CPC Definition - Subclass H05B
This place covers:
Electric heating
- Heat sources utilising ohmic resistance, electric, magnetic or electromagnetic fields, electric discharge, or combinations thereof;
- Light sources specially adapted for heating, e.g. infrared sources as used in light ovens.
This subclass covers not only the electric elements and circuitry designs but also the electric aspects of their arrangement, where these concern cases of general application.
Electric light sources
This subclass is residual as to electric light sources and covers in particular:
- Electric arc lamps, electroluminescent light sources and light sources using a combination of different types of light generation;
Circuit arrangements
- Circuit arrangements for operating electric light sources.
- Primary circuits, circuit arrangements and circuit elements for operating electric light sources.
Electric Heating
While this subclass covers electric aspects of heating, like electric elements, circuitry designs and their electric arrangement in heating apparatus or devices, the physical disposition of such electric elements as well as any other mechanical aspect of electric heating is covered by the subclasses of F24 and F27. Heating elements used in specific applications are classified in subclasses for those applications.
Electric light sources
This subclass is residual as to electric light sources: see section "References out of residual references" for a list of places covering electric light sources per se. Differently from this subclass, subclasses of class F21 cover the mechanical arrangement of parts including electrical elements, i.e. their geometrical or physical position in relation to one another, such as the structures or constructional features of lighting devices incorporating a light source (be it electric or otherwise).
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Domestic cooking | |
Heating or cooling appliances for medical or therapeutic treatment | |
Radiation therapy using microwaves | |
Forging by heat | |
Joining of preformed parts by heating of plastics or substances in a plastic state | |
Metallurgy | |
Domestic heating and stoves | |
Furnaces and ovens | |
Thermally-actuated switches |
Examples of places in relation to which this place is residual:
Electric light sources
Electric discharge tubes | |
Electric discharge lamps | |
Circuit elements structurally associated with the lighting element of an electric discharge lamp | |
Electric incandescent lamps | |
Laser | |
Plasma torches | |
Semiconductor devices having potential barriers, specially adapted for light emission, e.g. LEDs | |
Organic solid-state devices specially adapted for light emission, e.g. OLEDs or PLEDs |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electric light sources
Measuring characteristics of light; Colorimetry | |
Control of temperature in general | |
Regulating electric characteristics of arcs in general | |
Regulating electric power in general |
In this subclass the use of indexing codes H05B 2203/00 – H05B 2214/04 is mandatory.
This place covers:
General automatic switching arrangements specially adapted to heating applications, when no specific class exist for the particular heating application.
Control of heating devices, when no specific class exist for the particular heating application.
Further information:
H05B 1/0202 relates to automatic switching.
H05B 1/0227 relates to automatic control, classified according to the type of application.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Control of induction heating devices | |
Control of microwave heating devices | |
Control of electric discharge heating devices | |
Bakers' ovens; machines or equipment for baking | |
Industrial microwave ovens | |
Characteristic features of footwear; parts of footwear | |
Heated mirrors | |
Kitchen equipment; coffee mills; spice mills; apparatus for making beverages | |
Dentistry | |
Methods or apparatus for sterilising materials | |
Chemical or physical processes | |
Soldering or welding; cutting by applying heat locally | |
Shaping or joining of plastics | |
Vehicle heating | |
Car seats | |
Heated mirrors for cars | |
Heated windshield window (car) / heated rear window (car) | |
Helicopters de-icing | |
Airplane wings de-icing | |
Containers for storage or transport | |
Pop corn heating | |
Nanotechnology | |
Carbon nanotubes | |
Ceramics | |
Adhesives | |
Heat treatment of metals or alloys | |
Metal-spraying | |
Heating of sport playgrounds | |
Cleaning open waters, e.g. deicing | |
Roofs de-icing | |
Devices for securing together constructional elements or machine parts | |
Pipes; joints or fittings for pipes; supports for pipes or cables | |
Glow plugs | |
Electrical cooker / glow plug / gas cooker | |
Removal of fumes associated to cooking range (or microwave ovens) | |
Domestic- or space-heating systems e.g. central heating | |
Fluid heaters | |
Drying solid materials or objects by removing liquid there from | |
Electric furnaces | |
Details or accessories of furnaces | |
Electrography; electrophotography; magnetography | |
Controlling non-electric variables | |
Control of temperature in general | |
Controlling electric or magnetic variables | |
Resistors; methods of production | |
Electric switches | |
Thermally actuated switches | |
Aerials | |
Connectors | |
Removing snow from cables | |
Electric power conversion | |
Printed circuits | |
Semiconductor devices; methods of production |
This place covers:
Heating by applying a voltage to a material with a certain conductivity, so that an electric current is generated that, according to the resistivity of the material will dissipate energy in form of heat (Joule heating).
Accordingly, the heat can be generated in the same object that needs to be heated. Otherwise, the heat has to be transferred to the object that needs to be heated by a further process of radiation, conduction, or convection.
Further information:
H05B 3/0033- H05B 3/009 deal with heating devices using lamps
H05B 3/06 does not cover connectors (suitable) for heating elements, but covers the particular cases when the heater is structurally combined with the technical means allowing the electrical connection, otherwise only the classification in connectors, i.e. in H01R, applies.
H05B 3/10 deal with heater elements characterised by the composition or nature of the materials or by the arrangement of the conductor.
H05B 3/34 covers car seat heaters.
H05B 3/345 covers any heater to be used in a textile material (even if they are not clothes)
H05B 3/50 covers any car air heater (independently of the structure of the heater).
H05B 3/62-H05B 3/82 only cover electrical details, or details about the generation or transmission of heat. For other mechanical details the corresponding F24 or F27 class applies.
H05B 3/68- H05B 3/76 deal with heating arrangements specially adapted for cooking plates or analogous hot-plates
H05B 3/84 deal with heating arrangements specially adapted for transparent or reflecting areas
Further information about subgroups:
- H05B 3/0033 - H05B 3/009 cover heating devices using lamps.
- H05B 3/10 deal with heater elements characterised by the composition or nature of the materials or by the arrangement of the conductor.
- H05B 3/34 covers car seat heaters.
- H05B 3/345 covers any heater to be used in a textile material (even if they are not clothes).
- H05B 3/50 covers any car air heater (independently of the structure of the heater).
- H05B 3/84 deal with heating arrangements specially adapted for transparent or reflecting areas.
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Electric cigarettes | |
Devices for radiation therapy | |
Electrothermic treatment of ores | |
Ironing | |
Combustion engines heaters | |
Arrangements of heating elements in furnaces | |
Heat exchangers | |
Apparatus for thermal treatment of semiconductor or solid-state devices or of parts thereof |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Aquarium heaters | |
Bakers' ovens; machines or equipment for baking | |
Characteristic features of footwear; parts of footwear | |
Warming plates | |
Heated mirrors | |
Kitchen equipment; coffee mills; spice mills; apparatus for making beverages | |
Dentistry | |
Chemical or physical processes | |
Soldering or welding; cutting by applying heat locally | |
Shaping or joining of plastics | |
Layered products comprising glass | |
Thermal printers | |
Vehicle heating | |
Car seats | |
Heated mirrors (for cars) | |
Heated windshield window (car) / heated rear window (car) | |
Helicopters de-icing | |
Aircraft de-icing | |
Containers for storage or transport | |
Pop corn heating | |
Nanotechnology | |
Carbon nanotubes | |
Surface treatment of glass-plate materials | |
Ceramics | |
Adhesives | |
Heat treatment of metals or alloys | |
Metal-spraying | |
Heating of sport playgrounds | |
Cleaning open waters, e.g. deicing | |
Roofs de-icing | |
Devices for securing together constructional elements or machine parts | |
Pipes; joints or fittings for pipes; supports for pipes or cables | |
Glow plugs | |
Electrical cooker / glow plug / gas cooker | |
Removal of fumes associated to cooking ranges | |
Domestic- or space-heating systems e.g. central heating | |
Air-conditioning | |
Fluid heaters | |
Drying solid materials or objects by removing liquid there from | |
Electric furnaces | |
Details or accessories of furnaces | |
Electrography; electrophotography; magnetography | |
Image fixing devices | |
Controlling non-electric variables | |
Resistors-methods of production | |
Electric switches | |
Gas-filled discharge tubes | |
Aerials | |
Removing snow or ice from cables | |
Removing snow from cables | |
Electric power conversion | |
Printed circuits | |
Semiconductor devices; methods of production |
Usage or orthogonal indexing codes.
- Aspects relating to Ohmic resistive heating covered by group H05B 3/00 are classified in H05B 2203/00 and subgroups.
- Aspects relating to both to resistive heating and to induction heating, covered by H05B 3/00 and H05B 6/00 are classified in H05B 2213/00 and subgroups.
- Aspects relative to resistive heating, induction heating and heating using microwaves, covered by groups H05B 3/00, H05B 6/00 are classified in H05B 2214/00 and subgroups.
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
ELECTROTHERAPY; MAGNETOTHERAPY; RADIATION THERAPY; ULTRASOUND THERAPY |
This place does not cover:
Lamps specially adapted for non-metallic cooking plates |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Radiation therapy |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Non-metallic, non-adjustable resistors |
This place does not cover:
For semi-conductors manufacture |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Apparatus for thermal treatment of semiconductor or solid-state devices or of parts thereof |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Making textile fabrics |
This place does not cover:
Machine tool; metal-working |
This place covers:
- Induction heating
- Dielectric heating
- Microwave heating
Further information:
H05B 6/02 and subgroups relate to induction heating
H05B 6/46 and subgroups relate to dielectric heating
H05B 6/64 and subgroups relate to microwave heating
Control of cooking plates is covered by H05B 6/062. Control of cooking appliances other than cooking plates is covered by H05B 6/06.
Apportioning of the total heating power among the different heating coils is covered by H05B 6/065. Also apportioning in time, e.g. cyclic powering on and off of each heating coil. Also supplying a coil from multiple generators or multiple coils with a controlled amount of power from multiple generators. Also synchronisation, e.g. for avoiding generation of noise, or avoiding electromagnetic interferences. Not simply matrix heating plate per-se.
Induction heating apparatus, other than furnaces, for specific applications are covered by H05B 6/10.
Cooking devices are covered by H05B 6/12 but control of induction cooking devices is covered by H05B 6/06 and continuous movement of food is covered by H05B 6/10.
Induction cooking plates or the like and devices to be used in combination with them are covered by H05B 6/1209, but control for induction cooking plates is covered by H05B 6/062 and ohmic heating plates are covered by H05B 3/68.
H05B 6/1218 deals with induction cooking plates with arrangements using lights for the indication of the state of the heating zones. The typical application deals with the provision of LED's on a cooking area that are switched on when the induction heating power of that cooking area is switched on. Also particular details of the glass ceramic plate in order to achieve such effect, for example cut out, and darken areas to only illuminate the desired portion of the cooking area. Also glass plates having a substance or material sandwiched there inside that will interact with the magnetic field of the induction coils so that light is generated when the corresponding induction coil is switched on.
H05B 6/1227 deals with Induction cooking plates specially designed for wok pans, or similar shaped pans; also wok supports specially adapted for induction cooking (facilitating magnetic field transmission, coils provided inside the support...), cook-tops with wok-shaped upper surface (so substantially concave upper surface), but also cylinder surface with coils from top to bottom; wok is also called Chinese Pan.
H05B 6/1236 deals with Induction cooking plates adapted to induce current in a coil to supply power to a device and electrical heating devices powered in this way, If it is described any of the heating device itself or a particular control of the cook-top to recognise the load and correctly supply it with power. Typically the system acts as a transformer. The heating device is provided with a secondary coil for which the induction coil of the cook-top acts as primary.
H05B 6/1245 deals with induction cooking plates with special coil arrangements. The typical application deals with a particular coil material, coil shape, coil geometry , coil position within the plate or with respect to other coils.
H05B 6/1272 deals with induction cooking plates with more than one coil or coil segment per heating zone. Also when different concentric coils or coil segments or section with different coil distance or winding direction are provided . Also when coils are provided in different planes for the same heating zone.
H05B 6/1281 deals with induction cooking plates with flat coils. This means that the coil as a whole is constructed in a flat distribution, the coil conductor can however present a non-flat section. The typical application deals with coils particularly designed to be have a small total thickness, normally by printing a conductor on a substrate or by having a thin conductor embedded in a substrate. The flatness of the conductor used for the coil is not relevant.
H05B 6/129 deals with induction ovens. These are domestic appliances similar to a kitchen ovens wherein the heating means include at least an induction coil, (possibly in addition to any of the traditional heating means resistance heating, microwave heating, convection heating). Also induction heated trolleys, for catering, for example in airplanes. Also pop-corn machines (provided there is a closable / closed) cavity. Also vending machines in general (provided there is a closable / closed) cavity. Also induction warming drawers or the like (provided there is a closable / closed) cavity. Metal heat-treating apparatus only if there is a closable / closed cavity (therefore if it looks like a domestic oven). This class applies to cooking, de-freezing, warming, heat treating and re-heating appliances (the temperature achieved is unimportant).
H05B 6/14 can be assigned in combination with any of H05B 6/36, H05B 6/101 and H05B 6/105.
H05B 6/1209 takes precedence over H05B 6/34.
H05B 6/36 deals with coil arrangements with flat coil conductors. This means that the conductor used for the coil present a flat section (as a band), but the coil itself can have a (not flat) tri-dimensional distribution.
H05B 6/6402 deals with aspects relating to the microwave cavity but multiple cavity ovens are covered by H05B 6/80, continuous movement of material is covered by H05B 6/78, ovens specially adapted to a particular application are covered by H05B 6/80.
H05B 6/6408 deals with support or covers for the load inside the cavity. Supports or covers including microwave susceptors (e.g. browning plates) are additionally covered by H05B 6/6494.
H05B 6/6414 deals with aspects relating to the door of the microwave heating apparatus but microwave leakage is covered by H05B 6/76, and microwave leakage testing is covered by H05B 6/6432.
H05B 6/6417 deals with door interlocks of the microwave heating apparatus and related circuits. Also door position detecting circuits (e.g. with switches).
H05B 6/642 deals with the cooling of the microwave components and related air circulation systems, however if the refrigerating air is being re-circulated through the cavity for convection heating the class H05B 6/6476 is relevant instead.
H05B 6/6426 deals with any aspect relating to the exterior of the microwave heating apparatus, e.g. metal casing, power cord. Also handles (in portable microwave ovens) to allow carrying the microwave oven. Portable microwave ovens are additionally covered by H05B 6/80.
H05B 6/6432 deals with aspects relating to testing or detecting leakage in a microwave heating apparatus. This means detecting or testing the microwave radiation leaking out of the microwave oven but also microwave switching off upon detection of microwave leakage. Also testing the quality of microwave seals and screens by measuring the microwave leakage. However, detecting leaked or reflected microwaves going back to the magnetron is covered by H05B 6/76.
H05B 6/6447 deals with methods of operation or details of the microwave heating apparatus related to the use of detectors or sensors. However detecting reflected radiation for feedback control purposes is covered by H05B 6/705.
H05B 6/645 deals with the use of temperature sensor or thermistors for detecting the temperature of interior of the cavity or the product placed inside. However detecting the temperature of the magnetron or any related safety aspect is covered by H05B 6/666.
Details of particular circuits or particular components of the microwave generation circuit, e.g. a particular capacitor, a particular inductor... are classified under H05B 6/66 when no other more specific subgroup is provided for.
H05B 6/662 deals with aspects related to the boost transformer of the microwave heating apparatus. However cooling of the boost transformer is covered by H05B 6/642.
H05B 6/666 deals with safety circuits. The general idea in this subgroup is identifying situations where possible damage to the circuits (including inverter and magnetron) can occur. Also simply detecting the temperature of the magnetron/inverter or measuring anode current for limiting control, detecting status or detecting moding and eventually switching off the microwave oven/signalling alarm. Also soft start-up, control of preheating mode, controlled ramp up power supply at start up or at changing power level. However H05B 6/666 does not cover:
- fume or fire detection, covered by H05B 6/6461
- avoiding leakage, covered by H05B 6/76
- sensing leakage outside the microwave oven, covered by H05B 6/6432
- aspects related with door interlocks, even if relating to avoiding over-current at start up, covered by H05B 6/6417
- circuit where a variable (e.g. anode current) is measured on a power supplied feedback control (feedback power control with anode current), covered by H05B 6/683
- circuit for feedback power control with input current or inverter current being measured, covered by H05B 6/685
- avoiding radiation back into the waveguide or in the magnetron, covered by H05B 6/76
- avoiding generation of harmonics, covered by H05B 6/68
H05B 6/68 deals with circuits for monitoring or control. Typically the power supplied is controlled in a feedback loop. Includes monitoring input / output voltage / current / power in a feedback loop. Also if it is described compensation of the cooking time taking account of fluctuations in the power supply, temperature in the cavity or variables of the magnetron. If the presence of an inverter or of a solid state oscillator is not specified then this group is given and not the sub-groups. Also avoiding generation of harmonics. Also ZVS and ZCS.
However H05B 6/68 does not cover:
- limiting threshold control, (keeping a variable bellow a safety threshold value) covered by H05B 6/666
- soft start-up, control of preheating mode, controlled ramp up power supply at start up or at changing power level, covered by H05B 6/666
H05B 6/681 deals with circuits comprising an inverter, a boost transformer and a magnetron. Determinant is the presence of an inverter (there will always be a boost transformer and a magnetron). Includes methods of switching the inverter to regulate power (Duty-Ratio control and Frequency control). However, H05B 6/681 does not cover control based on sensors readings of non electrical variables (e.g. temperature, humidity... inside the cavity), covered by H05B 6/687 and H05B 6/6447.
H05B 6/686 deals with circuits comprising a signal generator and power amplifier, e.g. using solid state oscillators. Determinant is the presence of any of a power amplifier or a solid state oscillator (one implies the other).
H05B 6/687 deals with circuits for monitoring or control for cooking. The general idea is solving the problem of how to bring the cooked product to a certain status. Cooking is to be understood in the broad sense, therefore meaning also simply (re-)heating food or beverages. However, it is not enough the mere mention of cooking. It must be described a method of cooking with different steps in time or upon reaching certain status based on sensors readings. Also if a method of heating a particular type of food is described. H05B 6/688, H05B 6/6435, H05B 6/6447 and H05B 6/647 can be assigned in combination with H05B 6/687. However H05B 6/687 does not cover any of the following:
- a particular apparatus for heating a particular food product covered by H05B 6/80 or H05B 6/782
- switching off upon reaching a certain status for safety reasons covered by H05B 6/666
- circuits controlling the switching of the inverter covered by H05B 6/681
- compensation of the cooking time taking account of fluctuations in the power supply, temperature in the cavity, temperature of the magnetron or age of the magnetron covered by H05B 6/68.
H05B 6/688 is equivalent to H05B 6/687 but for the case of thawing.
H05B 6/70 deals with feed lines. This means the special way of providing microwave radiation to the load (not provided for in the sub-classes), like: application of microwaves using antennas inserted in the load; application of microwaves from multiple directions and/or with different parameters (frequency, phase, power); modification of the cavity (both periodically or according to a feedback control).
H05B 6/701 deals with the use of microwave applicators. It is not enough the mere mention of the word applicator (as any cavity can be called applicator, and this interpretation would be too broad). Typically for continuous movement of material (but not only). The waveguide ends with a particular shape that acts as a resonant cavity. To distinguish from the subject-matter covered by H05B 6/6402, it is considered an applicator when the applicator is a resonant cavity of dimensions similar to those of the waveguide and in this sense the applicator/cavity can be considered a continuation of the waveguide or waveguides.
However, magnetrons providing microwaves directly to the cavity or only using a coaxial cable (so no waveguide) are covered by H05B 6/70 or H05B 6/702.
H05B 6/702 takes precedence over H05B 6/707 and s.gr. when coaxial cables are used in combination with waveguides.
H05B 6/704 deals with the use of microwave polarisers. This includes when there is an explicit description of means for polarising the microwave radiation and also when it is described a method or apparatus where the use of polarised microwave radiation solves a technical problem.
H05B 6/705 deals with the use of microwave tuning. This includes changing the phase of the microwave radiation at the point of entering the cavity. Typically a waveguide with movable parts is used to change the phase of the standing wave generated. Microwave tuning comprises also impedance matching. Also changing the frequency with the intention of obtaining minimal impedance at the input of the cavity (in a feedback loop). Also detecting / sensing / measuring the microwave radiation reflected / not adsorbed, typically to make a feedback control on the power, frequency, phase applied (also with multiple microwave sources).
H05B 6/707 deals with the use of waveguides. Also when multiple waveguides are used.
However, waveguides used in combination with coaxial cables are covered by H05B 6/702.
H05B 6/72 deals with radiators or aerials. Also when multiple antennas are used. Antennas can receive microwaves directly from the magnetron, from a waveguide or from a coaxial cable.
H05B 6/725 deals with rotatable antennas. This also includes microwave stirring devices located inside the waveguide or at the opening of a waveguide to the cavity.
H05B 6/74 deals with mode transformers or mode stirrers. Stirrers are not antennas. The stirrers "only" reflect microwaves coming from the walls of the cavity. Also Cavity with moving walls or changing shape.
However, microwave stirring devices placed inside a waveguide or at the opening of a waveguide to the cavity are covered by H05B 6/72.
H05B 6/76 deals with the prevention of microwave leakage, e.g. door sealings. This includes also screens or deflectors for avoiding radiation back into the waveguide or in the magnetron. Also using dummy loads.
However, detection of microwave leakage is covered by H05B 6/6432.
H05B 6/763 deals with microwave radiation seals for doors.
However, mere air seals are covered by H05B 6/6414.
H05B 6/78 deals with arrangements for the continuous movement of material. However H05B 6/78 does not cover:
- arrangements for heating fluids covered by H05B 6/802
- the invention only refers to the applicator covered by H05B 6/701
H05B 6/782 deals with arrangements for the continuous movement of material wherein the material moved is food. This also includes particular apparatus for cooking / thawing a particular food product. However, H05B 6/782 does not cover:
- method of cooking / Thawing a particular food product in a normal microwave oven covered by H05B 6/687 and H05B 6/688
- the invention only refers to the applicator covered by H05B 6/701
H05B 6/80 deals with microwave apparatus for specific applications. Also particular apparatus for cooking / Thawing a particular food product. Also special type of microwave ovens, (e.g. portable, for vehicles or with DC power supply). Also multiple cavity oven. Also microwave oven with a separate cavity functioning as toaster, eventually in combination with other relevant classes (H05B 6/6414, H05B 6/6402).
However H05B 6/80 does not cover:
- methods of cooking / thawing a particular food product in a normal microwave oven covered by H05B 6/687 or H05B 6/688
- single cavity microwave including additionally radiating means (capable of toasting bread), covered by H05B 6/6482
- continuous movement of material covered by H05B 6/78
H05B 6/802 deals with microwave apparatus for heating fluids.
H05B 6/802 does not cover:
- methods of heating fluids in conventional microwave ovens covered by H05B 6/687
- documents where the invention only refers to the applicator covered by H05B 6/701
H05B 6/806 deals with microwave apparatus for laboratory use. Typically it is mentioned a chemical reactor or similar. H05B 6/806 takes precedence over H05B 6/802.
This place does not cover:
Radiation therapy using microwaves | |
Joining of preformed parts by heating of plastics or substances in a plastic state |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Single-crystal growth by zone-melting or refining by zone-melting using heating of the molten zone by induction, e.g. hot wire technique |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Trolleys with heating, cooling or ventilating means | |
Kitchen equipment of specific material or of particular construction | |
Warming devices with electrical heating means | |
Heat insulated warming chambers for heating food | |
Melt casting nozzles with heating means | |
Soldering | |
Shrink fit tools | |
Joining of preformed parts by heating of plastics or substances in a plastic state | |
Laser engraving of inorganic materials | |
Removing dry paint by electrically heating | |
Sealing of packages by induction welding | |
Containers, packaging elements or packages specially adapted to be heated by microwaves | |
Melting furnaces | |
Glass-plate processing | |
Heat treatment of metals or alloys | |
Refining or remelting of metals | |
Heating of cords using rolls | |
Heating of pipes | |
General details of cooking plates not related to the generation or transmission of heat | |
Transparent panels, e.g. for doors specially adapted for stoves or ranges | |
Tops with provisions of circulation of air | |
Tube through flow heaters | |
Furnaces, kilns, ovens or retorts and details thereof | |
Electro-photography | |
Vending machines in general | |
Inductive couplings | |
Inductive transmission of power in general, not directly related to heating | |
For wireless supply or distribution of electric power |
Usage of orthogonal indexing codes.
- Additional aspects relating to induction heating, as covered by group H05B 6/02, are classified in H05B 2206/00.
- Additional aspects relating to heating, as covered by H05B 6/64, are classified in H05B 2206/02.
- Additional aspects relating to both resistive heating and induction heating, as covered by H05B 3/00 and H05B 6/00, are classified in H05B 2213/00.
- Additional aspects relating to resistive heating, induction heating and microwave heating, as covered by groups H05B 3/00 and H05B 6/00, are classified in H05B 2214/00.
This place covers:
Induction heating apparatus, other than furnaces, for specific applications.
Further information:
H05B 6/101 relates to induction heating apparatus, other than furnaces, for local heating of metal pieces.
H05B 6/105 relates to induction heating apparatus, other than furnaces, for specific applications using a susceptor.
H05B 6/12 relates to induction cooking devices.
H05B 6/14 relates to induction tools, e.g. nozzles, rollers, calenders.
H05B 6/1218 deals with induction cooking plates with arrangements using lights for the indication of the state of the heating zones. The typical application deals with the provision of LED's on a cooking area that are switched on when the induction heating power of that cooking area is switched on.
H05B 6/1227 deals with induction cooking plates specially designed for wok pans, or similar shaped pans, also wok supports specially adapted for induction cooking (facilitating magnetic field transmission, coils provided inside the support), cook-tops with wok-shaped upper surface (so substantially concave upper surface), but also cylinder surface with coils from top to bottom; wok is also called Chinese pan.
H05B 6/1236 deals with induction cooking plates adapted to induce current in a coil to supply power to a device and electrical heating devices. Typically the system acts as a transformer. The heating device is provided with a secondary coil for which the induction coil of the cook-top acts as primary.
H05B 6/1245 deals with induction cooking plates with special coil arrangements. The typical application deals with a particular coil material, coil shape, coil geometry, coil position within the plate or with respect to other coils.
H05B 6/1272 deals with induction cooking plates with more than one coil or coil segment per heating zone. Also different concentric coils or coil segments or section with different coil distance or winding direction are provided in different planes for the same heating zone.
H05B 6/1281 deals with induction cooking plates with flat coils. This means that the coil as a whole is constructed in a flat distribution; the coil conductor can, however, present a non-flat section. The typical application deals with coils particularly designed to be a small total thickness, normally by printing a conductor on a substrate or by having a thin conductor embedded in a substrate. The flatness of the conductor used for the coil is not relevant.
H05B 6/129 deals with induction ovens. These are domestic appliances similar to kitchen ovens wherein the heating means include at least an induction coil (possibly, in addition to any of the traditional heating means resistance heating, microwave heating, convection heating), and also induction heated trolleys, for catering, for example in airplanes. This class applies to cooking, de-freezing, warming, heat treating and re-heating appliances (the temperature achieved is unimportant).
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Heating arrangements specially adapted for cooking plates | |
Soldering by means of induction heating | |
Joining of preformed parts by induction heating of plasticsor substances in a plastic state | |
Heat treatment of metals or alloys by induction heating, surface hardening by electric induction, induction heating, continuous furnaces with induction heating |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Induction heating with coil arrangements | |
Melting furnaces for glass; mineral or slag wool by induction heating | |
Refining or remelting of metals by induction | |
Furnaces, kilns, ovens or retorts and detailsthereof | |
Inductive transmission of power in general, notdirectly related to heating | |
For wireless supply or distribution of electric power using inductive coupling |
This place covers:
Details about the electrodes of electric discharge heating apparatus, including mounting of the electrodes, electrical and mechanical connections. Also methods of supplying current and controlling power in electric discharge apparatus. Also heating by glow discharge and heating by arc discharge.
Further information:
H05B 7/148 - H05B 7/156 cover power supplies for heating by electric discharge
H05B 7/16 covers heating by glow discharge
H05B 7/18 - H05B 7/225 cover heating by arc discharge
This place does not cover:
Plasma torches |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Soldering or welding; cutting by applying heat locally | |
Automatic feeding of electrodes for spot or seam welding or cutting | |
Electric furnaces | |
Details or accessories of furnaces | |
Disposition of electrodes in or on furnaces | |
Control of position in general | |
Regulating electric characteristics of arcs in general | |
Regulating electric power in general | |
Non-insulated conductors or conductive bodies in general | |
Insulated conductors or cables in general | |
Electron beam or ion beam tubes for localised treatment of objects | |
Gas-filled discharge tubes | |
Electric power networks; Circuit arrangements or systems for supplying or distributing electric power; Systems for storing electric energy | |
Electric power conversion |
This place covers:
Indirect Radiation from the arc is focused (e.g. by an ellipsoidal mirror) into a projection on a work being heated.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Heating by means of lamps | |
Spot arc welding | |
Investigating particle size or size distribution using imaging, e.g. a projected image of suspension; using holography | |
Imaging characterized by its optical setup | |
Reflectors or mirrors with curved faces | |
Gratings for image generation | |
Optical details of the image generation | |
Details of the optical system between the polygonal mirror and the image plane | |
Regulating electric characteristics of arcs |
This place covers:
Heating by combined application of ohmic heating, induction heating, dielectric heating or electric discharge heating.
This place does not cover:
Aspects related to microwave heating combined with other heating techniques |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Bakers' ovens; machines or equipment for baking | |
Industrial microwave ovens | |
Characteristic features of footwear; parts of footwear | |
Heated mirrors | |
Kitchen equipment; coffee mills; spice mills; apparatus for making beverages | |
Dentistry | |
Methods or apparatus for sterilising materials | |
Chemical or physical processes | |
Soldering or welding; cutting by applying heat locally | |
Shaping or joining of plastics | |
Vehicle heating | |
Car seats | |
Heated mirrors for cars | |
Heated windshield window (car) / heated rear window (car) | |
Helicopters de-icing | |
Airplane wings de-icing | |
Containers for storage or transport | |
Pop corn heating | |
Nanotechnology | |
Carbon nanotubes | |
Ceramics | |
Adhesives | |
Heat treatment of metals or alloys | |
Metal-spraying | |
Heating of sport playgrounds | |
Cleaning open waters, e.g. deicing | |
Roofs de-icing | |
Devices for securing together constructional elements or machine parts | |
Pipes; joints or fittings for pipes; supports for pipes or cables | |
Glow plugs | |
Electrical cooker / glow plug / gas cooker | |
Removal of fumes associated to cooking range (or microwave ovens) | |
Domestic- or space-heating systems e.g. central heating | |
Fluid heaters | |
Drying solid materials or objects by removing liquid there from | |
Electric furnaces | |
Details or accessories of furnaces | |
Electrography; electrophotography; magnetography | |
Controlling non-electric variables | |
Controlling electric or magnetic variables | |
Resistors; methods of production | |
Electric switches | |
Aerials | |
Connectors | |
Removing snow from cables | |
Electric power conversion | |
Printed circuits | |
Semiconductor devices; methods of production |
This place covers:
Lamps where an arc is established through air or a gas mixture using consumable electrodes (for example carbon rods).
This place does not cover:
Regulating electric characteristics of arcs | |
Electric arc lamps with non-consumable electrodes |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Circuit for gas discharge lamps | |
Electric lighting | |
Electric discharge tubes or discharge lamps | |
Electric arc lamps with non-consumable electrodes |
G05F 1/02 with non-consumable electrodes H01J 61/00
Circuit for gas discharge lamps in H05B 41/00
This place covers:
- Structural details of electroluminescent light sources
- Chemical elements, chemical compositions or chemical compounds capable of emitting light
- Circuit arrangements for driving said electroluminescent sources.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Luminescent scales or hands | |
Luminescent dials | |
Conductive layers on isolated substrate | |
Discharge lamps | |
Lasers | |
Pulse generation with electroluminescent elements | |
Electronic gates with electroluminescent elements | |
Semi-conductor devices with at least one particular jump barrier or surface barrier adapted for light emission | |
Organic light emitting devices |
This place does not cover:
Luminescent materials |
This place covers:
Circuits and apparatus for driving two dissimilar light sources, e.g. diverse light sources or light generators, e.g. a compact fluorescent lamp and LEDs (see illustrations below)
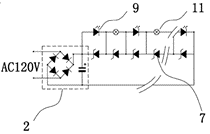
The two dissimilar light sources must be in the same casing or form a single unit
This group is meant for two types of light sources used simultaneously. Phosphors or different coloured LEDs are not to be considered as dissimilar light sources for the purpose of this group.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Circuit arrangements or apparatus for operating incandescent light sources | |
Circuit arrangements or apparatus for igniting or operating discharge lamps, e.g. fluorescent lamps | |
Driving electroluminescent panels | |
Circuit arrangements for operating light emitting diodes [LED] | |
Circuit arrangements for electric light sources in general | |
Lighting in general | |
Luminaries and their mechanical construction, e.g. combination of light sources | |
Gas-discharge or vapour-discharge lamps with light-emitting discharge path and separately-heated incandescent body within a common envelope. | |
Electric incandescent lamps | |
Circuit arrangements for emergency or stand-by power supply with automatic change-over |
In case of failure of the lamp, circuits providing for substitution: H05B 41/46.
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
LED | Light emitting diode |
OLED | Organic Light emitting diode |
CCFL | Cold Cathode Fluorescent lamp |
CFL | Compact Fluorescent lamp |
HID | High Intensity discharge lamp |
HPS | High Pressure lamp |
This place covers:
Circuit arrangements for controlling the light intensity of incandescent lamps.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Regulating electric variables in general |
This place covers:
Circuit arrangements, e.g. drivers, for discharge lamps.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arc lamps with consumable electrodes | |
Welding using accumulated energy | |
Electric lighting | |
Transformers or chokes for supplying discharge lamps | |
Circuit elements structurally associated with discharge lamps | |
Discharge lamps per se | |
Discharge lasers | |
Pulse technique | |
PCBs in general |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
DDBL | Dielectric Barrier Discharge Lamp |
CCFL | Cold cathode fluorescent Lamp |
CFL | Compact Fluorescent Lamp |
HID | High Intensity Discharge |
HPL | High Pressure Lamp |
HPS | High Pressure Sodium |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Switches in general | |
Igniting arrangements for discharge lamps |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Welding using accumulated energy | |
Circuit arrangements for gas discharge lasers | |
Electrical pulse generators with charge and discharge of an accumulating element |
This place covers:
Circuits for driving electroluminescent panels.
This place does not cover:
Circuit arrangements for operating light emitting diodes |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Circuit arrangements or apparatus for operating discharge lamps, e.g. fluorescent tubes | |
Control of light sources general | |
Electric lighting | |
Control arrangements or circuits for displays | |
Control arrangements or circuits for electroluminescent panels | |
Laser | |
Switching power supplies in general and inverters | |
Printed circuits [PCBs]; Details of electric apparatus, e.g. heatsinks | |
Inorganic light emitting devices [LED] | |
Organic light emitting devices [OLED] |
- Control of white light is classified in the colour section H05B 45/20 and subgroups.
This place covers:
Time switching, focus/target/beam control, LED flashes, LEDs as sensors, power saving aspects, shift registers control (simple sequences), emergency lights (when no other aspect is more relevant).
- Circuit arrangements for operating organic or inorganic light emitting diodes.
Circuit arrangements specially adapted or designed for operating light emitting diodes are classified in H05B 45/00, whereas circuit arrangements for operating light sources in general, i.e. where the type of the light source is not relevant, are classified in H05B 47/00, which is the corresponding function-oriented place.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Controlling of light sources in general | |
Controlling in response to parameters | |
Controlling by the ambient light | |
Control using timing means | |
Control using data bus linked networks | |
Control using power line carrier linked networks | |
Control using wireless networks | |
Arrangements or circuits for vehicle lighting devices | |
Arrangements or circuits for control of indicating devices using static means to present variable information | |
Control arrangements or circuits for displays using light-emitting diodes [LED] | |
Control arrangements or circuits for displays using organic light-emitting diodes [OLED] | |
Arrangements or circuits for control of laser diodes not provided for lighting | |
Solid state devices specially adapted for light emission including an organic material in the active part of the devices, e.g. organic light-emitting diodes [OLED] |
When classifying in H05B 45/00, further classification is made in H05B 47/00, for aspects, which are not lamp specific, whenever appropriate.
This place covers:
Controlling the intensity of the light using electrical feedback from LEDs or from LED-modules, e.g. involving detection of electric parameters.
This place covers:
Controlling the intensity of the light in response to the signal of a temperature sensor, e.g. for derating.
This place covers:
Transformations or calculations in a colour space, e.g. in the CIE colour space, to control the colour of the emitted light.
This place covers:
Controlling the colour of the light using electrical feedback from LEDs or from LED-modules, e.g. involving detection of load characteristics.
This place covers:
Circuits for supplying driving voltages or currents to LEDs, e.g. impedance circuits or active circuits.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
DC/DC or AC/DC conversion | |
Light or sound activated switches |
This place covers:
Circuits for supplying driving voltage or driving current of LEDs by controlling the operating frequency of a switching device.
This place covers:
Details of circuits providing leading edge phase control, e.g. triac circuits.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Bleeder circuits or dummy loads |
This place covers:
Details of circuits providing trailing edge phase control, e.g. AC switch circuits.
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used with the meaning indicated:
Reverse phase control | Trailing edge phase control |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Power conversion |
This place covers:
Driver circuits generating bursts of pulses, e.g. interrupted pulse trains, for dimming.
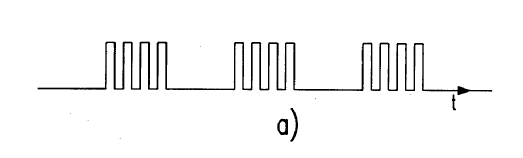
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Dynamic Headroom Control [DHC] | The term Dynamic Headroom Control refers to the dynamic adjustment of a LED power supply voltage to the lowest level that is sufficient to maintain correct operation of the current sources that supply the LED(s), thereby minimising wasteful power dissipation in the current sources. |
This place covers:
Circuits for equalising the currents through a plurality of LEDs or strings of LEDs arranged in parallel.
This place covers:
Driver circuits for LED retrofit light sources, i.e. LED light sources that directly replace incandescent bulbs and discharge lamps.
This place covers:
Circuits to maintain dimmer operation by the use of bleeder circuits or dummy loads.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Phase control circuits |
This place covers:
Emulating the electrical or functional characteristics of discharge lamps, e.g. emulating the presence of a discharge lamp by emulating filament resistance, ignition or lamp impedance.
This place covers:
Cuk or SEPIC – converter structures
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Circuits containing an inverter bridge |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Balancing circuits |
This place covers:
LED load circuits without active control in the LED matrix, other than in anti-parallel arrangements.
This place covers:
LED load circuits without active control in the LED matrix, in antiparallel arrangements 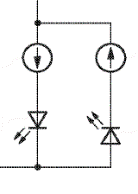
This place covers:
LED load circuits with active control inside the LED matrix, wherein the control switches are active devices.
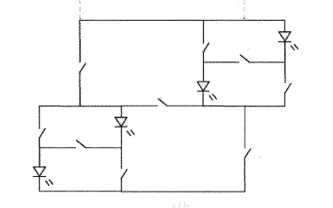
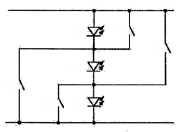
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
LED matrix with active control | An arrangement of LEDs and switches, whereby some of the LEDs may be switched into a series or a parallel configuration. |
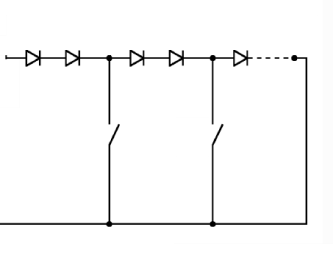
This place covers:
LED load circuits having a plurality of LED branches disposed in parallel with respect a power source, each branch comprising at least one LED and one control element arranged in series.
RGBs, current mirroring, active current balancers, minimum voltage selectors, in general when the parallel branches are gated for some purpose.
This symbol should be given as INV when the invention relates to the load configuration.
This symbol should be given as ADD when a load matching the definition can be observed in the document, but it is not the subject-matter of the invention or no details of it are provided.
This place covers:
LED load circuits having a plurality of LEDs units arranged in series with respect to a power source, each unit composed by at least one LED and one control element connected in parallel to the LEDs, e.g. a switch, transistor, MOSFET, Zener diode or resistor.
Examples:
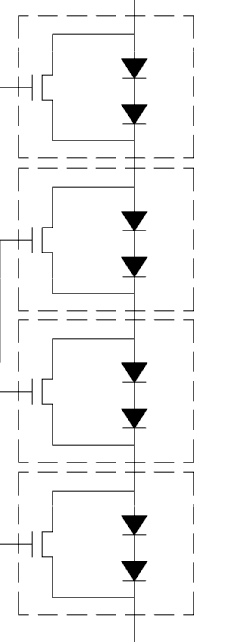
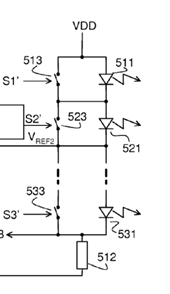
Typical problems appearing in the documents with this symbol are: accommodation of potential in a chain of series-connected LEDs, adaptation of the number of LEDs to various supplied voltages.
This symbol should be given as INV when the invention relates to the load configuration.
This symbol should be given as ADD when a load matching the definition can be observed in the document, but it is not the subject matter of the invention or no details of it are provided.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Circuit arrangements responsive to malfunctions of light sources or light sources life in general; Protective circuits of light sources in general | |
Monitoring vehicle lamps | |
Changing to a reserve source of current |
This place covers:
Circuits preventing general failure in case of a short circuit of at least one element of the array
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
LED matrixes disposed in parallel lines |
This place covers:
Circuits preventing general failure in case of an open circuit of at least one element of the array.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
LED matrixes organized in strings and incorporating parallel shunting devices |
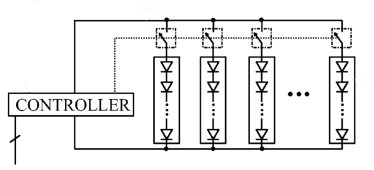
This place covers:
- The Internet of Things (IoT) applied to lighting
- The response to the presence or movement of objects or living beings
- The response to the environment luminance
- Program control or Logic control
- Remote control
- The response to malfunctions
- The monitoring of light source life
- The protection circuits or methods
Relative to the application-oriented places H05B 39/00, H05B 41/00, H05B 45/00 and H05B 46/00, H05B 47/00 is the function-oriented place, where the type of the light source is not relevant or it is in common use.
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Circuit arrangements or apparatus for operating incandescent light sources and not adapted to a particular application | |
Circuit arrangements or apparatus for igniting or operating discharge lamps | |
Circuit arrangements for operating light emitting diodes [LED] | |
Circuit arrangements for light sources using a charge of combustible material |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wake-up lights | |
Radiation therapy | |
Colour music | |
Vehicle lights | |
Monitoring vehicle lamps | |
Railways light signals | |
Lighting for photographic purposes | |
Time controlled switching | |
Building automation systems | |
Blinds or shutters | |
Regulating electric variables, e.g. voltage or current | |
Illuminated switch circuits | |
Traffic lights | |
Advertising | |
Light or sound activated switches | |
Transmission of digital information |
In this group, multiple classification is applied, so that subject matter characterized by aspects covered by more than one of its subgroups, which is considered to represent information of interest for search, may also be classified in each of those subgroups.
This place covers:
Controlling the light source in response to the presence or movement of objects or living beings, e.g. by radar or ultrasound.
This place covers:
Controlling the light source in response to the presence or movement of objects or living beings by detecting audible sound, e.g. speech or voice commands.
This place covers:
Controlling the light source in response to the presence or movement of objects or living beings using a camera, e.g. for gesture or traffic recognition.
This place covers:
Recognition of the type of lamp by determining non-electrical parameters, e.g. reading a lamp type identifier or label.
This place does not cover:
Electrical parameters of light source being controlled |
This place covers:
Controlling the light source by determining electrical characteristics of the light source, e.g. voltage, current or power; e.g. universal ballast.
This place covers:
Dynamic and interrelated control of two or more light sources, e.g. of their on/off pattern; e.g. gaming lighting.
This place covers:
Controlling the light source by timing means, e.g. circadian lights, timed lights or burglary deterrent circuits.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Time-controlled switching in general | |
Identifying, scaring or incapacitating burglars |
This place covers:
Controlling the light source on the basis of stored or streamed data, in e.g. theatre lighting or ambilights.
This place covers:
- Controlling operational modes of a light source, e.g. switching between manual and automatic modes
- Selectively permitting or prohibiting operations according to circumstances, e.g. preventing a street lamp from being lit during daylight, or a flashlamp from operating when there is sufficient light
- Configuration or calibration modes, switching from manual to automatic mode or prohibiting specific operations
This place covers:
Controlling the light source via data-bus transmission, e.g. DALI or DMX.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Current supply arrangements for data switching networks, e.g. power over Ethernet |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
DALI | Digital Addressable Lighting Interface |
DMX | Digital Multiplex |
PoE | Power over Ethernet |
This place covers:
Circuit arrangements for controlling light sources by remote control using power over ethernet supplies.
USB operations (power and control) are also classified in this group.
This place covers:
Controlling the light source via wireless transmission, e.g. RF or ZigBee.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
RF | Radio Frequency |
This place covers:
Controlling the light source via wireless transmission using visible or infrared light, e.g. Li-Fi
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
LIFI or Li-Fi | Light Fidelity |
This place covers:
Circuit arrangements for controlling light sources by remote control via wireless transmission using sound or voice control.
Configuration or calibration modes, switching from manual to automatic mode or prohibiting specific operations are classified in this group.
This place covers:
Circuit arrangements for controlling light sources by remote control via wireless transmission using gesture control.
The gestures being captured by cameras or touch pads or using wearable sensing devices are classified in this group.
This place covers:
- Monitoring for malfunctions such as earth faults.
- Protection of circuits when malfunctions of light sources occur, e.g. short circuits or open circuits.
- Control circuits and techniques responsive to ageing or degradation of the light source.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Monitoring vehicle lamps | |
Circuit arrangements for emergency or stand-by power supply, e.g. changing to a reserve source of current |