CPC Definition - Subclass F03D
This place covers:
Mechanisms for converting the energy of wind into useful mechanical power.
In particular:
Wind motors with rotation axis substantially parallel to the flow of air entering the machine.
Wind motors with rotation axis substantially at right angle to the flow of air entering the machine.
Other wind motors.
Controlling wind motors.
Adaptations of wind motors for special use.
Combinations of wind motors with apparatus driven thereby.
Wind motors specially adapted for installation in particular locations.
Assembly, mounting or commission of wind motors.
Arrangements specially adapted for transporting wind motor components.
Transmission of mechanical power.
Monitoring or testing of wind motors.
Other details, component parts, or accessories of wind motors.
F03D covers mechanisms for converting natural wind energy into useful mechanical energy, and the transmission of such mechanical energy to its point of use. Electrical power generation aspects of wind motors (e.g. dynamo-electric conversion and electric generators) are classified in H02P. Circuit arrangements or systems for supplying or distributing electric power are classified in H02J. Electric generators structurally associated with wind turbines are classified in H02K 7/183. F05B concerns a CPC internal scheme for indexing only relating, among others, to wind motors covered by subclass F03D.
This place does not cover:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Vehicles for transportation | |
Propulsive devices of ships or other waterborne vessels directly acted on by wind, using the Magnus effect | |
Rotors for airplanes and helicopters | |
Handling by cranes, hoisting, lifting | |
Machines or engines for liquids, Water turbines | |
Ventilators | |
Dynamo-electric machines | |
Structural association of electric generator with mechanical driving motor in dynamo-electric machines, e.g. turbine |
In this subclass, it is desirable to allocate the indexing codes of subclass F05B, if applicable.
The subclass F05B is used for indexing as follows:
F05D 2200/00: mathematical features
F05D 2210/00: working fluid
F05D 2220/00: application
F05D 2230/00: manufacture
F05D 2240/00: components
F05D 2250/00: geometry
F05D 2260/00: function
F05D 2270/00: control
F05D 2300/00: materials
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Motor | An apparatus for producing mechanical motion from any other form of energy; the motion may be continuous or in separate strokes |
Rotor | The wind-engaging parts of the wind motor and the rotary member carrying them |
Rotation axis | The axis of rotation of the rotor |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
HAWT | Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine |
VAWT | Vertical Axis Wind Turbine |
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms:
- "wind turbine", and "windmill"
- "azimuth angle", and "yaw angle"
- "rotor hub", "rotor cone" and "spinner"
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used with the meaning indicated:
Axial flow | Air flow parallel to the rotation axis. |
Savonius turbine | A wind turbine with at least two scoop-shaped wind-engaging surfaces. |
Darrieus turbine | A vertical axis wind turbine equipped with aerofoils mounted on a rotating shaft. |
This place covers:
Wind motors having their rotation axis substantially parallel to the flow of air entering the machine. When the flow has been guided into a direction other that the original wind direction, the final flow into the wind motor should be considered for classification.
This place does not cover:
Controlling of wind motors |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Solar updraft |
This place covers:
Wind motors having stationary wind-guiding means. The nacelle can be the wind guiding means, tip-shrouds are excluded.
This place does not cover:
Wind motors specially adapted for installation within towers |
This place covers:
Rotors characterised by their shape or form which is defining the aerodynamic property of the rotor.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
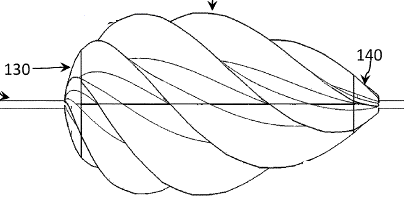
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Rotors characterised by their construction elements |
This place covers:
Rotors characterised by their construction and structural configuration, in particular:
- Construction and structural aspects of blades.
- Construction and structural aspects of the hub.
- Structural aspects of the link between the rotor hub and the blade, e.g. pitch arrangements.
- Assembly of blade or hub elements.
This place does not cover:
Assembly of wind motors; Arrangements for erecting wind motors | |
Installing rotor or blade |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Rotors characterised by their aerodynamic shape | |
Shaping, joining or repairing plastics | |
Manufacturing of plastic blades | |
Moulded wind turbine blades |
This place does not cover:
Controlling blade pitch |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Ring gears associated with pitch bearing |
This place covers:
Hydraulic mechanisms to control the pitch angle of the blade, e.g. hydraulic motors, cylinders, layout or linkage.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Power-supply to auxiliary components, e.g. reservoir tanks, pumps or circuits |
This place covers:
Electrical mechanisms to control the pitch angle of the blade, e.g. electric motors, electric circuit layout or linkage.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Power-supply to auxiliary components, e.g. batteries, electrical circuits, converters or back-up systems |
This place covers:
Blades made of several panels or skins.
This place covers:
Blades which are made of two or more elements in its longitudinal direction.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
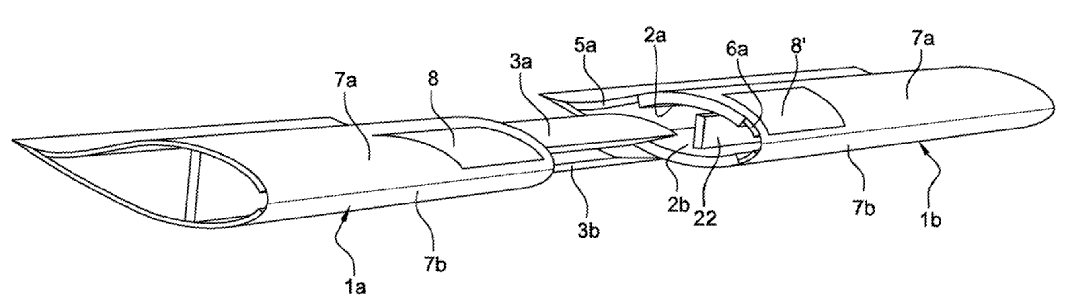
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Separate elements forming the blade tip, attachment thereof |
This place covers:
Wind turbine blades having an outer structure, e.g. shells, skins, which via its shape defines the aerodynamic property of the blade and an inner structure that carries the structural loads and provides stiffness. The inner structure may include beams, spar caps and shear webs as illustrated below.
Illustrative examples of subject matter classified in this group:
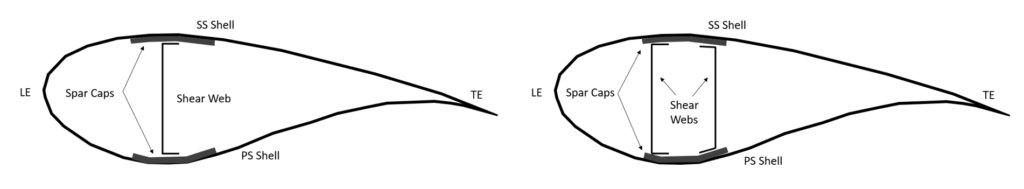
This place covers:
Mechanical aspects and layout of the yaw system, i.e. of the elements allowing rotation of the nacelle with respect to the tower.
Yaw actuator arrangements, e.g. yaw motors or hydraulic cylinders.
Other connecting aspects between the nacelle and the tower.
This place does not cover:
Controlling the orientation in relation to wind direction |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Power-supply to auxiliary components, e.g. batteries, electrical circuits, converters or back-up systems | |
Yaw bearings |
This place covers:
Wind motors having their rotation axis substantially perpendicular to the flow of air entering the machine. When the flow has been guided into a direction other that the original wind direction, the final flow into the wind motor should be considered for classification.
This place does not cover:
Controlling of wind motors |
This place covers:
A wind-guiding means positioned upstream, downstream or around a wind motor. The wind-guiding means directs wind to the rotor, or blocks wind from reaching a part of the rotor. The wind-guiding means may have a movement which is independent from the rotation of the rotor.
This place covers:
Wind motors characterised by the "effective area" of the rotor which is the cross section area of the rotor which contributes positively, i.e. causes a torque in/ to the desired rotation. The "augmenting" guiding means are those guiding means which intercept an area of flow greater than this "effective rotor area", and direct the flow into the rotor. The guiding means which fulfil this intercepting role are bounded on all sides from inlet to outlet into rotor, and therefore also accelerate or "concentrate" the flow into the rotor.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
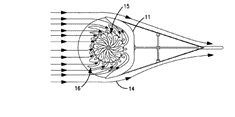
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
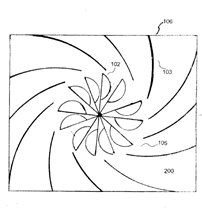
This place does not cover:
Guiding means forming also a shield means on one side of the rotor |
This place covers:
Wind motors with a concentrating means, i.e. the guiding means only increase the flow speed into the rotor without intercepting an area of flow greater than the effective rotor area (see definition of the effective area in F03D 3/0427).
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
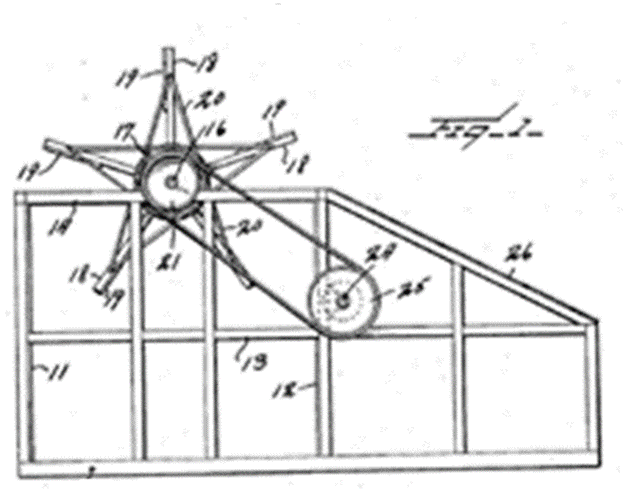
See channel 12
This place does not cover:
With augmenting action, i.e. the shield means intercepting an area greater than the effective rotor area |
This place covers:
Rotors characterised by their shape or form which is defining the aerodynamic property of the rotor.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Rotors characterised by their constructional elements |
This place covers:
Constructional aspects of the rotors.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Rotors characterised by their aerodynamic shape, e.g. aerofoil profile |
This place covers:
Wind motors where the wind engaging parts can be moved relative to the rotor, e.g. arrangements allowing pitching the wind engaging parts independently from the mechanical rotation of the rotor.
This place covers:
Wind motors wherein the wind engaging parts, i.e. the blades, vanes, paddles or cups, undergo a change of orientation within each cycle of rotation of the wind rotor, coming back to their original position after each revolution. This change of orientation happens of itself, passively, the direct result of the wind acting on the wind engaging parts as the relative wind direction changes with the rotation.
Example:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
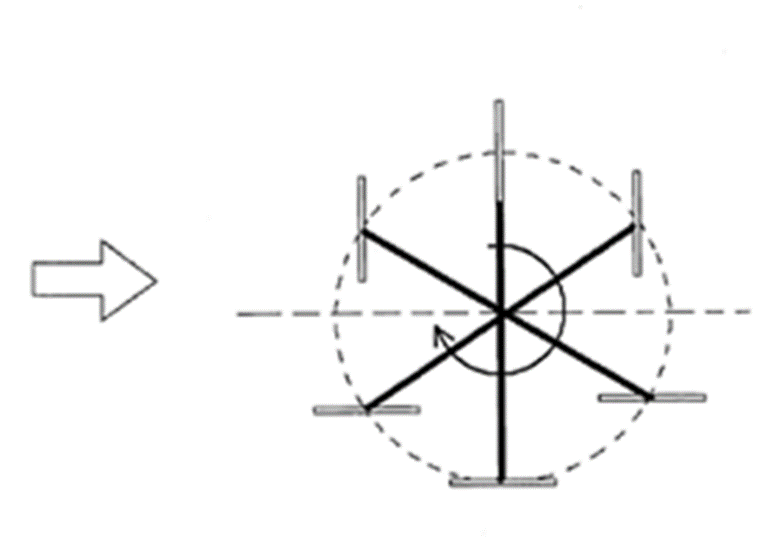
This place covers:
Wind motors whereby the cyclic movement of the wind engaging parts during each revolution of the rotor is mechanically related to the rotor rotation, and optionally the wind force or direction.
Examples:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
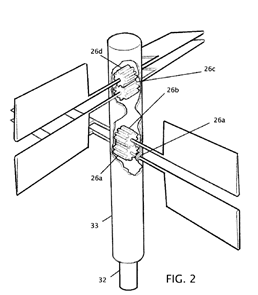
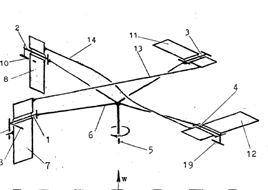
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
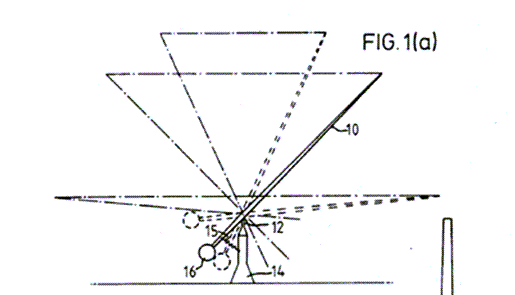
This place covers:
Tethered aircraft, e.g. kite or wings, having a particular flying pattern and getting energy from traction and retraction movement of the tether.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
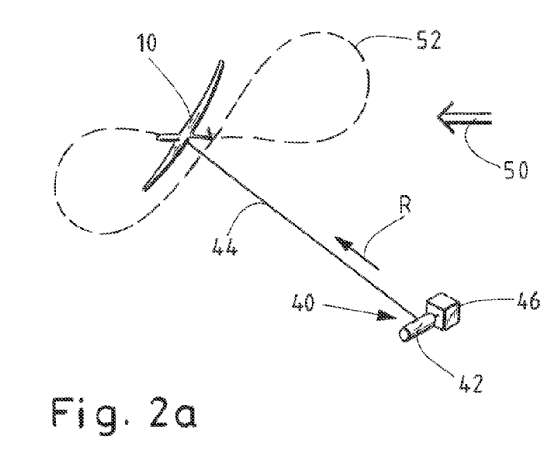

This place does not cover:
Controlling thereof |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wind motors being supported in air by airborne structures, e.g. by kites | |
Aircraft intended to be sustained without power plant |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
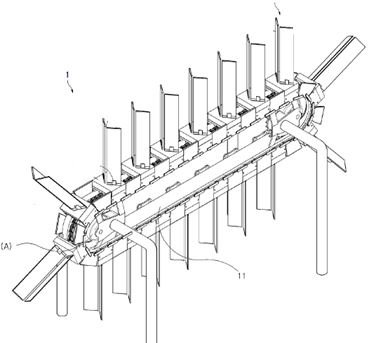
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
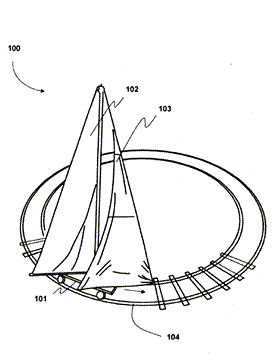
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
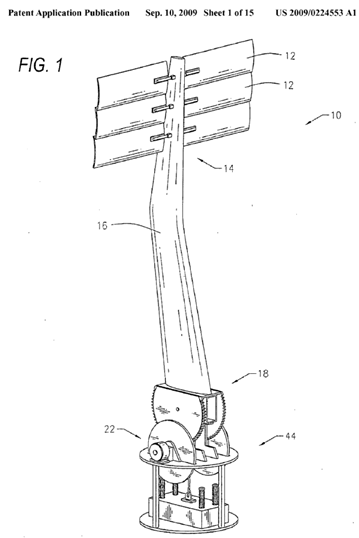
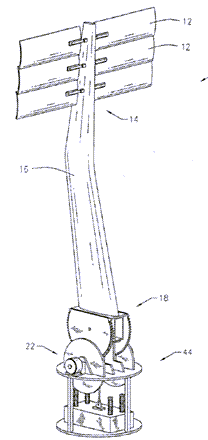
This place covers:
Control of wind motors and related control arrangements.
F03D 7/02 and F03D 7/06 covers essentially the two main types of wind motors according to groups F03D 1/00 and F03D 3/00. F03D 7/051 covers the control of wind motors according to groups F03D 5/015 and F03D 9/322. The head group F03D 7/00 covers all other types of wind motors.
Subgroups F03D 7/0204 - F03D 7/0296 cover the purpose of the control or the type of control actuators. Subgroups under F03D 7/04 cover the type of controllers and/or the control methods.
This place does not cover:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Pitch arrangements | |
Actuation arrangements for elements attached to or incorporated with the blade, e.g. flaps or slats | |
Yaw arrangements, rudders |
Documents should be classified in F03D 7/02 for purpose of control or the type of controller and in addition according to the control method or type of controller in group F03D 7/04. For example, a model-based controller acting on the pitch system to reduce rotor noise should be classified in groups F03D 7/045, F03D 7/0224 and F03D 7/0296.
Subgroups of F05B 2270/00, in particular control parameters under F05B 2270/30, should be used systematically in combination with classification in F03D 7/00 or its subgroups.
When monitoring aspects are relevant for the control, classification in F03D 17/00 should be considered as well.
This place covers:
Controlling wind motors, e.g. pitch, yaw, power output, while taking under consideration the behaviour of the floating support structure, e.g. ensuring wind motor stability or taking into account wave induced movements of the supporting platform.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Control of the floating platform as such to decrease unwanted movement, e.g. controlling ballast or anchoring |
This place covers:
Controlling each blade individually or independently, e.g. modulating the pitch angle based on the rotational angle of the blade to compensate for gravity or vertical wind shear.
This group is mainly used in combination with other groups of F03D 7/022 and its subgroups. For instance, individual control of a flap should be classified in F03D 7/0232 and F03D 7/024.
F03D 7/0208 covers the yawing movement of the rotor in a downwind position and the means to carry it. If the intention of the disclosed subject-matter is stopping or protecting the rotor, classifying in both groups, i.e. F03D 7/0208 and F03D 7/0264 should be considered.
This place does not cover:
Orientating out of wind |
This place covers:
Control of the generator to control the rotor, e.g. for regulating the rotor output torque or its speed. This can be done in various ways, e.g. control of the converter or of the generator speed.
The control of the generator or other electrical elements per se is covered by corresponding groups under H02P or H02M. Under F03D 7/0272, the generator is only seen as an abstract input-output black box element or actuator.
This place covers:
Controlling the output power of the wind rotor when acting on the rotor itself, i.e. by actuating some rotor or generator elements.
This place covers:
Control of the wind motor based on grid demand.
This place covers:
Controlling wind motors to prevent, counteract or reduce noise, e.g. modifying the control strategy and reducing rotor speed during night time.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangements for reducing noise pollution |
This place covers:
Control methods specially adapted to wind motors.
This place covers:
Control hardware or remote computing specially adapted to wind motors, e.g. redundant controllers, multi-processors architecture, decentralized cloud computing.
Data communication between SCADA system, turbine controllers or actuators.
This place covers:
Conjoint control of two or more wind motors located in relatively close proximity.
This place covers:
Control of airborne wind motors or tethered systems, in particular of their flying pattern.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wind motors of the tethered aircraft type, e.g. kites, with traction and retraction of the tether | |
Wind being motors supported in air by airborne structures, e.g. by kites |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangements for moving the wind engaging parts relative to the rotor |
This place covers:
Adaptations of wind motors for special use;
Combinations of wind motors with means for converting solar radiation into useful energy;
Combinations of wind motors with water energy converters, e.g. water turbines;
Combinations of wind motors with an apparatus storing energy;
Wind motors being characterised by the driven apparatus, e.g. heat pump, hydraulic pump, compressor, or electric generator;
Wind motors specially adapted for installation in particular locations, e.g. moving objects, stationary objects, infrastructure, or using landscape.
This place does not cover:
Hybrid wind-photovoltaic energy systems for the generation of electric power |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Pumps characterised by combination with wind motors |
This place covers:
Solar panels built in or on the blades or tower.
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Machines or engines for liquids |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Storage of energy relating to wind, spring, weight, inertia or like motors |
The mere disclosure of a trivial battery does not justify classification in this group.
This place does not cover:
Combinations of wind motors with apparatus storing energy |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Arrangements of propulsion units in vehicles in connection with power supply derived from wind power | |
Electric propulsion of vehicles using wind power | |
Propulsion of ships or other waterborne vessels by wind motors driving water-engaging propulsive elements | |
Driving auxiliaries on ships of other waterborne vessels using wind power |
This place covers:
Wind motors combined with the driven apparatus being an electric generator (not a routine electrical generator).
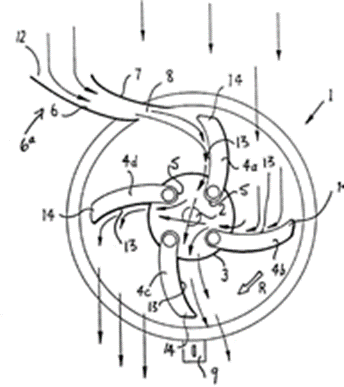
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
Generator mounted on top of the nacelle:
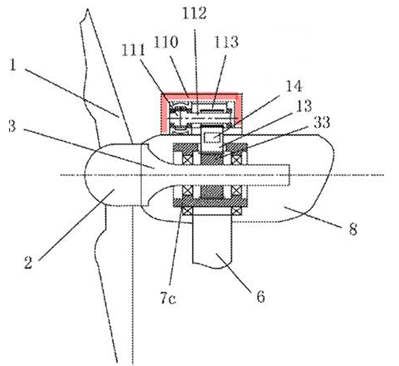
Generator 17 is activated by a special swash plate 15 and cams 13 on rotating shaft 12:
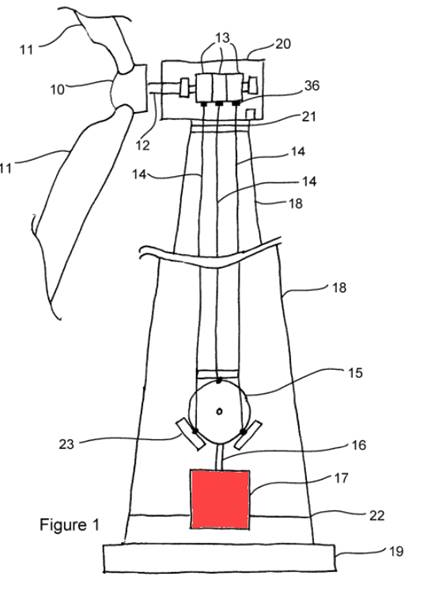
Classification in this group F03D 9/25 only applies when the combination of the electrical generator to the wind motor is disclosed. Structural features of the wind generator associated with a wind motor is classified in H02K 7/18. The mere disclosure of a state-of-the-art generator does not justify classification in this group. This generator type can be classified in F05B 2220/706.
This place does not cover:
Wind motors combined with the driven apparatus producing heat |
This place covers:
The connection or relative placement between the generator and the transformer to the electricity grid, e.g. by way of connecting elements, power cables, or the location of the transformer to the generator.
General electrical conduction between black-box elements, e.g. generator or transformer.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
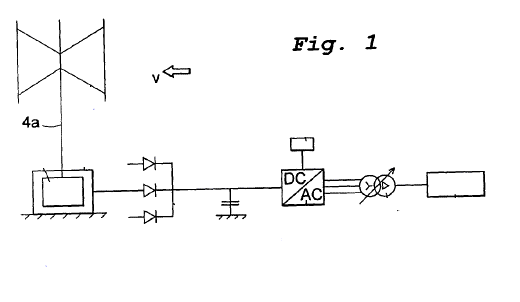
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangement of electrical components within nacelles or tower |
This place covers:
Electrical connection between wind motors, e.g. in an array or in series, other than a trivial disclosure of a wind turbine used in a wind park or a wind farm.
Multiple wind motors connected to a single transformer, different wind rated wind turbines placed in a pattern.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
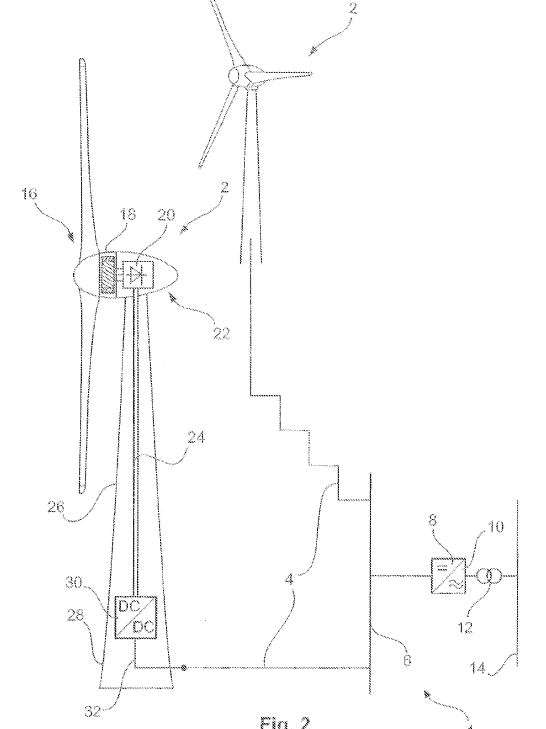
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Controlling wind farms | |
Mounting on supporting structures or systems as part of a wind turbine farm | |
Electric power networks; Circuit arrangements or systems for supplying or distributing electric power; Systems for storing electric energy |
Structures supporting multiple wind motors are not considered as a wind farm.
This place covers:
Adaptation of wind motors for driving a pump or a compressor.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
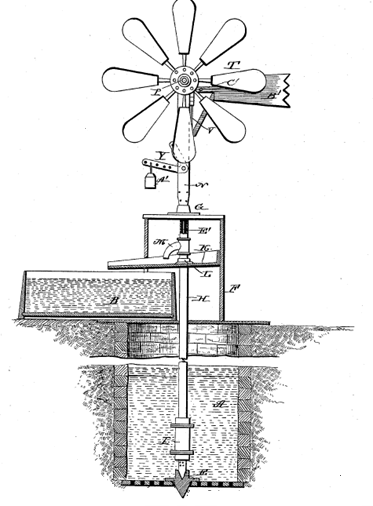
Wind motors combined with a heat pump or AC unit are classified in F03D 9/22.
Hydraulic transmissions, i.e. combination of hydraulic pump and motor, are classified in F03D 15/202.
This place does not cover:
Arrangements for mounting or supporting wind motors |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Anchoring arrangements for special vessels |
F03D 9/30 covers the location or place where the wind motors are installed and operated. F03D 13/20 covers the supporting structure of the wind motor or the way it is mounted to this structure.
For example, a wind motor positioned on a building should be classified in F03D 9/45 while the arrangements for attaching or supporting the wind motor on a building is classified by allocating F03D 13/20.
Classification in F05B 2240/90 as well as its subgroups is mandatory in combination with F03D 9/30 and F03D 13/20 to identify the supporting structure or location.
This place covers:
Wind motors specially adapted for installation on moving objects, e.g. vehicles, in which the movement of the object causes air flow through the rotor or places the wind motor in a different, typically increased, air flow.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangements for mounting or supporting wind motors on a floating support |
This place does not cover:
Controlling thereof |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wind motors of the tethered aircraft type, e.g. kites, with traction and retraction of the tether | |
Kite sails for water sports boards | |
Kite sails for vessels |
Mounting is typically understood as fixing something into position onto something, but in this group it is interpreted in a broader sense also encompassing the concept of supporting. Reference is made to the title of group F03D 13/20.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Cranes in general |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangement of components within nacelles or towers |
Foundations specially adapted for wind motors are classified in E02D 27/425.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wind motors kept aloft by an airborne structure | |
Floating buildings, stores, drilling platforms or workshops, e.g. carrying water-oil separating devices | |
Offshore structures for wind turbines mounted on piles or like supports | |
Foundations for poles, masts or chimneys | |
Foundations specially adapted for wind motors | |
Towers; Masts, poles; Methods of erecting such structures |
This place covers:
A wind motor supported on a structure which is of a design that has no interior access, similar to a flagpole or a sailboat mast.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
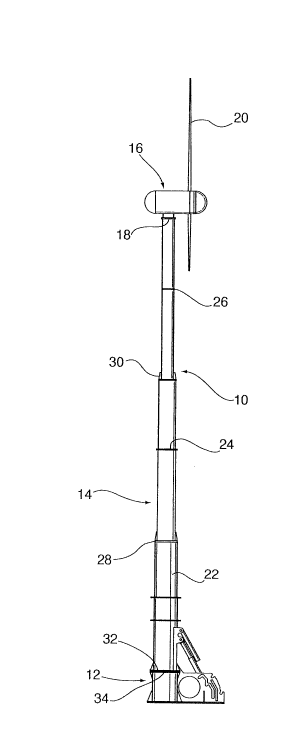
This place covers:
Tower-shaped wind motor support which is constructed to support a large nacelle or rotor. The tower may have access doors or be of a framed construction.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wind motors supported on masts or poles |
This place covers:
An opening, hatch, ingress or egress suitable for a person to enter or exit the tower.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
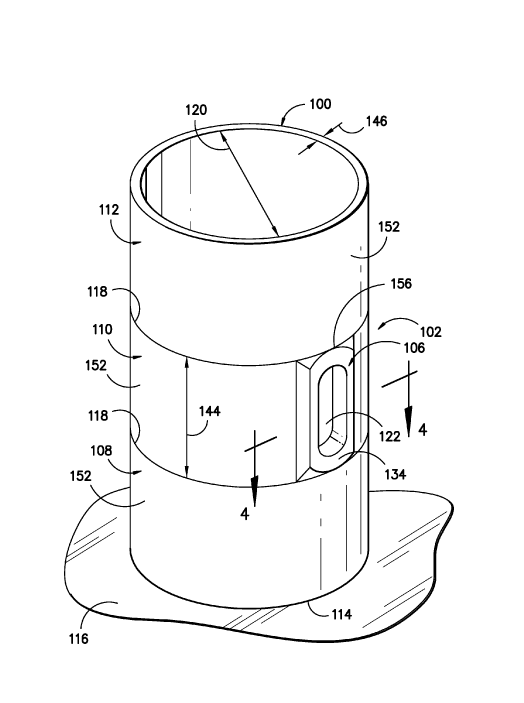
This place covers:
A wind motor tower made from circumferential segments joined together.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
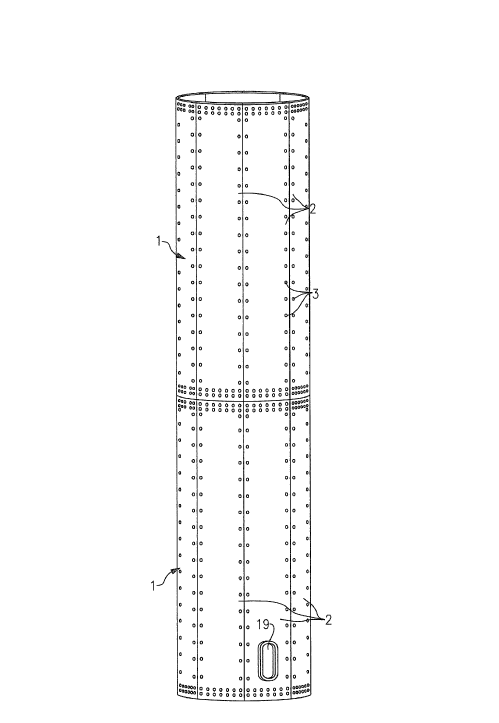
This place covers:
Means for connecting together adjacent segments of a wind motor tower.
Joints between adjacent segments. The adjacent segments may be either circumferentially or axially arranged.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
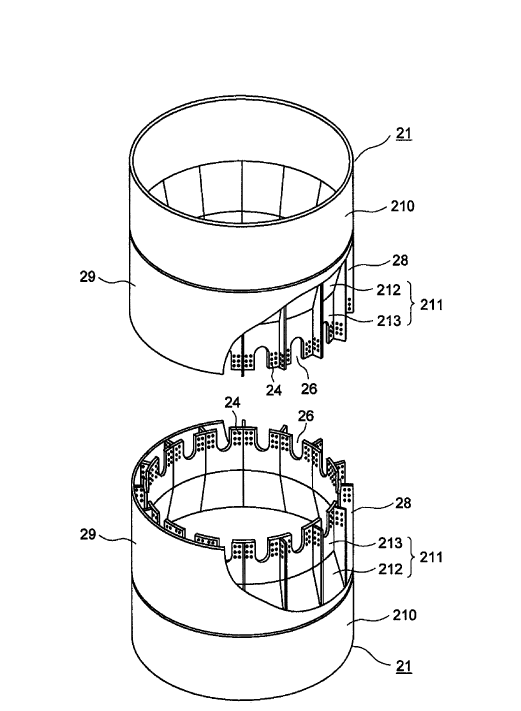
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
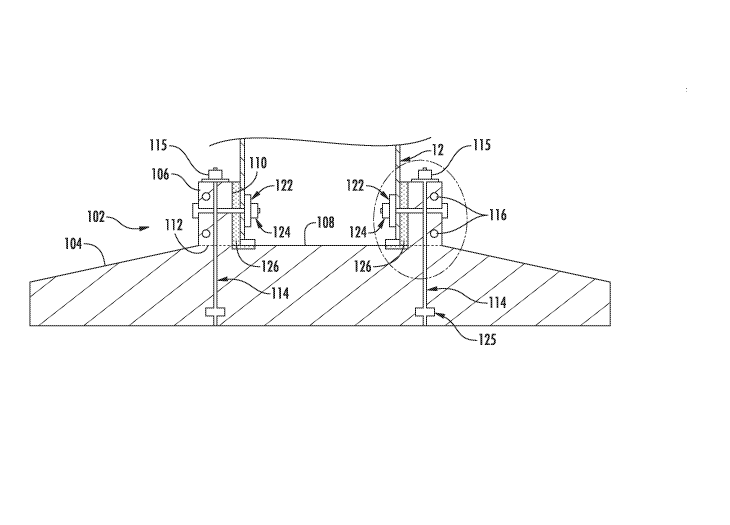
This place covers:
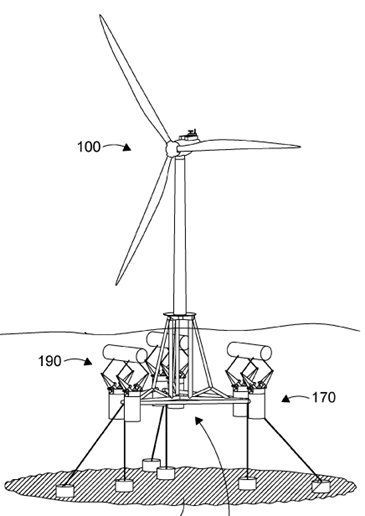
A wind motor supporting member having features specially adapted for offshore applications.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Anchoring arrangements for special vessels | |
Vessels or like floating structures adapted for special purposes | |
Artificial islands mounted on piles or like supports |
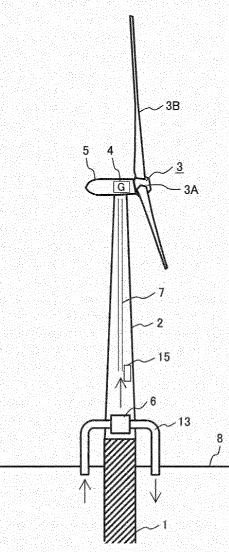
This place covers:
Offshore wind motors mounted on a floating support.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
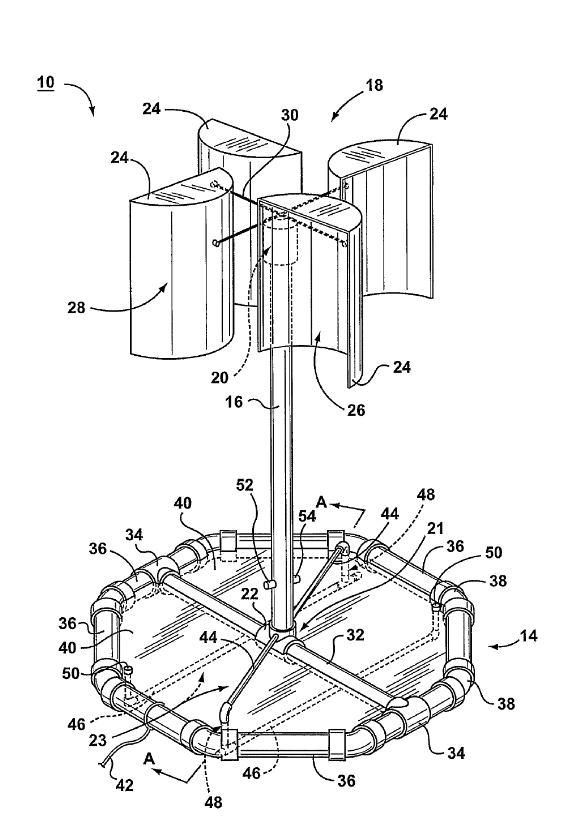
The floating structures per se are covered by groups in subclass B63B. F03D 13/256 covers the wind motors or linked elements, e.g. towers or masts, which are installed on or supported by a floating structure.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Controlling floating wind motors having rotation axis substantially parallel to the air flowing at the rotor | |
Transporting wind motors to their installation site |
This place covers:
Inspection, testing or adjustment of the wind motor before operating the wind motor to produce power.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Inspection or testing of the wind motor or components thereof, after commissioning | |
Micro-siting |
This place covers:
Transporting or storing of wind motor components.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Use of a wind motor mounted to a vehicle to produce power when the vehicle is either moving or stationary | |
Assembling the wind motor at the installation site | |
Vehicles adapted to transport or carry special loads or objects | |
Transporting offshore structures, specially adapted for electric power plants |
This place covers:
Transmission of mechanical power, i.e. mechanisms by which the wind-derived mechanical power is conveyed to its point of use
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Gearing |
This place covers:
Air flow through the blades, e.g. windmills creating a flow of air through the blade by their rotation.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
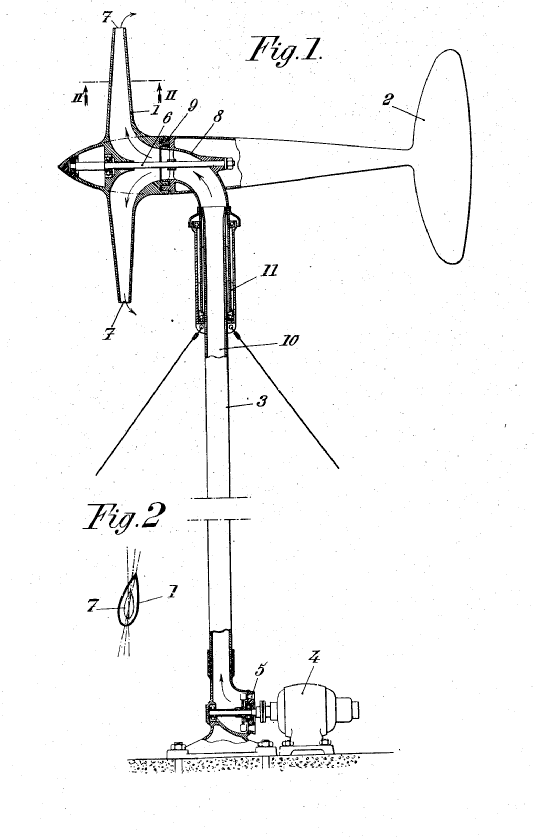
This place covers:
Wind motors transmitting mechanical power to their power generating device with a gear or gearbox. The gear is of any type, including rotary, as well as a rack and pinion gearing.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
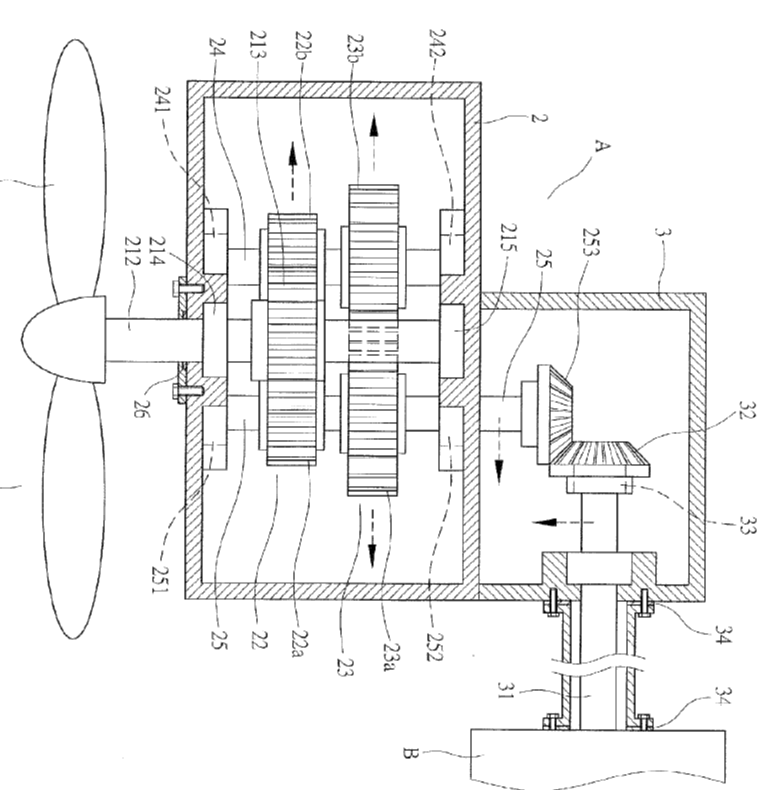
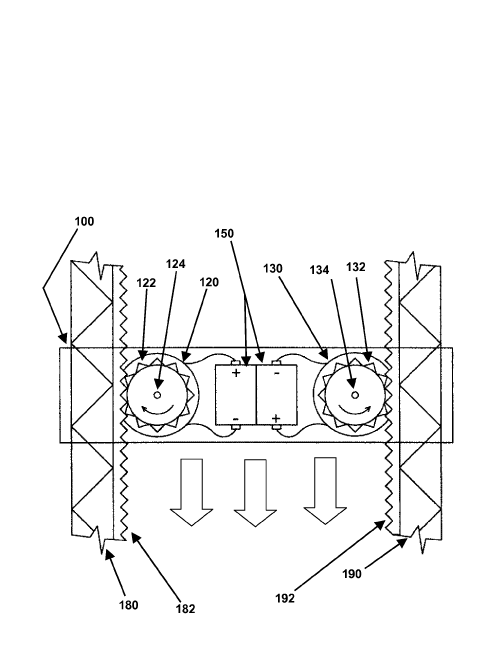
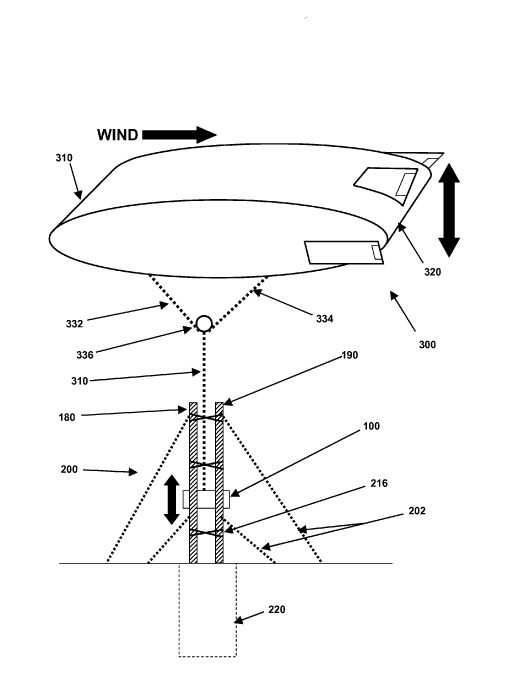
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wind motors with the wind-engaging parts swinging to-and-fro and not rotating |
This place covers:
Wind motors having the stroke length of a pump cylinder adjusted. The length of stroke is typically adjusted relative to the speed of the wind.
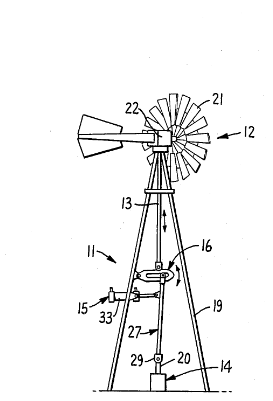
This place covers:
Gearless transmission arrangements in which the rotor shaft is directly coupled to the generator without intermediate gearing or other drive elements.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
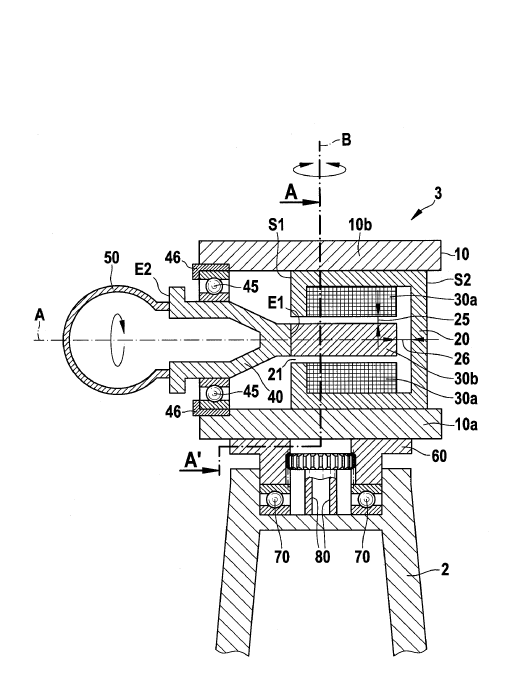
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Direct-drive | Gearless transmission arrangement in which the rotor shaft is attached directly to the generator without intermediate gearing. |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
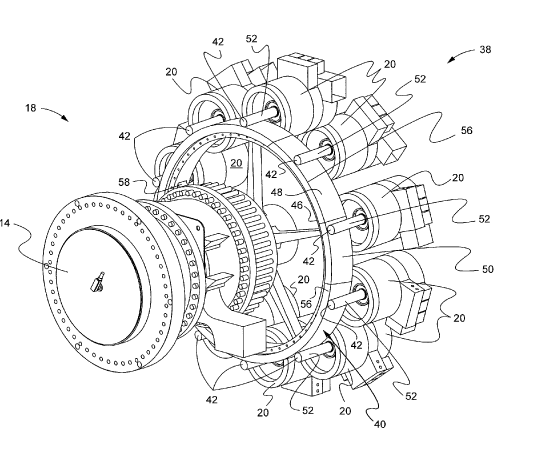
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
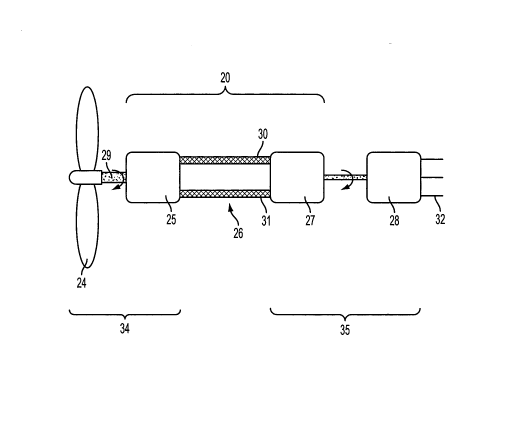
This place covers:
Transmissions coupling the rotor to a ground-based generator.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
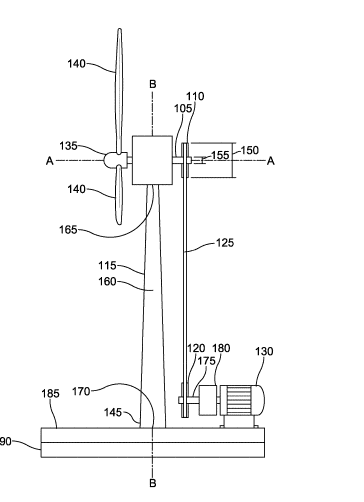
This place covers:
Arrangements for coupling multiple generators together.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
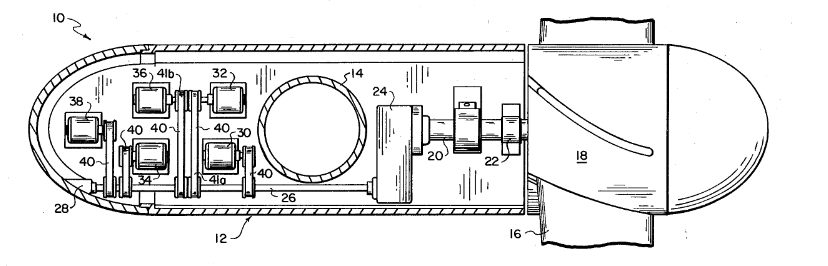
This place covers:
Monitoring or testing of wind motors, e.g. diagnostics or inspection.
This place does not cover:
Testing during commissioning of wind motors |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Ice detection | |
Testing static or dynamic balance of machines or structures; Testing of structures or apparatus, not otherwise provided for |
F03D 17/00 includes subgroups relating to the purpose (cf. F03D 17/009), and relating to the component being monitored or tested (cf. F03D 17/027). When appropriate, classification of the document should include the component of the wind motor being monitored or tested, together with the purpose of the monitoring or testing. For example, a wind motor tower being monitored for natural frequency vibrations should be allocated CPC symbols F03D 17/034 for the tower, and F03D 17/017 for monitoring natural frequencies thereof.
When control aspects are relevant, e.g. monitored parameters being used for controlling, classification in F03D 7/00 should be considered as well.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Monitoring or testing | Overseeing or analysing the operating conditions of the wind motor mechanism, typically to identify problematic conditions. This may involve reference to wind motor sensor signals indicating, e.g. wind speed and direction, pitch angle, vibration, rotary torque, blade load and strain. |
This place covers:
Inspection of the wind motor at the installation site. Inspection is performed on-demand or on a scheduled basis rather than a continuous monitoring.
The use of occupied vehicles, e.g. boats, helicopters for personnel to reach wind motor inspection sites.
This place covers:
Inspecting or checking the operation of the wind motor when implemented with a controlled input to verify the wind motor is performing to its specifications.
This place covers:
The use of optical devices during the inspection process.
The mere mentioning of a camera being used to take a picture during the inspection process does not justify classification in this group.
This place covers:
The inspection process being performed or assisted by the use of remote vehicles, e.g. remotely controlled robots or unmanned aerial vehicles.
This place covers:
The use of sensors to measure variables such as stress and strain which represent forces exposed on components of the wind motor.
Diagnosing the remaining useful life of a wind motor component.
Monitoring the wind motor with respect to the initiation and propagation of cracks due to cyclic loading.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Controlling wind motors to increase fatigue life | |
Strain gauges |
This place covers:
Monitoring the wind motor with respect to wear or clearance. Excessive wear can cause for clearances between parts to be outside of acceptable ranges.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Monitoring vibrations |
This place covers:
Detection of an abnormality or damage in the wind motor. Faults or failures are considered an extreme case of abnormalities and damage, i.e. the wind motor is still operable with the detection of an abnormality or damage, whereas a fault or failure detection indicates the inoperability of the wind motor. Detecting faults or failures are covered by subgroup F03D 17/014.
This place covers:
Monitoring wind motors with respect to a measured vibration.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Monitoring wear or clearances |
This place covers:
The vibration value is representative of the rotor imbalance.
Balancing rotors during or before commissioning is classified in F03D 13/35.
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms:
- Natural frequency
- Eigenfrequency
- Fundamental frequency
- Resonant frequency
This place covers:
Monitoring temperature of wind motor elements.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Cooling or heating of wind motors |
This group covers monitoring power or current associated with the electrical generator of the wind motor. Group H02P 9/00 covers arrangements for controlling electric generators for the purpose of obtaining a desired output.
This place covers:
Sensors or methods for determining and monitoring variables such as length or distance between components of the wind motor.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Displacement measuring means |
This place covers:
Sensors or methods for determining and monitoring noises emitted by the wind motor.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Controlling the wind motor to reduce noise emissions | |
Accessory devices for reducing noises emitted by the wind motor | |
Noise or sound levels as control parameters | |
Microphones |
This place covers:
Monitoring or diagnosing an error or offset of the wind motor, such as the yaw error, and implementing a correction to the measured error.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Controlling the wind motor to orient in relation to wind direction |
This place covers:
Estimating or predicting the power producing capabilities of the wind motor, e.g. based on predicted wind speed or on wind motor operability. Analysis of operating the wind motor above the power curve or above its rated power for a length of time.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Controlling wind motors | |
Micro-siting |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
AEP | Annual Energy Production |
This place covers:
The primary or redundant power-supply means for controlling a wind motor auxiliary component. For example, the use of any one of a: hydraulic circuit, battery, slip-ring, switch or controller to actuate a yaw or pitch drive motor.
Method or means for adjusting the power consumption of auxiliary components.
Examples of places in relation to which this place is residual:
Hydraulic actuators or electric actuators for changing the blade pitch of the wind motor |
This place covers:
Devices or processes for minimizing interaction between the wind motor and animals, e.g. birds or bats.
Detection of animals.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangements for warning air traffic |
This place covers:
Accessories used on the wind motor or in the vicinity of the wind motor to attenuate noise emissions therefrom.
Examples of places in relation to which this place is residual:
Noise reducers provided on blade surfaces | |
Controlling the wind motor to reduce noise emissions |
This place covers:
Rendering wind motors inoperative. Dismantling wind motors.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Assembly of wind motors | |
Commissioning of wind motors |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Traffic control systems for aircraft |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Shadow flicker | Periodic flickering effect due to repetitive shadows cast by rotating wind turbine blades. |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Installations of lightning conductors; Fastening thereof to supporting structure |
This place covers:
Temporary or permanent platforms associated with the wind motor for use during maintenance or repair.
This place covers:
Furnishing or upgrading the wind motor with a new or modified part.
Repurposing of a wind motor or component thereof into another useful item.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Cleaning |
This place covers:
Yaw bearings, pitch bearings or shaft bearings used on the wind motors.
Lubrication circuits and devices for supplying lubricant to wind motor components.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Monitoring or testing the blade pitch drive or yaw drive | |
Monitoring or testing the wind motor bearings | |
Lubricating of machines in general | |
Bearings |
This place covers:
The rolling elements, races and gears making up the bearings providing rotational movement between the blade and hub, or the tower and nacelle.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Pitch arrangements | |
Yaw arrangements |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Nacelle | The protective outer housing enclosing wind motor components such as the transmission, associated gearing and turbine. |