CPC Definition - Subclass B60K
This place covers:
Particular arrangements or mounting in vehicles of:
- Propulsion units or diverse prime movers (electrical, steam, internal-combustion, jet-propulsion, hybrid or other propulsion units),
- Transmissions.
- Diverse elements of propulsion units: cooling system, air intake or gas exhaust, fuel supply, element in connection with the power supply from force of nature (e.g. sun, wind),
- Auxiliary drives devices,
- Instrumentation or dashbord.
The following subject matters are not covered by this subclass:
- Subclass B60B and B60C embrace all vehicle wheels and tyres, except wheels for roller skates A63C 17/22, wheels for model railway vehicles A63H 19/22, and special adaptations of wheels or tyres for aircraft B64C 25/36.
- Subclass B60C embraces the connection of valves to inflatable elastic bodies in general, and in this respect it is not limited to vehicles.
- Subclass B60L embraces certain electric equipment of all electrically-propelled vehicles.
- Subclass B60M embraces certain power supply for, but external to, any kind of electrically-propelled vehicle
- Subclass B60R embraces safety belts or body harnesses used in all types of land vehicles
- Subclass B60S is a residual group for servicing, cleaning, repairing, supporting or lifting of vehicles.
- Subclass B60T includes brake control systems of general applicability, and in this respect it is not limited to vehicles. It also includes rail-vehicle power-brake systems and some features of rail-vehicle brake systems
Conjoint control of different drive units are not any more in this subclass; they are classified in subclass B60W.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wheel chairs | |
Suspension | |
Cooling, heating, venting devices especially for passenger, these groups comprise also the devices which are used for conjoint climatisation for the passenger space and for other devices (like a battery for example). | |
Seats in a vehicle | |
Power driven steering | |
Dynamo electric machines |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Automatic control | Using control systems for automatizing or assisting, to a full- or partial extent, tasks associated with driving of the vehicle, e.g. those normally carried out by the driver or those necessary to control the motion of the vehicle. |
Auxiliary equipment | A subsidiary or supplementary device of the propulsion, transmission or other units of the vehicle, e.g. a pump for supply of pressure for the control unit. |
Conjoint Control | A programmed or condition-responsive automatic controller on-board the vehicle, embodying control logic for plural vehicle sub-units and sends control signals to actuators of two or more vehicle sub-units, so that the sub-units act together to solve a particular problem or in response to a particular driving condition. |
Cruise control ACC | A system for automatically controlling vehicle speed, which may include additional functions e.g. control of distance between vehicles, so-called "Adaptive Cruise Control" (ACC). |
Drive control system | An electronic system in a road vehicle for automatically controlling the movement of that vehicle in order to take certain actions. |
Driving parameter | All input or output parameters of the road vehicle drive control systems, e.g. road specific parameters, driver or passenger related parameters, state variables of motion of the vehicle body or parameters related to the vehicle itself like load or weight of the vehicle |
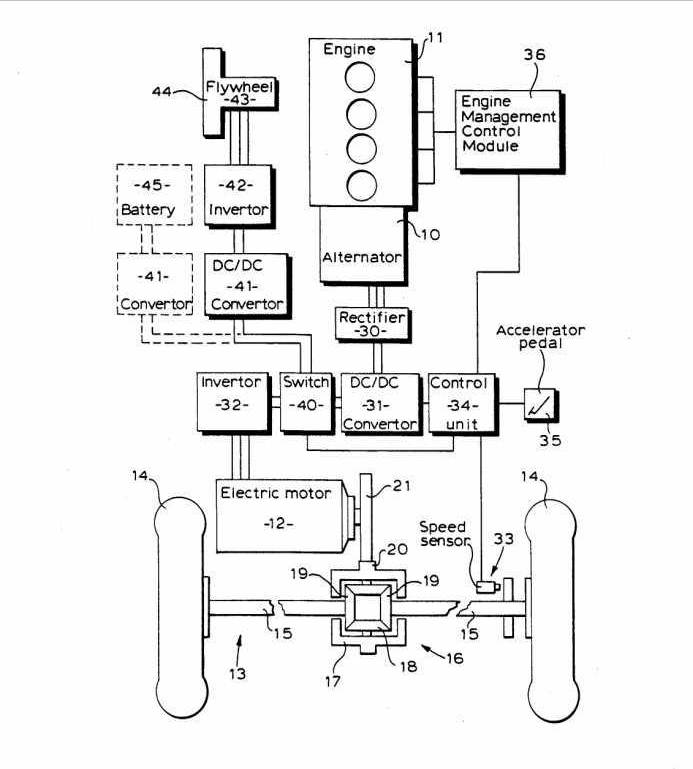
Hybrid vehicles HEV | Vehicles having two or more prime movers of more than one type for mutual or common propulsion, e.g. HEV: electrical and internal combustion motors, and that are either singularly or in combination used for propulsion of the vehicle. |
Road vehicle | A motorised passenger vehicle normally under the control of a human driver for transportation on roads, e.g. an automobile, truck or bus |
Drive-unit | Propulsion unit together with transmission, a "drive-unit" can additionally include the ultimate driven unit |
Sub-Unit | One of the following vehicle systems: propulsion systems; clutch system; change-speed gearing system; system for distributing drive torque between front and rear axles; axle differential system; brake system; steering system or suspension system; energy storage means; fuel cells or other auxiliary equipments |
Transmission | All propulsion parts linking propulsion units, e.g. engines, to ultimate propulsive elements, e.g. wheels |
Vehicle | All vehicles except those restricted to one of the following types of vehicles: rail vehicles, waterborne vessels, aircraft, space vehicles, hand carts, cycles, animal-drawn vehicles, and sledges, which are covered by the relevant subclasses of B61 - B64. Thus, the term "vehicle" includes:- vehicular characteristics which are common to more than one of the above listed types;- certain characteristics restricted to automobiles, road or cross-country trailers |
This place does not cover:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electric transmission arrangements | |
Four-wheel drive vehicles having fluid or electric motor for driving one or more wheels | |
Arrangement or mounting of propulsion-unit control devices in vehicles | |
Motor driven wheelchairs | |
Electric equipment or propulsion of electrically-propelled vehicles per se | |
Current-collectors for power supply lines of electrically-propelled vehicles | |
Methods, circuits or devices for controlling the traction-motor speed of electrically-propelled vehicles | |
Conjoint control of vehicle sub-units including control of electric propulsion units | |
Conjoint control system specially adapted for hybrid vehicles | |
Steering non-deflectable wheels by differentially driving ground-engaging elements on opposite vehicle sides | |
Superstructures for passenger vehicles | |
Dynamo-electric machines | |
Arrangements for handling mechanical energy structurally associated with dynamo-electric machines | |
Dynamo-electric machines with counter rotating rotors | |
Control of electric motors |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Cooling of the batteries using HVAC of the vehicle | |
Safety devices for electric storage systems in electric vehicles | |
Constructional details of batteries specially adapted for electric vehicles | |
Connecting elements for charging the batteries | |
Exchanging batteries for electrically-propelled vehicles | |
Arrangement of batteries specially adapted for vehicles and not otherwise provided for | |
Supplying batteries to, or removing batteries from, vehicles | |
Braking elements using wheel movement for accumulating energy, e.g. by driving air compressors | |
Floors or bottom sub-units | |
Electrochemical generators per se | |
Fuel cells | |
Heating of fuel cell | |
Heating and cooling of batteries in general | |
Heating and cooling of batteries specially adapted for applications in vehicles | |
Housings or holders for batteries | |
Fixing of the housing of the batteries to the vehicle if the invention is on the housing of the batteries |
If there exists a second prime mover, e.g. an internal combustion engine [ICE] or hydraulic accumulator, classification is additionally made in B60K 6/00.
This place covers:
This place does not cover:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangement or mounting of fluid gearing in vehicles | |
Arrangement or mounting of propulsion-unit control devices in vehicles | |
Engines using uniflow principle | |
Steam engines | |
Steam engine plants | |
Steam engine plants for driving vehicles | |
Gas turbine plants |
This place covers:
This group comprises documents concerning the arrangement of an internal combustion motor in the vehicle. A damping means, rubber or the control of a damping means per se are classified in F16F.
This place does not cover:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangement or mounting of propulsion-unit control devices in vehicles | |
Understructures of vehicles with resilient means for suspension | |
Understructures with impact absorbing front or rear frames | |
Internal-combustion piston engines; Combustion engines in general | |
Combinations of combustion engines with mechanical gearing | |
Springs; Shock absorbers; Means for damping vibration |
This group is given only if the fact that the crankshaft axis is parallel to the longitudinal centre line of the vehicle is important for the invention.
This group is given only if the fact that the crankshaft axis is transversal to the longitudinal centre line of the vehicle is important for the invention.
This group is given only if the fact that the crankshaft axis is vertical is important for the invention.
This place covers:
The arrangement and mounting of different prime-movers for common propulsion of a vehicle.
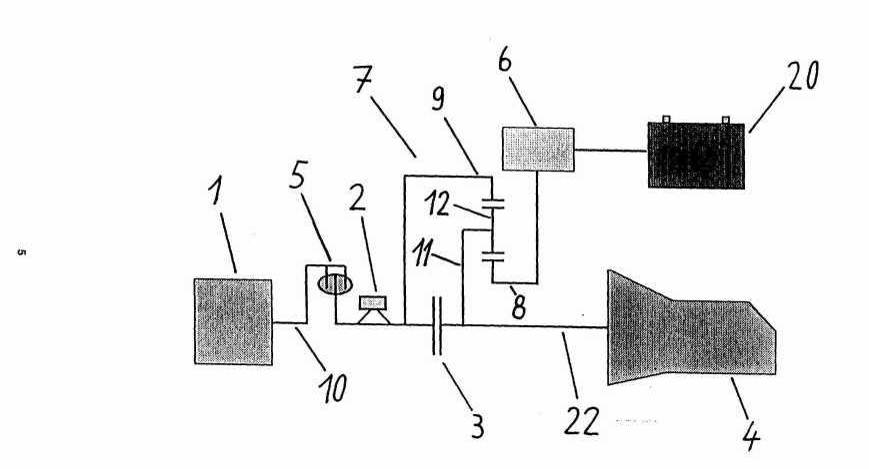
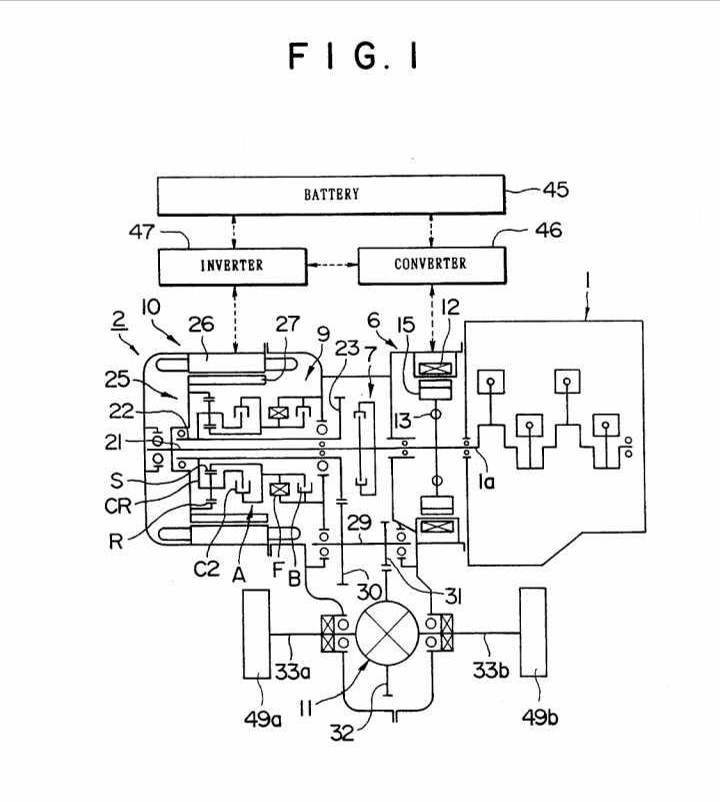
Hybrid propulsion systems comprising electrical and combustion engines.
Prime-movers comprising internal combustion motor and energy storing means.
B60K 6/00 is the place where the layout and arrangement of hybrid propulsion systems is classified. The control of these systems is classified in groups B60W 20/00 and B60W 10/00 for the type of the controlled unit with additional classification symbol in this group when the type of hybrid propulsion system is of interest. Combustion engine features are classified per se in the relevant subclasses F02B, F02D, F02N. Transmission or clutch features per se are classified in the relevant subclasses F16H or F16D.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Disposition of motor in, or adjacent to, traction wheel | |
Arrangement of fluid gearing in vehicles | |
Arrangement of electric gearing in vehicles | |
Transmission arrangements for driving front and rear wheels,having fluid or electric motor, for driving one or more wheels | |
Arrangement or mounting of propulsion-unit control devices in vehicles | |
Electric propulsion with power supplied within the vehicle | |
Electric propulsion with power supplied within the vehicle using propulsion power supplied by engine-driven generators | |
Control systems specially adapted for hybrid vehicles | |
Vehicle propulsion control with common controlling member for different functions | |
Prime movers comprising electric motors and ICE in a common engine block or housing | |
Electric motors or motor-generators used for starting the combustion engine | |
Electric motors for synchronising gearing | |
Mechanical gearings having orbital motion with secondary drive in order to vary speed continuously | |
Control of gear shifting per se | |
Control of hydrostatic gearing | |
Arrangements for handling mechanical energy structurally associated with the dynamo-electric machine | |
Dynamo-electric gears, i.e. dynamo-electric means for transmitting mechanical power from a driving shaft to a driven shaft and comprising structurally interrelated motor and generator parts |
Whenever one or more specific aspects of subunits are concerned, classification should be given for each of the different subunit in B60K 6/22 and a classification symbol should be added in the relevant place for the architecture B60K 6/42 and also for the driveline architecture B60K 6/50.
When classifying in one of groups B60K 6/22, B60K 6/42 or B60K 6/50, further technical classification, which is considered to represent information of interest for search should be classified in the other subgroups of B60K 6/00 to enable searching using combination of classification symbols. Where appropriate, classification symbols should be given for the architecture of the hybrid propulsion system in groups B60K 6/42 - B60K 6/485 and for the arrangement or kind of transmission units in groups B60K 6/50 - B60K 6/547.
The flywheel storing means are classified in B60K 6/105 if the power transmission is mechanical and in B60K 6/30 if the power transmission is purely electrical.
The power split transmission architecture B60K 6/445 is to be classified also in F16H 2037/0866 for distributing type, in F16H 2037/088 for summing type and F16H 2037/101 for parallel type, F16H 2037/102 or F16H 2037/104 for crossed connections of several planetary sets, F16H 2037/103 for Ravigneaux type.
Use of the Indexing Code scheme is mandatory. When classifying in group B60K 6/00 classification must also be made in groups B60K 6/00 – B60K 6/54 for additional features, in B60Y 2200/00 for vehicle type, in B60Y 2400/00 for special features in general, in B60Y 2300/00 in order to identify the purpose and in B60W 10/00 for multiple controlled sub-units and in B60W 2510/00 - B60W 2530/213 for controller input parameters and in B60W 2710/00 - B60W 2720/406 for the output target values.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
energy storing means | apparatus for storing propulsive energy and providing stored energy to drive the prime-mover or the ultimate propulsive elements, e.g. wheels |
hybrid electric vehicle | vehicles having an electric prime-mover and a combustion engine, in which the electric prime-mover and the combustion engine either singly or in combination, drive the ultimate propulsive elements, e.g. wheels |
motor-generator | an electric machine, such as a motor or a generator or a mechanical combination thereof, which can provide positive mechanical output force or torque and which can function at other times as an electric generator |
prime-mover | a propulsion unit or source of motive power providing a mechanical output, e.g. via a rotating shaft |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
HEV | Hybrid electric vehicle |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electric propulsion of vehicles with power supplied by engine-driven generators within the vehicle |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Transmission of prime-movers for changing ratio |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Series type or Range extender | HEVs having at least two motor-generators in which the first motor-generator is mechanically connected for driving or braking the wheels supplied by a battery which power is mostly generated by the second motor-generator mechanically connected to the combustion engine. Example: The combustion engine is mechanically connected to a motor-generator. The combustion engine is not mechanically connected to the wheels. All the output energy of the combustion engine is converted to electrical energy. The energy is used to drive a second electric machine connected to the wheels and/or to charge the energy storing means. The second electric machine will be used as generator during braking. (US5214358, example also classified in B60K 6/30 for mechanical accumulators ) |
Parallel type | HEVs having a single motor-generator in which both the combustion engine and the motor-generator can directly drive the wheels. Parallel type HEVs in which the motor-generator only assist the combustion engine and cannot drive the wheels alone are specially defined as 'motor assist type'. Therefore 'parallel type' is assigned to HEVs in which the motor generator can drive the wheels alone without the engine being connected to the wheels. Example: There is a single motor-generator and the combustion engine is mechanically connected to the motor-generator, via a clutch or via differential gearing. The motor-generator is also mechanically connected to the wheels. The vehicle is driven electrically by the motor-generator or mechanically by the engine or by both in combination. (EP941883) |
Motor-assist type | Parallel type HEV in which the motor-generator only assist the combustion engine and cannot drive the wheels alone. Example: The motor-generator is mechanically connected to the engine. There is no clutch or differential gearing between motor-generator and engine. The combustion engine is mechanically connected to the wheels. (FR2480042) |
Series-parallel type | HEV having at least two motor-generators, which include the functions of both the series type and the parallel type. |
Series-parallel switching type | Series-parallel type HEV in which the mode can be switched between series mode and parallel mode. Example: The combustion engine is directly connected to a first motor-generator. There is a second motor-generator mechanically connected to the wheels and a clutch between the two motor-generators. In the series mode the clutch will be disengaged and the second motor generator will drive the wheels by using the electric power generated by the first motor generator. In the parallel mode the clutch will be engaged and the engine directly drives the wheels with or without assistance by the motor generators. (US5513719) |
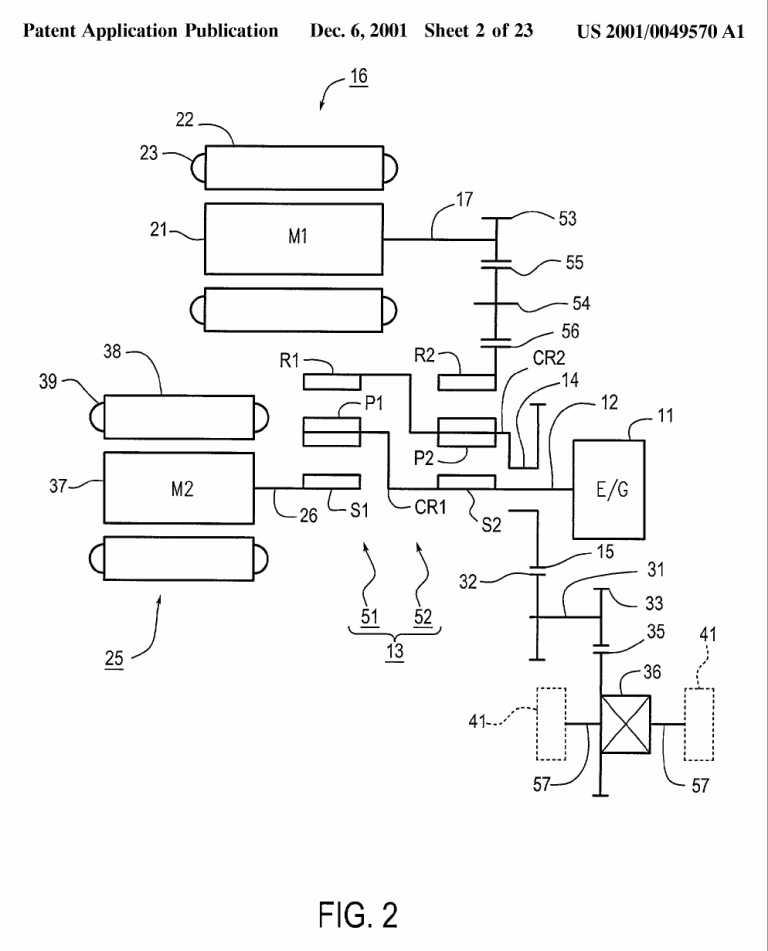
Differential gearing distribution type | Series-parallel type HEVs in which the combustion engine power is distributed or summed by a differential, e.g. a planetary gearing, to the first motor-generator and the wheels, and the electric power generated by the first motor-generator is used to drive the second motor-generator mechanically connected to either the wheels or the combustion engine. The series-mode energy flow path is established when the second motor-generator is driven by the electric power generated by the first motor-generator, while the parallel-mode energy flow path is established when the wheels are driven by both the combustion engine and the second motor-generator. Motor-generator currents are controlled to determine the energy flow path through the drive units.Example: The combustion engine is mechanically connected to a motor-generator via a first element of a differential gearing. A second motor-generator is connected to a second element of the differential gearing. The differential gearing also connects one or both of the motor-generators to the wheels. (US20010049570, example also classified in F16H 2037/102 ) |
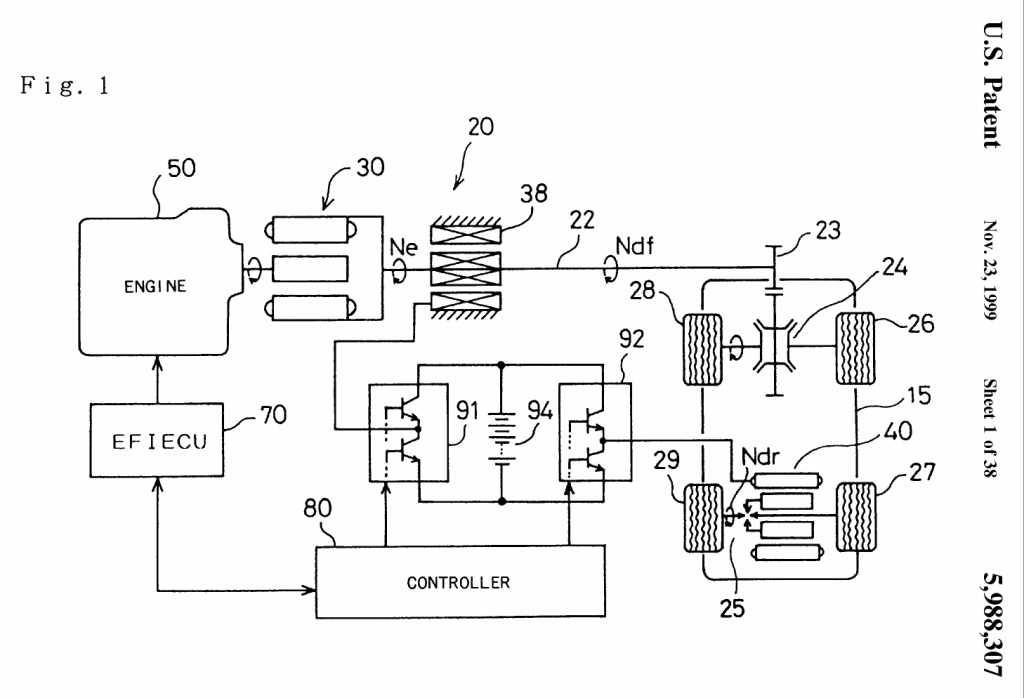
Electrical distribution type | Series-parallel type HEVs in which the engine power is distributed, using a first motor-generator which is specific as a double rotor-type motor-generator, into mechanical power for driving the wheels and electric power for driving a second motor-generator connected to either the wheels or the combustion engine. The series-mode energy flow path is established when the second motor-generator is driven by the electric power generated by the first motor-generator, while the parallel-mode energy flow path is established when the wheels are driven by both the combustion engine and the second motor-generator. Motor-generator currents are controlled to determine the energy flow path through the drive units. Example: The combustion engine shaft is mechanically connected to the inner rotor of a double-rotor type motor-generator. The outer rotor of the double-rotor type is connected to the second motor generator which is connected to the shaft driving the wheels. (US5988307) |
This place covers:
Particular arrangements of transmission units.
Kind or type of transmission units, e.g. CVT.
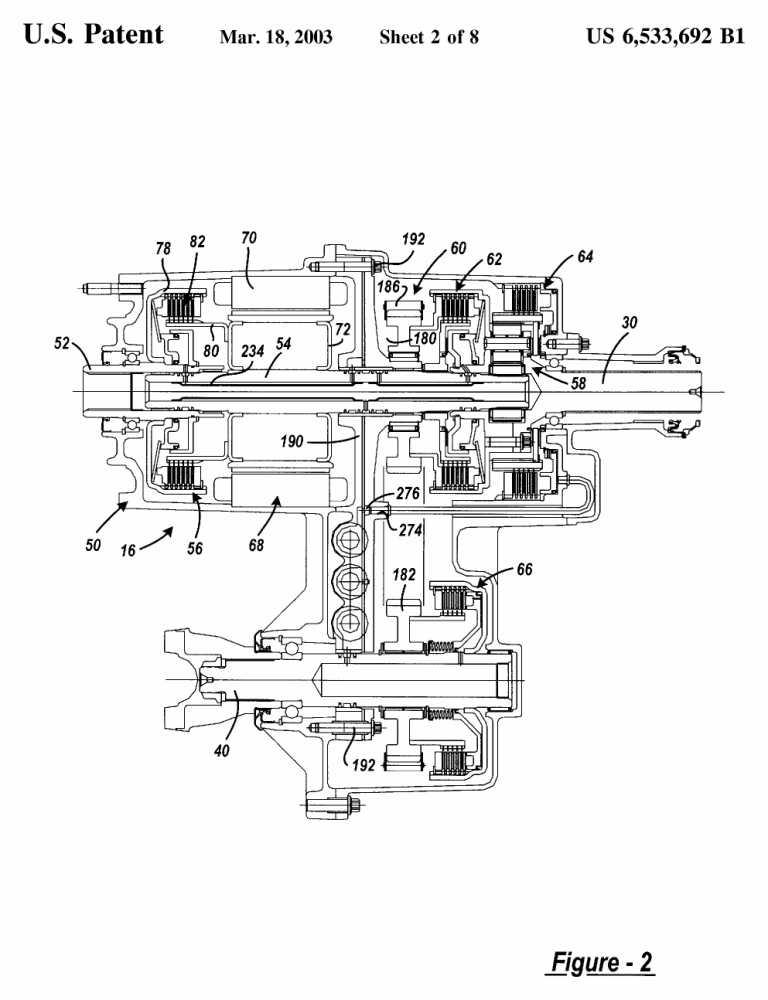
If the invention information is related to the transfer gearing independent of the hybrid layout it will be also classified in B60K 17/34. Example: US6533692
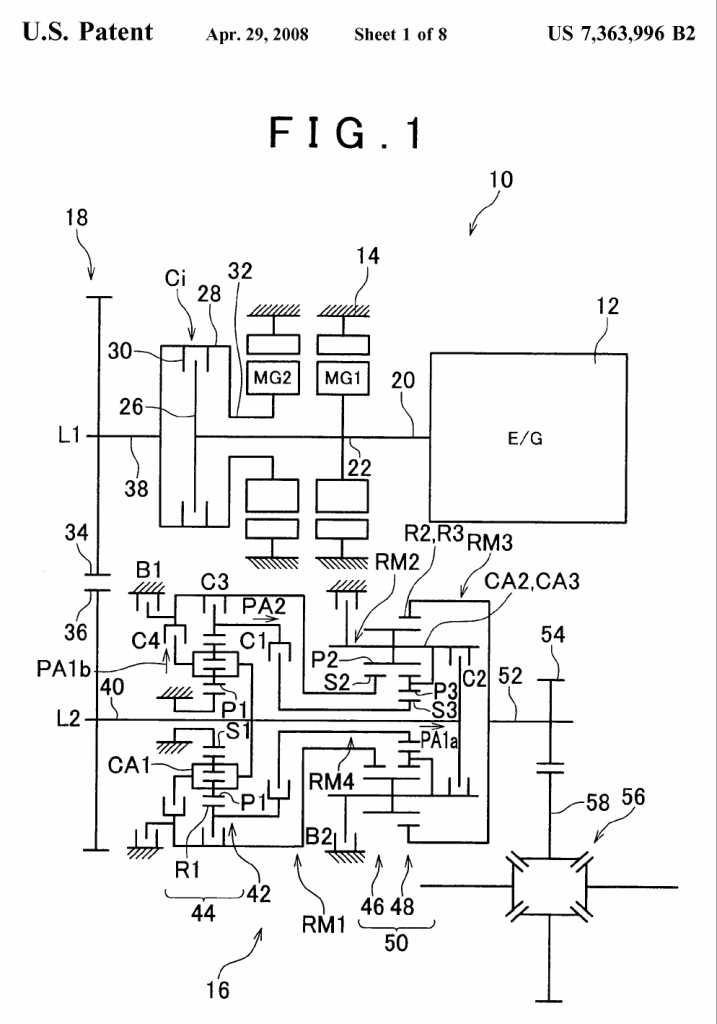
The aspect of the transmission unit per se are to be classified in the relevant groups of subclass F16H, for example if the invention is related to the Ravigneaux planetary set placed downstream of a power split electric transmission, the classification F16H 3/666 is also given. Example: US7363996
This place covers:
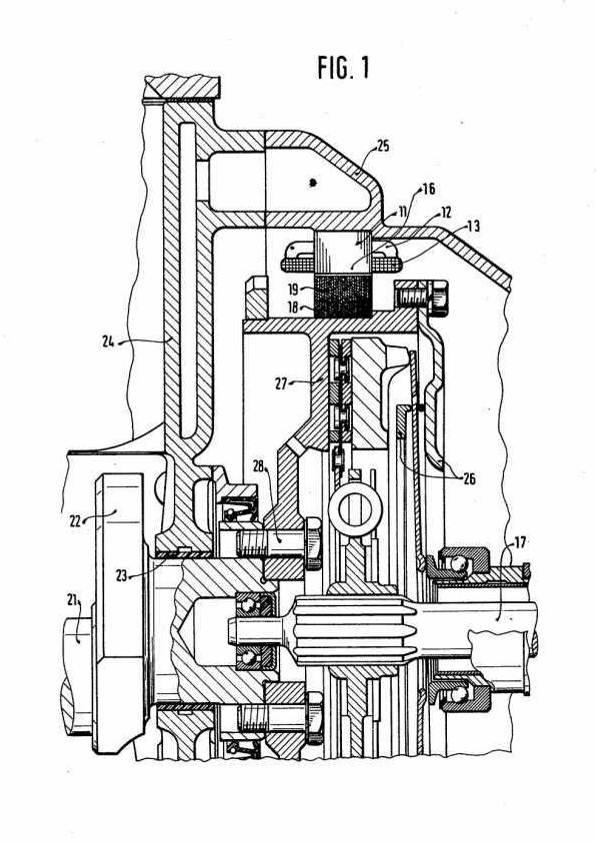
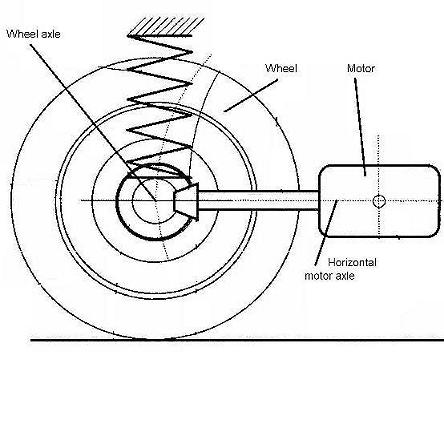
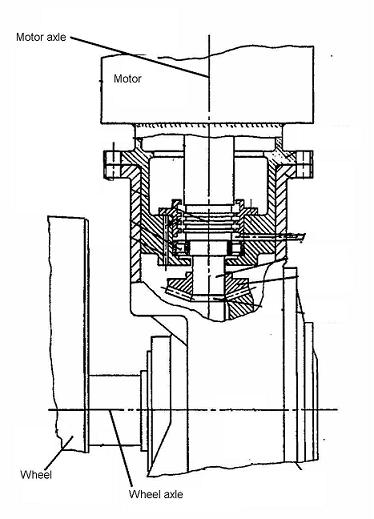
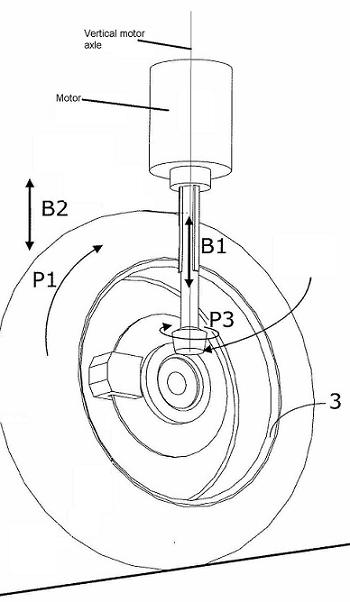
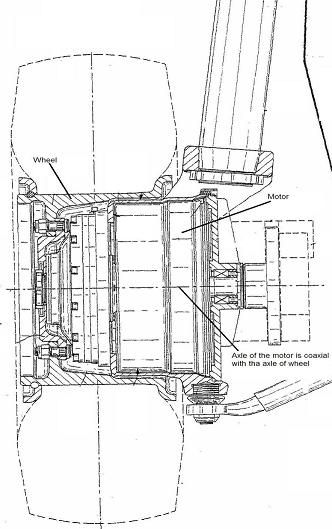
Inventions related to a particular disposition of the motor regarding the wheel. The term "in, or adjacent to" means there is one motor driving one wheel (or dual wheels forming a unit) without a differential in between.
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Arrangement or mounting of fluid or electric gearing in vehicles characterised by the motor of the fluid or electric gearing being disposed in, or adjacent to, traction wheel |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangement or mounting of electrical propulsion units in vehicles | |
One electric motor mounted directly on a propulsion axle for rotating right and left wheels of this axle, e.g. using a differential between the motors and the driven wheels | |
Hybrid propulsion systems for vehicles | |
Arrangement in connection with cooling of propulsion units | |
Arrangement of transmission units disposed in or near the vehicle wheel | |
Arrangement or mounting of propulsion-unit control devices in vehicles | |
Wheelchairs | |
Roller-skates or skateboards with driving mechanisms | |
Resilient suspension | |
Electric equipment or propulsion of electrically propelled vehicles | |
Arrangements of braking elements | |
Steering linkages | |
Dynamo-electric machines (electric motors) |
All documents showing in a schematic way a hybrid or electric vehicle having hub motors in the wheels should not be classified in this group. However, a code for additional information could be given.
Use of the Indexing Code scheme is mandatory for this main group. Additional information should be given in B60K 17/043 if a transmission is used.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Structural association of electro motor with clutches, brakes, gears, pulleys etc. |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group.
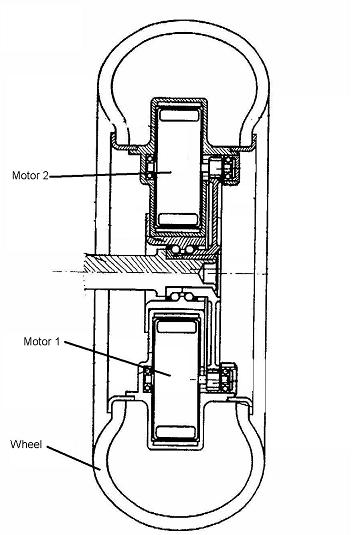
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group.
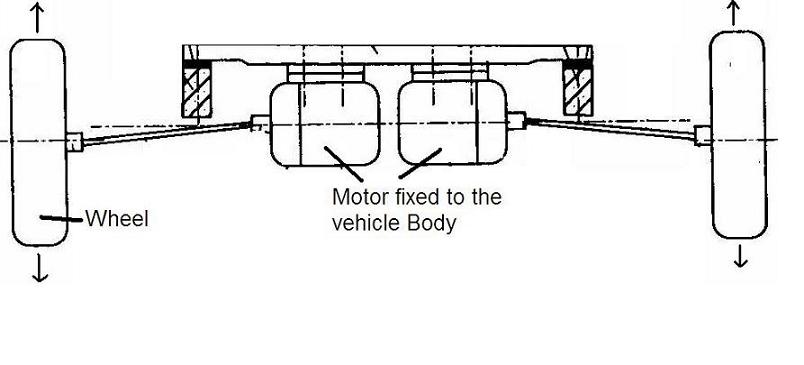
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group.
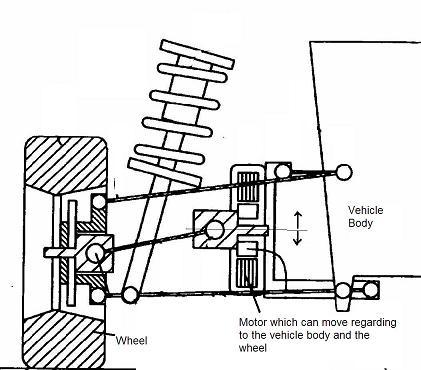
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group.
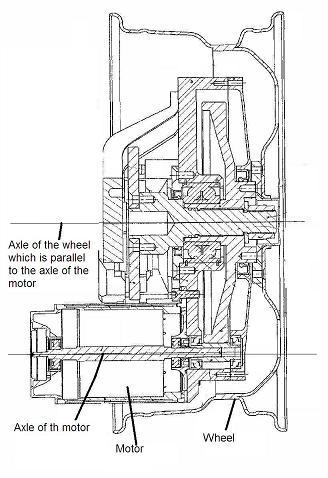
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group.
This place covers:
Illustrative examples of subject matter classified in this group.
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangement or mounting of electrical propulsion units | |
One motor mounted directly on a propulsion axle for rotating right and left wheels of this axle (for example using a differential between the motors and the driven wheels). | |
Hybrid vehicles | |
Arrangement in connection of cooling a propulsion unit | |
Transmission disposed in or adjacent the vehicle wheel | |
Wheelchairs | |
Resilient suspensions | |
Electric equipment or propulsion of electrically propelled vehicles | |
Arrangements of braking elements | |
Steering linkages | |
Dynamo electric machines (electric motors) |
Use of the Indexing Code scheme is mandatory for this main group. Addition information should be given in B60K 17/043 if a transmission is used.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
In, or adjacent to | there is one motor to drive one wheel (or one dual wheels). No differential therebetween. |
This place covers:
These groups comprise documents concerning the arrangement of a motor in a vehicle. The drive motor per se should be classified elsewhere.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangement or mounting of propulsion-unit control devices in vehicles | |
Hot gas displacement engines, use of waste heat of combustion engines | |
Spring, weight inertia or like motors |
This place covers:
Documents concerning the arrangement in connection with cooling of the propulsion units in the vehicle.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangement in connection with combustion air intake or exhaust of propulsion units in vehicles | |
Arrangement of heating devices for passenger or goods spaces of vehicles | |
Cooling devices for passenger or goods spaces of vehicles characterised by the arrangement or the type of heat exchanger, e.g. condenser or evaporator | |
Methods or circuit arrangements for cooling batteries, specially adapted for electric vehicles | |
Methods or circuit arrangements for cooling fuel cells, specially adapted for electric vehicles | |
Insulating elements for vehicles, e.g. for sound insulation | |
Cooling of internal combustion engines | |
Arrangements or mounting of liquid-to-air heat-exchangers for cooling of machines or engines other than in vehicles | |
Guiding or ducting cooling air to, or from, ducted fans | |
Guiding or ducting cooling air to, or from, liquid-to-air heat exchangers | |
Filtering, cooling or silencing cooling air | |
Non-positive-displacement pumps, e.g. ventilators or fans | |
Details of radiators | |
Arrangements for cooling or ventilating dynamoelectric machines |
This place covers:
These groups comprise an arrangement whereby the element to be cooled (for example the motor) is cooled by liquid.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Air inlets for cooling of propulsion units; Shutters or blinds therefor |
This place covers:
- Mounting or arrangement of radiators;
- Radiator shutters or blinds mounted directly on the radiator.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Air inlets for cooling of propulsion units in vehicles; Shutters or blinds therefor | |
Adjustable shutters or blinds for air inlets for cooling of propulsion units in vehicles | |
Arrangement in connection with combustion air intake or gas exhaust of propulsion units in vehicles | |
Arrangements or mounting of liquid-to-air heat-exchangers | |
Details of heat-exchange and heat-transfer apparatus, of general application |
This place covers:
These groups comprise an arrangement whereby the element to be cooled (for example the motor) is cooled by air. The way the air is ducted to a radiator (air to liquid heat exchanger) is therefore classified in groups B60K 11/02 or B60K 11/08.
This place covers:
Also air guiding walls in the air inlet passage.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangement or mounting of radiator shutters or radiator blinds, e.g. mounted directly on the radiator | |
Guiding or ducting cooling air to, or from, liquid to air heat exchangers |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
air inlet | space between the car body opening to the radiator |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Controlling of coolant flow for engines by throttling amount of air flowing to heat exchanger | |
Air flow control member (e.g. louvres, grilles or flaps) in air conditioning apparatus | |
Using more than one tilting member | |
With parallel lamellae |
This place covers:
Arrangement in the vehicle of combustion air intake or gas exhaust of propulsion unit.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Removing snow or ice from roads or like surfaces by application of heat | |
Exhaust silencers or exhaust apparatus for internal-combustion engines | |
Adding substances to exhaust gas | |
Supplying combustion engines with combustible mixtures or constituents thereof | |
Combustion-air cleaners, air intakes, intake silencers, or induction systems specially adapted for, or arranged on, internal-combustion engines | |
Pipes in general | |
Noise absorbing hangers or supports for pipes or pipe systems |
This place covers:
This group comprises for example arrangement of air intake in the car body and the arrangements made in the vehicle between the air intake to the air cleaner.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Bumpers | |
Intercoolers | |
Combustion-air cleaners, air intakes, intake silencers or induction systems for internal-combustion engines | |
Combustion-air filters for internal-combustion engines | |
Arrangement of the air intake system in the engine compartment |
This place covers:
Specific arrangement in the vehicle of exhaust element or structure used to fasten exhaust element to a vehicle if the invention is on the vehicle side (special adaptation of the vehicle structure) and not on the exhaust side.
Fixing element of the exhaust mounted on the vehicle frame and not on the exhaust apparatus, e.g. fixing bracket adapted to vehicle frame.
Arrangement of urea tanks in vehicles.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Exhaust silencers or exhaust apparatus for internal-combustion engines | |
Exhaust or silencing apparatus characterised by having thermal insulation | |
Exhaust or silencing apparatus characterised by means for fixing exhaust pipes or devices to vehicle bodies |
"Fixing means for the exhaust manifold or exhaust pipes to the vehicle body" are not classified in B60K 13/04 but in F01N 13/1805. These groups only comprise arrangement of the vehicle frame for mounting the exhaust, like for example, a specific fixing bracket on the vehicle frame. Further examples of documents classified in B60K 13/04 could be a pipe or a urea tank extending through a specific area in the vehicle.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
A specific form of the carroserie to duct the air in an air intake | |
Understructure forming fluid or electrical conduit means | |
Superstructure | |
Floor or bottom sub- units |
This place covers:
Arrangement of tanks in connection with fuel supply of combustion engines, as well as the arrangement of gas tanks in vehicles.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangement in connection with exhaust of propulsion units in vehicles, e.g. of urea tanks | |
Tank vehicles | |
Fuel tanks specially adapted for motorcycles | |
Tanks for aircraft | |
Tanks for storage or transport | |
Apparatus or devices for transferring liquids from bulk storage containers or reservoirs into vehicles | |
Tanks for the supply of substances, e.g. urea, to exhaust gases | |
Controlling the feeding of liquid fuel from storage containers to carburettors or fuel-injection apparatus | |
Supplying combustion engine with combustible mixtures or constituent thereof | |
Apparatus or systems for feeding liquid fuel from storage containers to carburettors or fuel-injection apparatus | |
Valves in general | |
Vessels for containing or storing compressed, liquefied or solidified gases | |
Indicating or measuring liquid level | |
Fuel cells | |
Reactant storage and supply for fuel cells |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Injection moulding | |
Chassis forming fluid conduit means | |
Pipes in general and connection thereof |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangement in connection with exhaust of propulsion units in vehicles, e.g. of urea tanks | |
Chassis comprising fluid storage compartment | |
Selective catalytic reduction [SCR] | |
Tanks for the supply of substances, e.g. urea, to exhaust gases | |
Constructional details; Manufacturing or assembly of elements of fuel system; Materials therefor | |
Details of the fuel feeding system related to multiple separate fuel tanks | |
Details of the fuel feeding system related to saddle tanks | |
Armoured vehicle |
This place does not cover:
Of gas tanks |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Engines characterised by operating on gaseous fuels; Plants including such engines | |
Controlling engines characterised by their use of non-liquid fuels, pluralities of fuels, or non-fuel substances added to the combustible mixtures | |
Apparatus for supplying engines with non-liquid fuels, e.g. gaseous fuels stored in liquid form | |
Vessels for containing or storing compressed, liquefied or solidified gases; fixed capacity gas holders | |
Pressure vessels, gas tank | |
Pipe-line systems for liquid gas |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Supplementary interior tanks inside the fuel tank |
This place does not cover:
Gas tanks |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Blow moulding | |
Blow moulding with insert | |
For specific joining process | |
Welding | |
Riveting | |
Joining elements to hollow article | |
Shaping techniques and joining techniques together | |
For layered tanks |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Control systems for LPG tanks |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Filter caps for fuel tanks provided with a lock | |
Locking means for the inlet cover of fuel tank |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Engine-pertinent apparatus for adding fuel vapours drawn from engine fuel reservoir to combustion air or fuel-air mixture | |
Valves | |
Arrangements for preventing explosion of gas bottles |
This place does not cover:
Adding fuel vapours drawn from engine fuel reservoir | |
Judging failure of purge control system | |
Arrangement of valves controlling the admission of fuel vapour to an engine, e.g. valve being disposed between fuel tank or absorption canister and intake manifold | |
Details of the absorption canister | |
Details of the fuel vapour pipes or conduits | |
Layout of the fuel vapour installation |
This place does not cover:
Arrangement of valves controlling the admission of fuel vapour to an engine, e.g. valve being disposed between fuel tank or absorption canister and intake manifold | |
Details of the fuel vapour pipes or conduits | |
Layout of the fuel vapour installation |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Mounting of venting tubes |
This place does not cover:
With means modifying or controlling distribution or motion of fuel | |
Inlet and filling arrangements for urea tanks |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Filters rigidly mounted on reservoirs or tanks | |
Manufacturing process | |
Supplying fuel to vehicle | |
Arrangements for controlling, indicating registering quantity or price of liquid transferred |
This place covers:
Filler caps is the detachable/movable cap at the end of the inlet pipe.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Closure caps for liquid coolant | |
Sealing in general |
A flap/baffle/trap door inside of the pipe is not considered as been a filler cap and should be classified in B60K 15/04
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Lock in general | |
Electrically actuated locks | |
For fuel inlet covers of vehicle |
This place covers:
Details of the inlet covers and inlet box
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Superstructure sub-units with access opening having movable or removable closures | |
Superstructure sub-units with access or drainage openings having movable or removable closures | |
Lock in general | |
Electrically actuated locks | |
For fuel inlet covers of vehicle | |
(for fuel inlet covers) | |
Hinges or pivots for doors in general |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Locking means for the inlet cover |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Filtering elements in the tanks | |
Fuel tanks specially adapted for motor cycles | |
Feeding apparatus for carburettors with multiple separate fuel tanks | |
Mounting of pumps on fuel tank | |
The pump being installed in a sub tank | |
Apparatus for feeding liquid fuel to the carburettors with a main and auxiliary pump |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Controlling the feeding of liquid fuel from the tank to the carburettors | |
Devices of the fuel feeding system inside the tank other than pumps or filter | |
Measuring liquid level |
This place covers:
In particular tanks having a specific position in the vehicle
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangement of the urea tank in the vehicle | |
Understructure having a fluid storage compartment | |
Floor and bottom sub units of the superstructure of the vehicle | |
Urea Tank | |
Engine working with a plurality of fuel |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Mounting arrangements for vessels |
This place covers:
Fuel container shape designed to fit framework
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Tanks specially adapted for motor cycles | |
Saddle tanks in feeding apparatus for the carburettors |
This place covers:
Container including devices to influence the motion or distribution of the fuel, e.g. swirl pots or fuel level control between dual tanks.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Anti-slosh devices in large containers | |
Details on the fuel return circuit | |
Feeding by a liquid fuel driven jet pump | |
Submerged in fuel, e.g. in reservoir | |
Mounting pumps on fuel tanks | |
The pump being installed in a sub-tank | |
Feeding apparatus characterized by main and auxiliary pump |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Float valves; Floats therefor |
This place covers:
Plants mounted in the vehicle and used for producing gas for the propulsion of the vehicle.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electric vehicles using power supplied by batteries or fuel cells | |
Production of gases containing carbon monoxide and hydrogen from solid carbonaceous materials by partial oxidation processes involving oxygen or steam | |
Engine plants characterised by the engines using gaseous fuel generated in the plant from solid fuel, e.g. wood | |
Fuel cells | |
Structural combinations of fuel cells with other electrochemical devices |
This place does not cover:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Rider propulsion of wheeled vehicle with additional power source comprising solar cells | |
Marine propulsion by wind motors driving water-engaging propulsive elements | |
Alleged perpetua mobilia using hydrostatic thrust | |
Wind motors | |
Controlling wind motors | |
Alleged perpetua mobilia with mechanical-power-producing mechanisms | |
Circuit arrangements for charging batteries comprising light sensitive cells |
This place covers:
This group is given only if there is a specific arrangement/mounting of the transmission in the vehicle. The different elements of the transmission per se are classified elsewhere and should not be classified in B60K 17/00 (e.g. F16H gearings, F16D clutches). Even the connection between the elements is to be classified elsewhere in most of the cases (see, for example, H02K 7/10 structural association of electric machines with clutches, brakes, gears).
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangement or mounting of control devices for vehicle transmissions | |
Torque-transmitting wheel axles | |
Vehicle suspension arrangements | |
Conjoin control of propulsion units | |
Steering of deflectable wheels | |
Steering non-deflectable wheels using gearings with differential power outputs on opposite sides | |
Understructures | |
Endless track vehicles | |
Assembling motor vehicles by joining sub-units or components, the components being engines, clutches or transmissions, with respect to the body shell or other sub-units or components | |
Combinations of combustion engines with mechanical gearing | |
Clutches | |
Suppression of vibrations | |
Gearing |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Braking elements acting on transmission parts | |
Control of drivelines clutches and change speed gearing speed in vehicles | |
Steering non deflectable wheels using brakes or clutches as main steering effecting means | |
Vehicles with variable number of ground engaging wheels | |
Clutches per se, e.g. construction thereof; Control of clutches | |
Clutches with interengaging parts | |
Friction clutches | |
Fluid actuated clutches | |
Magnetically actuated clutches | |
Automatic clutches |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangement or mounting of plural diverse prime-movers for mutual or common propulsion, e.g. hybrid propulsion systems | |
Hybrid electric vehicles characterised by the transmission gearings | |
Hybrid electric vehicles characterised by the assembly or relative disposition of components | |
Architecture of the driveline in hybrid electric vehicles | |
Arrangement of propulsion on amphibious vehicle | |
Electric equipment or propulsion of electrically-propelled vehicles per se | |
Combinations of mechanical gearings | |
Combinations of mechanical gearing with fluid gearing | |
Gearboxes; Mounting gearing therein | |
Support of gearboxes, e.g. torque arms, or attachment to other devices | |
Gearboxes using a combination of several standardised units | |
Features relating to lubrication or cooling of gearing |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Motor arranged in or near the wheels | |
Suspension | |
Brake | |
Steering linkage | |
Structural association of electric machines with clutches brakes, gears, pulleys or mechanical starter | |
Association of electric motors with gears | |
Counter rotating rotors of electric machines |
Code for additional information B60K 17/043 is systematically given for documents classified in group B60K 7/00 having a transmission gear between motor and vehicle wheel.
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
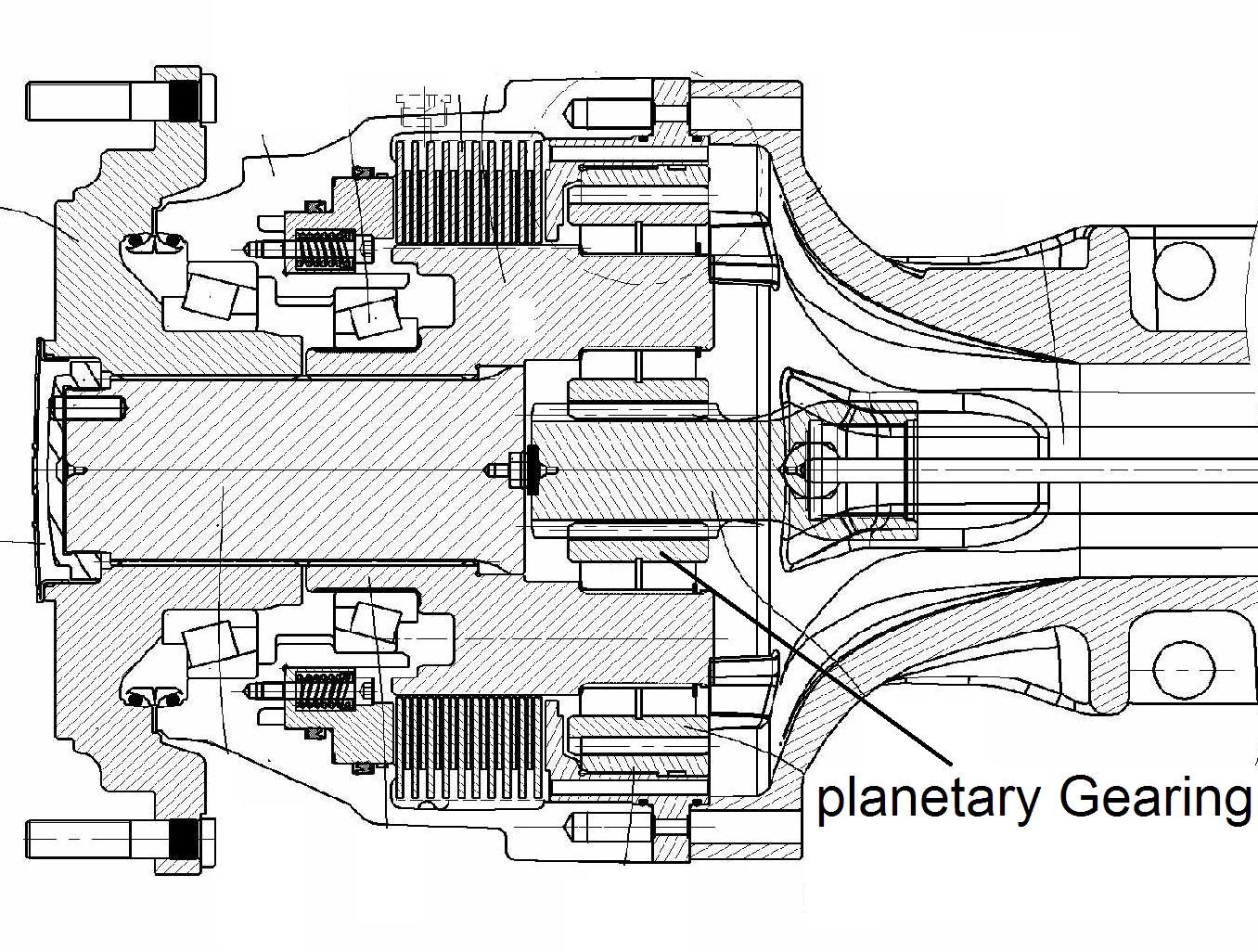
This place does not cover:
Gearings with gears having orbital motion | |
Gearing with variable gear ratio using gear having orbital motion | |
Lubrication/cooling of planetary gearings |
This place does not cover:
of fluid gearing | |
of differential gearing | |
Gearing with variable gear ratio |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangement or mounting of transmissions in vehicles characterised by arrangement, location or kind of clutch | |
Fluid or electric gearing in vehicles with motor being disposed in, or adjacent to, traction wheel | |
Positive-displacement machines for liquids; Pumps | |
Rotary-piston, or oscillating-piston, positive-displacement machines for liquids; Rotary-piston or oscillating-piston, positive-displacement pumps | |
Non-positive-displacement pumps | |
Pumping of fluid by direct contact of another fluid or by using inertia of fluid to be pumped | |
Rotary fluid gearing using pumps and motors of the volumetric type | |
Combinations of mechanical gearing with fluid clutches or fluid gearing | |
Control of hydrostatic gearing |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group.
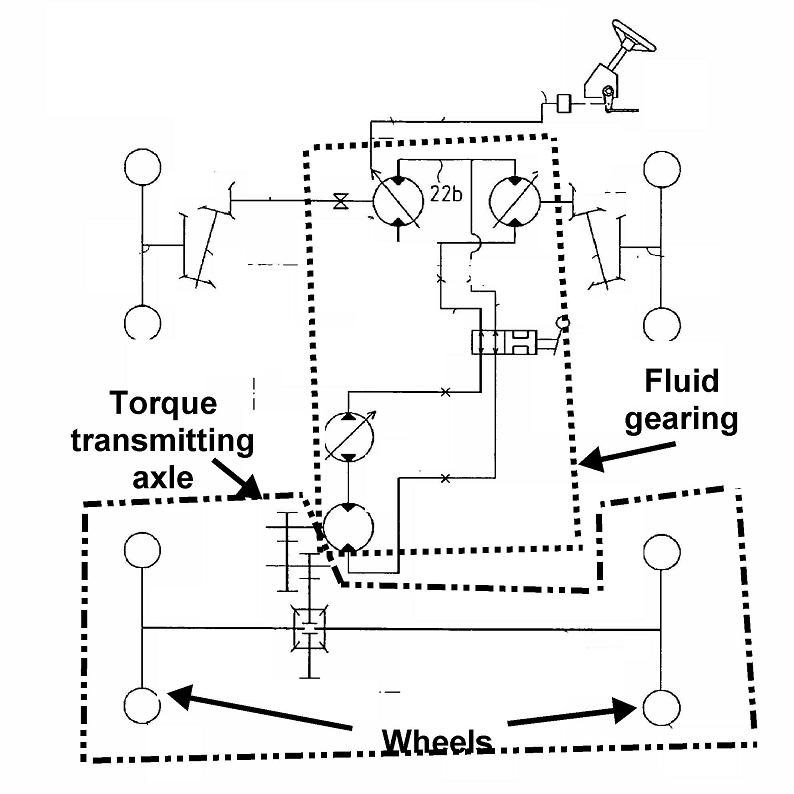
This place does not cover:
The motor of fluid or electric gearing being disposed in or adjacent to traction wheel |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangement or mounting of electrical propulsion units in vehicles | |
Disposition of motor in, or adjacent to, traction wheel | |
Arrangement or mounting of transmissions in vehicles characterised by arrangement, location or kind of clutch | |
Fluid or electric gearing in vehicles with motor being disposed in, or adjacent to, traction wheel | |
Electric equipment or propulsion of electrically propelled vehicles | |
Electric device for safety purposes, monitoring variables on electric vehicles | |
Methods for controlling the speed/torque of electric vehicles | |
Electric propulsion with power supplied within the vehicle | |
Conjoint control including the control of electric propulsion units | |
Arrangements for non-automatic engine control initiation means, e.g. operator initiated, characterised by electric type control linkages (Drive-by-wire) | |
Dynamo-electric clutches; Dynamo-electric brakes | |
Dynamo-electric gears, i.e. dynamo-electric means for transmitting mechanical power from a driving shaft to a driven shaft and comprising structurally interrelated motor and generator parts |
This place covers:
Electric or fluid gearing whereby the motor (electric or hydraulic) is disposed in or adjacent to the traction wheel. In these groups are in particular documents showing "electric or hydraulic differential".
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Disposition of motor in, or adjacent to, traction wheel | |
Arrangement or mounting of transmissions in vehicles for driving both front and rear wheels having fluid or electric motor, for driving one or more wheels | |
Steering non-deflectable wheels using gearings with differential power outputs on opposite sides, with additional power being supplied hydraulically to one side | |
Hydraulic motors | |
Rotary fluid gearing using pumps and motors of the volumetric type |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
in, or adjacent to | there is one motor driving one wheel (or dual wheels forming a unit) without a differential in between |
This place covers:
Arrangement of differential gearings in the vehicle.
This place does not cover:
Central differential for front and rear wheels driving | |
Mounting of ball or roller bearing, fixing them onto shaft or in housing | |
Universal joints | |
Differential gearing | |
Mechanical differentials gearings without member having orbital motion | |
Mounting or installation of gears in the gearbox casing | |
Housing for gearboxes with means for reducing vibrations | |
Gearboxes for accommodating differential gearings | |
Cooling/lubrication of differential gearings | |
Electric motor structurally associated with gears |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Gearings per se |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Axle units with differential | rigid casings comprising wheel drive shafts, bearings therefore and a differential, e.g. casing made of pressed sheet metal (see also axle units B60B 35/00, gearboxes with integrated axle drive). |
Differential gearing | Differential or means having the same function |
This place covers:
More the arrangement of such a differential in the vehicle
This place does not cover:
Arrangement or mounting of transmissions in vehicles in which the differential movement is obtained by resilient means | |
Arrangement or mounting of transmissions in vehicles in which the differential movement is limited | |
Steering deflectable wheels with means for differentially distributing power on the deflectable wheels during cornering | |
Arrangement for suppressing or influencing the differential action, e.g. locking devices |
This place covers:
Arrangement in the vehicle of differential means, whereby the difference of rotation speed between the two output shafts of the differential means is obtained using resilient means.
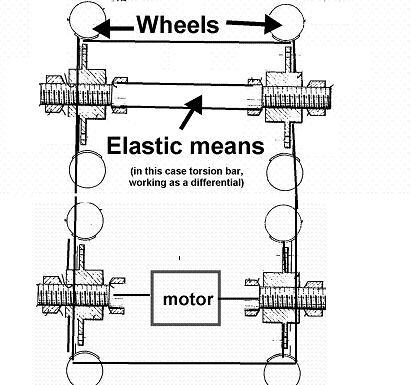
This place does not cover:
The transfer gear being a differential gear | |
Arrangement of control for differentials | |
Combinations of mechanical gearing having orbital motion with fluid clutches | |
Arrangement for suppressing or influencing the differential action, e.g. locking devices |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Differentials with electric motor for torque vectoring per se |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Torque transmitting axles for the wheels | |
Shafts | |
Shaft, axle | |
Bearings of crankshafts or connecting rod in general | |
Elastic or yielding bearings for exclusively rotary movement | |
Couplings fro transmitting rotation | |
Suppression of vibration |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangement of control for freewheels | |
Freewheels or freewheel clutches per see | |
Automatic clutches actuated entirely mechanically | |
Differential gearings without members having orbital motion |
This place covers:
Gearings comprising a power take off, which is for "extern" devices and not for other part of the vehicle like alternator, pump, fan for motor cooling etc.
This place does not cover:
Auxiliary drives from the transmission power take off (for example if the document describes a connection between the power take off shaft and the driven device | |
"Clutch-brake combinations" if it concerns the connection/disconnection of the power take off |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Auxiliary drives from the transmission power take-off if for example it is a connection between the power take-off shaft and the driven device | |
Tractors | |
Clutch-brake combinations if it concerns the connection disconnection of the power take off | |
Combination of mechanical gearing with fluid clutches or fluid gearings |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
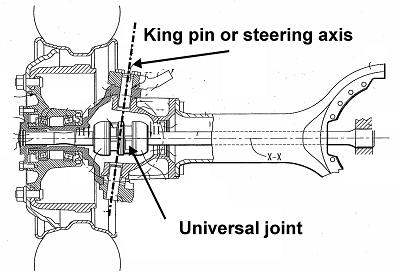
This place covers:
The ultimate propulsive element is steerable and the propulsive gearwheel being located on the steering knuckle or arranged in line with the kingpin axis.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
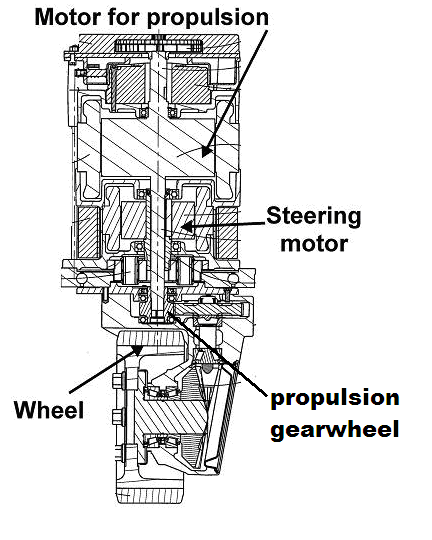
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Device for lifting or lowering bulky or heavy goods for loading and unloading purposes |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group.
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Suspensions | |
Vehicles with more than four wheels |
This place covers:
In this particular case, all four-wheel transmissions per se are classified in these groups and not only the arrangement in the vehicle.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangement or mounting of control devices for changing number of driven wheels |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangement of propulsion means on amphibious vehicles | |
Vehicles with more than four wheels |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group.
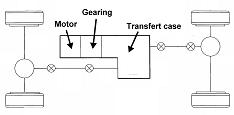
This place does not cover:
Cooling or lubrication of gearing |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Clutches |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group.
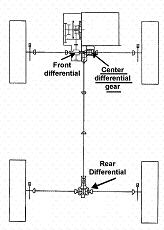
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Combinations of mechanical gearings with differential gearings and a plurality of driven shafts and one input shaft | |
Differential gearings per se | |
Cooling lubrication of differentials |
This place covers:
Transfer gears using for example clutches or differentials with a locking device. The locking device or other means for changing distribution of torque are arranged inside the transfer gear box.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangement of control devices for varying the torque distribution between the driven axles | |
Arrangements for regulating the brake forces specially adapted for four-wheel drive vehicles | |
Arrangements for suppressing or influencing the differential action per se |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
with | inside of the transfer gear box |
This place covers:
Using typically viscous couplings (difference of speed) or torque sensing differentials arranged inside the transfer gear box.
Illustrative example:
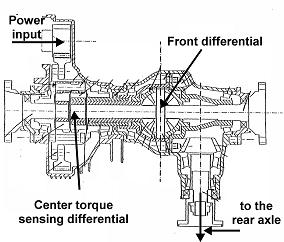
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group.
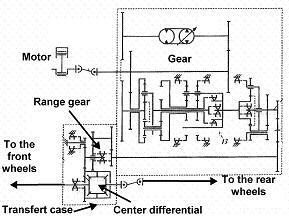
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Toothed gearings with variable gear ratio and having an orbital motion |
This place does not cover:
Arrangement of transmissions in vehicles for driving both front and rear wheels having a differential transfer gear |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangement of transmissions in vehicles for driving both front and rear wheels having a transfer gear | |
Arrangement of control devices for varying the torque distribution between the driven wheels |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
differential means | means which permit the front and the rear axles to rotate at different speed like for example: clutches, viscous connecting means |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this place:

Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangement or mounting of transfer gears for driving both front and rear wheels | |
Transfer gears with means for changing the distribution of torque between front and rear wheels | |
Arrangement of control devices for varying the torque distribution between driven axles | |
Differential gearing with arrangements for suppressing or influencing the differential action, e.g. locking devices |
This place covers:
Front and rear wheel driven vehicle comprising a particular self actuated arrangement for influencing the power transfert between the front and the rear wheels
This place does not cover:
Transfer gear with self actuating means for changing the distribution of torque between rear and front wheels |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Self actuated | without using an external command. For example: one way clutch, viscous clutch |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group.
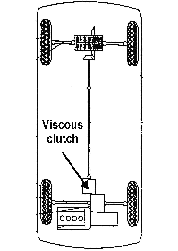
This place does not cover:
Transfer case having self actuated means (if for example the viscous clutch is in the transfer case housing) |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group.
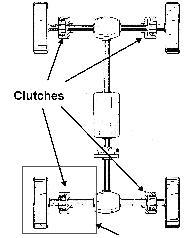
A driven wheel can be coupled independently.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Clutches |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Adjacent | between the wheel and the differential housing |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group.
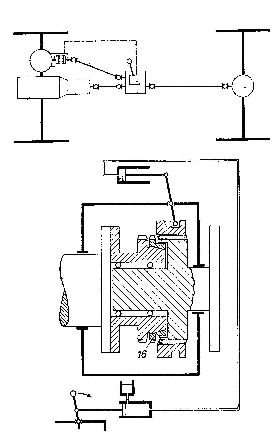
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Manually actuated mechanical control mechanisms |
This place covers:
Illustrative examples of subject matter classified in this group.
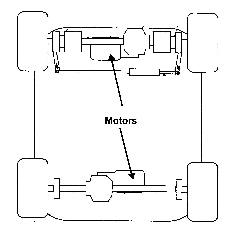
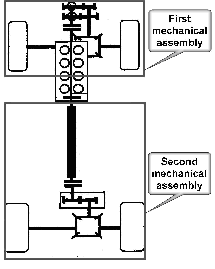
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Hybrid vehicles comprising electric and combustion engines | |
Hybrid vehicles driving a plurality of drive axles e.g. four wheel drive | |
Conjoin control including the control of driveline clutches | |
Conjoin control including the control of propulsion units | |
Conjoin control for hybrid vehicle characterized by a method for conjointly controlling different sub units |
This place covers:
The transmissions which comprise a main assembly for transmitting power and furthermore a fluid or electric motor(s) for driving one or more wheels.
Illustrative examples of subject matter classified in this place:

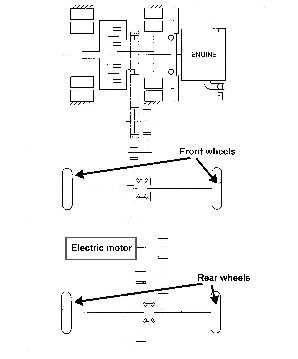
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Prime movers comprising combustion engines and mechanical or fluid energy storing means | |
Hybrid vehicles comprising electric and combustion engines | |
Hybrid vehicles driving a plurality of drive axles, e.g. with four-wheel drive | |
Disposition of motor in, or adjacent to, traction wheel | |
Conjoint control of vehicle sub-units of different type or different function, including the control of driveline clutches | |
Conjoint control of vehicle sub-units of different type or different function, including control of propulsion units | |
Control systems specially adapted for hybrid vehicles |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group.
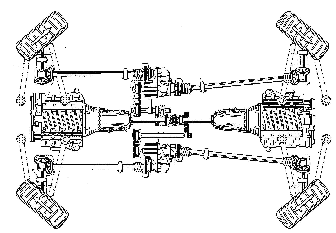
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Steering for trailer for centrally pivoted axles | |
Vehicles with more than four wheels |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group.

Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Tractors comprising traction increasing arrangements | |
Vehicles with more than four wheels |
This place covers:
The arrangement in the vehicle of the change speed gearing control devices. The change speed control device per se is classified in F16H 59/02.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Movable drivers' cabs characterised by special adaptations of vehicle control devices | |
Control inputs to change-speed- or reversing-gearings for conveying rotary motion | |
Selector apparatus to change-speed-, or reversing-gearings | |
Control functions within change-speed- or reversing-gearings for conveying rotary motion | |
Controlling members for hand actuation by pivoting movement in general, e.g. levers | |
Controlling members for hand actuation by rotary movement in general, e.g. hand wheels |
This place covers:
Only the arrangement or mounting in the vehicle. The change speed gearing control devices per se are classified in F16H 59/00.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adaptation for additional use of the arm-rests of vehicle seats | |
Adaptation of the arm-rests of vehicle seats for electrical control, e.g. by using switches | |
Selector apparatus to change-speed-, or reversing-gearings | |
Selector apparatus for automatic transmissions with means for range selection and manual shifting | |
Selector apparatus with means for suppression of vibrations or reduction of noise | |
Constructional features of the selector lever, e.g. grip parts, mounting or manufacturing | |
Ratio selector apparatus | |
Ratio selector apparatus consisting of electrical switches or sensors | |
Control devices or systems insofar as characterised by mechanical features only |
This place covers:
- Driver input members for controlling the main clutch comprising arrangements and mountings of pedals or paddles, clutch actuator transmission means of mechanical, electrical or hydraulic type and mounting of final actuators in the vehicle;
- Arrangements and mountings of automated clutch actuators using, e.g. mechanical, electromechanical or hydraulic means;
- Driver input members for controlling differential gearings comprising arrangements and mountings of levers, pedals or switches to lock a differential or to modify torque or speed distribution;
- Manual or automatic actuating means for locking or opening a freewheel device;
- Manual or automatic actuating means for switching from two to four-wheel drive;
- Automatic controllers for varying the torque distribution between axles, e.g. between the front and the rear wheels.
B60K 23/00 concerns the mountings or arrangements of control units related to a particular sub-unit not otherwise provided for in B60K.
The arrangements and mounting of input devices for change speed gearing are classified in B60K 20/00.
The arrangements and mounting of input devices for propulsion units are classified in B60K 26/00.
Vehicle drive control systems in general that are used for conjoint control and not related to a particular sub-unit are classified in B60W 30/00.
Arrangement or mounting of gearings for driving both front and rear wheels B60K 17/34.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangement or mounting of clutches in vehicles | |
Arrangement or mounting of differential gearing in vehicles | |
Arrangement or mounting of freewheel devices in vehicles | |
Control systems for conjoint control of vehicle sub-units of different type or different function comprising clutch units | |
Propulsion control with common controlling member for different functions, e.g. conjoint engine and clutch control member | |
Steering non-deflectable wheels using gearings with differential power outputs on opposite sides | |
Movable drivers' cabs characterised by special adaptations of vehicle control devices | |
Couplings for transmitting rotation; Clutches; Brakes | |
Fluid actuated clutches | |
Freewheel clutches in general | |
Control devices for clutches per se | |
Gearing | |
Control functions within change-speed- or reversing-gearings in general | |
Control of hydrostatic transmissions | |
Controlling members for hand actuation by pivoting movement in general, e.g. levers | |
Controlling members for hand actuation by rotary movement in general, e.g. hand wheels | |
Controlling members actuated by foot in general |
Use of the Indexing Code scheme is mandatory. When classifying in group B60K 23/00 classification must also be made in groups B60K 23/00 - B60K 2023/0841 for special features of clutch control, in B60Y 2400/00 for special features in general and in B60Y 2300/00 in order to identify the purpose and in B60W 10/00 for controlled sub-units B60W 2510/00 - B60W 2530/213 for controller input parameters and B60W 2710/00 - B60W 2720/406 for output target values.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Friction clutch adjustment for removing slack |
This place covers:
Drives for auxiliaries, including input power source, transmission and auxiliary output.
The driving power source is determinant for the subgroup and is either:
- directly from an engine shaft: B60K 25/02;
- from static or dynamic pressure or vacuum, developed by the engine: B60K 25/04;
- from a transmission power take-off, PTO shaft: B60K 25/06;
- from a ground wheel, e.g. engaging the wheel tread or rim: B60K 25/08;
- directly from oscillating movements due to vehicle running motion: B60K 25/10.
The drives are of any transmission type: belts, chains, gear trains, hydrostatic transmissions or electric transmissions using alternators/motors connected to a battery.
Auxiliary are all kind of vehicle auxiliaries as:
- Pumps for steering servos;
- Pumps for any hydraulic actuators for onboard implements;
- Compressors for air conditioning;
- Vacuum pumps for braking assistance;
- Alternators or generators.
B60K 25/00 concerns the mountings of auxiliary drives; the control of the auxiliary units is classified in the subclasses related to the particular auxiliary unit, as for example air conditioning.
The generator/motors drivingly connected to the engine crankshaft and driving also the vehicle are classified in subgroup B60K 6/485 for electric motor assisted hybrid vehicles.
This place does not cover:
Arrangement of tyre-inflating pumps mounted on vehicles |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangements in connection with power supply of propulsion units in vehicles from forces of nature, e.g. sun or wind | |
Arrangement, location or type of power take-off in vehicles | |
Driving arrangements for vehicle air-conditioning systems | |
Arrangements of pumps or compressors for control devices of brake systems | |
Pumps for power assisted steering | |
Engines characterised by the arrangement of auxiliary apparatus not being otherwise provided for | |
Starting of engines by means of electric motors, the motors being associated with current generators |
When classifying in group B60K 25/00, classification can also be made in codes for additional information:
- in B60K 25/00 - B60K 25/10 for additional information;
- in B60Y 2400/00 for special features in general;
- in B60Y 2200/00 for the vehicle types;
- in B60Y 2300/00 in order to identify the purpose;
- in B60W 10/00 for the type of controlled particular sub-unit, and further;
- in B60W 2510/00 - B60W 2530/213 for controller input parameters;
- in B60W 2710/00 - B60W 2720/406 for output target values.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangement, location or type of power take-off in vehicles |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Resilient suspensions having dampers accumulating utilisable energy, e.g. compressing air |
This place covers:
- Driver input members for controlling the propulsion unit, prime mowers comprising arrangements and mountings of accelerator pedals or paddles;
- Throttle or fuel injection actuator transmission means of mechanical, electrical or hydraulic type and mounting of control input devices in the vehicle;
- Arrangements and mountings of automatised actuators using actuating means, e.g. electromechanical or hydraulic, secondary throttles and drive by wire engine controls;
- Driver input members for controlling electric drive motors in electric vehicles;
- Haptic driver feedback in pedal or increasing pedal force in case of dangerous driving conditions;
- Electrical transmission means between accelerator pedals and propulsion units.
B60K 26/00 concerns the mountings of control units related to propulsion units of vehicles.
The operator initiation means for internal combustion engines control in general are classified in F02D 11/00.
The arrangements and mounting of clutch control input devices, e.g. arrangement or mounting of pedals for clutches are classified in B60K 23/00.
Vehicle drive control systems in general that are used for conjoint control and not related to a particular sub-unit are classified in B60W 30/00.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Human control setting devices for electrically propelled vehicles | |
Control systems for hybrid vehicles | |
Propulsion control with common controlling member for different functions, e.g. common control member for engine and brake control | |
Movable drivers' cabs characterised by special adaptations of vehicle control devices | |
Arrangements for, or adaptations to, operator-initiated engine control | |
Accelerator pedal transfer functions to engine controllers | |
Electrical control of supply of combustible mixture or its constituents | |
Circuits for controlling automatic idle-start-stop of engines | |
Ratio selector apparatus, the ratio being infinitely variable | |
Control of hydrostatic gearing | |
Controlling members for hand actuation by pivoting movement in general, e.g. levers | |
Controlling members for hand actuation by rotary movement in general, e.g. hand wheels | |
Controlling members by foot in general |
Use of the Indexing Code scheme is mandatory. When classifying in group B60K 26/00 classification must also be made in groups under B60K 26/00 for additional features of accelerator, in B60Y 2400/00 for special features in general, in B60Y 2300/00 in order to identify the purpose and in B60W 10/00 for the multiple controlled sub-units and in B60W 2510/00 - B60W 2530/213 for controller input parameters and B60W 2710/00 - B60W 2720/406 for the output target values.
This place covers:
The arrangements and mountings of safety systems responsive to:
- conditions relating to the driver, as presence or incapacity;
- conditions relating to the vehicle, as doors or cargo;
- skidding of the wheels;
for inhibiting the vehicle driving connection by acting on a single particular sub-unit:
- cutting ignition or fuel supply;
- switching off the battery;
- reducing engine torque;
- opening a clutch or other driving connection;
- sending a signal to the exterior.
B60K 28/00 is the place where the layout and arrangement of safety systems will be classified. The conjoint control of these systems will be classified in subclass B60W 10/00 for the type of the controlled unit with additional classification symbol in B60W 30/00 for the purpose. Combustion engine features per se are classified in the relevant subclasses F02B, F02D, F02N. Transmission or clutch features per se are classified in the relevant subclasses F16H or F16D.
This place does not cover:
Electric safety devices on electrically-propelled vehicles |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Control of airbags or occupant passive safety systems | |
Brake control systems for vehicle drive stability control of vehicle | |
Arrangements responsive to a speed condition, e.g. acceleration or deceleration for adjusting wheel breaking force | |
Road vehicle drive control systems for purposes not related to the control of a particular sub-unit | |
Driving stability by controlling multiple propulsion units | |
Active safety systems predicting or avoiding probable or impending collision by taking automatic action | |
Propulsion control with conjoint control of two or more sub-units for wheel slip | |
Means for informing the driver, warning the driver or prompting a driver intervention | |
Limiting control by the driver depending on vehicle state, e.g. interlocking means for the control input for preventing unsafe operation | |
Drive control systems specially adapted for autonomous road vehicles | |
Preventing wheel slippage by reducing power in rail vehicles | |
Alarms for ensuring the safety of persons, anti-dozing alarms |
Use of the Indexing Code scheme is mandatory. When classifying in group B60K 28/00 classification must also be made in groups B60K 28/00 - B60K 2028/003 for additional features of safety control, in B60Y 2400/00 for special features in general, in B60Y 2300/00 in order to identify the purpose and in B60W 10/00 for multiple particular sub-units and in B60W 2510/00 - B60W 2530/213 for controller input parameters and in B60W 2710/00 - B60W 2720/406 for the output target values.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Brake control systems for vehicle drive stability | |
Arrangements for adjusting wheel-braking force responsive to a speed condition | |
Control of vehicle driving stability not related to the control of a particular sub-unit | |
Preventing wheel slippage by reducing power in rail vehicles |
This place covers:
- Control systems for cruise control or speed limiting control of any particular single vehicle sub-unit;
- Control systems of a single vehicle sub-unit for adaptive cruise control [ACC] or for controlling distance between vehicles, in particular distance from a host vehicle to a preceding vehicle;
- Driver inputs to the cruise control systems comprising switches or levers for setting a target or reference vehicle speed;
- Control methods for controlling a single sub-unit or algorithms therefore for: selecting a target vehicle; detecting a distance and/or a speed of a target vehicle and comparing to a reference distance; setting or adapting the reference distance according to driving conditions; releasing or inhibiting the speed control, for example, in case of brake pedal actuation and resuming the speed control;
- Servomechanisms of electric, hydraulic or mechanical type to regulate the vehicle speed;
- Target outputs (analogue or digital) to the controller of a particular sub-unit to regulate a vehicle speed;
- Interactions with the driver, displaying target speeds, warning in case of excessive speeds.
B60K 31/00 concerns the vehicle speed controls related to a particular sub-unit, as for example engine or electrical drive motor or brakes, if the invention concerns a cruise control by acting on two or more sub-units as for example engine and brakes than it is classified in B60W 30/14 which is the application-oriented place covering vehicle drive control systems in general that are not related to a particular sub-unit or used for conjoint control.
Detecting means in general (e.g. ultrasonic radars G01S 7/00, TV cameras H04N, rear view cameras B60R 1/00, image processing, or measuring means) are covered by the classes G01, G06 or H04 and their appropriate subclasses.
Human-computer interfaces, e.g. keyboards are classified in G06F 3/00.
Displays in general are classified in B60K 35/22.
Driver warnings in general are classified in B60W 50/08.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Control systems for conjoint control of vehicle sub-units of different type or different function | |
Cruise control using conjoint control of vehicle sub-units | |
Estimations or calculations of driving parameters for road vehicle drive systems that are used for purposes of cruise control | |
Controlling combustion engines | |
Controlling combustion engines, such controlling being peculiar to the devices driven thereby, the devices being other than parts or accessories essential to engine operation, e.g. controlling of engines by signals external thereto | |
Electrical control of supply of combustible mixture or its constituents | |
Control of hydrostatic transmissions for achieving a target output speed | |
Speedometers | |
Systems for controlling position, course, altitude or attitude of land, water, air or space vehicles | |
Systems for controlling speed | |
Traffic control systems for road vehicles | |
Anti-collision systems |
Use of the Indexing Code scheme is mandatory. When classifying in group B60K 31/00 classification must also be made in groups B60K 31/00 - B60K 31/185 for additional features of cruise control, in B60Y 2400/00 for special features in general, in B60Y 2300/00 in order to identify the purpose and in B60W 10/00 for the controlled sub-units and in B60W 2510/00 - B60W 2530/213 for controller input parameters and in B60W 2710/00 - B60W 2720/406 for the output target values.
This place covers:
Arrangements of instruments for and aspects of display of information in a vehicle. The main group is in particular directed to all instruments located in the dashboard (and surrounding areas like windscreen or centre console) indicating information to the driver or passengers.
This main group covers all instruments that are in a vehicle dashboard if they are defined by particular aspects in their relation to the vehicle dashboard (e.g. the way they are mounted) or at least to control or indicate vehicle functions.
This group covers vehicle instruments, as well as their details or auxiliary aspects such as controlling, data transfer or information handling concerning vehicle functions.
This group does not cover details or auxiliary aspects relating to non-vehicle functions, unless the instruments are specially adapted for their use in a vehicle.
B60K 37/00 is directed to dashboards as such.
Whilst B60K 35/00 is directed to the adaptation of instruments in a dashboard, B62D 25/14 is related to the (internal) structure of the dashboard itself and to dashboards as superstructure sub units (e.g. dashboard structure, fixation).
Whilst B60K 35/00 is directed to the adaptation of vehicle instruments to the dashboard, B60R 11/00 is directed to mounting of electronic devices to dashboard (see in particular B60R 2011/0005).
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Indicating over speed | |
Monitoring tyres | |
Display devices for vehicle air conditioning | |
Arrangements or adaptations of lighting devices for vehicle interior | |
Lighting for dashboard | |
Arrangements for holding or mounting of radio sets, television sets, telephones or the like; Arrangement of controls thereof | |
Adaptations on rotatable parts of the steering wheel for accommodation of switches | |
Dashboard as superstructure | |
Arrangements or adaptations of instruments in aircraft | |
Measuring distances | |
Navigation | |
Devices specially adapted for navigation in a road network | |
Measuring combinations of speed and distance | |
Indicating measures values (analogue or digital) | |
Components of measuring arrangements | |
Components of indicators | |
Engine indicators | |
Measuring speed or acceleration | |
Head-up displays [HUD] | |
Input of data to computer | |
User interface programs, e.g. command shells, help systems, UIMS (interface arrangement | |
Remote windowing systems, e.g. X-windows; Or window cell phone displayed in vehicle display | |
Taximeters | |
Toll collection | |
Registering or indicating the working of vehicles | |
Traffic control systems for vehicles | |
Indicating arrangements for variable information in which the information is built-up on a support by selection or combination of individual elements | |
Mobile visual advertising | |
Accumulators combined with arrangements for measuring, testing or indicating the condition of cells, e.g. batteries with indicators | |
(Radio) receivers to be used in vehicles | |
Arrangements for broadcast, e.g. digital radio | |
Details of television systems |
In this group it is desirable to add the Orthogonal Indexing Codes of B60K 2360/00 – B60K 2360/96.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
HUD | head-up display |
LED | light emitting diode |
OLED | organic light emitting diode |
LCD | Liquid crystal display |
TFT | thin film transistor |
VFD | vacuum fluorescent display |
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms:
- "dashboard liner", "cladding" and "padding"
- "instrument cluster", "combined instrument" and "combi instrument"
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Input arrangements specially adapted for route navigation |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Control levers on arm rests | |
Arrangements of elements of electric circuits for voice control in vehicles | |
Controlling members, e.g. knobs or handles, in general | |
Input arrangements or combined input and output arrangements for interaction between user and computer in general | |
Touch screens | |
User interface programs, e.g. command shells, help systems or user interface management systems [UIMS] |
In this group it is desirable to add the Orthogonal Indexing Codes of B60K 2360/11 - B60K 2360/149.
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Output arrangements specially adapted for route navigation |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Means for informing the driver, warning the driver or prompting a driver intervention as part of control systems for road vehicle drive control not related to the control of a particular sub-unit |
In this group it is desirable to add the Orthogonal Indexing Codes of B60K 2360/151 - B60K 2360/1526.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Combined instruments indicating more than one navigational value, e.g. for aircraft |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Indicating arrangements for variable information in which the information is built-up on a support by selection or combination of individual elements in general |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Display screens | Integrated or non-integrated screens on which information is displayed |
G02B 27/01 covers head-up displays as optical elements or optical systems as such.
Contrary thereto, this subgroup relates to head-up displays as vehicle instruments.
Classification of technical characteristics of the head-up display relating to the vehicle instrument function is therefore classified in this subgroup. Technical characteristics of subject-matter referring to both optical aspects as well as to a vehicle instrument function is classified in G02B 27/01 as well as in this subgroup.
This place does not cover:
Optical aspects of head-up displays |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Head-up displays [HUD] | Substantially transparent displays that present information in one of the drivers' lines of sight to the outside of the vehicle |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Instrument input by detecting viewing direction not otherwise provided for |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Selective content distribution in pictorial communication, e.g. interactive television or video on demand in general |
In this group it is desirable to add the Orthogonal Indexing Codes of B60K 2360/16 - B60K 2360/179.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Optical viewing arrangements in vehicles not otherwise provided for |
In this group it is desirable to add the Orthogonal Indexing Codes of B60K 2360/18 - B60K 2360/199.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
This place does not cover:
Head-up displays characterised by their arrangement or structure for integration into vehicles |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangements for attaching the dashboard to the vehicle structure | |
Arrangements for holding or mounting radio sets, television sets or telephones | |
Devices for fastening or securing constructional elements or machine parts together | |
Arrangements of scales, pointers, lamps or acoustic indicators in automobile speedometers |
In this group it is desirable to add the Orthogonal Indexing Codes of B60K 2360/816 - B60K 2360/834.
This place does not cover:
Arrangements of lighting devices on dashboards |
In this group it is desirable to add the Orthogonal Indexing Codes of B60K 2360/77 - B60K 2360/797.
In this group it is desirable to add the Orthogonal Indexing Codes of B60K 2360/731 - B60K 2360/741.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Linings associated with the instrument panel or dashboard as occupant safety arrangement | |
Steering columns incorporating energy-absorbing arrangements, e.g. by being yieldable or collapsible | |
Shock-absorbers using plastic deformation of members in general |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electric circuits for transmission of signals between vehicle parts or subsystems | |
Network arrangements or protocols for supporting network services specially for special-purpose networking environments, e.g. networks in vehicles | |
User interfaces specially adapted for cordless or mobile telephones | |
Wireless communication networks for vehicles |
In this group it is desirable to add the Orthogonal Indexing Codes of B60K 2360/583 - B60K 2360/595.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Testing static or dynamic balance of machines or structures in general | |
Arrangements for locating electric faults | |
Camera calibration by analysis of captured images in general |
This place covers:
The adaptation of instruments in a vehicle dashboard. The main group is in particular directed to the mechanical mounting of instruments to the dashboard or the electrical integration of such instruments in the dashboard (e.g. connection to vehicle bus system). A dashboard related aspects must be present in all cases.
B60K 35/00 is the general home for documents comprising vehicle related aspects of indication devices.
B60K 37/00 is directed to dashboards and their adaptation in relation to instruments.
B62D 25/14 is related to the (internal) structure of the dashboard itself and to dashboards as superstructure sub units (e.g. dashboard structure, fixation).
B60R 11/00 is directed to mounting of electronic devices to dashboard (see in particular B60R 2011/0005).
This place does not cover:
Dashboard as road vehicle superstructure subunits |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangements or adaptations of lighting devices for vehicle interior | |
Lighting for dashboard | |
Arrangements for holding or mounting of radio sets, television sets, telephones or the like; Arrangement of controls thereof | |
Clips for joining vehicle mouldings or liners | |
Instruments in airplanes | |
Navigation | |
Components of measuring arrangements | |
Head-up displays (HUD) | |
Input of data to computer | |
Taximeters | |
Toll collection | |
Connectors | |
Electronic switching | |
Touch switches | |
(Radio) receivers to be used in vehicles |
In this main group it is desirable to add the Orthogonal Indexing Codes of B60K 2360/40 - B60K 2360/48, B60K 2360/65 - B60K 2360/6992 and B60K 2360/84.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
HUD | head-up display |
LED | light emitting diode |
OLED | organic light emitting diode |
LCD | Liquid crystal display |
TFT | thin film transistor |
VFD | vacuum fluorescent display |
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms:
- "dashboard liner", "cladding" and "padding"
- "instrument cluster", "combined instrument" and "combi instrument"
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Head-up displays with means for detecting the driver's gaze direction or eye points |
This indexing code covers all vehicle instruments input devices by detecting viewing direction excluding means for detecting the driver's gaze direction or eye points in head-up displays for which the main trunk symbol B60K 35/235 is provided.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electric circuits specially adapted for vehicles and not otherwise provided for; Arrangement of elements of electric circuits specially adapted for vehicles and not otherwise provided for | |
Electric constitutive elements, e.g. wire harnesses or grommets |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electric circuits for transmission of signals between vehicle parts or subsystems |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electric circuits for transmission of signals between vehicle parts or subsystems |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electric circuits for transmission of signals between vehicle parts or subsystems |