CPC Definition - Subclass F01N
This place covers:
Silencing apparatus in exhaust systems for reducing the noise emitted by machines or engines in general, but more particularly internal combustion engines.
Exhaust or silencing apparatus having means for purifying, rendering innocuous or otherwise treating exhaust. The main apparatus includes particulate filters, absorbents and other catalytic reactors. The means can also be an electric discharge or the addition of air or liquids.
Exhaust or silencing apparatus combined or associated with devices profiting by exhaust energy, mainly the devices using exhaust heat.
Electrical control, monitoring or diagnostic of exhaust gas treating apparatus.
Other constructional features common to the above apparatus or the exhaust conduits including manufacture, assembly, disassembly or material selection.
The treatment of recirculated exhaust gases [EGR] should be classified only in the F02M 26/00, unless the exhaust purifier also treats exhaust which is not recirculated.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Filters or filtering processes specially modified for separating dispersed particles from gases or vapours | |
Chemical or biological purification of waste gases, e.g. engine exhaust gases, smoke, fumes, flue gases or aerosols | |
Flow mixers; Mixers for falling materials, e.g. solid particles | |
Catalysts, in general, characterised by their form or physical properties | |
Separating dispersed particles from gases or vapour, e.g. air, by electrostatic effect | |
Application of procedures in order to alter the diameter of metal tube ends | |
Making hollow metal objects characterised by the use of the objects | |
Arrangement in connection with combustion air intake or gas exhaust of propulsion units | |
Arrangement in connection with gas exhaust of propulsion units | |
Insulating elements for body-finishing, identifying or decorating, e.g. for sound insulation | |
Arrangements, apparatus and methods for handling exhaust gas in outboard drives, e.g. exhaust gas outlets | |
Shaped ceramic products characterised by their composition; Ceramics compositions | |
Porous mortars, concrete, artificial stone or ceramic ware; Preparation thereof | |
Crankcase ventilating or breathing having means for purifying air before leaving crankcase, e.g. removing oil | |
Electrical control of supply of combustible mixture or its constituents with safety or indicating devices for abnormal conditions | |
Engine-pertinent apparatus for adding exhaust gases to combustion-air, main fuel or fuel-air mixture, e.g. by exhaust gas recirculation [EGR] systems | |
Combustion-air cleaners, air intakes, intake silencers or induction systems specially adapted for, or arranged on, internal-combustion engines | |
Combustion-air cleaners using filters | |
Pipes; Joints or fittings for pipes; Supports for pipes; Means for thermal insulation in general | |
Burners using a direct spraying action of liquid droplets or vaporised liquid into the combustion space | |
Arrangements of devices for treating smoke or fumes, e.g. catalytic treatment of flue gases from furnaces burning coal, gas or oil | |
Continuous combustion chambers using liquid or gaseous fuel characterised by the use of catalytic means, e.g. catalytic treatment of gases from exhaust from gas turbines | |
Heat-exchange apparatus having stationary conduit assemblies for one heat-exchange medium only, the media being in contact with different sides of the conduit wall, in which the other heat-exchange medium is a large body of fluid, e.g. domestic or motor car radiators | |
Measuring pressure in inlet or exhaust ducts of internal-combustion engines | |
Sampling; Preparing specimens for investigation | |
Sampling from a flowing stream of gas in a vehicle exhaust | |
Investigating or analysing materials by investigating resistance | |
Methods or devices for protecting against, or for damping, noise or other acoustic waves in general | |
Generating plasma |
References B60K 13/00, F02M 35/00 and G10K 11/16 are non-limiting in the subclass F01N. CPC will be corrected once this inconsistency is resolved in IPC.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Absorbent | Could also be found under the wording: trap, adsorbent or storage device, e.g. NOx-trap. It is an element which can absorb at least one compound and release/adsorb it again. The reduction or oxidation of the compound in the absorbent may or may not occur, depending of the presence of a suitable catalyst therefore. |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
SCR | Selective catalytic reduction |
DPF | Diesel particulate filter |
CRT | Continuous regenerating trap |
Absorbent | Trap, adsorber, absorber, occlusion element |
Silencer | Muffler |
This place covers:
Silencing apparatus for reducing or controlling the noise in exhaust emitted by internal combustion engines.
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Filters for removing solid constituents of exhaust, in combination with exhaust silencers in a single housing |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Catalytic reactors combined or associated with exhaust silencers in a single housing | |
Means for exhaust-air diffusion or for sound or vibration damping in suction cleaners | |
Arrangements of noise-damping means of exhaust silencers of portable power-driven percussive tools | |
Arrangements in connection with gas exhaust of propulsion units in vehicles | |
Arrangement or adaptation of acoustic signal devices, e.g. amplifying noise for the vehicle's passengers | |
Insulating elements for mounting around noise sources, e.g. air blowers | |
Silencer devices of power brake systems | |
Arrangement of marine propulsion power-unit exhaust uptakes | |
Arrangement of aircraft exhaust outlets or jet pipes | |
Ground installations for reducing aircraft engine or jet noise | |
Silencers specially adapted for steam engines | |
Use of kinetic or wave energy of charge in induction systems, or of combustion residues in exhaust systems, for improving quantity of charge or for increasing removal of combustion residues, in exhaust systems only, e.g. for sucking-off combustion gases | |
Acoustic insulation of combustion engines | |
Air-intakes for gas-turbine plants or jet-propulsion plants having provisions for noise suppression | |
Throttle valves specially adapted for controlling engines by throttling air or fuel-and-air induction conduits or exhaust conduits; Arrangements of such valves in conduits | |
Combustion-air intake silencers specially adapted for, or arranged on, internal-combustion engines | |
Pulsation or noise damping means of positive-displacement machines for liquids or pumps | |
Silencing of rotary-piston, or oscillating-piston, positive-displacement machines for liquids or positive displacement pumps | |
Combating cavitation, whirls, noise, vibration or the like in non-positive-displacement pumps | |
Means in valves for preventing water-hammer or noise | |
Noise absorbers for use in, or in connection with, pipes or pipe systems | |
Means for preventing or suppressing noise in air-conditioning or ventilation | |
Silencers for smallarms or ordnance | |
Methods or devices for transmitting, conducting or directing sound in general; Methods or devices for protecting against, or for damping, noise or other acoustic waves in general |
Remaining details of the silencers must be classified in the following codes:
- F01N 2210/00 for the combination of silencing methods;
- F01N 2230/00 for the combination of silencers and other devices;
- F01N 2290/00 for movable parts or members in exhaust systems for other than for control purposes;
- F01N 2470/00 for the structure or shape of gas passages, pipes or tubes;
- F01N 2490/00 for the structure, disposition or shape of gas-chambers;
- F01N 2310/00 or F01N 2450/06 for the filling of chambers with sound absorbing material;
- F01N 2590/00 for the particular use, i.e. the type of vehicle or machine.
This place covers:
Exhaust gas silencers with physical dimensions intended to alter, reduce or cancel sound at particular frequencies, often with little or no impedance to the passage of exhaust gas.
Resonance is achieved by placing a chamber or a channel in communication with the exhaust flow without the exhaust flow passing therethrough.
This place covers:
Illustrative example of the subject matter classified in this place:
![]()
This place covers:
Illustrative example of the subject matter classified in this place:

The Figure illustrates a porous member surrounding the chamber, constructed from, e.g. bronze or ceramics.
This place covers:
Illustrative examples of the subject matter classified in this place:
1.

2.

3.
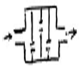
This place covers:
Illustrative examples of the subject matter classified in this place:
1.

2.

3.

This place covers:
Illustrative example of the subject matter classified in this place:
![]()
This place covers:
Illustrative example of the subject matter classified in this place:
![]()
This place does not cover:
Silencing by reducing exhaust energy by throttling or whirling using spirally or helically shaped channels |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of the subject matter classified in this place:
![]()
This place covers:
Illustrative example of the subject matter classified in this place:
1a.

1b.
![]()
This place covers:
Illustrative examples of the subject matter classified in this place:
1.
![]()
2.
![]()
3.
![]()
This place does not cover:
Silencing by reducing exhaust energy by throttling or whirling using transversal baffles defining a tortuous path for the gases or successively throttling gas flow | |
Silencing by reducing exhaust energy by throttling or whirling, the gases flowing through the silencer two or more times longitudinally in opposite directions, e.g. using parallel or concentric tubes | |
Silencing by reducing exhaust energy by throttling or whirling, with means to impart whirling motion to the gases |
This place covers:
Exhaust gas silencing using movable elements that modify the exhaust flow and its acoustic properties. These mechanisms may function by altering the flow path, varying the flow area, modulating pressure fluctuations, disrupting sound wave propagation or dynamically adjusting flow resistance.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Controlling engines by throttling air or fuel-and-air induction conduits or exhaust conduits |
This place covers:
Silencing by using movable parts for adjusting flow area, e.g. by means of a valve.
Illustrative example of the subject matter classified in this place:
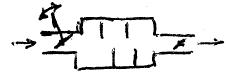
This place covers:
Illustrative examples of the subject matter classified in this place:
1.

2.

This place does not cover:
Silencing by using movable parts for adjusting flow area |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electrical control of exhaust gas treating apparatus | |
Monitoring or diagnostic devices for exhaust-gas treatment apparatus | |
Boiling apparatus for physical or chemical purposes | |
Filtration; Filtering material, regeneration thereof | B01D 24/00, B01D 25/00, B01D 27/00, B01D 29/00, B01D 33/00, B01D 35/00, B01D 36/00, B01D 37/00, B01D 39/00, B01D 41/00, B01D 43/00 |
Separating dispersed particles from gases or vapours | B01D 45/00, B01D 46/00, B01D 47/00, B01D 49/00, B01D 50/00, B01D 51/00, B01D 53/00, B01D 57/00, B01D 59/00 |
Catalysts, in general, characterised by their form or physical properties | |
Magnetic or electrostatic separation of solid material from solid materials or fluids; Separation by high-voltage electric fields | |
Layered products | |
Arrangement in connection with combustion air intake or gas exhaust of propulsion units | |
Arrangement in connection with gas exhaust of propulsion units | |
Arrangement in connection with fuel supply of combustion engines; Mounting or construction of fuel tanks | |
Production of hydrogen or of gaseous mixtures containing hydrogen | |
Preparation of ammonia from nitrogenous organic substances | |
Shaped ceramic products characterised by their composition; Ceramics compositions | |
Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres | |
Pulp or paper, comprising synthetic cellulose or non-cellulose fibres or web-forming material | |
Cooling of machines or engines in general; Cooling of internal-combustion engines | |
Engine-pertinent apparatus for adding exhaust gases to combustion-air, main fuel or fuel-air mixture, e.g. by exhaust gas recirculation [EGR] systems | |
Combustion-air cleaners, air intakes, intake silencers or induction systems specially adapted for, or arranged on, internal-combustion engines | |
Heating of pipes or pipe systems | |
Burners using a direct spraying action of liquid droplets or vaporised liquid into the combustion space | |
Arrangements of devices for treating smoke or fumes, e.g. catalytic treatment of flue gases from furnaces burning coal, gas or oil | |
Continuous combustion chambers using liquid or gaseous fuel characterised by the use of catalytic means, e.g. catalytic treatment of gases from exhaust from gas turbines | |
Water heaters, e.g. boilers, continuous-flow heaters or water-storage heaters | |
Indicating or measuring liquid level or level of fluent solid material, e.g. indicating in terms of volume or indicating by means of an alarm | |
Investigating or analysing materials by the use of refractometers | |
Coupling devices | |
Ohmic-resistance heating |
Details of electrical control or of the monitoring of the exhaust gas treating apparatus may also receive classification in F01N 2900/00.
References to F01N 9/00 and F01N 11/00 are non-limiting in main group F01N 3/00. CPC will be corrected once this inconsistency is resolved in IPC.
This place covers:
Physically separating particles from the exhaust with electric or electrostatic separators.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Rendering the exhaust gas innocuous with electric or magnetic treatment, e.g. dissociation of noxious components | |
Separating dispersed particles from gases or vapour, e.g. air, by electrostatic effect |
Mats that can be used as either a filter or a catalyst between a monolithic body and a housing should be classified in F01N 3/2853, and not in F01N 3/0211.
Structural details of catalyst supports or particle filters may be classified further in F01N 2330/00.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Particle separators, e.g. dust precipitators, using rigid hollow filter bodies characterised by the physical shape or structure of the filtering element | |
Shaped ceramic products characterised by their composition; Ceramics compositions; Processing powders of inorganic compounds preparatory to the manufacturing of ceramic products | |
Ceramic honeycomb structures |
Structural details of honeycomb supports may be classified further in F01N 2330/30.
Regeneration of a particulate filter by introducing corrections to engine control signals, e.g. by modifying the injection time delay or the exhaust/intake valve timing, are covered by F02D 41/029.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electrical control of filter regeneration, e.g. detection of clogging | |
Electrical control of supply of combustible mixture or its constituent with circuit arrangements for generating control signals to introduce corrections in relation with the state of the exhaust gas treating apparatus |
Catalytic coatings applied on filters to lower soot ignition temperature or otherwise promote soot ignition may be further classified in F01N 2510/065.
Details of bypassing exhaust may be further classified in F01N 2410/00.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electrical control of filter regeneration, e.g. detection of clogging |
This place covers:
Cooling, or removing solid constituents of, exhaust by means of filters in combination with catalytic reactors, e.g. catalysed diesel particulate filters.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Regenerating filters, e.g. by burning trapped particles | |
Regenerating filters using special exhaust apparatus upstream of the filter for producing nitrogen dioxide, e.g. for continuous filter regeneration systems [CRT] |
Catalytic coatings applied on filters may be further classified in F01N 2510/06.
This place covers:
Cooling, or removing solid constituents of, exhaust using liquids, e.g. water, and without chemical reactions directly involved.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Cooling an exhaust treating device using a liquid |
This place does not cover:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Control of additional air supply only to thermal or catalytic conversion of noxious components of exhaust, e.g. using by-passes or variable air pump drives | |
Other arrangements or adaptations of tailpipes, e.g. with means for mixing air with exhaust for exhaust cooling, dilution or evacuation | |
Cooling exhaust treating devices using air |
This place does not cover:
Exhaust or silencing apparatus having means for purifying, rendering innocuous or otherwise treating exhaust by means of electric or electrostatic separators | |
Chemical or biological purification of engine exhaust gases |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Catalysts, in general, characterised by their form or physical properties |
Arrangements for adding fuel to an absorbent should also receive classification in F01N 3/36 and F01N 2610/00.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Exhaust or silencing apparatus having means for purifying, rendering innocuous or otherwise treating exhaust by using absorbents or adsorbents, characterised by the absorbed or adsorbed substances | |
Exhaust treating apparatus eliminating, absorbing or adsorbing specific elements or compounds |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Filters in combination with catalytic reactors |
This place covers:
Control of the regeneration of the absorbent.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Introducing corrections to engine control signals to purge or regenerate exhaust gas treating apparatus | |
Introducing corrections to engine control signals to purge or regenerate NOx traps or adsorbents | |
Introducing corrections to engine control signals for desulphurisation of NOx traps or adsorbents | |
Introducing corrections to engine control signals to purge or regenerate SOx traps or adsorbents |
Control of the regeneration of the absorbent for releasing stored NOx is classified in F01N 3/0871.
Desulphurisation of NOx traps is classified in F01N 3/0885.
Details of bypassing exhaust may be further classified in F01N 2410/00.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Introducing corrections to engine control signals for desulphurisation of NOx traps or adsorbents |
This place covers:
Electric or magnetic treatment changing the gas structure at a molecular level, e.g. dissociation of noxious components, including by corona discharge.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Exhaust or silencing apparatus having electric or electrostatic separators for purifying, rendering innocuous or otherwise treating exhaust | |
Using electric or magnetic heating means for regenerating filters used for cooling, or for removing solid constituents of, exhaust | |
Using electric or magnetic heating means for periodically heating or cooling catalytic reactors |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Chemical or biological purification of waste gases |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Exhaust treating apparatus eliminating, absorbing or adsorbing specific elements or compounds |
Details of bypassing exhaust may be further classified in F01N 2410/00.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Using a fuel burner or introducing fuel into exhaust duct for periodically heating or cooling catalytic reactors, e.g. at cold starting or overheating |
This place covers:
Structural components of a selective catalytic reduction [SCR] system, and their arrangement within the system.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Combination or association of two or more different exhaust treating devices, or of at least one such device with an auxiliary device, not covered by indexing codes F01N 2230/00 or F01N 2250/00, one of the devices being an ammonia generator | |
Sprayers or atomisers used to supply substances to exhaust gases; Arrangement thereof in the exhaust apparatus |
Further details of arrangements for supplying substances other than fuel, e.g. ammonia or urea, may be classified in F01N 2610/00. This includes items like pumps, valves, conduits, nozzles and injectors.
This place covers:
Selective catalytic reduction [SCR] with means for generating a reducing substance from the exhaust gases, e.g. a NOx absorbent/reducing catalyst.
This place covers:
Electronic control of the SCR system.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Sprayers or atomisers used to supply substances to exhaust gases; Arrangement thereof in the exhaust apparatus |
This place covers:
- Construction of thermal reactors with afterburning of exhaust gases, often without using a catalyst.
- Supply of fuel to thermal reactors.
This place covers:
Construction of catalytic reactors, e.g. radial flow or a tapered catalyst carrier.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Structure of catalyst support or particle filter | |
Arrangements for fitting catalyst support or particle filter element in the housing | |
Selection of materials for exhaust purification | |
Methods or apparatus for fitting, inserting or repairing different elements | |
Surface coverings |
Simple methods of fitting the honeycomb in the housing may be further classified in F01N 2350/02.
This place covers:
Mats having a special shape or arrangement in the honeycomb housing.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Working or processing of sheet metal or metal tubes, rods or profiles without essentially removing material; Punching metal | |
Shaped ceramic products characterised by their composition; Ceramics compositions; Processing powders of inorganic compounds preparatory to the manufacturing of ceramic products | |
Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres |
F01N 2240/20 may be given along with F01N 3/2892 if the flow directors or deflectors are further combined with other exhaust treating devices or auxiliary devices.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adding substances to exhaust gases |
Further details of the arrangements for supply of additional fuel may be classified in F01N 2610/14.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Exhaust or silencing apparatus having means for cooling, or for removing solid constituents of, exhaust using heat exchangers | |
Construction of catalytic reactors combined or associated with heat exchangers in a single housing | |
Combination or association of two or more different exhaust treating devices, or of at least one such device with an auxiliary device, not covered by indexing codes F01N 2230/00 or F01N 2250/00, one of the devices being a heat exchanger | |
Movable parts or members in exhaust systems for other than for control purposes | |
Devices using kinetic or wave energy for charging the engine in exhaust systems only | |
Use of exhaust turbines for charging engines, i.e. turbocharging | |
Engines with prolonged expansion in exhaust turbines | |
Profiting from waste heat of exhaust gases | |
Thermoelectric devices in general |
This place covers:
Exhaust or silencing apparatus combined or associated with devices converting the exhaust energy into kinetic energy, e.g. exhaust-driven turbines coupled to electrical generators.
This place covers:
Methods of electrically controlling exhaust gas treating apparatus and of exhaust devices not provided elsewhere.
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Control of selective catalytic reduction [SCR], e.g. by adjusting the dosing of reducing agent | |
Electric control of additional air supply |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
By-passing absorbents or adsorbents | |
Exhaust or silencing apparatus having means for rendering innocuous by thermal or catalytic conversion of noxious components of exhaust characterised by methods of operation or control thereof | |
By-passing catalytic reactors, e.g. to prevent overheating | |
Monitoring or diagnostic devices for exhaust-gas treatment apparatus | |
Electrical control of supply of combustible mixture or its constituents in relation with the state of the exhaust gas treating apparatus | |
Conjoint electrical control of two or more combustion engine functions |
Details of electrical control or of the monitoring of the exhaust gas treating apparatus may also receive classification in F01N 2900/00.
References F01N 11/00 and F02D 43/00 are non-limiting in the subgroup F01N 9/00. CPC will be updated/corrected once this inconsistency is resolved in IPC.
This place covers:
Devices like engine control units [ECUs] or sensors used to monitor or diagnose the function of exhaust-gas treatment apparatuses, e.g. for catalytic activity.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Safety, indicating or supervising devices for internal combustion engines | |
Electrical control of supply of combustible mixture or its constituents with safety or indicating devices for abnormal conditions | |
Testing of machine parts |
Classification may occur in both F01N 9/00 and F01N 11/00 when an apparatus or an exhaust gas property is monitored and the results are used to introduce complex changes in the electrical control routine of the exhaust apparatus or to the exhaust flow.
When classifying in the F01N 11/00 group, when appropriate, the codes F01N 2550/00 should be given, to classify the type of apparatus or device being diagnosed.
When classifying in group F01N 11/00, it is desirable to add the indexing codes of group F01N 2900/00, relating to details of electrical monitoring or diagnosing of the exhaust gas treating apparatus.
This place covers:
Joints and assembling details of exhaust parts inside a housing or between exhaust conduits. Selection of particular materials, thermal insulation details, special arrangement of the exhaust conduits or devices on the vehicle or engine. Exhaust manifolds. Exhaust details of engines adapted for particular uses, model applications, marine propulsion.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Handling exhaust gas in outboard drives | |
Sealings in general | |
Pipes; Joints or fittings for pipes; Supports for pipes, cables or protective tubing; Means for thermal insulation in general |
Further details of subgroups
Regarding F01N 13/001, passages inside the cylinder head should be classified in F02F 1/00 and not in this subclass.
Regarding F01N 13/008, the construction details of a sensor itself are in G01N. Sensor arrangements in the exhaust of combustion engines, e.g. for temperature, misfire, air/fuel ratio or oxygen sensors: F02B 77/086.
Regarding F01N 13/007, the intake silencers are in F02M 35/12 and silencing methods are to be classified also using F01N 1/00.
Regarding F01N 13/14, other thermal insulation: mats or gaskets between catalyst or filter and housing, F01N 3/2839 or F01N 3/0211; thermal or acoustic insulation of combustion engines: F02B 77/11; insulating elements, e.g. for sound or heat insulation, for vehicles B60R 13/08; for mounting around heat sources, e.g. exhaust pipes: B60R 13/0876; heat shields for motor vehicles: B62D 25/2072; thermal insulation in general: F16L 59/00; means for preventing radiation, e.g. with metal foil: F16L 59/08; arrangements for the insulation of pipes or pipe systems: F16L 59/14.
Regarding F01N 13/002, here are mostly uses not covered by the more detailed F01N 2590/00, with the exception of some portable devices, e.g. chainsaws.
Regarding F01N 13/004, this subgroup is used in parallel with F01N 13/12 (submerged exhausting). Treating exhaust by using liquids: F01N 3/04.
Regarding F01N 13/008, to describe the type of sensor use F01N 2560/00, and when fitting exhaust sensors use F01N 2450/10.
Regarding F01N 13/02 and F01N 13/04, these subgroups are for silencers only. Other apparatus, like filters, absorbents and catalysts, are in F01N 3/02 - F01N 3/04.
Regarding F01N 13/08, this subgroup covers pipe details, curvature, deformation, and special position of pipe in relation to a vehicle part, and further details should be also classified in F01N 2470/00.
Regarding F01N 13/082, this subgroup can be used also with the subgroup F01N 13/20. However, F01N 13/20 should be used only for the bell-shaped or flared outlet shape. The remaining should be classified in F01N 13/082.
Regarding F01N 13/12, see above reference to F01N 13/004.
Regarding F01N 13/16, more specific material should be classified in F01N 2530/00.
Regarding F01N 13/1805, this subgroup covers connections of exhaust manifolds, exhaust pipes or pipe sections outside of the housing of a silencer of purifier, in contrast with F01N 13/1838.
Regarding F01N 13/1838, here are the connections regarding the inside of the housing of a silencer or purifier. That is the connection between housing and tubes or tubes and baffles, in contrast with F01N 13/1805.
Regarding F01N 13/20, see above references to F01N 13/082.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Methods or apparatus for fitting, inserting or repairing different elements of gas-flow silencers or exhausts apparatus by bolts, screws, rivets or the like |
This place covers:
Arrangement of the exhaust system, e.g. of the exhaust pipe, exhaust manifold or exhaust apparatus, relative to the vehicle or parts thereof, e.g. relative to the vehicle frame or to the vehicle body.
This place covers:
Series-connected exhaust apparatuses, e.g. series-connected purifying devices or series-connected silencers, mounted in a side-by-side spatial arrangement, e.g. U- or S-shaped.
Illustrative examples of subject matter classified in this place:
1.

Figure 1 illustrates first and second substrates (2 and 4) mounted in a U-shaped, side-by-side spatial arrangement. The output of the first purification member of the U-shaped purification device is connected to the input of the second purification member.
2.

Figure 2 shows the second additional exhaust aftertreatment unit (70) arranged downstream the first exhaust aftertreatment unit (40). Both exhaust aftertreatment units (40 and 70) are mounted in a U-shaped, side-by-side spatial arrangement.
3.

Figure 3 shows series-connected particle filter (5) and SCR catalyst (3) mounted in an S-shaped, side-by-side spatial arrangement.
4.

Figure 4 shows series-connected particle filter (1A) and SCR catalyst (1C) mounted in an S-shaped, side-by-side spatial arrangement.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Exhaust or silencing apparatus having two or more separate purifying devices arranged in series | |
Exhaust or silencing apparatus having two or more separate silencers in series |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Connection being realised by using bolts, screws, rivets or the like between parts of exhaust or silencing apparatus, e.g. between housing and tubes, between tubes and baffles |