CPC Definition - Subclass H01M
This place covers:
Constructional details or processes of manufacture of the non active parts, e.g. casings, mountings, vents, separators, current-conducting connections, arrangements for filling or emptying cases with or of liquid.
Electrodes composed of or comprising active material, processes of manufacture and active materials thereof, e.g. electrodes for primary cells, for lead-acid accumulator.
Inert electrodes with catalytic activity, processes of manufacture and catalytic materials thereof.
Primary cells, manufacture and servicing or maintenance thereof, e.g. cells with aqueous or non-aqueous electrolyte, deferred-action cells, printed batteries
Secondary cells, manufacture and servicing or maintenance thereof, heating or cooling; temperature control, e.g. lead-acid accumulators, alkaline accumulators, accumulators with non-aqueous electrolyte
Fuel cells or their stacks and manufacture thereof, e.g. alkaline fuel cell, polymer electrolyte fuel cell, solid oxide fuel cell, biochemical fuel cells comprising enzymes as catalysts
Combination of fuel cells with means for production of reactants, e.g. with reformer or for treatment of residues
Hybrid cells, e.g. Zinc-air battery, half-cell of a fuel cell type and half-cell of a primary or secondary cell type
Structural combinations of different types of electrochemical generators.
This subclass does not cover the preparations of chemical compounds as such, which subject matter is covered by classes C01 (inorganic chemistry), C07 (organic chemistry) and C08 (organic macromolecular compounds).
Specific chemical compounds for batteries and their preparation are classified in C01, C07 and C08 as well as in H01M.
Apparatus for testing electrical condition of accumulator or batteries are classified in G01R 31/36 and accumulators combined with arrangements for measuring, testing or indicating condition are classified in H01M 10/48
Electrochemical processes or apparatus otherwise than for generating energy C25
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Catalysts | |
Disposal of solid waste | |
Working or processing of sheet metal or metal tubes | |
Casting of metals | |
Shaping of substances in a plastic state | |
Producing particular articles from plastics or from substances in a plastic state. | |
Arrangement or mounting of plural diverse prime-movers characterised by the electric storing means, e.g. batteries | |
Arrangement or mounting of plural diverse prime-movers characterised by the fuel cells | |
Electric propulsion using power supplied from primary cells, secondary cells or fuel cells | |
Arrangement of batteries specially adapted for vehicles | |
Supplying batteries to, or removing batteries from vehicles | |
Conjoint control of vehicle sub-units of different type including control of energy storage means, e.g. batteries | |
Conjoint control of vehicle sub-units of different type including control of fuel cells | |
Measuring or testing processes involving enzymes | |
Electrodes for electrolytic processes | |
Electrodes for electrolytic or electrophoretic process for the production of compounds or non metals | |
Diaphragms; spacing elements for electrolytic or electrophoretic process for the production of compounds or non metals | |
Electrodes for electrolytic production, recovery or refining of metals | |
Diaphragms; spacing elements for electrolytic production, recovery or refining of metals | |
Electrodes for electrolytic coating | |
Indicating or measuring liquid | |
Investigating or analysing materials by determining their chemical or physical properties | |
Apparatus for testing electrical condition of accumulator or electric batteries | |
Control of temperature | |
Electrolytes for electrolytic capacitors | |
Electrolytic light sensitive devices | |
Lithium-ion capacitors | |
Electrically conductive connections | |
Conversion of DC power input into DC power output using batteries | |
Photovoltaic modules structurally associated with energy storage means, e.g. batteries | |
Semiconductor or other solid state devices for converting light or heat into electrical energy |
Every technical aspect of the invention is classified with inventive symbols and additional information from the description with additional symbols.
When the battery or fuel cell is characterised by the combination of a specific positive electrode, specific negative electrode and/or specific electrolyte: every specific component of the combination will be classified with inventive symbols.
When a breakdown Indexing Code represents the invention , the corresponding upper group should also be given.
When the type of battery is not mentioned, the classification of the invention is done in the primary and secondary type of battery classes.
When a group for a process does not exist, it is classified within the material of the object.
Additional orthogonal Indexing Codes are used for "additional information" and are always given together with a CPC group. Classification with these codes is highly desirable, since they provide an efficient search tool when combined with a CPC group.
They concern:
H01M 2200/00 and subgroups : Safety devices for primary or secondary batteries
H01M 2220/00 and subgroups : Batteries for particular applications
H01M 2250/00 and subgroups : Fuel cells for particular applications; Specific features of fuel cell system
H01M 2300/00 and subgroups : Electrolytes
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Active materials, active masses, active liquids | materials, masses, liquids participating in the electrochemical reactions |
Inert electrodes | Electrodes characterised by their catalytic activity |
Primary cells | Cells, where the cell energy present in chemical form is not regenerated |
Secondary cells, accumulator | Rechargeable cells, characterised by reversible electrochemical reactions |
Battery | Device comprising one or more electrochemical cells |
NTC, PTC | NTC (negative temperature coefficient) thermistors with their resistance decreasing with increasing temperature, PTC (positive temperature coefficient) thermistors with their resistance rising with increasing temperature |
Redox flow battery | Reversible fuel cell in which all electroactive components are dissolved in the electrolyte with a flow circulation system of the electrolyte |
Redox fuel cell, indirect fuel cell | Fuel cell where the oxydant or fuel is not reacted directly at the electrode but with the reduced/oxidised form of a redox couple and the oxidised/reduced species are fed to cathode/anode |
Electrochemical storage device | Galvanic primary cell or secondary cell (battery, accumulator), electrochemical capacitors (in particular pseudocapacitors and hybrid capacitors |
This place covers:
Electrodes comprising active material for primary, secondary and hybrid cell and electrodes with catalytic activity for fuel cells.
Processes of manufacture of the electrodes, selection of substances as active materials, carriers or collectors, inactive substances as ingredients in the electrode, e.g. binder, conductive material
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
General process for applying liquids to obtain a coating with specific electrical properties | |
Processing of sheet metal | |
Casting of metals | |
Working metallic powder | |
Soldering, welding | |
Layered products | |
Nanostructures | |
Carbon | |
Compounds of alkali metals | |
Compounds of Be, Mg, Al, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra, Th or rare earth metals | |
Compounds of manganese | |
Compounds of Nickel | |
Shaped ceramic products | |
Organic macromolecular compounds | |
Alloys | |
Coating metallic material, surface treatment of metallic material, e.g. vacuum evaporation | |
Electrodes for electrolytic processes | |
Electrolytic or electrophoretic processes for the production of compounds or non-metals, electrodes for those process | |
Carbon filaments | |
Conductors characterised by the conductive materials | |
Magnetic materials |
- The process of manufacture of a specific type of battery electrode is classified in H01M 4/16-H01M 4/23 or H01M 4/26-H01M 4/30 or H01M 4/139-H01M 4/1399 and in H01M 4/04-H01M 4/0428 (double classification).
- H01M 4/02 and H01M 4/04-H01M 4/0428 should not be used for fuel cell electrodes and their manufacture which are classified in H01M 4/86-H01M 4/8896
- All the steps of the process of the manufacture of an electrode (battery electrode or fuel cell electrode) should be classified if possible.
- When oxides are added in an electrode and when it' s not sure whether it's an active material or an additive, classes in H01M 4/48-H01M 4/57, H01M 4/62 and H01M 4/362 should be given
- H01M 4/366 is used for any coating (the coating being a second active material or not). In the case the coating is not a second active material, H01M 4/62 subgroup should be given.
- H01M 4/364 is only used for mixture of at least 2 active materials.
- Classification of alloys under H01M 4/38 relate to the composition before charging, e.g. before the addition of lithium.
- Electroactive polmyers classified in H01M 4/137 concern polymers where oxidation/reduction (redox) processes take place
- Electrode composed of Lithium or lithium based alloy is classified in H01M 4/134
- H01M 4/18 relates to Planté electrode process. It concerns lead dioxide generated by direct oxydation of lead that forms the conducting substrate.
- Alkaline earth metals oxides or hydroxides, oxides or hydroxides of metal other than manganese, nickel, iron, cobalt, silver, lead, mercury are classified in H01M 4/48 and if they insert or intercalate light metals, they are classified in H01M 4/485.
This place covers:
Electrodes for fuel cells, comprising catalysts
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Catalysts | |
Process for preparing catalyst |
Catalysts supported on carbon are not classified in H01M 4/96 but in H01M 4/9083 or H01M 4/926.
H01M 4/96 is only given if carbon is the catalytic species, e.g. for hybrid cells.
H01M 4/8647-H01M 4/8657 concern composite material, meaning comprising at least 2 catalysts having the same function and H01M 4/8615 concerns bifunctional electrode used in regenerative fuel cell with oxygen reduction catalyst and oxygen evolution reaction catalyst.
All the steps of the process of the manufacture of a fuel cell electrode
should be classified if possible within subgroups H01M 4/88-H01M 4/8896
The process for making electrocatalyst are classified within the catalyst material subgroups H01M 4/90-H01M 4/923. Catalysts used only in fuel cells are not classified in B01J.
This place covers:
- Primary batteries with aqueous electrolyte, non-aqueous electrolyte and solid electrolyte.
- primary batteries activated by addition of electrolyte, by physical means (thermal and mechanical)
- thin film or flat or printed primary batteries
- Methods or arrangements for maintenance of primary batteries including heating or cooling, primary batteries combined with cell condition or safety devices, regeneration of reactants or electrolyte, type recognition
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Thermoelectric solid state devices |
Classification for primary and secondary non aqueous batteries:
- When it concerns only primary battery : H01M 6/162-H01M 6/188
- When it concerns primary and secondary battery or in case of doubt : both subgroups are given : H01M 6/162-H01M 6/188 and H01M 10/056-H01M 10/0569
- When it concerns only secondary battery : H01M 10/056-H01M 10/0569
Solid polymer electrolyte of a battery is not classified in H01M 8/1018 unless the use in a fuel cell is mentioned.
Printed battery in H01M 6/40 concern thin film battery.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Primary cells | Electrochemical generators in which the cell energy is present in chemical form and is not regenerated |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Thermoelectric solid state devices |
This place covers:
Fuel cells or their stacks that can include:
- Collectors, separators, interconnectors, gas diffusion layer.
- Sealing or frame, its processes and materials.
- Membranes, matrices holding electrolytes solutions or melts.
- Means for temperature measurement or control, for reactant control or regulation.
- Methods for controlling fuel cells or fuel cell systems with detection and regulation of variables.
- Combination of fuel cells with means for production of reactants (e.g. with a reformer) or for treatment of residues.
- Types of fuel cell: with aqueous electrolytes (e.g. alkaline fuel cells), with solid electrolyte at low temperature (below 200-250°C) (e.g. polymer electrolyte fuel cells), with solid electrolyte at high temperature (e.g. solid oxide fuel cells), with molten electrolyte, biofuel cells/biochemical fuel cells comprising enzymes as catalysts.
- Manufacture thereof.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Constructional details, or processes of manufacture, of the non-active parts of cells other than fuel cells | |
Separation of gases or vapour | |
Semi-permeable membranes | |
Catalysts | |
Recycling of heat from fuel cell to other parts of a car | |
Fuel cells used to drive air conditioning | |
Prime movers consisting of electric motors and internal combustion engines characterised by the fuel cells | |
Electric propulsion using power supplied from fuel cells | |
Conjoint control of vehicle sub-units of different type including control of fuel cells | |
Arrangement or adaptations of fuel cells in cosmonautic vehicles | |
Hydrogen; Gaseous mixtures containing hydrogen; Separation of hydrogen from mixtures containing it; Purification of hydrogen | |
Shaped ceramic products (e.g. for use in solid oxide fuel cells) | |
Manufacture of shaped structures of ion-exchange resins | |
Production of combustibles gases containing carbon monoxide from solid carbonaceous fuels | |
Liquid carbonaceous fuels | |
Microorganisms or enzymes | |
Measuring or testing processes involving enzymes | |
Diaphragms or spacing elements for electrolytic or electrophoretic process for the production of compounds or non-metals | |
Diaphragms or spacing elements for electrolytic production, recovery or refining of metals | |
Vessels for containing or storing compressed, liquefied or solidified gases | |
Burners for combustion of a gas | |
Gas-turbine combustion chambers | |
Electrochemical sensors | |
Apparatus for testing electric properties | |
Control of temperature | |
Electrolytes for electrolytic capacitors | |
Hybrid capacitors | |
Electrically conductive connections | |
Semi-conductor or other solid state devices for converting light or heat into electrical energy |
- Membranes for immobilising electrolyte solutions or electrolyte melts are classified in H01M 8/0289-H01M 8/0295 and membranes used as support or mixed with polymer electrolytes are classified in H01M 8/1058-H01M 8/1062.
- Means for control of temperature, pressure, reactant, and electrolyte are classified in subgroups H01M 8/04007-H01M 8/04291 and methods for controlling fuel cells or fuel cell systems are classified in H01M 8/04298-H01M 8/04992.
- Reactant in a fuel cell is only what is delivered immediately to the fuel cell, e.g. liquid methanol is evaporated to gaseous methanol that is used then in a fuel cell; only H01M 8/04089 will be used.
- Means for preventing methanol crossover (gaseous or liquid methanol) are classified in H01M 8/04197.
- H01M 8/04119 concerns the humidification in the fuel cell.
- H01M 8/04291 is used for water management of the fuel cell system.
- Rules for H01M 8/04298-H01M 8/04992.
- When the claims refer to control and/or process/management of the fuel cell, then group symbols in H01M 8/04298-H01M 8/04992 should be given and it's the description and claims (if they are clear) that are classified. Every variable really disclosed/claimed and not just listed as part of a whole list should be classified.
- If only general details are given in the detected and/or regulated variables, then the upper groups H01M 8/04313 and/or H01M 8/04694 should be given.
- When control/management is detailed only in the description, then classification symbols from H01M 8/04298-H01M 8/04992 should be given as additional symbols.
- When the control of a fuel cell concerns the detection/measurement of environmental variables (e.g. temperature, pressure, humidity of the environment), classification in the group H01M 8/0432 should be given if it concerns the detection of ambient temperature or in the group H01M 8/0438 if it concerns ambient pressure.
- In a system with means for production of reactants or treatment of reactants or residues, if the fuel cell aspect is not the invention (only mentioned in the description or the last (sub)claim), the document should only be classified with an additional symbol H01M 8/06.
- If the fuel cell in combination with the other means is the invention, then it is classified as invention in the subgroups under H01M 8/06.
- H01M 8/188 is only allocated for redox flow battery or secondary fuel cells, the redox couple being reversible or regenerated.
- H01M 8/20 is only used for fuel cells with redox couple being irreversible.
- H01M 8/24 subgroups are used when the invention concerns the stack of fuel cells as such.
- The symbols H01M 8/083, H01M 8/086, H01M 2008/1095, H01M 2008/128, H01M 2008/1293, and H01M 2008/147 should be used for further classification to indicate the type of fuel cell.
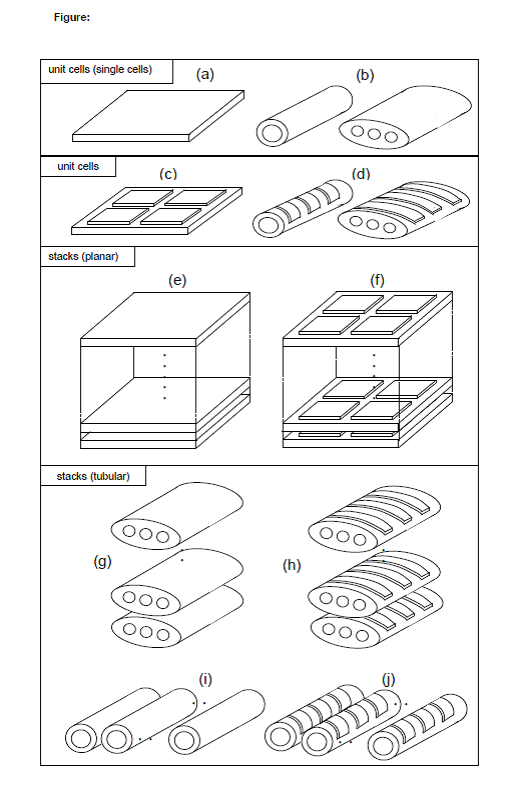
- Figures (c), (d) correspond to the group H01M 8/2428, figures (e), (f) correspond to the group H01M 8/2432, and figures (g), (h), (i), (j) correspond to the group H01M 8/243.
- Moreover, figure (f) also corresponds to the group H01M 8/2428 and figures (h), (j) also correspond to the group H01M 8/2428 if the emphasis of the invention is on the arrangement of the unit cells on a support.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Porous separator | gas diffusion layer |
Separator | bipolar plate, interconnector |
Fuel cell | Electrochemical generator wherein the reactants are supplied from outside |
Single cell | Fuel cell entity, containing one single anode, one single electrolyte and one single cathode [see figure: (a), (b)] |
Unit cell | Structural component, containing one or more single cells [see figure: (a), (b), (c), (d)] |
Stack | Group of components, where the components (unit cells) are arranged in vertical direction [see figure: (e), (f), (g), (h)] and/or horizontal direction [see figure: (i), (j)] |
Battery | Device comprising one or more electrochemical cells |
Redox flow battery | Reversible fuel cell in which all electroactive components are dissolved in the electrolyte with a flow circulation system of the electrolyte |
Redox fuel cell, indirect fuel cell | Fuel cell where the oxidant or fuel is not reacted directly at the electrode but with the reduced/oxidised form of a redox couple and the oxidised/reduced species are fed to cathode/anode |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
PEFC | Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cell |
PEMFC | Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell or Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell |
SOFC | Solid Oxide Fuel Cell |
AFC | Alkaline Fuel Cell |
MCFC | Molten Carbonate Fuel Cell |
DMFC | Direct Methanol Fuel Cell |
PAFC | Phosphoric Acid Fuel Cell |
MEA | Membrane Electrode Assembly |
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms:
- redox flow battery, regenerative fuel cell, and secondary fuel cell
This place does not cover:
Regenerative fuel cells |
The combination of fuel cell with means for production of reactants, e.g. reformer or for treatment of residues, e.g. removal of sulfur will be classified in H01M 8/06 subgroups.
If the invention concern specifically the mean associated with the fuel cell, the means is classified and the aspect of the combination of the fuel cell with that mean is classified in H01M 8/06 subgroups as additional symbol.
Temperature control means of a system combining fuel cell and for example a reformer will be classified in H01M 8/06 subgroups, H01M 8/04298 subgroups and in C01B 3/02 subgroups if the temperature control concerns the reformer.
Every means in a combination system will be classified as invention or additional symbol according to the specific aspect of the invention, e.g. emphasis on the system or on a specific mean.
Reformers are classified in C01B 3/02 subgroups
In a system comprising fuel cell and reformer, if the invention concerns only the reformer, the reformer will be classified in C01B 3/02 subgroups and the fuel cell (minor aspect) will be classified with H01M 8/06 as additional symbol.
If the invention concerns the whole system, then the invention is classified in H01M 8/06 subgroups.
This place covers:
Construction in general.
Several types of secondary batteries : lithium batteries, lead acid batteries, alkaline batteries, high temperature batteries.
Methods or arrangements for servicing or maintenance.
Cooling, heating, regulating temperature.
Recycling.
Circuits for charging or depolarising or for supplying loads from batteries are classified in H02J 7/00-H02J 7/36 and the methods for charging or discharging are classified in H01M 10/44-H01M 10/445.
Measuring electric variables are classified in G01R 31/36 if the measurement device is not structurally combined with the battery
Air conditioner of a car classified in B60H is also classified under H01M 10/60-H01M 10/667 if it's used for cooling/heating a battery.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Heating, cooling or ventilation devices in vehicles | |
Arrangement of electric storage means for propulsion | |
Prime movers consisting if electric motors and internal combustion engines | |
Vehicles using power form primary cells, secondary cells or fuel cells | |
Arrangement of batteries in a vehicle | |
Supplying batteries to, or removing batteries from vehicles | |
Specific uses or applications of nanostructures | |
Electrochemical actuator | |
Heat exchange or heat transfer apparatus | |
Indicating or measuring liquid in general | |
Investigating fluid tightness of structure | |
Measuring density | |
Investigating or analysing materials by the use of electric, electrochemical or magnetic means | |
Control of temperature in general | |
Arrangement for obtaining electrical energy form radioactive source | |
Generators in which kinetic energy is converted into electrical energy | |
Portable receivers and arrangement for mounting batteries or batteries chargers | |
Portable phone with battery compartment | |
Printed circuits | |
Semi-conductors devices |
- Small-sized batteries indicate batteries used in portable devices
- Large-sized batteries indicate batteries used in vehicles or standby power.
- Construction classes under H01M 10/12, H01M 10/28, H01M 10/058, H01M 10/38 take precedence over H01M 10/04.
- For non-aqueous secondary battery, a class indicating the type of battery, e.g. H01M 10/052 should always be given in addition to the classes related to construction H01M 10/058 - H01M 10/0587 or to the classes related to the type of electrolyte H01M 10/056- H01M 10/0569.
- Solid polymer electrolyte of a battery is not classified in H01M 8/1018-H01M 8/1093 unless the use of this polymer in a fuel cell is indicated.
- Special rules for the subgroups H01M 10/42-H01M 10/488
- Additives in electrolyte having the function of safety are classified in H01M 10/0567 for example and also in H01M 10/4235. Fusing, polymerising additives are also classified in H01M 10/4235.
- Structurally combination indicates attached to the battery or in the battery housing.
- Printed circuits integrated to the outside of the casing of the battery, e.g. on the cover) are classified in H01M 10/425
- H01M 10/4257 concern battery with incorporated memory, microchip, electronic circuit inside the housing of the cells or batteries.
- The use of printed circuit as a casing of a battery is classified in H01M 50/20.
- Apparatus for testing the cell or battery and not incorporated with the battery is classified in H01M 10/4285
- The regeneration of electrolyte or reactants done by non electrical means is classified in H01M 10/4242
- Any ratio between electrode/electrolyte, anode/cathode of a secondary battery is classified in H01M 2010/4292
- Removing gas inside the battery by water recombination is classified in H01M 10/52.
- Gel electrolytes are double classified in H01M 10/0565 if they concern gel-type polymeric material for non-aqueous accumulator and H01M 2300/0085
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Accumulator | secondary battery |
Secondary cells | Accumulators receiving and supplying electrical energy by means of reversible electrochemical reactions |
This place does not cover:
Constructional details of current conducting connections for detecting conditions inside cells or batteries, e.g. of voltage sensing terminals |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Methods for charging or discharging | |
Indicating or measuring level of liquid in general | |
Measuring density | |
Measuring electric variables |
This place covers:
hybrid cells, e.g. half-cell of fuel cell type and half-cell of primary or secondary cell type:
- half cell of capacitor type and half-cell of primary or secondary battery type
- half cell of fuel cell type and half cell of primary or secondary cell type
Solid electrolytic capacitors, double-layer capacitors, are classified in H01G 11/00
This place does not cover:
Hybrid capacitors; Electric double-layer [EDL] capacitors |
- The casing and the lid of the hybrid cells are classified in H01M 50/1385 and H01M 50/1537 respectively.
- Methods or arrangements for servicing or maintenance are classified in H01M 6/50 or H01M 10/42 according to the type of half battery cell. The control of half fuel cell type is classified under H01M 8/04298-H01M 8/04992.
- All hybrid cell concerning half capacitor, half battery should be circulated to H01G.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Hybrid cells | Electrochemical generators having two different types of half-cells, the half-cell being an electrode-electrolyte combination of either a primary, a secondary, or a fuel cell |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Methods or arrangements for servicing or maintenance |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Methods or arrangements for servicing or maintenance, e.g. for charging |
This place covers:
Every type of electrochemical cell that is not classified in the above groups.
Photoelectrochemical storage cells wherein the light causes a change in chemistry and the energy is stored and discharged at later stage.
Solar cells are classified in H01G 9/20 and only if the energy produced by the solar cell is stored then it will be also classified in H01M 14/005.
This place does not cover:
Light sensitive devices (photocells) |
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms:
- "photocells", "photoelectrochemical cells (PEC)", "photovoltaic cells" and "solar cells"
This place covers:
Photoelectrochemical storage cells wherein the light causes a change in chemistry and the energy is stored and discharged at later stage.
This group does not cover solar cells, photocells, photoelectrochemical cells or photovoltaic cells which are covered by the following groups:
- Semiconductor devices sensitive to light and adapted for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy are covered by group H10F, H10F 10/00, H10F 19/00
- Solid-state devices using organic materials as active part specially adapted for sensing light and adapted for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy are covered by group H10K 30/00
- Electrolytic light sensitive devices, e.g. dye-sensitised solar cells, are covered by group H01G 9/20
- Photovoltaic modules structurally associated with energy storage are covered by group H02S 40/38
This place does not cover:
Electrolytic light sensitive devices | |
Photovoltaic modules structurally associated with energy storage | |
Semiconductor devices sensitive to light | |
Solid-state devices using organic parts specially adapted for sensing light |
This place covers:
Association of fuel cells with other electrochemical generators, e.g. fuel cell + electrolysers, fuel cell+ battery, fuel cell + capacitor
This place does not cover:
Combination of secondary battery with capacitor |
This place covers:
Association of fuel cells with other electrochemical generators, e.g. fuel cell + electrolysers, fuel cell+ battery, fuel cell + capacitor
This place covers:
Constructional details of non-active parts of batteries, or details of their manufacture. Such parts may include:
- Primary and secondary casings, jackets or wrappings, lids or covers, carrying devices, racks, mountings, holders, fixing devices;
- Vents, vent plugs, mechanical arrangements for allowing the escape of gas;
- Separators, diaphragms, spacing elements inside a primary casing;
- Current-conducting connections for terminals for cells, means for affording protection against corrosion or for preventing undesired use;
- Arrangements or processes for filling or topping-up casings with liquid, arrangements or processes for draining liquids from casings;
- Arrangements for stirring or circulating electrolytes.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Constructional details or processes of manufacture of the non-active parts of fuel cells | |
Electrically operated smoking devices; Component parts thereof; Manufacture thereof; Maintenance or testing thereof; Charging means specially adapted therefor | |
Electrotherapy, e.g. implantable medical devices | |
Working or processing of sheet metal or metal tubes | |
Casting of metals | |
Tools for drilling machines | |
Portable power-driven tools | |
Shaping of substances in a plastic state | |
Producing particular articles from plastics or from substances in a plastic state | |
Arrangement of batteries specially adapted for vehicles | |
Supplying batteries to, or removing batteries from vehicles | |
Container for batteries | |
Diaphragms; spacing elements for electrolytic or electrophoretic process for the production of compounds or non-metals | |
Diaphragms; spacing elements for electrolytic production, recovery or refining of metals | |
Sealing | |
Valves | |
Apparatus for testing electrical condition of accumulators or electric batteries | |
Electrically conductive connectors connecting the battery to the load or electric system |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
primary casing | casing containing the electrochemical cell, i.e. arranged closest to the electrodes, the electrolyte and any separators |
secondary casing | housing/casing/structure comprising or enveloping one or more primary casing(s) |
single cell, battery | a cell is a primary casing containing a single electrochemical cell. A battery is a primary casing containing more than one cell. The term "battery" is sometimes loosely used to mean a single cell |
battery pack, module | secondary casing containing one (or more) (single) cell(s) or batteries |
button cell, coin cell | cells having a button- or coin-shaped casing, often of circular, elliptical or polygonal shape, and having a height-to-width ratio of less than 1 |
pouch or flexible bag | generally made of a flexible multi-layered laminate sheet sealed along at least an overlapping edge |
jacket, wrapping | additional layer of material around at least a portion of a primary casing; not intrinsically formed with primary casing; generally having an additional functionality such as displaying information, additional external protection |
separator, diaphragm | an electronically insulating, but ion-permeable porous body to be arranged between two electrochemically active electrodes; a separator or diaphragm may also be used for preventing liquids from being intermixed, e.g. in redox flow batteries |
spacer, spacing element | an inert object to be arranged between two other objects for keeping a defined distance there between; usually electronically insulating; can be placed inside or outside primary casing battery; to be clearly distinguished from a separator by its positioning if inside a primary casing |
terminal | electrical contact exposed at and accessible from the outside of a primary or secondary casing |
interconnector | external electrical contacting element between terminals on a battery case (including primary and secondary cases) |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
[PCB] | Printed circuit board |
This place covers:
Any primary casing characterised by shape or physical structure, e.g. cable-shaped casings being intrinsically flexible and having a height to diameter (or width) ratio of approximately 10 or more.
This place covers:
Prismatic or rectangular casings that are generally hard, rigid casings often comprising a distinct lid. The edges may also be rounded.
Illustrative examples of prismatic or rectangular shaped casing (50 of first drawing and 34 of second drawing):
1.
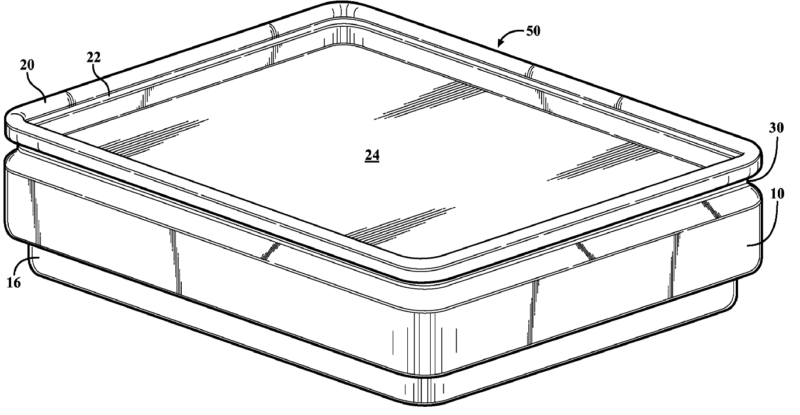
2.
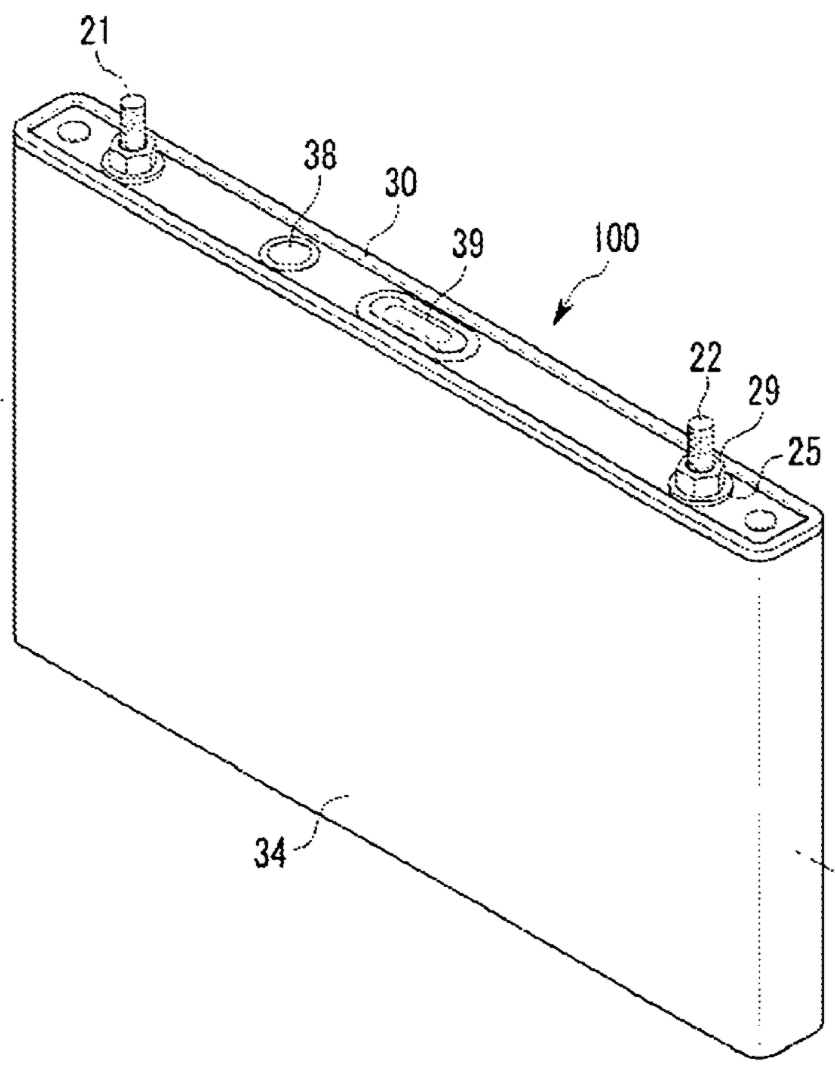
This place does not cover:
Primary casings of button or coin shape | |
Primary casings having a structure in the form of a chip |
This place covers:
Casings of pouch cells or flexible bag cells generally made of a flexible multi-layered laminate sheet sealed along at least an overlapping edge.
Illustrative example of pouch type battery casing (111-113a):
1.
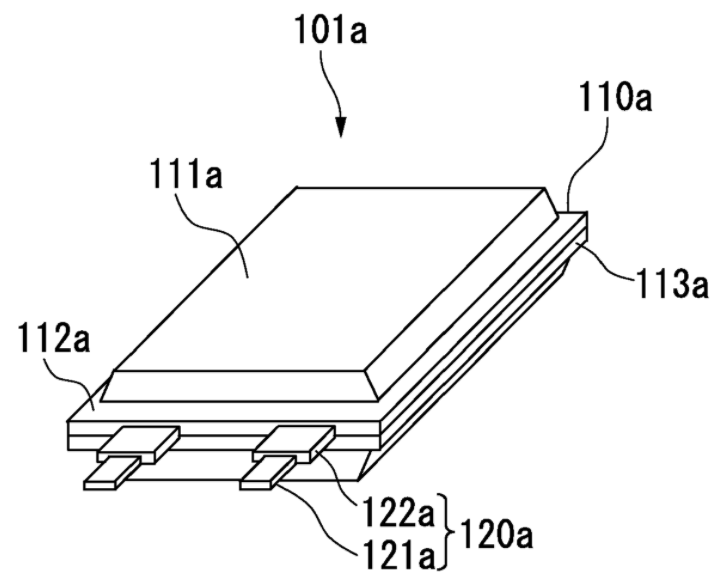
This place covers:
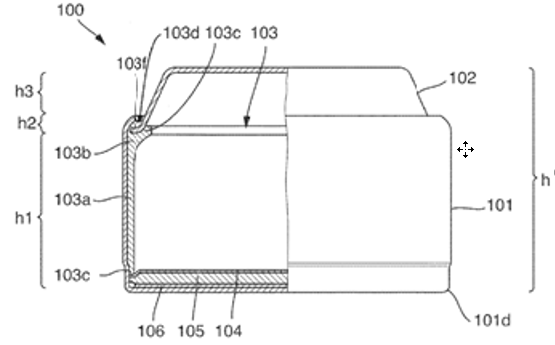
Button or coin-shaped casings having a cylindrical or an elliptical shape, and, further, having a height to diameter ratio of less than 1.
Illustrative example of a button or coin shaped casing (101, 102):
1.
This place covers:
Structures of microsized batteries and miniature power sources integrated on chips, e.g. structures of thin-film micro lithium-ion batteries or rolled-up microtube lithium-ion batteries.
Illustrative example of a casing having a chip structure:
1.
This place covers:
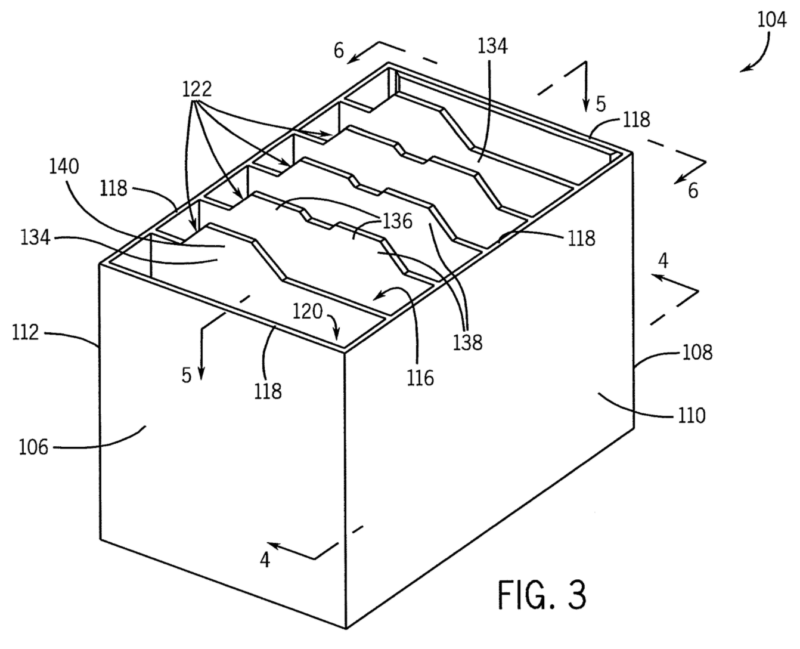
Casings consisting of an integral housing with multiple compartments for holding bare electrochemical cells.
Illustrative example of monobloc casing (106) with multiple compartments (122):
1.
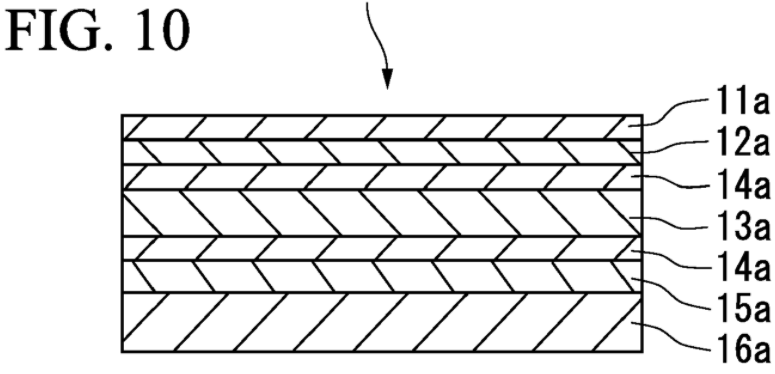
Classification of multilayered casings, jackets or wrappings in this group or in groups H01M 50/126, H01M 50/128 or H01M 50/129 requires consideration of the number of layers present.
In multilayered objects, adhesive layers are not considered as distinct layers for determining the number of layers.
Any layer providing functionality beyond simple adhesion should be counted as a distinct layer.
Layered structures are further classified according to the material of each layer, e.g. a layered structure comprising a metal layer should be classified in H01M 50/119 and H01M 50/124.
This place covers:
Casings comprising three or more layers with two or more layers of only inorganic material.
Illustrative example:
1.
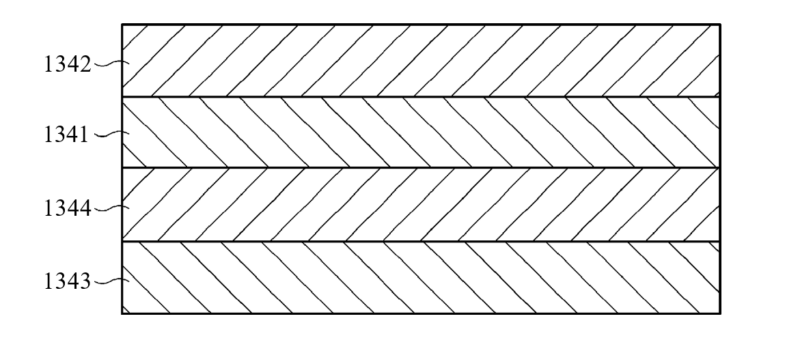
A pouch for a battery may be formed as a layer structure. The layer structure may include an outermost surface protection layer 1342 made of a first polymer and an innermost sealant layer 1343 made of a second polymer. A gas barrier layer 1341 made of a metal and a heat dissipation layer 1344 made of a ceramic may be stacked between the outer and inner layers.
The pouch of this example is classified in H01M 50/128 and in H01M 50/129.
This place covers:
Illustrative example:
1. 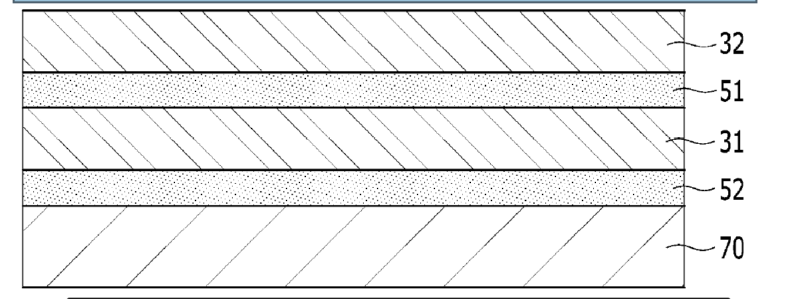
An outer case for a secondary battery may include a first polymer resin layer 31, a second polymer resin layer 32 disposed on a first surface of the first polymer resin layer 31 and attached by interposing a first adhesive layer 51, and an inner resin layer 70 disposed on a second surface of the first polymer resin layer 31 and attached by interposing a second adhesive layer 52, wherein each of the first polymer resin layer and the second polymer resin layer comprises a fluorine-containing resin.
This place covers:
Primary casings, jackets or wrappings of a single cell or a single battery characterised by physical properties such as flexibility or heat resistance.
Primary casings, jackets or wrappings with heat resistant properties related to protection against damage by fire or explosion caused by external factors are classified in H01M 50/143.
This place covers:
Electrochemical cell operating at high temperatures, e.g. molten salt electrolyte batteries, thermal batteries or sodium sulfur batteries [NAS].
Air batteries, e.g. zinc air or lithium air batteries.
Deep sea batteries. Deferred-action cells.
Illustrative example:
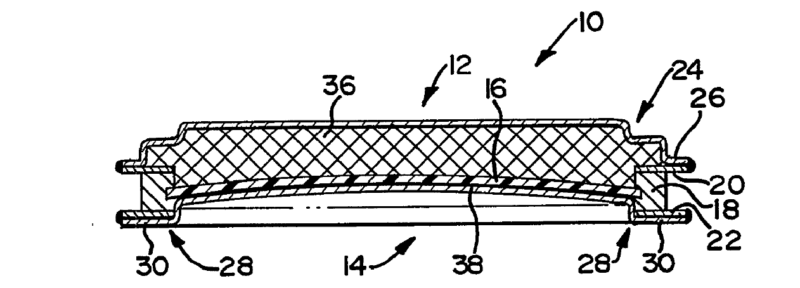
A high temperature rechargeable electrochemical cell (10) may comprise a cell casing defining an anode compartment for containing an alkali metal anode and a cathode compartment containing a liquid electrolyte. The cell may have an operating temperature at which the anode and liquid electrolyte are molten. The anode compartment may be separated from the cathode compartment by a separator (16) comprising a solid electrolyte which is a conductor of ions of the alkali metal of the anode at the operating temperature of the cell. The casing may comprise a cathode cover (12) of sheet material enclosing the cathode-side surface of the separator and an anode cover (14) of sheet material enclosing the anode-side surface of the separator. The cathode cover and the anode cover may be electronically conductive and electronically insulated from each other and may respectively form a cathode terminal and an anode terminal of the cell.
1.
This place covers:
Primary casings, jackets or wrappings for protecting against humidity or preventing the ingress of moisture, e.g. waterproofing wrappings.
This place covers:
Primary casings, jackets or wrappings for protecting against fire or explosion, e.g. thermally insulating layer for preventing a thermal runaway.
Example:
A battery comprising a fire-resistant sheet comprising a fire-resistant resin composition comprising an endothermic agent having a thermal decomposition onset temperature of 800°C or lower and an amount of heat absorbed of 300 J/g or larger, and a resin, a content of the endothermic agent per 100 parts by mass of the resin being 10 to 10000 parts by mass; and a battery cell, wherein the fire-resistant sheet is attached to the surface of the battery cell.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangements for facilitating escape of gases |
Primary casings, jackets or wrappings with heat resistant properties not related to protection against damage by fire or explosion are classified in H01M 50/131.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
fireproof or fire-resistant material | material that withstands heat and prevents the spread of fire |
heat-resistant material | material that remains unaffected by heat |
This place covers:
The protection of primary casings against corrosion, e.g. the protection of metallic casings against corrosion caused by water.
Documents related to corrosion resistance and protection against humidity are classified in H01M 50/141 and H01M 50/145.
In the subgroups, lids or covers are classified according to the geometrical shape of the primary casing.
In the below example, the circular lid is classified in H01M 50/103 as it concerns prismatic cells. 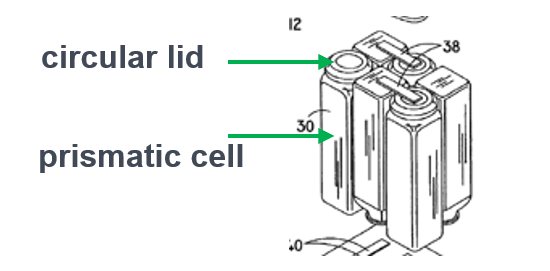
A lid or cover for a chip-shaped casing is classified in H01M 50/148.
This place covers:
Methods of assembling casing with lid by crimping.
Illustrative example:
1.
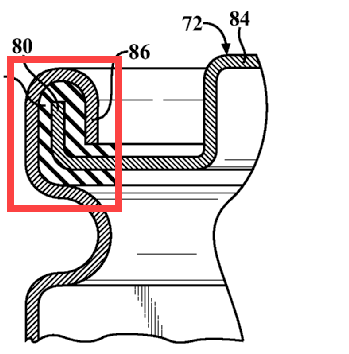
The upper part of the casing (86) is assembled with the lid (80) by crimping.
This place covers:
Methods of assembling casing with lid by welding, brazing or soldering.
The welding processes concern welding metal to metal and the fusion of plastic materials.
This place covers:
Primary casings, jackets or wrappings of a single cell or a single battery characterised by physical properties of the sealing material and supported by numerical values or exemplifying the solution of the problem to be solved, e.g. adhesiveness.
This place covers:
Constructional details or processes of manufacture. Such details may include:
- Secondary casings, modules, packs, racks, holders;
- Suspension devices, shock absorbers, transport or carrying devices;
- Materials;
- Adaptation to shape of encompassed primary casing batteries;
- Physical properties of casings or racks;
- Methods of mounting;
- Lids or covers for racks or secondary casings;
- Details of integrating PCBs;
- Spacing elements;
- Fastening means; or
- Terminals of battery packs.
This place does not cover:
Structural combination of accumulators with charging apparatus |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Electrically operated smoking devices; Component parts thereof; Manufacture thereof; Maintenance or testing thereof; Charging means specially adapted therefor | |
Electrotherapy, e.g. implantable medical devices | |
Tools for drilling machines | |
Portable power-driven tools | |
Arrangement of batteries specially adapted for vehicles | |
Adaptation of battery structures of electric vehicles, e.g. integration into control or safety systems, crash-resistant casings or vibration-damping means | |
Exchange of the energy storage elements for electric vehicles | |
Supplying batteries to, or removing batteries from, vehicles |
This place covers:
Constructional details or processes of manufacture of secondary casings or frames around the primary casing of a single cell or a single battery.
Illustrative example of a single primary battery housed in a secondary casing:
1.
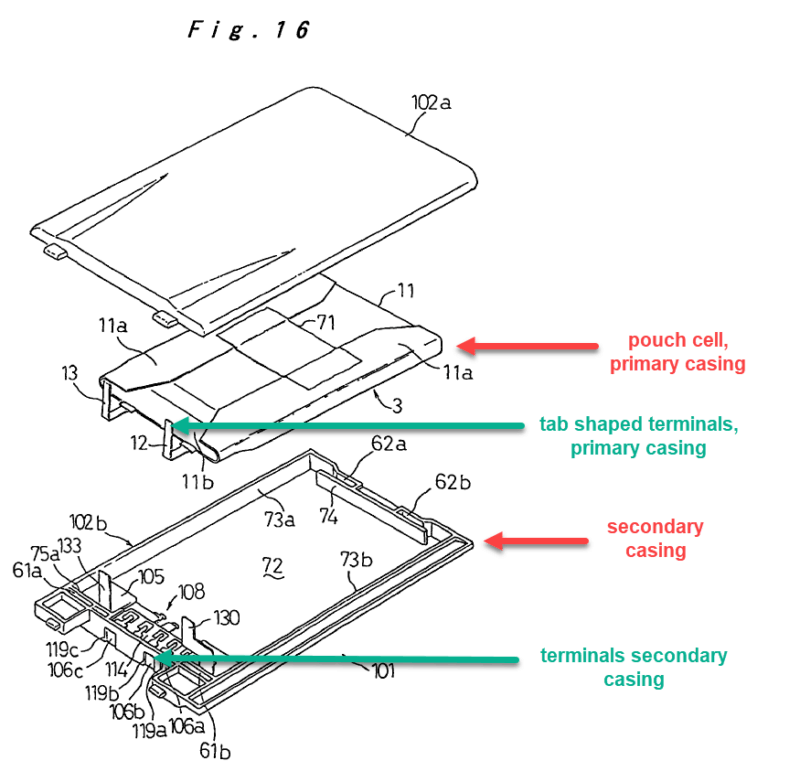
Physical properties should only be classified if supported by numerical values or exemplifying the solution of the problem to be solved (e.g. flexibility, foldability; protection against vibrations/impact/swelling).
This place covers:
Methods and mounting arrangements for secondary casings, racks, suspension devices, carrying devices and holders per se.
The mounting of cells or batteries within these casings, racks, etc.
Methods and arrangements for mounting secondary casings, racks, etc. in finished products, e.g. appliances or vehicles, are classified in H01M 50/247, H01M 50/249, H01M 50/251 if the invention relates to the battery casings.
Methods of mounting casings in finished products such as appliances or cars are classified in places appropriate to the finished product if the invention relates to the product, appliance or vehicle.
This place covers:
Illustrative example:
1.
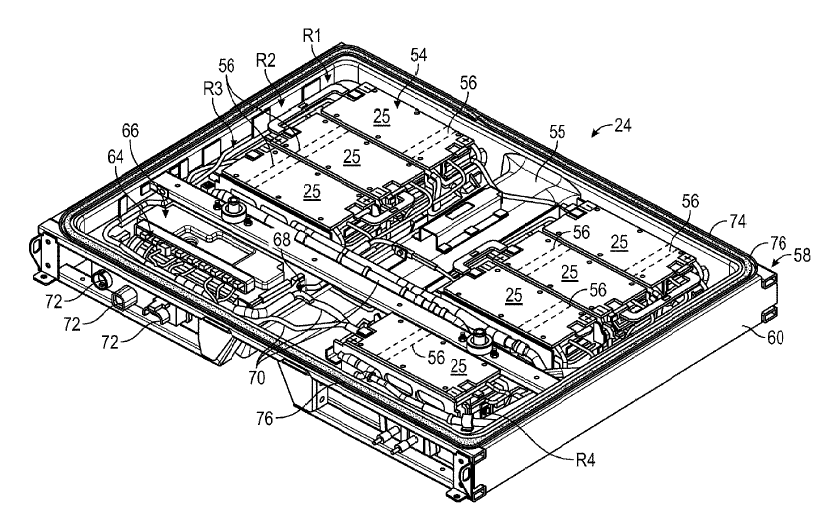
Battery pack 24 that can be used in an electric vehicle.
The battery pack 24 include a battery system 54 housed in a housing assembly 58. The housing assembly 58 may be a sealed housing, and may be embodied in any size, shape, and configuration within the scope of the present disclosure. In an embodiment, the housing assembly 58 includes a tray 60 and a cover. During assembly, the battery system 54 can be positioned within the tray 60, and then the cover can be fixedly secured to the tray 60 to seal the battery system 54 therein (discussed further below). The tray 60 and the cover can be made of any material or combination of materials, including metal and/or polymer materials.
The battery system 54 includes a plurality of battery cells 56 that store energy used to power various electrical loads of the electric vehicle 12. The battery cells 56 of the battery system 54 may be stacked side by side to form a group of battery cells 56, sometimes referred to as a battery array. In the embodiment, the battery cell 56 is a prismatic lithium ion battery cell.
The battery system 54 depicted in the figure above includes a plurality of adjacent rows R1-R4 of the battery array 25. In the embodiment, for a total of seven battery arrays, the rows R1 to R3 of the battery system 54 each include two battery arrays, and the row R4 includes one battery array.
The battery array 25 may be arranged in the housing assembly 58 in any configuration. In an embodiment, adjacent battery arrays 25 of rows R1 to R3 are separated by structural beams 55 extending between opposing side walls of tray 60.
B60L 50/64 covers adaptation of battery structures of electric vehicles, e.g. integration into control or safety systems, crash-resistant casings or vibration-damping means.
This place does not cover:
Constructional details of batteries specially adapted for electric vehicles |
This place covers:
Illustrative example for switching between "in series" and "mixed" ("series-parallel") wiring by means of reconfigurable connection pins (40).
Illustrative examples:
1.
In-series" connection configuration
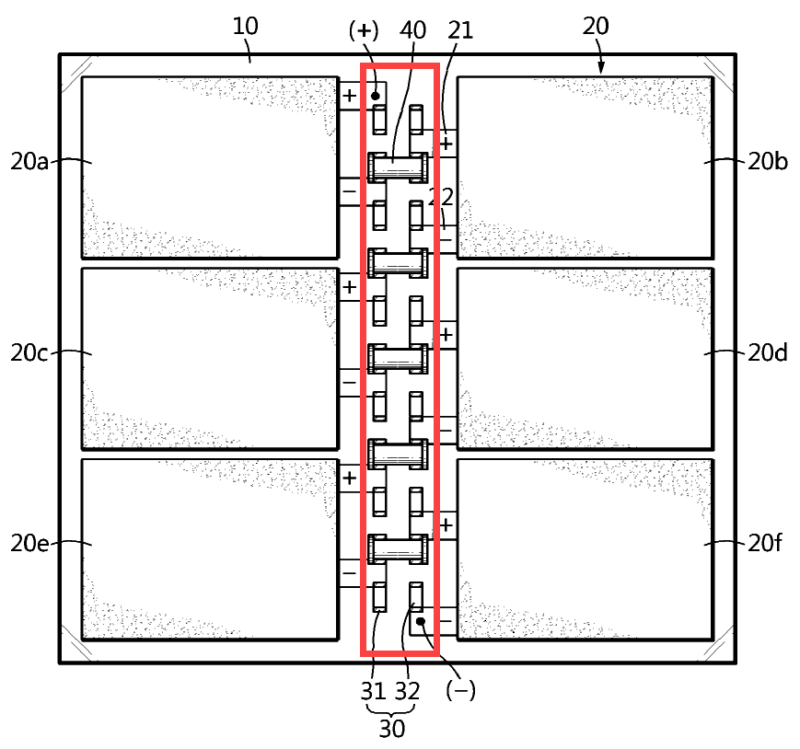
"Mixed" connection configuration
2.
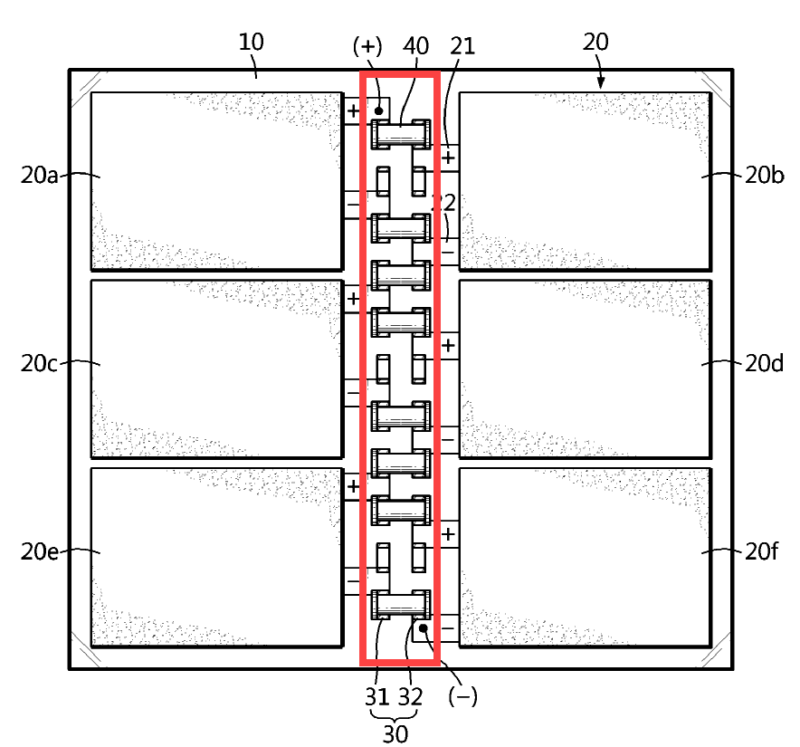
This place does not cover:
Methods or arrangements for servicing or maintenance |
This place covers:
Printed circuit boards [PCB] integrated within mountings, secondary casings, racks, modules or packs, suspension devices, shock absorbers, transport or carrying devices, or holders.
Printed circuit boards [PCB] combined with or integrated in interconnectors are classified in H01M 50/519. This also encompasses the releasable fixing of PCB to an interconnector.
This place does not cover:
Spacing elements inside cells other than separators, membranes or diaphragms |
Cooling plates that do not provide a spacing function are classified in H01M 10/60 and subgroups.
Battery modules assembled by alternately stacking frames and batteries should be classified in H01M 50/289 and in H01M 50/204 and subgroups.
This place covers:
Illustrative example of spacing elements (140):
1.
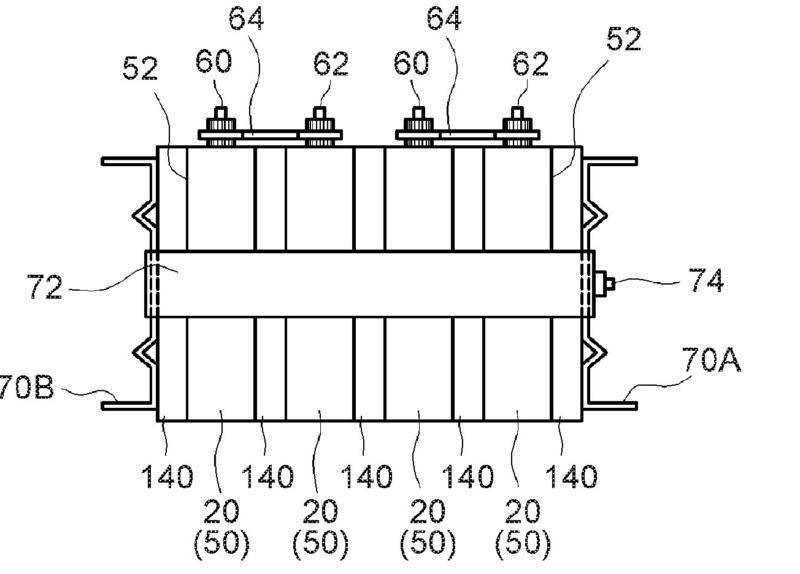
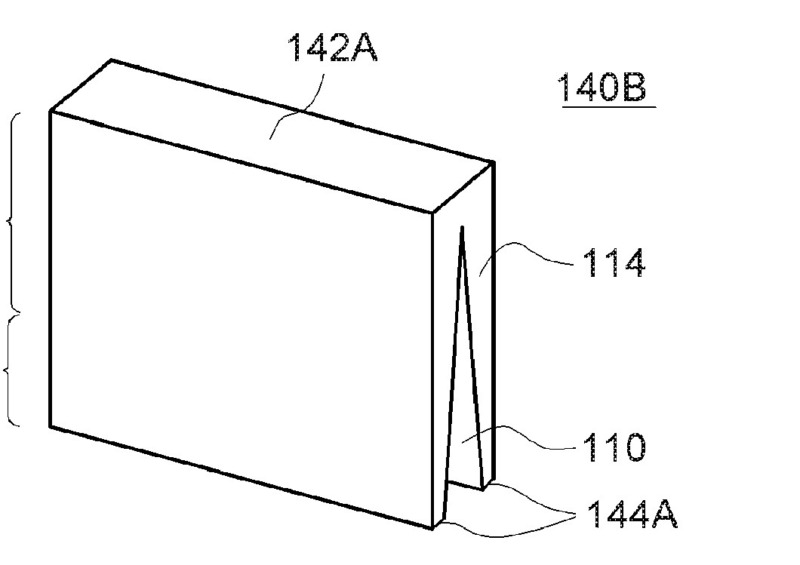
This place covers:
Terminals of secondary casings/battery packs.
This place does not cover:
Terminals of batteries |
Terminals of secondary casing battery are classified in H01M 50/296 only.
Terminals of primary casing battery or terminals formed by the primary casing itself, on the contrary, are classified in subgroups of H01M 50/543.
Illustrative example for distinction between a terminal of primary casing battery and a terminal of a secondary casing battery:
1.

This place covers:
Illustrative example of wiring module (W) of batteries (12):
1.
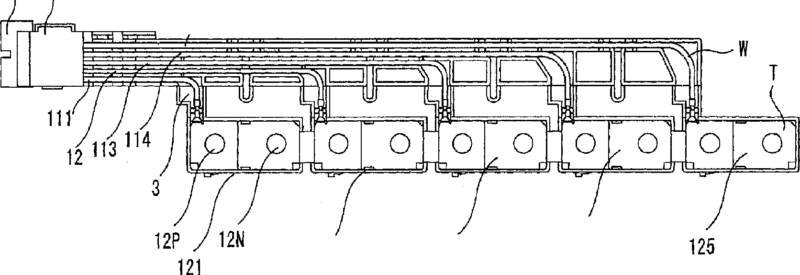
This place covers:
Gas exhaust passages that are external to the cover/lid and located on the cover or case.
Illustrative example for an external gas exhaust passage on the lids:
1.
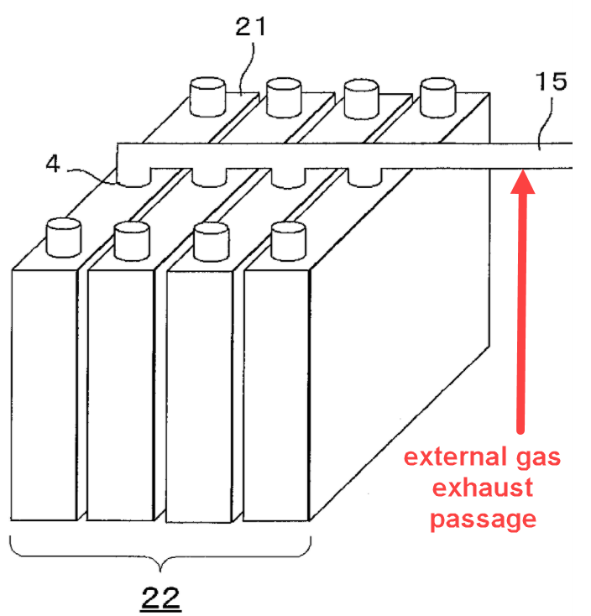
This place covers:
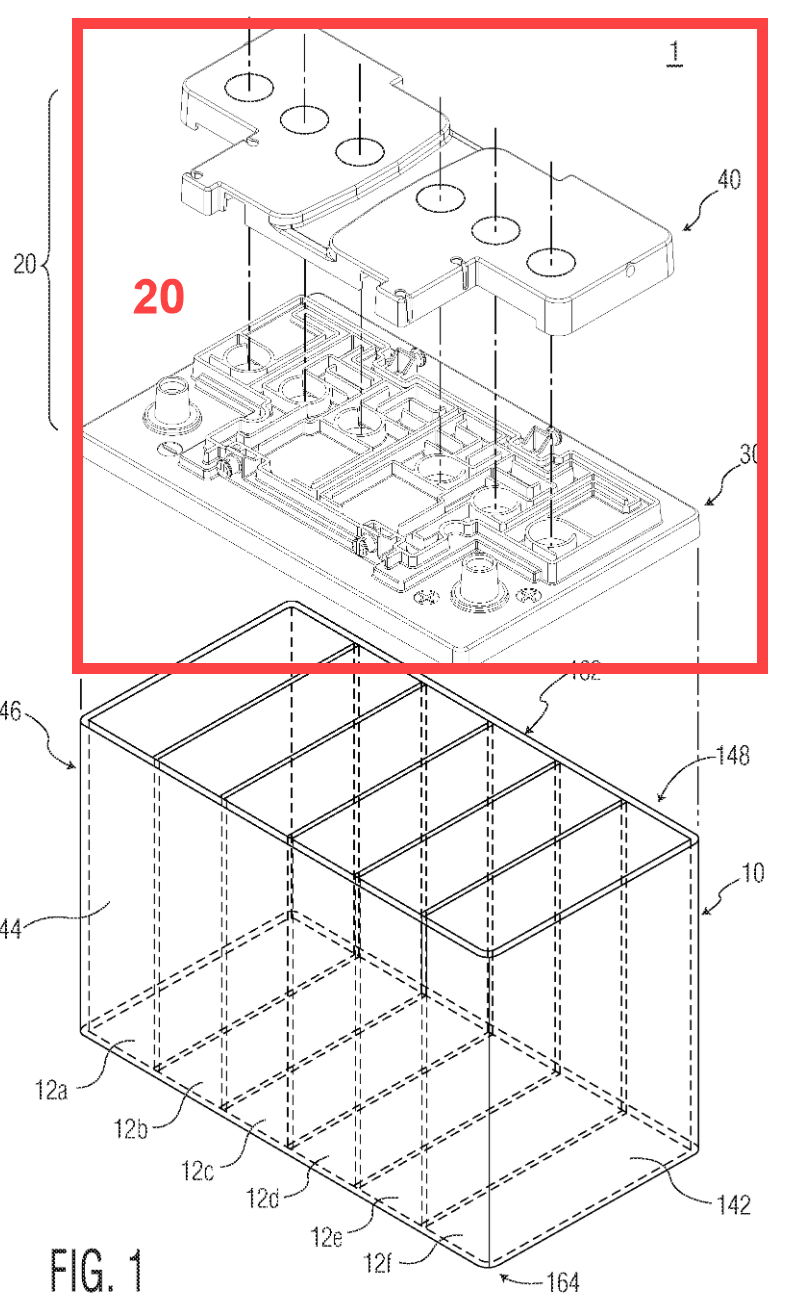
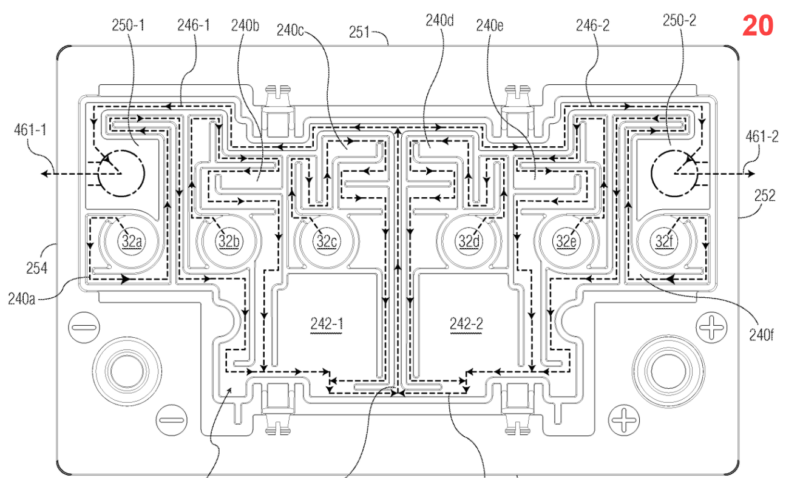
Gas exhaust passages that are internal, i.e. integrated within the cover, lid or casing.
Illustrative example for an internal gas exhaust passage (shown: double cover vent system 20):
1.
2.
Solid electrolytes acting as separators are classified in the application place, such as H01M 10/056 or H01M 12/08, and H01M 50/40 and subgroups for the details concerning composition, structure or manufacturing processes.
This place covers:
Separators comprising layers of only organic material and layers containing inorganic material.
Organic binders can be used in the inorganic layers to hold the inorganic materials together.
This place covers:
Spacing elements.
Note:
Spacing elements are elements arranged within the primary casing but not between opposing electrochemically active electrodes.
Spacing elements differ from separators or diaphragms by virtue of their positioning inside the primary casing.
Illustrative example of spacer (glass wool 46 in head spacer: H01M 50/474 and H01M 50/483):
1.
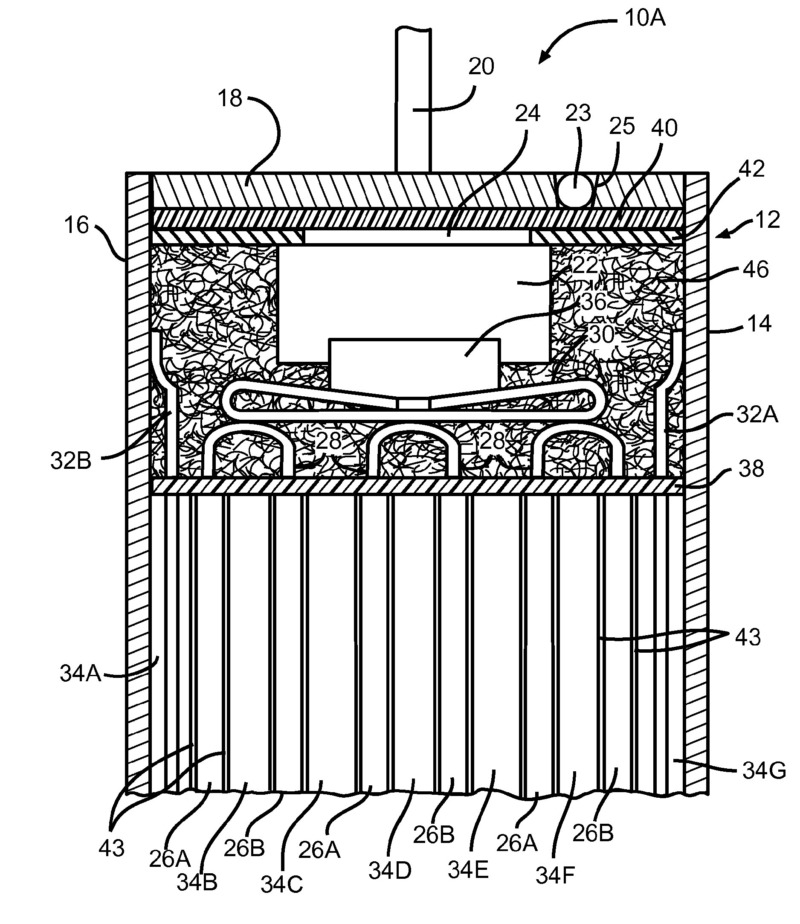
This place does not cover:
Spacing elements for preventing incorrect contact inside or outside batteries |
This place covers:
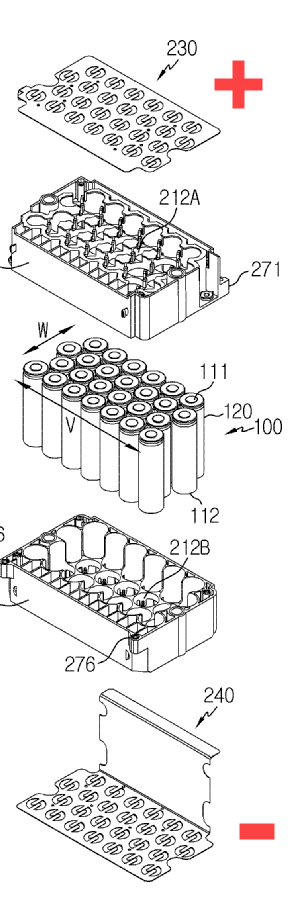
Illustrative example of series-parallel connections:
One portion 240 of a plate connects the negative terminals of a first group of cells together in parallel. Another portion 230 of the plate connects the positive terminals of a second group of cells together in parallel. Another portion 244 of the plate connects the groups of cells in series, forming the basis of a series-parallel group (when the opposite ends of the cells are similarly connected to additional plates).
1.
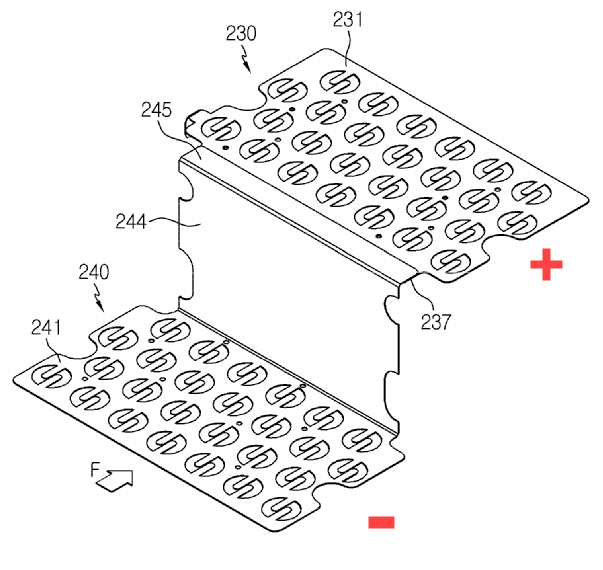
Illustrative example for interconnection only parallel (H01M 50/512):
2.
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms:
"series-parallel" and "mixed connections"
This place covers:
Interconnectors comprising printed circuit boards [PCB].
The PCB is located on or attached directly to the interconnector.
Illustrative examples for PCB fixed to an interconnector:
1.
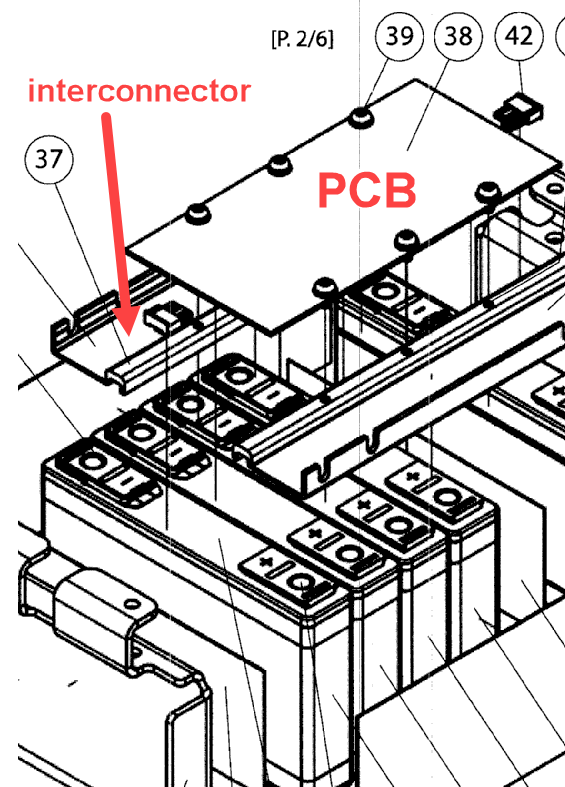
2.
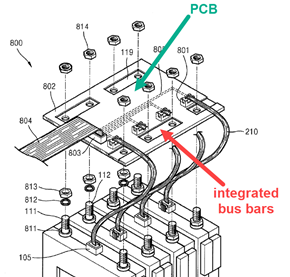
3.
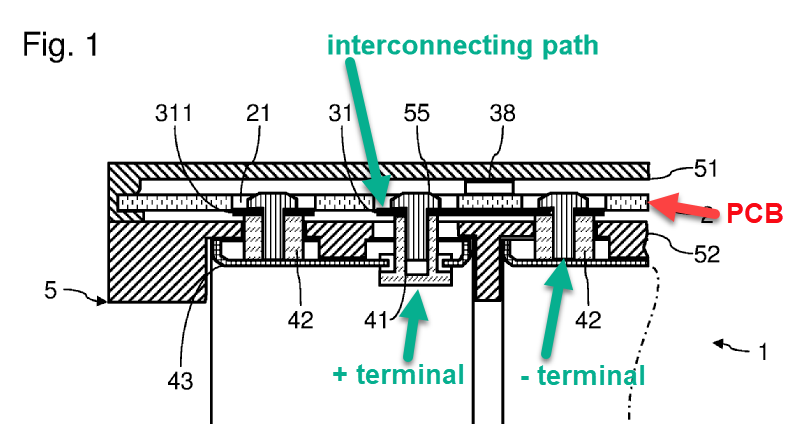
This place covers:
Connections not intended for disconnection in the primary or secondary casing.
Illustrative example:
Connection members (30 and 33), which are not intended for disconnection, are welded to the primary casing battery terminal tabs (12 and 13, respectively) for connection to the protective circuit and the external terminals of the secondary casing battery:
1.
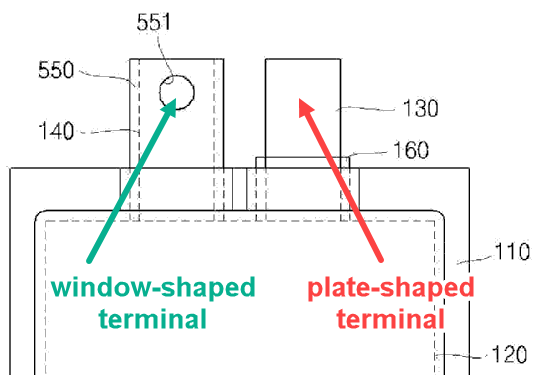
This place covers:
Terminals of primary casing batteries adapted to prismatic, pouch or rectangular cells.
Illustrative example for a pouch cell having both a window-shaped terminal (H01M 50/555) and a plate-shaped terminal (H01M 50/557):
1.
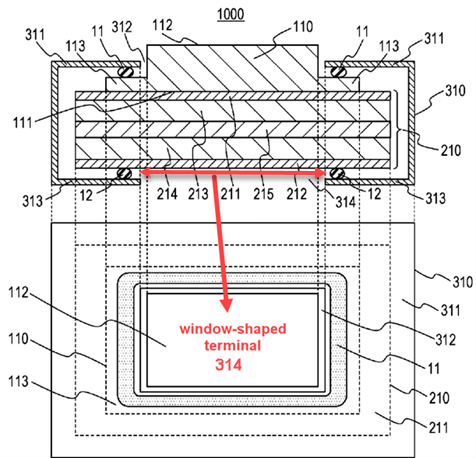
Illustrative example for a solid-state primary casing battery having two different terminals, namely a window-shaped terminal (H01M 50/555) and a knob-shaped terminal (H01M 50/553):
2.
This place covers:
Processes of manufacturing terminals, including fixing the terminals of primary casing batteries to the lid, to the casing or to inner connectors.
If terminals are electrically connected to cell internal contacts during the process, then it is classified in H01M 50/564 and H01M 50/528.
This place covers:
Illustrative example for a fixing process by welding:
1.
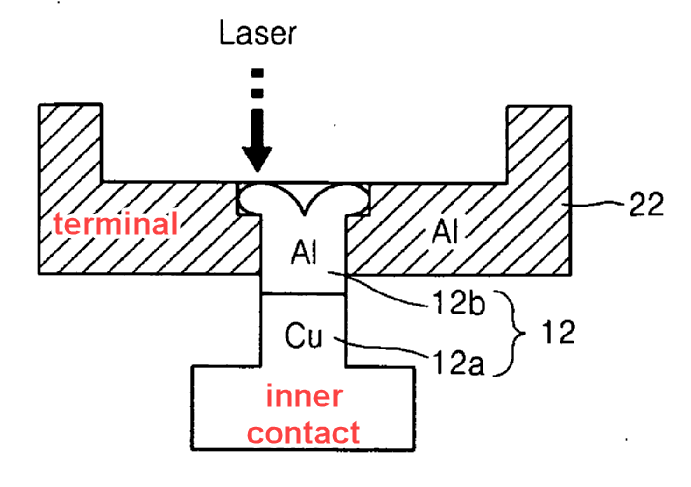
This place covers:
Illustrative example for a fixing process by riveting:
1.
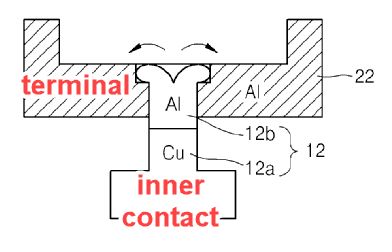
This place covers:
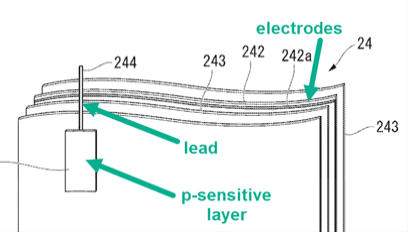
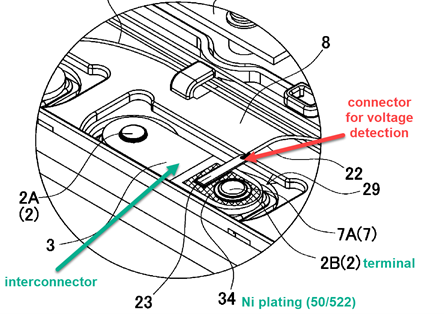
Arrangements of current conducting connections for detecting conditions inside cells or batteries.
Illustrative example of the integration of a pressure sensitive detector inside a battery:
1.
Illustrative example of an electrical connection probe specifically fixed to an interconnector for detecting voltage:
2.
This place does not cover:
Battery terminal connectors with integrated measuring arrangements |
This place covers:
Means for preventing incorrect electrical contact inside or outside a (primary or secondary) casing.
This place covers:
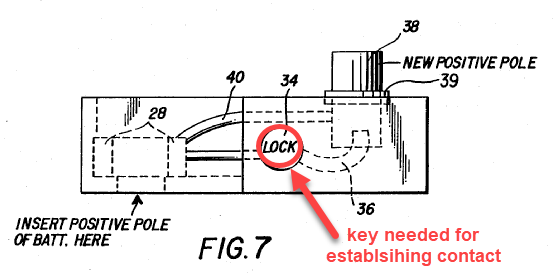
This encompasses aspects relating to the interruption of an established current connection and to aspects denying establishment of a current connection in the event of a (detected) theft or the absence of authorizing features (as a result of theft).
Illustrative example of a device requiring authorization by means of a key:
1.
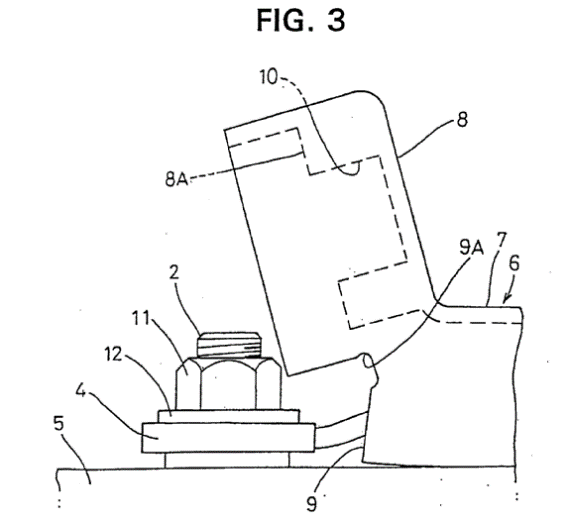
This place covers:
Covers for preventing incorrect or inadvertent electrical contact inside or outside a casing, e.g. for protecting terminals.
Illustrative example for a cover-like contact preventing means (H01M 50/591) being outside the casing (H01M 50/588):
1.
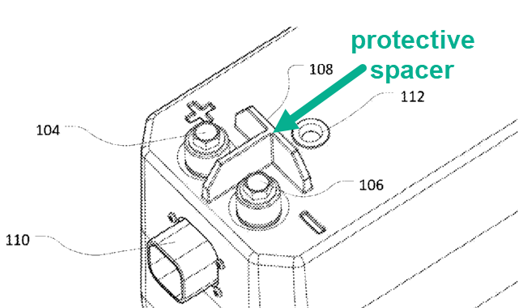
This place covers:
Spacers, insulating plates or barriers outside a primary or secondary casing for preventing incorrect or inadvertent electrical contact, e.g. short circuits between terminals.
Illustrative example for a spacer-like contact preventing means (H01M 50/593) being outside the casing (H01M 50/588):
1.
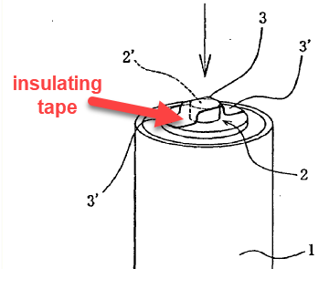
This place covers:
Means for preventing incorrect electrical contact inside or outside a (primary or secondary) casing having the shape of a tape.
Illustrative example for a tape-like contact preventing means (H01M 50/595) being outside the casing (H01M 50/588):
1.
This place covers:
Means capable of indicating improper use of a battery.
As an example, submersion labels are cited, irreversibly changing their colour, for instance, when having had contact with liquid water or excessive humidity. The manufacturer can then challenge the guarantee due to proven improper use.
Labels, e.g. guarantee labels, may be visibly located at the outside of the housing or be hidden inside, to identify if the battery has been used.
Illustrative example for a guarantee label (H01M 50/598) being outside the casing (H01M 50/588):
1.
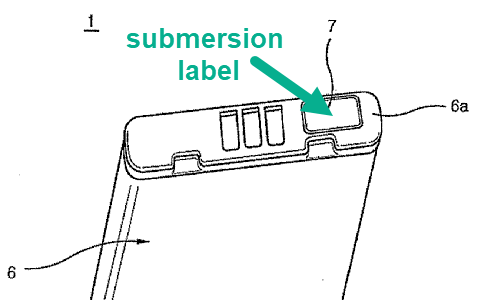
This place covers:
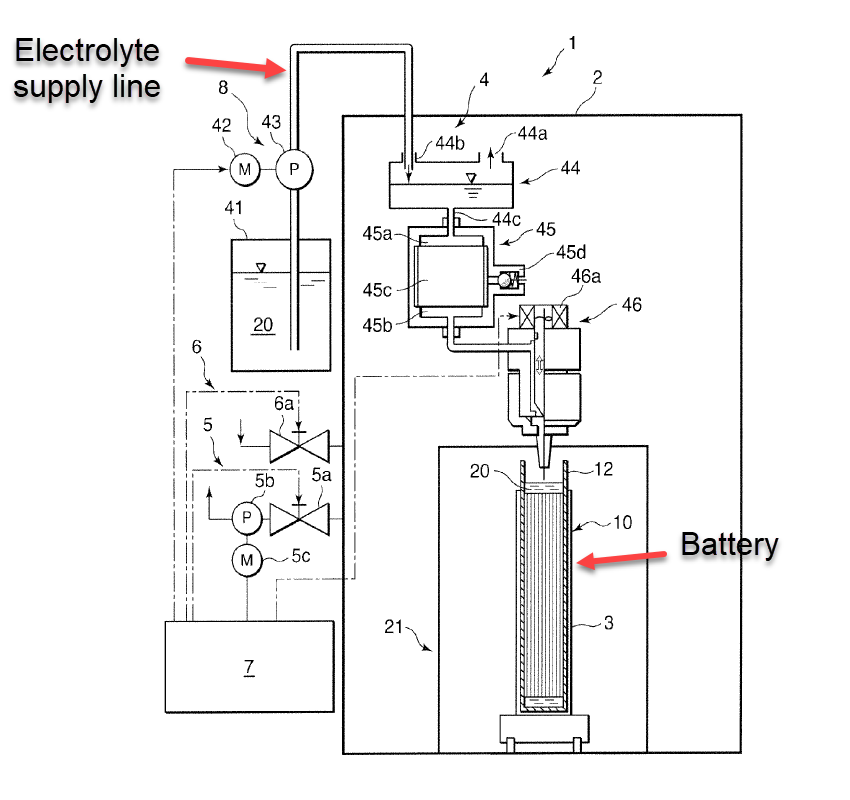
Constructional details or processes for filling/topping-up with liquids or for draining liquids from casings.
Liquids may be an electrolyte, liquids for rinsing, liquids poured into casing in exceptional cases such as an emergency.
Illustrative example for a fire extinguishing liquid deliverable into casing by means of delivery conduits (H01M 50/673) for supplying electrolyte to a battery:
1.
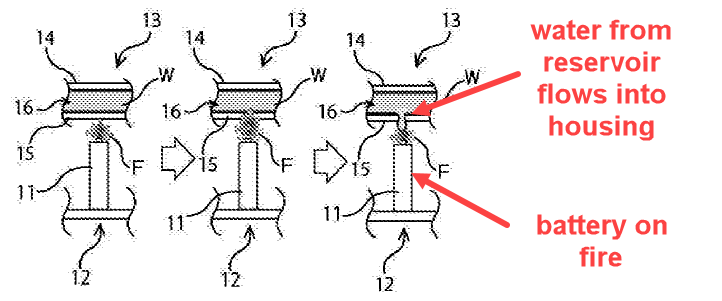
Illustrative example for a (fire extinguishing) liquid poured into casing from a container integrated in the lid of a battery casing (H01M 50/682):
2.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Combination of fuel cells with other electrochemical generators, e.g. capacitors, electrolysers |