SECTION I - CLASS DEFINITION
This class provides for active solid-state electronic devices, that
is, electronic devices or components that are made up primarily
of solid materials, usually semiconductors, which
operate by the movement of charge carriers - electrons
or holes - which undergo energy level changes within the
material and can modify an input voltage to achieve rectification, amplification, or switching
action, and are not classified elsewhere.
SCOPE OF THE CLASS
Active solid-state electronic devices include diodes, transistors, thyristors, etc., but
exclude pure resistors, capacitors, inductors, or
combinations solely thereof. The latter class of devices
is characterized as passive.
The subject matter to be found here includes only active solid-state
devices, per se. It may include one or more such
devices combined with contacts or leads, or structures
configured to be tested on a semiconductor chip, or merely
semiconductor material without contacts or leads where the sole
disclosed use is an active solid-state device.
This subject matter does not include
active solid-state devices combined with significant circuits.
Claims reciting an integrated circuit nominally with significant
metallization will be classified in Class 257, whereas
otherwise, nominal recitation of an integrated circuit (i.e., without
significant active solid-state device recitation) will
not be sufficient to permit the device to be classified in Class
257.
KEY CONCEPTS
See Subclass References to the Current Class, below, for references
that relate to key concepts and terms found in Class 257.
An indication that a particular concept or term occurs in one or
more subclasses does not mean that the indicated subclass or subclasses
are the only places that subject matter may be found.
That subject matter may possibly be found elsewhere in Class 257 listed
under a related term or concept that may be broader or narrower
or of the same scope.
OTHER CLASSIFICATION SYSTEMS
Each subclass definition may contain an OTHER CLASSIFICATION
SYSTEMS listing that is to be used for informational purposes only.
These classification listings may change at any time after their
publication and are therefore not guaranteed to be current.
In addition, the classification listing does not necessarily
indicate the sole relationship between the U.S. Patent Classification
System and foreign classifications. Even where a single
classification is listed for a single U.S. subclass, a
one-to-one correlation should not be inferred.
As a result, information contained therein is considered
to be only a guide to related subject matter.
SECTION II - LINES WITH OTHER CLASSES AND WITHIN THIS CLASS
A. Classes related to Class 257 subject matter in
the sense that they employ active solid-state devices in
electronic circuits and the relationship of these classes to Class
257 is mainly that of a combination to a subcombination or of a
genus to a specie. See References to Other Classes, below, referencing
this section.
B. Classes related to Class 257 subject matter in
the sense that they employ active solid-state devices in
electronic circuits and the use of active solid-state electronic devices
primarily as a perfecting feature. See References to Other
Classes, below, referencing this section.
C. See References to Other Classes below for classes that
provide for materials used in active solid-state electronic
devices.
D. See References to Other Classes, below, for
classes related to Class 257 because they provide for methods of
making, cleaning, coating, etc., active
solid-state devices, e.g., Class
438, Semiconductor Device Manufacturing: Process.
E. See References to Other Classes, below, for
Classes related to Class 257 because they provide for active solid-state
electronic devices structures with a specified use, e.g., Class
136, Batteries: Thermoelectric and Photoelectric.
F. See References to Other Classes, below, for
classes providing for provide for subcombination subject matter
that can be used as component part of active solid-state
electronic devices (e.g., lead
frames) or perfect the device (e.g., a
heat sink).
G. Classes which provide for passive solid-state
electronic devices with names that may refer to either active or
passive solid-state electronic devices, e.g., coherers, varistors, varactors. luminescent
or electroluminescent devices. The devices may be part
of the main subject matter of the class or may be used as circuit
elements in circuits or control or measuring systems which form
the main subject matter of the class.
See References to Other Classes, below, referencing
this section.
SECTION III - SUBCLASS REFERENCES TO THE CURRENT CLASS
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1, | through 8, for bulk effect device. |
| 2, | - 5, 16, 52-63, and
646, for amorphous semiconductor material. |
| 4, | 72, 91, 144, 150, 151, 175-177, 181, 182, 207-211, 246-250, 276, 309, 317, 401, 448, 457, 459, 503, 508, 573, 584, 587, 602, 621, 625, 666-676, and
692-697, for configuration of electrode, contact, lead
or pad. |
| 4, | 32, 33, 81, 91, 99, 144, 150-153, 177-179, 181, 182, 203, 207-211, 276, 377, 382-385, 459, 503, 522, 554, 573, 576, 584, 602, 621, 625, 661-677, 690-700, and
734-786, for electrical contact or lead. |
| 6, | through 8, for Gunn effect (intervalley
transfer). |
| 7, | for intervalley transfer (e.g., Gunn) device
in integrated circuit. |
| 10, | through 11, and 407, for controlled
work function material. |
| 10, | and 11, for electron emissive layer. |
| 10, | through 27, and 104-106, for
heterojunction involving quantum-mechanical tunneling. |
| 10, | and 11, for photocathode. |
| 10, | 54, 73, 155, 192-195, 217, 260, 267, 269, 275-277, 280-284, 449-457, 471-486, and
928, for Schottky barrier. |
| 10, | 11, 30-39, and 314-326, for
tunneling-insulator layer. |
| 10, | 11, and 407, for work function
of material, controlled, e.g., low. |
| 13, | 76, 78, 85, 90, and
94-97, for heterojunction light emitter. |
| 13, | 79-103, and 918, for
light emitting device. |
| 13, | through 25, for quantum well device. |
| 15, | through 22, and 28, for superlattice. |
| 16, | 55, 63, and 65, for heterojunction
in non-single-crystal material. |
| 18, | 19, and 190, for mismatched or
strained lattice. |
| 18, | 19, and 190, for mismatch of lattice
constant. |
| 18, | and 19, for strained layer superlattice
heterojunction. |
| 19, | 76, 78, 103, 200-201, and
613-616, for alloy of two different semiconductors (e.g., GaxIn1-xAs). |
| 20, | 24, 27, 57-61, 66-72,
133-145, 192-195, 202-211, 213, and
252-413, for field effect devices. |
| 20, | 24, and 194, for HEMT (High
electron mobility transistor). |
| 20, | 27, 187, and 192-195, for
heterojunction FETs. |
| 21, | 85, 184-189, for heterojunction
in light responsive device. |
| 21, | for light responsive or activated device (superlattice
quantum well heterojunction). |
| 21, | 53-56, 59, 72, 80-85, 113-118, 184-189, 222, 223, 225-234, 257, 258, 290-294, 325, 428-466, 680, 681, and
749, for radiation responsive. |
| 21, | and 187, for light responsive heterojunction transistor. |
| 21, | 187, 443, and 462, for
photosensitive bipolar transistor. |
| 26, | 27, and 29, for ballistic transport
device. |
| 26, | 27, and 29, for ballistic transport
transistor. |
| 31, | through 36, for Josephson device. |
| 31, | through 36, and 661-663, for
superconductive element/device. |
| 31, | through 36, 468, and 661-663, for
thermal device operated at cryogenic temperature. |
| 33, | for high temperature (30 K) Josephson
device. |
| 40, | for organic semiconductor material. |
| 41, | for point contact device. |
| 42, | for Selenium (elemental). |
| 44, | through 47, for alloyed junction. |
| 45, | for thermal gradient zone melting (TGZM). |
| 46, | 104, and 105, for Esaki diode. |
| 46, | and 104-106, for p-n
junction type (Esaki type) tunneling. |
| 47, | 197, 205, 273, 350, 361, 370, 378, 423, 462, 477
though 479, 511, 512, 517, 518, 525, 526, 539-543, and
552-593, for bipolar transistor structure. |
| 47, | for alloyed junction bipolar transistor. |
| 48, | and 797, for calibration or test structure.5, for array
of bulk effect amorphous switches. |
| 48, | for test structures. |
| 49, | through 75, for non-single crystal, as
active layer. |
| 49, | through 51, 64-75, 359, 377, 380-382, 385, 412, 505, 518, 520, 524-527, 538, 554, 576, 581, 588, and
754-757, for polycrystalline semiconductor material. |
| 49, | through 51, and 64-75, for
polycrystalline active junction material. |
| 49, | through 51, and 64-75, for
recrystallized active semiconductor layer. |
| 50, | and 530, for anti-fuse component
or element. |
| 50, | 530, and 928, for shorted devices, in
general, e.g., anti-fuse
elements. |
| 53, | through 56, for amorphous semiconductor material
device. |
| 53, | through 56, 108, 225, 252, and
414, for responsiveness to nonelectric signal. |
| 55, | and 63, for alloy of
amorphous semiconductor materials. |
| 55, | 63, and 65, and 646,
for silicon nitride to increase band gap of amorphous or polycrystalline
silicon. |
| 56, | 58, 62, and 65, for for
dangling bond. |
| 56, | 58, 62, and 68, for passivation
of dangling bonds in nonsingle crystal semiconductor. |
| 57, | through 61, 66-72, and
368-401, for insulated gate FET in integrated
circuit. |
| 57, | through 61, and 66-72, for
FET in non-single crystal or recrystallized semiconductor
material (e.g., amorphous or
polycrystalline semiconductor as channel). |
| 59, | 72, and 88-93, for array
as imager, or with transparent electrode, or as
display (with plural light emitters). |
| 59, | 72, 449-457, and 749, for
electrical contact or lead transparent to light. |
| 59, | 72, and 293, for photoresistor
combined with accessing FET. |
| 59, | 72, 453, and 749, for
transparent electrode. |
| 60, | 135, 136, 263-267, 302, and
328-334, for vertical channel field effect device. |
| 64, | 255, 521, 627, and 628, for
crystal axis or plane. |
| 65, | for alloy of polycrystalline semiconductor materials. |
| 66, | 67, 69, 379-381, 903, and
904, for static memory cell using FET. |
| 67, | through 70, for stacked FETs. |
| 67, | 69, 70, and 74, for stacked
FETs. |
| 68, | through 71, 296-313, 296, 298, 300, 906, and 908, for
capacitance combined with insulated gate device. (e.g., DRAM). |
| 68, | 71, and 295-313, for
insulated gate device (capacitor or combined with capacitor). |
| 68, | 71, 296-313, and 905-908, for
memory device component involving a capacitor (e.g., dynamic
memory cell). |
| 68, | 71, 303, and 306-309, for
stacked capacitors in DRAM cell. |
| 68, | and 301-305, for capacitor in
trench. |
| 68, | 283, 284, 330-334, 374, 397, 513, 514, 622, 647, and
648, for vertical walled groove in semiconductor. |
| 69, | 195, 204, 206, 338, 350, 351, 357-359, and 365-377, for
CMOS. |
| 69, | 195, 204, 206, 274, 338, 350, 351, 357-359, and
369-377, for complementary field effect transistors. |
| 74, | and 278, for three-dimensional
integrated circuit. |
| 76, | through 78, and 183-201, for
heterojunction, generally. |
| 76, | through 78, for wide band gap semiconductor material
other than GaAsP or GaAlAs. |
| 80, | through 85, for light responsive or activated device
combined with light emitting device. |
| 81, | 99, 177-181, 584, 625, 675, 688, 689, 705, 707, 712-722, and
796, for heat sink. |
| 81, | 82, and 99, for housing or package
for light emitter. |
| 81, | and 82, for housing or package for light
emitter combined with light receiver. |
| 81, | 82, 433, 434, 680, 681, for
housing or package for light responsive device. |
| 81, | 99, and 666-677, for
lead frame. |
| 83, | for light coupled transistor structure. |
| 86, | and 87 for indirect band gap active layer - light emitter. |
| 87, | 131, 156, 439, 523, 590, and
608-612, for deep level dopant/impurity. |
| 87, | 126, 131, 156, 523, 590, 609-612, and
617, for recombination centers. |
| 91, | 98, 151, 175, 176, 249, 250, 276, 282-284, 309, 317, 401, 418, 435, 448, 457, 459, 503, 508, 534, 573, 587, 602, 621, 662, and
664, for shape(d) contact, electrode, conductor, or
terminal. |
| 91, | 98, 294, 323, 435, and
659, for optical shield. |
| 93, | for plural light emitters in integrated circuit. |
| 93, | 374, 446, 499 and 564, for
electrical isolation of components in integrated circuit. |
| 95, | 117, 118, 127, 170, 244, 283, 284, 301-305, 330-334, 418, 419, 447, 460, 466, 496, 534, 571, 586, and
618-628, for grooves, generally. |
| 95, | 170, 171, 452, 466, 496, 571,
586, 594, 600, 618, and 623-626, for
mesa structure. |
| 95, | for shaped contact, electrode, etc., external
of heterojunction light emitter. |
| 98, | 116, 117, 294, and 432, for
light fiber, guide, or pipe. |
| 98, | for luminescent material used with light emitter. |
| 98, | 181, 418, 688, 710, 711, 728, and
730, for shaped housing or package. |
| 98, | 99, 116, 434, 680, and
681, for window (optical) for housing. |
| 100, | 433, 434, 667, 687, 767-and
796, for encapsulated. |
| 101, | 194, 219-221, 264, 269, 285, 335-345, 404, 430, 450, 458, 463, 492, 493, 497, 498, 543, 545, 548, 558, 583, 591, 592, 596, 597, 605, 606, 655-657, 927, and
929, for dopant/impurity concentration, incl., graded
profile. |
| 102, | 227, 439, and 607-612, for
specified, generally (e.g., photoionizable). |
| 106, | for reverse conducting diode (tunnel diode). |
| 106, | for Zener diode. |
| 107, | through 182, and 918, for regenerative
switching device. |
| 108, | 252, and 421-427, for
magnetic field responsive. |
| 108, | 225, 254, and 415 and-419, for
device responsive to pressure. |
| 108, | 222, 225, 254, and 417-419, for
strain sensor. |
| 108, | 225, 252, and 467-470, for
passivating device responsive to temperature. |
| 109, | for Shockley diode. |
| 110, | and 119-131, for bidirectional
device (diac, rectifier). |
| 113, | through 118, for regenerative-type
switching device. |
| 115, | 123, and 157-161, for
amplified gate in thyristor. |
| 121, | for reverse conducting thyristor. |
| 121, | for Static Induction Transistor (SIT) - Bipolar transistor
as reverse path of bidirectional conducting thyristor. |
| 122, | 141, 146, and 162, for
lateral structure in regenerative device. |
| 124, | 125, and 133-145, for
FET in or combined with thyristor. |
| 125, | 137, 138, 143, and 149, for
shunt, regenerative device. |
| 125, | 137, 138, 143, 149, and
154, for shorted emitter, anode or cathode, in
thyristor. |
| 127, | 446, 510-522, 571, 577, and
594, for groove to define plural devices. |
| 127, | 170, 339, 372-376, 394-400, 409, 452, 484, 490, 493-495, and
605, for guard ring or region. |
| 131, | 156, 376, 424, 523, 590, and
617, for crystal damage. |
| 133, | 145, 195, 205, 273, 337, 350, 361, 362, 370, and
378, for field effect combined with bipolar type (including
regenerative type) device. |
| 134, | through 136, 217, 256-287, and
504, for JFET. |
| 136, | 205, 264, 268, 269, 392, for
enhancement mode. |
| 139, | through 145, and 212, for conductivity
modulated transistor. |
| 139, | through 145, 147-153, for
extended latching current device. |
| 139, | through 145, 147-153, and
372-376, for means to prevent latchup. |
| 139, | through 145, and 211, for conductivity
modulated transistor. |
| 142, | 148, 376, 553, and 583, for
doping for gain reduction. |
| 146, | 476-479, and 499-564, for
structure with elec. isolated components. |
| 150, | 151, 177-181, for housing
or package for regenerative type switching device. |
| 154, | 169, 194, 195, 218, 264, 523, 646, and
656, for high resistivity semiconductor region - see, also,
intrinsic material; PIN device. |
| 154, | 350, 358, 359, 363, 379-381, 516, 533, 536-543, 571, 572, 577, 580-582,
and 904, for resistive element (resistor) (passive
device). |
| 164, | and 580-582, for ballasting of
current (e.g., by resistors). |
| 164, | through 166, 560-561, 563, and
579- 581, for multiple/plural emitter. |
| 170, | for edge, beveled - preventing
breakdown. |
| 171, | 496, 586, and 618+, for
bevel. |
| 171, | 452, 483, and 484, for
protection against edge breakdown. |
| 171, | and 496, for reverse bevels. |
| 173, | 174, 328, 355-363, 487-496, and
546, for protection against overcurrent or overvoltage. |
| 173, | 529, 665, and 910, for
fuse/fusible link. |
| 173, | for overvoltage protection means in thyristor. |
| 177, | through 181, 467, 468, 573, 625, 675, 688, 705-707, and
712-722, for cooling. |
| 178, | 179, and 746-748, for
stress avoidance between electrode and semiconductor. |
| 178, | through 179, 633, 747, and
748, for thermal expansion matching or compensation. |
| 180, | and 733, for stud-type mount for
housing. |
| 180, | and 733, for stud mount. |
| 181, | 182, 688, 689, 726, 727, and
785 for press contact of electrode and semiconductor. |
| 183.1,
193, | 215-251, and 912, for
charge transfer device. |
| 184, | through 189, for heterojunction. |
| 185, | and 191, for graded band gap. |
| 185, | for staircase (light responsive heterojunction). |
| 187, | 197, and 198, for heterojunction
bipolar transistor. |
| 198, | for wide band gap emitter heterojunction bipolar
transistor. |
| 199, | 481, 482, 551, and 603-606, for
avalanche diode. |
| 199, | 482, and 604, for IMPATT. |
| 199, | 259, 275-277, 482, 523, 604, 624, 625, 659, 662, 664, and
728, for for microwave device component. |
| 202+, | and 909, for master slice (gate
array). |
| 202+, | and 909, for gate arrays. |
| 202, | through 211, and 909, for gate
arrays. |
| 205, | 273, 350, 361, 370, and
378, for bipolar combined with field effect type device. |
| 205, | 273, 350, 361, 370, and
378, for bipolar transistor structure combined with FET. |
| 206, | 208, 210, and 211, for
configuration of elements in gate array. |
| 209, | for gate array with programmable signal paths. |
| 210, | and 758-760, for multi-level
metallization. |
| 212, | for double-base diode (unijunction
transistor). |
| 212, | for Static Induction Transistor (SIT) - Unijunction
transistor. |
| 212, | for unijunction transistor. |
| 214, | for charge injection device. |
| 215, | 218, and 225-251, for
surface channel charge transfer device. |
| 216+, | for bulk channel device. |
| 216, | and 285, for buried channel. |
| 219, | through 221, for nonuniform channel doping
in buried channel CCD. |
| 223, | 230, and 445, for antiblooming. |
| 223, | 230, and 445, for suppression
of blooming in light imager. |
| 224, | and 243, for channel confinement. |
| 225, | 253, and 414, for chemical sensor. |
| 225, | for CCD with fixed pattern memory as ROM. |
| 228, | 447, 460, for backside illumination. |
| 239, | for floating diffusion as CCD Output Tap. |
| 239, | 261, and 315-323, for
floating gate. |
| 240, | for nonuniform channel thickness in CCD. |
| 241, | for parallel channels in CCD. |
| 245, | 364, and 489, for resistive electrode. |
| 246, | through 248, for nonuniform channel doping
in CCD, for directionality. |
| 249, | 317, 359, 363, 364, 377, 380-382,
384, 385, 387, 407, 412, 413, 489, 505, 518, 520, 524-527, 538, 554, 576, 581, 588, 646, 754-756, 904, and
914, for polycrystalline material (including polysilicon
contacts) other than active junction material. |
| 251, | for bucket-brigade device. |
| 254, | and 416, for acoustic
energy detector. |
| 256, | and 257, for light responsive PIN device
combined with JFET. |
| 257, | and 258, for JFET. |
| 227, | and 439, for photoionization. |
| 258, | 291-294, 443-448, and
911, for array of electrode field effect devices. |
| 260, | and 262, in or combined with a JFET device. |
| 260, | and 261, for memory device component involving
a JFET (e.g., taper isolated
or floating pn junction gate type). |
| 265, | for vertical current path JFET in integrated circuit. |
| 266, | 267, and 287, for parallel channels
in JFET. |
| 269, | and 285, for nonuniform channel doping
in JFET. |
| 272, | through 278, for JFET in integrated circuit. |
| 275, | through 278, 662, and 664, for
stripline lead. |
| 276, | for air bridge electrical lead. |
| 276, | for air bridge contact. |
| 283, | and 284, for groove alignment of Schottky
gate to source region in MESFET. |
| 283, | through 284, 330-334, for
gate electrode of FET formed in groove. |
| 286, | for nonuniform channel thickness in JFET. |
| 290, | and 294, for IGFET. |
| 291, | through 294, 326, 334, 337, 338, 347-363, and 368-401, for
insulated gate device (IGFET in integrated circuit). |
| 294, | 297, 340, 409, 435, 488-490, 503, 508, 630, 659-660, and
662, for shield electrode. |
| 295, | 298, and 314-326, for
EPROM/EEPROM. |
| 295, | 298, 314, and 324-326, for
MNOS insulated gate-type memory device component. |
| 297, | 349, 547, and 620, for
means to prevent charge leakage or leakage current. |
| 297, | 349, 354, 372-376, 503, 547, and
620, for means to prevent leakage current or charge leakage. |
| 297, | 660, and 921, for protection against
radiation (e.g., alpha particles). |
| 297, | 660, and 921, for radiation protection. |
| 297, | 422, and 659-660, for
ionizing radiation shield, charged particles, electric
or magnetic fields. |
| 298, | and 315-326, for insulated gate
device (floating gate memory device). |
| 298, | and 315-323, for floating insulated
gate memory-type memory device component. |
| 299, | for substrate bias (electrical generator. |
| 301, | through 305, 534, and 599, for
groove involving a capacitor. |
| 305, | 354, 376, 398-400, 519, 620, 648, and
652, for channel stop. |
| 305, | 333, 374, 389, 395-399, 510-521, and
632-651, for field oxide. |
| 312, | 480, and 595-602, for
voltage variable capacitance device. |
| 314, | through 326 for variable threshold insulated gate
device (e.g., EEPROM, non-volatile
memory MOSFET). |
| 322, | for programming of floating gate MISFET (avalanche
breakdown). |
| 323, | 680, and 681, for light erasure
of EPROM. |
| 325, | for oxynitride as insulator in MNOS memory IGFET. |
| 327, | through 346, for short channel. |
| 328, | and 355-363, for overvoltage protection
means in IGFET. |
| 328, | and 355-363, for MOSFET gate protection. |
| 331, | 341, 342, and 401, for
parallel channels in IGFET. |
| 332, | 346, 387, 388, 412, and
413, for self-aligned MOSFET gate. |
| 333, | 340, and 386-389, for
reduction of gate capacitance (FET). |
| 333, | 346, 387, and 388, for
overlap of gate electrode with source or drain in IGFET. |
| 334, | 337, and 338, for VMOS or DMOS
short channel IGFET in integrated circuit. |
| 336, | 344, 408, and 900, for
LDD (lightly doped drain) device. |
| 339, | 409, 483, 484, and 487-496, for
preventing avalanche breakdown. |
| 339, | 409, and 488-490, for
field relief electrode. |
| 339, | 409, 490, and 495, for
floating pn junction guard region. |
| 340, | 394, and 630, for field shield
electrode. |
| 345, | and 404, for nonuniform channel doping
in IGFET. depletion mode. |
| 347, | through 354, and 507, for insulating
substrate integrated circuit. |
| 347, | through 354, and 507, for single
crystal insulating substrate. |
| 347, | through 354, and 507, for single
crystal semiconductor layer on insulating substrate (SOI). |
| 348, | 391, 392, and 402-407, for
depletion mode Insulated Gate FET. |
| 349, | 354, 372-376, 503, and
547, for controlling, reducing, etc. parasitics. |
| 350, | 511, 512, 525, and 555-562, for
lateral bipolar transistor in integrated circuit. |
| 354, | through 374, 395-399, 501, and
506-527, for dielectric isolation. |
| 355, | through 363, for gate insulator breakdown
protection in IGFET integrated circuit. |
| 360, | and 367, for insulated gate device (controlling pn
junction breakdown). |
| 361, | 362, and 497-499, for
punch-device. |
| 366, | for overlap of plural gate electrodes in IGFET. |
| 368, | through 401, for PN junction isolation
in MOSFET integrated circuit. |
| 374, | 394-398, 626, 631-651, and
758-760, for insulating/passivating coating. |
| 374, | 396-398, 510-521, 647, and
648, for groove (dielectric isolation means). |
| 377, | 382-385, 388, 412, 413, 454-458, 486, 518, 554, 576, 588, 747, 748, 754-757, 761, 763-764, and
768-770, for refractory electrode material. |
| 377, | 382-384, 388, 412, 413, 454-456, 485, 486, 576, 587, 751, 754-757, and
768-770, for silicide. |
| 379, | through 381, and 903-904, for
static RAM arrangement. |
| 379, | through 381, 516, 528-543, 903, 904, 919, and 924, for
passive components in integrated circuits. |
| 382, | through 384, 576, 757, 768, and
769, for metal or silicide of platinum group metal, as
ohmic contact. |
| 383, | 388, 412, 485, 486, 763, 764, and
770, for pure or alloyed titanium. |
| 388, | 407, 412, and 413, for
metal or silicide of platinum group metal, as MOSFET gate. |
| 390, | and 391, for array of IGFETs. |
| 390, | and 391, for nonerasable (e.g., ROM). |
| 390, | and 391, for mask-programmed MOSFET ROM. |
| 401, | for nonuniform channel thickness in IGFET. |
| 410, | 411, 639-641, 649, and
760, for silicon nitride. |
| 411, | and 760, for composite insulator material. |
| 411, | for oxynitride as gate insulator in IGFET, in general. |
| 422, | and 659, for magnetic field shielding |
| 423, | 511, 512, 525, 526, 556, 557-562, 575, and 576, for
lateral bipolar transistor structure. |
| 423, | for magnetic field sensing bipolar transistor. |
| 426, | and 469, for passivating means to reduce
temperature sensitivity. |
| 427, | for magnetic field sensor in integrated circuit. |
| 430, | and 458, for light or radiation responsive
PIN device, in general. |
| 431, | 466, for light responsive or activated
device generally. |
| 437, | for anti-reflection coating. |
| 444, | for matrix or array of light sensor elements overlying
active switching elements in integrated circuit. |
| 446, | for matrix or array of light sensors with specific
isolation means in integrated circuit. |
| 449, | through 457, for Schottky barrier. |
| 453, | through 455, 485, and 486, for
metal or silicide of platinum group metal, as Schottky
barrier material. |
| 458, | 523, 538, and 656, for
intrinsic material or region. |
| 458, | for PIN diode. |
| 459, | 676, and 786, for bonding flag
or pad |
| 465, | 592, 599, 653, and 654, for
configuration of junction geometry. |
| 466, | 496, 571, 586, 594, 599, 600, and
618-628, for configuration of external portion
of active device. |
| 474, | for bipolar transistor with Schottky barrier transistor
as emitter-base or base-collector junction. |
| 474, | through 479, 512, 525, 555, 556, and
574-576, for integrated injection logic. |
| 477, | through 479, for bipolar transistor in
integrated circuit with Schottky barrier diode. |
| 479, | and 570, for anti-saturation diode. |
| 479, | for baker clamp. |
| 486, | 740, 751, and 767, for
diffusion barrier. |
| 491, | and 492, for means to increase breakdown
voltage in integrated circuit. |
| 492, | and 493, for RESURF device. |
| 494, | for reverse biased (electrical) pn
junction guard region. |
| 494, | for reverse biased guard ring to prevent breakdown. |
| 497, | and 498, for punchthrough transistor. |
| 504, | for JFET isolation in integrated circuit (i.e., pinched-off
region used for integrated circuit isolation). |
| 509, | through 521, 544-556, and
929, for isolated PN junction. |
| 509, | through 521, for PN junction isolation
in integrated circuit combined with dielectric isolation. |
| 511, | 512, 525, 555, 556, 569, and
574-576, for complementary bipolar transistor
structure. |
| 511, | 512, 525, 555, 556, 569, and
574-576, for complementary bipolar transistors. |
| 511, | 512, 514, 515, 517, 518, 525, 526, 539-543, and
552-563, for bipolar transistors in integrated
circuit. |
| 511, | 512, 514, 517, 518, and
552-556, for bipolar transistors with pn junction
isolation. |
| 512, | 569, and 574-576, for
bipolar transistor structure with common active region. |
| 512, | 569, and 574-576, for
complementary bipolar transistors with common active region. |
| 512, | 555, 556, and 574-576, for
logic device (superintegrated) using Integrated
Injection Logic (I2L). |
| 514, | and 515, for walled emitter bipolar transistor. |
| 522, | for air isolation of integrated circuit. |
| 531, | for inductance in integrated circuit. |
| 532, | through 535, for capacitance as passive
component in non-FET I.C. |
| 540, | for dynamic isolation pocket bias (electrical). |
| 541, | for pinch resistor. |
| 544, | through 556, for PN junction isolation
in integrated circuit in general. |
| 545, | for reduction of isolation junction capacitance. |
| 546, | for overvoltage protection means in pn junction isolated
integrated circuit. |
| 546, | for reverse voltage polarity protection, in
pn junction isolated integrated circuit. |
| 549, | for collector diffused type isolation. |
| 559, | lateral transistor formed along groove. |
| 560, | through 564, for multiple/plural
collectors. |
| 560, | 563, and 579-581, for
plural emitters in bipolar transistor. |
| 562, | for logic device (superintegrated) using
Current Hogging Logic (CHL). |
| 565, | through 593, for bipolar transistor structure, in general. |
| 571, | for groove resistor in Darlington bipolar device. |
| 573, | and 584, for housing or package for bipolar transistor
devices. |
| 592, | for configuration of bipolar transistor base region. |
| 602, | for housing or package for voltage-variable capacitance
device. |
| 607, | and 917, for plural dopants of same conductivity
type. |
| 610, | for platinum (as deep level dopant). |
| 620, | for scribe line or region. |
| 624, | for prevention of skin effect, microwave device, by
low resistance ohmic contact along mesa surface. |
| 626, | and 629-652, for passivation of
semiconductor surface. |
| 634, | for passivating glass with ingredient to adjust
softening or melting temperature. |
| 639, | and 649, for oxynitride as passivating
insulating layer. |
| 642, | 643, and 759, for organic insulating
material or layer. |
| 643, | 759, and 788, for polyamide. |
| 643, | 759, and 792, for polyimide. |
| 653, | 654, for shaped PN junction. |
| 655, | for reverse doping concentration gradient profile. |
| 656, | for PIN device in general. |
| 657, | for stepped profile. |
| 657, | for stepped dopant concentration profile. |
| 660, | for housing or package for radiation shielded device. |
| 662, | and 664, for transmission line lead. |
| 663, | for superconductive contact or lead on integrated
circuit. |
| 669, | 670, 673, 674, 676, 688, 689, 692-697, 728, 735-739, 752, 758, 773-776, and
780-786, for shaped contact, electrode, etc. |
| 669, | for lead frame having stress relief. |
| 676, | for die bonding flag. |
| 676, | for lead frame-type mount for chip. |
| 678, | through 733, for housing or package, generally. |
| 679, | and 922, for smart card (e.g., "credit
card" integrated circuit package). |
| 686, | for stacked housings. |
| 700, | 701, and 703-707, for
ceramic housing or package material. |
| 705, | for high thermal conductivity ceramic for package. |
| 711, | for metal housing with mount for chip. |
| 713, | for cooling of housing or contents for integrated
circuit. |
| 714, | through 716, for liquid coolant. |
| 719, | for press contact of heat sink and semiconductor. |
| 720, | for high thermal conductivity insert in heat sink. |
| 731, | for mount for housing. |
| 732, | for flanged type mount for housing. |
| 735, | through 739, 746, 758-760, 773-776, 780-781, 786, 920, 923, 926, for
configuration of electrode, etc. |
| 738, | 780, and 781, for ball-shaped
leads, contacts or bonds. |
| 740, | for prevention of spiking of contact metal. |
| 741, | through 745, and 751, for gold (deep
level dopant as contact or electrode). |
| 742, | and 743, for dopant/impurity conductivity
type in electrical contact material. |
| 746, | for composite electrode material. |
| 746, | for electrode material. |
| 749, | for electrode transparent to light. |
| 751, | 767, and 915, for titanium nitride. |
| 758, | through 760, for multiple metallization
layers separated by insulating layer on integrated circuit. |
| 760, | for oxynitride between metal levels in integrated
circuit. |
| 764, | 765, and 768-771, for
alloy of materials forming electrical contacts. |
| 767, | for electromigration prevention or reduction. |
| 777, | for chip on chip mount for chip. |
| 778, | for flip chip mount for chip. |
| 779, | and 780-784, for die or lead bond. |
| 782, | and 783, for die bond. |
| 900, | for MOSFET type gate sidewall insulating spacer. |
| 901, | for MOSFET substrate bias (electrical). |
| 901, | for MOSFET substrate bias. |
| 902, | for FET with metal source region. |
| 903, | and 904, for configuration of FETs for
Static Memory Cell (SRAM). |
| 905, | through 908, for configuration of Dynamic Memory (DRAM). |
| 905, | for trench shared by plural DRAM cells. |
| 906, | Electrode use for accessing capacitance, in DRAM. |
| 910, | for array of diodes. |
| 911, | for vidicon array (cross-reference
collection). |
| 915, | for titanium nitride. |
| 919, | for parallel electrical connections to average out
manufacturing variations. |
| 920, | for parallel electrical connections to reduce resistance. |
| 922, | for anti-tamper device. |
| 922, | for diode arrays. |
| 922, | for anti-tamper or inspection means for |
| 923, | for conductor aspect ratio. |
| 925, | for bridge rectifier module. |
| 927, | for shaped depletion layer. |
| 930, | for Peltier cooling (cross-reference
collection). |
SECTION IV - REFERENCES TO OTHER CLASSES
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 29, | Metal Working,
subclasses 25.01+ for process and apparatus for making barrier layer
or semiconductor devices not elsewhere classified; subclass
25.35 for piezoelectric device making not elsewhere classified; subclasses
25.41+ for electric condenser making not elsewhere
classified; subclasses 592.1+ for process
of mechanical manufacture of electrical devices, not elsewhere
classified; and subclasses 825+ for electrical
conductor manufacturing processes, including subclass 827
regarding beam lead frames and beam leads. (class
providing for methods of making, cleaning, coating, etc., active
solid-state devices, See Lines With Other Classes
and Within This Class, D). |
| 29, | Metal Working,
subclass 612 for making thermally variable resistors. (See
G, Lines With Other Classes and Within This Class, above). |
| 29, | Metal Working, appropriate subclasses for manufacturing methods
of beam lead frame or beam lead devices. (Class
providing for subcombination subject matter used as component part
of active solid-state electronic devices. See Lines
with Other Clases and Within This Class, F, above). |
| 40, | Card, Picture, or Sign Exhibiting,
subclass 544 for electroluminescent signs. (See
B, Lines With Other Classes and Within This Class, above.) |
| 62, | Refrigeration,
subclasses 3.2+ for thermoelectric, e.g., Peltier
effect cooling processes and apparatus. (See B, Lines
With Other Classes and Within This Class, above.) |
| 65, | Glass Manufacturing,
subclasses 138+ for Electronic envelope header, terminal, or
stem making means and subclass 155 for electronic device making
involving fusion bonding. (Class providing for
methods of making, cleaning, coating, etc., active
solid-state devices, See Lines With Other Classes
and Within This Class, D). |
| 73, | Measuring and Testing,
subclass 31.06 for gas analysis semiconductor detector details; subclass
777 for semiconductor stress sensor structure; and subclass
754 for semiconductor type fluid pressure gauges. (Class
employing active solid-state devices in electronic circuits. See Lines
With Other Classes and Within This Class, A, above). |
| 84, | Music,
subclasses 676 and 678 for transistorized analog oscillator circuits. (See
B, Lines With Other Classes and Within This Class, above.) |
| 102, | Ammunition and Explosives,
subclass 202.4 for semiconductor voltage variable resistance shunts
in devices used to prevent accidental fuse ignition. (See
G, Lines With Other Classes and Within This Class, above) |
| 102, | Ammunition and Explosives,
subclass 202.4 for semiconductor fuse shunts and subclass 220 for
silicon controlled rectifier ignition or detonation switch devices. (See
B, Lines With Other Classes and Within This Class, above.) |
| 116, | Signals and Indicators, digest 35 for electroluminescent dials. (See
B, Lines With Other Classes and Within This Class, above.) |
| 117, | Single-Crystal, Oriented-Crystal, and
Epitaxy Growth Processes; Non-Coating Apparatus Therefor, for processes and non-coating apparatus
for growing therein-defined single-crystal of
all types of materials, including those which may be suitable
as or to produce an active solid-state device.
Class 118 generally provides for coating apparatus, including
single-crystal (e.g., epitaxy) coating
means. (Class providing for methods of making, cleaning, coating, etc., active
solid-state devices, See Lines With Other Classes
and Within This Class, D). |
| 118, | Coating Apparatus,
subclass 900 for semiconductor vapor doping. (Class
providing for methods of making, cleaning, coating, etc., active
solid-state devices, See Lines With Other Classes
and Within This Class, D) |
| 123, | Internal-Combustion Engines,
subclasses 650+ for ignition systems with power supplies having
diode and transistor features. (See B, Lines With
Other Classes and Within This Class, above.) |
| 134, | Cleaning and Liquid Contact With Solids,
subclasses 1.2 , 1.3, and 902 for semiconductor wafer
cleaning. (Class providing for methods of making, cleaning, coating, etc., active
solid-state devices, See Lines With Other Classes and
Within This Class, D, above). |
| 136, | Batteries: Thermoelectric and Photoelectric,
subclasses 203+ for Peltier effect device; subclasses
200+ for batteries which generate electricity under the
action of heat (thermoelectric); and
subclasses 243+ for batteries which generate electricity
under the action of light, such as photovoltaic batteries, some
of these batteries utilize potential barrier layers. (class
providing for active solid-state electronic devices structures
with a specified use.) |
| 148, | Metal Treatment,
subclasses 33+ for PN type barrier layer stock material treatment
and numerous digests concerning treatment of semiconductor materials, dopants, and
active solid-state electronic devices. (Class
providing for methods of making, cleaning, coating, etc., active
solid-state devices, See Lines With Other Classes
and Within This Class, D, above). |
| 148, | Metal Treatment, digest 171 for metal treatment involving varistors. (See
G, Lines With Other Classes, above). |
| 165, | Heat Exchange,
subclasses 80.2+ and 104.33 for electrical device or component
heat exchangers. (Class providing for subcombination
subject matter used as component part of active solid-state
electronic devices. See Lines with Other Clases and Within
This Class, F, above). |
| 174, | Electricity: Conductors and Insulators,
subclasses 15.1 through 16.3for fluid cooling of electrical conductors or insulator; subclasses 250-268
for printed circuit devices; and subclasses 520-64
for housings with electric devices or mounting means. (Class
employing active solid-state devices in electronic circuits. See
Lines With Other Classes and Within This Class, A, above). |
| 178, | Telegraphy,
subclass 117 for coherer type AC systems. (See
B, Lines With Other Classes and Within This Class, above.) |
| 178, | Telegraphy,
subclass 117 for coherer type AC systems. (See
G, Lines With Other Classes and Within This Class, above). |
| 194, | Check-Actuated Control Mechanisms,
subclasses 216+ for value accumulator having solid-state
circuitry. (See B, Lines With Other Classes
and Within This Class, above.) |
| 204, | Chemistry: Electrical and Wave Energy,
subclasses 400+ for active solid-state devices used in
measuring and testing involving electrolytic analysis. (Class
employing active solid-state devices in electronic circuits. See
Lines With Other Classes and Within This Class, A, above). |
| 204, | Chemistry: Electrical and Wave Energy,
subclass 192.25 for semiconductor coating, forming, or
etching by sputtering. (Class providing for
methods of making, cleaning, coating, etc., active
solid-state devices, See Lines With Other Classes
and Within This Class, D, above) |
| 216, | Etching a Substrate: Processes,
subclass 16 for active solid state devices involved in an etching
process. (Class providing for methods of making, cleaning, coating, etc., active solid-state
devices, See Lines With Other Classes and Within This Class, D, above). |
| 219, | Electric Heating,
subclass 501 for automatic regulation or control means for heating
devices which include semiconductor, e.g., transistor, means. (See
B, Lines With Other Classes and Within This Class, above.) |
| 228, | Metal Fusion Bonding,
subclass 123 for processes of bonding metal to semiconductor-type material
and subclasses 179+ for processes of bonding electrical
device (e.g., semiconductor) joints.
(Class providing for methods of making, cleaning, coating, etc., active
solid-state devices, See Lines With Other Classes and
Within This Class, D, above). |
| 250, | Radiant Energy,
subclass 492.2 for irradiation of semiconductor devices. (Class
providing for methods of making, cleaning, coating, etc., active
solid-state devices, See Lines With Other Classes
and Within This Class, D, above). |
| 250, | Radiant Energy,
subclass 338.4 for infrared responsive semiconductor devices, subclasses 370.01-370.15
for invisible radiant energy responsive semiconductor devices; subclass 371
for invisible radiant energy responsive methods using semiconductor
devices; subclass 492.2 for irradiation of semiconductor devices; subclasses
552 and 553 for photocell circuits and apparatus involving solid-state light
sources; subclasses 211 for photocells including photosensitive
junctions; and subclasses 208.1-208.6
for plural photosensitive elements, including arrays. (Class
employing active solid-state devices in electronic circuits. See
Lines With Other Classes and Within This Class, A, above). |
| 264, | Plastic and Nonmetallic Article Shaping or Treating: Processes,
subclass 272.11 for electrical component encapsulating processes, including
subclass 272.17 for encapsulating semiconductor or barrier
layer device. (Class providing for methods of
making, cleaning, coating, etc., active
solid-state devices, See Lines With Other Classes
and Within This Class, D, above). |
| 252, | Compositions,
subclass 62.3 for barrier layer device compositions, e.g., N-material, P-material
and, subclasses 500+ for electrically conductive
or emissive compositions. (Class providing for
materials used in active solid-state devices, Lines
With Other Classes and Within This Class, C, above). |
| 273, | Amusement Devices: Games, digest 24 for luminescent devices. (See
B, Lines With Other Classes, above.) |
| 307, | Electrical Transmission or Interconnection Systems,
subclasses 401+ for nonlinear reactor systems which typically employ
active solid-state devices; subclass 91 for magnetic
or electrostatic field shielding; and subclasses 109+ for
systems involving capacitors. |
| 310, | Electrical Generator or Motor Structure,
subclass 303 for energy conversion devices employing pn semiconductor
junction devices, and digest 3 for Hall effect generators
and converters. (See B, Lines With Other
Classes and Within This Class, above.) |
| 313, | Electric Lamp and Discharge Devices,
subclasses 498+ for electric lamp and discharge devices having
solid-state luminescent materials, including nominally
recited luminescent semiconductor type materials; subclasses
329 and 367+ for mosaic electrodes; subclasses 366+ for
semiconductor depletion layer type image pickup tubes; subclass
463 for electroluminescent cathoderay tube screens; subclasses 346
and 346 for photoemissive cathodes; and subclass 504 for
solid-state organic phosphor material luminescent devices. (Class
employing active solid-state devices in electronic circuits. See
Lines With Other Classes and Within This Class, A, above). |
| 315, | Electric Lamp and Discharge Devices: Systems,
subclass 12.1 for secondary emissive stage in a cathoderay
tube; subclass 407 for a deflection coil circuit including
a diode; subclass 408 for deflection coil circuits including
a solid-state switch; and digest 7 for starting
and control circuits using transistors. (Class employing
active solid-state devices in electronic circuits. See
Lines With Other Classes and Within This Class, A, above). |
| 323, | Electricity: Power Supply or Regulation
Systems,
subclasses 229+ for power supply or regulation systems using a
diode in shunt with a source or load; subclasses 237+, 254, 257, 258, 263, 265+, and
292 for output level devices employing three or more terminal semiconductor
devices; subclass 300 for input level devices or systems
employing three or more terminal semiconductor devices; subclasses 311+ for
self-regulating systems employing three or more terminal
semiconductor devices; subclasses 325+, 339, 343, and
349+ for external or operator controlled systems employing three
or more terminal semiconductor devices; subclass 360 for
superconductor type transformers or inductors; digest 902
for device with optical coupling to a semiconductor; and digest
907 for temperature compensation of a semiconductor. (Class
employing active solid-state devices in electronic circuits. See
Lines With Other Classes and Within This Class, A, above). |
| 318, | Electricity: Motive Power Systems,
subclass 681 for positional servomechanisms using solid-state
servo amplifiers. (see B, Lines With Other
Classes and Within This Class, above.) |
| 315, | Electric Lamp and Discharge Devices: Systems,
subclass 311 for variable impedance device in automatic regulator
in supply circuit of an electric lamp or discharge device. (See
G, Lines With Other Classes and Within This Class, above). |
| 318, | Electricity: Motive Power Systems,
subclass 662 for variable capacitor type positional servo systems
and subclasses 788 and 792 for variable temperature impedance (e.g., resistor) elements
in induction motor systems. (See G, Lines
With Other Classes and Within This Class, above). |
| 320, | Electricity: Battery or Capacitor Charging
or Discharging, appropriate subclass for an active solid-state
device included in a charging or discharging circuit for a battery
or capacitor. (See B, Lines With Other
Classes, above.) |
| 322, | Electricity: Single Generator Systems, digest 5 for Hall effect elements. (see
B, Lines With Other Classes and Within This Class, above.) |
| 323, | Electricity: Power Supply or Regulation
Systems,
subclass 298 for output level responsive devices including a
variable resistor. (See G, Lines With
Other Classes and Within This Class, above). |
| 324, | Electricity: Measuring and Testing,
subclasses 762.01 through 762.1for testing semiconductor devices, SCR
and transistor testing and subclasses 244+ for magnetometers
many of which employ active solid-state devices, e.g., subclasses
248 (thin film), 251 (Hall plate) and
252 (semiconductor type solid-state or magneto
resistive). (Class employing active solid-state
devices in electronic circuits. See Lines With Other Classes
and Within This Class, A, above). |
| 327, | Miscellaneous Active Electrical Nonlinear Devices, Circuits, and
Systems, appropriate subclasses for miscellaneous nonlinear
circuits utilizing an active device. (Class employing active
solid-state devices in electronic circuits. See
Lines With Other Classes and Within This Class, A, above). |
| 327, | Miscellaneous Active Electrical Nonlinear Devices, Circuits, and
Systems,
subclasses 185+ for a stable state circuit utilizing an electron
tube and a transistor and subclasses 568+ for a miscellaneous
negative resistance circuit. (See B, Lines
With Other Classes and Within This Class, above.) |
| 329, | Demodulators,
subclass 370 for diode demodulators and subclass 371 for coherer
type demodulators. (See B, Lines With
Other Classes and Within This Class, above.) |
| 329, | Demodulators,
subclass 370 for diode demodulators and subclass 371 for coherer
type demodulators. (See G, Lines With
Other Classes and Within This Class, above). |
| 330, | Amplifiers,
subclass 145 for diode type variable impedances for signal channel
controlled by a separate control path and subclasses 282+ for
semiconductor amplifier devices with gain control means and feedback
means acting as a variable impedance. |
| 330, | Amplifiers,
subclass 4.9 for semiconductor type parametric amplifiers; subclass
183 for DC interstage coupling with as nonlinear device; and
subclasses 250+ for semiconductor amplifying devices. (Class
employing active solid-state devices in electronic circuits. See Lines
With Other Classes and Within This Class, A, above). |
| 331, | Oscillators,
subclass 51 for semiconductor type cascade or tandem connected
oscillators and subclasses 107-117 for solid-state
active element oscillators. (Class employing active solid-state
devices in electronic circuits. See Lines With Other Classes
and Within This Class, A, above). |
| 331, | Oscillators,
subclasses 36+ for AFC devices using particular frequency control
means, including reactance devices (e.g., variable capacitors) and
subclass 177 for voltage sensitive capacitor type frequency adjusting
means. (See G, Lines With Other Classes
and Within This Class, above). |
| 332, | Modulators,
subclasses 105 , 116, 135+, 146, 152, 168, and
178 for modulators with discrete semiconductor devices (subclass
136 includes varactors). (See B, Lines
With Other Classes and Within This Class, above.) |
| 332, | Modulators,
subclasses 105 , 116, 135+, 146, 152, 168, and
178 for modulators with discrete semiconductor devices (subclass
136 includes varactors). (See G, Lines
With Other Classes and Within This Class, above). |
| 333, | Wave Transmission Lines and Networks,
subclass 263 for variable impedance devices connected in circuit
with a long line element or component. (See G, Lines
With Other Classes and Within This Class, above). |
| 333, | Wave Transmission Lines and NetWorks,
subclasses 103 and 104 for branched circuits with switching means
having semiconductor operating means; subclass 165 for
frequency or time domain filters using charge transfer devices; subclasses
216 and 217 for negative impedance devices; subclass 247
for semiconductor mounts for strip type long line elements; and subclass
99 for super conductive devices. (class employing
active solid-state devices in electronic circuits. See
Lines With Other Classes and Within This Class, A, above) |
| 334, | Tuners,
subclasses 66 and 69 for series tuned circuits with variable
impedance elements. |
| 334, | Tuners,
subclass 15 for semiconductor reactance tuning circuits. (See
B, Lines With Other Classes and Within This Class, above.) |
| 338, | Electrical Resistors,
subclass 1 for coherer type resistors, subclass 22
for semiconductor type thermistors, and subclass 32 for
magnetic field responsive devices, including Hall effect
types and super conductive types. (Class employing active
solid-state devices in electronic circuits. See
Lines With Other Classes and Within This Class, A, above). |
| 338, | Electrical Resistors,
subclass 1 for coherer type resistors; subclass 22
for semiconductor type thermistors; and subclass 32 for
magnetic field responsive devices, including Hall effect
types and superconductive types. (See G, Lines
With Other Classes and Within This Class, above). |
| 343, | Communications: Radio Wave Antennas,
subclass 745 for antennas with variable reactance tuning; subclass
750 for adjustable lumped reactance antenna tuning; and
subclass 861 for adjustable impedance matching network leadins. (See
G, Lines With Other Classes and Within This Class, above). |
| 340, | Communications: Electrical,
subclass 598 for barrier layer thermal sensors in condition responsive
device; subclass 815.03 for a visual indicator
using a light emitting diode; subclasses 2.2-2.31
for a channel selecting matrix; and subclasses 14.1-14.69
for a decoder matrix. |
| 341, | Coded Data Generation or Conversion,
subclasses 133+ for analog-to-digital conversion with
particular solid-state devices; subclass 150 for
digital to analog conversion using charge coupled devices or switched
capacitances; and subclass 172 for analog to digital conversion
using charge transfer devices. (See B, Lines
With Other Classes and Within This Class, above.) |
| 345, | Computer Graphics Processing and Selective Visual
Display Systems,
subclasses 30+ for selective visual display systems which may employ
active solid-state device light sources, including
subclasses 44 and 82 for visual display systems having solid-state
light emitters. (class employing active solid-state
devices in electronic circuits. See Lines With Other Classes
and Within This Class, A, above). |
| 348, | Television,
subclasses 272+ and 294+ for solid-state image
sensors in television cameras and subclasses 800+ for electroluminescent video
display with solid-state scanned matrix. (class
employing active solid-state devices in electronic circuits. See
Lines With Other Classes and Within This Class, A, above). |
| 358, | Facsimile and Static Presentation Processing,
subclasses 482 and 483 solid-state picture generators, including
charge coupled devices. (Class employing active
solid-state devices in electronic circuits. See
Lines With Other Classes and Within This Class, A, above). |
| 359, | Optical: Systems and Elements,
subclass 248 for semiconductor polarization type light modulators
and subclasses 321+ for modulators having significant chemical
composition or structure. (Class employing active
solid-state devices in electronic circuits. See
Lines With Other Classes and Within This Class, A, above). |
| 361, | Electricity: Electrical Systems and Devices,
subclass 2 for solid-state switch type arc suppressors; subclasses
98, 100, and 101 for current fault responsive
sensors involving semiconductor active solid-state devices; subclasses
196+ for semiconductor time delay devices; subclass
205 for threshold devices including SCR thyratrons; subclasses
275.1+ for electrical, e.g., fuse
element for electrolytic capacitors; subclasses 277+ for
variable capacitor not involving active solid-state devices; subclasses
525 for solid electrolytic capacitors with significant semiconductor; subclasses 679.01-679.61
for cooling devices, housings, supports, electrical
contacts, etc., for diverse electrical
components; subclass 421 for lead frames; and
subclasses 523+ for solid electrolytic capacitors. (class
employing active solid-state devices in electronic circuits. See
Lines With Other Classes and Within This Class, A, above) |
| 361, | Electricity: Electrical Systems and
Devices,
subclass 188 for variable impedance condition responsive devices
for relay or solenoid safety or protection; and subclasses
277+ for variable electrostatic capacitors. (See
G, Lines With Other Classes and Within This Class, above) |
| 361, | Electricity: Electrical Systems and
Devices,
subclass 421 for lead frames. (Class providing for
subcombination subject matter used as component part of active
solid-state electronic devices. See Lines with
Other Clases and Within This Class, F, above) |
| 362, | Illumination,
subclass 84 for light source or light source support and luminescent
material and subclass 800 (cross-reference art
collection) for light emitting diode light sources. (See B, Lines
With Other Classes and Within This Class, above.) |
| 363, | Electric Power Conversion Systems,
subclasses 10+ for combined phase and frequency conversion using
a semiconductor device converter, and subclasses 13-147
for current conversion devices many of which explicitly call for
semiconductor active solid-state devices, and
subclasses 159-163 for frequency conversion using semiconductor
type devices. (See B, Lines With Other
Classes and Within This Class, above.) |
| 365, | Static Information Storage and Retrieval,
subclasses 52+ for hardware, including shields, for storage
elements; subclass 71 for negative resistance; and
subclass 72 for transistor or diode interconnection arrangement; subclass 96
for fusible link storage elements; subclasses 103-105
for semiconductive semipermanent read only systems; subclasses
106+ for systems involving radiant energy, including
subclasses 109-115 for photoconductive, electroluminescent, amorphous, semiconductive
and diode devices; subclasses 129+ for systems
using a particular element, including subclasses 154-188
for systems using particular elements including active solid-state
devices; subclasses 185.01+ for floating
gate memory storage (e.g., flash
memory); and subclasses 208 and 212 for semiconductive
differential (e.g., thermal) noise
suppression means in read/write circuits. (Class
employing active solid-state devices in electronic circuits. See
Lines With Other Classes and Within This Class, A, above). |
| 367, | Communications, Electrical: Acoustic
Wave Systems and Devices,
subclasses 140+ for signal transducers which may be active solid-state devices, and
including support structures, diaphragm, and pressure
compensation means. (See B, Lines With
Other Classes and Within This Class, above.) |
| 368, | Horology: Time Measuring Systems or Devices,
subclass 83 for solid body light emitters, e.g., diodes; subclasses
86 and 87 for transistorized pulse transforming means; subclasses
56+ for solid-state oscillating time base circuits; and
subclasses 239+ for optical display devices, including
subclass 241 for solid-state, e.g., LED
light emitting displays. (See B, Lines
With Other Classes and Within This Class, above.) |
| 369, | Dynamic Information Storage or Retrieval,
subclass 44.12 for optical servo systems having solid-state
optical elements; subclasses 121+ for light sources, including
solid-state light source; subclass 145 for semiconductive
information handling transducers. (class employing active
solid-state devices in electronic circuits. See
Lines With Other Classes and Within This Class, A, above) |
| 372, | Coherent Light Generator,
subclasses 43 through 50for semiconductor layers and subclass 75 for semiconductor
optical laser pump devices. (class employing active
solid-state devices in electronic circuits. See
Lines With Other Classes and Within This Class, A, above). |
| 374, | Thermal Measuring and Testing,
subclass 178 for barrier layer (e.g., semiconductor
junction) heat sensors and subclasses 183+ for
current modifying sensors. (Class employing active
solid-state devices in electronic circuits. See
Lines With Other Classes and Within This Class, A, above). |
| 377, | Electrical Pulse Counters, Pulse Dividers, or Shift
Registers: Circuits and Systems,
subclasses 57 through 63for charge transfer device systems; subclass
74 for input circuits involving field-effect transistors; subclass
79 and 117 for transfer means including a field effect transistor; and
subclass 93 for superconductive elements. (class
employing active solid-state devices in electronic circuits. See Lines
With Other Classes and Within This Class, A, above) |
| 378, | X-Ray or Gamma Ray Systems or Devices,
subclass 104 for X-ray source power supplies with specified
rectifier. (See B, Lines With Other Classes
and Within This Class, above.) |
| 379, | Telephonic Communications,
subclass 294 for semiconductor line finders. (See
B, Lines With Other Classes, above.) |
| 381, | Electrical Audio Signal Processing Systems and
Devices,
subclass 100 for crossover filters with active devices and subclass
175 for semiconductor junction microphones. (see
B, Lines With Other Classes and Within This Class, above.) |
| 388, | Electricity: Motor Control Systems,
subclasses 917 through 920for thyristor or SCR devices or control circuit
elements and subclass 926 for a specific feedback control or device which
controls a solid-state device in a motor circuit. |
| 388, | Electricity: Motor Control Systems,
subclass 807 for variable impedance type field control circuits
and subclasses 855+ for selectable or variable impedance
armature control devices. (see G, Lines
With Other Classes and Within This Class, above) |
| 427, | Coating Processes,
subclasses 58 through 126.6, especially subclasses 62 and 63, 66, 74-76, 79-81, 96.1-99.5, 100, and
101-103 for coating processes to make an electrical product (for
methods of making, cleaning, coating, etc., active
solid-state devices, see Lines With Other Classes
and Within This Class, D., above). |
| 428, | Stock Material or Miscellaneous Articles,
subclass 620 for composite metallic stock having a semiconductor
component, subclasses 690 and 691 for fluorescent, phosphorescent
or luminescent inorganic layer composites; subclasses 917
for electroluminescent material; and subclasses 928-931
for materials with special properties, including magnetic
properties, electrical contact features and superconductivity. (Class
providing for materials used in active solid-state devices, Lines
With Other Classes and Within This Class, C, above). |
| 430, | Radiation Imagery Chemistry: Process, Composition, or
Product Thereof,
subclasses 56 through 96for radiation sensitive compositions or products; subclass
139 for luminescent imaging process, composition or product; and subclass
900 for donor-acceptor complex photoconductors. (Class
providing for materials used in active solid-state devices, Lines
With Other Classes and Within This Class, C, above) |
| 430, | Radiation Imagery Chemistry: Process, Composition, or
Product Thereof,
subclasses 56 through 96for radiation sensitive compositions or products; subclass
139 for luminescent imaging process, composition or product; and subclass
900 for donor-acceptor complex photoconductors. (Class
providing for methods of making, cleaning, coating, etc., active
solid-state devices, See Lines With Other Classes and
Within This Class, D, above). |
| 438, | Semiconductor Device Manufacturing:
Process, for (a) combined operations (steps) for producing
a semiconductor substrate having a junction, usually between
p-type and n-type material or (b) a
unit operation involving semiconductor material, not elsewhere
provided; see the search notes therein. (class
providing for methods of making, cleaning, coating, etc., active
solid-state devices, See Lines With Other Classes
and Within This Class, D, above). |
| 439, | Electrical Connectors, appropriate subclasses for features related or analogous
to electrical contact or housing features of active solid-state devices, e.g.,
subclasses 271+ for sealing elements, or subclasses 449+ for
stress relief means for conductor to terminal joint. (class employing
active solid-state devices in electronic circuits. See
Lines With Other Classes and Within This Class, A, above). |
| 455, | Telecommunications,
subclass 253.1 for semiconductor gain, level or volume
control; subclass 291 for receivers having a wave collector with
coupling to a stage of the receiver using an active device, and
subclass 333 for transistorized or integrated circuit type frequency conversion
structure or circuitry. (see B, Lines With
Other Classes and Within This Class, above.) |
| 455, | Telecommunications,
subclasses 261 and 262 for variable reactance, e.g., variable
capacitance type automatic local oscillator control devices. (see
G, Lines With Other Classes and Within This Class, above) |
| 505, | Superconductor Technology: Apparatus, Material, Process,
subclasses 150+ for high temperature (Tc >
30 K) superconducting devices, and particularly
subclasses 161 and 162 for bolometers or SQUIDs, subclasses 190+ for
Josephson junctions, per se, and subclasses 191+ for
other thin film solid-state devices; and pertinent
cross-reference art collections, including subclasses
831+, for static information storage and retrieval
system or device; subclasses 857+ for nonlinear
solid-state device, system, or circuit; subclasses 873+ for
active solid-state devices; subclass 883 for housing
and mounting assemblies with plural diverse electrical components; subclasses
884+ for conductors; and subclasses 900+ for
heat exchangers. (see B, Lines With Other
Classes and Within This Class, above.) |
| 505, | Superconductor Technology: Apparatus, Material, Process,
subclasses 150+ for high temperature (Tc >
30 K) superconducting devices, and particularly
subclasses 161 and 162 for bolometers or SQUIDs, subclasses 190+ for
Josephson junctions, per se, and subclasses 191+ for
other thin film solid-state devices; and pertinent
cross-reference art collections, including subclasses
831+, for static information storage and retrieval
system or device; subclasses 857+ for nonlinear
solid-state device, system, or circuit; subclasses 873+ for
active solid-state devices; subclass 883 for housing
and mounting assemblies with plural diverse electrical components; subclasses
884+ for conductors; and subclasses 900+ for
heat exchangers. (Class providing for materials
used in active solid-state devices, Lines With
Other Classes and Within This Class, C, above) |
| 600, | Surgery,
subclasses 486+ and 505 for active solid-state devices
inserted inside a body and used for measuring and testing. (class
employing active solid-state devices in electronic circuits. See
Lines With Other Classes, A, above) |
| 708, | Electrical Computers: Arithmetic Processing and
Calculating,
subclass 190 for integrated circuit type digital computers. |
| 716, | Computer-Aided Design and Analysis of
Circuits and Semiconductor Masks,
subclasses 50 through 56for design and analysis of a semiconductor mask
or reticle and subclasses 100 through 139 for the design and analysis
of circuit systems and integrated circuit structure by data processing
and computer programming techniques. |
| 902, | Electronic Funds Transfer,
subclass 26 for identification, means with a semiconductor chip, e.g., a
smart card. (see B, Lines With Other
Classes and Within This Class, above.) |
| D10, | Measuring, Testing or Signalling Instruments,
subclass 77 for transistor testers. (see
B, Lines With Other Classes and Within This Class, above.) |
| D13, | Equipment for Production, Distribution
or Transformation of Energy, appropriate subclass for semiconductor, transistor
or integrated circuit energy conversion or transformation. (see
B, Lines With Other Classes and Within This Class, above.) |
SECTION V - GLOSSARY
ACCEPTOR IMPURITY
An atom or ion different from or foreign to, but
present in, a semiconductor material and which has insufficient valence
electrons to complete the normal bonding arrangement in the semiconductor
crystal structure. An acceptor impurity accepts an electron
from an adjacent atom to create a hole. Acceptor impurities
are also referred to as p-type impurities. Common
acceptor impurities in silicon or germanium are boron, gallium, and
indium.
ACTINIDES
Ac, Th, Pa, U, Np, Pu, Am, Cm, Bk, Cf, E, Fm, Mv, No, Lw.
ALKALI METALS
Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr.
ALKALINE-EARTH METALS
Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra.
ACTIVE solid-state ELECTRONIC DEVICE
An electronic device or component that is made up primarily
of solid materials, usually semiconductors, which
operates by the movement of charge carriers - electrons
or holes - which undergo energy level changes within the
material and can modify an input voltage to achieve rectification, amplification, or
switching action. Active solid-state electronic
devices include diodes, transistors, thyristors, etc., but
exclude pure resistors, capacitors, inductors, or
combinations solely thereof. The latter class of devices
is characterized as passive.
ALLOY JUNCTION
A fused junction produced by combining one or more elemental
impurity metals with a semiconductor. Typical alloyed
junctions include indium- germanium and aluminum-silicon.
ALLOY TRANSISTOR
A transistor in which the emitter-base and collector-base junctions
are alloy junctions.
AVALANCHE BREAKDOWN
A sudden change from high dynamic electrical resistance
to very low dynamic resistance in a reverse biased semiconductor
device, e.g., a reverse biased
junction between p-type and n-type semiconductor
materials, wherein current carriers are created by electrons
or holes which have gained sufficient speed to dislodge valence
electrons. Avalanche breakdown can cause structural damage
to a semiconductor device.
AXIAL LEAD
A wire lead coming from the end of and along the axis of
a resistor, capacitor, or other component.
BACK BONDED
The bonding of active chips to a substrate using the back
of the chip opposite the side containing active solid-state
devices.
BALL BOND
A bond formed by a round, ball-shaped
lead on a semiconductor device.
BALLISTIC TRANSPORT DEVICE
An active solid-state electronic device in which
an active layer is present through which carriers* pass, wherein
the active layer is thinner than the mean free path of the carriers* in
the material in that layer, so that carriers* can
pass through the layer without scattering. Carriers* are
typically injected into the ballistic transport layer as "hot" carriers*, having
an energy, in the case of electrons, substantially
greater than the minimum of the conduction band*, or
in the case of holes, substantially lower than the maximum
of the valence band. Ballistic electron injectors include
heterojunctions, tunnel barriers, and punchthrough (e.g., planar doped
or camel) barriers.
BAND GAP
The difference between the energy levels of electrons bound
to their nuclei (valence electrons) and the energy levels
that allow electrons to migrate freely (conduction electrons).
The band gap depends on the particular semiconductor involved.
BARRIER REGION OR LAYER
A region which extends on both sides of a semiconductor
junction in which all carriers are swept away from the junction
region. The region is depleted of carriers. This
is also referred to as a depletion region.
BARRITT DIODE
Barrier injection transit time diode. A bipolar
or device in which a type of breakdown known as punchthrough occurs
and wherein the punchthrough structure device is operable at
microwave frequencies. In bipolar transistors a direct
current path is formed from emitter to collector due to the formation
of a depletion region throughout the base region and charge carriers
from the emitter punch through to the collector. Carriers
flowing from the emitter to the collector take a controlled time
to pass through the depletion layer, leading to a controlled delay
in current after a voltage is applied, and effective negative
impedance.
BASE REGION
The region between the emitter and collector of a bipolar
transistor into which minority carriers are injected by the emitter.
BASE CURRENT
The electrical current that flows in the base terminal
of a bipolar transistor.
BEAM LEADS
Flat, metallic leads which extend beyond the
edges of a chip component like wooden beams extend from a roof overhang.
Beam leads are used to interconnect a component to film circuitry.
BIAS
A direct current or voltage applied to an active solid-state
device that establishes certain operating characteristics of the
device.
BI-FET
An active solid-state electronic device that
contains both bipolar and field effect transistors.
BILATERAL
A characteristic of an active solid-state electronic
device that permits it to support current flow in opposite directions.
BINARY COMPOUND
A substance that always contains the same two elements in
a fixed atomic ratio.
BIPOLAR
An active solid-state electronic device in which
both positive and negative current carriers are used to support current
flow.
BIPOLAR TRANSISTOR
An active solid-state electronic device with
a base electrode and two or more junction electrodes in which both
positive and negative current carriers are used to support current
flow.
BLOCH WAVELENGTH
The effective wavelength of electrons in a semiconductor
crystal, sometimes referred to as a wave packet or wave function.
It can be an order of magnitude larger than the de
broglie wavelength of electrons having the same energy.
BONDING AREA
The area, defined by the extent of a metallization
land or the top surface of a terminal, to which a lead
is or is to be bonded.
BONDING PAD
A metallized area to which an electrical connection is
to be made. It is also called a bonding island or a controlled
collapse chip connection.
BONDING WIRE
Fine wire for making electrical connections in hybrid circuits
between various bonding pads on the semiconductor device substrate
and device terminals or substrate lands.
BREAKDOWN
A sudden change from high dynamic electrical resistance
to a very low dynamic resistance in a reverse biased semiconductor
device, e.g., a reverse biased junction
between p-type and n-type semiconductor materials, wherein
reverse current increases rapidly for a small increase in reverse
applied voltage, and the device behaves as if it had negative
electrical resistance.
BREAKDOWN POINT/VOLTAGE
The voltage value at which breakdown occurs.
BREAKOVER
The start of current flow in a silicon controlled rectifier.
BUCKET BRIGADE DEVICE
A charge transfer device in which only a portion of the charge
carriers (electrons or holes) at each storage
site are transferred to the next storage site.
BUMP CONTACT
A term used to describe, typically, solder
bumps on a chip or substrate which are found on only one side of
the chip or substrate as, for example, on a flip-chip.
BULK-CHANNEL CCD
A charge coupled device in which charge is stored and transferred
below the surface of the device.
BULK-EFFECT DEVICE
An active solid-state device made up of a semiconductor material
whose electrical characteristics and electronic properties are exhibited
throughout the entire body of the material, rather than
in just a localized region thereof, e.g., the
surface.
BURIED CHANNEL CCD
See BULK-CHANNEL CCD.
CB JUNCTION
The collector-base junction of a bipolar transistor.
CAPACITOR
A component used in electrical and electronic circuits which
stores a charge of electricity, usually for very brief
periods of time, with the ability to rapidly charge and
discharge. A capacitor is usually considered a passive
component since it does not rectify, amplify, or switch
and because charge carriers do not undergo energy level changes
therein, although some active solid-state devices
function as voltage variable capacitors.
CARRIER
A mobile free electron or hole.
CARRIER CONCENTRATION
The number of electrical charge carriers in a given volume, usually
a cubic centimeter, of semiconductor material.
CELL
An individual integrated circuit element located on a large, or
master chip of, semiconductor material.
CHANNEL
A path for conducting current between a source and drain
of a field effect transistor.
CHANNEL LENGTH EFFECTS
Operating characteristics of FETs which depend on the length (distance
between source and drain) of the channel regions.
Such effects include switching speed change and threshold voltage
change with channel length change.
CHANNEL WIDTH EFFECTS
Operating characteristics of FETs which depend on the width (horizontal
distance perpendicular to channel length and parallel to upper surface
of device) of the channel. Such effects include
conductance and threshold voltage change with channel width change.
CHANNEL STOP
Means for limiting channel formation in a semiconductor
device by surrounding the affected area with a ring of highly doped, low
resistivity semiconductor material. In a field effect
transistor, it is a region of highly doped material of
the same type as the lightly doped substrate used to prevent leakage
paths along the chip surface from developing. Also referred
to as "chanstop."
CHANNEL PINCH-OFF REGION
The location in a current channel portion of a field
effect transistor (FET) where the current is reduced
to a minimum value due to its diameter being reduced to a minimum.
CHARACTERISTIC CURVE
A graph showing the relationship between two or more changing
parameters, e.g., current and
voltage of an electronic device.
CHARGE CARRIER
A mobile conduction electron or hole in a semiconductor.
CHARGE CONFINEMENT
Restriction of electrical charge carriers, e.g., electrons
or holes, to specified locations, e.g., by
quantum wells, gate electrode potentials, etc.
CHARGE-COUPLED DEVICE
A charge transfer device in which all carriers (electrons or
holes) are transferred from one storage site to the next upon
application of a shifting voltage.
CHARGE INJECTION DEVICE
A field effect device in which storage sites for packets of
electric charge are induced at or below the surface of an active
solid-state device by an electric field applied to the
device and wherein carrier potential energy per unit charge minima
are established at a given storage site and such charge packets
are injected into the device substrate or into a data bus.
This type device differs from a charge transfer device in that, in
the latter, charge is transferred to adjacent charge storage
sites in a serial manner, whereas, in a charge
injection device, the charge is injected in a non-serial
manner to the device substrate or to a data bus.
CHARGE TRANSFER DEVICE
A semiconductor device in which discrete packets of electrical
charge are transferred from one location to another. Examples
of charge transfer devices include charge-coupled devices (CCDs) and
bucket-brigade devices (BBDs).
CHIP
A single crystal substrate of semiconductor material
on which one or more active or passive solid-state electronic
devices are formed. A chip may contain an integrated circuit.
A chip is not normally ready for use until packaged and provided
with external connectors.
CHIP CARRIER
A package with terminals, for solid-state
electronic devices, including chips which facilitates handling
of the chip during assembly of the chip to other electronic elements.
CHIP COMPONENT
A circuit element (active or passive) for
use in microelectronics. Besides integrated circuits, the
term includes diodes, transistors, resistors, and
capacitors.
CIRCUIT
A number of devices interconnected in a one or more closed
paths to perform a desired electrical or electronic function.
CLADDING BARRIER
A higher band gap material which encases a lower band gap
material that defines the walls of a quantum well.
CMOS
See COMPLEMENTARY METAL OXIDE SEMICONDUCTOR.
COHERENCE LENGTH
The typical distance an electron can travel before it
is scattered (e.g., by a phonon, a
defect, or an impurity).
COHERER
A term which encompasses both active and passive type devices, the
passive type being a resistor whose resistance decreases when subjected
to a high frequency signal, and the active type being a
rectifier which is made up of active solid-state particles
which conduct and rectify current when connected into a cohesive
element but which loses that characteristic when the particles are separated (e.g., by
shaking a container in which the particles are located).
COLLECTOR
That end region of a bipolar transistor which forms one of
the main current regions and which is reverse biased in operation
with respect to the base region.
COLLECTOR CURRENT
The current which flows through the terminal of the collector
region of a bipolar transistor.
COLLECTOR DIFFUSION ISOLATION (CDI)
An electrical isolation technology used for bipolar devices
which employs an epitaxial layer, which forms transistor
base regions, laid on a substrate of the same conductivity
type (p or n) as the epitaxial layer, with
an opposite conductivity type region, more heavily doped than
the epitaxial base layer and located between the layer and the substrate, forming
the collector and isolating the transistor from the substrate.
COMMON-BASE CONFIGURATION
A bipolar transistor in which the base region is common to
both the input and output circuit. This is also known as
a grounded-base bipolar transistor circuit.
COMMON-COLLECTOR CONFIGURATION
A bipolar transistor in which the collector region is common
to both the input and output circuit. It is also known
as an emitter-follower bipolar transistor circuit.
COMMON-DRAIN CONFIGURATION
A unipolar transistor in which the drain region is common
to both the input and output circuit.
COMMON-EMITTER CONFIGURATION
A bipolar transistor in which the emitter region is common
to both the input and output circuit. It is also known
as a grounded-emitter bipolar transistor circuit.
COMMON- or GATE-CONFIGURATION
A unipolar transistor in which the gate region is common
to both input and output circuits.
COMPLEMENTARY METAL OXIDE SEMICONDUCTOR (CMOS)
Both n-type and p-type metal oxide
semiconductor devices, e.g., transistors, formed
on the same substrate.
COMPONENT
An electronic device - active or passive - which
has distinct electrical characteristics and has terminals for connection
to other components to form a circuit.
COMPOUND
A homogeneous material which has definite proportions of
chemically combined atoms or ions.
CONCENTRATION GRADIENT
A difference in dopant concentration (p- or
n-type) from one position to another in a semiconductor.
CONDUCTION BAND
A partially filled energy band in which electrons can move
freely, permitting a material to carry electric current
where electrons are the current carriers.
CONDUCTION ELECTRONS
In a conductor or n-type semiconductor, outer
shell electrons that are bound so loosely that they can move freely
in the conduction band of a solid material under the influence of
an electric field.
CONDUCTIVITY
The ability of a material to conduct electric current.
Its converse is resistivity.
CONDUCTOR
A material which offers comparatively little resistance to
the flow of current.
CONDUCTOR SPACING
The distance between adjacent edges (not centerline
to centerline) of isolated conductive patterns in a conductor
layer.
CONNECTOR AREA
That portion of metallized conductors used for providing
external electrical connections from a component to a chip or other
component.
CONTACT
The parts of a conductor designed to touch or be touched
by other such parts of an electrical conductor to carry current
to or from the conductor.
CONTACT WINDOW
An opening in an insulating layer to expose an underlying
conductor to permit electrical contact thereto. It is also
called a via hole.
COVALENT BONDING
The sharing of electrons by atoms in which each atom contributes
one of a pair of electrons shared by another atom and forming a
bond between those two atoms.
CRYOSAR
An active solid-state device which operates
at cryogenic temperatures, i.e., at
temperatures at or below 77 degrees Kelvin, by avalanche
breakdown caused by impact ionization of device impurities.
CRYSTAL
A solid substance whose atoms are arranged with periodic
geometric regularity, called a lattice.
CRYSTAL DEFECT
Any nonuniformity in a crystal lattice. There
are four categories of crystal defects: (1) point
defects, (2) line defects, (3) area
defects, and (4) volume defects.
Point defects include any foreign atom at a regular lattice site (substitutional
site) or between lattice sites (interstitial site), anti-site
defects in compound semiconductors, e.g., Ga
in As or As in Ga, missing lattice atoms, and host
atoms located between lattice sites and adjacent to a vacant site (Frenkel
defects). Line defects, also called edge
dislocations, include extra planes of atoms in a lattice.
Area defects include twins or twinning (a change in crystal
orientation across a lattice) and grain boundaries (a
transition between crystals having no particular positional orientation
to one another. Volume defects include precipitates of
impurity or dopant atoms caused by volume mismatch between a host
lattice and precipitates.
CUTOFF
A minimum value of voltage or current applied to an active
device which stops the device from operating in a particular manner.
DE BROGLIE WAVELENGTH
The wavelength of a particle, based on L.V. de
Broglie"s theory that particles exhibit wavelike characteristics.
DEEP DEPLETION
The condition in which a depletion layer formed in
a MOS active device due to voltage applied to the gate electrode
of the device, is deeper than the maximum depth at which
inversion would normally be expected to occur at room temperature
in a semiconductor device at the surface closest to the gate electrode, without
formation of an inversion layer.
DEEP GROOVE ISOLATION
Electrical isolation of adjacent devices in a single
monolithic semiconductor chip by grooves extending deeply into
and below the surface of the chip between the devices.
DEEP-LEVEL CENTERS
Energy levels that can act as traps located in the forbidden
band of a semiconductor material that are not near the conduction
or valence band edges.
DEGENERATION
Doping of a semiconductor to such an extent that the Fermi
level lies within the conduction band (N+ semiconductor) or
within the valence band (P+ semiconductor).
Also, in circuit applications, negative feedback between
two or more active solid-state devices.
DEPLETION LAYER
See DEPLETION REGION.
DEPLETION MODE
The operation of a field-effect transistor having
appreciable channel conductivity for zero gate- source
voltage and whose channel conductivity may be increased or decreased
according to the polarity of the applied gate-source voltage, by
changing the gate-to-source voltage from zero
to a finite value, resulting in a decrease in the magnitude
of the drain current.
DEPLETION REGION
The region extending on both sides of a reverse biased semiconductor
junction in which free carriers are removed from the vicinity of
the junction. It is also called a space charge region, a
barrier region, or an intrinsic semiconductor region.
DEVICE (ACTIVE)
The physical realization of an individual electrical
element in a physically independent body which cannot be further
divided without destroying its stated function. Examples
are transistors, pnpn structures, and tunnel diodes.
DIE
A tiny piece of semiconductor material, separated
from a semiconductor slice, on which one or more active electronic
components are formed. Sometimes called a chip.
DIE BOND
Attachment of a semiconductor chip to a substrate or chip
carrier or package, usually with an epoxy, eutectic, or
solder alloy.
DIFFUSED JUNCTION
A junction between two different conductivity regions within
a semiconductor and which is formed by diffusion of appropriate
impurity atoms into the material.
DIFFUSED TRANSISTOR
A transistor in which the emitter and collector junctions are
formed by diffusion of dopant atoms into the semiconductor material.
DIFFUSION
(1) The movement of carriers from a
region of concentration to one of lower concentration; (2) a
process of adding impurities to a semiconductor material to change its
electrical characteristics.
DIFFUSION BARRIER
An obstacle to the diffusion of charge carriers in an active
solid-state device.
DIFFUSION CURRENT
Current caused by charge carriers diffusing from a volume
of high carrier concentration to a volume of lower carrier concentration
in a solid-state material.
DIFFUSION LENGTH
In a homogeneous semiconductor material, the
average distance minority carriers move during their lifetime (i.e., between
generation and recombination).
DIODE
An electronic device which has two terminals and an asymmetrical
or nonlinear voltage-current characteristic.
DIODE ISOLATION
A technique in which a high electrical resistance between
an integrated circuit element and its substrate is achieved by surrounding
the element with a reverse biased pn junction.
DIP (DUAL-IN-LINE PACKAGE)
A chip carrier or package consisting of a plastic or ceramic
body with two rows of vertical leads in which a semiconductor integrated
circuit is assembled and sealed. The leads are typically
inserted into a circuit board and secured by soldering.
DIRECT BAND GAP SEMICONDUCTOR
A semiconductor material in which an electron transition
from the conduction to the valence band, or vice versa, does
not require a change in crystal momentum for the electron.
Gallium arsenide is a direct band gap semiconductor material.
DISCRETE CIRCUIT
A circuit which has an individual identity and which
is fabricated prior to installation, or is separately packaged and
is not part of an integrated circuit.
DISLOCATION
A region in a crystal in which the atoms are not arranged
in a perfect lattice-like structure. See CRYSTAL
DEFECT for examples of crystal defects/dislocations.
DMOSFET
Depletion type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor.
Such devices are normally in the on condition with no applied gate
voltage.
DONOR IMPURITY
An element which when added to a semiconductor provides
unbound or free electrons to the semiconductor which may serve
as current carriers. Typically, donors are atoms
which have more valence electrons than the atoms of the semiconductor
material into which they are introduced in small quantities as an
impurity or dopant. Since such donor impurities have more
valence electrons than the semiconductor, a semiconductor doped
with donor impurities is an n-type semiconductor.
DOPANT
An impurity added to a semiconductor material to change
its electrical conductivity or other characteristics.
N-type (negative) dopants, such
as phosphorus, for a group IV semiconductor such as silicon
typically come from group V of the periodic table. When
added to silicon n-type dopants create a material that
contains conduction electrons. P-type (positive) dopants, such
as boron, for a group IV semiconductor such as silicon, typically
come from group III and result in holes.
DOPING PROFILE
The point to point concentration throughout a semiconductor
of an impurity atom doped into the semiconductor.
DOUBLE-DIFFUSED MOS (DMOS)
A metal oxide semiconductor having diffused junctions in
which successive diffusions of different impurity types are made
in the same well-defined region of the semiconductor.
DRAIN
The electrode of a field effect transistor which receives charge
carriers which pass through the transistor channel from the source
electrode.
DRAIN CURRENT
The flow of charge carriers in the drain region of a
field effect transistor.
DRAIN-SOURCE SATURATION CURRENT
The maximum amount of current carried by the drain of a
field-effect transistor when the gate- source
voltage equals zero volts.
DRIFT CURRENT
Current produced in a solid-state electronic
device by charge carriers (e.g., holes
or electrons) drifting in the direction of an applied electric
field.
DUAL GUARD-BAND ISOLATION
A type of electrical isolation of functional elements
of an integrated circuit comprised of two distinct unused areas
of chip surface area adjacent to the elements desired to be electrically
isolated.
DUAL-IN-LINE (DIP)
See DIP.
DYNAMIC RANDOM ACCESS MEMORY (DRAM)
solid-state memory in which the information
decays over time and needs to be periodically refreshed.
EB JUNCTION
Emitter base junction in a bipolar transistor.
ELECTRON
The negatively charged particle in an atom that orbits the
nucleus in specific energy levels.
ELECTRON FLOW
Movement of electrons from a source of negative potential
to a positive potential.
ELECTRON-HOLE PAIR
A positive charge carrier (i.e., hole) and
a negative charge carrier (i.e., electron) considered
together as being created or destroyed as part of one and the same event.
EMITTER
The region of a bipolar junction transistor from which charge
carriers flow through the emitter-base junction into the
base region of the device.
EMITTER CURRENT
The amount of current flowing from the emitter across the
emitter-base junction into the base region of the device.
E-MOSFET
Enhancement mode metal oxide semiconductor device. See
ENHANCEMENT MODE and MOSFET.
ENERGY LEVELS
The possible energy values that an atom or molecule or subatomic
particle (e.g., an electron) can
have.
ENHANCEMENT MODE
The operation of a field effect transistor which has
a channel formed therein between its source and drain regions and
which normally does not conduct current through its channel with
zero voltage applied to its gate electrode. Voltage of
the correct polarity will accumulate minority carriers in the channel
to permit conduction of current in the channel, thus turning
on the transistor.
EPITAXY
The growth of a crystal of one substance on the surface of
a crystal of the same or another substance so that the crystal lattice
of the base substance controls the orientation of the atoms in the
grown crystal.
EPITAXIAL LAYER
An added layer of crystal that takes on the same crystalline
orientation as the substrate crystal.
ESAKI DIODE
A heavily doped pn junction diode where conduction occurs
through the junction potential barrier due to a quantum mechanical
effect even though the carriers which tunnel through the potential
barrier do not have enough energy to overcome the potential barrier.
Esaki tunneling involves a tunneling barrier formed by a macroscopic
depletion layer between n-type and p-type regions.
It does not involve a resonant
tunneling barrier using controlled quantum confinement, a
layer located between junctions, nor a thin superlattice
layer.
EXCESS CARRIERS
Charge carriers present in a semiconductor in excess
of those present in thermal equilibrium.
EXTRINSIC SEMICONDUCTOR
A semiconductor whose charge carrier concentration and, therefore, electrical
properties depend on impurity, atoms introduced therein.
FACE BONDED
A chip mounting technique wherein semiconductor chips
are provided with small mounting pads, turned face down, and
bonded directly to conductors on a substrate.
FANNED LEADS
Leads placed through a package wall at closer intervals than
normal and radiated (fanned) out on the exterior
of the package until a desired center-to-center
lead spacing is achieved.
FET
Acronym for field effect transistor.
FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR
A unipolar transistor in which current carriers are injected
at a source terminal and pass to a drain terminal through a channel
of semiconductor material whose conductivity depends largely on
an electric field applied to the semiconductor from a control electrode.
There are two main types of FET, a junction FET and an
insulated-gate FET. In the junction FET, the
gate is isolated from the channel by a pn junction. In
an insulated-gate FET, the gate is isolated from
the channel by an insulating layer, so that the gate and
channel form a capacitor with the insulating layer as the capacitor
dielectric.
FIELD OXIDE
A thin (on a macroscopic scale) film
made up of an oxide of a material which overlies a device substrate
to reduce parasitic capacitive coupling between conductors overlying
the oxide and the substrate or devices below the oxide layer (e.g., in
the substrate).
FLAT PACK
An integrated circuit package with leads extending from
it in the same plane as that of the package. It has a low
profile.
FLIP-CHIP
A term which describes the situation wherein a semiconductor
device which has all terminations on one side thereof in the form
of bump contacts, has a passivated surface and has been
flipped over and attached to a matching substrate.
FLOATING DIFFUSION
A region of a semiconductor device in which impurity atoms
have been doped and which is electrically floating, that
is, has no direct electrical connection.
FLOATING GATE
A gate electrode that is electrically floating, that
is, has no direct electrical connection.
FOOTPRINT
Also called a land pattern. It is a combination
of lands used to mount a surface mount component. Metal
pads on a substrate surface are arranged in the same pattern as
the leads or pads on the component itself.
FORBIDDEN ENERGY BAND/REGION/GAP
The energy band of a material which is located between a
solid material"s conduction and valence bands. It is defined
by the amount of energy that is needed to release an electron from
its valence band to its conduction band. Electrons cannot
exist in this gap. They are either below it, and
bound to an atom, or above it, and able to move
freely.
FORWARD BIAS
An external voltage applied in the conducting direction of
a pn junction. A positive potential is connected to the
p-type material and a negative potential to the n-type semiconductor
material.
FORWARD BREAKOVER POTENTIAL
The value of positive terminal voltage at which a regenerative
device (e.g., a silicon controlled
rectifier), with its gate circuit open, becomes
conductive.
FORWARD CURRENT
The current which flows across a semiconductor junction
when a forward bias is applied across the junction.
FOUR-LAYER DIODE
A semiconductor diode with three junctions and only two
terminals connected to the outer layers forming the junctions. This
includes two terminal pnpn thyristors.
FOUR-PHASE CCD
A charge coupled device having four electrode sets and four
gate voltages.
FOUR-SIDE LEAD LAYOUT
The situation wherein there are leads through all four sides
of an integrated circuit package.
FRAME TRANSFER CCD
A charge coupled device area imager array with a separate
image area, storage area, and read-out
register area, the storage area being located between the
image area and the readout area. This is distinguished
from an interline-transfer CCD in which the sensing and
storage/readout function areas are located next to each
other.
FREE ELECTRON
An electron not bound to a particular atom, but
free to circulate among the atoms of a solid material.
GAIN
The ratio of the magnitude of the electrical output of
a device to the magnitude of its electrical input.
GALLIUM ARSENIDE
A semiconducting chemical compound which is often used
in active solid-state devices.
GATE
The control electrode or region of a field effect transistor, located
between the source and drain electrodes, and regions thereof.
GATE ARRAY
A repeating geometric arrangement of groups of active solid-state
devices, each group being connectable into a logic circuit, in
one integrated, monolithic semiconductor chip.
GATE CHARGE
The electrical charge on a gate electrode.
GATE CONTROLLED DIODE
A three terminal semiconductor diode with the ability
to be turned on or off by a pulse applied to its gate electrode.
GATE TRIGGER CURRENT
The amount of current needed to commence gate current flow
in a four layer semiconductor device (e.g., a
thyristor).
GATE TRIGGER VOLTAGE
The amount of voltage needed to begin gate current flow
in a four layer semiconductor device (e.g., a
silicon controlled rectifier).
GERMANIUM
A semiconductor material used in active solid-state devices.
GULL-WING
The name given to lead configurations of some surface mounted
devices. Gull wings extend from the side of a component
package and have an L-shaped bend at component ends, which
extend down to the substrate surface and away from the component.
GUNN DIODE
A diode in which electrons under the influence of sufficiently
high electric fields are transferred between energy valleys of different
momentum in the conduction band of the active semiconductor device
material or holes under the influence of sufficiently high electric fields
are transferred between energy valleys of different momentum in
the valence band of the active semiconductor device material.
A Gunn diode does not normally have a pn junction and cannot be
used as a rectifier.
GUNN EFFECT
An inter valley transfer effect wherein electrons under the
influence of sufficiently high electric fields are transferred between
energy valleys of different momentum in the conduction band of
the active semiconductor device material, or holes under
the influence of sufficiently high electric fields are transferred
between energy valleys of different momentum in the valence band
of the active semiconductor device material.
HALL EFFECT DEVICE
An active solid-state device in which a current
is flowing and is in a magnetic field perpendicular to the current, and
in which a voltage is produced that is perpendicular to both the
current flow direction and the magnetic field direction.
HALOGENS
F, Cl, Br, I, At.
HEADER
A slab-like or flat plug-in base for
a package that is designed to be used with a cover or lid.
HEAT SINK
Devices used to absorb or transfer heat away from heat sensitive
devices or device components.
HEAVY METALS
Metals other than light metals - see LIGHT METALS.
HETEROJUNCTION /HETEROINTERFACE
An interface between two dissimilar semiconductor materials.
For example, one material may by InAs and the other may
be InAlAs, or one material may be GaAs and the other material
may be GaAlAs.
HETEROSTRUCTURE
See HETEROJUNCTION.
HIGH ELECTRON (HOLE) MOBILITY TRANSISTOR (HEMT)
A heterojunction field effect transistor with impurity ions
located on the side of the hetero junction with lower affinity for
the charge carriers (holes or
electrons) injected at the source that pass to the drain
via a channel adjacent the hetero junction.
HOLDING CURRENT
The minimum current needed to maintain a generative type
active solid-state device (e.g., a
thyristor) in an "on" or conducting condition.
HOLE
An empty energy level in the valence band of a semiconductor
crystal which exhibits properties of a real particle and can act
as a mobile positive charge carrier.
HOLE FLOW
The current in a semiconductor material due to the movement
of holes therein.
HOMOJUNCTION
An interface between regions of opposite polarity in
the same semiconductor material.
HOT CARRIER DIODE
A diode in which electrons (or holes) have
energies greater than those that are in thermal equilibrium with the
material of at least one of the regions forming the diode.
Schottky barrier diodes typically have "hot carriers" (hot
electrons) injected into the metal from the semiconductor.
HOT ELECTRONS
See HOT CARRIER DIODE.
HYBRID CIRCUIT
A small printed circuit having miniature components, which
may include passive components (resistors, capacitors, and
inductors, deposited on a printed circuit board.
A "hybrid circuit" is NOT an integrated circuit, and
is not classifiable in this class.
IMPURITY
A foreign material present in a semiconductor crystal, such
as boron or arsenic in silicon, which is added to the
semiconductor to produce either p-type or n-type semiconductor
material, or to otherwise result in material whose electrical
characteristics depend on the impurity dopant atoms.
INDIRECT BAND GAP SEMICONDUCTOR
A semiconductor material in which a change in semiconductor
crystal momentum for an electron is required when it moves from
the conduction band to the valence band and vice versa.
Silicon is an indirect band gap semiconductor.
INSULATED-GATE FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR (IGFET)
A unipolar transistor with source, gate, and
drain regions and electrodes, in which conduction takes
place in a channel controlled by action of the voltage applied to
the gate electrode of the device, in which the gate electrode
is separated from the channel by an insulator layer.
INSULATOR
A material which has a high resistance to the flow of electric
current. It has such low electrical conductivity that
the flow of current therethrough can usually be neglected.
INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
See MONOLITHIC DEVICE (e.g., IC) as
contrasted to HYBRID CIRCUIT.
INTRINSIC CONCENTRATION
The number of minority carriers in a semiconductor due to
thermal generation of electron-hole pairs.
INTRINSIC SEMICONDUCTOR
A pure semiconductor, i.e., one
with no impurity atoms introduced therein.
INVERSION
A condition in a semiconductor material in which the concentration
of minority carriers exceeds the concentration of majority carriers.
INVERSION LAYER/CHANNEL
A region in a semiconductor material in which the concentration
of minority carriers exceeds the concentration of majority carriers.
IRON GROUP METALS
Fe, Co, Ni.
ISOLATION
Prevention of the flow of electric current between electronic
component parts of a solid-state electronic device.
ISOPLANAR CMOS
A semiconductor device in which relatively thick regions
of silicon dioxide, recessed into the semiconductor surface, are
used to electrically isolate device areas and prevent parasitic
device formation. More commonly called LOCOS CMOS.
ISOPLANAR ISOLATION
A type of electric isolation in which relatively thick regions
of silicon dioxide, recessed into the semiconductor surface, are
used to electrically isolate device areas and prevent parasitic
device formation. More commonly called LOCOS ISOLATION.
J-LEAD
A rolled-under, J-shaped configuration
of some surface mounted component leads.
JUNCTION
A joining of two different semiconductors or of a semiconductor
and a metal at an interface. Types of junctions include
HETEROJUNCTIONS, SCHOTTKY BARRIER JUNCTIONS, and
PN JUNCTIONS.
JUNCTION BARRIER
The opposition to the diffusion of majority carriers across
a pn junction due to the charge of the fixed donor and acceptor
ions.
JUNCTION CAPACITANCE
The capacitance across a pn junction. It depends
on the width of the depletion layer, which increases with increased
reverse bias voltage across the junction.
JUNCTION GATE FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR (JFET)
See FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR.
JUNCTION ISOLATION
Electrical isolation of devices on a monolithic integrated circuit
chip using a reverse biased junction diode to establish a depletion
layer that forms the electrical isolation between devices.
JUNCTION RESISTANCE
The electrical resistance across a semiconductor PN junction.
LAND
The conductive areas, normally metal patterns, on
a semiconductor integrated circuit, which form part of
the contacts and interconnections between components on the integrated
circuit.
LAND PATTERN
A combination of lands on an integrated circuit.
LANTHANIDE ELEMENTS
La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Pm, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho,Er, Tm, Yb, Lu.
LATCHING/LATCHED/LATCHUP
The state or condition of a regenerative feedback device, e.g., a
thyristor, in which the device remains ON when the initializing
signal is removed.
LCCC
An abbreviation for a leadless ceramic chip carrier which
is a hermetically-sealable ceramic package in which an
integrated chip can be placed to create a surface mounted component.
It has pads around its perimeter for connection to a substrate.
LEAD
The conductor brought out from a component.
LEAD FRAME
A metal frame which provides support for an integrated circuit
chip or die as well as electrical leads to interconnect the integrated
circuit on the die or chip to other electrical components or contacts.
LEAKAGE CURRENT
Unwanted current flow.
LIFETIME
The average time interval between the introduction of and
recombination of minority charge carriers in a semiconductor.
LIGHT EMITTING DIODE (LED)
Junction diodes which give off light when energized.
LIGHT METALS
Alkali metals, alkaline-earth metals, Be, Al, Mg.
LINE DEFECT
A planar crystal defect (e.g., an
extra plane of atoms in a crystal). It is also
called an edge dislocation.
LOCAL OXIDE CMOS (LOCMOS)
Local oxide complementary metal oxide semiconductor structure
which features oxide isolation which is recessed into the semiconductor
surface.
LOCOS
(Local Oxidation of Silicon) Patterns
of oxide isolation which are recessed into the semiconductor surface. Sometimes
also called isoplanar, ROX (Recessed Oxide Isolation), or
planox.
LUMINESCENCE
Emission of light by directly converting some other type of
energy. Types include thermoluminescence, photoluminescence, cathodoluminescence, and
electroluminescence. It includes fluorescence and phosphorescence. Active
solid-state luminescent devices are semiconductors which
operate via injection luminescence. Active devices include
pn junctions (including heterojunctions), Schottky
barrier junctions, metal-insulator-semiconductor (MIS) structures, and
high speed traveling domains, e.g., Gunn
domain and acoustoelectric wave generated domains; whereas
passive solid-state electroluminescent devices (phosphors) are
insulators which operate in an intrinsic luminescence phenomena, i.e., where
an applied electric field generates free carriers (there
being no free carriers in an insulator to be accelerated by an applied
field unless the field also generates them) to initiate
the light emission mechanism.
MAJORITY CARRIER
The predominant charge carrier in a semiconductor. Electrons
are majority carriers in n-type semiconductors.
Holes are majority carriers in p-type semiconductors.
MAJORITY CURRENT
Current caused by the flow of majority carriers.
MASTERSLICE ARRAY/MASTERCHIP
A substrate that contains active and passive electronic components
in a predetermined pattern which may be connected into different
logic or analog circuits.
MBM JUNCTION
Active solid-state devices having metal-barrier-metal layer
junctions.
METAL-OXIDE SEMICONDUCTOR FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR (MOSFET)
See INSULATED GATE FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR.
METAL-GATE FET
A field effect transistor having a gate conductor made
of metal, rather than polycrystalline semiconductor material.
METALLIZATION
A single or multilayer film pattern of electrically conductive
material deposited on a substrate to interconnect electronic components, or
the metal film on the bonding area of a substrate which becomes
part of the bond and performs both an electrical and a mechanical
function.
METALS
Elements other than non-metals. See
NON-METALS.
MIM DIODE
A junction diode with a thin insulating layer of material sandwiched
between two metallic surface layers which operates as a tunneling (direct
or Fowler-Nordheim type) diode.
MINORITY CARRIER
The less predominant charge carrier in a semiconductor. In
a p-type semiconductor, minority carriers are
electrons, whereas in n-type semiconductor material, minority
carriers are holes.
MINORITY CURRENT
The current caused by flowing minority carriers.
MIS
Acronym for metal-insulator-semiconductor.
Typically active solid-state devices with MIS technology
have a silicon dioxide layer formed on a single crystal silicon substrate.
A polysilicon conductor layer is formed on the oxide.
MOBILITY
The facility with which carriers move through a semiconductor
when subjected to an applied electric field. Electrons
and holes typically have different mobilities in the same semiconductor.
MODFET
Acronym for a modulation doped field effect transistor. A
high speed semiconductor FET in which dopant atom containing semiconductor
layers alternate with non-doped semiconductor layers, so
that the carriers (electrons or holes) resulting
from the dopant atoms can travel in the undoped material, so
that there is little scattering of carriers from dopant atoms.
Typically, the dopant atoms are in semiconductor material
having a lower carrier affinity than the undoped layers, to
facilitate carrier spill over into the undoped layers.
Such a structure may typically constitute a superlattice.
See also HIGH ELECTRON MOBILITY TRANSISTOR (HEMT).
MODULATION DOPING
Spatial modulation of dopant atoms in a semiconductor crystal.
MONOLITHIC DEVICE (e.g., IC)
A device in which all components are fabricated on a single
chip of silicon. Interconnections among components are
provided by means of metallization patterns on the surface of the
chip structure, and the individual parts are not separable
from the complete circuit. External connecting wires are
taken out to terminal pins or leads.
MSM
Acronym for metal-semiconductor-metal
semiconductors. Active solid-state semiconductor
devices having a semiconductor layer sandwiched between two layers
of metal.
MULTILAYER METALLIZATION
Two or more layers of interconnecting metallization patterns
in a monolithic integrated circuit separated by insulator material
except in interconnection areas.
N-TYPE SEMICONDUCTOR
An extrinsic semiconductor in which electron density exceeds
hole density.
NDM
Negative differential mobility (e.g., Gunn
effect) intervalley active semiconductor devices wherein
an applied electric field imparts energy to electrons or holes
to permit them to jump to higher quantum electronic intervalley
energy levels in which electrons have lowered electron mobility.
NEGATIVE RESISTANCE REGION
An operating region of an active solid-state
electronic device in which an increase in applied voltage results
in a decrease in output current.
NEGATIVE TEMPERATURE COEFFICIENT
The amount of reduction in a device parameter, such
as capacitance or resistance, for each degree of device operating
temperature.
NMOS
N-channel metal oxide semiconductor devices
which use electrons as majority carriers.
NOBLE GASES
He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn.
NON-METALS
H, B, C, Si, N, P, O, S, Se, Te, noble
gases, halogens.
NPN TRANSISTOR
A transistor in which the base is made of p-type
material and both source and drain are made of n-type semiconductor
material.
N-CHANNEL FET
A field effect transistor that has an n-type
conduction channel.
N-TYPE SEMICONDUCTOR
An extrinsic semiconductor having n-type dopant atoms, e.g., atoms
with one more valence electron than the host atoms.
ORGANIC SEMICONDUCTOR
A semiconductor compound in which the molecule is characterized
by two or more carbon atoms bonded together, one atom of
carbon bonded to at least one atom of hydrogen or halogen (i.e., chlorine, fluorine, bromine, iodine) or
one atom of carbon bonded to at least one atom of nitrogen by a
single or double bond.
| | (1)
Note. Exceptions to thisrule
include HCN, CN-CN, HNCO, HNCS, cyanogen
halides, cyanamide, fulminic acid, and
metal carbides. These are not regarded as organic semiconductor
materials. Also, note that graphite and diamond
are not regarded as organic semiconductors since they are not compounds; silicon
carbide is not regarded as organic. |
OXIDE ISOLATION
Electrical isolation of semiconductor electronic devices in
a monolithic integrated circuit by an oxide (e.g., silicon
oxide).
PACKAGE
A container, case, or enclosure for
protecting a solid-state electronic device from the environment.
PAD
(1) The portion of a conductive pattern
on a solid-state electronic device for making external
connection thereto; (2) the portion of
a conductive pattern on a chip or a printed circuit board designed
for mounting or attaching a substrate or solid-state active
electronic device.
PARASITIC CURRENT
Unintended current which flows between devices in an integrated
circuit, or which flows between device regions and isolation
regions.
PARASITIC DEVICES/CHANNELS
Junctions forming unintended active solid-state
devices which interconnect intended active solid-state
devices, which unintended devices are not designed to carry
current flow.
PARASITIC THYRISTOR ACTION
Unwanted active solid-state device formation
in which four adjacent complementary doped regions not designed
to act as an active solid-state device, lack sufficient
isolation therebetween and act as a thyristor. Parasitic
thyristor action is typically a problem encountered in CMOS integrated
circuits.
PARASITIC TRANSISTOR ACTION
Unwanted transistor formation in an integrated circuit structure.
PASSIVE DEVICE
A solid-state electronic device or component
in which charge carriers do not change their energy levels and that
does not provide rectification, amplification, or switching, but
which does react to voltage and current. Examples are
pure resistors, capacitors, and inductors.
P-CHANNEL
A conduction path, made of p-type
semiconductor material, located between the source and
drain of a field effect device.
PERISTALTIC CCD
See BULK CHANNEL CCD.
PERMISSIBLE ENERGY LEVEL
An energy level in a conduction or valence band which
a charge carrier (electron or hole) may have.
PHOTODIODE
A diode in which charge carriers are created by light which
illuminates the diode junction. It is a photovoltaic as
well as a photoconductive device.
PHOTOTRANSISTOR
A transistor having no base terminal and in which charge
carriers are created by light which illuminates its collector-base
junction.
PHOTOVOLTAIC CELL
An active solid-state device with a pn junction
that generates a voltage in response to light impinging on the junction.
PINCH-EFFECT RESISTOR
A monolithic integrated circuit resistor having a layer
of one conductivity type, typically a P-layer
formed at the same time as integrated circuit bipolar transistor
base regions, which is thinned by an inset region of opposite conductivity
type, typically an N-layer formed at the same
time as integrated circuit bipolar transistor emitter regions.
PINCH-OFF
The condition in a depletion mode field effect transistor wherein
the conducting channel is depleted of majority carriers and is thereby
pinched off, no path remaining for the source-to-drain
majority carrier (e.g., electron) flow.
PIN DIODE/DEVICE
A diode having an intrinsic semiconductor (i.e., one with
no dopants) sandwiched between a p-type layer and
an n-type layer. The depletion region (the
intrinsic semiconductor layer) thickness can be tailored
to optimize quantum efficiency for use as a photo diode or frequency
response for use as a microwave diode.
PIN-GRID ARRAY
A semiconductor chip package having leads in the form of
pins arranged in columns and rows.
PLANAR TRANSISTOR
A bipolar transistor in which the emitter base and collector
regions terminate at the same plane surface without indentations
in or protrusions from the surface. Hence, the
emitter and base regions form dish shaped portions extending into
the semiconductor from the common surface.
PLUG-IN PACKAGE
An electronic package for an active solid-state
device in which the lead pins are perpendicular to the mounting area
of the substrate, as contrasted with a flat package in which
the leads are in the same plane as the substrate.
P-MOSFET
A metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor having
p-type source and drain regions and a p-type conduction
channel which may be formed by a p type doped region (depletion
mode) or induced by a voltage on the gate (enhancement
mode).
PN-JUNCTION
The interface and region of transition between p-type and
n-type semiconductors.
PN-JUNCTION DIODE
A semiconductor device having two terminals connected
to opposite type semiconductor materials with a junction therebetween
and exhibiting a non-linear voltage-current characteristic, usually
used for switching or rectification.
PNP TRANSISTOR
A bipolar transistor with a p type emitter, an
n-type base and a p-type collector.
POINT DEFECT
A crystal defect occurring at a point in a crystal. Examples
include, (1) a foreign atom incorporated
into the crystal lattice at either a substitutional (regular
lattice) site or interstitial (between regular
lattice sites) site, (2) a missing
atom in the lattice, or (3) a host atom
located between regular lattice sites and adjacent to a vacancy (called
a Frenkel defect).
POLYCRYSTALLINE
A material composed of more than one crystal.
POLYSILICON
A polycrystalline form of silicon.
POSITIVE CARRIER
A charge carrier which has a net positive charge (e.g., a hole).
POSITIVE IONS
Atoms which are missing a valence shell electron.
POTENTIAL BARRIER
The difference in electrical potential across a pn junction
in a semiconductor.
POTENTIAL HILL
See POTENTIAL BARRIER.
POTTING
An embedding process in which an electronic component
is placed in a can, shell, or other container
and buried in a liquid dielectric polymer which subsequently changes
to a solid material. The container is not removed from
the finished part, and a release agent is not used.
This process differs from casting - which involves a removable
mold.
PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD
A structure formed on one or more layers of electrically insulating
material having electrical terminals and conductive material deposited
thereon, in continuous paths, from terminal to
terminal, to form circuits for electronic apparatus such
as chips or substrates.
P-TYPE CONDUCTIVITY
Electrical conductivity associated with positive charge carriers (holes) in
a semiconductor material.
P-TYPE SEMICONDUCTOR
An extrinsic semiconductor in which the hole density exceeds
the conduction electron density.
PUNCHTHROUGH
Expansion of a depletion region* from one junction
to another junction in an active solid-state device.
PURPLE PLAGUE
A brittle, inter metallic electrically conductive
compound which has a purplish color and is formed when aluminum
and gold, used as electrical contact materials in semiconductor
electronic devices, contact each other and interact.
It is usually considered undesirable because it breaks easily, reduces
device reliability, and lowers product yield.
QUANTIZED STATES
Discrete energy levels due to the quantum mechanical properties
of a material.
QUANTUM TRANSISTOR
Transistors whose operation is based on the properties of
electrons confined in quantum wells - semiconductor films
only a hundred or so angstroms thick sandwiched between high confining
walls made of a second semiconductor material.
QUANTUM WELL
Semiconductor films only a hundred or so angstroms thick
sandwiched between high confining walls made of a second material.
RARE EARTHS
Sc, Y, Lanthanides.
READ-OUT REGISTER
Gated semiconductor devices which receive and accumulate
charges and make them available to an output device.
RECOMBINATION
The process by which excess holes and electrons in a semiconductor
crystal recombine and and no longer function as charge carriers
in the semiconductor. Basic recombination processes are
band-to-band recombination which occurs when an
electron in the conduction band recombines with a hole in the valence
band, and trapping recombination which occurs when an electron or
hole is captured by a deep energy level, such as produced
by a deep level dopant, before recombining with an opposite
conductivity type carrier.
REFRACTORY METALS
Ti, V, Cr, Zr, Nb, Mo, Hf, Ta, W.
RESISTIVITY
A measure of the resistance of a material to electric
current. Resistivity is a bulk material property, measured
in ohm-cm.
RESONANT TUNNELLING DEVICE
A device that works on the principle of resonant electron (or
hole) tunneling through a pair of matched potential barriers.
This occurs when the energy of the electrons (or holes) matches
that of a quantum energy level in the quantum well formed between
the barriers.
REVERSE BIAS
A voltage applied across a semiconductor junction in the
reverse direction, i.e., wherein
a positive potential is connected to the n-type semiconductor
and a negative potential is applied to the p-type semiconductor.
REVERSE BREAKDOWN VOLTAGE
The reverse bias voltage value at which electrical resistance
drops appreciably and operating current sharply increases.
REVERSE CURRENT
The current flowing through a rectifying junction with
a reverse voltage thereacross.
SATURATION
The current between the base and collector of a bipolar transistor
when an increase in emitter to base voltage causes no further increase
in the collector current.
SCATTERING CENTERS
The impurities (dopants) in semiconductors
that cause electrons or holes flowing through the semiconductor to
scatter. These reduce carrier mobility and represent a problem
in quantum devices because they affect electron coherence length.
SCHOTTKY BARRIER
A metal to semiconductor interface in which the carrier affinity
and doping level of the semiconductor are such that a rectifying
junction is formed. Usually, minority carriers
in the semiconductor do not significantly contribute to the current
flowing in a device with such a barrier.
SCHOTTKY DIODE
A diode with a Schottky barrier.
SEMICONDUCTOR
A material whose electrical resistivity is between that of
insulators and conductors. The resistivity is commonly
changed by light, heat, electric, or
magnetic fields incident on the material. Current flow
is achieved by transfer of positive holes as well as by movement
of electrons.
SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE
A device in which current conduction takes place within a
semiconductor.
SEMICONDUCTOR LASER
A light emitting diode that uses stimulated emission
of radiation to produce coherent light output.
SILICON BILATERAL SWITCH (SBS)
A silicon controlled switch that can conduct current
in both directions.
SILICON CONTROLLED RECTIFIER (SCR)
A four layer pnpn device that, when in a normal
state, blocks applied voltage in either direction.
Application of a correct voltage to a gate terminal permits the
device to conduct in a forward direction.
SILICON CONTROLLED SWITCH (SCS)
A four layer pnpn semiconductor switching device that can
be triggered into conduction by applying either positive or negative
pulses.
SILICON-GATE FET
A field effect transistor which has a gate electrode
made of silicon.
SILICON ON INSULATOR (SOI)
A semiconductor structure using an insulating substrate, instead
of silicon as a substrate material, with an overlying active
layer of single crystal silicon containing active solid-state
devices. The substrate may typically be of the form of
an insulating layer which is itself formed on a single crystal substrate.
SILICON ON SAPPHIRE (S0S) CMOS
A complementary metal oxide semiconductor device (e.g., a
transistor) wherein single crystal silicon is grown on
a passive insulating base of sapphire (single crystal alpha
phase aluminum oxide) with complementary MOS transistors
formed in the silicon in one or more island portions.
SILICON TRANSISTOR
A transistor which uses silicon as the semiconductor material.
SINGLE-IN-LINE PACKAGE
A plug-in semiconductor device package with
one row of pins with specified spacings therebetween.
SINGLE CRYSTAL
A body of material having atoms regularly located at periodic
lattice sites throughout.
SINKER
A buried electrically conductive, low resistance
path in an integrated circuit which connects an electrical contact
to a conductive region buried in the integrated circuit.
It may be made up of a heavily doped impurity region.
SIS
An MIS structure (Metal-Insulator-Semiconductor) in which
the "metal" layer is made of semiconductor material, typically
polycrystalline silicon.
SOLAR CELL
A photovoltaic cell in the form of a semiconductor diode, usually
made of silicon, that generates electricity directly from
sunlight impingent on the cell.
SOLID-STATE DEVICE
An electronic device or component that uses current flow
through solid (as opposed to liquid), gas, or
vacuum materials. solid-state devices may be
active or passive.
SOURCE
In a field effect transistor, the electrode
to which the source of charge carriers is connected.
SPACE CHARGE REGION
The region around a pn junction in which holes and electrons
recombine to leave no mobile charge carriers and a net charge density
due to the residual dopant ions.
STEP RECOVERY DIODE
A pn junction active solid-state device in which
a forward bias voltage injects charge carriers across the junction
but prior to recombination of the carriers, a reverse voltage
is applied to return the charge carriers to their source as a group.
SUBSTRATE
The supporting material on or in which the components of
an integrated circuit are fabricated or attached.
SUBSTRATE BIAS
The electric potential applied to a substrate, which
typically serves as the reference potential against which other
voltages are measured. Also, in a MISFET, a
voltage applied to the substrate with respect to the source region.
SUPERLATTICE
A periodic sequence of variations in carrier potential energy
in a semiconductor, of such magnitude and spacing that
the current carrier wave function is spread out over many periods, so
that carrier energy and other properties are determined in part
by the periodic variations. The variation may be in chemical
composition of the material, as in a sequence of heterojunctions, or
in impurity concentration, forming a doping superlattice, or
both.
SURFACE-CHANNEL CCD
A charge coupled device in which charge resides at the semiconductor
surface.
SURFACE MOUNT DEVICES
Active or passive solid-state devices which
are structured and configured to be mounted directly to a printed circuit
board surface. This type of mounting is distinguished
from "through-hole" mounting which involves the
electrical and physical connection of devices to a printed circuit
board using drilled and plated holes through the conductive pattern
of the board.
SURFACE RESISTIVITY
The resistance of a material between two opposite sides of
a unit square of its surface. Also called Sheet Resistance.
Measured in ohms, often written as "ohms per square" in
this case.
TEST PROBES
Mechanical points of contact used for electrical measurement.
THERMISTOR
A semiconductor device whose electrical resistance varies
with temperature. Its temperature coefficient of resistance
is high, nonlinear, and usually negative.
THICK-FILM DEVICES
Printed thin-film circuits. Silk screen
printing techniques are used to make the desired circuit patterns
on a ceramic substrate. Active devices may be added thereto as
separate devices (see HYBRID CIRCUIT).
THIN-FILM DEVICES
solid-state electronic devices which are constructed
by depositing films of conducting material on the surface of electrically
insulating bases.
THYRISTOR
A four layer p-n-p-n bistable
switching device that changes from an off or blocking state to an
on or conducting state which uses both electron and hole type carrier
transport.
THRESHOLD VOLTAGE
The voltage at which a pn junction begins to conduct current.
THROUGH-HOLE MOUNTING
The electrical and physical connection of components
to the surface of a conductive pattern using drilled and plated
holes through the conductive and insulating layers of a printed
circuit board.
TRANSFERRED ELECTRON DEVICE
See GUNN EFFECT. In such devices, advantage
is taken of the negative differential mobility of electrons or
holes in certain semiconducting compounds, particularly
GaAs or InP.
TRANSISTOR
An active solid-state semiconductor device having
three or more electrodes in which the current flowing between two
specified electrodes is modulated by the voltage or current applied
to one or more specified electrodes, and is capable of
performing switching or amplification.
TRANSITION ELEMENTS
Sc, Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Y, Zr, Nb, Mo, Te, Ru, Rh, Pd, Ag, Cd, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Pm, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu, Hf, Ta, W, Re, Os, Ir, Pt, Au, Hg, Ac, Th, Pa, U, Np, Pu, Am, Cm, Bk, Cf, E, Fm, Mv, No, Lw.
TRAPATT DEVICE
An acronym for trapped plasma avalanche triggered transit
diodes, which are biased into avalanche condition.
As the diode breaks down, a highly conducting electron-hole
plasma quickly fills the entire n-type region, and
the voltage across the diode drops to a low value. The
plasma is then extracted from the diode by the low residual electric
field, thus causing a large current flow even though the
voltage is low. Once extraction of the plasma is completed, the
current drops and the voltage rises.
TRENCH ISOLATION
Electrical isolation of electronic components in a monolithic
integrated circuit by the use of holes or other indentations in
the surface of the device filled with dielectric material.
TUNNEL DIODE
A semiconductor diode in which the electrons penetrate a
quantum barrier that is impenetrable in terms of classical physics, but
which is penetrable in terms of quantum physics due to the quantum
mechanical uncertainty in position of current carriers.
TUNNEL EFFECT/TUNNELLING
See TUNNEL DIODE and RESONANT TUNNELING DEVICE.
TWIN-TUB STRUCTURE
CMOS device structure in which both p-type
and n-type deep wells are formed into a substrate for
the n-channel and p-channel device (e.g., a
transistor), respectively.
TWO-DIMENSIONAL ELECTRON GAS
A description of the motion of electrons which are confined
in only one direction, such as electrons in the conducting
channel of a MOSFET. In an electron gas, the electrons
move around without apparent restriction. The behavior
of electrons in conducting metals (e.g., copper) is
an example of a three-dimensional electron gas.
In a two dimensional electron gas, motion is restricted
to a single plane (two dimensions).
UNIPOLAR
An active solid-state electronic device in
which only one type of charge carrier, positive or negative, is used to support
current flow.
UNIPOLAR TRANSISTOR
A transistor in which the source to drain current involves
only one type of charge carrier.
VARACTOR
A semiconductor diode that changes capacitance with a change
in applied voltage, comprising a two terminal active device
using the voltage variable capacitance of a pn junction or a Schottky
junction.
VARISTOR
A term applied to both passive and active solid-state devices.
A varistor is a two-electrode semiconductor device with
a voltage dependent nonlinear resistance which falls significantly
as the voltage is increased. In an active device, the
non-linear property is due to the presence of one or more
potential barriers, whereas, in a passive type
varistor, it is due to electrical heating of the material
due to current flow therethrough. Varistors are to be
contrasted with passive variable resistors such as rheostats or
potentiometers.
VERTICAL JUNCTION
A junction of finite width which has a vertical axis.
The materials which form it lie on either horizontal side thereof.
VIA
A metallized or plated-through hole, in
an insulating layer, e.g., a
substrate, chip or a printed circuit board which forms
a conduction path itself and is not designed to have a wire or
lead inserted therethrough.
WAFER
A thin slice of semiconductor material with parallel faces
used as the substrate for active solid-state devices in
discrete or monolithic integrated circuit form.
WIRE BOND
Attachment of a tiny wire, as by thermocompression bonding, to
a bonding pad on a semiconductor chip.
WIRING CHANNEL
An area on an integrated circuit, such as a
gate array, which is left free of active devices and in
which interconnection metallization patterns are formed.
WORK FUNCTION
The minimum energy required to remove an electron from
the Fermi level of a material and liberate it to free space outside
the solid.
ZENER CURRENT
The current generated by a Zener diode when its reverse
voltage is increased above the Zener breakdown value.
ZENER DIODE
A single pn junction, two terminal semiconductor
diode reversed biased into breakdown caused by the Zener effect, i.e., by
field emission of charge carriers in the device"s depletion layer.
NOTE: True Zener breakdown occurs in silicon at values
below 6 volts. It is to be distinguished from the avalanche
breakdown mechanism that occurs in reverse biased diodes at higher (about
6 volts) voltages.
SUBCLASSES
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 1]](../ps.gif) 1 1 | BULK EFFECT DEVICE: |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter in which the active device is made up of
a semiconductor material whose electrical characteristics are due
to the electronic properties of the semiconductor material, which
are exhibited throughout the entire body of material rather than
in just a localized region thereof (e.g., the surface).
| | (1)
Note. Excluded from this subclass are semiconductive devices
whose nonlinear characteristic is due to a junction rather than
to the bulk properties of the semiconductor, whether they are homojunctions
(i.e., made up of the same semiconductor material with different dopant
ions on opposite sides of a junction) or heterojunctions (i.e.,
made up of different materials on either side of a junction). |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 289, | for insulated electrode devices having significant
semiconductor compound in bulk crystal. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 438, | Semiconductor Device Manufacturing: Process,
subclass 900 for methods of making a bulk effect semiconductor
device. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 2]](../ps.gif) 2 2 | Bulk effect switching in amorphous material: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1. Subject matter wherein the bulk material is an amorphous
material, i.e., one in which active solid material is non-crystalline
in the sense that (1) there is either complete disorder in the arrangement
of atoms/mole or molecules of the material or (2) there
is an absence of any long range structural order that is detectable
by electron or X-ray diffraction patterns of the material and the
device is used as an electronic switch. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 5]](../ps.gif) 5 5 | In array: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 2. Subject matter in which the amorphous bulk effect switch
has a group of individual switch elements with a predetermined (often
regular) spacing extended in one or more directions.
| | (1)
Note. The elements often extend in two dimensions to form
two-dimensional arrays. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 6]](../ps.gif) 6 6 | Intervalley transfer (e.g., Gunn effect): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1. Subject matter wherein electrons under the influence of
sufficiently high electric fields are transferred between energy
minima having different momentum in the conduction band of the active
semiconductor material, or holes under the influence of sufficiently
high electric fields are transferred between energy minima having different
momentum in the valence band of the active semiconductor material.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 331, | Oscillators,
subclass 107 for Gunn-type bulk effect device oscillators. |
| 341, | Coded Data Generation or Conversion,
subclass 133 for analog to or from digital conversion with particular
solid-state devices (e.g., Gunn effect devices). |
| 365, | Static Information Storage and Retrieval,
subclass 169 for systems using a Gunn effect device. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 7]](../ps.gif) 7 7 | In monolithic integrated circuit: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 6. Subject matter wherein the intervalley transfer devices
are integrally combined with one or more other active (e.g., diode
or transistor) or passive (e.g., resistor or capacitor) devices
in a single solid-state electronic device. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 9]](../ps.gif) 9 9 | THIN ACTIVE PHYSICAL LAYER WHICH IS (1) AN ACTIVE POTENTIAL WELL
LAYER THIN ENOUGH TO ESTABLISH DISCRETE QUANTUM ENERGY LEVELS OR
(2) AN ACTIVE BARRIER LAYER THIN ENOUGH TO PERMIT QUANTUM MECHANICAL TUNNELING
OR (3) AN ACTIVE LAYER THIN ENOUGH TO PERMIT CARRIER TRANSMISSION
WITH SUBSTANTIALLY NO SCATTERING (E.G., SUPERLATTICE QUANTUM WELL,
OR BALLISTIC TRANSPORT DEVICE): |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter wherein the active material is a thin physical
layer of material located between materials which have different
electrical properties than the thin layer and wherein the thin active
physical layer is (1) a potential well layer thin enough to establish
discrete quantum energy levels or (2) a potential barrier layer
thin enough to permit quantum mechanical tunneling or (3) a layer
thin enough to permit carrier transmission therethrough with substantially
no scattering of the carriers.
| | (1)
Note. Examples of such devices are superlattice, quantum
well, and ballistic transport devices. |
| | (2)
Note. Esaki tunneling is not the
type of tunneling which this subclass and those indented thereunder
contemplate. Esaki tunneling, while being quantum mechanical in
nature, merely involves a tunneling barrier formed by a macroscopic depletion
layer between n-type and p-type regions, but which neither a resonant
tunneling barrier using controlled quantum mechanical charge confinement,
a layer located between junctions, a thin layer as defined above.
Esaki tunneling devices are found classified below, in subclasses
104+. |
| | (3)
Note. Active junction devices may employ a plurality of barrier
junctions forming layers of material therebetween, but those layers
are only classified in this subclass if they are thin enough to
have the properties set forth in the definition. If those layers
do not meet the definition, then the devices are classified below. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 372, | Coherent Light Generators,
subclasses 43.01+ for semiconductor lasers which may contain thin
layer devices of this type for producing coherent light. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 10]](../ps.gif) 10 10 | Low workfunction layer for electron emission (e.g., photocathode
electron emissive layer): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 9. Subject matter wherein a layer of material from which electrons
are emitted with less input energy than that necessary to emit them
from adjacent material is provided.
| | (1)
Note. The adjacent material and the low workfunction layer
form either a heterojunction or a Schottky barrier, depending on
whether both materials are semiconductors or one of the materials
is a metal. |
| | (2)
Note. Typical low workfunction layer devices include cold
cathode emitters in electron tubes. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 313, | Electric Lamp and Discharge Devices,
subclasses 346+ and 373+ for photoemissive cathodes and
subclasses 527, 530, 541, and 542+ for photocathodes in
general. |
| 438, | Semiconductor Device Manufacturing: Process,
subclass 20 for processes of making an electron emissive device
utilizing a semiconductor substrate. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 11]](../ps.gif) 11 11 | Combined with a heterojunction involving a III-V compound: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 10. Subject matter in which the thin active layer and low workfunction
layer for electron emission are combined with a heterojunction,
i.e., a transition region between two materials with different energy
band gaps, one material of which is a III-V compound, i.e., a compound wherein
one material is found in group III of the periodic table and another
material is found in group V of the periodic table. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 12]](../ps.gif) 12 12 | Heterojunction: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 9. Subject matter wherein the device includes at least two
adjacent active layers, one of which is made of a substance that
differs from that of the other.
| | (1)
Note. See the illustration of a heterojunction device, in
subclass 183. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 194, | for heterojunction FETs having doping on the side
of the heterojunction with lower carrier affinity. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 13]](../ps.gif) 13 13 | Incoherent light emitter: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 12. Subject matter wherein the device emits incoherent light.
| | (1)
Note. Coherent light generators are explicitly excluded from
this subclass. This means that cross-references from Class 372,
Coherent Light Generators, are not to be placed in this subclass.
It is not desired to create a duplicate set of heterostructure
lasers in this subclass. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 372, | Coherent Light Generators,
subclasses 43.01+ for coherent semiconductor light generators. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 14]](../ps.gif) 14 14 | Quantum well: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 12. Subject matter wherein at least two heterojunctions are
formed with a thin active layer of material having a relatively
large carrier affinity between two materials with smaller carrier affinities,
resulting in a quantum mechanical energy well located in the thin
active layer with the relatively large carrier affinity.
| | (1)
Note. Quantum well devices appear in many forms, including
(a) heterostructures; (b) only those high electron mobility transistors
(HEMTs) which use a quantum well or a plurality of quantum wells;
(c) superlattices which comprise many quantum wells so tightly coupled that
the individual wells are not distinguishable, but rather the wells
become analogous to atoms in a lattice and superlattice devices
may behave more like new types of materials rather than as groups
of coupled quantum wells; and (d) resonant tunneling devices - which exhibit
quantum coupling, charge confinement and resonant tunneling. |
| | (2)
Note. See the illustration, below, for a graphic example
of a quantum well device.
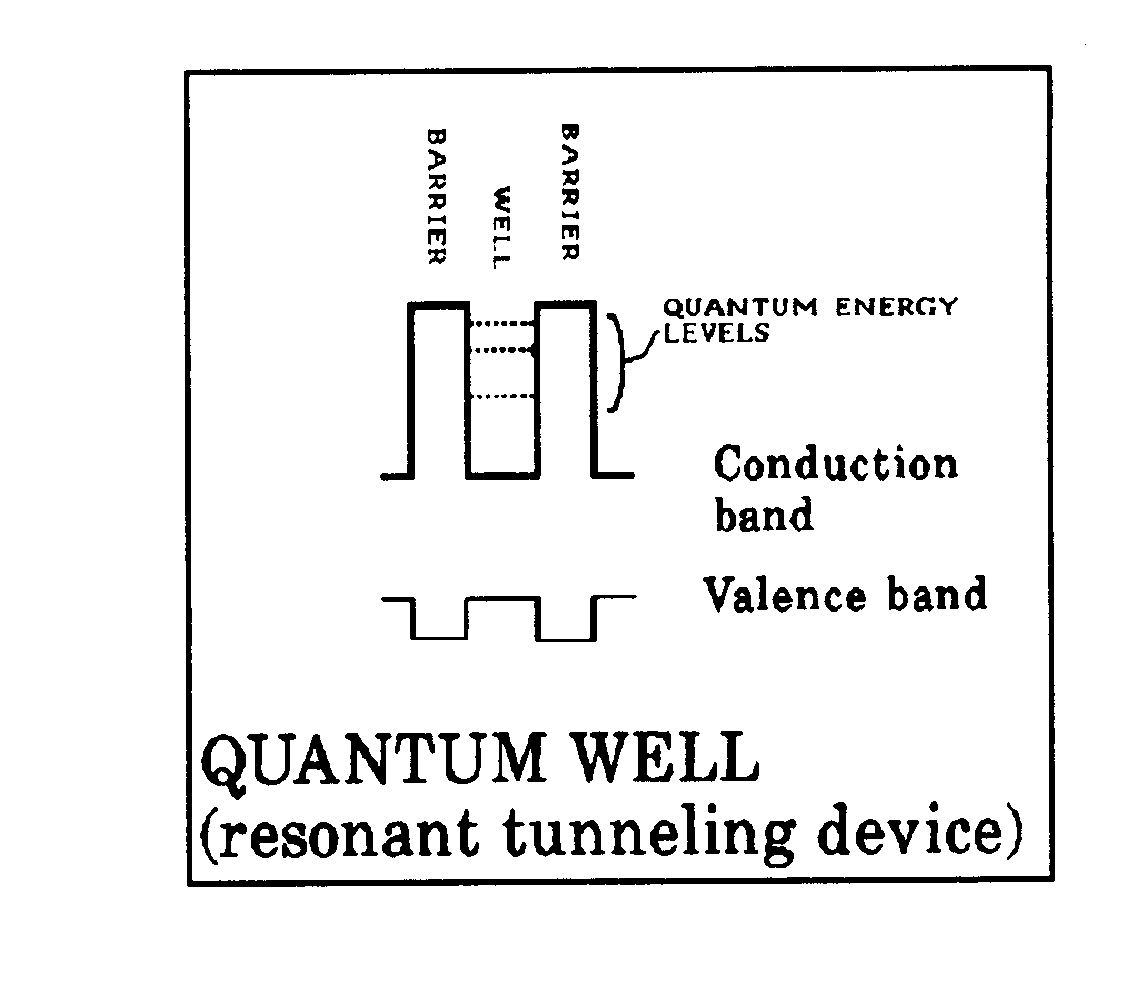
| |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 15]](../ps.gif) 15 15 | Superlattice: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 14. Subject matter wherein a large number of quantum wells are
present, the quantum wells being sufficiently close to each other
that carrier quantum wave functions are spread out over plural quantum
wells and the intervening barriers formed by the boundaries between adjacent
layers having different carrier affinities.
| | (1)
Note. Thicknesses of both the quantum well layers and the
barrier layers are typically a few angstroms to a few hundred angstroms
(10-10 meter) thick. |
| | (2)
Note. See the illustration, below, for energy level diagrams
showing band edge energy discontinuities at four types of superlattice
heterointerfaces.
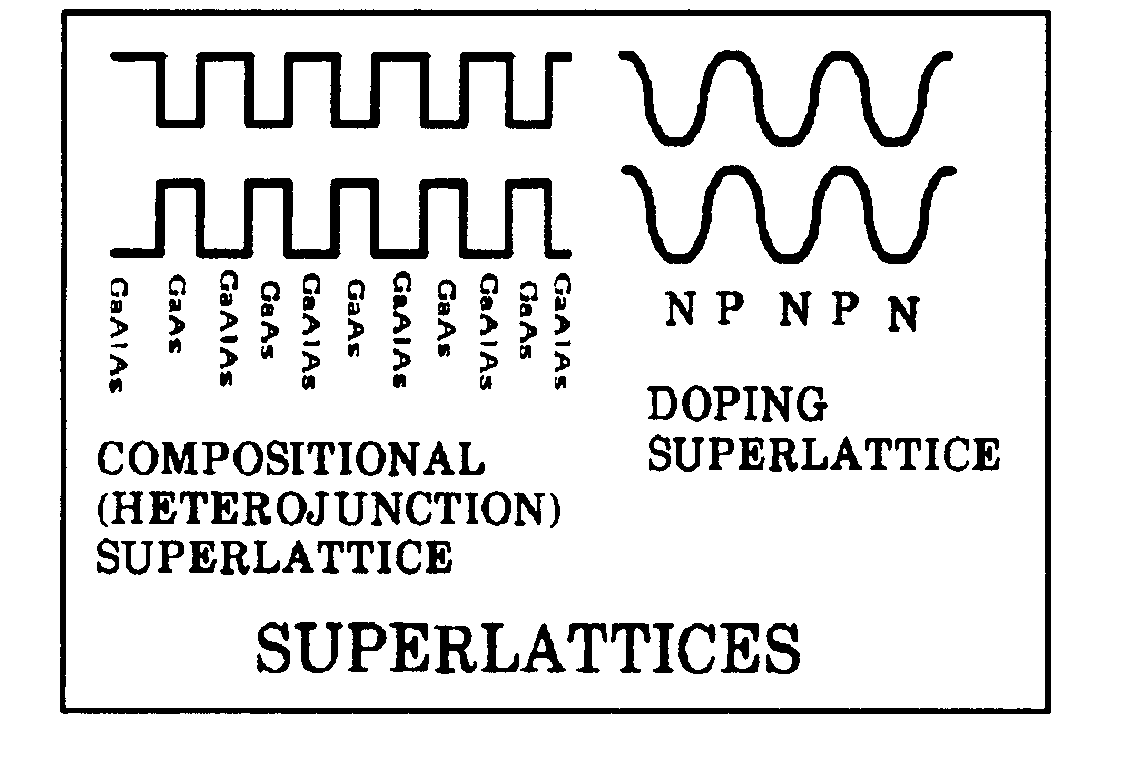
| SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 148, | Metal Treatment, digest 160 for superlattice treatment. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 18]](../ps.gif) 18 18 | Strained layer superlattice: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 15. Subject matter wherein the crystalline lattice characteristics
of adjacent thin active superlattice layers are mismatched so that
alternate layers are in elastic tension or compression. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 19]](../ps.gif) 19 19 | SixGe1-x: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 18. Subject matter wherein at least one of the strained superlattice
materials is a silicon-germanium alloy. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 20]](../ps.gif) 20 20 | Field effect device: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 15. Subject matter wherein the superlattice active layer forms
the conduction channel of a field effect device (i.e., one which
has two or more terminals denoted as source and gate with a conduction
channel therebetween, and in which the current through the conducting
channel is controlled by an electric field coming from a voltage
which is applied between the gate and source terminals thereof). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 21]](../ps.gif) 21 21 | Light responsive structure: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 15. Subject matter wherein absorption of light (ultraviolet,
visible, or infrared) by a superlattice active layer or junction
causes a change in the current-voltage characteristic of the device. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 23]](../ps.gif) 23 23 | Current flow across well: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 14. Subject matter wherein the device operation involves flow
of carriers (electrons or holes) across the quantum well (as contrasted
with tunneling through the well).
| | (1)
Note. Current flow is considered to be "across" the
well if the carriers have sufficient energy to pass over the barrier layers
confining the quantum well, as contrasted to passing through the
barriers by quantum mechanical tunneling. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 25, | for devices which operate by resonant tunneling
through the barriers, rather than over them. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 24]](../ps.gif) 24 24 | Field effect device: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 14. Subject matter wherein the quantum well device is a field
effect device, i.e., one which has two or more terminals denoted
as source and gate, with a conduction channel therebetween, and
in which the current through the conducting channel is controlled
by an electric field coming from a voltage which is applied between
the gate and source terminals thereof.
| | (1)
Note. See illustration under subclass 213 for various field
effect devices. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 25]](../ps.gif) 25 25 | Employing resonant tunneling: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 14. Subject matter wherein the operation of the device depends
not only on carrier charge confinement by the quantum well, but
the quantum well layer also acts as an intermediate layer through
which carriers pass by resonantly tunneling through both confining
barriers and the well. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 26]](../ps.gif) 26 26 | Ballistic transport device: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 12. Subject matter in which an active layer is present through
which carriers pass, wherein the active layer is thinner than the
mean free path of the carriers in the material in that layer, so
that carriers can pass through the layer without scattering.
| | (1)
Note. Carriers are typically injected into the ballistic
transport layer as "hot" carriers, having an energy,
in the case of electrons, substantially greater than the minimum
of the conduction band, or in the case of holes, substantially lower than
the maximum of the valence band. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 27]](../ps.gif) 27 27 | Field effect transistor: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 26. Subject matter wherein the ballistic transport device is
a field effect transistor, i.e., one which has two or more terminals
denoted as source and gate with a conduction channel therebetween,
and in which the current through the conducting channel is controlled
by an electric field coming from a voltage which is applied between
the gate and source terminals thereof.
| | (1)
Note. See illustration, below, of various field effect devices
under subclass 213. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 28]](../ps.gif) 28 28 | Non-heterojunction superlattice (e.g., doping superlattice
or alternating metal and insulator layers): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 9. Subject matter wherein there are a plurality of active layers
and barrier regions, the active layers being sufficiently close
to each other that carrier quantum wave functions are spread out over
plural active layers and the intervening barriers, and wherein the
active layers and barrier regions do not form heterojunctions between
different semiconductor materials.
| | (1)
Note. Typically the active layers and barrier layers may
be doped with opposite conductivity type dopants. Thicknesses of
both the active layers and the barrier layers are typically a few
angstroms to a few hundred angstroms (10-10 meter)
thick. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 29]](../ps.gif) 29 29 | Ballistic transport device (e.g., hot electron transistor): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 9. Subject matter in which an active layer is present through
which carriers pass, which active layer is thinner than the mean
free path of the carriers in the material in that layer, so that
carriers can pass through the layer without scattering.
| | (1)
Note. Carriers are typically injected into the ballistic transport
layer as "hot" carriers, having an energy, in
the case of electrons, substantially greater than the minimum of
the conduction band, or in the case of holes, substantially lower than
the maximum of the valence band. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 30]](../ps.gif) 30 30 | Tunneling through region of reduced conductivity: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 9. Subject matter wherein the active layer through which carrier
tunnelling occurs has lower electrical conductivity than the material
adjacent thereto.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 29, | Metal Working,
subclass 25.01 for methods of making barrier layer devices of
the metal-insulator-metal type. |
| 331, | Oscillators,
subclass 107 for superconductive element and tunneling element
oscillators. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 31]](../ps.gif) 31 31 | Josephson: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 30. Subject matter wherein the device is of the form of a pair
of superconductive electrodes separated by a thin, less conductive,
portion, through which superconductive tunneling may occur.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 29, | Metal Working,
subclass 25.01 for methods of making barrier layer devices possessing
a Josephson junction. |
| 216, | Etching a Substrate: Processes,
subclass 3 for Josephson Junction device manufacture involving
etching. |
| 505, | Superconductor Technology: Apparatus, Material,
Process,
subclass 1 for high temperature superconductor Josephson devices
with particular electrode materials and pertinent cross-reference
art collections, including subclasses 857+ for nonlinear solid-state
device, system, or circuit; and subclasses 873+ active
solid-state devices. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 33]](../ps.gif) 33 33 | High temperature (i.e., >30° Kelvin): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 32. Subject matter wherein the device can operate at temperatures
above 30 degrees on the Kelvin temperature scale.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 505, | Superconductor Technology: Apparatus, Material,
Process,
subclass 1 for high temperature superconductor materials and
devices. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 40]](../ps.gif) 40 40 | ORGANIC SEMICONDUCTOR MATERIAL: |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter comprising a semiconductor compound that
includes an organic material characterized by two or more carbon
atoms bonded together, one atom of carbon bonded to at least one
atom of hydrogen or halogen (i.e., chlorine, fluorine, bromine,
iodine), or one atom of carbon bonded to at least one atom of nitrogen
by a single or double bond.
| | (1)
Note. Certain compounds are exceptions to this rule, i.e.,
HCN, CN-CN, HNCO, HNCS, cyanogen halides, cyanamide, fulminic acid,
and metal carbides. These are not regarded as organic materials. |
| | (2)
Note. Graphite and diamond are not regarded as organic, since
they are not compounds; silicon carbide is not regarded as organic.
Active solid-state devices using silicon carbide or diamond as
the semiconductor are in subclass 77 of this class. |
| | (3)
Note. Organic insulating materials, as opposed to semiconducting
materials, do not go in this subclass. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 136, | Batteries: Thermoelectric and Photoelectric,
subclass 263 for photoelectric cells containing organic active material. |
| 260, | Chemistry of Carbon Compounds, and other classes which form integral parts of Class
260, appropriate subclasses for organic materials |
| 313, | Electric Lamp and Discharge Devices,
subclass 504 for solid-state organic phosphor material luminescent
devices. |
| 361, | Electricity: Electrical Systems and Devices,
subclass 527 for solid electrolytic capacitors containing an organic
salt. |
| 438, | Semiconductor Device Manufacturing: Process,
subclass 82 for processes of making a light responsive device
utilizing an organic semiconductor, and subclass 99 for methods of
making an electrical device utilizing as a semiconductor component
an organic semiconductor. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 41]](../ps.gif) 41 41 | POINT CONTACT DEVICE: |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter including a junction between a semiconductor
and a metallic element (e.g., wire) at a single point of contact therebetween. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 42]](../ps.gif) 42 42 | SEMICONDUCTOR IS SELENIUM OR TELLURIUM IN ELEMENTAL FORM: |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter including a semiconductor material comprised
of selenium or tellurium in elemental form (i.e., not in a compound).
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 430, | Radiation Imagery Chemistry: Process, Composition
or Product,
subclass 57.8 for electrophotographic plates containing selenium
or a selenium alloy. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 43]](../ps.gif) 43 43 | SEMICONDUCTOR IS AN OXIDE OF A METAL (E.G., CuO, ZnO) OR
COPPER SULFIDE: |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter wherein a semiconductor material includes
a metal oxide or copper sulfide.
| | (1)
Note. Those variable resistors known as "coherers" which
are active solid-state devices, and are
made of a metal oxide, are found in this subclass. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 798, | for other active solid-state device type coherers. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 338, | Electrical Resistors,
subclasses 1 and 223+ for passive solid-state coherers. |
| 438, | Semiconductor Device Manufacturing: Process,
subclass 85 for processes of making a light responsive device
utilizing as the semiconductive component a metal oxide or copper sulfide
and subclasses 104 for methods of forming an electrical device utilizing
as a semiconductive component a metal oxide or copper sulfide. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 44]](../ps.gif) 44 44 | WITH METAL CONTACT ALLOYED TO ELEMENTAL SEMICONDUCTOR TYPE PN
JUNCTION IN NONREGENERATIVE STRUCTURE: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 107. Subject matter under the class definition wherein the active
solid-state device has a pn junction formed by alloying one or
more impurity metal contacts to an elemental semiconductor, and
wherein the active solid-state device is not a
regenerative device of this class.
| | (1)
Note. The impurity metal contact alloys with a semiconductor
material to form a p-region or n-region, depending on the impurity
used. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 46]](../ps.gif) 46 46 | In pn junction tunnel diode (Esaki diode): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 44. Subject matter wherein the alloyed pn junction device
is a tunnel diode, i.e., wherein the active solid-state device includes
a heavily doped pn junction wherein conduction occurs through the
junction potential barrier due to a quantum mechanical effect even
though the carriers which tunnel through the potential barrier do
not have enough energy to overcome the barrier potential. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 47]](../ps.gif) 47 47 | In bipolar transistor structure: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 44. Subject matter wherein the alloyed pn junction device is
a bipolar transistor, i.e., a transistor structure whose working
current passes through semiconductor material of both polarities
(p and n). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 48]](../ps.gif) 48 48 | TEST OR CALIBRATION STRUCTURE: |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter in which structures are provided on active
solid-state devices to permit or facilitate the measurement, test,
or calibration of the characteristics of the devices.
| | (1)
Note. Active solid-state device standards are also included
herein. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 324, | Electricity: Measuring and Testing,
subclass 158 for semiconductor device test apparatus and methods. |
| 438, | Semiconductor Device Manufacturing: Process, particularly
subclass 18 for methods under the class definition having
combined therewith a step of measuring an electrical condition utilizing
a test element. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 49]](../ps.gif) 49 49 | NON-SINGLE CRYSTAL, OR RECRYSTALLIZED, SEMICONDUCTOR MATERIAL
FORMS PART OF ACTIVE JUNCTION (INCLUDING FIELD-INDUCED ACTIVE JUNCTION): |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter wherein there is an active junction (e.g.,
a junction between dissimilar materials, or a junction induced by
an applied electric field, which exhibits non-linear current-voltage
characteristics) and at least part of the active junction is formed
by a semiconductor material in polycrystalline or amorphous form.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 136, | Batteries: Thermoelectric and Photoelectric,
subclass 258 for photoelectric cells with polycrystalline or
amorphous semiconductor material. |
| 438, | Semiconductor Device Manufacturing: Process, particularly
subclass 96 and 482+ for methods of depositing amorphous
semiconductive material functioning as an active region for an electrical
device and subclasses 97 and 488+ for methods of depositing polycrystalline
semiconductive material functioning as an active region for an electrical
device. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 52]](../ps.gif) 52 52 | Amorphous semiconductor material: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 49. Subject matter wherein the non-single crystal semiconductor
material is amorphous, i.e., non-crystalline in the sense that (1)
there is either complete disorder in the arrangement of atoms or
molecules of the material or (2) there is an absence of any long
range structural order that is detectable by electron or X-ray diffraction
patterns of the material.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 2, | through 5, for bulk effect switching in amorphous
material. |
| 16, | for superlattice quantum well heterojunction devices
of amorphous semiconductor material. |
| 646, | for amorphous semiconductor material coating to
control surface effects. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 136, | Batteries: Thermoelectric and Photoelectric,
subclass 258 for photoelectric cells with polycrystalline or
amorphous semiconductor material. |
| 438, | Semiconductor Device Manufacturing: Process, particularly
subclasses 482+ for methods for depositing amorphous semiconductor. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 53]](../ps.gif) 53 53 | Responsive to nonelectrical external signals (e.g., light): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 52. Subject matter wherein the amorphous semiconductor active
junction generates an electrical signal when subjected to non-electrical (e.g.,
optical, thermal, or vibratory) signals.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 430, | Radiation Imagery Chemistry: Process, Composition
or Product,
subclass 57.4 for electrophotographic plates containing amorphous
silicon. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 57]](../ps.gif) 57 57 | Field effect device in amorphous semiconductor material: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 52. Subject matter wherein the amorphous semiconductor active
junction is a field effect device, i.e., one which has a conducting
channel and two or more electrodes, one of which is denoted a source
and the other a drain electrode, and in which the current through
the conducting channel is controlled by an electric field coming
from a voltage which is applied between the gate and source terminals
thereof.
| | (1)
Note. See illustration under subclass 213 for various field
effect devices. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 438, | Semiconductor Device Manufacturing: Process, particularly
subclasses 149+ for methods of forming a field effect transistor
on an insulating substrate or layer (e.g., SOS, SOI, etc.). |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 58]](../ps.gif) 58 58 | With impurity other than hydrogen to passivate dangling
bonds (e.g., halide): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 57. Subject matter wherein the semiconductor active junction
amorphous field effect device is doped with an impurity other than
hydrogen (e.g., a halide) for providing electrical stability by
completing chemical bonds between semiconductor atoms which were
not completed due to the amorphous nature of the semiconductor active
layer material. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 59]](../ps.gif) 59 59 | In array having structure for use as imager or display,
or with transparent electrode: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 57. Subject matter wherein a plurality of semiconductor active
junction amorphous field effect devices are interconnected in a
monolithic chip device for generating an image of an object, light
from which is incident on the device, or for displaying signals
applied to the device, or having an electrode that transmits optical
radiation in the infrared, visible, or ultraviolet wavelength bands. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 62]](../ps.gif) 62 62 | With impurity other than hydrogen to passivate dangling
bonds (e.g., halide): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 52. Subject matter wherein the semiconductor active junction
amorphous field effect device is doped with an impurity other than
hydrogen (e.g., a halide) for providing electrical stability by
completing chemical bonds between semiconductor atoms which were
not completed due to the amorphous nature of the semiconductor active
layer material. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 70]](../ps.gif) 70 70 | Recrystallized semiconductor material: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 67. Subject matter wherein the combined device contains a non-single
semiconductor region of recrystallized material.
| | (1)
Note. Recrystallized semiconductor material has been processed,
typically by heat or laser irradiation to cause growth of large
regions of substantially single crystal material to obtain properties approximating
those of completely single crystal material. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 72]](../ps.gif) 72 72 | In array having structure for use as imager or display,
or with transparent electrode: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 66. Subject matter wherein a plurality of field effect devices
in non-single crystal, or recrystallized, semiconductor material
are interconnected in a monolithic chip device for generating an
image of an object, light from which is incident on the device,
or for displaying signals applied to the device, or having an electrode
that transmits optical radiation in the infrared, visible, or ultraviolet
wavelength bands. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 76]](../ps.gif) 76 76 | SPECIFIED WIDE BAND GAP (1.5eV) SEMICONDUCTOR MATERIAL
OTHER THAN GaAsP or GaAlAs: |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter including a semiconductor material with a
band gap (between its valance and conduction bands) greater that
1.5 electron volts which is not gallium arsenide phosphide or gallium
aluminum arsenide. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 78]](../ps.gif) 78 78 | II-VI compound: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 76. Subject matter wherein the specified wide band gap material
is a compound, one element of which comes from group II, and the
other element of which comes from group VI of the periodic table
of elements. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 79]](../ps.gif) 79 79 | INCOHERENT LIGHT EMITTER STRUCTURE: |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter wherein the active solid-state device generates
incoherent light when subjected to an appropriate input signal.
| | (1)
Note. Lasers (coherent light generators) are classified in
Class 372, and patents directed to lasers are not to be cross-referenced
in this or indented subclasses unless such patent contains disclosure
of a light emitting semiconductor device which is NOT a laser or
coherent light generator. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 13, | for incoherent thin physical layer light emitter
devices with operating principles as specified therein. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 250, | Radiant Energy,
subclasses 552+ for solid-state light source circuits. |
| 313, | Electric Lamp and Discharge Devices,
subclasses 498+ for electric lamp and discharge devices having solid-state
luminescent materials, including nominally recited luminescent semiconductor
type materials; and subclass 504 for solid-state organic phosphor
material luminescent devices. |
| 340, | Communications: Electrical,
subclasses 760+ and 766+ for solid-state light emitting
arrays and array elements. |
| 362, | Illumination,
subclass 84 for light source or light source support and luminescent
material and subclass 800 (cross-reference art collection) for light
emitting diode light sources. |
| 438, | Semiconductor Device Manufacturing: Process, particularly
subclasses 22+ for methods of forming a semiconductor device which
may be emissive of either coherent or incoherent radiation. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 80]](../ps.gif) 80 80 | In combination with or also constituting light responsive
device: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 79. Subject matter wherein the light emitting active semiconductor
device is combined with a separate device which generates an electrical
signal when light impinges upon it or the active device both emits
light when stimulated and generates an electrical signal in response
to light impingent thereupon.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 250, | Radiant Energy,
subclass 551 for signal isolators involving a light source and
photodetector. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 83]](../ps.gif) 83 83 | Light coupled transistor structure: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 80. Subject matter wherein the active solid-state device has
a pair of rectifying junctions, a first of which when forward biased
produces light which, when absorbed in the depletion region of the
second junction when reverse biased, produces a current through
the second junction, with the first junction functioning similarly
to the emitter-base junction, and the second junction functioning
similarly to the base-collector junction, of an ordinary bipolar
transistor.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 250, | Radiant Energy,
subclass 551 for signal isolator for optically coupled light emitter
and light detector combinations wherein the devices are used to isolate
electrical signals. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 85]](../ps.gif) 85 85 | With heterojunction: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 84. Subject matter wherein the device contains a heterojunction,
i.e., wherein the junction separates semiconductor materials of
different chemical composition. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 86]](../ps.gif) 86 86 | Active layer of indirect band gap semiconductor: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 79. Subject matter wherein the light emitting active region
is in or between semiconductor materials in which direct transitions
of electrons from conduction to valance bands do not take place.
| | (1)
Note. Transitions may take place in steps due to trapping
levels located in the forbidden band between the conduction and
valance bands. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 90]](../ps.gif) 90 90 | With heterojunction: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 89. Subject matter wherein there is at least one heterojunction,
i.e., wherein the junction separates semiconductor materials of
different chemical composition. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 91]](../ps.gif) 91 91 | With shaped contacts or opaque masking: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 88. Subject matter wherein the plural light emitting devices
have electrical contacts with specific shapes or are combined with
optical elements which are impervious to light emitted by the devices
and are placed in the path of light emitted by the devices. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 92]](../ps.gif) 92 92 | Alphanumeric segmented array: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 88. Subject matter wherein the plural light emitting devices
are structured and arranged in segments of Arabic numerals or alphabet
letters.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 340, | Communications: Electrical,
subclasses 760+ and 766+ for solid-state light emitting
arrays and array elements. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 94]](../ps.gif) 94 94 | With heterojunction: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 79. Subject matter wherein there is at least one junction between
semiconductor materials of different chemical compositions.
| | (1)
Note. See the illustration of a heterojunction device in
subclass 183. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 98]](../ps.gif) 98 98 | With reflector, opaque mask, or optical element (e.g.,
lens, optical fiber, index of refraction matching layer, luminescent material
layer, filter) integral with device or device enclosure or package: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 79. Subject matter wherein the light emitting active junction
device is combined with one or more optical elements (e.g., to transmit
or shape or otherwise affect light emitted by the device); and the
optical element is an integral part of the device or of the housing,
encapsulant, or other device enclosure or package. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 100]](../ps.gif) 100 100 | Encapsulated: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 79. Subject matter wherein the light emitting active junction
device is embedded in a protective coating.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 174, | Electricity: Conductors and Insulators,
subclass 521 for potted or encapsulated electrical devices. |
| 439, | Electrical Connectors,
subclass 936 for potting material or coating for electrical
conductors. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 104]](../ps.gif) 104 104 | TUNNELING PN JUNCTION (E.G., ESAKI DIODE) DEVICE: |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter wherein the active solid-state device includes
a heavily doped pn junction where conduction occurs through the
junction potential barrier due to a quantum mechanical effect even
though the carriers which tunnel through the potential barrier do not
have enough energy to overcome the barrier potential.
| | (1)
Note. PN Junction tunnel diodes operated under forward bias
are often referred to as Esaki diodes. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 46, | for an Esaki diode having a metal contact alloyed
to elemental semiconductor type pn junction in a non-regenerative
structure. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 326, | Electronic Digital Logic Circuitry,
subclass 134 for a digital logic device which includes a tunnel
diode. |
| 327, | Miscellaneous Active Electrical Nonlinear Devices,
Circuits, and Systems,
subclass 195 for stable state circuits utilizing a tunnel diode;
subclass 326 for limiting, clipping, or clamping using a tunnel
diode; subclass 402 for a delay controlled switch with tunnel diode;
subclasses 420 and 499 for gating circuits utilizing transistors
or diodes respectively which use tunnel diodes; and subclass 570
for miscellaneous tunnel diode circuits. |
| 331, | Oscillators,
subclass 107 for tunnel diode oscillators. |
| 361, | Electricity: Electrical Systems and Devices,
subclass 100 for tunnel diode current responsive fault sensors. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 105]](../ps.gif) 105 105 | In three or more terminal device: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 104. Subject matter wherein the tunnel junction is part of an
active solid-state electronic device which has three or more electrical
terminals (e.g., transistors or thyristors). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 106]](../ps.gif) 106 106 | Reverse bias tunneling structure (e.g., "backward" diode,
true Zener diode): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 104. Subject matter wherein the tunnel junction is structured
to permit quantum mechanical tunneling of carriers in a reverse
bias mode, i.e., when the p-side of the junction is connected to a
negative voltage source and the n-side of the junction is connected
to a positive voltage source.
| | (1)
Note. In silicon, such conduction occurs when the junction
breakdown voltage is less than approximately 5.6 volts. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 148, | Metal Treatment, digest 174 for treatment of Zener diodes. |
| 323, | Electricity: Power Supply or Regulation Systems,
subclass 231 for systems using a Zener diode and being in shunt
with a load. |
| 327, | Miscellaneous Active Electrical Nonlinear Devices,
Circuits, and Systems,
subclasses 194 and 195 for stable state circuits with a zener
or back diode respectively; subclass 326 for limiting, clipping,
or clamping utilizing a zener diode; subclass 421 for gating circuits
having a transistor which utilizes a zener effect; subclass 502
for a gating circuit with zener diode; and subclass 584 for a miscellaneous
circuit utilizing a zener diode. |
| 361, | Electricity: Electrical Systems and Devices,
subclass 197 , for relay time delay safety or protection devices including,
for example, a Zener diode. |
| 377, | Electrical Pulse Counters, Pulse Dividers, or
Shift Registers: Circuits and Systems,
subclass 128 for pulse counting or dividing chains which include
bi-stable semiconductor devices with only two electrodes, e.g., tunnel
diodes. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 107]](../ps.gif) 107 107 | REGENERATIVE TYPE SWITCHING DEVICE (E.G., SCR, COMFET,
THYRISTOR): |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter wherein the active solid-state device acts
as if it has two or more active emitter junctions each of which
is associated with a separate, equivalent transistor having an individual
gain and, when initiated by a base region current, the equivalent
transistors mutually drive each other in a regenerative manner to
lower the voltage drop between the emitters.
| | (1)
Note. If the current is above a level IH, called
the "holding current", then the device will remain
ON when the triggering signal is removed by the regenerative feedback
therebetween, and is then said to be "latched". |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 123, | Internal-Combustion Engines,
subclass 648 for circuits employing silicon controlled rectifiers
(SCRs). |
| 327, | Miscellaneous Active Electrical Nonlinear Devices,
Circuits, and Systems,
subclasses 199+ for a bistable circuit which includes diverse solid-state devices
such as an SCR, subclasses 392+ for a delay controlled
switch which may include an SCR, and subclasses 438+ for
gating circuits which may use a thyristor or SCR. |
| 361, | Electricity: Electrical Systems and Devices,
subclasses 100+ and 205 for circuits employing thyristors (e.g.,
silicon controlled rectifiers (SCRs)). |
| 363, | Electric Power Conversion Systems,
subclasses 27+ , 54, 57+, 68, 85+, 96+,
128+, 135+, and 160+ for circuits employing
thyristors (e.g., silicon controlled rectifiers (SCRs)). |
| 388, | Electricity: Motor Control Systems,
subclasses 917+ for circuits employing thyristors (e.g., silicon
controlled rectifiers (SCRs)). |
| 438, | Semiconductor Device Manufacturing: Process, particularly
subclasses 133+ for methods of forming a regenerative type switching
device. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 111]](../ps.gif) 111 111 | Triggered by VBO overvoltage means: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 109. Subject matter wherein the two terminal device with no control
electrode includes means to apply a voltage larger than the breakover
voltage VBO to initiate operation of the device. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 113]](../ps.gif) 113 113 | With light activation: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 107. Subject matter wherein the regenerative switching device
is activated (e.g., turned on and/or off) by light impinging
on a light sensitive portion of the device. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 118]](../ps.gif) 118 118 | With groove or thinned light sensitive portion: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 113. Subject matter wherein the light sensitive portion is located
in a groove in the surface of the device or is located close to
the surface of the device in a thinned region of the device so that only
a relatively thin portion of the device has to be traversed by light. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 119]](../ps.gif) 119 119 | Bidirectional rectifier with control electrode (gate) (e.g.,
Triac): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 107. Subject matter wherein the regenerative switching device
has a control electrode, can conduct in both forward and reverse
directions, and can be triggered into conduction by a pulse applied
to its control electrode.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 110, | for bidirectional rectifiers with no control electrode. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 323, | Electricity: Power Supply or Regulation Systems,
subclasses 240 and 325 for circuit having unidirectional elements
with bidirectional pass. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 121]](../ps.gif) 121 121 | With diode or transistor in reverse path: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 119. Subject matter wherein a diode (i.e., a device which passes
current in only one direction) is connected to conduct current in
one direction, with a regenerative switching device with a control
electrode connected to conduct current in the other direction to
produce a bi-directionally conducting regenerative switching device. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 122]](../ps.gif) 122 122 | Lateral: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 119. Subject matter wherein the bidirectional rectifier with
control electrode is of the lateral type, i.e., when viewed in cross
section, the two main electrodes (e.g., anode and cathode) are arranged
horizontally, side-by-side in the same surface of the semiconductor
body. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 124]](../ps.gif) 124 124 | Combined with field effect transistor structure: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 119. Subject matter wherein the bidirectional rectifier with
control electrode includes or is combined with a field effect transistor
structure, i.e., a transistor in which the current through a conducting
channel is controlled by an electric field coming from a voltage
which is applied between the gate and source terminals thereof.
| | (1)
Note. See illustration under subclass 213 for various field
effect devices. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 125]](../ps.gif) 125 125 | Controllable emitter shunting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 124. Subject matter wherein the field effect transistor structure
is connected to shunt one of the emitter-base junctions of the regenerative structure
under control of the voltage applied to the gate of the field effect
transistor. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 127]](../ps.gif) 127 127 | Guard ring or groove: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 126. Subject matter wherein the means to separate portions of
the device having different conductive polarity is or includes a
groove, or a guard ring, i.e., a pn junction region in the body
of the device located and/or configured to reduce electric
field strength at a given applied voltage. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 131]](../ps.gif) 131 131 | Recombination centers or deep level dopants: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 130. Subject matter wherein the switching speed enhancement means
include (1) centers wherein excess holes and electrons recombine and
are removed as charge carriers in the device or (2) dopant ions
with energy levels that are located in the forbidden band of the active
semiconductor material of the device. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 132]](../ps.gif) 132 132 | Five or more layer unidirectional structure: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 107. Subject matter wherein the regenerative active solid-state
device has five or more layers of semiconductor material producing
at least four active junctions, and is operable in a single electrical
direction. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 133]](../ps.gif) 133 133 | Combined with field effect transistor: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 107. Subject matter wherein the regenerative device includes
or is combined with a field effect transistor, i.e., a transistor
in which the current through a conducting channel is controlled
by an electric field coming from a voltage which is applied between
the gate and source terminals thereof. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 134]](../ps.gif) 134 134 | J-FET (junction field effect transistor): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 133. Subject matter wherein the field effect transistor combined
with the regenerative action junction type switching device is a
junction field effect transistor, i.e., a field effect transistor wherein
the gate region is isolated from the conducting channel by a rectifying
pn junction or Schottky barrier junction.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 287, | for power JFET devices. |
| 504, | for JFET type isolation. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 136]](../ps.gif) 136 136 | Enhancement mode (e.g., so-called SITs): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 135. Subject matter in which no current flows except for leakage
current, when the gate to source voltage is zero.
| | (1)
Note. Conduction does not begin until the gate voltage reaches
a finite threshold value. |
| | (2)
Note. Compare this with depletion mode J-FETS in which maximum
current is passed by the transistor at a zero gate potential and
current decreases as the gate voltage increases. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 137]](../ps.gif) 137 137 | Having controllable emitter shunt: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 133. Subject matter wherein the regenerative switching device
is combined with a junction field effect transistor that is connected
across an emitter-base junction of the regenerative device to controllably
divert current from the emitter-base junction. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 142]](../ps.gif) 142 142 | Having impurity doping for gain reduction: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 139. Subject matter wherein the extended latchup current level
device has impurity dopant to reduce device regenerative gain, i.e.,
the gain or amplification of one or more of the active junction
portions connected in regenerative fashion. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 143]](../ps.gif) 143 143 | Having anode shunt means: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 139. Subject matter wherein the extended latchup current level
device has means connected across the emitter-base junction of the
PNP transistor portion of the regenerative device to controllably
divert current from the emitter-base junction. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 145]](../ps.gif) 145 145 | Low impedance channel contact extends below surface: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 139. Subject matter wherein the extended latchup current level
device has an electrical contact extending from the device surface
into the body of the device which is connected to the channel of
the field effect transistor portion and wherein the contact has
a relatively low electrical impedance. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 148]](../ps.gif) 148 148 | Having impurity doping for gain reduction: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 147. Subject matter wherein the regenerative switching device
has impurity dopant to reduce device gain of one of the equivalent
transistors.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 142, | for this subject matter in a COMFET device. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 149]](../ps.gif) 149 149 | Having anode shunt means: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 147. Subject matter wherein the regenerative switching device
has means connected across the emitter-base junction of the PNP
transistor section of the regenerative device to divert current
from the emitter-base junction. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 156]](../ps.gif) 156 156 | Having deep level dopants or recombination centers: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 155. Subject matter wherein the regenerative device has deep
level dopants or electron-hole recombination centers with energy
levels that are within the forbidden energy band and widely spaced
from the conduction and valence bands of the semiconductor device. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 157]](../ps.gif) 157 157 | With integrated trigger signal amplification means (e.g.,
amplified gate, "pilot thyristor", etc.): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 107. Subject matter wherein the regenerative switching device
has means to amplify the control current of the device, which is
physically integrated with the regenerative switching device.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 115, | for light activated regenerative devices with trigger
signal amplification. |
| 123, | for bidirectional regenerative devices with trigger
signal amplification. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 330, | Amplifiers,
subclasses 250+ for semiconductor amplifying devices (e.g., transistors |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 159]](../ps.gif) 159 159 | Transistor as amplifier: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 157. Subject matter wherein the amplification means is a transistor
(i.e., an active semiconductor device having three or more electrodes). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 160]](../ps.gif) 160 160 | With distributed amplified current: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 157. Subject matter wherein the regenerative device with amplification
means produces amplified current which is distributed by electrodes
to other portions of the device. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 161]](../ps.gif) 161 161 | With a turn-off diode: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 157. Subject matter wherein the regenerative device with amplification
means is integrally provided with a diode, i.e., a solid-state active
rectifying two terminal device, to bypass the amplifying stage(s),
in order to switch OFF the regenerative device. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 162]](../ps.gif) 162 162 | Lateral structure: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 107. Subject matter wherein the regenerative active junction
type switching device has a lateral structure, i.e., one in which
the active junctions are arranged so that electric current flows
from side to side, rather than from top to bottom of the device. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 163]](../ps.gif) 163 163 | Emitter region feature: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 107. Subject matter wherein the active emitter junction region
of the regenerative device has a particular characteristic. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 166]](../ps.gif) 166 166 | Radially symmetric regions: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 164. Subject matter wherein the plural emitters are located in
regions of the device which are symmetrical extending radially in
a horizontal direction from a predetermined emitter location. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 169]](../ps.gif) 169 169 | High resistivity base layer: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 168. Subject matter wherein the means for increasing breakdown
voltage includes a base (as contrasted with emitter or collector)
layer which has a relatively high electrical resistivity. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 172]](../ps.gif) 172 172 | With means to lower "ON" voltage drop: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 107. Subject matter wherein the regenerative active junction
type switching device comprises means to lower the voltage drop
across the main terminals when the switch is operated in the ON
mode. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 173]](../ps.gif) 173 173 | Device protection (e.g., from overvoltage): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 107. Subject matter wherein the regenerative active junction
type switching device includes means for protecting the device from
destructive overloads (e.g., from operating voltage above a particular
threshold level).
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 361, | Electricity: Electrical Systems and Devices,
subclasses 91.1+ for overvoltage protection in safety and protection
of systems and devices. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 175]](../ps.gif) 175 175 | With means to control triggering (e.g., gate electrode
configuration, Zener diode firing, dV/Dt control, transient
control by ferrite bead, etc.): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 107. Subject matter wherein the regenerative active junction
type switching device includes means for controlling device turn-on.
| | (1)
Note. Transient electrical phenomena, e.g., damped oscillations
or surges in operation current or voltage following a sudden change
in the applied voltage or current to the device, may be controlled, for
example, by use of ferrite bead or capacitive input means. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 177]](../ps.gif) 177 177 | With housing or external electrode: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 107. Subject matter wherein the regenerative active junction
type switching device includes a structure in which to place the
device.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 81, | and 82, for a light emitting device in combination
with or constituting a light responsive device, with specific housing
structure. |
| 99, | for light emitting device with specific housing
structure. |
| 433, | and 434, for light responsive device with housing
or encapsulation means. |
| 573, | for Darlington configuration bipolar transistor
structure with housing or contact structure. |
| 584, | for enlarged emitter device bipolar transistor means
having housing or contact. |
| 602, | for a voltage variable capacitance device with specified
housing or contact. |
| 660, | for means to shield a device contained in a housing. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 180]](../ps.gif) 180 180 | Stud mount: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 177. Subject matter wherein the housing is provided with a threaded
or serrated insert or post used for connecting heat sinks or terminals
to the device. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 183]](../ps.gif) 183 183 | HETEROJUNCTION DEVICE: |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter wherein the active solid-state device contains
a heterojunction, i.e., a boundary between different regions, one
of which is made of a material that differs from that of the other
region.
| | (1)
Note. See illustration, below, for an example of a heterojunction
bipolar transistor.
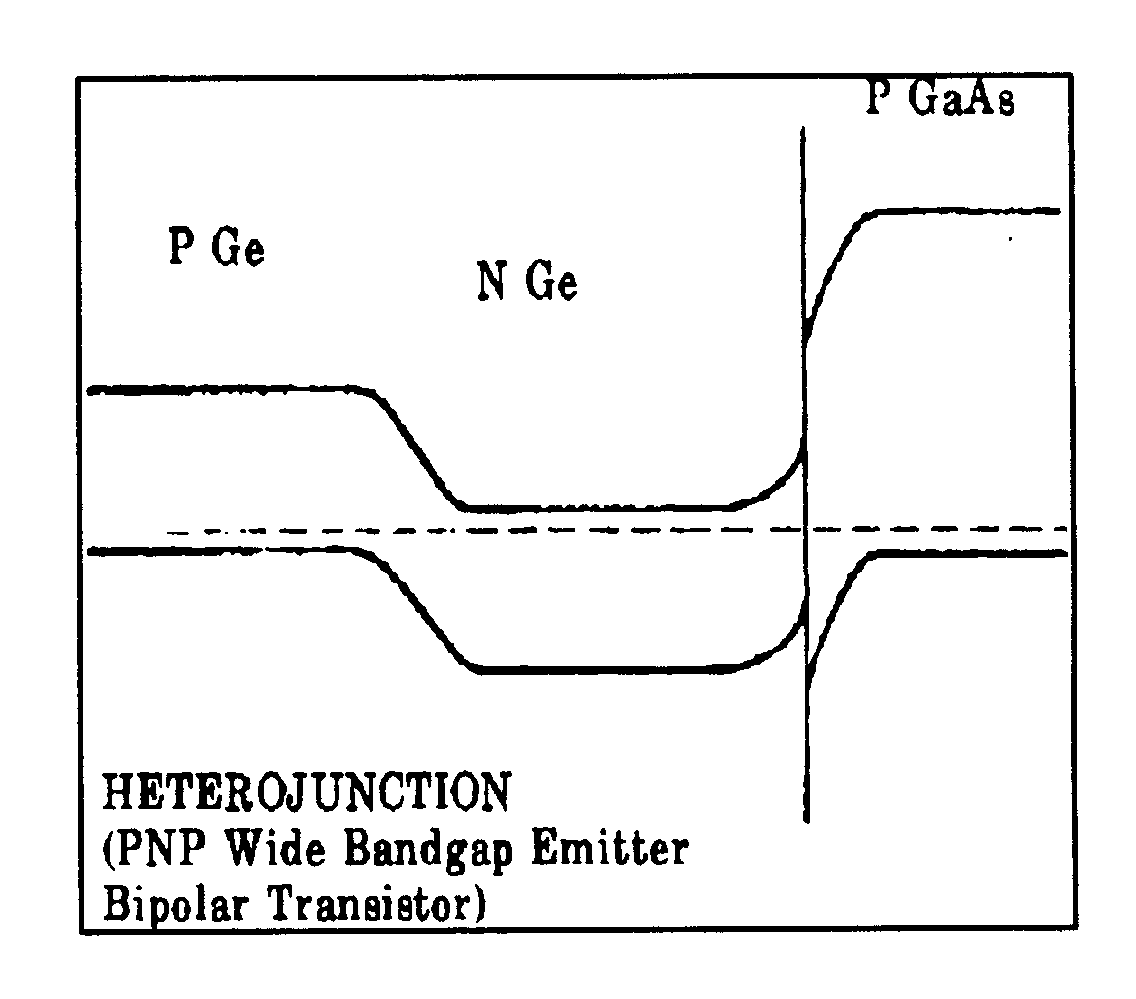
| SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 10, | and 11, for a heterojunction involving a low workfunction
layer for electron emission. |
| 12, | through 27, for heterojunction devices which involve
quantum well, superlattice or ballistic (hot carrier) transport
devices. |
| 51, | for a non-single crystal material/monocrystal
heterojunction device. |
| 85, | for a light emitting structure device combined with
a light responsive device in an integrated structure wherein the
light responsive device has a heterojunction. |
| 90, | for plural light emitting heterojunction devices. |
| 94, | through 97, for heterojunction light emitter structures. |
| 183.1, | for a heterojunction charge transfer device. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 372, | Coherent Light Generators,
subclasses 43 through 50for semiconductor lasers which may contain heterojunctions. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 183.1]](../ps.gif) 183.1 183.1 | Charge transfer device: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 183. Subject matter in which storage sites for packets of electric
charge are induced at or below the surface of the active solid-state
(semiconductor) device by an electric field applied to the device
and wherein carrier potential energy per unit charge minima is established
at a given storage site and such minima is transferred to one or
more adjacent storage sites in a serial manner and which contains
a junction between two semiconductor materials of different chemical
compositions each different composition having a different carrier
affinity.
| | (1)
Note. Typically, heterojunctions are between materials which
additionally have different band gaps, but that is not true of all
heterojunctions. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 215, | for charge transfer devices which do not involve
heterojunctions. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 185]](../ps.gif) 185 185 | Staircase (including graded composition) device: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 184. Subject matter wherein the active region contains a number
of layers forming plural heterojunctions and the carrier (i.e.,
electron or hole) affinities of each layer incrementally increase or
decrease progressively across the active region thickness, so that
the energy level diagram of the active region, when under electrical
bias, resembles a staircase.
| | (1)
Note. Staircase effect devices may also be provided with
a graded composition, i.e., wherein the chemical composition of
the semiconductor forming the heterojunction varies in a direction
either perpendicular or parallel to the junction. |
| | (2)
Note. See illustration, below, for an example of a staircase
bandgap.
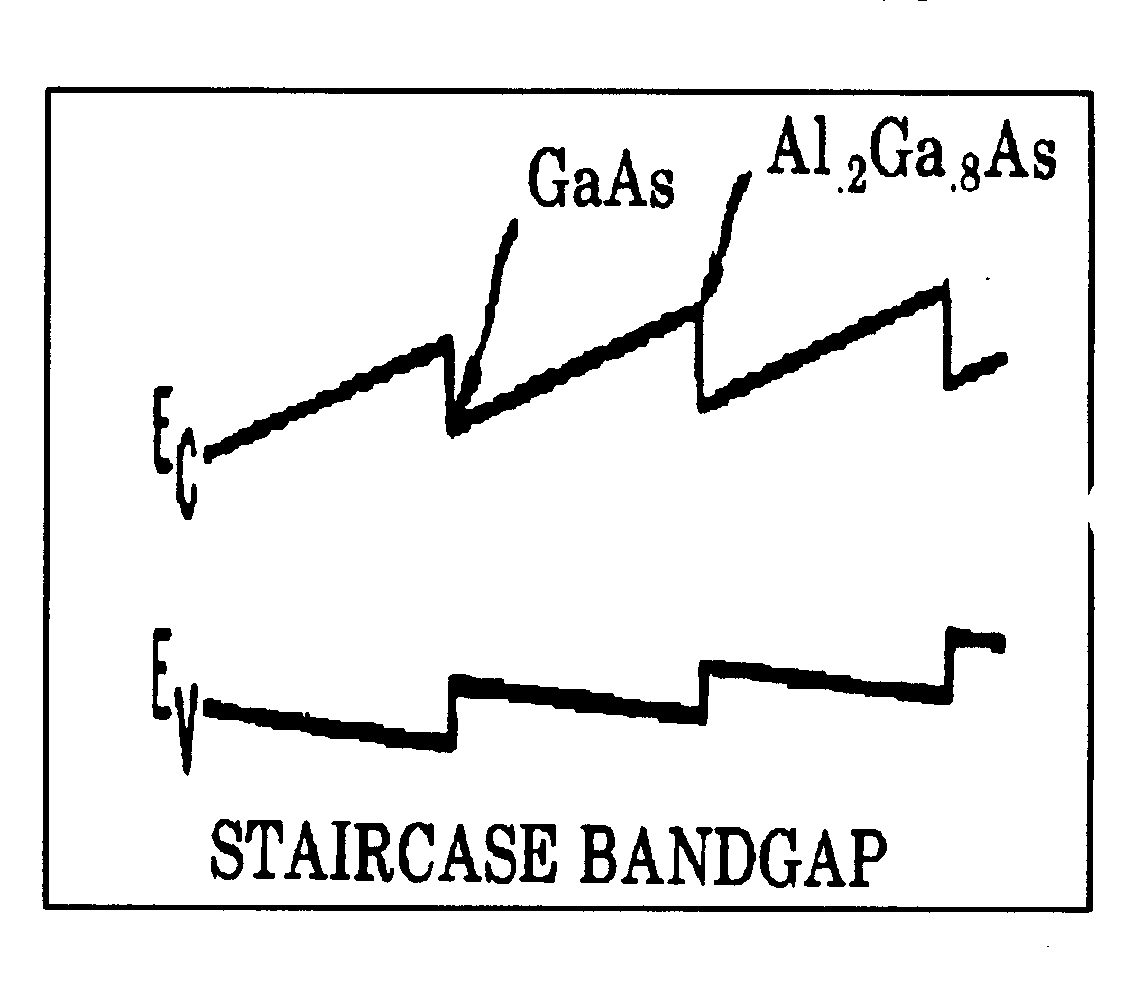
| |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 186]](../ps.gif) 186 186 | Avalanche photodetection structure: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 184. Subject matter wherein carriers generated in the active
region of the device in response to light incident thereupon, achieve
enough kinetic energy to knock further carriers from the crystalline
lattice of the active region producing an avalanche or snowball
increase in operating current level.
| | (1)
Note. Avalanche photodetector devices may have bipolar transistor
structure, i.e., wherein the heterojunction device has three terminals
- an emitter, a collector and a base, the operating current comprising
both positive and negative electrical charges. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 187]](../ps.gif) 187 187 | Having transistor structure: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 184. Subject matter wherein the light responsive heterojunction
device has three terminals - an emitter, collector, and a base;
a source, drain, and gate; or a hybrid combination of each, which
can provide gain or can be used as a switch. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 189]](../ps.gif) 189 189 | Layer is a group III-V semiconductor compound: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 188. Subject matter wherein the narrow energy band gap layer
is a semiconductor compound made of one element taken from periodic
table group III elements and another element taken from periodic
table group V elements. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 190]](../ps.gif) 190 190 | With lattice constant mismatch (e.g., with buffer layer
to accommodate mismatch): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 183. Subject matter wherein at least one of the materials that
form the heterojunction has a crystalline lattice constant which
is made to differ from the lattice constant of the other material which
forms the heterojunction.
| | (1)
Note. Typically, lattice mismatches are sought to be avoided.
However, sometimes they are desired, as for example, when the resulting
strain favorably affects the properties of the strained semiconductor. |
| | (2)
Note. A buffer layer may be provided to accommodate a lattice
mismatch, i.e., a layer of material which mechanically separates
the layers which have different lattice constants. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 18, | for strained layer heterojunctions in a superlattice. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 191]](../ps.gif) 191 191 | Having graded composition: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 183. Subject matter wherein the chemical composition of the semiconductor
forming the heterojunction varies continuously in a direction either
perpendicular or parallel to the junction. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 192]](../ps.gif) 192 192 | Field effect transistor: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 183. Subject matter wherein the heterojunction is part of a field
effect transistor, i.e., wherein the current through the active
heterojunction is controlled by a voltage applied between gate and
source terminals of the device. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 194]](../ps.gif) 194 194 | Doping on side of heterojunction with lower carrier affinity
(e.g., high electron mobility transistor (HEMT)): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 192. Subject matter wherein the heterojunction field effect transistor
has impurity dopant on the side of the heterojunction with lower
affinity for the charge carriers (holes or electrons)
supplied by the dopant, so that the charge carriers spill over the
heterojunction into the side with higher carrier affinity.
| | (1)
Note. Typically, the spilled over charge carriers constitute
the conductive channel connecting the source and drain electrodes. |
| | (2)
Note. Such devices may be provided with a channel layer of
semiconductor material other than group III-V compound semiconductor
(e.g., IV-VI compound semiconductor, germanium semiconductor, etc.). |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 12, | through 27, for other closely related quantum well
and ballistic transport field effect devices. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 195]](../ps.gif) 195 195 | Combined with diverse type device: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 194. Subject matter wherein the heterojunction field effect transistor
with impurity dopant on the side of the heterojunction with lower
affinity for the charge carriers supplied by the dopant is combined
with another electronic device.
| | (1)
Note. Typical diverse devises include complementary field
effect transistors, i.e., a field effect transistor of opposite conductivity
type to the heterojunction field effect transistor; and field effect transistors
of different threshold voltages (e.g., enhancement and depletion HEMTs
in same integrated circuit). | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 197]](../ps.gif) 197 197 | Bipolar transistor: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 183. Subject matter wherein the heterojunction is part of a bipolar
transistor, i.e., a transistor structure whose working current passes through
semiconductor material of both polarities (p and n) which form a
heterojunction portion of the transistor.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 438, | Semiconductor Device Manufacturing: Process, particularly
subclasses 312+ for methods of forming a heterojunction bipolar
transistor. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 198]](../ps.gif) 198 198 | Wide band gap emitter: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 197. Subject matter wherein the bipolar transistor with an active
heterojunction region involves a charge carrier emitter region made
of a semiconductor material having an energy gap between its conduction
and valence bands which is greater than the energy gap of the base region
forming a heterojunction therewith. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 199]](../ps.gif) 199 199 | Avalanche diode (e.g., so-called "Zener" diode
having breakdown voltage greater than 6 volts, including heterojunction IMPATT
type microwave diodes): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 183. Subject matter wherein the heterojunction device is a diode
in which conduction under reverse bias conditions is caused by avalanche
breakdown at an applied voltage greater than 6 volts.
| | (1)
Note. One example of such a device is a microwave transit
time device (e.g., IMPATT diode). |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 481, | for a Schottky barrier avalanche diode. |
| 551, | for an avalanche diode used as a voltage reference
element combined with pn junction isolation means in an integrated
circuit. |
| 603, | through 606, for avalanche diodes not classified
above those subclasses in this schedule, i.e., not involving a heterojunction
in a non-charge transfer device, or a Schottky barrier, or one used
as a voltage reference element with pn junction isolation means
in an integrated circuit. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 331, | Oscillators,
subclasses 107+ for solid-state active element oscillators. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 202]](../ps.gif) 202 202 | GATE ARRAYS: |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter comprising a repeating geometric arrangement
of individual structural units of solid-state devices, the solid-state devices
of each individual structural unit being connectable into various
different types of logic circuits in one integrated, monolithic chip.
| | (1)
Note. The significant distinction between a "gate
array" and other arrays of active solid state devices,
such as read-only memories (ROMs), and programmable logic arrays
(PLAs), is that the solid-state devices of each individual structural
of a "gate array" can be connected into various
different types of logic circuits, whereas in a ROM or PLA, each
of the individual structural units is configured so that they must
be connected into the same type of logic circuit (e.g., wherein
all individual structural units are connected as NOR gates). |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 438, | Semiconductor Device Manufacturing: Process, particularly
subclasses 128+ for methods of forming an array of devices upon
a semiconductor substrate and selectively interconnecting the same. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 203]](../ps.gif) 203 203 | With particular chip input/output means: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 202. Subject matter wherein the gate array integrated circuit
is provided with specific means to input and output electrical signals
to operate the device.
| | (1)
Note. Examples of particular chip input/output means
include (a) interface circuits, i.e., circuits that connect the
chip to another device or to a circuit and which produces necessary
current and voltage characteristics for the interconnected devices
and circuits to function properly, with particular active solid-state
devices used in the interface circuits; (b) structure permitting
electrical interconnection to either receive an input signal or
to output an output signal; or (c) specific bonding pad or electrode configurations
(i.e., wherein the input/output means includes a particular
electrically conductive surface to which electrical interconnecting
element (e.g., electrical leads) can be connected, or has a specified
electrode configuration such as a power supply bus for the input/output
means separate from those used to power the gate array devices. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 210]](../ps.gif) 210 210 | With wiring channel area: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 208. Subject matter wherein the signal paths in the array are
located in an area separate from the active devices forming the
elements of the array. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 211]](../ps.gif) 211 211 | Multi-level metallization: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 208. Subject matter wherein the particular signal path connections
include more than one layer of conductive metal deposited on a substrate.
| | (1)
Note. The multilayer metallization may include a layer of
material made up of silicon in polycrystalline form or a silicide
compound. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 212]](../ps.gif) 212 212 | CONDUCTIVITY MODULATION DEVICE (E.G., UNIJUNCTION TRANSISTOR,
DOUBLE-BASE DIODE, CONDUCTIVITY-MODULATED TRANSISTOR): |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter wherein the active solid-state device has
a high resistivity semiconductor region of one conductivity type
having a region of opposite conductivity type forming a pn junction
with a central portion of the high resistivity layer, with structural
means provided to forward bias the pn junction to inject minority
carriers into the high resistivity region to increase its conductivity
through conductivity modulation.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 327, | Miscellaneous Active Electrical Nonlinear Devices,
Circuits, and Systems,
subclasses 397 and 402 for a delay controlled switch using a unijunction transistor
and having a variable or fixed delay respectively; subclasses 438+ for
gating circuits utilizing a unijunction transistor, and subclass 569
for a miscellaneous circuit which utilizes a unijunction transistor. |
| 361, | Electricity: Electrical Systems and Devices,
subclass 91.3 for overvoltage protection with time delay, and subclass
198 for time delay with unijunction devices. |
| 388, | Electricity: Motor Control Systems,
subclass 919 for unijunction transistor circuit trigger control
means. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 213]](../ps.gif) 213 213 | FIELD EFFECT DEVICE: |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter comprising a field effect transistor, in
which the density of electrical charge (electrons or holes) in a
semiconductor region is controlled by a voltage applied to an adjacent
region or electrode which in operation is prevented from conducting
direct electrical current to or from the semiconductor region by an
insulator or barrier region.
| | (1)
Note. The conduction of current in a field effect device
is along a path called a channel. |
| | (2)
Note. See Illustration, below, for various types of field
effect devices.
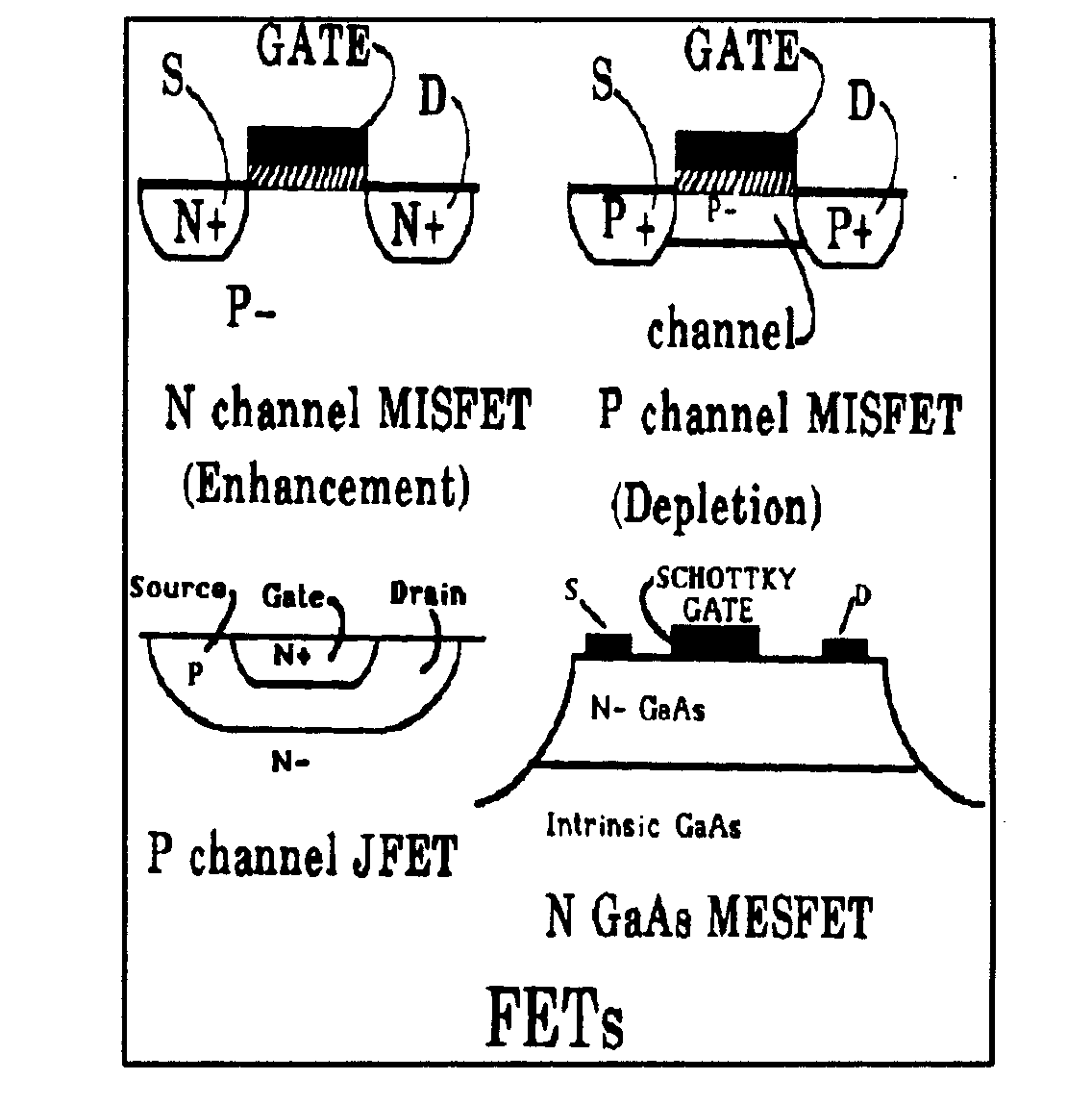
| SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 331, | Oscillators,
subclasses 116 and 117 for field effect transistor oscillator active
elements. |
| 341, | Coded Data Generation or Conversion,
subclass 136 for analog to or from digital conversion devices
with a field effect transistor. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 214]](../ps.gif) 214 214 | Charge injection device: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 213. Subject matter wherein the field effect device is a device
in which storage sites for packets of electric charge are induced
at or below the surface of the active solid-state (semiconductor) device
by an electric field applied to the device and wherein carrier potential
energy per unit charge minima are established at a given storage
site and such charge packets are injected into the device substrate
or into a data bus.
| | (1)
Note. This type device differs from a charge transfer device
in that, in the latter, charge is transferred to adjacent charge
storage sites in a serial manner whereas in the former, the charge
is injected in a non-serial manner to the device substrate or a
data bus. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 215]](../ps.gif) 215 215 | Charge transfer device: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 213. Subject matter in which storage sites for packets of electric
charge are induced at or below the surface of the active solid-state
(semiconductor) device by an electric field applied to the device
and wherein carrier potential energy per unit charge minima are
established at a given storage site and such minima are transferred
to one or more adjacent storage sites in a serial manner.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 183.1, | for heterojunction type charge transfer devices. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 438, | Semiconductor Device Manufacturing: Process,
subclass 60 for methods of making a photo-responsive semiconductor
integrated circuit having a charge transfer device combined with
another electrical device, subclasses 75+ for methods of
making a photoresponsive charge transfer device, and subclasses
144+ for methods of making a charge transfer device. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 217]](../ps.gif) 217 217 | Having a conductive means in direct contact with channel
(e.g., non-insulated gate): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 216. Subject matter wherein an electrical conductor (e.g., electrode)
directly contacts the channel region of the charge transfer device
(e.g., a non-insulated gate (control) electrode).
| | (1)
Note. The conductive means in direct contact with the channel
may be directly connected to the substrate. |
| | (2)
Note. The conductive means in direct contact with the channel
may be made of metal, forming a Schottky contact with the semiconductor
channel material, i.e., a metal-semiconductor junction. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 219]](../ps.gif) 219 219 | Impurity concentration variation: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 216. Subject matter wherein the majority signal carrier charge
transfer device contains impurity dopant ions which vary in terms
of concentration in all or part of the channel of the device.
| | (1)
Note. The impurity dopant ion concentration may vary across
the channel and channel substrate interface. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 220]](../ps.gif) 220 220 | Vertically within channel (e.g., profiled): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 219. Subject matter wherein the impurity dopant ion concentration
in the channel of the device varies across the channel in a direction
perpendicular to a main surface of the device, regardless of the
orientation of the channel (e.g., parallel or perpendicular to a
main surface of the device). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 224]](../ps.gif) 224 224 | Channel confinement: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 216. Subject matter wherein the majority carrier charge transfer
device has means to restrict the dimensions of the thin semiconductor
conductive path region (charge transfer channel) between the source
and drain of the device. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 228]](../ps.gif) 228 228 | Light responsive, back illuminated: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 225. Subject matter wherein the non-electrical input responsive
device has two major opposed surfaces, the channel containing the
charge carrier storage sites being at or below one surface, and wherein
the device is responsive to light which is incident on the other
major surface. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 229]](../ps.gif) 229 229 | Having structure to improve output signal (e.g., exposure
control structure): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 225. Subject matter wherein the non-electrical input responsive
device contains structural means to improve the electrical signal
it generates in response to the non-electrical input signal.
| | (1)
Note. The structural means to improve the output signal may
control the amount of charge generated by light incident on the
device which is transferred as output signal charge. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 230]](../ps.gif) 230 230 | With blooming suppression structure: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 229. Subject matter wherein the structural means to improve the
output signal prevents spill over of a large amount of signal charge
generated at a storage site which receives a non-electrical input
signal of very high intensity to adjacent storage sites.
| | (1)
Note. The antiblooming suppression structure may include
a drain structure for removing charge from storage sites. |
| | (2)
Note. The antiblooming drain structure may be located in
the device beneath storage sites rather than on its surface. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 231]](../ps.gif) 231 231 | 2-dimensional area architecture: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 225. Subject matter wherein the device has a plurality of non-electrical
input responsive means spread out over a two dimensional area, e.g.,
a matrix or array of such means.
| | (1)
Note. One 2-dimensional architecture area may be provided
for light imaging elements and a separate 2-dimensional architecture
area may be provided for electrical signal storage elements. |
| | (2)
Note. The imaging element sites may also be charge transfer
storage sites (e.g., frame transfer imaging device). | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 234]](../ps.gif) 234 234 | Single strip of sensors (e.g., linear imager): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 225. Subject matter wherein the non-electrical input responsive
device is in the form of a line of individual sensors.
| | (1)
Note. The single strip of sensors may be combined with a
structure forming readout registers, i.e., short term storage devices
for accumulating charge packets generated by the sensors and for
transferring charge packets to an amplifier or output device, and
wherein the sensors are placed adjacent to the readout register
structure. |
| | (2)
Note. The device may have plural readout register structures. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 235]](../ps.gif) 235 235 | Electrical input: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 215. Subject matter wherein the input to the charge transfer
device to create the charge to be transferred is an electrical signal. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 236]](../ps.gif) 236 236 | Signal applied to field effect electrode: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 235. Subject matter wherein means is provided to apply an electrical
signal to an electrode which has an electrical potential barrier
between the electrode and the semiconductor material of the device
(e.g., a MOS dielectric or Schottky contact or reverse-biased junction),
as contrasted with an ohmic electrical contact to the semiconductor. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 239]](../ps.gif) 239 239 | Signal charge detection type (e.g., floating diffusion
or floating gate non-destructive output): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 215. Subject matter wherein means is provided to detect the amount
of charge being transferred in the device.
| | (1)
Note. The charge being transferred may be measured without
destroying the charge, i.e., the charge packet remains intact. |
| | (2)
Note. The charge transfer device may have a region diffused
with impurity ions not electrically connected to ground to detect
the magnitude of charge being transferred in the device and to output
a signal proportional to that sensed charge. This is known as a
floating diffusion output device. One example of such a device
is a floating diffusion amplifier (FDA). |
| | (3)
Note. The charge transfer device may have a control electrode
not electrically connected to ground to detect the magnitude of
charge being transferred in the device and to output a signal proportional
to that sensed charge. This type device is known as a floating
gate output device. One example of such a device is a floating
gate amplifier (FGA). Devices with plural floating gate outputs
include distributed floating gate amplifiers (DFGA). | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 241]](../ps.gif) 241 241 | Multiple channels (e.g., converging or diverging or parallel
channels): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 215. Subject matter wherein the charge transfer device contains
more than one channel for charge transfer path.
| | (1)
Note. The channels may converge or diverge, i.e., they are
not parallel to each other, but change direction either toward or
away from each other along their length. |
| | (2)
Note. In such devices, the charge transfer path may lie in
two different (e.g., orthogonal) directions. |
| | (3)
Note. The device may include two or more parallel channels
(e.g., serial- parallel-serial) wherein the charge transfer takes
place in different directions, but the device includes charge transfer
paths that are parallel to each other. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 242]](../ps.gif) 242 242 | Vertical charge transfer: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 215. Subject matter wherein the charge transfer device is provided
with structure for vertical charge transfer perpendicular to a main
device surface. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 243]](../ps.gif) 243 243 | Channel confinement: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 215. Subject matter containing means (e.g., pn junctions or dielectric
layers) to restrict the boundaries of the charge transfer path through
the device.
| | (1)
Note. Typical channel confinement means include use of (a)
an electrically insulating medium; (b) a layer of silicon polymer
material (polysilicon) used to reduce electric field interaction
with charge to be transferred via the channel; or (c) an impurity
ion located in the device substrate, i.e., in the material on which
the device is fabricated (e.g., an implanted channel stop). | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 244]](../ps.gif) 244 244 | Comprising a groove: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 215. Subject matter wherein a surface of the device includes
an elongated indentation.
| | (1)
Note. The location of the groove relative to the charge storage
sites of the device is deliberately not specified in this definition. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 246]](../ps.gif) 246 246 | Phase structure (e.g., doping variations to provide asymmetry
for 2-phase operation; more than four phases or "electrode
per bit"): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 245. Subject matter including a plurality of gate regions or
doping variation regions to permit unidirectional charge packet
transfer by symmetrical or unsymmetrically phased electrical control
signals applied to the device gate or gates.
| | (1)
Note. The phase structure may be multiphase (e.g., 3-phase
or 4-phase), i.e., with three sets or four sets of electrodes, respectively. |
| | (2)
Note. Search subclass 249, below, for 2-phase structure devices. |
| | (3)
Note. Means may also be provided to generate a traveling
wave of non-electrical energy (e.g., acoustic energy) in the device. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 248]](../ps.gif) 248 248 | 2-phase: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 246. Subject matter wherein the device has two sets of gate electrodes. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 250]](../ps.gif) 250 250 | Plural gate levels: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 249. Subject matter wherein the electrode structures include
more than one level of gate electrodes relative to a main surface
of the device. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 256]](../ps.gif) 256 256 | Junction field effect transistor (unipolar transistor): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 213. Subject matter wherein the field effect device is a junction
field effect transistor, i.e., in which current flow through a
thin channel of semiconductor material is controlled by an electric
field applied to a control region or electrode in rectifying contact
(i.e., a pn junction or Schottky barrier junction) with the semiconductor
material of the channel, so that the depletion region extending
into the channel from the rectifying contact reduces the thickness
of the undepleted portion of the channel to reduce the current flow
through the channel.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 438, | Semiconductor Device Manufacturing: Process, particularly
subclasses 167+ for methods of forming a Schottky gate field effect
device and subclasses 186+ for methods of forming a junction
gate field effect device. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 258]](../ps.gif) 258 258 | In imaging array: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 257. Subject matter wherein a plurality of light responsive JFETs
or JFETs combined with a light responsive device are in the form
of a one or two dimensional array (e.g., line or area array) for
forming an image of an object, light from which is incident upon
the array. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 259]](../ps.gif) 259 259 | Elongated active region acts as transmission line or distributed
active element (e.g., "transmission line" field
effect transistor): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 256. Subject matter including at least one elongated active region
(source, gate, or drain) which transmits or distributes charge carriers.
| | (1)
Note. When the impedance of an element at the operating frequency
is due primarily to the parameters of the element itself, and in
considering the inductance, capacitance, and resistance of the element
they must be considered as mixed together and spread out along the element
rather than being considered as separate discrete lumps or components as
in the case of simple series and parallel circuits, the element
may be said to have distributed parameters. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 333, | Wave Transmission Lines and Networks, appropriate subclasses for transmission lines or
distributed elements, per se. |
| 438, | Semiconductor Device Manufacturing: Process, particularly
subclasses 167+ for methods of forming a Schottky gate field effect
device and subclasses 186+ for methods of forming a junction
gate field effect device. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 260]](../ps.gif) 260 260 | Same channel controlled by both junction and insulated
gate electrodes, or by both Schottky barrier and pn junction gates
(e.g., "taper isolated" memory cell): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 256. Subject matter including plural gate electrodes or regions,
at least one of which is isolated from the channel by a rectifying
junction and at least another of which is isolated from the channel
by an insulating layer therebetween, or wherein one rectifying junction
may be a metal-to-semiconductor (Schottky) type and the other a
pn junction.
| | (1)
Note. In such devices, the junction gate region may be free
of direct electrical connection (e.g., "taper isolated" memory
cell), i.e., wherein the JFET has at least one gate electrode region
which is isolated from the channel by a rectifying junction and
is not directly provided with an electrical connection or terminal. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 261]](../ps.gif) 261 261 | Junction gate region free of direct electrical connection
(e.g., floating junction gate memory cell structure): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 256. Subject matter including at least one gate electrode region
which is isolated from the channel by a rectifying junction and
is not directly provided with an electrical connection or terminal.
| | (1)
Note. This type of gate is a floating junction gate, as contrasted
with a floating insulated gate. |
| | (2)
Note. See this class, subclass 315, for floating insulated
gate field effect devices. |
| | (3)
Note. The floating gate region may capacitively store electrical
charge and be used as a memory element. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 262]](../ps.gif) 262 262 | Combined with insulated gate field effect transistor (IGFET): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 256. Subject matter including a field effect transistor having
a gate (control) electrode which is electrically insulated from
the channel and other electrodes of the transistor.
| | (1)
Note. The combined JFET and IGFET may be electrically connected
so that the source or drain electrode of one FET is connected to
the gate electrode of the other FET. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 263]](../ps.gif) 263 263 | Vertical controlled current path: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 256. Subject matter wherein the operating current of the JFET
has a path perpendicular to a main surface of the JFET and is controlled
by the gate electrode of the device. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 264]](../ps.gif) 264 264 | Enhancement mode or with high resistivity channel (e.g.,
doping of 1015cm-3 or
less): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 263. Subject matter wherein an increase in the magnitude of the
gate bias voltage increases the operating current, only leakage
current flows when the gate voltage is zero, and conduction does
not begin until the gate voltage reaches a threshold value; or the
JFET has a channel made of relatively high electrical resistivity, e.g.,
due to doping with impurity ions of 1015 cm-3or
less. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 268]](../ps.gif) 268 268 | Enhancement mode: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 256. Subject matter wherein an increase in the magnitude of the
gate bias voltage increases the operating current, only leakage
current flows when the gate voltage is zero, and conduction does
not begin until the gate voltage reaches a threshold value. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 273]](../ps.gif) 273 273 | With bipolar device: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 272. Subject matter located in an integrated circuit with a device
which operates using both positive and negative charge carriers.
| | (1)
Note. An active solid-state electronic device that contains
both bipolar and field effect transistors may be referred to as
a BI-FET device. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 280]](../ps.gif) 280 280 | With Schottky gate: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 256. Subject matter including a metal to semiconductor rectifying
(i.e., Schottky barrier) gate electrode.
| | (1)
Note. A Schottky barrier gate JFET is referred to commonly
as a MESFET (MEtal-Semiconductor field effect
transistor). | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 286]](../ps.gif) 286 286 | With non-uniform channel thickness or width: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 256. Subject matter wherein the channel has a non-uniform width
or thickness (which lies in a plane perpendicular to both the channel
length and width).
| | (1)
Note. Channel length is measured along a line connecting
the source and drain, while channel width is measured perpendicular
to the length. Both length and width lie in a plane, parallel to
the device surface. See the illustration, below.
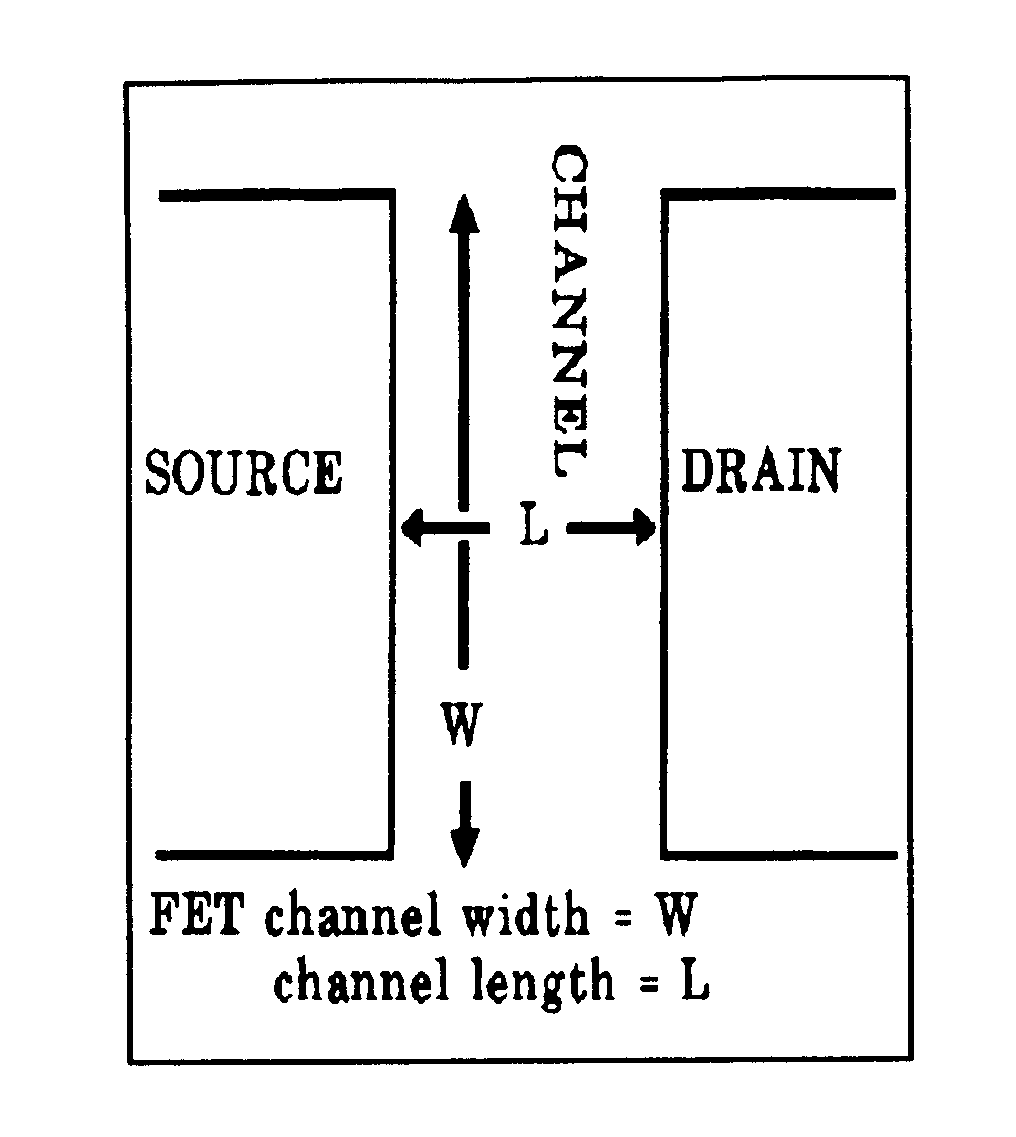
| |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 288]](../ps.gif) 288 288 | Having insulated electrode (e.g., MOSFET, MOS diode): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 213. Subject matter including an electrode which is electrically
insulated from the active semiconductor region of the device (e.g.,
a metal oxide semiconductor insulated electrode).
| | (1)
Note. Typically the insulated electrode is the control or
gate electrode. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 438, | Semiconductor Device Manufacturing: Process, particularly
subclasses 197+ for methods of forming an insulated gate field
effect device. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 291]](../ps.gif) 291 291 | Imaging array: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 290. Subject matter comprising a one or more dimensional array
of light responsive devices which generate an electronic image of
light from an object incident thereupon. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 294]](../ps.gif) 294 294 | With shield, filter, or lens: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 291. Subject matter including means to shield the array from
unwanted light, to filter light incident on the array, or to refract
light incident on the array (e.g., to focus an image of an object on
the array). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 296]](../ps.gif) 296 296 | Insulated gate capacitor or insulated gate transistor combined
with capacitor (e.g., dynamic memory cell): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 288. Subject matter wherein the device gate acts as a capacitor
(i.e., wherein a positive potential placed on the gate electrode
creates a negative charge on the other side of the insulator in
the semiconductor material of the device, and vice versa) or the
device is a transistor and it is combined with a capacitor.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 438, | Semiconductor Device Manufacturing: Process, particularly
subclasses 239+ for methods of forming an insulated gate field
effect transistor combined with a capacitor and subclasses 386 through
399 for manufacture of a capacitors, per se, utilizing a semiconductor
substrate. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 297]](../ps.gif) 297 297 | With means for preventing charge leakage due to minority
carrier generation (e.g., alpha generated soft error protection
or "dark current" leakage protection): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 296. Subject matter wherein the device further includes means
(1) to prevent electrical charge in the capacitor or capacitive
type insulated gate region of the transistor to leak therefrom, or
(2) to prevent excess leakage currents across pn junctions due
to generation of minority carriers in the device for example (a)
alpha particles incident on the device or (b) thermal generation
of electron-hole pairs, or (c) minority carriers injected into
the semiconductor substrate by other devices in the same substrate.
| | (1)
Note. Junctions across which excess leakage is sought to
be prevented typically include (a) the source or drain junction
of an insulated gate field effect transistor or (b) a connecting
BIT line of a memory array which is isolated by a pn junction from
a semiconductor substrate. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 302]](../ps.gif) 302 302 | Vertical transistor: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 301. Subject matter combined with a vertical transistor (i.e.,
one in which the operating current flow is perpendicular to a main
surface of the device). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 303]](../ps.gif) 303 303 | Stacked capacitor: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 301. Subject matter wherein the trench capacitor device contains
a number of capacitor electrode regions stacked vertically above
each other or wherein the capacitor and the transistor are located
such that one overlies the other. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 306]](../ps.gif) 306 306 | Stacked capacitor: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 296. Subject matter wherein the capacitor device contains a number
of capacitor electrode regions overlying each other or where the capacitor
and the transistor are located such that one overlies the other. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 313]](../ps.gif) 313 313 | Inversion layer capacitor: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 296. Subject matter wherein one plate of the capacitor device
is a layer of minority carriers opposite in conductivity type to
the doping of the semiconductor which are induced by applied voltage. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 314]](../ps.gif) 314 314 | Variable threshold (e.g., floating gate memory device): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 288. Subject matter wherein the device has a threshold voltage
for current conduction which may be varied (e.g., by storage of
charge in an insulator layer adjacent the channel in response to an
electrical "write" signal).
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 239, | for a floating gate signal charge detection type
charge transfer device. |
| 261, | for a floating gate JFET. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 365, | Static Information Storage and Retrieval, appropriate subclass for read/write static storage
systems, and
subclasses 185.01+ for predominate structure of floating gate memory storage
(e.g., flash memory), particularly subclass 185.24 for threshold setting
(e.g., conditioning). |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 315]](../ps.gif) 315 315 | With floating gate electrode: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 314. Subject matter including a gate electrode which is free
of direct electrical connection.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 365, | Static Information Storage and Retrieval, appropriate subclass for read/write static storage
systems, and
subclasses 185.01+ for predominate structure of floating gate memory storage
(e.g., flash memory), particularly subclass 185.24 for threshold setting
(e.g., conditioning). |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 323]](../ps.gif) 323 323 | With means to facilitate light erasure: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 315. Subject matter including means to make erasure of the electrical
charge content of the device by light easier (e.g., by providing
an ultraviolet light window layer over the floating gate electrode
to reduce absorption of erasing light). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 327]](../ps.gif) 327 327 | Short channel insulated gate field effect transistor: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 288. Subject matter wherein the field effect device is an insulated
gate field effect transistor with a short channel (i.e., one wherein
the length of the channel is sufficiently short that the threshold
voltage of the transistor depends on the length of the channel,
or where the channel is specified to be less than 2 micrometers
in length). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 329]](../ps.gif) 329 329 | Gate controls vertical charge flow portion of channel (e.g.,
VMOS device): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 327. Subject matter wherein the short channel IGFET has a channel
portion in which charge flows in a substantially vertical direction
and wherein the charge flowing therein is controlled by the gate
electrode.
| | (1)
Note. An IGFET"s short channel may have horizontal
as well as vertical charge flow portions. This subclass provides for
those devices in which the vertical charge flow portion, i.e., the
portion of the channel in which charge is flowing substantially
in a vertical direction, of the channel is controlled by the gate. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 330]](../ps.gif) 330 330 | Gate electrode in groove: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 329. Subject matter wherein the gate controlled vertical channel
device has a groove located therein and a gate electrode located
in the groove. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 337]](../ps.gif) 337 337 | In integrated circuit structure: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 335. Subject matter wherein the graded channel doping short channel
IGFET is contained in a single monolithic chip with other active
or passive solid-state electronic devices. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 338]](../ps.gif) 338 338 | With complementary field effect transistor: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 337. Subject matter wherein the graded channel doping short channel
IGFET is contained in a single monolithic chip with a field effect
transistor with a polarity type opposite to that of the graded channel
doping short channel IGFET. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 339]](../ps.gif) 339 339 | With means to increase breakdown voltage: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 335. Subject matter wherein the graded channel doping short channel
IGFET includes means to increase the voltage that may be applied
to the device without electrical breakdown of the device occurring. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 347]](../ps.gif) 347 347 | Single crystal semiconductor layer on insulating substrate
(SOI): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 288. Subject matter wherein the field effect device has a single
crystal semiconductor layer located on a substrate made of electrically
insulating material.
| | (1)
Note. See this class, subclass 49, for active solid-state
devices in non-single crystalline layers which may be on insulating
substrates. See this class, subclass 506, for active devices in
single crystal layers which are dielectrically isolated, but do
not include field effect devices. |
| | (2)
Note. Material deposited as polycrystalline or amorphous
and then recrystallized, as by a scanning laser beam, is considered
to be non-single crystalline for purposes of determining classification
between this subclass and subclass 49, since such recrystallization
typically leaves residual grain boundaries and is thus large grained
polycrystalline material, rather than true single crystal material. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 438, | Semiconductor Device Manufacturing: Process, particularly
subclasses 149+ for methods of forming a field effect transistor
on an insulating substrate or layer (e.g., SOS, SOI, etc.). |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 348]](../ps.gif) 348 348 | Depletion mode field effect transistor: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 347. Subject matter wherein the SOI device is a field effect
transistor which operates in the depletion mode, i.e., a FET which
passes maximum operating current with the gate to source biased
to zero volts. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 361]](../ps.gif) 361 361 | For operation as bipolar or punchthrough element: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 360. Subject matter wherein the insulated gate transistor structure
protection device is configured to operate as a bipolar transistor
or to conduct by punchthrough of a depletion region from one pn
junction to another pn junction upon application of an overvoltage. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 362]](../ps.gif) 362 362 | Punchthrough or bipolar element: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 356. Subject matter wherein the means for protecting against
insulator breakdown is a bipolar device or is configured to conduct
by punchthrough of a depletion region from one pn junction to another
pn junction upon application of an overvoltage. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 370]](../ps.gif) 370 370 | Combined with bipolar transistor: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 369. Subject matter including at least one bipolar transistor.
| | (1)
Note. An active solid-state electronic device that contains
both bipolar and field effect transistors may be referred to as
a BI-FET device. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 372]](../ps.gif) 372 372 | With means to prevent latchup or parasitic conduction channels: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 369. Subject matter including means to prevent conduction between
regions of complementary IGFETs which form a (parasitic) regenerative structure
which remains ON in the absence of a triggering signal.
| | (1)
Note. For a definition of the regenerative structure of this
subclass type, see subclass 107. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 378]](../ps.gif) 378 378 | Combined with bipolar transistor: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 368. Subject matter wherein the IGFET is combined with a bipolar
transistor in a single semiconductor chip.
| | (1)
Note. An active solid-state electronic device that contains
both bipolar and field effect transistors may be referred to as
a BI-FET device. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 382]](../ps.gif) 382 382 | With contact to source or drain region of refractory material
(e.g., polysilicon, tungsten, or silicide): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 368. Subject matter wherein the device has an electrical contact
to its source region or drain region wherein the contact is made
of a refractory or platinum group metal, or of other material which
has a melting point above that of the iron group of metals and which
is resistant to heat (e.g., of polysilicon, tungsten or silicide).
| | (1)
Note. Refractory materials include refractory metals and
platinum group metals which include metals found in groups IVA,
VA, VIA, or VIIIA (other than iron (Fe), nickel (Ni) or cobalt (Co)) of
the periodic table of the elements. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 395]](../ps.gif) 395 395 | Thick insulator portion: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 394. Subject matter wherein the means to prevent parasitic conduction
channels from forming includes a thick insulator portion. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 397]](../ps.gif) 397 397 | In vertical-walled groove: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 396. Subject matter wherein the recessed thick isolator portion
is in a groove in the surface of the overall device which extends
perpendicular to the surface of the overall device. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 414]](../ps.gif) 414 414 | RESPONSIVE TO NON-ELECTRICAL SIGNAL (E.G., CHEMICAL, STRESS, LIGHT,
OR MAGNETIC FIELD SENSORS): |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter wherein the device generates an electrical
signal in response to a non-electrical signal (e.g., light, heat,
pressure) incident thereon. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 415]](../ps.gif) 415 415 | Physical deformation: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 414. Subject matter wherein the non-electrical signal incident
upon the active solid-state device is a force which physically deforms
the device.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 438, | Semiconductor Device Manufacturing: Process, particularly
subclasses 50+ for methods of forming semiconductor devices which
are responsive to physical deformation. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 416]](../ps.gif) 416 416 | Acoustic wave: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 415. Subject matter wherein the physically deforming force is
in the form of a traveling vibration made up of sound energy.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 254, | for field effect acoustic wave responsive devices. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 417]](../ps.gif) 417 417 | Strain sensors: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 415. Subject matter wherein the physically deforming force is
that of an applied stress.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 254, | for field effect strain sensor devices. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 421]](../ps.gif) 421 421 | Magnetic field: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 414. Subject matter wherein the non-electrical signal to which
the active solid-state device responds, is a magnetic field.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 108, | for regenerative type magnetic field responsive
devices |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 428]](../ps.gif) 428 428 | Electromagnetic or particle radiation: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 414. Subject matter wherein the electrical signal is generated
by the device in response to radiant energy in the electromagnetic
energy spectrum or in the form of neutral or charged particles (e.g.,
alpha or beta particles). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 431]](../ps.gif) 431 431 | Light: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 428. Subject matter wherein the non-electrical signal to which
the device responds is electromagnetic energy in the light frequency/wavelength range
(i.e., from infrared (except where the response is mainly due to
thermal heating due to the infrared radiation) to visible and ultraviolet).
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 21, | for light responsive superlattice quantum well heterojunction
tunneling devices. |
| 53, | through 56, for amorphous semiconductor junction
material devices which are responsive to non-electrical (e.g., light)
signals. |
| 80, | through 85, for light emitters combined with or
also constituting a light responsive device. |
| 113, | through 118, for light activated regenerative type
devices. |
| 184, | through 189, for light responsive heterojunction
devices in non-charge transfer devices. |
| 225, | through 234, for charge transfer devices with non-electrical
(e.g., light) input. |
| 257, | through 258, for light responsive JFET devices. |
| 290, | through 294, for light responsive insulated electrode
field effect devices. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 438, | Semiconductor Device Manufacturing: Process, particularly
subclasses 54+ for methods of making a temperature responsive
semiconductor device. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 432]](../ps.gif) 432 432 | With optical element: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 431. Subject matter wherein the light incident upon the active
region passes through an optical element (e.g., a fiber, lens, filter,
etc.). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 434]](../ps.gif) 434 434 | With window means: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 433. Subject matter with means to optically couple the light
to the device through a transparent window. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 435]](../ps.gif) 435 435 | With optical shield or mask means: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 431. Subject matter with means to spatially or temporally block
all or part of the light incident on the portions of the device
receptor region, other than the intended region. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 437]](../ps.gif) 437 437 | Antireflection coating: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 436. Subject matter wherein the means for increasing light absorption
by the junction is a coating applied to the device which reduces
reflection of the incident light (e.g., by use of interference films). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 438]](../ps.gif) 438 438 | Avalanche junction: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 431. Subject matter wherein the device has a junction which is
operated in the avalanche portion of its operating curve to utilize
the avalanche multiplication of photocurrent by means of hole-electron
pairs created by absorbed photons.
| | (1)
Note. When the reverse bias voltage applied to the device
approaches breakdown level, the holes or electrons collide with
substrate atoms to produce an avalanche of hole-electron pairs. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 445]](../ps.gif) 445 445 | With antiblooming means: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 443. Subject matter with means to prevent more than one individual
light responsive element from being activated by a very bright spot
of light incident on a point of the matrix or array.
| | (1)
Note. The anti-blooming means may drain charge from adjacent
individual array elements to some other area, e.g., the substrate.
This is known as an overflow drain. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 455]](../ps.gif) 455 455 | Silicide of Platinum group metal: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 454. Subject matter wherein the Schottky layer is a silicide
of a metal found in the period table listed as a platinum group
metal (i.e., ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, osmium, iridium, and
platinum). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 461]](../ps.gif) 461 461 | Light responsive pn junction: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 431. Subject matter wherein the device has a junction between
p-type and n-type material which responds to light incident upon
it by generating a signal proportional thereto. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 462]](../ps.gif) 462 462 | Phototransistor: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 461. Subject matter wherein the pn junction device is a transistor
wherein the device generates an electrical signal in response to
light incident on the transistor. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 467]](../ps.gif) 467 467 | Temperature: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 414. Subject matter wherein the non-electrical signal to which
the device responds is thermal energy.
| | (1)
Note. Infrared energy incident on the active junction which
does not cause significant thermal heating of the device is classified
in subclass 431. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 438, | Semiconductor Device Manufacturing: Process, particularly
subclasses 54+ for methods of making a temperature responsive
semiconductor device. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 470]](../ps.gif) 470 470 | Pn junction adapted as temperature sensor: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 467. Subject matter wherein the active junction is a pn junction
(i.e., forms a boundary between p-type and n-type carrier materials)
and generates an electrical signal in response to thermal energy
incident upon the active junction. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 471]](../ps.gif) 471 471 | SCHOTTKY BARRIER: |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter wherein the device contains a Schottky barrier
(i.e., a rectifying interface between a semiconductor material and
a metal).
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 54, | for Schottky barrier to amorphous semiconductor
material device. |
| 73, | for Schottky barrier to polycrystalline semiconductor
material device. |
| 155, | for a regenerative type switching device with switching
speed enhancement means (e.g., a Schottky contact). |
| 260, | for JFET having the same channel controlled by,
for example, Schottky barrier and PN junction gates. |
| 280, | through 284, for JFETs with a Schottky gate electrode. |
| 449, | through 457, for a light responsive device with
a Schottky barrier. |
| 928, | for a shorted pn or Schottky junction device. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 438, | Semiconductor Device Manufacturing: Process, particularly
subclasses 570+ for methods of forming a rectifying (Schottky)
contact to a semiconductor. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 475]](../ps.gif) 475 475 | With doping profile to adjust barrier height: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 471. Subject matter wherein the difference in electrical potential
from one side of an active junction to the other has been adjusted
by a distribution of impurity dopant in the semiconductor adjacent
the Schottky junction. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 477]](../ps.gif) 477 477 | With bipolar transistor: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 476. Subject matter wherein the Schottky barrier device is located
in a single integrated monolithic semiconductor chip with a bipolar
transistor. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 481]](../ps.gif) 481 481 | Avalanche diode (e.g., so-called "Zener" diode
having breakdown voltage greater than 6 volts): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 471. Subject matter wherein the Schottky barrier is in a device
designed to operate in avalanche breakdown.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 199, | for an avalanche diode in a non-charge transfer
device having a heterojunction. |
| 551, | for an avalanche diode used as a voltage reference
element combined with pn junction isolation means in an integrated
circuit. |
| 603, | through 606, for avalanche diodes not classified
above those subclasses in this schedule, i.e., not involving a heterojunction
in a non-charge transfer device, or a Schottky barrier, or one used
as a voltage reference element with pn junction isolation means
in an integrated circuit. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 484]](../ps.gif) 484 484 | Guard ring: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 483. Subject matter wherein the means to prevent edge breakdown
is a guard ring (e.g., a pn junction surrounding the periphery of
the Schottky metal). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 487]](../ps.gif) 487 487 | WITH MEANS TO INCREASE BREAKDOWN VOLTAGE THRESHOLD: |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter wherein the device is provided with means
to increase the voltage that may be applied thereto without causing
electrical breakdown. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 488]](../ps.gif) 488 488 | Field relief electrode: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 487. Subject matter wherein the means to increase breakdown voltage
comprises an electrode insulated from the semiconductor material
of the active solid-state device, and configured so as to reduce
the electric field strength at a given voltage applied to the device. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 489]](../ps.gif) 489 489 | Resistive: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 488. Subject matter wherein the field relief electrode is a high
resistance layer adapted to have a current flow therethrough and
a corresponding voltage variation therein. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 490]](../ps.gif) 490 490 | Combined with floating pn junction guard region: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 488. Subject matter wherein the means for increasing breakdown
voltage includes, in addition to a field relief electrode, a floating
pn junction guard region, i.e., a region free of direct electrical
connection located in the material forming one side of an active
pn, or other rectifying semiconductor junction, which region forms
a pn junction with the material of the one side of the active junction,
the guard region being spaced from the active junction, but sufficiently
close thereto that the reverse bias depletion region from the active
junction can reach the guard junction, whereby the guard junction modifies
the shape of the depletion region from the active junction thus
lowering the electric field intensity at a given applied reverse
voltage across the active junction. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 491]](../ps.gif) 491 491 | In integrated circuit: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 487. Subject matter wherein the device with means to increase
breakdown voltage is combined in a unitary monolithic semiconductor
chip with other active or passive electronic devices.
| | (1)
Note. The means for increasing breakdown voltage in the integrated
circuit active device may include a floating pn junction guard
region, that is, a region, free of direct electrical connection, located
in the material forming one side of an active pn or other rectifying
semiconductor junction, which region forms a pn junction with the
material of the one side of the active junction, the guard region
being spaced from the active junction but sufficiently close thereto that
the reverse bias depletion region from the active junction can reach
the guard junction, whereby the guard junction modifies the shape
of the depletion region from the active junction thus lowering the
electric field intensity at a given applied reverse voltage across
the active junction. |
| | (2)
Note. The means for increasing the breakdown voltage of the
integrated circuit device may include a semiconductor surface portion
having a physical configuration, such as a bevel or mesa, to reduce
electric field strength at a given applied voltage. Typically,
the physical configuration will be such that the depletion region
from a reverse biased junction in the active device reaches the physically
configured surface and is forced by the shape of the surface to spread
wider at a given applied reverse voltage than it would otherwise,
thus reducing the electric field strength in the depletion layer. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 492]](../ps.gif) 492 492 | With electric field controlling semiconductor layer having
a low enough doping level in relationship to its thickness to be
fully depleted prior to avalanche breakdown (e.g., RESURF devices): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 491. Subject matter wherein the means to increase breakdown voltage
of the device includes a layer of semiconductor material having
a sufficiently low doping concentration that it may be fully depleted
by the depletion region of a reverse biased junction of the active
device prior to avalanche breakdown of the active device, so that
upon depletion of the layer of semiconductor material, the effective
width of the depletion layer of the reverse biased junction of the
active device is greatly expanded, thus resulting in smaller increases
in electric field intensity with further increases of reverse voltage.
| | (1)
Note. Devices provided with such a layer are sometimes called "RESURF" (Reduced
SURFace Field) devices. |
| | (2)
Note. In silicon, to be fully depleted without avalanche
breakdown, a layer must typically have an integrated doping density
(the line integral of doping density along a path through the thickness
of the layer) of less than 2x1012 dopant atoms/cm2.
The critical integrated doping density varies depending on the properties
of the particular semiconductor material. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 494]](../ps.gif) 494 494 | Reverse-biased pn junction guard region: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 487. Subject matter wherein the means for increasing breakdown
voltage in the device includes a reverse biased pn junction guard
region, that is, a region located in the material forming one side
of an active pn or other rectifying semiconductor junction, which
region forms a pn junction with the material of the one side of
the active junction, the guard region being adapted to be reverse
biased with respect to the material forming one side of the active
junction, and being spaced from the active junction, but sufficiently
close thereto that the reverse bias depletion region from the active
junction can reach the depletion region from the reverse biased
guard junction, whereby the depletion region of the guard junction
modifies the shape of the depletion region from the active junction thus
lowering the electric field intensity at a given applied reverse
voltage across the active junction. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 495]](../ps.gif) 495 495 | Floating pn junction guard region: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 487. Subject matter wherein the means for increasing breakdown
voltage in the device includes a floating pn junction guard region,
that is, a region, free of direct electrical connection, located
in the material forming one side of an active pn or other rectifying
semiconductor junction, which region forms a pn junction with the
material of the one side of the active junction, the guard region
being spaced from the active junction, but sufficiently close thereto
that the reverse bias depletion region from the active junction
can reach the guard junction, whereby the guard junction modifies the
shape of the depletion region from the active junction thus lowering
the electric field intensity at a given applied reverse voltage across
the active junction. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 496]](../ps.gif) 496 496 | With physical configuration of semiconductor surface to
reduce electric field (e.g., reverse bevels, double bevels, stepped mesas,
etc.): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 487. Subject matter wherein the means to increase breakdown voltage
includes a semiconductor surface portion having a physical configuration,
such as a bevel or mesa, to reduce electric field strength at a
given applied voltage. Typically, the physical configuration will
be such that the depletion region from a reverse biased junction
in the active device reaches the physically configured surface and
is forced by the shape of the surface to spread wider at a given applied
reverse voltage than it would otherwise, thus reducing the electric
field strength in the depletion layer. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 497]](../ps.gif) 497 497 | PUNCHTHROUGH STRUCTURE DEVICE (E.G., PUNCHTHROUGH TRANSISTOR,
CAMEL BARRIER DIODE): |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter having at least one active pn, Schottky barrier,
or other rectifying junction which can be reverse biased to produce
a depletion layer, the active junction being spaced from a second
junction by a layer of semiconductor material in which the depletion region
extending from the active junction is produced, the second junction
being one capable of supplying minority carriers to the layer of
semiconductor material upon forward bias of the second junction,
and in which the second junction is located sufficiently close to
the active junction that the depletion region from the active junction
can reach the second junction, thereby forward biasing the second
junction and causing the injection of minority carriers therefrom
which traverse the depletion layer and reach the active junction.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 361+, | for punchthrough structure elements used to protect
against overvoltage gate insulator breakdown of insulated gate devices. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 499]](../ps.gif) 499 499 | INTEGRATED CIRCUIT STRUCTURE WITH ELECTRICALLY ISOLATED COMPONENTS: |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter wherein at least one active solid-state device
is provided in a single, monolithic semiconductor chip along with other
active or passive elements in the chip, and means are provided to
electrically isolate different devices in the monolithic chip from each
other.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 7, | for intervalley transfer bulk effect devices (e.g.,
Gunn effect devices) in a monolithic integrated circuit. |
| 93, | for plural light emitting devices with electrical
isolation means in integrated circuit structure. |
| 265, | for JFET devices having vertical current path in
integrated circuit. |
| 272, | through 278, for JFET devices in integrated circuits. |
| 334, | for short channel IGFET devices having a gate electrode
controlling the vertical portion of the channel and being in a groove
in an integrated circuit. |
| 337, | and 338, for graded channel short channel IGFET
devices in integrated circuit structure. |
| 357, | through 359, for insulated electrode field effect
devices with gate insulator overvoltage protection means in complementary
field effect transistor integrated circuit devices. |
| 368, | through 401, for IGFET devices in integrated circuit. |
| 427, | for a magnetic field sensor in an integrated circuit. |
| 446, | for matrix or array type photodetectors with specific
isolation means in an integrated circuit. |
| 491, | and 492, for devices with means to increase breakdown
voltage in an integrated circuit, including, for example, RESURF
devices. |
| 663, | for a superconductive contact or lead on an integrated
circuit. |
| 713, | for cooling means for an integrated circuit device. |
| 758, | through 760, for multi-level metallization in, e.g.,
an integrated circuit device. |
| 922, | for a device with means to prevent inspection of
or tampering with an integrated circuit. |
| 929, | for pn junction isolated integrated circuits with
isolation walls having minimum dopant concentration at intermediate
depth in epitaxial layer. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 438, | Semiconductor Device Manufacturing: Process, particularly
subclasses 294+ for methods of making laterally spaced, electrically
isolated semiconductor regions in combination with insulated gate
field effect transistors; subclasses 353+ for methods of
making laterally spaced, electrically isolated semiconductor regions
in combination with bipolar transistors; and subclasses 400+ for
methods of making laterally spaced, electrically isolated semiconductor
regions or various |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 500]](../ps.gif) 500 500 | Including high voltage or high power devices isolated from
low voltage or low power devices in the same integrated circuit: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 499. Subject matter wherein the monolithic chip includes both
electronic components specifically configured for operation at high
voltages or high power levels, along with other electronic components
which are configured for operation only at low voltages or power
levels.
| | (1)
Note. See this class, subclass 491 for monolithic chips which
include active components with specific means provided to increase
the breakdown voltage of those active components. The combination
of high voltage and low voltage active solid-state devices on the
same monolithic chip will only be classified in this subclass (500),
if no particular structure is provided to increase the breakdown
voltage of the high voltage components. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 501]](../ps.gif) 501 501 | Including dielectric isolation means: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 500. Subject matter wherein the means to electrically isolate
different devices in the same monolithic chip, containing both high
voltage or power and low voltage or power devices, from each other
includes a region of electrical insulator material. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 503]](../ps.gif) 503 503 | With contact or metallization configuration to reduce parasitic
coupling (e.g., separate ground pads for different parts of integrated circuit): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 499. Subject matter wherein the chip includes contacts or electrical
interconnections, such as metal strips deposited on the surface
of the chip, which contacts or interconnections are configured in
such a manner as to reduce or eliminate unwanted parasitic coupling
of electrical signals from one part or component of the integrated
circuit to another.
| | (1)
Note. Such configuration might be, for example, a shielding
conductive layer connected to fixed potential, or large area metal
pads for connection to external supply voltages with plural separate pads
provided to connect different parts or components of the same integrated circuit
to the same external voltage, to prevent voltage drops from electrical current
flowing between a pad and one component from producing a parasitic varying
voltage applied to another component. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 659, | for electrical shielding, in general, in active
solid-state devices. |
| 664, | for transmission line connections, in general, in
active solid-state devices. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 505]](../ps.gif) 505 505 | With polycrystalline semiconductor isolation region in
direct contact with single crystal active semiconductor material: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 499. Subject matter wherein the means for electrically isolating
different devices in the chip from each other includes at least
one region of polycrystalline (i.e., made up of many small crystals)
semiconductor material, which polycrystalline isolation region is
in direct contact with at least one region of single crystal semiconductor
material which forms part of an active solid-state device in the
chip.
| | (1)
Note. The polycrystalline isolation region may be either
undoped or doped with recombination center doping, in order to make
it high resistivity and thus, effectively, an electrical insulator,
or may be doped with a p or n dopant in order to form a pn junction
with the single crystal material of the active solid-state device
so that the rectifying junction between the doped isolation region and
the single crystal active portion, when reverse biased, electrically
isolates the devices in the chip from each other. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 507]](../ps.gif) 507 507 | With single crystal insulating substrate (e.g., sapphire): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 506. Subject matter wherein the means to electrically isolate
different devices from each other includes a substrate of single
crystal insulating material, upon which the semiconductor material
of the active devices is grown in heteroepitaxial relationship therewith.
| | (1)
Note. The substrate may typically be the alpha crystalline
phase of aluminum oxide, commonly called sapphire or single crystalline
beryllium oxide or single crystal magnesium aluminate known as spinel. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 509]](../ps.gif) 509 509 | Combined with pn junction isolation (e.g., isoplanar, LOCOS): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 506. Subject matter wherein the means for electrically isolating
components in the chip from each other includes, in addition to
portions of electrical insulator material, pn junctions separating
regions of active devices from each other and/or from a
supporting semiconductor substrate.
| | (1)
Note. There are several names in common use for isolation
of this type, particularly where the pn junctions provide isolation
between active devices and the supporting semiconductor substrate
with the dielectric material recessed into the semiconductor between
active devices and extending down to the isolating pn junctions
to separate devices laterally from each other. Such common names include
LOCOS (Local Oxidation of Silicon), ROI (Recessed Oxide Isolation), Isoplanar,
and Planox. These terms do not represent different isolation structures,
but are merely alternative names for the same type of isolation. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 510]](../ps.gif) 510 510 | Dielectric in groove: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 509. Subject matter wherein the electrical insulator material
forming part of the isolation means is located in grooves in the
semiconductor surface (e.g., LOCOS)
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 374, | for CMOS FET dielectric isolation means (e.g., dielectric
layer in vertical groove.) |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 512]](../ps.gif) 512 512 | Complementary devices share common active region (e.g.,
integrated injection logic, I2L): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 511. Subject matter wherein the device includes structures wherein
a pnp transistor shares a semiconductor region with an npn transistor, e.g.,
where the base region of the pnp transistor serves also as the emitter
of the npn transistor and the collector of the pnp transistor serves
as the base region of the npn transistor.
| | (1)
Note. Search this class, subclass 107 for regenerative switching
devices, which typically are in the form of a pnp transistor and
an npn transistor, the collector and base of the pnp transistor
forming the base and collector, respectively, of the npn transistor. |
| | (2)
Note. A typical structure in which pnp transistors and npn
transistors share regions in common is that called Integrated injection
logic, I2L (formerly alternatively called merged
transistor logic, MTL), in which a pnp transistor serves to supply
base region current to a multicollector npn transistor, with the base
region of the npn being the logic circuit input and the multiple
collectors providing logic fan out to plural further logic gates. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 513]](../ps.gif) 513 513 | Vertical walled groove: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 510. Subject matter wherein the dielectric isolation is located
in grooves in the surface of the overall device which extend perpendicular
to the surface of the overall device. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 514]](../ps.gif) 514 514 | With active junction abutting groove (e.g., "walled
emitter"): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 513. Subject matter wherein at least one pn junction forming
a part of an active solid-state device terminates against the dielectric
filling in the vertical walled isolation groove.
| | (1)
Note. If the emitter-base junction terminates against a dielectric
isolation sidewall, this is termed a "walled emitter" transistor
structure. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 521]](../ps.gif) 521 521 | Sides of grooves along major crystal planes (e.g., (111),
(100) planes, etc.): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 510. Subject matter wherein the device has grooves for the isolation
whose sides are oriented along one or more major crystal planes
of the semiconductor material in which the grooves are formed.
| | (1)
Note. Major crystal planes are considered to be the (111),
(110), and (100) planes in a crystal with cubic symmetry. |
| | (2)
Note. See illustration, below.
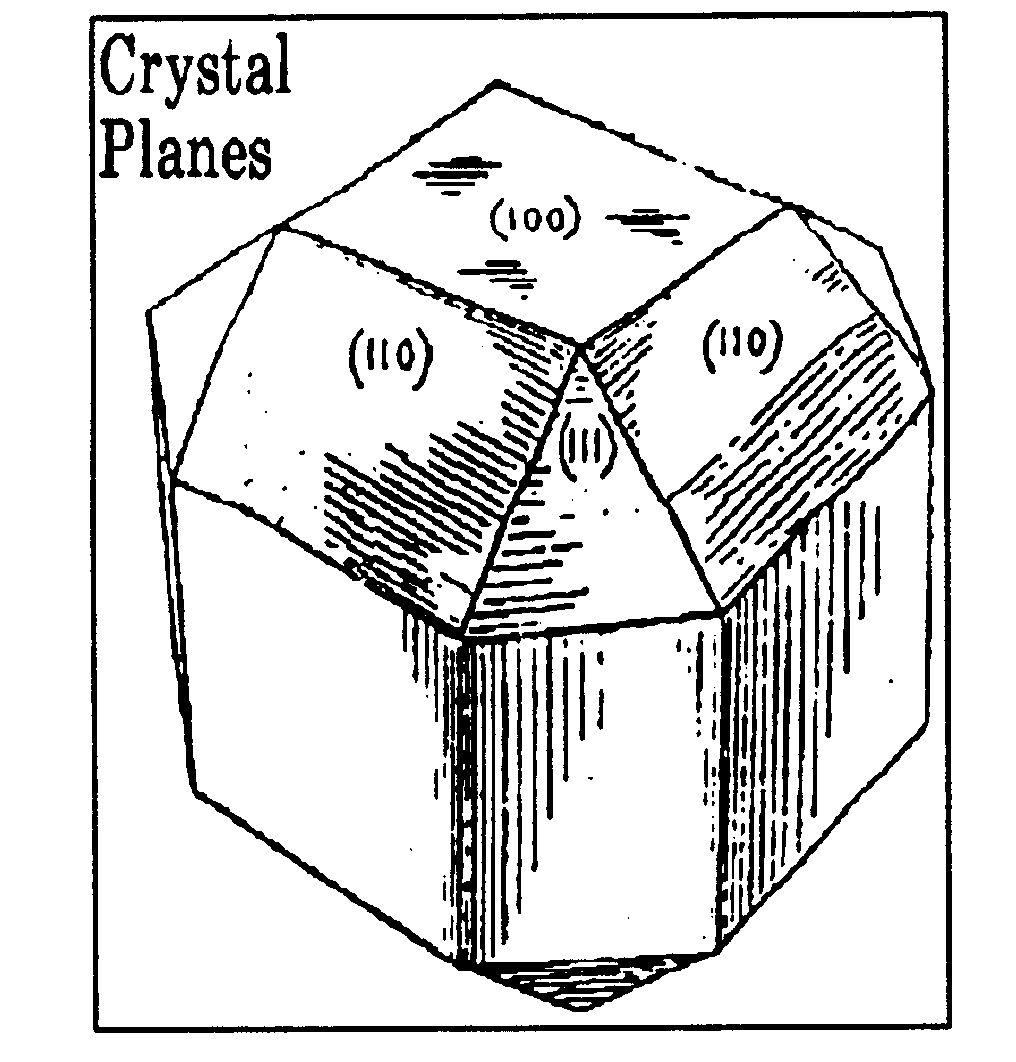
| |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 522]](../ps.gif) 522 522 | Air isolation (e.g., beam lead supported semiconductor
islands): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 506. Subject matter wherein the isolation means is air (e.g.,
islands of semiconductor material supported by beam leads and separated
by air).
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 438, | Semiconductor Device Manufacturing: Process, particularly
subclass 411 for methods of forming electrically isolated semiconductor
islands held in place by beam lead metallization; subclass 461 for
methods of forming beam leads on a semiconductor substrate combined
with dicing of the substrate into plural separate bodies; and subclass
611 for methods of forming beam lead metallization on a semiconductor
substrate. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 528]](../ps.gif) 528 528 | Passive components in ICs: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 499. Subject matter wherein the device is contained in a single,
monolithic chip with electrical components which are passive, i.e.,
which do not have gain, for example, pure capacitors, inductors,
or resistors.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 379, | for a passive component combined with an IGFET device
in an integrated circuit. |
| 516, | for passive components in an integrated circuit
with dielectric in groove and pn junction isolation. |
| 904, | for a FET combined with passive components adapted
for use as a static memory cell. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 529]](../ps.gif) 529 529 | Including programmable passive component (e.g., fuse): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 528. Subject matter wherein a passive component is programmable,
i.e., may be permanently altered (e.g., a fuse - a protective device designed
to open a circuit in response to an excessive current).
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 438, | Semiconductor Device Manufacturing: Process, particularly
subclasses 467 , 600, and 601 for methods of forming or modifying
electrically alterable structures for selectively interconnecting
electrical devices on a semiconductor substrate. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 530]](../ps.gif) 530 530 | Anti-fuse: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 529. Subject matter wherein an element which is normally non-conductive
is made conductive (e.g., a capacitor) that is, that can be selectively electrically
shorted. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 531]](../ps.gif) 531 531 | Including inductive element: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 528. Subject matter wherein the device includes an electrical
inductor, i.e., an element that tends to oppose any change of current
applied thereto because of a magnetic field generated by the inductor
itself. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 532]](../ps.gif) 532 532 | Including capacitor component: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 528. Subject matter wherein the device includes an electrical
capacitor, i.e., a passive element with electrical conductors separated
by a dielectric material which stores electrical charge when potential
differences exist between the conductive elements of the capacitor. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 541]](../ps.gif) 541 541 | Pinch resistor: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 539. Subject matter wherein the resistor element has a structure
in the form of a layer of one conductivity type sandwiched between
a pair of regions of opposite conductivity type, so that the upper
region of opposite conductivity type restricts the thickness of
the resistive layer and thus increases its resistivity.
| | (1)
Note. Typically, the resistor will have the same doping profile
as the base region of the bipolar transistor, while the lower opposite
conductivity type region will have the same doping profile as the
bipolar transistor collector, and the upper, or "pinching" region,
will have the same doping profile as the bipolar transistor emitter. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 542]](../ps.gif) 542 542 | Resistor has same doping as emitter or collector of bipolar
transistor: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 539. Subject matter wherein the resistor region has the same
doping concentration and profile (e.g., is formed in the same step
as) either the emitter or the collector region of the bipolar transistor
with which the resistor is combined in the same integrated circuit.
| | (1)
Note. Most resistors in bipolar integrated circuits are
formed with the same doping step as the bipolar transistor base regions.
Resistors that are instead formed at the same doping step as the emitter
or collector, rather than the base, go in this subclass. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 543]](../ps.gif) 543 543 | Lightly doped junction isolated resistor (e.g., ion implanted
resistor): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 539. Subject matter wherein the resistive element is of the form
of a lightly doped layer of one conductivity type located in a region
of opposite conductivity type, such that the pn junction between
the resistor region and its containing opposite conductivity type
region serves to isolate the resistor.
| | (1)
Note. A resistor region is considered to be lightly doped
if it is substantially less heavily doped than the base region of
the bipolar transistors in the same integrated circuit, or if it
is has a doping density not greater than 100 times that of the opposite
conductivity type region in which it is contained. |
| | (2)
Note. Such lightly doped resistors are typically formed by
the process of ion implantation, wherein desired dopant atoms are
placed in the semiconductor body by ionizing the dopant material
and accelerating the resulting ions through a carefully controlled
voltage to impinge on the surface of the semiconductor material,
so that the depth of the resulting dopant atoms is determined by
the accelerating voltage and the doping density is determined by
the flux of the ion beam. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 544]](../ps.gif) 544 544 | With pn junction isolation: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 499. Subject matter wherein the means for electrically isolating
different devices from each other includes a pn junction located
between the devices to be isolated. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 548]](../ps.gif) 548 548 | At least three regions of alternating conductivity types
with dopant concentration gradients decreasing from surface of semiconductor
(e.g., "triple-diffused" integrated circuit): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 544. Subject matter including at least three regions of alternating
conductivity type (p or n), with each successive region contained
within the previous region, and each of the regions having a doping
concentration which decreases with distance from the same external
surface of the semiconductor body.
| | (1)
Note. Junction isolated integrated circuits of this type
are typically manufactured by starting with an uniformly doped p-type
semiconductor body to serve as the substrate, then diffusing spaced
n-type regions into the P substrate to form collectors of npn transistors,
and then successively diffusing p-type base and n-type emitters
into the spaced n-type regions. Junction isolated integrated circuits
of this type are simple to manufacture, due to the reduced number
of processing steps involved, but suffer from non-optimum doping concentration
profiles, particularly in the collector regions. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 551]](../ps.gif) 551 551 | Including voltage reference element (e.g., avalanche diode,
so-called "Zener diode" with breakdown voltage
greater than 6 volts or with positive temperature coefficient of breakdown
voltage): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 544. Subject matter including a voltage reference element, i.e.,
a device which limits the operating voltage of one or more active
devices in the integrated circuit (e.g., an avalanche diode, so-called "Zener
diode" with breakdown voltage greater than 6 volts, or
with positive temperature coefficient of breakdown voltage).
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 199, | for an avalanche diode in a non-charge transfer
device having a heterojunction. |
| 481, | and 482, for Schottky barrier avalanche diodes. |
| 603, | through 606, for avalanche diodes not classified
above those subclasses in this schedule, i.e., not involving a heterojunction
in a non-charge transfer device or a Schottky barrier, or one used
as a voltage reference element with pn junction isolation means
in an integrated circuit. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 552]](../ps.gif) 552 552 | With bipolar transistor structure: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 544. Subject matter wherein the junction isolation is formed
in an integrated circuit between active devices at least one of
which has a bipolar transistor structure. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 556]](../ps.gif) 556 556 | Including lateral bipolar transistor structure: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 555. Subject matter wherein at least one of the pnp or npn complementary
bipolar transistors is a lateral structure (i.e., has current flow
between its emitter and collector parallel to a major surface of
the semiconductor chip). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 557]](../ps.gif) 557 557 | Lateral bipolar transistor structure: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 499. Subject matter wherein the device includes at least one
bipolar transistor which has a lateral structure (i.e., has current
flow between its emitter and collector parallel to a major surface of
the semiconductor chip). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 565]](../ps.gif) 565 565 | BIPOLAR TRANSISTOR STRUCTURE: |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter wherein the active solid-state device comprises
at least one bipolar transistor.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 47, | for bipolar transistor structure having a metal
contact alloyed to elemental semiconductor type pn junction in a non-regenerative
structure. |
| 511, | for complementary bipolar transistor structure having
dielectric-in-groove isolation and pn junction isolation in an integrated
circuit. |
| 517, | and 518, for bipolar transistor structure having
dielectric-in-groove isolation and pn junction isolation in an integrated
circuit. |
| 525, | for complementary bipolar structure with full dielectric
isolation in an integrated circuit. |
| 526, | for bipolar structure with full dielectric isolation
in an integrated circuit. |
| 552, | through 556, for bipolar transistor structure combined
with pn junction isolation in an integrated circuit. |
| 557, | through 562, for integrated circuits with electrically
isolated lateral bipolar transistor structure. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 148, | Metal Treatment, digests 10 and 11 for bipolar transistor devices. |
| 326, | Electronic Digital Logic Circuitry, particularly
subclasses 18+ , 42+, 48, 75+, 89+,
109+, and 124+ for logic circuits utilizing bipolar
transistors. |
| 327, | Miscellaneous Active Electrical Nonlinear Devices,
Circuits, and Systems, particularly
subclasses 204 , 207, 405, 411+, 417, 432+, 439,
459, 462, 463, 474, 475, and 478+ for miscellaneous nonlinear
circuits with explicitly recited bipolar transistors. |
| 330, | Amplifiers,
subclasses 250+ for amplifiers with transistors which may be bipolar
transistors and subclass 300 which explicitly provides for bipolar or
field effect transistors. |
| 341, | Coded Data Generation or Conversion,
subclasses 127+ for bipolar analog to or from digital converters
and subclass 133 for such device with a drift (graded base) transistor
element. |
| 438, | Semiconductor Device Manufacturing: Process,
subclasses 309+ for methods of forming bipolar transistors. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 566]](../ps.gif) 566 566 | Plural non-isolated transistor structures in same structure: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 565. Subject matter wherein the bipolar structure includes more
than one bipolar transistor in a structure without electrical isolation
between transistors.
| | (1)
Note. See subclass 499, above, for integrated circuits with
electrical isolation, including with bipolar transistors. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 569]](../ps.gif) 569 569 | Complementary Darlington-connected transistors: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 567. Subject matter wherein the Darlington configuration comprises
two bipolar transistors which have a complementary connection,
i.e., the input transistor is of one conductivity type (e.g., npn)
and the other is of the opposite conductivity type (e.g., pnp). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 575]](../ps.gif) 575 575 | Including lateral bipolar transistor structure: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 574. Subject matter wherein at least one of the complementary
bipolar transistors sharing a common region is a lateral bipolar
transistor (i.e., has current flow between its emitter and collector
parallel to a major surface of the semiconductor chip).
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 423, | for lateral and other bipolar transistor magnetic
field responsive structure. |
| 557+, | for electrically isolated lateral bipolar transistor
structures in an integrated circuit. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 589]](../ps.gif) 589 589 | Avalanche transistor: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 565. Subject matter wherein the device is a bipolar transistor
designed to be operated with its base-collector junction biased
into avalanche breakdown. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 594]](../ps.gif) 594 594 | WITH GROOVE TO DEFINE PLURAL DIODES: |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter wherein the active solid-state device has
more than one diode and has a groove therein to separate the diodes. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 595]](../ps.gif) 595 595 | VOLTAGE VARIABLE CAPACITANCE DEVICE: |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter wherein the active solid-state device has
a capacitance which varies with the voltage applied thereto.
| | (1)
Note. This type of voltage variable capacitor device is to
be distinguished from voltage variable capacitors (also referred
to as varactors) which are passive devices only and which may be found,
for example, in Class 361, Electricity: Electrical Systems and
Devices, subclass 277, and Class 332, Modulators, subclass 136,
modulators with varactors. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 312, | for insulated gate type voltage variable capacitor
devices or voltage variable capacitor devices combined with an insulated
gate transistor. |
| 438, | Semiconductor Device Manufacturing: Process, subclass
379 for methods of forming a voltage variable capacitance device
utilizing a semiconductor substrate. |
| 480, | for a voltage variable capacitor diode with a Schottky
barrier. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 603]](../ps.gif) 603 603 | AVALANCHE DIODE (E.G., SO-CALLED "ZENER" DIODE
HAVING BREAKDOWN VOLTAGE GREATER THAN 6 VOLTS): |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter configured to operate in a manner in which
an external voltage is applied in the reverse-conducting direction
of the device junction with sufficient magnitude to cause the potential
barrier at the junction to breakdown due to electrons or holes gaining sufficient
speed to dislodge valence electrons and thus create more hole-electron
current carriers by an avalanche process.
| | (1)
Note. This includes the so-called "Zener" diode
using silicon as a semiconductor which has a breakdown voltage greater
than 6 volts. True Zener diodes conduct by reverse tunneling, and are
classified in subclass 106. However, many avalanche breakdown diodes which
are classifiable in subclass 603 are called "Zener" diodes
even though the breakdown mechanism is avalanche multiplication,
rather than tunneling. In silicon, pn junctions which break down at
less than 5 volts, do so by reverse tunneling, while those that
break down at above 6 volts, do so by avalanche multiplication. |
| | (2)
Note. See the illustration, below:
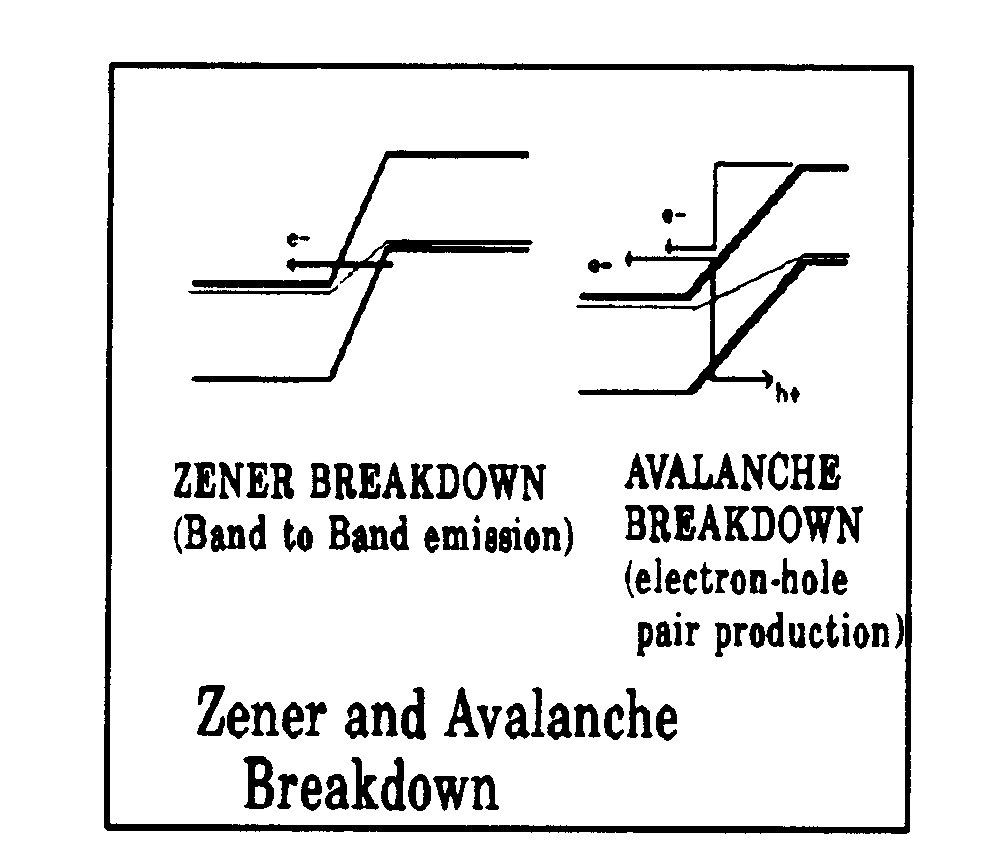
| SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 106, | for a reverse bias tunneling diode (Zener diode). |
| 199, | for an avalanche diode having a heterojunction. |
| 481, | for a Schottky barrier avalanche diode. |
| 551, | for an avalanche diode used as a voltage reference
element combined with pn junction isolation means in an integrated
circuit. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 327, | Miscellaneous Active Electrical Nonlinear Devices,
Circuits, and Systems,
subclasses 185+ for stable state circuits which may include an
avalanche diode; subclass 326 for limiting, clipping, or clamping
utilizing an avalanche diode; subclass 502 for gating circuits utilizing
an avalanche diode; and subclass 584 for miscellaneous circuits
utilizing an avalanche diode. |
| 438, | Semiconductor Device Manufacturing: Process,
subclass 91 for methods of making a light responsive avalanche
diode and subclass 380 for making an avalanche diode utilizing a semiconductor
substrate. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 604]](../ps.gif) 604 604 | Microwave transit time device (e.g., IMPATT diode): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 603. Subject matter wherein the device is structured to operate
as a transit time device at microwave frequencies, the frequency
at which it operates being determined by the transit time of charge carriers
through the depletion region which extends on both sides of the
reverse biased junction (e.g., an Impact
ionization avalanche transit time
(IMPATT) diode). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 607]](../ps.gif) 607 607 | WITH SPECIFIED DOPANT (e.g., plural dopants of same conductivity
in same region): |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter wherein the active solid-state device contains
impurity dopant atoms which are specified and are used to change
the conductive properties of the semiconductor material.
| | (1)
Note. If the dopant is in Si or Ge, it may be a shallow level
dopant, other than an element from group III or group V of the periodic
table (e.g., a dopant such as Li in Ge). | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 610]](../ps.gif) 610 610 | Deep level dopant: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 607. Subject matter including a specified dopant which establishes
traps in the forbidden band of a semiconductor into which carriers
may drop or rise. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 613]](../ps.gif) 613 613 | INCLUDING SEMICONDUCTOR MATERIAL OTHER THAN SILICON OR
GALLIUM ARSENIDE (GaAs) (E.G., PbxSn1-xTe): |
| | Subject matter under the subclass definition which includes
semiconducting material other than silicon or gallium arsenide (GaAs). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 617]](../ps.gif) 617 617 | INCLUDING REGION CONTAINING CRYSTAL DAMAGE: |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter wherein the device includes a region which
has crystal damage.
| | (1)
Note. The crystal damage may have been caused by charged
or elementary particles bombardment of a particular region. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 618]](../ps.gif) 618 618 | PHYSICAL CONFIGURATION OF SEMICONDUCTOR (E.G., MESA, BEVEL, GROOVE,
ETC.): |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter wherein the device has a particular physical
form, such as a mesa or bevel or groove.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 171, | for regenerative devices with edge features (e.g.,
bevels). |
| 496, | for devices with physical configuration (e.g., bevels)
to increase breakdown voltage threshold. |
| 586, | for bipolar transistor devices with non-planar semiconductor
surfaces (e.g., bevels). |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 622]](../ps.gif) 622 622 | Groove: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 618. Subject matter in which there is a physical groove in a
surface of the semiconductor device.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 117, | and 118, for light activated regenerative type devices
having a groove, e.g., that contains a light conductor. |
| 127, | for a bidirectional rectifier with control electrode
and a groove or guard ring to separate the device into sections
having different conductive polarity. |
| 170, | for a regenerative type device with a groove or
other surface feature to increase breakdown voltage. |
| 244, | for a charge transfer device having a groove. |
| 283, | for a JFET with Schottky gate closely aligned with
source region with a groove or overhang for alignment. |
| 284, | for a JFET with Schottky gate in a groove. |
| 330, | through 334, for a short channel IGFET with a gate
electrode in a groove for controlling a vertical portion of the
device channel. |
| 397, | for an IGFET in an integrated circuit with a thick
insulator portion recessed in a vertical walled groove in the semiconductor
surface to prevent parasitic conduction channels. |
| 466, | for a light responsive device with a physical configuration
feature (e.g., a groove). |
| 534, | for a passive component located in a groove in an
integrated circuit device. |
| 571, | for Darlington configuration bipolar transistor
structure having a nonplanar structure (e.g., a groove). |
| 586, | for a bipolar transistor structure with a nonplanar
surface (e.g., a groove). |
| 589, | for a voltage variable capacitance device with means
to increase active junction area (e.g., a groove). |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 629]](../ps.gif) 629 629 | WITH MEANS TO CONTROL SURFACE EFFECTS: |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter wherein the active junction device has means
to modify (e.g., reduce, or eliminate) electrical field effects
which take place at the device surface or to modify (e.g., reduce
or eliminate) inhomogeneities in electrical properties of a semiconductor
crystal region due to effects caused by the discontinuity of the crystal
lattice at the surface.
| | (1)
Note. Such effects include formation of an inversion layer
of minority carriers at the semiconductor surface, or depletion of
majority carriers at the semiconductor surface, due to charge in
an insulating coating on the surface or due to dangling bonds where
the crystal structure of the semiconductor ends at the surface,
leakage current via charge flow over a surface rather than through
it, etc. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 487, | for a semiconductor device provided with means to
increase breakdown voltage of the device (which may involve surface
effects). |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 630]](../ps.gif) 630 630 | With inversion-preventing shield electrode: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 629. Subject matter wherein the means to control surface effects
includes an electrode, insulated from the semiconductor surface,
which electrode is configured to prevent inversion of the conductivity
type of the surface due to surface effects. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 632]](../ps.gif) 632 632 | Insulating coating: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 629. Subject matter wherein there is a surface coating of electrically
insulating material on the semiconductor body to control surface
effects. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 633]](../ps.gif) 633 633 | With thermal expansion compensation (e.g., thermal expansion
of glass passivant matched to that of semiconductor): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 632. Subject matter wherein the insulating coating includes means
to compensate for mismatches in thermal expansion coefficient between
different portions of the device, such as forming the insulating
coating of a material which closely matches the thermal expansion
coefficient of the underlying semiconductor.
| | (1)
Note. Typical semiconductor materials, such as silicon, have
extremely low thermal expansion coefficients, and thus, low thermal
expansion materials such as Corning Code 7740 PYREX® borosilicate
glass closely match the expansion coefficient of the semiconductor,
and help to prevent thermal expansion induced stress or cracking. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 634]](../ps.gif) 634 634 | Insulating coating of glass composition containing component
to adjust melting or softening temperature (e.g., low melting point glass): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 632. Subject matter wherein the insulating coating comprises
a glass composition containing a component to adjust the melting
or softening temperature.
| | (1)
Note. A commonly used additive to lower the melting point
of silica (silicon dioxide) is phosphorous oxide, producing phosphosilicate
glass. |
| | (2)
Note. Such layers are typically provided so that the device
can be heated to the softening point of the glass to cause it to flow
and smooth out sharp edges on the semiconductor surface that might adversely
affect subsequently deposited layers. Hence, such a layer is often called
a reflow glass layer. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 635]](../ps.gif) 635 635 | Multiple layers: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 632. Subject matter wherein the insulating coating comprises
multiple layers on the surface of the semiconductor body. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 641]](../ps.gif) 641 641 | Combined with glass layer: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 640. Subject matter wherein in addition to the layer of silicon
nitride, there is at least one layer of glass in the multiple insulating
layers on the semiconductor body.
| | (1)
Note. For purposes of the definitions of this class, a material
is considered to be a glass if it is amorphous (i.e., non-crystalline,
and its major constituents are a mixture of oxides of more than one element). An oxide of a
single element, such as silicon dioxide, is not regarded as a glass layer,
while a mixture of phosphorus oxide and silicon dioxide (phosphosilicate
glass) would be regarded as a glass. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 642]](../ps.gif) 642 642 | At least one layer of organic material: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 635. Subject matter wherein at least one insulating layer comprises
an organic compound, i.e., one which has a molecule characterized
by two carbon atoms bonded together, one atom of carbon being bonded
to at least one atom of hydrogen or a halogen, or one atom or carbon bonded
to at least one atom of nitrogen by a single or double bond, certain
compounds such as HCN, CN-CN, HNCO, HNCS, cyanogen halides, cyanamide,
fulminic acid and metal carbides, being exceptions to this rule.
| | (1)
Note. The definition of an organic compound here is the same
as in Class 260, Chemistry of Carbon Compounds. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 643]](../ps.gif) 643 643 | Polyimide or polyamide: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 642. Subject matter wherein the at least one organic insulating
layer comprises polyamide (i.e., a polymeric compound) resulting
from replacement of an atom of hydrogen in an organic amine by an
organic univalent acid radical, or polyimide, i.e., a polymeric
compound resulting from replacement of both atoms of hydrogen in
an organic amine by organic univalent acid radicals or by an organic
divalent acid radical.
| | (1)
Note. Polyamides are copolymers (polymers formed from at
least two different starting organic materials) which have a linkage,
as illustrated below, between the starting materials, where R is
typically hydrogen and Q1 and Q2are
the organic residues of the starting monomers. |
| | (2)
Note. Linkage between the starting materials, illustrated
below. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 644]](../ps.gif) 644 644 | At least one layer of glass: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 635. Subject matter wherein there is at least one layer of glass
in the multiple insulating layers on the semiconductor body.
| | (1)
Note. For purposes of the definitions of this class, a material
is considered to be a glass if it is amorphous (i.e., non-crystalline)
and its major constituents are a mixture of oxides of more than one element. An oxide of a
single element, such as silicon dioxide, is not regarded as a glass
layer, while a mixture of phosphorus oxide and silicon dioxide (phosphosilicate
glass) would be regarded as a glass. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 647]](../ps.gif) 647 647 | Insulating layer recessed into semiconductor surface (e.g.,
LOCOS oxide): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 632. Subject matter wherein the insulating layer is recessed
into the semiconductor surface.
| | (1)
Note. This type of recessed insulator may typically be LOCOS
(Local Oxidation of Silicon) oxide, which is formed by oxidizing
the silicon surface in areas not covered by an oxidation resistant mask,
so that oxide is formed which is recessed into the semiconductor
by approximately 1/2 of its thickness due to consumption
of silicon to form the silicon oxide. LOCOS oxide may also be recessed
fully to be substantially flush with the surface (except in areas
at the edge of the oxide, wherein ridges known as "birdheads" (due
to their shape) occur, which taper off to small thickness oxide
portions in areas protected by the oxidation resistant mask (these
tapering portions are called the "bird"s beak"). | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 648]](../ps.gif) 648 648 | Combined with channel stop region in semiconductor: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 647. Subject matter wherein the recessed insulating layer is
combined with a channel stop region, i.e., a region of heavy doping
concentration in the underlying semiconductor surface to prevent
inversion of the surface by formation of a layer of induced minority
carriers. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 650]](../ps.gif) 650 650 | Insulating layer of glass: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 632. Subject matter wherein the insulating layer is composed
of glass.
| | (1)
Note. For purposes of the definitions of this class, a material
is considered to be a glass if it is amorphous (i.e., non-crystalline)
and its major constituents are a mixture of oxides of more than one element. An oxide of a
single element, such as silicon dioxide, is not regarded as a glass
layer, while a mixture of phosphorus oxide and silicon dioxide (phosphosilicate
glass) would be regarded as a glass. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 652]](../ps.gif) 652 652 | Channel stop layer: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 629. Subject matter wherein the means to control surface effects
comprises a channel stop region (i.e., a region of heavy doping
concentration in the underlying semiconductor surface to prevent
inversion of the surface by formation of a layer of induced minority
carriers).
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 305, | for insulated gate capacitor in trench or insulated
gate transistor combined with capacitor in trench with a channel
stop. |
| 349, | for SOI devices with buried channel stop layer. |
| 354, | for SOI devices with channel stop regions in single
crystal island edges. |
| 376, | and 398 through 400, for IGFET integrated circuit
devices with channel stop layers used to prevent parasitic conduction
channels. |
| 519, | for integrated circuit devices with PN junction
and dielectric in groove isolation with heavily doped channel stop
region adjacent to groove. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 653]](../ps.gif) 653 653 | WITH SPECIFIED SHAPE OF PN JUNCTION: |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter wherein the device has at least one junction
between semiconductor regions of opposite conductivity type (P and N),
and wherein the interface between at least one P region and its
adjoining N region has a specified shape or geometrical configuration. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 654]](../ps.gif) 654 654 | Interdigitated pn junction or more heavily doped side of
junction is concave: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 653. Subject matter wherein the device has at least one pn junction
which is interdigitated (i.e., in which plural layers or fingers
of n type material alternate with plural layers or fingers of
p-type material, with then-type layers or fingers being parts
of a single unitary n region and the p-type layers or fingers being
parts of a single unitary p-region).
| | (1)
Note. Interdigitated configurations are frequently used to
increase the amount of PN junction area in a given volume of semiconductor
material. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 655]](../ps.gif) 655 655 | WITH SPECIFIED IMPURITY CONCENTRATION GRADIENT: |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter wherein the active solid-state device includes
at least one region of semiconductor material with a specified profile or
gradient of impurity doping concentration.
| | (1)
Note. Examples of impurity concentration gradients include
reverse gradient profiles (i.e., wherein the doping concentration
is lighter toward the semiconductor surface or away from a pn junction) or
a radial concentration profile). |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 101, | for light emitting devices with specified dopant
concentration or concentration profile. |
| 219, | through 221, for charge transfer field effect majority
signal carrier devices with impurity concentration variations (e.g.,
in the device channel). |
| 335, | through 343, for short channel IGFETs with graded
dopant concentration in the active channel region that decreases
with distance from the source region. |
| 548, | for integrated circuits with pn junction isolation
having at least three regions of alternating conductivity types
with dopant concentration gradients decreasing from the surface
of the semiconductor. |
| 596, | and 597, for a voltage variable capacitance device
with specified dopant profile (e.g., retrograde dopant profile). |
| 929, | for a pn junction isolated integrated circuit with
isolation walls having minimum dopant concentration at an intermediate
depth in an epitaxial layer. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 657]](../ps.gif) 657 657 | Stepped profile: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 655. Subject matter wherein the device includes at least one
region of the same conductivity type (P or N) wherein the doping
concentration varies abruptly (e.g., a P+ to P- junction). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 658]](../ps.gif) 658 658 | PLATE TYPE RECTIFIER ARRAY: |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter in which the device comprises plates of material
each of which is coated with a layer of semiconductor material (e.g.,
copper oxide or selenium) which forms a rectifying barrier junction,
the device being made up of several flat conductive plates and semiconductor
material layers to form a rectifier array.
| | (1)
Note. Typical rectifiers of this type include (a) copper
oxide rectifiers in which the rectifying barrier is a junction between
metallic copper plate and cuprous oxide layer coated on one side of
the plate and (b) selenium rectifier in which a thin layer of selenium
is formed on one side of an aluminum plate with a highly conductive
metal coated over the selenium. If the semiconductor material is
specifically recited as selenium or tellurium, or an oxide of a
metal such as copper oxide, the patent will be classified in the
appropriate one of subclasses 42 or 43. |
| | (2)
Note. This type of device has generally been replaced with
more modern devices, including silicon rectifiers. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 659]](../ps.gif) 659 659 | WITH SHIELDING (E.G., ELECTRICAL OR MAGNETIC SHIELDING,
OR FROM ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION OR CHARGED PARTICLES): |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter in which means is provided for protecting
an active solid-state device by providing a barrier to prevent electrical
or magnetic radiation or fields or charged particles from reaching
the device, or to limit the amount of such radiation or particles
reaching the device.
| | (1)
Note. This subject matter is to be distinguished from that
found in the cross-reference art collection entitled "radiation hardening",
which encompasses subject matter which does not attempt to shield the
device from electric or magnetic or electromagnetic radiation or
charged particles, but is used to prevent or limit the damage caused
to a device by such radiation or particles which reach the device. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 297, | for shielding against alpha particles in dynamic
random access memory (DRAM) structures. |
| 422, | for magnetic field shielding in magnetic field sensor
active solid-state devices. |
| 435, | for light shields in light responsive active solid-state
devices. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 174, | Electricity: Conductors and Insulators,
subclasses 32 through 397for miscellaneous anti-inductive structures, particularly
subclasses 350-397 for miscellaneous electrical shields and screen
structures not elsewhere classifiable. |
| 307, | Electrical Transmission or Interconnection Systems,
subclass 91 for anti-induction or coupling to other systems with
magnetic or electrostatic field control (e.g., shielding). |
| 315, | Electric Lamp and Discharge Devices: Systems,
subclass 85 for gaseous tube systems with electromagnetic wave
radiation prevention or shielding means. |
| 330, | Amplifiers,
subclass 68 for amplifiers with shielding means. |
| 331, | Oscillators,
subclass 67 for oscillators combined with electromagnetic or
electrostatic shield means. |
| 333, | Wave Transmission Lines and Networks,
subclass 12 for transmission line inductive or radiation interference systems. |
| 334, | Tuners,
subclass 85 for radio tuners with shielding means. |
| 336, | Inductor Devices,
subclass 84 for induction devices with electric or magnetic
shield means. |
| 338, | Electrical Resistors,
subclass 64 for electrical resistors with electrical shield
means. |
| 343, | Communications: Radio Wave Antennas,
subclasses 841+ for antenna structure with electric shield means. |
| 348, | Television,
subclasses 825+ a for cathode-ray tube support and 836+ for cabinet
or chassis of a television receiver in general. |
| 361, | Electricity: Electrical Systems and Devices,
subclasses 816+ for radio interference type shielding means. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 661]](../ps.gif) 661 661 | SUPERCONDUCTIVE CONTACT OR LEAD: |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter wherein an active solid-state device contains,
or is connected to, an electrical contact or lead (pronounced "leed") which
is made of a material whose electrical resistivity drops to zero
at a particular temperature called a critical transition temperature (Tc).
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 174, | Electricity: Conductors and Insulators,
subclasses 15.4+ and 125.1 for superconducting conductors. |
| 438, | Semiconductor Device Manufacturing: Process, particularly
subclass 2 for methods of forming an semiconductor device
having a superconductive component thereon. |
| 505, | Superconductor Technology: Apparatus, Material,
Process,
subclass 1 for high temperature superconductor materials and
subclasses 884+ for superconductive electrical conductors. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 662]](../ps.gif) 662 662 | Transmission line or shielded: |
| | Subject matter under 661 in which the superconductive electrical
lead has controlled electrical characteristics designed to convey
high frequency (e.g., greater than 3 megahertz) signals or narrow
pulse signals; or is surrounded by a separate electrical conductor
or envelope, called a shield, designed to minimize the effects of
nearby electrical circuits.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 174, | Electricity: Conductors and Insulators,
subclasses 32 through 397for miscellaneous anti-inductive structures, particularly
subclasses 350-397 for miscellaneous electrical shields and screen
structures not elsewhere classifiable. |
| 307, | Electrical Transmission or Interconnection Systems,
subclass 91 for anti-induction or coupling to other systems with
magnetic or electrostatic field control (e.g., shielding). |
| 315, | Electric Lamp and Discharge Devices: Systems,
subclass 85 for gaseous tube systems with electromagnetic wave
radiation prevention or shielding means. |
| 330, | Amplifiers,
subclass 68 for amplifiers with shielding means. |
| 331, | Oscillators,
subclass 67 for oscillators combined with electromagnetic or
electrostatic shield means. |
| 333, | Wave Transmission Lines and Networks,
subclass 12 for transmission line inductive or radiation interference systems. |
| 334, | Tuners,
subclass 85 for radio tuners with shielding means. |
| 336, | Inductor Devices,
subclass 84 for induction devices with electric or magnetic
shield means. |
| 338, | Electrical Resistors,
subclass 64 for electrical resistors with electrical shield
means. |
| 343, | Communications: Radio Wave Antennas,
subclasses 841+ for antenna structure with electric shield means. |
| 348, | Television,
subclass 820 for a cathode-ray tube video display with electric
or magnetic shielding means. |
| 361, | Electricity: Electrical Systems and Devices,
subclasses 816+ for radio interference type shielding means. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 663]](../ps.gif) 663 663 | On integrated circuit: |
| | Subject matter under 661 in which the superconductive contact
or lead is associated with an electrical network made up of more
than one electronic device, including at least one active solid-state
electronic device, in a unitary structure. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 664]](../ps.gif) 664 664 | TRANSMISSION LINE LEAD (E.G., STRIPLINE, COAX, ETC.): |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter wherein an active solid-state device is provided
with an electrical connection or lead with controlled electrical
characteristics used to transmit high-frequency, e.g., greater than
3 megahertz, or narrow pulse signals to or from the device.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 333, | Wave Transmission Lines and Networks, appropriate subclasses for transmission lines, per
se. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 665]](../ps.gif) 665 665 | CONTACTS OR LEADS INCLUDING FUSIBLE LINK MEANS OR NOISE
SUPPRESSION MEANS: |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter wherein an active solid-state device is provided
with electrical contacts or leads (pronounced "leeds")
which contain portions which have a composition or are made so that
they will melt at a relatively low temperature to form an open circuit
and thereby protect the device in case excessive current, e.g.,
a current spike from lightning, or voltage is provided to the contact
or lead, or contains means designed to suppress unwanted electrical
disturbances in the electrical contacts or leads.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 365, | Static Information Storage and Retrieval,
subclass 96 for a fusible link storage member. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 666]](../ps.gif) 666 666 | LEAD FRAME: |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter wherein the active solid-state device is
provided with a conductive metal network which may have relatively
large area portions, commonly called pads or flags, for direct contact
with semiconductor chips or dice, and lead elements for facilitating
electrical interconnection of the chips or dies via intermediate
(e.g., jumper) connections to other electronic devices or components.
| | (1)
Note. Lead frames also have other portions, usually called "ties",
which interconnect the pad or flag portions with the lead portions
prior to assembly of the lead frame in an electronic package or housing,
but which are removed during package assembly. |
| | (1)
Note. See the illustration, below:
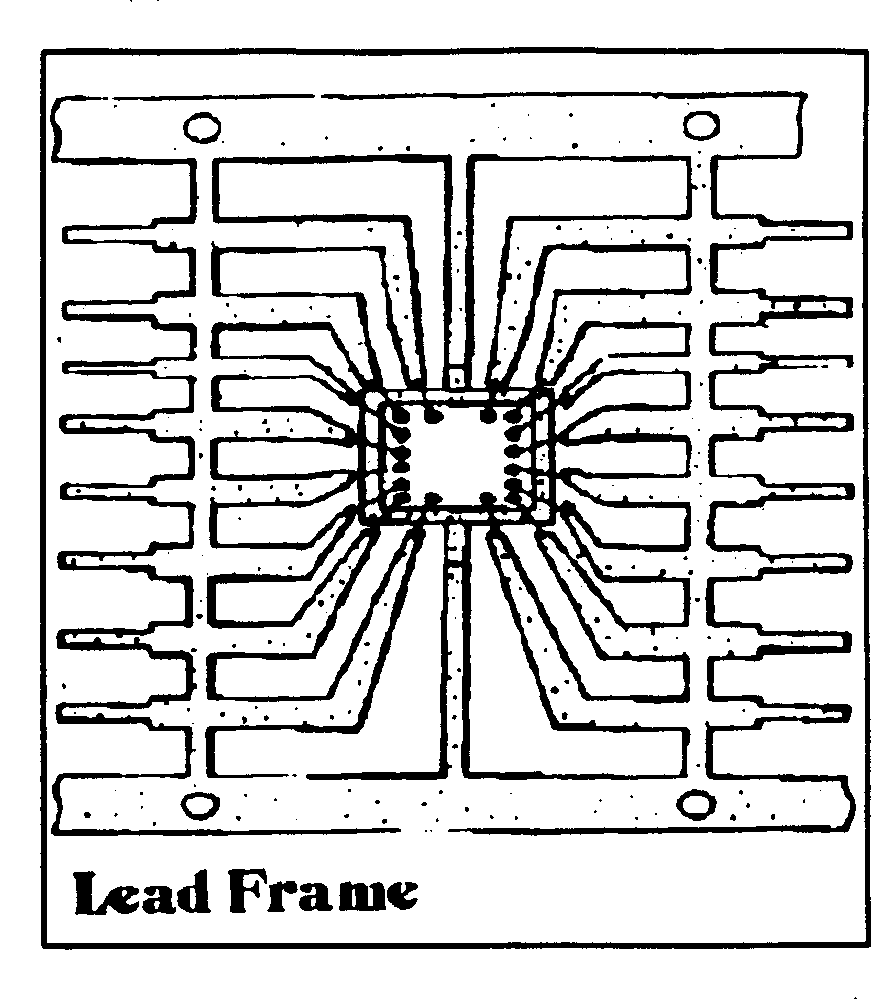
| SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 29, | Metal Working,
subclasses 739+ , especially subclass 741, for means to fasten electrical
component to wiring means, base, or substrate, including a multi-lead
component; and subclass 834 for beam lead frames or beam lead devices. |
| 174, | Electricity: Conductors and Insulators,
subclass 529 for flat pack electronic device mounting means. |
| 361, | Electricity: Electrical Systems and Devices,
subclass 813 for lead frames, per se, not associated with a
solid-state active electronic device of the type classified in Class
257. |
| 428, | Stock Material or Miscellaneous Articles,
subclasses 571+ for stock materials of metal which have marginal indexing
features or weakened portion for severing. Lead frames are commonly
made in long strips of repeating patterns with such indexing and/or severing
features. |
| 438, | Semiconductor Device Manufacturing: Process, particularly
subclasses 111+ and 123+ for methods of packaging utilizing
a lead frame; see the search notes therein. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 667]](../ps.gif) 667 667 | With dam or vent for encapsulant: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 666. Subject matter with a portion or portions to block encapsulant
flow, typically from flowing out of a mold during an encapsulation
process, or vent means (e.g., grooves in lead frame leads) to permit
egress to the atmosphere for air or other gases which are inside
a mold during encapsulation. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 668]](../ps.gif) 668 668 | On insulating carrier other than a printed circuit board: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 666. Subject matter wherein the lead frame is mounted on an insulating
carrier other than a printed circuit board.
| | (1)
Note. Printed circuit boards alone, or with one or more solid-state
electronic devices mounted thereon are not classified herein, but
are found in Class 174, Electricity: Conductors and Insulators, or
Class 361, Electricity: Electrical Systems and Devices. See the
class definitions for Classes 174 and 361 for the line of demarkation
between these two classes. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 174, | Electricity: Conductors and Insulators,
subclasses 260 and 520 for printed circuit boards in combination with
one or more electronic solid-state devices. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 669]](../ps.gif) 669 669 | With stress relief: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 666. Subject matter wherein means are provided to alleviate stresses
and strains (e.g., mechanical or thermal stresses) to which a lead
frame is subjected. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 670]](../ps.gif) 670 670 | With separate tie bar element or plural tie bars: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 666. Subject matter in which a frame element used to tie or connect
a semiconductor chip pad/flag and/or lead fingers
frame members is a separate element and not part of the lead frame itself
or wherein plural tie bar elements are provided as part of a lead
frame. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 671]](../ps.gif) 671 671 | Of insulating material: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 670. Subject matter wherein the separate tie bar element or
the plural tie bars are made of electrically insulating material. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 674]](../ps.gif) 674 674 | With means for controlling lead tension: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 666. Subject matter wherein means are provided for controlling
the tension under which an electrical lead is placed including,
for example, a bend in the lead, an area of reduced lead thickness,
etc. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 675]](../ps.gif) 675 675 | With heat sink means: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 666. Subject matter wherein a heat sink means is provided, either
as part of the lead frame or in addition to the lead frame for cooling
the active solid-state device. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 678]](../ps.gif) 678 678 | HOUSING OR PACKAGE: |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter wherein preformed physical means to cover
or protect a solid-state electronic device is provided therefor.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 81, | and 82, for a light emitting device in combination
with or also constituting a light responsive device and with specific
housing structure. |
| 99, | for light emitting device with specific housing
structure. |
| 177, | through 182, for a regenerative type switching device
with housing or external electrode. |
| 433, | and 434, for light responsive device with housing
or encapsulation means. |
| 573, | for Darlington configuration bipolar transistor
structure with housing or contact structure. |
| 584, | for enlarged emitter device bipolar transistor means
having housing or contact. |
| 602, | for a voltage variable capacitance device with specified
housing or contact. |
| 660, | for means to shield a device contained in a housing. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 361, | Electricity: Electrical Systems and Devices,
subclass 679.01 for housings and mounting assemblies for electronic
devices and components. |
| 438, | Semiconductor Device Manufacturing: Process, particularly
subclasses 106+ for methods of packaging; see the search notes
therein. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 679]](../ps.gif) 679 679 | Smart (e.g., credit) card package: |
| | Subject matter under 678 wherein the housing or package
is in a form which permits it to be used as a credit card.
| | (1)
Note. A smart card is one which contains a microprocessor
chip. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 235, | Registers,
subclass 487 and indented subclasses for coded records including
electronic credit cards, per se. |
| 361, | Electricity: Electrical Systems and Devices,
subclasses 736+ and 752+ for modules for printed circuits
or housing or chassis for printed circuit boards. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 680]](../ps.gif) 680 680 | With window means: |
| | Subject matter under 678 wherein the housing or package
has a physical opening or area otherwise transparent to ultraviolet,
visible, or infrared light. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 681]](../ps.gif) 681 681 | For erasing EPROM: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 680. Subject matter wherein the window means is provided for
transmitting light to erase an electrically programmable read-only
memory (EPROM). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 682]](../ps.gif) 682 682 | With desiccant, getter, or gas filling: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 678. Subject matter including a desiccant (i.e., a material for
absorbing moisture); a getter (i.e., a material which absorbs undesirable
semiconductor, housing or package contaminants); or wherein a gaseous
material fills the housing or package. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 684]](../ps.gif) 684 684 | With semiconductor element forming part (e.g., base, of
housing): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 678. Subject matter wherein part of the housing is formed by
a semiconductor element.
| | (1)
Note. The semiconductor element may have an inactive portion
connected to the rest of the housing, and another portion forming
an active device, for example. Frequently the semiconductor element forms
the base of the housing, through which leads are inserted. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 685]](../ps.gif) 685 685 | Multiple housings: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 678. Subject matter wherein more than one housing is provided
for a solid-state active electronic device, or wherein plural housings,
each containing one or more solid-state active devices, are constructed
as a unitary structure.
| | (1)
Note. One housing may be located within another housing. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 687]](../ps.gif) 687 687 | Housing or package filled with solid or liquid electrically
insulating material: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 678. Subject matter wherein the housing or package is filled
with a solid or liquid electrically insulating material.
| | (1)
Note. Encapsulated devices are excluded from this subclass
and are not considered to be housings or packages as defined in
subclass 678 which requires them to be preformed. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 361, | Electricity: Electrical Systems and Devices,
subclasses 729 , 730+, and 744+ for various modules
for printed circuit boards. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 689]](../ps.gif) 689 689 | Rigid electrode portion: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 688. Subject matter wherein the large area electrodes are rigid
in whole or in part.
| | (1)
Note. These type devices typically employ relatively massive
electrodes to operate at large current densities. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 690]](../ps.gif) 690 690 | With contact or lead: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 678. Subject matter wherein the device is provided with a contact
or lead, in addition to or as part of the package or housing. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 692]](../ps.gif) 692 692 | With particular lead geometry: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 690. Subject matter wherein the contact or lead provided as part
of or in addition to the package or housing has a specified geometrical
configuration. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 693]](../ps.gif) 693 693 | External connection to housing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 692. Subject matter wherein the contact or lead having a specified
geometry comprises an electrical connection for connecting the package
or housing and its contained active solid-state device to other
electrical devices or circuits. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 694]](../ps.gif) 694 694 | Axial leads: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 693. Subject matter wherein the leads or contacts which form
an external connection to the housing or package extend out opposite
ends along an axis of symmetry of a housing or package. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 695]](../ps.gif) 695 695 | Fanned/radial leads: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 693. Subject matter wherein the leads or contacts which form
an external connection to the housing or package extend radially
outward from the package.
| | (1)
Note. See illustration, below.
| |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 696]](../ps.gif) 696 696 | Bent (e.g., J-shaped) lead: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 693. Subject matter wherein the leads or contacts which form
an external connection to the housing or package include one or
more leads which have a curved end portion (e.g., for mounting on
the top surface of a printed circuit board).
| | (1)
Note. See illustration, below.
| |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 697]](../ps.gif) 697 697 | Pin grid type: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 693. Subject matter wherein the leads or contacts which form
an external connection to the housing or package are in the form
of a grid or matrix of elongated pins.
| | (1)
Note. See illustration, below.
| |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 699]](../ps.gif) 699 699 | Housing entirely of metal except for feedthrough structure: |
| | Subject matter under 698 wherein the housing or package
is made entirely of metal except for the portion wherein the electrical
contacts or leads are fed through.
| | (1)
Note. Typically, an insulator is placed in the feedthrough
portion of a metal housing to prevent electrical short circuiting of
the leads to the housing. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 702]](../ps.gif) 702 702 | Of insulating material other than ceramic: |
| | Subject matter under 701 wherein the housing is made of
electrically insulating material other than ceramic (e.g., the housing
is made of glass or of a single crystal insulator material).
| | (1)
Note. A ceramic is a polycrystalline, non-metallic, non-organic
material, such as fired polycrystalline aluminum oxide, typically
made by firing a compressed and shaped powder at high temperatures to
fuse the powder together. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 704]](../ps.gif) 704 704 | Cap or lid: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 701. Subject matter wherein the housing or package is provided
with a cap or lid. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 706]](../ps.gif) 706 706 | With heat sink: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 701. Subject matter wherein the insulating housing has a heat
sink to dissipate heat.
| | (1)
Note. The heat sink may be located in a cavity in a base
member made of ceramic material. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 174, | Electricity: Conductors and Insulators, appropriate subclasses directed to cooling means. |
| 361, | Electricity: Electrical Systems and Devices,
subclasses 688 through 723for cooling means for electronic devices or components
with housings or mounting assemblies. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 708]](../ps.gif) 708 708 | Entirely of metal except for feedthrough: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 678. Subject matter wherein the housing or package is made entirely
of metal except for the portion wherein the electrical contacts
or leads are fed through.
| | (1)
Note. Typically, an insulator is placed in the feedthrough
portion of a metal housing to prevent electrical short circuiting of
the leads to the housing. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 709]](../ps.gif) 709 709 | With specified insulator to isolate device from housing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 708. Subject matter wherein a specific insulator means is provided
to electrically isolate the active solid-state device contained
in the metal package or housing from the metal package or housing
to prevent electrical short circuits due to the housing or package. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 712]](../ps.gif) 712 712 | With provision for cooling the housing or its contents: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 678. Subject matter wherein means for cooling the housing or
its contents are provided in addition to natural cooling processes.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 174, | Electricity: Conductors and Insulators, appropriate subclasses directed to cooling means. |
| 361, | Electricity: Electrical Systems and Devices,
subclasses 688 through 723,for cooling means for electronic devices or components
with housings or mounting assemblies. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 713]](../ps.gif) 713 713 | For integrated circuit: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 712. Subject matter wherein the solid-state electronic device
for which cooling means is provided is an integrated circuit, which
is a semiconductor substrate which contains a plurality of active
solid-state electronic devices. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 714]](../ps.gif) 714 714 | Liquid coolant: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 712. Subject matter wherein the means provided for cooling the
housing or its contents is a liquid. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 715]](../ps.gif) 715 715 | Boiling (evaporative) liquid: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 714. Subject matter wherein the cooling means involves boiling
a liquid to provide evaporative cooling.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 174, | Electricity: Conductors and Insulators, appropriate subclasses directed to liquid cooling
means. |
| 361, | Electricity: Electrical Systems and Devices,
subclasses 699+ for liquid cooling means for electronic devices or
components with housings or mounting assemblies. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 716]](../ps.gif) 716 716 | Cryogenic liquid coolant: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 714. Subject matter wherein the cooling means uses a liquid to
maintain device temperatures at or below 100 degrees Kelvin.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 174, | Electricity: Conductors and Insulators, appropriate subclasses directed to liquid cooling
means. |
| 361, | Electricity: Electrical Systems and Devices,
subclasses 699+ for liquid cooling means for electronic devices or
components with housings or mounting assemblies. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 721]](../ps.gif) 721 721 | With gas coolant: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 712. Subject matter wherein the cooling means uses a gas to provide
the cooling (e.g., by convection). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 722]](../ps.gif) 722 722 | With fins: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 721. Subject matter wherein the cooling means has fins, i.e.,
long, thin, blade like structures used to dissipate heat to the
gas coolant. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 723]](../ps.gif) 723 723 | For plural devices: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 678. Subject matter wherein a package or housing is provided
for more than one electronic device, at least one of the electronic
devices being an active solid-state device.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 174, | Electricity: Conductors and Insulators,
subclasses 50+ for housings and printed circuits. |
| 361, | Electricity: Electrical Systems and Devices,
subclasses 729 and 730+ for plural housing modules. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 724]](../ps.gif) 724 724 | With discrete components: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 723. Subject matter wherein at least some of the electronic components
are in the form of an individual device per semiconductor chip,
as contrasted to a single integrated circuit containing plural semiconductor
devices. The discrete components may be active solid-state devices or
passive components such as resistors, capacitors, or inductors. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 728]](../ps.gif) 728 728 | For high frequency (e.g., microwave) device: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 678. Subject matter wherein the active solid-state device provided
with a housing or package is a high frequency solid-state electronic
device operating at high frequencies, such as microwave frequencies
or above. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 731]](../ps.gif) 731 731 | With housing mount: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 678. Subject matter wherein the housing or package has means
(e.g., a flange or threaded stud) for attaching the housing to a
support.
| | (1)
Note. Search this class, subclass 180 for housings or packages
of this type which specifically contain a regenerative type switching
device such as an SCR or thyristor. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 732]](../ps.gif) 732 732 | Flanged mount: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 731. Subject matter wherein the housing mount is a flange with
openings therein (e.g., threaded holes) to permit the housing to
be attached (e.g., by fasteners) to a support. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 733]](../ps.gif) 733 733 | Stud mount: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 731. Subject matter wherein the housing mount is a threaded element
shaped like a bolt extending from the housing for fastening into
a threaded hole in a support. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 734]](../ps.gif) 734 734 | COMBINED WITH ELECTRICAL CONTACT OR LEAD: |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter wherein the active solid-state device is
provided with one or more electrical contacts or leads.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 41, | for point contact rectifiers. |
| 44, | through 47, for devices with a metal contact alloyed
to elemental semiconductor type PN junction in a non-regenerative
structure. |
| 54, | for Schottky barrier to amorphous semiconductor
material device. |
| 73, | for Schottky barrier to polycrystalline semiconductor
material device. |
| 81, | and 82, for light emitter combined with or also
constituting a light responsive device and having a specific housing
or contact structure. |
| 91, | for plural light emitting devices with shaped contacts
or opaque masking. |
| 99, | for light emitting devices with specified housing
or contact structure. |
| 145, | for a regenerative type device combined with a FET
with extended latching current level and a low impedance channel
contact extending below the device surface. |
| 155, | and 156, for a regenerative type device with switching
speed enhancing means (e.g., a Schottky contact). |
| 177, | through 182, for a regenerative type device with
housing or external electrode. |
| 217, | for a majority signal carrier charge transfer device
with a conductive means in direct contact with channel (e.g., a
non-insulated gate). |
| 260, | for JFET having the same channel controlled by,
for example, Schottky barrier and pn junction gates. |
| 276, | for a JFET in a microwave integrated circuit with
a contact or heat sink extending through a hole in the semiconductor. |
| 280, | through 284, for JFETs with a Schottky gate electrode. |
| 316, | through 322, for a variable threshold insulated
electrical field effect device with additional contacted control
electrode. |
| 343, | for graded channel dopant IGFET device with plural
sections connected in parallel and having all contacts on the same
surface. |
| 382, | through 385, for an IGFET in an integrated circuit
with a refractory material contact to source or drain region. |
| 449, | through 457, for Schottky contacts in light responsive
devices. |
| 471, | through 486, for Schottky contact devices. |
| 502, | for high power integrated circuit devices with electrical
isolation and a backside collector contact. |
| 503, | for an integrated circuit device with electrically
isolated components having a contact or metallization configuration
to reduce parasitic coupling. |
| 522, | for beam-lead supported semiconductor islands in
integrated circuits. |
| 573, | for Darlington configuration non-isolated bipolar
transistors with resistance means connected between transistor base
regions and with housing or contact structure or configuration. |
| 576, | for complementary bipolar transistors sharing a
common active region (e.g., IIL, I2L) including
lateral bipolar transistor structure and having contacts of a refractory
material. |
| 584, | for bipolar transistor device with enlarged emitter
area and with housing or contact means. |
| 602, | for a voltage variable capacitance device with specified
housing or contact. |
| 621, | for a semiconductor device with electrical contact
in a hole in the semiconductor (e.g., lead extends through semiconductor
body). |
| 624, | for mesa structure device having a low resistance
ohmic connection along a mesa edge. |
| 661, | through 663, for superconductive contacts or leads. |
| 664, | for transmission line leads. |
| 665, | for contacts or leads including fusible link or
noise suppression means. |
| 666, | through 677, for lead frames. |
| 688, | and 689, for housings with large area flexible electrodes
in press contact with opposite sides of active semiconductor chip
and surrounded by an insulating element. |
| 690, | through 700, for housings with specified contact
or lead. |
| 905, | for plural DRAM cells sharing a common contact or
common trench. |
| 926, | for a device with an elongated lead extending axially
through another elongated lead. |
| 928, | for shorted pn or Schottky junction other than an
emitter junction. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 174, | Electricity: Conductors and Insulators,
subclasses 99+ for bus bar structure, per se. |
| 361, | Electricity: Electrical Systems and Devices,
subclasses 772 through 776for specific lead configurations connecting electronic
systems and devices to printed circuit boards. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 735]](../ps.gif) 735 735 | Beam leads (i.e., leads that extend beyond the ends or
sides of a chip component): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 734. Subject matter wherein electrical contact leads extend like
beams beyond the ends of a chip component.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 438, | Semiconductor Device Manufacturing: Process, particularly
subclass 411 for methods of forming electrically isolated semiconductor
islands held in place by beam lead metallization; subclass 461 for
methods of forming beam leads on a semiconductor substrate combined
with dicing of the substrate into plural separate bodies; and subclass
611 for methods of forming beam lead metallization on a semiconductor
substrate. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 736]](../ps.gif) 736 736 | Layered: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 735. Subject matter wherein the leads are made of at least two
separate layers of the same or different material. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 737]](../ps.gif) 737 737 | Bump leads: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 734. Subject matter wherein an electrical contact is in the form
of a relatively abrupt protuberance on the surface of a solid-state
electronic device or chip/die containing such a device. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 738]](../ps.gif) 738 738 | Ball shaped: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 737. Subject matter wherein the bump contacts have the spherical
shape of a ball.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 780, | for ball shaped bonds, generally. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 739]](../ps.gif) 739 739 | With textured surface: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 734. Subject matter wherein the surface of the contact or lead
is rough or has a characteristic of a closely interwoven fabric,
rather than being smooth. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 743]](../ps.gif) 743 743 | For compound semiconductor material: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 742. Subject matter in which the electrical contact material
contacts and contains a dopant for a semiconductor material which
is a chemical compound, as contrasted to an elemental semiconductor. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 745]](../ps.gif) 745 745 | Contact for III-V material: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 744. Subject matter in which the compound semiconductor material
is a group III-V compound, i.e., one component is from periodic
table group III and the other is from periodic table group V. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 747]](../ps.gif) 747 747 | With thermal expansion matching of contact or lead material
to semiconductor active device: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 741. Subject matter in which the electrical contact or lead material
is chosen to have a coefficient of thermal expansion which closely
matches that of the semiconductor active device material.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 178, | for regenerative device with housing and means to
avoid stress (e.g., thermal matching of electrode to semiconductor). |
| 633, | for thermal expansion compensation between semiconductor
and insulating coating. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 750]](../ps.gif) 750 750 | Layered: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 741. Subject matter wherein the specified contact material is
layered. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 751]](../ps.gif) 751 751 | At least one layer forms a diffusion barrier: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 750. Subject matter wherein at least one layer forms a barrier
to the diffusion of the contact material into the semiconductor
or into another contact layer.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 486, | for Schottky barrier layers including a diffusion
barrier material. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 754]](../ps.gif) 754 754 | At least one layer of silicide or polycrystalline silicon: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 750. Subject matter wherein at least one layer of material is
made up of a silicide or polycrystalline silicon.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 381, | and 538, for polycrystalline silicon resistive elements
connected to active semiconductor electronic devices. |
| 554, | and 588, for bipolar transistor devices with a polycrystalline
semiconductor connection electrode. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 755]](../ps.gif) 755 755 | Polysilicon laminated with silicide: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 754. Subject matter wherein the layers include a polysilicon
laminated with a silicide.
| | (1)
Note. Such laminated contacts of polysilicon and silicide
are sometimes called "polycide" contacts. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 757]](../ps.gif) 757 757 | Silicide of refractory or platinum group metal: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 754. Subject matter wherein a layered electrical contact or lead
includes a silicide of a metal found in groups IVA, VA, VIA or VIIIA
(other than iron (Fe), nickel (Ni) or cobalt (Co)) of the periodic
table of the elements. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 758]](../ps.gif) 758 758 | Multiple metal levels on semiconductor, separated by insulating
layer (e.g., multiple level metallization for integrated circuit): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 750. Subject matter wherein there are plural layers of metal
forming electrical contact material, the layers being separated
by intervening layers of insulator material.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 211, | for gate arrays with multi-level metallization. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 156, | Adhesive Bonding and Miscellaneous Chemical Manufacture,
subclasses 60+ , for processes of uniting plural bodies via an
adhesive material. |
| 438, | Semiconductor Device Manufacturing: Process, particularly
subclasses 118+ for methods of packaging a semiconductor device
including a step of bonding utilizing an adhesive material; see
the search notes therein. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 759]](../ps.gif) 759 759 | Including organic insulating material between metal levels: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 758. Subject matter wherein there is at least one layer of organic
insulating material between different layers of metal. An organic
compound is one which fulfills the requirements of the Class 260
definition, i.e., has a molecule characterized by two carbon atoms
bonded together, one atom of carbon being bonded to at least one
atom of hydrogen or a halogen, or one atom or carbon bonded to at
least one atom of nitrogen by a single or double bond, certain compounds
such as HCN, CN-CN, HNCO, HNCS, cyanogen halides, cyanamide, fulminic
acid and metal carbides, being exceptions to this rule. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 768]](../ps.gif) 768 768 | Refractory or platinum group metal or alloy or silicide
thereof: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 741. Subject matter wherein the specified contact or lead material
is a refractory metal or a platinum group metal, i.e., a metal found
in groups IVA, VA, VIA or VIIIA (other than iron (Fe), nickel (Ni)
or cobalt (Co)) of the periodic table of the elements or a silicide
(i.e., a binary compound of silicon), usually with a more electropositive element
or radical, thereof. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 769]](../ps.gif) 769 769 | Platinum group metal or silicide thereof: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 768. Subject matter wherein the specified contact or lead material
is a platinum group metal (i.e., platinum (Pt), palladium (Pd),
rhodium (Rh), ruthenium (Ru), osmium (Os) or iridium (Ir)) or a
silicide i.e., a binary compound of silicon, usually with a more
electropositive element or radical, thereof. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 772]](../ps.gif) 772 772 | Solder composition: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 741. Subject matter wherein the specific contact or lead material
is a solder composition (i.e., a metal or metallic alloy that melts
at relatively low temperatures).
| | (1)
Note. Solder is normally used to join metals with higher
melting points than the solder composition. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 774]](../ps.gif) 774 774 | Via (interconnection hole) shape: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 773. Subject matter wherein the shape or configuration of an
electrical contact or lead is determined by the shape of a hole
through an insulating layer through which the contact extends. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 776]](../ps.gif) 776 776 | Cross-over arrangement, component or structure: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 773. Subject matter wherein means are provided for electrically
insulating electrical contact elements or leads which cross each
other to do so without a short circuit therebetween.
| | (1)
Note. Electrically insulating components or structures associated
with electrical contact crossovers may be referred to as bridges,
tunnels, overpasses, underpasses, etc. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 777]](../ps.gif) 777 777 | Chip mounted on chip: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 734. Subject matter wherein a semiconductor substrate of an active
solid-state device is electrically connected to, and positioned
on, another semiconductor substrate.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 361, | Electricity: Electrical Systems and Devices,
subclasses 760+ for plural modules or means of connection of components
to a printed circuit board. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 778]](../ps.gif) 778 778 | Flip chip: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 734. Subject matter wherein a semiconductor substrate which contains
an active solid-state electronic device has electric contacts on
the top side thereof, the top side being that which contains an
active solid-state electronic device, and which is flipped so that
the contact side becomes the bottom side for connection with a substrate
which has matching electrical contacts. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 780]](../ps.gif) 780 780 | Ball or nail head type contact, lead, or bond: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 734. Subject matter wherein a contact, lead, or bond is in the
form of a wire having an end for connection to the semiconductor
which is in the shape of a ball or nail head.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 738, | for ball shaped bump contacts. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 782]](../ps.gif) 782 782 | Die bond: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 734. Subject matter wherein a semiconductor chip containing at
least one active solid-state device and provided with a contact
or lead is provided with a means for attaching the chip to a supporting
member.
| | (1)
Note. The supporting member or attachment may form part of
the contacts or leads for the chip, or be separate therefrom. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 783]](../ps.gif) 783 783 | With adhesive means: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 782. Subject matter wherein adhesive means (e.g., a layer) is
provided to secure a die (chip) which contains an active solid-state
electronic device to a supporting member.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 156, | Adhesive Bonding and Miscellaneous Chemical Manufacture,
subclasses 60+ for processes of uniting plural bodies via an adhesive
material. |
| 438, | Semiconductor Device Manufacturing: Process, particularly
subclasses 118+ for methods of packaging a semiconductor device
including a step of bonding utilizing an adhesive material; see
the search notes therein. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 784]](../ps.gif) 784 784 | Wire contact, lead, or bond: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 734. Subject matter wherein the contact, lead or bond is a very
flexible, elongated, small diameter filament made of electrically
conductive material. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 785]](../ps.gif) 785 785 | By pressure alone: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 734. Subject matter wherein the electrical contact, lead or bond
is held in place by pressure alone (e.g., by a spring clip).
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 181+, | and 688+, for other electrodes in press contact
with an active semiconductor device. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 786]](../ps.gif) 786 786 | Configuration or pattern of bonds: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 734. Subject matter wherein the electrical contact, lead or bond,
has a specific configuration or pattern.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 459, | for light activated devices with particular bonding
pad arrangement. |
| 625, | for mesa structure semiconductor device bonded to
heat sink or thick electrical conductor. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 787]](../ps.gif) 787 787 | ENCAPSULATED: |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter wherein an active solid-state electronic
device, often part of a semiconductor chip, is surrounded by an
electrically insulating material which forms a sealed encasement
therefor.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 100, | for encapsulated light emitter device. |
| 433+, | for light responsive devices with housing or encapsulation. |
| 687, | for a housing containing an encapsulant material. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 29, | Metal Working, particularly
subclasses 841 and 855 for methods of assembling an electrical
component to a base or lead and encapsulating the same. |
| 65, | Glass Manufacturing, appropriate subclasses for the manufacturing of glass
encapsulated electronic devices or components thereof. |
| 174, | Electricity: Conductors and Insulators,
subclass 251 for a printed circuit with an encapsulated wire. |
| 264, | Plastic and Nonmetallic Article Shaping or Treating:
Processes,
subclass 272.11 for encapsulation of electrical components. |
| 343, | Communications: Radio Wave Antennas,
subclass 873 for embedded, potted, or coated radio wave antennas. |
| 361, | Electricity: Electrical Systems and Devices,
subclasses 600 and 679.01 for enclosures, including encapsulated types,
for electrical and electronic devices. |
| 438, | Semiconductor Device Manufacturing: Process, particularly
subclasses 112 and 127 for methods of encapsulating; see the search
notes therein. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 788]](../ps.gif) 788 788 | With specified encapsulant: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 787. Subject matter wherein the chemical composition of the material
that encapsulates the active solid-state electronic device is specified. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 789]](../ps.gif) 789 789 | With specified filler material: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 788. Subject matter wherein a particular material has been added
to an encapsulant material to give it desirable mechanical, thermal,
electrical, or other desirable characteristics, and the material
is specified. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 791]](../ps.gif) 791 791 | Including polysiloxane (e.g., silicone resin): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 788. Subject matter wherein the encapsulant includes polysiloxane
(i.e., any of various polymeric compounds which contain alternate silicon
and oxygen atoms in either a linear or cyclic arrangement), often
with one or two organic groups attached to each silicon atom. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 792]](../ps.gif) 792 792 | Including polyimide: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 788. Subject matter wherein the encapsulant includes polyimide
i.e., a polymeric compound resulting from replacement of both atoms
of hydrogen in an organic amine by organic univalent acid radicals
or by an organic divalent acid radical.
| | (1)
Note. Polyimides are copolymers (polymers formed from at
least two different starting organic materials) which have a linkage,
as illustrated below, between the starting materials, wherein R
is typically hydrogen and Q1 and Q2 are
the organic residues of the starting monomers. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 793]](../ps.gif) 793 793 | Including epoxide: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 788. Subject matter wherein the encapsulant includes an epoxy
compound (i.e., a compound containing three membered ring consisting
or one oxygen and two carbon atoms). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 794]](../ps.gif) 794 794 | Including glass: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 788. Subject matter wherein the encapsulant contains glass (i.e.,
an amorphous inorganic, usually transparent or translucent substance consisting
of a mixture of silicates or borates or phosphates formed by fusion
of silica or of oxides of boron or phosphorous with a flux and stabilizer
that cools to a rigid condition without crystallization). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 795]](../ps.gif) 795 795 | With specified filler material: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 787. Subject matter wherein a particular material has been added
to an encapsulant material to give it desirable mechanical, thermal,
electrical, or other desirable characteristics, and the material
is specified. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 796]](../ps.gif) 796 796 | With heat sink embedded in encapsulant: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 787. Subject matter wherein a heat sink is embedded in the encapsulant.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 174, | Electricity: Conductors and Insulators, appropriate subclasses. |
| 361, | Electricity: Electrical Systems and Devices,
subclasses 704 through 723 for thermal conduction means. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 797]](../ps.gif) 797 797 | ALIGNMENT MARKS: |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter wherein the active solid-state device is
provided with one or more indicia or marks used during fabrication
of the device to facilitate accurate alignment of regions in the
device. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 798]](../ps.gif) 798 798 | MISCELLANEOUS: |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter wherein the subject matter is not otherwise
provided for. |
| | |
E-SUBCLASSES
The E-subclasses in U.S. Class 257 provide for active solid-state
electronic devices, that is, electronic devices or components that
are made primarily of solid materials, usually semiconductors, which
operate by the movement of charge carriers - electrons or holes
- which undergo energy level changes within the material and can
modify an input voltage or electro-magnetic signal to achieve rectification,
amplification, oscillating, radiation emission, or switching action,
or capacitors or resistors with potential-jump or surface barrier;
the E-subclasses include processes or apparatus peculiar to the manufacture
or treatment of such active solid-state devices or of parts of such
devices.
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.001]](../ps.gif) E21.001 E21.001 | PROCESSES OR APPARATUS ADAPTED FOR MANUFACTURE OR TREATMENT OF
SEMICONDUCTOR OR SOLID-STATE DEVICES OR OF PARTS THEREOF (EPO): |
| | This main group provides for processes or apparatus that
are employed in the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or
solid-state devices or of parts thereof. This subclass is substantially
the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/00.
| | (1)
Note. This subclass will take subject matter where the manufactured
or treated device/component (or part thereof) will have
at least one of the following capabilities:
| | (a)
The conduction or modification of an electrical current, |
| | (b)
The storage of electrical energy for subsequent discharge
within a microelectronic integrated circuit, or |
| | (c)
The conversion of electromagnetic wave energy to electrical
energy or electrical energy to electromagnetic energy. | |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E31.001, | E33.001, E39.001, E45.001, E47.001, E49.001, and
E51.001, for processes or apparatus adapted for manufacture or treatment
of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.004]](../ps.gif) E21.004 E21.004 | Of resistor (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.003. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/02B2. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.008]](../ps.gif) E21.008 E21.008 | Of capacitor (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.003. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/02B3. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.022]](../ps.gif) E21.022 E21.022 | Of inductor (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.003. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/02B4. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.025]](../ps.gif) E21.025 E21.025 | For lift-off process (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.024. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/027B2. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.028]](../ps.gif) E21.028 E21.028 | Using laser (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.027. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/027B6B2. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.045]](../ps.gif) E21.045 E21.045 | Making electrode (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.041. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/04D20. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.046]](../ps.gif) E21.046 E21.046 | Ohmic electrode (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.045. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/04D20A. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.047]](../ps.gif) E21.047 E21.047 | Schottky electrode (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.045. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/04D20C. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.053]](../ps.gif) E21.053 E21.053 | Diode (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.052. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/04D40C2. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.057]](../ps.gif) E21.057 E21.057 | Using ion implantation (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.056. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/04H4A.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E21.054, | for processes where ion implantation of boron and
subsequent annealing does not produce a p-doped region. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.058]](../ps.gif) E21.058 E21.058 | Using masks (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.057. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/04H4A10. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.059]](../ps.gif) E21.059 E21.059 | Angled implantation (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.057. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/04H4A12. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.061]](../ps.gif) E21.061 E21.061 | Making electrode (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.054. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/04H10. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.062]](../ps.gif) E21.062 E21.062 | Ohmic electrode (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.061. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/04H10A. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.064]](../ps.gif) E21.064 E21.064 | Schottky electrode (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.061. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/04H10C. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.077]](../ps.gif) E21.077 E21.077 | Heat treating (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.076. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/145. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.088]](../ps.gif) E21.088 E21.088 | By direct bonding (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.087. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/18B2. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.124]](../ps.gif) E21.124 E21.124 | Heteroepitaxy (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.123. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/20B6B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.139]](../ps.gif) E21.139 E21.139 | Lithium-drift (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.135. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/22L. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.14]](../ps.gif) E21.14 E21.14 | Diffusion source (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.135. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/22N. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.147]](../ps.gif) E21.147 E21.147 | By ion implantation (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.146. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/225A2D. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.161]](../ps.gif) E21.161 E21.161 | Of conductive layer (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.16. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/285B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.171]](../ps.gif) E21.171 E21.171 | Selective deposition (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.17. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/285B4H2. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.177]](../ps.gif) E21.177 E21.177 | MOS-gate structure (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.176. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/28B2. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.178]](../ps.gif) E21.178 E21.178 | Joint-gate structure (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.177. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/28B2C. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.195]](../ps.gif) E21.195 E21.195 | Characterized by conductor (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.191. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/28E2B.
| | (1)
Note. This subclass includes the final conductor comprising
a superconductor. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.219]](../ps.gif) E21.219 E21.219 | Chemical etching (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.215. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/306B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.222]](../ps.gif) E21.222 E21.222 | Vapor phase etching (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.22. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/306B4C. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.224]](../ps.gif) E21.224 E21.224 | Chemical cleaning (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.215. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/306N. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.226]](../ps.gif) E21.226 E21.226 | Dry cleaning (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.224. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/306N2. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.228]](../ps.gif) E21.228 E21.228 | Wet cleaning only (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.224. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/306N4. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.231]](../ps.gif) E21.231 E21.231 | Using mask (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.215. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/308. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.241]](../ps.gif) E21.241 E21.241 | Post-treatment (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.24. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/3105. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.242]](../ps.gif) E21.242 E21.242 | Of organic layer (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.241. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/3105P. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.248]](../ps.gif) E21.248 E21.248 | By ion implantation (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.247. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/3115B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.251]](../ps.gif) E21.251 E21.251 | By chemical means (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.25. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/311B2. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.252]](../ps.gif) E21.252 E21.252 | By dry-etching (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.251. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/311B2B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.255]](../ps.gif) E21.255 E21.255 | By chemical means (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.254. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/311C2. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.256]](../ps.gif) E21.256 E21.256 | By dry-etching (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.255. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/311C2B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.257]](../ps.gif) E21.257 E21.257 | Using mask (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.249. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/311D. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.258]](../ps.gif) E21.258 E21.258 | Using masks (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.24. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/32. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.266]](../ps.gif) E21.266 E21.266 | Inorganic layer (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.24. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/314. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.268]](../ps.gif) E21.268 E21.268 | Of silicon (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.266. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/314B1. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.279]](../ps.gif) E21.279 E21.279 | On silicon body (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.278. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/316B2B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.281]](../ps.gif) E21.281 E21.281 | On a silicon body (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.28. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/316B3B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.282]](../ps.gif) E21.282 E21.282 | Formed by oxidation (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.271. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/316C. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.284]](../ps.gif) E21.284 E21.284 | By thermal oxidation (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.283. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/316C2B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.285]](../ps.gif) E21.285 E21.285 | Of silicon (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.284. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/316C2B2. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.287]](../ps.gif) E21.287 E21.287 | By anodic oxidation (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.283. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/316C2C. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.288]](../ps.gif) E21.288 E21.288 | Of silicon (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.287. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/316C2C2. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.291]](../ps.gif) E21.291 E21.291 | By anodic oxidation (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.29. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/316C3B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.293]](../ps.gif) E21.293 E21.293 | Of silicon nitride (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.292. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/318B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.3]](../ps.gif) E21.3 E21.3 | Post treatment (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.294. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/321. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.303]](../ps.gif) E21.303 E21.303 | Planarization (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.3. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/321P. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.31]](../ps.gif) E21.31 E21.31 | By vapor etching only (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.308. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/3213C4. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.311]](../ps.gif) E21.311 E21.311 | Using plasma (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.31. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/3213C4B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.314]](../ps.gif) E21.314 E21.314 | Using mask (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.305. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/3213D. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.315]](../ps.gif) E21.315 E21.315 | Doping layer (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.3. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/3215. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.323]](../ps.gif) E21.323 E21.323 | Of diamond body (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.317. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/322D. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.328]](../ps.gif) E21.328 E21.328 | Radiation treatment (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.085. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/26. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.337]](../ps.gif) E21.337 E21.337 | Through-implantation (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.336. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/265A2B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.338]](../ps.gif) E21.338 E21.338 | Recoil-implantation (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.335. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/265A3. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.342]](../ps.gif) E21.342 E21.342 | Through-implantation (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.341. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/265B2B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.344]](../ps.gif) E21.344 E21.344 | In diamond (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.334. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/265D. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.346]](../ps.gif) E21.346 E21.346 | Using mask (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.334. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/266. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.348]](../ps.gif) E21.348 E21.348 | Using X-ray laser (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.347. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/268B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.352]](../ps.gif) E21.352 E21.352 | Diode (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.351. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/329B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.353]](../ps.gif) E21.353 E21.353 | Tunnel diode (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.352. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/329B2. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.356]](../ps.gif) E21.356 E21.356 | Zener diode (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.355. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/329B4B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.357]](../ps.gif) E21.357 E21.357 | Avalanche diode (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.355. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/329B4C. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.358]](../ps.gif) E21.358 E21.358 | Rectifier diode (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.352. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/329B5. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.359]](../ps.gif) E21.359 E21.359 | Schottky diode (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.352. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/329B6. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.36]](../ps.gif) E21.36 E21.36 | Planar diode (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.352. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/329B7. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.366]](../ps.gif) E21.366 E21.366 | Diode (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.365. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/329P4. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.368]](../ps.gif) E21.368 E21.368 | Schottky diode (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.366. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/329P4C. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.37]](../ps.gif) E21.37 E21.37 | Transistor (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.369. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/331. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.371]](../ps.gif) E21.371 E21.371 | Heterojunction transistor (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.37. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/331B.
| | (1)
Note: for multi-step processes, a junction between two regions
of the same material but in different crystalline state, e.g., amorphous
Si or poly Si emitters on a single crystalline Si, is not considered
an heterojunction. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.373]](../ps.gif) E21.373 E21.373 | Lateral transistor (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.37. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/331C. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.374]](../ps.gif) E21.374 E21.374 | Schottky transistor (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.037. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/331D. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.376]](../ps.gif) E21.376 E21.376 | Planar transistor (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.375. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/331F2. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.378]](../ps.gif) E21.378 E21.378 | Inverse transistor (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.375. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/331F4. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.384]](../ps.gif) E21.384 E21.384 | With recessed gate (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.383. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/331G2R. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.388]](../ps.gif) E21.388 E21.388 | Thyristor (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.369. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/332.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E21.362, | for gated diode structure, e.g., FCTh, SITh, and
FCD. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.41]](../ps.gif) E21.41 E21.41 | Vertical transistor (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.409. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/336A.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E21.411 | through E21.416, for vertical thin film transistor, with the exception
of monocrystalline vertical thin film transistor. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.412]](../ps.gif) E21.412 E21.412 | Amorphous silicon or polysilicon transistor (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.411. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/336D2.
| | (1)
Note: This subclass includes amorphous silicon or polysilicon
transistor with Gate All Around. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.419]](../ps.gif) E21.419 E21.419 | With recessed gate (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.418. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/336B2R. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.422]](../ps.gif) E21.422 E21.422 | With floating gate (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.409. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/336F. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.438]](../ps.gif) E21.438 E21.438 | Using self-aligned silicidation, i.e., salicide (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.409. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/336M.
| | (1)
Note: documents are classified in this subclass when they
are directed to avoiding short circuit between source/drain and
gate. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E21.165, | for improving the source or drain contact. |
| E21.199, | for improving the gate. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.457]](../ps.gif) E21.457 E21.457 | With insulated gate (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.456. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/339B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.458]](../ps.gif) E21.458 E21.458 | With Schottky gate (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.456. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/339C. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.459]](../ps.gif) E21.459 E21.459 | Device having semiconductor body other than carbon, Si,
Ge, SiC, Se, Te, Cu 2O, CuI, and Group III-V
compounds with or without impurities, e.g., doping materials (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.04 This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/34. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.46]](../ps.gif) E21.46 E21.46 | Multistep process (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.459. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L21/34B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.471]](../ps.gif) E21.471 E21.471 | Radiation treatment (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.459. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/42. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.474]](../ps.gif) E21.474 E21.474 | Using mask (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.473. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/426. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.486]](../ps.gif) E21.486 E21.486 | Using mask (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.485. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/467. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.488]](../ps.gif) E21.488 E21.488 | Using mask (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.487. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/475. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.49]](../ps.gif) E21.49 E21.49 | Etching layer (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.489. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/4757B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.491]](../ps.gif) E21.491 E21.491 | Doping layer (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.489. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/4757C. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.493]](../ps.gif) E21.493 E21.493 | Inorganic layer (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.487. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/471. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.504]](../ps.gif) E21.504 E21.504 | Moulds (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.502. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/56M. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.512]](../ps.gif) E21.512 E21.512 | Right-up bonding (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.511. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/60C4B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.53]](../ps.gif) E21.53 E21.53 | For structural parameters, e.g., thickness, line width,
refractive index, temperature, warp, bond strength, defects, optical
inspection, electrical measurement of structural dimensions, metallurgic
measurement of diffusions (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.529. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/66M2. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.573]](../ps.gif) E21.573 E21.573 | Air gaps (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.54. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/764. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.577]](../ps.gif) E21.577 E21.577 | By forming via holes (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.576. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/768B2. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.578]](../ps.gif) E21.578 E21.578 | Tapered via holes (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.577. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/768B2B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.581]](../ps.gif) E21.581 E21.581 | Dielectric comprising air gaps (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.576. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/768B6.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E21.243, | for planarization of insulating materials, per
se. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.583]](../ps.gif) E21.583 E21.583 | Planarization; smoothing (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.582. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/768C2.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E21.195, | for electrode structure characterized by conductor. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.595]](../ps.gif) E21.595 E21.595 | Modifying pattern (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.591. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/768C8L. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.608]](../ps.gif) E21.608 E21.608 | Bipolar technology (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.606. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/8222. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.613]](../ps.gif) E21.613 E21.613 | Memory structures (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.608. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/8229. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.616]](../ps.gif) E21.616 E21.616 | MIS technology (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.615. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/8234. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.645]](../ps.gif) E21.645 E21.645 | Memory structures (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.616. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/8239. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.657]](../ps.gif) E21.657 E21.657 | Making bit line (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.656. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/8242D2. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.659]](../ps.gif) E21.659 E21.659 | Making word line (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.656. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/8242D6. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.666]](../ps.gif) E21.666 E21.666 | PROM (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.662. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/8246P. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.667]](../ps.gif) E21.667 E21.667 | ROM only (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.662. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/8246R. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.693]](../ps.gif) E21.693 E21.693 | For vertical channel (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E21.692. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L21/8247M8V. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.001]](../ps.gif) E23.001 E23.001 | PACKAGING, INTERCONNECTS, AND MARKINGS FOR SEMICONDUCTOR OR
OTHER SOLID-STATE DEVICES (EPO): |
| | This main group provides for preformed physical means to
cover or protect semiconductor or other solid state devices, electrical
interconnection of such devices and lead elements for facilitating
electrical interconnection of the chips or dies via intermediate
(e.g., jumper) connections to other devices or components, and marks
applied to chips or dies such as test patterns or alignment marks.
This subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L23/00. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.014]](../ps.gif) E23.014 E23.014 | Beam leads (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E23.012. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L23/482B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.017]](../ps.gif) E23.017 E23.017 | Materials (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E23.012. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L23/482M. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.022]](../ps.gif) E23.022 E23.022 | Overhang structure (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E23.019. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L23/485H. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.029]](../ps.gif) E23.029 E23.029 | Semiconductor (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E23.028. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L23/492M2. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.03]](../ps.gif) E23.03 E23.03 | Carbon (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E23.028. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L23/492M3. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.031]](../ps.gif) E23.031 E23.031 | Lead frames or other flat leads (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E23.023. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L23/495.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E23.141, | for lead frame interconnections between components. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.032]](../ps.gif) E23.032 E23.032 | Additional leads (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E23.031. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L23/495C. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.041]](../ps.gif) E23.041 E23.041 | Multi layer (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E23.031. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L23/495D. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.07]](../ps.gif) E23.07 E23.07 | Geometry or layout (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E23.06. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L23/498G. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.072]](../ps.gif) E23.072 E23.072 | Characterized by materials (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E23.06. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L23/498M.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E23.005, | for materials of the substrates. |
| E23.053, | for materials of the lead-frames. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.074]](../ps.gif) E23.074 E23.074 | Carbon, e.g., fullerenes (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E23.072. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L23/498M3.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E39.008, | for superconducting fullerenes. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.091]](../ps.gif) E23.091 E23.091 | Bellows (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E23.09. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L23/433B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.098]](../ps.gif) E23.098 E23.098 | By flowing liquids (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E23.097. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L23/473. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.1]](../ps.gif) E23.1 E23.1 | Jet impingement (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclassE23.099. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L23/473J. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.103]](../ps.gif) E23.103 E23.103 | Foil-like cooling fins or heat sinks (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E23.102. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L23/367F.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E23.051, | for foil-like cooling fins or heat sinks being part
of lead-frames. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.109]](../ps.gif) E23.109 E23.109 | Metallic materials (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E23.106. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L23/373M. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.111]](../ps.gif) E23.111 E23.111 | Diamond (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E23.11. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L23/373D. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.115]](../ps.gif) E23.115 E23.115 | Against alpha rays (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E23.114. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L23/556. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.121]](../ps.gif) E23.121 E23.121 | Containing filler (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E23.119. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L23/29P4. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.129]](../ps.gif) E23.129 E23.129 | Partial encapsulation or coating (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E23.123. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L23/ 31P.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E21.240, | for mask layer used as insulation layer. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.13]](../ps.gif) E23.13 E23.13 | Coating being foil (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E23.129. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L23/31P4. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.134]](../ps.gif) E23.134 E23.134 | Multilayer coating (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E23.129. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L23/31P12. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.159]](../ps.gif) E23.159 E23.159 | Aluminum alloys (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E23.158. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L23/532M1A2. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.173]](../ps.gif) E23.173 E23.173 | Multilayer substrates (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E23.169. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L23/538D.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E23.169, | for multilayer metallisation on monolayer substrates. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.18]](../ps.gif) E23.18 E23.18 | Containers; seals (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E23.001. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L23/02. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E25.001]](../ps.gif) E25.001 E25.001 | ASSEMBLIES CONSISTING OF PLURALITY OF INDIVIDUAL SEMICONDUCTOR
OR OTHER SOLID-STATE DEVICES (EPO): |
| | This main group provides for housing or mounting arrangements
of a plurality of discrete semiconductor or other solid state devices,
e.g., side-by-side and/or stacked arrangement of devices
such as solar cells and diodes. This subclass is substantially the
same in scope as ECLA classification H01L25/00.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E23.031 | through E23.059, for assembly including lead frames interconnection. |
| E27.001, | for devices consisting of a plurality of solid
state components formed in or on a common substrate. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E25.002]](../ps.gif) E25.002 E25.002 | All devices being of same type, e.g., assemblies of rectifier
diodes (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E25.001. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L25/03.
| | (1)
Note. This subclass includes assembly of all the devices being
of a type provided for in the same main groups of E27.001, E29.001,
E31.001, E33.001, E39.001, E43.001, E45.001, E47.001, and E49.001. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E25.025]](../ps.gif) E25.025 E25.025 | Mixed assemblies (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E25.024. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L25/11M. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E25.029]](../ps.gif) E25.029 E25.029 | Devices being of two or more types, e.g., forming hybrid
circuits (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E25.001. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L25/16.
| | (1)
Note. This subclass includes assembly of the devices being
of types provided for in two or more different main groups of E27.001,
E29.001, E31.001, E33.001, E39.001, E43.001, E45.001, E47.001, and
E49.001. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E25.031]](../ps.gif) E25.031 E25.031 | Containers (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E25.029. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L25/16H. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.001]](../ps.gif) E27.001 E27.001 | DEVICE CONSISTING OF A PLURALITY OF SEMICONDUCTOR OR OTHER SOLID
STATE COMPONENTS FORMED IN OR ON A COMMON SUBSTRATE, E.G., INTEGRATED
CIRCUIT DEVICE (EPO): |
| | This main group provides for device which includes a plurality
of semiconductor or other solid state components with specific
structural features related to the device, material, or layout,
and integrated on a common substrate. This subclass is substantially
the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L27/00.
| | (1)
Note. See E21.001, E31.001, E33.001, E39.001, E45.001, E47.001,
E49.001, and E51.001 for processes or apparatus adapted for manufacture
or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts
thereof. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.01]](../ps.gif) E27.01 E27.01 | With semiconductor substrate only (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E27.009. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L27/04.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E27.111, | for substrate comprising other than a semiconductor
material |
| E27.112, | for substrate including insulator on semiconductor
or vise versa, e.g., silicon on insulator (SOI) |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.029]](../ps.gif) E27.029 E27.029 | Including component of the field-effect type (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E27.028. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L27/07F.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E27.059, | for integrated circuit device containing field effect
components of single kind only. |
| E27.081, | for integrated circuit device including of plurality
of field effect components in a repetitive configuration. |
| E27.107, | for masterslice integrated circuit using field effect
structure. |
| E27.148, | for Junction field effect transistor imager. |
| E29.242, | for electrodes controlled by field effect transistor. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.047]](../ps.gif) E27.047 E27.047 | Resistor only (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E27.046. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L27/08B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.048]](../ps.gif) E27.048 E27.048 | Capacitor only (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E27.046. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L27/08C. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.049]](../ps.gif) E27.049 E27.049 | Varactor diode (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E27.048. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L27/08C2. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.051]](../ps.gif) E27.051 E27.051 | Diode only (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E27.046. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L27/08D. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.052]](../ps.gif) E27.052 E27.052 | Thyristor only (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E27.046. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L27/08U. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.062]](../ps.gif) E27.062 E27.062 | Complementary MIS (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E27.06. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L27/092. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.079]](../ps.gif) E27.079 E27.079 | Thyristor (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E27.072. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L27/102U. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.091]](../ps.gif) E27.091 E27.091 | Transistor in trench (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E27.078. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L27/108F6. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.092]](../ps.gif) E27.092 E27.092 | Capacitor in trench (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E27.078. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L27/108F8. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.096]](../ps.gif) E27.096 E27.096 | Vertical transistor (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E27.095. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L27/108F10V. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.105]](../ps.gif) E27.105 E27.105 | Masterslice integrated circuit (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E27.07. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L27/118.
| | (1)
Note: Masterslice integrated circuit is a gate array wherein
the circuit elements can be interconnected by more than one wirings
pattern to have different designed devices. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.108]](../ps.gif) E27.108 E27.108 | CMOS gate array (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E27.107. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L27/118G4. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.115]](../ps.gif) E27.115 E27.115 | Thick-film circuits (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E27.114. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L27/01B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.116]](../ps.gif) E27.116 E27.116 | Thin-film circuits (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E27.114. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L27/01C. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.134]](../ps.gif) E27.134 E27.134 | Color imager (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E27.133. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L27/146F2. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.136]](../ps.gif) E27.136 E27.136 | Infrared imager (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E27.133. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L27/146F3. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.139]](../ps.gif) E27.139 E27.139 | Anti-blooming (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E27.133. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L27/146F4.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E27.145, | for anti-blooming in imager using a photoconductor
layer |
| E27.162, | for anti-blooming in charge coupled imager |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.142]](../ps.gif) E27.142 E27.142 | Color imager (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E27.141. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L27/146P2. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.143]](../ps.gif) E27.143 E27.143 | Infrared imager (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E27.141. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L27/146P3. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.145]](../ps.gif) E27.145 E27.145 | Anti-blooming (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E27.141. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L27/146P4. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.15]](../ps.gif) E27.15 E27.15 | Charge coupled imager (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E27.13. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L27/148.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E29.065, | for individual charge coupled devices. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.153]](../ps.gif) E27.153 E27.153 | Linear CCD imager (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E27.15. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L27/148B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.154]](../ps.gif) E27.154 E27.154 | Area CCD imager (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E27.15. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L27/148C. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.156]](../ps.gif) E27.156 E27.156 | Interline transfer (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E27.154. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L27/148C4. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.157]](../ps.gif) E27.157 E27.157 | Frame transfer (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E27.154. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L27/148C6. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.162]](../ps.gif) E27.162 E27.162 | Anti-blooming (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E27.15. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L27/148M. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.001]](../ps.gif) E29.001 E29.001 | Semiconductors devices adapted for rectifying, amplifying,
oscillating, or switching, capacitors, or resistors with at least
one potential-jump barrier or surface barrier (EPO): |
| | This main group provides for semiconductor devices which
operate by the movement of charge carriers, i.e. electrons and holes,
from one energy level to another within the semiconductor material
and can modify an input voltage to achieve rectification, amplification, oscillation
or switching action, or capacitors or resistors with at least one
potential-jump barrier or surface barrier. This subclass is substantially
the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/00.
| | (1)
Note: See E21.001 for processes or apparatus adapted for
manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices
or of parts thereof. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.026]](../ps.gif) E29.026 E29.026 | Surface layout of device (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.024. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L29/06D3.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E29.066, | for surface shape of the base only. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.035]](../ps.gif) E29.035 E29.035 | Pedestal collectors (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.034. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L29/08C2. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.04]](../ps.gif) E29.04 E29.04 | Of field-effect transistors with insulated gate (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.039. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L29/08E2.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E29.062, | with a passive supplementary region between source
or drain and substrate related to punch-through, capacity or isolation
phenomena. |
| E29.266, | with LDD or DDD structure. |
| E29.277, | for thin film transistors. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.042]](../ps.gif) E29.042 E29.042 | Tunneling barrier (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.029. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L29/08T. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.051]](../ps.gif) E29.051 E29.051 | With insulated gate (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.05. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29//10D2B.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E29.135, | with channel and gate aligned in the lengthwise
direction. |
| E29.270, | with buried channel. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.052]](../ps.gif) E29.052 E29.052 | Nonplanar channel (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.051. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L29/10D2B1.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E29.130, | if characterised only by the shape of a non-planar
gate structure. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.057]](../ps.gif) E29.057 E29.057 | With PN junction gate: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.05. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L29/10D2C. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.062]](../ps.gif) E29.062 E29.062 | With insulated gate (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.061. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/10F2B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.069]](../ps.gif) E29.069 E29.069 | Single quantum well structures (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.068. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L29/12W.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E29.081, | E29.085, E29.091, E29.097, for single heterojunctions,
couples of materials. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.08]](../ps.gif) E29.08 E29.08 | Amorphous materials (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.79. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/26E. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.083]](../ps.gif) E29.083 E29.083 | Amorphous materials (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.082. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L29/16E. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.088]](../ps.gif) E29.088 E29.088 | Amorphous materials (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.087. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L29/18E. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.092]](../ps.gif) E29.092 E29.092 | Amorphous materials (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.089. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L29/20E. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.095]](../ps.gif) E29.095 E29.095 | Amorphous materials (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.094. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L29/22E. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.101]](../ps.gif) E29.101 E29.101 | Amorphous materials (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.1. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/24E. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.111]](../ps.gif) E29.111 E29.111 | Electrodes (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.001. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L29/40. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.128]](../ps.gif) E29.128 E29.128 | With insulated gate (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.127. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L29/423D2B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.13]](../ps.gif) E29.13 E29.13 | Gate electrodes for nonplanar MOSFET (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.128. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L29/423D2B4.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E29.267, | for MOSFET"s with lightly doped drain (LDD)
structure. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.143]](../ps.gif) E29.143 E29.143 | Ohmic electrodes (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.139. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L29/45. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.146]](../ps.gif) E29.146 E29.146 | On silicon (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.143. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L29/45S. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.15]](../ps.gif) E29.15 E29.15 | Electrodes for IGFET (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.139. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L29/49. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.151]](../ps.gif) E29.151 E29.151 | For TFT (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.15. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/49B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.155]](../ps.gif) E29.155 E29.155 | Multiple silicon layers: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.154. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L29/49C2
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E29.154, | with only a vertical doping structure or vertical
doping variation. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.159]](../ps.gif) E29.159 E29.159 | Diverse conductors (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.158. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L29/49D2. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.161]](../ps.gif) E29.161 E29.161 | Silicide (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.16. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L29/49E2. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.162]](../ps.gif) E29.162 E29.162 | Insulating materials for IGFET (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.15. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L29/51.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E29.151, | for MIS structures on thin film semiconductor. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.165]](../ps.gif) E29.165 E29.165 | Multiple layers (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.162. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L29/51B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.167]](../ps.gif) E29.167 E29.167 | Controllable by plural effects that include variations
in magnetic field, mechanical force, or electric current/potential
applied to device or one or more electrodes of device (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.166. Subject
matter wherein the performance of the device is regulated by varying
the application of two or more forces (i.e., magnetic field, mechanical
force, electric current/potential to the device or one
or more of its electrodes). This subclass is substantially the same
in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/96.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E29.169, | for control by a signal. |
| E29.323, | for control by variation in a magnetic field, per
se. |
| E29.324, | for control by variation of mechanical force, per
se. |
| E29.325, | for control by variation of electrical current/potential
applied. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.168]](../ps.gif) E29.168 E29.168 | Quantum effect device (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.166. Subject
matter wherein the device operation uses a quantum effect. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L29/66Q.
| | (1)
Note. Examples include using quantum reflection, diffraction
or interference effects, (i.e., Bragg-or Aharonov-Bohmeffects). | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.171]](../ps.gif) E29.171 E29.171 | Bipolar device (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.169. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L29/70. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.172]](../ps.gif) E29.172 E29.172 | Double-base diode (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.171. This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L29/70B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.179]](../ps.gif) E29.179 E29.179 | Tunnel transistors (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.174. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/73E. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.183]](../ps.gif) E29.183 E29.183 | Vertical transistor (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.174. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/732. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.187]](../ps.gif) E29.187 E29.187 | Lateral transistor (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.174. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/735. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.202]](../ps.gif) E29.202 E29.202 | Thin-film device (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.197. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/739C1. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.219]](../ps.gif) E29.219 E29.219 | Combined with diode (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.217. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/74B4. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.22]](../ps.gif) E29.22 E29.22 | Antiparallel diode (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.219. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/74B4B.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E29.037, | for shorted anode structures enabling reverse conduction. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.224]](../ps.gif) E29.224 E29.224 | Asymmetrical thyristor (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.211. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/74E.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E29.037, | with a particular shorted anode structure. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.225]](../ps.gif) E29.225 E29.225 | Lateral thyristor (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.211. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/74F. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.226]](../ps.gif) E29.226 E29.226 | Unipolar device (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.169. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/76. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.23]](../ps.gif) E29.23 E29.23 | Input structure (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.229. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/768B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.231]](../ps.gif) E29.231 E29.231 | Output structure (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.229. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/768C. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.233]](../ps.gif) E29.233 E29.233 | Buried channel CCD (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.229. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/768E. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.234]](../ps.gif) E29.234 E29.234 | Two-phase CCD (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.233. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/768E2. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.235]](../ps.gif) E29.235 E29.235 | Three-phase CCD (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.233. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/768E3. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.236]](../ps.gif) E29.236 E29.236 | Four-phase CCD (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.233. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/768E4. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.237]](../ps.gif) E29.237 E29.237 | Surface channel CCD (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.229. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/768F. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.238]](../ps.gif) E29.238 E29.238 | Two-phase CCD (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.237. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/768F2. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.239]](../ps.gif) E29.239 E29.239 | Three-phase CCD (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.237. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/768F3. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.24]](../ps.gif) E29.24 E29.24 | Four-phase CCD (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.237. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/768F4. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.262]](../ps.gif) E29.262 E29.262 | Vertical transistor (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.255. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/78C.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E29.131, | for gate electrodes for channels having a nonvertical
component. |
| E29.257, | for vertical transistors with a drain drift region
contacting the channel. |
| E29.274, | for unipolar insulated gate field effect thin film
vertical transistors. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.264]](../ps.gif) E29.264 E29.264 | With multiple gate structure (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.255. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/78E.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.27]](../ps.gif) E29.27 E29.27 | With buried channel (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.255. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/78G. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.273]](../ps.gif) E29.273 E29.273 | Thin-film transistor (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.255. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/786.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E29.021, | for transistors having only the source or the drain
region on an insulator layer. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.274]](../ps.gif) E29.274 E29.274 | Vertical transistor (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.273. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/786C. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.275]](../ps.gif) E29.275 E29.275 | With multiple gates (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.273. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/786D.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E29.285 | through E29.299, the materials specified for the transistors are
the material of the channel region. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.282]](../ps.gif) E29.282 E29.282 | With light shield (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.276. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/786B5. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.285]](../ps.gif) E29.285 E29.285 | Silicon transistor (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.273. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/786E. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.286]](../ps.gif) E29.286 E29.286 | Monocrystalline only (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.285. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/786E2. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.287]](../ps.gif) E29.287 E29.287 | SOS transistor (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.286. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/786E2B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.288]](../ps.gif) E29.288 E29.288 | Nonmonocrystalline (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.285. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/786E4. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.29]](../ps.gif) E29.29 E29.29 | With top gate (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.289. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/786E4B2. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.293]](../ps.gif) E29.293 E29.293 | With top gate (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.292. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/786E4C2. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.3]](../ps.gif) E29.3 E29.3 | With floating gate (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.255. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/788. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.313]](../ps.gif) E29.313 E29.313 | Vertical transistors (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.312. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/808B.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.314]](../ps.gif) E29.314 E29.314 | Thin-film JFET (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.312. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/808C. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.317]](../ps.gif) E29.317 E29.317 | With Schottky gate (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.31. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/812.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E29.315, | for Schottky contact on top of heterojunction gate. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.318]](../ps.gif) E29.318 E29.318 | Vertical transistors (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.317. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/812B.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.319]](../ps.gif) E29.319 E29.319 | With multiple gate (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.317. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/812C. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.32]](../ps.gif) E29.32 E29.32 | Thin-film MESFET (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.317. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/812D. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.321]](../ps.gif) E29.321 E29.321 | With recessed gate (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.317. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/812E. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.327]](../ps.gif) E29.327 E29.327 | Diode (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.325. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/861. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.333]](../ps.gif) E29.333 E29.333 | Point contact diode (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.327. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/862. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.336]](../ps.gif) E29.336 E29.336 | PIN diode (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.327. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/868. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.338]](../ps.gif) E29.338 E29.338 | Schottky diode (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.327. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/872. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.339]](../ps.gif) E29.339 E29.339 | Tunneling diode (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.327. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/88. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.341]](../ps.gif) E29.341 E29.341 | Esaki diode (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.339. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/885. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.346]](../ps.gif) E29.346 E29.346 | Trench capacitor (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E29.345. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L29/94B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.001]](../ps.gif) E31.001 E31.001 | Semiconductor devices responsive or sensitive to electromagnetic
radiation (e.g., infrared radiation, adapted for conversion of radiation
into electrical energy or for control of electrical energy by such
radiation, processes or apparatus peculiar to manufacture or treatment
of such devices, or of parts thereof) (EPO): |
| | This main group provides for semiconductor devices that
are sensitive to infra-red radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation
of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and adapted either
for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical
energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation,
and processes or apparatus peculiar to the manufacture or treatment
of such devices or of parts thereof. This subclass is substantially
the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L31/00. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.004]](../ps.gif) E31.004 E31.004 | Inorganic materials (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E31.003. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L31/0264. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.038]](../ps.gif) E31.038 E31.038 | Shape of body (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E31.037. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L31/0352C2. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.071]](../ps.gif) E31.071 E31.071 | Photothyristor (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E31.07. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L31/111B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.074]](../ps.gif) E31.074 E31.074 | With Schottky gate (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E31.073. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L31/112B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.076]](../ps.gif) E31.076 E31.076 | Photo MESFET (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E31.074. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L31/112B3. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.117]](../ps.gif) E31.117 E31.117 | Encapsulation (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E31.11. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L31/0203.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E33.059, | for encapsulation of other light-emitting semiconductor
device. |
| E51.02, | for encapsulation of radiation-sensitive organic
semiconductor device. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.119]](../ps.gif) E31.119 E31.119 | Coatings (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E31.11. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L31/0216.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E33.06, | for coating details of light-emitting semiconductor
device. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.124]](../ps.gif) E31.124 E31.124 | Electrode (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E31.11. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L31/0224. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.13]](../ps.gif) E31.13 E31.13 | Texturized surface (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E31.11. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L31/0236. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.001]](../ps.gif) E33.001 E33.001 | Light emitting semiconductor devices having potential or
surface barrier, processes or apparatus peculiar to manufacture
or treatment of such devices, or of parts thereof (EPO): |
| | This main group provides for semiconductor devices with
at least one potential-jump barrier or surface barrier adapted for
light emission, e.g. infra-red emission, and processes or apparatus
peculiar to the manufacture or treatment of such devices or of parts
thereof. This subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA
classification H01L33/00.
| | (1)
Note: This main group does not include semiconductor lasers. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.014]](../ps.gif) E33.014 E33.014 | In different regions (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E33.013. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L33/00C4G2. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.016]](../ps.gif) E33.016 E33.016 | With heterojunction (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E33.015. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L33/00C4B2. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.018]](../ps.gif) E33.018 E33.018 | Including porous Si (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E33.015. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L33/00C4B4. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.021]](../ps.gif) E33.021 E33.021 | With heterojunction (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E33.02. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L33/00C4C2B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.027]](../ps.gif) E33.027 E33.027 | With heterojunction (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E33.026. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L33/00C4D3B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.03]](../ps.gif) E33.03 E33.03 | Nitride compound (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E33.029. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L33/00C4D4B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.046]](../ps.gif) E33.046 E33.046 | P-I-N device (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E33.045. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L33/00D2B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.056]](../ps.gif) E33.056 E33.056 | Packaging (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E33.055. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L33/00B2. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.058]](../ps.gif) E33.058 E33.058 | Housing (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E33.056. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L33/00B2C. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.059]](../ps.gif) E33.059 E33.059 | Encapsulation (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E33.056. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L33/00B2D.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E31.117, | for encapsulation of other radiation-sensitive semiconductor
device. |
| E51.02, | for encapsulation of radiation-sensitive organic
semiconductor device. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.06]](../ps.gif) E33.06 E33.06 | Coatings (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E33.055. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L33/00B3.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E31.119, | for coating details of radiation-sensitive semiconductor
device. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.062]](../ps.gif) E33.062 E33.062 | Electrodes (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E33.055. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L33/00B4. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.072]](../ps.gif) E33.072 E33.072 | Reflective means (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E33.071. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L33/00B6C2. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.075]](../ps.gif) E33.075 E33.075 | With means for cooling or heating (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E33.055. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L33/00B7.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E31.131, | for cooling means for radiation-sensitive semiconductor
device. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E39.001]](../ps.gif) E39.001 E39.001 | DEVICES USING SUPERCONDUCTIVITY, PROCESSES, OR APPARATUS PECULIAR
TO MANUFACTURE OR TREATMENT OF SUCH DEVICES, OR OF PARTS THEREOF
(EPO): |
| | This main group provides for semiconductor or solid state
devices with at least one potential-jump barrier or surface barrier
which include superconductive material, processes or apparatus peculiar
to the manufacture or treatment of such devices or of parts thereof.
This subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L39/00.
| | (1)
Note. Superconductive material is a material that is characterized
by zero electrical resistivity and, ideally, zero permeability. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E39.007]](../ps.gif) E39.007 E39.007 | Organic materials (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E39.006. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L39/12B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E39.009]](../ps.gif) E39.009 E39.009 | Ceramic materials (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E39.006. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L39/12C. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E39.02]](../ps.gif) E39.02 E39.02 | Field-effect devices (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E39.019. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L39/14C2. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E43.001]](../ps.gif) E43.001 E43.001 | SEMICONDUCTOR OR SOLID-STATE DEVICES USING GALVANO-MAGNETIC
OR SIMILAR MAGNETIC EFFECTS, PROCESSES, OR APPARATUS PECULIAR TO
MANUFACTURE OR TREATMENT OF SUCH DEVICES, OR OF PARTS THEREOF (EPO): |
| | This main group provides for semiconductor or solid state
devices which respond to a magnetic field signal, processes or
apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment of
such devices, or of parts thereof. This subclass is substantially
the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L43/00. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E43.002]](../ps.gif) E43.002 E43.002 | Hall-effect devices (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E43.43.001 This
subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L43/06. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E45.001]](../ps.gif) E45.001 E45.001 | SOLID-STATE DEVICES ADAPTED FOR RECTIFYING, AMPLIFYING,
OSCILLATING, OR SWITCHING WITHOUT POTENTIAL-JUMP BARRIER OR SURFACE
BARRIER, E.G., DIELECTRIC TRIODES; OVSHINSKY-EFFECT DEVICES, PROCESSES,
OR APPARATUS PECULIAR TO MANUFACTURE OR TREATMENT THEREOF, OR OF PARTS
THEREOF (EPO): |
| | This main group provides for solid state devices which change
from non-conductive state to semiconductive state to achieve rectification,
amplification, oscillation or switching action, upon application
of a minimum voltage, and processes or apparatus peculiar to the
manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L45/00.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E29.001, | for semiconductors devices adapted for rectifying,
amplifying, oscillating, or switching, capacitors, or resistors with
at least one potential-jump barrier or surface barrier. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E47.001]](../ps.gif) E47.001 E47.001 | BULK NEGATIVE RESISTANCE EFFECT DEVICES, E.G., GUNN-EFFECT DEVICES,
PROCESSES, OR APPARATUS PECULIAR TO MANUFACTURE OR TREATMENT OF
SUCH DEVICES, OR OF PARTS THEREOF (EPO) |
| | This main group provides for active devices which exhibit
the characteristic of decreasing current rate with increasing applied
voltage, processes or apparatus peculiar to the manufacture or treatment
of such devices or of parts thereof. This subclass is substantially
the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L47/00. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E47.004]](../ps.gif) E47.004 E47.004 | Gunn diodes (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E47.002. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L47/02C. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E49.001]](../ps.gif) E49.001 E49.001 | SOLID-STATE DEVICES WITH AT LEAST ONE POTENTIAL-JUMP BARRIER
OR SURFACE BARRIER USING ACTIVE LAYER OF LOWER ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY
THAN MATERIAL ADJACENT THERETO AND THROUGH WHICH CARRIER TUNNELING
OCCURS, PROCESSES OR APPARATUS PECULIAR TO MANUFACTURE OR TREATMENT
OF SUCH DEVICES, OR OF PARTS THEREOF (EPO): |
| | This main group provides for solid state devices with at
least one potential-jump barrier or surface barrier using active
layer of lower electrical conductivity than the material adjacent
thereto, e.g., metal sandwiched between thin or thick film insulator
or organic semiconductor material, and through which carrier tunneling
occurs, and processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or
treatment of such devices, or of parts thereof. This subclass is
substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L49/00. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.001]](../ps.gif) E51.001 E51.001 | Organic solid state devices, processes or apparatus peculiar
to manufacture or treatment of such devices, or of parts thereof
(EPO): |
| | This main group provides for solid state device using organic
material or a combination of organic material with other material
as active part of the device, processes or apparatus specially adapted
for the manufacture or treatment of such devices, or of parts thereof.
This subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification
H01L51/00. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.003]](../ps.gif) E51.003 E51.003 | Organic solid-state device adapted for rectifying, amplifying,
oscillating, or switching, or capacitors or resistors with potential
or surface barrier (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E51.002. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L51/20B.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E29.001, | and its indents, for details of other solid-state
devices adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating, or switching,
or capacitors or resistors with a potential or surface barrier. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.012]](../ps.gif) E51.012 E51.012 | Radiation-sensitive organic solid-state device (EPO): |
| | Subject matter under subclass E51.002 wherein the solid-state
device is responsive or sensitive to electromagnetic radiation (e.g.,
infrared radiation), adapted for a conversion of the radiation into
electrical energy or for a control of electrical energy by such
radiation. This subclass is substantially the same in scope as ECLA
classification H01L51/20C.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E31.001, | and its indents, for other radiation-sensitive semiconductor
devices. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.019]](../ps.gif) E51.019 E51.019 | Electrode (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E51.018. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L51/20D2B. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.02]](../ps.gif) E51.02 E51.02 | Encapsulation (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E51.019. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L51/20D2C.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| E31.117, | for encapsulation of other radiation-sensitive semiconductor
devices. |
| E33.059, | for encapsulation of other light-emitting semiconductor
devices. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.036]](../ps.gif) E51.036 E51.036 | Copolymers (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E51.027. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L51/30D6. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.037]](../ps.gif) E51.037 E51.037 | Ladder-type polymer (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E51.027. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L51/30D8. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.039]](../ps.gif) E51.039 E51.039 | Fullerenes (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E51.038. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L51/30F2. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.04]](../ps.gif) E51.04 E51.04 | Carbon nanotubes (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E51.038. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L51/30F4. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.042]](../ps.gif) E51.042 E51.042 | Phthalocyanine (EPO): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass E51.041. This subclass
is substantially the same in scope as ECLA classification H01L51/30M2. |
| | |
CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 900]](../ps.gif) 900 900 | MOSFET TYPE GATE SIDEWALL INSULATING SPACER: |
| | Subject matter wherein a metal oxide semiconductor field
effect transistor with a gate electrode includes a relatively thick
layer of electrically insulating material along the side wall of
the gate electrode and wherein the source or drain region of the
transistor has a distinct portion which is distant from the gate electrode
and is aligned with the edge of the insulating material, so that
the source or drain region is spaced from the gate electrode by
the thickness of the insulating material. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 901]](../ps.gif) 901 901 | MOSFET SUBSTRATE BIAS: |
| | Subject matter wherein an electrical bias is applied between
the substrate and the source electrode of a metal oxide field effect
transistor.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 299, | for an insulated gate capacitor, or transistor combined
with capacitor, with a substrate bias generator. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 902]](../ps.gif) 902 902 | FET WITH METAL SOURCE REGION: |
| | Subject matter including a field effect transistor with
a source region that comprises a metal material (e.g., a Schottky
barrier or ohmic contact to the channel region). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 903]](../ps.gif) 903 903 | FET CONFIGURATION ADAPTED FOR USE AS STATIC MEMORY CELL: |
| | Subject matter wherein a field effect transistor is structurally
arranged to be used in a static memory element (i.e., one in which
information need not be periodically refreshed). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 904]](../ps.gif) 904 904 | WITH PASSIVE COMPONENTS, (e.g., POLYSILICON RESISTORS): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 903. Subject matter including a solid-state electronic part/component
in which charge carriers do not change their energy levels and
that does not provide rectification, amplification, or switching,
but which does react to voltage and current. Examples are pure resistors,
capacitors and inductors. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 905]](../ps.gif) 905 905 | PLURAL DRAM CELLS SHARE COMMON CONTACT OR COMMON TRENCH: |
| | Subject matter comprising plural dynamic random access memory
elements which share an electrical contact or trench. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 906]](../ps.gif) 906 906 | DRAM WITH CAPACITOR ELECTRODES USED FOR ACCESSING (E.G., BIT
LINE IS CAPACITOR PLATE): |
| | Subject matter comprising a dynamic random access memory
element having an electrode which forms one plate of a storage capacitor, which
electrode is adapted to be supplied with varying electrical signals
to get information into or out of the memory element. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 907]](../ps.gif) 907 907 | FOLDED BIT LINE DRAM CONFIGURATION: |
| | Subject matter comprising an array of dynamic random access
memory elements including differential sense amplifiers each connected
to two different rows of memory cells, wherein the two rows of memory
cells connected to a specific sense amplifier lie adjacent and parallel
to each other on the same side of the sense amplifier. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 908]](../ps.gif) 908 908 | DRAM CONFIGURATION WITH TRANSISTORS AND CAPACITORS OF PAIRS OF
CELLS ALONG A STRAIGHT LINE BETWEEN ADJACENT BIT LINES: |
| | Subject matter comprising dynamic random access memory elements
having transistors and capacitors, where memory elements connected to
adjacent bit lines have transistors and capacitors which are not
staggered but which lie along a straight line which is located between the
adjacent bit lines of the device. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 909]](../ps.gif) 909 909 | MACROCELL ARRAYS (E.G., GATE ARRAYS WITH VARIABLE SIZE
OR CONFIGURATION OF CELLS): |
| | Subject matter comprising plural geometric arrangements
of groups of active solid-state devices, each group being connectable
into a logic circuit, in one integrated, monolithic semiconductor
chip. in which different groups differ from each other in size,
complexity, or number of components. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 910]](../ps.gif) 910 910 | DIODE ARRAYS (E.G., DIODE READ-ONLY MEMORY ARRAY): |
| | A repeating geometric arrangement of electronic devices
which have two terminals and an asymmetrical or nonlinear voltage-current characteristic. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 911]](../ps.gif) 911 911 | LIGHT SENSITIVE ARRAY ADAPTED TO BE SCANNED BY ELECTRON
BEAM (E.G.,VIDICON DEVICE): |
| | A repeating geometric arrangement of light sensitive devices
structured to be scanned by an electron beam. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 912]](../ps.gif) 912 912 | CHARGE TRANSFER DEVICE USING BOTH ELECTRON AND HOLE SIGNAL CARRIERS: |
| | Subject matter wherein a charge transfer device* uses
both electron and hole carriers in the same transfer or storage
regions of the charge transfer device. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 913]](../ps.gif) 913 913 | WITH MEANS TO ABSORB OR LOCALIZE UNWANTED IMPURITIES OR DEFECTS
FROM SEMICONDUCTORS (E.G., HEAVY METAL GETTERING): |
| | Subject matter including a semiconductor device having means
to absorb or localize semiconductor impurities or defects which would
adversely affect the performance of the device, e.g., phosphosilicate
glass coating to absorb deep level impurities. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 914]](../ps.gif) 914 914 | POLYSILICON CONTAINING OXYGEN, NITROGEN, OR CARBON (E.G., SIPOS): |
| | Subject matter comprising polycrystalline silicon which
contains oxygen, nitrogen, or carbon. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 915]](../ps.gif) 915 915 | WITH TITANIUM NITRIDE PORTION OR REGION: |
| | Subject matter wherein an active solid-state device includes
a portion or region of the device which contains titanium nitride. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 916]](../ps.gif) 916 916 | NARROW BAND GAP SEMICONDUCTOR MATERIAL (<<1eV): |
| | Subject matter wherein an active solid-state device material
is a semiconductor in which the difference between the energy levels
of electrons bound to their nuclei (valence electrons) and the energy
levels that allow electrons to migrate freely (conduction electrons)
is less than one electron volt. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 917]](../ps.gif) 917 917 | PLURAL DOPANTS OF SAME CONDUCTIVITY TYPE IN SAME REGION: |
| | Subject matter wherein an active solid-state device has
a region or portion which contains at least two different impurity
elements which have the same electrical conductivity type (i.e., both
p-type or both n-type). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 918]](../ps.gif) 918 918 | LIGHT EMITTING REGENERATIVE SWITCHING DEVICE (E.G., LIGHT EMITTING
SCR) ARRAYS, CIRCUITRY, ETC.: |
| | Subject matter wherein an active solid-state device acts
as if it has two or more active emitter junctions each of which
is associated with a separate, equivalent transistor having an individual
gain and, when initiated by a base region* current, the
equivalent transistors mutually drive each other in a regenerative manner
to lower the voltage drop between the emitters, and which active
solid-state device can generate light.
| | (1)
Note. If the current is above a level IH, called the "holding
current*", then the device will remain ON when
the triggering signal is removed by the regenerative feedback therebetween,
and is then said to be "latched*". | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 919]](../ps.gif) 919 919 | ELEMENTS OF SIMILAR CONSTRUCTION CONNECTED IN SERIES OR
PARALLEL TO AVERAGE OUT MANUFACTURING VARIATIONS IN CHARACTERISTICS: |
| | Subject matter comprising devices wherein components or
portions or regions of the devices having similar structure are
electrically connected in series or parallel to average out manufacturing
variations in their operational characteristics. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 920]](../ps.gif) 920 920 | CONDUCTOR LAYERS ON DIFFERENT LEVELS CONNECTED IN PARALLEL (E.G.,
TO REDUCE RESISTANCE): |
| | Subject matter wherein a device contains layers of electrical
conductors and different conductor layers are electrically connected
in parallel, to improve device operation (e.g., to reduce conductor
resistance). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 921]](../ps.gif) 921 921 | RADIATION HARDENED SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE: |
| | Subject matter in which an active solid-state device is
provided with means to render it relatively less susceptible to
being damaged or deleteriously affected in any way by radiant energy
(e.g., alpha particles).
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 659+, | for means to shield active solid-state devices from
harmful radiation. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 922]](../ps.gif) 922 922 | WITH MEANS TO PREVENT INSPECTION OF OR TAMPERING WITH AN INTEGRATED
CIRCUIT (E.G., "SMART CARD", ANTI-TAMPER): |
| | Subject matter comprising an integrated circuit with means
to prevent inspection of, or tampering with the integrated circuit
(e.g., an integrated circuit used in a "smart card" credit
or bank card). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 923]](../ps.gif) 923 923 | WITH MEANS TO OPTIMIZE ELECTRICAL CONDUCTOR CURRENT CARRYING
CAPACITY (E.G., PARTICULAR CONDUCTOR ASPECT RATIO): |
| | Subject matter in which an active solid-state device includes
means to optimize the current carrying capacity of an electrical
conductor of the device, e.g., by using a particular conductor cross-sectional
configuration. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 924]](../ps.gif) 924 924 | WITH PASSIVE DEVICE (E.G., CAPACITOR), OR BATTERY, AS INTEGRAL PART
OF HOUSING OR HOUSING ELEMENT (E.G., CAP): |
| | Subject matter which includes a distinct solid-state electronic
device in which charge carriers do not change their energy levels
and that does not provide rectification, amplification or switching,
but which does react to voltage and current (e.g., resistors, capacitors,
and inductors), or contains a battery, as an integral part of a
housing or housing element for an active solid-state device. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 925]](../ps.gif) 925 925 | BRIDGE RECTIFIER MODULE: |
| | Subject matter comprising a self-contained element which
includes two or more junction diodes structurally interconnected
as a rectifier bridge circuit. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 926]](../ps.gif) 926 926 | ELONGATED LEAD EXTENDING AXIALLY THROUGH ANOTHER ELONGATED
LEAD: |
| | Subject matter wherein an active solid-state device includes
more than one electrical lead wherein one relatively long lead is
coaxially located within another relatively long lead. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 927]](../ps.gif) 927 927 | DIFFERENT DOPING LEVELS IN DIFFERENT PARTS OF PN JUNCTION
TO PRODUCE SHAPED DEPLETION LAYER: |
| | Subject matter wherein a pn junction device contains impurity
dopants with differing concentrations of dopant in different parts
of the PN junction such that a depletion region associated with
the PN junction has a controlled shape. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 928]](../ps.gif) 928 928 | WITH SHORTED PN OR SCHOTTKY JUNCTION OTHER THAN EMITTER JUNCTION: |
| | Subject matter wherein a device has a pn or Schottky junction
electrode which is electrically short circuited (i.e., there is
a direct connection to both sides of the junction). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 929]](../ps.gif) 929 929 | PN JUNCTION ISOLATED INTEGRATED CIRCUIT WITH ISOLATION WALLS
HAVING MINIMUM DOPANT CONCENTRATION AT INTERMEDIATE DEPTH IN EPITAXIAL
LAYER (E.G., DIFFUSED FROM BOTH SURFACES OF EPITAXIAL LAYER): |
| | Subject matter comprising an integrated circuit with pn
junction isolation and having boundary walls isolating the integrated
circuit from its substrate, wherein the walls have a minimum concentration
of dopant at an intermediate depth in an epitaxial layer substrate
(e.g., diffused from both surfaces of an epitaxial layer). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 930]](../ps.gif) 930 930 | THERMOELECTRIC (E.G., PELTIER EFFECT) COOLING: |
| | Subject matter comprising means thermally connected to an
active solid-state device which, when subjected to the application
of an electric or magnetic field or electric current, causes heat
to be absorbed and thereby to cool the active solid-state device. |
| | |
![[Search a list of Patent Appplications for class 257]](../as.gif) CLASS 257,
CLASS 257,![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 1]](../ps.gif) 1
1![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 2]](../ps.gif) 2
2![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 3]](../ps.gif) 3
3![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 4]](../ps.gif) 4
4![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 5]](../ps.gif) 5
5![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 6]](../ps.gif) 6
6![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 7]](../ps.gif) 7
7![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 8]](../ps.gif) 8
8![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 9]](../ps.gif) 9
9![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 10]](../ps.gif) 10
10![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 11]](../ps.gif) 11
11![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 12]](../ps.gif) 12
12![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 13]](../ps.gif) 13
13![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 14]](../ps.gif) 14
14![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 15]](../ps.gif) 15
15![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 16]](../ps.gif) 16
16![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 17]](../ps.gif) 17
17![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 18]](../ps.gif) 18
18![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 19]](../ps.gif) 19
19![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 20]](../ps.gif) 20
20![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 21]](../ps.gif) 21
21![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 22]](../ps.gif) 22
22![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 23]](../ps.gif) 23
23![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 24]](../ps.gif) 24
24![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 25]](../ps.gif) 25
25![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 26]](../ps.gif) 26
26![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 27]](../ps.gif) 27
27![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 28]](../ps.gif) 28
28![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 29]](../ps.gif) 29
29![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 30]](../ps.gif) 30
30![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 31]](../ps.gif) 31
31![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 32]](../ps.gif) 32
32![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 33]](../ps.gif) 33
33![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 34]](../ps.gif) 34
34![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 35]](../ps.gif) 35
35![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 36]](../ps.gif) 36
36![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 37]](../ps.gif) 37
37![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 38]](../ps.gif) 38
38![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 39]](../ps.gif) 39
39![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 40]](../ps.gif) 40
40![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 41]](../ps.gif) 41
41![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 42]](../ps.gif) 42
42![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 43]](../ps.gif) 43
43![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 44]](../ps.gif) 44
44![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 45]](../ps.gif) 45
45![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 46]](../ps.gif) 46
46![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 47]](../ps.gif) 47
47![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 48]](../ps.gif) 48
48![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 49]](../ps.gif) 49
49![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 50]](../ps.gif) 50
50![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 51]](../ps.gif) 51
51![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 52]](../ps.gif) 52
52![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 53]](../ps.gif) 53
53![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 54]](../ps.gif) 54
54![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 55]](../ps.gif) 55
55![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 56]](../ps.gif) 56
56![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 57]](../ps.gif) 57
57![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 58]](../ps.gif) 58
58![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 59]](../ps.gif) 59
59![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 60]](../ps.gif) 60
60![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 61]](../ps.gif) 61
61![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 62]](../ps.gif) 62
62![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 63]](../ps.gif) 63
63![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 64]](../ps.gif) 64
64![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 65]](../ps.gif) 65
65![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 66]](../ps.gif) 66
66![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 67]](../ps.gif) 67
67![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 68]](../ps.gif) 68
68![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 69]](../ps.gif) 69
69![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 70]](../ps.gif) 70
70![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 71]](../ps.gif) 71
71![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 72]](../ps.gif) 72
72![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 73]](../ps.gif) 73
73![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 74]](../ps.gif) 74
74![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 75]](../ps.gif) 75
75![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 76]](../ps.gif) 76
76![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 77]](../ps.gif) 77
77![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 78]](../ps.gif) 78
78![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 79]](../ps.gif) 79
79![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 80]](../ps.gif) 80
80![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 81]](../ps.gif) 81
81![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 82]](../ps.gif) 82
82![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 83]](../ps.gif) 83
83![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 84]](../ps.gif) 84
84![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 85]](../ps.gif) 85
85![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 86]](../ps.gif) 86
86![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 87]](../ps.gif) 87
87![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 88]](../ps.gif) 88
88![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 89]](../ps.gif) 89
89![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 90]](../ps.gif) 90
90![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 91]](../ps.gif) 91
91![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 92]](../ps.gif) 92
92![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 93]](../ps.gif) 93
93![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 94]](../ps.gif) 94
94![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 95]](../ps.gif) 95
95![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 96]](../ps.gif) 96
96![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 97]](../ps.gif) 97
97![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 98]](../ps.gif) 98
98![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 99]](../ps.gif) 99
99![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 100]](../ps.gif) 100
100![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 101]](../ps.gif) 101
101![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 102]](../ps.gif) 102
102![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 103]](../ps.gif) 103
103![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 104]](../ps.gif) 104
104![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 105]](../ps.gif) 105
105![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 106]](../ps.gif) 106
106![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 107]](../ps.gif) 107
107![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 108]](../ps.gif) 108
108![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 109]](../ps.gif) 109
109![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 110]](../ps.gif) 110
110![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 111]](../ps.gif) 111
111![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 112]](../ps.gif) 112
112![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 113]](../ps.gif) 113
113![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 114]](../ps.gif) 114
114![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 115]](../ps.gif) 115
115![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 116]](../ps.gif) 116
116![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 117]](../ps.gif) 117
117![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 118]](../ps.gif) 118
118![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 119]](../ps.gif) 119
119![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 120]](../ps.gif) 120
120![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 121]](../ps.gif) 121
121![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 122]](../ps.gif) 122
122![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 123]](../ps.gif) 123
123![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 124]](../ps.gif) 124
124![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 125]](../ps.gif) 125
125![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 126]](../ps.gif) 126
126![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 127]](../ps.gif) 127
127![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 128]](../ps.gif) 128
128![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 129]](../ps.gif) 129
129![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 130]](../ps.gif) 130
130![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 131]](../ps.gif) 131
131![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 132]](../ps.gif) 132
132![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 133]](../ps.gif) 133
133![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 134]](../ps.gif) 134
134![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 135]](../ps.gif) 135
135![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 136]](../ps.gif) 136
136![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 137]](../ps.gif) 137
137![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 138]](../ps.gif) 138
138![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 139]](../ps.gif) 139
139![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 140]](../ps.gif) 140
140![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 141]](../ps.gif) 141
141![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 142]](../ps.gif) 142
142![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 143]](../ps.gif) 143
143![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 144]](../ps.gif) 144
144![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 145]](../ps.gif) 145
145![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 146]](../ps.gif) 146
146![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 147]](../ps.gif) 147
147![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 148]](../ps.gif) 148
148![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 149]](../ps.gif) 149
149![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 150]](../ps.gif) 150
150![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 151]](../ps.gif) 151
151![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 152]](../ps.gif) 152
152![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 153]](../ps.gif) 153
153![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 154]](../ps.gif) 154
154![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 155]](../ps.gif) 155
155![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 156]](../ps.gif) 156
156![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 157]](../ps.gif) 157
157![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 158]](../ps.gif) 158
158![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 159]](../ps.gif) 159
159![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 160]](../ps.gif) 160
160![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 161]](../ps.gif) 161
161![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 162]](../ps.gif) 162
162![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 163]](../ps.gif) 163
163![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 164]](../ps.gif) 164
164![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 165]](../ps.gif) 165
165![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 166]](../ps.gif) 166
166![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 167]](../ps.gif) 167
167![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 168]](../ps.gif) 168
168![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 169]](../ps.gif) 169
169![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 170]](../ps.gif) 170
170![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 171]](../ps.gif) 171
171![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 172]](../ps.gif) 172
172![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 173]](../ps.gif) 173
173![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 174]](../ps.gif) 174
174![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 175]](../ps.gif) 175
175![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 176]](../ps.gif) 176
176![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 177]](../ps.gif) 177
177![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 178]](../ps.gif) 178
178![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 179]](../ps.gif) 179
179![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 180]](../ps.gif) 180
180![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 181]](../ps.gif) 181
181![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 182]](../ps.gif) 182
182![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 183]](../ps.gif) 183
183![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 183.1]](../ps.gif) 183.1
183.1![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 184]](../ps.gif) 184
184![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 185]](../ps.gif) 185
185![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 186]](../ps.gif) 186
186![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 187]](../ps.gif) 187
187![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 188]](../ps.gif) 188
188![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 189]](../ps.gif) 189
189![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 190]](../ps.gif) 190
190![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 191]](../ps.gif) 191
191![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 192]](../ps.gif) 192
192![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 194]](../ps.gif) 194
194![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 195]](../ps.gif) 195
195![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 196]](../ps.gif) 196
196![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 197]](../ps.gif) 197
197![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 198]](../ps.gif) 198
198![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 199]](../ps.gif) 199
199![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 200]](../ps.gif) 200
200![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 201]](../ps.gif) 201
201![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 202]](../ps.gif) 202
202![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 203]](../ps.gif) 203
203![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 204]](../ps.gif) 204
204![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 205]](../ps.gif) 205
205![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 206]](../ps.gif) 206
206![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 207]](../ps.gif) 207
207![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 208]](../ps.gif) 208
208![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 209]](../ps.gif) 209
209![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 210]](../ps.gif) 210
210![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 211]](../ps.gif) 211
211![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 212]](../ps.gif) 212
212![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 213]](../ps.gif) 213
213![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 214]](../ps.gif) 214
214![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 215]](../ps.gif) 215
215![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 216]](../ps.gif) 216
216![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 217]](../ps.gif) 217
217![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 218]](../ps.gif) 218
218![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 219]](../ps.gif) 219
219![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 220]](../ps.gif) 220
220![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 221]](../ps.gif) 221
221![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 222]](../ps.gif) 222
222![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 223]](../ps.gif) 223
223![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 224]](../ps.gif) 224
224![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 225]](../ps.gif) 225
225![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 226]](../ps.gif) 226
226![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 227]](../ps.gif) 227
227![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 228]](../ps.gif) 228
228![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 229]](../ps.gif) 229
229![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 230]](../ps.gif) 230
230![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 231]](../ps.gif) 231
231![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 232]](../ps.gif) 232
232![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 233]](../ps.gif) 233
233![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 234]](../ps.gif) 234
234![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 235]](../ps.gif) 235
235![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 236]](../ps.gif) 236
236![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 237]](../ps.gif) 237
237![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 238]](../ps.gif) 238
238![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 239]](../ps.gif) 239
239![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 240]](../ps.gif) 240
240![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 241]](../ps.gif) 241
241![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 242]](../ps.gif) 242
242![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 243]](../ps.gif) 243
243![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 244]](../ps.gif) 244
244![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 245]](../ps.gif) 245
245![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 246]](../ps.gif) 246
246![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 247]](../ps.gif) 247
247![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 248]](../ps.gif) 248
248![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 249]](../ps.gif) 249
249![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 250]](../ps.gif) 250
250![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 251]](../ps.gif) 251
251![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 252]](../ps.gif) 252
252![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 253]](../ps.gif) 253
253![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 254]](../ps.gif) 254
254![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 255]](../ps.gif) 255
255![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 256]](../ps.gif) 256
256![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 257]](../ps.gif) 257
257![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 258]](../ps.gif) 258
258![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 259]](../ps.gif) 259
259![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 260]](../ps.gif) 260
260![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 261]](../ps.gif) 261
261![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 262]](../ps.gif) 262
262![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 263]](../ps.gif) 263
263![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 264]](../ps.gif) 264
264![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 265]](../ps.gif) 265
265![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 266]](../ps.gif) 266
266![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 267]](../ps.gif) 267
267![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 268]](../ps.gif) 268
268![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 269]](../ps.gif) 269
269![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 270]](../ps.gif) 270
270![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 271]](../ps.gif) 271
271![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 272]](../ps.gif) 272
272![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 273]](../ps.gif) 273
273![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 274]](../ps.gif) 274
274![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 275]](../ps.gif) 275
275![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 276]](../ps.gif) 276
276![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 277]](../ps.gif) 277
277![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 278]](../ps.gif) 278
278![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 279]](../ps.gif) 279
279![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 280]](../ps.gif) 280
280![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 281]](../ps.gif) 281
281![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 282]](../ps.gif) 282
282![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 283]](../ps.gif) 283
283![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 284]](../ps.gif) 284
284![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 285]](../ps.gif) 285
285![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 286]](../ps.gif) 286
286![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 287]](../ps.gif) 287
287![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 288]](../ps.gif) 288
288![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 289]](../ps.gif) 289
289![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 290]](../ps.gif) 290
290![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 291]](../ps.gif) 291
291![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 292]](../ps.gif) 292
292![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 293]](../ps.gif) 293
293![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 294]](../ps.gif) 294
294![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 295]](../ps.gif) 295
295![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 296]](../ps.gif) 296
296![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 297]](../ps.gif) 297
297![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 298]](../ps.gif) 298
298![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 299]](../ps.gif) 299
299![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 300]](../ps.gif) 300
300![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 301]](../ps.gif) 301
301![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 302]](../ps.gif) 302
302![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 303]](../ps.gif) 303
303![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 304]](../ps.gif) 304
304![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 305]](../ps.gif) 305
305![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 306]](../ps.gif) 306
306![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 307]](../ps.gif) 307
307![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 308]](../ps.gif) 308
308![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 309]](../ps.gif) 309
309![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 310]](../ps.gif) 310
310![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 311]](../ps.gif) 311
311![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 312]](../ps.gif) 312
312![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 313]](../ps.gif) 313
313![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 314]](../ps.gif) 314
314![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 315]](../ps.gif) 315
315![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 316]](../ps.gif) 316
316![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 317]](../ps.gif) 317
317![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 318]](../ps.gif) 318
318![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 319]](../ps.gif) 319
319![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 320]](../ps.gif) 320
320![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 321]](../ps.gif) 321
321![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 322]](../ps.gif) 322
322![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 323]](../ps.gif) 323
323![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 324]](../ps.gif) 324
324![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 325]](../ps.gif) 325
325![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 326]](../ps.gif) 326
326![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 327]](../ps.gif) 327
327![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 328]](../ps.gif) 328
328![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 329]](../ps.gif) 329
329![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 330]](../ps.gif) 330
330![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 331]](../ps.gif) 331
331![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 332]](../ps.gif) 332
332![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 333]](../ps.gif) 333
333![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 334]](../ps.gif) 334
334![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 335]](../ps.gif) 335
335![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 336]](../ps.gif) 336
336![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 337]](../ps.gif) 337
337![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 338]](../ps.gif) 338
338![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 339]](../ps.gif) 339
339![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 340]](../ps.gif) 340
340![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 341]](../ps.gif) 341
341![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 342]](../ps.gif) 342
342![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 343]](../ps.gif) 343
343![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 344]](../ps.gif) 344
344![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 345]](../ps.gif) 345
345![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 346]](../ps.gif) 346
346![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 347]](../ps.gif) 347
347![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 348]](../ps.gif) 348
348![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 349]](../ps.gif) 349
349![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 350]](../ps.gif) 350
350![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 351]](../ps.gif) 351
351![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 352]](../ps.gif) 352
352![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 353]](../ps.gif) 353
353![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 354]](../ps.gif) 354
354![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 355]](../ps.gif) 355
355![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 356]](../ps.gif) 356
356![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 357]](../ps.gif) 357
357![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 358]](../ps.gif) 358
358![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 359]](../ps.gif) 359
359![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 360]](../ps.gif) 360
360![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 361]](../ps.gif) 361
361![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 362]](../ps.gif) 362
362![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 363]](../ps.gif) 363
363![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 364]](../ps.gif) 364
364![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 365]](../ps.gif) 365
365![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 366]](../ps.gif) 366
366![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 367]](../ps.gif) 367
367![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 368]](../ps.gif) 368
368![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 369]](../ps.gif) 369
369![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 370]](../ps.gif) 370
370![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 371]](../ps.gif) 371
371![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 372]](../ps.gif) 372
372![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 373]](../ps.gif) 373
373![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 374]](../ps.gif) 374
374![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 375]](../ps.gif) 375
375![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 376]](../ps.gif) 376
376![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 377]](../ps.gif) 377
377![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 378]](../ps.gif) 378
378![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 379]](../ps.gif) 379
379![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 380]](../ps.gif) 380
380![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 381]](../ps.gif) 381
381![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 382]](../ps.gif) 382
382![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 383]](../ps.gif) 383
383![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 384]](../ps.gif) 384
384![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 385]](../ps.gif) 385
385![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 386]](../ps.gif) 386
386![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 387]](../ps.gif) 387
387![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 388]](../ps.gif) 388
388![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 389]](../ps.gif) 389
389![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 390]](../ps.gif) 390
390![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 391]](../ps.gif) 391
391![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 392]](../ps.gif) 392
392![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 393]](../ps.gif) 393
393![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 394]](../ps.gif) 394
394![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 395]](../ps.gif) 395
395![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 396]](../ps.gif) 396
396![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 397]](../ps.gif) 397
397![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 398]](../ps.gif) 398
398![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 399]](../ps.gif) 399
399![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 400]](../ps.gif) 400
400![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 401]](../ps.gif) 401
401![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 402]](../ps.gif) 402
402![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 403]](../ps.gif) 403
403![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 404]](../ps.gif) 404
404![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 405]](../ps.gif) 405
405![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 406]](../ps.gif) 406
406![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 407]](../ps.gif) 407
407![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 408]](../ps.gif) 408
408![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 409]](../ps.gif) 409
409![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 410]](../ps.gif) 410
410![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 411]](../ps.gif) 411
411![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 412]](../ps.gif) 412
412![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 413]](../ps.gif) 413
413![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 414]](../ps.gif) 414
414![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 415]](../ps.gif) 415
415![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 416]](../ps.gif) 416
416![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 417]](../ps.gif) 417
417![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 418]](../ps.gif) 418
418![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 419]](../ps.gif) 419
419![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 420]](../ps.gif) 420
420![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 421]](../ps.gif) 421
421![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 422]](../ps.gif) 422
422![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 423]](../ps.gif) 423
423![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 424]](../ps.gif) 424
424![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 425]](../ps.gif) 425
425![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 426]](../ps.gif) 426
426![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 427]](../ps.gif) 427
427![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 428]](../ps.gif) 428
428![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 429]](../ps.gif) 429
429![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 430]](../ps.gif) 430
430![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 431]](../ps.gif) 431
431![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 432]](../ps.gif) 432
432![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 433]](../ps.gif) 433
433![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 434]](../ps.gif) 434
434![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 435]](../ps.gif) 435
435![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 436]](../ps.gif) 436
436![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 437]](../ps.gif) 437
437![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 438]](../ps.gif) 438
438![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 439]](../ps.gif) 439
439![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 440]](../ps.gif) 440
440![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 441]](../ps.gif) 441
441![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 442]](../ps.gif) 442
442![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 443]](../ps.gif) 443
443![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 444]](../ps.gif) 444
444![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 445]](../ps.gif) 445
445![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 446]](../ps.gif) 446
446![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 447]](../ps.gif) 447
447![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 448]](../ps.gif) 448
448![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 449]](../ps.gif) 449
449![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 450]](../ps.gif) 450
450![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 451]](../ps.gif) 451
451![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 452]](../ps.gif) 452
452![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 453]](../ps.gif) 453
453![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 454]](../ps.gif) 454
454![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 455]](../ps.gif) 455
455![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 456]](../ps.gif) 456
456![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 457]](../ps.gif) 457
457![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 458]](../ps.gif) 458
458![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 459]](../ps.gif) 459
459![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 460]](../ps.gif) 460
460![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 461]](../ps.gif) 461
461![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 462]](../ps.gif) 462
462![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 463]](../ps.gif) 463
463![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 464]](../ps.gif) 464
464![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 465]](../ps.gif) 465
465![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 466]](../ps.gif) 466
466![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 467]](../ps.gif) 467
467![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 468]](../ps.gif) 468
468![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 469]](../ps.gif) 469
469![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 470]](../ps.gif) 470
470![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 471]](../ps.gif) 471
471![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 472]](../ps.gif) 472
472![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 473]](../ps.gif) 473
473![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 474]](../ps.gif) 474
474![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 475]](../ps.gif) 475
475![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 476]](../ps.gif) 476
476![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 477]](../ps.gif) 477
477![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 478]](../ps.gif) 478
478![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 479]](../ps.gif) 479
479![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 480]](../ps.gif) 480
480![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 481]](../ps.gif) 481
481![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 482]](../ps.gif) 482
482![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 483]](../ps.gif) 483
483![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 484]](../ps.gif) 484
484![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 485]](../ps.gif) 485
485![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 486]](../ps.gif) 486
486![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 487]](../ps.gif) 487
487![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 488]](../ps.gif) 488
488![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 489]](../ps.gif) 489
489![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 490]](../ps.gif) 490
490![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 491]](../ps.gif) 491
491![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 492]](../ps.gif) 492
492![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 493]](../ps.gif) 493
493![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 494]](../ps.gif) 494
494![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 495]](../ps.gif) 495
495![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 496]](../ps.gif) 496
496![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 497]](../ps.gif) 497
497![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 498]](../ps.gif) 498
498![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 499]](../ps.gif) 499
499![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 500]](../ps.gif) 500
500![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 501]](../ps.gif) 501
501![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 502]](../ps.gif) 502
502![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 503]](../ps.gif) 503
503![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 504]](../ps.gif) 504
504![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 505]](../ps.gif) 505
505![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 506]](../ps.gif) 506
506![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 507]](../ps.gif) 507
507![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 508]](../ps.gif) 508
508![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 509]](../ps.gif) 509
509![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 510]](../ps.gif) 510
510![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 511]](../ps.gif) 511
511![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 512]](../ps.gif) 512
512![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 513]](../ps.gif) 513
513![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 514]](../ps.gif) 514
514![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 515]](../ps.gif) 515
515![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 516]](../ps.gif) 516
516![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 517]](../ps.gif) 517
517![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 518]](../ps.gif) 518
518![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 519]](../ps.gif) 519
519![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 520]](../ps.gif) 520
520![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 521]](../ps.gif) 521
521![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 522]](../ps.gif) 522
522![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 523]](../ps.gif) 523
523![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 524]](../ps.gif) 524
524![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 525]](../ps.gif) 525
525![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 526]](../ps.gif) 526
526![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 527]](../ps.gif) 527
527![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 528]](../ps.gif) 528
528![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 529]](../ps.gif) 529
529![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 530]](../ps.gif) 530
530![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 531]](../ps.gif) 531
531![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 532]](../ps.gif) 532
532![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 533]](../ps.gif) 533
533![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 534]](../ps.gif) 534
534![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 535]](../ps.gif) 535
535![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 536]](../ps.gif) 536
536![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 537]](../ps.gif) 537
537![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 538]](../ps.gif) 538
538![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 539]](../ps.gif) 539
539![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 540]](../ps.gif) 540
540![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 541]](../ps.gif) 541
541![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 542]](../ps.gif) 542
542![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 543]](../ps.gif) 543
543![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 544]](../ps.gif) 544
544![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 545]](../ps.gif) 545
545![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 546]](../ps.gif) 546
546![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 547]](../ps.gif) 547
547![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 548]](../ps.gif) 548
548![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 549]](../ps.gif) 549
549![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 550]](../ps.gif) 550
550![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 551]](../ps.gif) 551
551![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 552]](../ps.gif) 552
552![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 553]](../ps.gif) 553
553![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 554]](../ps.gif) 554
554![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 555]](../ps.gif) 555
555![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 556]](../ps.gif) 556
556![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 557]](../ps.gif) 557
557![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 558]](../ps.gif) 558
558![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 559]](../ps.gif) 559
559![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 560]](../ps.gif) 560
560![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 561]](../ps.gif) 561
561![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 562]](../ps.gif) 562
562![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 563]](../ps.gif) 563
563![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 564]](../ps.gif) 564
564![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 565]](../ps.gif) 565
565![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 566]](../ps.gif) 566
566![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 567]](../ps.gif) 567
567![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 568]](../ps.gif) 568
568![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 569]](../ps.gif) 569
569![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 570]](../ps.gif) 570
570![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 571]](../ps.gif) 571
571![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 572]](../ps.gif) 572
572![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 573]](../ps.gif) 573
573![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 574]](../ps.gif) 574
574![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 575]](../ps.gif) 575
575![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 576]](../ps.gif) 576
576![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 577]](../ps.gif) 577
577![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 578]](../ps.gif) 578
578![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 579]](../ps.gif) 579
579![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 580]](../ps.gif) 580
580![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 581]](../ps.gif) 581
581![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 582]](../ps.gif) 582
582![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 583]](../ps.gif) 583
583![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 584]](../ps.gif) 584
584![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 585]](../ps.gif) 585
585![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 586]](../ps.gif) 586
586![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 587]](../ps.gif) 587
587![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 588]](../ps.gif) 588
588![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 589]](../ps.gif) 589
589![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 590]](../ps.gif) 590
590![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 591]](../ps.gif) 591
591![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 592]](../ps.gif) 592
592![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 593]](../ps.gif) 593
593![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 594]](../ps.gif) 594
594![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 595]](../ps.gif) 595
595![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 596]](../ps.gif) 596
596![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 597]](../ps.gif) 597
597![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 598]](../ps.gif) 598
598![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 599]](../ps.gif) 599
599![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 600]](../ps.gif) 600
600![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 601]](../ps.gif) 601
601![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 602]](../ps.gif) 602
602![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 603]](../ps.gif) 603
603![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 604]](../ps.gif) 604
604![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 605]](../ps.gif) 605
605![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 606]](../ps.gif) 606
606![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 607]](../ps.gif) 607
607![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 608]](../ps.gif) 608
608![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 609]](../ps.gif) 609
609![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 610]](../ps.gif) 610
610![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 611]](../ps.gif) 611
611![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 612]](../ps.gif) 612
612![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 613]](../ps.gif) 613
613![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 614]](../ps.gif) 614
614![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 615]](../ps.gif) 615
615![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 616]](../ps.gif) 616
616![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 617]](../ps.gif) 617
617![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 618]](../ps.gif) 618
618![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 619]](../ps.gif) 619
619![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 620]](../ps.gif) 620
620![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 621]](../ps.gif) 621
621![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 622]](../ps.gif) 622
622![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 623]](../ps.gif) 623
623![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 624]](../ps.gif) 624
624![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 625]](../ps.gif) 625
625![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 626]](../ps.gif) 626
626![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 627]](../ps.gif) 627
627![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 628]](../ps.gif) 628
628![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 629]](../ps.gif) 629
629![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 630]](../ps.gif) 630
630![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 631]](../ps.gif) 631
631![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 632]](../ps.gif) 632
632![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 633]](../ps.gif) 633
633![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 634]](../ps.gif) 634
634![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 635]](../ps.gif) 635
635![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 636]](../ps.gif) 636
636![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 637]](../ps.gif) 637
637![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 638]](../ps.gif) 638
638![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 639]](../ps.gif) 639
639![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 640]](../ps.gif) 640
640![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 641]](../ps.gif) 641
641![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 642]](../ps.gif) 642
642![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 643]](../ps.gif) 643
643![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 644]](../ps.gif) 644
644![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 645]](../ps.gif) 645
645![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 646]](../ps.gif) 646
646![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 647]](../ps.gif) 647
647![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 648]](../ps.gif) 648
648![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 649]](../ps.gif) 649
649![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 650]](../ps.gif) 650
650![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 651]](../ps.gif) 651
651![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 652]](../ps.gif) 652
652![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 653]](../ps.gif) 653
653![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 654]](../ps.gif) 654
654![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 655]](../ps.gif) 655
655![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 656]](../ps.gif) 656
656![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 657]](../ps.gif) 657
657![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 658]](../ps.gif) 658
658![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 659]](../ps.gif) 659
659![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 660]](../ps.gif) 660
660![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 661]](../ps.gif) 661
661![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 662]](../ps.gif) 662
662![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 663]](../ps.gif) 663
663![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 664]](../ps.gif) 664
664![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 665]](../ps.gif) 665
665![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 666]](../ps.gif) 666
666![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 667]](../ps.gif) 667
667![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 668]](../ps.gif) 668
668![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 669]](../ps.gif) 669
669![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 670]](../ps.gif) 670
670![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 671]](../ps.gif) 671
671![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 672]](../ps.gif) 672
672![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 673]](../ps.gif) 673
673![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 674]](../ps.gif) 674
674![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 675]](../ps.gif) 675
675![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 676]](../ps.gif) 676
676![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 677]](../ps.gif) 677
677![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 678]](../ps.gif) 678
678![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 679]](../ps.gif) 679
679![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 680]](../ps.gif) 680
680![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 681]](../ps.gif) 681
681![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 682]](../ps.gif) 682
682![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 683]](../ps.gif) 683
683![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 684]](../ps.gif) 684
684![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 685]](../ps.gif) 685
685![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 686]](../ps.gif) 686
686![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 687]](../ps.gif) 687
687![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 688]](../ps.gif) 688
688![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 689]](../ps.gif) 689
689![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 690]](../ps.gif) 690
690![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 691]](../ps.gif) 691
691![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 692]](../ps.gif) 692
692![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 693]](../ps.gif) 693
693![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 694]](../ps.gif) 694
694![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 695]](../ps.gif) 695
695![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 696]](../ps.gif) 696
696![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 697]](../ps.gif) 697
697![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 698]](../ps.gif) 698
698![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 699]](../ps.gif) 699
699![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 700]](../ps.gif) 700
700![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 701]](../ps.gif) 701
701![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 702]](../ps.gif) 702
702![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 703]](../ps.gif) 703
703![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 704]](../ps.gif) 704
704![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 705]](../ps.gif) 705
705![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 706]](../ps.gif) 706
706![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 707]](../ps.gif) 707
707![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 708]](../ps.gif) 708
708![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 709]](../ps.gif) 709
709![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 710]](../ps.gif) 710
710![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 711]](../ps.gif) 711
711![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 712]](../ps.gif) 712
712![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 713]](../ps.gif) 713
713![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 714]](../ps.gif) 714
714![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 715]](../ps.gif) 715
715![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 716]](../ps.gif) 716
716![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 717]](../ps.gif) 717
717![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 718]](../ps.gif) 718
718![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 719]](../ps.gif) 719
719![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 720]](../ps.gif) 720
720![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 721]](../ps.gif) 721
721![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 722]](../ps.gif) 722
722![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 723]](../ps.gif) 723
723![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 724]](../ps.gif) 724
724![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 725]](../ps.gif) 725
725![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 726]](../ps.gif) 726
726![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 727]](../ps.gif) 727
727![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 728]](../ps.gif) 728
728![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 729]](../ps.gif) 729
729![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 730]](../ps.gif) 730
730![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 731]](../ps.gif) 731
731![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 732]](../ps.gif) 732
732![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 733]](../ps.gif) 733
733![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 734]](../ps.gif) 734
734![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 735]](../ps.gif) 735
735![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 736]](../ps.gif) 736
736![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 737]](../ps.gif) 737
737![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 738]](../ps.gif) 738
738![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 739]](../ps.gif) 739
739![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 740]](../ps.gif) 740
740![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 741]](../ps.gif) 741
741![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 742]](../ps.gif) 742
742![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 743]](../ps.gif) 743
743![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 744]](../ps.gif) 744
744![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 745]](../ps.gif) 745
745![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 746]](../ps.gif) 746
746![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 747]](../ps.gif) 747
747![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 748]](../ps.gif) 748
748![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 749]](../ps.gif) 749
749![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 750]](../ps.gif) 750
750![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 751]](../ps.gif) 751
751![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 752]](../ps.gif) 752
752![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 753]](../ps.gif) 753
753![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 754]](../ps.gif) 754
754![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 755]](../ps.gif) 755
755![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 756]](../ps.gif) 756
756![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 757]](../ps.gif) 757
757![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 758]](../ps.gif) 758
758![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 759]](../ps.gif) 759
759![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 760]](../ps.gif) 760
760![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 761]](../ps.gif) 761
761![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 762]](../ps.gif) 762
762![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 763]](../ps.gif) 763
763![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 764]](../ps.gif) 764
764![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 765]](../ps.gif) 765
765![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 766]](../ps.gif) 766
766![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 767]](../ps.gif) 767
767![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 768]](../ps.gif) 768
768![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 769]](../ps.gif) 769
769![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 770]](../ps.gif) 770
770![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 771]](../ps.gif) 771
771![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 772]](../ps.gif) 772
772![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 773]](../ps.gif) 773
773![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 774]](../ps.gif) 774
774![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 775]](../ps.gif) 775
775![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 776]](../ps.gif) 776
776![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 777]](../ps.gif) 777
777![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 778]](../ps.gif) 778
778![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 779]](../ps.gif) 779
779![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 780]](../ps.gif) 780
780![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 781]](../ps.gif) 781
781![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 782]](../ps.gif) 782
782![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 783]](../ps.gif) 783
783![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 784]](../ps.gif) 784
784![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 785]](../ps.gif) 785
785![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 786]](../ps.gif) 786
786![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 787]](../ps.gif) 787
787![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 788]](../ps.gif) 788
788![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 789]](../ps.gif) 789
789![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 790]](../ps.gif) 790
790![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 791]](../ps.gif) 791
791![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 792]](../ps.gif) 792
792![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 793]](../ps.gif) 793
793![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 794]](../ps.gif) 794
794![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 795]](../ps.gif) 795
795![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 796]](../ps.gif) 796
796![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 797]](../ps.gif) 797
797![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 798]](../ps.gif) 798
798![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.001]](../ps.gif) E21.001
E21.001![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.002]](../ps.gif) E21.002
E21.002![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.003]](../ps.gif) E21.003
E21.003![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.004]](../ps.gif) E21.004
E21.004![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.005]](../ps.gif) E21.005
E21.005![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.006]](../ps.gif) E21.006
E21.006![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.007]](../ps.gif) E21.007
E21.007![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.008]](../ps.gif) E21.008
E21.008![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.009]](../ps.gif) E21.009
E21.009![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.01]](../ps.gif) E21.01
E21.01![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.011]](../ps.gif) E21.011
E21.011![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.012]](../ps.gif) E21.012
E21.012![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.013]](../ps.gif) E21.013
E21.013![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.014]](../ps.gif) E21.014
E21.014![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.015]](../ps.gif) E21.015
E21.015![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.016]](../ps.gif) E21.016
E21.016![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.017]](../ps.gif) E21.017
E21.017![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.018]](../ps.gif) E21.018
E21.018![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.019]](../ps.gif) E21.019
E21.019![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.02]](../ps.gif) E21.02
E21.02![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.021]](../ps.gif) E21.021
E21.021![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.022]](../ps.gif) E21.022
E21.022![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.023]](../ps.gif) E21.023
E21.023![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.024]](../ps.gif) E21.024
E21.024![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.025]](../ps.gif) E21.025
E21.025![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.026]](../ps.gif) E21.026
E21.026![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.027]](../ps.gif) E21.027
E21.027![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.028]](../ps.gif) E21.028
E21.028![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.029]](../ps.gif) E21.029
E21.029![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.03]](../ps.gif) E21.03
E21.03![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.031]](../ps.gif) E21.031
E21.031![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.032]](../ps.gif) E21.032
E21.032![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.033]](../ps.gif) E21.033
E21.033![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.034]](../ps.gif) E21.034
E21.034![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.035]](../ps.gif) E21.035
E21.035![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.036]](../ps.gif) E21.036
E21.036![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.037]](../ps.gif) E21.037
E21.037![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.038]](../ps.gif) E21.038
E21.038![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.039]](../ps.gif) E21.039
E21.039![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.04]](../ps.gif) E21.04
E21.04![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.041]](../ps.gif) E21.041
E21.041![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.042]](../ps.gif) E21.042
E21.042![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.043]](../ps.gif) E21.043
E21.043![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.044]](../ps.gif) E21.044
E21.044![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.045]](../ps.gif) E21.045
E21.045![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.046]](../ps.gif) E21.046
E21.046![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.047]](../ps.gif) E21.047
E21.047![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.048]](../ps.gif) E21.048
E21.048![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.049]](../ps.gif) E21.049
E21.049![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.05]](../ps.gif) E21.05
E21.05![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.051]](../ps.gif) E21.051
E21.051![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.052]](../ps.gif) E21.052
E21.052![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.053]](../ps.gif) E21.053
E21.053![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.054]](../ps.gif) E21.054
E21.054![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.055]](../ps.gif) E21.055
E21.055![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.056]](../ps.gif) E21.056
E21.056![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.057]](../ps.gif) E21.057
E21.057![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.058]](../ps.gif) E21.058
E21.058![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.059]](../ps.gif) E21.059
E21.059![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.06]](../ps.gif) E21.06
E21.06![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.061]](../ps.gif) E21.061
E21.061![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.062]](../ps.gif) E21.062
E21.062![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.063]](../ps.gif) E21.063
E21.063![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.064]](../ps.gif) E21.064
E21.064![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.065]](../ps.gif) E21.065
E21.065![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.066]](../ps.gif) E21.066
E21.066![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.067]](../ps.gif) E21.067
E21.067![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.068]](../ps.gif) E21.068
E21.068![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.069]](../ps.gif) E21.069
E21.069![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.07]](../ps.gif) E21.07
E21.07![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.071]](../ps.gif) E21.071
E21.071![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.072]](../ps.gif) E21.072
E21.072![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.073]](../ps.gif) E21.073
E21.073![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.074]](../ps.gif) E21.074
E21.074![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.075]](../ps.gif) E21.075
E21.075![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.076]](../ps.gif) E21.076
E21.076![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.077]](../ps.gif) E21.077
E21.077![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.078]](../ps.gif) E21.078
E21.078![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.079]](../ps.gif) E21.079
E21.079![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.08]](../ps.gif) E21.08
E21.08![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.081]](../ps.gif) E21.081
E21.081![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.082]](../ps.gif) E21.082
E21.082![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.083]](../ps.gif) E21.083
E21.083![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.084]](../ps.gif) E21.084
E21.084![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.085]](../ps.gif) E21.085
E21.085![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.086]](../ps.gif) E21.086
E21.086![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.087]](../ps.gif) E21.087
E21.087![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.088]](../ps.gif) E21.088
E21.088![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.089]](../ps.gif) E21.089
E21.089![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.09]](../ps.gif) E21.09
E21.09![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.091]](../ps.gif) E21.091
E21.091![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.092]](../ps.gif) E21.092
E21.092![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.093]](../ps.gif) E21.093
E21.093![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.094]](../ps.gif) E21.094
E21.094![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.095]](../ps.gif) E21.095
E21.095![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.096]](../ps.gif) E21.096
E21.096![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.097]](../ps.gif) E21.097
E21.097![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.098]](../ps.gif) E21.098
E21.098![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.099]](../ps.gif) E21.099
E21.099![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.1]](../ps.gif) E21.1
E21.1![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.101]](../ps.gif) E21.101
E21.101![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.102]](../ps.gif) E21.102
E21.102![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.103]](../ps.gif) E21.103
E21.103![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.104]](../ps.gif) E21.104
E21.104![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.105]](../ps.gif) E21.105
E21.105![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.106]](../ps.gif) E21.106
E21.106![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.107]](../ps.gif) E21.107
E21.107![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.108]](../ps.gif) E21.108
E21.108![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.109]](../ps.gif) E21.109
E21.109![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.11]](../ps.gif) E21.11
E21.11![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.111]](../ps.gif) E21.111
E21.111![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.112]](../ps.gif) E21.112
E21.112![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.113]](../ps.gif) E21.113
E21.113![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.114]](../ps.gif) E21.114
E21.114![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.115]](../ps.gif) E21.115
E21.115![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.116]](../ps.gif) E21.116
E21.116![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.117]](../ps.gif) E21.117
E21.117![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.118]](../ps.gif) E21.118
E21.118![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.119]](../ps.gif) E21.119
E21.119![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.12]](../ps.gif) E21.12
E21.12![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.121]](../ps.gif) E21.121
E21.121![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.122]](../ps.gif) E21.122
E21.122![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.123]](../ps.gif) E21.123
E21.123![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.124]](../ps.gif) E21.124
E21.124![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.125]](../ps.gif) E21.125
E21.125![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.126]](../ps.gif) E21.126
E21.126![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.127]](../ps.gif) E21.127
E21.127![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.128]](../ps.gif) E21.128
E21.128![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.129]](../ps.gif) E21.129
E21.129![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.13]](../ps.gif) E21.13
E21.13![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.131]](../ps.gif) E21.131
E21.131![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.132]](../ps.gif) E21.132
E21.132![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.133]](../ps.gif) E21.133
E21.133![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.134]](../ps.gif) E21.134
E21.134![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.135]](../ps.gif) E21.135
E21.135![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.136]](../ps.gif) E21.136
E21.136![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.137]](../ps.gif) E21.137
E21.137![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.138]](../ps.gif) E21.138
E21.138![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.139]](../ps.gif) E21.139
E21.139![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.14]](../ps.gif) E21.14
E21.14![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.141]](../ps.gif) E21.141
E21.141![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.142]](../ps.gif) E21.142
E21.142![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.143]](../ps.gif) E21.143
E21.143![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.144]](../ps.gif) E21.144
E21.144![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.145]](../ps.gif) E21.145
E21.145![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.146]](../ps.gif) E21.146
E21.146![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.147]](../ps.gif) E21.147
E21.147![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.148]](../ps.gif) E21.148
E21.148![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.149]](../ps.gif) E21.149
E21.149![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.15]](../ps.gif) E21.15
E21.15![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.151]](../ps.gif) E21.151
E21.151![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.152]](../ps.gif) E21.152
E21.152![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.153]](../ps.gif) E21.153
E21.153![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.154]](../ps.gif) E21.154
E21.154![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.155]](../ps.gif) E21.155
E21.155![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.156]](../ps.gif) E21.156
E21.156![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.157]](../ps.gif) E21.157
E21.157![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.158]](../ps.gif) E21.158
E21.158![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.159]](../ps.gif) E21.159
E21.159![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.16]](../ps.gif) E21.16
E21.16![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.161]](../ps.gif) E21.161
E21.161![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.162]](../ps.gif) E21.162
E21.162![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.163]](../ps.gif) E21.163
E21.163![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.164]](../ps.gif) E21.164
E21.164![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.165]](../ps.gif) E21.165
E21.165![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.166]](../ps.gif) E21.166
E21.166![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.167]](../ps.gif) E21.167
E21.167![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.168]](../ps.gif) E21.168
E21.168![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.169]](../ps.gif) E21.169
E21.169![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.17]](../ps.gif) E21.17
E21.17![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.171]](../ps.gif) E21.171
E21.171![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.172]](../ps.gif) E21.172
E21.172![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.173]](../ps.gif) E21.173
E21.173![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.174]](../ps.gif) E21.174
E21.174![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.175]](../ps.gif) E21.175
E21.175![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.176]](../ps.gif) E21.176
E21.176![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.177]](../ps.gif) E21.177
E21.177![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.178]](../ps.gif) E21.178
E21.178![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.179]](../ps.gif) E21.179
E21.179![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.18]](../ps.gif) E21.18
E21.18![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.181]](../ps.gif) E21.181
E21.181![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.182]](../ps.gif) E21.182
E21.182![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.183]](../ps.gif) E21.183
E21.183![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.184]](../ps.gif) E21.184
E21.184![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.185]](../ps.gif) E21.185
E21.185![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.186]](../ps.gif) E21.186
E21.186![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.187]](../ps.gif) E21.187
E21.187![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.188]](../ps.gif) E21.188
E21.188![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.189]](../ps.gif) E21.189
E21.189![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.19]](../ps.gif) E21.19
E21.19![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.191]](../ps.gif) E21.191
E21.191![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.192]](../ps.gif) E21.192
E21.192![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.193]](../ps.gif) E21.193
E21.193![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.194]](../ps.gif) E21.194
E21.194![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.195]](../ps.gif) E21.195
E21.195![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.196]](../ps.gif) E21.196
E21.196![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.197]](../ps.gif) E21.197
E21.197![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.198]](../ps.gif) E21.198
E21.198![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.199]](../ps.gif) E21.199
E21.199![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.2]](../ps.gif) E21.2
E21.2![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.201]](../ps.gif) E21.201
E21.201![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.202]](../ps.gif) E21.202
E21.202![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.203]](../ps.gif) E21.203
E21.203![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.204]](../ps.gif) E21.204
E21.204![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.205]](../ps.gif) E21.205
E21.205![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.206]](../ps.gif) E21.206
E21.206![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.207]](../ps.gif) E21.207
E21.207![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.208]](../ps.gif) E21.208
E21.208![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.209]](../ps.gif) E21.209
E21.209![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.21]](../ps.gif) E21.21
E21.21![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.211]](../ps.gif) E21.211
E21.211![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.212]](../ps.gif) E21.212
E21.212![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.213]](../ps.gif) E21.213
E21.213![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.214]](../ps.gif) E21.214
E21.214![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.215]](../ps.gif) E21.215
E21.215![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.216]](../ps.gif) E21.216
E21.216![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.217]](../ps.gif) E21.217
E21.217![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.218]](../ps.gif) E21.218
E21.218![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.219]](../ps.gif) E21.219
E21.219![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.22]](../ps.gif) E21.22
E21.22![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.221]](../ps.gif) E21.221
E21.221![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.222]](../ps.gif) E21.222
E21.222![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.223]](../ps.gif) E21.223
E21.223![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.224]](../ps.gif) E21.224
E21.224![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.225]](../ps.gif) E21.225
E21.225![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.226]](../ps.gif) E21.226
E21.226![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.227]](../ps.gif) E21.227
E21.227![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.228]](../ps.gif) E21.228
E21.228![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.229]](../ps.gif) E21.229
E21.229![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.23]](../ps.gif) E21.23
E21.23![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.231]](../ps.gif) E21.231
E21.231![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.232]](../ps.gif) E21.232
E21.232![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.233]](../ps.gif) E21.233
E21.233![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.234]](../ps.gif) E21.234
E21.234![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.235]](../ps.gif) E21.235
E21.235![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.236]](../ps.gif) E21.236
E21.236![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.237]](../ps.gif) E21.237
E21.237![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.238]](../ps.gif) E21.238
E21.238![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.239]](../ps.gif) E21.239
E21.239![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.24]](../ps.gif) E21.24
E21.24![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.241]](../ps.gif) E21.241
E21.241![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.242]](../ps.gif) E21.242
E21.242![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.243]](../ps.gif) E21.243
E21.243![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.244]](../ps.gif) E21.244
E21.244![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.245]](../ps.gif) E21.245
E21.245![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.246]](../ps.gif) E21.246
E21.246![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.247]](../ps.gif) E21.247
E21.247![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.248]](../ps.gif) E21.248
E21.248![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.249]](../ps.gif) E21.249
E21.249![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.25]](../ps.gif) E21.25
E21.25![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.251]](../ps.gif) E21.251
E21.251![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.252]](../ps.gif) E21.252
E21.252![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.253]](../ps.gif) E21.253
E21.253![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.254]](../ps.gif) E21.254
E21.254![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.255]](../ps.gif) E21.255
E21.255![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.256]](../ps.gif) E21.256
E21.256![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.257]](../ps.gif) E21.257
E21.257![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.258]](../ps.gif) E21.258
E21.258![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.259]](../ps.gif) E21.259
E21.259![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.26]](../ps.gif) E21.26
E21.26![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.261]](../ps.gif) E21.261
E21.261![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.262]](../ps.gif) E21.262
E21.262![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.263]](../ps.gif) E21.263
E21.263![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.264]](../ps.gif) E21.264
E21.264![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.265]](../ps.gif) E21.265
E21.265![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.266]](../ps.gif) E21.266
E21.266![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.267]](../ps.gif) E21.267
E21.267![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.268]](../ps.gif) E21.268
E21.268![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.269]](../ps.gif) E21.269
E21.269![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.27]](../ps.gif) E21.27
E21.27![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.271]](../ps.gif) E21.271
E21.271![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.272]](../ps.gif) E21.272
E21.272![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.273]](../ps.gif) E21.273
E21.273![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.274]](../ps.gif) E21.274
E21.274![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.275]](../ps.gif) E21.275
E21.275![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.276]](../ps.gif) E21.276
E21.276![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.277]](../ps.gif) E21.277
E21.277![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.278]](../ps.gif) E21.278
E21.278![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.279]](../ps.gif) E21.279
E21.279![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.28]](../ps.gif) E21.28
E21.28![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.281]](../ps.gif) E21.281
E21.281![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.282]](../ps.gif) E21.282
E21.282![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.283]](../ps.gif) E21.283
E21.283![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.284]](../ps.gif) E21.284
E21.284![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.285]](../ps.gif) E21.285
E21.285![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.286]](../ps.gif) E21.286
E21.286![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.287]](../ps.gif) E21.287
E21.287![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.288]](../ps.gif) E21.288
E21.288![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.289]](../ps.gif) E21.289
E21.289![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.29]](../ps.gif) E21.29
E21.29![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.291]](../ps.gif) E21.291
E21.291![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.292]](../ps.gif) E21.292
E21.292![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.293]](../ps.gif) E21.293
E21.293![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.294]](../ps.gif) E21.294
E21.294![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.295]](../ps.gif) E21.295
E21.295![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.296]](../ps.gif) E21.296
E21.296![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.297]](../ps.gif) E21.297
E21.297![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.298]](../ps.gif) E21.298
E21.298![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.299]](../ps.gif) E21.299
E21.299![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.3]](../ps.gif) E21.3
E21.3![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.301]](../ps.gif) E21.301
E21.301![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.302]](../ps.gif) E21.302
E21.302![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.303]](../ps.gif) E21.303
E21.303![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.304]](../ps.gif) E21.304
E21.304![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.305]](../ps.gif) E21.305
E21.305![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.306]](../ps.gif) E21.306
E21.306![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.307]](../ps.gif) E21.307
E21.307![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.308]](../ps.gif) E21.308
E21.308![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.309]](../ps.gif) E21.309
E21.309![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.31]](../ps.gif) E21.31
E21.31![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.311]](../ps.gif) E21.311
E21.311![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.312]](../ps.gif) E21.312
E21.312![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.313]](../ps.gif) E21.313
E21.313![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.314]](../ps.gif) E21.314
E21.314![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.315]](../ps.gif) E21.315
E21.315![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.316]](../ps.gif) E21.316
E21.316![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.317]](../ps.gif) E21.317
E21.317![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.318]](../ps.gif) E21.318
E21.318![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.319]](../ps.gif) E21.319
E21.319![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.32]](../ps.gif) E21.32
E21.32![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.321]](../ps.gif) E21.321
E21.321![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.322]](../ps.gif) E21.322
E21.322![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.323]](../ps.gif) E21.323
E21.323![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.324]](../ps.gif) E21.324
E21.324![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.325]](../ps.gif) E21.325
E21.325![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.326]](../ps.gif) E21.326
E21.326![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.327]](../ps.gif) E21.327
E21.327![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.328]](../ps.gif) E21.328
E21.328![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.329]](../ps.gif) E21.329
E21.329![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.33]](../ps.gif) E21.33
E21.33![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.331]](../ps.gif) E21.331
E21.331![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.332]](../ps.gif) E21.332
E21.332![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.333]](../ps.gif) E21.333
E21.333![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.334]](../ps.gif) E21.334
E21.334![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.335]](../ps.gif) E21.335
E21.335![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.336]](../ps.gif) E21.336
E21.336![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.337]](../ps.gif) E21.337
E21.337![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.338]](../ps.gif) E21.338
E21.338![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.339]](../ps.gif) E21.339
E21.339![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.34]](../ps.gif) E21.34
E21.34![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.341]](../ps.gif) E21.341
E21.341![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.342]](../ps.gif) E21.342
E21.342![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.343]](../ps.gif) E21.343
E21.343![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.344]](../ps.gif) E21.344
E21.344![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.345]](../ps.gif) E21.345
E21.345![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.346]](../ps.gif) E21.346
E21.346![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.347]](../ps.gif) E21.347
E21.347![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.348]](../ps.gif) E21.348
E21.348![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.349]](../ps.gif) E21.349
E21.349![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.35]](../ps.gif) E21.35
E21.35![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.351]](../ps.gif) E21.351
E21.351![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.352]](../ps.gif) E21.352
E21.352![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.353]](../ps.gif) E21.353
E21.353![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.354]](../ps.gif) E21.354
E21.354![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.355]](../ps.gif) E21.355
E21.355![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.356]](../ps.gif) E21.356
E21.356![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.357]](../ps.gif) E21.357
E21.357![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.358]](../ps.gif) E21.358
E21.358![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.359]](../ps.gif) E21.359
E21.359![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.36]](../ps.gif) E21.36
E21.36![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.361]](../ps.gif) E21.361
E21.361![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.362]](../ps.gif) E21.362
E21.362![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.363]](../ps.gif) E21.363
E21.363![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.364]](../ps.gif) E21.364
E21.364![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.365]](../ps.gif) E21.365
E21.365![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.366]](../ps.gif) E21.366
E21.366![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.367]](../ps.gif) E21.367
E21.367![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.368]](../ps.gif) E21.368
E21.368![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.369]](../ps.gif) E21.369
E21.369![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.37]](../ps.gif) E21.37
E21.37![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.371]](../ps.gif) E21.371
E21.371![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.372]](../ps.gif) E21.372
E21.372![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.373]](../ps.gif) E21.373
E21.373![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.374]](../ps.gif) E21.374
E21.374![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.375]](../ps.gif) E21.375
E21.375![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.376]](../ps.gif) E21.376
E21.376![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.377]](../ps.gif) E21.377
E21.377![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.378]](../ps.gif) E21.378
E21.378![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.379]](../ps.gif) E21.379
E21.379![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.38]](../ps.gif) E21.38
E21.38![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.381]](../ps.gif) E21.381
E21.381![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.382]](../ps.gif) E21.382
E21.382![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.383]](../ps.gif) E21.383
E21.383![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.384]](../ps.gif) E21.384
E21.384![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.385]](../ps.gif) E21.385
E21.385![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.386]](../ps.gif) E21.386
E21.386![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.387]](../ps.gif) E21.387
E21.387![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.388]](../ps.gif) E21.388
E21.388![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.389]](../ps.gif) E21.389
E21.389![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.39]](../ps.gif) E21.39
E21.39![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.391]](../ps.gif) E21.391
E21.391![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.392]](../ps.gif) E21.392
E21.392![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.393]](../ps.gif) E21.393
E21.393![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.394]](../ps.gif) E21.394
E21.394![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.395]](../ps.gif) E21.395
E21.395![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.396]](../ps.gif) E21.396
E21.396![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.397]](../ps.gif) E21.397
E21.397![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.398]](../ps.gif) E21.398
E21.398![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.399]](../ps.gif) E21.399
E21.399![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.4]](../ps.gif) E21.4
E21.4![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.401]](../ps.gif) E21.401
E21.401![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.402]](../ps.gif) E21.402
E21.402![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.403]](../ps.gif) E21.403
E21.403![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.404]](../ps.gif) E21.404
E21.404![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.405]](../ps.gif) E21.405
E21.405![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.406]](../ps.gif) E21.406
E21.406![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.407]](../ps.gif) E21.407
E21.407![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.408]](../ps.gif) E21.408
E21.408![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.409]](../ps.gif) E21.409
E21.409![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.41]](../ps.gif) E21.41
E21.41![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.411]](../ps.gif) E21.411
E21.411![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.412]](../ps.gif) E21.412
E21.412![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.413]](../ps.gif) E21.413
E21.413![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.414]](../ps.gif) E21.414
E21.414![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.415]](../ps.gif) E21.415
E21.415![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.416]](../ps.gif) E21.416
E21.416![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.417]](../ps.gif) E21.417
E21.417![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.418]](../ps.gif) E21.418
E21.418![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.419]](../ps.gif) E21.419
E21.419![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.42]](../ps.gif) E21.42
E21.42![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.421]](../ps.gif) E21.421
E21.421![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.422]](../ps.gif) E21.422
E21.422![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.423]](../ps.gif) E21.423
E21.423![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.424]](../ps.gif) E21.424
E21.424![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.425]](../ps.gif) E21.425
E21.425![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.426]](../ps.gif) E21.426
E21.426![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.427]](../ps.gif) E21.427
E21.427![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.428]](../ps.gif) E21.428
E21.428![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.429]](../ps.gif) E21.429
E21.429![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.43]](../ps.gif) E21.43
E21.43![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.431]](../ps.gif) E21.431
E21.431![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.432]](../ps.gif) E21.432
E21.432![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.433]](../ps.gif) E21.433
E21.433![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.434]](../ps.gif) E21.434
E21.434![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.435]](../ps.gif) E21.435
E21.435![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.436]](../ps.gif) E21.436
E21.436![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.437]](../ps.gif) E21.437
E21.437![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.438]](../ps.gif) E21.438
E21.438![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.439]](../ps.gif) E21.439
E21.439![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.44]](../ps.gif) E21.44
E21.44![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.441]](../ps.gif) E21.441
E21.441![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.442]](../ps.gif) E21.442
E21.442![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.443]](../ps.gif) E21.443
E21.443![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.444]](../ps.gif) E21.444
E21.444![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.445]](../ps.gif) E21.445
E21.445![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.446]](../ps.gif) E21.446
E21.446![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.447]](../ps.gif) E21.447
E21.447![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.448]](../ps.gif) E21.448
E21.448![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.449]](../ps.gif) E21.449
E21.449![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.45]](../ps.gif) E21.45
E21.45![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.451]](../ps.gif) E21.451
E21.451![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.452]](../ps.gif) E21.452
E21.452![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.453]](../ps.gif) E21.453
E21.453![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.454]](../ps.gif) E21.454
E21.454![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.455]](../ps.gif) E21.455
E21.455![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.456]](../ps.gif) E21.456
E21.456![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.457]](../ps.gif) E21.457
E21.457![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.458]](../ps.gif) E21.458
E21.458![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.459]](../ps.gif) E21.459
E21.459![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.46]](../ps.gif) E21.46
E21.46![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.461]](../ps.gif) E21.461
E21.461![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.462]](../ps.gif) E21.462
E21.462![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.463]](../ps.gif) E21.463
E21.463![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.464]](../ps.gif) E21.464
E21.464![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.465]](../ps.gif) E21.465
E21.465![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.466]](../ps.gif) E21.466
E21.466![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.467]](../ps.gif) E21.467
E21.467![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.468]](../ps.gif) E21.468
E21.468![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.469]](../ps.gif) E21.469
E21.469![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.47]](../ps.gif) E21.47
E21.47![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.471]](../ps.gif) E21.471
E21.471![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.472]](../ps.gif) E21.472
E21.472![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.473]](../ps.gif) E21.473
E21.473![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.474]](../ps.gif) E21.474
E21.474![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.475]](../ps.gif) E21.475
E21.475![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.476]](../ps.gif) E21.476
E21.476![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.477]](../ps.gif) E21.477
E21.477![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.478]](../ps.gif) E21.478
E21.478![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.479]](../ps.gif) E21.479
E21.479![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.48]](../ps.gif) E21.48
E21.48![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.481]](../ps.gif) E21.481
E21.481![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.482]](../ps.gif) E21.482
E21.482![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.483]](../ps.gif) E21.483
E21.483![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.484]](../ps.gif) E21.484
E21.484![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.485]](../ps.gif) E21.485
E21.485![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.486]](../ps.gif) E21.486
E21.486![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.487]](../ps.gif) E21.487
E21.487![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.488]](../ps.gif) E21.488
E21.488![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.489]](../ps.gif) E21.489
E21.489![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.49]](../ps.gif) E21.49
E21.49![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.491]](../ps.gif) E21.491
E21.491![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.492]](../ps.gif) E21.492
E21.492![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.493]](../ps.gif) E21.493
E21.493![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.494]](../ps.gif) E21.494
E21.494![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.495]](../ps.gif) E21.495
E21.495![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.496]](../ps.gif) E21.496
E21.496![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.497]](../ps.gif) E21.497
E21.497![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.498]](../ps.gif) E21.498
E21.498![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.499]](../ps.gif) E21.499
E21.499![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.5]](../ps.gif) E21.5
E21.5![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.501]](../ps.gif) E21.501
E21.501![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.502]](../ps.gif) E21.502
E21.502![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.503]](../ps.gif) E21.503
E21.503![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.504]](../ps.gif) E21.504
E21.504![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.505]](../ps.gif) E21.505
E21.505![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.506]](../ps.gif) E21.506
E21.506![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.507]](../ps.gif) E21.507
E21.507![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.508]](../ps.gif) E21.508
E21.508![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.509]](../ps.gif) E21.509
E21.509![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.51]](../ps.gif) E21.51
E21.51![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.511]](../ps.gif) E21.511
E21.511![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.512]](../ps.gif) E21.512
E21.512![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.513]](../ps.gif) E21.513
E21.513![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.514]](../ps.gif) E21.514
E21.514![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.515]](../ps.gif) E21.515
E21.515![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.516]](../ps.gif) E21.516
E21.516![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.517]](../ps.gif) E21.517
E21.517![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.518]](../ps.gif) E21.518
E21.518![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.519]](../ps.gif) E21.519
E21.519![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.52]](../ps.gif) E21.52
E21.52![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.521]](../ps.gif) E21.521
E21.521![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.522]](../ps.gif) E21.522
E21.522![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.523]](../ps.gif) E21.523
E21.523![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.524]](../ps.gif) E21.524
E21.524![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.525]](../ps.gif) E21.525
E21.525![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.526]](../ps.gif) E21.526
E21.526![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.527]](../ps.gif) E21.527
E21.527![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.528]](../ps.gif) E21.528
E21.528![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.529]](../ps.gif) E21.529
E21.529![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.53]](../ps.gif) E21.53
E21.53![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.531]](../ps.gif) E21.531
E21.531![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.532]](../ps.gif) E21.532
E21.532![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.533]](../ps.gif) E21.533
E21.533![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.534]](../ps.gif) E21.534
E21.534![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.535]](../ps.gif) E21.535
E21.535![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.536]](../ps.gif) E21.536
E21.536![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.537]](../ps.gif) E21.537
E21.537![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.538]](../ps.gif) E21.538
E21.538![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.539]](../ps.gif) E21.539
E21.539![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.54]](../ps.gif) E21.54
E21.54![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.541]](../ps.gif) E21.541
E21.541![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.542]](../ps.gif) E21.542
E21.542![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.543]](../ps.gif) E21.543
E21.543![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.544]](../ps.gif) E21.544
E21.544![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.545]](../ps.gif) E21.545
E21.545![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.546]](../ps.gif) E21.546
E21.546![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.547]](../ps.gif) E21.547
E21.547![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.548]](../ps.gif) E21.548
E21.548![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.549]](../ps.gif) E21.549
E21.549![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.55]](../ps.gif) E21.55
E21.55![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.551]](../ps.gif) E21.551
E21.551![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.552]](../ps.gif) E21.552
E21.552![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.553]](../ps.gif) E21.553
E21.553![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.554]](../ps.gif) E21.554
E21.554![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.555]](../ps.gif) E21.555
E21.555![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.556]](../ps.gif) E21.556
E21.556![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.557]](../ps.gif) E21.557
E21.557![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.558]](../ps.gif) E21.558
E21.558![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.559]](../ps.gif) E21.559
E21.559![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.56]](../ps.gif) E21.56
E21.56![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.561]](../ps.gif) E21.561
E21.561![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.562]](../ps.gif) E21.562
E21.562![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.563]](../ps.gif) E21.563
E21.563![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.564]](../ps.gif) E21.564
E21.564![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.565]](../ps.gif) E21.565
E21.565![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.566]](../ps.gif) E21.566
E21.566![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.567]](../ps.gif) E21.567
E21.567![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.568]](../ps.gif) E21.568
E21.568![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.569]](../ps.gif) E21.569
E21.569![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.57]](../ps.gif) E21.57
E21.57![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.571]](../ps.gif) E21.571
E21.571![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.572]](../ps.gif) E21.572
E21.572![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.573]](../ps.gif) E21.573
E21.573![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.574]](../ps.gif) E21.574
E21.574![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.575]](../ps.gif) E21.575
E21.575![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.576]](../ps.gif) E21.576
E21.576![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.577]](../ps.gif) E21.577
E21.577![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.578]](../ps.gif) E21.578
E21.578![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.579]](../ps.gif) E21.579
E21.579![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.58]](../ps.gif) E21.58
E21.58![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.581]](../ps.gif) E21.581
E21.581![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.582]](../ps.gif) E21.582
E21.582![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.583]](../ps.gif) E21.583
E21.583![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.584]](../ps.gif) E21.584
E21.584![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.585]](../ps.gif) E21.585
E21.585![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.586]](../ps.gif) E21.586
E21.586![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.587]](../ps.gif) E21.587
E21.587![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.588]](../ps.gif) E21.588
E21.588![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.589]](../ps.gif) E21.589
E21.589![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.59]](../ps.gif) E21.59
E21.59![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.591]](../ps.gif) E21.591
E21.591![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.592]](../ps.gif) E21.592
E21.592![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.593]](../ps.gif) E21.593
E21.593![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.594]](../ps.gif) E21.594
E21.594![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.595]](../ps.gif) E21.595
E21.595![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.596]](../ps.gif) E21.596
E21.596![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.597]](../ps.gif) E21.597
E21.597![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.598]](../ps.gif) E21.598
E21.598![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.599]](../ps.gif) E21.599
E21.599![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.6]](../ps.gif) E21.6
E21.6![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.601]](../ps.gif) E21.601
E21.601![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.602]](../ps.gif) E21.602
E21.602![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.603]](../ps.gif) E21.603
E21.603![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.604]](../ps.gif) E21.604
E21.604![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.605]](../ps.gif) E21.605
E21.605![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.606]](../ps.gif) E21.606
E21.606![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.608]](../ps.gif) E21.608
E21.608![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.609]](../ps.gif) E21.609
E21.609![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.61]](../ps.gif) E21.61
E21.61![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.611]](../ps.gif) E21.611
E21.611![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.612]](../ps.gif) E21.612
E21.612![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.613]](../ps.gif) E21.613
E21.613![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.614]](../ps.gif) E21.614
E21.614![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.615]](../ps.gif) E21.615
E21.615![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.616]](../ps.gif) E21.616
E21.616![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.617]](../ps.gif) E21.617
E21.617![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.618]](../ps.gif) E21.618
E21.618![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.619]](../ps.gif) E21.619
E21.619![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.62]](../ps.gif) E21.62
E21.62![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.621]](../ps.gif) E21.621
E21.621![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.622]](../ps.gif) E21.622
E21.622![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.623]](../ps.gif) E21.623
E21.623![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.624]](../ps.gif) E21.624
E21.624![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.625]](../ps.gif) E21.625
E21.625![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.626]](../ps.gif) E21.626
E21.626![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.627]](../ps.gif) E21.627
E21.627![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.628]](../ps.gif) E21.628
E21.628![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.629]](../ps.gif) E21.629
E21.629![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.63]](../ps.gif) E21.63
E21.63![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.631]](../ps.gif) E21.631
E21.631![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.632]](../ps.gif) E21.632
E21.632![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.633]](../ps.gif) E21.633
E21.633![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.634]](../ps.gif) E21.634
E21.634![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.635]](../ps.gif) E21.635
E21.635![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.636]](../ps.gif) E21.636
E21.636![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.637]](../ps.gif) E21.637
E21.637![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.638]](../ps.gif) E21.638
E21.638![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.639]](../ps.gif) E21.639
E21.639![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.64]](../ps.gif) E21.64
E21.64![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.641]](../ps.gif) E21.641
E21.641![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.642]](../ps.gif) E21.642
E21.642![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.643]](../ps.gif) E21.643
E21.643![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.644]](../ps.gif) E21.644
E21.644![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.645]](../ps.gif) E21.645
E21.645![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.646]](../ps.gif) E21.646
E21.646![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.647]](../ps.gif) E21.647
E21.647![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.648]](../ps.gif) E21.648
E21.648![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.649]](../ps.gif) E21.649
E21.649![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.65]](../ps.gif) E21.65
E21.65![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.651]](../ps.gif) E21.651
E21.651![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.652]](../ps.gif) E21.652
E21.652![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.653]](../ps.gif) E21.653
E21.653![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.654]](../ps.gif) E21.654
E21.654![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.655]](../ps.gif) E21.655
E21.655![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.656]](../ps.gif) E21.656
E21.656![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.657]](../ps.gif) E21.657
E21.657![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.658]](../ps.gif) E21.658
E21.658![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.659]](../ps.gif) E21.659
E21.659![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.66]](../ps.gif) E21.66
E21.66![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.661]](../ps.gif) E21.661
E21.661![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.662]](../ps.gif) E21.662
E21.662![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.663]](../ps.gif) E21.663
E21.663![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.664]](../ps.gif) E21.664
E21.664![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.665]](../ps.gif) E21.665
E21.665![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.666]](../ps.gif) E21.666
E21.666![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.667]](../ps.gif) E21.667
E21.667![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.668]](../ps.gif) E21.668
E21.668![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.669]](../ps.gif) E21.669
E21.669![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.67]](../ps.gif) E21.67
E21.67![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.671]](../ps.gif) E21.671
E21.671![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.672]](../ps.gif) E21.672
E21.672![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.673]](../ps.gif) E21.673
E21.673![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.674]](../ps.gif) E21.674
E21.674![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.675]](../ps.gif) E21.675
E21.675![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.676]](../ps.gif) E21.676
E21.676![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.677]](../ps.gif) E21.677
E21.677![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.678]](../ps.gif) E21.678
E21.678![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.679]](../ps.gif) E21.679
E21.679![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.68]](../ps.gif) E21.68
E21.68![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.681]](../ps.gif) E21.681
E21.681![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.682]](../ps.gif) E21.682
E21.682![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.683]](../ps.gif) E21.683
E21.683![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.684]](../ps.gif) E21.684
E21.684![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.685]](../ps.gif) E21.685
E21.685![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.686]](../ps.gif) E21.686
E21.686![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.687]](../ps.gif) E21.687
E21.687![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.688]](../ps.gif) E21.688
E21.688![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.689]](../ps.gif) E21.689
E21.689![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.69]](../ps.gif) E21.69
E21.69![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.691]](../ps.gif) E21.691
E21.691![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.692]](../ps.gif) E21.692
E21.692![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.693]](../ps.gif) E21.693
E21.693![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.694]](../ps.gif) E21.694
E21.694![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.695]](../ps.gif) E21.695
E21.695![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.696]](../ps.gif) E21.696
E21.696![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.697]](../ps.gif) E21.697
E21.697![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.698]](../ps.gif) E21.698
E21.698![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.699]](../ps.gif) E21.699
E21.699![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.7]](../ps.gif) E21.7
E21.7![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.701]](../ps.gif) E21.701
E21.701![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.702]](../ps.gif) E21.702
E21.702![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.703]](../ps.gif) E21.703
E21.703![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.704]](../ps.gif) E21.704
E21.704![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E21.705]](../ps.gif) E21.705
E21.705![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.001]](../ps.gif) E23.001
E23.001![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.002]](../ps.gif) E23.002
E23.002![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.003]](../ps.gif) E23.003
E23.003![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.004]](../ps.gif) E23.004
E23.004![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.005]](../ps.gif) E23.005
E23.005![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.006]](../ps.gif) E23.006
E23.006![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.007]](../ps.gif) E23.007
E23.007![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.008]](../ps.gif) E23.008
E23.008![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.009]](../ps.gif) E23.009
E23.009![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.01]](../ps.gif) E23.01
E23.01![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.011]](../ps.gif) E23.011
E23.011![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.012]](../ps.gif) E23.012
E23.012![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.013]](../ps.gif) E23.013
E23.013![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.014]](../ps.gif) E23.014
E23.014![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.015]](../ps.gif) E23.015
E23.015![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.016]](../ps.gif) E23.016
E23.016![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.017]](../ps.gif) E23.017
E23.017![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.018]](../ps.gif) E23.018
E23.018![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.019]](../ps.gif) E23.019
E23.019![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.02]](../ps.gif) E23.02
E23.02![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.021]](../ps.gif) E23.021
E23.021![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.022]](../ps.gif) E23.022
E23.022![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.023]](../ps.gif) E23.023
E23.023![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.024]](../ps.gif) E23.024
E23.024![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.025]](../ps.gif) E23.025
E23.025![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.026]](../ps.gif) E23.026
E23.026![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.027]](../ps.gif) E23.027
E23.027![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.028]](../ps.gif) E23.028
E23.028![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.029]](../ps.gif) E23.029
E23.029![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.03]](../ps.gif) E23.03
E23.03![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.031]](../ps.gif) E23.031
E23.031![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.032]](../ps.gif) E23.032
E23.032![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.033]](../ps.gif) E23.033
E23.033![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.034]](../ps.gif) E23.034
E23.034![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.035]](../ps.gif) E23.035
E23.035![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.036]](../ps.gif) E23.036
E23.036![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.037]](../ps.gif) E23.037
E23.037![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.038]](../ps.gif) E23.038
E23.038![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.039]](../ps.gif) E23.039
E23.039![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.04]](../ps.gif) E23.04
E23.04![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.041]](../ps.gif) E23.041
E23.041![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.042]](../ps.gif) E23.042
E23.042![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.043]](../ps.gif) E23.043
E23.043![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.044]](../ps.gif) E23.044
E23.044![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.045]](../ps.gif) E23.045
E23.045![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.046]](../ps.gif) E23.046
E23.046![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.047]](../ps.gif) E23.047
E23.047![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.048]](../ps.gif) E23.048
E23.048![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.049]](../ps.gif) E23.049
E23.049![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.05]](../ps.gif) E23.05
E23.05![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.051]](../ps.gif) E23.051
E23.051![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.052]](../ps.gif) E23.052
E23.052![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.053]](../ps.gif) E23.053
E23.053![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.054]](../ps.gif) E23.054
E23.054![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.055]](../ps.gif) E23.055
E23.055![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.056]](../ps.gif) E23.056
E23.056![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.057]](../ps.gif) E23.057
E23.057![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.058]](../ps.gif) E23.058
E23.058![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.059]](../ps.gif) E23.059
E23.059![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.06]](../ps.gif) E23.06
E23.06![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.061]](../ps.gif) E23.061
E23.061![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.062]](../ps.gif) E23.062
E23.062![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.063]](../ps.gif) E23.063
E23.063![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.064]](../ps.gif) E23.064
E23.064![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.065]](../ps.gif) E23.065
E23.065![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.066]](../ps.gif) E23.066
E23.066![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.067]](../ps.gif) E23.067
E23.067![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.068]](../ps.gif) E23.068
E23.068![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.069]](../ps.gif) E23.069
E23.069![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.07]](../ps.gif) E23.07
E23.07![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.071]](../ps.gif) E23.071
E23.071![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.072]](../ps.gif) E23.072
E23.072![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.073]](../ps.gif) E23.073
E23.073![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.074]](../ps.gif) E23.074
E23.074![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.075]](../ps.gif) E23.075
E23.075![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.076]](../ps.gif) E23.076
E23.076![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.077]](../ps.gif) E23.077
E23.077![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.078]](../ps.gif) E23.078
E23.078![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.079]](../ps.gif) E23.079
E23.079![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.08]](../ps.gif) E23.08
E23.08![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.081]](../ps.gif) E23.081
E23.081![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.082]](../ps.gif) E23.082
E23.082![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.083]](../ps.gif) E23.083
E23.083![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.084]](../ps.gif) E23.084
E23.084![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.085]](../ps.gif) E23.085
E23.085![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.086]](../ps.gif) E23.086
E23.086![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.087]](../ps.gif) E23.087
E23.087![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.088]](../ps.gif) E23.088
E23.088![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.089]](../ps.gif) E23.089
E23.089![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.09]](../ps.gif) E23.09
E23.09![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.091]](../ps.gif) E23.091
E23.091![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.092]](../ps.gif) E23.092
E23.092![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.093]](../ps.gif) E23.093
E23.093![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.094]](../ps.gif) E23.094
E23.094![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.095]](../ps.gif) E23.095
E23.095![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.096]](../ps.gif) E23.096
E23.096![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.097]](../ps.gif) E23.097
E23.097![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.098]](../ps.gif) E23.098
E23.098![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.099]](../ps.gif) E23.099
E23.099![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.1]](../ps.gif) E23.1
E23.1![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.101]](../ps.gif) E23.101
E23.101![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.102]](../ps.gif) E23.102
E23.102![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.103]](../ps.gif) E23.103
E23.103![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.104]](../ps.gif) E23.104
E23.104![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.105]](../ps.gif) E23.105
E23.105![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.106]](../ps.gif) E23.106
E23.106![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.107]](../ps.gif) E23.107
E23.107![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.108]](../ps.gif) E23.108
E23.108![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.109]](../ps.gif) E23.109
E23.109![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.11]](../ps.gif) E23.11
E23.11![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.111]](../ps.gif) E23.111
E23.111![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.112]](../ps.gif) E23.112
E23.112![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.113]](../ps.gif) E23.113
E23.113![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.114]](../ps.gif) E23.114
E23.114![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.115]](../ps.gif) E23.115
E23.115![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.116]](../ps.gif) E23.116
E23.116![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.117]](../ps.gif) E23.117
E23.117![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.118]](../ps.gif) E23.118
E23.118![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.119]](../ps.gif) E23.119
E23.119![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.12]](../ps.gif) E23.12
E23.12![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.121]](../ps.gif) E23.121
E23.121![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.122]](../ps.gif) E23.122
E23.122![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.123]](../ps.gif) E23.123
E23.123![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.124]](../ps.gif) E23.124
E23.124![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.125]](../ps.gif) E23.125
E23.125![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.126]](../ps.gif) E23.126
E23.126![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.127]](../ps.gif) E23.127
E23.127![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.128]](../ps.gif) E23.128
E23.128![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.129]](../ps.gif) E23.129
E23.129![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.13]](../ps.gif) E23.13
E23.13![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.131]](../ps.gif) E23.131
E23.131![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.132]](../ps.gif) E23.132
E23.132![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.133]](../ps.gif) E23.133
E23.133![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.134]](../ps.gif) E23.134
E23.134![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.135]](../ps.gif) E23.135
E23.135![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.136]](../ps.gif) E23.136
E23.136![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.137]](../ps.gif) E23.137
E23.137![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.138]](../ps.gif) E23.138
E23.138![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.139]](../ps.gif) E23.139
E23.139![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.14]](../ps.gif) E23.14
E23.14![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.141]](../ps.gif) E23.141
E23.141![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.142]](../ps.gif) E23.142
E23.142![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.143]](../ps.gif) E23.143
E23.143![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.144]](../ps.gif) E23.144
E23.144![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.145]](../ps.gif) E23.145
E23.145![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.146]](../ps.gif) E23.146
E23.146![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.147]](../ps.gif) E23.147
E23.147![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.148]](../ps.gif) E23.148
E23.148![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.149]](../ps.gif) E23.149
E23.149![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.15]](../ps.gif) E23.15
E23.15![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.151]](../ps.gif) E23.151
E23.151![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.152]](../ps.gif) E23.152
E23.152![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.153]](../ps.gif) E23.153
E23.153![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.154]](../ps.gif) E23.154
E23.154![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.155]](../ps.gif) E23.155
E23.155![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.156]](../ps.gif) E23.156
E23.156![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.157]](../ps.gif) E23.157
E23.157![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.158]](../ps.gif) E23.158
E23.158![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.159]](../ps.gif) E23.159
E23.159![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.16]](../ps.gif) E23.16
E23.16![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.161]](../ps.gif) E23.161
E23.161![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.162]](../ps.gif) E23.162
E23.162![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.163]](../ps.gif) E23.163
E23.163![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.164]](../ps.gif) E23.164
E23.164![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.165]](../ps.gif) E23.165
E23.165![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.166]](../ps.gif) E23.166
E23.166![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.167]](../ps.gif) E23.167
E23.167![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.168]](../ps.gif) E23.168
E23.168![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.169]](../ps.gif) E23.169
E23.169![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.17]](../ps.gif) E23.17
E23.17![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.171]](../ps.gif) E23.171
E23.171![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.172]](../ps.gif) E23.172
E23.172![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.173]](../ps.gif) E23.173
E23.173![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.174]](../ps.gif) E23.174
E23.174![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.175]](../ps.gif) E23.175
E23.175![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.176]](../ps.gif) E23.176
E23.176![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.177]](../ps.gif) E23.177
E23.177![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.178]](../ps.gif) E23.178
E23.178![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.179]](../ps.gif) E23.179
E23.179![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.18]](../ps.gif) E23.18
E23.18![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.181]](../ps.gif) E23.181
E23.181![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.182]](../ps.gif) E23.182
E23.182![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.183]](../ps.gif) E23.183
E23.183![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.184]](../ps.gif) E23.184
E23.184![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.185]](../ps.gif) E23.185
E23.185![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.186]](../ps.gif) E23.186
E23.186![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.187]](../ps.gif) E23.187
E23.187![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.188]](../ps.gif) E23.188
E23.188![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.189]](../ps.gif) E23.189
E23.189![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.19]](../ps.gif) E23.19
E23.19![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.191]](../ps.gif) E23.191
E23.191![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.192]](../ps.gif) E23.192
E23.192![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.193]](../ps.gif) E23.193
E23.193![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E23.194]](../ps.gif) E23.194
E23.194![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E25.001]](../ps.gif) E25.001
E25.001![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E25.002]](../ps.gif) E25.002
E25.002![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E25.003]](../ps.gif) E25.003
E25.003![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E25.004]](../ps.gif) E25.004
E25.004![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E25.005]](../ps.gif) E25.005
E25.005![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E25.006]](../ps.gif) E25.006
E25.006![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E25.007]](../ps.gif) E25.007
E25.007![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E25.008]](../ps.gif) E25.008
E25.008![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E25.009]](../ps.gif) E25.009
E25.009![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E25.01]](../ps.gif) E25.01
E25.01![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E25.011]](../ps.gif) E25.011
E25.011![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E25.012]](../ps.gif) E25.012
E25.012![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E25.013]](../ps.gif) E25.013
E25.013![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E25.014]](../ps.gif) E25.014
E25.014![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E25.015]](../ps.gif) E25.015
E25.015![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E25.016]](../ps.gif) E25.016
E25.016![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E25.017]](../ps.gif) E25.017
E25.017![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E25.018]](../ps.gif) E25.018
E25.018![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E25.019]](../ps.gif) E25.019
E25.019![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E25.02]](../ps.gif) E25.02
E25.02![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E25.021]](../ps.gif) E25.021
E25.021![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E25.022]](../ps.gif) E25.022
E25.022![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E25.023]](../ps.gif) E25.023
E25.023![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E25.024]](../ps.gif) E25.024
E25.024![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E25.025]](../ps.gif) E25.025
E25.025![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E25.026]](../ps.gif) E25.026
E25.026![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E25.027]](../ps.gif) E25.027
E25.027![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E25.028]](../ps.gif) E25.028
E25.028![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E25.029]](../ps.gif) E25.029
E25.029![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E25.03]](../ps.gif) E25.03
E25.03![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E25.031]](../ps.gif) E25.031
E25.031![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E25.032]](../ps.gif) E25.032
E25.032![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.001]](../ps.gif) E27.001
E27.001![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.002]](../ps.gif) E27.002
E27.002![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.003]](../ps.gif) E27.003
E27.003![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.004]](../ps.gif) E27.004
E27.004![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.005]](../ps.gif) E27.005
E27.005![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.006]](../ps.gif) E27.006
E27.006![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.007]](../ps.gif) E27.007
E27.007![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.008]](../ps.gif) E27.008
E27.008![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.009]](../ps.gif) E27.009
E27.009![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.01]](../ps.gif) E27.01
E27.01![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.011]](../ps.gif) E27.011
E27.011![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.012]](../ps.gif) E27.012
E27.012![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.013]](../ps.gif) E27.013
E27.013![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.014]](../ps.gif) E27.014
E27.014![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.015]](../ps.gif) E27.015
E27.015![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.016]](../ps.gif) E27.016
E27.016![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.017]](../ps.gif) E27.017
E27.017![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.018]](../ps.gif) E27.018
E27.018![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.019]](../ps.gif) E27.019
E27.019![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.02]](../ps.gif) E27.02
E27.02![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.021]](../ps.gif) E27.021
E27.021![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.022]](../ps.gif) E27.022
E27.022![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.023]](../ps.gif) E27.023
E27.023![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.024]](../ps.gif) E27.024
E27.024![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.025]](../ps.gif) E27.025
E27.025![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.026]](../ps.gif) E27.026
E27.026![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.027]](../ps.gif) E27.027
E27.027![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.028]](../ps.gif) E27.028
E27.028![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.029]](../ps.gif) E27.029
E27.029![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.03]](../ps.gif) E27.03
E27.03![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.031]](../ps.gif) E27.031
E27.031![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.032]](../ps.gif) E27.032
E27.032![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.033]](../ps.gif) E27.033
E27.033![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.034]](../ps.gif) E27.034
E27.034![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.035]](../ps.gif) E27.035
E27.035![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.036]](../ps.gif) E27.036
E27.036![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.037]](../ps.gif) E27.037
E27.037![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.038]](../ps.gif) E27.038
E27.038![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.039]](../ps.gif) E27.039
E27.039![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.04]](../ps.gif) E27.04
E27.04![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.041]](../ps.gif) E27.041
E27.041![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.042]](../ps.gif) E27.042
E27.042![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.043]](../ps.gif) E27.043
E27.043![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.044]](../ps.gif) E27.044
E27.044![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.045]](../ps.gif) E27.045
E27.045![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.046]](../ps.gif) E27.046
E27.046![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.047]](../ps.gif) E27.047
E27.047![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.048]](../ps.gif) E27.048
E27.048![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.049]](../ps.gif) E27.049
E27.049![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.05]](../ps.gif) E27.05
E27.05![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.051]](../ps.gif) E27.051
E27.051![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.052]](../ps.gif) E27.052
E27.052![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.053]](../ps.gif) E27.053
E27.053![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.054]](../ps.gif) E27.054
E27.054![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.055]](../ps.gif) E27.055
E27.055![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.056]](../ps.gif) E27.056
E27.056![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.057]](../ps.gif) E27.057
E27.057![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.058]](../ps.gif) E27.058
E27.058![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.059]](../ps.gif) E27.059
E27.059![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.06]](../ps.gif) E27.06
E27.06![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.061]](../ps.gif) E27.061
E27.061![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.062]](../ps.gif) E27.062
E27.062![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.063]](../ps.gif) E27.063
E27.063![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.064]](../ps.gif) E27.064
E27.064![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.065]](../ps.gif) E27.065
E27.065![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.066]](../ps.gif) E27.066
E27.066![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.067]](../ps.gif) E27.067
E27.067![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.068]](../ps.gif) E27.068
E27.068![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.069]](../ps.gif) E27.069
E27.069![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.07]](../ps.gif) E27.07
E27.07![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.071]](../ps.gif) E27.071
E27.071![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.072]](../ps.gif) E27.072
E27.072![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.073]](../ps.gif) E27.073
E27.073![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.074]](../ps.gif) E27.074
E27.074![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.075]](../ps.gif) E27.075
E27.075![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.076]](../ps.gif) E27.076
E27.076![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.077]](../ps.gif) E27.077
E27.077![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.078]](../ps.gif) E27.078
E27.078![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.079]](../ps.gif) E27.079
E27.079![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.08]](../ps.gif) E27.08
E27.08![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.081]](../ps.gif) E27.081
E27.081![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.082]](../ps.gif) E27.082
E27.082![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.083]](../ps.gif) E27.083
E27.083![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.084]](../ps.gif) E27.084
E27.084![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.085]](../ps.gif) E27.085
E27.085![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.086]](../ps.gif) E27.086
E27.086![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.087]](../ps.gif) E27.087
E27.087![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.088]](../ps.gif) E27.088
E27.088![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.089]](../ps.gif) E27.089
E27.089![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.09]](../ps.gif) E27.09
E27.09![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.091]](../ps.gif) E27.091
E27.091![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.092]](../ps.gif) E27.092
E27.092![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.093]](../ps.gif) E27.093
E27.093![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.094]](../ps.gif) E27.094
E27.094![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.095]](../ps.gif) E27.095
E27.095![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.096]](../ps.gif) E27.096
E27.096![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.097]](../ps.gif) E27.097
E27.097![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.098]](../ps.gif) E27.098
E27.098![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.099]](../ps.gif) E27.099
E27.099![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.1]](../ps.gif) E27.1
E27.1![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.101]](../ps.gif) E27.101
E27.101![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.102]](../ps.gif) E27.102
E27.102![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.103]](../ps.gif) E27.103
E27.103![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.104]](../ps.gif) E27.104
E27.104![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.105]](../ps.gif) E27.105
E27.105![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.106]](../ps.gif) E27.106
E27.106![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.107]](../ps.gif) E27.107
E27.107![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.108]](../ps.gif) E27.108
E27.108![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.109]](../ps.gif) E27.109
E27.109![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.11]](../ps.gif) E27.11
E27.11![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.111]](../ps.gif) E27.111
E27.111![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.112]](../ps.gif) E27.112
E27.112![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.113]](../ps.gif) E27.113
E27.113![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.114]](../ps.gif) E27.114
E27.114![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.115]](../ps.gif) E27.115
E27.115![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.116]](../ps.gif) E27.116
E27.116![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.117]](../ps.gif) E27.117
E27.117![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.118]](../ps.gif) E27.118
E27.118![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.119]](../ps.gif) E27.119
E27.119![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.12]](../ps.gif) E27.12
E27.12![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.121]](../ps.gif) E27.121
E27.121![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.122]](../ps.gif) E27.122
E27.122![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.123]](../ps.gif) E27.123
E27.123![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.124]](../ps.gif) E27.124
E27.124![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.125]](../ps.gif) E27.125
E27.125![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.126]](../ps.gif) E27.126
E27.126![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.127]](../ps.gif) E27.127
E27.127![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.128]](../ps.gif) E27.128
E27.128![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.129]](../ps.gif) E27.129
E27.129![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.13]](../ps.gif) E27.13
E27.13![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.131]](../ps.gif) E27.131
E27.131![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.132]](../ps.gif) E27.132
E27.132![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.133]](../ps.gif) E27.133
E27.133![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.134]](../ps.gif) E27.134
E27.134![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.135]](../ps.gif) E27.135
E27.135![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.136]](../ps.gif) E27.136
E27.136![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.137]](../ps.gif) E27.137
E27.137![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.138]](../ps.gif) E27.138
E27.138![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.139]](../ps.gif) E27.139
E27.139![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.14]](../ps.gif) E27.14
E27.14![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.141]](../ps.gif) E27.141
E27.141![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.142]](../ps.gif) E27.142
E27.142![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.143]](../ps.gif) E27.143
E27.143![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.144]](../ps.gif) E27.144
E27.144![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.145]](../ps.gif) E27.145
E27.145![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.146]](../ps.gif) E27.146
E27.146![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.147]](../ps.gif) E27.147
E27.147![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.148]](../ps.gif) E27.148
E27.148![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.149]](../ps.gif) E27.149
E27.149![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.15]](../ps.gif) E27.15
E27.15![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.151]](../ps.gif) E27.151
E27.151![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.152]](../ps.gif) E27.152
E27.152![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.153]](../ps.gif) E27.153
E27.153![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.154]](../ps.gif) E27.154
E27.154![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.155]](../ps.gif) E27.155
E27.155![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.156]](../ps.gif) E27.156
E27.156![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.157]](../ps.gif) E27.157
E27.157![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.158]](../ps.gif) E27.158
E27.158![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.159]](../ps.gif) E27.159
E27.159![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.16]](../ps.gif) E27.16
E27.16![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.161]](../ps.gif) E27.161
E27.161![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.162]](../ps.gif) E27.162
E27.162![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E27.163]](../ps.gif) E27.163
E27.163![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.001]](../ps.gif) E29.001
E29.001![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.002]](../ps.gif) E29.002
E29.002![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.003]](../ps.gif) E29.003
E29.003![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.004]](../ps.gif) E29.004
E29.004![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.005]](../ps.gif) E29.005
E29.005![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.006]](../ps.gif) E29.006
E29.006![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.007]](../ps.gif) E29.007
E29.007![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.008]](../ps.gif) E29.008
E29.008![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.009]](../ps.gif) E29.009
E29.009![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.01]](../ps.gif) E29.01
E29.01![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.011]](../ps.gif) E29.011
E29.011![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.012]](../ps.gif) E29.012
E29.012![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.013]](../ps.gif) E29.013
E29.013![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.014]](../ps.gif) E29.014
E29.014![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.015]](../ps.gif) E29.015
E29.015![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.016]](../ps.gif) E29.016
E29.016![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.017]](../ps.gif) E29.017
E29.017![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.018]](../ps.gif) E29.018
E29.018![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.019]](../ps.gif) E29.019
E29.019![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.02]](../ps.gif) E29.02
E29.02![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.021]](../ps.gif) E29.021
E29.021![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.022]](../ps.gif) E29.022
E29.022![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.023]](../ps.gif) E29.023
E29.023![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.024]](../ps.gif) E29.024
E29.024![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.025]](../ps.gif) E29.025
E29.025![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.026]](../ps.gif) E29.026
E29.026![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.027]](../ps.gif) E29.027
E29.027![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.028]](../ps.gif) E29.028
E29.028![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.029]](../ps.gif) E29.029
E29.029![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.03]](../ps.gif) E29.03
E29.03![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.031]](../ps.gif) E29.031
E29.031![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.032]](../ps.gif) E29.032
E29.032![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.033]](../ps.gif) E29.033
E29.033![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.034]](../ps.gif) E29.034
E29.034![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.035]](../ps.gif) E29.035
E29.035![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.036]](../ps.gif) E29.036
E29.036![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.037]](../ps.gif) E29.037
E29.037![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.038]](../ps.gif) E29.038
E29.038![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.039]](../ps.gif) E29.039
E29.039![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.04]](../ps.gif) E29.04
E29.04![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.041]](../ps.gif) E29.041
E29.041![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.042]](../ps.gif) E29.042
E29.042![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.043]](../ps.gif) E29.043
E29.043![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.044]](../ps.gif) E29.044
E29.044![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.045]](../ps.gif) E29.045
E29.045![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.046]](../ps.gif) E29.046
E29.046![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.047]](../ps.gif) E29.047
E29.047![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.048]](../ps.gif) E29.048
E29.048![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.049]](../ps.gif) E29.049
E29.049![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.05]](../ps.gif) E29.05
E29.05![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.051]](../ps.gif) E29.051
E29.051![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.052]](../ps.gif) E29.052
E29.052![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.053]](../ps.gif) E29.053
E29.053![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.054]](../ps.gif) E29.054
E29.054![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.055]](../ps.gif) E29.055
E29.055![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.056]](../ps.gif) E29.056
E29.056![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.057]](../ps.gif) E29.057
E29.057![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.058]](../ps.gif) E29.058
E29.058![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.059]](../ps.gif) E29.059
E29.059![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.06]](../ps.gif) E29.06
E29.06![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.061]](../ps.gif) E29.061
E29.061![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.062]](../ps.gif) E29.062
E29.062![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.063]](../ps.gif) E29.063
E29.063![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.064]](../ps.gif) E29.064
E29.064![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.065]](../ps.gif) E29.065
E29.065![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.066]](../ps.gif) E29.066
E29.066![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.067]](../ps.gif) E29.067
E29.067![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.068]](../ps.gif) E29.068
E29.068![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.069]](../ps.gif) E29.069
E29.069![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.07]](../ps.gif) E29.07
E29.07![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.071]](../ps.gif) E29.071
E29.071![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.072]](../ps.gif) E29.072
E29.072![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.073]](../ps.gif) E29.073
E29.073![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.074]](../ps.gif) E29.074
E29.074![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.075]](../ps.gif) E29.075
E29.075![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.076]](../ps.gif) E29.076
E29.076![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.077]](../ps.gif) E29.077
E29.077![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.078]](../ps.gif) E29.078
E29.078![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.079]](../ps.gif) E29.079
E29.079![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.08]](../ps.gif) E29.08
E29.08![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.081]](../ps.gif) E29.081
E29.081![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.082]](../ps.gif) E29.082
E29.082![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.083]](../ps.gif) E29.083
E29.083![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.084]](../ps.gif) E29.084
E29.084![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.085]](../ps.gif) E29.085
E29.085![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.086]](../ps.gif) E29.086
E29.086![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.087]](../ps.gif) E29.087
E29.087![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.088]](../ps.gif) E29.088
E29.088![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.089]](../ps.gif) E29.089
E29.089![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.09]](../ps.gif) E29.09
E29.09![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.091]](../ps.gif) E29.091
E29.091![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.092]](../ps.gif) E29.092
E29.092![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.093]](../ps.gif) E29.093
E29.093![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.094]](../ps.gif) E29.094
E29.094![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.095]](../ps.gif) E29.095
E29.095![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.096]](../ps.gif) E29.096
E29.096![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.097]](../ps.gif) E29.097
E29.097![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.098]](../ps.gif) E29.098
E29.098![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.099]](../ps.gif) E29.099
E29.099![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.1]](../ps.gif) E29.1
E29.1![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.101]](../ps.gif) E29.101
E29.101![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.102]](../ps.gif) E29.102
E29.102![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.103]](../ps.gif) E29.103
E29.103![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.104]](../ps.gif) E29.104
E29.104![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.105]](../ps.gif) E29.105
E29.105![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.106]](../ps.gif) E29.106
E29.106![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.107]](../ps.gif) E29.107
E29.107![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.108]](../ps.gif) E29.108
E29.108![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.109]](../ps.gif) E29.109
E29.109![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.11]](../ps.gif) E29.11
E29.11![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.111]](../ps.gif) E29.111
E29.111![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.112]](../ps.gif) E29.112
E29.112![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.113]](../ps.gif) E29.113
E29.113![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.114]](../ps.gif) E29.114
E29.114![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.115]](../ps.gif) E29.115
E29.115![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.116]](../ps.gif) E29.116
E29.116![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.117]](../ps.gif) E29.117
E29.117![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.118]](../ps.gif) E29.118
E29.118![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.119]](../ps.gif) E29.119
E29.119![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.12]](../ps.gif) E29.12
E29.12![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.121]](../ps.gif) E29.121
E29.121![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.122]](../ps.gif) E29.122
E29.122![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.123]](../ps.gif) E29.123
E29.123![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.124]](../ps.gif) E29.124
E29.124![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.125]](../ps.gif) E29.125
E29.125![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.126]](../ps.gif) E29.126
E29.126![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.127]](../ps.gif) E29.127
E29.127![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.128]](../ps.gif) E29.128
E29.128![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.129]](../ps.gif) E29.129
E29.129![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.13]](../ps.gif) E29.13
E29.13![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.131]](../ps.gif) E29.131
E29.131![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.132]](../ps.gif) E29.132
E29.132![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.133]](../ps.gif) E29.133
E29.133![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.134]](../ps.gif) E29.134
E29.134![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.135]](../ps.gif) E29.135
E29.135![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.136]](../ps.gif) E29.136
E29.136![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.137]](../ps.gif) E29.137
E29.137![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.138]](../ps.gif) E29.138
E29.138![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.139]](../ps.gif) E29.139
E29.139![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.14]](../ps.gif) E29.14
E29.14![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.141]](../ps.gif) E29.141
E29.141![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.142]](../ps.gif) E29.142
E29.142![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.143]](../ps.gif) E29.143
E29.143![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.144]](../ps.gif) E29.144
E29.144![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.145]](../ps.gif) E29.145
E29.145![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.146]](../ps.gif) E29.146
E29.146![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.147]](../ps.gif) E29.147
E29.147![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.148]](../ps.gif) E29.148
E29.148![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.149]](../ps.gif) E29.149
E29.149![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.15]](../ps.gif) E29.15
E29.15![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.151]](../ps.gif) E29.151
E29.151![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.152]](../ps.gif) E29.152
E29.152![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.154]](../ps.gif) E29.154
E29.154![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.155]](../ps.gif) E29.155
E29.155![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.156]](../ps.gif) E29.156
E29.156![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.157]](../ps.gif) E29.157
E29.157![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.158]](../ps.gif) E29.158
E29.158![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.159]](../ps.gif) E29.159
E29.159![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.16]](../ps.gif) E29.16
E29.16![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.161]](../ps.gif) E29.161
E29.161![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.162]](../ps.gif) E29.162
E29.162![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.164]](../ps.gif) E29.164
E29.164![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.165]](../ps.gif) E29.165
E29.165![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.166]](../ps.gif) E29.166
E29.166![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.167]](../ps.gif) E29.167
E29.167![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.168]](../ps.gif) E29.168
E29.168![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.169]](../ps.gif) E29.169
E29.169![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.17]](../ps.gif) E29.17
E29.17![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.171]](../ps.gif) E29.171
E29.171![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.172]](../ps.gif) E29.172
E29.172![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.173]](../ps.gif) E29.173
E29.173![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.174]](../ps.gif) E29.174
E29.174![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.175]](../ps.gif) E29.175
E29.175![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.176]](../ps.gif) E29.176
E29.176![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.177]](../ps.gif) E29.177
E29.177![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.178]](../ps.gif) E29.178
E29.178![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.179]](../ps.gif) E29.179
E29.179![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.18]](../ps.gif) E29.18
E29.18![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.181]](../ps.gif) E29.181
E29.181![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.182]](../ps.gif) E29.182
E29.182![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.183]](../ps.gif) E29.183
E29.183![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.184]](../ps.gif) E29.184
E29.184![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.185]](../ps.gif) E29.185
E29.185![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.186]](../ps.gif) E29.186
E29.186![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.187]](../ps.gif) E29.187
E29.187![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.188]](../ps.gif) E29.188
E29.188![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.189]](../ps.gif) E29.189
E29.189![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.19]](../ps.gif) E29.19
E29.19![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.191]](../ps.gif) E29.191
E29.191![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.192]](../ps.gif) E29.192
E29.192![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.193]](../ps.gif) E29.193
E29.193![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.194]](../ps.gif) E29.194
E29.194![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.195]](../ps.gif) E29.195
E29.195![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.196]](../ps.gif) E29.196
E29.196![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.197]](../ps.gif) E29.197
E29.197![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.198]](../ps.gif) E29.198
E29.198![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.199]](../ps.gif) E29.199
E29.199![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.2]](../ps.gif) E29.2
E29.2![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.201]](../ps.gif) E29.201
E29.201![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.202]](../ps.gif) E29.202
E29.202![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.211]](../ps.gif) E29.211
E29.211![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.212]](../ps.gif) E29.212
E29.212![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.213]](../ps.gif) E29.213
E29.213![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.214]](../ps.gif) E29.214
E29.214![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.215]](../ps.gif) E29.215
E29.215![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.216]](../ps.gif) E29.216
E29.216![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.217]](../ps.gif) E29.217
E29.217![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.218]](../ps.gif) E29.218
E29.218![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.219]](../ps.gif) E29.219
E29.219![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.22]](../ps.gif) E29.22
E29.22![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.221]](../ps.gif) E29.221
E29.221![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.222]](../ps.gif) E29.222
E29.222![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.223]](../ps.gif) E29.223
E29.223![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.224]](../ps.gif) E29.224
E29.224![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.225]](../ps.gif) E29.225
E29.225![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.226]](../ps.gif) E29.226
E29.226![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.227]](../ps.gif) E29.227
E29.227![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.228]](../ps.gif) E29.228
E29.228![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.229]](../ps.gif) E29.229
E29.229![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.23]](../ps.gif) E29.23
E29.23![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.231]](../ps.gif) E29.231
E29.231![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.232]](../ps.gif) E29.232
E29.232![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.233]](../ps.gif) E29.233
E29.233![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.234]](../ps.gif) E29.234
E29.234![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.235]](../ps.gif) E29.235
E29.235![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.236]](../ps.gif) E29.236
E29.236![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.237]](../ps.gif) E29.237
E29.237![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.238]](../ps.gif) E29.238
E29.238![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.239]](../ps.gif) E29.239
E29.239![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.24]](../ps.gif) E29.24
E29.24![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.241]](../ps.gif) E29.241
E29.241![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.242]](../ps.gif) E29.242
E29.242![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.243]](../ps.gif) E29.243
E29.243![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.244]](../ps.gif) E29.244
E29.244![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.245]](../ps.gif) E29.245
E29.245![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.246]](../ps.gif) E29.246
E29.246![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.247]](../ps.gif) E29.247
E29.247![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.248]](../ps.gif) E29.248
E29.248![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.249]](../ps.gif) E29.249
E29.249![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.25]](../ps.gif) E29.25
E29.25![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.251]](../ps.gif) E29.251
E29.251![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.252]](../ps.gif) E29.252
E29.252![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.253]](../ps.gif) E29.253
E29.253![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.254]](../ps.gif) E29.254
E29.254![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.255]](../ps.gif) E29.255
E29.255![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.256]](../ps.gif) E29.256
E29.256![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.257]](../ps.gif) E29.257
E29.257![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.258]](../ps.gif) E29.258
E29.258![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.259]](../ps.gif) E29.259
E29.259![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.26]](../ps.gif) E29.26
E29.26![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.261]](../ps.gif) E29.261
E29.261![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.262]](../ps.gif) E29.262
E29.262![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.263]](../ps.gif) E29.263
E29.263![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.264]](../ps.gif) E29.264
E29.264![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.265]](../ps.gif) E29.265
E29.265![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.266]](../ps.gif) E29.266
E29.266![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.267]](../ps.gif) E29.267
E29.267![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.268]](../ps.gif) E29.268
E29.268![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.269]](../ps.gif) E29.269
E29.269![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.27]](../ps.gif) E29.27
E29.27![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.271]](../ps.gif) E29.271
E29.271![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.272]](../ps.gif) E29.272
E29.272![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.273]](../ps.gif) E29.273
E29.273![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.274]](../ps.gif) E29.274
E29.274![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.275]](../ps.gif) E29.275
E29.275![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.276]](../ps.gif) E29.276
E29.276![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.277]](../ps.gif) E29.277
E29.277![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.278]](../ps.gif) E29.278
E29.278![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.279]](../ps.gif) E29.279
E29.279![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.28]](../ps.gif) E29.28
E29.28![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.281]](../ps.gif) E29.281
E29.281![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.282]](../ps.gif) E29.282
E29.282![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.283]](../ps.gif) E29.283
E29.283![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.284]](../ps.gif) E29.284
E29.284![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.285]](../ps.gif) E29.285
E29.285![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.286]](../ps.gif) E29.286
E29.286![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.287]](../ps.gif) E29.287
E29.287![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.288]](../ps.gif) E29.288
E29.288![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.289]](../ps.gif) E29.289
E29.289![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.29]](../ps.gif) E29.29
E29.29![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.291]](../ps.gif) E29.291
E29.291![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.292]](../ps.gif) E29.292
E29.292![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.293]](../ps.gif) E29.293
E29.293![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.294]](../ps.gif) E29.294
E29.294![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.295]](../ps.gif) E29.295
E29.295![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.296]](../ps.gif) E29.296
E29.296![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.297]](../ps.gif) E29.297
E29.297![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.298]](../ps.gif) E29.298
E29.298![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.299]](../ps.gif) E29.299
E29.299![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.3]](../ps.gif) E29.3
E29.3![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.301]](../ps.gif) E29.301
E29.301![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.302]](../ps.gif) E29.302
E29.302![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.303]](../ps.gif) E29.303
E29.303![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.304]](../ps.gif) E29.304
E29.304![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.305]](../ps.gif) E29.305
E29.305![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.306]](../ps.gif) E29.306
E29.306![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.307]](../ps.gif) E29.307
E29.307![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.308]](../ps.gif) E29.308
E29.308![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.309]](../ps.gif) E29.309
E29.309![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.31]](../ps.gif) E29.31
E29.31![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.311]](../ps.gif) E29.311
E29.311![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.312]](../ps.gif) E29.312
E29.312![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.313]](../ps.gif) E29.313
E29.313![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.314]](../ps.gif) E29.314
E29.314![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.315]](../ps.gif) E29.315
E29.315![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.316]](../ps.gif) E29.316
E29.316![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.317]](../ps.gif) E29.317
E29.317![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.318]](../ps.gif) E29.318
E29.318![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.319]](../ps.gif) E29.319
E29.319![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.32]](../ps.gif) E29.32
E29.32![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.321]](../ps.gif) E29.321
E29.321![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.322]](../ps.gif) E29.322
E29.322![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.323]](../ps.gif) E29.323
E29.323![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.324]](../ps.gif) E29.324
E29.324![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.325]](../ps.gif) E29.325
E29.325![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.326]](../ps.gif) E29.326
E29.326![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.327]](../ps.gif) E29.327
E29.327![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.328]](../ps.gif) E29.328
E29.328![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.329]](../ps.gif) E29.329
E29.329![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.33]](../ps.gif) E29.33
E29.33![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.331]](../ps.gif) E29.331
E29.331![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.332]](../ps.gif) E29.332
E29.332![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.333]](../ps.gif) E29.333
E29.333![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.334]](../ps.gif) E29.334
E29.334![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.335]](../ps.gif) E29.335
E29.335![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.336]](../ps.gif) E29.336
E29.336![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.337]](../ps.gif) E29.337
E29.337![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.338]](../ps.gif) E29.338
E29.338![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.339]](../ps.gif) E29.339
E29.339![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.34]](../ps.gif) E29.34
E29.34![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.341]](../ps.gif) E29.341
E29.341![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.342]](../ps.gif) E29.342
E29.342![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.343]](../ps.gif) E29.343
E29.343![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.344]](../ps.gif) E29.344
E29.344![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.345]](../ps.gif) E29.345
E29.345![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.346]](../ps.gif) E29.346
E29.346![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E29.347]](../ps.gif) E29.347
E29.347![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.001]](../ps.gif) E31.001
E31.001![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.002]](../ps.gif) E31.002
E31.002![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.003]](../ps.gif) E31.003
E31.003![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.004]](../ps.gif) E31.004
E31.004![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.005]](../ps.gif) E31.005
E31.005![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.006]](../ps.gif) E31.006
E31.006![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.007]](../ps.gif) E31.007
E31.007![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.008]](../ps.gif) E31.008
E31.008![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.009]](../ps.gif) E31.009
E31.009![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.01]](../ps.gif) E31.01
E31.01![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.011]](../ps.gif) E31.011
E31.011![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.012]](../ps.gif) E31.012
E31.012![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.013]](../ps.gif) E31.013
E31.013![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.014]](../ps.gif) E31.014
E31.014![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.015]](../ps.gif) E31.015
E31.015![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.016]](../ps.gif) E31.016
E31.016![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.017]](../ps.gif) E31.017
E31.017![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.018]](../ps.gif) E31.018
E31.018![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.019]](../ps.gif) E31.019
E31.019![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.02]](../ps.gif) E31.02
E31.02![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.021]](../ps.gif) E31.021
E31.021![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.022]](../ps.gif) E31.022
E31.022![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.023]](../ps.gif) E31.023
E31.023![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.024]](../ps.gif) E31.024
E31.024![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.025]](../ps.gif) E31.025
E31.025![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.026]](../ps.gif) E31.026
E31.026![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.027]](../ps.gif) E31.027
E31.027![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.028]](../ps.gif) E31.028
E31.028![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.029]](../ps.gif) E31.029
E31.029![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.03]](../ps.gif) E31.03
E31.03![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.031]](../ps.gif) E31.031
E31.031![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.032]](../ps.gif) E31.032
E31.032![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.033]](../ps.gif) E31.033
E31.033![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.034]](../ps.gif) E31.034
E31.034![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.035]](../ps.gif) E31.035
E31.035![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.036]](../ps.gif) E31.036
E31.036![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.037]](../ps.gif) E31.037
E31.037![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.038]](../ps.gif) E31.038
E31.038![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.039]](../ps.gif) E31.039
E31.039![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.04]](../ps.gif) E31.04
E31.04![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.041]](../ps.gif) E31.041
E31.041![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.042]](../ps.gif) E31.042
E31.042![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.043]](../ps.gif) E31.043
E31.043![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.044]](../ps.gif) E31.044
E31.044![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.045]](../ps.gif) E31.045
E31.045![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.046]](../ps.gif) E31.046
E31.046![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.047]](../ps.gif) E31.047
E31.047![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.048]](../ps.gif) E31.048
E31.048![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.049]](../ps.gif) E31.049
E31.049![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.05]](../ps.gif) E31.05
E31.05![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.051]](../ps.gif) E31.051
E31.051![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.052]](../ps.gif) E31.052
E31.052![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.053]](../ps.gif) E31.053
E31.053![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.054]](../ps.gif) E31.054
E31.054![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.055]](../ps.gif) E31.055
E31.055![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.056]](../ps.gif) E31.056
E31.056![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.057]](../ps.gif) E31.057
E31.057![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.058]](../ps.gif) E31.058
E31.058![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.059]](../ps.gif) E31.059
E31.059![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.06]](../ps.gif) E31.06
E31.06![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.061]](../ps.gif) E31.061
E31.061![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.062]](../ps.gif) E31.062
E31.062![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.063]](../ps.gif) E31.063
E31.063![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.064]](../ps.gif) E31.064
E31.064![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.065]](../ps.gif) E31.065
E31.065![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.066]](../ps.gif) E31.066
E31.066![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.067]](../ps.gif) E31.067
E31.067![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.068]](../ps.gif) E31.068
E31.068![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.069]](../ps.gif) E31.069
E31.069![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.07]](../ps.gif) E31.07
E31.07![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.071]](../ps.gif) E31.071
E31.071![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.072]](../ps.gif) E31.072
E31.072![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.073]](../ps.gif) E31.073
E31.073![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.074]](../ps.gif) E31.074
E31.074![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.075]](../ps.gif) E31.075
E31.075![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.076]](../ps.gif) E31.076
E31.076![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.077]](../ps.gif) E31.077
E31.077![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.078]](../ps.gif) E31.078
E31.078![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.079]](../ps.gif) E31.079
E31.079![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.08]](../ps.gif) E31.08
E31.08![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.081]](../ps.gif) E31.081
E31.081![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.082]](../ps.gif) E31.082
E31.082![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.083]](../ps.gif) E31.083
E31.083![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.084]](../ps.gif) E31.084
E31.084![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.085]](../ps.gif) E31.085
E31.085![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.086]](../ps.gif) E31.086
E31.086![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.087]](../ps.gif) E31.087
E31.087![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.088]](../ps.gif) E31.088
E31.088![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.089]](../ps.gif) E31.089
E31.089![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.09]](../ps.gif) E31.09
E31.09![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.091]](../ps.gif) E31.091
E31.091![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.092]](../ps.gif) E31.092
E31.092![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.093]](../ps.gif) E31.093
E31.093![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.094]](../ps.gif) E31.094
E31.094![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.095]](../ps.gif) E31.095
E31.095![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.096]](../ps.gif) E31.096
E31.096![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.097]](../ps.gif) E31.097
E31.097![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.098]](../ps.gif) E31.098
E31.098![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.099]](../ps.gif) E31.099
E31.099![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.1]](../ps.gif) E31.1
E31.1![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.101]](../ps.gif) E31.101
E31.101![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.102]](../ps.gif) E31.102
E31.102![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.103]](../ps.gif) E31.103
E31.103![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.104]](../ps.gif) E31.104
E31.104![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.105]](../ps.gif) E31.105
E31.105![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.106]](../ps.gif) E31.106
E31.106![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.107]](../ps.gif) E31.107
E31.107![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.108]](../ps.gif) E31.108
E31.108![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.109]](../ps.gif) E31.109
E31.109![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.11]](../ps.gif) E31.11
E31.11![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.111]](../ps.gif) E31.111
E31.111![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.112]](../ps.gif) E31.112
E31.112![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.113]](../ps.gif) E31.113
E31.113![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.114]](../ps.gif) E31.114
E31.114![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.115]](../ps.gif) E31.115
E31.115![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.116]](../ps.gif) E31.116
E31.116![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.117]](../ps.gif) E31.117
E31.117![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.118]](../ps.gif) E31.118
E31.118![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.119]](../ps.gif) E31.119
E31.119![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.12]](../ps.gif) E31.12
E31.12![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.121]](../ps.gif) E31.121
E31.121![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.122]](../ps.gif) E31.122
E31.122![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.123]](../ps.gif) E31.123
E31.123![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.124]](../ps.gif) E31.124
E31.124![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.125]](../ps.gif) E31.125
E31.125![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.126]](../ps.gif) E31.126
E31.126![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.127]](../ps.gif) E31.127
E31.127![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.128]](../ps.gif) E31.128
E31.128![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.129]](../ps.gif) E31.129
E31.129![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.13]](../ps.gif) E31.13
E31.13![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E31.131]](../ps.gif) E31.131
E31.131![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.001]](../ps.gif) E33.001
E33.001![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.002]](../ps.gif) E33.002
E33.002![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.003]](../ps.gif) E33.003
E33.003![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.004]](../ps.gif) E33.004
E33.004![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.005]](../ps.gif) E33.005
E33.005![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.006]](../ps.gif) E33.006
E33.006![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.007]](../ps.gif) E33.007
E33.007![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.008]](../ps.gif) E33.008
E33.008![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.009]](../ps.gif) E33.009
E33.009![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.01]](../ps.gif) E33.01
E33.01![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.011]](../ps.gif) E33.011
E33.011![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.012]](../ps.gif) E33.012
E33.012![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.013]](../ps.gif) E33.013
E33.013![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.014]](../ps.gif) E33.014
E33.014![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.015]](../ps.gif) E33.015
E33.015![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.016]](../ps.gif) E33.016
E33.016![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.017]](../ps.gif) E33.017
E33.017![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.018]](../ps.gif) E33.018
E33.018![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.019]](../ps.gif) E33.019
E33.019![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.02]](../ps.gif) E33.02
E33.02![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.021]](../ps.gif) E33.021
E33.021![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.022]](../ps.gif) E33.022
E33.022![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.023]](../ps.gif) E33.023
E33.023![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.024]](../ps.gif) E33.024
E33.024![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.025]](../ps.gif) E33.025
E33.025![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.026]](../ps.gif) E33.026
E33.026![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.027]](../ps.gif) E33.027
E33.027![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.028]](../ps.gif) E33.028
E33.028![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.029]](../ps.gif) E33.029
E33.029![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.03]](../ps.gif) E33.03
E33.03![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.031]](../ps.gif) E33.031
E33.031![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.032]](../ps.gif) E33.032
E33.032![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.033]](../ps.gif) E33.033
E33.033![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.034]](../ps.gif) E33.034
E33.034![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.035]](../ps.gif) E33.035
E33.035![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.036]](../ps.gif) E33.036
E33.036![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.037]](../ps.gif) E33.037
E33.037![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.038]](../ps.gif) E33.038
E33.038![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.039]](../ps.gif) E33.039
E33.039![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.04]](../ps.gif) E33.04
E33.04![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.041]](../ps.gif) E33.041
E33.041![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.042]](../ps.gif) E33.042
E33.042![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.043]](../ps.gif) E33.043
E33.043![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.044]](../ps.gif) E33.044
E33.044![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.045]](../ps.gif) E33.045
E33.045![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.046]](../ps.gif) E33.046
E33.046![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.047]](../ps.gif) E33.047
E33.047![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.048]](../ps.gif) E33.048
E33.048![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.049]](../ps.gif) E33.049
E33.049![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.05]](../ps.gif) E33.05
E33.05![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.051]](../ps.gif) E33.051
E33.051![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.052]](../ps.gif) E33.052
E33.052![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.053]](../ps.gif) E33.053
E33.053![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.054]](../ps.gif) E33.054
E33.054![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.055]](../ps.gif) E33.055
E33.055![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.056]](../ps.gif) E33.056
E33.056![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.057]](../ps.gif) E33.057
E33.057![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.058]](../ps.gif) E33.058
E33.058![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.059]](../ps.gif) E33.059
E33.059![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.06]](../ps.gif) E33.06
E33.06![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.061]](../ps.gif) E33.061
E33.061![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.062]](../ps.gif) E33.062
E33.062![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.063]](../ps.gif) E33.063
E33.063![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.064]](../ps.gif) E33.064
E33.064![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.065]](../ps.gif) E33.065
E33.065![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.066]](../ps.gif) E33.066
E33.066![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.067]](../ps.gif) E33.067
E33.067![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.068]](../ps.gif) E33.068
E33.068![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.069]](../ps.gif) E33.069
E33.069![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.07]](../ps.gif) E33.07
E33.07![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.071]](../ps.gif) E33.071
E33.071![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.072]](../ps.gif) E33.072
E33.072![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.073]](../ps.gif) E33.073
E33.073![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.074]](../ps.gif) E33.074
E33.074![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.075]](../ps.gif) E33.075
E33.075![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.076]](../ps.gif) E33.076
E33.076![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E33.077]](../ps.gif) E33.077
E33.077![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E39.001]](../ps.gif) E39.001
E39.001![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E39.002]](../ps.gif) E39.002
E39.002![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E39.003]](../ps.gif) E39.003
E39.003![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E39.004]](../ps.gif) E39.004
E39.004![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E39.005]](../ps.gif) E39.005
E39.005![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E39.006]](../ps.gif) E39.006
E39.006![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E39.007]](../ps.gif) E39.007
E39.007![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E39.008]](../ps.gif) E39.008
E39.008![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E39.009]](../ps.gif) E39.009
E39.009![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E39.01]](../ps.gif) E39.01
E39.01![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E39.011]](../ps.gif) E39.011
E39.011![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E39.012]](../ps.gif) E39.012
E39.012![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E39.013]](../ps.gif) E39.013
E39.013![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E39.014]](../ps.gif) E39.014
E39.014![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E39.015]](../ps.gif) E39.015
E39.015![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E39.016]](../ps.gif) E39.016
E39.016![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E39.017]](../ps.gif) E39.017
E39.017![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E39.018]](../ps.gif) E39.018
E39.018![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E39.019]](../ps.gif) E39.019
E39.019![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E39.02]](../ps.gif) E39.02
E39.02![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E43.001]](../ps.gif) E43.001
E43.001![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E43.002]](../ps.gif) E43.002
E43.002![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E43.003]](../ps.gif) E43.003
E43.003![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E43.004]](../ps.gif) E43.004
E43.004![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E43.005]](../ps.gif) E43.005
E43.005![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E43.006]](../ps.gif) E43.006
E43.006![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E43.007]](../ps.gif) E43.007
E43.007![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E45.001]](../ps.gif) E45.001
E45.001![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E45.002]](../ps.gif) E45.002
E45.002![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E45.003]](../ps.gif) E45.003
E45.003![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E45.004]](../ps.gif) E45.004
E45.004![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E45.005]](../ps.gif) E45.005
E45.005![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E45.006]](../ps.gif) E45.006
E45.006![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E47.001]](../ps.gif) E47.001
E47.001![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E47.002]](../ps.gif) E47.002
E47.002![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E47.003]](../ps.gif) E47.003
E47.003![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E47.004]](../ps.gif) E47.004
E47.004![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E47.005]](../ps.gif) E47.005
E47.005![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E49.001]](../ps.gif) E49.001
E49.001![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E49.002]](../ps.gif) E49.002
E49.002![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E49.003]](../ps.gif) E49.003
E49.003![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E49.004]](../ps.gif) E49.004
E49.004![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.001]](../ps.gif) E51.001
E51.001![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.002]](../ps.gif) E51.002
E51.002![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.003]](../ps.gif) E51.003
E51.003![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.004]](../ps.gif) E51.004
E51.004![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.005]](../ps.gif) E51.005
E51.005![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.006]](../ps.gif) E51.006
E51.006![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.007]](../ps.gif) E51.007
E51.007![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.008]](../ps.gif) E51.008
E51.008![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.009]](../ps.gif) E51.009
E51.009![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.01]](../ps.gif) E51.01
E51.01![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.011]](../ps.gif) E51.011
E51.011![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.012]](../ps.gif) E51.012
E51.012![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.013]](../ps.gif) E51.013
E51.013![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.014]](../ps.gif) E51.014
E51.014![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.015]](../ps.gif) E51.015
E51.015![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.016]](../ps.gif) E51.016
E51.016![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.017]](../ps.gif) E51.017
E51.017![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.018]](../ps.gif) E51.018
E51.018![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.019]](../ps.gif) E51.019
E51.019![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.02]](../ps.gif) E51.02
E51.02![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.021]](../ps.gif) E51.021
E51.021![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.022]](../ps.gif) E51.022
E51.022![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.023]](../ps.gif) E51.023
E51.023![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.024]](../ps.gif) E51.024
E51.024![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.025]](../ps.gif) E51.025
E51.025![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.026]](../ps.gif) E51.026
E51.026![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.027]](../ps.gif) E51.027
E51.027![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.028]](../ps.gif) E51.028
E51.028![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.029]](../ps.gif) E51.029
E51.029![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.03]](../ps.gif) E51.03
E51.03![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.031]](../ps.gif) E51.031
E51.031![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.032]](../ps.gif) E51.032
E51.032![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.033]](../ps.gif) E51.033
E51.033![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.034]](../ps.gif) E51.034
E51.034![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.035]](../ps.gif) E51.035
E51.035![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.036]](../ps.gif) E51.036
E51.036![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.037]](../ps.gif) E51.037
E51.037![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.038]](../ps.gif) E51.038
E51.038![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.039]](../ps.gif) E51.039
E51.039![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.04]](../ps.gif) E51.04
E51.04![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.041]](../ps.gif) E51.041
E51.041![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.042]](../ps.gif) E51.042
E51.042![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.043]](../ps.gif) E51.043
E51.043![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.044]](../ps.gif) E51.044
E51.044![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.045]](../ps.gif) E51.045
E51.045![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.046]](../ps.gif) E51.046
E51.046![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.047]](../ps.gif) E51.047
E51.047![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.048]](../ps.gif) E51.048
E51.048![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.049]](../ps.gif) E51.049
E51.049![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.05]](../ps.gif) E51.05
E51.05![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.051]](../ps.gif) E51.051
E51.051![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass E51.052]](../ps.gif) E51.052
E51.052![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 900]](../ps.gif) 900
900![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 901]](../ps.gif) 901
901![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 902]](../ps.gif) 902
902![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 903]](../ps.gif) 903
903![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 904]](../ps.gif) 904
904![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 905]](../ps.gif) 905
905![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 906]](../ps.gif) 906
906![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 907]](../ps.gif) 907
907![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 908]](../ps.gif) 908
908![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 909]](../ps.gif) 909
909![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 910]](../ps.gif) 910
910![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 911]](../ps.gif) 911
911![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 912]](../ps.gif) 912
912![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 913]](../ps.gif) 913
913![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 914]](../ps.gif) 914
914![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 915]](../ps.gif) 915
915![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 916]](../ps.gif) 916
916![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 917]](../ps.gif) 917
917![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 918]](../ps.gif) 918
918![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 919]](../ps.gif) 919
919![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 920]](../ps.gif) 920
920![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 921]](../ps.gif) 921
921![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 922]](../ps.gif) 922
922![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 923]](../ps.gif) 923
923![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 924]](../ps.gif) 924
924![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 925]](../ps.gif) 925
925![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 926]](../ps.gif) 926
926![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 927]](../ps.gif) 927
927![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 928]](../ps.gif) 928
928![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 929]](../ps.gif) 929
929![[List of Patents for class 257 subclass 930]](../ps.gif) 930
930










