CPC Definition - Subclass H04R
This place covers:
- loudspeakers, microphones, acoustic transducers therefor producing acoustic waves or variations of electric current or voltage, or gramophone pick-ups
- arrangements actuated by variations of electric current or voltage for cutting grooves in records;
- circuits for the above-mentioned loudspeakers, microphones, acoustic transducers, gramophone pick-ups or arrangements;
- monitoring or testing of the above-mentioned loudspeakers, microphones, acoustic transducers, gramophone pick-ups, arrangements or circuits therefor.
Regarding producing sound, this subclass covers producing sound with a frequency determined by the frequency of the electrical signal applied to the transducer, whereas G10K covers producing sounds with frequency not so determined.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
- Classification of invention information and additional information is obligatory.
- Further detail not provided for in any of the main groups is provided for in the subgroups of Indexing Code groups H04R 2201/00 - H04R 2231/00, H04R 2307/00 and H04R 2400/00 – H04R 2499/00. These indexing code groups should be used in combination with CPC main trunk symbols to classify information highly relevant to the invention only. Classification is obligatory as indicated for each of the indexing groups concerned.
- Of Indexing Code groups H04R 2201/00 - H04R 2231/00, H04R 2307/00 and H04R 2400/00 - H04R 2499/00 and of Indexing Code groups H04R 2201/02, H04R 2201/10 and H04R 2201/40 ONLY the subgroups should be used for classification.
- Further detail not provided for in any of the main groups is provided for in the subgroups of Indexing Code groups H04S 2400/00 and H04S 2420/00 below. Classification is obligatory.
- Modifications to the transducers itself (e.g. a Helmholtz resonator attached to a through-hole in the magnetic circuit or zeolytes attached to the frame) in order to modify the frequency response are to be classified in the appropriate place for the type of transducer (H04R 9/00 - H04R 23/00) as invention information in combination with H04R 1/22 as additional information.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Acoustic, Sound | cover the technical field dealing with ultrasonic, sonic or infrasonic waves |
Deaf aid | hearing aid |
Loudspeaker | transducer mounted in a casing for producing sound |
Microphone | transducer mounted in a casing for collecting sound |
Stereophonic system | two- or more channel system, e.g. quadraphonic, ambisonic or similar system |
Transducer | a device that converts an electrical signal to an acoustic signal with a frequency which is determined by the frequency of the electrical signal applied to the transducer, or vice versa |
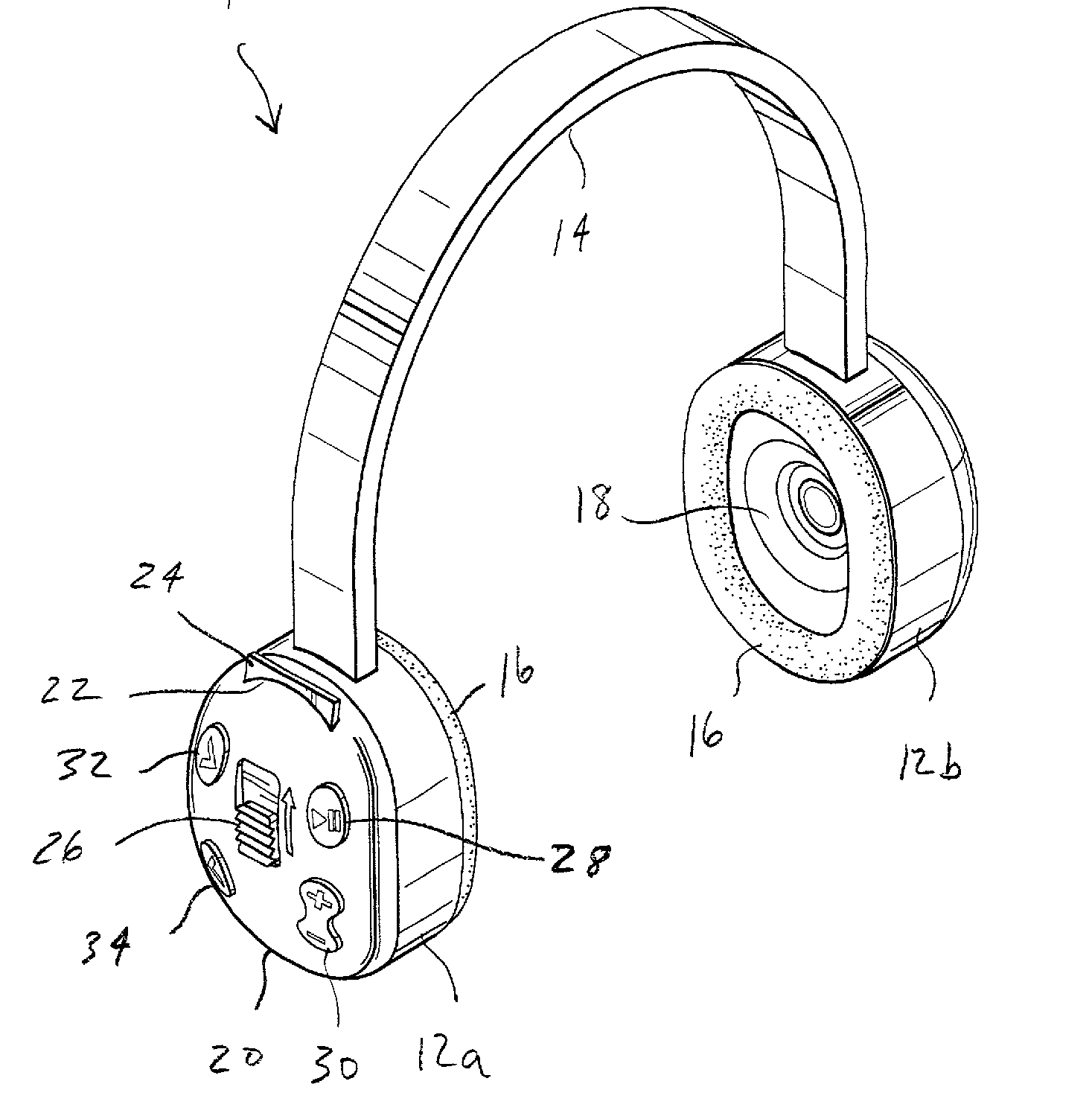
Microstructural device | 1. micromechanical devices comprising movable, flexible or deformable elements; 2. three-dimensional structures without movable, flexible or deformable elements, comprising microformations designed to accomplish an essential structural function for interacting with their environment, as opposed to purely electronic or chemical functions, regardless of whether the structures are combined with microelectronic devices or formed from specific materials; |
Microstructural system | 1. systems of cooperating microstructural devices; 2. microelectro-mechanical or microopto-mechanical systems, which combine on a common substrate the specific features of microstructural devices and electrical or optical components, e.g. for controlling, analysing or signalling the functioning of microstructural devices. |
This place covers:
Details of transducers, loudspeakers or microphones.
This place does not cover:
Diaphragms for acoustic transducers | |
Details of transducers characterised by the nature of the transducer |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Mountings specially adapted for telephone equipment |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Mounting radio sets or communication systems in helmets |
Further detail is covered by the Indexing Code group H04R 2201/003 listed below. Classification is obligatory.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Casing | housing, cabinet, enclosure |
Deaf aid | hearing aid, auditory prosthesis |
Stereophonic system | two- or more channel system, e.g. quadraphonic, ambisonic or similar systems |
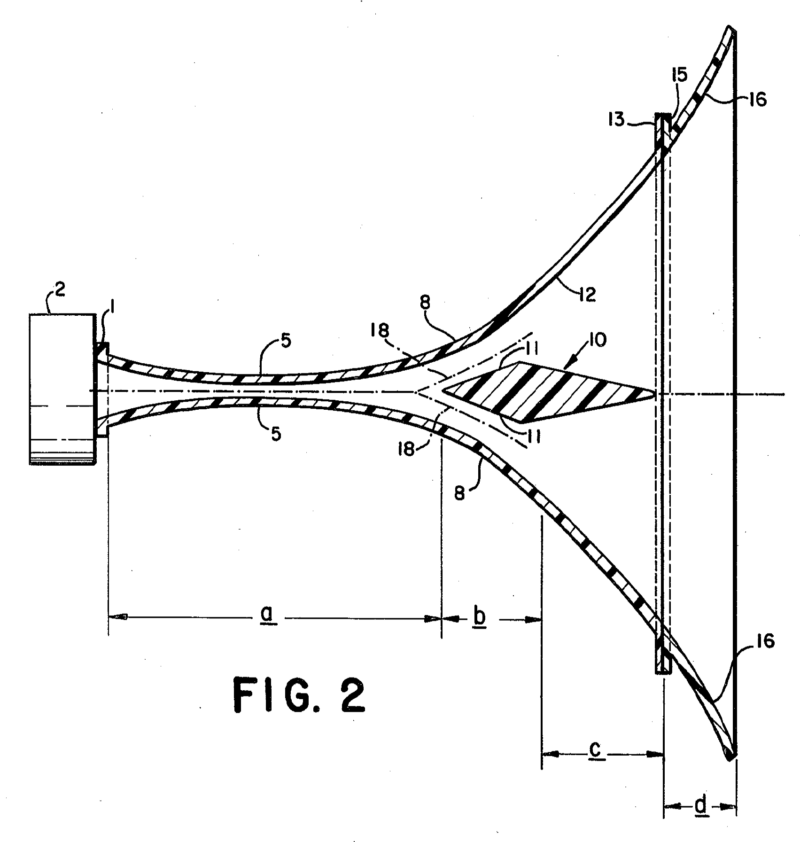
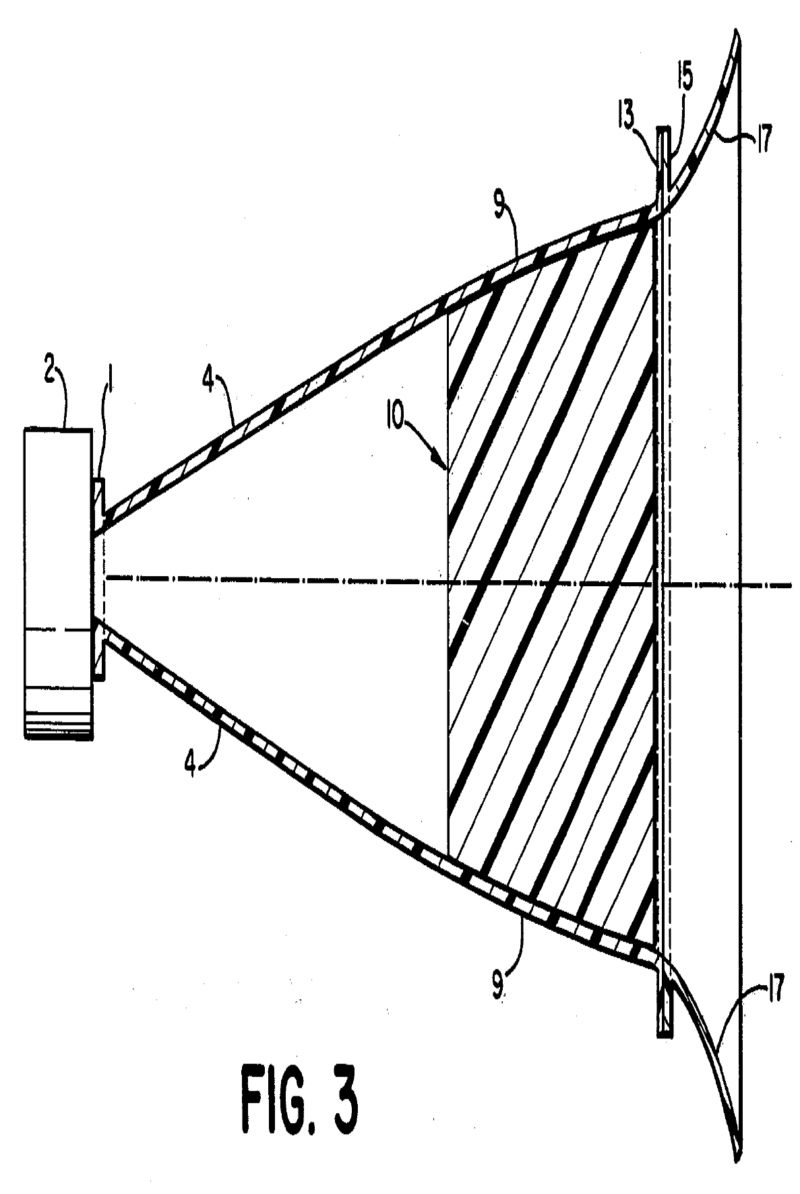
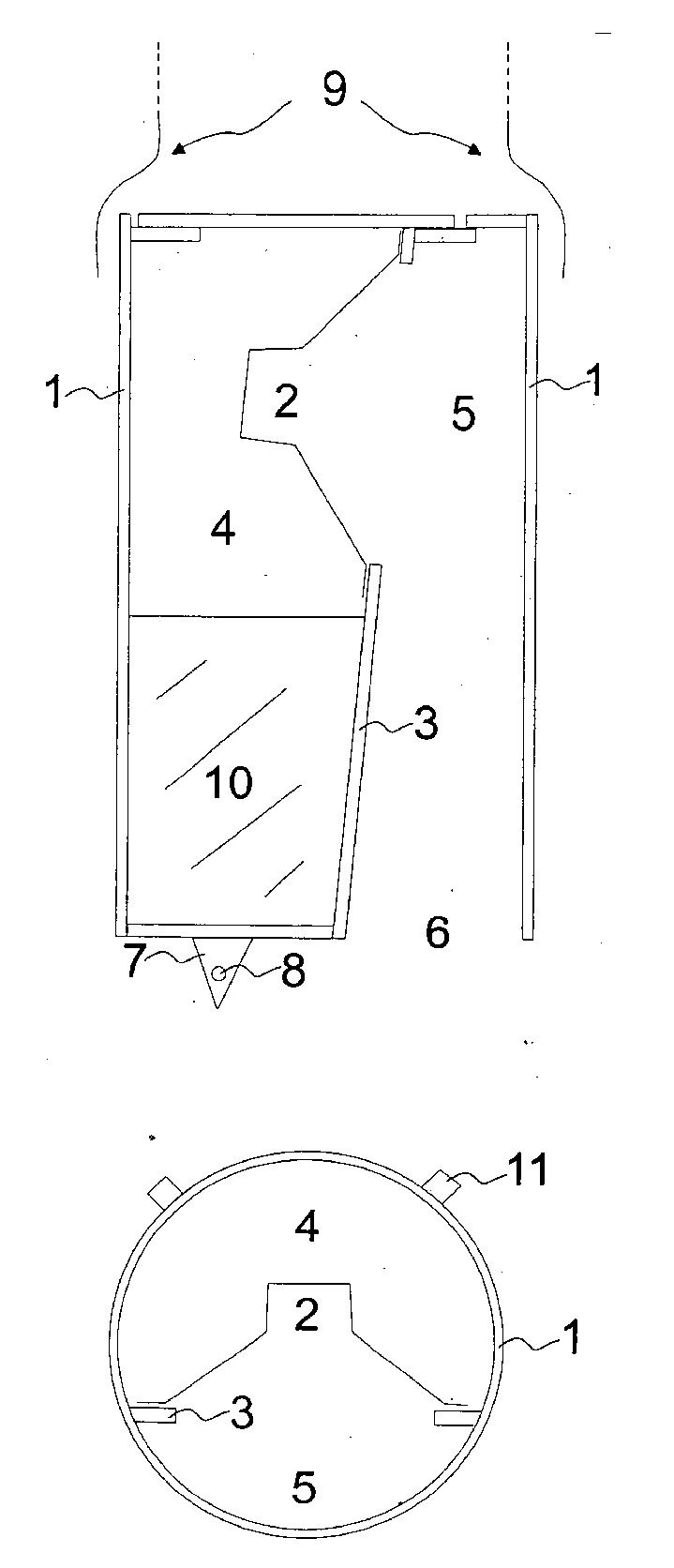
This place covers:
Example for a loudspeaker transducer (the number of windings of the 15 coils ranges from 20-214)
Example for a microphone transducer:
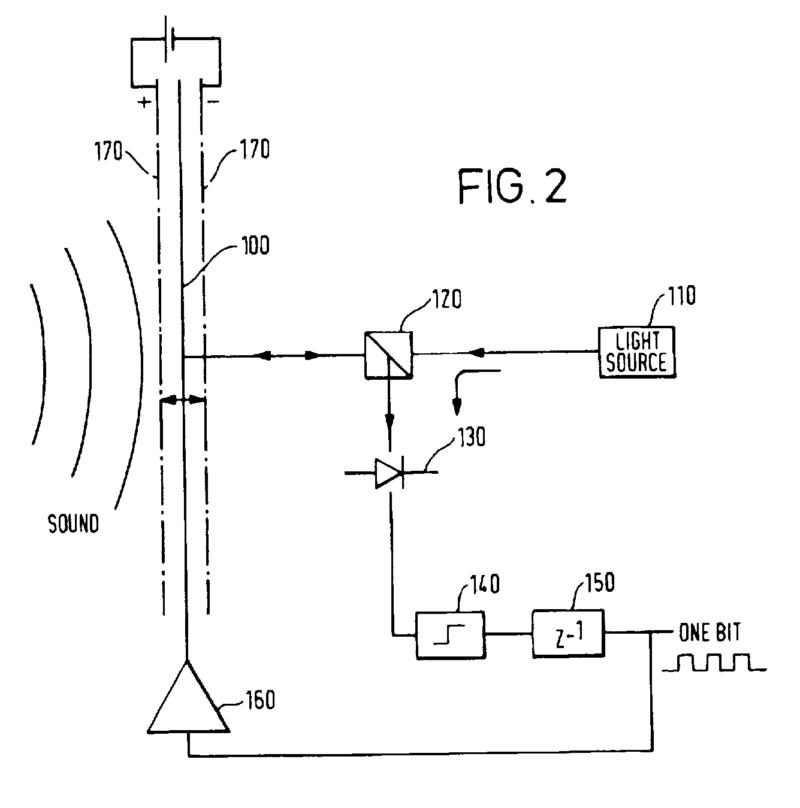
This place covers:
Casings, cabinets for transducers, their manufacture, their support, or mountings for transducers therein.
This place does not cover:
Attachments for microphones | |
Mounting of transducers in earpieces | |
Transducer mountings or enclosures modified by provision of mechanical or acoustic impedances, e.g. resonator, damping means |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Mounting of acoustic transducers in vehicles |
Further detail is covered by the subgroups of Indexing Code group H04R 2201/02 listed below. Classification is obligatory.
This place covers:
A mesh or grating covering the loudspeaker transducer or a sound path leading to the loudspeaker transducer
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Furniture aspects of radio, television | |
Adaptations of chairs or stools for incorporating lamps, radio sets, bars, telephones, ventilation, heating or cooling arrangements or the like |
This place covers:
Means to hold a loudspeaker casing for and during use
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Decoupling of vibrations by means of point-of-contact supports, e.g. ball bearings | |
Supports and stands in general |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of the subject matter classified in this place:
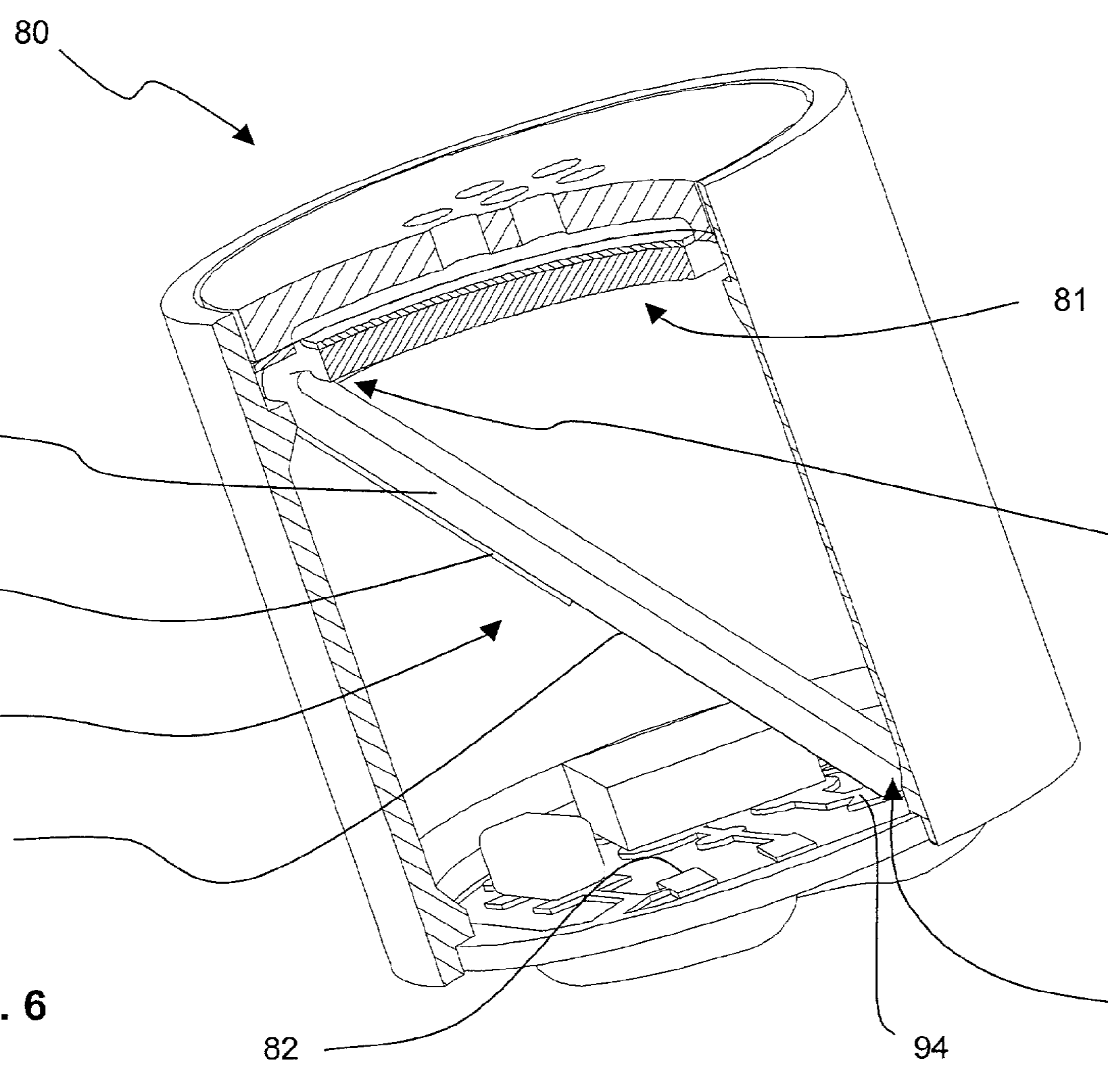
The Figure illustrates circuitry (81) that can be mounted inside the microphone (80).
This place does not cover:
Structural association of microphone with electric circuitry therefor in electric hearing aids |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
MEMS packages | |
Microstructural systems comprising a MEMS connected to control electronics, i.e. smart-MEMS | |
Packaging of Smart-MEMS, i.e. packaging together processing unit and MEMS |
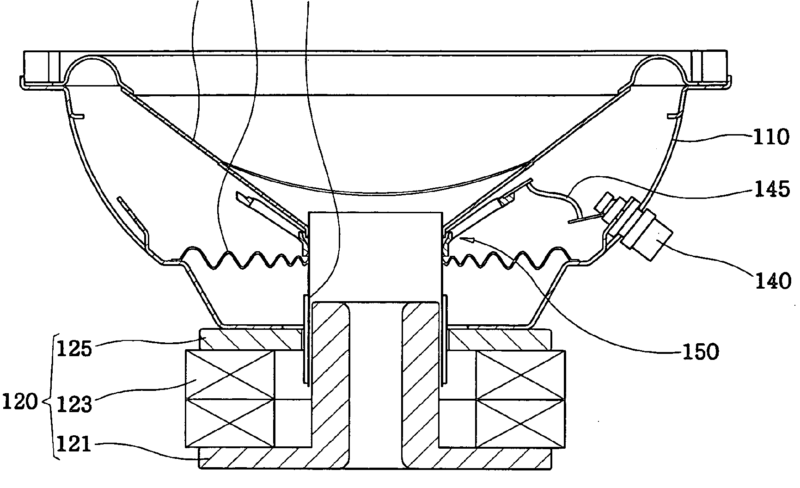
This place covers:
Connection or contacting arrangements specially adapted to transducers, loudspeakers or headphones.
In the example the tinsel wire 145 is prevented from contacting the diaphragm during vibration, by ring structure 150.
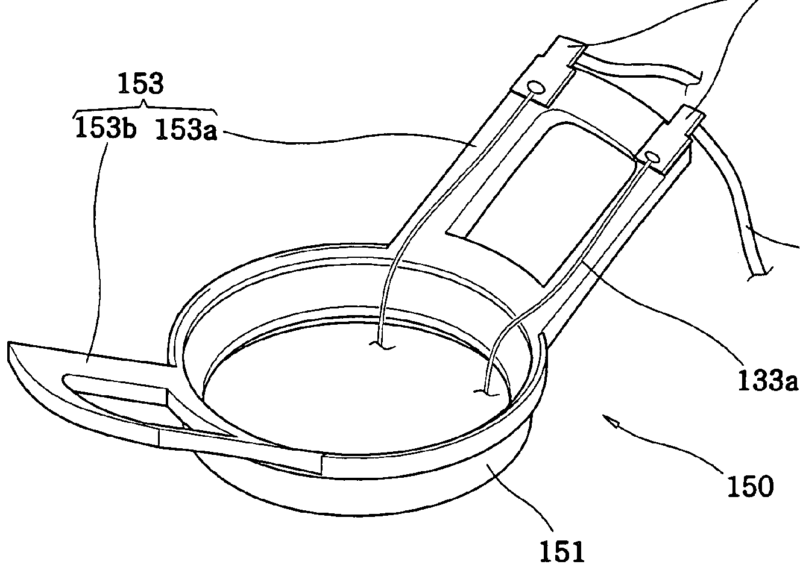
In the example, the terminal 30 is prevented from bending too much during mounting, by stopper 29.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Interconnections between the MEMS and external electrical signals | |
Connecting electric signal lines from the MEMS device with external electrical signal lines, e.g. through vias | |
Means for relieving strain on wire connection, e.g. cord grip, for avoiding loosening of connections between wires and terminals within a coupling device terminating a cable or for flat or ribbon cables |
Further detail is covered by the subgroup of Indexing Code group H04R 2420/09 listed below. Classification is obligatory.
This place covers:
Microphones, mouthpieces or attachments therefor, e.g. spiders or microphone booms, or protective screens therefor, e.g. all weather or wind screens.
This place does not cover:
Throat mountings for microphones |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Supports and stands in general |
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used with the meaning indicated:
"spider" | "shock mount to elastically fasten microphones to stands". |
Further detail is covered by the subgroup of Indexing Code group.
Further detail is covered by Indexing Code group H04R 2410/07. Classification is obligatory.
This place covers:
- Earphones or monophonic headphones;
- Attachments therefor, e.g. ear hooks;
- Details of headphones both of monophonic and stereophonic type, e.g. earpieces, e.g. intra-aural or supra-aural, or mechanical or electronic switches or control elements peculiar thereto, or accumulators or arrangements for charging peculiar thereto;
- Assembly or manufacture thereof, e.g. ear pads;
- Mechanical or electrical reduction of external noise.
This place does not cover:
Transducer mountings or enclosures modified by provision of mechanical or acoustic impedances, e.g. resonator, damping means | |
Stereophonic headphones |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Sanitary or hygienic devices for earpieces | |
Badges | |
Ornaments for ears | |
Earphones measuring physiological sounds (e.g. heart rate, breathing, pulse) | |
Transceivers carried on the body, e.g. in helmets |
- When classifying in this group or in its subgroups, aspects relating to stereophonic headphones are to be classified in H04R 5/033 (additional information) as well.
- Concerning inventions relating to hearing devices, if an application describes and shows the invention using only embodiments relating to ear- or headphones then H04R 1/10 or subgroups or H04R 5/033 or subgroups should be given as invention information. Dependent on the case, the mere statement that the invention is also applicable to hearing aids may render classification under H04R 25/00 useful, but only as additional information. Only if specific non-trivial embodiments for hearing aids are also shown, classification under H04R 25/00 as invention information may be considered as well.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Ear moulds for hearing aids | |
Hybrid ear moulds for customisation | |
Earplugs for protection |
Further detail is covered by the subgroups of Indexing Code group H04R 2460/09 and H04R 2460/11 listed below. Classification is obligatory.
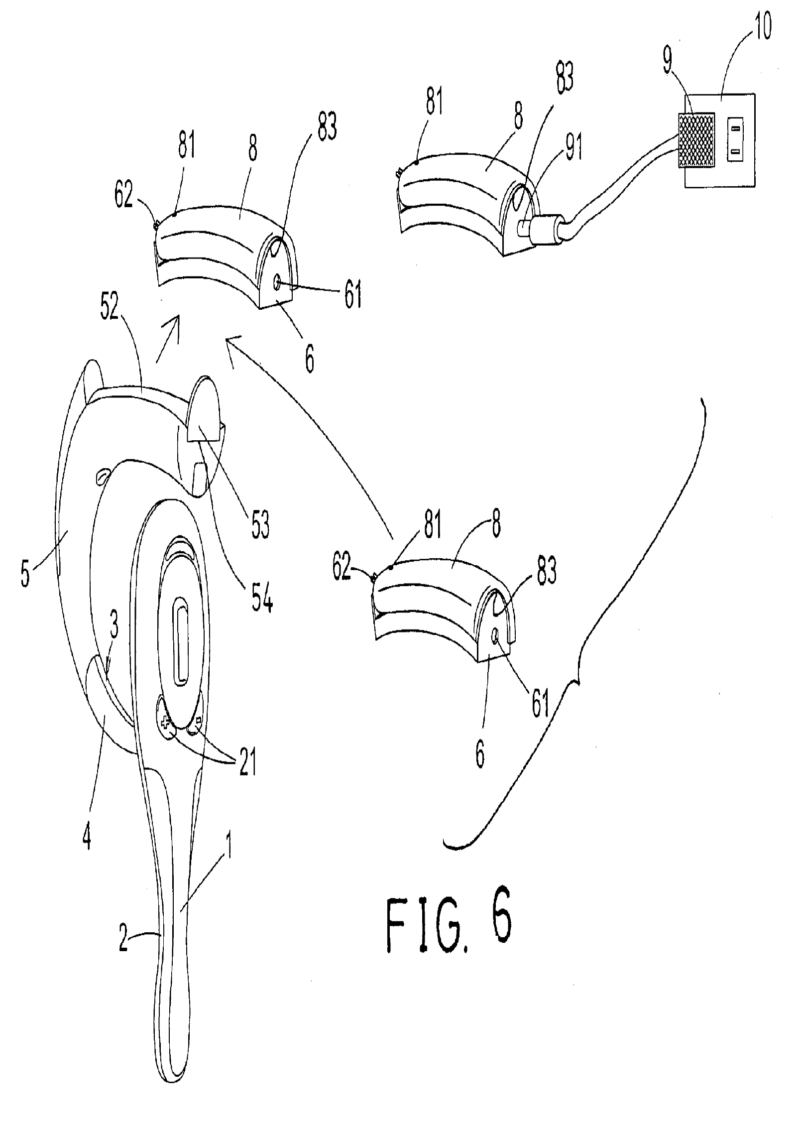
This place covers:
Adaptations to earpieces to enable charging.
For example:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Aspects of accumulators, e.g. rechargeable batteries, fuel cells, in hearing aids | |
Secondary cells per se | |
Charging in general | |
Battery chargers characterised by the mechanical construction, e.g. adapted for holding portable devices containing batteries |
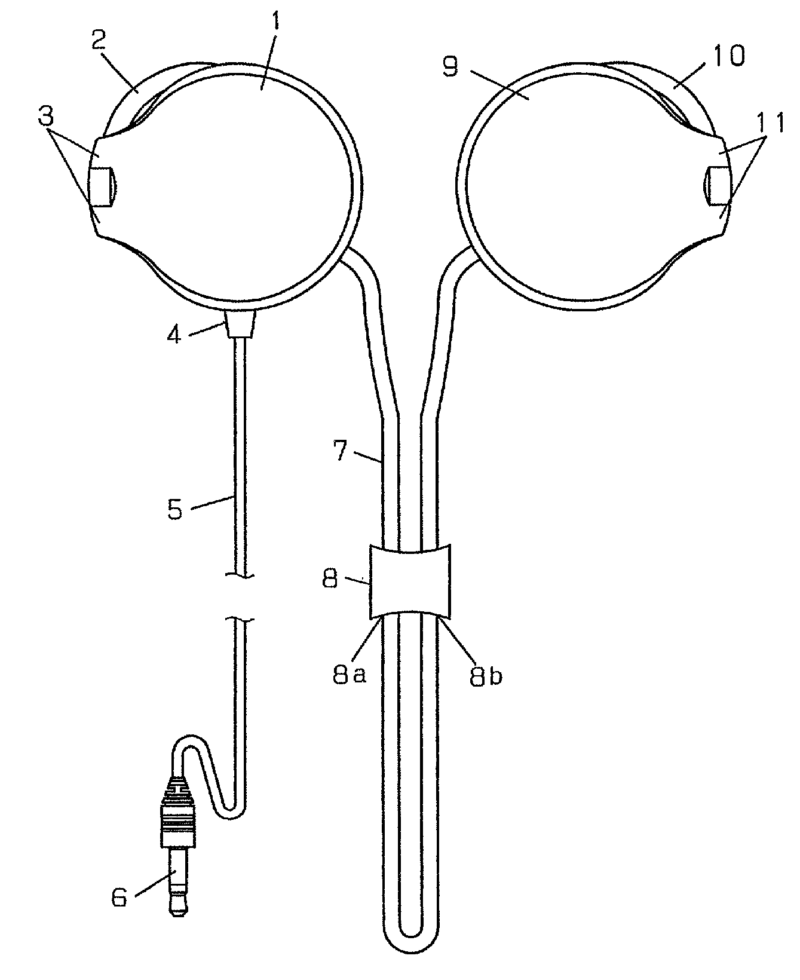
This place covers:
For example:
A stereophonic earphone with two earpieces each with a cable (4,5). The cable is wound on a spool (8) for storing the cables when the earphone is not in use.
For example:
A stereophonic headphone with a U-shaped slider (8) to adjust the length of the cable.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangements for storing and repeatedly paying-out and re-storing lengths of conductors or cables | |
Extensible conductors or cables, e.g. self-coiling cords | |
Insulated conductors or cables characterised by their form with arrangements for facilitating mounting or securing | |
Cord reels per se | |
Protection of telephone cord; Guiding telephone cord; Winding-up telephone cord |
This place covers:
For example (electronic switch/control elements)
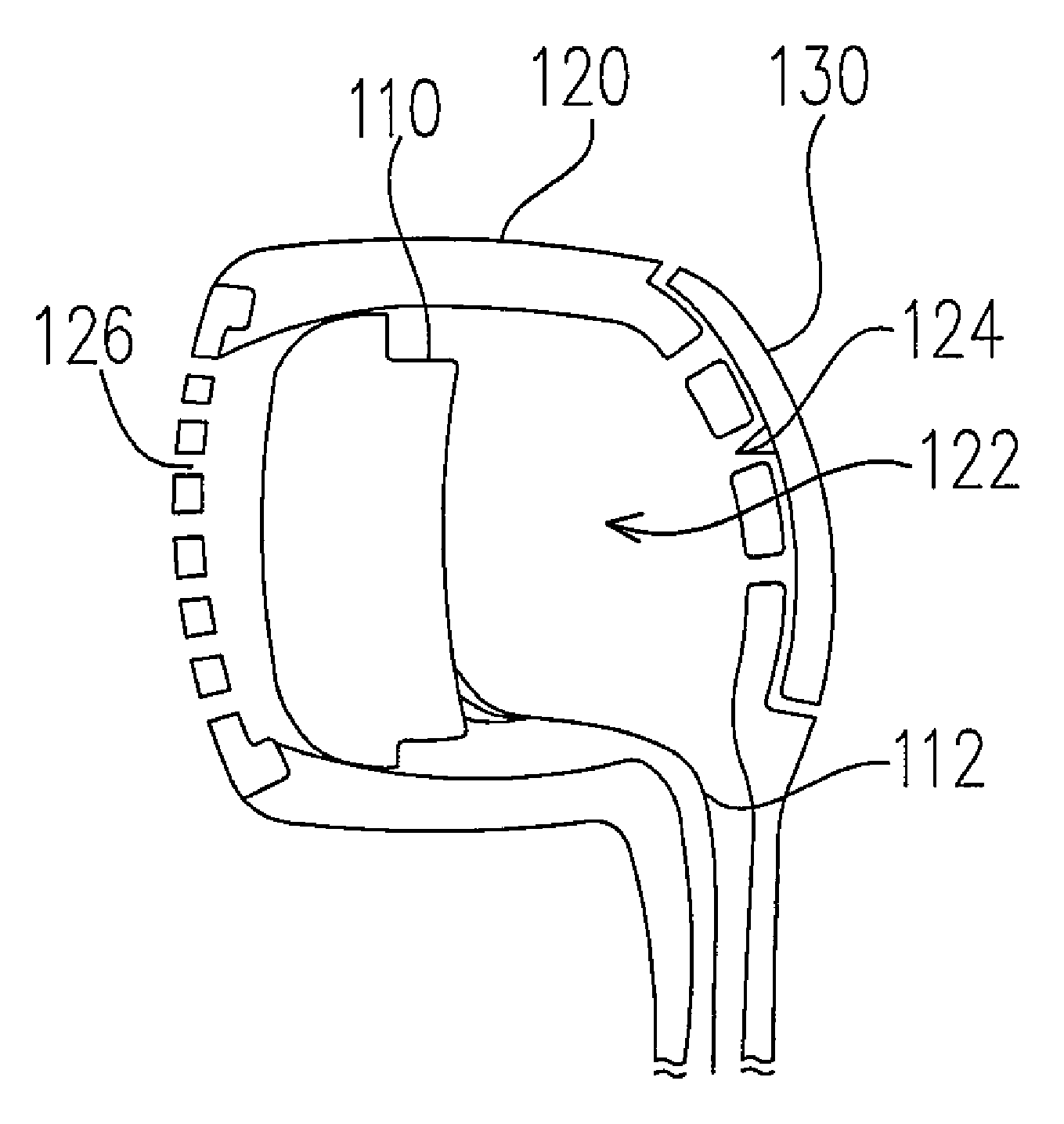
For example (mechanical control element):
Earphone wherein the frequency response can be changed by changing (with slide 130) the number of holes (124) that are open/closed. Please take note of precedence rule referring to H04R 1/28.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Mounting or interconnection of switches or control elements in hearing aids | |
Aspects relating to switches or control elements for hearing aids, e.g. functioning | |
Switches in general | |
Line cord switches | |
Hand-held casings specially adapted for remote control, e.g. of audio or video apparatus |
This place covers:
For example:
Earpiece support 30 is used to attach headset to the ear. The arms 31 of support 30 are rotatable around hinge H.
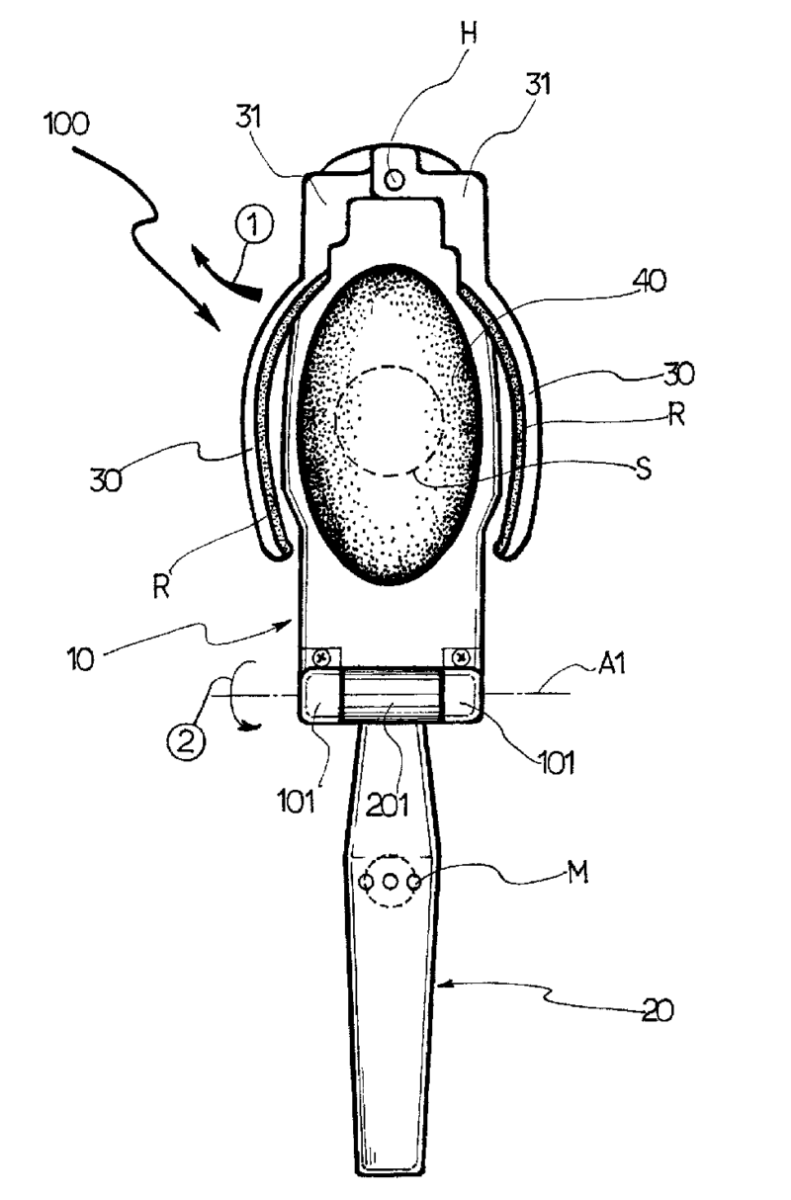
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Earpiece supports for stereophonic headphones |
This place covers:
Methods of manufacture or assembling as well as the way devices are assembled or constructed
For example:
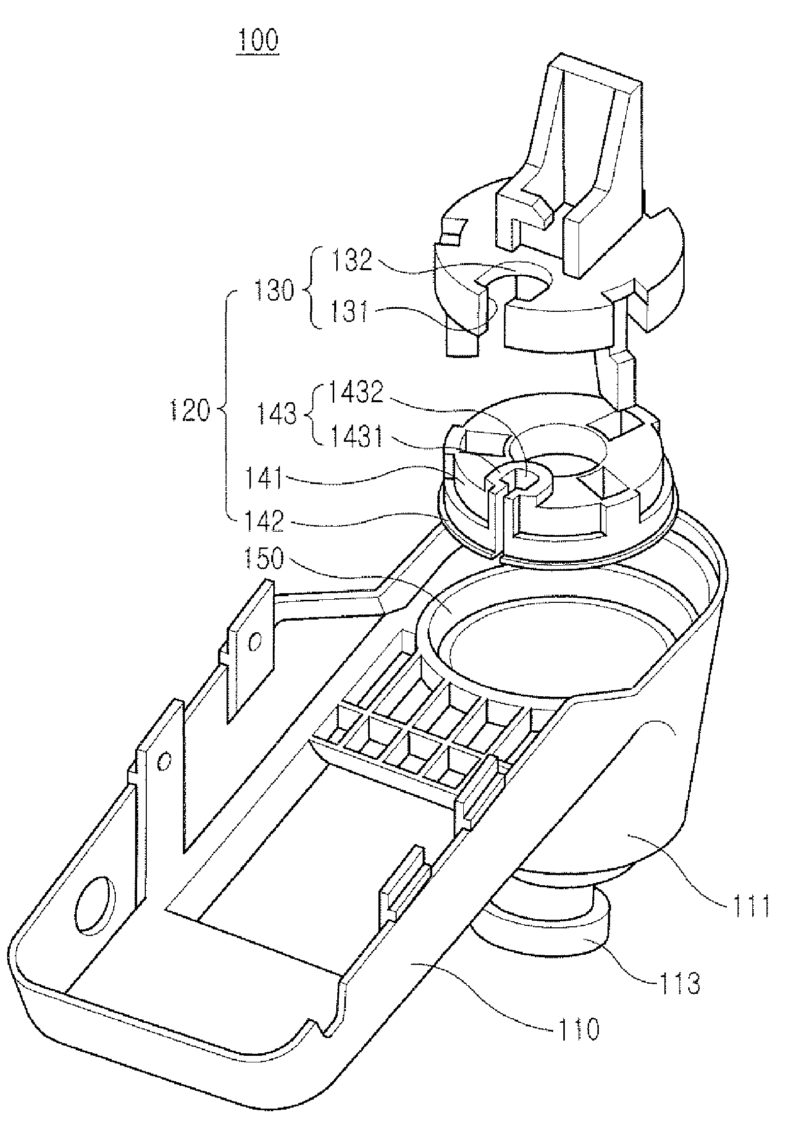
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Manufacture of mono- or stereophonic headphone parts not otherwise provided for in H04R, e.g. moulding of ear pads |
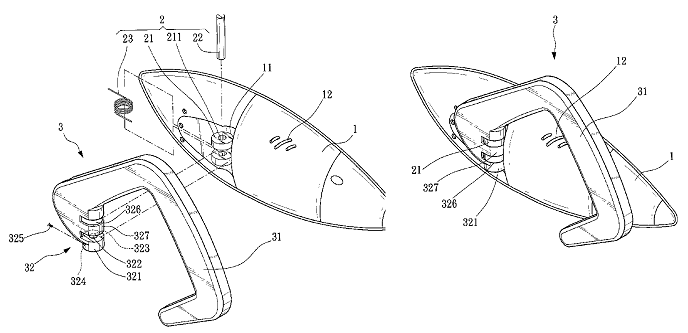
This place covers:
Example (ear hook):
Example (headband):
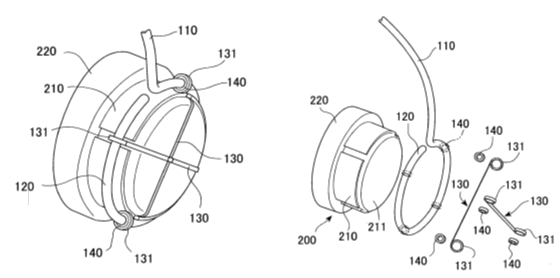
Example (headband):

Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Earpiece support for monophonic headphones | |
Earpiece support for stereophonic headphones |
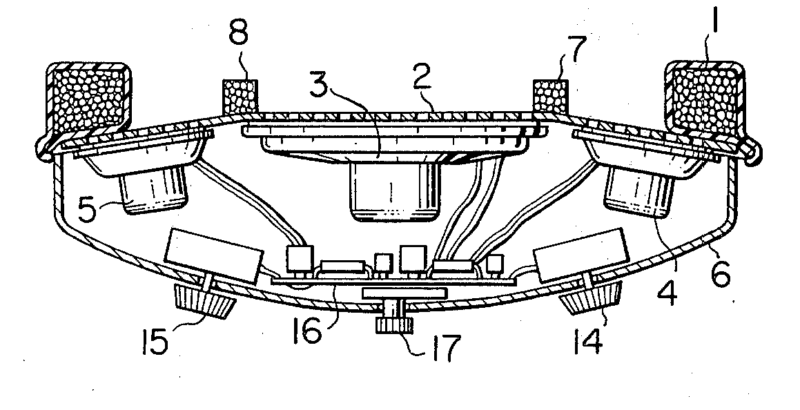
This place covers:
For example: (positioning of the transducers (4, 5, 6) in the earpiece)
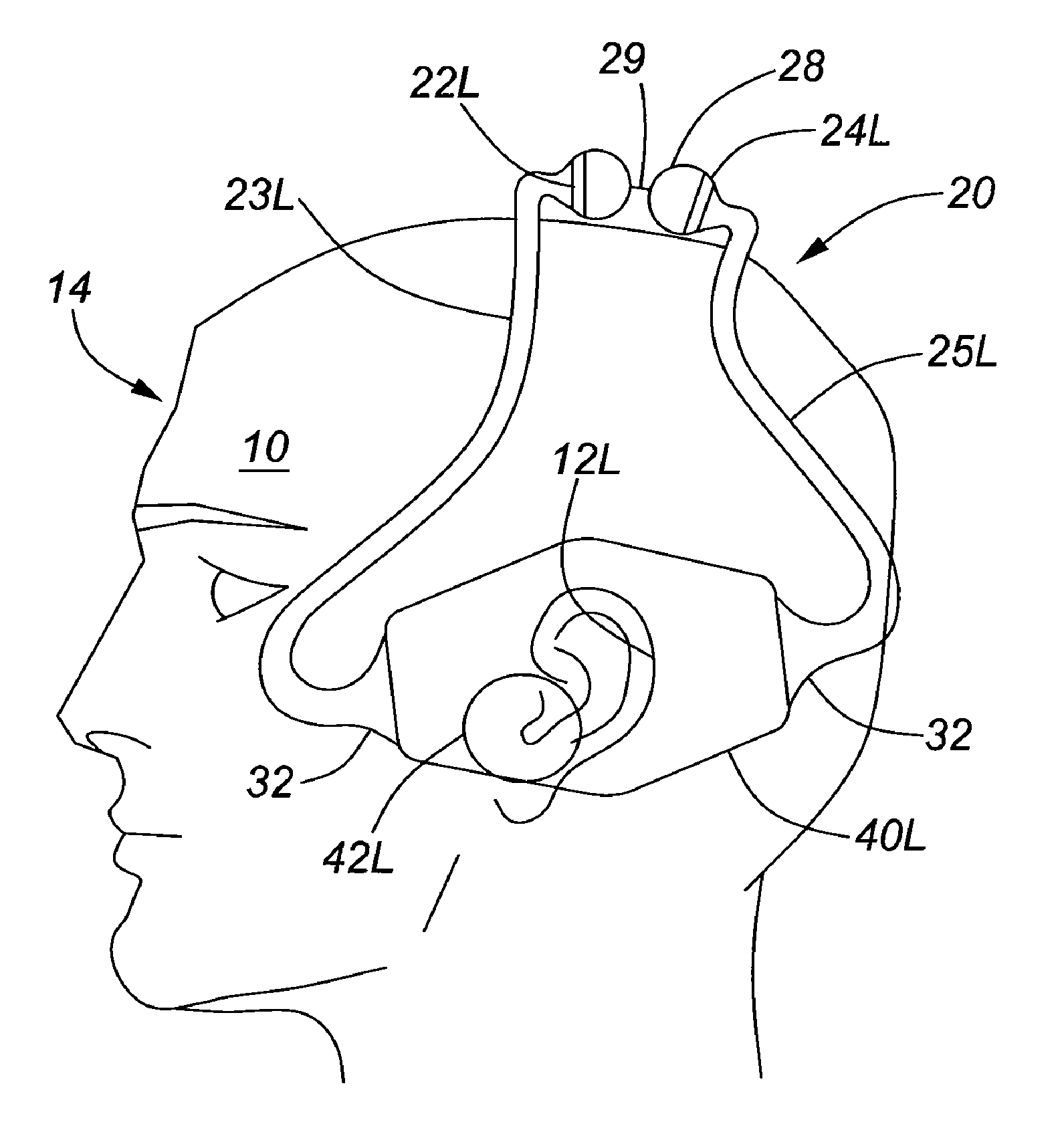
For example: (mounting of the loudspeakers mounted on the head support (in figure only the left side: left front 22L and left rear 24L both ported to the left ear)
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Mounting transducers in general |
This place covers:
For example:
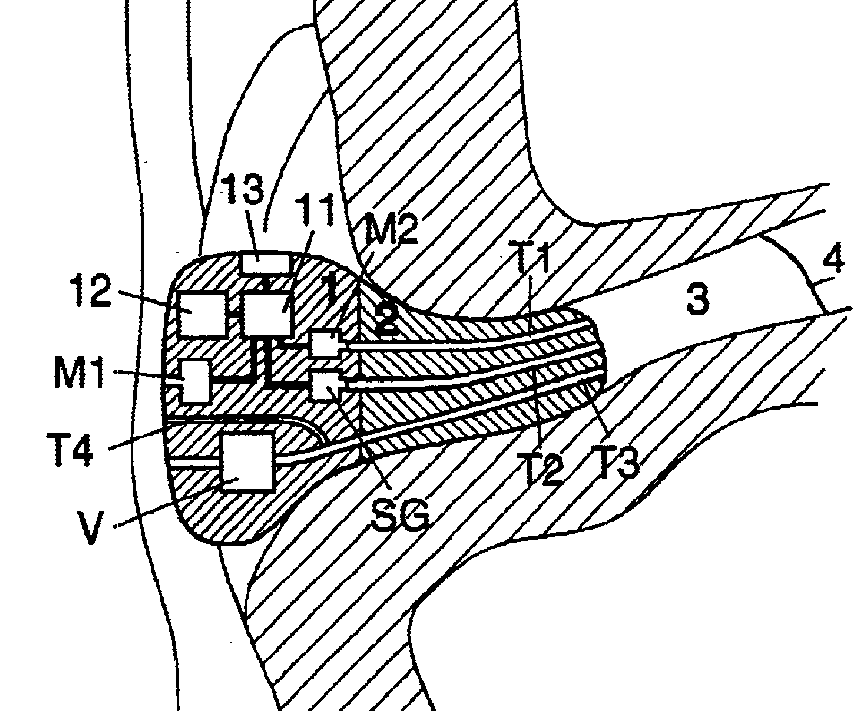
A personal noise exposure dose meter integrated in an active hearing protective communications earplug, comprising a main section 1 containing two microphones an outer microphone M1 and an inner microphone M2, and a sound generator SG, which are used for active noise control. A sealing section 2 is attached to the main section. An acoustic transmission channel T1 connects microphone M2 to the inner portion of the meatus 3. Microphone M2 therefore picks up the sound present in the meatus 3, just outside the eardrum (tympanum) 4. An acoustic transmission channel T2 connects sound generator SG to the inner portion of the meatus 3. The sound generator SG may provide audible information to the user, in form of warning signals or synthetic speech.
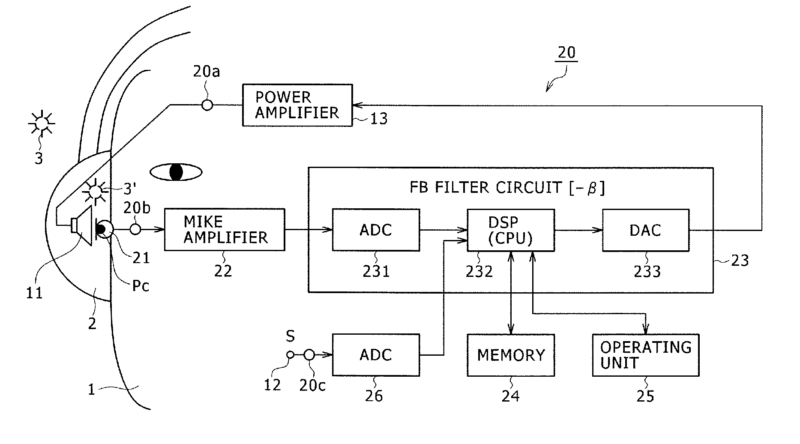
For example:
Noise reduction using feedback (23):
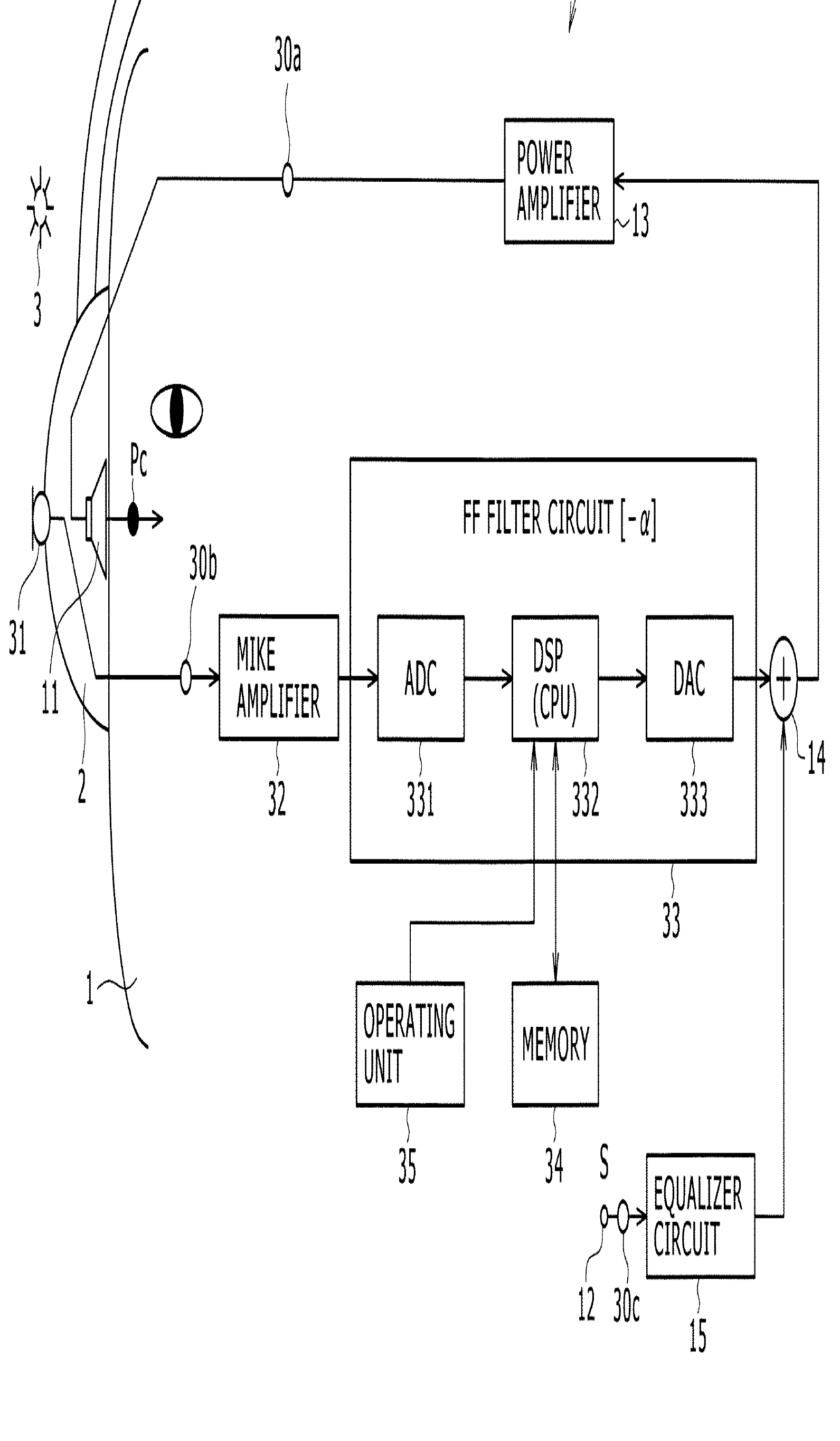
Noise reduction using feedforward (33).
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Protective devices for the ear, e.g. providing acoustic protection | |
Active noise reduction per se | |
Active noise control in general for microphones or earphones |
Further detail is covered by Indexing Code group H04R 2460/01. Classification is obligatory.
Examples of places in relation to which this place is residual:
Earpieces of the supra-aural or circum-aural type | |
Earpieces of the intra-aural type | |
Accumulators or arrangements for charging | |
Cables or cables storage, e.g. cable reels | |
Mechanical or electronic switches, or control elements | |
Earpiece supports, e.g. ear hooks | |
Manufacture or assembly | |
Reduction of ambient noise |
Further detail is covered by Indexing Code groups H04R 2201/103, H04R 2201/105, H04R 2201/107, H04R 2201/109, H04R 2420/07, H04R 2420/09, H04R 2460/03, H04R 2460/05, H04R 2460/07, H04R 2460/13, H04R 2460/15 and H04R 2460/17. Classification is obligatory.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Mouthpieces in general | |
Earpieces in general | |
Ear wax barrier for hearing aids | |
Hygienic or sanitary devices on telephone equipment |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Mouthpieces in general | |
Special adaptations for use as contact microphones | |
Transceivers carried on the body, e.g. in helmets |
This place does not cover:
Arrangements for obtaining desired frequency or directional characteristics for stereophonic purposes |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Speech enhancement by processing of the speech signal |
This place covers:
Arrangements where the focus lies in the way the desired frequency characteristic is obtained
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Arrangements in hearing aids for obtaining desired frequency characteristic |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Circuits for combining transducers having different responses |
If a directivity effect is also addressed classification in H04R 1/32 or subgroups as additional information is required as well
This place covers:
Transducer enclosure modified by provision of mechanical or acoustic impedances to achieve a desired frequency or phase response, e.g. enclosures:
- of the bass reflex type,
- of the bandpass type,
- using passive membranes,
- using acoustic labyrinths or transmission lines,
- using back-loaded horns.
- with adjustable volume
- Virtual enlargement by e.g. zeolytes.
Transducer mountings or enclosures modified to reduce undesired resonances, i.e. standing waves within enclosure, or of vibrations, i.e. of the enclosure itself, by e.g.:
- damping materials in the enclosure,
- enclosure stiffening structures,
- Helmholtz resonators,
- special mountings of transducers.
This place does not cover:
Combinations of transducers with horns, i.e. front loaded horns |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Transducer mounting in telephone equipment improving the acoustic characteristics by means of constructional features of the housing, e.g. ribs, walls, resonating chambers or cavities. |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Mountings for loudspeaker in general | |
Mountings for microphones in general | |
Circuits for combining transducers having different responses |
Applications of the mountings or enclosures for loudspeaker transducers is to be classified in H04R 1/2803.
Further detail is covered by the subgroup of Indexing Code group H04R 2201/029. Classification is obligatory.
This place covers:
Example for porous material (12) for virtual volume increase, to improve bass response:
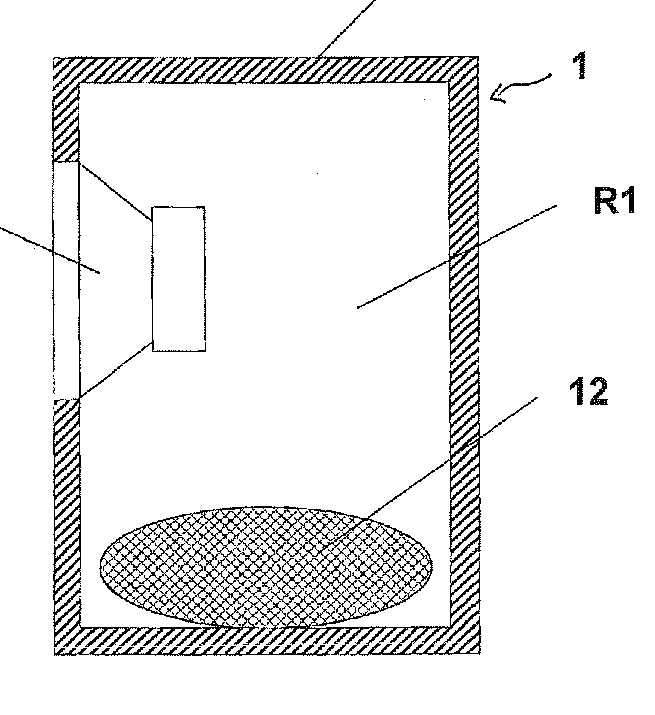
Example for porous carbon material (20) for virtual volume increase, to improve bass response, membrane (22) is to prevent moisture from reaching the porous carbon material; membrane acoustically transparent)
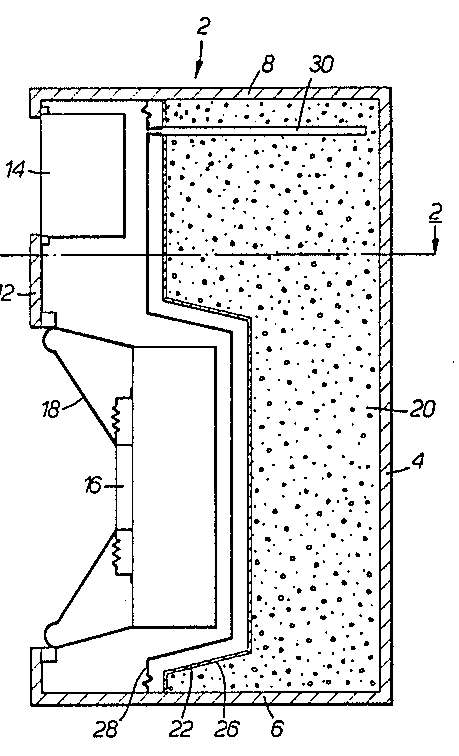
The use of porous materials in loudspeaker enclosures for equivalent volume increase is classified under H04R 1/2803). For mid- and high-frequencies the porous material works as a damping material too. Thus classification in H04R 1/2876 or Indexing Code may be required if this aspect is addressed as well.
This place covers:
Example (for H04R 1/2811): movable side wall (4) for varying volume to adapt frequency response:
Example (for H04R 1/2811): left-hand figure amplified bass, and right-hand figure normal bass:

This place covers:
Illustrative examples of subject matter classified in this place:
1. Vent with variable length

2. Shape of the vent
3. Shape and structure of the vent
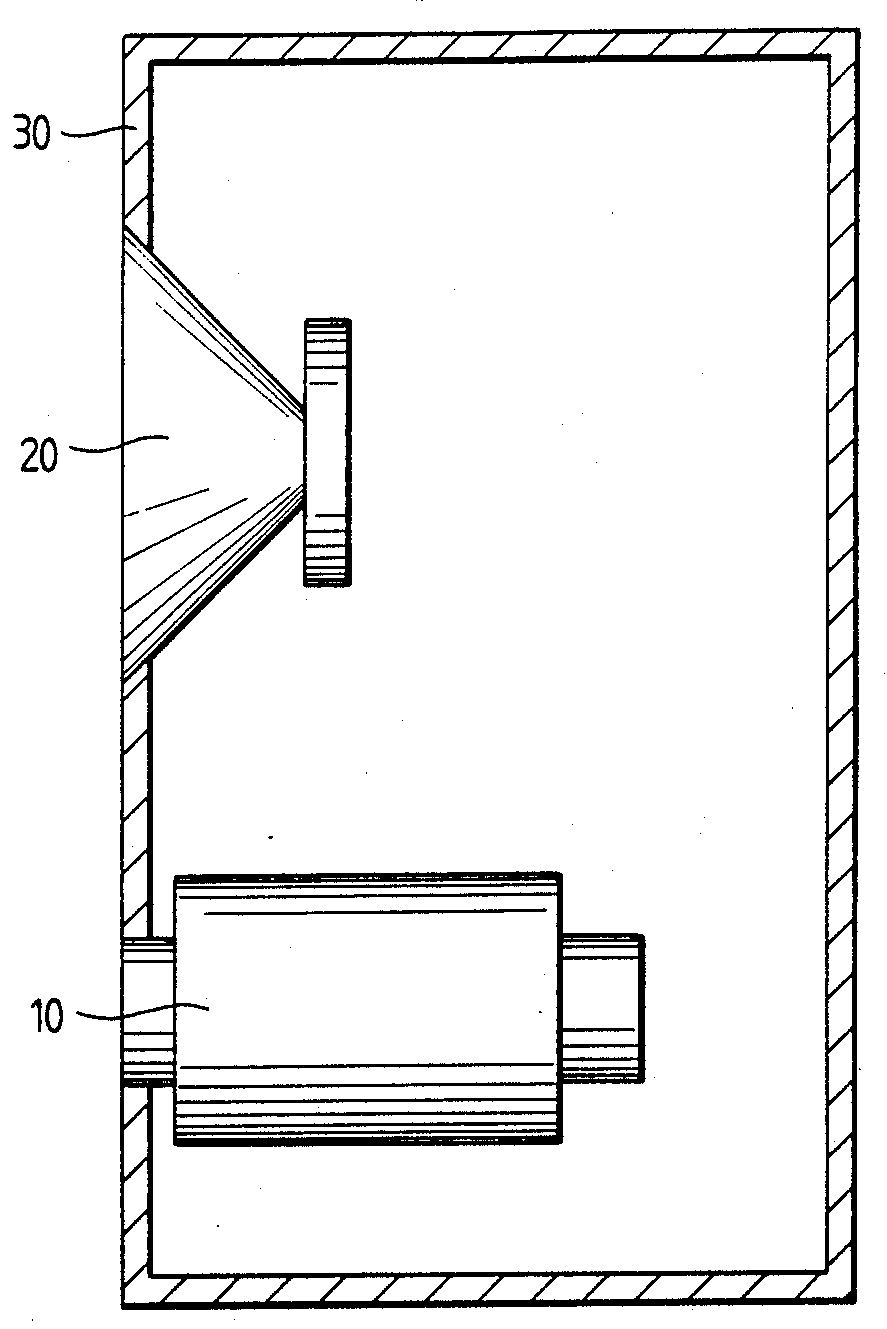
4.

Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Vents in bandpass type enclosures |
- Passive diaphragms or their suspension (invention) and being used in a bandpass type enclosure is classified in in H04R 1/283 or H04R 1/2834 (invention information), but H04R 1/2838 or H04R 1/2842 (additional information) is to be given as well;
- Passive diaphragms or their suspension themselves are to be classified as diaphragms for transducers, i.e. in H04R 7/00 or H04R 31/003 (invention or additional information) where appropriate, but H04R 1/283 or H04R 1/2834 (additional information) is to be given as well.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Passive diaphragm | Diaphragm driven by a fluid and providing an acoustic impedance |
This place covers:
For example (for H04R 1/2842):
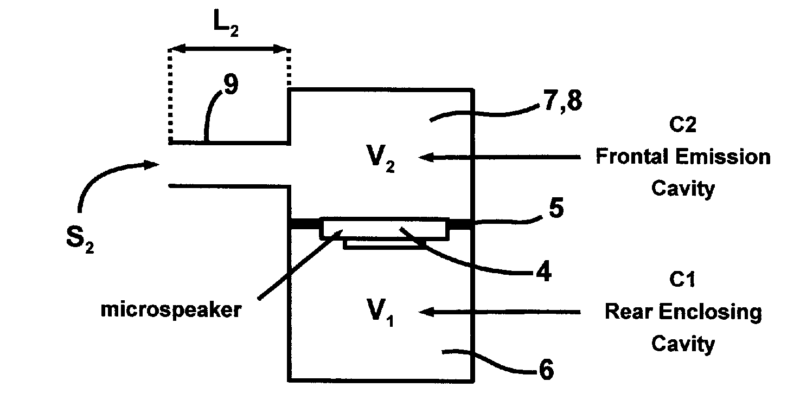
(vent 9 is not tuned to the wavelength)
Example 1st classification rule (the vent is replaced by a passive membrane):

Example 2nd classification rule (vent replaced by tube tuned to the wavelength)
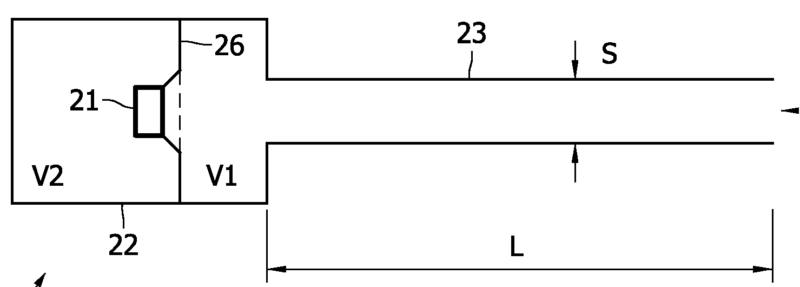
- Bandpass type enclosures (invention) and using a passive membrane should be classified in H04R 1/2838 or H04R 1/2842 (invention information), but H04R 1/283 or H04R 1/2834 (additional information) is to be given as well.
- Bandpass type enclosures (invention) and using an acoustic labyrinth of transmission line should be classified in H04R 1/2838 or H04R 1/2842 (invention information) but H04R 1/2853 or H04R 1/2857 (additional information) is to be given as well.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Vents in bass reflex type enclosures |
This place covers:
Enclosures using an acoustic labyrinth or a transmission line. The acoustic labyrinth or the transmission line can be open or closed.
For example (for H04R 1/2857):
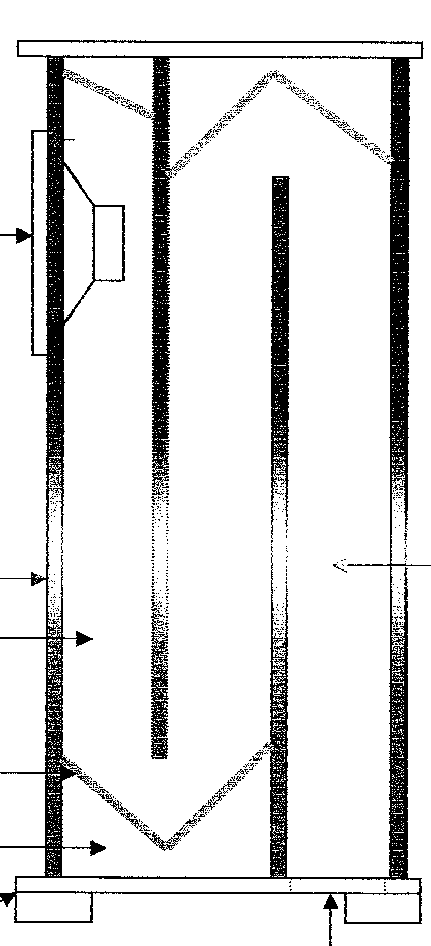
The length of the top tubular part is tuned to the wavelength.
Acoustic labyrinths or transmission lines (invention) and being used in a bandpass type enclosure is classified in H04R 1/2853 or H04R 1/2857 (invention information), but H04R 1/2838 or H04R 1/2842 (additional information) is to be given as well.
This place covers:
Enclosures using a back-loaded horn. The horn has an aperture surface area that increases with distance from the transducer along the horn axis.
This place covers:
Reduction of undesired resonances not covered by its subgroups, e.g. by means of Helmholtz resonators
This place does not cover:
The use of damping material to tune vents | |
The use of damping material to tune transmission lines |
This place covers:
Illustrative examples of subject matter classified in this place:
1. Stiffening panels inside the enclosure

2. Shape of the enclosure to reduce reflexions within the enclosure

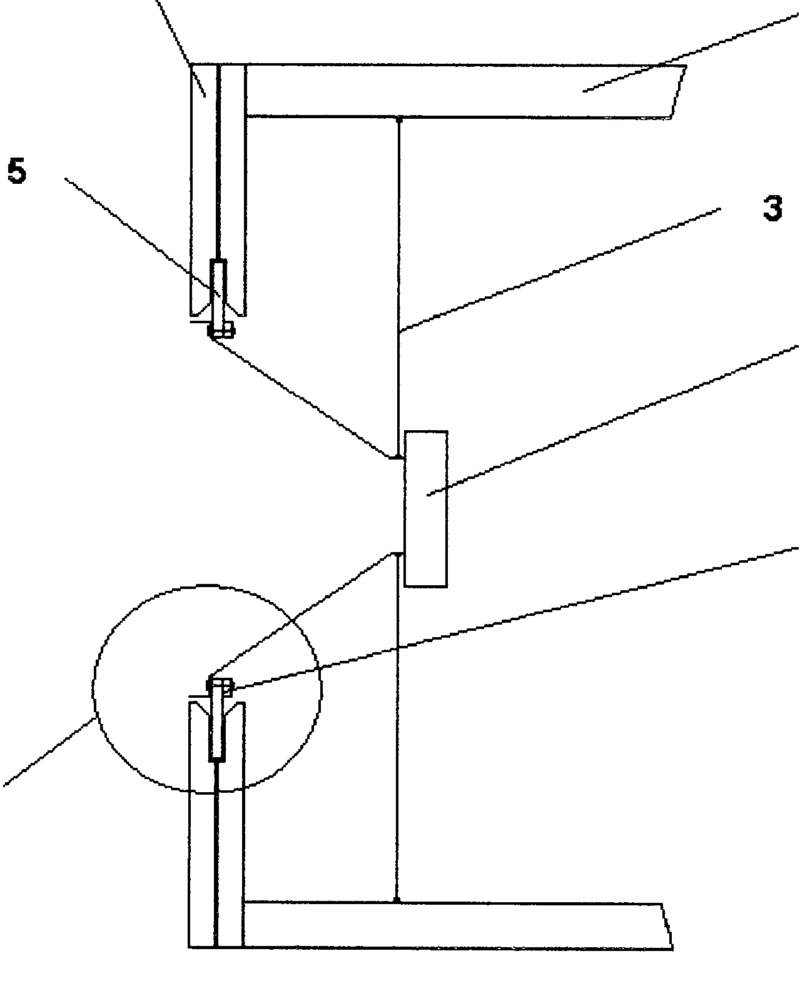
This place covers:
For example (for H04R 1/2896): DE202004017450U (rubber transducer mounting), US2005152570.
For example (for H04R 1/2896):
Rubber transducer mounting (5) combined with flexible cables (3):
Elastic mounting (20) with dampening buffer element (30)
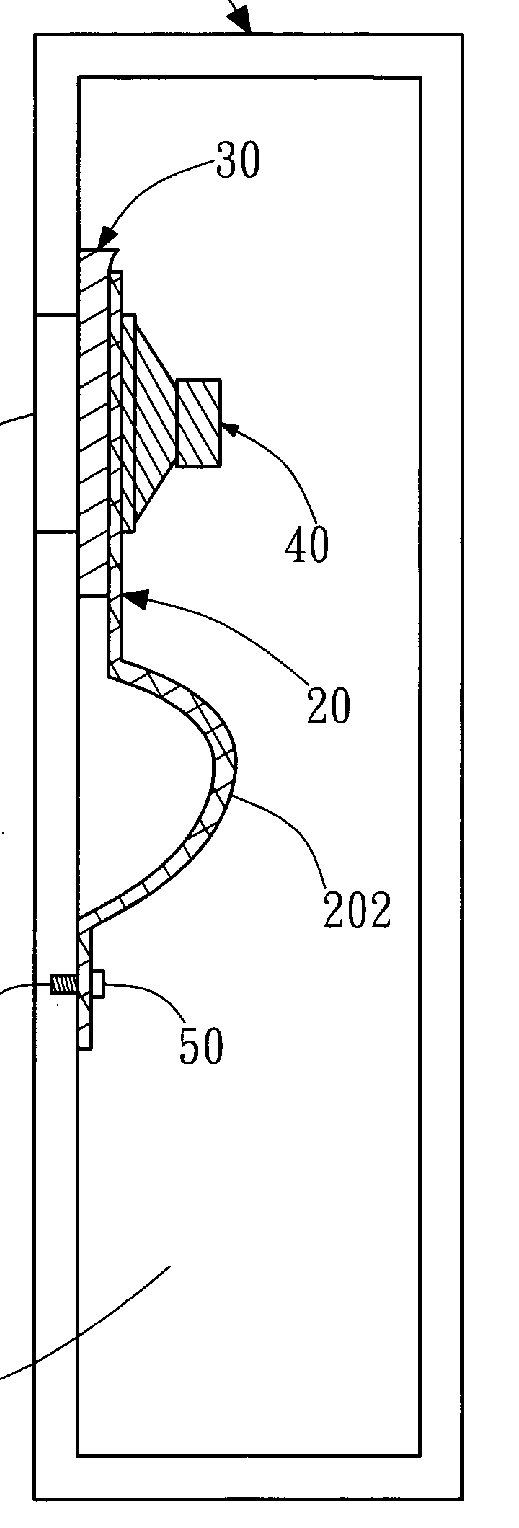
This place covers:
Combinations of transducers with front-loaded horns; Enclosures using front-loaded horns, the acoustic horns predominantly being characterised by the mechanical matching, even though a directivity effect is also present
The horn has an aperture surface area that increases with distance from the transducer along the horn axis
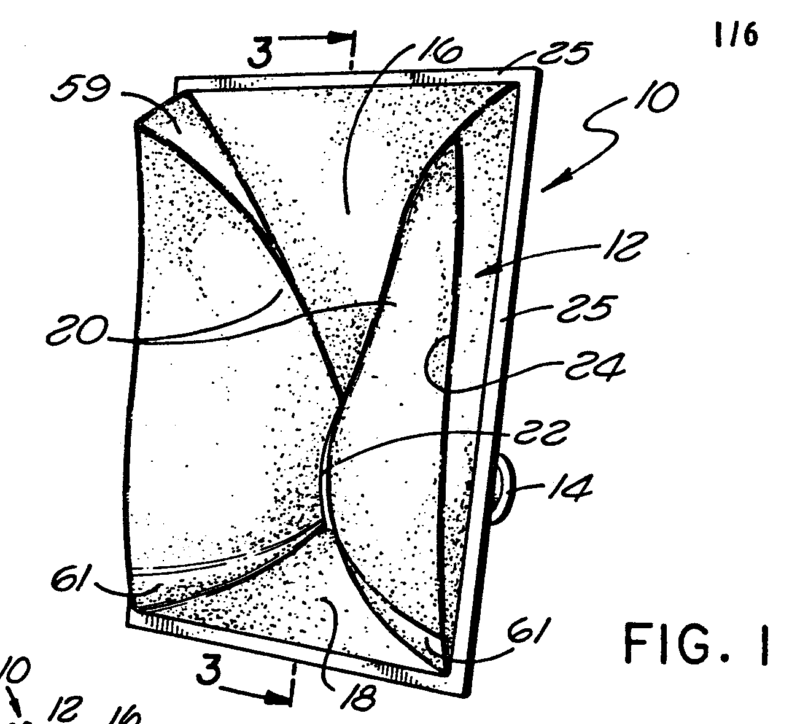
For example:
In the example shown on the left the exponential area increase is obtained by the combination of a cylindrical housing (1) with a flat sloped plate (3).
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Transducer enclosures or mountings using a back-loaded horn | |
Application of horns as guiding means to obtain a predetermined directivity characteristic | |
Horn in general |
Further detail is covered by the subgroup of Indexing Code group H04R 2400/13 listed below. Classification is obligatory.
This place covers:
Arrangements where the focus lies in the way the desired directional characteristic is obtained
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Arrangements in electric hearing aids for obtaining desired directional characteristic |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Mounting transducers, e.g. provided with mechanical moving or orienting device |
- If a frequency effect is also addressed, classification in H04R 1/22 or subgroups as additional information is required as well.
- Further detail is covered by Indexing Code H04R 2410/01. Classification is obligatory.
This place covers:
Sound reflecting, diffracting, directing or guiding means, e.g. horns to obtain a desired directivity characteristic, acoustic lenses, tubes, or phase plugs
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Arrangements specially adapted for hearing aids |
This place covers:
For example: (horn (top figure) used to obtain predetermined directivity (lower figures)

For example: (plurality of plates (210) functioning as an acoustic lens).
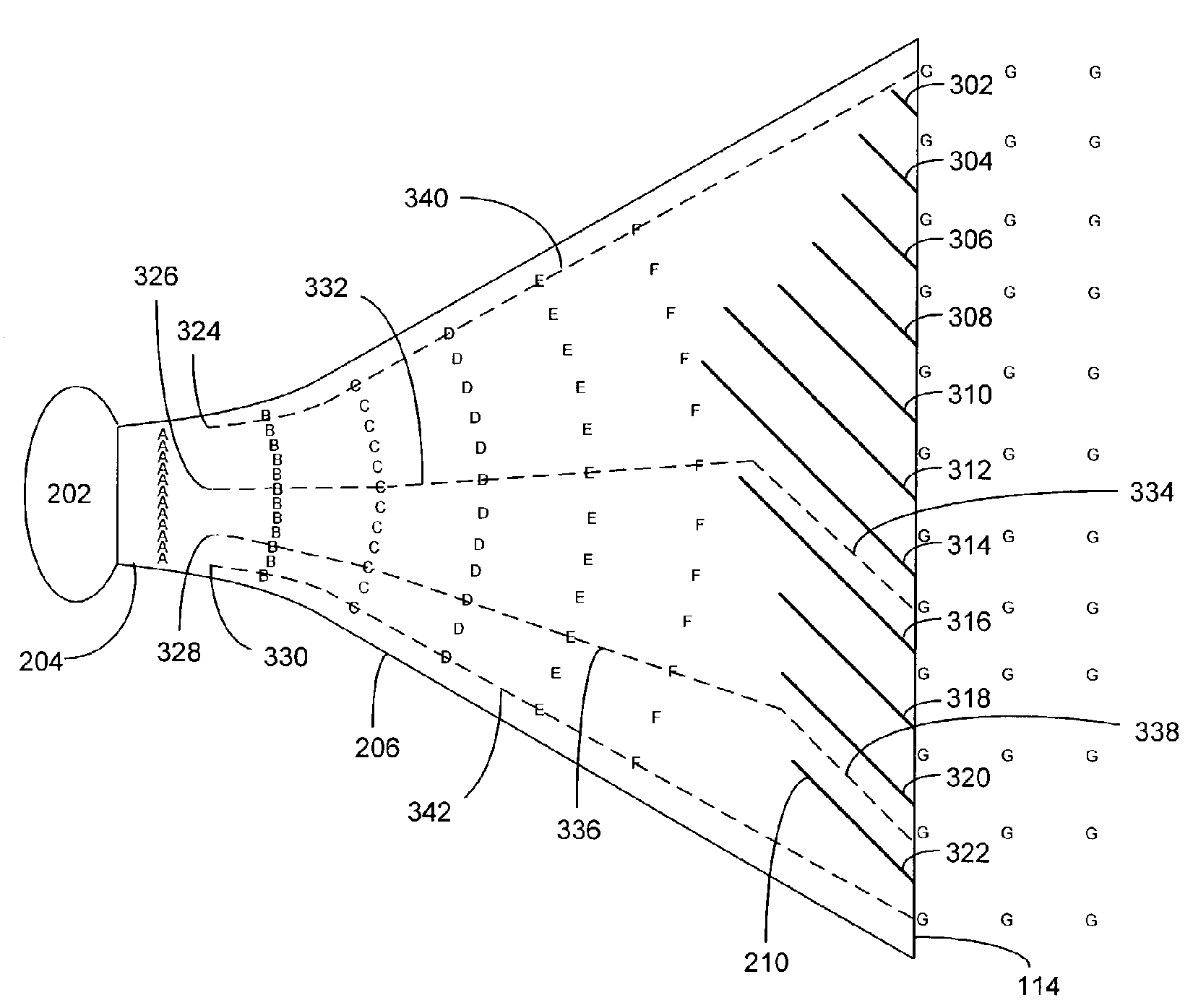
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Horn-loaded compression drivers and impedance frequency matching | |
Single aperture acoustic lenses | |
Methods or devices for sound-focusing or directing |
Further detail is covered by Indexing Code group H04R 2201/34 listed below. Classification is obligatory.
This place covers:
For example:
This place covers:
Such an aperture functions as an acoustic lens
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Other types of acoustic lenses |
This place does not cover:
Combining a number of identical transducers for stereophonic purpose |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Combining a number of identical transducers specially adapted for electric hearing aids |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Circuits for distributing signals to two or more loudspeakers | |
Constructional aspects of beam steering | |
Sound-focusing or directing using electrical steering of transducer arrays, e.g. beam steering |
Further detail is covered by the subgroups of Indexing Code group H04R 2201/40. Classification is obligatory.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Circuits for distributing signals of two or more loudspeakers |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Circuits for combining the signals of two or more microphones |
Further detail is covered by the subgroup of Indexing Code group H04R 2410/05. Classification is obligatory.
This place covers:
Circuits for transducers, e.g.:
- Motional feedback or like circuit arrangements for transducers.
- Circuits for combining the signals of two or more microphones.
- Protection circuits for transducers.
- Circuits for preventing acoustic reaction.
- Circuits for distributing a signal to a plurality of loudspeakers.
- Circuits for correcting the frequency response of transducers.
This place does not cover:
Arrangements for producing a reverberation or echo sound | |
Amplifiers |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Circuits for combining the signals of two or more microphones or loudspeakers specially adapted for electric hearing aids | |
Public address systems, e.g. circuits therefor |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Circuits for stereophonic arrangements | |
Driving circuits for generating mechanical vibrations of infrasonic, sonic or ultrasonic frequency (specially adapted for particular applications, see the relevant subclass) | |
Audio-frequency transformers or mutual inductances, i.e. not suitable for handling frequencies considerably beyond the audio range | |
Low frequency amplifiers, e.g. audio preamplifiers | |
Power amplifiers using a combination of several semiconductor amplifiers | |
Combinations of amplifiers using coupling networks with distributed constants | |
Combinations of amplifiers, e.g. multi-channel amplifiers for stereophonics | |
Control of amplification | |
Remote control of amplification, tone or bandwidth | |
Arrangements for preventing acoustic feedback | |
Two-way loud-speaking telephone systems with means for conditioning the signal, e.g. for suppressing echoes for one or both directions of traffic | |
Stereophonic systems |
Further detail is covered by the subgroups of Indexing Code groups H04R 2201/401, H04R 2201/403, H04R 2201/405, H04R 2203/12, H04R 2410/07, H04R 2420/01, H04R 2420/03, H04R 2420/05, H04R 2430/01 and H04R 2430/03. Classification is obligatory.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Deaf aid | hearing aid, auditory prosthesis |
Stereophonic system | two- or more channel system, e.g. quadraphonic, ambisonic or similar systems |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Circuits for combining the signals of two or more microphones to obtain desired directional characteristics specially adapted for hearing aids | |
Circuits for combining the signals of two or more microphones, i.e. mixing, specially adapted for hearing aids |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Combining a number of identical transducers | H04R 1/40 and the subgroups of H04R 2201/40 |
Spatial or constructional stereophonic arrangement of microphones | |
Direction-finders for determining the direction from which infrasonic, sonic, ultrasonic, not having a directional significance, are being received | |
Systems for determining distance or velocity not using reflection or re-radiation and using ultrasonic, sonic, or infrasonic waves | |
Circuits for sound-focusing or directing using electrical steering of transducer arrays, e.g. beam steering | |
Speech recognition techniques specially adapted for robustness in adverse environments | |
Combining signals of a signal microphone and a noise microphone for speech processing | |
Beamforming for speech processing | |
Telephonic conference arrangements | |
Video conference systems |
Further detail is covered by Indexing Code groups H04R 2410/01, H04R 2410/05 and H04R 2430/20 and its subgroups. Classification is obligatory.
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Circuits for prevention of acoustic reaction specially adapted for electric hearing aids |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Synergistic effects of band splitting and sub-band processing | |
Tone control or bandwidth control in amplifiers |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Circuits for combining the signals of two or more loudspeakers to obtain a desired directivity characteristic specially adapted for hearing aids | |
Public address systems |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Directing sound using electrical steering of transducer arrays, e.g. beam steering |
Further detail is covered by Indexing Code groups H04R 2203/12 and H04R 2430/20. Classification is obligatory.
This place covers:
Spatial or constructional arrangements of loudspeakers or of electro-acoustic devices for stereophonic purposes or specific circuit arrangements therefor, e.g.
- aspects relating to docking-station type assemblies to obtain an acoustical effect,
- positioning of loudspeakers for spatial sound reproduction,
- plurality of transducers corresponding to a plurality of sound channels in each earpiece of headphones or in a single enclosure,
- single (sub)woofer with two or more satellite loudspeakers for higher frequency band reproduction driven via the (sub)woofer,
- sound field microphones, or
- dummy heads
This place does not cover:
Stereophonic pick-ups, i.e. wherein signals are recorded or played back by vibration of a stylus in two orthogonal directions simultaneously |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Stereophonic system | two- or more channel system, e.g. quadraphonic, ambisonic or similar systems |
This place covers:
Spatial or constructional arrangements of loudspeakers or loudspeaker transducers for stereophonic reproduction, e.g.
- aspects relating to docking-station type assemblies to obtain an acoustical effect,
- positioning of loudspeakers for spatial sound reproduction,
- plurality of transducers corresponding to a plurality of sound channels in each earpiece of headphones or in a single enclosure, or
- single (sub)woofer with two or more satellite loudspeakers for higher frequency band reproduction driven via the (sub)woofer.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Mounting radio sets or communication systems in helmets | |
Mounting of acoustic transducers in vehicles |
Further detail is covered by Indexing Code groups H04R 2205/021, H04R 2205/022, H04R 2205/024 and H04R 2205/026. Classification is obligatory.
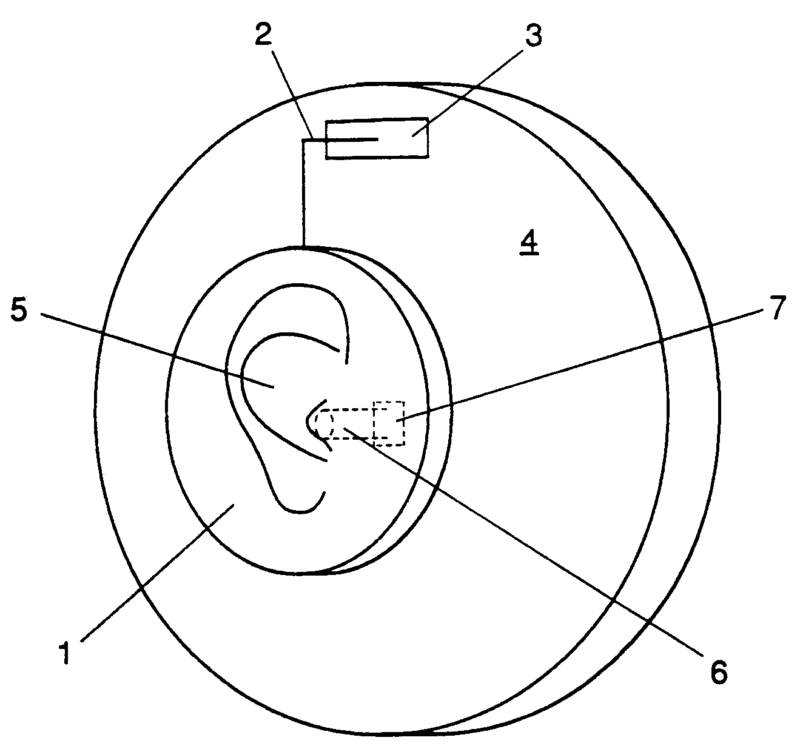
This place covers:
Spatial or constructional arrangements of microphones or microphone transducers for stereophonic sound capture.
For example (dummy head):
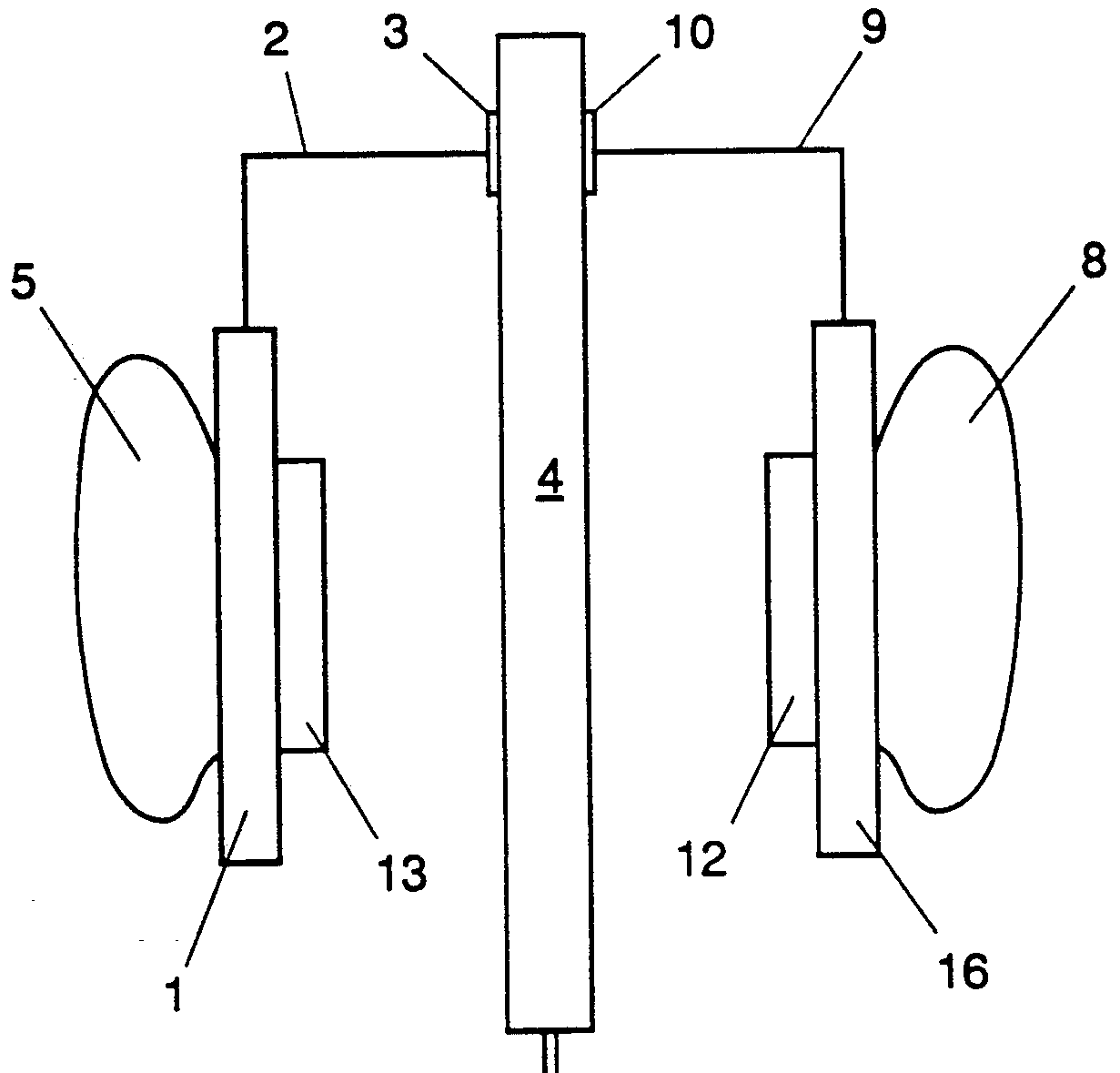
For example (sound field microphone):
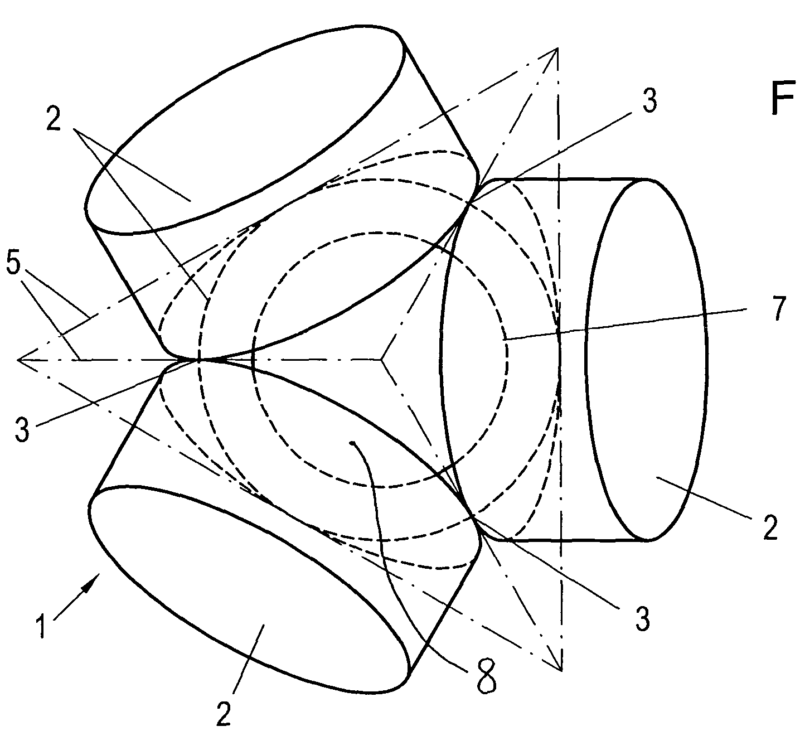
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangements for obtaining desired frequency or directional characteristics by combining a number of identical transducers microphones | |
Circuits for combining the signals of two or more microphones for non-stereophonic purposes | |
Hearing aid circuits for combining signals of transducers | |
Binaural hearing aids | |
Details of transducer arrays |
This place does not cover:
Details thereof, e.g. relating to batteries, cables or control elements | |
Transceivers carried on the body, e.g. in helmets | |
Sound field enhancement in stereophonic headphones |
- Concerning inventions relating to hearing devices, if an application describes and shows the invention using only embodiments relating to ear- or headphones then H04R 1/10 or subgroups or H04R 5/033 or subgroups should be given as invention information. Dependent on the case, the mere statement that the invention is also applicable to hearing aids may render classification under H04R 25/00 useful, but only as additional information. Only if specific non-trivial embodiments for hearing aids are also shown, classification under H04R 25/00 as invention information may be considered as well.
- Further detail is covered by the subgroups of Indexing Code groups H04R 2201/103, H04R 2201/105, H04R 2420/09 and H04R 2460/03. Classification is obligatory.
This place covers:
For example: segmented headband for easy storage of the headphone
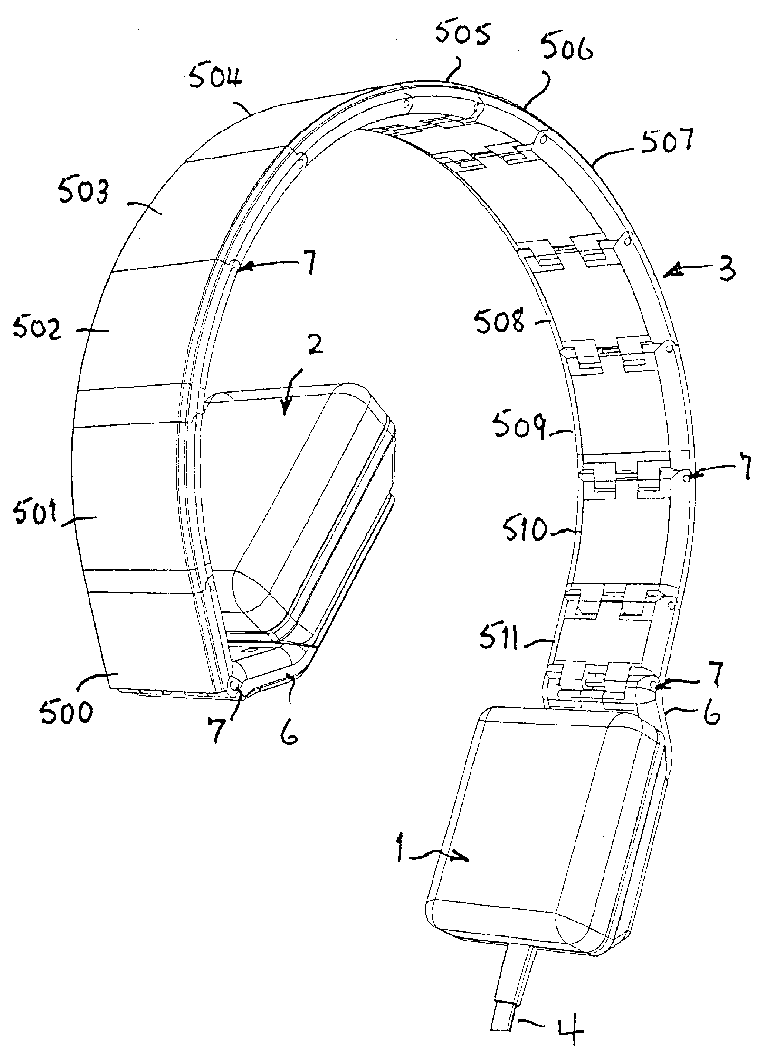
For example: (head support with loudspeakers mounted thereon (in figure only the left side: left front speaker 22L and left rear speaker 24L both ported to the left ear)

Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Earpiece support for monophonic headphones, e.g. earhooks |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Circuits or components specially adapted for stereophonic broadcast systems | |
Broadcast systems for the distribution of stereophonic information | |
Circuits or components specially adapted for stereophonic broadcast receiving | |
Stereophonic systems |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Testing of transducer, loudspeaker or microphone connection for non-stereophonic purposes | |
Amplifiers | |
Low frequency amplifiers, e.g. audio preamplifiers | |
Power amplifiers using a combination of several semiconductor amplifiers | |
Combinations of amplifiers using coupling networks with distributed constants | |
Combinations of amplifiers, e.g. multi-channel amplifiers for stereophonics | |
Control of amplification | |
Remote control of amplification, tone, or bandwidth | |
Transmission systems for stereophonic reception | |
Powerline communication in general | |
Audio/video applications of powerline communications |
Further detail is covered by Indexing Code groups H04R 2205/041, subgroups of H04R 2420/00, and H04R 2430/01. Classification is obligatory.
This place covers:
- Diaphragms for electromechanical transducers.
- Cones
- Mountings thereof, e.g. outer suspension.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Apparatus or processes specially adapted for the manufacture of diaphragms or surrounds for transducers | |
MEMS structures allowing for movement | |
Type of movement | |
Diaphragms in general | |
Pressure measurement / constructional details associated with semiconductive diaphragm sensors, e.g. etching of diaphragms | |
Cones, diaphragms or the like, for emitting or receiving sound in general |
Further detail is covered by Indexing Code groups H04R 2207/021, H04R 2231/001, H04R 2231/003 and H04R 2307/021 - H04R 2307/029. Classification is obligatory.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
In vehicles | |
Projection screens allowing free passage of sound |
Further detail is covered by Indexing Code groups H04R 2440/01 and H04R 2440/07. Classification is obligatory.
This place covers:
For example: Upon excitation of diaphragm 1 by piezoelectric exciter 15 the diaphragm generating bending wave in itself and eventually produces sound by resonating.
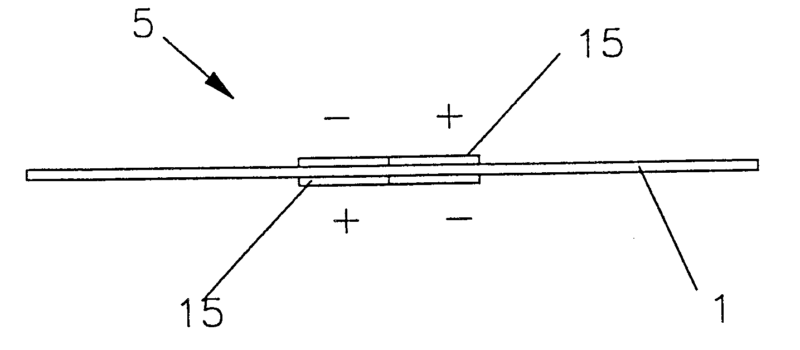
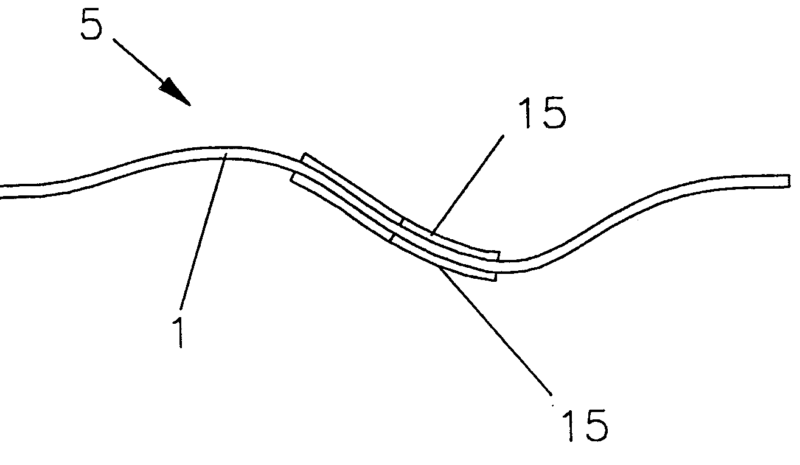
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Using non-resonant travelling waves | |
Touch screens using propagation of acoustic waves |
Further detail is covered by Indexing Code groups H04R 2440/03 and H04R 2440/05. Classification is obligatory.
This place covers:
For example: DE202007016414 (air motion transformer).
For example: ribs to provide rigidity to the central part of the loudspeaker diaphragm
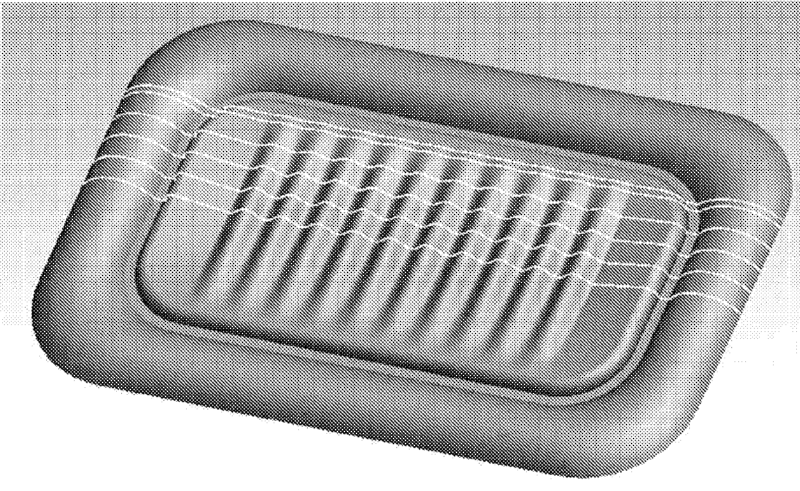
For example: air motion transformer (AMT) with a meander shaped diaphragm and air pockets (6). Upon energising the transformer (current through conductors 2) and due to the magnetic field perpendicular to the current, the air in the pockets is pushed out or pulled in, thus producing sound.
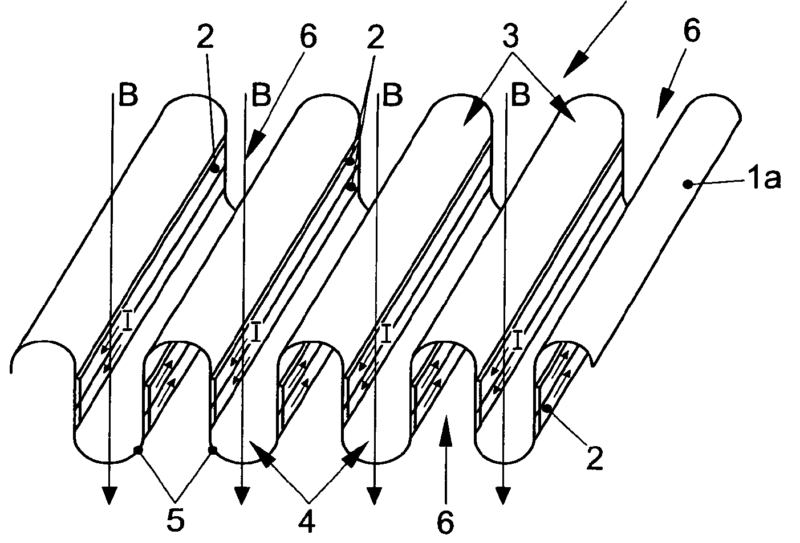
This place covers:
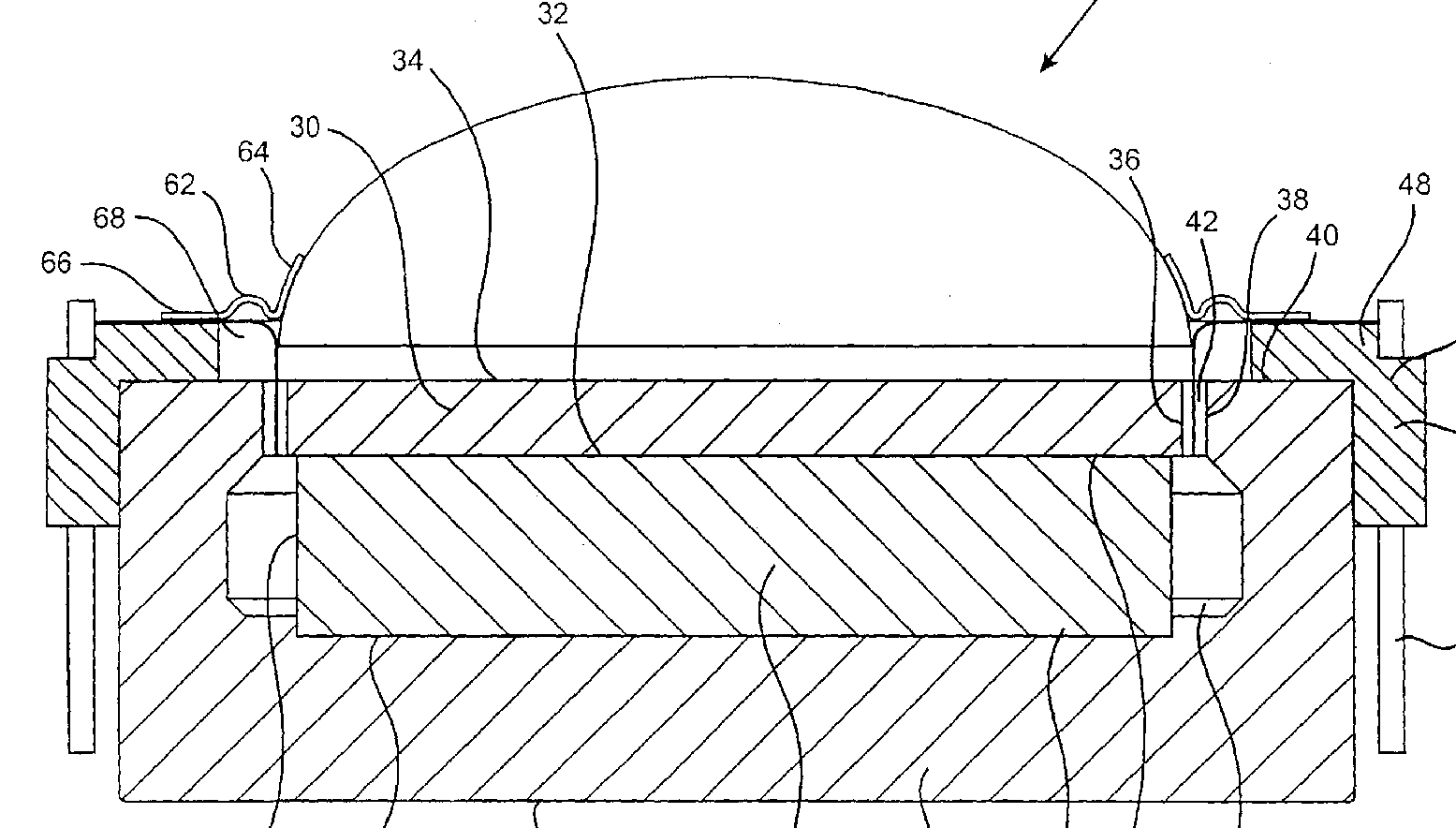
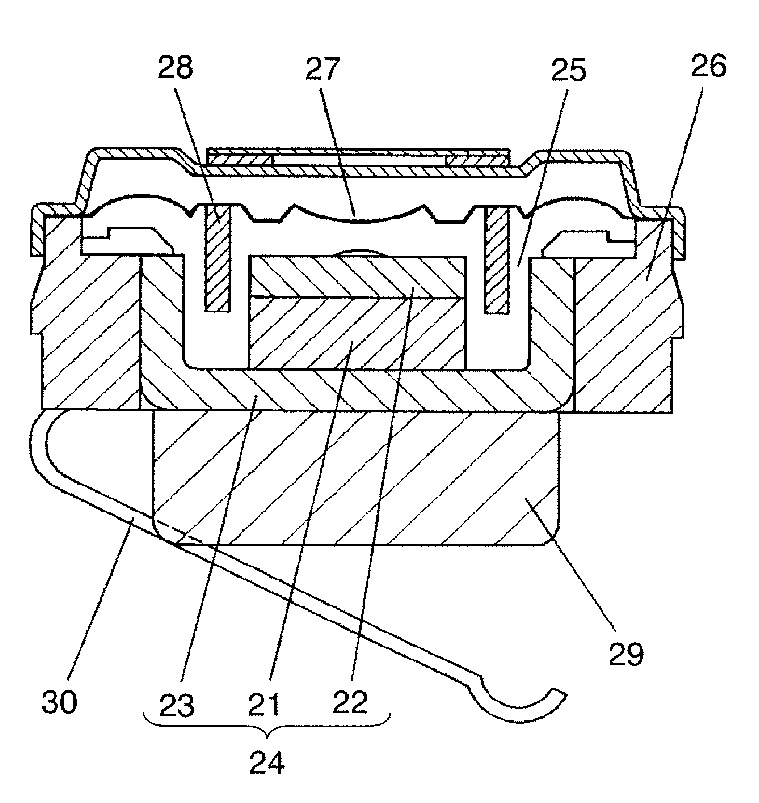
For example: diaphragm is mounted to the frame (26) by surround (29) which is connected to the membrane (27) within its periphery (at 200)
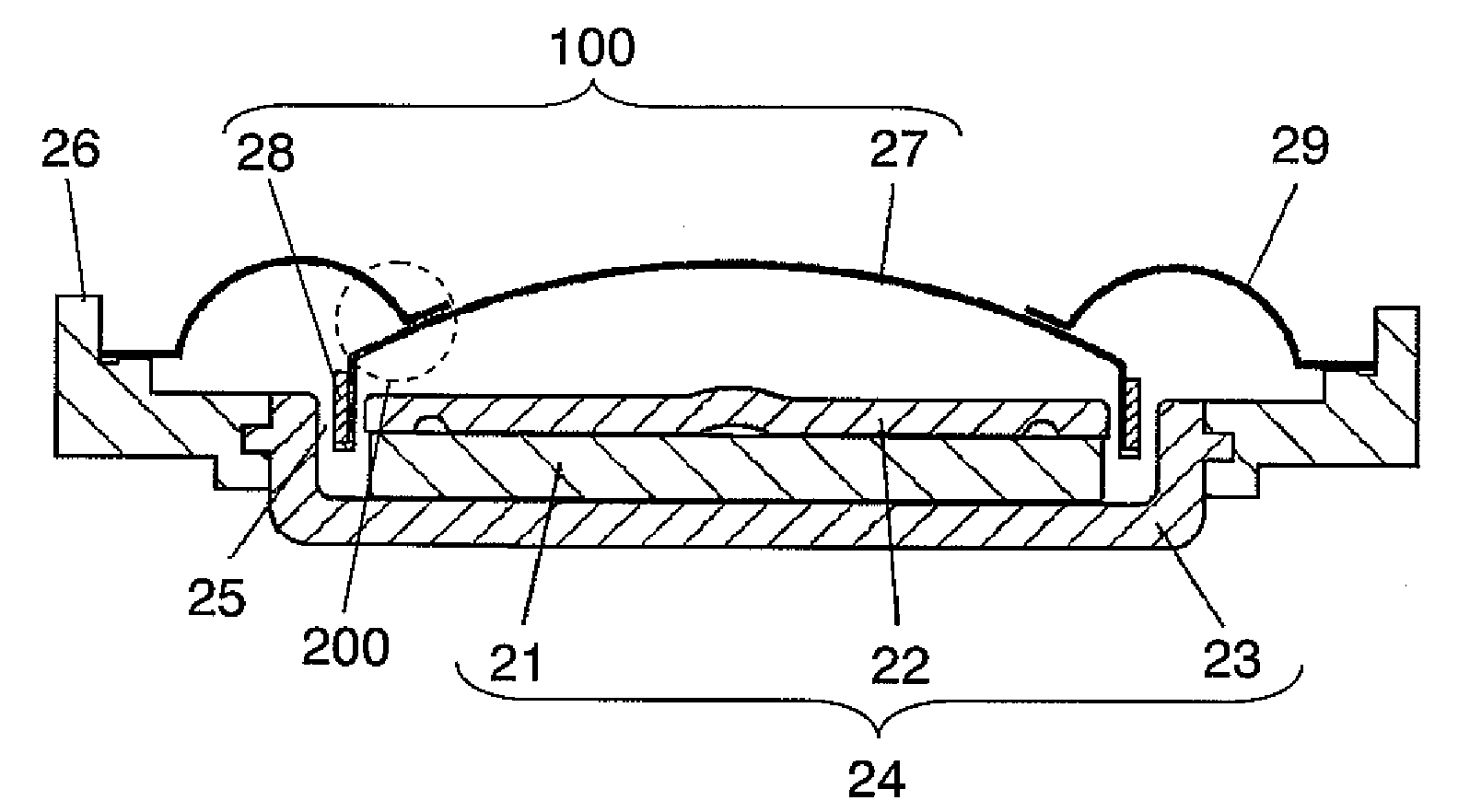
This place covers:
For example: membrane (2) is extended to form outer suspension (21), whose elastic properties are adapted by the elastic layer (22).

For example: membrane (34) divided in a suspension part (34A, 34B) and a central sound producing part (34C)
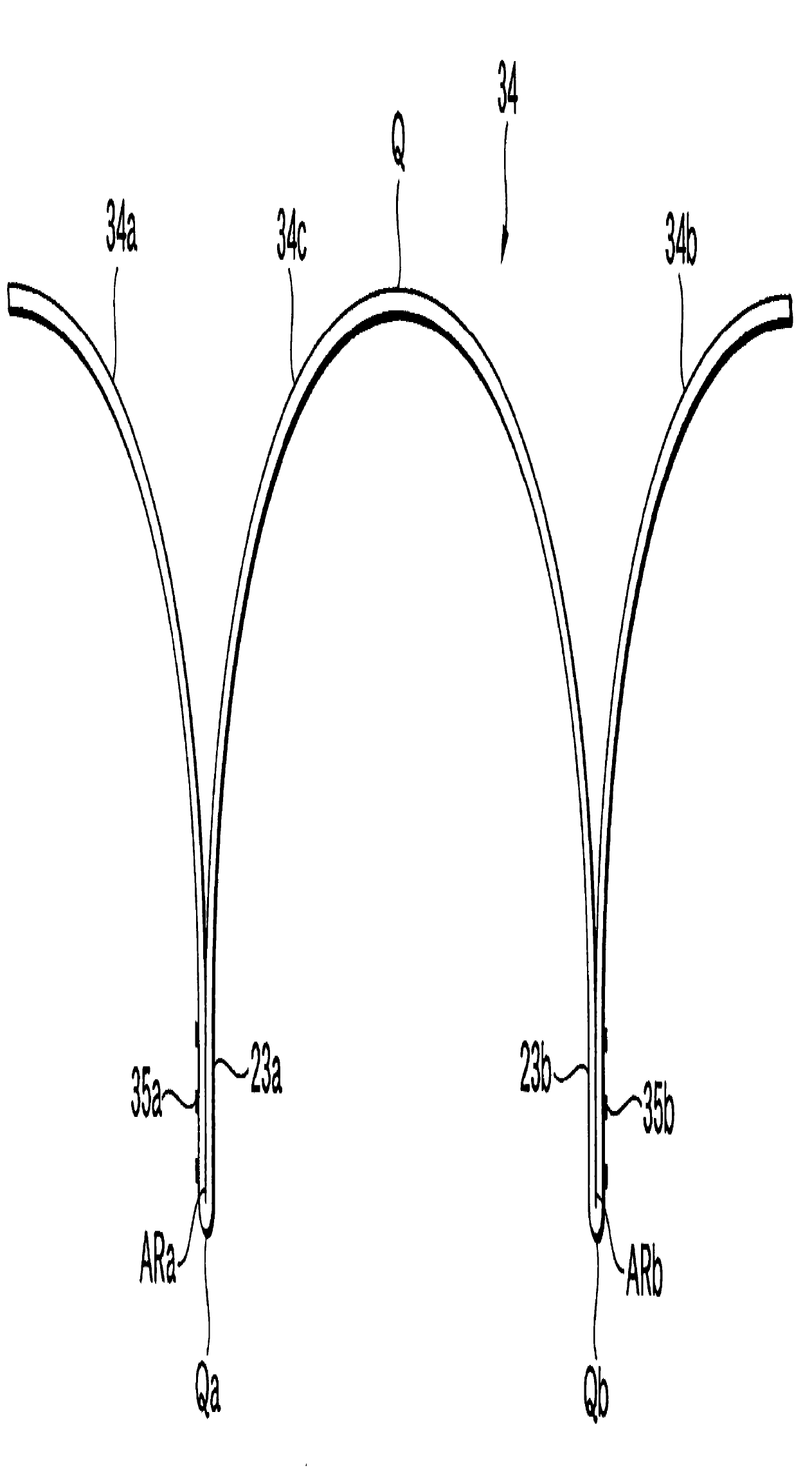
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Manufacture of surrounds |
This place covers:
For example:

Further detail is covered by Indexing Code groups H04R 2231/001, H04R 2231/003, H04R 2307/201 - H04R 2307/207. Classification is obligatory.
This place covers:
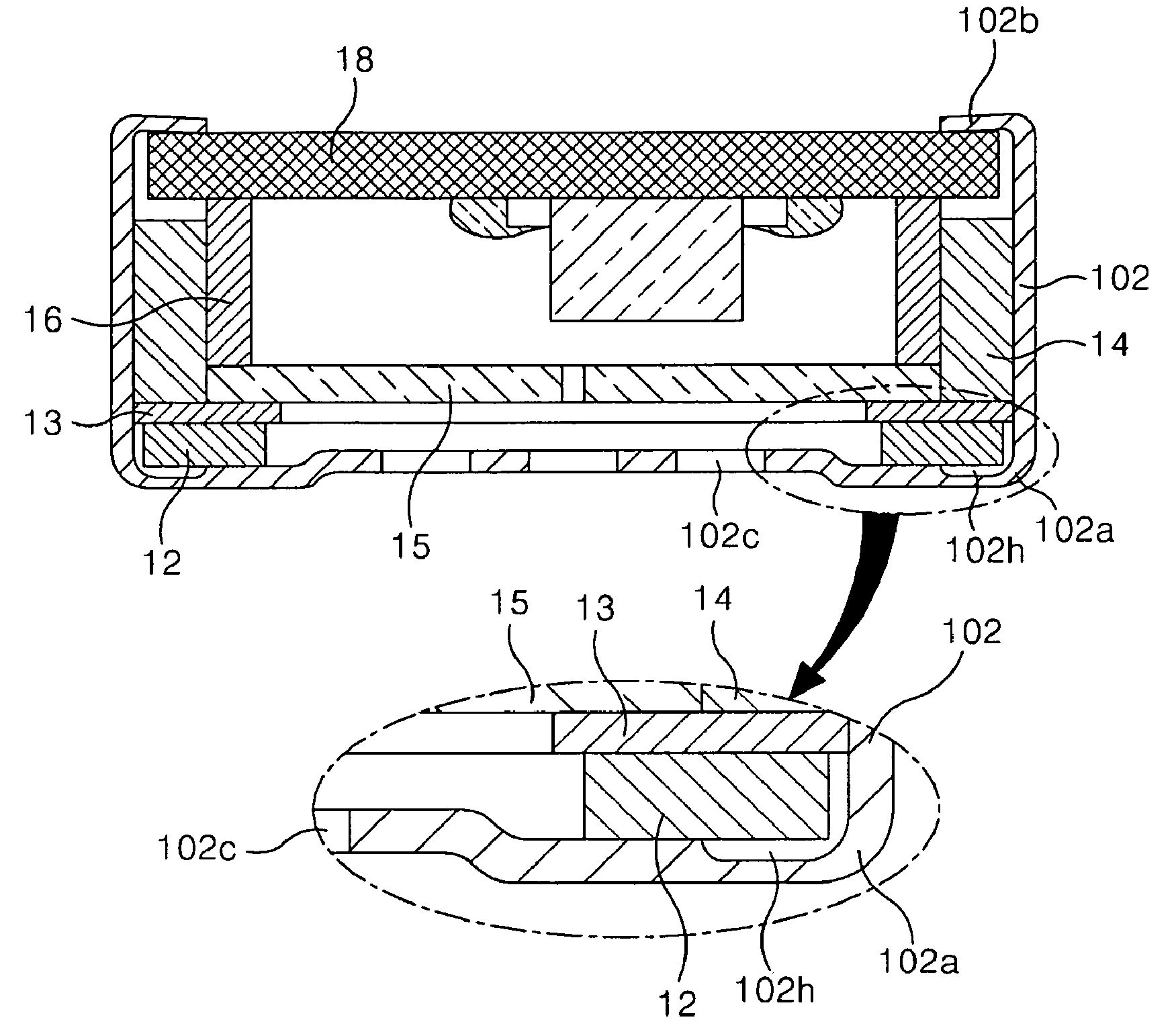
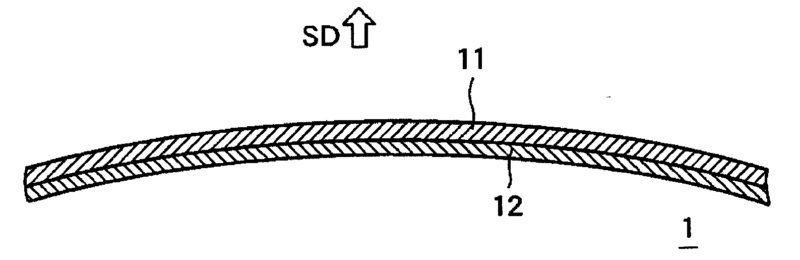
For example: Microphone comprising a vibrating plate (12) with polar ring which is clamped via a spacer (13) between base (14, 16) and the casing (102). Groove 102h is formed to prevent deformation of the polar ring which would negatively affect the acoustic properties membrane (2) is extended to form outer suspension (21), whose elastic properties are adapted by the elastic layer (22).
This place covers:
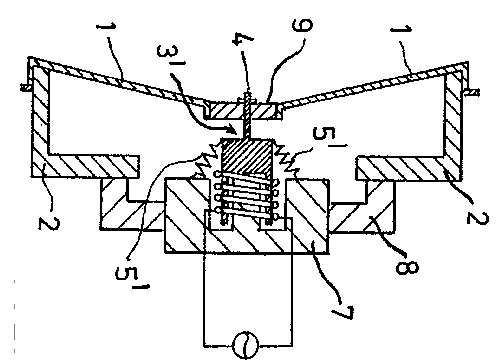
For example: EP0330423.
For example: tensioning by springs 5'
This place covers:
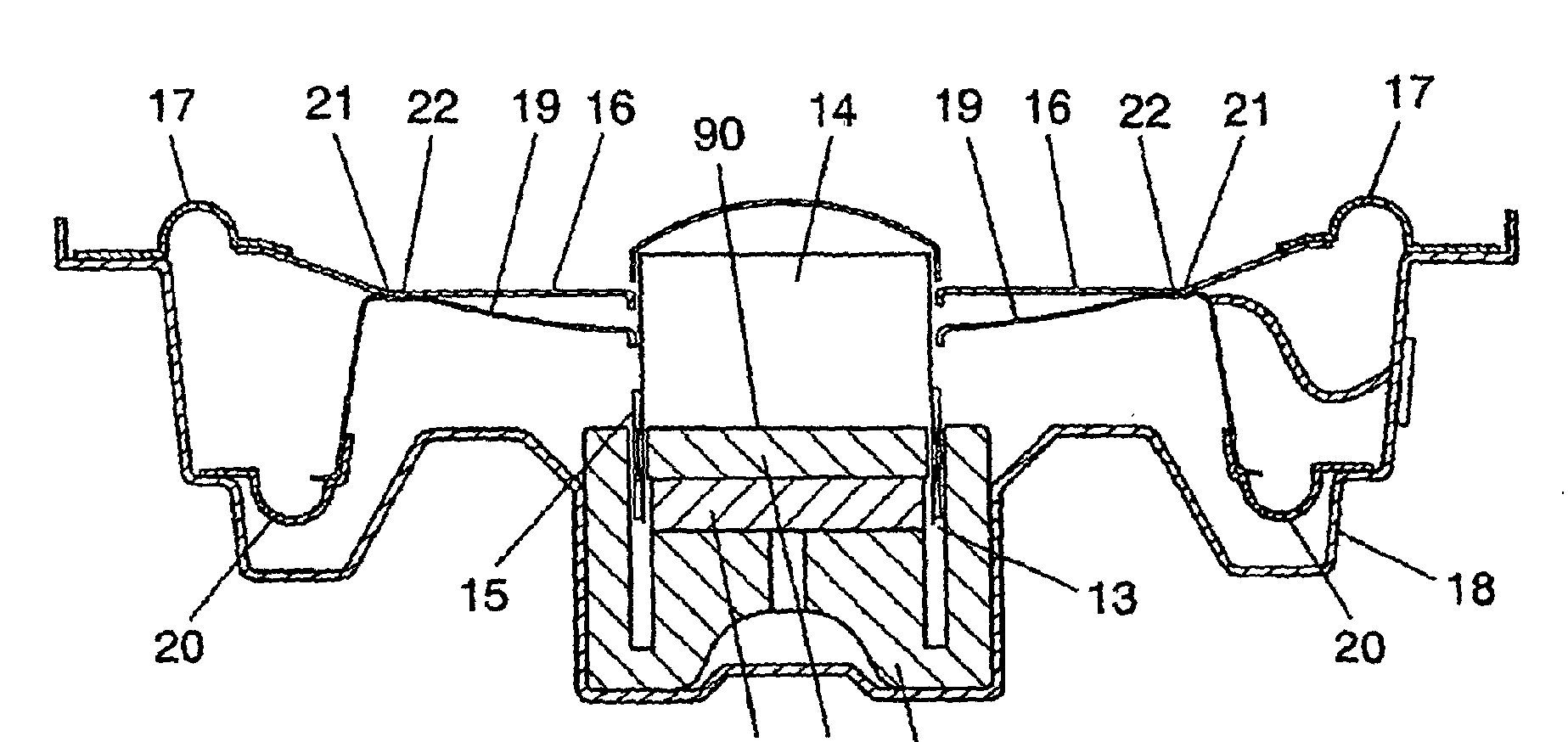
For example: damping by elastic material 27
For example: sound producing diaphragm provided with a damping layer (12) to dampen vibration in the diaphragm
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Transducer mountings or enclosures providing mechanical or acoustic impedances by air damping |
This place covers:
Transducers of moving-coil, moving-strip, or moving-wire type, e.g.
- general constructional aspects thereof
- cooling aspects;
- constructional aspects of the magnetic circuit, e.g. to reduce eddy currents or stray flux;
- aspects of the voice coil, i.e. mounting, construction or centring thereof
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Generating mechanical vibrations of infrasonic, sonic, or ultrasonic frequency operating with electromagnetism, e.g. using vibrating magnet, armature or coil system | |
Dynamo-electric motors with vibrating magnet, armature or coil system |
Further detail is covered by Indexing Code group H04R 2201/003 and the subgroups of Indexing Code group H04R 2440/00. Classification is obligatory.
This place covers:
- General constructional aspects of the transducers;
- Cooling aspects;
- Constructional aspects of the magnetic circuit, e.g. to reduce eddy currents or stray flux;
- Aspects of the voice coil, i.e. mounting, construction or centring thereof.
Further detail is covered by Indexing Code groups H04R 2209/021 - H04R 2209/027 and the subgroups of Indexing Code group H04R 2400/00. Classification is obligatory.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Manufacturing aspects of the magnetic circuit of loudspeaker or microphone transducers |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Magnetic liquids in general, e.g. ferrofluids |
Further detail is covered by the subgroups of Indexing Code groups H04R 2209/041 and H04R 2209/043 listed below. Classification is obligatory.
This place covers:
For example: the inner suspension (13) is formed with leg portions (13b, 13c) having equal length, to prevent lateral vibration of the bobbin (8). Thus excursion of suspension and thus of the diaphragm can be increase without increasing the diameter of the inner suspension.
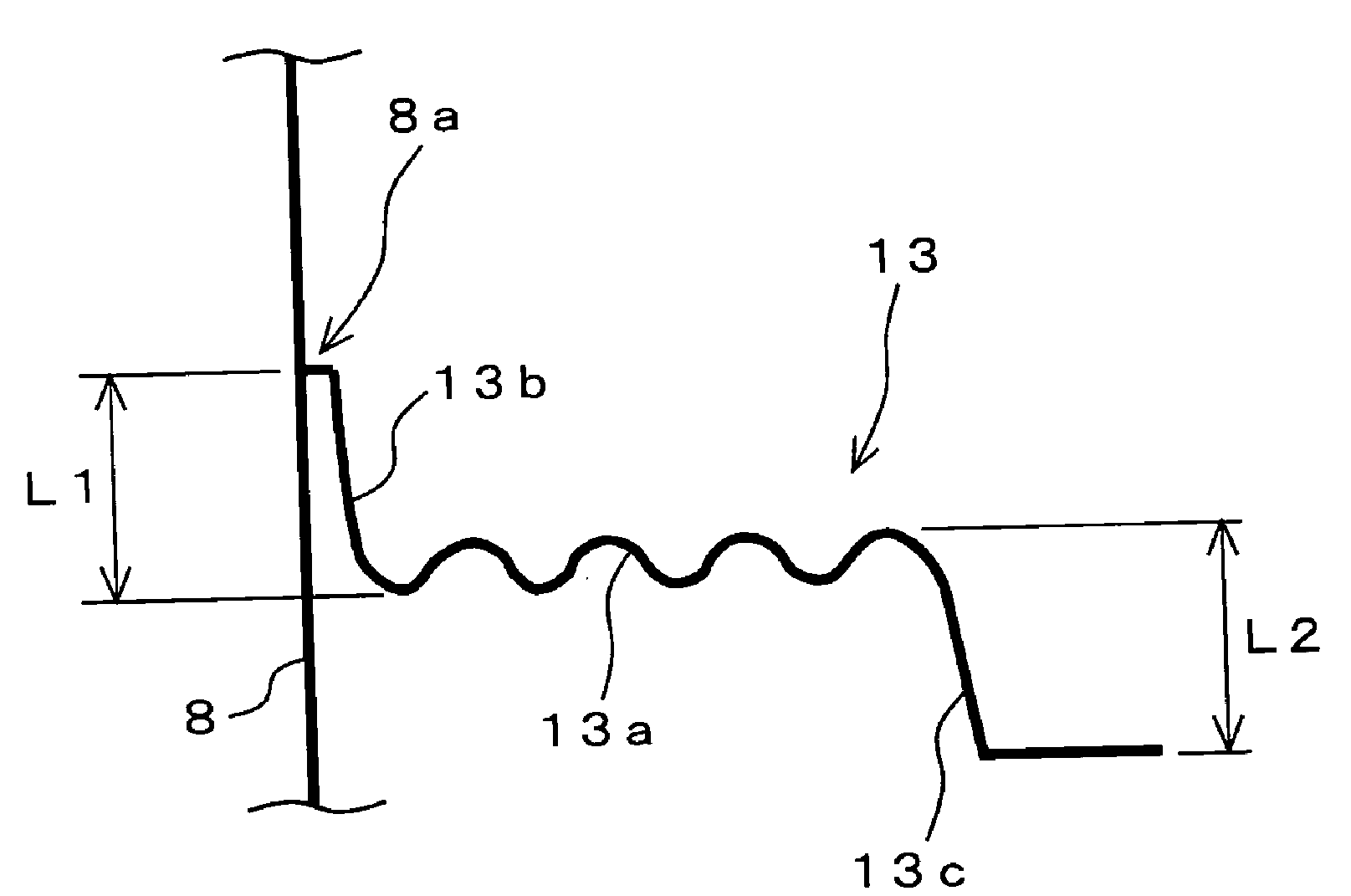
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Outer suspension or surround |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
spider | inner suspension usually placed between voice coil former and frame, for providing a restoring force enabling the return of the transducer membrane to its normal resting position and for centring the voice coil |
This place covers:
Mounting of the voice coil or the bobbin on which the voice coil is wound
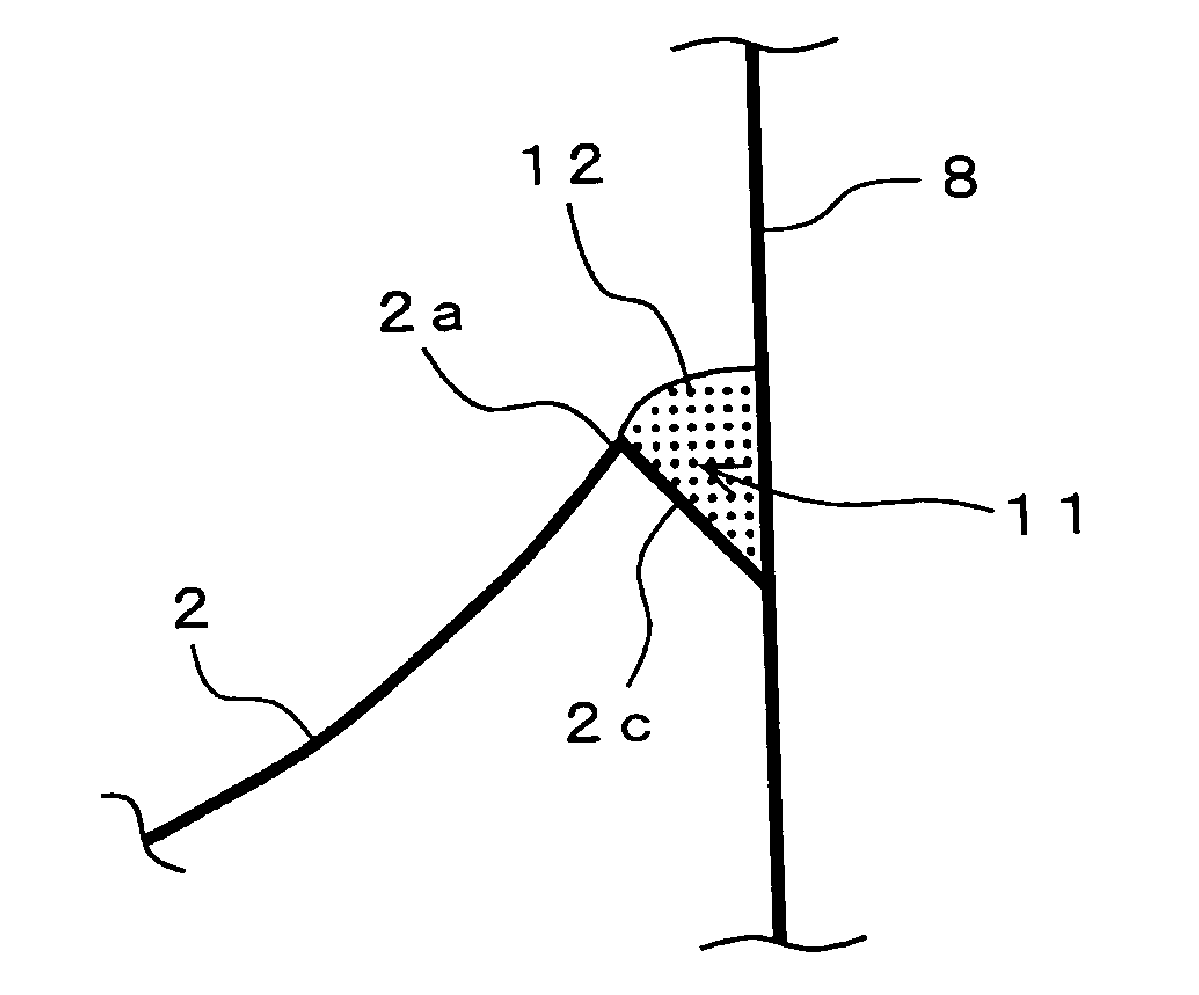
For example: the connection between bobbin (8) and diaphragm (2) is provided with a groove, which is filled with glue to strengthen the connection.
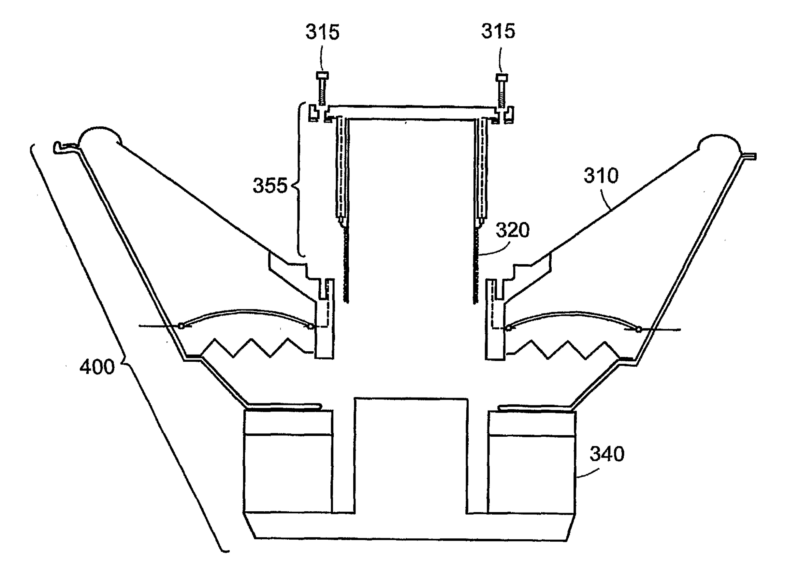
Example: bobbin assembly (355) removably mounted to the inner circumference of the diaphragm (310). Thus replacement of damaged assembly requires minimal effort.
Example: bobbin (140) is mounted at its top directly to outer suspension and in the middle via bridge (160). Thus the bobbin is prevented from bending.
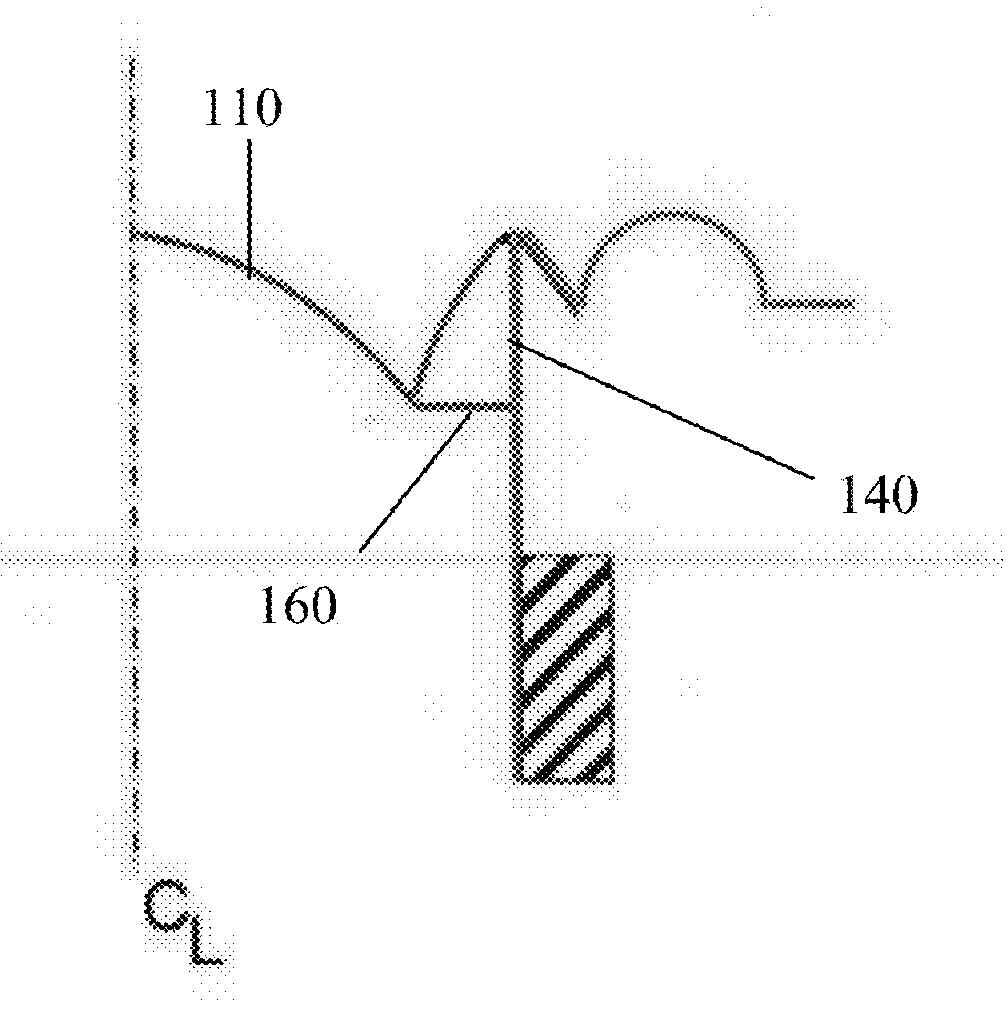
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Inner suspension or damper |
This place covers:
- Constructional aspects of the voice coil, e.g. shape of the coil, the winding angle, shape or material of the windings,
- Constructional aspects of the bobbin on which a voice coil is to be wound, e.g. material, shape, connection with voice coil
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Coils per se and their manufacture |
This place covers:
- Transducers for loudspeakers of the pistonic type, e.g. compression drivers, or of the distributed mode type;
- Inertial transducers, i.e. transducers for loudspeakers wherein the voice coil is directly mounted to vibrating diaphragm and the magnetic circuit is floating but suspended with respect to the diaphragm and voice coil.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Telephone receivers |
Further detail is covered by Indexing Code group and by H04R 2400/13. Classification is obligatory.
This place covers:
Transducers for loudspeakers wherein the voice coil is directly mounted to vibrating diaphragm and the magnetic circuit is floating but suspended with respect to the diaphragm and voice coil.
For example: body sensed speaker, that can be placed in e.g. waistcoats, cushions, matrasses, belts
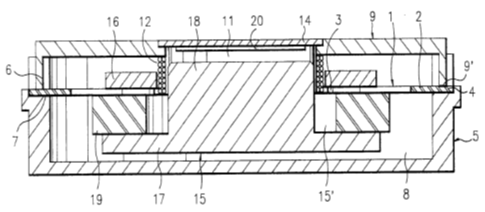
For example: exciter for distributed mode loudspeakers (DML)
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Transducers of moving-armature or moving-core type |
Further detail is covered by Indexing Code group H04R 2400/07. Classification is obligatory.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Transducers having separately controllable opposing diaphragms, e.g. for ring-tone and voice, or for combined microphone/-receiver in telephones | |
Transducers used as a loudspeaker to generate sound as well as a microphone to detect sound |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Transducers having separately controllable opposing diaphragms, e.g. for ring-tone and voice | |
Transducers used as a loudspeaker to generate sound as well as a microphone to detect sound | |
Transducers capable of generating both sound as well as tactile vibration e.g. as used in cellular phones | |
Generating mechanical vibrations of infrasonic, sonic, or ultrasonic frequency using vibrating magnet, armature or coil system | |
Generating vibrations with systems involving rotary unbalanced masses | |
Tactile signalling systems |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Transducers of moving-coil, moving-strip, or moving-wire type | |
Loudspeaker transducers using the principle of inertia | |
Acoustic diaphragm of magnetisable material directly co-acting with electromagnet | |
Generating mechanical vibrations of infrasonic, sonic, or ultrasonic frequency operating with electromagnetism, e.g. using vibrating magnet, armature or coil system | |
Dynamo-electric motors with vibrating magnet, armature or coil system |
Further detail is covered by the subgroups of Indexing Code groups H04R 2400/01, H04R 2400/03, and H04R 2440/01 - H04R 2440/07.
This place covers:
For example:
The voice coil (2) is static. Upon energising the magnets (4-6) move.

Example of a hearing aid receiver:
Armature 136 has a fixed (146) and a movable arm (144). When coils 134 is energised, movable arm 144 moves and drives membrane (118) via a linkage 138, thus producing sound.
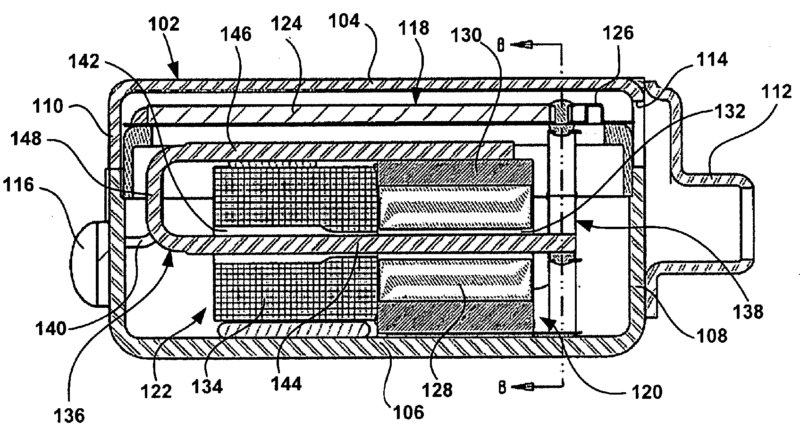
Example of a bone conduction speaker:
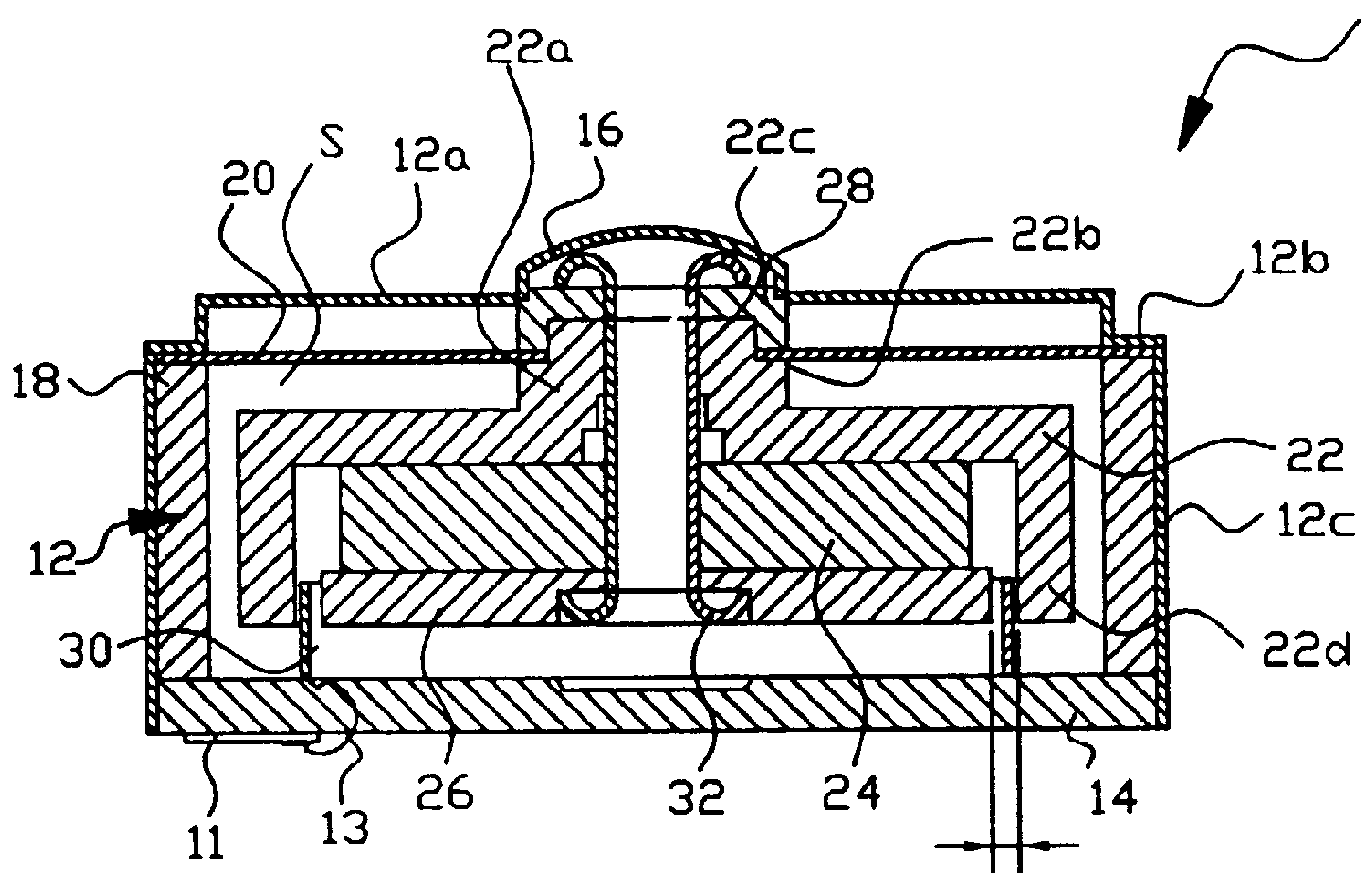
Voice coil 30 is mounted directly to base plate 14 which is part of the transducer frame. The magnetic circuit (yoke 22, magnet 24, base plate 26) is movably attached to the frame 12 via damper 20, such that upon energising the voice coil the armature moves.
This place does not cover:
Telephone receivers of the moving-armature or moving-core type |
Further detail is covered by Indexing Code group H04R 2400/07 and H04R 2400/11. Classification is obligatory.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Transducers having separately controllable opposing diaphragms, e.g. for ring-tone and voice | |
Transducers used as a loudspeaker to generate sound as well as a microphone to detect sound | |
Transducers capable of generating both sound as well as tactile vibration e.g. as used in cellular phones | |
Generating vibrations with systems involving rotary unbalanced masses | |
Tactile signalling systems |
This place covers:
Transducers for loudspeakers or microphones, in which the membrane is part of the magnetic circuit.
For example:
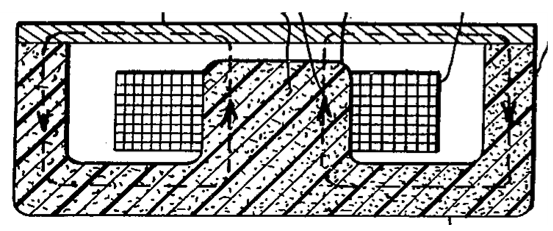
Further detail is covered by the subgroup of Indexing Code group H04R 2400/11 listed below. Classification is obligatory.
This place covers:
In the example shown in the figure below a configuration of the magnetostrictive actuator 103 is presented. The magnetostrictive actuator 103 has a rod-like magnetostrictive element 151 that is displaced along its extension direction, a solenoid coil 152 for generating a magnetic field, which is positioned around this magnetostrictive element 151, a driving rod 103a as driving member, which is connected to an end of the magnetostrictive element 151 and transmits any displacement output of the magnetostrictive actuator 103, and a container 154 that contains the magnetostrictive element 151 and the solenoid coil 152 therein.
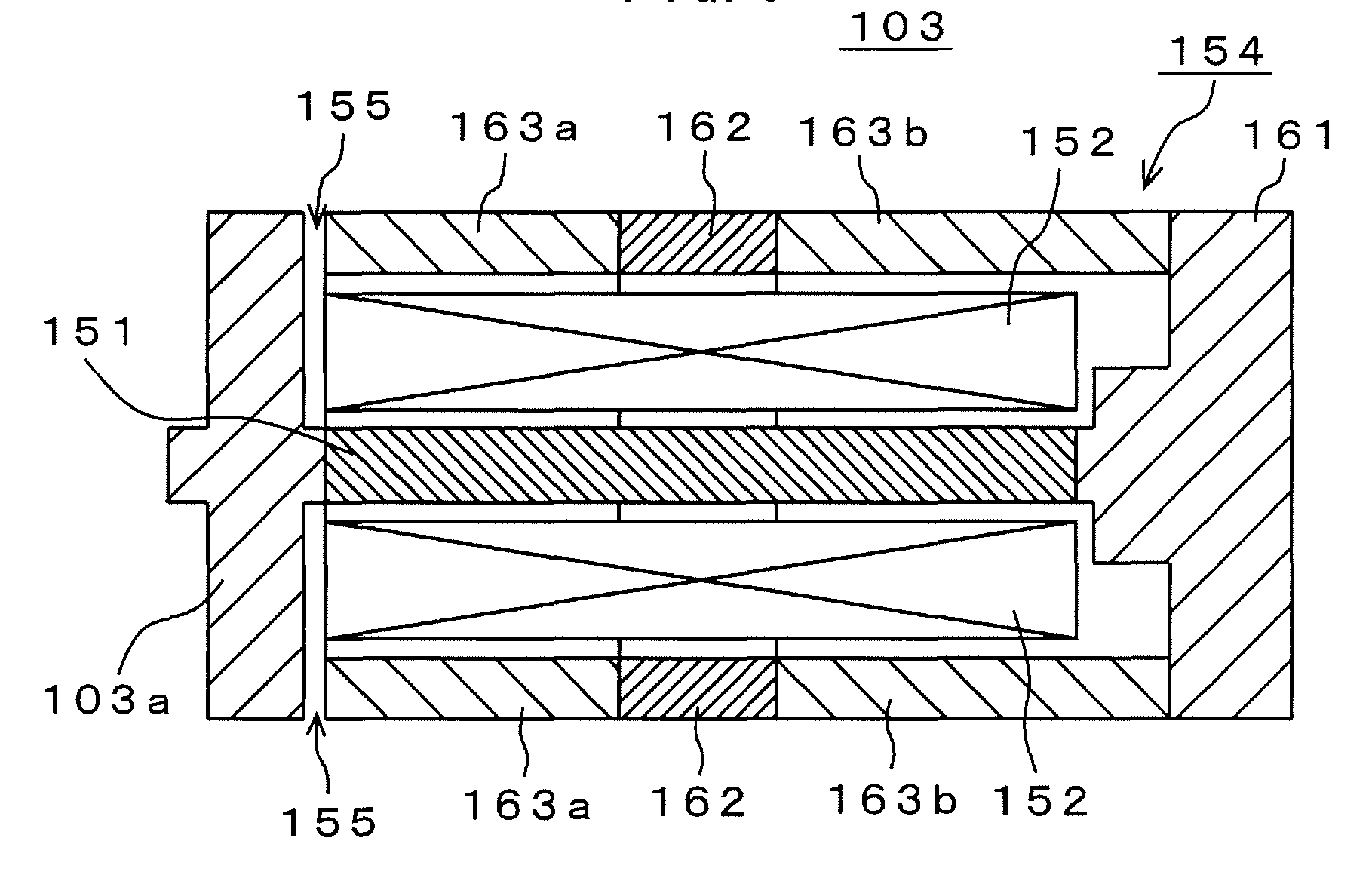
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Magnetostrictive elements in general | |
Materials; Manufacture of magnetostrictive devices | |
Details of magnetostrictive devices |
Further detail is covered by Indexing Code group H04R 2201/003, H04R 2217/01, H04R 2400/03 and H04R 2400/11. Classification is obligatory.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Details of piezoelectric or electrostrictive motors, generators or positioners | |
Piezoelectric or electrostrictive elements in general | |
Manufacture of piezoelectric or electrostrictive devices | |
Details of piezoelectric or electrostrictive devices | |
Selection of materials for piezoelectric or electrostrictive devices |
Further detail is covered by Indexing Code group H04R 2201/003, H04R 2217/01, H04R 2400/03, H04R 2400/11 and the subgroups of Indexing Code group H04R 2440/00. Classification is obligatory.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Piezoelectric or electrostrictive devices of macromolecular compositions |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Piezoelectric or electrostrictive devices with mechanical input and electrical output |
Further detail is covered by Indexing Code group H04R 2410/03. Classification is obligatory.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Piezoelectric or electrostrictive devices of macromolecular compositions |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Generating mechanical vibrations of infrasonic, sonic, or ultrasonic frequency using electrostatic transducers, e.g. electret-type |
Further detail is covered by Indexing Code groups H04R 2400/11 and H04R 2410/03. Classification is obligatory.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Transducers other than those covered by groups H04R 9/00 - H04R 21/00 using solid state devices | |
Arrangements for avoiding sticking of the flexible or moving parts of MEMS devices having such parts | |
MEMS packages and encapsulations | |
Microphones and microspeakers | |
MEMS structures allowing for movement | |
Type of movement | |
Pressure measurement / constructional details associated with semiconductive diaphragm sensors, e.g. etching of diaphragms |
This place does not cover:
Electrostatic transducers characterised by the use of electrets | |
for loudspeakers |
This place does not cover:
Electrostatic transducers characterised by the use of electrets | |
for microphones |
This place does not cover:
Gaseous resistance transducers | |
Magneto resistive transducers |
Examples of places in relation to which this place is residual:
Transducers of moving-coil, moving-strip or moving-wire type | |
Transducers of moving-armature or moving-core type | |
Transducers having an acoustic diaphragm of magnetisable material directly co-acting with electromagnet | |
Magnetostrictive transducers | |
Piezoelectric transducers; Electrostrictive transducers | |
Electrostatic transducers | |
Variable-resistance transducers |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Diaphragms for transducers of the distributed-mode type |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Sound producing devices using optical excitation, e.g. laser bundle | |
Sound producing devices using electric discharge |
This place covers:
Acoustic transducers using solid state devices and not covered by H04R 9/00 - H04R 21/00
This place does not cover:
Electrostatic transducers using semiconductor materials |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Solid state devices per se |
This place covers:
Electric hearing aids providing an auditory perception.
Electrical or mechanical aspects thereof, e.g.:
- Electro-acoustic or electro-mechanical hearing aids.
- Electric tinnitus maskers providing an auditory perception.
- Signal processing, e.g. beamforming, prevention of acoustic reaction or noise reduction, noise reduction, in dependence of listening situation.
- Electronic fitting, i.e. initial or subsequent adaptation using audiological test signals, e.g. by a hearing aid acoustician, testing or monitoring.
- Wired or wireless external connection or remote control.
- Manufacture or assembly, e.g. mounting of transducers or batteries.
- Ear tips, ear moulds or their manufacture.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Constructions of transducers per se | |
Amplifying systems for the deaf | |
Monitoring arrangements; Testing arrangements in general | |
Ornaments for ears | |
Earphones measuring physiological sounds, e.g. heartrate, breathing, pulse | |
Methods or devices for treatment of the ears, e.g. surgery | |
Devices or methods enabling ear patients to replace direct auditory perception | |
Internal protective devices for the ears, e.g. earplugs | |
Non-electric hearing aids | |
Cochlear implants | |
Structural combination of hearing aids with spectacle frames | |
Teaching or communicating with deaf persons | |
Directing sound using electrical steering of transducer arrays, e.g. beam steering | |
Coding or decoding of speech or audio signal, using source filter models or psychoacoustic analysis | |
Processing of speech signals | |
Automatic gain control in audio amplifiers | |
Telephone sets for the hearing impaired | |
Mobile telephones for the hearing impaired |
Classification should be directed to groups H04R 25/02, H04R 25/04 and H04R 25/50 and its subgroups, if and only if the technical subject in consideration cannot be classified elsewhere under this main group.
Concerning inventions relating to hearing devices, if an application describes and shows the invention using only embodiments relating to hearing aids, then H04R 25/00 or subgroups should be given as invention information. Dependent on the case, the mere statement that the invention is also applicable to ear- or headphones may render classification under H04R 1/10 or H04R 5/033 useful, but only as additional information. Only if specific non-trivial embodiments for ear- or headphones are also shown, classification under H04R 1/10 or H04R 5/033 as invention information may be considered as well.
Further details are covered by indexing groups H04R 2225/31, H04R 2225/33, H04R 2410/07, H04R 2430/03, H04R 2460/03, H04R 2460/13 and H04R 2460/17. Classification is obligatory.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Electro-acoustic or electro-mechanical hearing aids | hearing aids acting indirectly, e.g. acoustically, or directly on the ear drum, mastoid, ossicles or cochlea and providing an auditory perception |
Monitoring | encompasses indication |
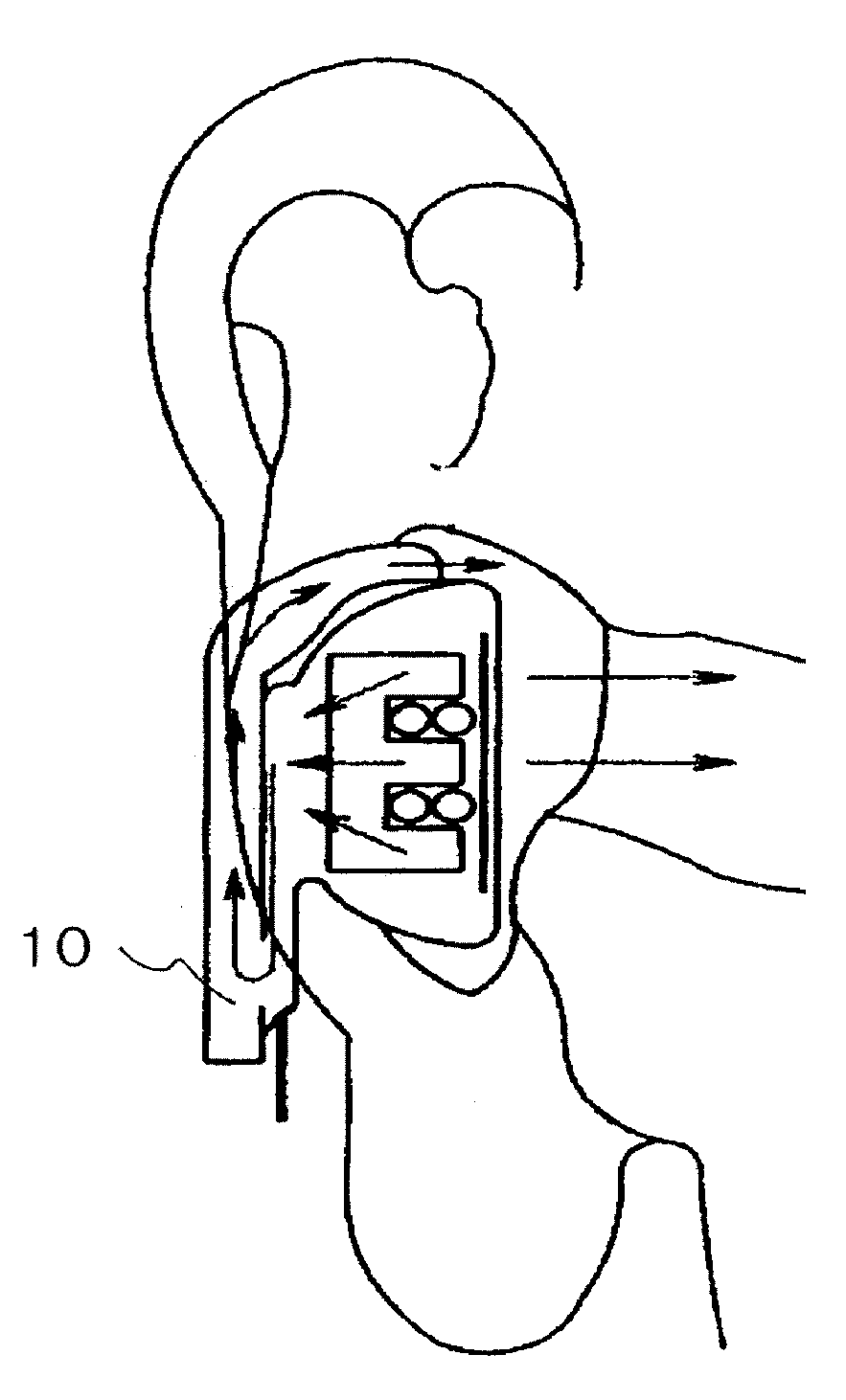
This place covers:
The signal processing is done external to the hearing aid part that is in the ear (as for example shown in the figure)
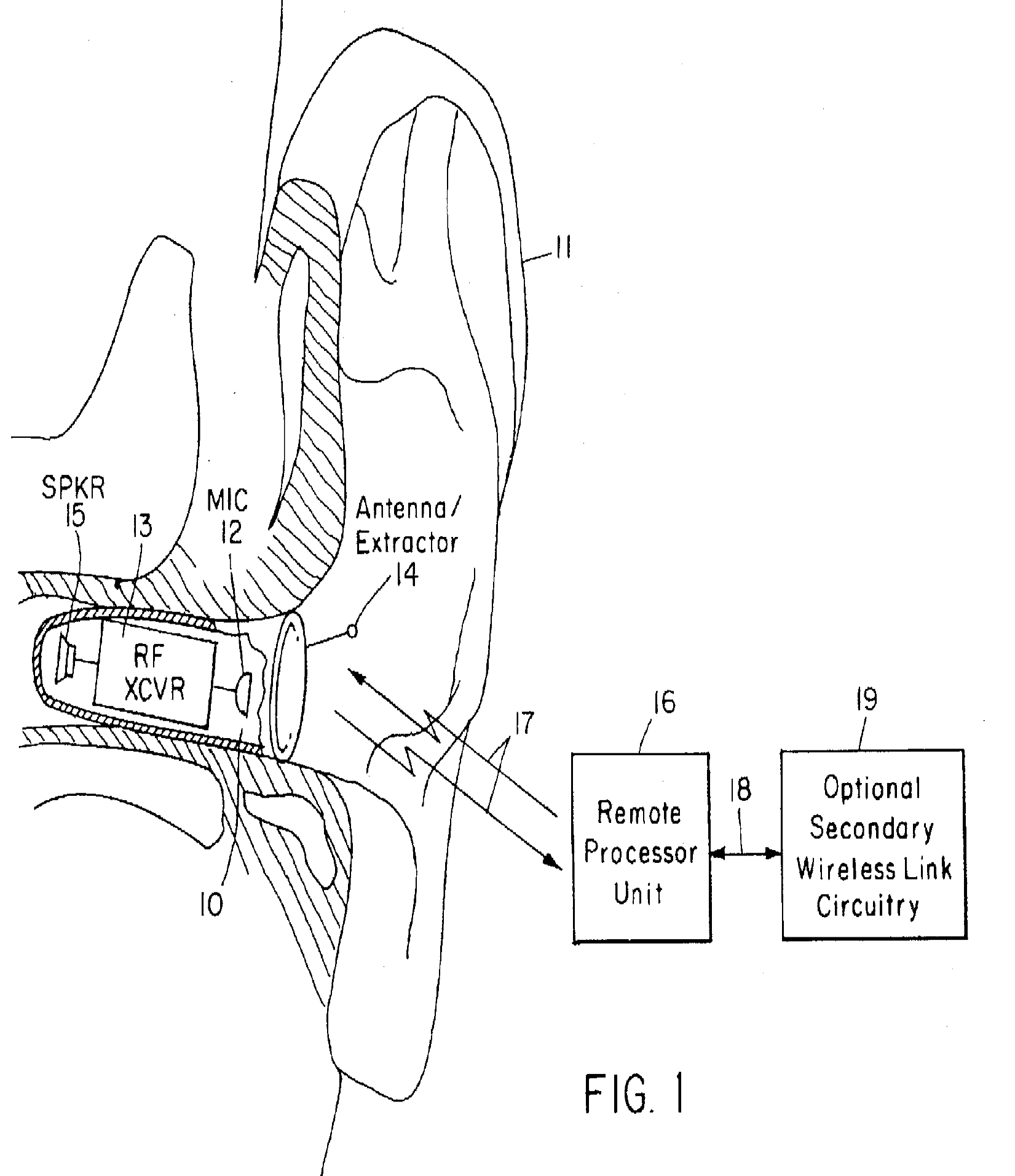
This place covers:
For example testing of the functioning of an amplifier in a hearing aid (see figure). Switching circuit 20 measures a time period T, and interrupts the signal from the microphone 10 once every such period T. The interruption, or test time interval, lasts for another measured time segment t where t is less than T. During the interruption, the switching circuit 20 transmits the signal from the signal generator 22 to the hearing aid amplifier 12 to act as a test signal. Difference detector 24 detects malfunction of the amplifier. Difference detector 34 low battery status.
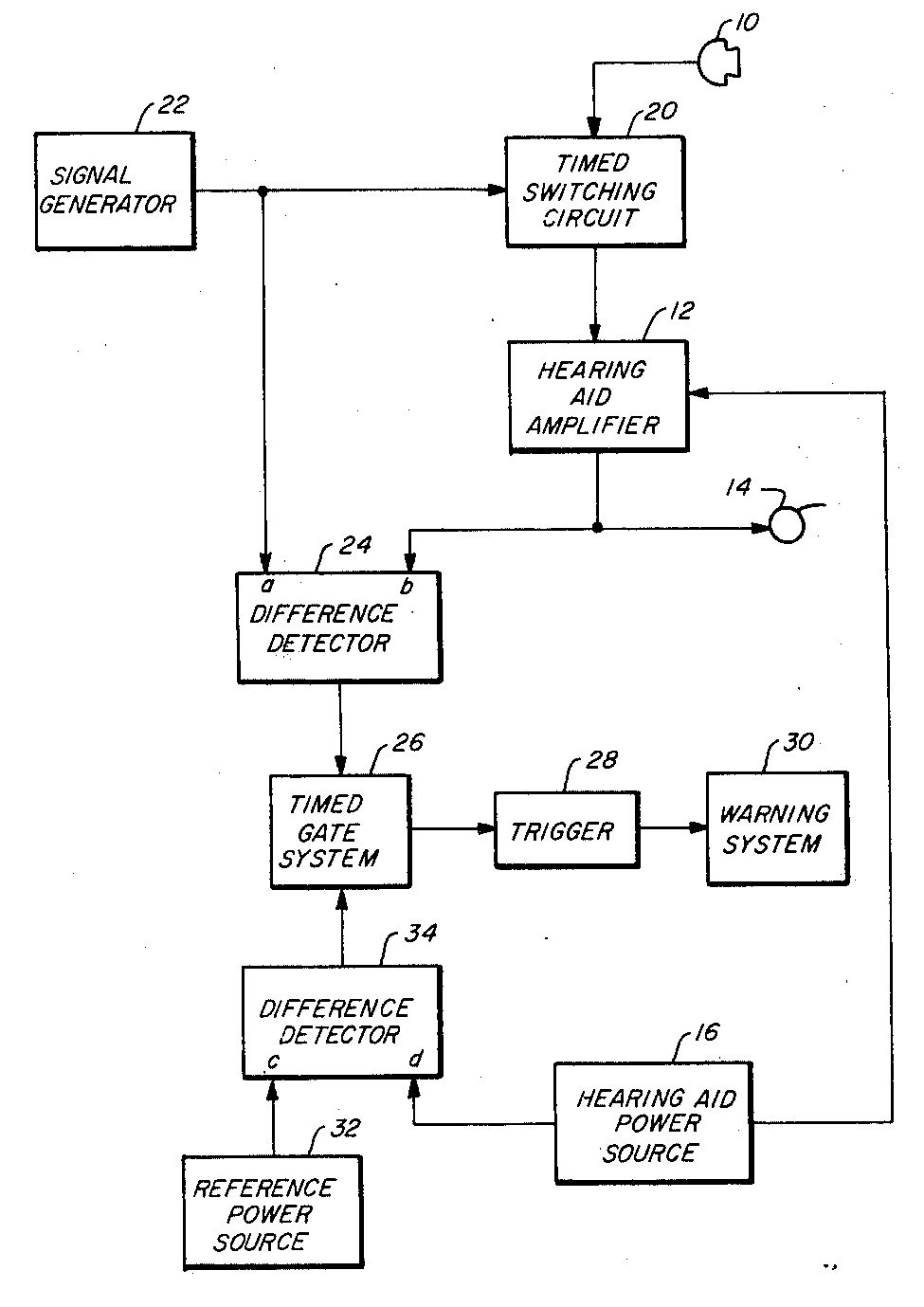
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Testing arrangements for electro-acoustic transducers in general | |
Testing arrangements for cochlear implants | |
Battery testing in general | |
Indicators for indicating switching condition |
For example: US4049930.
Further detail is covered by Indexing Code group H04R 2460/15. Classification is obligatory.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Monitoring | also encompasses indicating |
This place covers:
Example of a self-diagnosis system with which the transducers and other component can be checked, see figure.
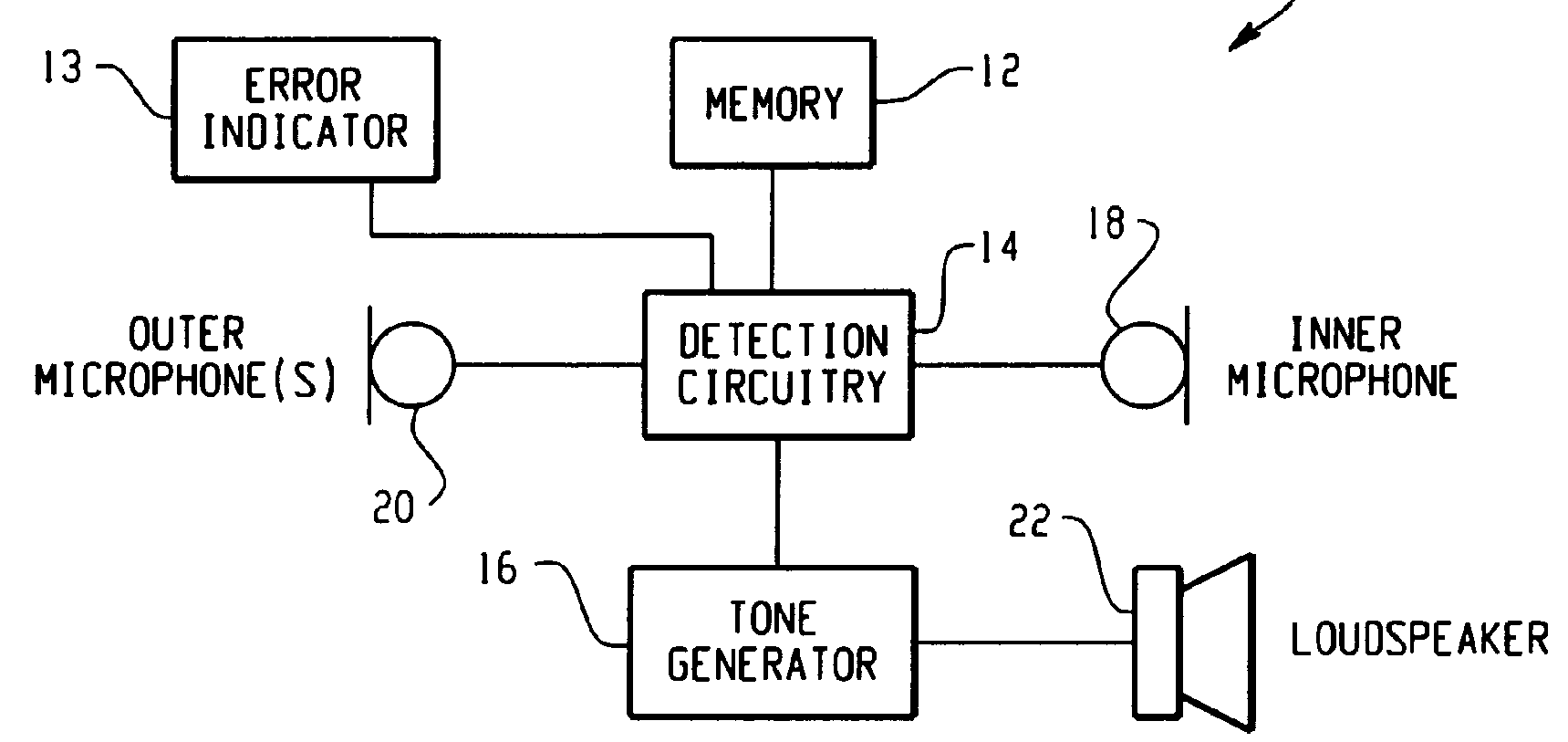
Further detail is covered by Indexing Code subgroup H04R 2225/39. Classification is obligatory.
This place covers:
For example:
This place covers:
For example:
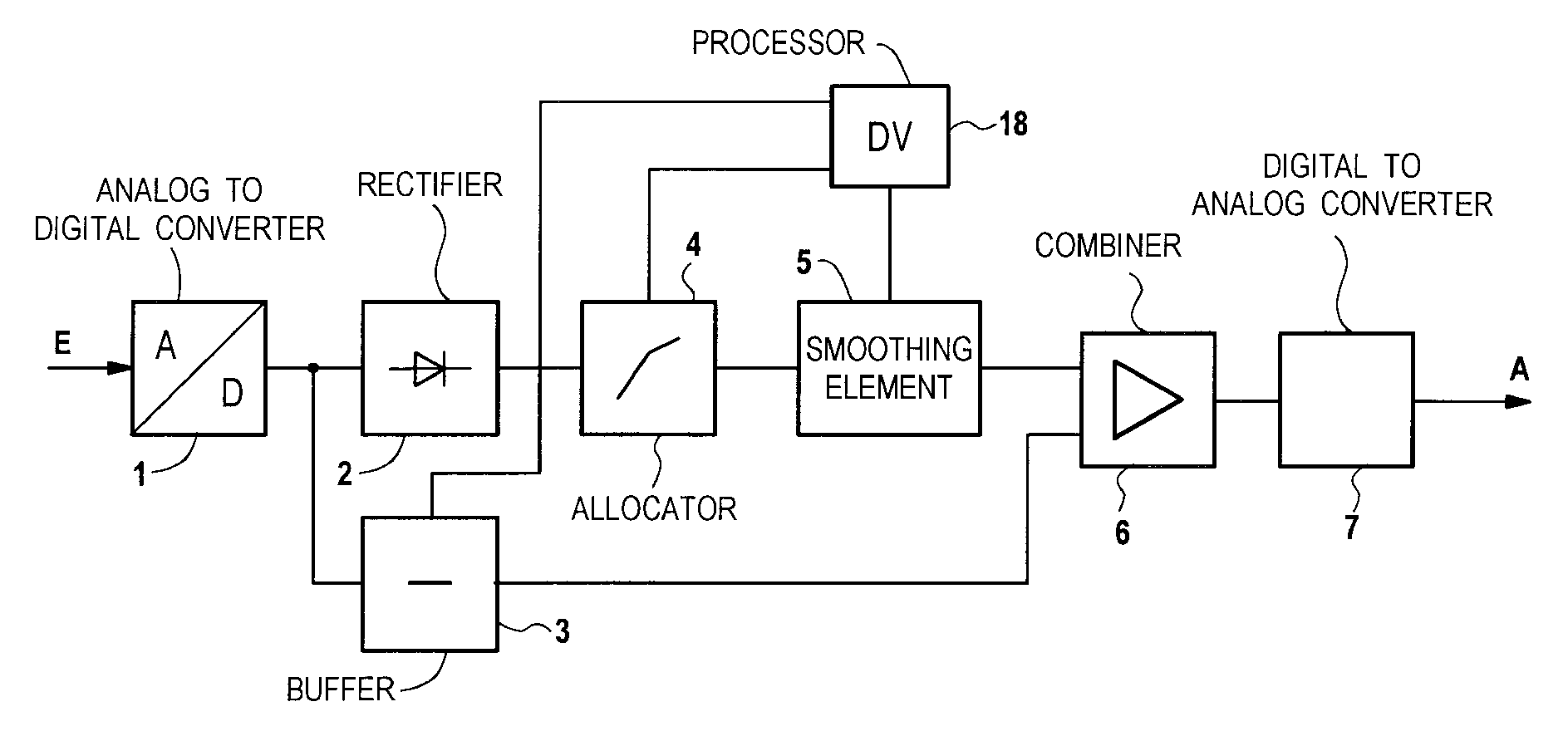
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Compression/ expansion | |
Frequency-dependent volume compression or expansion in general, e.g. multiple-band systems |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Obtaining a desired directivity characteristic using constructional means in general |
This place covers:
Mechanical aspects, e.g. orientation, relative placement, of acoustic transducers in hearing aids to obtain a desired directional characteristic.
For example microphone openings (17A-17C) arranged along a straight line (see figure):
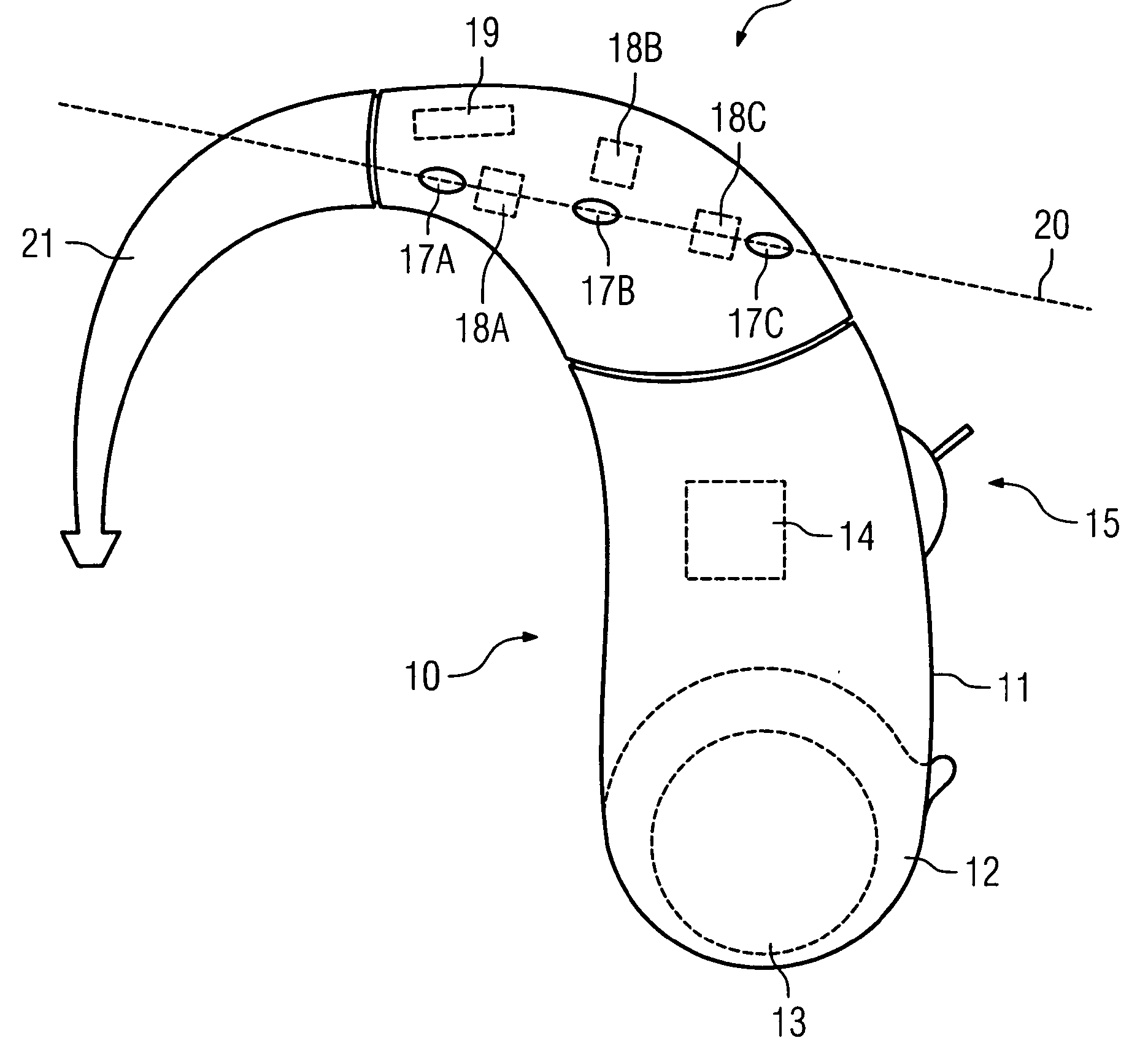
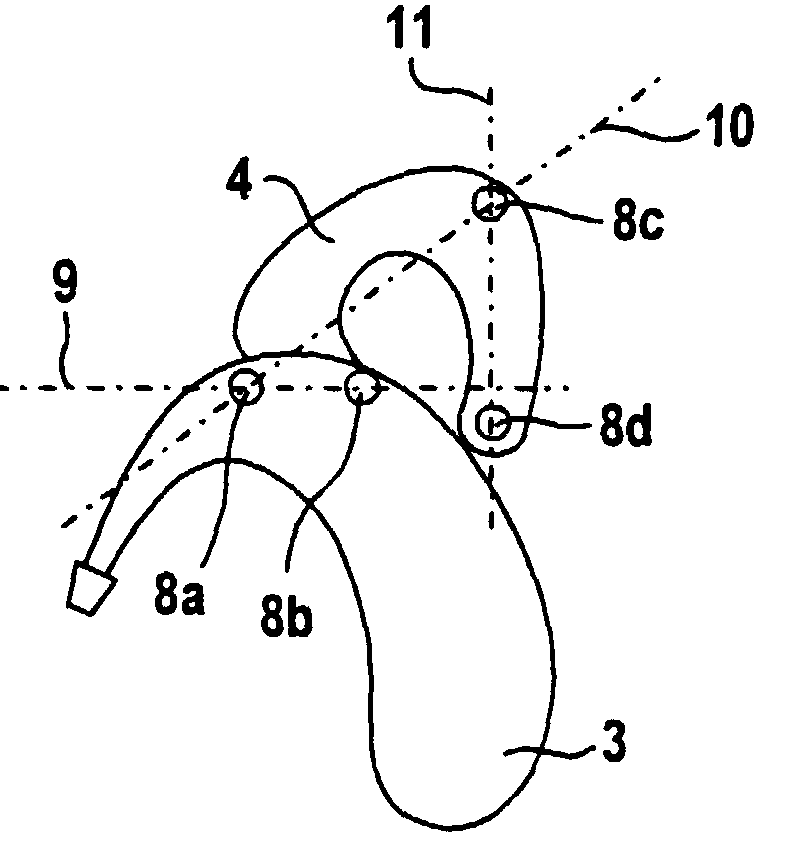
For example microphones (8a,8b) mounted in a BTE housing and additional microphones (8c, 8d) mounted in a lever (4) which can be swung away from the housing to adapt the directivity of the hearing aid.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangements for obtaining a desired directional characteristic by combining a number of identical acoustic transducers |
The mere fact that more than one microphone is used to obtain a desired directivity need not be classified, especially if H04R 25/407 has to be given anyway (cf. the first 2 EXAMPLES given for H04R 25/407).
Further detail is covered by Indexing Code group H04R 2410/01. Classification is obligatory.
This place covers:
For example:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Circuits for combining signals of a plurality of acoustic transducers in general | |
Direction-finders for determining the direction from which infrasonic, sonic, ultrasonic, not having a directional significance, are being received | |
Systems for determining distance or velocity not using reflection or re-radiation and using ultrasonic, sonic, or infrasonic waves | |
Circuits for sound-focusing or directing using electrical steering of transducer arrays, e.g. beam steering | |
Speech recognition techniques specially adapted for robustness in adverse environments | |
Speech enhancement using two microphones, one receiving mainly the noise signal and the other one mainly the speech signal | |
Speech enhancement using microphone arrays or beamforming | |
Telephonic conference arrangements | |
Video conference systems |
Further detail is covered by Indexing Code groups H04R 2410/01 and H04R 2430/20 listed below. Classification is obligatory.
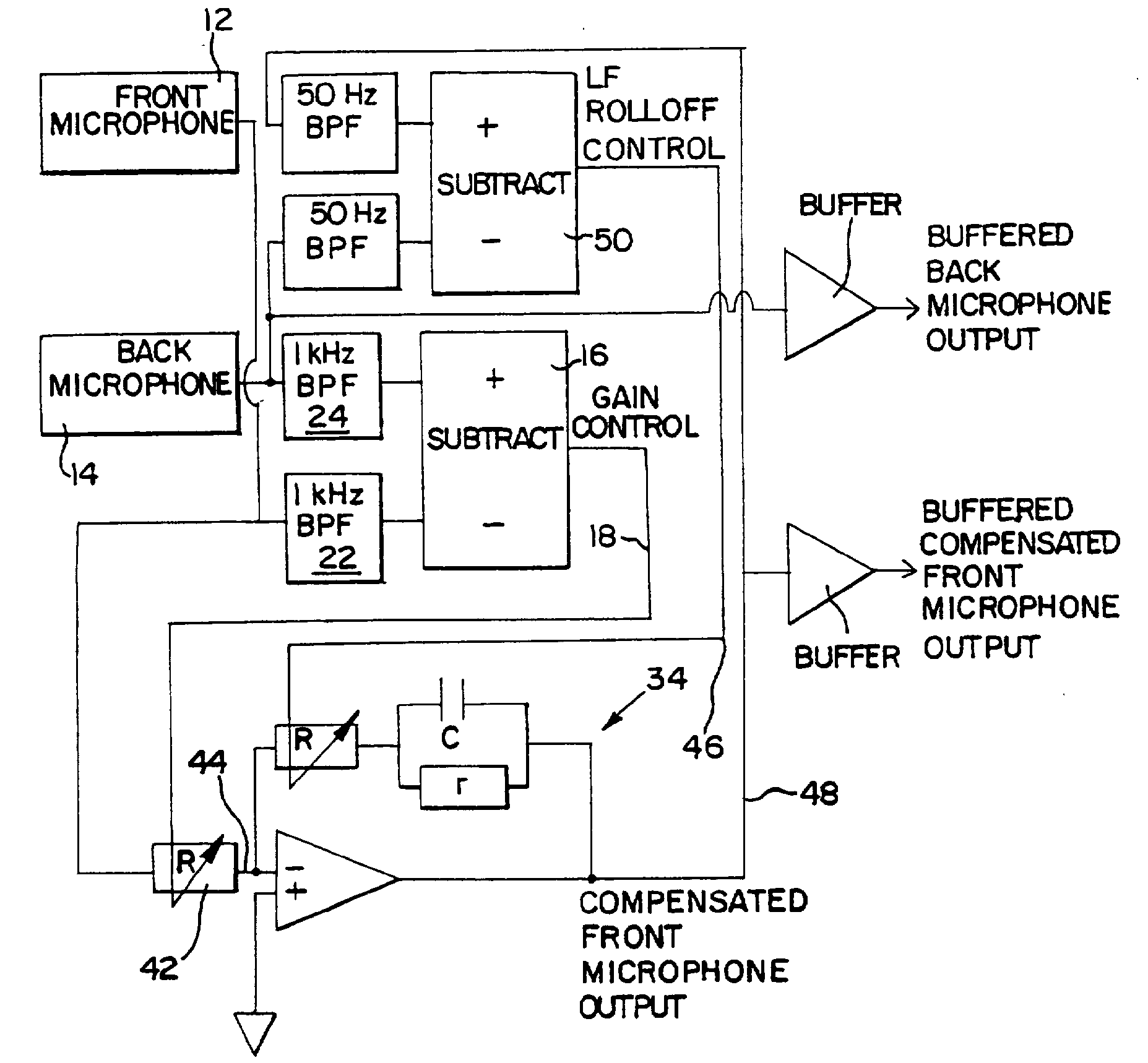
This place covers:
Example for input selection:
Example for mixing:
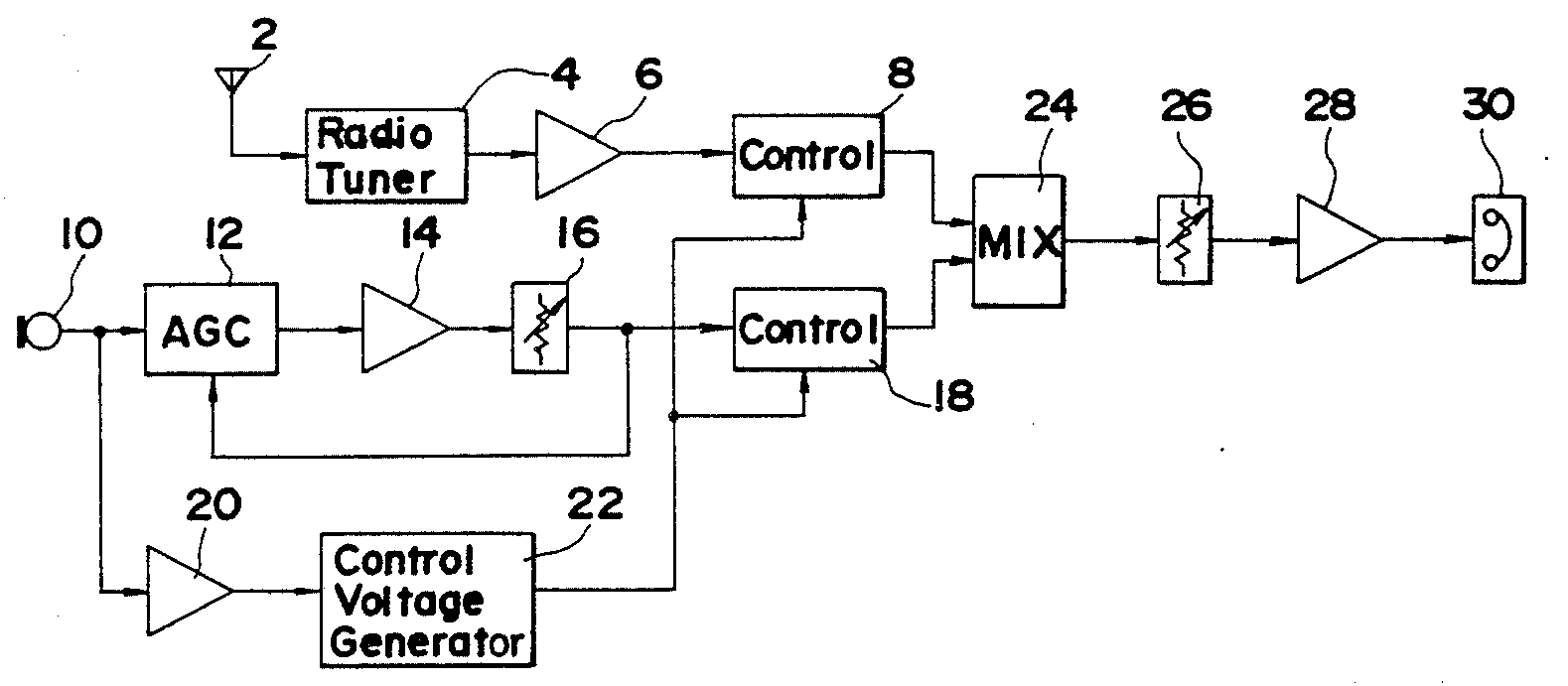
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Prevention of acoustic reaction in general |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Mounting and assembly of hearing aids | |
Housing parts, e.g. shells, tips or moulds | |
Aspects relating to vents in hearing devices |
This place does not cover:
Ear tips; Ear moulds |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Constructional means for obtaining a desired frequency response in general |
This place covers:
General analog or digital signal processing in hearing aid not provided for in H04R 25/00 or its subgroups.
- Classification should be directed to this group and its subgroups, if and only if the technical subject in consideration cannot be classified elsewhere under this main group
- Inventions relating to the interaction of analogue and digital signal processing are to be classified here in combination with both H04R 25/502 and H04R 25/505 as additional information.
- Further detail is covered by Indexing Code subgroups H04R 2225/41, H04R 2225/49, H04R 2225/49, H04R 2460/01, H04R 2460/05, H04S 2420/01 and H04S 2420/05. Classification is obligatory.
This place covers:
External connection for the purpose of data exchange between hearing aids, e.g. binaural hearing aids, or between hearing aid and external device, e.g. telecoil, remote control, or for charging of batteries in hearing aids
Example for wirelessly charging accumulators in a hearing aid (see figure)
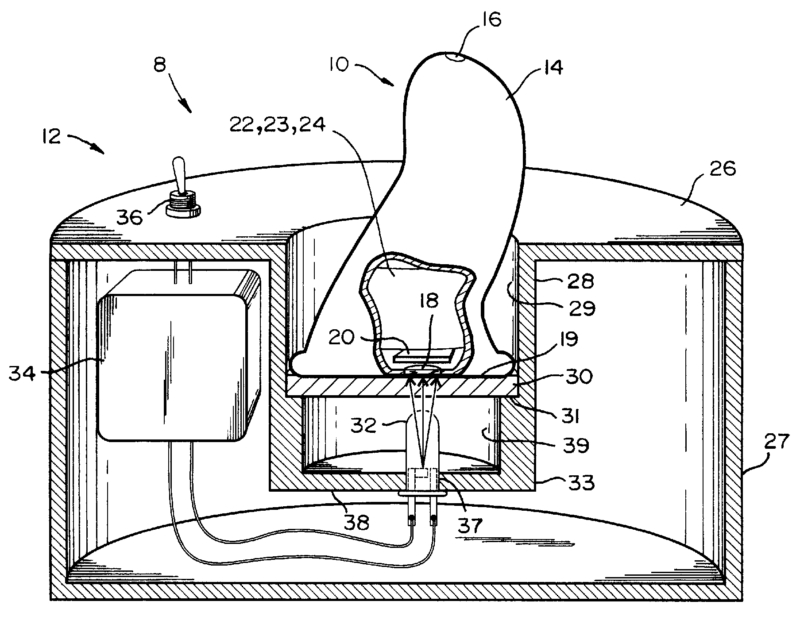
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Transmission systems in which the medium consists of the human body |
- If battery charging is wireless only H04R 25/55 is to be given in combination with H04R 2225/31. If however charging is wired H04R 25/556 (as additional information) is to be added as well.
- Further detail is covered by subgroups H04R 2225/51, H04R 2225/53, H04R 2225/55 and H04R 2460/07. Classification is obligatory.
This place covers:
Binaural control, e.g. control of one hearing aid in dependence of the other; Data exchange between hearing aids to enable binaural control, e.g. type of data, timing, ...
The mere fact that binaural control of data exchange is wired or wireless needs not be classified.
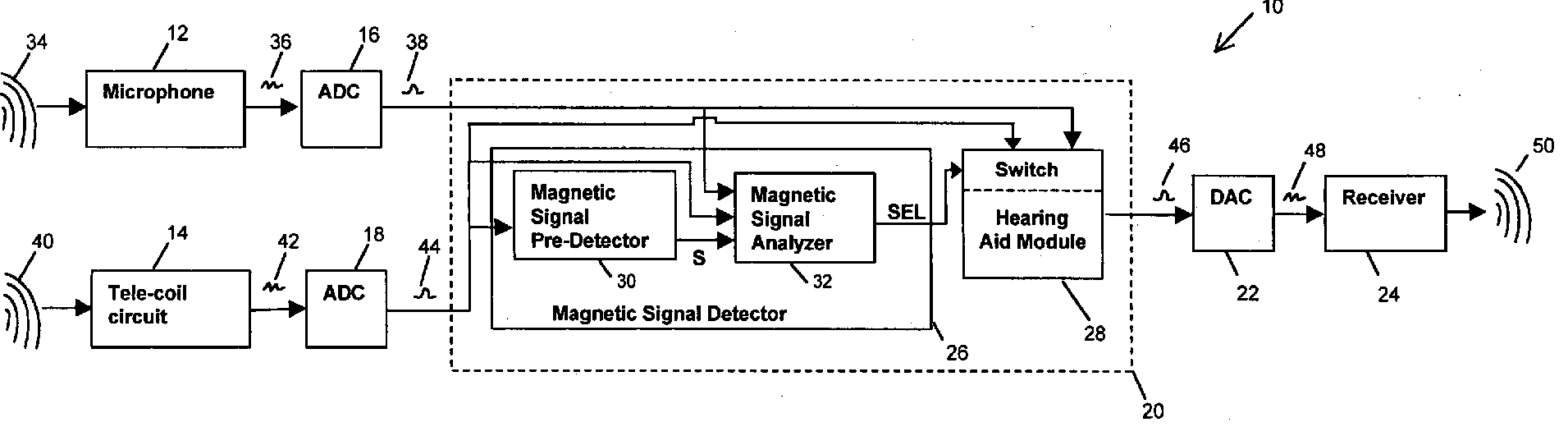
This place covers:
Electric hearing aids using wireless connection for the transmission audio representative data, e.g. T-coils, FM receivers (see e.g. the figure below)
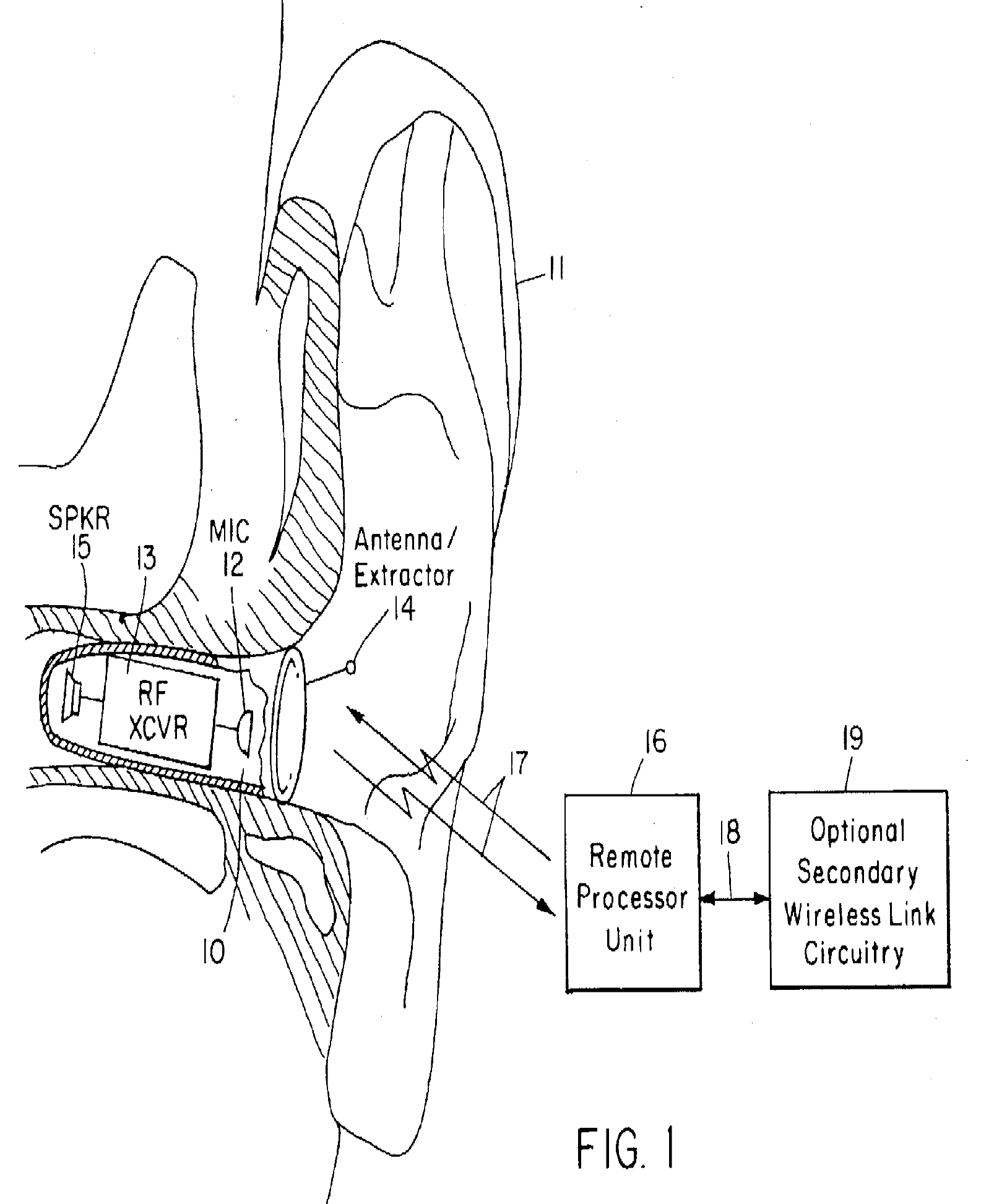
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wireless connection in general | |
Near field transmission in general | |
Transmission systems in which the medium consists of the human body | |
Non-intrusive coupling means between telephone set and auxiliary equipment |
Binaural hearing aids (invention) are not to be classified in this group but in H04R 25/552. No classification in H04R 25/554 (as invention of additional information) is in principle needed.
This place covers:
Example for an ITE hearing aid connected to a programmer (5):
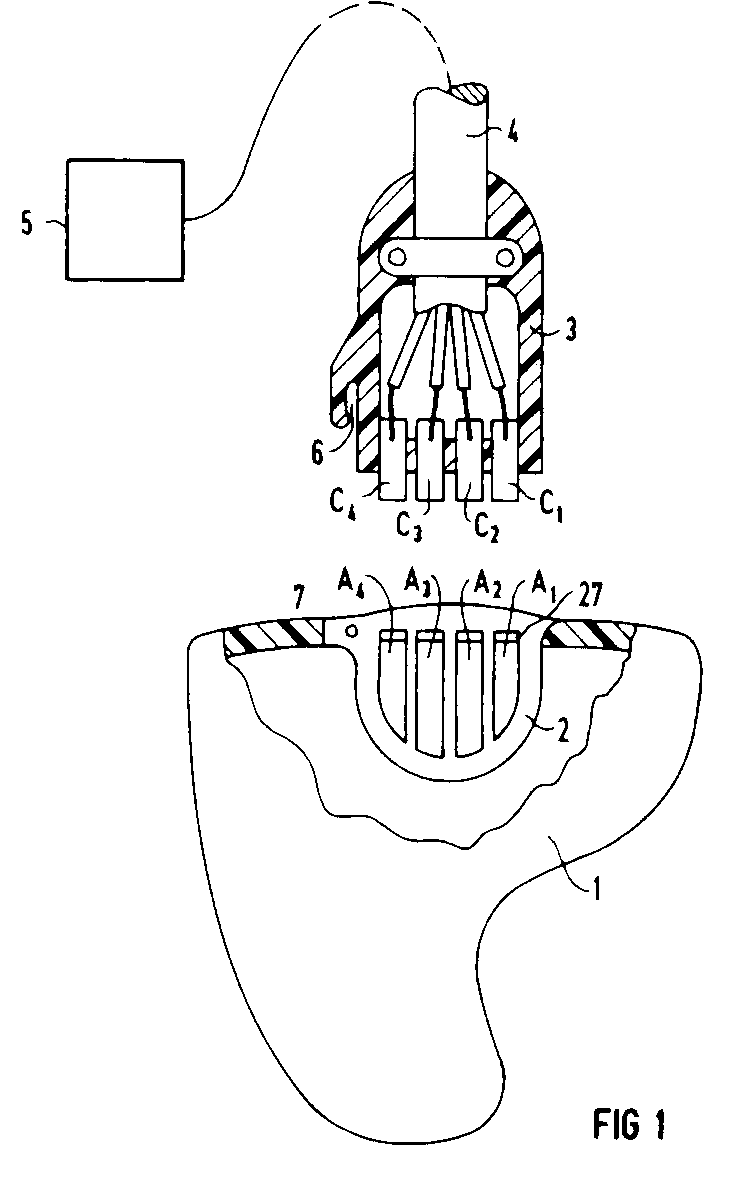
Example for a BTE hearing aid additionally provided with an FM receiver (3):
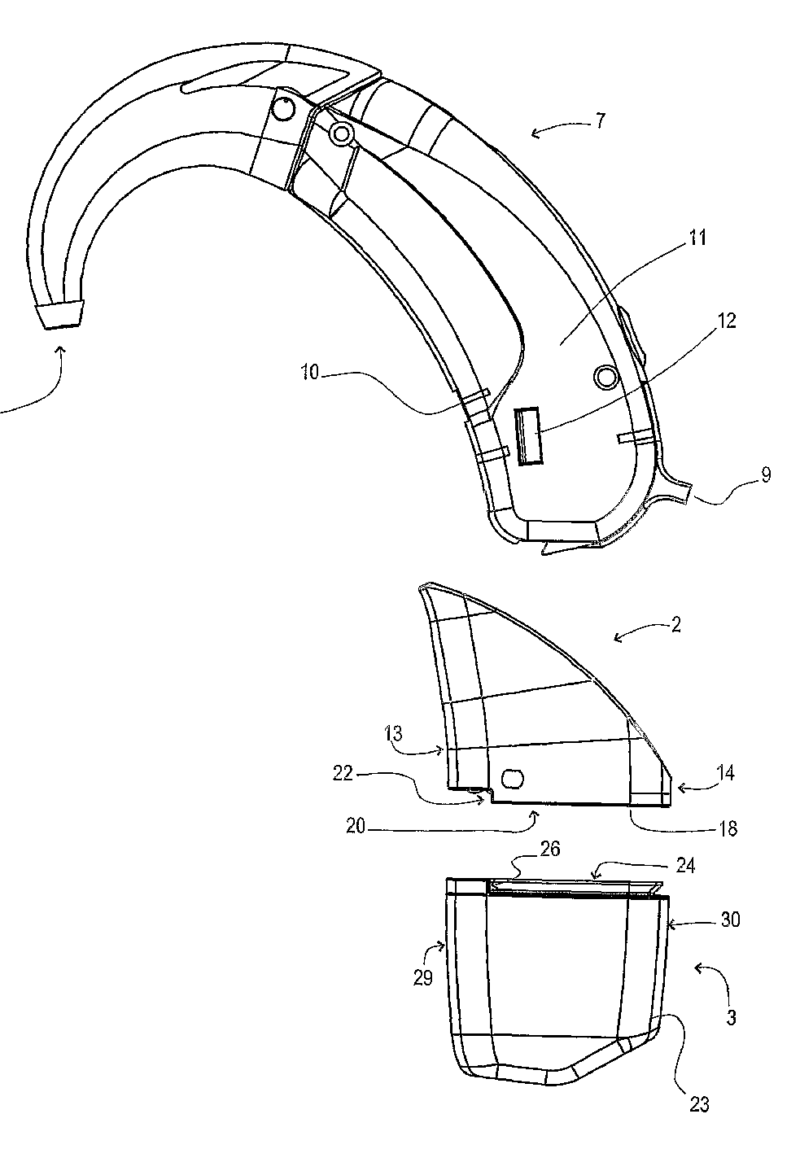
This place does not cover:
Earhooks |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Local control of medical devices, e.g. graphical user interfaces, dedicated hardware interfaces | |
Connectors in general |
Connection between the BTE housing and the earmould via an earhook is not to be classified here but in H04R 25/60 in combination with H04R 2225/0213.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Telemetry systems for implants such as pace makers or cochlear implants | |
Input or output devices integrated in time-pieces | |
Remote control in general | |
Audio-frequency transformers or mutual inductances, i.e. not suitable for handling frequencies considerably beyond the audio range | |
Indicators for indicating switching condition | |
Remote control of amplification, tone, or bandwidth | |
Combined remote-control of tuning and other functions, e.g. brightness, amplification | |
remote control, e.g. for HiFi systems or audio/video combinations | |
Hi-Fi systems or audio/video combinations |
This place covers:
Arrangements for mounting or interconnection of hearing aid parts.
Example: Details of mounting of ear tip (11) via tube (21 to BTE housing (30):
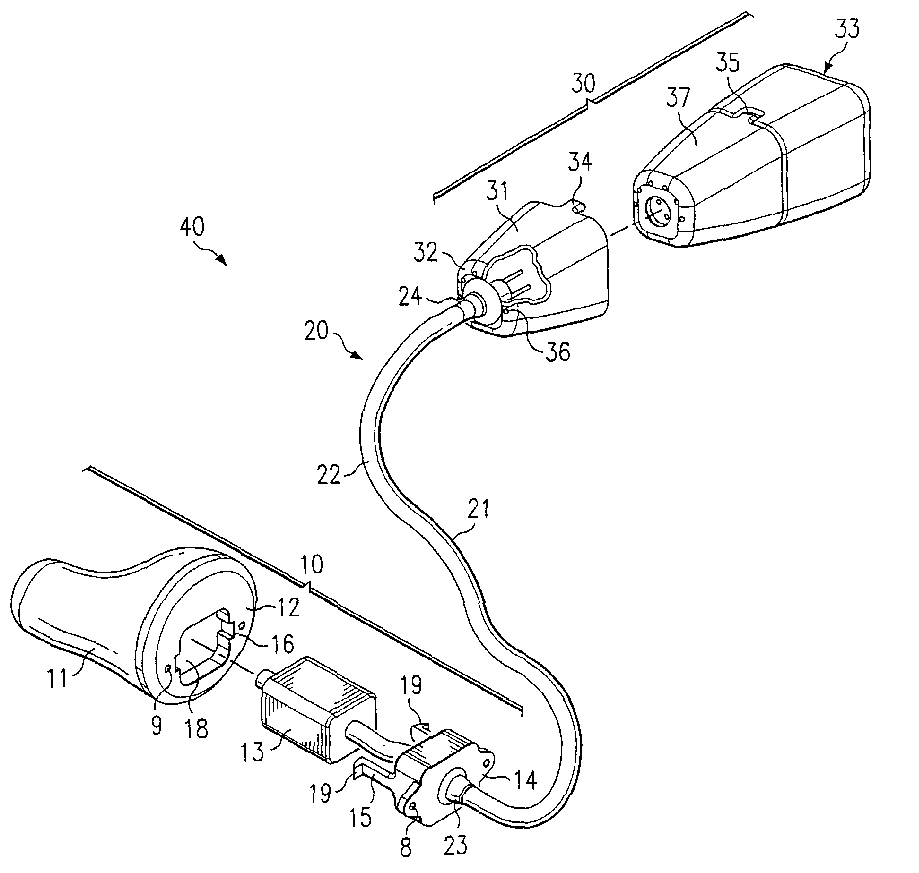
This place does not cover:
Ear wax retarders, e.g. their mounting |
Further detail is covered by Indexing Code subgroups H04R 2225/0213, H04R 2225/49, H04R 2225/59, H04R 2225/61, and H04R 2225/67. Classification is obligatory.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Interconnection | covers both mechanical as well as electrical interconnection |
This place covers:
Arrangements for mounting or interconnection of batteries in hearing aids
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electrical supply for implants, e.g. pace makers or cochlear implants | |
Secondary cells; Manufacture thereof, Details, Construction or manufacture in general, small-sized flat cells or batteries portable equipment | |
Primary casings, jackets or wrappings of a single cell or a single battery | |
Mountings; Secondary casings or frames; Racks, modules or packs; Suspension devices; Shock absorbers; Transport or carrying devices; Holders | |
Circuit arrangements for charging or depolarising batteries or for supplying loads from batteries |
This place covers:
Arrangements for mounting or interconnection of transducers in hearing aids
This place covers:
Mounting or interconnection aspects of implantable hearing aid transducers
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Earphones or headphones using bone-conduction transducers | |
Constructions of transducers per se | |
Implantable hearing aids or parts thereof | |
Electrode placement of cochlear implants | |
Controlling aspects of cochlear implants | |
Electrical supply for implants |
This place covers:
Interconnection or mounting of electrical aspects of implantable hearing aid transducers
This place does not cover:
of electronic switches or control elements |
This place covers:
Example CIC: housing (15) and ear tip (18)

Example ITE: housing (15) and ear mould (21)
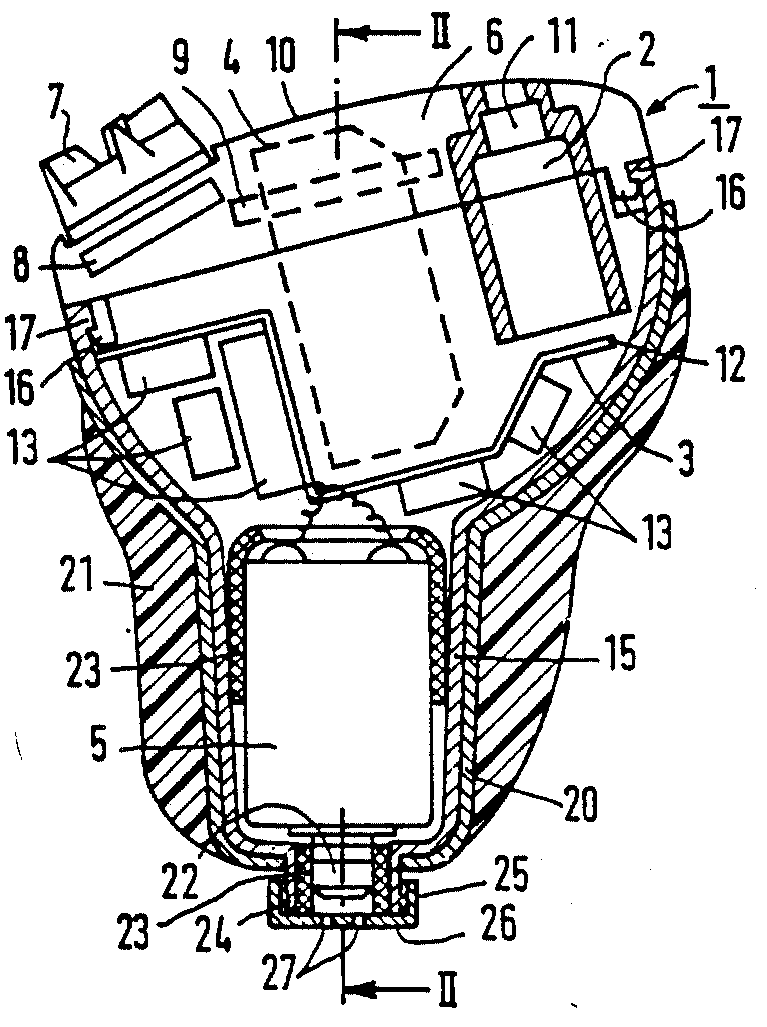
Example BTE: housing (17) and ear tip (20).
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Constructional arrangements, e.g. casings, for implants | |
Storage case for drying purposes | |
Housing specially adapted for small components |
Further detail is covered by Indexing Code group H04R 2225/77. Classification is obligatory.
This place covers:
For examples, please see H04R 25/65.
This place does not cover:
Hybrid ear moulds or post-processing thereof for their customisation |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Earpieces of the intra-aural type | |
Measuring physical dimensions, e.g. size of the entire body or parts thereof | |
Earplugs for protection | |
Computer-aided design | |
Three dimensional (3D) modelling, e.g. data description of 3D objects |
Further detail is covered by Indexing Code groups H04R 2460/09 and H04R 2460/11. Classification is obligatory.
This place covers:
Means for protecting electric components, e.g. receivers, microphones, in hearing aids against e.g. earwax, oil, moisture, debris, and other foreign material; Their mounting or interconnection
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Screens for loudspeakers | |
Protective screens for microphones, e.g. all weather or wind screens | |
Mounting or interconnection of hearing aid parts in general, e.g. inside tips, housing or to ossicles |
This place covers:
Example BTE:
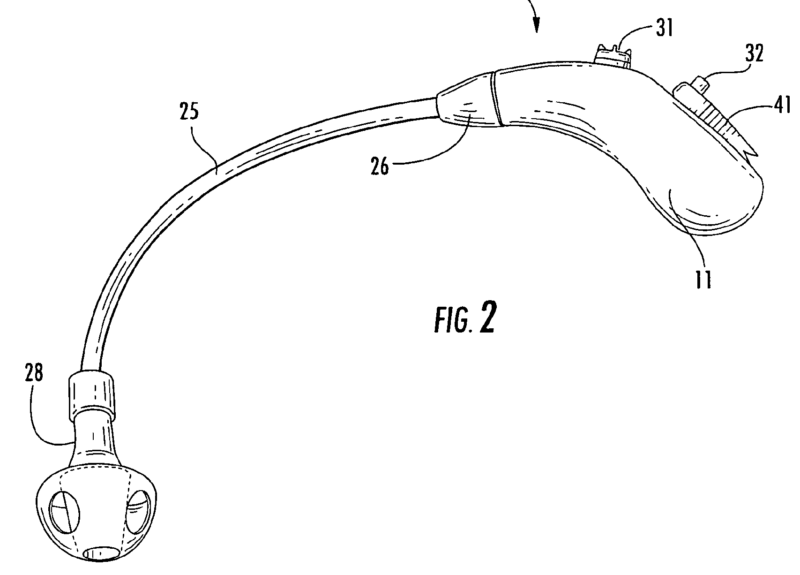
Example ITE:
Example CIC:

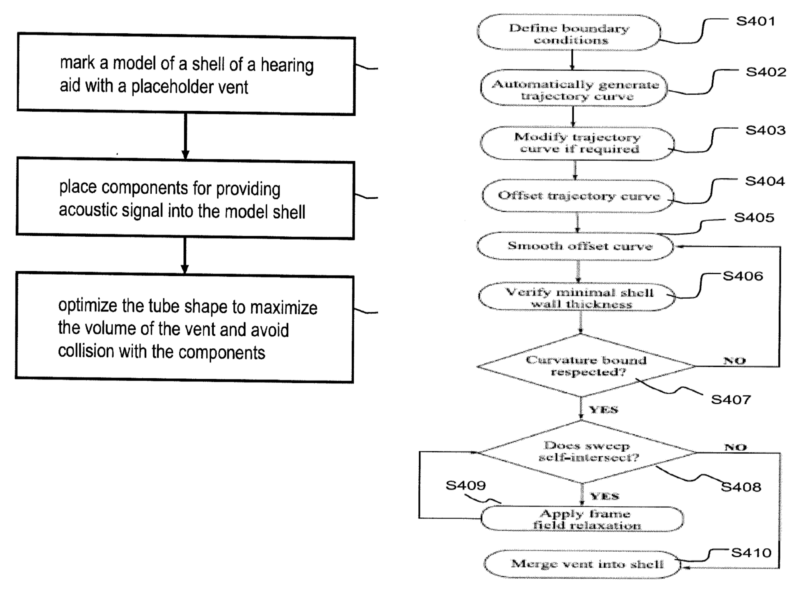
This place covers:
Aspects of design and manufacturing of housing parts
Example of design and subsequent manufacture of ear mould:

Example of design of a vent in a hearing aid shell (left-hand figure: general modelling and right-hand figure a method for optimising the shape of the vent)
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Moulding of plastics | |
Shaping of plastics in general |
This place covers:
Electronic adaptation of the hearing aid settings in response to audiological test signals to compensate for hearing aid loss or changes therein, i.e. initial or subsequent fitting.
Initial fitting is generally carried out by an acoustician. Subsequent fitting can be carried out by the acoustician or by the user, e.g. with audiological test signals generated in the hearing aid.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Ear tip or ear moulds for hearing aids | |
Audiometering |
Further detail is covered by Indexing Code subgroups H04R 2225/39, H04R 2225/81 and H04R 2225/83. Classification is obligatory.
This place covers:
Electric tinnitus maskers providing an auditory perception e.g. an acoustic noise signal around the tinnitus frequency. The tinnitus maskers can be stand-alone devices or can be integrated in a hearing aid.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Evaluating tinnitus | |
Devices or methods to cause a change in the state of consciousness | |
Masking sound in general |
This place covers:
Audio distribution systems for buildings, e.g. stations or religious facilities, for venues, e.g. in stadiums or in concerts halls, or for domestic use, i.e. multiroom.
Public address systems for buildings, e.g. stations or religious facilities, for open air, for indoor and outdoor venues, e.g. in stadiums or in concerts halls, or for domestic use, i.e. multiroom.
This place does not cover:
Circuits for preventing acoustic reaction | |
Monitoring or testing arrangements for public address systems |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Circuits for distributing signals to loudspeakers in general | |
Audible signalling systems and audible personal calling systems | |
Audible advertising | |
Combined visual and audible advertising or displaying, e.g. for public address | |
Speech enhancement, e.g. noise reduction, echo cancellation in public address systems | |
Installations of electric cables or lines in or on buildings or equivalent structures | |
Amplifiers | |
Powerline communication in general | |
Audio/video applications of powerline communications | |
Broadcasting |
Further detail is covered by the subgroups of Indexing Code group H04R 2227/00 and by Indexing Code groups H04R 2420/05 and H04R 2430/03. Classification is obligatory.
This place covers:
Inductive loop or similar systems to enable communication with the hard of hearing.
This place does not cover:
Electric hearing aids | |
Cochlear implants | |
Teaching or communicating with deaf persons |
This place covers:
- Monitoring or testing arrangements for transducers, loudspeakers, microphones or public address systems;
- Testing of transducer, loudspeaker or microphone connection
- Visual indication of acoustic signal levels.
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Detection of loudspeaker or microphone connection for stereophonic purposes | |
Monitoring or testing of hearing aids | |
Circuits or components specially adapted for stereophonic broadcast systems |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measurement of mechanical vibrations or ultrasonic, sonic or infrasonic waves, e.g. sound dosimeter | |
Testing of electronic circuits in household appliances or professional audio/video equipment | |
Sound-field adaptation dependent on speaker detection |
Further detail is covered by the subgroup of Indexing Code groups H04R 2420/05 and H04R 2430/03. Classification is obligatory.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Monitoring | encompasses indication |
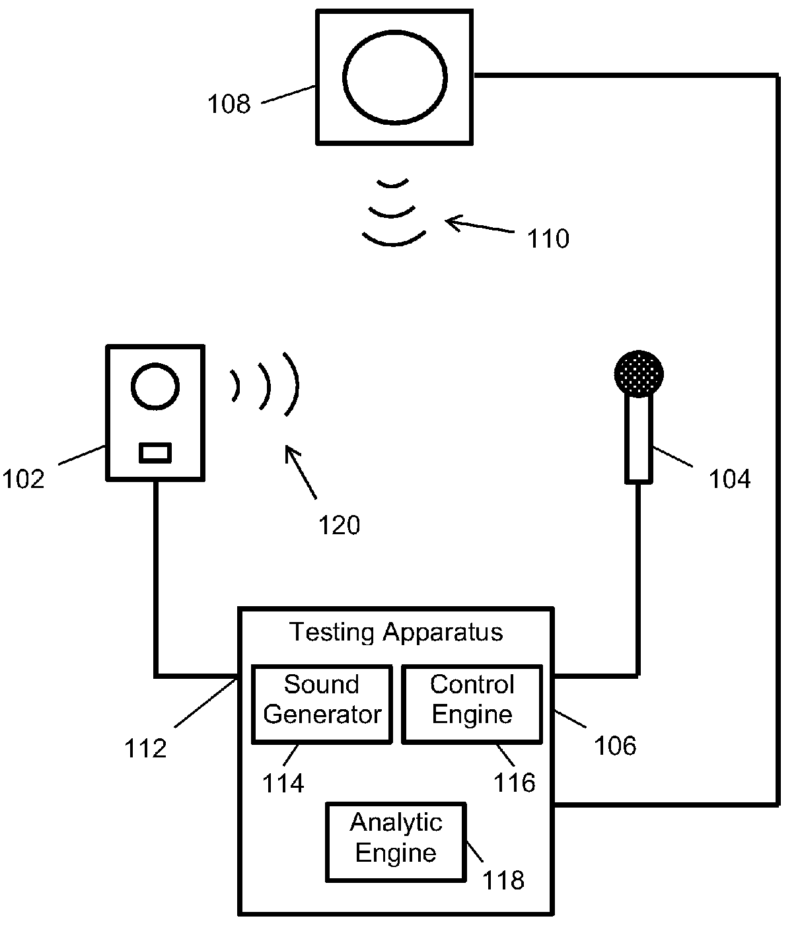
This place covers:
Loudspeaker 102 the one under test is in the exemplary figures below.
Loudspeaker 108 is the reference loudspeaker.

This place does not cover:
Testing or monitoring arrangements for public address systems |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Signal processing adapting stereophonic sound system to listener position |
This place covers:
Example for test method:
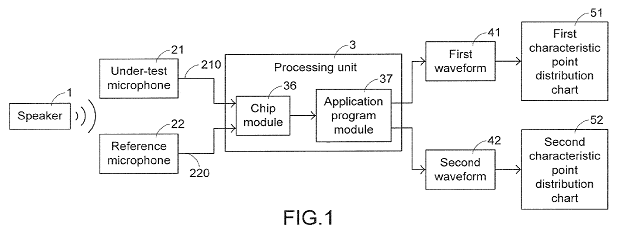
Example for testing arrangement to test a plurality of microphones:
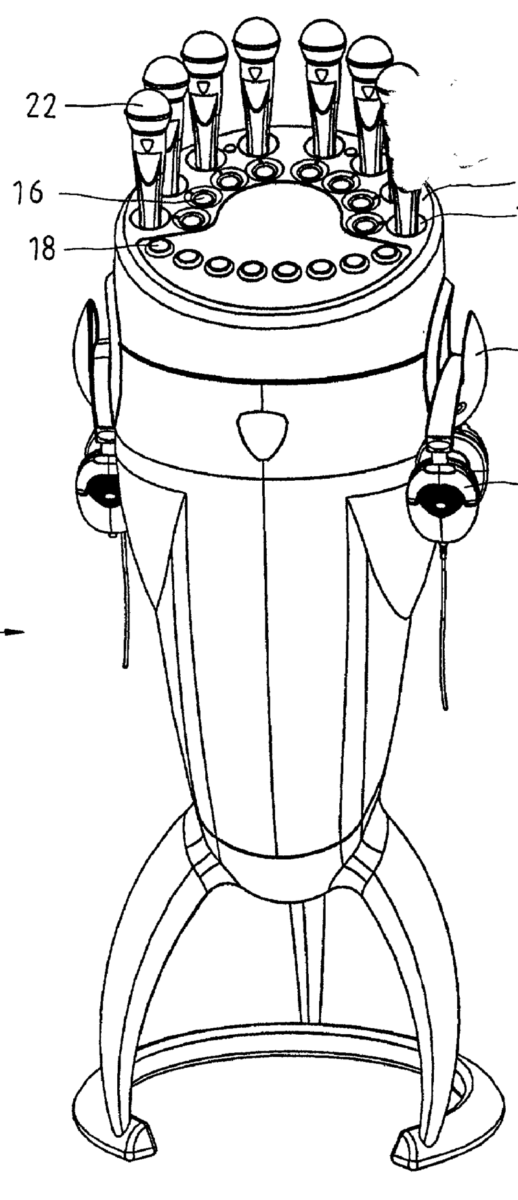
This place does not cover:
Testing or monitoring arrangements for public address systems |
This place covers:
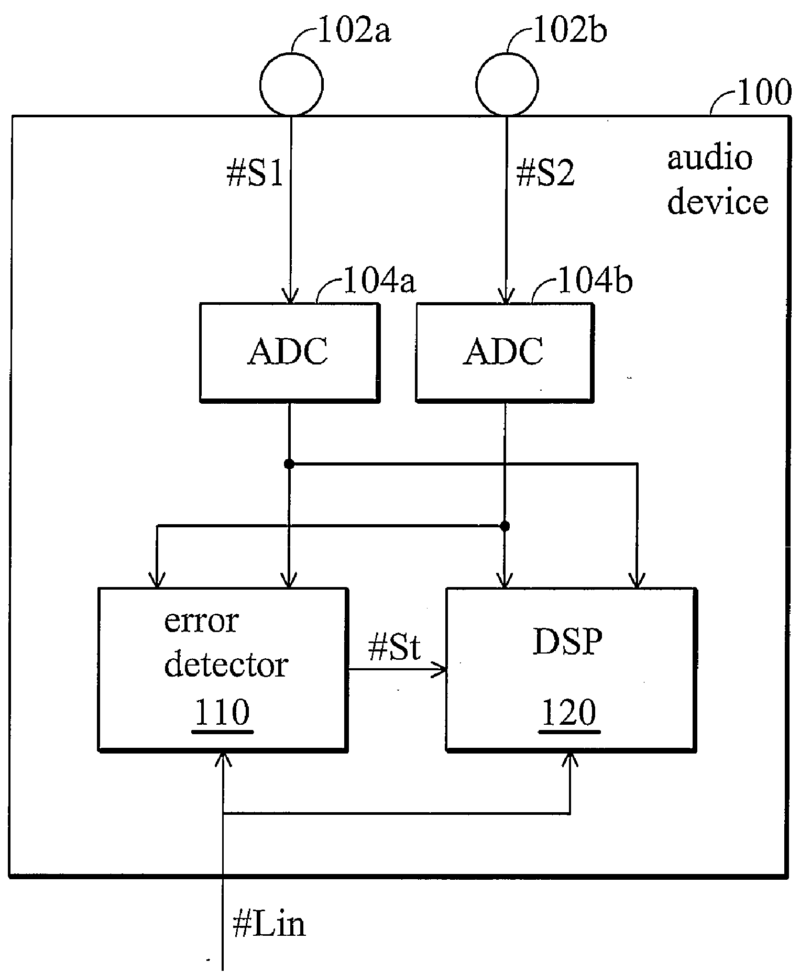
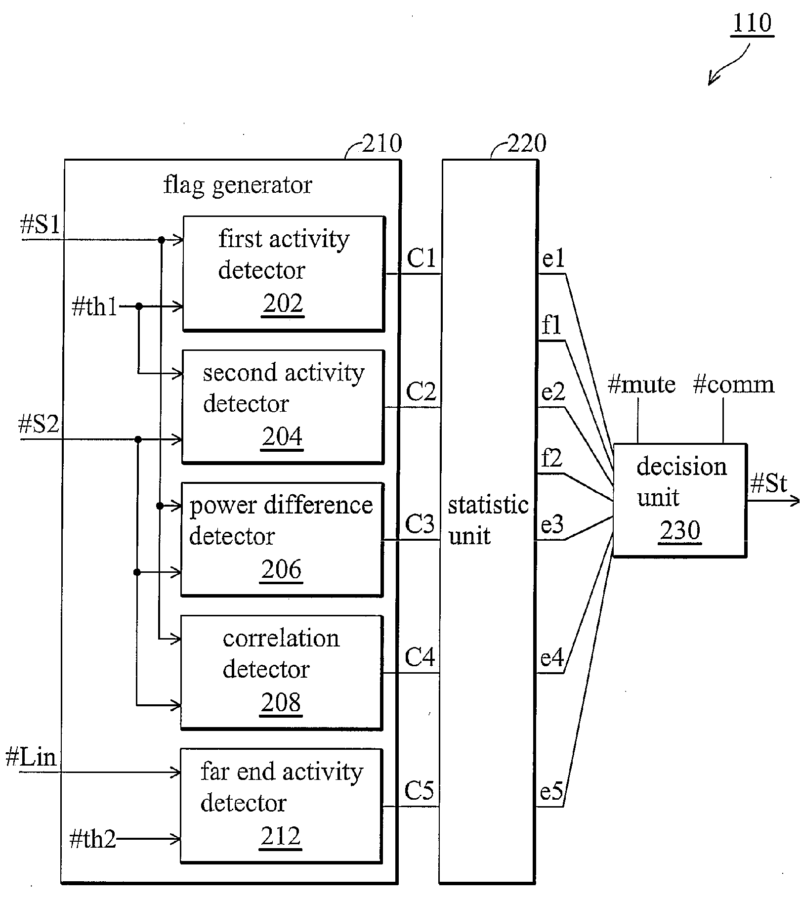
For example:
Functioning of the microphones (102a, 102b) is monitored (error detection 110) and if one microphone is considered defect, its signal is not used for further processing.
This place covers:
For example: US6272229.
For example: microphone matching in a microphone array in general
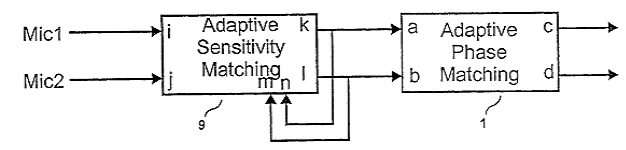
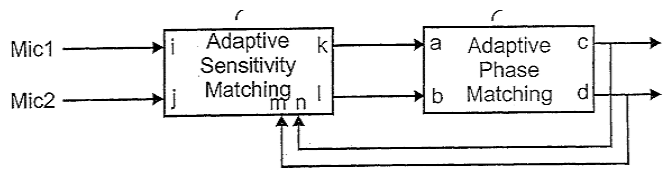
For example: microphone matching (CABLE) in an adaptive interference canceller (side-lobe canceller):
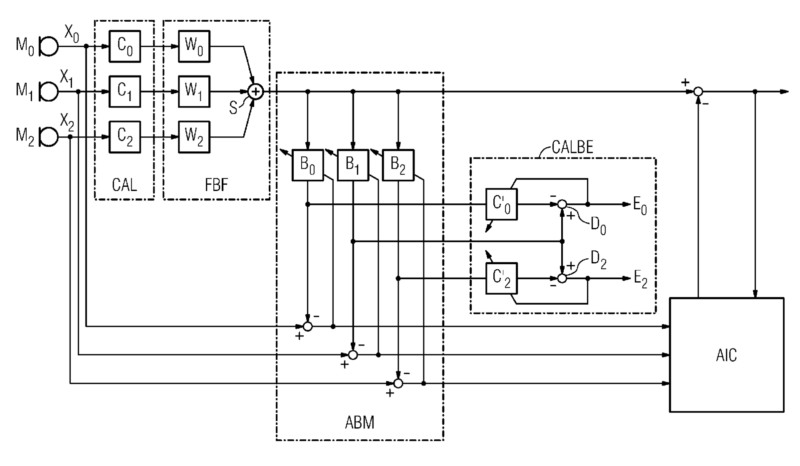
This place covers:
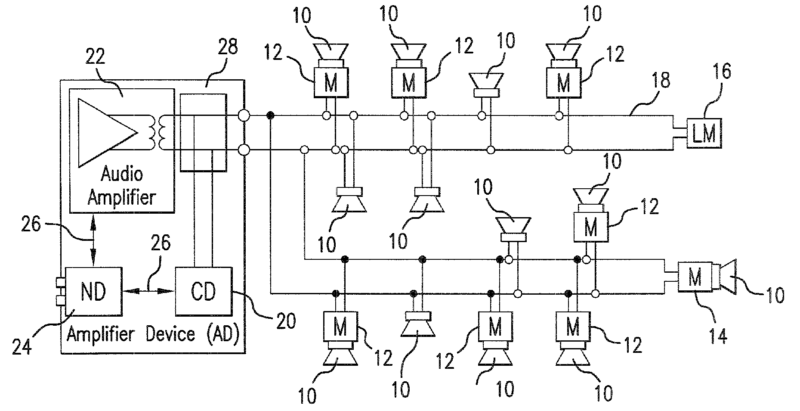
For example:
In the PA system shown in the figure control device (CD) polls all monitoring devices 12,14 and line monitoring devices 16 to check if errors have occurred: Monitoring 12 checks for example whether the voice coil in the loudspeaker is an open connection (e.g. loudspeaker is defect)
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Public address systems per se | |
Testing and monitoring for signalling and alarm systems |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Indicating measured values | |
Arrangements for displaying electric variables or waveforms | |
Visual indication of stereophonic sound image |
This place covers:
Apparatus or processes specially adapted for the manufacture of
- acoustic transducers, including MEMS acoustic transducers
- diaphragms therefor;
- means for securing diaphragm or cone resiliently to support by flexible material, springs, cords, or strands for diaphragms.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Microphones and microspeakers | |
Manufacture of microstructural arrangements of deformable or non-deformable structures in general | |
Packaging of Smart-MEMS, i.e. packaging together processing unit and MEMS | |
Interconnecting the MEMS and the processing unit | |
Processes for packaging MEMS | |
Pressure measurement / constructional details associated with semiconductive diaphragm sensors, e.g. etching of diaphragms |
Further detail is covered by Indexing Code groups H04R 2201/003, H04R 2231/001 and H04R 2231/003. Classification is obligatory.
This place covers:
For example: Aluminium diaphragm (1) is pressed (5-7) out of an aluminium plate. The diaphragm is chemically treated cleaned (8-10) and the resulting diaphragm is treated with anodic oxidation to form an amorphous ceramic diaphragm of Al2O3. The amorphous diaphragm is heat treated to create corundum, a crystalline form of Al2O3.
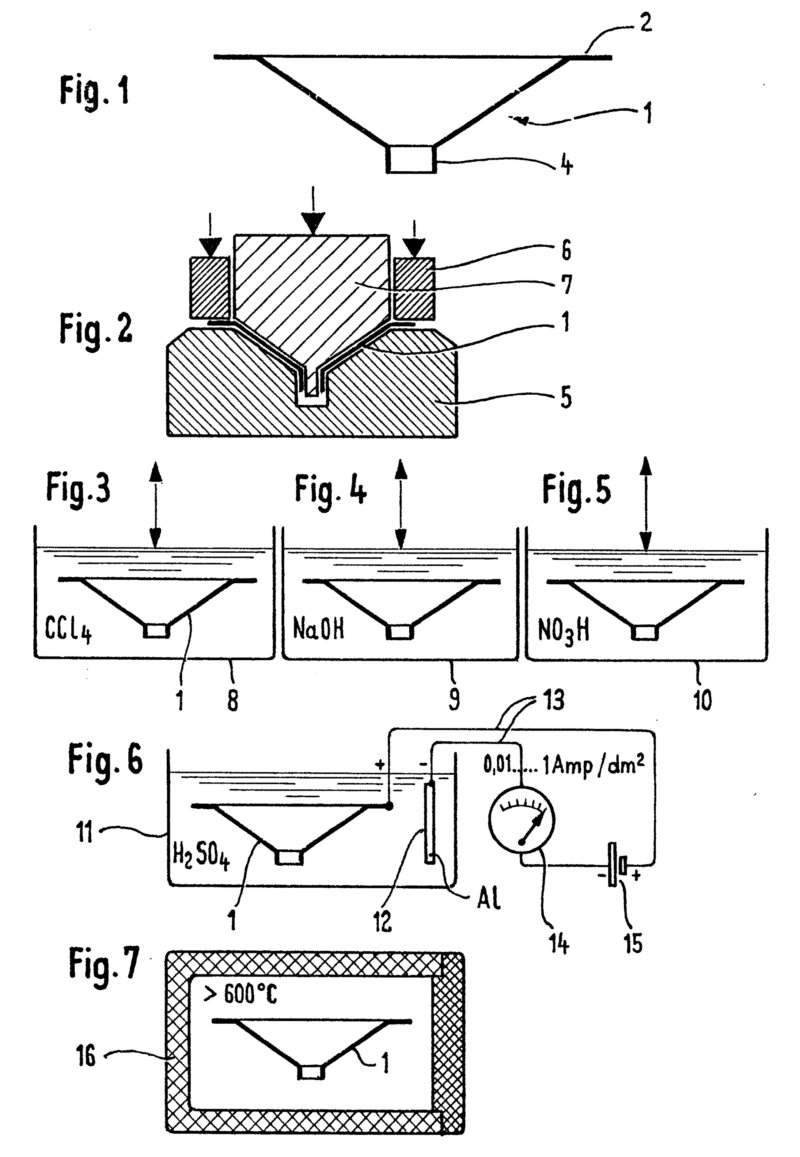
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Diaphragms for electromechanical transducers characterised by the construction | |
Securing diaphragm or cone resiliently to support by flexible material, springs, cords, or strands | |
Moulding of plastics | |
Shaping of plastics in general | |
Manufacture of micromechanical membranes and diaphragms | |
Electroplating | |
Anodizing of metals |
Further detail is covered by Indexing Code group H04R 2207/021 and the subgroups of H04R 2307/00. Classification is obligatory.
This place covers:
For example: A transducer is assembled with the help of jig 1 and jig 12 used for relative positioning of the parts during assembly. Jig 12 is removed before mounting of bottom frame 8. Jig 1 is removed after complete assembly.
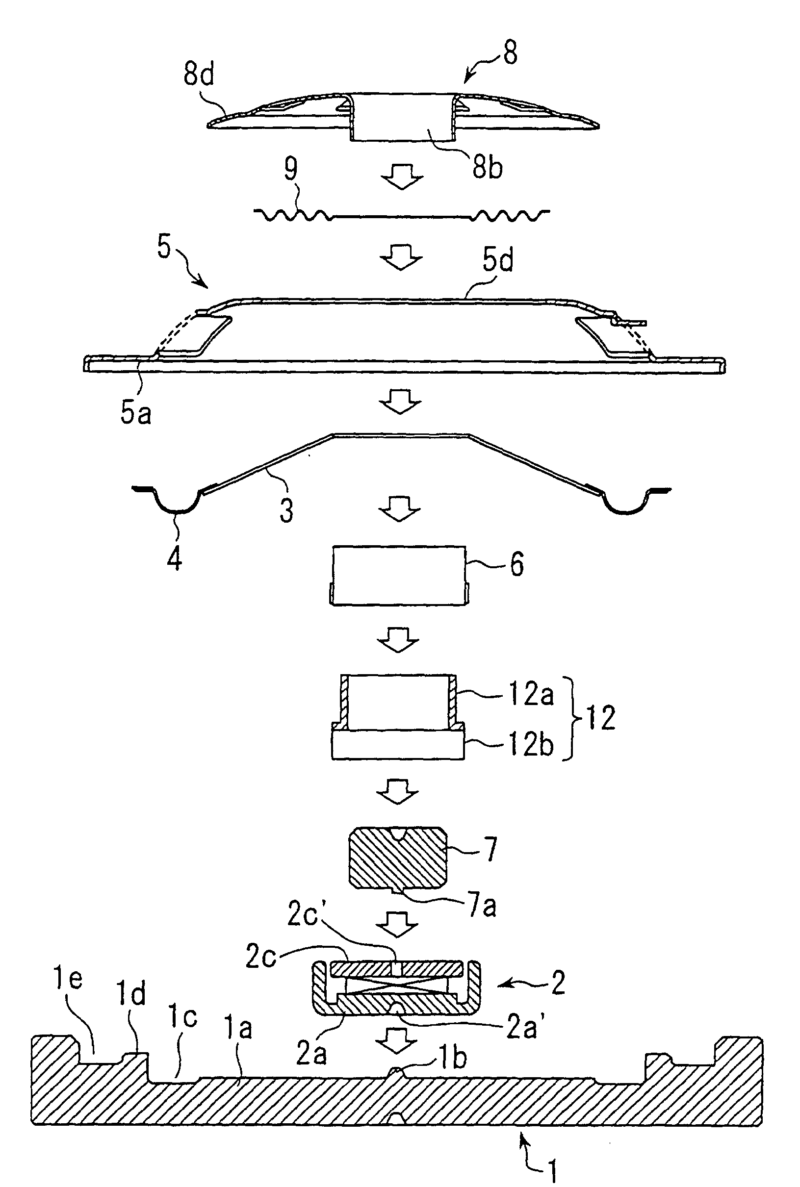
For example: A centre pole cap 88 is formed with cap die press 82. With help of pattern roller 82 an axial griping surface 92 is formed on the centre pole 16, after which the cap is pressed on the pole with press 86. The cap is held in place by interference fit.

Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Assembly of magnetic circuit for electrodynamic transducers | |
Adhesives |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
MEMS transducers of the electrostatic type | |
Arrangements for avoiding sticking of the flexible or moving parts of MEMS devices having such parts | |
MEMS packages and encapsulations | |
Microphones and microspeakers | |
MEMS structures allowing for movement | |
Type of movement |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
MEMS | Microelectromechanical system |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Sound or noise insulation, absorption, or reflection | |
Sound or noise insulation, absorption, or reflection of floors or ceilings | |
Sound or noise insulation, absorption, or reflection of flooring | |
Room acoustics, i.e. forms of, or arrangements in, rooms for influencing or directing sound |
This place covers:
For example:
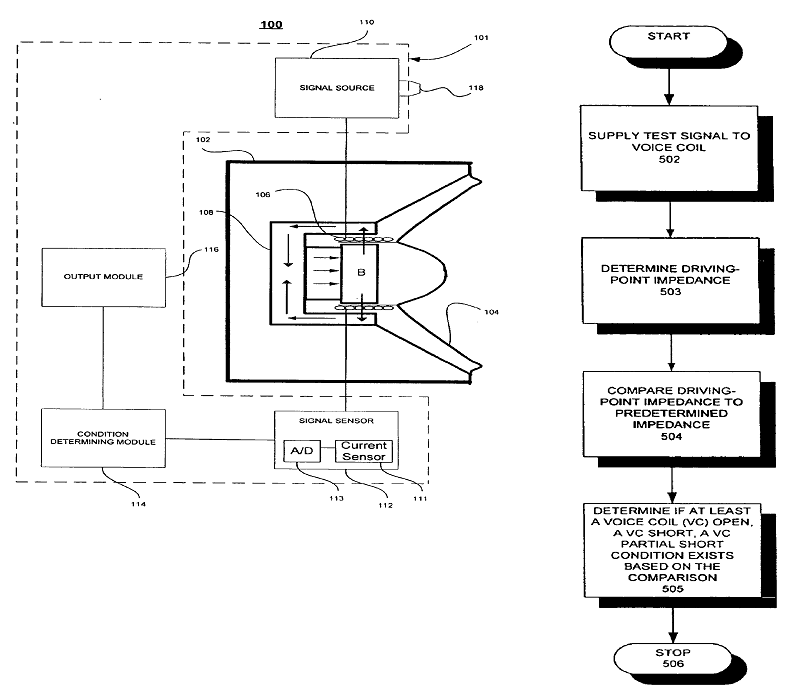
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Garments adapted to accommodate electronic equipment | |
Footwear with sound or music sources |
This place covers:
For example: (amplifier (10) mounted to transducer (20))
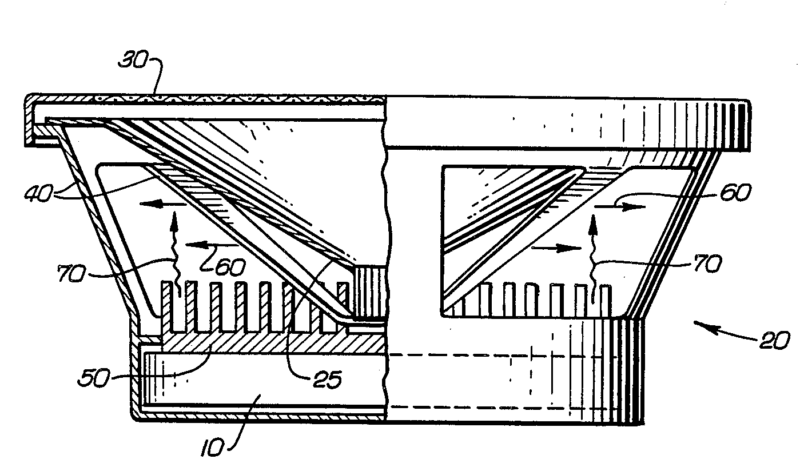
(amplifier mounted to loudspeaker enclosure)
For example: (the active loudspeaker (311,312) is placed in a separate enclosure (11,12) used in a television)
This place does not cover:
General applications |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Single (sub)woofer with two or more satellite loudspeakers for mid- and high-frequency band reproduction driven via the (sub)woofer |
This place covers:
For example: manufacture of loudspeaker casing with backloaded horn using two lateral plates (1) and a plurality of intermediate plates (2) which are screwed together (6,7).
For example: assembly of loudspeaker.
This place covers:
Typical components are earpiece supports, ear tips, and ear cushions, transducers specially adapted for earphones or headphones.
This place does not cover:
Manufacture of diaphragms for acoustic transducers |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Manufacture or assembly of earphones or headphones | |
Manufacturing aspects of the magnetic circuit of loudspeaker or microphone transducers |
This place covers:
For example: (monophonic: microphone (40)).
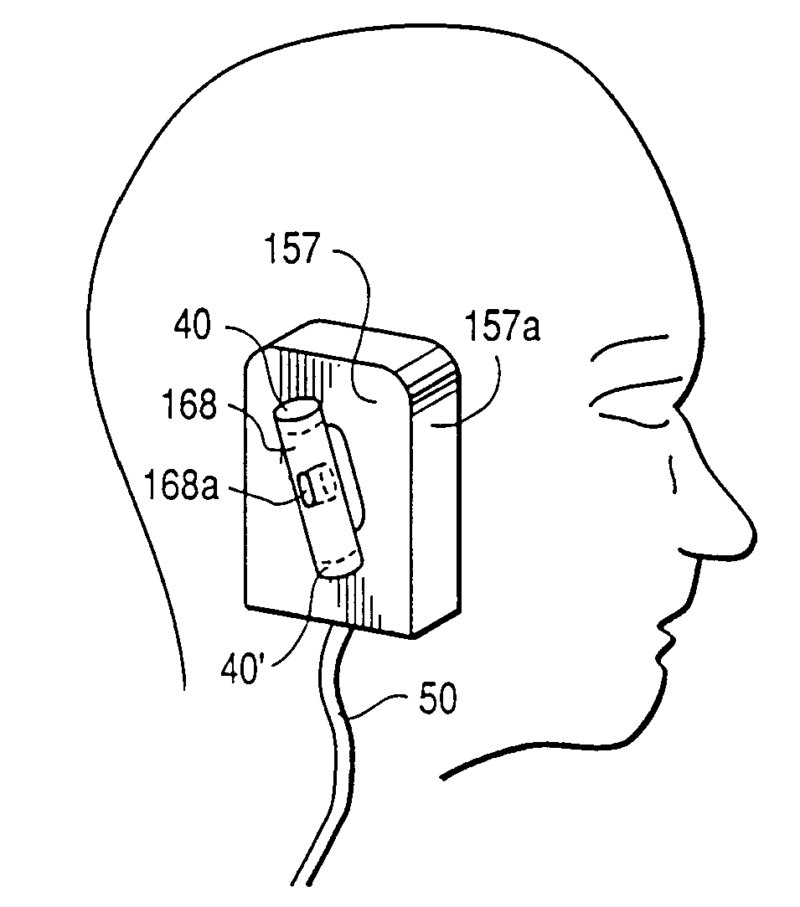
For example: (stereophonic; microphone (30)).
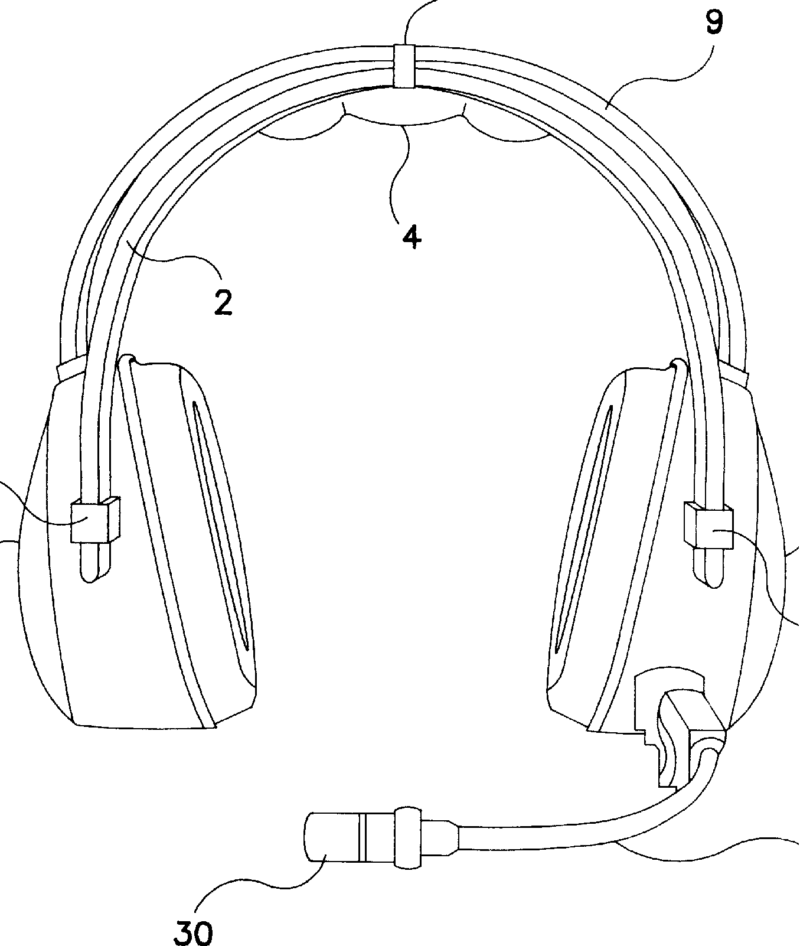
This place covers:
First illustrative example of the subject matter classified in H04R 2201/109:
- Monophonic: rotatable joint 25 enables rotation about axes B and C.

Second illustrative example of subject matter classified in H04R 2201/109:
- Monophonic: rotatable joints 28a and 28b enable rotation of the microphone arm 24 and of the earpiece, respectively.
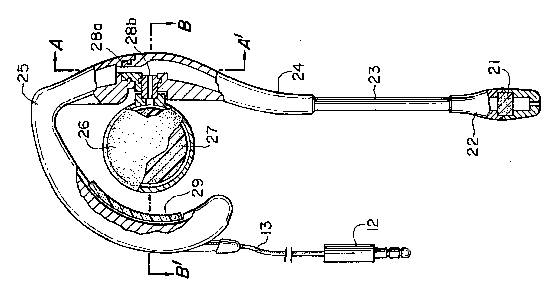
Third illustrative example of subject matter classified in H04R 2201/109:
- Stereophonic earpieces are releasably mounted using hook-and-loop type fastener.
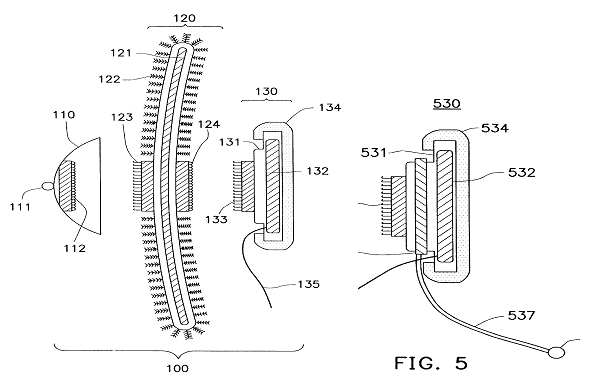
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Mouthpieces and attachments therefor in general | |
Throat mountings for microphones | |
Transceivers carried on the body, e.g. in helmets | |
Substation equipment including speech amplifiers providing hands-free use or loudspeaker mode |
This place covers:
For example:US5933508 (phase plug of a compression driver), US2006153412 (phase plug used with a transducer).
For example: (phase plug (30) of a compression driver)
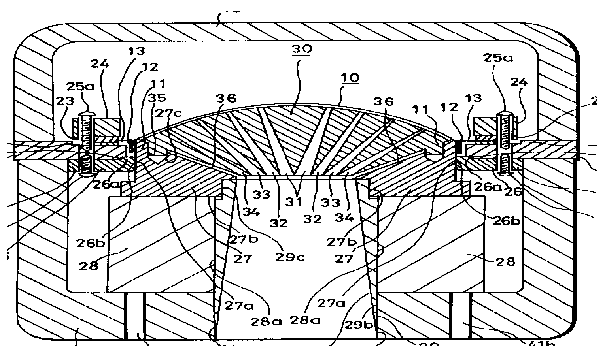
For example: (phase plug used with a transducer)
This place covers:
See for example: generation of multiple sound channels (12-1, 12-2) to reproduce stereophonic sound
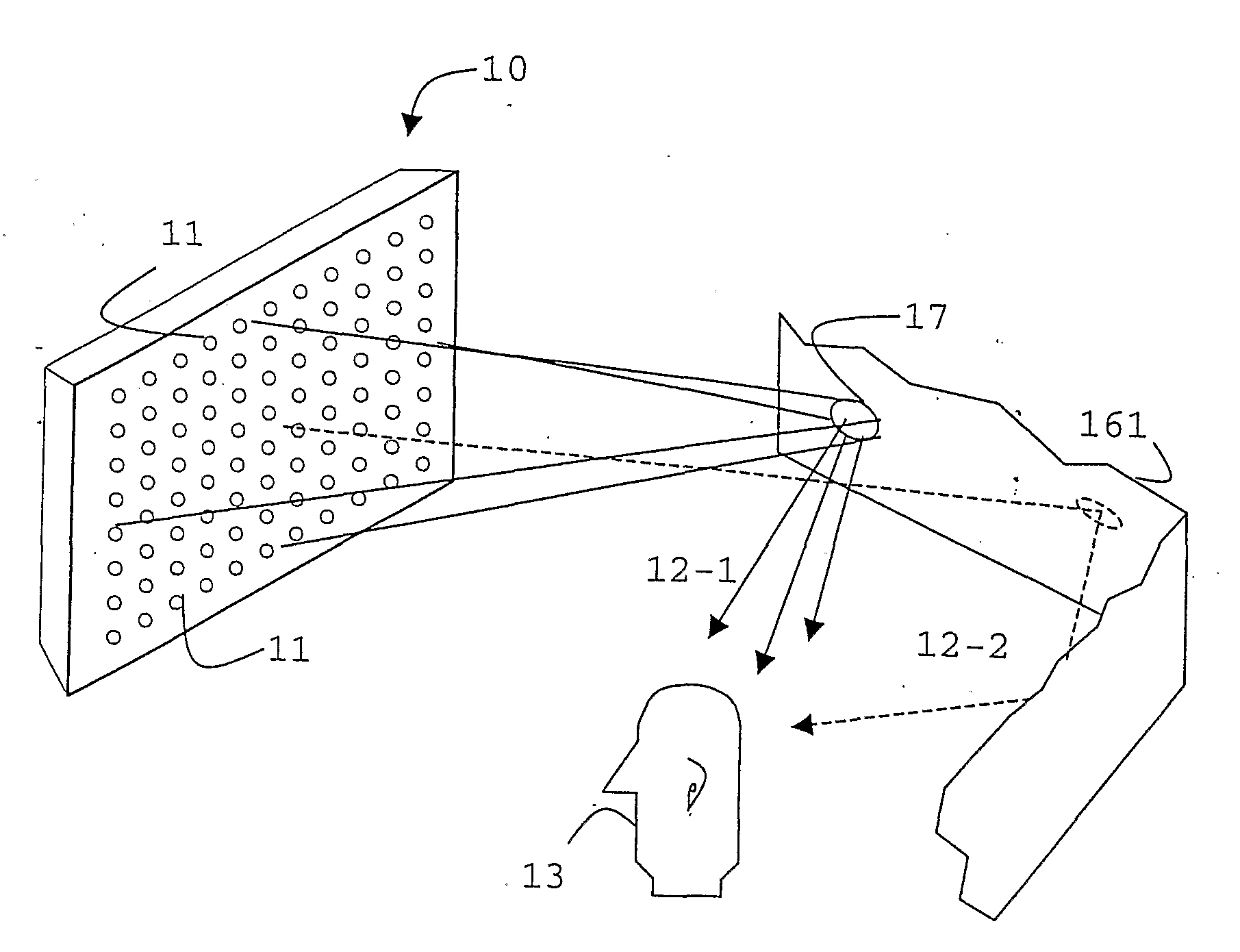
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Beamforming aspects for sound reproduction in general |
This place covers:
For example: (electric connection)
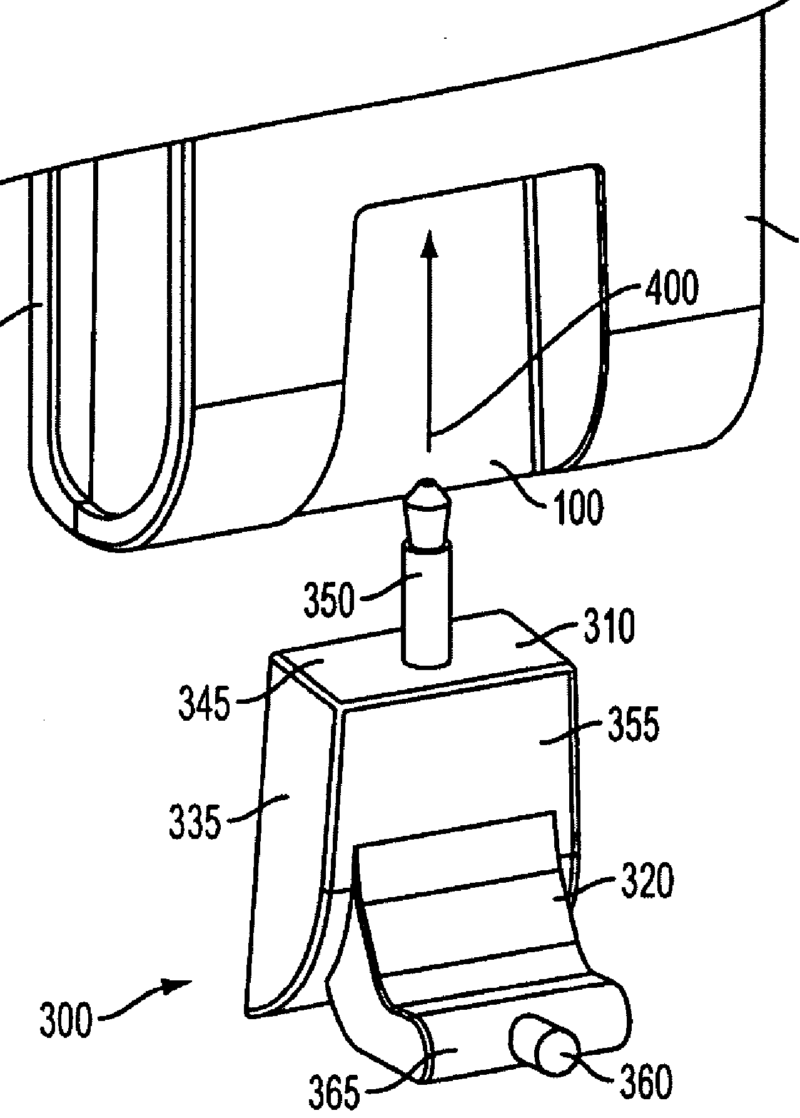
JP2005136895 (acoustic connection)
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
External expansion units, e.g. docking stations | |
Cabinets for information storage devices; Cases; Stands; Disposition of apparatus therein or thereon | |
Disposition of constructional parts in the apparatus for information storage devices, e.g. of power supply, of modules | |
Side-by-side or stacked arrangements for casings, cabinets or drawers for electric apparatus |
This place covers:
For example: (two-channel microphones in earpiece (2a, 2b) mounted on a spherical structure (1) for four-channel sound capture).
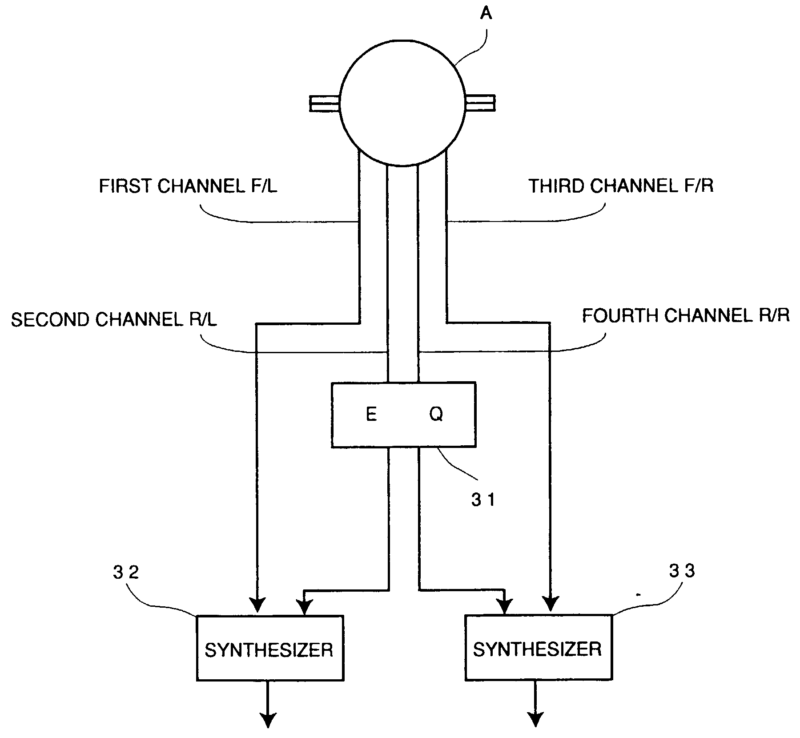
For example: (multiple channels (20, 20') in earpiece (30) of headphones).
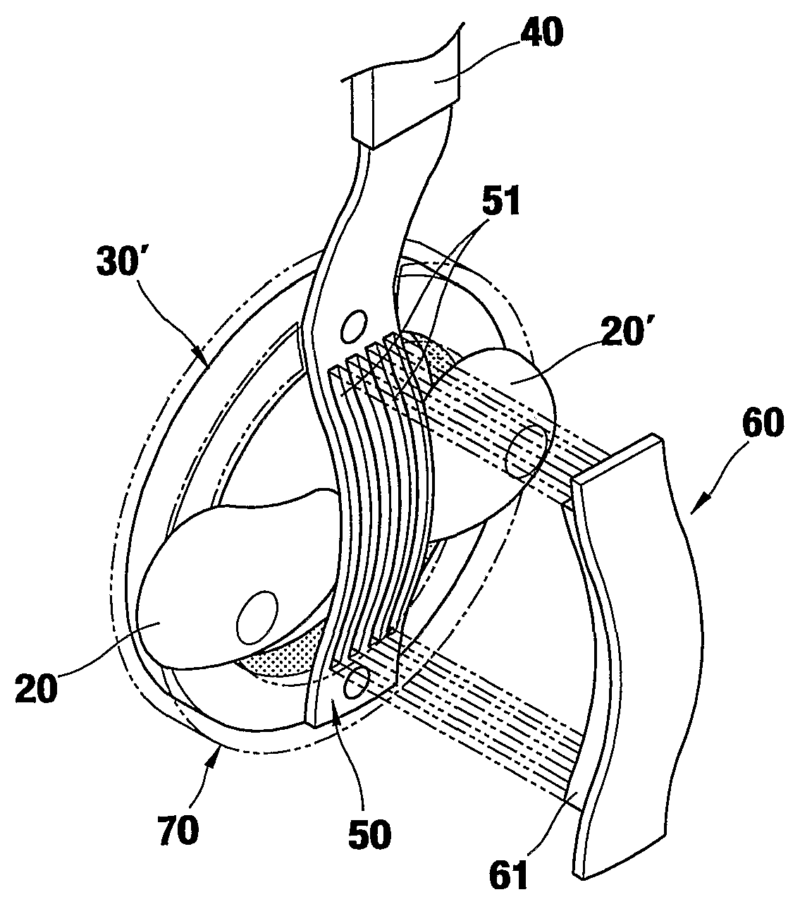
For example: (multiple channels in single loudspeaker box).
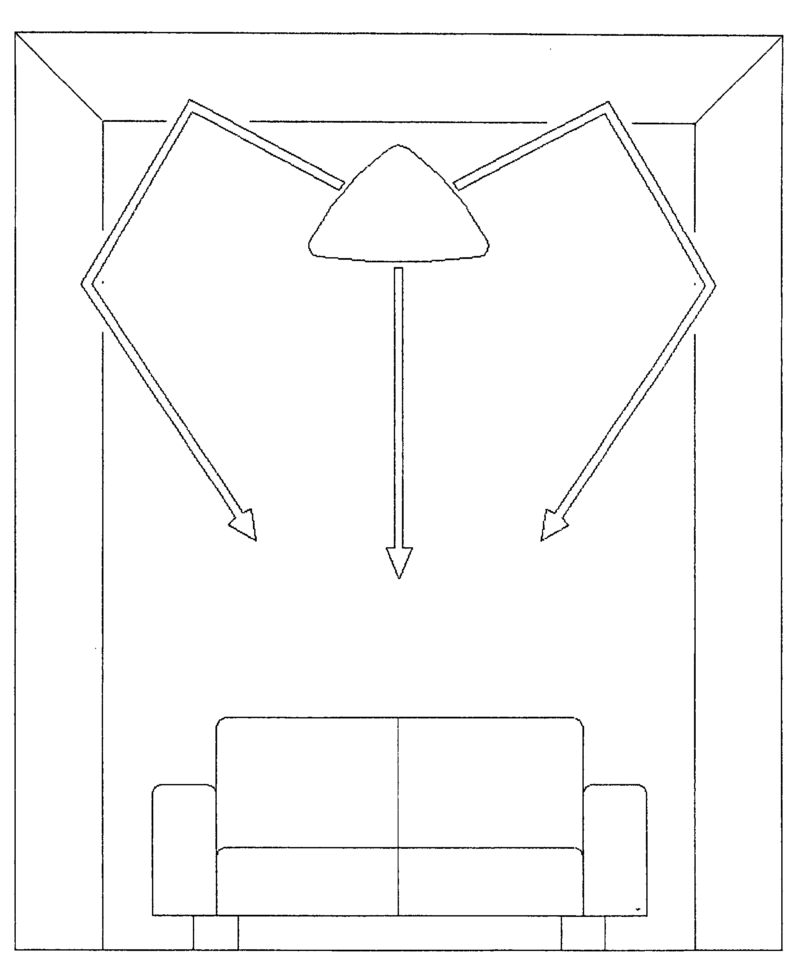
For example: (multiple channels in single loudspeaker box, comprising a pistonic loudspeaker transducer (7) and a distributed mode panel (3) with exciters (5)).

Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Positioning of loudspeaker enclosures for spatial sound reproduction | |
Positioning of microphones for spatial sound recording in general |
This place covers:
Aspect relating to the relative positioning of loudspeaker enclosures, e.g. determination of their actual position
This place does not cover:
Mounting of transducers in earphones or headphones | |
Public address systems | |
Electronic adaptation of stereophonic sound system to listener position or orientation |
This place covers:
For example:
This place does not cover:
Deaf-aid sets |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Telephone sets for the hearing impaired | |
Mobile telephones for the hearing impaired |
This place covers:
For example: (flange (a) to prevent deformation of dome during firing to obtain a ceramic diaphragm
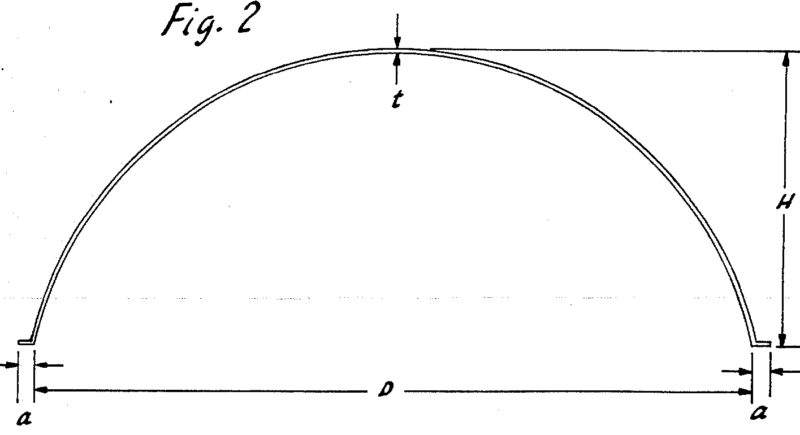
For example: (annular skirt (54) extending from the dome (52), around which a voice coil is wound)
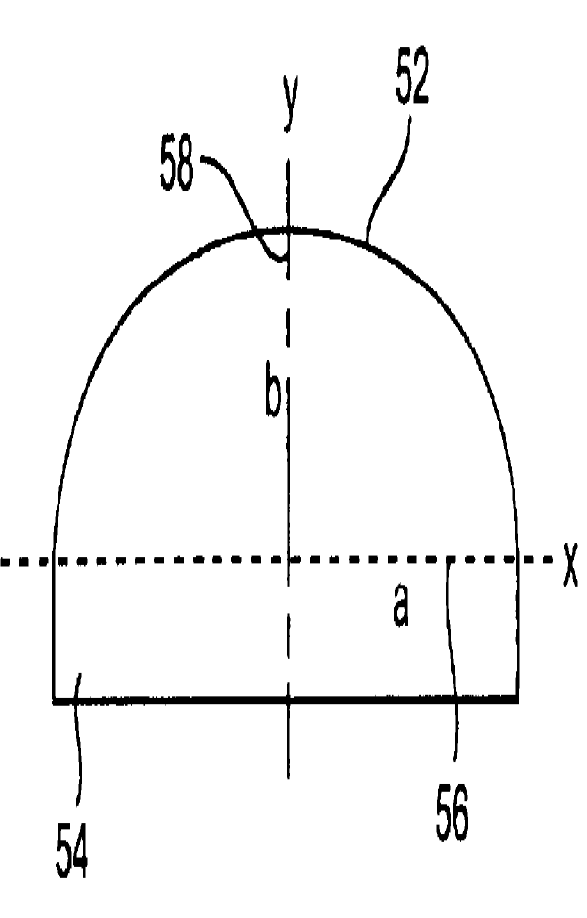
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Magnetic circuits for electrodynamic loudspeaker transducers | |
Magnetic materials, cores, yokes and magnets in general, and their manufacture |
This place does not cover:
Transducers capable of generating both sound as well as tactile vibration e.g. as used in cellular phones |
This place covers:
For example: (passive reduction with the help of a weight (23) mounted at the rear side of the magnetic circuit (25) of loudspeaker transducer (25)).
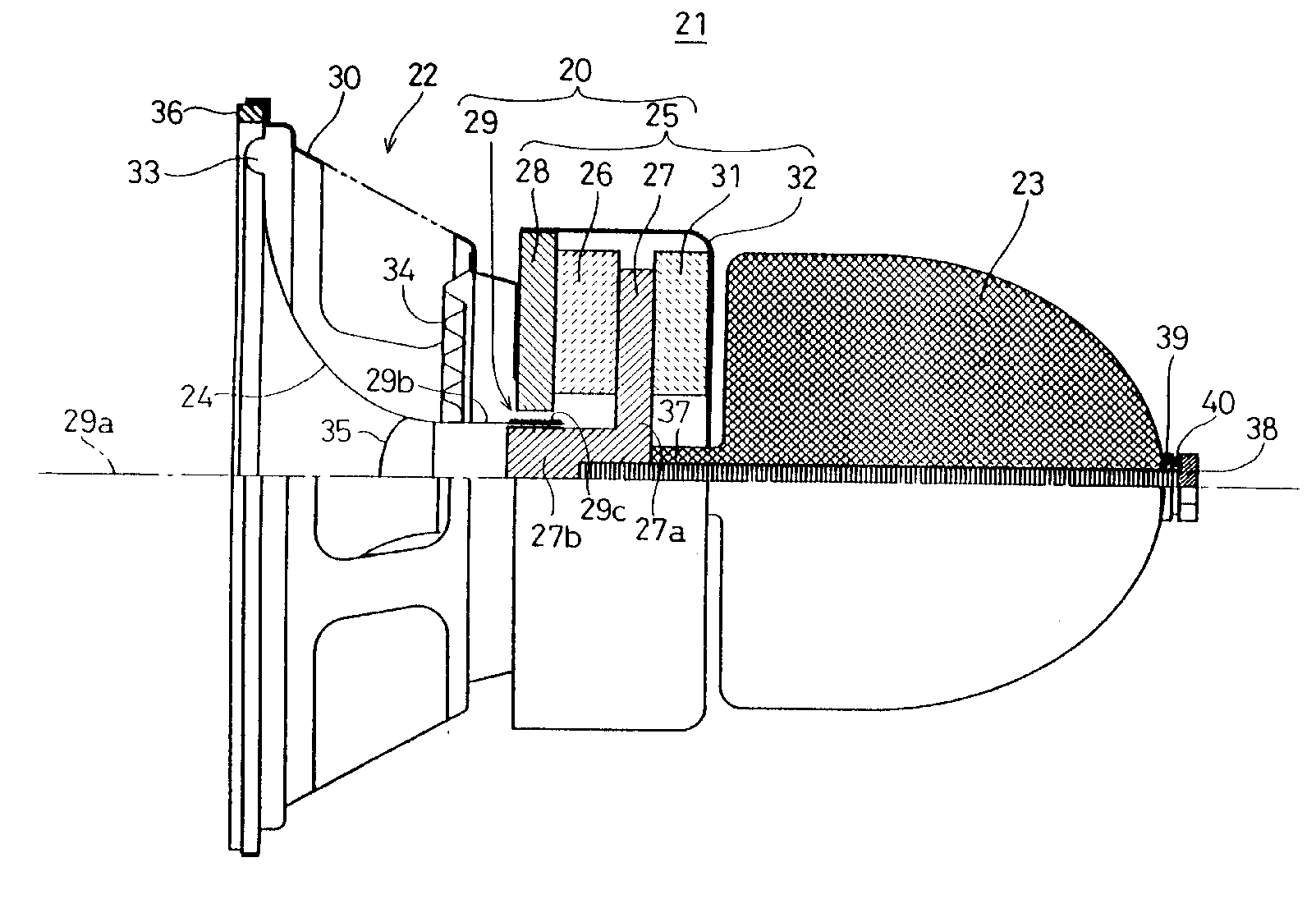
For example (active reduction with the help of a second magnetic circuit (5B). This second magnetic circuit is similar to the first magnetic circuit (5A) driving the diaphragm (8 and attached thereto. Voice coil 7B is driven with part of the signal with which voice coil 7A is driven, such that a weight coupled to the coil 7B move in a direction opposite to that of the diaphragm (8)).
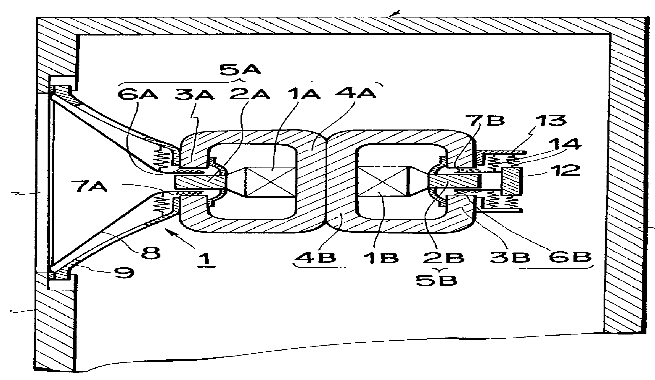
This place covers:
For example: (short circuited moving coil (28) and static driving coil (23)
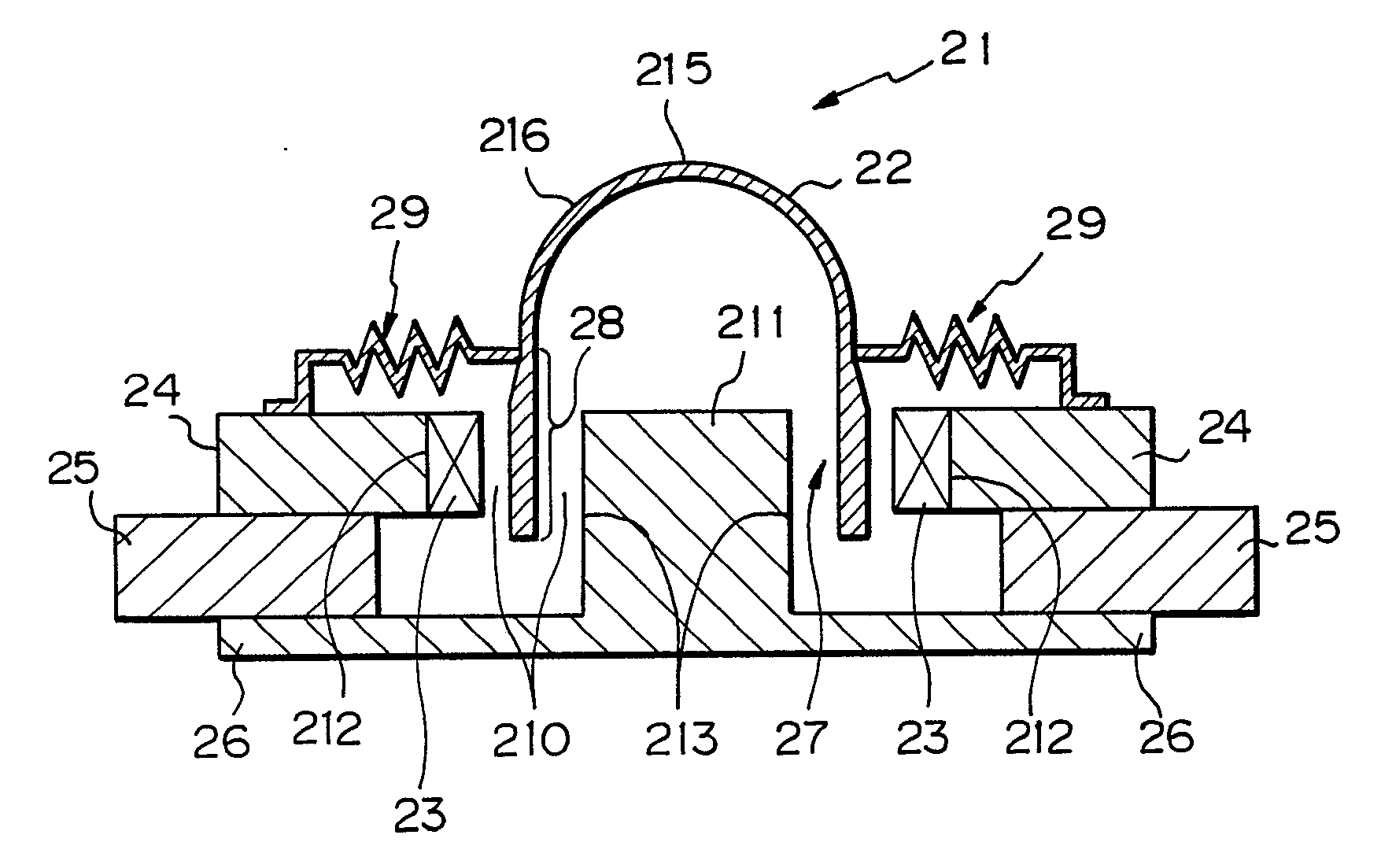
This place covers:
For example: a flat bi-layer tape (21) extending around a minor axis (24) in a helix to form a helical electro-active structure extending along the minor axis (24). The tape can be used as shown in the right-hand figure to obtain a loudspeaker driver (480).
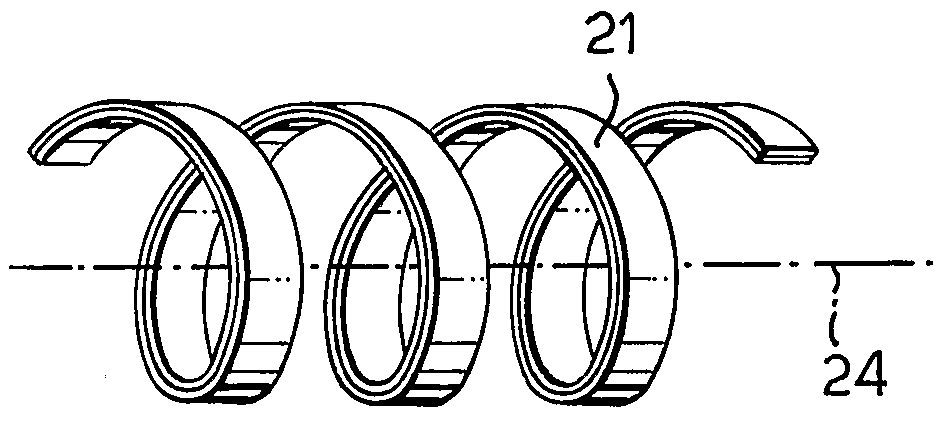
This place covers:
Construction or application of such transducers. Sound generation may be using piezoelectric, electrostatic, or other principles.
For example: schematic driving circuit (14, 6, 27) for a parametric loudspeaker array comprising a plurality of modules (12, 29).
An example for the modules used with the driving circuit above is shown in the figure directly below. A conductive electrode unit (32), a dielectric spacer (34) provided with an array of apertures (36), and a metallized polymer membrane (38). The components (32-38) are compressed against the spring (30) by an upper ring (40) that bears against the film (38) and threadably engages a base member (42) that supports the spring (30). The module (29) comprises a plurality of electrostatic transducers, corresponding with the respective apertures (36) in the polymer spacer (34).
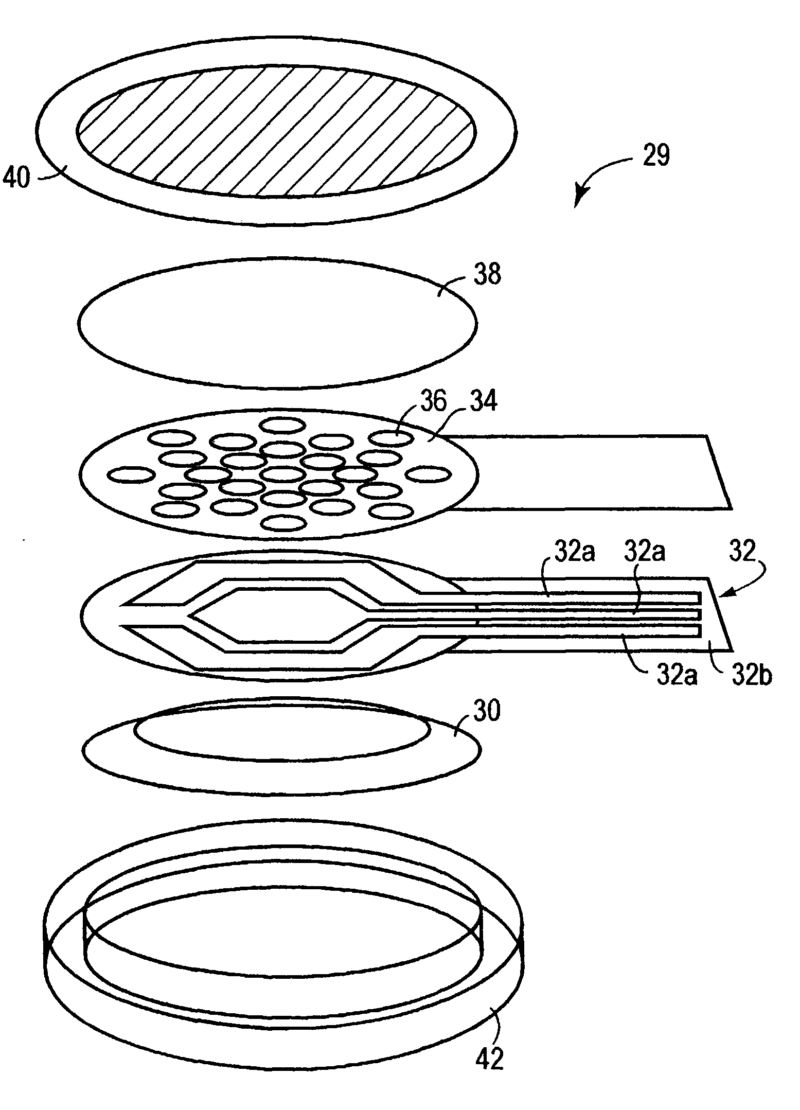
For example: sound reproduction for a TV, one parametric loudspeaker and one conventional nonparametric loudspeaker per channel.
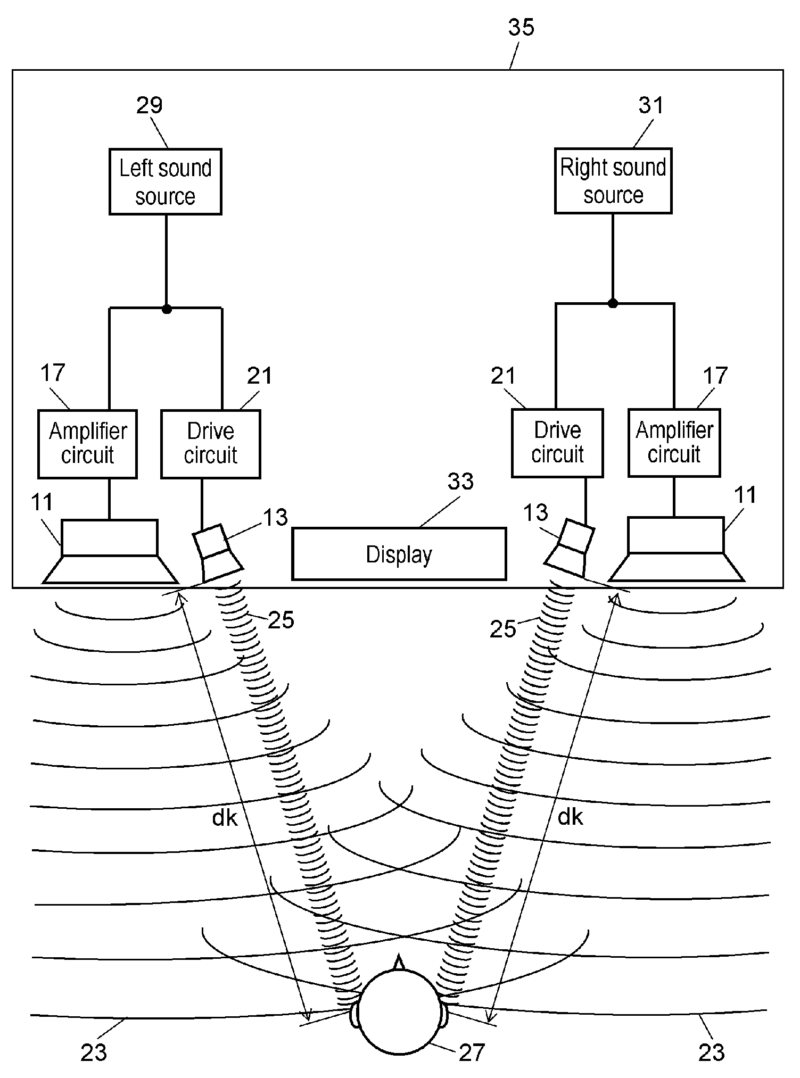
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used with the meaning indicated:
"parametric loudspeaker" | "superdirective loudspeaker". |
This place covers:
For example: Rechargeable battery (31) and battery charger 5 with charging contacts (51, 51')
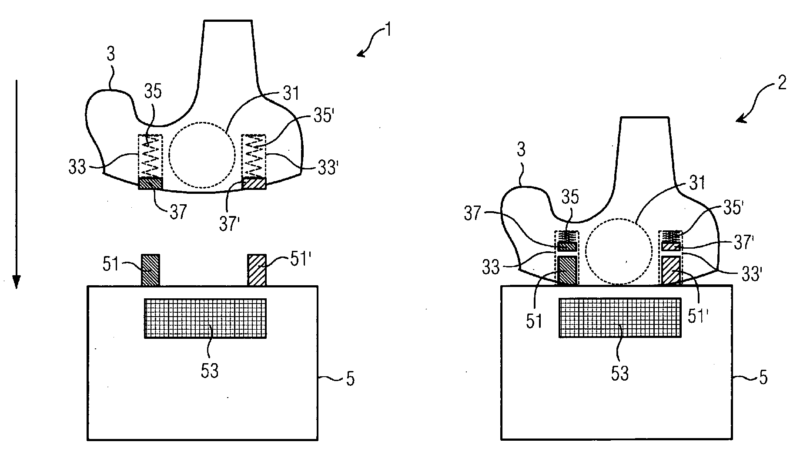
For example: Fuel cell (6) with fuel cell tank (8). Valve (9) is used for filling the tank and with the help of window (10) the amount of fuel can be checked.

For example: Thermic semiconductor elements (2) arranged on the outer surface of hearing aid.
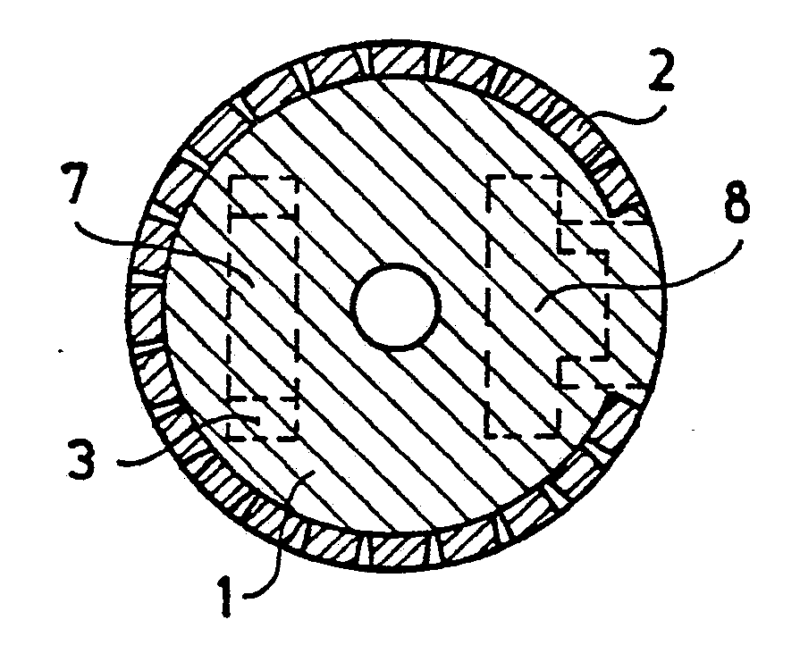
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
For earphones and headphones | |
Reduction of energy consumption in hearing aids | |
Electrical supply for implants | |
Fuel cells | |
Secondary cells (accumulators) | |
Circuit arrangements for charging or depolarising batteries or for supplying loads from batteries |
This place covers:
For example: A hearing aid comprises a step-down/step-up converter (3) as voltage regulator, which transforms both higher as well as lower operating voltage into at least one stabilised supply voltage.
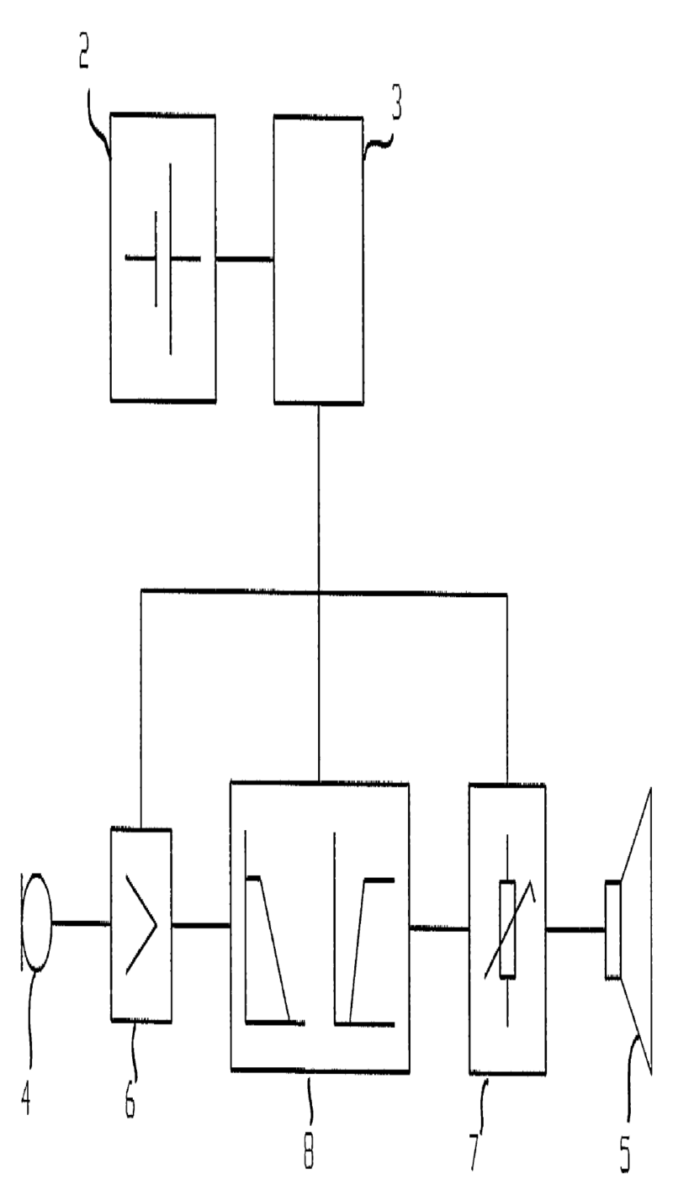
For example: Power source (206) is connected to a charge pump and voltage regulator (208), which generates a larger or smaller output voltage depending on the value of the power source (206) and stabilises the output voltage.
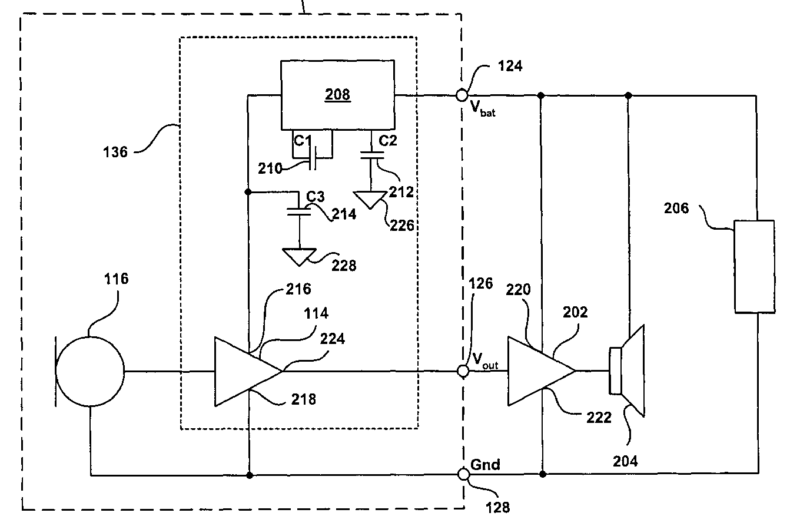
This place covers:
For example: Hearing aid with data logger (60) which logs data relating to sound environment, programs used, etc. The data stored can be used by subsequent fitting.
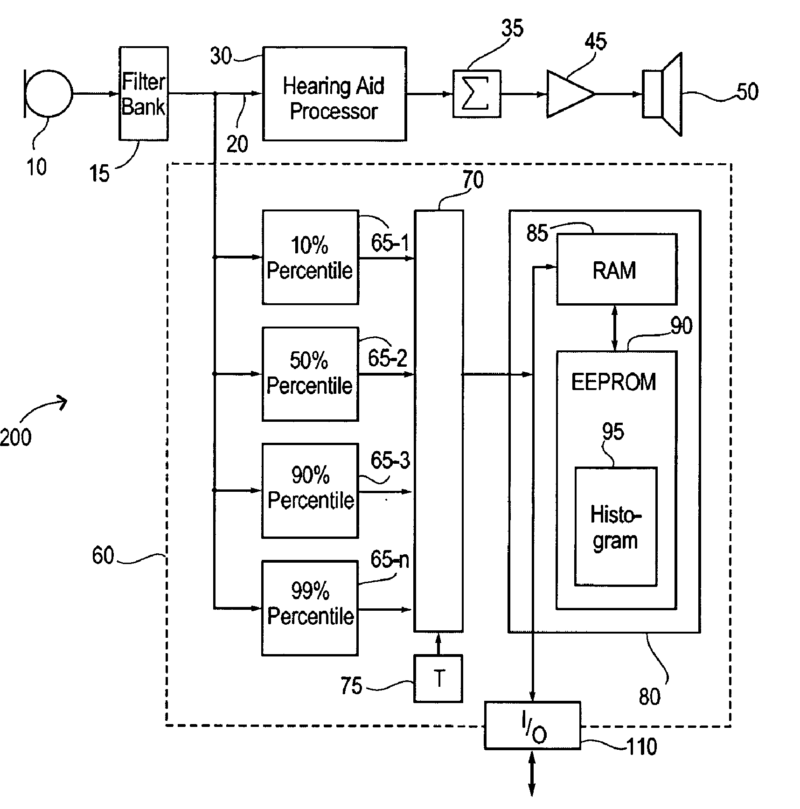
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Hearing aid fitting | |
Adaptation of hearing aid parameters to listening situation |
This place covers:
For example: Acoustic scene identification method for hearing device, which involves extracting characteristic feature of input signal and generating revised class information in processing stages to characterize and identify acoustic scenes. The settings can be adapted to the encountered acoustic scene, if its characteristics are detected.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Listening situation | Acoustic scene, acoustic environment |
This place covers:
Application of speech processing techniques, e.g. formant processing, determination or use of speech intelligibility threshold, detection of voiced speech, to control a hearing aid to enhance speech intelligibility.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Speech enhancement, e.g. noise reduction or echo cancellation | |
Speech enhancement using noise filtering characterised by the method used for estimating noise |
The mere mentioning of increasing speech intelligibility, which is a general aim for hearing aids, should not be classified.
This place covers:
For example: Passive shielding of a microphone transducer (21) by metal jacket (30)

For example: Active shielding by attenuation loops (8, 9) to attenuate electromagnetic interference resulting from supply lines (6C, 6D, coming from battery (6)) or the amplifier (3) and receiver (4) at the site of antenna (7)
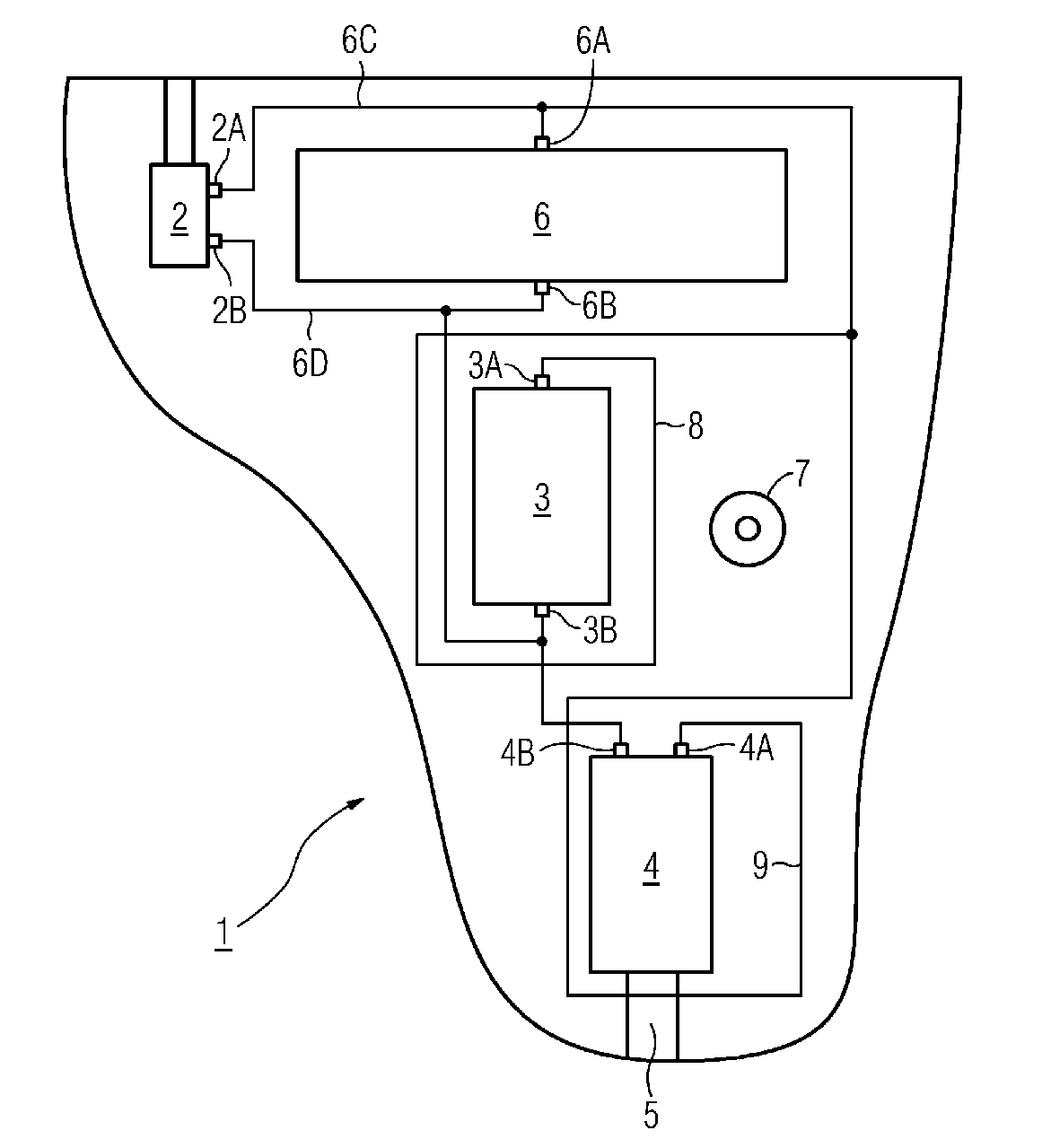
For example: Compensation for em-noise in signal processing:
A hearing aid receives the electromagnetic disturbance signal (14) via the detector element (12) and therefore detects the presence of, for example, a GSM telephone in the D1 network. The detector element (12) transmits the information about the detected noise field type (namely GSM telephone, D1 network) to the DSP element (3), so that the filter element (13) can be configured in a way that is adapted to the detected noise field type for the particularly effective noise field suppression.).
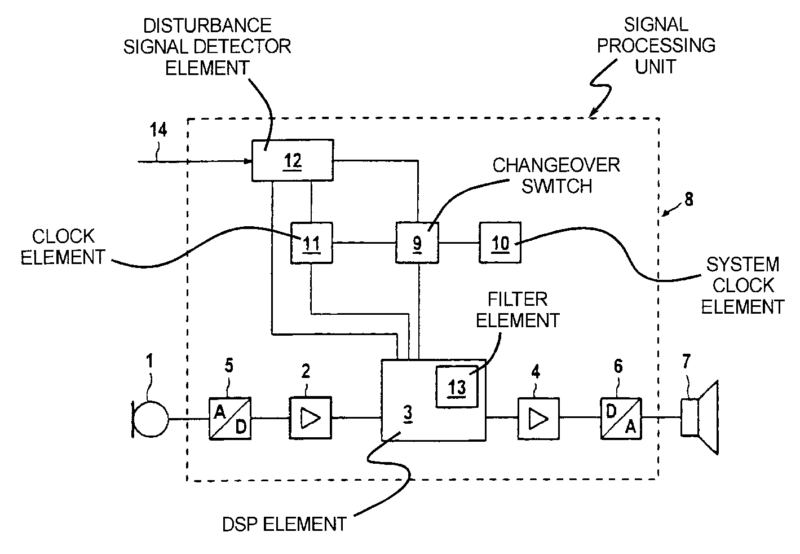
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
MEMS packages for protecting against electromagnetic or electrostatic interferences | |
Measuring electromagnetic field characteristics | |
Screening of apparatus or components against electric or magnetic fields |
This place covers:
For example: Construction of the antenna
For example: Circuitry for transmitting signal between hearing aid (2) and an external device (1):
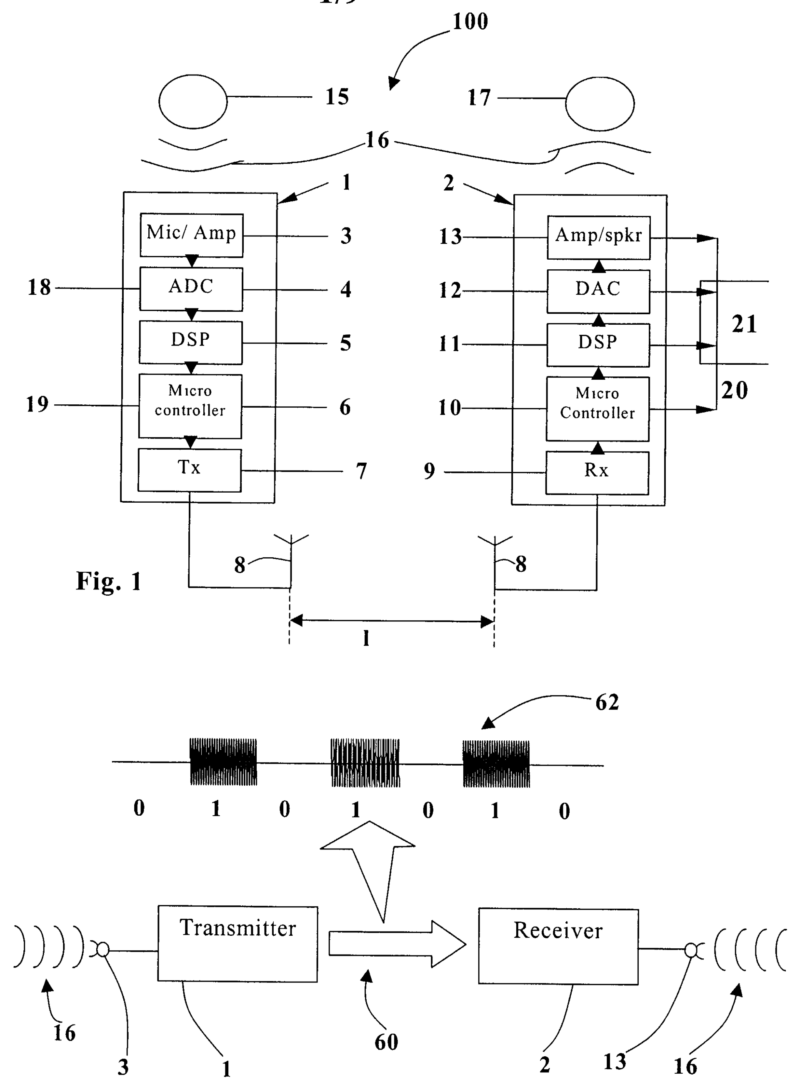
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adaptation of aerials for carrying or wearing by persons or animals | |
Aerials using equipment having another main function to serve additionally as an aerial | |
Loop aerials |
This place covers:
For example: Sound delivered to the deaf ear (18) is sent to the other ear (19) and processed to maintain some directional hearing.
If the other ear is also impaired it is called Bi-CROS.

This place covers:
For example:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Remote monitoring using telemetry, e.g. using a communication network | |
Home automation networks, e.g. Home Audio Video Interoperability [HAVI] networks |
This place covers:
For example: multiple amplifiers to one single receivers
For example: multiple amplifiers to multiple receivers, with same or different characteristics
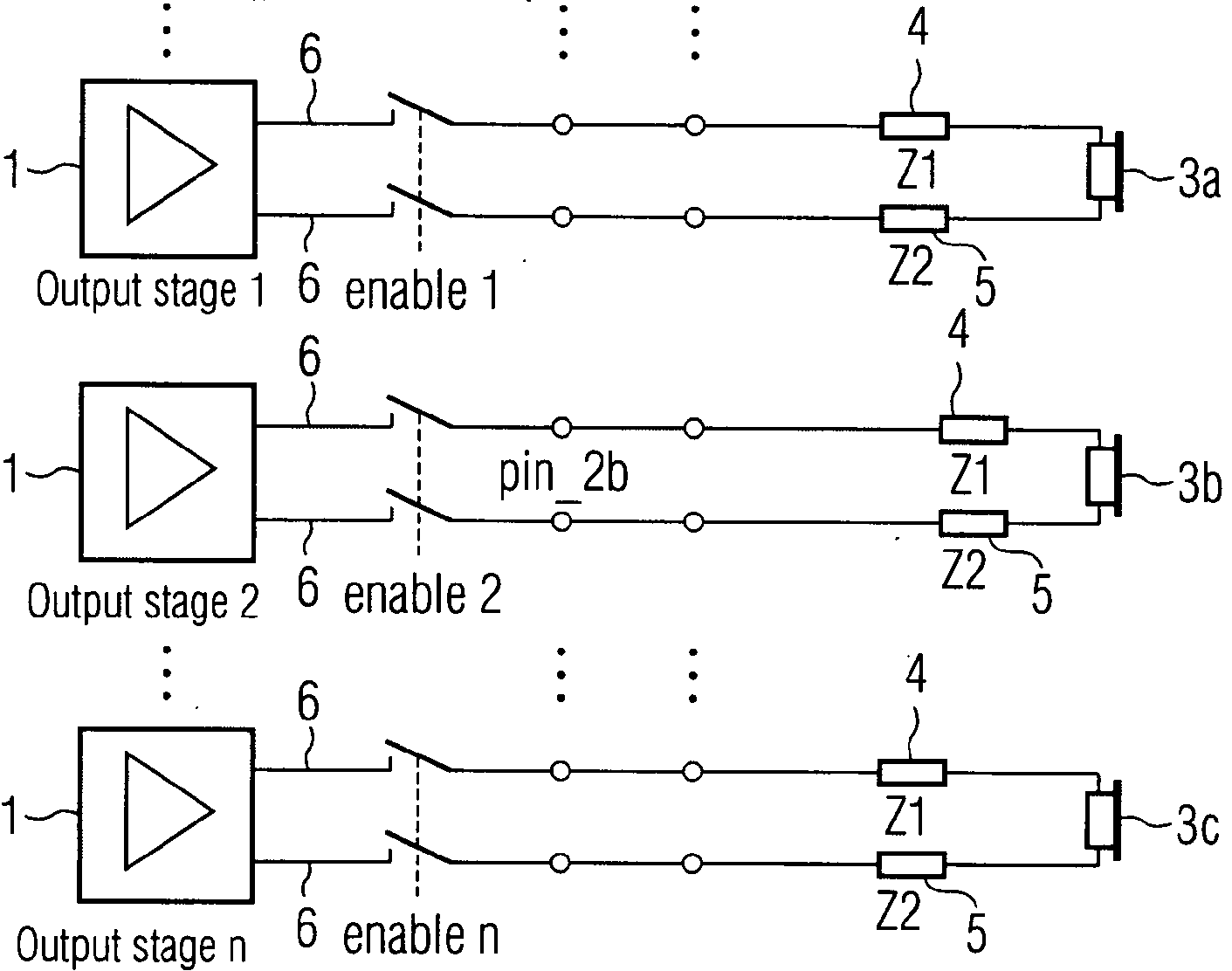
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
For stereophonic purposes | |
Connection circuits to selectively connect loudspeakers or headphones to amplifiers |
This place covers:
For example:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
For earphones or headphones | |
Electronic input selection or mixing based on input signal analysis, e.g. mixing or selection between microphone and telecoil or between microphones with different directivity characteristics (H04R 25/407 takes precedence) | |
Signal processing in hearing aids to enhance the speech intelligibility | |
Switching (mechanical) in general | |
Switches in or for hearing aids in general | |
Electronic switching in general |
This place covers:
Implantable hearing aids or parts thereof, e.g. receivers, housings, whereas in H04R 25/606 the emphasis is on the mounting of the transducers.
This place covers:
For example:
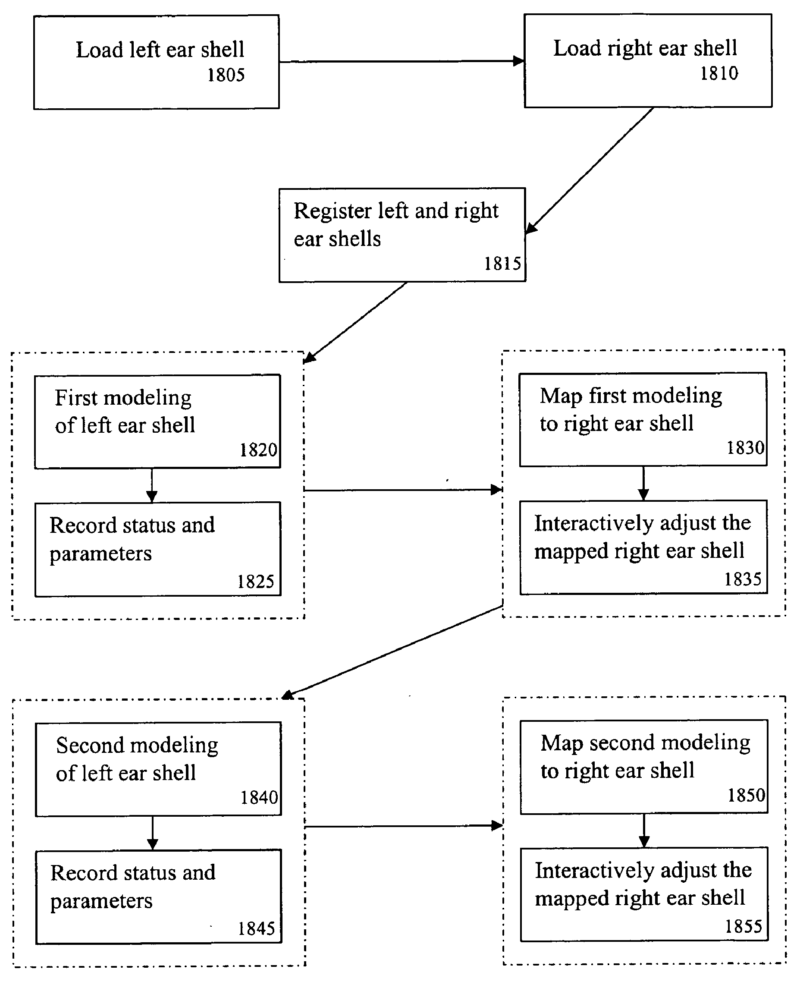
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Computer aided design in general |
This place covers:
For example: The ohmic resistance of the skin is measured. Under stress the ohmic resistance reduces due to sweating. Thus this resistance can be taken as a measure of psychoacoustic variables, e.g. loudness, sharpness, audio stress, etc.
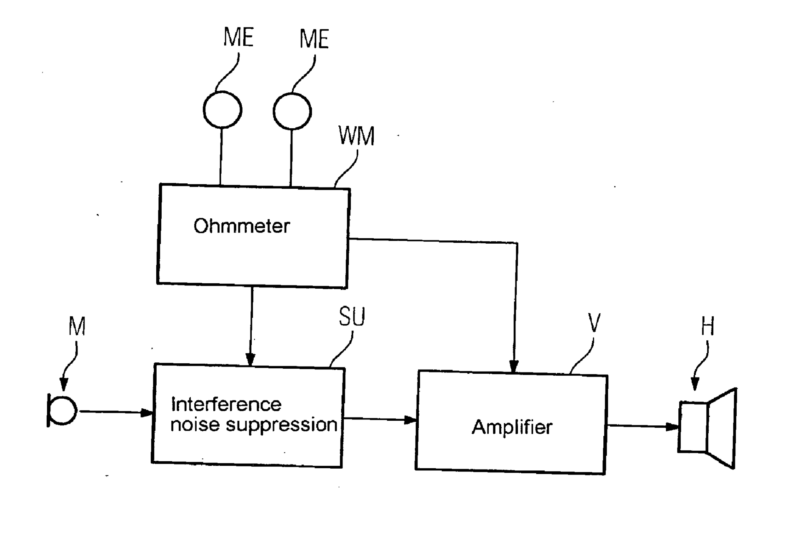
This place covers:
For example: compensation for the change in characteristics of a child's ear during growth
This place covers:
Adaptation of the signal processing is generally done by sensing the interference signal or noise. For example: A PA system has two audio inputs (6, 7) provided for interference signal and a utility signal, respectively. An adjustment device (11) adjusts the utility signal with the interference signal in such manner that a modified utility signal is produced. An audio output is provided for the modified utility signal. The interference signal contains information about local distribution of static noises.
This place covers:
For example:

Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Home automation networks, e.g. Home Audio Video Interoperability [HAVI] networks |
This place covers:
For example:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Receiver circuits for HiFi systems or audio/video combinations | |
Audio mixers |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Room | zone |
This place covers:
For example: reverberation adaptation for indoor or outdoor venues for PA-systems.
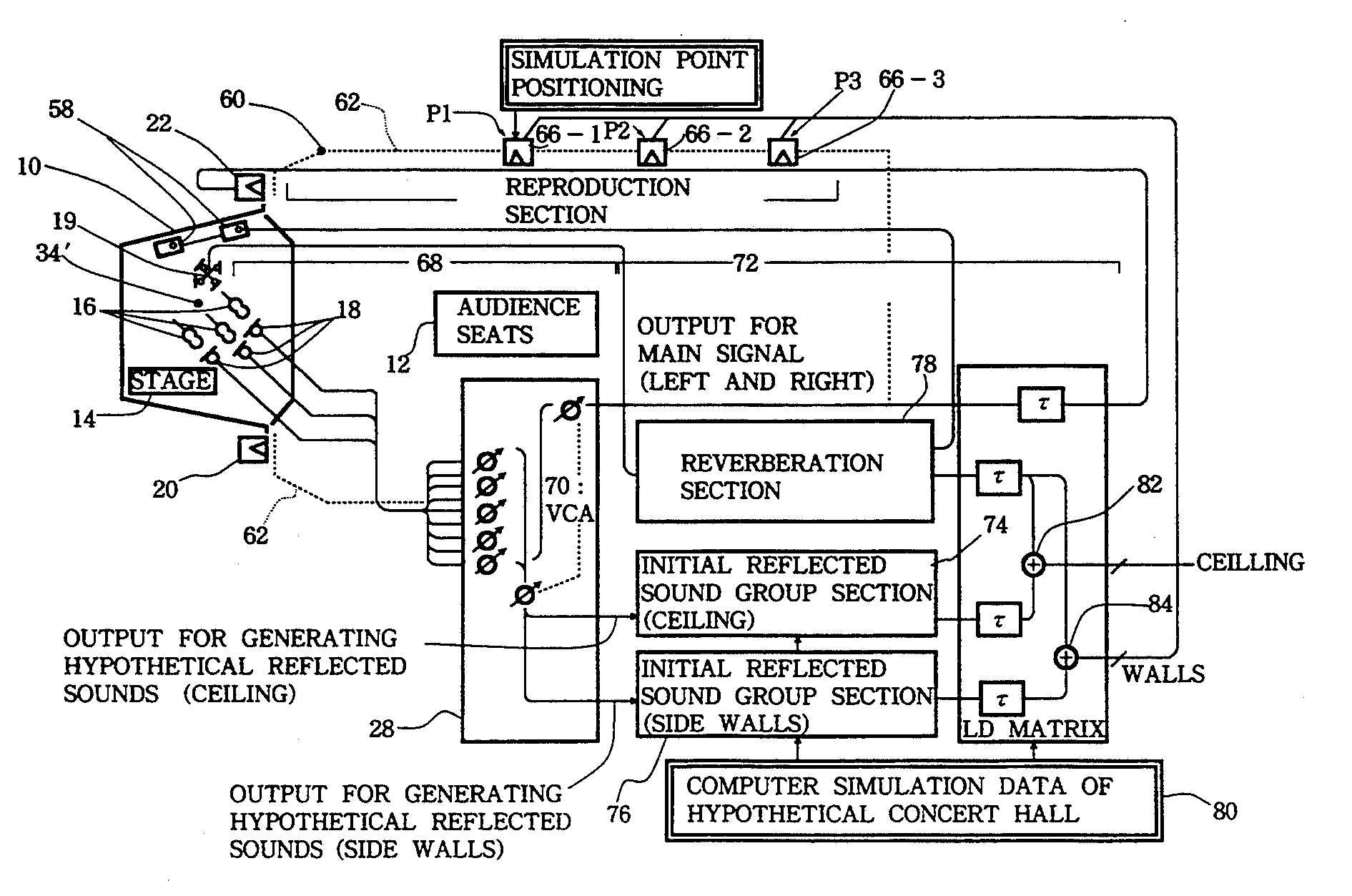
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring reverberation time; Room acoustic measurements | |
Arrangements for producing a reverberation or echo sound | |
For stereophonic systems |
This place covers:
For example: Amplifiers (312) have the amplification gain, which is the function of the bandwidth (308) of the filter (306), thus effectively augmenting the speech in noisy conditions, and hence preserving the overall sound pressure level and increasing speech intelligibility. The appropriate amplifier/filter combination is selected by a switch (304), which can be manually or automatically controlled by a switch controller (316) (cf. figure).
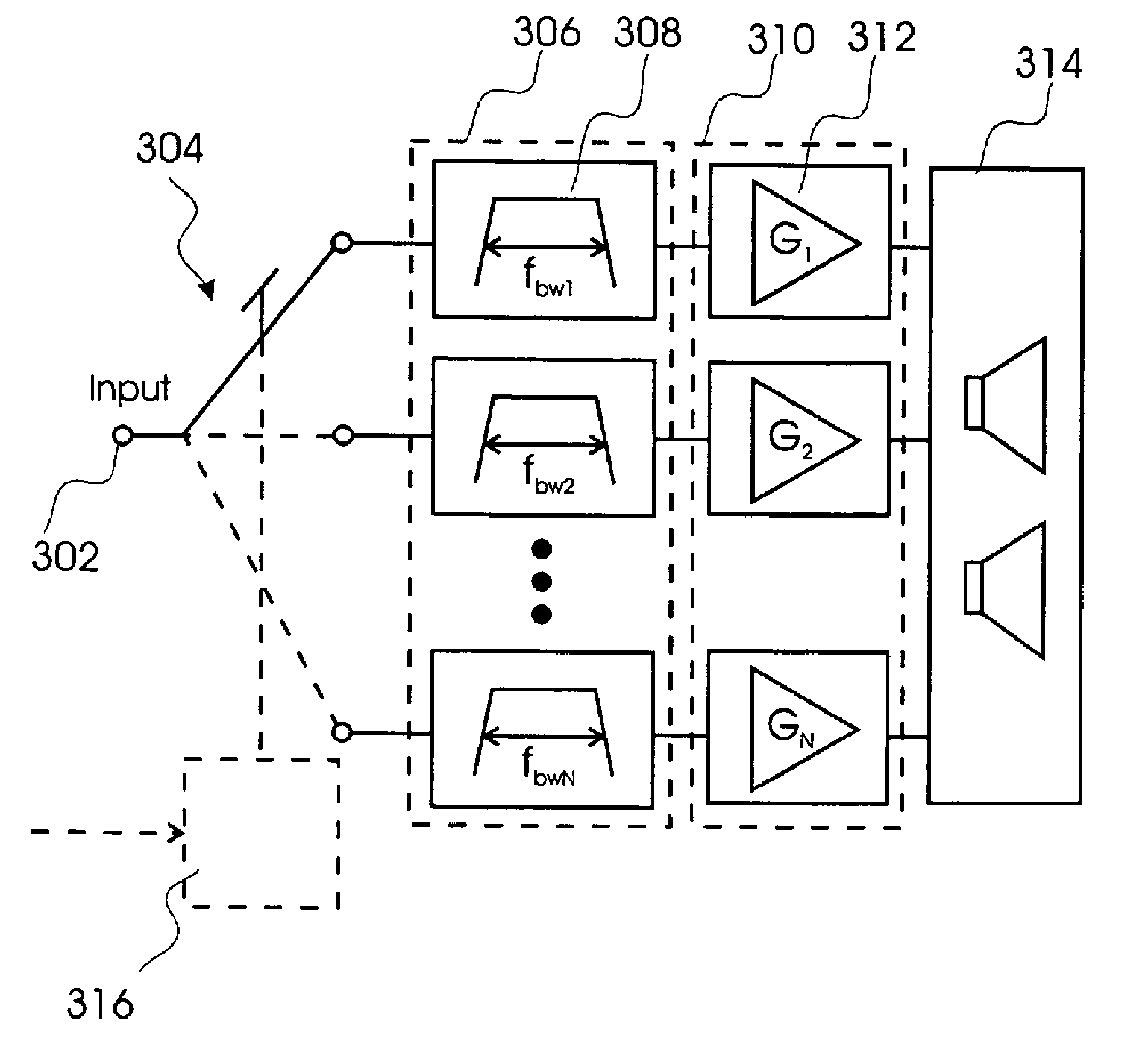
For example: A method involves sensing the ambient sound in a region for a predetermined time interval, analyzing sensed ambient sound and overlaying ambient sound with test audio signals having predetermined characteristics. The overlaid ambient sound is sensed. The degradation of speech intelligibility beyond acceptable level is determined by analyzing ambient sound pressure level and ambient frequency domain characteristics (cf. figure).

Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Speech enhancement using two microphones, one receiving mainly the noise signal and the other one mainly the speech signal |
This place covers:
For example: Polypropylene pellets (61) are grinded (S01) to prepare granulated polypropylene resin (62). Fibres 63 are partly cut (S02; 64) and mixed (S03) with the resin to produce a compound (15 which can be injection moulded (S04, S05) to produce a loudspeaker diaphragm.

This place covers:
For example: Surround press-moulded onto a loudspeaker diaphragm (7)
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Anodizing of metals |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Moulding aspects of diaphragm or surround | |
Moulding of plastics | |
Shaping of plastics in general |
This place covers:
For example: membrane (2) is extended to form outer suspension (21), whose elastic properties are adapted by the elastic layer (22).

For example: dampening material (20) for the edge (14a)
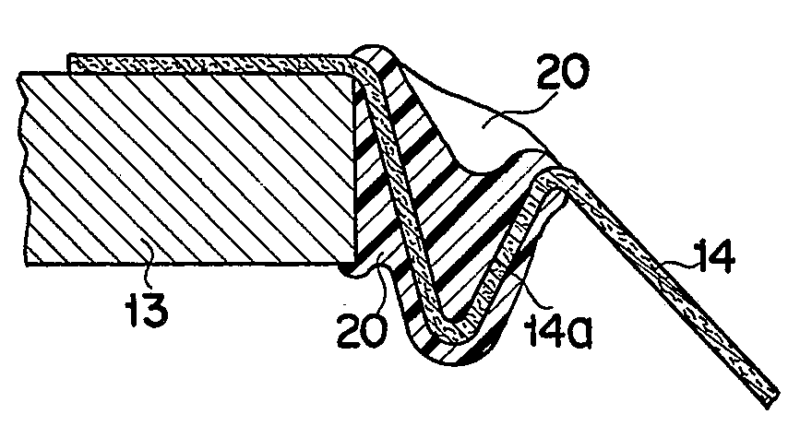
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Outer suspension | surround |
This place covers:
For example: Pleats (26,27, 28,32, 33,34, 38,39, 40) are provided in the outer suspension in such a way the vibration of membrane is more uniform over the frequency range the transducer is to be used for.
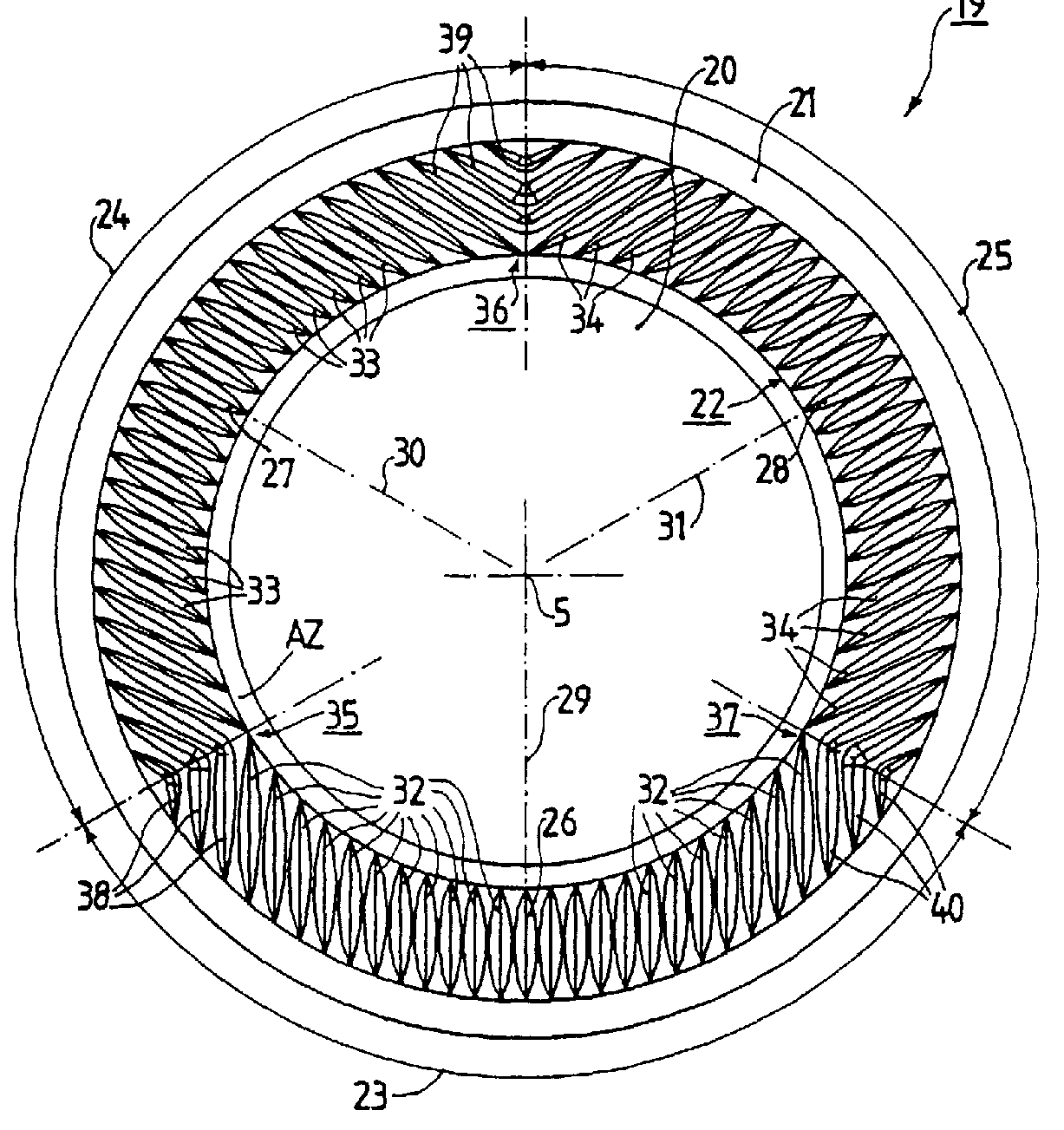
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Outer suspension | surround |
Only for those cases where the classification does not allow specification the type of transducer and the type is important, e.g. frequency control circuit (H04R 3/04 and subgroups) may require different circuit for microphones or for loudspeakers
This place covers:
For example: US2002137478.
For example: Cellular telephone (1) has pair of transducers (8A,8B) functioning as stereo speakers during sound reproduction and functioning separately as speaker (8A) and microphone (8B) during conversation.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Moving coil loudspeaker transducers | |
Moving armature loudspeaker transducers | |
Generating mechanical vibrations with vibrating magnet, armature or coil system; | |
Tactile signalling systems |
This place covers:
For example: The transducer shown in the figure below, comprises magnetic circuit (103, 104, 105) and a movable diaphragm (101) to produce sound when the voice coil (102) is supplied with a signal having a higher frequency. When the magnetic circuit and a weight (106) constitute a vibrator which is elastically supported against the case (110) by an upper and a lower suspension (107, 108). If the voice coil is supplied with a low frequency signal the vibrator starts vibrating, resulting in a tactile vibration.
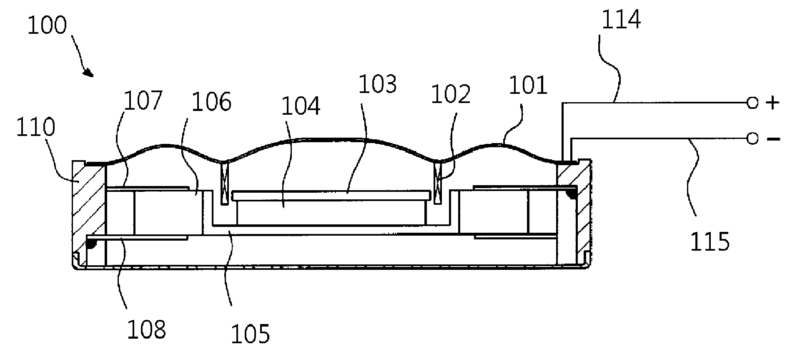
For example: an inertial transducer with a flexible membrane (3') and magnetic circuit elastically supported by a suspension (9). Upon energising the voice coil (4b) the membrane starts producing sound and the magnetic circuit move as well, causing a tactile vibration to be simultaneously generated.
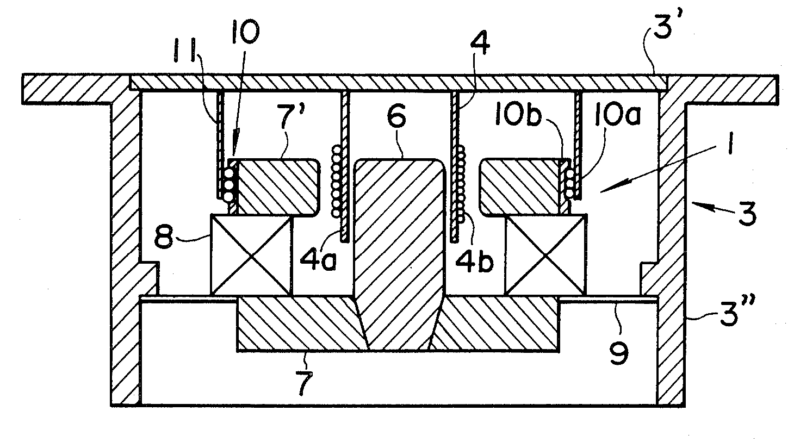
This place covers:
For example: Details of construction of a compression driver.
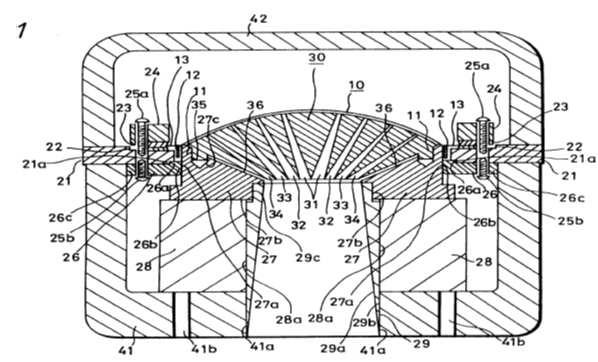
Only for those cases where the classification does not allow specification the type of transducer and the type is important, e.g. frequency control circuit (H04R 3/04 and subgroups) may require different circuit for microphones or for loudspeakers
This place covers:
For example: In this particular example the far field microphone is omnidirectional and the near field microphone is directional
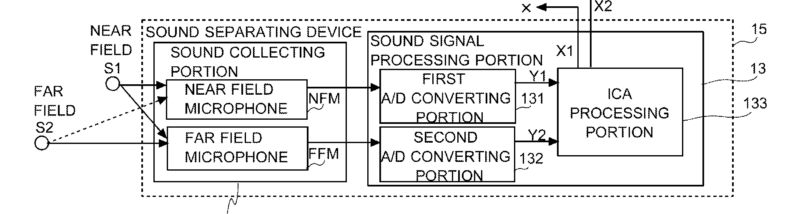
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electronic input selection in hearing aids based on input signal analysis |
This place covers:
Intrinsic noise is the noise which is generated inside the microphone (transducer) without any ambient acoustic signal (noise) being present, e.g. noise caused by parasitic capacitances in MEMS microphones or thermal noise.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Speech enhancement using two microphones, one receiving mainly the noise signal, and the other one mainly the speech signal |
This place covers:
For example: mechanical reduction with the help of a mesh (6,6',6'') over the sound openings (5,5',5'') of a microphone

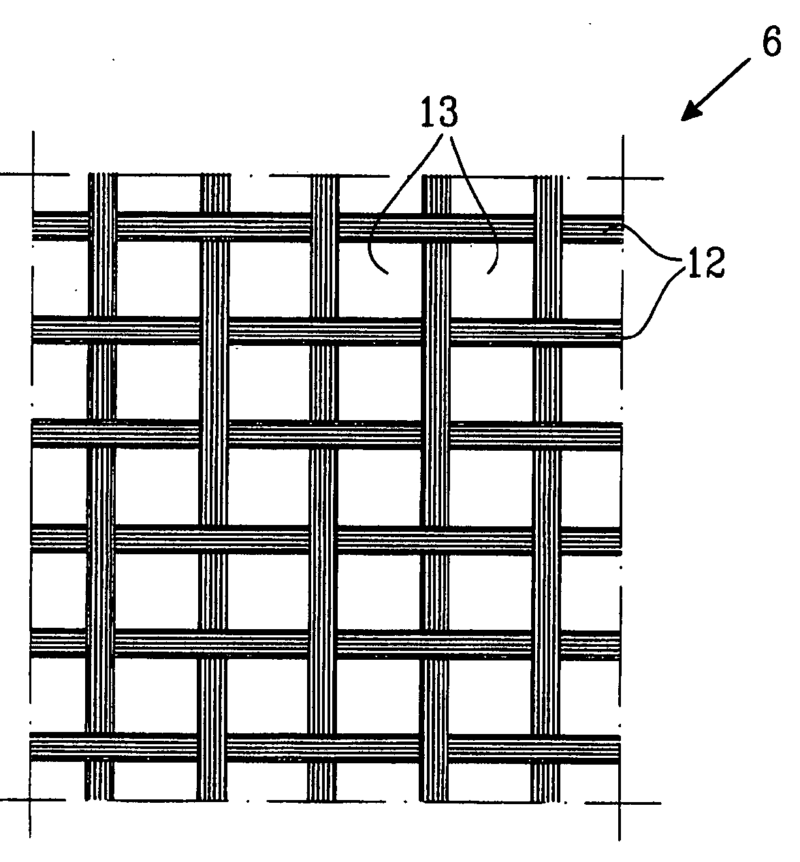
For example: electrical reduction using primary microphone (1) and a reference microphone (2) placed closely together. The microphone signals are input to adaptive noise canceller (6) (cf. Figure below).
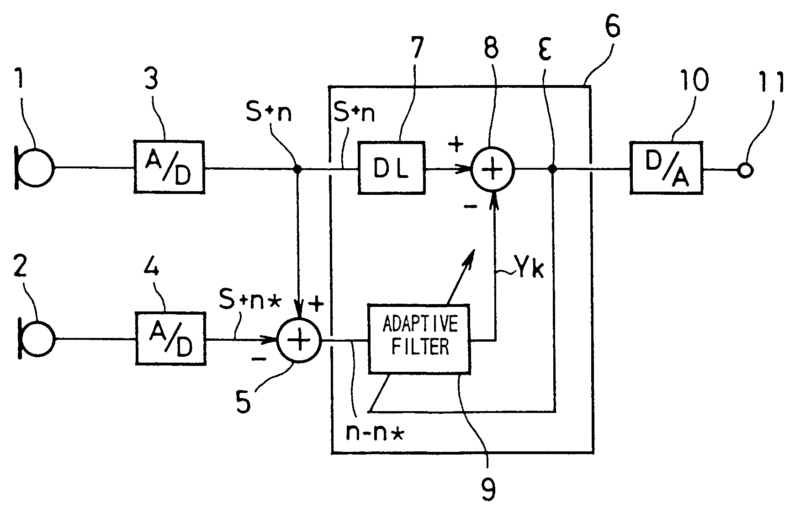
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Speech enhancement using noise filtering | |
Speech enhancement using noise filtering characterised by the method used for estimating noise |
This place covers:
Illustrative examples of subject matter classified in this place:
1.
Example of selection
2.
Example of mixing
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electronic input selection or mixing based on input signal analysis for deaf-aid sets | |
Audio mixers |
This place covers:
For example:
This place does not cover:
Public address systems |
This place covers:
Detection of state of connection of acoustic transducers, microphones, loudspeakers and headphones to amplifiers
For example: The information apparatus (100) includes speakers (FLS, FRS, RLS, RRS) connected to the amplifiers (12a-12d). An input switch circuit (22) performs the input of a predetermined inspection signal into the amplifier. A microcomputer (23) determines whether the speaker is connected to the amplifier based on a signal to be inspected which is produced from the input inspection signal in the input switch circuit (cf. Figure).
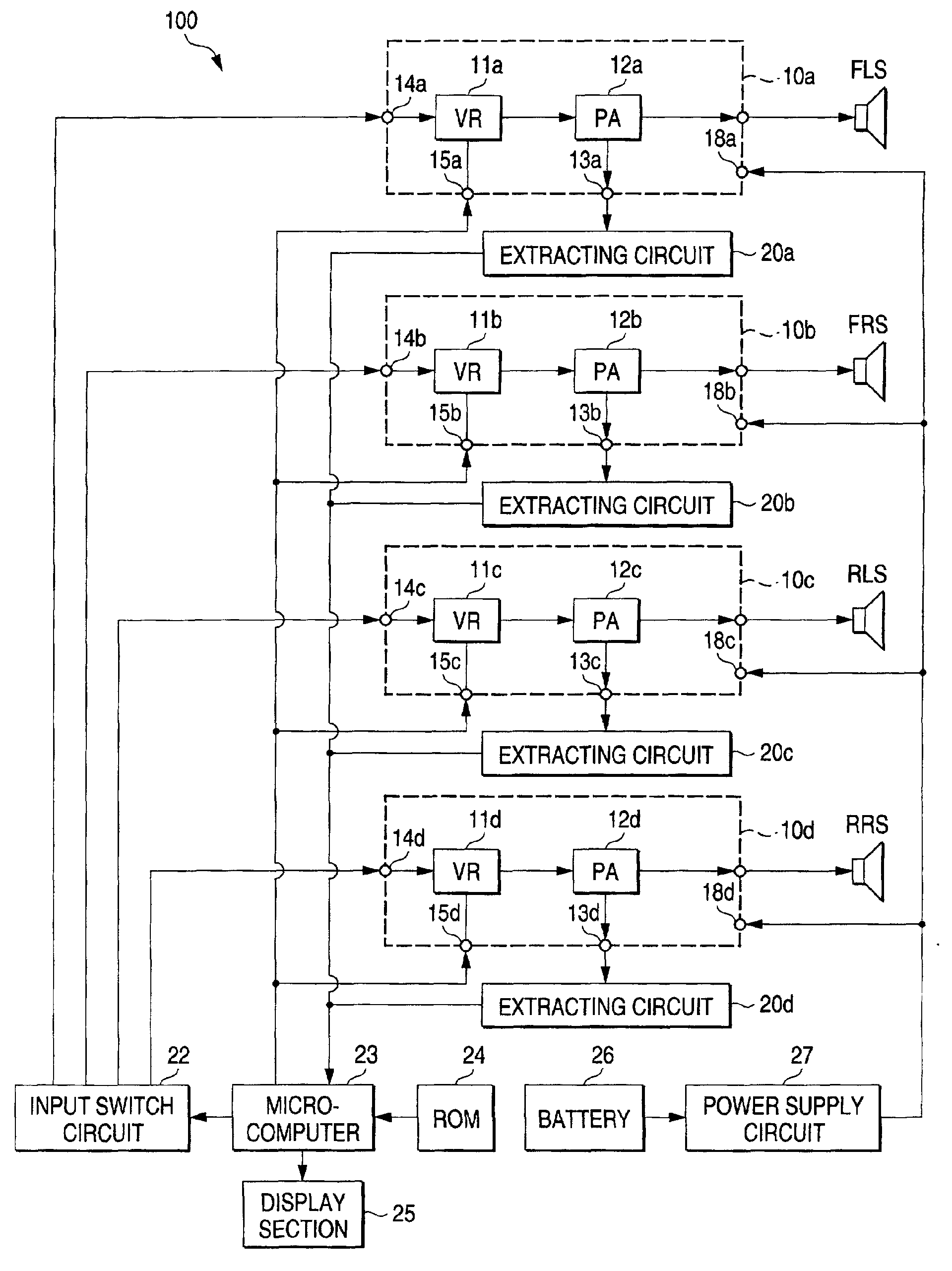
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Means for preventing incorrect coupling by indicating incorrect coupling; by indicating correct or full engagement |
To be used in combination with H04R 5/04 (stereophonic) or H04R 29/00 (not stereophonic) (or its subgroups) to indicate detection of connection.
This place covers:
For example: stand for a microphone (not shown) having an antenna (3) and a transmitter (45))
For example: loudspeaker
This place does not cover:
Wireless connection for hearing aids |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangements for transmitting signals characterised by the use of a wireless electrical link. | |
Portable transmitters | |
Near-field transmission systems | |
Indoor or near-field type systems for optical communication | |
Hands-free substation equipment including a wireless connection or interface |
The mere fact that a wireless connection for data transfer is used should not be classified.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
External connectors, e.g. plugs, modules for hearing aids |
This place covers:
Electronic aspects of volume control, e.g. for control based on sensor signals or for limiting the maximum sound level, or aspects of elements used for volume control, e.g. for simplicity in use or the construction of control element.
The mere presence of a volume control should not be classified.
Example (electronic aspects of volume control): The volume level set by the gain controller (205) of a headphone is determined in dependence of the ambient signal (B) picked up by a microphone (109) and an attenuated version (A) thereof.
Example (aspects of the element used for control): The earphone 10 has a front side 12, from which sound is emitted from a speaker, and a back side 14 which the user can press with the user's finger or hand 15 in order to activate a switch that raises the volume level of the sound produced by the earphone 10.
This place covers:
For example: EP1471765, US4953216, DE19632734.
Only if additional effects due to the combination of band splitting and sub-band processing are present (cf. the examples below).
The mere fact that band splitting and sub-band processing is applied should not be classified.
For example: Adaptive feedback cancellation for individual frequency band, which reduces computational effort, thus making cancellation faster and a good sound quality can be maintained.
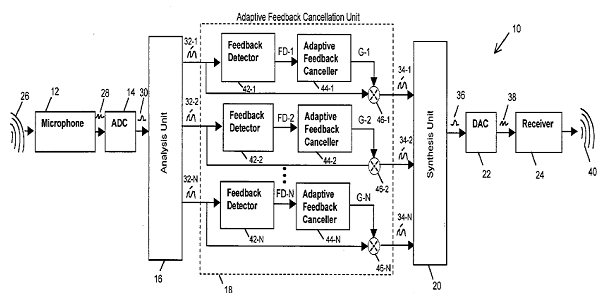
For example: For each frequency band (122a, 12b, ...) an automatic threshold switch (13a, 13b, ...) is opened if speech is present. Thus noise is only transmitted in the presence of louder speech in a frequency band and is suppressed if no speech is present in said band. Because the unwanted signals are transmitted only in those frequency channels wherein louder speech signals are simultaneously present, the unwanted signals are always covered by the louder speech signals, and the unwanted signals are thus no longer audible.
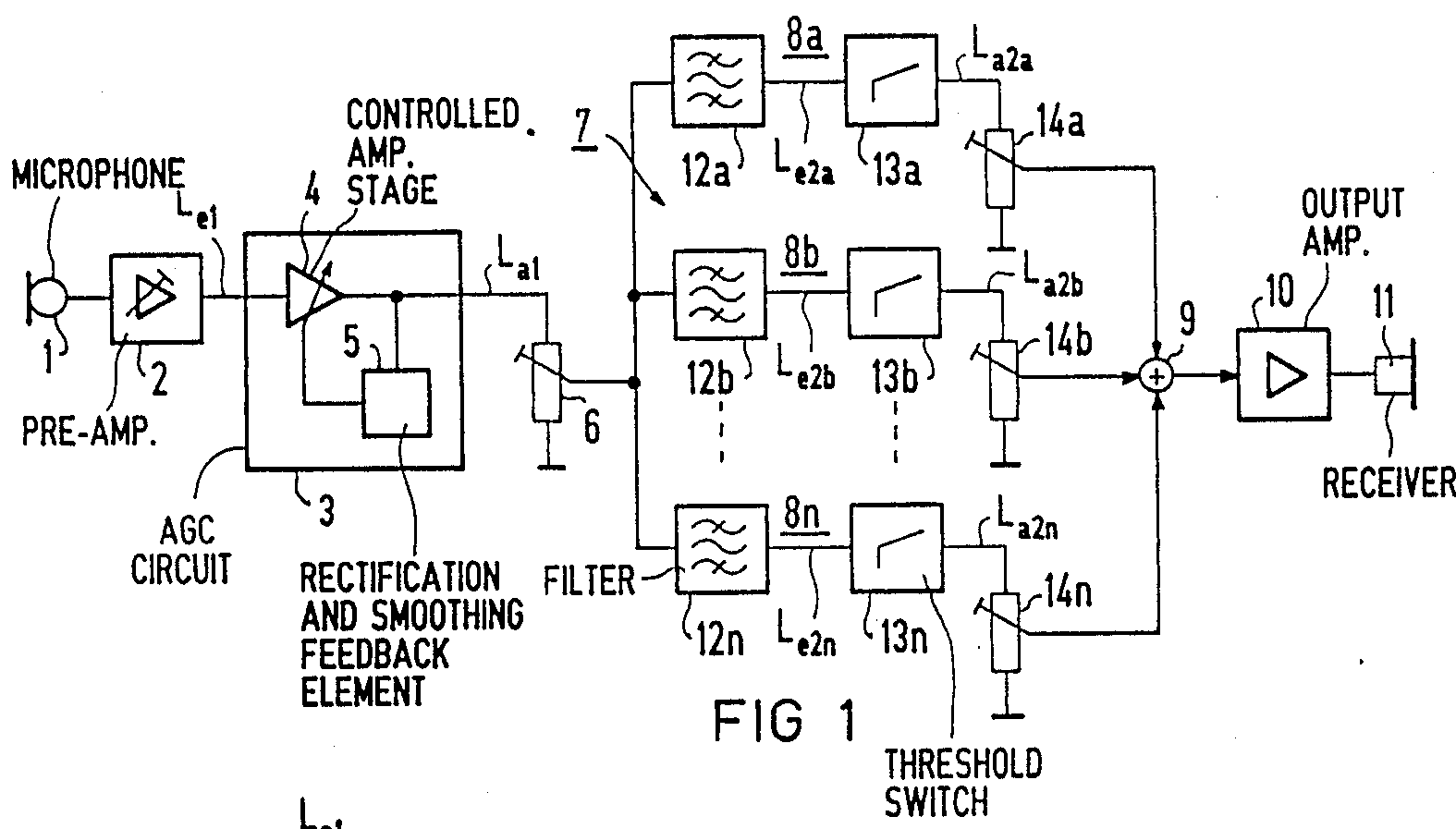
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Crossover filters for loudspeakers | |
Digital filter banks |
The mere band splitting or presence of a filter bank (e.g. FFT or FIR) should not be classified.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Deaf aid | hearing aid, auditory prosthesis |
Stereophonic system | two- or more channel system, e.g. quadraphonic, ambisonic or similar systems |
This place covers:
Signal processing of the output signals of an array of microphones for direction finding or of the input signals of an array of loudspeakers for steering sound in a desired direction
This place does not cover:
Beamforming aspects for stereophonic sound reproduction with loudspeaker arrays |
This place covers:
For example: microphone array
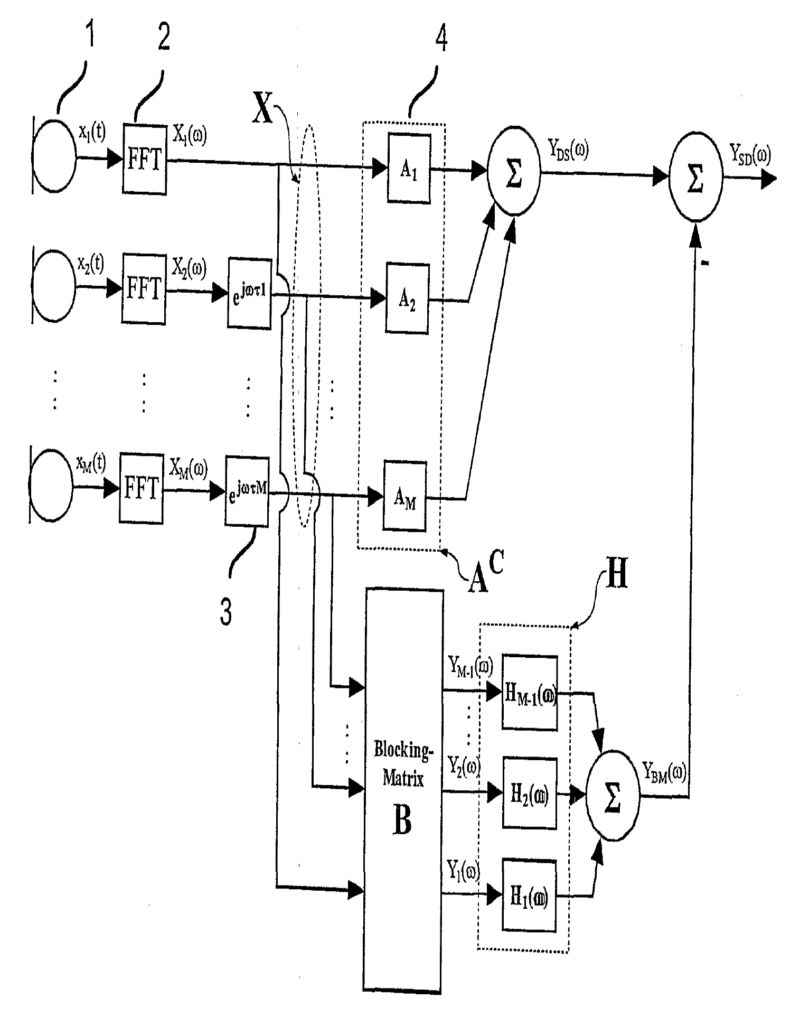
For example: loudspeaker array comprising additionally high-directivity edge loudspeakers which are driven with only low-frequency signal, to cancel side-lobes.
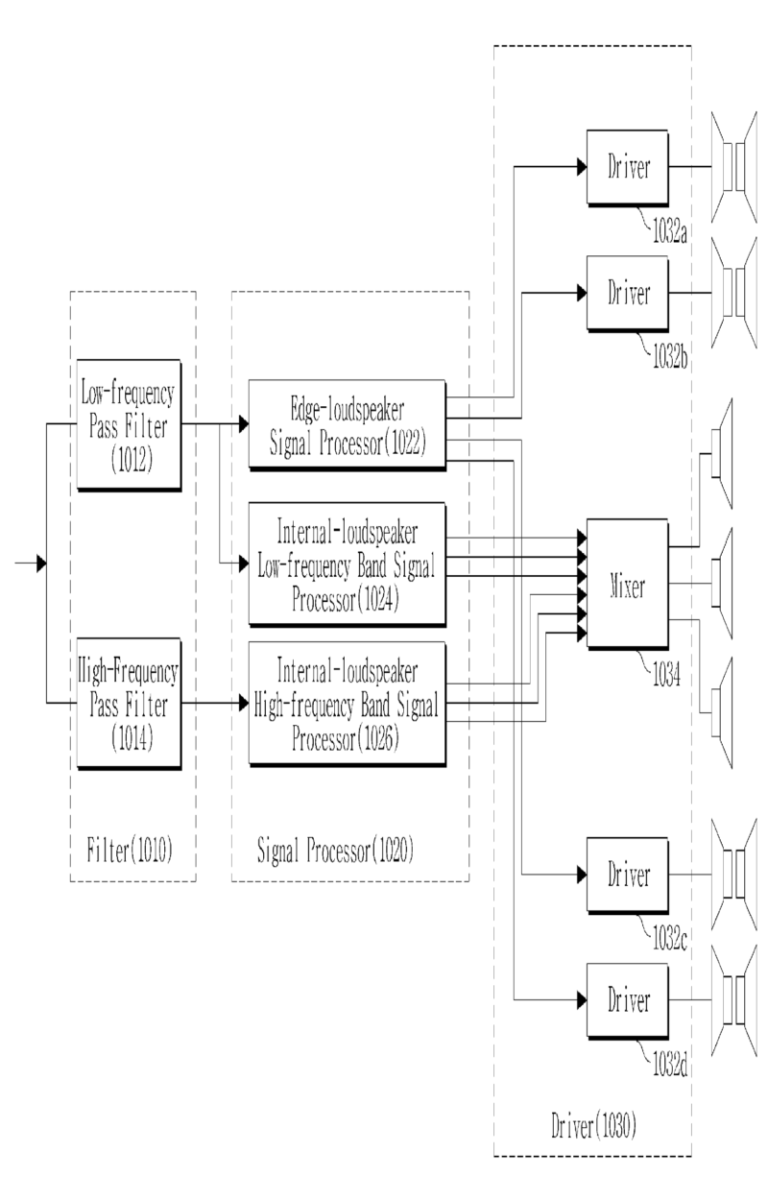
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Plane diaphragms using the distributed mode principle |
This place covers:
For example: Repositioning of central exciter (42) which has to be positioned at the edge of a transparent panel to be used for a visual display.
For example: mounting of the exciter (9) in the panel (2) (upper figure) or on the panel (2) (lower figure).
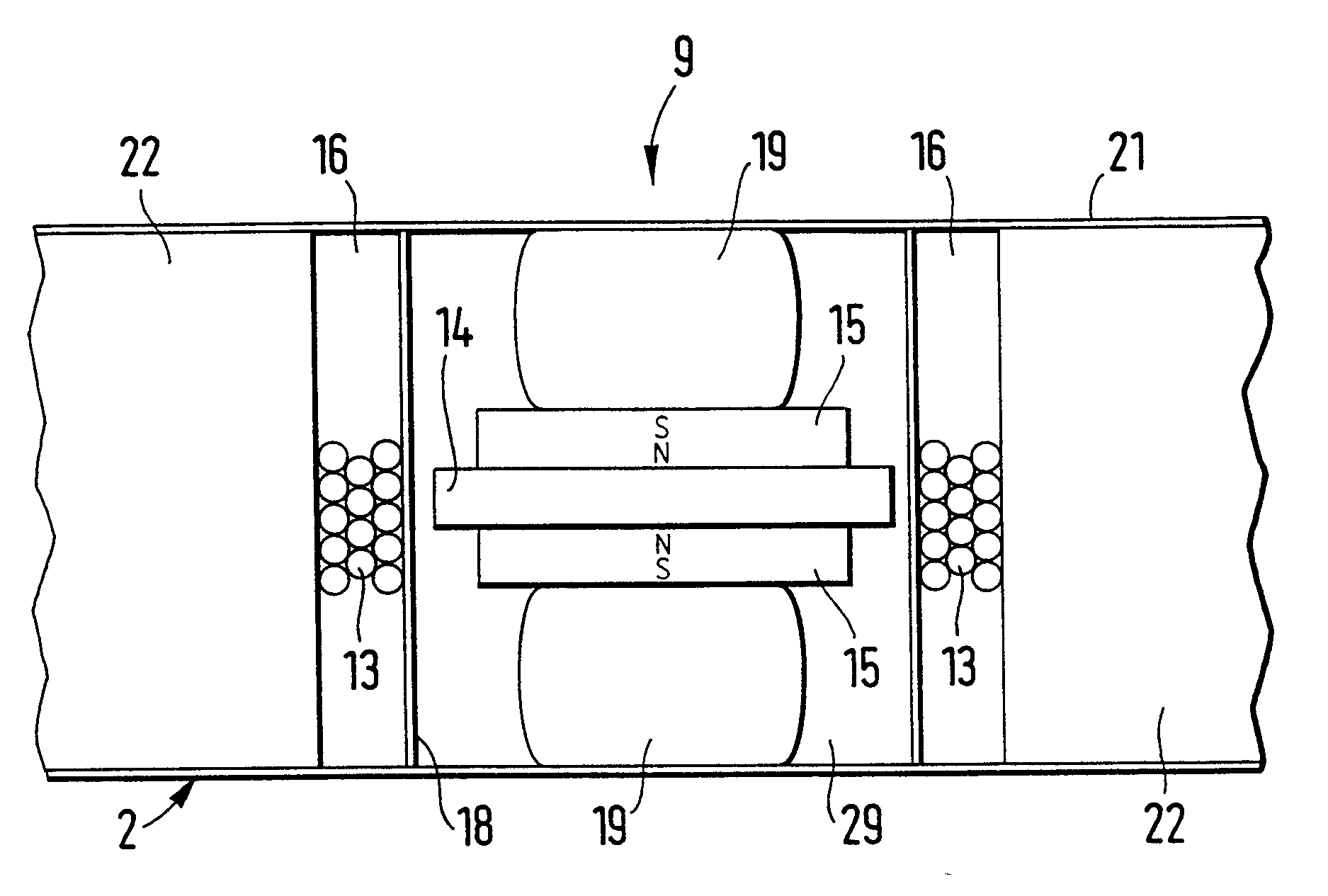
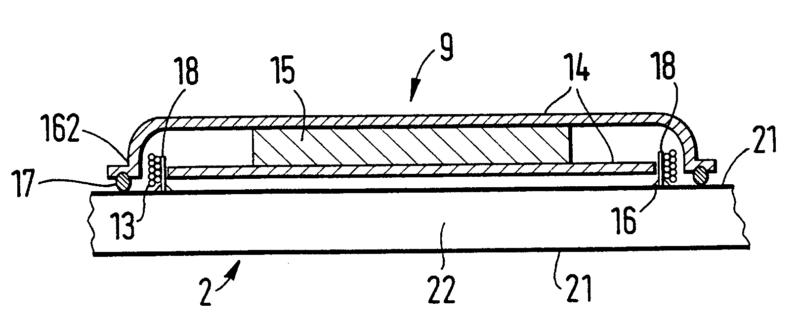
This place covers:
For example: Bending wave resonance speaker (1) for surround channels and pistonic loudspeaker transducer (7) for the main channel
For example: The membrane (2) of loudspeaker (81) is actively driven with resonant bending waves by an exciter (9) for the high frequencies and is passively driven by a pistonic loudspeaker transducer (42) for the low frequencies.
This place covers:
For example: US6661901 (earphone and hearing aid).
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Reduction of ambient noise in headphones in general | |
Ear defenders (electric or acoustic) | |
Active noise cancellation in general | |
Active noise control in general for earphones or microphones |
This place covers:
For example:

Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Battery saving arrangements in cordless telephones |
This place covers:
For example: Fitting a hearing aid including occlusion compensation filter (C).
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Non-occlusive ear tips, i.e. leaving the ear canal open, for both custom and non-custom tips | |
Aspects relating to vents, e.g. shape, orientation, acoustic properties in ear tips of hearing aids to prevent occlusion |
This place covers:
For example:

This place does not cover:
Aspects relating to vents, e.g. shape, orientation, acoustic properties in ear tips of hearing aids to prevent occlusion |
This place covers:
For example: Improved venting of the ear canal due to the opposite orientation of valves (25, 26), which enables circulation (29) of air in the ear canal.
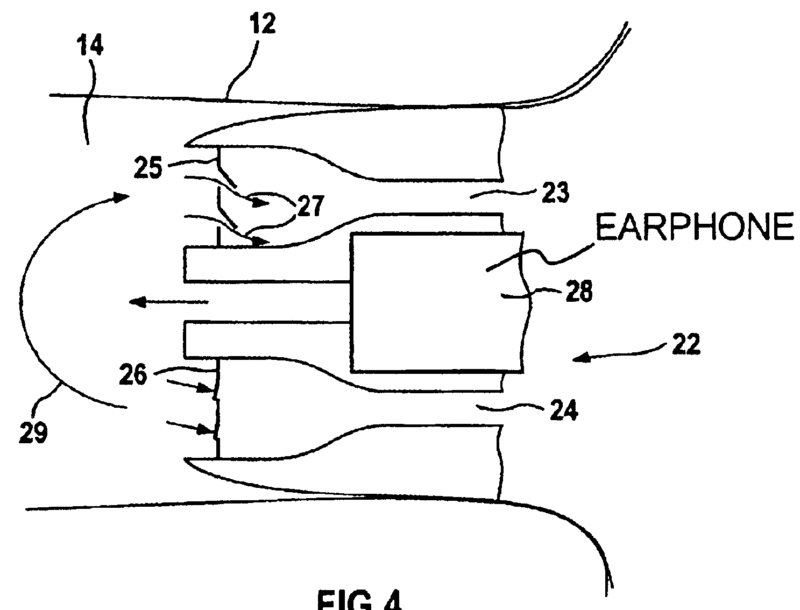
For example: hearing aid device with a ventilation channel (5), cross-section of which can be adapted (6, 7) to the respective acoustic situation (e.g. acoustic feedback) in a fast and simple manner.
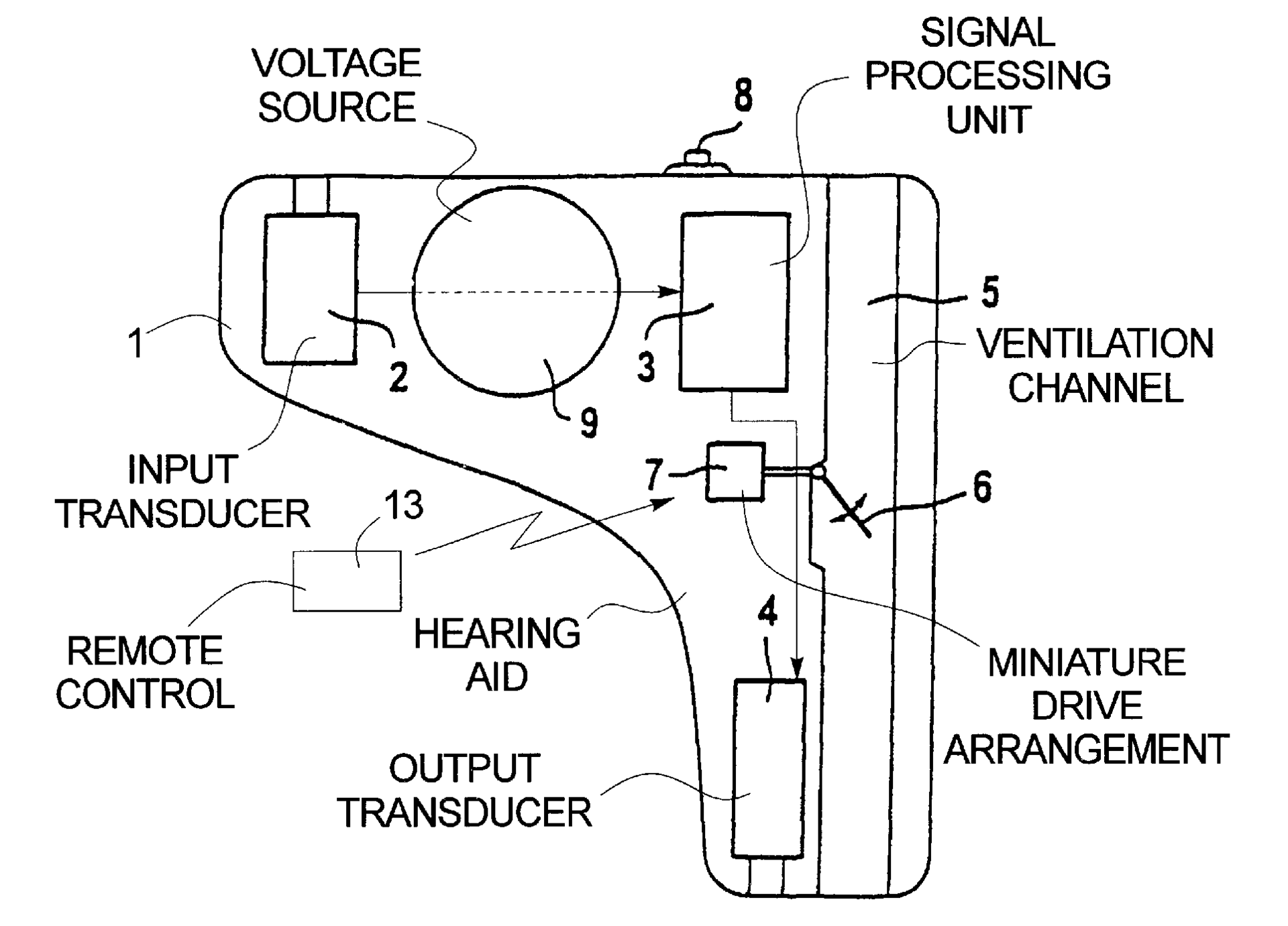
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Prevention of acoustic feedback in hearing aids mechanically | |
Electronic compensation of the occlusion effect |
This place covers:
For example:
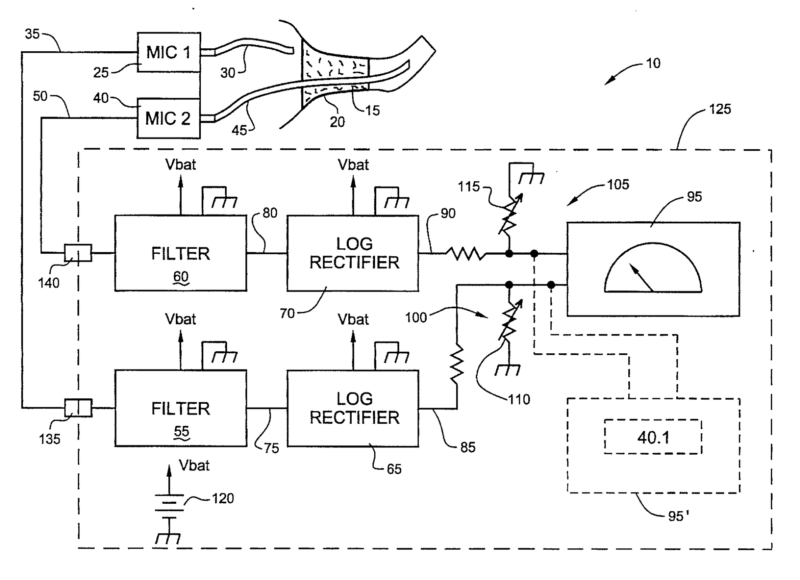
This place covers:
For example: Haring aid (12) cleaning: a cleaning liquid (28) is pump up (with a pump system (252)) from a cartridge (224) into a reservoir (229) (cf. figure)

For example: Tool for replacement of cerumen barriers: a cerumen barrier (19) is provided with two holes (21, 22) (upper figure). The tool (lower figure) (31) is provided with two pins (35, 36) which fit in said holes (21, 22) of the cerumen barrier. Thus the barrier can be easily screwed onto the outside thread (4) of the neck (3) of the ITE hearing aid module (1).
For example: hearing aid storage box: When the lid (5) is closed the protrusion (7) pushes the on/off switch (3) in the off position.
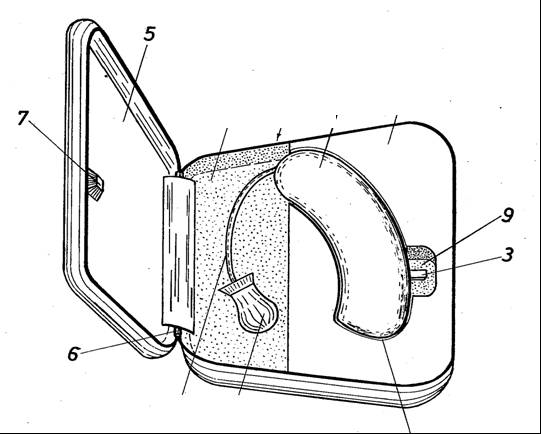
For example: safety loop for securing an earbud to e.g. a shirt.
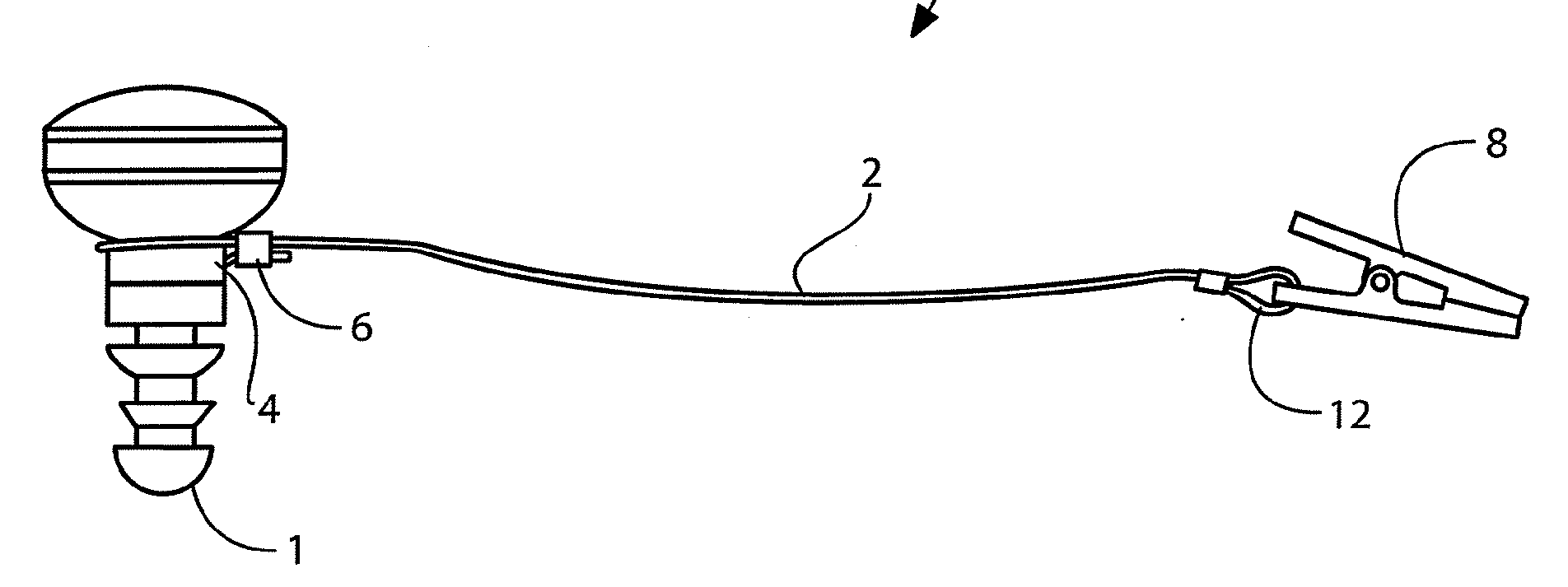
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Mountings specially adapted for telephone equipment | |
Improving the acoustic characteristics by means of constructional features of the housing (of telephone equipment), e.g. ribs, walls, resonating chambers or cavities | |
Supports for telephone transmitters and receivers | |
Substation equipment with increased funcionallity, e.g. for playing back music files |
This place covers:
For example: US6389147, EP1482763.
Subject matter relating to mounting of transducers on or within a vehicle, e.g. automobile, aircraft, motorcycle, and to electronic control of the sound field within a vehicle, e.g. automobile, aircraft, motorcycle.
For example: Mounting of transducers in vehicles
For example: Sound control in vehicles
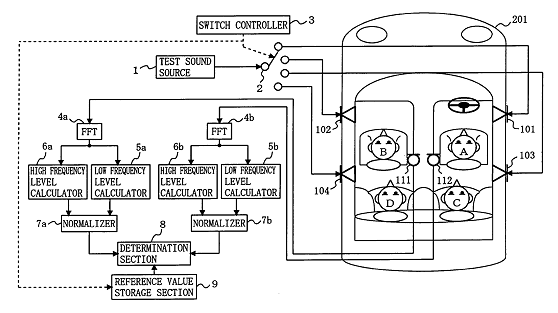
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Mounting of acoustic transducers in vehicles | |
Automatic control of amplifiers dependent upon ambient noise level or sound level |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Stereophonic system | two- or more channel system, e.g. quadraphonic, ambisonic or similar systems |
Multi-channel system | three- or more channel system |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Details related to the integrated loudspeakers in data processing equipment | |
Loudspeakers in televisions |