![[Search a list of Patent Appplications for class 74]](../as.gif) CLASS 74, CLASS 74, | MACHINE ELEMENT OR MECHANISM |
| Click here for a printable version of this file | |
SECTION I - CLASS DEFINITION
Mechanical combinations, contrivances, or devices constituting portions of machines, instruments and apparatus and consisting of two or more fixed and movable parts so combined that the motion of one compels a completely controlled or constrained motion of the other according to a law of operation inherent in and depending on the nature of the combination, and also the elemental parts of such machines not provided for in other machine element classes.
SECTION II - LINES WITH OTHER CLASSES AND WITHIN THIS CLASS
This class is intended as a generic class for mechanism and machine parts not otherwise classified. Other machine element classes subgeneric hereto are Class 384, Bearings; Class 464, Rotary Shafts, Gudgeons, Housings, and Flexible Couplings for Rotary Shafts.
This class does not include machines and instruments or apparatus claimed as such, for which see the appropriate art classes. It does not include the special tools, instruments, and subcombinations peculiar to the special arts and provided for in the classification of the art classes.
SECTION III - REFERENCES TO OTHER CLASSES
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 70, | Locks, appropriate subclasses and particularly subclasses 174+ , for machine elements combined with locks wherein the element or its associated structure is modified solely to accommodate the lock, or where the device is modified for the reception of a locking device, whether or not claimed. |
| 73, | Measuring and Testing, subclasses 488+ for a speed responsive device, per se. |
| 92, | Expansible Chamber Devices, for the line between Class 74 and Class 92, see References to Other Classes of the class definition of Class 92 under SEARCH CLASS 74. |
| 123, | Internal-Combustion Engines, subclasses 90.1+ and 188.1+, for valve operating mechanism. |
| 173, | Tool Driving or Impacting, appropriate subclass for subject matter directed to driving or impacting a tool, when such subject matter includes combined features peculiar to tool driving, but which does not include features limiting the subject matter to a specific tool art, such as specific shape of the work contacting portion of the tool, related tools, or an opposed work support. See References to Other Classes of the Class 173 class definition for a statement of the line with Class 74. |
| 187, | Elevator, Industrial Lift Truck, or Stationary Lift for Vehicle, appropriate subclasses. |
| 188, | Brakes, appropriate subclasses and especially subclasses 105 through 108for brake operators. |
| 192, | Clutches and Power-Stop Control, appropriate subclasses and especially subclasses 82+ , for clutch operators. |
| 193, | Conveyors, Chutes, Skids, Guides, and Ways, appropriate subclasses. |
| 198, | Conveyors: Power-Driven, appropriate subclasses. |
| 242, | Winding, Tensioning, or Guiding, appropriate subclasses. |
| 251, | Valves and Valve Actuation, subclasses 213+ for mechanical movement valve actuators. |
| 267, | Spring Devices, appropriate subclasses. |
| 279, | Chucks or Sockets, appropriate subclasses. |
| 296, | Land Vehicles: Bodies and Tops, various subclasses for bodies and tops having movable components which may be actuated by mechanical means. |
| 384, | Bearing, appropriate subclasses, and see (1) Note above. |
| 464, | Rotary Shafts, Gudgeons, Housings, and Flexible Couplings for Rotary Shafts, see (1) Note supra. |
| 474, | Endless Belt Power Transmission Systems or Components, appropriate subclasses, and see particularly (5) Note under Lines With Other Classes in the class definition of Class 474. |
| 475, | Planetary Gear Transmission Systems or Components, for planetary gear transmissions. |
| 476, | Friction Gear Transmission Systems or Components, for friction gear transmissions. |
| 477, | Interrelated Power Delivery Controls, Including Engine Control, for interrelated control between an engine and a transmission. |
SUBCLASSES
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 1]](../ps.gif) 1 1 | MISCELLANEOUS: | ||
| This subclass is indented under the class definition. Miscellaneous mechanisms and not provided for below.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 1.5]](../ps.gif) 1.5 1.5 | ESCAPEMENTS: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under the class definition. Mechanisms comprising devices in which a unidirectionally
biased power member, during at least a portion of its movement, imparts
motion to an element which, as a result of such movement, alternately
locks and releases the biased member for intermittent operation.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 2]](../ps.gif) 2 2 | AUTOMATIC OPERATION OR CONTROL (E.G., TRIPS): | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| This subclass is indented under the class definition. Mechanisms for releasing or tripping portions of machines
to cause other portions to automatically operate due to the expenditure
of the potential energy possessed by such parts.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 3]](../ps.gif) 3 3 | Speed controlled: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 2. Mechanisms wherein the releasing or tripping is initiated
by a speed responsive device.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 3.2]](../ps.gif) 3.2 3.2 | Valve gear trips (e.g., steam engine "Corliss" type): | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 3. Mechanisms wherein a flow controlling valve is the released
or tripped device.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 3.5]](../ps.gif) 3.5 3.5 | Retarded: | ||||||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 2. Mechanisms preset to cause the releasing or tripping at
a particular time of day or at the termination of a particular time
interval following the setting.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 3.52]](../ps.gif) 3.52 3.52 | Plural, sequential, trip actuations: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 3.5. Mechanism preset to cause sequential tripping of a single part or tripping of several parts in sequence. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 3.54]](../ps.gif) 3.54 3.54 | Clock train: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 3.5. Mechanism including a clock, a clock train or similar gearing. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 3.56]](../ps.gif) 3.56 3.56 | Winding knob trip (e.g., alarm mechanism): |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 3.54. Mechanism wherein the trip includes the winding knob of a spring powered clock train or the winding knob of a spring powered operator (e.g., alarm mechanism) under the control of the clock train. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 4]](../ps.gif) 4 4 | Hit and miss: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 2. Mechanism wherein the releasing or tripping is intermittent and the mechanism is intended to insure a uniform speed output. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 5]](../ps.gif) 5 5 | GYROSCOPES: | ||||||||||||||||
This subclass is indented under the class definition. Devices defined in (1) Note, below and known as gyroscopes.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 5.1]](../ps.gif) 5.1 5.1 | With caging or parking means: | ||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 5. Gyroscopes combined with mechanism to hold the rotor axis
fixed, when the rotor is not spinning, or if spinning, when it is
desired to take the gyroscope out of useful operation.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 5.12]](../ps.gif) 5.12 5.12 | Rotor spin and cage release type: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 5.1. Devices having a mechanism to impart spin to a rotor and
a further means to release the holding means after the rotor is
up to speed.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 5.14]](../ps.gif) 5.14 5.14 | And resetting means: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 5.1. Devices wherein further means is provided to adjust or vary the position held. This may be done by having the means which holds the rotor axis adjustable to vary the position held, or by having the first means restrain movement in one plane and a second means to position the rotor axis in that plane. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 5.2]](../ps.gif) 5.2 5.2 | With gimbal lock preventing means: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 5. Gyroscopes wherein means is provided to prevent alignment of the rotor axis with a gimbal axis. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 5.22]](../ps.gif) 5.22 5.22 | Combined: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 5. Gyroscopes combined with structure other than the gyroscope,
except means to control and/or drive the mechanism.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 5.34]](../ps.gif) 5.34 5.34 | Multiple gyroscopes: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 5. Gyroscopes comprising two or more gyroscopes. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 5.37]](../ps.gif) 5.37 5.37 | With rotor drives: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 5.34. Devices having means for driving the gyroscopes.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 5.4]](../ps.gif) 5.4 5.4 | Gyroscope control: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 5. Gyroscopes having means to apply one or more forces to the rotor axis to control the movement of the rotor axis about its center of suspension. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 5.41]](../ps.gif) 5.41 5.41 | Erecting: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 5.4. Devices wherein one or more forces act to move the rotor
axis to a given position, usually to a vertical position.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 5.42]](../ps.gif) 5.42 5.42 | By plural diverse forces: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 5.41. Devices where at least two diverse forces are used for erection.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 5.43]](../ps.gif) 5.43 5.43 | By jet: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 5.41. Devices wherein the force of a fluid jet is used for erection. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 5.44]](../ps.gif) 5.44 5.44 | By weight: | ||||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 5.41. Devices wherein the gravitational force upon a weight is
utilized for erection.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 5.45]](../ps.gif) 5.45 5.45 | By friction: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 5.41. Devices wherein the application of a frictional force is
utilized for erection.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 5.46]](../ps.gif) 5.46 5.46 | By magnetic field: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 5.41. Devices wherein the force of a magnetic field is utilized for erection. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 5.47]](../ps.gif) 5.47 5.47 | By motor torque: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 5.41. Devices where the torque of a prime mover constitutes the force used for erection. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 5.5]](../ps.gif) 5.5 5.5 | Damping: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 5.4. Devices having means to dampen the oscillation of the gimbals, or of the rotor axis. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 5.6]](../ps.gif) 5.6 5.6 | With pick off: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 5. Gyroscopes having a means to sense the relative position
or change of position of the rotor axis, and/or its gimbals.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 5.7]](../ps.gif) 5.7 5.7 | With rotor drive: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 5. Gyroscopes having means to drive the rotor.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 5.8]](../ps.gif) 5.8 5.8 | Vertical gyroscopes: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 5. Gyroscopes peculiarly constructed for operating with the spin axis in a vertical position only. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 5.9]](../ps.gif) 5.9 5.9 | Horizontal gyroscopes: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 5. Gyroscopes peculiarly constructed for operating with the spin axis in a horizontal position only. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 5.95]](../ps.gif) 5.95 5.95 | Flywheel structure: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 5. Subject matter including a motion-smoothing component
generally made up of a massive disk-like member.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 6]](../ps.gif) 6 6 | ENGINE STARTERS: | ||||||||||
This subclass is indented under the class definition. Mechanical movements and/or gearing, combined as
a unit, for initiating the starting of a machine, in which operative
engagement with the machine to be started is initiated and controlled
and power is applied to the gearing by some conventional means.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 7]](../ps.gif) 7 7 | Automatic: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 6. Starters in which the operative engagement with the machine to be started is automatic. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 8]](../ps.gif) 8 8 | Radial meshing: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 6. Starters in which meshing of the gears with the machine to be started takes place in a radial direction. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 9]](../ps.gif) 9 9 | Cam operated: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 6. Starters in which meshing of the gearing with the machine to be started is accomplished by a cam device other than a screw. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 10]](../ps.gif) 10 10 | SHAFT OPERATORS (RADIO TUNER TYPE): | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This subclass is indented under the class definition. Assemblies particularly adapted for mechanically rotating
one or more shafts of electronic tuning devices into desired angular positions.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 10.1]](../ps.gif) 10.1 10.1 | Preselected position: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 10. Devices having interengaging means by which the rotation of the shaft may be halted at a plurality of predetermined angular positions. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 10.15]](../ps.gif) 10.15 10.15 | Step by step: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 10.1. Devices having means interposed between a single initiator
and the shaft for rotating the shaft through a series of successive
predetermined positions, the rotation of the shaft being halted
at each such successive position.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 10.2]](../ps.gif) 10.2 10.2 | Rotatable stop and projectable abutment: | ||||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 10.1. Devices having a rotatable stop element for halting shaft
movement and a movable abutment for the stop element, and means
for moving the abutment into a position in which the stop element
may contact the abutment.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 10.22]](../ps.gif) 10.22 10.22 | Digital dial type: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 10.1. Devices in which the shaft operator is a dial and is provided
with a series of single finger-receiving openings.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 10.27]](../ps.gif) 10.27 10.27 | Plural operator: | ||||||||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 10.1. Devices having more than one operator for controlling the
shaft.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 10.29]](../ps.gif) 10.29 10.29 | Cam and follower: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 10.27. Devices wherein a cam and follower is interposed between
the operator and the shaft.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 10.31]](../ps.gif) 10.31 10.31 | Adjustable cam: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 10.29. Devices wherein the cam is adjustable.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 10.33]](../ps.gif) 10.33 10.33 | Sliding operator: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 10.31. Devices where the cam is carried by a sliding operator. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 10.35]](../ps.gif) 10.35 10.35 | Adjustable follower: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 10.29. Devices wherein the follower is adjustable.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 10.37]](../ps.gif) 10.37 10.37 | Sliding operator: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 10.35. Devices where the cam is carried by a sliding operator. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 10.39]](../ps.gif) 10.39 10.39 | Rack and pinion: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 10.27. Devices wherein a rack and pinion gearing is interposed
between at least one of the operators and the shaft.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 10.41]](../ps.gif) 10.41 10.41 | With detent or clicker: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 10.1. Devices in which a detent or click device tends to hold
the shaft in the predetermined positions.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 10.45]](../ps.gif) 10.45 10.45 | Plural shafts: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 10. Devices in which a plurality of shafts are rotated by a
single operator.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 10.5]](../ps.gif) 10.5 10.5 | Plural speed: | ||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 10. Devices in which the shaft may be rotated at a plurality
of speeds.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 10.52]](../ps.gif) 10.52 10.52 | Planetary: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 10.5. Devices wherein a planetary gearing is interposed between
the operator and the shaft.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 10.54]](../ps.gif) 10.54 10.54 | Separate operators: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 10.5. Devices having separate operators for each speed.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 10.6]](../ps.gif) 10.6 10.6 | Cam and follower: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 10. Devices wherein a cam and follower is interposed between
the operator and the shaft.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 10.7]](../ps.gif) 10.7 10.7 | Tensioned flexible operator: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 10. Devices wherein the operator includes a flexible strand
operating in tension only, usually in the nature of a belt and pulley
drive, although the strand may be anchored to one of the pulleys.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 10.8]](../ps.gif) 10.8 10.8 | Gear drive: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 10. Devices wherein gearing is interposed between the operator
and the shaft.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 10.85]](../ps.gif) 10.85 10.85 | Worm or screw: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 10.8. Devices where the gearing is of the worm or screw type.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 10.9]](../ps.gif) 10.9 10.9 | Lever and linkage drive: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 10. Devices wherein a lever and linkage system is interposed
between the operator and the shaft.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 11]](../ps.gif) 11 11 | POWER TAKE-OFF: | ||||||||||||||||||||
This subclass is indented under the class definition. Devices comprising a subordinate power transmitting assembly,
additional to and driven by one of the elements of a main power
line, or by the prime mover therefor.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||||||||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 12]](../ps.gif) 12 12 | Speedometer: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 11. Assemblies, in which the auxiliary driven element is a speedometer. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 13]](../ps.gif) 13 13 | Wheel take-off: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 11. Mechanisms, in which the power is taken directly from or
transmitted directly to, the wheels of a vehicle.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 14]](../ps.gif) 14 14 | Wheel bed type: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 13. Mechanisms, in which the mechanisms are provided with power transmitting or receiving elements which contact with and support at least one wheel of the vehicle. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 15]](../ps.gif) 15 15 | Supported pulley: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 13. Mechanisms, in which power is delivered from or to a vehicle
wheel through a device attached thereto, the wheel being out of
peripheral contact with any other object.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 15.2]](../ps.gif) 15.2 15.2 | Plural take-off shafts: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 11. Devices having a plurality of power take-off shafts.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 15.4]](../ps.gif) 15.4 15.4 | With independent change speed gearing: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 11. Devices in which independent gearing means are provided
to effect a change in output speed of, and/or a forward
or reverse drive for, the take-off.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 15.6]](../ps.gif) 15.6 15.6 | From shaft extension: | ||||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 11. Devices in which either a prime mover shaft, a main power
line shaft, or an auxiliary driven shaft is extended to constitute
a power take-off.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 15.63]](../ps.gif) 15.63 15.63 | Prime mover shaft, e.g., crank shaft: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 15.6. Devices in which a shaft in a prime mover for the power
line (e.g., a crank shaft or a cam shaft) is extended to constitute
a take-off.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 15.66]](../ps.gif) 15.66 15.66 | Change speed transmission shaft: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 15.6. Devices in which a shaft in a change speed transmission is extended to constitute the take-off. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 15.69]](../ps.gif) 15.69 15.69 | Vehicle propeller shaft: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 15.6. Devices in which the propeller shaft of a vehicle is extended
to constitute a take-off.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 15.8]](../ps.gif) 15.8 15.8 | Intermediate ends of power transmitting line: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 11. Devices which are driven by a connection in the main power
transmitting line and intermediate its driving and driven ends.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 15.82]](../ps.gif) 15.82 15.82 | Vehicle propulsion transmitting line: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 15.8. Devices in which the power transmitting line is used for vehicle propulsion. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 15.84]](../ps.gif) 15.84 15.84 | Between prime mover shaft and transmission: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 15.82. Devices in which the connection to the transmitting line is located between the prime mover output shaft and the transmission. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 15.86]](../ps.gif) 15.86 15.86 | Drive from transmission gear: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 15.82. Devices in which the driving connection comprises a gear in mesh with a second gear, which second gear is part of the transmission gearing. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 15.88]](../ps.gif) 15.88 15.88 | Between transmission and propeller shaft: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 15.82. Devices in which the driving connection to the transmitting
line is located between the driven shaft of the transmission and
the propeller shaft.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 16]](../ps.gif) 16 16 | POWER TABLES AND STANDS: | ||||||||||||||||
This subclass is indented under the class definition. Portable assemblies designed to drive one or more auxiliary
attachments.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 17]](../ps.gif) 17 17 | WASHER AND WRINGER: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under the class definition. Assemblies particularly adapted for the operation of a washing
and wringing machine.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 17.5]](../ps.gif) 17.5 17.5 | FULL STROKE MECHANISM: | ||
| This subclass is indented under the class definition. Devices for compelling a reciprocating part to be actuated
to its full extent before it can be returned.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 17.8]](../ps.gif) 17.8 17.8 | MOTION TRANSFER THROUGH IMPERFORATE FLEXIBLE SEAL: | ||||||
This subclass is indented under the class definition. Devices having an imperforate member functioning as a seal
for an aperture in a partition or for a passageway, the member being flexible
at least in part to permit movement with respect to the partition
and being fixed to the partition or walls of the passageway, there being
means contacting one side of the seal member to receive or transfer
motion from or to the member, and there being relative motion between
the seal member and the means at the point of contact.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 18]](../ps.gif) 18 18 | FLEXIBLE SEALING DIAPHRAGM ATTACHED TO MOVING ROD AND TO CASING: | ||||||||||||||
| This subclass is indented under the class definition. Devices in which motion is transmitted through a sealed
casing by means of a flexible sealing material attached to the casing
and to a moving rod which passes through the sealing material.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 18.1]](../ps.gif) 18.1 18.1 | Pivoting or nutating rod: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 18. Devices in which the rod pivots or nutates. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 18.2]](../ps.gif) 18.2 18.2 | Longitudinally reciprocating rod: | ||||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 18. Devices in which the rod reciprocates longitudinally. Mechanical
Movements. Devices under the class definition other than gearing
for imparting motion to one body from the motion of another body,
wherein the two motions, or some intermediate motion, are of different form,
type or degree.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 20]](../ps.gif) 20 20 | Oscillating to reciprocating and alternating rotary: |
| Mechanical Movements for converting oscillating motion to the compound motion of reciprocation and alternating rotary motion. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 21]](../ps.gif) 21 21 | Oscillating to reciprocating and intermittent rotary: |
| Mechanical Movements for converting oscillating motion to the compound motion of reciprocation and intermittent rotary motion. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 22]](../ps.gif) 22 22 | Rotary to reciprocating and rotary: | ||||||
| Mechanical Movements for converting rotary motion to the
combined motion of reciprocation and rotary motion.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 23]](../ps.gif) 23 23 | Rotary to reciprocating and alternating rotary: |
| Mechanical Movements for converting rotary motion to the compound motion of reciprocation and alternating rotary motion. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 24]](../ps.gif) 24 24 | Rotary to reciprocating and intermittent rotary: |
| Mechanical Movements for converting rotary motion to the compound motion of reciprocation and intermittent rotary motion. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 25]](../ps.gif) 25 25 | Rotary to or from reciprocating or oscillating: | ||||||||
| Mechanical Movements for converting rotary motion to or
from reciprocating or oscillating motion.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 26]](../ps.gif) 26 26 | Head motions: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 25. Mechanisms, especially adapted for shaking screens in which
the screen is not claimed as a positive element and excepting those
driven by unbalanced weights.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 27]](../ps.gif) 27 27 | Reciprocating carriage motions: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 25. Mechanisms for converting rotary motion to or from reciprocating
or oscillating motion of a carriage in which the driven member is
driven by different types of mechanism during different parts of
its stroke.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 28]](../ps.gif) 28 28 | Phonograph type: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 27. Mechanisms, especially adapted for moving the tone arm of
a phonograph across the record.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 29]](../ps.gif) 29 29 | Rack and pinion type: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 25. Mechanisms, in which the mechanism involved is a rack and pinion and cannot be classified in any of the subclasses under this subclass. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 30]](../ps.gif) 30 30 | Shifting rack: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 29. Mechanisms, in which the rack moves in and out of engagement with the pinion. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 31]](../ps.gif) 31 31 | Shiftable pinion: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 29. Mechanisms, in which the pinion moves in and out of engagement with the rack. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 32]](../ps.gif) 32 32 | Segmental pinion: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 29. Mechanisms, in which the teeth on the pinion cover less than 360 degrees of the circumference of the pinion. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 33]](../ps.gif) 33 33 | Alternately rotated pinion: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 29. Mechanisms, in which the pinion is always in mesh with the rack but its direction of rotation is alternated. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 34]](../ps.gif) 34 34 | Clutchable gears: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 29. Mechanisms, in which the pinion or pinions are constantly in mesh with the rack but are clutched and declutched to the shaft by which they are carried. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 35]](../ps.gif) 35 35 | Bevel: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 34. Mechanisms, in which the pinion or pinions are constantly in mesh with the rack but are clutched and declutched to the shaft by which they are carried, the pinions being of the bevel type. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 36]](../ps.gif) 36 36 | Overcoming dead center: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 25. Mechanisms, in which the mechanisms involved either prevents the device from stopping on dead center or has some auxiliary mechanism for throwing the device off of dead center. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 37]](../ps.gif) 37 37 | Belt or chain carried member: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 25. Mechanisms, which change the motion by means of a chain or belt. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 38]](../ps.gif) 38 38 | Crank, lever, toggle, and slide: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 25. Mechanisms, including a crank, lever, toggle, and slide. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 39]](../ps.gif) 39 39 | Crank, lazy-tong, and slide: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 25. Mechanisms, including a crank, lazy-tong, and slide. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 40]](../ps.gif) 40 40 | Crank, pitman, lever, and slide: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 25. Mechanisms, including a crank, pitman, lever, and slide.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 41]](../ps.gif) 41 41 | Pump jack type: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 40. Mechanisms, including a crank, pitman, lever and slide of the pump jack type. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 42]](../ps.gif) 42 42 | Crank, pitman, and lever: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 25. Mechanisms, including a crank, pitman, and lever.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 43]](../ps.gif) 43 43 | Multiple levers: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 42. Mechanisms, including a crank, pitman, and a plurality of levers. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 44]](../ps.gif) 44 44 | Crank, pitman, and slide: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 25. Mechanisms, including a crank, pitman, and slide. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 45]](../ps.gif) 45 45 | Crank, lever, and slide: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 25. Mechanisms, including a crank, lever, and slide.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 46]](../ps.gif) 46 46 | Rack connections: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 45. Mechanisms, including a crank, lever, and slide and the connection between part of the members including a rack. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 47]](../ps.gif) 47 47 | Crank and lever: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 25. Mechanisms, including a crank and lever.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 48]](../ps.gif) 48 48 | Slidable connections: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 47. Mechanisms, including a crank and lever with a slidable connection between the crank and lever. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 49]](../ps.gif) 49 49 | Crank and slide: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 25. Mechanisms, including a crank and slide.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 50]](../ps.gif) 50 50 | Slidable connections (e.g., scotch yoke): |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 49. Mechanisms, including a crank and slide with a slidable connection between the crank and slide. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 51]](../ps.gif) 51 51 | Crank and multiple pitmans: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 25. Mechanisms, including a crank and more than one pitman. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 52]](../ps.gif) 52 52 | Planetary gearing and slide: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 25. Mechanisms, including planetary gearing and a slide. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 53]](../ps.gif) 53 53 | Cam, lever, and slide: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 25. Mechanisms, including a cam, lever, and slide. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 54]](../ps.gif) 54 54 | Cam and lever: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 25. Mechanisms, including a cam and lever.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 55]](../ps.gif) 55 55 | Cam and slide: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 25. Mechanisms, including a cam and slide.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 56]](../ps.gif) 56 56 | Axial cam: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 55. Mechanisms, including a cam and slide, the cam being of
the axial type.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 57]](../ps.gif) 57 57 | Grooved: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 56. Mechanisms, including a cam and slide, the cam being of the axial type and the cam surface being in the form of a groove in the cam surface. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 58]](../ps.gif) 58 58 | Multiple screw: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 57. Mechanisms, including two axially grooved cams or screws rotating in opposite directions, one of which drives or is driven by the reciprocated or oscillated member or slide in one direction and the other in the opposite direction. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 59]](../ps.gif) 59 59 | Alternately rotated screw: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 57. Mechanisms, including an axially grooved cam connected to a slide, the cam being alternately rotated as the slide alternately changes its direction. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 60]](../ps.gif) 60 60 | Wabbler type: | ||||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 55. Mechanisms, including an axial cam and slide, the cam being
of the wabbler type.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 61]](../ps.gif) 61 61 | Unbalanced weights: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 25. Mechanisms, in which the mechanism involved makes use of
unbalanced weights to produce the reciprocating or oscillating motion.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 62]](../ps.gif) 62 62 | Trammel-pitman: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 25. Mechanisms, in which the mechanism involved includes a cam
having a plurality of intersecting slots, in which slide projections
on a beam or connecting rod.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 63]](../ps.gif) 63 63 | Rotary to rotary: |
| Mechanical movements for changing rotary motion to rotary motion. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 64]](../ps.gif) 64 64 | Inertia or centrifugal transmitters: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 63. Mechanisms, in which the motion is changed by means of inertia
or centrifugal means.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 65]](../ps.gif) 65 65 | Crank, pitman, lever, and crank: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 63. Mechanisms in which the motion is changed by means of a crank, pitman, lever, and crank. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 66]](../ps.gif) 66 66 | Crank, lever, and crank: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 63. Mechanisms, in which the motion is changed by means of a crank, lever, and crank. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 67]](../ps.gif) 67 67 | Crank, pitman, and crank: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 63. Mechanisms, in which the motion is changed by means of a crank, pitman, and crank. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 68]](../ps.gif) 68 68 | Cranks, link connected: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 63. Mechanisms, in which the motion is changed by means of cranks which are connected together by links. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 69]](../ps.gif) 69 69 | Cranks, slidable connections: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 63. Mechanisms, in which the motion is changed by cranks which are slidably connected together. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 70]](../ps.gif) 70 70 | Rotary to alternating rotary: | ||
| Mechanical Movements for converting rotary motion to alternating
rotary motion.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 71]](../ps.gif) 71 71 | Mangle connections: | ||||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 70. Mechanisms, in which the motion is changed by means of a
mangle and gearing and the driving member is the shiftable member.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 72]](../ps.gif) 72 72 | Shiftable driven gear: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 71. Mechanisms, in which the motion is changed by means of a mangle and gearing and the driven member is the shiftable member. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 73]](../ps.gif) 73 73 | Central teeth: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 72. Mechanisms, the driven gear being shiftable and the teeth on the mangle being located along the center line of the mangle. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 74]](../ps.gif) 74 74 | Multilated gearing connections: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 71. Mechanisms, in which the motion is changed by means of a mangle and gearing and the gearing is mutilated. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 75]](../ps.gif) 75 75 | Crank, pitman, and lever: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 70. Mechanisms, in which the motion is changed by means of a crank, pitman, and lever. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 76]](../ps.gif) 76 76 | Reciprocating rack connections: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 70. Mechanisms, in which the motion is changed by means of a reciprocating rack. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 77]](../ps.gif) 77 77 | Crank and pitman actuator: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 76. Mechanisms, in which the motion is changed by means of a reciprocating rack driven by a crank and pitman. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 78]](../ps.gif) 78 78 | Simple crank actuator: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 76. Mechanisms, in which the motion is changed by means of a reciprocating rack driven directly by the crank. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 79]](../ps.gif) 79 79 | Oscillating rack connections: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 70. Mechanisms, in which the motion is changed by means of an oscillating rack. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 80]](../ps.gif) 80 80 | Mangle actuated: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 79. Mechanisms, in which the rack is mangle actuated. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 81]](../ps.gif) 81 81 | Crank and pitman actuator: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 79. Mechanisms, in which the rack is driven by a crank and pitman. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 82]](../ps.gif) 82 82 | Flexible connector type: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 70. Mechanisms, in which the motion is changed by means of a
flexible member.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 83]](../ps.gif) 83 83 | Associated inertia devices: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 70. Mechanisms, in which the motion is changed by inertia devices.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 84]](../ps.gif) 84 84 | Rotary to intermittent unidirectional motion: | ||||||
| Mechanical Movements for changing rotary motion to intermittent
unidirectional motion.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 86]](../ps.gif) 86 86 | Rotary to gyratory: | ||
| Mechanical Movements for converting rotary motion to gyratory
motion.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 87]](../ps.gif) 87 87 | Unbalanced weight: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 86. Mechanisms, in which the motion is changed by means of unbalanced
weights.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 88]](../ps.gif) 88 88 | Reciprocating or oscillating to intermittent unidirectional motion: |
| Mechanical Movements for converting reciprocating or oscillating motion to intermittent unidirectional motion. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 89]](../ps.gif) 89 89 | Reciprocating or oscillating to or from alternating rotary: | ||
| Mechanical movement for converting oscillating or reciprocating
motion to or from alternating rotary motion, all such motions as
defined in the Glossary of this subclass.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
| GLOSSARY | |||
| ALTERNATING MOTION | |||
|
The intermittent movement along a path, first in one direction and then in the opposite along such path. | |||
| OSCILLATING MOTION | |||
|
Alternating motion of less than 360 degrees along an arcuate path. | |||
| RECIPROCATING MOTION | |||
|
Alternating motion along a straight-line path. | |||
| ROTARY MOTION | |||
|
The turning of a rigid body about an internal axis such that a point on the body travels through an arcuate path, about the axis, having an extent of 360 degrees or more. | |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 89.1]](../ps.gif) 89.1 89.1 | Including inertia device: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 89. Mechanical movement comprising movable input and output
elements, movable means drivingly interconnecting said elements
and a movable member having substantial mass joined to either of
said elements or said means by a force-transmitting connection which
is effective to vary the speed of the movable member at some time
during its operation.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 89.11]](../ps.gif) 89.11 89.11 | With rack and pinion: | ||
Mechanical movement under subclasses 89.1 including a straight
or curved member having a series of teeth or recesses to mesh with
a gear, such series having determinate effective length.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 89.12]](../ps.gif) 89.12 89.12 | Rectilinear rack: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 89.11. Mechanical movement wherein the rack teeth or recesses lie in a straight line. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 89.13]](../ps.gif) 89.13 89.13 | Including bevel gears: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 89. Mechanical movement comprising at least one pair of toothed
elements, rotatable about nonparallel axes, having meshing toothed
surfaces which are inclined to said axes.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 89.14]](../ps.gif) 89.14 89.14 | Including worm: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 89. Mechanical movement comprising a rotatable screw member
for meshing with a complementary toothed gear or rack.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 89.16]](../ps.gif) 89.16 89.16 | Including spur gear: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 89. Mechanical movement comprising a wheel having radially projecting
teeth located parallel to the axis of said wheel for meshing with another
toothed member.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 89.17]](../ps.gif) 89.17 89.17 | With rack: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 89.16. Mechanical movement including a straight or curved member having a series of teeth or recesses to mesh with a gear, such series having determinate effective length. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 89.18]](../ps.gif) 89.18 89.18 | Curvilinear rack: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 89.17. Mechanical movement wherein the teeth or recesses lie in a curved line. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 89.19]](../ps.gif) 89.19 89.19 | With biasing means: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 89.18. Mechanical movement comprising yieldable means which assists the motion of the movement in one direction or the other (e.g., spring, counter weight, etc.). | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 89.2]](../ps.gif) 89.2 89.2 | Including flexible drive connector (e.g., belt, chain, strand, etc.): | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 89. Mechanical movement including a yieldable transmission member
engaged with the periphery of a pulley, or of a sprocket or other
type wheel.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 89.21]](../ps.gif) 89.21 89.21 | With sprocket wheel: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 89.2. Mechanical movement including a member with peripheral cogs or teeth for engaging the flexible drive connector. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 89.22]](../ps.gif) 89.22 89.22 | With pulley: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 89.2. Mechanical movement including a sheave or wheel with a grooved rim for receiving and frictionally cooperating with the flexible drive connector in driving or driven relationship. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 89.23]](../ps.gif) 89.23 89.23 | Including screw and nut: | ||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 89. Subject matter including mechanical movement comprising
a rotatable element having spiral threads or grooves encircling
its axis of rotation and a second element enmeshed therewith for
relative movement along the axis.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||
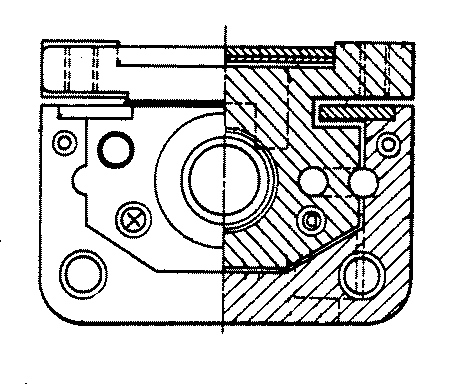
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 89.24]](../ps.gif) 89.24 89.24 | Shaft shorter than nut: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 89.23. Subject matter. Subject matter in which the area of meshing
engagement of the threads of the screw and nut extends substantially
from one end of the thread bearing portion of the screw to the other
and the thread bearing portion of the nut is longer than that of
the screw.
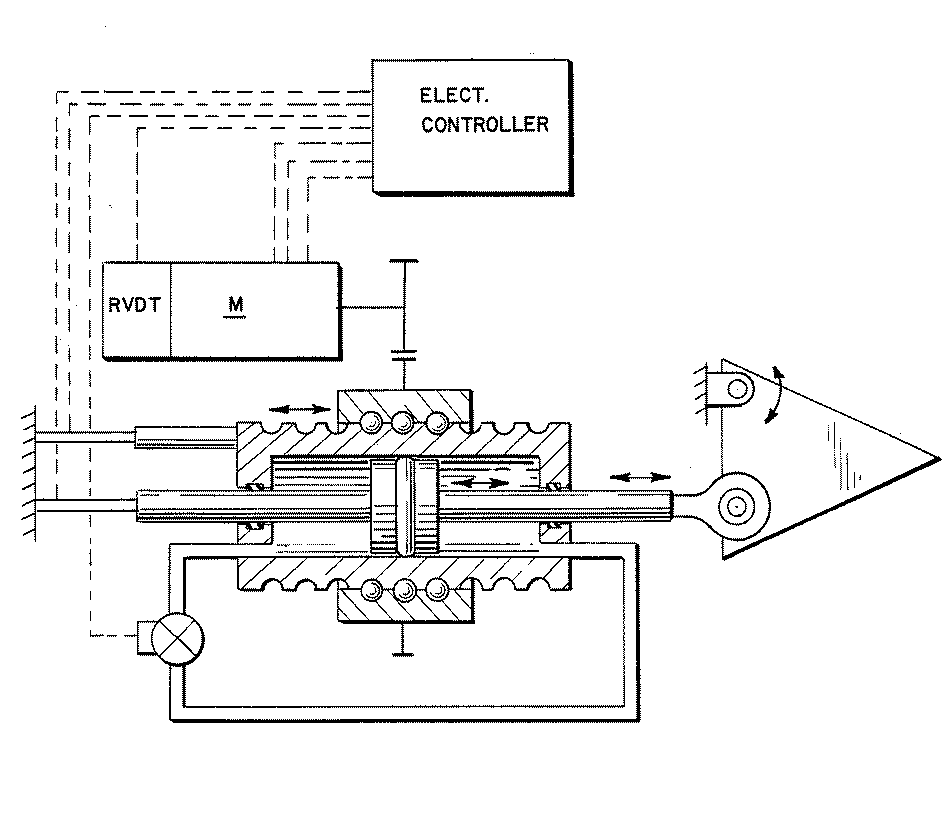
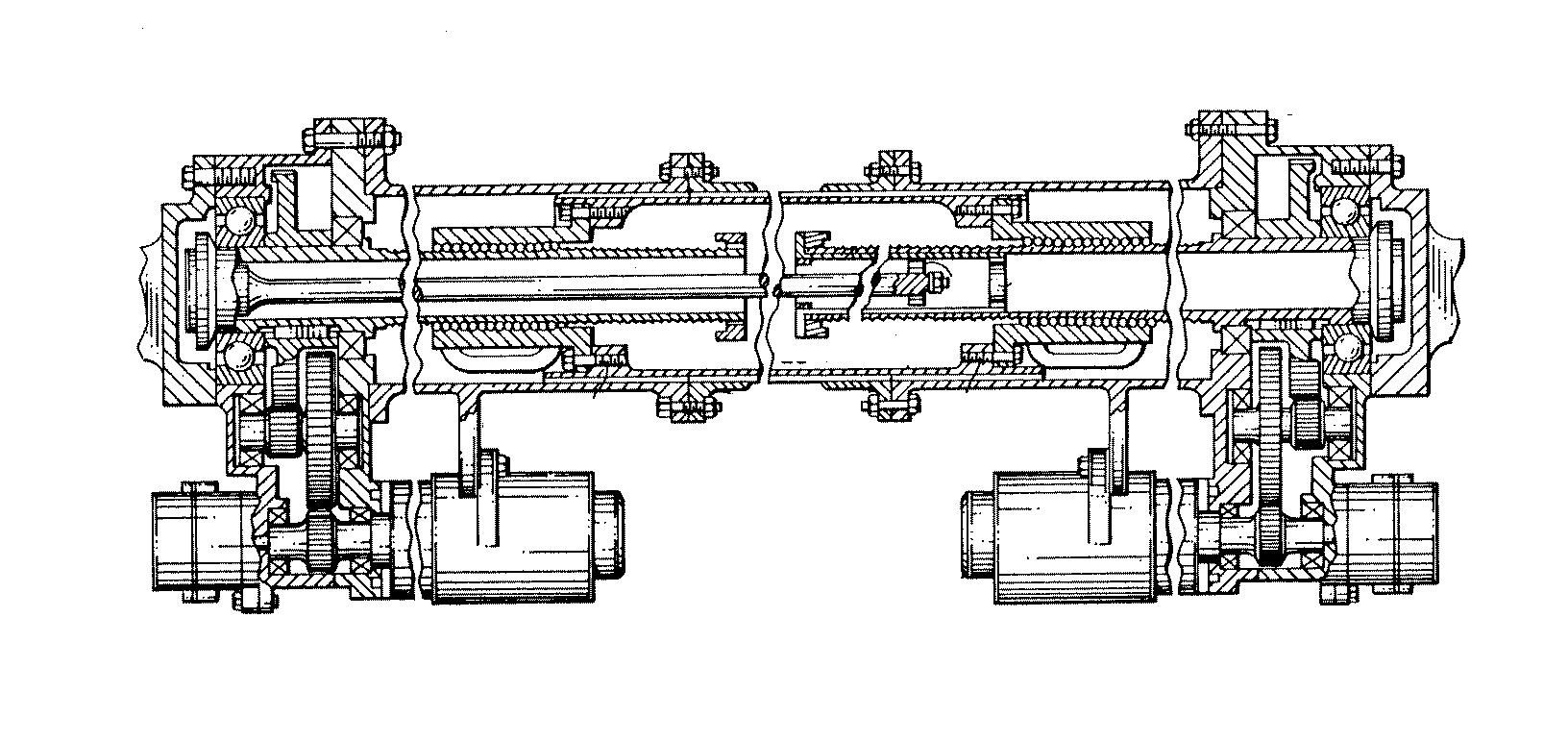
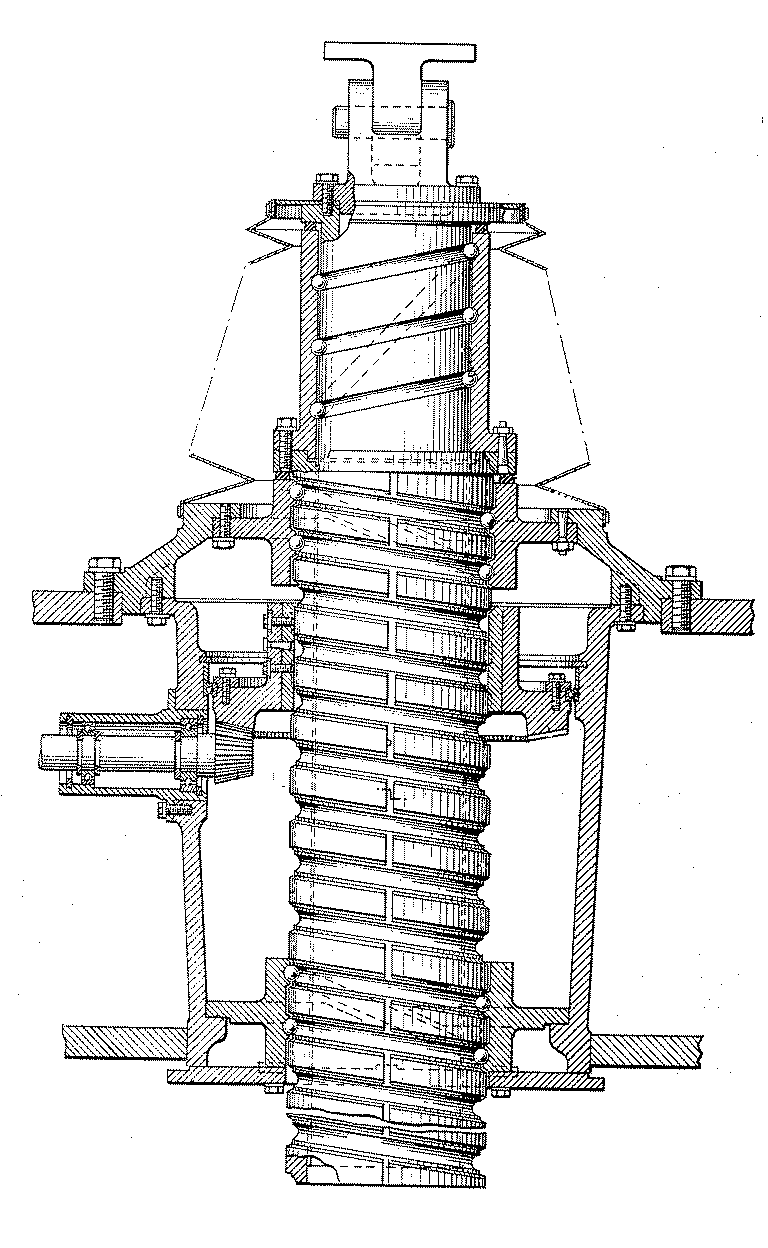
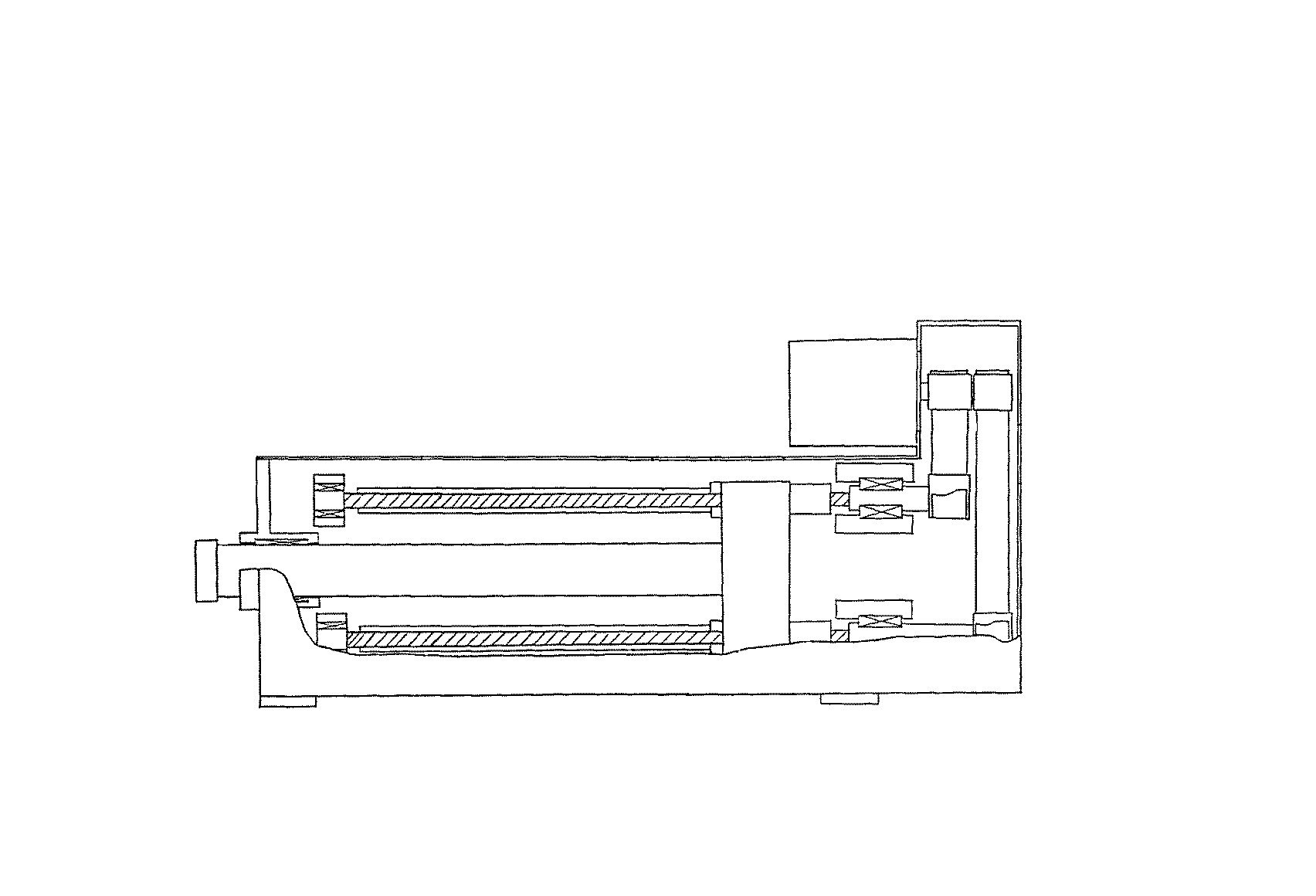
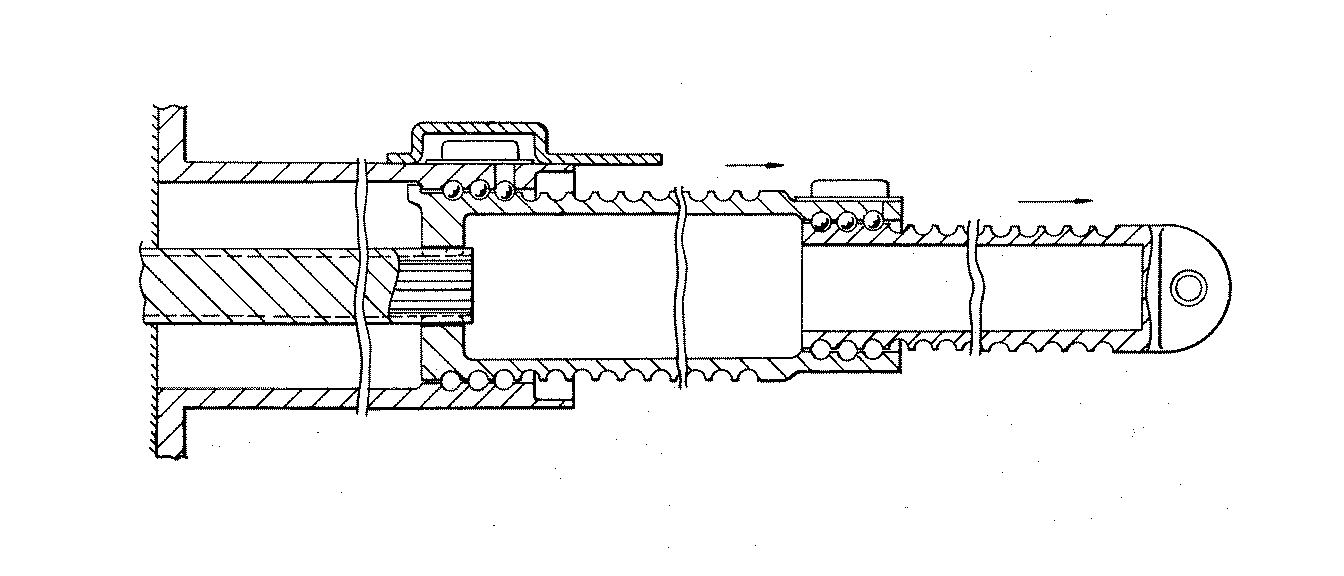
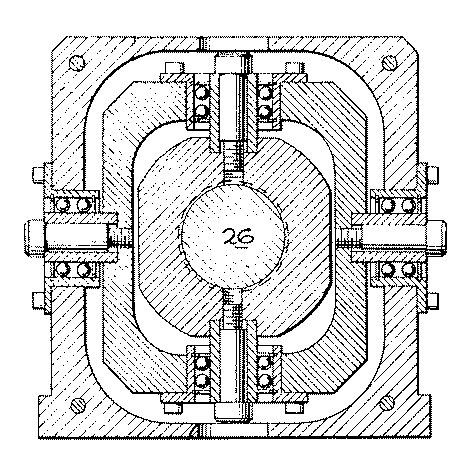
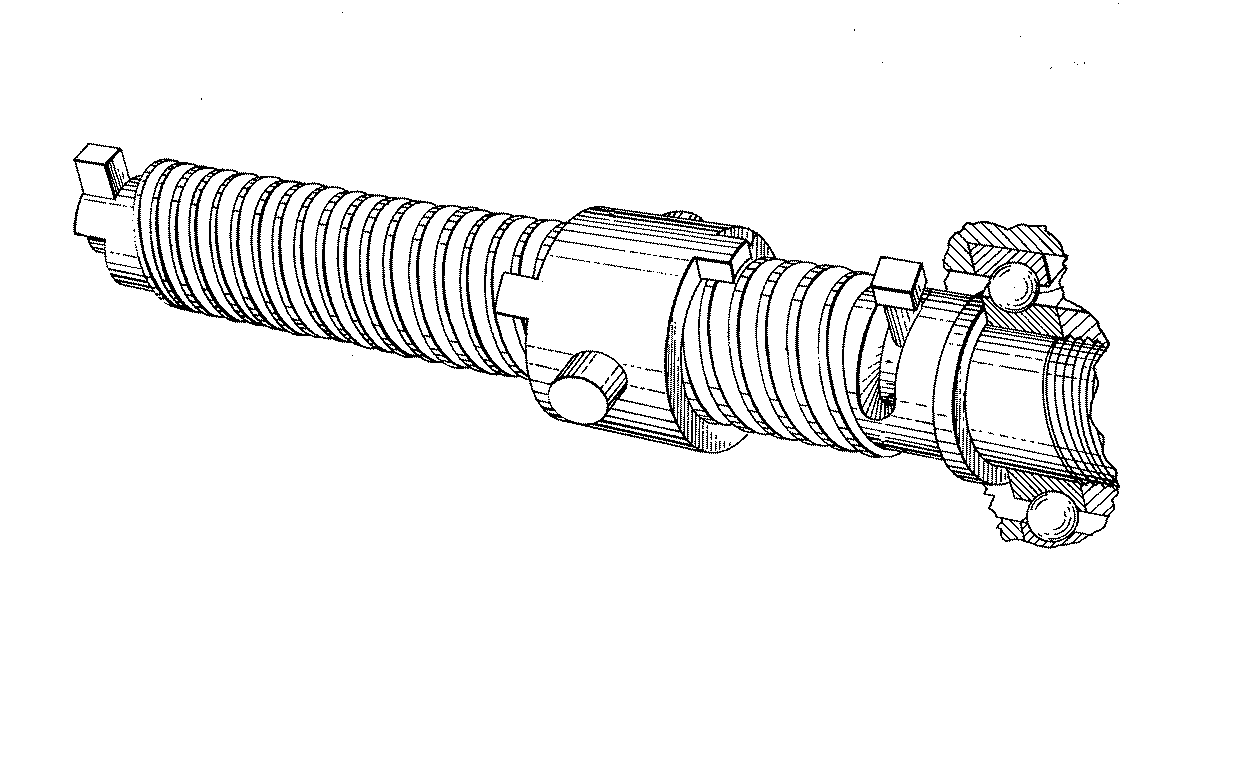
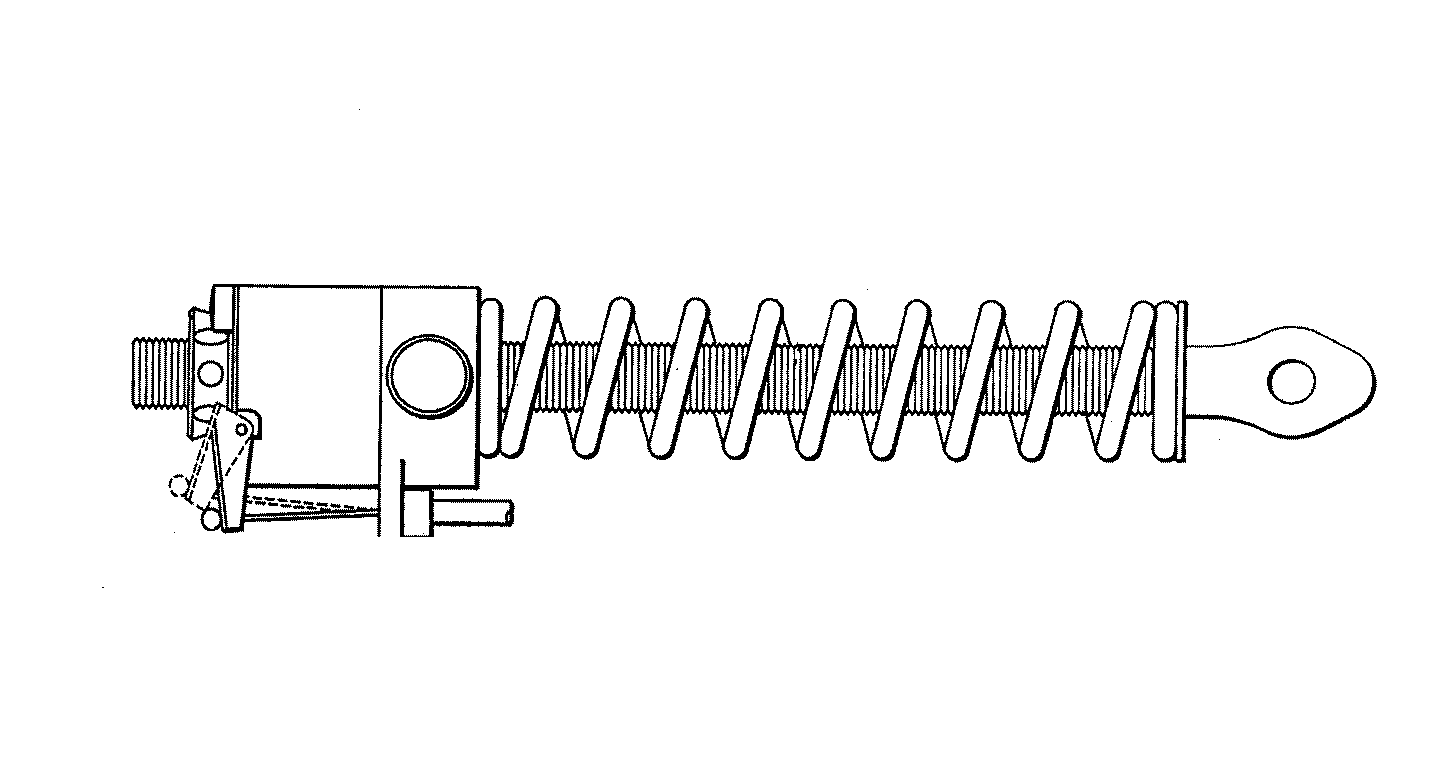
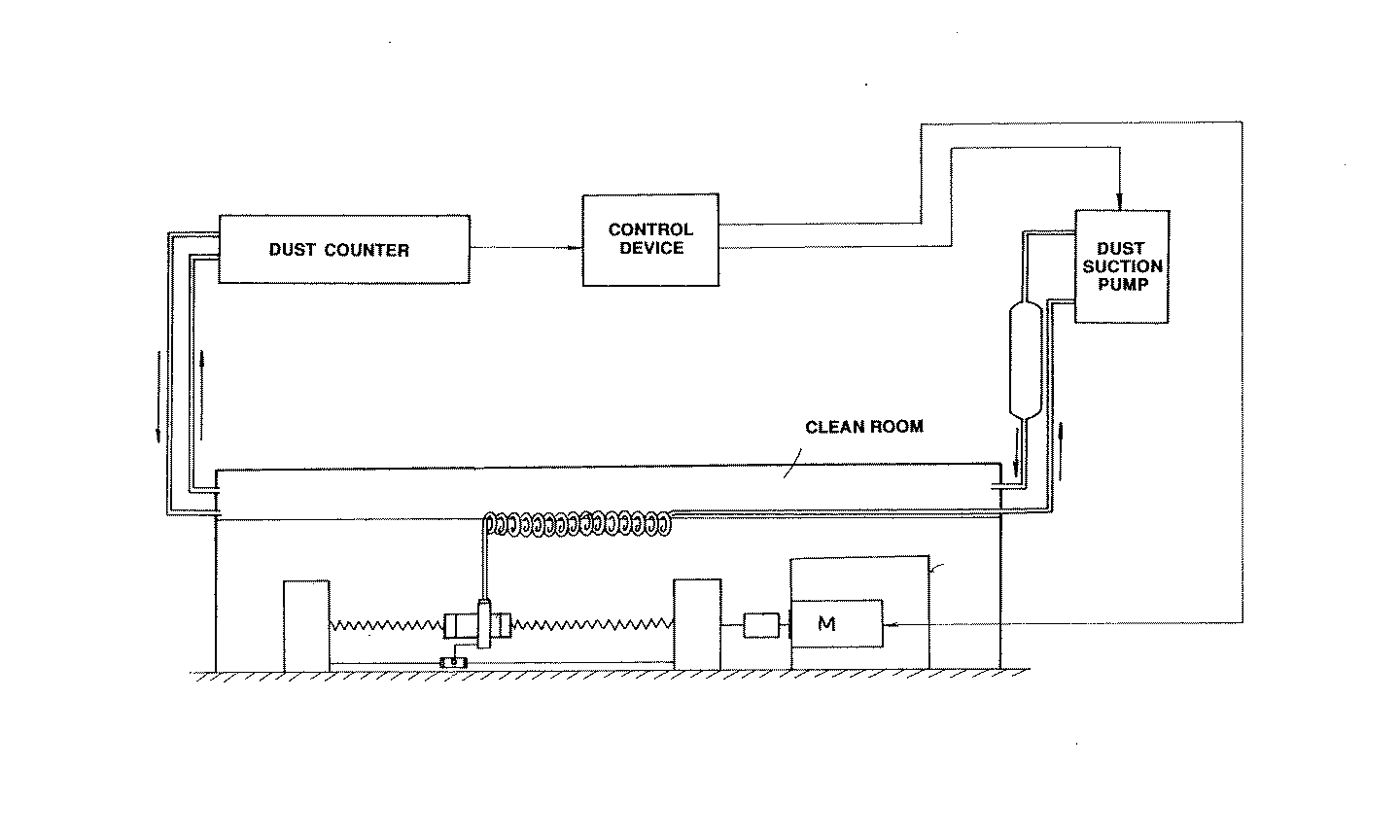
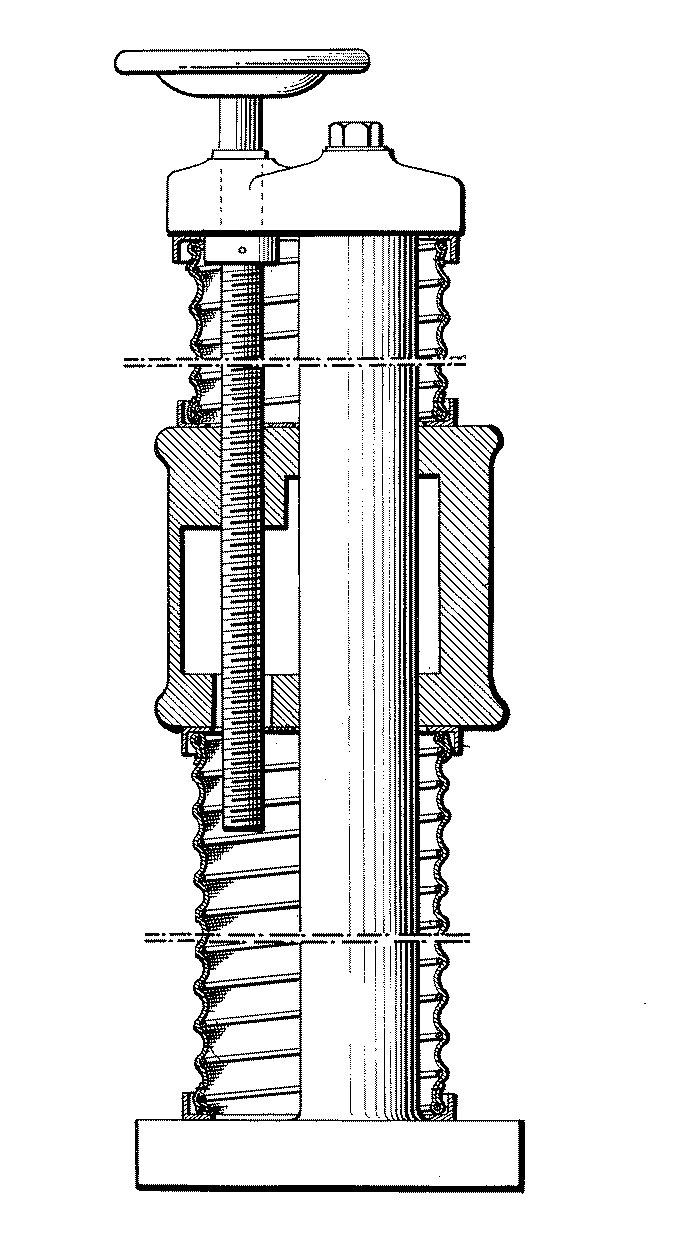
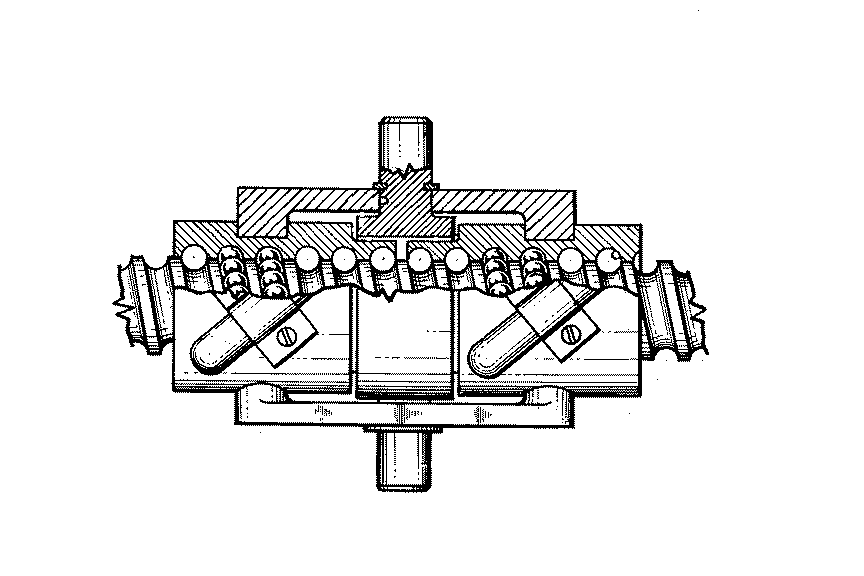
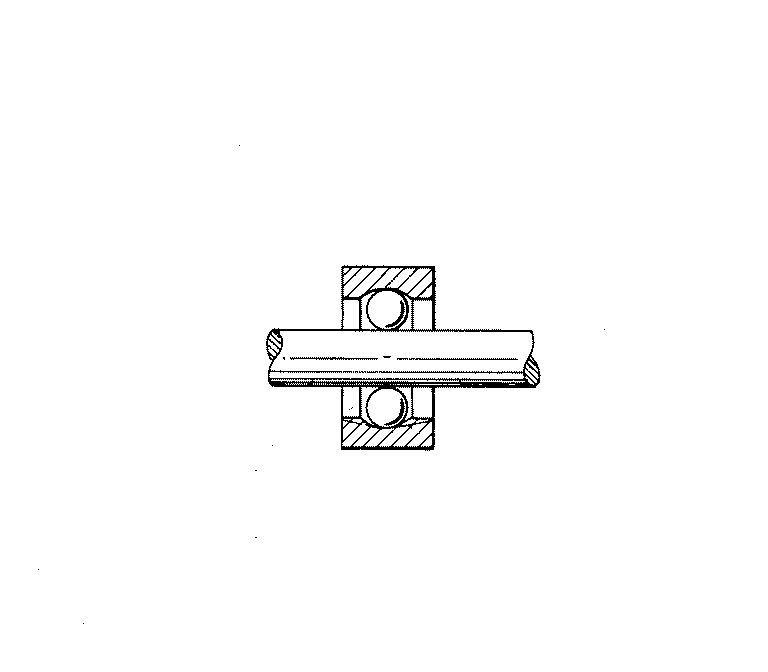
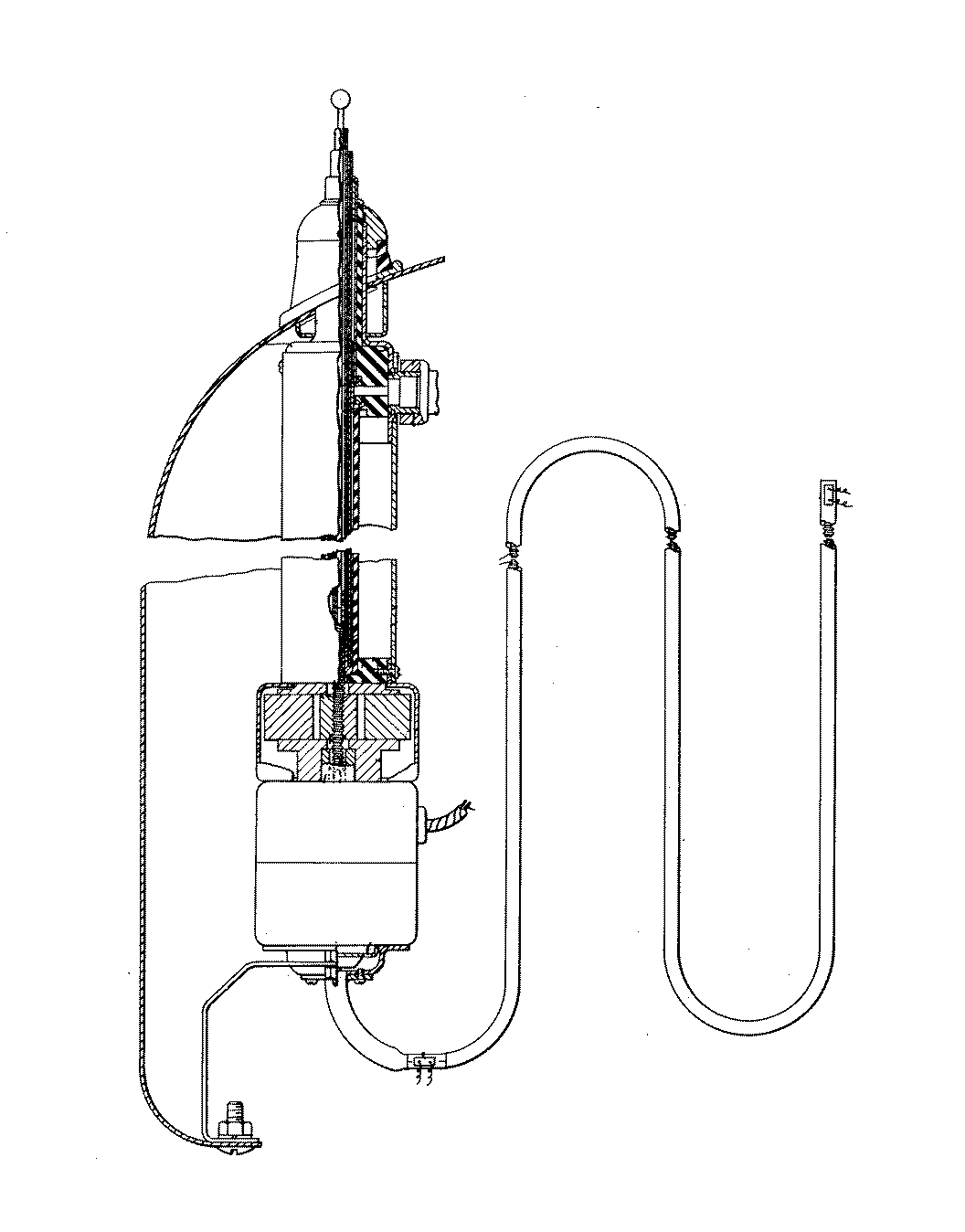
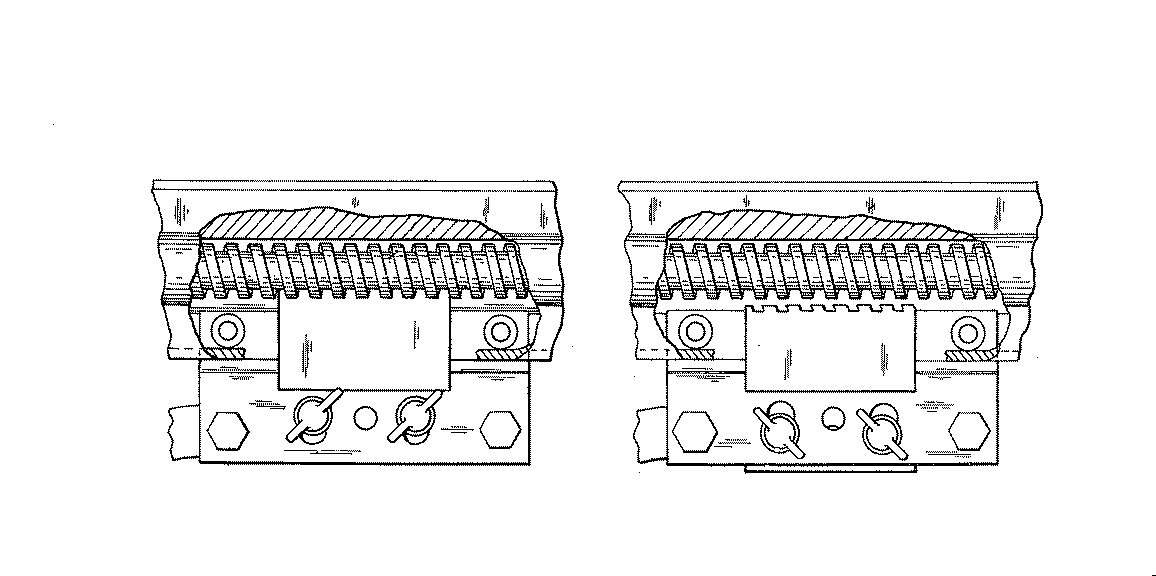
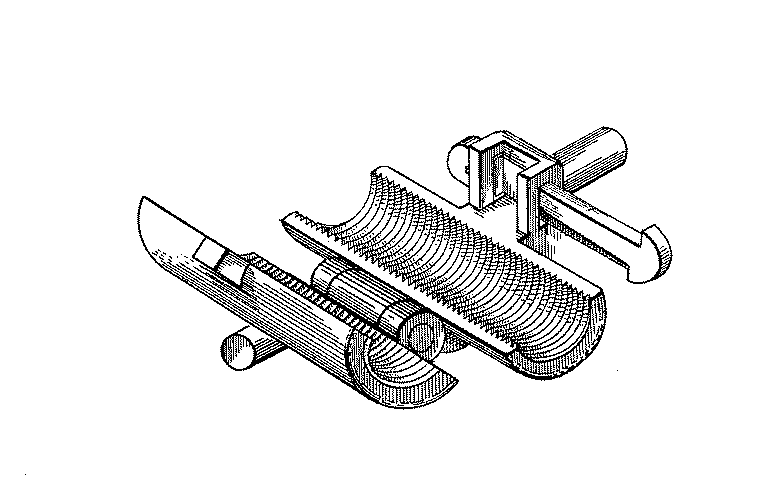
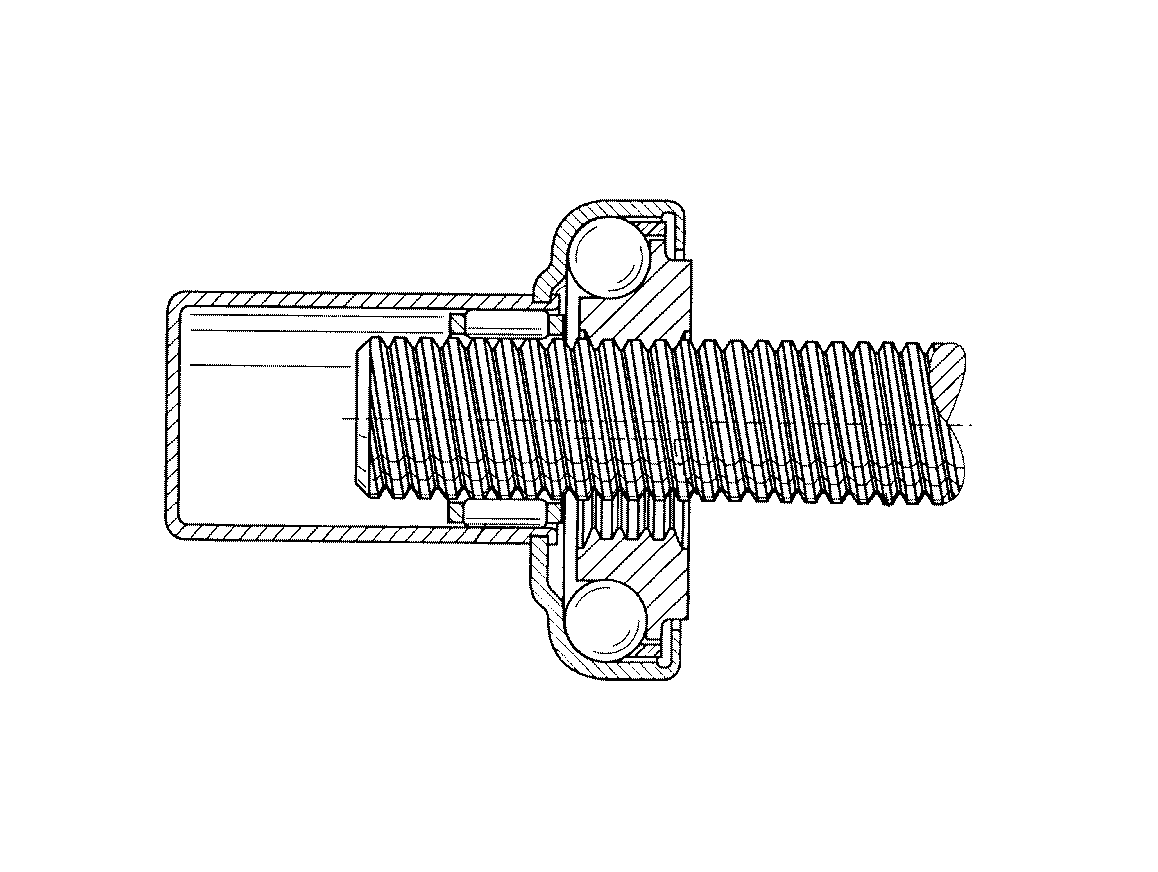
Figure 1. A typical example of the subject matter. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 89.25]](../ps.gif) 89.25 89.25 | Auxiliary drive (e.g., fluid piston, etc.) for load: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 89.23. Subject matter including drive means in addition to drive
means for the screw and nut and connected to the same load and capable
of moving the nut when the screw and nut are not operating.
Figure 1. A typical example of the subject matter. SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 89.26]](../ps.gif) 89.26 89.26 | Alternate power path operable on failure of primary: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 89.23. Subject matter in which there are plural distinct power
paths between an input and output of the mechanism only one of which
is active at an initial point in time and the mechanism includes
means to activate the other power path upon failure of the initially
active one to produce movement of the output.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 89.27]](../ps.gif) 89.27 89.27 | Single input split into two intermediate outputs that are subsequently superposed into a single output: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 89.23. Subject matter in which there are two power paths between
a single input and a single output of the mechanical movement that
are in use simultaneously.
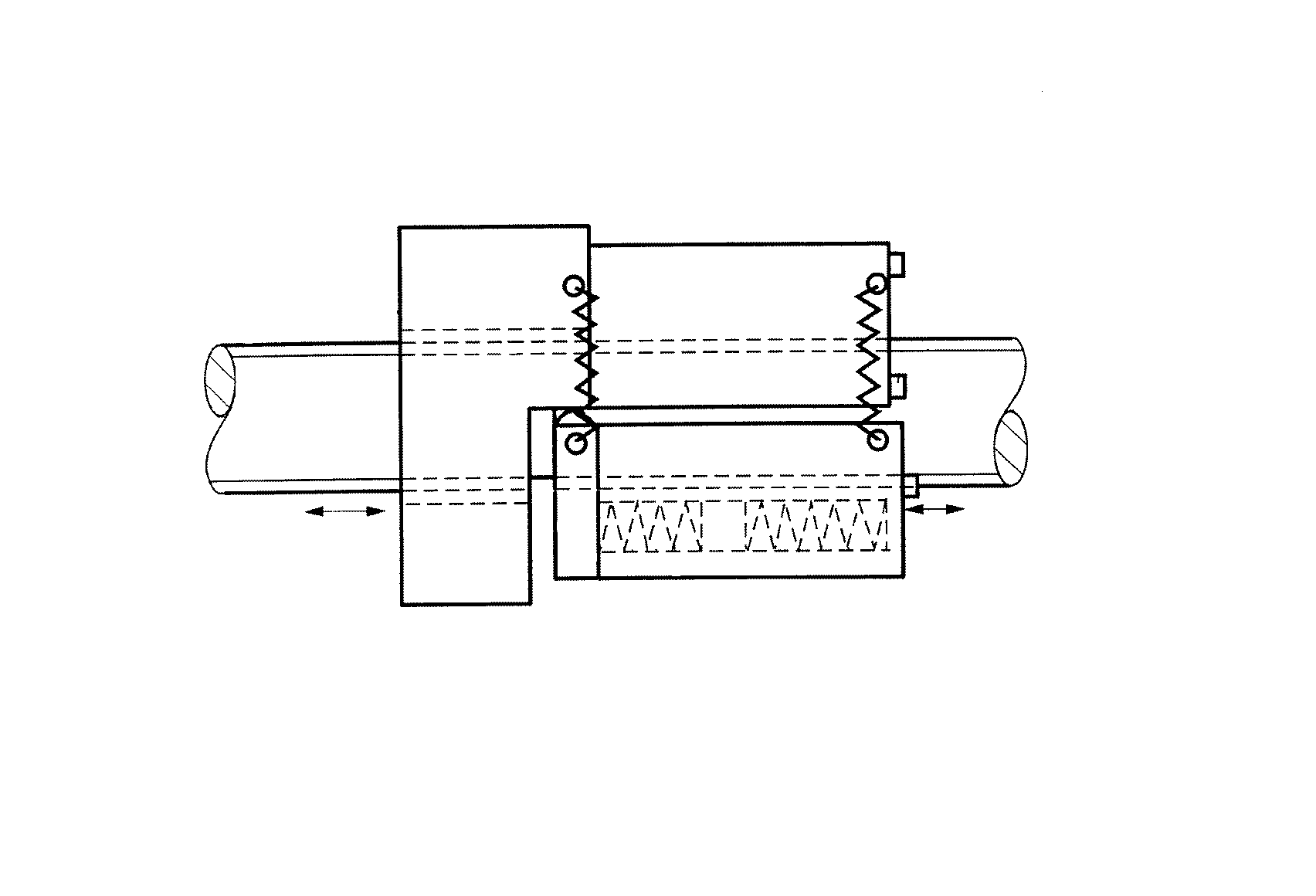
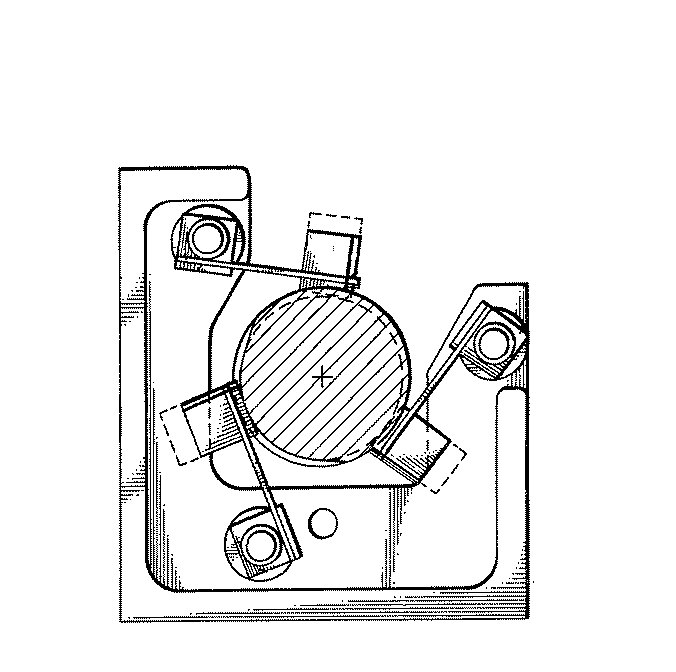
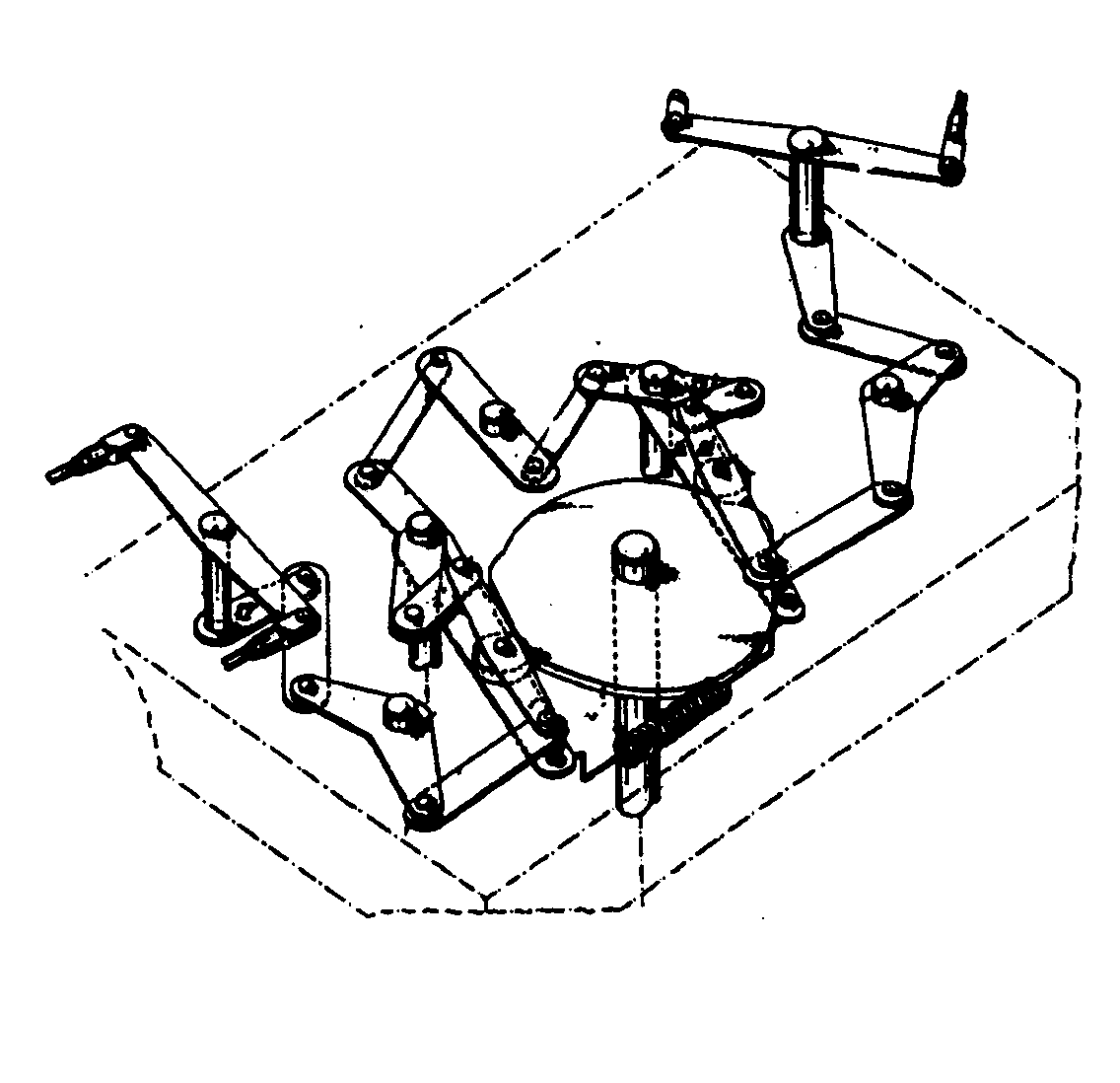
Figure 1. A typical example of the subject matter. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 89.28]](../ps.gif) 89.28 89.28 | Single input, plural outputs: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 89.23. Subject matter in which a single input drives plural outputs.
Figure 1. A typical example of the subject matter. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 89.29]](../ps.gif) 89.29 89.29 | Plural inputs, single output: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 89.23. Subject matter including plural power paths between plural
inputs and a single output.
Figure 1. A typical example of the subject matter. SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
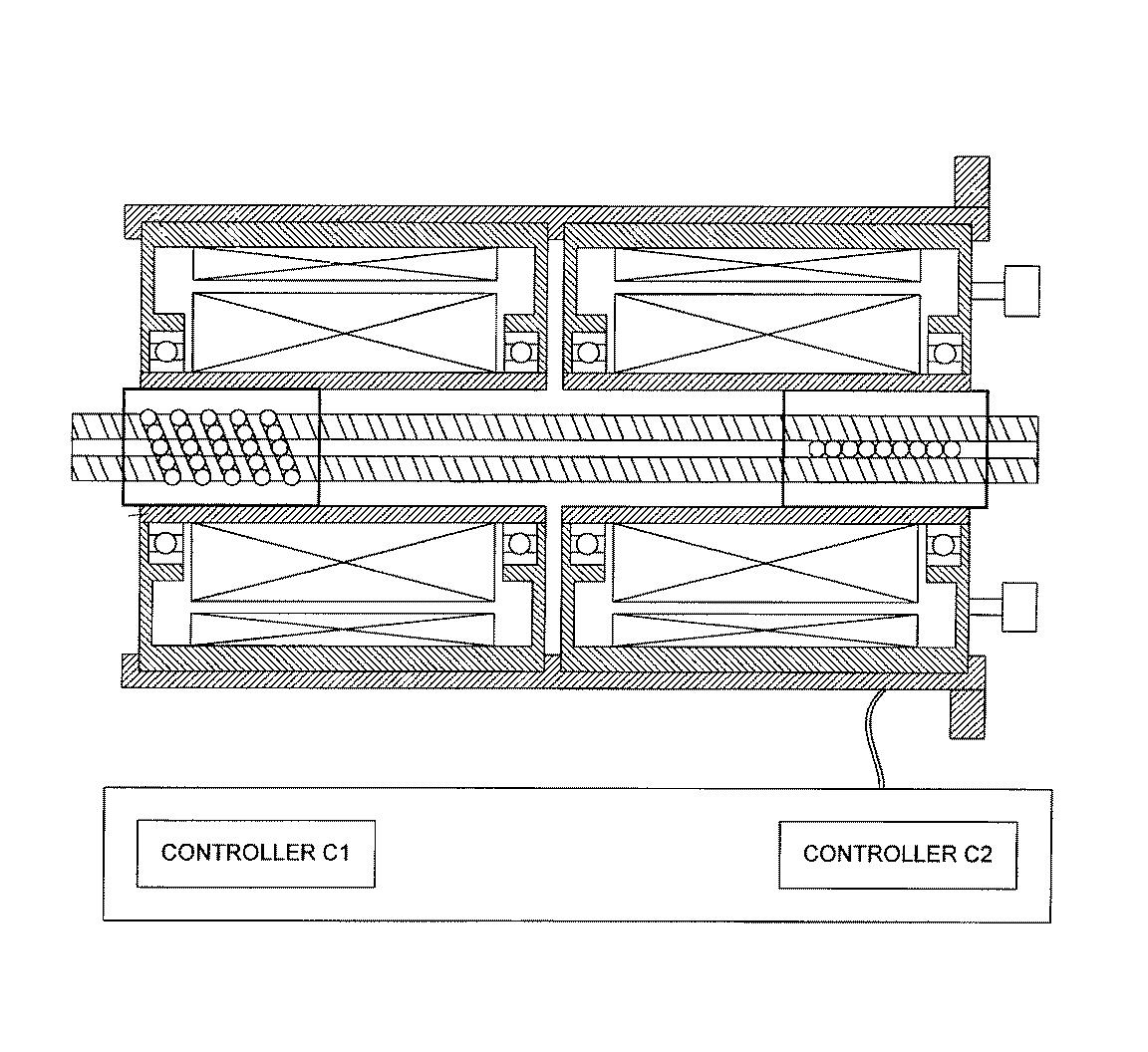
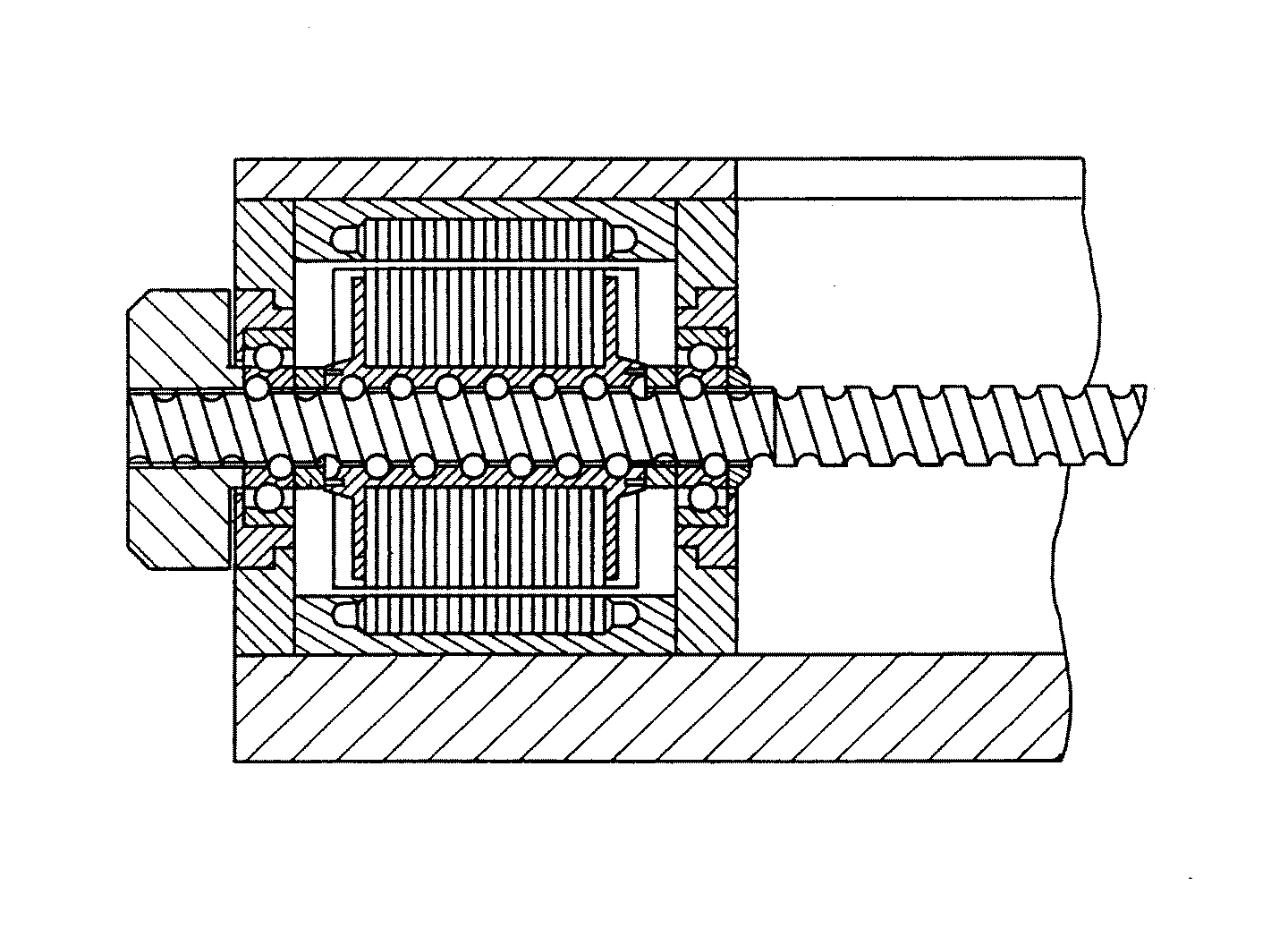
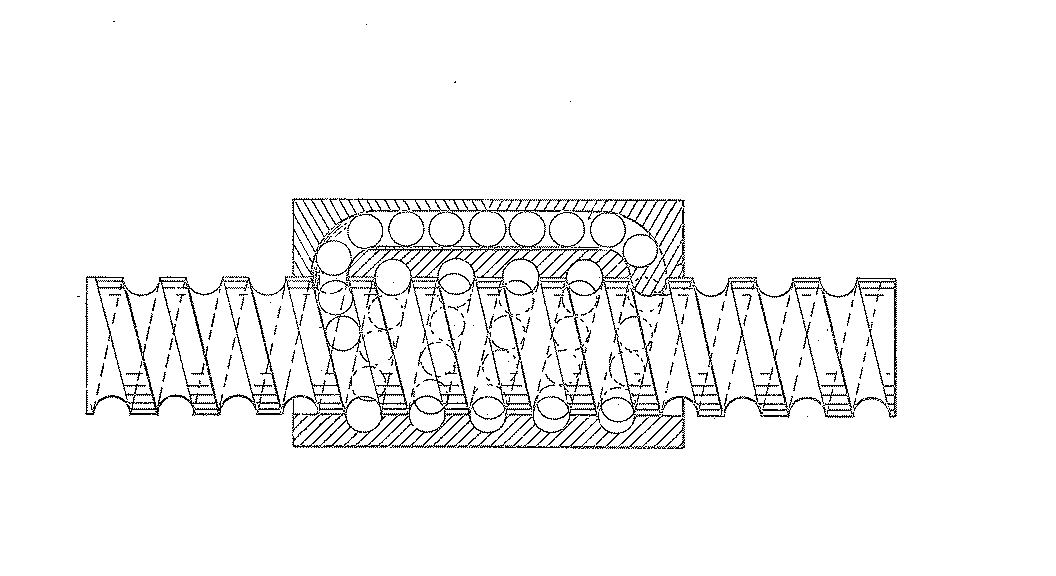
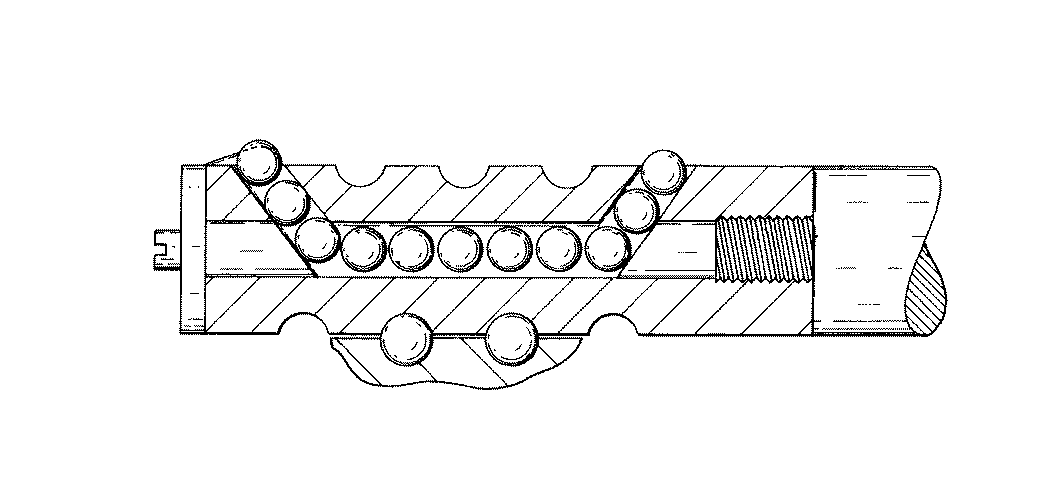
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 89.3]](../ps.gif) 89.3 89.3 | Plural nuts driving shaft: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 89.29. Subject matter in which there are plural nuts on a single
integral shaft, both of which nuts are simultaneously driven to
drive the shaft.
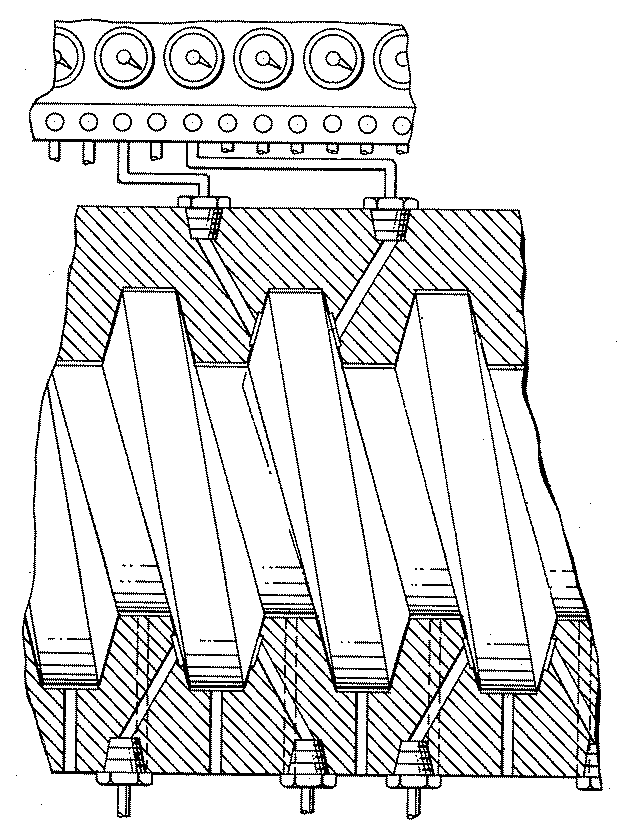
Figure 1. A typical example of the subject matter. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 89.31]](../ps.gif) 89.31 89.31 | Shaft and nut driven: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 89.29. Subject matter in which the shaft and nut are simultaneously driven. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 89.32]](../ps.gif) 89.32 89.32 | Carriage surrounding, guided by, and primarily supported by member other than screw (e.g., linear guide, etc.): |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 89.23. Subject matter in which the screw and nut drive a carriage
that at least partially surrounds a fixed structure (guide) that
supports substantially all of a load on the carriage transverse
to the screw.
Figure 1. A typical example of the subject matter. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 89.33]](../ps.gif) 89.33 89.33 | Carriage surrounded, guided, and primarily supported by member other than screw (e.g., linear guide, etc.): |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 89.23. Subject matter in which the screw and nut drive a carriage
that is at least partially surrounded by a fixed structure (guide)
that supports substantially all of a load on the carriage transverse
to the screw.
Figure 1. A typical example of the subject matter. | |
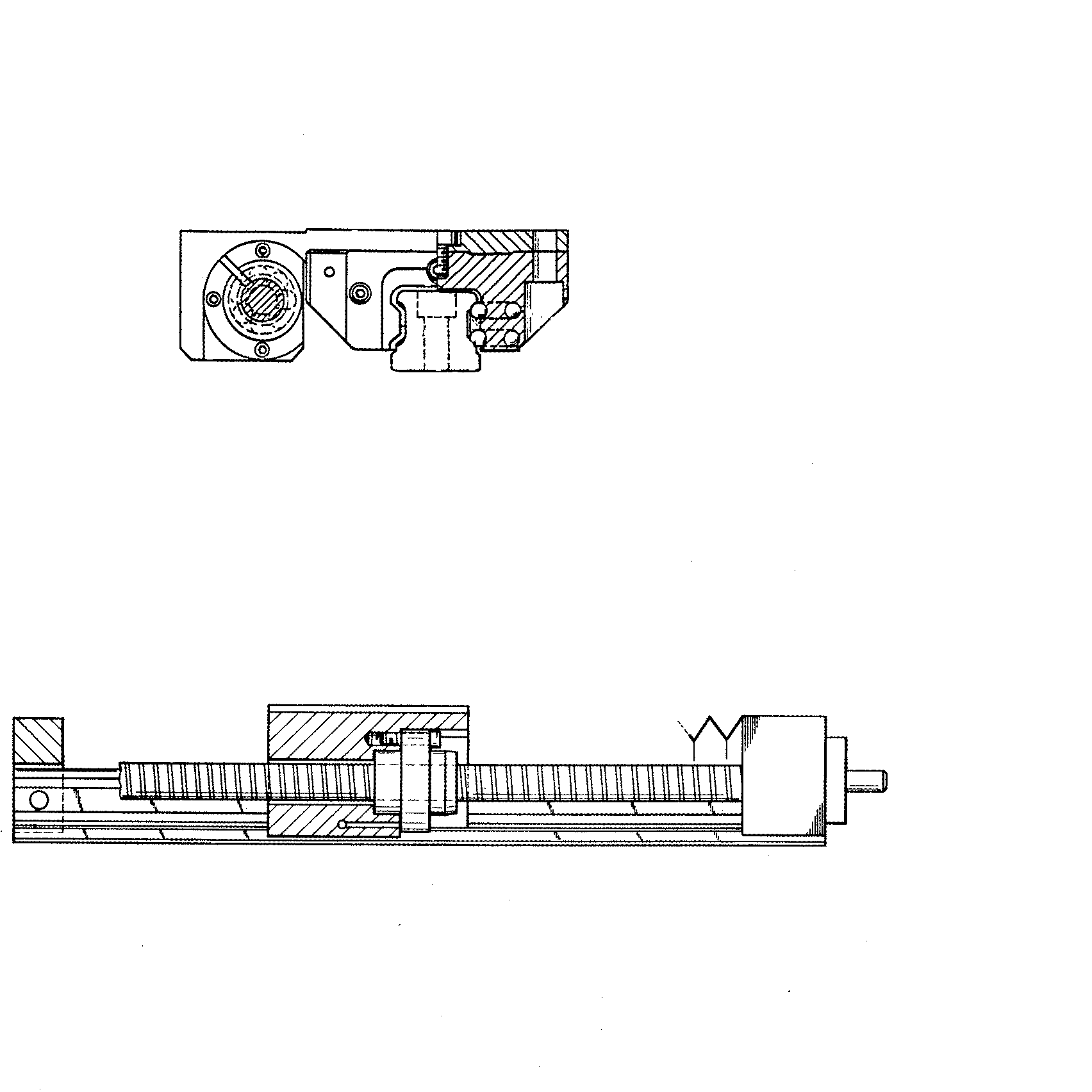
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 89.34]](../ps.gif) 89.34 89.34 | Shaft moves through rotary drive means: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 89.23. Subject matter including means for rotating the screw
that includes a rotating hollow member through which the screw passes.
Figure 1. A typical example of the subject matter. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 89.35]](../ps.gif) 89.35 89.35 | Plural screws in series (e.g., telescoping, etc.): |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 89.23. Subject matter in which plural screws each associated
with a different driving or driven nut form a single power path
in which a nut on one screw drives a second screw.
Figure 1. A typical example of the subject. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 89.36]](../ps.gif) 89.36 89.36 | Deflection related: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 89.23. Subject matter constructed to accommodate, prevent, reduce,
or mitigate lateral deflection or misalignment of the screw and
nut.
Figure 1. A typical example of the subject matter. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 89.37]](../ps.gif) 89.37 89.37 | Limit stop: | ||||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 89.23. Subject matter including means to stop motion of the output
of the screw and nut mechanism at a predetermined position of the
output.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 89.38]](../ps.gif) 89.38 89.38 | Including means to selectively transmit power (e.g., clutch, etc.): | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 89.23. Subject matter including structure in the power path that
may be altered in normal use to assume a state in which it connects
two points in the power path so as to be capable of transmitting
drive force between the two points and a state in which it is not
capable of transmitting such force.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 89.39]](../ps.gif) 89.39 89.39 | Means to selectively lock or retard screw or nut: | ||||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 89.23. Subject matter including a structure mounted on a stationary
support constructed to selectively apply a force to the nut or screw
(1) tending to retard the motion of the nut or screw or (2) maintaining
the nut or screw in a stationary state.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 89.4]](../ps.gif) 89.4 89.4 | Contamination related: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 89.23. Subject matter including means for impeding the movement
of material onto or from the screw or nut from or to the surrounding
environment.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 89.41]](../ps.gif) 89.41 89.41 | Imperforate enclosure: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 89.4. Subject matter including a barrier surrounding a space
containing both the screw and nut so as to prevent movement of material
into and out of the space.
Figure 1. A typical example of the subject matter. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 89.42]](../ps.gif) 89.42 89.42 | Backlash: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 89.23. Subject matter related to reduction or mitigation of play
between the threads of the screw and nut.
Figure 1. A typical example of the subject matter. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 89.43]](../ps.gif) 89.43 89.43 | Pressurized fluid introduced between nut and screw: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 89.23. Subject matter having structure in the screw or nut for
introducing fluid under pressure into the space between the screw
and nut so as to maintain a separation between their threads.
Figure 1. A typical example of the subject matter. SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 89.44]](../ps.gif) 89.44 89.44 | Lubrication: | ||||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 89.23. Subject matter in which the screw or nut has specific
structure for reducing sliding friction between the screw and nut.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 89.45]](../ps.gif) 89.45 89.45 | Manually driven: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 89.23. Subject matter in which the mechanism is constructed to permit a person to supply its input power without the use of tools. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 96]](../ps.gif) 96 96 | Oscillating to oscillating: |
| Mechanical movements for converting oscillating motion to oscillating motion. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 97.1]](../ps.gif) 97.1 97.1 | Snap action: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 96. Mechanism wherein the energy of the driving member is stored
during the beginning of the stroke and is imparted to the driven
member during the latter part of the stroke to impart a rapid motion
to the driven member.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 97.2]](../ps.gif) 97.2 97.2 | Plate spring: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 97.1. Mechanism wherein the driving member is a thin, resilient
element which is in a distorted condition in either one of the two
positions which it customarily occupies, and which, when moved by
an external force away from one position in the direction of the
other position, undergoes a reversal of distortion, resulting in
a rapid movement between the two positions.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 98]](../ps.gif) 98 98 | Geared connections: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 96. Mechanisms, in which the motion is changed by means of gears. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 99]](../ps.gif) 99 99 | Reciprocating to or from oscillating: |
| Mechanical movements for converting reciprocating motion to or from oscillating motion. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 100.1]](../ps.gif) 100.1 100.1 | Snap action: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 99. Mechanism wherein the energy of the driving member is stored
during the beginning of the stroke and is imparted to the driven
member during the latter part of the stroke to impart a rapid motion
to the driven member.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 100.2]](../ps.gif) 100.2 100.2 | Plate spring: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 100.1. Mechanism wherein the driving member is a thin, resilient
element which is in a distorted condition in either one of the two
positions which it customarily occupies, and which, when moved by
an external force away from one position in the direction of the
other position, undergoes a reversal of distortion, resulting in
a rapid movement between the two positions.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 101]](../ps.gif) 101 101 | Compound lever and slide: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 99. Mechanisms, in which the motion is changed by means of a compound lever and slide. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 102]](../ps.gif) 102 102 | Lever and slide: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 99. Mechanisms, in which the motion is changed by means of a lever and slide. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 103]](../ps.gif) 103 103 | Straight line motions: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 102. Mechanisms, in which the motion is changed by means of a lever and slide and the path of the reciprocating member is a straight line. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 104]](../ps.gif) 104 104 | Slidable connections: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 102. Mechanisms in which the motion is changed by means of a lever and slide and the connection between the lever and slide is slidable. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 105]](../ps.gif) 105 105 | Link connections: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 102. Mechanisms, in which the motion is changed by means of a lever and slide which are connected together by a link. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 106]](../ps.gif) 106 106 | Toggle transmissions: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 102. Mechanisms, in which the motion is changed by means of a
lever and slide which are connected together by a toggle.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 107]](../ps.gif) 107 107 | Cam connections: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 102. Mechanisms, in which the motion is changed by means of a lever and slide which are connected together by cams. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 108]](../ps.gif) 108 108 | Flexible connections: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 102. Mechanisms, in which the motion is changed by means of a lever and slide which are connected together by a flexible member. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 109]](../ps.gif) 109 109 | Rack and pinion: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 99. Mechanisms, in which the motion is changed by means of a rack and pinion. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 110]](../ps.gif) 110 110 | Reciprocating to reciprocating: |
| Mechanical movements for changing reciprocating motion to reciprocating motion. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 111]](../ps.gif) 111 111 | MECHANICAL MOVEMENTS (INTERMITTENT GRIP TYPE): | ||||||||||||
This subclass is indented under the class definition. Mechanisms, provided with parts adapted to impart step-by-step
motion to a unidirectionally driven member.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 112]](../ps.gif) 112 112 | Rotary to intermittent unidirectional motion: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 111. Mechanisms having a rotary driving member and provided with
parts adapted to impart step-by-step motion to a unidirectionally
driven member.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 113]](../ps.gif) 113 113 | Automatically controlled: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 112. Mechanisms in which the transmission ratio is controlled automatically. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 114]](../ps.gif) 114 114 | Speed: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 113. Mechanisms in which the transmission ratio is controlled
automatically by speed responsive elements.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 116]](../ps.gif) 116 116 | Rotary crank or eccentric drive: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 112. Mechanisms having a rotary crank or eccentric driving member
and provided with parts adapted to impart step-by-step motion to
a unidirectionally driven member.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 117]](../ps.gif) 117 117 | Adjustable: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 116. Mechanisms, having an adjustable driving member.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 118]](../ps.gif) 118 118 | Lever transmitter: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 116. Mechanisms in which the parts include an intermediate lever pivoted to some supporting structure. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 119]](../ps.gif) 119 119 | Adjustable leverage: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 118. Mechanisms, in which the parts include an intermediate lever of adjustable ratio pivoted to some supporting structure. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 120]](../ps.gif) 120 120 | Rack and pinion transmitter: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 116. Mechanisms, in which the parts include rack and pinion transmitting elements. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 121]](../ps.gif) 121 121 | Adjustable throw: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 120. Mechanisms, in which the parts include rack and pinion transmitting
elements, and means are provided for varying the extent of effective movement
of those elements.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 122]](../ps.gif) 122 122 | Rotary cam drive: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 116. Mechanisms, having a rotary cam driving member and provided
with parts adapted to impart step-by-step motion to a unidirectionally
driven member.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 123]](../ps.gif) 123 123 | Adjustable throw: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 122. Mechanisms, in which the extent of movement of the transmitting
parts may be varied.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 124]](../ps.gif) 124 124 | Radial cam: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 123. Mechanisms and having a radial cam.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 125]](../ps.gif) 125 125 | Radial cam: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 122. Mechanisms and having a radial cam.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 125.5]](../ps.gif) 125.5 125.5 | Intermittently engaged clutch: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 112. Mechanisms in which the parts include periodically engageable
clutch elements.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 126]](../ps.gif) 126 126 | Oscillation or reciprocation to intermittent unidirectional motion: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 111. Mechanisms and having either an oscillating or reciprocating driving member and provided with parts adapted to impart step-by-step motion to a unidirectionally driven member. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 127]](../ps.gif) 127 127 | Screw and nut devices: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 126. Mechanisms, in which the parts include relatively movable
screw and nut elements.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 128]](../ps.gif) 128 128 | Slide actuator: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 126. Mechanisms, in which the driving member is in the form of
a slidable actuator.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 129]](../ps.gif) 129 129 | Multiple acting: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 128. Mechanisms, in which a slidable actuator is adapted to impart motion to the driven member in both directions of its movement or in which a plurality of slidable actuators are adapted to impart motion to the driven member in sequence. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 130]](../ps.gif) 130 130 | Rack actuator: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 126. Mechanisms, in which the driving member is provided with
rack teeth.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 131]](../ps.gif) 131 131 | Multiple acting: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 130. Mechanisms, in which a single driving member having rack teeth is capable of imparting motion to the driven member in both directions of its movement or in which a plurality of driving members having rack teeth are adapted to impart motion to the driven member in sequence. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 132]](../ps.gif) 132 132 | Inwardly facing racks: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 131. Mechanisms, in which the driving member is provided with inwardly facing rack teeth and is effective in both directions of its movement to impart motion to the driven member. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 133]](../ps.gif) 133 133 | Oscillating: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 130. Mechanisms, in which the rack is oscillatable. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 134]](../ps.gif) 134 134 | Multiple acting: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 133. Mechanisms, in which the oscillatable rack is adapted to impart motion to the driven member in both directions of its movement or in which a plurality of oscillatable racks are adapted to impart motion to the driven member in sequence. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 135]](../ps.gif) 135 135 | Inwardly facing racks: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 134. Mechanisms, in which the rack is provided with inwardly facing teeth and is effective in both directions of its movement. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 136]](../ps.gif) 136 136 | Multiple acting: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 126. Mechanisms, in which a single driving member in the form of a strap, chain, belt, etc., is adapted to impart motion to the driven member in both directions of its movement or in which a plurality of straps are adapted to impart motion to the driven member in sequence. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 137]](../ps.gif) 137 137 | Spring or weight return: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 136. Mechanisms, in which a spring or weight moves the strap in one direction. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 138]](../ps.gif) 138 138 | Single acting: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 126. Mechanisms, in which the driving member is in the form of a strap, chain, or belt and is effective in only one direction of movement to impart motion to the driven member. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 139]](../ps.gif) 139 139 | Engine starter type: | ||||||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 138. Mechanisms in which the entire device is particularly designed
for uses as an engine starter but is adapted for other uses.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 140]](../ps.gif) 140 140 | Spring or weight return: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 139. Mechanisms, in which a spring or weight is adapted to return
the strap to its initial position.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 141]](../ps.gif) 141 141 | Spring or weight return: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 138. Mechanisms, in which a spring or weight is adapted to return the strap to its initial position. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 141.5]](../ps.gif) 141.5 141.5 | Lever actuator: | ||||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 126. Mechanisms in which the driving member is a lever effective
in its oscillation to impart motion to the driven member.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 142]](../ps.gif) 142 142 | Rotary driven element: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 141.5. Mechanisms in which the intermittently driven member revolves around a relatively fixed axis. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 143]](../ps.gif) 143 143 | Multiple acting: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 142. Mechanisms in which a single driving member in the form
of a lever, is adapted to impart motion to the driven member in
both directions of oscillation of the lever or in which a plurality
of levers are adapted to impart motion to the driven member in sequence.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 144]](../ps.gif) 144 144 | Grip units and features: | ||||||||||||||||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 111. Devices, adapted to form parts of more complex intermittent
grip mechanisms and to impart step-by-step motion directly to a
unidirectionally driven member.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||||||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 145]](../ps.gif) 145 145 | Compound movement handle: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 144. Devices, including a handle capable of movement in a plurality of planes. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 146]](../ps.gif) 146 146 | Reversible: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 145. Devices, including a handle capable of movement in a plurality of planes and adapted to impart either forward or reverse motion to the driven member. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 147]](../ps.gif) 147 147 | Transverse pivots: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 145. Devices, in which the handle is swingable about an axis transverse to the axis of rotation of the driven member. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 148]](../ps.gif) 148 148 | Gripper releasing devices: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 144. Devices, in which means are provided for releasing a gripper
from the driven member.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 149]](../ps.gif) 149 149 | Power pawl lifter: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 148. Devices, in which the pawl disengaged is the driving or power transmitting pawl. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 150]](../ps.gif) 150 150 | Automatic: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 149. Devices, in which means are provided for automatically disengaging a power transmitting pawl from the driven member. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 151]](../ps.gif) 151 151 | Idle stroke: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 150. Devices, in which means are provided for automatically disengaging a power transmitting pawl from the driven member during the idle or return movement of the pawl. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 152]](../ps.gif) 152 152 | Cooperating holding pawl: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 151. Devices, in which a holding pawl is adapted to prevent retrograde
movement of the driven member.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 153]](../ps.gif) 153 153 | Power stroke: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 150. Devices, in which means are provided for automatically disengaging a power transmitting pawl from the driven member during the power or working movement of the pawl. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 154]](../ps.gif) 154 154 | Cooperating holding pawl: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 149. Devices, in which means are provided for disengaging a power pawl from the driven member and an auxiliary holding pawl is adapted to prevent retrograde movement of the driven member. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 155]](../ps.gif) 155 155 | Holding pawl lifter: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 148. Devices, provided with a holding pawl for preventing retrograde movement of the driven member, the said holding pawl being disengaged from the driven member by the movement of some part of the device. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 156]](../ps.gif) 156 156 | Gripper mountings, lever: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 144. Devices, in which the element which engages the driven member
is mounted on a lever actuator.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 157]](../ps.gif) 157 157 | Reversible: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 156. Devices, in which the element which engages the driven member may be shifted to impart either forward or reverse motion to the driven member. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 158]](../ps.gif) 158 158 | Multiple acting: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 156. Devices, in which a plurality of elements are adapted to engage one or more driven members and are mounted on one or more lever actuators. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 159]](../ps.gif) 159 159 | Single ratchet or clutch: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 158. Devices, in which the driven member is in the form of a single ratchet or clutch to provide only one set of teeth for cooperation with the plurality of elements. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 160]](../ps.gif) 160 160 | Gripper mountings, slide: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 144. Devices, having the element adapted to engage the driven
member mounted on a slidable actuator.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 161]](../ps.gif) 161 161 | Multiple acting: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 160. Devices, in which a plurality of elements are adapted to
engage one or more driven members and are mounted on one or more
slide actuators.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 162]](../ps.gif) 162 162 | Grip features: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 144. Devices, limited to the combination of the details of the
power imparting element, per se, and the driven member.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 163]](../ps.gif) 163 163 | Driving band: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 162. Devices, in which the power imparting element is in the form of a band surrounding the driven member. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 164]](../ps.gif) 164 164 | Clamping: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 163. Devices, in which the power imparting element is in the form of a band surrounding the driven member and which actuates the driven member intermittently by being clamped thereto and unclamped therefrom. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 165]](../ps.gif) 165 165 | Driven band and gripper: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 162. Devices, in which the driven member is in the form of an endless band, such as a chain or belt. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 166]](../ps.gif) 166 166 | Positive grip: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 165. Devices, provided with means to prevent slippage between the power imparting elements and the driven member. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 167]](../ps.gif) 167 167 | Driving ratchet-bar or rack: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 162. Devices, in which the power imparting element is in the form of a ratchet bar or rack. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 168]](../ps.gif) 168 168 | Multiple acting: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 167. Devices, in which a plurality of power imparting elements in the form of ratchet bars or racks actuate the driven member. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 169]](../ps.gif) 169 169 | Driven ratchet-bar and power dog: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 162. Devices, in which the power imparting element is in the
form of a pawl adapted to cooperate with the teeth of a ratchet
bar which comprises the driven member.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
| Gearing Frictional. | |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 640. Gearing, comprising rotary elements having substantially smooth surfaces in contact with each other, or in line or point contact with an interposed member, to produce a relative rolling motion between them due to contact of surfaces. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 216.3]](../ps.gif) 216.3 216.3 | Toothed gear and recirculated unconnected elements: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 640. Gearing which includes a guide tube in the form of a closed
path, a plurality of free running independent bodies (e.g., balls)
within and substantially filling said tube, and one or more notched
rotary elements tangentially engaging the bodies axially of the
run thereof to thereby transmit and/or receive power axially
of the run by the compressive action of the bodies upon each other
in the forward run of the path.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 318]](../ps.gif) 318 318 | Alternating rotary or continuous: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 640. Gearing combinations comprising one or more trains of gears
for converting the continuous rotation of a driving gear to an alternating
rotation of a driven element and in which additional elements may
be provided for continuing the rotation of the driven element in
one direction.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 319]](../ps.gif) 319 319 | Alternating rotary: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 640. Gearing combinations comprising one or more trains of gears
for converting the continuous rotation of a driving element to an
alternating rotation of a driven element.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 320]](../ps.gif) 320 320 | Progressive: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 319. Gearing, in which the driven element is rotated a greater amount in one direction than in the other. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 321]](../ps.gif) 321 321 | Shiftable and/or slidable gears: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 319. Gearing, embodying shiftable and/or slidable gears
for effecting an alternating rotation of the driven member.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 322]](../ps.gif) 322 322 | Clutchable gears: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 319. Gearing, embodying engageable and disengageable clutches
for effecting an alternating rotation of the driven members.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 323]](../ps.gif) 323 323 | On single driven member: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 322. Alternating rotary gearing, in which the clutches are all mounted on the alternating driven member. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 324]](../ps.gif) 324 324 | On single driving member: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 322. Alternating rotary gearing, in which the clutches are all mounted on the continuously rotating driving member. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 325]](../ps.gif) 325 325 | Interchangeably locked: | ||||||||||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 640. Transmissions in which a plurality of speeds are transmitted
from one shaft to another by optionally engaging or meshing selected
gears or clutches or gears and clutches, to their supporting shafts.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 329]](../ps.gif) 329 329 | Disconnectable counter shaft: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 325. Transmissions involving change of speed in which the counter shaft is disconnected from the drive shaft when the drive is not through the counter shaft. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 330]](../ps.gif) 330 330 | Multiple concentric clutch shafts: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 325. Transmissions either (1) wherein the drive from the prime
mover to the transmission is through a manually selected one of
a plurality of concentric drive shafts, each of which has a clutch
for engagement with the engine clutch; or (2) wherein the drive
from the transmission to the propeller shaft is by means of a manually selected
one of a plurality of concentric driven shafts each of which has
a clutch for engagement with a clutch on the propeller shaft.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 331]](../ps.gif) 331 331 | Plurality of counter shafts: | ||||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 325. Transmission in which the change of speed from the drive
shaft to the driven shaft may be through a selected one of a plurality
of counter shafts.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 332]](../ps.gif) 332 332 | Internal-external gears: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 325. Transmissions wherein the transmission of power from the drive shaft to the driven shaft is by means of internal-external gears in conjunction with shiftable gears, or shiftable clutches, with constantly meshed gears, or both, in a single unit. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 333]](../ps.gif) 333 333 | Combined gear and clutch: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 325. Transmissions composed of shiftable gears, and shiftable
clutches, or shiftable gears provided with clutch elements, all
in one gearing combination, wherein selected gears or clutches are
manually shifted into or out of mesh with cooperating gears or clutches.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 334]](../ps.gif) 334 334 | Preselector: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 333. Transmissions, wherein the selected gears or clutches are
manually shifted into or out of mesh with cooperating gears or clutches
by operation of a clutch pedal after a separate preselective change
speed device has been set.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 335]](../ps.gif) 335 335 | Control mechanism: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 325. Transmissions composed of shiftable gears, or shiftable clutches with constantly meshed gears, or shiftable gears and shiftable clutches, wherein the shifting is accomplished by mechanical power driven means. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 336]](../ps.gif) 336 336 | Speed responsive: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 335. Transmissions, wherein the shifting is accomplished either
by means responsive to the speed of some part of the transmission
or by means responsive to both speed and torque conditions of the
transmission.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 336.5]](../ps.gif) 336.5 336.5 | Governor: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 336. Transmissions, wherein the shifting is accomplished by a
governor responsive to the speed of some part of the transmission.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 337]](../ps.gif) 337 337 | Torque responsive: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 335. Transmissions, wherein the shifting is automatically accomplished
by means operated in response to either the torque of the engine
or of the driven shaft.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 337.5]](../ps.gif) 337.5 337.5 | Cam operated: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 335. Transmissions, wherein the shifting is accomplished by means
of a manually operable cam which is connected to the shiftable member
so that operation of the cam produces progressive changes in gear
ratios.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 339]](../ps.gif) 339 339 | Meshing assisters: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 325. Transmissions, wherein a means is provided for synchronizing
the speed of the member which is being shifted with the speed of
the member to be engaged by the shiftable member prior to engagement
thereof.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 340]](../ps.gif) 340 340 | Double clutch and interposed transmission: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 339. Transmissions, having a clutch at each end thereof, which
are simultaneously engaged or disengaged to simultaneously engage
the transmission as a unit with or disengage it from the engine
and the propeller shaft.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
| Interchangeably locked, Longitudinally slidable: | |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 325. Transmissions wherein one or more gears may be moved along the axis of rotation into mesh with cooperating gears. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 341]](../ps.gif) 341 341 | With tumbler gear: | ||||||||
| Transmissions under Longitudinally slidable composed of
multiple spur gears on a tumbler carrier for cooperating with different
sized driving and driven gears.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 342]](../ps.gif) 342 342 | Selective: |
| Transmissions under Longitudinally slidable composed of selective, multiple, sliding spur gears on a plurality of shafts. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 343]](../ps.gif) 343 343 | Direct clutch and drive: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 342. Transmissions, but having means to directly clutch the drive and driven shafts together. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 344]](../ps.gif) 344 344 | Progressive: | ||
| Transmissions under Longitudinally slidable composed of
multiple sliding spur gears on a plurality of shafts, which gears
may be shifted manually to provide a progressive plurality of speeds.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 345]](../ps.gif) 345 345 | Direct clutch and drive: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 344. Transmissions, but which have means to directly clutch together the drive and driven shafts. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 346]](../ps.gif) 346 346 | Fluid operated: | ||||
| Transmissions under Longitudinally slidable containing a
plurality of slidable spur gears which are adapted to be shifted
into and out of engagement by fluid pressure means under manual
control.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 347]](../ps.gif) 347 347 | Multiple bevel gears: |
| Transmissions under Longitudinally slidable composed of a plurality of slidable bevel gears which may mesh with a disk or with other bevel gears. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 348]](../ps.gif) 348 348 | Tumbler and cone: | ||||
Transmissions under Longitudinally slidable comprising a
plurality of spur gears of varying diameters arranged on a single
shaft in cone form, and a single slidable spur tumbler gear adapted
to be progressively slid into mesh with the gears of the cone whereby
either the tumbler, or any one of the cone gears, may be driven
by the other in mesh therewith.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 349]](../ps.gif) 349 349 | Multiple cone: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 348. Transmissions in which a plurality of cone type gears are used and the single slidable tumbler gear is interposed between the cone type gears and acts to transmit power from one to the other. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 350]](../ps.gif) 350 350 | Single bevel gear: | ||
| Transmissions under Longitudinally slidable in which there
is a single slidable bevel gear in mesh with a toothed disk, or
one of a plurality of bevel gears for changing the speed.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 351]](../ps.gif) 351 351 | Pin or crown gears: | ||
| Transmissions under Longitudinally slidable in which pin
or crown gears, either single or multiple, are shifted to provide
a change of speed.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 352]](../ps.gif) 352 352 | Laterally slidable gears: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 325. Transmissions wherein the gears are supported by a shiftable carrier whereby the gears may be moved laterally with respect to the longitudinal axis of the transmission into mesh with cooperating gears. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 353]](../ps.gif) 353 353 | Rotary carriage: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 352. Transmissions wherein the gears are supported by a rotary carrier and are adapted to be moved laterally into mesh with cooperating gears. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 354]](../ps.gif) 354 354 | Swinging carriage: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 352. Transmissions wherein the gears are supported by a swingable carrier and are adapted to be moved laterally into mesh with cooperating gears. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 355]](../ps.gif) 355 355 | Single forward and reverse speeds: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 325. Transmissions wherein a single forward or a single reverse speed is obtained by means of slidable toothed gears of any type. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 356]](../ps.gif) 356 356 | Alternative clutch shaft: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 325. Transmissions composed of a single shiftable driving shaft which can be progressively or selectively clutched to any one of a plurality of intermediate shafts or counter shafts, which in turn are connected by constant mesh gearing to a final driven shaft, the drive shaft and the intermediate shafts or counter shafts being provided with cooperating clutch faces. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 357]](../ps.gif) 357 357 | Progressive: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 325. Transmissions wherein there are a plurality of slidable
keys or clutches splined to a plurality of shafts which are connected
to each other by constant mesh gears revoluble on the shafts, and
provided with clutch elements adapted to be engaged by the slidable
clutches or keys, the keys or clutches being manually shifted in
a manner to provide a progressive change in gear ratio.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 358]](../ps.gif) 358 358 | Keys simultaneously slidable: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 357. Transmissions, wherein the slidable keys or clutches are manually operated simultaneously to provide progressive changes in gear ratios. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 359]](../ps.gif) 359 359 | Selective: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 325. Transmissions wherein there are a plurality of slidable
keys or clutches splined to a plurality of shafts which are connected
to each other by constant mesh gears revoluble on the shafts, and
provided with clutch elements adapted to be engaged by the slidable
clutches or keys, the slidable keys or clutches being manually shifted
to provide selected changes in gear ratios.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 360]](../ps.gif) 360 360 | Multiple forward and reverse: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 325. Transmissions wherein there are a plurality of manually operable slidable keys or clutches splined to a plurality of shafts which are connected to each other by constant mesh gears revoluble on the shafts, the gears being provided with clutch elements adapted to be engaged by the slidable clutches or keys to provide a plurality of selective forward speeds and a plurality of reverse speeds. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 361]](../ps.gif) 361 361 | Single forward and reverse: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 325. Transmissions wherein there are a plurality of manually operable slidable keys or clutches splined to a plurality of shafts which are connected to each other by constant mesh gears, revoluble on the shafts, the gears being provided with clutch elements adapted to be engaged by the slidable clutches or keys to provide a single forward speed and a single reverse speed. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 362]](../ps.gif) 362 362 | Multiple key: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 325. Transmissions where there are a plurality of manually operable slidable keys or clutches splined to a single clutch shaft, the clutch shaft being connected to the other shafts of the transmission by constant mesh gears revoluble on the shafts, which shafts have clutch elements adapted to be engaged by the slidable keys or clutches to provide progressive change in gear ratios. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 363]](../ps.gif) 363 363 | Spur: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 362. Transmissions, in which the rotatable constantly meshed
gears are of the spur type.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 364]](../ps.gif) 364 364 | Fluid operated: | ||||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 363. Transmissions, in which the clutches or keys are
shifted by manually controlled fluid operated means, or
the clutches are of the fluid type.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 365]](../ps.gif) 365 365 | Electrically operated: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 363. Transmissions, where the clutches or keys are shifted by
manually controlled electrically operated means.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 366]](../ps.gif) 366 366 | Single key: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 325. Transmissions wherein there are constant mesh gears, some
of which are rotatably mounted on a shaft and adapted to be clutched
to the shaft by a single clutch or key which is manually shifted
to provide progressive changes in gear ratio.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 368]](../ps.gif) 368 368 | Clutch and ratchet: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 366. Transmissions comprising a gear train connecting driving
and driven shafts and a manually operable positive clutch for directly
connecting the shafts, together with a one-way clutch in the gear
train which acts like a ratchet mechanism which permits the gear
train to overrun when the shafts are directly coupled together.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 369]](../ps.gif) 369 369 | Spur gears: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 366. Transmissions, wherein the gears of the transmission are
spur gears.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 370]](../ps.gif) 370 370 | Intermediate clutch: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 369. Transmissions, providing two speeds only, wherein constant
mesh spur gears connect the drive and driven shafts, the gears being
loosely mounted on the shafts and being adapted to be connected
to their respective shafts by a single manually operable slidable
key or clutch intermediate the loosely mounted gears.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 371]](../ps.gif) 371 371 | Sliding clutch carrier: | ||||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 369. Transmissions comprising a plurality of spur gears loosely
mounted on a hollow shaft, the gears meshing with cooperating spur
gears fixed to a second shaft, and also comprising a member slidably
mounted in the hollow shaft, which member carries a single clutch
element, the latter of which is manually shiftable to progressively
and successively clutch the loose gears to the shaft on which they
are mounted.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 372]](../ps.gif) 372 372 | Sliding clutch operator: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 369. Transmissions comprising a plurality of spur gears loosely mounted on a hollow shaft, the gears meshing with cooperating spur gears fixed to a second shaft, and also comprising a member slidably mounted in the hollow shaft, the gears carrying clutches and the slidable member carrying means for operating the clutches to progressively connect any one of the gears to its shaft. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 373]](../ps.gif) 373 373 | Selective: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 325. Transmissions wherein there are a plurality of manually
operable slidable keys or clutches splined to a single shaft which
are connected to each other by constant mesh gears, revoluble on
the shafts, the gears being provided with a single key to selectively
connect certain of the gears to their respective shafts.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 374]](../ps.gif) 374 374 | Multiple key: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 373. Transmissions, but provided with constantly meshed gears,
some of which are loosely mounted on the same shaft and wherein
manually operable keys are provided for connecting a selected one
of the gears to its shaft.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 375]](../ps.gif) 375 375 | Spur gears: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 374. Transmissions wherein the gears of the transmission are
spur gears.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 376]](../ps.gif) 376 376 | Single speed forward and reverse: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 325. Miscellaneous transmissions comprising combinations of spur
gears with either pulleys and belts or chains and sprockets and
provided with manually operable slidable clutches mounted on a single
shaft for clutching either the pulleys, the sprockets, or the gears
thereto in order to provide either a single forward or a single reverse
speed.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 377]](../ps.gif) 377 377 | Spur gears: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 376. Transmissions having spur gears in constant mesh, certain of which are rotatable on a shaft and are adapted to be connected to the shaft by manually operated shiftable clutches. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 378]](../ps.gif) 378 378 | Bevel gears: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 376. Transmissions wherein a bevel driving gear is in constant
mesh with a plurality of driven bevel gears, loosely mounted on
the driven shaft with a manually operated slidable clutch for connecting
either of the loosely mounted gears to its shaft and wherein the
drive shaft is at an angle to the driven shaft.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 379]](../ps.gif) 379 379 | Bevel and idler gears: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 376. Transmissions wherein a bevel driving gear is in constant mesh with a plurality of driven bevel gears, loosely mounted on the driven shaft with a manually operated slidable clutch for connecting either of the loosely mounted gears to its shaft and wherein the drive and driven shafts are in alignment, and the common bevel gear, which is in mesh with both loose gears, acts as an idler to reverse the drive. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 380]](../ps.gif) 380 380 | Pivotally supported: | ||||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 640. Gearing mounted on a pivotal support to permit the driving
and driven gears of a gear train to be pivotally moved relative
to each other in a single plane without permitting a change of speed.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 381]](../ps.gif) 381 381 | Windmill turntable: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 380. Gearing of the windmill type. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 383]](../ps.gif) 383 383 | Screw: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 380. Screw gearing, | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 384]](../ps.gif) 384 384 | Spur: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 380. Spur gearing. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 385]](../ps.gif) 385 385 | Bevel: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 380. Bevel gearing.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 386]](../ps.gif) 386 386 | Wheel type: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 385. Bevel gearing associated with the wheels of a vehicle.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 387]](../ps.gif) 387 387 | Wringer type: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 385. Bevel gearing associated with the wringer of a washing machine.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 388]](../ps.gif) 388 388 | Follow-up mechanism: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 640. Gearing provided with means whereby in response to actuation
of one of its elements the movement of such element is continued
or augmented by some other means.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 390]](../ps.gif) 390 390 | Eccentric driving shaft and axle: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 640. Gearing usually for driving a motor vehicle wheel, which
is mounted adjacent a wheel and in which the driving shaft is offset
with respect to the driven shaft or axle.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 391]](../ps.gif) 391 391 | Central driving shaft in axle: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 640. Gearing usually for driving a motor vehicle wheel, which
is mounted adjacent a wheel and in which the driving shaft is centrally
disposed with respect to the vehicle axle.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 392]](../ps.gif) 392 392 | Parallel shafts, adjustable gear mesh: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 640. Gearing in which the gears are carried by parallel shafts
which are movable from or toward each other to such a limited extent
that the gears always remain in engagement.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 393]](../ps.gif) 393 393 | Varying speed ratio: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 640. Gearing in which the speed of the driven element is varied
during each revolution.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 395]](../ps.gif) 395 395 | Adjustable: | ||||||||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 640. Gearing in which one of the elements is adjustable relatively
to bring it into adjusted relationship with another.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 396]](../ps.gif) 396 396 | Relative movable axes: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 395. Gearing, in which either gear or shaft is adapted to be
moved for the purpose of adjustment.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 397]](../ps.gif) 397 397 | Parallel shafts: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 396. Gearing, in which the gear shafts are parallel.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 398]](../ps.gif) 398 398 | Automatic control: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 396. Gearing in which the gears or gear shafts are adjustable by automatic means. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 399]](../ps.gif) 399 399 | Parallel shafts: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 398. Gearing, the gears or gear shafts being parallel to each other. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 400]](../ps.gif) 400 400 | Fixed axes: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 395. Gearing, in which one of the elements is adapted to be moved manually in the direction along its axis for the purpose of adjustment. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 401]](../ps.gif) 401 401 | Parallel shafts: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 400. Gearing, the gear shafts being parallel to each other. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 402]](../ps.gif) 402 402 | Automatic control: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 400. Gearing, gear shafts being adjusted by automatic means. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 403]](../ps.gif) 403 403 | Parallel shafts: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 402. Gearing, the gear shafts being parallel to each other. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 404]](../ps.gif) 404 404 | Reversing means: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 640. Miscellaneous gearing in which the direction of rotation
of the driven shaft is reversible and in which there is no change
of speed.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 404.5]](../ps.gif) 404.5 404.5 | Governor control: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 404. Gearing, in which there is no change of speed, in which
the direction of rotation of the driven shaft is reversible, and
in which the change of direction is controlled by a governor.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 405]](../ps.gif) 405 405 | Disconnecting means: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 640. Miscellaneous gearing provided with means for disconnecting
the gear train.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 406]](../ps.gif) 406 406 | Displaceable elements: | ||||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 640. Gearing in which one of the elements moves linearly or angularly
about a center other than the axis of rotation of the gear.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 409]](../ps.gif) 409 409 | Backlash take-up: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 640. Gear trains provided with means to eliminate backlash in
some element of the combination.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 410]](../ps.gif) 410 410 | Pressure distributing: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 640. Gear trains provided with means by which the pressure of
the teeth of one unit is compensated for by that of another unit.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 411]](../ps.gif) 411 411 | Yieldability in gear trains: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 640. Gearing having one element provided with a yielding means
through which torque is transmitted.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 411.5]](../ps.gif) 411.5 411.5 | With brake means for gearing: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 640. Gearing in which means are provided to selectively stop
or prevent rotation of a gearing element.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 412]](../ps.gif) 412 412 | Directly cooperating gears: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 640. Gearing consisting of two meshed gears mounted on shafts.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 413]](../ps.gif) 413 413 | Parallel axes or shafts: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 412. Gearing, wherein the gear axes or shafts are parallel.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 414]](../ps.gif) 414 414 | External type: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 413. Gearing, in which all of the gears have external teeth. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 415]](../ps.gif) 415 415 | Pin teeth: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 414. Gearing, in which one of the gears has pin teeth.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 416]](../ps.gif) 416 416 | Intersecting axes: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 412. Gearing not otherwise classified, consisting of two gears in combination with a particular form of mounting, the axes thereof intersecting each other. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 417]](../ps.gif) 417 417 | Bevel gear type: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 416. Gearing, the gears being of the bevel type. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 420]](../ps.gif) 420 420 | Spur and bevel: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 412. Gearing consisting of a combination of spur and of bevel
gears.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 421]](../ps.gif) 421 421 | Spur: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 412. Gearing, consisting of gears of the spur type.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 422]](../ps.gif) 422 422 | Rack and pinion: | ||||||||||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 412. Gearing, the gearing embodying racks and pinions.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 423]](../ps.gif) 423 423 | Bevel: | ||||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 412. Gearing of the bevel type.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 424]](../ps.gif) 424 424 | Motor vehicle drive: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 423. Gearing, in which the bevel gearing drives the differential
and rear axle shafts of a motor vehicle.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 424.5]](../ps.gif) 424.5 424.5 | Spiral: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 412. Gearings of the spiral type. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 424.6]](../ps.gif) 424.6 424.6 | Driven rack or shaft: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 424.5. Spiral gearing, in which the driven element is a rack or chain. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 424.7]](../ps.gif) 424.7 424.7 | Screw: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 424.5. Gearing, the two gears being spiral and nonintersecting.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 424.71]](../ps.gif) 424.71 424.71 | Screw and nut: | ||||||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 424.5. Subject matter including gearing including a rotatable
element having spiral threads or grooves encircling its axis of
rotation and a second element enmeshed with it for relative movement
along the axis.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 424.72]](../ps.gif) 424.72 424.72 | Plural longitudinally variably spaced nuts: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 424.71. Subject matter including a plurality of nuts on the same
screw that are moveable to permit the spacing between the nuts to
change.
Figure 1. A typical example of the subject matter. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 424.73]](../ps.gif) 424.73 424.73 | Threadless: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 424.71. Subject matter in which the shaft and nut have no threads
at the interface between them, i.e., power is transmitted by frictional contact.
Figure 1. A typical example of the subject matter. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 424.74]](../ps.gif) 424.74 424.74 | Non-linear screw: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 424.71. Subject matter in which a portion of the axis of the screw
is curved.
Figure 1. A typical example of the subject matter. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 424.75]](../ps.gif) 424.75 424.75 | Thread geometry: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 424.71. Subject matter including particular structure or shape of
the threads.
Figure 1. A typical example of the subject matter. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 424.76]](../ps.gif) 424.76 424.76 | Thread pitch varies over axial length: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 424.75. Subject matter in which the distance between successive turns of the helical threads varies from one point on the shaft to another. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 424.77]](../ps.gif) 424.77 424.77 | Shaft thread is spirally wound wire: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 424.75. Subject matter in which the screw thread includes a wire extending along the helix of the thread. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 424.78]](../ps.gif) 424.78 424.78 | Nut disengageable from screw: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 424.71. Subject matter in which the nut is constructed to be readily
moved out of contact with the screw.
Figure 1. A typical example of the subject matter. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 424.79]](../ps.gif) 424.79 424.79 | Nut segments hinged parallel to shaft (e.g., clam shell-type, etc.): | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 424.78. Subject matter in which the nut includes two portions joined
together so as to be pivotable relative to each other along an axis that
is generally parallel with the axis of relative rotation of the
nut and screw when the nut is in operable engagement with the screw.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 424.81]](../ps.gif) 424.81 424.81 | Rolling element engaging thread: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 424.71. Subject matter including an element between the screw and nut that engages and rolls in the threads of the screw and nut to effect the meshing of the threads. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 424.82]](../ps.gif) 424.82 424.82 | Recirculating rolling elements: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 424.81. Subject matter including elements between the screw and
nut that engage and roll in the threads of the screw and nut to
effect the meshing of the threads, the elements traveling along
a closed loop path, a portion of which is outside of the screw nut
interface and not in meshing force transmitting relationship with the
screw and nut.
Figure 1. A typical example of the subject matter. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 424.83]](../ps.gif) 424.83 424.83 | Plural independent recirculating element paths: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 424.82. Subject matter including additional elements that roll in the threads of the screw and nut and travel along a second closed loop path, the paths having substantially no portions in common. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 424.84]](../ps.gif) 424.84 424.84 | Single thread common to plural paths: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 424.82. Subject matter in which portions of each of the two closed loop paths lie in different portions of the same screw or nut thread. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 424.85]](../ps.gif) 424.85 424.85 | Roller return path in shaft: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 424.82. Subject matter in which a portion of the closed loop path
is located within the body of the screw.
Figure 1. A typical example of the subject matter. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 424.86]](../ps.gif) 424.86 424.86 | Return path geometry: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 424.82. Subject matter including particular structure for guiding the rolling elements along the portion of the path that is not in meshing engagement with the screw and nut threads (i.e., outside the screw nut interface). | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 424.87]](../ps.gif) 424.87 424.87 | Rolling element deflector: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 424.86. Subject matter including particular structure for directing the rolling elements between the portions of the paths that lie inside and outside the screw nut interface. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 424.88]](../ps.gif) 424.88 424.88 | Interconnected or cooperating rollers or roller structure: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 424.82. Subject matter in which (1) at least two of the roller elements are connected or cooperate in a manner involving other than mere pushing contact or (2) including the particular shape or construction of an individual roller element. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 424.89]](../ps.gif) 424.89 424.89 | Non-recirculating rolling elements: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 424.81. Subject matter including elements between the screw and nut that engage and roll in the threads of the screw and nut to effect the meshing of the threads, the elements being held in at least one thread at all times during operation. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 424.9]](../ps.gif) 424.9 424.9 | Captured sphere: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 424.89. Subject matter in which the rolling elements are spherical and including means for restricting there movement so as to prevent engagement with one another. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 424.91]](../ps.gif) 424.91 424.91 | Cylindrical or quasi-cylindrical roller element (e.g., inclined roller, etc.): |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 424.89. Subject matter in which the rolling elements are substantially cylindrical (i.e., they have a single axis of symmetry about which they roll). | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 424.92]](../ps.gif) 424.92 424.92 | Parallel to shaft: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 424.91. Subject matter in which the axes of the rolling elements are substantially parallel to the axis of relative rotation of the screw and nut during operation. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 424.93]](../ps.gif) 424.93 424.93 | Perpendicular to shaft: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 424.91. Subject matter in which the axes of the rolling elements are substantially perpendicular to the axis of relative rotation of the screw and nut (i.e., tangent to a cylinder centered on the axis) during operation. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 424.94]](../ps.gif) 424.94 424.94 | Less than 360 degrees of contact between nut and screw: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 424.71. Subject matter in which the screw and nut engage over an
arc that totals substantially less than 360 degrees.
Figure 1. A typical example of the subject matter. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 424.95]](../ps.gif) 424.95 424.95 | Independent nut segments: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 424.94. Subject matter in which the nut includes a plurality of
relatively moveable threaded portions each engaging the screw.
Figure 1. A typical example of the subject matter. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 424.96]](../ps.gif) 424.96 424.96 | Integral deformable tangs engaging screw: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 424.95. Subject matter in which the relatively moveable threaded
portions of the nut are integrally connected by means including
a flexible member.
Figure 1. A typical example of the subject matter. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 425]](../ps.gif) 425 425 | Worm: | ||||||||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 424.5. Gearing of the worm type.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 425.5]](../ps.gif) 425.5 425.5 | Variable speed: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 425. Gearing, the worm gearing being of a structure to impart a variable speed to the driven member. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 426]](../ps.gif) 426 426 | Intermittent motion: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 425. Gearing, the worm gearing being of a structure to impart
an intermittent motion to the driven element.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 427]](../ps.gif) 427 427 | Distribution of pressure: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 425. Gearing, the pressure of the teeth of one of the elements
being compensated for by that of another.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 431]](../ps.gif) 431 431 | Gear and rotary bodies: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 640. Gearing comprising a combination of a gear with a rotary body or bodies, not a gear, fixed thereto and mounted upon a common shaft. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 432]](../ps.gif) 432 432 | Laterally-spaced wheels: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 431. Gearing, the rotary elements being laterally spaced. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 433]](../ps.gif) 433 433 | Radially-spaced wheels: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 431. Gearing, the rotary elements being spaced radially. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 433.5]](../ps.gif) 433.5 433.5 | With flywheel: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 431. Subject matter including a motion-smoothing component
generally made up of a massive disk-like member.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 434]](../ps.gif) 434 434 | Rotary bodies: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 640. Gearing comprising structure and details of rotary bodies,
per se, constituting gearing elements.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 435]](../ps.gif) 435 435 | Mutilated: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 434. Inventions, having teeth which extend only partially around the periphery, producing upon rotation an intermittent drive. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 436]](../ps.gif) 436 436 | Geneva: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 434. Gearing, of the star-wheel type adapted to give intermittent
rotation to a driven element during each revolution thereof.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 437]](../ps.gif) 437 437 | Irregular teeth and bodies: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 434. Devices, having peripheries of noncircular form or irregularly shaped teeth, or both. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 438]](../ps.gif) 438 438 | External and internal teeth: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 434. Devices, provided with teeth both on the inner and outer periphery. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 439]](../ps.gif) 439 439 | Sectional: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 434. Gears, which are made up of a plurality of sections. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 440]](../ps.gif) 440 440 | Backlash take-up: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 439. Devices, provided with means for the elimination of backlash.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 441]](../ps.gif) 441 441 | Screw and nut: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 440. Devices, the gears being of the screw and nut type. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 443]](../ps.gif) 443 443 | Sound deadening: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 439. Gears including means for deadening sound in operation.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 444]](../ps.gif) 444 444 | Differential disks: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 439. Gears mounted upon a single shaft and connected thereto
by means which permits of a differential action between them.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 445]](../ps.gif) 445 445 | Multiple disks: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 439. Devices, made up of laminations.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 446]](../ps.gif) 446 446 | Separate rim: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 439. Bodies, having separate rims and webs.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 447]](../ps.gif) 447 447 | Detachable: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 446. Bodies, having the rim secured to the web by means permitting the detachment of the rim. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 448]](../ps.gif) 448 448 | Segmental rim: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 439. Bodies, having rims made up of a plurality of segments.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 449]](../ps.gif) 449 449 | Sheet metal: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 439. Bodies, fabricated wholly or in part of sheet metal.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 450]](../ps.gif) 450 450 | Diametrically split: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 439. Gears, in which the line of division between the sections occurs along a diameter. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 451]](../ps.gif) 451 451 | Shaft-admitting insert: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 439. Gears, provided with removable inserts whereby the shafts may be removed laterally through the opening occurred by the inserts. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 457]](../ps.gif) 457 457 | Teeth: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 640. Subcombinations comprising the gear teeth of meshing gears. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 458]](../ps.gif) 458 458 | Worm and helical: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 457. Devices directed to the structure and details of worm and
helical gear teeth.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 459.5]](../ps.gif) 459.5 459.5 | Bevel: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 457. Devices comprising bevel teeth. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 460]](../ps.gif) 460 460 | Spur: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 457. Devices comprising spur teeth. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 461]](../ps.gif) 461 461 | Yieldable: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 460. Devices wherein the spur teeth are combined with yieldable elements. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 462]](../ps.gif) 462 462 | Form: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 460. Devices wherein the spur teeth are of a modified tooth form. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 464]](../ps.gif) 464 464 | Antifriction: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 462. Devices, in which the teeth embody antifriction means. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 465]](../ps.gif) 465 465 | Roller: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 464. Devices, in which the teeth are provided with or operate
against rollers.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 466]](../ps.gif) 466 466 | Twisted: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 462. Devices, in which the teeth are twisted. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 467]](../ps.gif) 467 467 | Lubrication: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 640. Gears specifically modified for purposes of lubrication.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 468]](../ps.gif) 468 468 | Teeth: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 467. Gearing having teeth specifically modified for purposes
of lubrication.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 469]](../ps.gif) 469 469 | CONTROL LEVER AND LINKAGE SYSTEMS: | ||||||||
This subclass is indented under the class definition. Mechanisms which are made up of (1) such links as cranks,
levers and rods, with turning and sliding pairs, and (2) links consisting
of bodies which have two or more rigid elements, which links may
be connected to other bodies for the purpose of transmitting force
or motion, not otherwise classified.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 470]](../ps.gif) 470 470 | Resilient connections: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 469. Systems which have a resilient member as one of the elements. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 471]](../ps.gif) 471 471 | Multiple controlled elements: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 469. Systems in which there is a single control element which
selectively operates a plurality of controlled elements.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 473.1]](../ps.gif) 473.1 473.1 | Transmission control: | ||||||||||||||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 471. Multiple controlled elements for manually controlling an
assembly of gears or associated parts for the transfer of power
from a prime mover to a driving or propelling means.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 473.11]](../ps.gif) 473.11 473.11 | Fluid actuator: | ||||||||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 473.1. Transmission control wherein the operation or engagement
of a multiple controlled transmission element is initialized by
a fluid means.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 473.12]](../ps.gif) 473.12 473.12 | Electrical actuator: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 473.1. Transmission control wherein the operation or engagement of a multiple controlled transmission element is initialized by an electrical pulse or current. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 473.13]](../ps.gif) 473.13 473.13 | Occupant propelled vehicle: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 473.1. Transmission control wherein the multiple controlled transmission
elements are in a vehicle moved via the action of a rider or occupant
of the vehicle.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 473.14]](../ps.gif) 473.14 473.14 | Transmission controlled by flexible cable: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 473.13. Occupant propelled vehicle wherein the multiple controlled
transmission elements are manipulated or moved by a pliable cable.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 473.15]](../ps.gif) 473.15 473.15 | Transmission controlled by flexible cable: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 473.1. Transmission control wherein the multiple controlled transmission
elements are actuated by a pliable cable.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 473.16]](../ps.gif) 473.16 473.16 | Foot operated: | ||||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 473.1. Transmission control wherein the multiple controlled element
is engaged or disengaged via movement of a lever engaged by the
terminal part of a human leg.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 473.17]](../ps.gif) 473.17 473.17 | Multiple foot-operated controls: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 473.16. Foot operated control having a plurality of independent foot operated levers. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 473.18]](../ps.gif) 473.18 473.18 | Control convertible between automatic and manual operation: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 473.1. Transmission control capable of selectively operating in a system controlled mode or an operator manipulated mode. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 473.19]](../ps.gif) 473.19 473.19 | Control of plural mechanisms (e.g., control of transmission and control of 4 - wheel drive): |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 473.1. Transmission control capable of operating more than one transmission or related mechanism. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 473.2]](../ps.gif) 473.2 473.2 | Separate control levers: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 473.19. Control of plural mechanisms having individual controls
for each controlled transmission or mechanism.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 473.21]](../ps.gif) 473.21 473.21 | Restriction of shift, gear selection, or gear engagement: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 473.1. Transmission control wherein movement of a shifting element
is regulated, limited, or prohibited.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 473.22]](../ps.gif) 473.22 473.22 | Prevention of reverse shift: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 473.21. Restricted shift, gear selection or gear engagement wherein
a reverse shift, selection, or engagement is averted, impeded, or
prohibited.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 473.23]](../ps.gif) 473.23 473.23 | Separate actuator to disengage restrictor: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 473.21. Restricted shift, gear selection or gear engagement further comprising a releasable mechanism for manually enabling the shifting, selecting, or engaging element. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 473.24]](../ps.gif) 473.24 473.24 | Shift element interlock: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 473.21. Restricted shift, gear selection or gear engagement wherein the shifting elements are releasably interconnected. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 473.25]](../ps.gif) 473.25 473.25 | With detent, recess, notch, or groove: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 473.24. Shift rod interlock wherein the interlock comprises a stop or checking device to hold the shifting element in a predetermined position until moved therefrom by an application of a force transmitted to the element. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 473.26]](../ps.gif) 473.26 473.26 | Resiliently biased interlock: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 473.24. Shift rod interlock wherein the interlock is flexabily urged in a locking position. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 473.27]](../ps.gif) 473.27 473.27 | Spherical restrictor: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 473.21. Restricted shift, gear selection, or gear engagement wherein the restrictor is generally round in three dimensional space. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 473.28]](../ps.gif) 473.28 473.28 | Resiliently biased restrictor: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 473.21. Restricted shift, gear selection, or gear engagement wherein the restrictor is flexabily urged in a locking position. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 473.29]](../ps.gif) 473.29 473.29 | Having vibration damper: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 473.1. Transmission control having a means to shunt frequencies generated by the transmission. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 473.3]](../ps.gif) 473.3 473.3 | Manually operated selector (e.g., remotely controlled device, lever, push button, rotary dial, etc.): |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 473.1. Transmission control wherein the transmission is manipulated by the vehicle or machine operator using a hand operated device. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 473.31]](../ps.gif) 473.31 473.31 | Control lever on steering column: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 473.3. Manually operated selector located on the steering column of a vehicle. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 473.32]](../ps.gif) 473.32 473.32 | Control lever movable through plural planes: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 473.31. Steering column mounted control level wherein the control
lever movement is not confined to a single plane.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 473.33]](../ps.gif) 473.33 473.33 | Control lever movable through plural planes: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 473.3. Hand operated selector wherein the control lever movement
is not confined to a single plane.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 473.34]](../ps.gif) 473.34 473.34 | Spherical mount (e.g., ball and socket): |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 473.33. Control lever movable through plural planes wherein the control lever is mounted using a spherical portion and complementary cavity mount. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 473.35]](../ps.gif) 473.35 473.35 | Resiliently biased control lever: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 473.34. Spherical mounted control lever wherein the control lever is resiliently biased or urged in a particular orientation. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 473.36]](../ps.gif) 473.36 473.36 | Particular element (e.g., shift fork, template, etc.): |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 473.1. Transmission control having specific structure of a transmission control element or related mechanism. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 473.37]](../ps.gif) 473.37 473.37 | Shift fork structure: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 473.36. Particular element wherein the transmission control element or related mechanism is a shift fork. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 478]](../ps.gif) 478 478 | Foot operated: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 471. Systems in which there are foot operated controls which
selectively operates a plurality of controlled members.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 478.5]](../ps.gif) 478.5 478.5 | Offset extension: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 478. Devices wherein there are at least two foot operated controllers
for separate systems, and one of the controllers has either an extension
or a remote operator attached or connected thereto and so positioned
with respect to at least one other of the controllers that a single
foot may be manipulated to effect operation of at least two of the
controllers.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 479.01]](../ps.gif) 479.01 479.01 | Multiple controlling elements for single controlled element: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 469. Systems in which there are a plurality of controlling elements
providing input to control a single element output.
| |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 480]](../ps.gif) 480 480 | Interconnected: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 479. Systems in which there are a plurality of independently
operable systems which may be connected and operated by a single
controlling member.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 481]](../ps.gif) 481 481 | Hand and foot: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 480. Systems, when one control is a foot operated member and
the other a hand operated member.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 482]](../ps.gif) 482 482 | Accelerator: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 481. Systems, for controlling a carburetor.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 483]](../ps.gif) 483 483 | Interlocked: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 479. Systems located between and cooperating with elements of
a plurality of control lever and linkage systems which prevent the
simultaneous operation of the control systems, and permit the operation
of only one control system at a time.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 484]](../ps.gif) 484 484 | Steering and controls assemblies: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 479. Systems where the controlling elements are grouped around a steering post. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 485]](../ps.gif) 485 485 | Rotary control shaft: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 484. Systems in which the control members are rotary shafts.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 486]](../ps.gif) 486 486 | Reciprocating control elements: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 484. Systems in which the controlling elements have a part reciprocating in a line parallel to the steering post axis. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 487]](../ps.gif) 487 487 | Flexible: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 486. Systems in which the reciprocating member is flexible. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 488]](../ps.gif) 488 488 | Handle bar type: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 486. Systems in which the rotary shafts are grouped about a handle bar and in which one of the shafts reciprocates. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 489]](../ps.gif) 489 489 | Flexible control element: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 488. Systems in which one element of the controls is a flexible
member.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 490]](../ps.gif) 490 490 | Antirattling elements: | ||||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 479. Systems in which a plurality of controlling elements are
grouped about each other, and a device is interposed between the
controlling elements to prevent rattling.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 490.01]](../ps.gif) 490.01 490.01 | Robotic arm: | ||||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 479.01. Systems in which the controlled element is a member of a
robotic linkage system which may include a base and its associated supporting
structure.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 490.02]](../ps.gif) 490.02 490.02 | Including power cable or connector: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 490.01. Subject matter in which the controlled member has associated
therewith an electrical cable, a pneumatic tube, a hydraulic conduit,
or a connector which will handle either single or plural energy
paths.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 490.03]](../ps.gif) 490.03 490.03 | Including electric motor: | ||||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 490.01. Subject matter in which one or more electric motors are
used to move a robotic linkage system to a desired location within
the range of motion of the linkage.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 490.04]](../ps.gif) 490.04 490.04 | Including flaccid drive element: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 490.01. Subject matter in which the robotic linkage system is moveable
to a desired location by drive inputs from one or more nonrigid flexible
elements.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 490.05]](../ps.gif) 490.05 490.05 | Joint between elements: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 490.01. Subject matter in which the controlled member is a drive
path connection between two or more members of a robot linkage.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 490.06]](../ps.gif) 490.06 490.06 | Wrist: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 490.05. Subject matter in which the joint, typically between the
robot linkage and the end effector mount member, permits rotation
about a plurality of orthogonal axes.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 490.07]](../ps.gif) 490.07 490.07 | Power elements as controlling elements: | ||||||||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 479.01. Subject matter in which the controlling elements include
power devices which include, but are not limited to electric motors, fluid
motors, spring motors, heat engines (e.g., thermostatic actuator),
electromagnetic devices (e.g., solenoids), etc.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 490.08]](../ps.gif) 490.08 490.08 | Planar surface with orthogonal movement and rotation: | ||||||||||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 490.07. Subject matter in which the power elements control both
linear movement of a planar surface member (constrained to move
along at least one of the three orthogonal spacial axes) and its
rotary movement about at least one axis.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 490.09]](../ps.gif) 490.09 490.09 | Planar surface with orthogonal movement only: | ||||||||||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 490.07. Subject matter in which the power elements control linear
movement of a planar surface member that is constrained to move
along at least one of the three orthogonal spacial axes.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 490.1]](../ps.gif) 490.1 490.1 | Pair of power elements: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 490.07. Subject matter in which there are only two power elements
in the linkage system.
| |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 490.11]](../ps.gif) 490.11 490.11 | Power and manual controlling elements: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 479.01. Subject matter in which there is a combination of at least
one power driven element and at least one manually operated element
which together control the system"s single output element.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 490.12]](../ps.gif) 490.12 490.12 | Manual controlling elements: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 479.01. Subject matter in which there is a plurality of exclusively
hand or exclusively foot operated devices which together provide
inputs to control the system"s single output element.
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 490.13]](../ps.gif) 490.13 490.13 | Planar surface with orthogonal movement or rotation: | ||||||||||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 490.12. Subject matter in which hand operated elements control both
linear movement of a planar surface member (constrained to move along
at least one of the three orthogonal spacial axes) or its rotary
movement about at least one axis.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 490.14]](../ps.gif) 490.14 490.14 | Levers: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 490.12. Subject matter in which the manual controlling elements
are a plurality of first, second, or third degree levers which are
either operated by hand or by foot.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 490.15]](../ps.gif) 490.15 490.15 | Pair of levers: | ||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 490.14. Subject matter in which there are only two control elements
in the linkage system that are exclusively either hand or foot operated.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 491]](../ps.gif) 491 491 | Hand operated: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 469. Systems which are hand operated. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 492]](../ps.gif) 492 492 | Steering posts: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 491. Hand operated steering posts.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 493]](../ps.gif) 493 493 | Adjustable: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 492. Hand operated steering posts which are angularly or axially
adjustable.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 494]](../ps.gif) 494 494 | Auxiliary operators: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 492. Auxiliary devices to be used alternately with the conventional steering wheel or arm for operating steering posts. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 495]](../ps.gif) 495 495 | Position controllers: | ||||||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 492. Devices acting on a steering post or wheel to position it
in a selected position.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 496]](../ps.gif) 496 496 | Motion translating mechanism: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 492. Devices for transferring power from steering posts to steering
linkage.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 497]](../ps.gif) 497 497 | Cam type: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 496. Mechanisms in which cams are used for transferring power
from the steering posts to the steering linkage.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 498]](../ps.gif) 498 498 | Gear type: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 496. Mechanisms in which gears are used for transferring power
from steering posts to steering linkages.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 499]](../ps.gif) 499 499 | Screw and nut: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 498. Mechanisms in which screw and nut gearing is used.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 500]](../ps.gif) 500 500 | Worm: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 498. Mechanisms in which worm gearing is used.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 500.5]](../ps.gif) 500.5 500.5 | Flexible transmitter (e.g., bowden cable): | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 491. Mechanism including an elongated element for transmitting
force or motion from a hand to operate a device, wherein the element
is formed of a flexible or pilant material or a series of pivoted
links, such that the force or motion may be transmitted along a
curved path.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 501.5]](../ps.gif) 501.5 501.5 | Constant tension sustaining: | ||||||||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 500.5. Devices comprising means for maintaining an established
static stretch or pull in the flexible elements, effective upon
change in said stretch or pull, for concurrently restoring the same
to the established value.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 501.6]](../ps.gif) 501.6 501.6 | And hand operator: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 500.5. Mechanism including a particular input portion which is
directly contacted and manipulated by the hand.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 502]](../ps.gif) 502 502 | Slidable: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 501.6. Device wherein the particular input portion which is directly
contacted and manipulated by the hand comprises a reciprocating
rod slidably engaged in fixed support structure.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 502.1]](../ps.gif) 502.1 502.1 | For moving a mirror: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 501.6. Mechanism wherein the elongated flexible element is connected to a device having a polished or smoothed surface that forms an image by reflection, and is intended to transmit motion from a hand to the device. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 502.2]](../ps.gif) 502.2 502.2 | Single rotatable lever (e.g., for bicycle brake or deraileur): | ||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 501.6. Mechanism wherein the particular input portion comprises
a pivoted link or bar having a first section adapted to be contacted
and moved by the hand, and a second portion connected directly to
the flexible element or an intermediate fastener.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 502.3]](../ps.gif) 502.3 502.3 | Including rolling antifriction elements: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 500.5. Mechanism including a plurality of discrete rotatable elements
located between and contacting the flexible element and its surrounding or
supporting structure, to eliminate frictional contact between the
two.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 502.4]](../ps.gif) 502.4 502.4 | And sheath support, connector, or anchor: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 500.5. Mechanism including a flexible tubular housing covering
a substantial length of the flexible element and which allows axial
movement of the element therein, wherein one of the following is
provided: (a) means to hold up or provide a foundation for the flexible
housing or (b) means to fasten an end of the flexible housing either
to another section of flexible housing or to a structure which is
fixed with respect to the flexible element.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 502.5]](../ps.gif) 502.5 502.5 | Specific cable or sheath structure: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 500.5. Mechanism wherein significance is attributed to the particular
composition or form of either the elongated flexible element or
a flexible tubular housing which covers a substantial length of
the flexible element and allows axial movement of the element therein.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 502.6]](../ps.gif) 502.6 502.6 | Specific cable connector or guide: | ||||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 500.5. Mechanism wherein particular significance is attributed
to either (a) a device or structure for fastening an end of the
flexible element to something, or (b) a rigid element which defines a
path through which the flexible element moves and which limits lateral
movement of the flexible element.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 503]](../ps.gif) 503 503 | Sliding rod: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 491. Devices comprising hand operated, rigid, control members
which operate by sliding movement in the direction of their longitudinal
axes.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 504]](../ps.gif) 504 504 | Rotatable rod, shaft, or post: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 491. Devices, comprising miscellaneous hand operated controls which consist of a rigid rotatable member. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 505]](../ps.gif) 505 505 | Gear, drum, and cable: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 504. Systems in which the control member is a rotatable rod,
shaft, or post which transmits motion through a gear to a drum and
cable.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 506]](../ps.gif) 506 506 | Drum and cable: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 504. Devices directly connected to a drum and cable. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 507]](../ps.gif) 507 507 | Gear: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 504. Devices connected to gearing for operating it. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 508]](../ps.gif) 508 508 | Variable ratio: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 507. Devices which translate the forces applied thereto with
varying ratios.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 509]](../ps.gif) 509 509 | Screw and nut: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 507. Devices in the form of screw and nut gearing used for transmitting force and motion from the rotatable control member to the controlled linkage. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 510]](../ps.gif) 510 510 | Adjustable: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 504. Devices consisting of rigid rotatable control members which are collapsible when not in use and adjustable either axially or transversely. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 511]](../ps.gif) 511 511 | Mountings: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 504. Devices for supporting and mounting hand operated rotatable rods, shafts, or posts, and their motion translating mechanisms. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 512]](../ps.gif) 512 512 | Foot operated: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 469. Systems which are operated by foot controlled members.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 513]](../ps.gif) 513 513 | Accelerator: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 512. Systems in which the foot operated member operates a linkage system which controls a carburetor. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 514]](../ps.gif) 514 514 | Signal: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 512. Systems in which the foot operated member operates a linkage system which controls a signal. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 515]](../ps.gif) 515 515 | Knee operated: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 469. Systems operated by a knee controlled member. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 516]](../ps.gif) 516 516 | Variable output force: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 469. Systems having a mechanical unit which automatically varies the out-put force during the operation. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 517]](../ps.gif) 517 517 | Flexible: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 516. Systems wherein one element of the mechanical force varying unit is flexible. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 518]](../ps.gif) 518 518 | Variable input leverage: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 516. Systems which have an additional device for varying the leverage of a control element so as to vary the input force. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 519]](../ps.gif) 519 519 | Levers: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 469. Elements consisting of rigid structures which turn freely
on a fixed pivot and impart pressure or motion from a source of
power.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 520]](../ps.gif) 520 520 | Toggle: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 519. Elements hinged together and employed to transmit a varying
force by lateral pressure on the hinge.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 521]](../ps.gif) 521 521 | Lazy tongs: | ||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 520. Devices consisting of a series of diagonal levers pivoted
together in the middle and at the ends by which arrangement the
device can be extended.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 522]](../ps.gif) 522 522 | Adjustable: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 519. Levers in which the relationship of parts may be varied as by varying the length of the lever or work arms or by varying the point of application of force or the position of the fulcrum. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 522.5]](../ps.gif) 522.5 522.5 | Swing posts: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 519. Devices which have one end fulcrumed on a fixed base and pivotally supporting at or adjacent the opposite end a reciprocating motion transmitting member. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 523]](../ps.gif) 523 523 | Hand: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 519. Levers specially designed for operation by hand.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 524]](../ps.gif) 524 524 | Jointed: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 523. Levers which are formed of a plurality of parts which are
jointed together.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 525]](../ps.gif) 525 525 | Adjustable: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 523. Levers provided with means for adjusting their length or their arms with respect to each other. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 526]](../ps.gif) 526 526 | Stops: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 519. Devices positioned in the path of movement of levers to
limit their movements.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 527]](../ps.gif) 527 527 | Detents: | ||||||||||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 469. Elements used in connection with fixed and movable members
and especially adapted to check or arrest motion.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 528]](../ps.gif) 528 528 | Hand crank: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 527. Detents cooperating with hand cranks to prevent accidental
movement.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 529]](../ps.gif) 529 529 | Interrelated lever release: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 527. Devices in which a detent acts on one element of the system
to hold it in a predetermined position, the detent being connected
to a second member of the system, and in order to release the element,
the second member must first be operated to release the detent.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 530]](../ps.gif) 530 530 | Gear: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 527. Detents which consist of a body with a plurality of teeth which cooperate with similar teeth on the positioned member. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 531]](../ps.gif) 531 531 | Friction: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 527. Detents which have friction surfaces engaging the positioned
member.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 532]](../ps.gif) 532 532 | Lever engaging: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 527. Detents consisting of hooks or struts which are engaged by a lever when it moves to a predetermined position. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 533]](../ps.gif) 533 533 | Lever engaging rack: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 527. Detents consisting of a toothed rack member with which a lever is adapted to be moved into engagement, the engaged tooth of the rack acting as a detent. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 534]](../ps.gif) 534 534 | Pivoted: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 533. Devices wherein the toothed rack member is pivoted. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 535]](../ps.gif) 535 535 | Lever carried pawl: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 533. Detents consisting of devices pivoted on a lever and adapted to fall into notches or teeth in a fixed member to restrain the lever from back motion. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 536]](../ps.gif) 536 536 | Handle release: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 533. Devices in which the detent is released by a handle carried
by the lever.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 537]](../ps.gif) 537 537 | Finger lever release: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 533. Devices in which the detent is released by a lever which is so positioned on the control lever that it can be actuated by the fingers at the time of operation of the control lever. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 538]](../ps.gif) 538 538 | Slidable: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 537. Devices wherein finger levers are connected to the detent by a member slidably mounted on the control lever. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 539]](../ps.gif) 539 539 | Pedal controlled: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 533. Detents which are controlled by a pedal connected to the pawl. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 540]](../ps.gif) 540 540 | Lever carried rack: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 527. Detents which consist of a fixed member which cooperates with the teeth of a rack which is carried by a lever. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 541]](../ps.gif) 541 541 | Pivoted: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 540. Devices in which the rack is pivoted to the lever. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 542]](../ps.gif) 542 542 | Pedal controlled: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 540. Devices in which the racks are connected to a pedal which controls their position and effects their release from an operative position. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 543]](../ps.gif) 543 543 | Handles: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 469. Elements adapted to be grasped by the hand in lifting or
using when claimed in combination with essential mechanical movement
structure or which is definitely limited in use or application to
the mechanical movement art.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 544]](../ps.gif) 544 544 | Extension: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 543. Devices which are adapted to be detachably secured to handles
to facilitate their control from a remote point.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 545]](../ps.gif) 545 545 | Hand crank: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 543. Devices for causing rotation about an axis, consisting of a member extending at right angles to the axis and a hand grip attached to the free end of the member. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 546]](../ps.gif) 546 546 | Extensible: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 545. Devices in which the length of the crank arm is adjustable.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 547]](../ps.gif) 547 547 | Collapsible: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 545. Devices in which the handle or crank arm may be folded or otherwise collapsed when not in use. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 548]](../ps.gif) 548 548 | Shaft connections: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 543. Devices for connecting a handle to a shaft in which the
connections between the shaft and handle are either controlled by
the handle itself or by a mechanism mounted on the handle.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 550]](../ps.gif) 550 550 | Engine starter type: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 548. Devices between an engine crank shaft and the hand crank
where there is no back-fire protective device incorporated.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 551]](../ps.gif) 551 551 | Holders: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 550. Devices for holding an engine starter crank in a predetermined position when not in use. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 551.1]](../ps.gif) 551.1 551.1 | Handle bars: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 543. Devices in the form of a handle bar for a bicycle or like
device.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 551.2]](../ps.gif) 551.2 551.2 | Spring biased or supported: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 551.1. Devices in which the bar is spring biased or supported for shock absorbing purposes. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 551.3]](../ps.gif) 551.3 551.3 | Folding or adjustable: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 551.1. Devices in which the bar is foldable or adjustable relative to the post. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 551.4]](../ps.gif) 551.4 551.4 | Sectional: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 551.3. Devices in which the bar is made up of separate sections. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 551.5]](../ps.gif) 551.5 551.5 | Simultaneously movable: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 551.4. Devices in which the sections are constrained to move simultaneously. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 551.6]](../ps.gif) 551.6 551.6 | Continuous: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 551.3. Devices in which the bar is continuous from end to end. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 551.7]](../ps.gif) 551.7 551.7 | With handle latch: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 551.6. Devices in which the bar is locked in adjusted position
by means of a latch operable from hand grip of the bar.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 551.8]](../ps.gif) 551.8 551.8 | Attachments and accessories: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 551.1. Attachments and accessories specially designed for use with handle bars. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 551.9]](../ps.gif) 551.9 551.9 | Handholds and grips: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 551.1. Handholds and grips for handle bars.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 552]](../ps.gif) 552 552 | Hand wheels: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 543. Devices comprising hand operated control wheels, e.g., steering
wheels.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 553]](../ps.gif) 553 553 | Knob or dial: | ||||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 552. Devices comprising hand operated rounded or wheel-shaped
members adapted for attachment to a rotary shaft.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 554]](../ps.gif) 554 554 | Slidable: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 552. Hand wheels having connections with rotary shafts which permit the hand wheel to be slid to inoperative positions relative to the shafts when not is use. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 555]](../ps.gif) 555 555 | Pivoted: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 552. Hand wheels which are pivoted to a rotary shaft, the pivoted connection permitting movement of the hand wheel to an inoperative position by rotary motion about the pivotal axis. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 556]](../ps.gif) 556 556 | Releasable: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 555. Pivoted hand wheels with locking means for holding the hand
wheel in a predetermined position relative to its pivotal axis.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 557]](../ps.gif) 557 557 | Handles: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 552. Handles adapted to be grasped by the hand which are attached to a hand wheel to facilitate its operation. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 558]](../ps.gif) 558 558 | Rim grips and covers: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 552. Devices attached to the wheel rim to facilitate gripping
of the wheel.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 558.5]](../ps.gif) 558.5 558.5 | Caps and covers: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 543. Devices for covering or cushioning a hand engaging portion
of an existing handle.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 559]](../ps.gif) 559 559 | Rocker arms: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 469. Elements comprising crank arms fixedly attached to oscillatable
shafts.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 560]](../ps.gif) 560 560 | Pedals: | ||||||||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 469. Elements comprising foot engaging levers.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 561]](../ps.gif) 561 561 | Treadles: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 560. Levers designed to impart motion to a mechanism through
a connecting rod and crank.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 562]](../ps.gif) 562 562 | Extension: | ||||||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 560. Devices having means connected to or contacting the pedal
which constitutes an additional foot engaging portion.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 562.5]](../ps.gif) 562.5 562.5 | Offset: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 562. Devices wherein the additional foot engaging mechanism is
so mounted that its zone of operation is to one side of the zone
of operation of the pedal.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 563]](../ps.gif) 563 563 | Pads and covers: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 560. Devices comprising coverings for the foot engaging portions
of pedals.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 564]](../ps.gif) 564 564 | Foot rests: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 469. Elements located adjacent pedals to support a portion of
the foot during the pedal operation.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 565]](../ps.gif) 565 565 | Controller checks: | ||||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 469. Elements placed in the path of controllers to limit their
speed of operation to a predetermined maximum.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 566]](../ps.gif) 566 566 | Slot closers and lever guards: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 469. Elements which are (1) attached to levers to close slots
in which such levers move so as to prevent the passage of dust and
oil; (2) movable in front of operating members to prevent their
accidental operation.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 567]](../ps.gif) 567 567 | Cams: | ||
| This subclass is indented under the class definition. Elements comprising a rotatable, oscillatable, or reciprocable
machine element (usually a plate or a cylinder) having a surface
or a groove formed therein of predetermined contour which will impart
a prescribed motion of reciprocation or oscillation such as generally cannot
be obtained by gear wheels or link motion, to a follower slidably
contacting with such surface or groove.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 568]](../ps.gif) 568 568 | Adjustable: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 567. Devices comprising a cam or a part thereof adjustable longitudinally
or transversely of its axis of rotation.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 569]](../ps.gif) 569 569 | Follower: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 567. Devices comprising an element adapted to slidably contact with and to be moved by a cam. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 570.1]](../ps.gif) 570.1 570.1 | Eccentric: | ||
| Subject matter under subclass entitled ELEMENTS comprising
a mass having a center of gravity offset from geometrical center.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 570.2]](../ps.gif) 570.2 570.2 | Plural, movable relative to each other (including ball(s)): |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 570.1. Subject matter having at least two masses that can travel independently. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 570.21]](../ps.gif) 570.21 570.21 | Concentric: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 570.2. Subject matter wherein the plural movable eccentric masses are located one inside the other. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 570.3]](../ps.gif) 570.3 570.3 | Having anti-friction means, e.g., roller bearing, lubrication, etc.: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 570.1. Subject matter wherein the eccentric has structure to
facilitate the reduction of resistance generated by two moving parts.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 571.1]](../ps.gif) 571.1 571.1 | Adjustable: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 570.1. Subject matter wherein the eccentric has structure allowing the mass to change position relative to a fixed datum, e.g., a shaft, etc. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 571.11]](../ps.gif) 571.11 571.11 | Radially: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 571.1. Subject matter wherein the eccentric has structure allowing the mass to change position relative to a radius of a fixed datum, e.g., a shaft radius, etc. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 572.1]](../ps.gif) 572.1 572.1 | Power generating-type flywheel: | ||||||||||
Subject matter under subclass entitled ELEMENTS comprising
a mass used in a system to produce mechanical or electrical energy.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 572.11]](../ps.gif) 572.11 572.11 | Structural detail, e.g., material, configuration, superconductor, discs, laminated, etc.: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 572.1. Subject matter for a power generating flywheel subcombination highlighting a specific feature of the mass, such as chemical, electrical, or mechanical make-up, etc. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 572.12]](../ps.gif) 572.12 572.12 | Containing fiber or filament: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 572.11. Subject matter wherein the power generating flywheel specific feature is a thread-like or strand-like member. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 572.2]](../ps.gif) 572.2 572.2 | Flywheel, motion smoothing-type: | ||||||||||
Subject matter under subclass entitled ELEMENTS comprising
a mass used to modulate or control the inertia or momentum of a mechanical
system.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 572.21]](../ps.gif) 572.21 572.21 | Structural detail, e.g., fiber, held by magnet, etc.: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 572.2. Subject matter highlighting a specific feature of the mass, such as chemical, electrical, or mechanical make-up, etc. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 572.4]](../ps.gif) 572.4 572.4 | Balancing for drum, e.g., washing machine or arm-type structure, etc., e.g., centrifuge, etc.: |
| Subject matter under subclass entitled ELEMENTS comprising structure for maintaining the equilibrium of (a) a barrel-like structure rotatable about a single axis, used in a clothes cleaning system, or (b) a long, slender support rotatable at one end about a single axis, used in a spinning system to separate material. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 573.1]](../ps.gif) 573.1 573.1 | With fluid balancing means: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 572.2. Subject matter in which the flywheel has a liquid or gas to maintain equilibrium or stability. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 573.11]](../ps.gif) 573.11 573.11 | And pressure compensation: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 573.1. Subject matter in which the flywheel has fluid balancing including a device, e.g., a valve, etc., to regulate the force generated by the liquid or gas in the system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 573.12]](../ps.gif) 573.12 573.12 | And elastic device: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 573.1. Subject matter in which the flywheel has fluid balancing including a device, e.g. elastomeric blocks, etc., to absorb vibration. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 573.13]](../ps.gif) 573.13 573.13 | And bearings: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 573.1. Subject matter in which the flywheel has fluid balancing including an anti-friction device comprising spheres movable inside a track. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 574.1]](../ps.gif) 574.1 574.1 | With electrical or magnetic damping: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 572.2. Subject matter in which the flywheel utilizes the flow of electrons or the attractive-repulsive property of materials to suppress vibration. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 574.2]](../ps.gif) 574.2 574.2 | Damping using swinging masses, e.g., pendulum-type, etc.: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 572.2. Subject matter wherein vibration is suppressed by the flywheel utilizing an additional movable mass mounted on a support, in which the mass moves away from the support to a rotating member, e.g. shaft, connection, etc. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 574.3]](../ps.gif) 574.3 574.3 | Damping by increasing frictional force: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 572.2. Subject matter in which the flywheel utilizes resistance generated by two moving parts to suppress vibration. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 574.4]](../ps.gif) 574.4 574.4 | Damping by absorbing vibration force (via rubber, elastomeric material, etc.): |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 572.2. Subject matter in which the flywheel utilizes the property of some materials to suppress an asymmetric motion of the flywheel from a state of equilibrium. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 575]](../ps.gif) 575 575 | Pawls and ratchets: | ||||||||||||||||
| This subclass is indented under the class definition. Elements limited to the structural details of a pawl or
ratchet.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 576]](../ps.gif) 576 576 | Noiseless: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 575. Devices comprising pawls held out of engagement with the ratchet wheel during rotation of the latter in one direction and moved into engagement with said ratchet wheel on the reverse rotation of the latter. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 577]](../ps.gif) 577 577 | Pivoted pawls: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 575. Devices comprising pawls mounted for oscillation on a pivot. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 578]](../ps.gif) 578 578 | Sliding pawls: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 575. Devices comprising pawls mounted for sliding movement. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 579]](../ps.gif) 579 579 | Pitmans and connecting rods: | ||||||||||||
| This subclass is indented under the class definition. Elements comprising an intermediate connector having a bearing
at each end for transmitting motion by a push and pull movement.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 580]](../ps.gif) 580 580 | Radial: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 579. Devices comprising two or more connecting rods operatively
connected to the same crank pin.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 581]](../ps.gif) 581 581 | Yieldable: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 579. Devices comprising connecting rods having yieldable means embodied therein for allowing limited relative movement between the ends thereof. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 582]](../ps.gif) 582 582 | Longitudinal springs: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 581. Devices comprising yieldable means consisting of coil springs, the axes of which extend coincident with or parallel to the longitudinal axis of the connecting rod, giving only linear yieldability. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 583]](../ps.gif) 583 583 | Fluid cushion: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 581. Devices comprising yieldable means consisting of fluid means. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 584]](../ps.gif) 584 584 | Automatic release: | ||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 581. Devices wherein the yieldable means yields only after predetermined
pressure has been applied to ends of the link.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 585]](../ps.gif) 585 585 | Toggle link type: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 584. Devices wherein the yieldable means consists of a toggle
mechanism.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 586]](../ps.gif) 586 586 | Longitudinally adjustable: | ||||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 579. Devices comprising connecting rods having an adjusting means
embodied therein for regulating the length thereof.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 587]](../ps.gif) 587 587 | Hollow rod, lubricated: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 579. Devices comprising connecting rods having a hollow shank
or an oil conduit incorporated therewith, between the opposite bearing
ends, whereby lubricant can be supplied to said ends.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 588]](../ps.gif) 588 588 | Sheet metal type: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 579. Devices comprising connecting rods fabricated from sheet
metal.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 589]](../ps.gif) 589 589 | Counterbalanced: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 579. Devices comprising connecting rods having counterweights
directly attached thereto for balancing the same about a bearing
end.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 590]](../ps.gif) 590 590 | Weight type: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 589. Weight devices for assisting connecting rods to move a load connected thereto. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 591]](../ps.gif) 591 591 | Rotating: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 590. Weight devices attached to a rotating arm for assisting
the connecting rod to move a load connected thereto.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 592]](../ps.gif) 592 592 | Spring: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 589. Spring devices for assisting the connecting rod to move a load connected thereto. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 593]](../ps.gif) 593 593 | Section coupled: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 579. Devices in which the rod comprises a pair of sections, each section sliding on a portion of the other, and having a means thereon for coupling and uncoupling said sections whereby one section will move simultaneously with or relatively to the other for transmitting or interrupting the flow of power from one bearing end to the other. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 594]](../ps.gif) 594 594 | Bearings, adjustable: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 579. Devices comprising connecting rods having the end bearings thereof adjustable relative to the shank of the rod. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 594.1]](../ps.gif) 594.1 594.1 | Cranks and pedals: | ||||||||||||
This subclass is indented under the class definition. Elements comprising a unit consisting of an arm rotating
about an axis and a crank pin projecting transversely from said
arm for the attachment of a foot pedal, the first mentioned axis
and the axis of the pin being substantially parallel to each other.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 594.2]](../ps.gif) 594.2 594.2 | With attached gear: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 594.1. Units which have a gear attached thereto. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 594.3]](../ps.gif) 594.3 594.3 | Variable: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 594.1. Units having incorporated therewith a self-actuated means
for adjusting the axis of the pin relative to the axis of rotation
of the arm continuously throughout the complete revolution of the
arm.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 594.4]](../ps.gif) 594.4 594.4 | Pedals: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 594.1. Foot engaging units and their attachment to the crank arm.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 594.5]](../ps.gif) 594.5 594.5 | Counterbalanced: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 594.4. Pedals which have means to counterbalance them so that the foot engaging portion always remains up. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 594.6]](../ps.gif) 594.6 594.6 | With toe or shoe clips: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 594.4. Pedals having some means to hold the toe of a shoe on the pedal. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 594.7]](../ps.gif) 594.7 594.7 | Adjustable or folding: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 594.4. Pedals which are adjustable for various width shoes or are
adapted to be folded against the crank arm.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 595]](../ps.gif) 595 595 | Cranks and wrist pins: | ||||||||||
| This subclass is indented under the class definition. Elements comprising a unit consisting of an arm rotating
or oscillating about an axis and a crank pin projecting transversely
from said arm for the attachment of a connecting rod, the first
mentioned axis and the axis of the pin being substantially parallel
to each other.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 596]](../ps.gif) 596 596 | Multiple throw: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 595. Units integrally united, the axes of rotation of the arms of each unit being coaxial with each other. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 597]](../ps.gif) 597 597 | Sectional: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 596. Units made in sections and subsequently united by bolting, riveting, or welding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 598]](../ps.gif) 598 598 | Sectional: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 595. Units made in sections and subsequently united by bolting, riveting, or welding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 599]](../ps.gif) 599 599 | Yieldable: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 595. Units having a yieldable joint between the ends of the crank
arm whereby said ends are capable of angular movement relative to
each other.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 600]](../ps.gif) 600 600 | Adjustable: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 595. Units having incorporated therewith a means for adjusting
the axis of the pin relative to the axis of rotation of the arm
to adjust the throw of the crank.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 601]](../ps.gif) 601 601 | Automatically: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 600. Units having incorporated therewith means for automatically adjusting the axis of the pin relative to the axis of rotation of the arm according to the speed of rotation of said arm to automatically adjust the throw of the crank. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 602]](../ps.gif) 602 602 | Variable: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 595. Units having incorporated therewith a self-actuated means
for adjusting the axis of the pin relative to the axis of rotation
of the arm continuously throughout the complete revolution of the
arm.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 603]](../ps.gif) 603 603 | Counterbalanced: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 595. Units having means attached to the arm thereof for counter-acting
the centrifugal force exerted by the unit.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 604]](../ps.gif) 604 604 | Vibration dampers: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 603. Units having a device connected thereto for damping vibrations
created in/by the unit.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 605]](../ps.gif) 605 605 | Lubricated: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 595. Units having the arm and/or the pin thereof modified for lubricating the peripheral surfaces of the pin. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 606]](../ps.gif) 606 606 | Gear casings: | ||||||||||||||
This subclass is indented under the class definition. Elements for inclosing and supporting gearing in assembled
relationship.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 607]](../ps.gif) 607 607 | Axle and torque tubes: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 606. Housings for inclosing and holding automotive differential
gearing in assembled relationship.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 608]](../ps.gif) 608 608 | Guards: | ||||
This subclass is indented under the class definition. Housings for merely inclosing gearing for the express purpose
of preventing injury to/by said gearing.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 609]](../ps.gif) 609 609 | For rotary member: | ||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 608. Housings, the portion of the gearing inclosed is a wheel
member thereof.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 612]](../ps.gif) 612 612 | Guard mechanisms: | ||
| This subclass is indented under the class definition. Elements for preventing injury to an operator of a machine
during the operation thereof.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 613]](../ps.gif) 613 613 | Automatic: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 612. Mechanisms comprising guards actuated into protective position
by some part of the machines.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 614]](../ps.gif) 614 614 | Oscillating member actuator: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 613. Mechanisms wherein a part of the machine is an oscillating member. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 615]](../ps.gif) 615 615 | Reciprocating member actuator: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 613. Mechanisms wherein a part of the machine is a reciprocating member. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 616]](../ps.gif) 616 616 | Operator controlled: | ||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 612. Means actuated by the operator simultaneously with the starting
device of a machine for preventing injury to the operator of such
a machine during operating thereof.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 617]](../ps.gif) 617 617 | Set screw: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 612. Devices for shielding the heads of set screws against injury thereto and/or to persons. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 625]](../ps.gif) 625 625 | ALTERNATE MANUAL OR POWER OPERATORS: | ||||||||||||||
| This subclass is indented under the class definition. Devices having provision for operation of a single driven
device alternately by either manual or power means.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 640]](../ps.gif) 640 640 | GEARING: | ||||||||||||||||||||
This subclass is indented under the class definition. Mechanism comprising relatively rotatable bodies or combinations
of such bodies provided with teeth or interengaging elements, chains
and sprockets, belts, and pulleys or other means not otherwise classified,
whereby a rotatable body will impart to or receive motion or power
from some other member by rolling contact.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||||||||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 650]](../ps.gif) 650 650 | Nonplanetary gearing differential type (e.g., gearless differentials): | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 640. Gearing, not of the planetary type, wherein a differential
action is obtained through some mechanisms other than a planetary
gearing, such as e.g., overrunning clutches acting between a driving
member and a plurality of driven members, a fluid drive involving
plural power paths combined with other gearing, etc. Such structures
are commonly designated "gearless" differentials.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 655]](../ps.gif) 655 655 | Single gearing unit includes fluid drive: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 640. Gearing units wherein a fluid drive mechanism is included
as a part of the intermediate internal mechanism of a single gearing
unit.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 661]](../ps.gif) 661 661 | Plural prime movers selectively coupled to common output: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 640. Gearing in which means are provided to connect plural prime
motors either individually or unitarily to the same load.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 664]](../ps.gif) 664 664 | Plural power paths from prime mover: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 640. Gearing wherein a single prime mover drives plural power
paths, at least one path involving a gearing.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 665]](../ps.gif) 665 665 | Plural power paths to and/or from gearing: | ||||||||||||||||||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 640. Gearing in which a plurality of power paths constitute either
the input or the output of the gearing.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||||||||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 670]](../ps.gif) 670 670 | Alternate input connections single hand crank: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 665. Gearing in which a separable operating crank may be applied
at any one of a plurality of points to actuate the driven shaft
directly or through gearing.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 718]](../ps.gif) 718 718 | Fluid drive divides or combines alternate paths: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 665. Gearing wherein a fluid drive either divides or combines
alternate plural power paths to and/or from the gearing.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 720]](../ps.gif) 720 720 | One path includes fluid drive: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 665. Gearing wherein a fluid drive is included in one of the plural paths. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 721]](../ps.gif) 721 721 | Friction-type gearing: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 665. Gearing in which the gearing is of the friction type.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 724]](../ps.gif) 724 724 | Worm-type gearing: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 665. Gearing wherein the gearing unit is of worm gear type.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 730.1]](../ps.gif) 730.1 730.1 | With fluid drive: | ||||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 640. Subject matter wherein gearing is combined with a fluid
force torque transmitting device to form a drive train.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 731.1]](../ps.gif) 731.1 731.1 | Condition responsive control: | ||||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 730.1. Subject matter wherein means are provided to sense a condition
or change of condition in the drive train and in response to such
sensing effect a control function on the drive train.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 732.1]](../ps.gif) 732.1 732.1 | With one or more controllers for gearing, fluid drive, or clutch: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 730.1. Subject matter wherein means is provided to regulate the operation of the gearing or fluid drive; or to regulate the operation of a clutch. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 733.1]](../ps.gif) 733.1 733.1 | With interrelated controls: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 732.1. Subject matter wherein two of the regulating means are either
controlled by a single actuator or are otherwise related such that
the operation of one affects the operation of the other.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 745]](../ps.gif) 745 745 | In series plural interchangeably locked nonplanetary units: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 640. Gearing comprising a plurality of interchangeably locked
nonplanetary gearing units arranged in series.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 810.1]](../ps.gif) 810.1 810.1 | Reversal of direction of power flow changes power transmission to alternate path: | ||||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 640. Subject matter having two alternately usable parallel power
transmitting paths between a single input and a single output so
arranged that (1) the interchange of the input and output relationship
or (2) the change of direction of rotation of the input, changes
the path through which the power is transmitted.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 810.2]](../ps.gif) 810.2 810.2 | Input and output exchange functions: | ||||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 810.1. Subject matter wherein in response to the interchange of
roles between the transmission input member and the transmission
output member the path through which power is transmitted is changed.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 813]](../ps.gif) 813 813 | ROTARY MEMBER OR SHAFT INDEXING, E.G., TOOL OR WORK TURRET: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This subclass is indented under the class definition. Assemblies having (1) means for applying torque to a shaft
or other rotatably mounted device to turn the shaft or other device
about its axis to one or more selected loci, and (2) means to prevent
or hold against rotation in at least one direction at such loci.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 814]](../ps.gif) 814 814 | With safety device or drive disconnect: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 813. Devices including mechanism which prevents the assembly from improper functioning and/or responds to some imperfection, deficiency or fault in the functioning of the assembly to prevent further functioning. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 815]](../ps.gif) 815 815 | With locating point adjusting: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 813. Devices having one member on one part and another member on the other part which, by contact together, constitute a means for determining the angular position of the shaft, and in which at least one member is provided with means to change its position on the part and/or its point of contact with the other member. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 816]](../ps.gif) 816 816 | Preselected indexed position: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 813. Devices having means to interrupt and stop rotation of the
shaft at a physically predestined position.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 817]](../ps.gif) 817 817 | Sequential: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 816. Devices having a single initiator or source of power for rotating the shaft or load and having means to halt the shaft or load at each of a series of successive, predetermined positions. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 818]](../ps.gif) 818 818 | Skip position: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 817. Devices having means to cause the load or shaft to pass one or more preselected positions without stopping thereat. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 819]](../ps.gif) 819 819 | Held by torque: | ||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 817. Devices having means to generate a rotating force to provide
the angular repositioning of the shaft or load and using all or
part of that force to hold the body against a position stop.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 820]](../ps.gif) 820 820 | Geneva or multilated gear drive: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 817. Devices having either a mutilated or a Geneva type gearing
as defined in this class, subclasses 435 and 436, respectively.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 821]](../ps.gif) 821 821 | Velocity control: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 817. Devices having additional means to vary the speed of rotation
of the shaft or load as a predetermined position is approached.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 822]](../ps.gif) 822 822 | Interlocked rotator and brake: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 817. Devices wherein a common initiator or common source of power both turns the shaft or load and either permits rotation or prevents further rotation - the operation of turning is a condition precedent or subsequent to the operation of permitting or preventing rotation. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 823]](../ps.gif) 823 823 | Diverse-type brakes: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 822. Devices wherein the means permitting or preventing rotation comprises at least two distinct types of holding means, e.g., friction brake and positive brake. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 824]](../ps.gif) 824 824 | With axially acting friction brake: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 823. Devices wherein the operation of one of the holding means is effected by relative movement between radial face brake surfaces along the axis of the shaft or load. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 825]](../ps.gif) 825 825 | Plural operators or input drives: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 813. Devices having at least two means for applying torque to the shaft or rotatably mounted device. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 826]](../ps.gif) 826 826 | With means to axially shift shaft: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 813. Devices wherein the means to prevent or hold against shaft or load rotation includes a means to effect relative movement between radial surfaces along the axis of the shaft or load. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 827]](../ps.gif) 827 827 | Single revolution input effects desired fractional output: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 813. Devices wherein a rotary input, in multiples of 360° rotation, provides a turning of the shaft or rotatably mounted device, one increment of predestined angular rotation per multiple. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 828]](../ps.gif) 828 828 | ALTERNATING-MOTION DRIVEN DEVICE WITH MEANS DURING OPERATION TO ADJUST STROKE: | ||||||||
This subclass is indented under the class definition. Mechanism comprising a reciprocating or oscillating-motion
driven device provided with means to adjust the length and/or
position of the stroke of the driven device while the mechanism
continues in operation.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 829]](../ps.gif) 829 829 | Constant length stroke with means to displace end limits: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 828. Mechanisms wherein the driven device has a stroke of nonvariable length with means for changing the position of the stroke relative to a stationary part of the mechanism. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 830]](../ps.gif) 830 830 | Cyclical displacement responsive to the alternating-motion: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 829. Mechanisms wherein changing of the position of the stroke is caused mechanically by the alternating-motion imparted to the driven device. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 831]](../ps.gif) 831 831 | Stroke adjustable to zero and/or reversible in phasing: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 828. Mechanisms wherein the stroke can be diminished to the point of no motion and/or be caused to act in a direction cyclically opposite to that in which it has been operating. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 832]](../ps.gif) 832 832 | Plural driving means to jointly drive the driven device: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 831. Mechanisms having two or more driving motions for simultaneously
or commonly driving the alternating motion driven device.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 833]](../ps.gif) 833 833 | Device driven from selected points on oscillating link: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 831. Mechanisms having an oscillating link driving the alternating-motion driven device from chosen positions along the link. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 834]](../ps.gif) 834 834 | Driving lever with adjustable pivot point: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 831. Mechanisms wherein the means to diminish or reverse the stroke includes a lever having a driving input connection, a driven output connection, and a pivot connection for the lever which is adjustable along the lever to vary the movement arm thereof. | |
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 835]](../ps.gif) 835 835 | Eccentric and strap drive, shiftable eccentric: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 831. Mechanisms wherein the means to diminish or reverse the
stroke includes an eccentric and strap drive with the position of
the eccentric being adjustable relative to a stationary part of the
machine.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 836]](../ps.gif) 836 836 | Changing the extent of eccentricity: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 835. Mechanisms having means to vary the amount of eccentricity.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 837]](../ps.gif) 837 837 | Crank pin drive, shiftable pin: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 831. Mechanisms having an off-center pin drive with the position
of the pin being adjustable to diminish or reverse the stroke.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 838]](../ps.gif) 838 838 | Cam and follower drive: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 831. Mechanisms having a cam-driven follower causing movement
of the driven device.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 839]](../ps.gif) 839 839 | Axial-type cam (e.g., wabbler type): | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 838. Mechanisms having a rotating or oscillating cam which causes
movement of its follower substantially parallel to the cam axis.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 840]](../ps.gif) 840 840 | ROTARY DRIVEN DEVICE ADJUSTABLE DURING OPERATION RELATIVE TO ITS SUPPORTING STRUCTURE: | ||||
This subclass is indented under the class definition. Mechanisms comprising means to drive a load device in a
circular or orbital path about a fixed axis lying either within
or outside the confines of the device and having means operable
while the mechanism is in motion to change the location of the device
relative to supporting structure which does not partake of all motions of
the device.
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 841]](../ps.gif) 841 841 | Screw and nut adjusting means: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 840. Mechanisms wherein the location changing means include a
screw and nut mechanism.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 842]](../ps.gif) 842 842 | Rack and pinion adjusting means: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 840. Mechanisms wherein the location changing means includes
a rack and pinion mechanism.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS
![[List of Patents for class 74 subclass 900]](../ps.gif) 900 900 | PARTICULAR SHIFT PATTERN: |
| Collection of art disclosing a transmission control element or mechanism manipulated through a specific pattern or path. | |
The definitions for FOR 100-FOR 104 below correspond to the definitions of the abolished subclasses under Class 74 from which these collections were formed. See the Foreign Art Collections schedule for specific correspondences. [Note: The titles and definitions for indented art collections include all the details of the one (s) that are hierarchically superior. | |
| FOR 100 | TRANSMISSION CONTROL: |
| Foreign Art Collections for systems for manually controlling transmissions. | |
| FOR 101 | Foot operated: |
| Foreign Art Collections for systems for manually controlling transmissions in which the control member is foot operated. | |
| FOR 102 | With detent mechanism: |
| Foreign Art Collections for systems in which there are stop or checking devices used in conjunction with a member of the transmission control system to hold that member in a predetermined position until moved therefrom by an application of force transmitted to the member from the control system. | |
| FOR 103 | With reverse lockout: |
| Foreign Art Collections for systems in which there are stops which prevent accidental or unintentional shifting into reverse. | |
| FOR 104 | With interlocked elements: |
| Foreign Art Collections for systems in which there are devices which are operated by elements of the system for preventing simultaneous movement of the shift rods. | |