CPC Definition - Subclass C09J
This place covers:
- Adhesives and adhesive processes (but see below for adhesive processes), including adhesives characterised by their physical nature or by the effects produced.
- Adhesives based on polysaccharides or their derivatives, based on rubbers or their derivatives, based on natural or unspecified macromolecular compounds or their derivatives, or based on organic macromolecular compounds, obtained by (or obtained otherwise than by) reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds.
- Adhesives based on inorganic substances or on organic non-macromolecular compounds having at least one polymerisable carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bond.
- Adhesives in the form of films or foils, including releasable films.
- Heat seal adhesives and hot melts.
- Use of materials as adhesives, e.g. the use of known or new polymers or products.
- Other features of adhesives, e.g. additives for adhesives.
This subclass is residual in respect of adhesive processes. Please see the "References out of a residual place" section below, for details of other places for classifying some adhesive processes.
In cases where an adhesive contains an organic non-macromolecular compound as an additive but not as an essential ingredient, and such a compound is of interest, classification could be made in subclass C08K or as an additive in groups C08J 3/00 or C09J 11/02. This may be in addition to classification in groups C09J 123/00 - C09J 149/00.
Processes for applying liquids or other fluent materials to surfaces in general are classified in subclass B05D.
Organic dyes or closely-related compounds for producing dyes, mordants or lakes per se, are classified in subclass C09B.
Treatment of inorganic materials other than fibrous fillers used as pigments or fillers is classified in subclass C09C.
Natural resins, French polish, drying-oils, driers, turpentine, per se, are classified in subclass C09F.
Compositions of macromolecular compounds are classified in subclass C08L. Coating compositions or adhesive compositions are classified in subclasses C09D and C09J, respectively.
Subclasses C09D and C09J are seen as "related fields" of subclass C08L, so this structure has implications on search and classification.
For classification:
If the claims only pertain to an "adhesive composition...", then classification is only done in subclass C09J.
This place does not cover:
Preparation of glue or gelatine |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Electrically-conducting adhesives | |
Electrically conductive adhesives specially adapted for use in therapy or testing in vivo | |
Adhesive bandages, dressings or absorbent pads | |
Surgical adhesives | |
Joining of preformed parts; Apparatus therefor using adhesives | |
Layered products characterised by the relation between layers, i.e. products essentially comprising layers having different physical properties or products characterised by the interconnection of layers where at least one layer has inter-reactive properties | |
Layered products characterised by the relation between layers, i.e. products essentially comprising layers having different physical properties or products characterised by the use of interposed adhesives or interposed materials with adhesive properties | |
Cling foils | |
Bonding of a preformed macromolecular material to the same or other solid material such as metal, glass, leather, e.g. using adhesives | |
Using adhesives in the production of multi-layer textile fabrics | |
Adhesive labels, tag tickets or similar identification or indication means |
Examples of places in relation to which this place is residual:
Spraying apparatus; Atomising apparatus, e.g. devices for applying liquids or adhesives, to surfaces, including wood surfaces, which are to be joined together | |
Apparatus for applying fluent materials to surfaces, in general | |
Processes for applying liquids or other fluent materials, e.g. adhesives, to surfaces, in general | |
Accessory machines or apparatus for working wood or similar materials or tools therefor for applying adhesives or glue to surfaces of wood to be joined; Safety devices for woodworking machines or tools | |
Shaping or joining of plastics, e.g. bonding of non-plastics to plastics or bonding substances in a plastic state, in general | |
Labelling fabrics or comparable materials or articles with deformable surfaces using adhesives | |
Joining glass to other inorganic material; Joining glass to glass other than by fusing |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Containers, packaging elements or packages for web or tape-like material, e.g. dispenser for dispensing tape | |
Polishing compositions; Ski waxes | |
Soaps or detergent compositions | |
Connecting constructional elements or machine parts by sticking or pressing them together, e.g. cold pressure welding |
Classification guidance:
- In this subclass, adhesives containing specific organic macromolecular substances are classified only according to the macromolecular substance, non-macromolecular substances not being taken into account. Example: an adhesive containing polyethylene and amino-propyltrimethoxysilane is classified in group C09J 123/06.
- However, adhesives containing combinations of organic non-macromolecular compounds having at least one polymerisable carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bond with prepolymers or polymers other than unsaturated polymers of groups C09J 159/00 - C09J 187/00 are classified according to the unsaturated non-macromolecular component in group C09J 4/06. Example: an adhesive containing polyethylene and styrene monomer is classified in group C09J 4/06.
- Aspects relating to the physical nature of the adhesives or to the effects produced, as defined in group C09J 9/00, if clearly and explicitly stated, are also classified in this subclass.
- Unspecified adhesives (when the macromolecular constituent is not specified) characterised by additives are classified in group C09J 11/00.
- In this subclass, adhesives comprising two or more macromolecular constituents are classified according to the macromolecular constituent or constituents present in the highest proportion, i.e. the constituent on which the composition is based. If the composition is based on two or more constituents, present in equal proportions, the adhesive is classified according to each of these constituents. Example: an adhesive containing 80 parts of polyethylene and 20 parts of polyvinylchloride is classified in group C09J 123/06. An adhesive containing 40 parts of polyethylene and 40 parts of polyvinylchloride is classified in groups C09J 123/06 and C09J 127/06.
- In groups C09J 101/00 - C09J 201/00, any macromolecular constituent of an adhesive which is not identified by the classification according to Note (3) after the title of subclass C09J, and the use of which is determined to be novel and non-obvious, must also be classified in a group chosen from groups C09J 101/00 - C09J 201/00.
- In groups C09J 123/00 - C09J 149/00, in the absence of an indication to the contrary, a copolymer is classified according to the major monomeric component.
- In groups C09J 165/00 - C09J 185/00, in the absence of an indication to the contrary, adhesives based on macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions forming two different linkages in the main chain are classified only according to the linkage present in excess.
- When the adhesive is a specified organic polymer, classification is in groups C09J 101/00 - C09J 201/00. When the adhesive is a specified inorganic constituent, classification is in group C09D 1/00.
- Adhesive compositions containing specific organic macromolecular substances are classified according to the macromolecular substance.
- Adhesive compositions comprising specific macromolecular substances with other macromolecular substances and/or non-macromolecular substances are also classified under the form of C-Sets as explained below.
Allocation of indexing codes:
- Orthogonal indexing codes may be allocated in conjunction with combination-set symbols. In these situations, allocations of specific indexing codes are indicated with the related C-Sets in C-Sets classification.
Combination sets (C-Sets):
In this subclass, C-Sets classification is applied to the following groups, listed in the table below, if the document discloses a pertinent combination of technical features that cannot be covered by the allocation of a single symbol. The fourth column of the table indicates the place where the detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules can be found, in the section Special rules of classification.
C-SETS ID | BASE SYMBOLS | SUBSEQUENT SYMBOLS | C-SETS FORMULA; LOCATION OF C-SETS RULES |
#C9Ja | C08F 210/00 - C08F 246/00 (excluding breakdown indexing codes) | (C09J 4/00, C08F); an adhesive composition based on at least one monomer; see C09J 4/00 | |
#C9Jb | (C09J 4/06, C08F); an adhesive composition based on at least one monomer and at least one polymer; see C09J 4/06 | ||
#C9Jc | C08L 1/00 - C08L 101/16 (excluding breakdown indexing codes) | (C09J, C08L …); an adhesive composition of two or more polymers; see C09J 101/00 | |
#C9Jc(Si) | C09J 101/00 - C09J 201/10 (excluding C09J 183/02 - C09J 183/16) | (C09J, C08L 83/02 - C08L 83/16, C08L 83/00, ...); an adhesive composition comprising one non-Si-based polymer in majority and two or more Si-based polymers; see C09J 101/00 | |
#C9Jc(Si)2 | C08L 83/00 and optionally C08L 1/00 - C08L 101/16 (excluding C08L 83/02 - C08L 83/16 and excluding breakdown indexing codes) | (C09J 183/02 - C09J 183/16, C08L 83/00, …, C08L, ...); an adhesive composition comprising one Si-based polymer in majority and one or more Si-based polymers and optionally non-Si-based polymer(s); see C09J 183/00 | |
#C9Je | C08K 3/00 - C08K 13/08 (excluding breakdown indexing codes) | (C09J, C08K, ...); an adhesive composition of one polymer with additive(s); see C09J 101/00 | |
#C9Jf | C08L 1/00 - C08L 101/16 (excluding breakdown indexing codes), C08K 3/00 - C08K 13/08 (excluding breakdown indexing codes) | (C09J, C08L, …C08K, ...); an adhesive composition of two or more polymers with additive(s); see C09J 101/00 | |
#C9Jf(Si) | C09J 101/00 - C09J 201/10 (excluding C09J 183/02 - C09J 183/16) | C08L 83/02 - C08L 83/16, C08L 83/00, C08K 3/00 - C08K 13/08 (excluding breakdown indexing codes) | (C09J, C08L 83/02 - C08L 83/16, C08L 83/00, ..., C08K, ...); an adhesive composition comprising one non-Si-based polymer in majority and two or more Si-based polymers and additive(s); see C09J 101/00 |
#C9Jf(Si)2 | C08L 83/00 and optionally C08L 1/00 - C08L 101/16 (excluding C08L 83/02 - C08L 83/16) and excluding breakdown indexing codes), C08K 3/00 – C08K 13/08 (excluding breakdown indexing codes) | (C09J 183/02 - C09J 183/16, C08L 83/00, ..., C08L, ... C08K, ...); an adhesive composition comprising one Si-based polymer in majority with one or more Si-based polymers and optionally non-Si polymer(s) and additive(s); see C09J 183/00 | |
#C9J(z) | (C09J, C08L 2666/00 - C08L 2666/26); an adhesive composition of two or more polymers; see C09J 101/00 | ||
#C9Jg | C09J 2400/00 – C09J 2499/008 (exclusions apply, see C-Set rules) | C09J 2400/00 - C09J 2499/008 (exclusions apply, see C-Set rules) | (C09J 2400/00 - C09J 2499/008, C09J 2400/00 - C09J 2499/008, blends of material or resins used within the same layer of adhesives in the form of films or foils or in adhesive processes in general; see C09J 2400/00 |
#C9Jh | C09J 2400/00 - C09J 2499/008 (exclusions apply, see C-Set rules) | C09J 2400/00 - C09J 2499/008 (exclusions apply, see C-Set rules) | (C09J 2400/00 - C09J 2499/008, C09J 2400/00 - C09J 2499/008, …), C09J 2301/414 (co)polymers used within the same layer of adhesives in the form of films or foils or in adhesive processes in general; see C09J 2400/00 |
The specific C-Sets rule is located at only one place of the base symbol in the section Special rules of classification in the definition. If the C-Sets rule is applicable to all groups of a subclass, it is located at the subclass level only. If the same C-Sets rule is applicable to multiple groups or subgroups within the same subclass, the C-Sets rule is placed at the highest group or subgroup of the multiple groups.
In this subclass, all exemplified compositions should be classified as separate C-Sets. In the absence of examples, at least one C-Set is given on the basis of sufficient disclosure in the document.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
aliphatic radical | an acyclic or a non-aromatic carbocyclic carbon skeleton which is considered to be terminated by every bond: to an element other than carbon; a carbon atom having a double bond to one atom other than carbon; or an aromatic carbocyclic ring or a heterocyclic ring |
use of materials as adhesives | the use of known or new polymers or products as adhesives |
rubber | includes natural or conjugated diene rubbers or rubber in general (for a specific rubber, other than a natural rubber or a conjugated diene rubber), see the group provided for adhesives based on such macromolecular compounds) |
This place covers:
Adhesives based on inorganic constituents unless they are based on compositions of mortars, concrete, artificial stone or hydraulic cement.
This place does not cover:
Hydraulic cement | |
Compositions of mortars, concrete or artificial stone |
This place covers:
Coating compositions for adhesives based on non-macromolecular compounds that are able to be polymerized during the film formation step (in-situ polymerization) in the absence of a pre-formed polymer.
Any composition for adhesives comprising at least one polymerisable ethylenically unsaturated monomer or oligomer and able to be polymerized by means of the known methods leading, during the film formation, to macromolecular compounds of C08F 210/00 - C08F 246/00 or coating compositions based on non-macromolecular compounds that are able to react, during the film formation, to form macromolecular compounds of groups C08G 77/00 -C08G 77/62.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adhesives based on blends from polymers |
Classification guidance:
- In the case of adhesive compositions based on non-macromolecular compounds that are able to react, during the film formation, to form macromolecular compounds of groups C08G 77/00 - C08G 77/80 (e.g. by hydrolysis condensation of siloxane-type of monomers), C09J 4/00 is given together with a single symbol taken from groups C08G 77/00 - C08G 77/62 to indicate the nature of the polymer formed and a single symbol taken from groups C09J 183/02 - C09J 183/16 to indicate the nature of the adhesive composition which is assumed to be formed by the in situ polymerization of these monomers.
- An adhesive composition comprising phenyltriethoxysilane and aminopropyl trimethoxy silane in minority is classified in C09J 4/00 together with C08G 77/26 and in C09J 183/08.
Combination sets (C-Sets):
C-Sets statement: #C9Ja
- In group C09J 4/00, the adhesive compositions based on organic non-macromolecular compounds having at least one polymerizable carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bond are classified in the form of C-Sets.
- In #C9Ja, the base symbol, representing adhesive composition, is taken from the group C09J 4/00, whereas the subsequent symbol representing a representative monomer or a monomer in majority is taken from the groups C08F 210/00 - C08F 246/00.
- In addition, a separate C-Set representing the copolymer that is formed according to the monomers of C08F must be given.
C-Sets syntax rules:
- Each C-Set shall contain exactly two symbols.
- Duplicate symbols are not allowed in these C-Sets.
- Breakdown indexing codes are not allowed as either base or subsequent symbols.
- The order of symbols in these C-Sets is relevant as it reflects the adhesive composition and the monomer.
C-Sets examples:
- #C9Ja: An adhesive composition consisting of 2-ethylhexylacrylate is classified as (C09J 4/00, C08F 220/18)
- #C9Ja: An adhesive composition comprising butylacrylate in majority and ethylene glycol dimethacrylate in minority is classified as (C09J 4/00, C08F 220/18) and as (C08F 220/1804, C08F 222/102) for the resulting copolymer.
For searches using C-Sets:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
This place covers:
Coating compositions for adhesives based on non-macromolecular compounds that are able to be polymerized during the film formation step (in-situ polymerization) in the presence of a pre-formed polymer.
This includes any composition comprising at least one polymerisable ethylenically unsaturated monomer or oligomer that has at least another polymer and is able to be polymerized by means of the known methods leading to macromolecular compounds of C08F 251/00 - C08F 291/185.
C-Sets classification:
C-Sets statement: #C9Jb
- In group C09J 4/06, the adhesive compositions based on organic non-macromolecular compounds having at least one polymerizable carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds in combination with a macromolecular compound are classified in the form of C-Sets.
- In #C9Jb, the base symbol, representing adhesive composition, is taken from the group C09J 4/06, whereas the subsequent symbol representing the resulting graft copolymer in accordance with C08F is taken from the groups C08F 251/00 - C08F 291/185.
- A separate C-Set representing the graft copolymer that is formed according to the monomers of C08F must also be given.
C-Sets syntax rules:
- Each C-Set shall contain exactly two symbols.
- Duplicate symbols are not allowed in these C-Sets.
- Breakdown indexing codes are not allowed as either base or subsequent symbols.
- The order of symbols in these C-Sets is relevant as it reflects the adhesive composition and the grafted copolymer.
C-Sets examples:
- #C9Jb: An adhesive composition comprising methyl methacrylate and polybutylacrylate is classified as the C-Set (C09J 4/06, C08F 265/06) and (C08F 265/06, C08F 220/14) for the resulting grafted copolymer.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
This place covers:
Adhesive processes characterised by process features, e.g. heating; Pre-treatment of the surface to be joined, e.g. by use of a primer; Separate application of adhesive ingredients to the different surfaces to be joined.
Processes of joining materials by welding overlapping edges with an insertion of plastic material.
Processes of debonding substrates which were glued together beforehand.
- Glue sticks are classified in C09J 9/005.
- Processes in which the steps predominately modify the chemical nature of specifically defined substrates joined by an adhesive are generally classified in subgroups of C09J 5/02.
- Processes and articles in which macromolecular material substrates are heat bonded without the application of a separate adhesive are classified in C08J 5/121.
- Processes characterised by the chemical or physical nature of the adhesive, rather than the substrate(s), are generally classified in C09J 5/00 and its subgroups.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Processes for applying adhesives to surfaces | |
Removing scrap from containers, e.g. removing labels | |
Welding with interposition of material for facilitating bonding | |
Applying adhesives or glue to surfaces of wood to be joined | |
Methods or apparatus for laminating multiple layers | |
Hand-held desk devices for applying adhesives by contact to surfaces | |
Labelling machines and processes | |
Bonding of preformed macromolecular material to the same or other solid material |
Classification guidance:
Use of Indexing Codes:
C09J 2203/00 - C09J 2499/008 are indexing codes related to the use of materials in adhesive processes in general or adhesives in the form of films or foils used in conjunction with C09J 5/00 and C09J 7/00 groups.
C09J 2203/00-C09J 2499/008 are used as single symbols and C09J 2400/00 may also be used in C-Sets (in the case of blends or copolymers). C-Sets rules are explained in C09J 2400/00.
Use of indexing codes as single symbols:
- The nature of the polymer in the adhesive is indicated by the orthogonal indexing code C09J 2400/22 or by an orthogonal indexing code taken only in the head groups of the range C09J 2401/00 – C09J 2499/008. For example, for a (meth) acrylic adhesive is classified with the orthogonal indexing code C09J 2433/00.
- The nature of the polymer in the barrier layer is indicated by the orthogonal indexing code C09J 2400/221 or the orthogonal indexing code corresponding to the barrier layer taken in the range C09J 2401/00 – C09J 2499/008. For example, a barrier layer composition comprising a polyvinyl alcohol is classified with the orthogonal indexing code C09J 2429/00.
- The nature of the polymer in the primer coating is indicated by the orthogonal indexing code C09J 2400/223 or by the orthogonal indexing code corresponding to the primer coating taken in the range C09J 2400/00 – C09J 2499/008. For example, for a primer coating comprising an epoxy resin is classified with the orthogonal indexing code C09J 2463/003.
- The nature of the polymer in the release coating is indicated by the orthogonal indexing code C09J 2400/225 or by the orthogonal indexing code corresponding to the release coating taken in the range C09J 2400/00 – C09J 2499/008. For example, for a release coating comprising an epoxy resin is classified with the orthogonal indexing code C09J 2463/005.
- The nature of the substrate to be bonded is indicated by the appropriate orthogonal indexing code taken in the range C09J 2400/00 – C09J 2499/008. For example, a substrate made of a polyolefin is classified with the orthogonal indexing code C09J 2423/006.
- The nature of the pre-treated substrate to be bonded, irrelevant to what the pre-treatment might be, e.g. plasma or corona, is indicated by the appropriate orthogonal indexing code taken in the range C09J 2400/00 – C09J 2499/008. For example, a pre-treated polyolefin substrate is classified with the orthogonal indexing code C09J 2423/008.
- A process of debonding, is indicated by the orthogonal indexing code C09J 2301/502.
- Applications, chemical or physical properties or process features are indicated by the corresponding orthogonal indexing codes in the range C09J 2203/00 – C09J 2203/37 and C09J 2301/00 – C09J 2301/416.
This place covers:
Preparing the surfaces to promote bonding such as using a solvent.
The nature of the pre-treated substrate to be bonded, irrelevant to what the pre-treatment might be, e.g. plasma or corona, is indicated by an Indexing Code in the group C09J 2400/00 - C09J 2499/008. For example, a pre-treated polyolefin substrate is classified with the Indexing Code C09J 2423/008.
This place covers:
Adhesive tapes, films or sheets characterised by having an outer adhesive layer to be applied to a substrate. The outer adhesive layer might be covered by a release liner or a release sheet (see illustrative example).
Adhesives in the form of films or foils without carriers.
Adhesives in the form of films or foils on carriers, e.g. plastics, paper, textile fabrics, laminated material.
Carriers with adhesive in the form of films or foils.
Release liners of adhesives in the form of films or foils.
Release coatings on the carrier.
Primer between the carrier and the adhesive.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this place:
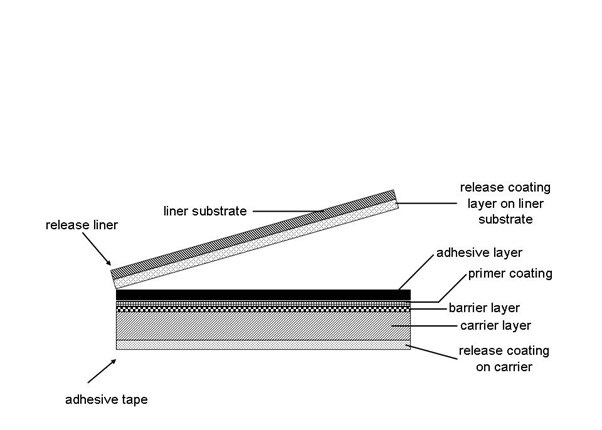
The illustrative example shows a carrier mounted adhesive film with a barrier layer, a primer coating, a release coating on the carrier layer and a release liner.
Relationship between C09J 7/00 and H10P 95/00:
Subgroups of C09J 7/00 are generally chemistry-oriented subgroups, whereas subgroups of H10P 95/00 are generally process related subgroups.
Relationship between C09J 7/00 and other groups of the subclass: Adhesives in the form of film or foils with or without a carrier layer and being specified by the macromolecular constituent are classified in C09J 101/00 - C09J 201/00.
For example, if a document discloses an adhesive tape having a carrier and being characterised by an acrylic adhesive layer (covered by C09J 7/385), this document should also be classified in one of the subgroups of C09J 133/00.
Layered structures in which the adhesive layer is between other layers that are not removable are classified in appropriate B32B areas. When the adhesive layer represents the outermost layer, which may be covered by only a removable release layer, it is classified as an adhesive tape in the appropriate subgroups of C09J 7/00.
See Table 1 below as an example.
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Hook and loop tape or fasteners | |
Bandages or dressings | |
Adhesive bandages or dressings | |
Auxiliary appliances for wound dressings | |
Adhesive bandages, dressing or adsorbent pad, e.g. plasters | |
Surgical adhesives or cements; Adhesives for colostomy devices | |
Laminates comprising at least two layers which are bonded permanently by means of an adhesive layer | |
Non-metallic flexible elongated elements for bundling or supporting articles, e.g., adhesive tapes | |
Labels fastened or secured by an adhesive layer | |
Sealing materials for batteries | |
Back sheet for solar cell panels | |
Adhesive tapes used in dicing/grinding of semiconductors and wafers | |
Wafer tapes | |
Adhesive tapes used for connecting semiconductor devices |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adhesives in the form of films or foils without a carrier and being specified by the macromolecular constituent | |
Masking elements for spraying apparatus | |
Attaching together paper or cardboard sheets, strips or webs by adhesive tape | |
Machines or apparatus for gluing labels or articles to be labelled | |
Attaching a replacement web to an expiring web in a machine, e.g. flying splice | |
Microstructured surfaces having tips, pillars, i.e. raised structures | |
Coated paper | |
Release paper | |
Signs, plates, panels or boards with readily detachable symbols attached with adhesive |
Use of Indexing Codes:
C09J 2203/00 and C09J 2400/00 are indexing schemes that are related to the use of materials in adhesive processes in general or adhesives in the form of films or foils and are used as single symbols or in C-Sets (in the case of blends or copolymers) in conjunction with groups C09J 5/00 and C09J 7/00.
C-Sets rules are explained in C09J 2400/00.
Use of indexing codes as single symbols:
- The nature of the polymer in the adhesive is indicated by the orthogonal indexing code C09J 2400/22 or by an orthogonal indexing code taken only in the head groups of the range C09J 2401/00 – C 09J 2499/008. For example, a (meth) acrylic adhesive is classified with the orthogonal indexing code C09J 2433/00.
- The nature of the polymer in the barrier layer is indicated by the orthogonal indexing code C09J 2400/221 or the orthogonal indexing code corresponding to the barrier layer taken in the range C09J 2401/00 – C 09J 2499/008. For example, a barrier layer composition comprising a polyvinyl alcohol is classified with the orthogonal indexing code C09J 2429/00.
- The nature of the polymer in the primer coating is indicated by the orthogonal indexing code C09J 2400/223 or by the orthogonal indexing code corresponding to the primer coating taken in the range C09J 2400/00 – C09J 2499/008. For example, a primer coating comprising an epoxy resin is classified with the orthogonal indexing code C09J 2463/003.
- The nature of the polymer in the release coating is indicated by the orthogonal indexing code C09J 2400/225 or by the orthogonal indexing code corresponding to the release coating taken in the range C09J 2400/00 –C09J 2499/008. For example, a release coating comprising an epoxy resin is classified with the orthogonal indexing code C09J 2463/005.
- The nature of the substrate to be bonded is indicated by the appropriate orthogonal indexing code taken in the range C09J 2400/00 – C09J 2499/008. For example, a substrate made of a polyolefin is classified with the orthogonal indexing code C09J 2423/006.
- The nature of the pre-treated substrate to be bonded, irrelevant to what the pre-treatment might be, e.g. plasma or corona, is indicated by the appropriate orthogonal indexing code taken in the range C09J 2400/00 – C09J 2499/008. For example, a pre-treated polyolefin substrate is classified with the orthogonal indexing code C09J 2423/008.
- A process of debonding is indicated by the orthogonal indexing code C09J 2301/502.
- Applications, chemical or physical properties or process features are indicated by the corresponding orthogonal indexing codes in the range C09J 2203/00 – C09J 2203/37 and C09J 2301/00 – C09J 2301/416.
- For example, the use of an adhesive tape for bundling cables should be indicated by the orthogonal indexing code C09J 2203/302. The presence of an adhesive layer being formed by alternating adhesive areas being chemically different is indicated by the orthogonal indexing code C09J 2301/21.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this place:
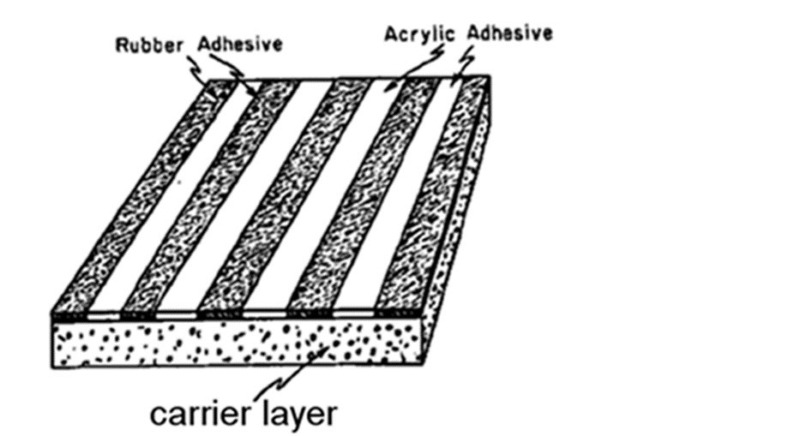
- In contrast, the presence of different adhesive layers opposing each other is indicated by the orthogonal indexing code C09J 2301/1242.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this place:

- In case the adhesive layer is interrupted by non-adhesive protrusions extending from the surface of the carrier layer, the orthogonal indexing code C09J 2301/206 is given.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this place:

- In case the adhesive coating is discontinuous, the orthogonal indexing code C09J 2301/204 is given.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this place:
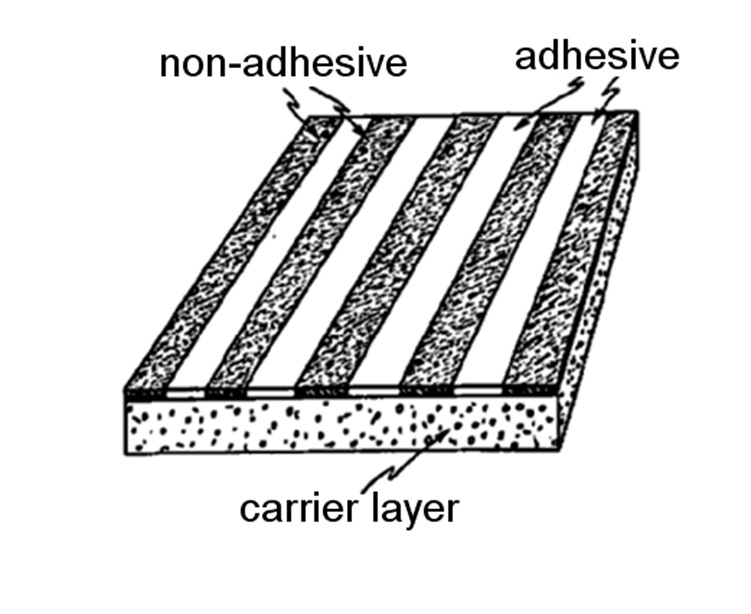
- The presence of an additive in the adhesive or substrate layer is indicated by the corresponding orthogonal indexing codes in the range C09J 2301/408 – C09J 2301/41.
- The nature of the non-macromolecular additive is subsequently indicated by a symbol from C08K 3/00 – C08K 13/08, as additional information. For example, the adhesive layer of an adhesive tape comprising an inorganic flame proofing agent is classified in C09J 2301/408, which is the indexing code that indicates the presence of an additive in the adhesive layer, as well as in C08K 3/016 (ADD), as the inorganic flame proofing agent is considered an essential feature of the adhesive layer.
Further details of subgroups
The subgroups of C09J 7/40 cover release liners used to cover the adhesive surface of an adhesive tape as illustrated in the definition statement. Release coating layers being part of the adhesive tape (cf. the illustrative example in the definition statement) itself are classified in C09J 7/203, C09J 7/22 and C09J 7/203, C09J 7/21.
This subgroup is given where the release coating composition is applied to the carrier layer (cf. illustrative example in the definition statement).
Classification in this subgroup concerns carrier constituted by a metal sheet only.
Classification in this subgroup concerns adhesive tapes having a carrier constituted by a laminate. The presence of a foam, metal, paper, textile or other material layer in the laminate is indicated by the corresponding orthogonal indexing code of C09J 2400/123 – C09J 2499/006. The presence of only resin layers in the laminate is indicated by the orthogonal indexing code C09J 2301/162.
In general, the nature of the resin in the laminate support layer is indicated by the corresponding orthogonal indexing codes of C09J 2401/00 – C09J 2499/006. For example, for a laminate carrier comprising a layer made of a polyolefin, the Indexing Code C09J 2423/006 should be given.
Metallised films or foils are classified in C09J 7/22 or C09J 7/29 depending on the relationship between the metal layer and the adhesive. See Table 2 below.
Table 2: Difference between a metallised film or foil (C09J 7/22) and a laminate carrier layer having one metal layer (C09J 7/29)
Carrier layer is constituted by metallised plastic sheet C09J 7/22 bearing a thin metal layer. |
|
Carrier layer is constituted by a laminated material C09J 7/29 wherein eventually one layer is a metal layer C09J 2400/163. |
|
Adhesive tape with a laminate carrier that has a textile fabric or paper layer is NOT classified in the subgroups of C09J 7/21.
The presence of a barrier layer, a release coating layer, or a primer layer does not constitute a laminate carrier layer. These layers are considered forming part of the carrier layer (cf. the illustrative example in the definition statement). In contrast, a carrier layer being coated with an ink receptive layer is considered as a laminate support layer.
Subgroups of C09J 7/21 are given to adhesive tapes having a carrier made of paper or textile fabrics. In order to indicate whether a paper or a textile fabrics carrier layer is present, the corresponding orthogonal indexing code of C09J 2400/283 and C09J 2400/263, respectively, is given.
Laminate carrier layers comprising a layer made of paper of textile fabrics are NOT classified in the subgroups of C09J 7/21, instead laminated carriers are classified in the subgroup of C09J 7/29.
This subgroup is given where the release adhesive composition is applied to the paper or textile fabrics carrier layer. (cf. the illustrative example in the definition statement).
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
adhesive film | a free-standing film or sheet of adhesive (adhesive without carrier) or coating of adhesive on a film or sheet rather than a larger substrate. For example, the adhesive as a film on a tape rather than a generic substrate disclosed as generally a non-tape or sheet entity. |
metal foil | a free-standing thin metal substrate as the only adhesive carrying component on which the adhesive is applied. |
pressure-sensitive adhesive | pressure-sensitive adhesive (PSA, self-adhesive, self-stick adhesive) is adhesive which forms a bond when pressure is applied to adhere the adhesive with the adherend. No solvent, water or heat is needed to activate the adhesive. |
metallised plastic | metallised plastics are plastics coated with a thin layer of metal, usually aluminium. Metallisation is generally performed using physical vapour deposition, plating or thermal/cold spraying processes. This coating is much thinner than a metal foil could be made, in the range of 0.5 micrometres. |
heat-activated adhesives | heat-activated adhesives are designed to bond parts or components through the use of heat (over 30oC). |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
AA | Acrylic acid |
MAA | Methacrylic acid |
PSA | Pressure-sensitive adhesive |
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms:
- "carrier", "support", "substrate", "facestock" or "backing"
- "adhesive", "glue", "fixative", "bonding agent" or "sealant"
This place covers:
Adhesives that are specified (when the macromolecular constituent is known) and where the emphasis is on the physical nature or the effect produced.
In this place, the physical nature or effect produced refers to non-mechanical, physical nature and/or effects such as optical, electrical or thermal conductivity of the adhesive rather than mechanical properties such as tensile strength, moduli or peel strength.
Adhesives characterised by their mechanical properties are classified according to the specific adhesive or the unspecified adhesive as discussed throughout the C09J definition statement. In other words, the adhesive would be classified as if the mechanical properties were not present.
Classification in C09J 9/00 shall only be done when the adhesive is specified and when the effect due to the presence of an additive cannot appropriately be classified in C08K. The additive responsible for the physical nature or effect produced when the adhesive is specified is classified according to the adhesive and the appropriate C08K symbol for the additive.
Example:
Electrically conductive adhesive comprising a polyurethane adhesive and metallic particles is classified in C09J 9/02 (when the focus of the invention is on the effect obtained), C09J 175/04 (polyurethane) and C08K 3/08 (ADD) (for the additive itself), since C08K 3/08 classifies the metallic particle and not its effect.
Adhesives characterised by their physical nature or effect produced when the adhesive itself is unspecified and the additive is known are classified in C09J 11/00 according to the additive responsible for the physical nature or effect produced.
Example:
Adhesive comprising an unspecified polymer and metallic particles is classified in C09J 11/04 (for the presence of the additive) and in C08K 3/08 (ADD) (for the additive itself).
This place does not cover:
Adhesives in the form of films or foils |
This place covers:
Additives in adhesive formulations where the adhesive itself is unspecified and the additive is known.
Additives in adhesive formulations where the adhesive itself is specified are classified in the appropriate group in C09J 101/00 – C09J 201/10 and in C08K in the form of a C-Set. See C09J definitions.
This place covers:
Adhesives based on cellulose, modified cellulose or cellulose derivatives corresponding to the following groups:
Covalently or ionically crosslinked gels are classified in C08B.
A composition based on cellulose, modified cellulose or cellulose derivatives is classified in C08L.
Coating compositions based on cellulose, modified cellulose or cellulose derivatives are classified in C09D.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Cellulose or derivatives thereof per se | |
Composition comprising cellulose or cellulose derivative | |
Composition based on lignin-containing materials, e.g. lignin, cork, lignocellulose or wood | |
Composition of natural macromolecular compounds or of derivatives thereof not provided for in C08L 89/00 - C08L 97/00, e.g. flours | |
Coating composition comprising cellulose or cellulose derivative |
Last place priority rule:
Within each group of this subclass, in the absence of an indication to the contrary, classification is made in the last appropriate place.
Classification guidance:
- The subject matter disclosed in both the claims and the examples of a patent document is to be classified.
- Adhesive compositions of cellulose or derivatives thereof in solution, together with other macromolecular compounds, or together with an inorganic or non-macromolecular organic additive are considered as an adhesive composition and are thus classified according to the rules of C09J.
C-sets classification:
C-Sets statement: #C9Jc, #C9Je, and #C9Jf
- In groups C09J 101/00 - C09J 201/10 adhesive composition based on polymers, and when present non-macromolecular additive(s), are classified in the form of C-Sets according to the relative proportions by weight percentage of the macromolecular constituents.
- In #C9Jc, the base symbol, representing the polymer in majority, is taken from the groups C09J 101/00 - C09J 201/10, whereas the subsequent symbol(s) representing the polymer(s) in minority is (are) taken from the groups C08L 1/00 - C08L 101/16.
- In #C9Je, the base symbol, representing the polymer, is taken from the groups C09J 101/00 - C09J 201/10, whereas the subsequent symbol(s) representing compound(s) used as an additive(s), is (are) taken from the groups C08K 3/00 - C08K 13/08.
- In #C9Jf, the base symbol, representing the polymer in majority, is taken from the groups C09J 101/00 - C09J 201/10, whereas the subsequent symbol(s) representing the polymer(s) in minority is (are) taken from the groups C08L 1/00 - C08L 101/16 and further subsequent symbols representing compound(s) used as an additive(s), is (are) taken from the groups C08K 3/00 - C08K 13/08.
- In addition, a single symbol is given according to the macromolecular constituent present in the highest proportion.
- If all the constituents are present in equal proportions, the composition is classified according to each of these constituents.
- In the case that several polymers are in the majority, separate C-Sets should be made based on each polymer in the majority and its component(s) in the minority.
- Attention is drawn to adhesive compositions comprising, next to a major macromolecular compound according to C09J 101/00 - C09J 201/00 (excluding C09J 183/02 - C09J 183/16), two or more Si-based macromolecular compounds in accordance with C08G 77/00 which are classified according to #C9Jc(Si) or C9Jf(Si) as explained below.
- Orthogonal indexing codes C09J 2203/00 - C09J 2499/008 must also be allocated as separate symbols when applicable.
C-Sets syntax rules:
- C-Set of #C9Jc and #C9Je shall contain at least two symbols.
- C-Set of #C9Jf shall contain at least three symbols.
- Duplicate subsequent symbols are allowed in these C-Sets for the subsequent symbols only.
- Breakdown indexing codes are not allowed as either base or subsequent symbols.
- For #C9Jf the symbols for the additives always appear after the symbols for the polymers regardless their relative amounts.
C-Sets examples:
- #C9Jc: An adhesive composition comprising poly-2-ethylhexyl acrylate (C09J 133/08) and polyvinyl chloride (C08L 27/06) is classified as (C09J 133/08, C08L 27/06).
- #C9Jc: An adhesive composition consisting of 60 wt.% of microcrystalline cellulose (C09J 101/04) and 40 wt.% of maltodextrin (C08L 3/02) is classified as (C09J 101/04, C08L 3/02).
- #C9Je: An adhesive composition comprising poly-2-ethylhexyl acrylate in majority and a triaryl phosphate fire retardant (C08K 5/523) is classified as (C09J 133/08, C08K 5/523).
- #C9Je: An adhesive composition consisting of carboxymethyl cellulose and glycerol (plasticiser) is classified as (C09J 101/286, C08K 5/053) and in C08K 5/0016.
- #C9Jf: An adhesive composition comprising poly-2-ethylhexyl acrylate in majority, polyvinyl chloride and a triaryl phosphate fire retardant (C08K 5/523) is classified as: C09J 133/08, C08L 27/06, C08K 5/523.
C-Sets statement: #C9Jc(Si), #C9Jf(Si)
- #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si) are a special use of #C9Jc and #C9Jf and are applied for an adhesive composition comprising two or more Si-based polymers in accordance with C08G 77/00.
- In #C9Jc(Si), the base symbol, representing the polymer in majority, is taken from the groups C09J 101/00 - C09J 201/10 (excluding C09J 183/02 - C09J 183/16), whereas the subsequent symbols representing the polymers in minority are taken from the groups C08L 83/02 - C08L 83/16 for the Si-based polymer in majority, and in C08L 83/00 for the Si-based polymer in minority.
- In #C9Jf(Si), the base symbol, representing the polymer in majority, is taken from the groups C09J 101/00 - C09J 201/10 (excluding C09J 183/02 - C09J 183/16), whereas the subsequent symbols representing the polymers in minority are taken from the groups C08L 83/02 - C08L 83/16 (for the Si-based polymer in majority), and in C08L 83/00 (for the Si-based polymer in minority) and further subsequent symbols representing compound(s) used as an additive(s), is (are) taken from the groups C08K 3/00 - C08K 13/08.
- The classification is further described by adding, as one or more additional codes, one or more symbols selected from the range C08G 77/02 - C08G 77/62 corresponding to each of the silicon-based macromolecular compound components detailed in the C-Set.
- In all cases, a single symbol is also given according to the macromolecular constituent present in the highest proportion.
C-Sets syntax rules:
- C-Set of #C9Jc(Si) shall contain at least three symbols.
- C-Set of #C9Jf(Si) shall contain at least four or more symbols.
- Duplicate subsequent symbols are allowed in these C-Sets for subsequent symbols, only one symbol selected from the range C08L 83/02 - C08L 83/16 is permitted per C-Set.
- Breakdown indexing codes are not allowed as either base or subsequent symbols.
- The order of symbols in these C-Sets is relevant as it reflects the relative amounts of each polymer; C09J always appears as the base symbol.
- The order of C08K symbols of additives is not relevant if there is more than one additive in the composition
- For #C9Jf(Si), the symbols for the additive(s) always appear(s) after the symbols for the polymers of regardless their relative amounts.
C-Sets examples:
- #C9Jc(Si): An adhesive composition comprising, in descending amounts by weight, a polyester in accordance with C08G 63/02 (C09J 167/02), an amine-substituted polysiloxane in accordance with C08G 77/26 and an epoxy-substituted polysiloxane in accordance with C08G 77/14 is classified as (C09J 167/02, C08L 83/08, C08L 83/00) and in C08G 77/14 (ADD) and C08G 77/26 (ADD).
- #C9Jf(Si): An adhesive composition comprising, in descending amounts by weight, a polyester in accordance with C08G 63/02 (C09J 167/02), an amine-substituted polysiloxane in accordance with C08G 77/26 and an epoxy-substituted polysiloxane in accordance with C08G 77/14 and carbon black is classified as (C09J 167/02, C08L 83/08, C08L 83/00, C08K 3/04) and C08G 77/14 (ADD) and C08G 77/26 (ADD).
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses, e.g. C08L and C09D.
In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
Search rules #C9Jz:
- To search an adhesive composition of 2 polymers, build search queries as follows:
(C09J of the polymer in majority, C08L 2666/00 - C08L 2666/26).
The subsequent symbol is selected from the most appropriate subgroup of C08L 2666/02 - C08L 2666/26 (last place rule).
The search statement can also be further refined by searching the polymer in minority by using its C08L as ADD for documents classified between 2003 and April 2012.
Example 1: An adhesive composition based on a 60 parts of a polyamide (C09J 177/00) and 40 parts of a graft polymer
Search queries: (C09J 177/00, C08L 2666/24).
Example 2: An adhesive composition based on a polysiloxane (C09J 183/04) and containing a second polysiloxane, a phenol and silica
Search queries: (C09J 183/04, C08L 83/00, C08K 5/13, C08K 3/36) and optionally C08L 2205/02.
#C9Jz search rules do not apply when polysiloxane is in majority and when there is a second polysiloxane; C08L 83/00 is used as subsequent symbol(s) in that case.
- To search for a composition of 3 or more polymers, build search queries as follows:
(C09J of the polymer in majority, C08L 2666/00 - C08L 2666/26) and C08L 2205/03 (ADD)
The search statement can also be further refined by searching the polymers in minority by using their C08L as ADD for documents classified between 2003 and April 2012.
In the case of a composition of three or more polymers, the subsequent symbol is taken from the common C08L 2666/00 - C08L 2666/26 group that covers all minority polymers.
This place covers:
Adhesives compositions of starch, amylose or amylopectin or of their derivatives or degradation products corresponding to the following groups:
A composition based on starch or derivatives thereof is classified in C08L.
Covalently or ionically crosslinked gels are classified in C08B.
Coating compositions based on such starches are classified in C09D.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Starch and derivatives thereof per se | |
Composition comprising cellulose or cellulose derivative starch, amylose, amylopectin or their derivatives or degradation products | |
Composition of natural macromolecular compounds or of derivatives thereof not provided for in groups C08L 89/00 - C08L 97/00, e.g. flours | |
Coating composition comprising starch, amylose, amylopectin or their derivatives or degradation products |
Last place priority rule:
Within each group of this subclass, in the absence of an indication to the contrary, classification is made in the last appropriate place.
Classification guidance:
- The subject-matter disclosed in both the claims and the examples of a patent document is to be classified.
- Adhesive composition of starch or derivatives thereof in solution, together with other macromolecular compounds, or together with an inorganic or non-macromolecular organic additive are considered as an adhesive composition and are thus classified according to the rules of C09J.
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
- The adhesive compositions of this group are classified in the form of C-Sets according to the relative proportions by weight percentage of the macromolecular constituents.
- In addition, a single symbol is given according to the macromolecular constituent present in the highest proportion.
- If all the constituents are present in equal proportions, the composition is classified according to each of these constituents.
Example 1: Adhesive composition of starch acetate in solution is classified in C09J 103/06.
Example 2: An adhesive composition consisting of 60 wt. % of crosslinked starch and 40 wt.% of maltodextrin is classified in (C09J 103/04, C08L 3/02) and C08L 2205/02.
Example 3: An adhesive composition consisting of carboxymethyl starch and glycerol (plasticiser) is classified in (C09J 103/08, C08K 5/053) and C08K 5/0016.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
This place covers:
Adhesives based on polysaccharides, other than cellulose and starch, or on derivatives thereof corresponding to the following groups:
Covalently or ionically crosslinked gels are classified in C08B.
A composition based on such polysaccharides or derivatives thereof is classified in C08L.
Coating compositions based on such polysaccharides are classified in C09D.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Polysaccharides per se | |
Polysaccharides per se | |
Composition comprising polysaccharide or polysaccharide derivative | |
Coating composition comprising polysaccharide or polysaccharide derivative |
Last place priority rule:
Within each group of this subclass, in the absence of an indication to the contrary, classification is made in the last appropriate place.
Classification guidance:
- The subject-matter, disclosed in both the claims and the examples of a patent document, is to be classified.
- Adhesive compositions of polysaccharides or derivatives thereof in solution, or together with other macromolecular compounds, or together with an inorganic or non-macromolecular organic additive are considered as a composition and are thus classified according to the rules of C09J.
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
- The adhesive compositions of this group are classified in the form of C-Sets (i.e. #C9J(c)) according to the relative proportions by weight percentage of the macromolecular constituents.
- In addition, a single symbol is given according to the macromolecular constituent present in the highest proportion.
- If all the constituents are present in equal proportions, the composition is classified according to each of these constituents.
Example 1: Adhesive composition of ethers of cyclodextrin in solution is classified in C09J 105/16.
Example 2: An adhesive composition consisting of 60 wt.% of hyaluronic acid and 40 wt.% of maltodextrin is classified as (C09J 105/08, C08L 3/02).
Example 3: An adhesive composition consisting of carboxymethyl dextran and glycerol (plasticiser) is classified as (C09J 105/02, C08K 5/053) and (C09D 105/02, C08K 5/0016).
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions of natural rubbers or latex.
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
This place covers:
- Adhesive compositions of copolymers with acrylonitrile or latex
- Adhesive compositions of copolymers with styrene or latex
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions of homopolymers or copolymers of chloroprene or latex.
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions of rubbers containing carboxyl groups containing monomers in minority, e.g. acrylic acid or acrylic acid esters.
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions based on rubber derivates, meaning a rubber treated according to C08C.
See C09J 107/00.
This place does not cover:
Adhesives based on copolymers of chloroprene | |
Adhesives based on rubbers containing carboxyl groups |
An additional symbol from C08C may be given for the treatment.
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions based on reclaimed rubber meaning the reuse of unvulcanised or devulcanised rubber.
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
This place covers:
- Adhesives based on natural or synthetic elastic material not classifiable in groups C09J 107/00 - C09J 117/00
- Adhesive compositions comprising vulcanised or crosslinked rubber which are classified in C09J 119/003
- Adhesive compositions containing rubbers with functional groups, e.g. telechelic diene rubbers which are classified in C09J 119/006.
- Compositions comprising diene rubbers or their derivatives are classified in C08L 7/00 - C08L 21/00
- Coating compositions comprising diene rubbers or their derivatives are classified in C09D 107/00 - C09D 121/00
- Treatment or chemical modification of diene rubber is classified in C08C 1/00 - C08C 19/44.
- Recycling of polymers is classified in C08J 11/04 - C08J 11/28
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adhesive compositions of copolymers of etheylne-propylene or ethylene-propylene-diene, e.g. EPM or EPDM rubber | |
Adhesive compositions of copolymers of isobutene with minor part of conjugated dienes monomers, e.g. butyl rubber | |
Adhesive compositions of polyacrylates | |
Adhesive compositions of unconjugated dienes | |
Adhesive compositions of graft copolymers | |
Adhesive compositions of block copolymers | |
Adhesive compositions of ABS | |
Chemical compositions of tyres | |
Preparation of rubber compounds | |
Recycling of polymers | |
Inorganic or non-macromolecular organic materials as compounding agents | |
Compositions of diene rubbers or their derivatives in minority |
Last place priority rule:
Within each group of this subclass, in the absence of an indication to the contrary, classification is made in the last appropriate place.
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Rubber | a. natural or conjugated diene rubbers b. rubber in general (for a specific rubber, other than a natural rubber or a conjugated diene rubber, see the group provided for compositions of such macromolecular compounds) |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
ABS | Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene |
BR | Butadiene rubber |
CR | Chloroprene rubber |
EPDM | Ethene propene diene rubber |
EPM | Ethene propene rubber |
IIR | Butyl rubber |
IR | Isoprene rubber |
NBR | Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber |
NR | Natural rubber |
SAN | Styrene acrylonitrile copolymer |
SBR | Styrene butadiene rubber |
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions based on unspecified rubbers.
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
This place covers:
Adhesives based on homopolymers or copolymers of unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond; Adhesives based on derivatives of such polymers. Adhesive compositions based on modified polymers are classified as such in C08F 8/00 subgroups.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Organic labelling fabrics, comparable materials or articles with deformable surface using adhesives | |
Organic labelling fabrics or comparable materials or articles with deformable surface using thermo-activatable adhesives | |
Applications or uses of polymer compositions in films | |
Working-up, compounding, after-treatment of macromolecular compounds | |
Use of Inorganic of non-macromolecular organic substances as compounding ingredients | |
Materials for sealing or packing joints or covers | |
Materials for stopping leaks | |
Organic labelling fabrics or comparable materials or articles with deformable production of multi-layer textile fabrics | |
Adhesive labels, tag tickets or similar identification of indication means | |
Encapsulation of solar cells |
Last place priority rule:
Within each group of this subclass, in the absence of an indication to the contrary, classification is made in the last appropriate place.
Classification guidance:
- Documents are preferably classified according to the examples in the documents, not according to general claims, e.g. if the examples only describe adhesives based on polyethylene, but if subject matter of the claim is an adhesive of polyolefin, the document is classified under adhesives of polyethylene (C09J 123/06).
- In C09J, adhesives which have only one polymeric component are also classified, e.g. C09J 123/0815 represents an adhesive of only one ethylene vinylacetate polymer.
- Single polymers and their preparation are to be classified in C08F 210/00 on the basis of sufficient disclosure in the document.
Choice of symbol for copolymer:
- A composition of copolymers gets the symbol of the major component, except if there is a lower class which specifies the comonomer in minority (see also last place rule), e.g. ethylene butylene copolymers (ethene comonomer in majority) would be classified in C09J 123/0815, and not in C09J 123/20, but ethylene butylene copolymers (butene in majority) would be classified in C09J 123/20, not in C09J 123/0815.
- In addition, a separate C-Set representing the copolymer that is formed according to the monomers of C08F must also be given.
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of classification section in C09J 101/00.
- If C09J 123/00 relates to a composition and two or more polymers are present, classification is given in the form of C-Sets (i.e. #C9J(c)) according to the relative weight percentage of the polymer constituents.
- The polymer in majority is given a symbol as a base symbol, and the polymers in minority are given symbols as subsequent symbols in the form of C-Sets.
- If all the constituents are present in equal weight percentage, the composition is classified according to each of these constituents.
- In the case that several polymers can be in majority, separate C-Sets should be made based on each polymer in majority and its component(s) in minority.
- Orthogonal indexing codes C08L 2201/00 - C08L 2555/86 are also given if applicable.
Example 1: An adhesive of a blend of 60 parts polyethylene (C09J 123/06) and 40 parts polyamide (C09J 177/00) is classified as (C09J 123/06, C08L 77/00).
Example 2: An adhesive of a blend of 50 parts polyethylene (C09J 123/06) and 50 parts polyamide (C09J 177/00) is classified as (C09J 123/06, C08L 77/00) and (C09J 177/00, C08L 23/06).
Example 3: An adhesive based on a composition of polyethylene and containing CaCO3 is classified as (C09J 123/06, C08K 3/26). If this composition also contains a polyamide, then the classification will be (C09J 123/06, C08L 77/00, C08K 3/26).
Example 4: An adhesive based on a composition based on a first polyethylene (C09J 123/06) and containing a second polyethylene, a phenol and silica is classified as (C09J 123/06, C08L 23/06, C08K 5/13, C08K 3/36) and in C08L 2205/02.
Example 5: An adhesive based on a composition containing a polyamide in majority, a polyester and a polyethylene is classified as (C09J 177/00, C08L 67/00, C08L 23/06) and C08L 2205/03.
Example 6: Adhesives of compositions containing two polymers of the same subgroup, for example compositions of two ethylene vinylacetate copolymers, are characterised by the orthogonal indexing code C08L 2205/025. The complete classification for such a composition therefore would be (C09J 123/0853, C08L 23/0853) and C08L 2205/025. The same applies for compositions of two polymers only distinguished by physical properties, e.g. molecular weight or density.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Addition polymers | Polymers in which unsaturated monomer molecules join together to form a polymer in which the molecular formula of the repeat unit is identical (except for the double bond) with that of the monomer. |
Aliphatic cyclic olefins | A carbocyclic monomer with an endocyclic double bond. |
Block polymers | Polymers formed by polymerization of monomers on to a macromolecule having groups capable of inducing the formation of new polymer chains bound at one or both ends of the starting macromolecule, or by polymerization using successively different catalyst types or successively different monomer systems without deactivating the intermediate polymer. |
Condensation polymers | Polymers in which water or some other simple molecule is eliminated from 2 or more monomer molecules as they combine to form the polymer or crosslinks between polymer chains. |
Copolymer | Usually denotes a polymer of 2 chemically distinct monomers, and sometimes denotes a terpolymer containing more than 2 types of monomer unit. |
EPR or EPDM, elastomeric ethylene propylene (diene) copolymers | Elastomeric copolymer rubbers defined by similar amounts of ethylene and propene, e.g. 30-70wt% ethylene and 70-30wt% propene. |
Graft polymers | Macromolecular compounds obtained by polymerizing monomers on to preformed polymers or on to inorganic materials. Such preformed polymers could be rubbers, polysaccharides, condensation polymers, homopolymers or copolymers of the addition polymer type. |
Homopolymers | Polymers resulting from the polymerisation of a single monomer or polymer with a single type of repeating unit. |
Ionomer | Polymers containing monomers carrying ionic groups, usually salts of carboxylic acids. |
Iso-olefin | Non-linear olefinic monomers, e.g. isobutylene, isopentene. |
Modified by chemical after treatment | Modification of the polymer after polymerisation, with the exception that (a) neutralisation of carboxylic acid containing copolymers to form epoxide containing esters (C08L 23/0884) and (b) saponified copolymers, e.g. ethylene vinyl alcohol [EVA] copolymers (C08L 23/0861) are not regarded as after treatments in the sense of C08L 23/00 |
Repeat(ing) unit | The unit in an addition polymer which is repeated throughout the molecule; for example in polyethylene the repeat unit is:–CH2-CH2-. |
Rubber | a. Natural or conjugated diene rubbers; b. Rubber in general. |
Saponified vinylacetate | Ethylene copolymers with vinyl alcohol. |
In patent documents the following abbreviations are often used:
Attention is drawn to the table at the beginning of C09J.
This group should only be used in cases without examples.
This group should only be used in cases without examples.
This group should only be used if there are examples both of polymers of C09J 123/06 or C09J 123/0807 and C09J 123/0846.
Classification in this place can be further characterised by the indexing codes C08L 2207/062, C08L 2207/066, C08L 2207/068, C08L 2207/07 or C08L 2314/02 - C08L 2314/08.
This group should only be used if there are examples both of polymers of C09J 123/0807 and C09J 123/0846.
C09J 123/16 takes precedence over this group.
This group can be further characterised by Indexing Codes C08L 2207/062-C08L 2207/07 or C08L 2314/02-C08L 2314/08.
It is preferable to classify in C09J 123/0815.
The polymers in this group can be further characterised by Indexing Codes C08L 2207/062-C08L 2207/07 or C08L 2314/02-C08L 2314/08.
When ethylene is in majority, ethylene-propene copolymers are only classified when propene is clearly the minor component, e.g. LLDPE with the comonomer propene is classified in C09J 123/0815, whereas EPR is classified in C09J 123/16.
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions of copolymers of ethene with aliphatic cyclic olefins, e.g. ethylene, propene and norbornene.
This place does not cover:
Adhesive compositions of copolymers with a majority of norbornene |
This group takes precedence over C09J 123/0815, e.g. a copolymer of ethylene, propene and norbornene.
Copolymers with majority of norbornene see C09J 145/00.
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions of copolymers of ethene with aliphatic polyenes, i.e. containing more than one unsaturated bond, e.g. a copolymer of ethylene, butene (small amount) and norbornene (smaller amount).
This group takes precedence over C09J 123/0815.
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions of copolymers of ethene with aromatic monomers, e.g. copolymer of ethylene, butene (small amount) and styrene (smaller amount).
This group takes precedence over C09J 123/0815.
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions of copolymers of ethene with unsaturated hydrocarbons containing other atoms than carbon or hydrogen atoms, e.g. copolymer of ethylene, butene (small amount) and acrylate (smaller amount).
This group takes precedence over C09J 123/0815.
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions of saponified vinylacetate (EVA), e.g. copolymer of ethylene, vinylacetate (small amount) and vinylalcohol (smaller amount).
This group takes precedence over C09J 123/0861.
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions of ethene with acids or derivatives thereof, e.g. ethylene copolymers with vinyl sulfonic acids.
C09J 123/0892 takes precedence over this group.
This place covers:
Ethylene carboxylic acid copolymers where H+ is replaced by M+.
This group takes precedence over C09J 123/0892.
In this group, M+ is not regarded as "other atom".
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions of ethene with epoxide containing esters, e.g. ethylene copolymers with glycidyl methacrylate.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adhesive compositions with copolymers of ethane with copolymers of ethene with monomers with other atoms than carbon, hydrogen or oxygen atoms when the olefin is in minority |
This group takes precedence over C09J 123/0869.
This group can be further characterised by Indexing Codes C08L 2207/10-C08L 2207/14 or C08L 2314/02-C08L 2314/08.
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions of homopolymers.
This group can be further characterised by Indexing Codes C08L 2207/10-C08L 2207/14 or C08L 2314/02-C08L 2314/08.
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions of copolymers of propene, when the propene is in majority, e.g. ethylene-propene copolymers when ethylene is clearly the minor component.
Rubbery polymers, e.g. high a-olefin content or atactic, but no propene.
This place does not cover:
Adhesive compositions of copolymers of etheylne-propylene or ethylene-propylene-diene, e.g. EPM or EPDM rubber |
This group can be further characterised by Indexing Codes C08L 2207/10-C08L 2207/14 or C08L 2314/02-C08L 2314/08.
This group takes precedence over C09J 123/14 or C09J 123/142 in the case of terpolymers even if the polyene unit is the monomer in the lowest concentration.
This group takes preference over C09J 123/14 or C09J 123/142 in the case of terpolymers even if the heteroatom carrying unit is the monomer in the lowest concentration.
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions based on elastomeric ethylene-propylene or ethylene-propylene-diene copolymers, e.g. ethylene-propylene rubber [EPR] or ethylene-propylene-diene rubber [EPDR] copolymers with similar amounts of each monomer.
Although these adhesive compositions containing ethylene-propylene copolymers are adhesives of rubbers or elastomers, group C08L 23/16 is used when the diene monomers are not in majority; whereas group C08L 9/00 is used for copolymers where diene monomers are in majority.
C09J 123/0861 takes precedence in the case of saponified EVA.
C09J 123/0876 takes precedence in the case of neutralised ethylene carboxylic acid copolymers (iononers).
For chlorosulfonation, C09J 123/32 takes precedence over this group.
This place covers:
- Homo- and copolymers of styrene,
- General purpose polystyrene (GPS),
- High impact polystyrene (HIPS).
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
SBR rubber | |
Grafted (co)polymers | |
Block (co)polymers | |
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) |
Classification guidance:
- Classification should be made based on the examples, but not the general claims in the documents. The use of main group symbols should be avoided if there are subgroups which cover the subject matter to be classified. The classification should be made in the most indented subgroup that covers the subject matter.
- For example, a document claiming adhesive compositions of a polymer of an aromatic vinyl monomer, wherein the examples are limited to e.g. polystyrene, should be allocated the symbol C09J 125/06 and not C09J 125/04, C09J 125/02 or C09J 125/00.
- General purpose PS, GPS is classified in C09J 125/06. High impact polystyrene HIPS is classified in C09J 125/06, unless the rubber or rubber content is of relevance, in which case it should be classified in C09J 151/04.
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
GPS | General purpose polystyrene |
HIPS | High impact polystyrene |
PS | Polystyrene |
SAN | Styrene acrylonitrile copolymer |
SPS | Syndiotactic polystyrene |
This place does not cover:
Copolymers with allyl alcohol, even when allyl alcohol monomer is in minority | |
Copolymers with monomers according to C09D 135/06, even in minority | |
Copolymers with monomers according to C09D 141/00, even in minority | |
Copolymers with monomers according to C09D 143/00, even in minority |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Styrene butadiene rubber SBR | |
Grafted copolymers comprising styrene and dienes | |
Block copolymers comprising styrene and dienes |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Copolymers of unsaturated nitriles | |
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene copolymers ABS |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Copolymers with unsaturated carboxylic acids and esters thereof |
This place covers:
- Adhesives based on homo- and copolymers of vinyl mono-, di-, tri- or tetra- halogenide(s) e.g. vinyl(idene) chloride, vinyl(idene) fluoride, chlorotrifluoroethylene, tetrafluoroethylene, hexafluoropropene, etc.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
(per)Halogenated esters of unsaturated carboxylic acids | |
(per)Halogenated polyethers | |
Chemically modified, (post)halogenated polymers |
Classification guidance:
- Classification should be made based on the examples, but not the general claims in the documents. The use of main group symbols should be avoided if there are subgroups which cover the subject matter to be classified. The classification should be made in the most indented subgroup that covers the subject matter.
- For example, a document claiming adhesive compositions of a fluorinated polymer, wherein the examples are limited to e.g. poly(tetrafluoroethylene), should be classified in C09J 127/18 and not in C09J 127/12.
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
CTFE | Chlorotrifluoroethene, chlorotrifluoroethylene |
HFP | Hexafluoropropene, hexafluoropropylene |
PTFE | Poly (tetrafluoroethene), poly (tetrafluoroethylene) |
PVC | Poly (vinyl chloride) |
PVDC | Poly (vinylidene chloride) |
PVDF | Poly (vinylidene fluoride) |
PVF | Poly (vinyl fluoride) |
This place covers:
- Adhesives based on (co)polymers of fluorine containing unsaturated monomers other than those covered by C09J 127/14-C09J 127/20.
- Adhesives based on (co)polymers of fluorine containing unsaturated monomers having additional halogen atom(s) other than fluorine, e.g. (co)polymers of chlorotrifluoroethylene
This place covers:
Adhesives based on homopolymers or copolymers
- of unsaturated alcohols, e.g. polyvinyl alcohol
- of unsaturated ketones
- of acetals or ketals obtained by polymerisation of unsaturated acetals or ketals or by after-treatment of polymers of unsaturated alcohols
Adhesives based on partially hydrolysed homopolymers or copolymers of esters of unsaturated alcohols with saturated carboxylic acids, e.g. copolymers of allyl alcohol.
Classification guidance:
- Classification should be made based on the examples, but not the general claims in the documents. The use of main group symbols should be avoided if there are subgroups which cover the subject matter to be classified. The classification should be made in the most indented subgroup that covers the subject matter.
- For example, a document claiming adhesive compositions of a polymer of an unsaturated alcohol monomer, wherein the examples are limited to e.g. polyvinyl alcohol, should be classified in C09J 129/04 and not in C09J 129/02 or C09J 129/00.
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
EVA or E-VA | Ethylene vinyl alcohol copolymer or ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer |
PVA | Poly(vinyl alcohol) or poly(vinyl acetate) |
PVB | Poly (vinyl butyral) |
PVOH | Poly (vinyl alcohol) |
This place covers:
Homo- and co-polymers of vinyl alcohol
Saponified or hydrolysed (co)polymers of vinyl esters of saturated acids, e.g. saponified or hydrolysed (co)polymers of vinyl acetate.
This place does not cover:
Ethylene/vinyl alcohol copolymers in which ethylene is in majority |
This place covers:
Copolymers with styrene, even when styrene is in majority.
C09J 135/08 takes precedence over this group, i.e. copolymers with monomers according to C09J 135/08, e.g. unsaturated dicarboxylic acids, anhydrides or esters, are classified in C09J 135/08 only, even when these monomers are in minority.
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions based on homopolymers or copolymers of
- esters of monocarboxylic acids, e.g. of vinyl acetate
- esters of polycarboxylic acids, e.g. of phthalic acid.
This place does not cover:
Hydrolised or saponified polymers thereof |
Classification guidance:
- Classification should be made based on the examples, but not the general claims in the documents. The use of main group symbols should be avoided if there are subgroups which cover the subject matter to be classified. The classification should be made in the most indented subgroup that covers the subject matter.
- For example, a document claiming adhesive compositions of a (co)polymer of an unsaturated ester of a saturated carboxylic acid monomer, wherein the examples are limited to, e.g. polyvinyl acetate, should receive the symbol C09J 131/04 and not C09J 131/02 or C09J 131/00.
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
EVA or E-VA | Ethylene Vinyl Acetate copolymer or Ethylene Vinyl Alcohol copolymer |
PVA | Poly(Vinyl Acetate) or Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) |
PVAC or PVAc | Poly (Vinyl Acetate) |
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions of homopolymers or copolymers having one or more unsaturated aliphatic radicals, each having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond, and at least one being terminated by only one carboxyl radical, or of salts, anhydrides, esters, amides, imides, or nitriles thereof, e.g. acrylamide, methacrylamide or acrylic acid esters.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adhesives from diene rubbers containing carboxylic groups | |
Adhesives for nail coating | |
Diapers | |
Applications or uses of polymer compositions in films | |
Polymer compositions | |
Coatings | |
Electrical cables and wires | |
Encapsulation of solar cells |
Last place priority rule:
Within each subgroup of this group, in the absence of an indication to the contrary, classification is made in the last appropriate place.
- For example, adhesives comprising terpolymers of styrene, vinyl acetate and methyl methacrylate in similar proportions would be classified in C09J 133/12 instead of C09J 125/00 or C09J 131/00.
Classification guidance:
- The monomer composition of the main polymer component can be characterised by a C-Set in C08F on the basis of sufficient disclosure in the description or claims.
- Documents are preferably classified according to the examples in the documents, not according to general claims, e.g. if the examples only describe adhesives of acrylic copolymers, but subject matter of the claim is a composition of acrylamide copolymer, the document is classified as adhesive of acrylamide copolymers (C09J 133/26, C08L 23/00).
- The classification of the main component polymer of the composition should be according to the most specific, or reactive monomer, e.g. glycidyl methacrylate and not methyl methacrylate in a copolymer of glycidyl methacrylate and methyl methacrylate. All comonomers of the main polymeric component should be characterised by symbols in C08F, e.g. C08F 220/32 and C08F 220/14.
Choice of symbol for copolymers:
- In an adhesive comprising a copolymer, the copolymer is given the symbol on the basis of the major monomer component, except if there is a lower symbol which specifies the comonomer in minority.
- An adhesive composition based on a copolymer of ethylene and acrylic acid therefore is to be classified in C09J 123/0869 (ethylene in majority), but in C09J 133/02 if acrylic acid is in majority. However, an adhesive based on a copolymer of acrylic ester and acrylonitrile (acrylic ester in majority) would be classified in C09J 133/20.
- The classification of the main component polymer of the adhesive should be according to the most specific, or reactive monomer (i.e. glycidyl methacrylate and not methyl methacrylate in a copolymer of glycidyl methacrylate and methyl methacrylate).
- Thus adhesives comprising copolymers wherein anhydride, carboxylic acid or metal salt containing monomers are present are classified in C09J 133/064; copolymers wherein hydroxyl-containing monomers are present are classified in C09J 133/064, copolymers wherein glycidyl-containing monomers are present are classified in C09J 133/068.
- In addition, a separate C-Set representing the copolymer that is formed according to the monomers of C08F must also be given.
C-sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
- If C09J 133/00 relates to a composition and two or more polymers are present, classification is given in the form of C-Sets (i.e. #C9J(c)) according to the relative weight percentage of the polymer constituents.
- The polymer in majority is given a symbol as a base symbol, and the polymers in minority are given symbols as subsequent symbols in the form of C-Sets.
- In addition, a single symbol is given according to the macromolecular constituent present in the highest proportion.
- If all the constituents are present in equal weight percentage, the composition is classified according to each of these constituents.
- In the case that several polymers can be in majority, separate C-Sets should be made based on each polymer in majority and its component(s) in minority.
- Orthogonal indexing codes C08L 2201/00 - C08L 2555/86 are also given if applicable.
Example 1: An adhesive composition of 60 parts polymethyl methacrylate (C09J 133/12) and 40 parts polyamide (C08L 77/00) is classified as (C09J 133/12, C08L 77/00).
Example 2: An adhesive composition of 50 parts polymethyl methacrylate (C09J 133/12) and 50 parts polyamide (C09J 177/00) is classified as (C09J 133/12, C08L 77/00) and (C09J 177/00, C08L 33/12).
Example 3: An adhesive composition based on polymethyl methacrylate and containing CaCO3 is classified as (C09J 133/12, C08K 3/26). If this composition contains also a polyamide, then the classification will be (C09J 133/12, C08L 77/00, C08K 3/26).
Example 4: An adhesive composition based on a first polymethyl methacrylate (C09J 133/12) and containing as a second polymer a copolymer of acrylic acid, a phenol and silica is classified as (C09J 133/12, C08L 33/02, C08K 5/13, C08K 3/36) and in C08L 2205/02.
Example 5: A composition containing a polyamide in majority, a polyester and a polymethyl methacrylate is classified as (C09J 177/00, C08L 67/00, C08L 33/12) and in C08L 2205/03.
Example 6: Adhesive compositions containing two polymers of the same dot group, for example compositions of two polymers amhydroxyl containing acrylic ester, are characterised by the orthogonal indexing code C08L 2205/025. The complete classification for such compositions, therefore, would be (C09J 133/066, C08L 33/066) and C08L 2205/025. The same applies for compositions of two polymers only distinguished by physical properties, e.g. molecular weight or density.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Attention is drawn to the glossary of C09J 123/00.
In patent documents the following abbreviations are often used:
Attention is drawn to the table after the title of C09J.
This place does not cover:
Copolymers containing bicarboxylic acids in majority |
All of C09J 137/00-C09J 143/04, C09J 133/064-C09J 133/068 and C09J 133/14-C09J 133/26 take precedence over this group, even if the corresponding monomers are in minority.
This group should be used if the nature of the acrylic ester polymer is not specified.
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions based on all alkyl alkylacrylate monomers.
This place does not cover:
Adhesive compositions based on acrylic acid esters or methacrylic acid esters with alkanols or phenols, without having additional functional groups, e.g. methyl ethylacrylate |
This place does not cover:
Adhesive compositions based on monomers which have OH, glycidyl, anhydride or additional acid groups | |
Adhesive compositions based on monomers which have halogen, nitrogen, sulfur, or oxygen |
This place covers:
Acrylic adhesive compositions based on maleic acid or derivative containing polymers having maleic acid in minority.
This place does not cover:
Acrylic adhesive compositions based on maleic acid or derivative containing polymers having an olefin acid in majority | |
Acrylic adhesive compositions based on maleic acid or derivative containing polymers having maleic acid in majority |
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions based on polymers containing hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA).
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions based on polymers containing glycidyl methacrylate.
This place covers:
Adhesive composition based on homopolymers or copolymers which are esters of acrylic acid or methacrylic acid.
This place does not cover:
Adhesive composition based on copolymers of other alkylacrylates |
All of C09J 137/00-C09J 143/00, C09J 133/062-C09J 133/068 and C09J 133/14-C09J 133/26 take precedence over this group even if the corresponding monomers are in minority.
In copolymers, all of C09J 137/00-C09J 143/04, C09J 133/062-C09J 133/068 and C09J 133/14-C09J 133/26 take precedence over this group even if the corresponding monomers are in minority.
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions based on acrylic esters of polyethylene ethers, methoxymethacrylate or amino substituted acrylate esters.
All of C09J 133/064-C09J 133/068, C09J 137/00-C09J 143/00 and C09J 133/18-C09J 133/26 take precedence over this group.
This place covers:
Adhesives based on homopolymers or copolymers of compounds having one or more unsaturated aliphatic radicals, each having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond, and at least one being terminated by a carboxyl radical, and containing at least another carboxyl radical in the molecule, or of salts, anhydrides, esters, amides, imides or nitriles thereof; Adhesives based on derivatives of such polymers. Bonding using organic-inorganic elastomer and elastomeric substances obtained by co-polymerisation of maleic anhydride, vinyl stearate and a vinyl alkoxy silane with or without vinyl formate.
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Applications or uses of polymer compositions in laminates | |
Applications or uses of polymer compositions in films | |
Working-up, compounding, after-treatment of macromolecular compounds |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adhesives based on compositions of polymerisable monomers | |
Adhesives for nail coatings | |
Adhesives for diapers | |
Use of Inorganic of non-macromolecular organic substances as compounding ingredients | |
Polymer compositions | |
Coatings |
Last place priority rule:
Within each subgroup of this group, in the absence of an indication to the contrary, classification is made in the last appropriate place.
Classification guidance:
- Documents are preferably classified according to the examples in the documents, not according to general claims, e.g. if the examples only describe adhesives of compositions of styrene-maleic anhydride, but subject matter of the claim is an adhesive of a composition of a vinyl aromatic copolymer, the document is classified as adhesive composition of styrene maleic anhydride copolymer C09J 135/06.
- In C09J, adhesives which have only one polymeric component is also classified, e.g. C09J 135/06 for an adhesive of only one maleic anhydride copolymer.
- For Copolymers
In an adhesive comprising a copolymer, the copolymer is given the symbol on the basis of the major component, except if there is a lower symbol which specifies the comonomer in minority (see also last place rule), i.e. ethylene maleic anhydride copolymers (ethylene in majority) would be classified in C09J 123/0869, and not in C09J 135/00, but ethylene maleic anhydride copolymers (maleic anhydride in majority) would be classified in C09J 135/00, not in C09J 123/0869.
C-sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
- If C09J 135/00 relates to a composition and two or more polymers are present, classification is given in the form of C-Sets (i.e. #C9Jc) according to the relative weight percentage of the polymer constituents.
- The polymer in majority is given a symbol as a base symbol, and the polymers in minority are given symbols as subsequent symbols in the form of C-Sets.
- In addition, a single symbol is given according to the macromolecular constituent present in the highest proportion.
- If all the constituents are present in equal weight percentage, the composition is classified according to each of these constituents.
- In the case that several polymers can be in majority, separate C-Sets should be made based on each polymer in majority and its component(s) in minority.
- Orthogonal indexing codes C08L 2201/00 - C08L 2555/86 are also given if applicable.
Example 1: An adhesive of a blend of 60 parts styrene-maleic anhydride copolymer (C09J 135/06) and 40 parts polyamide (C09J 177/00) is classified as (C09J 135/06, C08L 77/00).
Example 2: An adhesive of a blend of 50 parts styrene-maleic anhydride copolymer (C09J 135/06) and 50 parts polyamide (C09J 177/00) is classified as (C09J 135/06, C08L 77/00) and (C09J 177/00, C08L 35/06).
Example 3: An adhesive of a composition based on styrene-maleic anhydride copolymer and containing CaCO3 is classified as (C09J 135/06, C08K 3/26). If this composition contains also a polyamide, then the classification will be (C09J 135/06, C08L 77/00, C08K 3/26).
Example 4: An adhesive of a composition based on a first styrene-maleic anhydride copolymer (C09J 135/06) and containing a second styrene-maleic anhydride copolymer, a phenol and silica is classified as (C09J 135/06, C08L 35/06, C08K 5/13, C08K 3/36) and in C08L 2205/025.
Example 5: An adhesive of a composition containing a polyamide in majority, a polyester and a styrene-maleic anhydride copolymer is classified as (C09J 177/00, C08L 67/00, C08L 35/06) and in C08L 2205/03.
Example 6: An adhesive of compositions containing two polymers of the same dot group, for example compositions of two styrene-maleic anhydride copolymer polymers, are characterised by the orthogonal indexing code C08L 2205/025. The complete classification for such compositions therefore would be (C09J 135/06, C08L 35/06) and C08L 2205/025. The same applies for adhesive compositions of two polymers only distinguished by physical properties, i.e. molecular weight or density.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Attention is drawn to the glossary of C09J 123/00.
In patent documents the following abbreviations are often used:
Attention is drawn to the table after the title of C09J.
This place does not cover:
Adhesives based on copolymers of unsaturated esters, e.g. acrylic ester with a monomer of C09J 135/00, e.g. maleic anhydride which have the ester in majority |
Maleic anhydride should be characterised by an Indexing Code of C08F, e.g. C08F 222/04.
Groups C09J 135/06 and C09J 135/08 take precedence over this group.
This place does not cover:
Adhesives of copolymers of unsaturated nitriles, e.g. acrylonitrile with a monomer of C09J 135/00, e.g. maleic anhydride which have the nitrile in majority |
Maleic anhydride should be characterised by an Indexing Code of C08F , e.g. C08F 222/04.
Groups C09J 135/06 and C09J 135/08 take precedence over this group.
This place does not cover:
Adhesives based on copolymers of vinyl aromatic compounds, e.g. styrene with a monomer of C09J 135/00, e.g. maleic anhydride which have the vinyl aromatic compound in majority |
Maleic anhydride should be characterised by an Indexing Code of C08F, e.g. C08F 222/04.
Groups C09J 135/06 and C09J 135/08 take precedence over this group.
This place does not cover:
Adhesives based on copolymers of vinylethers with a monomer of C09J 135/00, e.g. maleic anhydride which have the vinylether in majority |
Maleic anhydride should be characterised by an Indexing Code of C08F, e.g. C08F 222/04.
This place covers:
Adhesives based on homopolymers or copolymers of compounds having one or more unsaturated aliphatic radicals, each having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond, and at least one being terminated by a heterocyclic ring containing oxygen; adhesives based on derivatives of such polymers, bonding using a non-volatile organic binder having 2-vinyl-1,3cyclic acetal radicals.
This place does not cover:
Adhesives based on polymers of cyclic esters of polyfunctional acids; based on polymers of cyclic anhydrides of unsaturated acids | |
Adhesives based on polymers of cyclic anhydrides of unsaturated acids |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adhesives based on compositions of polymerisable monomers | |
Adhesives for nail coatings | |
Adhesives in diapers | |
ß Applications or uses of polymer compositions in films | |
Polymer compositions | |
Coatings | |
Encapsulation of solar cells |
Last place priority rule:
Within each subgroup of this group, in the absence of an indication to the contrary, classification is made in the last appropriate place.
Classification guidance
- Documents are preferably classified according to the examples in the documents, not according to general claims, e.g. if the examples only describe adhesives of compositions of diene vinylfuran copolymers, but subject matter of the claim is an adhesive of a composition of a diene copolymer, the document is classified as adhesive composition of a vinyl furan copolymer C09J 137/00.
- In C09J, adhesives having only one polymeric component are also classified, e.g. C09J 137/00, an adhesive consisting of one vinyl furan copolymer.
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
- If C09J 137/00 relates to a composition and two or more polymers are present, classification is given in the form of C-Sets (i.e. #C9J(c)) according to the relative weight percentage of the polymer constituents.
- The polymer in majority is given a symbol as a base symbol, and the polymers in minority are given symbols as subsequent symbols in the form of C-Sets.
- A single symbol is given according to the macromolecular constituent present in the highest proportion.
- If all the constituents are present in equal weight percentage, the composition is classified according to each of these constituents.
- In the case that several polymers can be in majority, separate C-Sets should be made based on each polymer in majority and its component(s) in minority.
- Orthogonal indexing codes C08L 2201/00 - C08L 2555/86 are also given if applicable.
- Common adhesive ingredients like tackifying resins or waxes only get a C-Set classification in C09J 137/00 if they have characterising features for the composition.
Example 1: An adhesive of a blend of 60 parts diene vinylfuran copolymer (C09J 137/00) and 40 parts polyamide (C09J 177/00) is classified as (C09J 137/00, C08L 77/00).
Example 2: An adhesive of a blend of 50 parts diene vinylfuran copolymer (C09J 137/00) and 50 parts polyamide (C09J 177/00) is classified as (C09J 137/00, C08L 77/00) and (C09J 177/00, C08L 37/00).
Example 3: An adhesive of a composition based on diene vinylfuran copolymer and containing CaCO3 is classified as (C09J 137/00, C08K 3/26). If this composition contains also a polyamide, then the classification will be (C09J 137/00, C08L 77/00, C08K 3/26).
Example 4: An adhesive of a composition based on a first diene vinylfuran copolymer (C09J 137/00) and containing a second diene vinylfuran copolymer, a phenol and silica is classified as (C09J 137/00, C08L 37/00, C08K 5/13, C08K 3/36) and in C08L 2205/025.
Example 5: An adhesive of a composition containing a polyamide in majority, a polyester and a diene vinylfuran copolymer is classified as (C09J 177/00, C08L 67/00, C08L 37/00) and in C08L 2205/03.
Example 6: An adhesive of compositions containing two polymers of the same dot group, for example compositions of two diene vinylfuran copolymer polymers, are characterised by the orthogonal indexing code C08L 2205/025. The complete classification for such compositions therefore would be (C09J 137/00, C08L 37/00) and C08L 2205/025. The same applies for adhesive compositions of two polymers only distinguished by physical properties, e.g. molecular weight or density.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Attention is drawn to the glossary of C09J 123/00.
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms:
Attention is drawn to the table after the title of C09J.
This place covers:
Adhesives based on homopolymers or copolymers of compounds having one or more unsaturated aliphatic radicals, each having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond, and at least one being terminated by a single or double bond to nitrogen or by a heterocyclic ring containing nitrogen; Adhesives based on derivatives of such polymers
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Acrylic copolymers of amides and imides | |
Adhesives for nail coatings | |
Adhesives in diapers | |
Applications or uses of polymer compositions in films | |
Polymer compositions | |
Applications or uses of polymer compositions in coatings | |
Encapsulation of solar cells |
Last place priority rule:
Within each subgroup of this group, in the absence of an indication to the contrary, classification is made in the last appropriate place.
Classification guidance:
- Documents are preferably classified according to the examples in the documents, not according to general claims, e.g. if the examples only describe adhesives based on an acrylic polymer containing vinyl pyrrolidone, but subject matter of the claim is an acrylic adhesive, the document is classified under adhesives of vinyl pyrrolidone copolymer C09J 139/06.
- In C09J, adhesives which have only one polymeric component are classified, e.g. C09J 139/06 represents an adhesive of only one vinyl pyrrolidone copolymer.
For Copolymers:
- C09J 139/00 may also be given when the monomer described therein is in minority in the copolymer of an adhesive composition. An adhesive based on a copolymer of acrylic ester and vinyl pyridine, which has a lower content of vinyl pyridine than acrylic ester, would also be classified in C09J 139/08. Additional classification in C09D 133/08 should be considered.
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
- If C09J 139/00 relates to a composition and two or more polymers are present, classification is given in the form of C-Sets (i.e. #C9J(c)) according to the relative weight percentage of the polymer constituents.
- The polymer in majority is given a symbol as a base symbol, and the polymers in minority are given symbols as subsequent symbols in the form of C-Sets.
- In addition, a single symbol is given according to the macromolecular constituent present in the highest proportion.
- If all the constituents are present in equal weight percentage, the composition is classified according to each of these constituents.
- In the case that several polymers can be in majority, separate C-Sets should be made based on each polymer in majority and its component(s) in minority.
- Orthogonal indexing codes C08L 2201/00 - C08L 2555/86 are also given if applicable.
- Common adhesive ingredients like tackifying resins or waxes only get a C-Set classification in C09J 139/00 if they have characterising features for the composition.
Example 1: An adhesive of a blend of 60 parts vinyl pyridine copolymer (C09J 139/08) and 40 parts polyamide (C09J 177/00) is classified as (C09J 139/00, C08L 77/00).
Example 2: An adhesive of a blend of 50 parts vinyl pyridine copolymer (C09J 139/08) and 50 parts polyamide (C09J 177/00) is classified as (C09J 139/08, C08L 77/00) and (C09J 177/00, C08L 39/08).
Example 3: An adhesive based on a composition of vinyl pyridine copolymer and containing CaCO3 is classified as (C09J 139/08, C08K 3/26). If this composition contains also a polyamide, then the classification will be (C09J 139/08, C08L 77/00, C08K 3/26).
Example 4: An adhesive based on a composition based on a first vinyl pyridine copolymer (C09J 139/08) and containing a second vinyl pyridine copolymer, a phenol and silica is classified as (C09J 139/08, C08L 39/08, C08K 5/13, C08K 3/36) and in C08L 2205/025.
Example 5: An adhesive based on a composition containing a polyamide in majority, a polyester and a vinyl pyridine copolymer is classified as (C09J 177/00, C08L 67/00, C08L 39/08) and in C08L 2205/03.
Example 6: Adhesives of compositions containing two polymers of the same subgroup, for example compositions of two vinyl pyridine copolymers, are characterised by the orthogonal indexing code C08L 2205/025. The complete classification for such a composition therefore would be (C09J 139/08, C08L 39/08) and C08L 2205/025. The same applies for compositions of two polymers only distinguished by physical properties (e.g. molecular weight, density etc.)
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Attention is drawn to the glossary of C09J 123/00.
In patent documents the following abbreviations are often used:
Attention is drawn to the table after the title of C09J.
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00 .
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions based on homopolymers or copolymers of compounds corresponding to groups C08F 30/00, C08F 130/00 or C08F 230/00.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adhesive tapes, glue sticks, other features of adhesives | |
Adhesives of ethylene copolymers of silane or phosphorous containing compounds | |
Adhesives of propene copolymers of silane or phosphorous containing compounds | |
Acrylic adhesive compositions | |
Adhesives for nail coatings | |
Adhesives for diapers | |
Applications or uses of polymer compositions in films | |
Polymer compositions | |
Applications or uses of polymer compositions in coatings | |
Encapsulation of solar cells |
Last place priority rule:
Within each subgroup of this group, in the absence of an indication to the contrary, classification is made in the last appropriate place.
Classification guidance:
- Documents are preferably classified according to the examples in the documents, not according to general claims, e.g. if the examples only describe adhesives based on an acrylic polymer containing vinyl silane, but subject matter of the claim is an acrylic adhesive, the document is classified under adhesives of vinyl silane copolymer (C09J 143/04).
- In C09J 143/00, adhesives which have only one polymeric component are also classified, e.g. C09J 143/04, an adhesive consisting of only one vinyl silane polymer.
- Further subdivisions:
C09J 143/02: Adhesive compositions based on copolymers of ethylene or propene are not classified in this group.
C09J 143/04: Adhesive compositions based on copolymers of ethylene or propene are not classified in this group.
- For Copolymers:
C09J 143/00 may also be given when the monomer described therein is in minority in the copolymer of a coating composition. An adhesive based on a copolymer of acrylic ester and vinyl silane, which has a lower content of vinyl silane than acrylic ester, would also be classified in C09J 143/04. Additional classification in C09J 133/08 should be considered.
The comonomer in majority should get a symbol in C08F, e.g. C08F 220/10 for acrylic esters.
However, if the major comonomer is ethylene or propene, the corresponding copolymer compositions are classified in C09J 123/0892 or C09J 123/147.
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
- If C09J 143/00 relates to a composition and two or more polymers are present, classification is given in the form of C-Sets (i.e. #C9J(c)) according to the relative weight percentage of the polymer constituents.
- The polymer in majority is given a symbol as a base symbol, and the polymers in minority are given symbols as subsequent symbols in the form of C-Sets.
- In addition, a single symbol is given according to the macromolecular constituent present in the highest proportion.
- If all the constituents are present in equal weight percentage, the composition is classified according to each of these constituents.
- In the case that several polymers can be in majority, separate C-Sets should be made based on each polymer in majority and its component(s) in minority.
- Orthogonal indexing codes C08L 2201/00 - C08L 2555/86 are also given if applicable.
- Common adhesive ingredients like tackifying resins or waxes only get a C-Set classification in C09J 143/00 if they have characterising features for the composition.
Example 1: An adhesive of a blend of 60 parts vinyl silane copolymer (C09J 143/04) and 40 parts polyamide (C09J 177/00) is classified as (C09J 143/04, C08L 77/00).
Example 2: An adhesive of a blend of 50 parts vinyl silane copolymer (C09J 143/04) and 50 parts polyamide (C09J 177/00) is classified as (C09J 143/04, C08L 43/04) and (C09J 177/00, C08L 43/04).
Example 3: An adhesive based on a composition of vinyl silane copolymer and containing CaCO3 is classified as (C09J 143/04, C08K 3/26). If this composition contains also a polyamide, then the classification will be (C09J 143/04, C08L 77/00, C08K 3/26).
Example 4: An adhesive based on a composition based on a first vinyl silane copolymer (C09J 143/04) and containing a second vinyl silane copolymer, a phenol and silica is classified as (C09J 143/04, C08L 43/04, C08K 5/13, C08K 3/36) and in C08L 2205/025.
Example 5: An adhesive based on a composition containing a polyamide in majority, a polyester and a vinyl silane copolymer is classified as (C09J 177/00, C08L 67/00, C08L 43/04) and in C08L 2205/03.
Example 6: Adhesives of compositions containing two polymers of the same dot group, for example compositions of two vinyl silane copolymers, are characterised by the orthogonal indexing code C08L 2205/025. The complete classification for such a composition therefore would be (C09J 143/04, C08L 43/04) and C08L 2205/025. The same applies for compositions of two polymers only distinguished by physical properties (e.g. molecular weight, density etc.)
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Attention is drawn to the glossary of C09J 123/00.
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
Attention is drawn to the table after the title of C09J.
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions based on homopolymers or copolymers of compounds corresponding to groups C08F 32/00, C08F 132/00, C08F 232/00 or C08F 244/00.
Adhesive compositions based on (co)polymers of cyclic olefins, e.g. norbornene or bicyclopentadiene, where the cyclic monomer is the major component in the copolymer.
This place does not cover:
Adhesives based on polymers of cyclic esters of polyfunctional acids | |
Adhesives based on polymers of cyclic anhydrides or imides |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adhesives based on copolymers of monomers terminated by a heterocyclic ring containing Oxygen | |
Adhesives based on copolymers of monomers terminated by a heterocyclic ring containing Nitrogen | |
Applications or uses of polymer compositions in films | |
Polymer compositions | |
Coatings |
Last place priority rule:
Within each subgroup of this group, in the absence of an indication to the contrary, classification is made in the last appropriate place.
Classification guidance:
- Documents are preferably classified according to the examples in the documents, not according to general claims, e.g. if the examples only describe adhesives based on polynorbornene, but subject matter of the claim is an adhesive of polyolefin, the document is classified under adhesives of polynorbornene (C09J 145/00).
- For Copolymers:
Copolymers get the class of the major component, except if there is a lower class which specifies the comonomer in minority (see also last place rule), i.e. ethylene copolymers (ethylene comonomer in majority) would be classified in C09J 123/0807 , and not in C09J 145/00, but ethylene norbornene copolymers (norbornene in majority) would be classified in C09J 145/00, not in C09J 123/08.
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
- If C09J 145/00 relates to a composition and two or more polymers are present, classification is given in the form of C-Sets (i.e. #C9J(c)) according to the relative weight percentage of the polymer constituents.
- The polymer in majority is given a symbol as a base symbol, and the polymers in minority are given symbols as subsequent symbols in the form of C-Sets.
- In addition, a single symbol is given according to the macromolecular constituent present in the highest proportion.
- If all the constituents are present in equal weight percentage, the composition is classified according to each of these constituents.
- In the case that several polymers can be in majority, separate C-Sets should be made based on each polymer in majority and its component(s) in minority.
- Orthogonal indexing codes C08L 2201/00 - C08L 2555/86 are also given if applicable.
Example 1: An adhesive of a blend of 60 parts poly-norbornene (C09J 145/00) and 40 parts polyamide (C09J 177/00) is classified as (C09J 145/00, C08L 77/00).
Example 2: An adhesive of a blend of 50 parts poly norbornene (C09J 145/00) and 50 parts polyamide (C09J 177/00) is classified as (C09J 145/00, C08L 77/00) and (C09J 177/00, C08L 45/00).
Example 3: An adhesive based on a composition of polynorbornene and containing CaCO3 is classified as (C09J 145/00, C08K 3/26). If this composition contains also a polyamide, then the classification will be (C09J 145/00, C08L 77/00, C08K 3/26).
Example 4: An adhesive based on a composition based on a first polynorbornene (C09J 145/00) and containing a second polynorbornene, a phenol and silica is classified as (C09J 145/00, C08L 45/00, C08K 5/13, C08K 3/36) and in C08L 2205/02.
Example 5: An adhesive based on a composition containing a polyamide in majority, a polyester and a polynorbornene is classified as (C09J 177/00, C08L 67/00, C08L 45/00) and in C08L 2205/03.
Example 6: Adhesives of compositions containing two polymers of the same dot group, for example compositions of two polynorbornenes, are characterised by the orthogonal indexing code C08L 2205/025. The complete classification for such a composition therefore would be (C09J 145/00, C08L 45/00) and C08L 2205/025. The same applies for compositions of two polymers only distinguished by physical properties, e.g. molecular weight or density.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Attention is drawn to the table of the glossary of C09J 123/00.
In patent documents the following abbreviations are often used:
Attention is drawn to the table after the title of C09J.
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions of homopolymers or copolymers of compounds having one or more unsaturated aliphatic radicals, at least one having two or more carbon-to-carbon double bonds, i.e. unconjugated dienes.
Adhesive compositions of derivatives of such polymers.
This place does not cover:
Adhesive compositions of conjugated diene polymers | |
Adhesive compositions of coumarone-indene polymers |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adhesive compositions of copolymers of ethylene-propylene or ethylene-propylene-diene, e.g. adhesive compositions of EPM or EPDM rubber | |
Adhesive compositions of copolymers of isobutene with minor part of conjugated dienes monomers (butyl rubber) |
Classification guidance:
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
ABS | Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene |
BR | Butadiene rubber |
CR | Chloroprene rubber |
EPDM | Ethene propene diene rubber |
EPM | Ethene propene rubber |
IIR | Butyl rubber |
IR | Isoprene rubber |
NBR | Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber |
NR | Natural rubber |
SAN | Styrene acrylonitrile copolymer |
SBR | Styrene butadiene rubber |
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions based on homopolymers or copolymers of compounds corresponding to groups C08F 38/00, C08F 138/00 and C08F 238/00.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Applications or uses of polymer compositions in films | |
Polymer compositions | |
Artificial filaments or fibres | |
Textile treating compositions | |
Coatings of electrical wires | |
Encapsulation of solar cells |
Last place priority rule:
Within each subgroup of this group, in the absence of an indication to the contrary, classification is made in the last appropriate place.
Classification guidance:
- Documents are preferably classified according to the examples in the documents, not according to general claims, e.g. if the examples only describe adhesive compositions based on polyacetylene, but subject matter of the claim is an adhesive composition of polyolefin, the document is classified under adhesive compositions of polyacetylene (C09J 149/00).
- For Copolymers:
In an adhesive comprising a copolymer, the copolymer is given the symbol on the basis of the major component, except if there is a lower group which specifies the comonomer in minority (see also last place rule), e.g. ethylene copolymers (ethylene comonomer in majority) would be classified in C09J 123/0807, and not in C09J 149/00, but ethylene acetylene (acetylene in majority) would be classified in C09J 149/00, not in C09J 123/08.
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
- If C09J 149/00 relates to a composition and two or more polymers are present, classification is given in the form of C-Sets (i.e. #C9J(c)) according to the relative weight percentage of the polymer constituents.
- The polymer in majority is given a symbol as a base symbol, and the polymers in minority are given symbols as subsequent symbols in the form of C-Sets.
- In addition, a single symbol is given according to the macromolecular constituent present in the highest proportion.
- If all the constituents are present in equal weight percentage, the composition is classified according to each of these constituents.
- In the case that several polymers can be in majority, separate C-Sets should be made based on each polymer in majority and its component(s) in minority.
- Orthogonal indexing codes C08L 2201/00 - C08L 2555/86 are also given if applicable.
Example 1: An adhesive composition of a blend of 60 parts polyacetylene (C09J 149/00) and 40 parts polyamide (C09J 177/00) is classified as (C09J 149/00, C08L 77/00).
Example 2: An adhesive composition of a blend of 50 parts poly acetylene (C09J 149/00) and 50 parts polyamide (C09J 177/00) is classified as (C09J 149/00, C08L 77/00) and (C09J 177/00, C08L 49/00).
Example 3:An adhesive composition based on a composition of polyacetylene and containing CaCO₃ is classified as (C09J 149/00, C08K 3/26). If this composition contains also a polyamide, then the classification will be (C09J 149/00) C08L 77/00, C08K 3/26).
Example 4: An adhesive composition based on a composition based on a first polyacetylene (C09J 149/00) and containing a second polyacetylene, a phenol and silica is classified as (C09J 149/00, C08L 49/00, C08K 5/13, C08K 3/36) and in C08L 2205/02.
Example 5: An adhesive composition on a composition containing a polyamide in majority, a polyester and a polyacetylene is classified as (C09J 177/00, C08L 67/00, C08L 49/00) and C08L 2205/03.
Example 6: An adhesive composition containing two polymers of the same dot group, for example compositions of two polyacetylenes, are characterised by the orthogonal indexing code C08L 2205/025. The complete classification for such a composition therefore would be (C09J 149/00, C08L 49/00) and C08L 2205/025. The same applies for compositions of two polymers only distinguished by physical properties (e.g. molecular weight, density etc.)
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Attention is drawn to the glossary of C09J 123/00.
In patent documents the following abbreviations are often used:
Attention is drawn to the table after the title of C09J.
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions comprising graft polymers of C08F 251/00-C08F 292/00.
Graft copolymers in which the grafted component is obtained by reactions involving C=C per se are classified in C08F 251/00-C08F 292/00.
Compositions (other than coating or adhesive) comprising a grafted polymer in majority and other polymer(s) are classified in C08L 51/00-C08L 51/10.
Adhesive compositions comprising graft polymers in which the graft polymer is in minority are classified in C08L 51/00-C08L 51/10.
This place does not cover:
Adhesive compositions comprising ABS polymers |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adhesive compositions comprising an unsaturated monomer and a polymer, e.g. grafting in situ | |
Adhesives in the form of films or foils | |
Adhesive compositions comprising an unsaturated monomer and a polymer of C08L 59/00 - C08L 87/00 | |
Adhesive compositions comprising block or graft copolymers containing polysiloxane sequences (not obtained by reaction of C=C monomer(s) onto polysiloxane) | |
Adhesive compositions comprising graft polymers obtained by interreacting polymers in the absence of monomers, i.e. graft polymer of C08G 81/00 - C08G 81/028 | |
Presence of graft polymer |
Classification guidance:
For adhesive compositions comprising grafted rubbers, several symbols are given if the rubber is specific.
If the rubber is EPR: C09J 151/04 and C09J 151/06
If the rubber is EPDM, SBR or acrylate rubber: C09J 151/04 and C09J 151/003
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions of block polymers of classes C08F 293/00-C08F 297/08.
Block polymers obtained by reactions only involving C=C per se are classified in C08F 293/00-C08F 297/08.
Compositions (other than coating or adhesive) comprising block polymer in majority and other polymer(s), are classified in C08L 53/00-C08L 53/025.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adhesives in the form of films or foils | |
Adhesive compositions comprising block or graft copolymers containing polysiloxane sequences (not obtained by reaction of C=C monomer(s) onto polysiloxane) | |
Adhesive compositions comprising block polymers obtained by interreacting polymers in the absence of monomers (Block polymer of C08G 81/00 - C08G 81/028) | |
Presence of block polymer |
Classification guidance:
- Further subdivisions:
C09J 153/005 and C09J 153/025 cover adhesive compositions comprising modified block polymers. In particular, adhesive compositions comprising hydrogenated styrene-diene block copolymers are classified in C09J 153/025.
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adhesives in the form of films or foil | |
Presence of ABS polymer | |
Polymerisation by the diene synthesis | |
ABS polymers per se | |
Macromolecular compounds obtained by polymerising monomers on to polymers modified by introduction of aliphatic unsaturated end or side groups | |
Polymeric compositions comprising homopolymers or copolymers, obtained by polymerisation reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, not provided for in groups C08L 23/00 - C08L 53/00 |
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
This place covers:
Adhesives based on polymers obtained by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds which are not limited to a particular polymer type as defined in groups C09J 107/00-C09J 155/00.
Adhesive compositions of polymers obtained by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds which are not specific enough as to fit in the preceding groups C09J 107/00-C09J 155/00.
Use of C09J 157/00-C09J 157/12 symbols should be avoided by classifying the specific examples, whenever practicable, in the corresponding classes of C09J 107/00-C09J 155/00.
Classification guidance:
Classification should be made based on the examples, but not the general claims in the documents. The use of main group symbols should be avoided if there are subgroups which cover the subject matter to be classified. The classification should be made in the most indented subgroup that covers the subject matter.
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adhesives based on (co)polymers of compounds having one or more unsaturated aliphatic radicals, each having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond, and at least one being terminated by a halogen |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Polysaccharides | |
Unsaturated alcohols, ethers, ketones, acetals or ketals | |
Saturated carboxylic acid, carbonic acid or haloformic acid esters of unsaturated alcohols | |
Unsaturated carboxylic acids, esters | |
Unsaturated dicarboxylic acids, esters, anhydrides | |
Unsaturated aliphatic radicals, terminated by a heterocyclic ring containing oxygen |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Polymers of unsaturated nitriles amides or imides | |
Unsaturated dicarboxylic amides, imides, nitriles | |
Unsaturated aliphatic radicals, terminated by a heterocyclic ring containing nitrogen |
This place covers:
Adhesives based on polyacetals, which are addition polymers of aldehydes or cyclic oligomers thereof or of ketones and correspond to groups C08G 2/00 - C08G 16/00 and their subgroups.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adhesives based on polyvinyl acetals |
Classification guidance:
When a document specifies an adhesive based on polyacetal in general, or both homopolyacetals and copolyacetals, classification is done in the main group C09J 159/00; only when the document specifically mentions homopolyacetals or copolyacetals, then classification in C09J 159/02 and C09J 159/04 is given.
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
This place covers:
- Adhesives based on condensation polymers of
- aldehydes or ketones with polyalcohols which correspond to subgroups C08G 4/00,
- aldehydes or ketones only which correspond to subgroups C08G 6/00,
- aldehydes or ketones with phenols only which correspond to subgroups C08G 8/00,
- aldehydes or ketones with aromatic hydrocarbons or halogenated
- aromatic hydrocarbons only which correspond to subgroups C08G 10/00,
- aldehydes or ketones with only compounds containing hydrogen attached to nitrogen which correspond to subgroups C08G 12/00.
- aldehydes or ketones corresponding to C08G 14/00 - C08G 16/06.
This place does not cover:
Adhesives based on condensation polymers of aldehydes or ketones with polyalcohols | |
Adhesives based on condensation polymers of aldehydes or ketones with polynitriles |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions based on polycondensates having more than one epoxy group per molecule, with or without other components.
C08L 63/00 relates to compositions based on epoxy resins.
C09D 163/00 relates to coating compositions based on epoxy resins.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adhesives in the form of films or foils | |
Adhesives in the form of films or foils, characterised by the carrier | |
Adhesives in the form of films or foils, characterised by the carrier, based on macromolecular compounds obtained otherwise than by reactions involving only carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds |
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
- If C09J 163/00 relates to a composition and two or more polymers are present, classification is given in the form of C-Sets (i.e. #C9J(c)) according to the relative weight percentage of the polymer constituents.
- The polymer in majority is given a symbol as a base symbol, and the polymers in minority are given symbols as subsequent symbols in the form of C-Sets.
- In addition, a single symbol is given according to the macromolecular constituent present in the highest proportion.
- If all the constituents are present in equal weight percentage, the composition is classified according to each of these constituents.
- In the case that several polymers can be in majority, separate C-Sets should be made based on each polymer in majority and its component(s) in minority.
- Orthogonal indexing codes C08L 2201/00 - C08L 2555/86 are also given if applicable.
Example 1: An adhesive composition comprising a blend of 60 parts non-specified epoxy resin (C09J 163/00) and 40 parts polyamide (C09J 177/00) is classified as (C09J 163/00, C08L 77/00).
Example 2: An adhesive composition comprising a blend of 50 parts non-specified epoxy resin (C09J 163/00) and 50 parts Novolak epoxy resin (C09J 163/04) is classified as (C09J 163/00, C08L 63/04), (C09J 163/04, C08L 63/00) and in C08L 2205/02.
Example 3: An adhesive composition based of a polyepoxide and containing CaCO3 is classified as (C09J 163/00, C08K 3/26). If this composition contains also a polyamide, then the classification will be (C09J 163/00, C08L 77/00, C08K 3/26).
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Adhesive compositions | Bonding compositions |
Bisphenol A | 4,4'-(Propane-2,2-diyl)diphenol |
Bisphenol F | 2-[(2-Hydroxyphenyl)methyl]phenol |
Bisphenol S | 4-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)sulfonylphenol |
DGEBA | Diglycidyl ether of bisphenol A |
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions comprising aromatic epoxy resins, which are multifunctional (three functions or more per molecule), from the condensation of phenol-formaldehyde resins and epichlorhydrin.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Epoxy resins containing three or more epoxy groups per molecule |
Novolak | Novolac |
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions comprising cyclic heteroaromatic resin with three glycidyl groups: from the reaction of cyanuric acid with excess epichlorhydrin.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Epoxy compounds containing three or more epoxy groups, heterocyclic compounds | |
Compositions of triglycidylisocyanurates |
Teroxirone Tris(2,3-epoxypropyl) isocyanurate: TGICTEPIC |
|
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions comprising macromolecular unsaturated compounds, which are epoxidised in a further step (e.g. oxidation by H2O2), such as fatty acid-based polymers or epoxidised rubbers
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Epoxy resins obtained by epoxydation of unsaturated precursor | |
Compositions of epoxidised polymersied polyenes |
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions comprising epoxy resins chemically modified by the reaction of unsaturated compounds
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Epoxy-functional Polycondensates modified by chemical after treatment | |
Epoxy-functional Polycondensates modified by chemical after treatment, with unsaturated monoacids | |
Epoxy-functional Polycondensates modified by chemical after-treatment, with acrylic or methacrylic acids | |
Epoxy-functional Polycondensates modified by chemical after treatment, with fatty acids |
This place covers:
Adhesives and adhesive processes (but see below for adhesive processes) based on macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions forming a carbon-carbon bond in the main chain other than polymers obtained by reactions only involving the polyaddition of carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds (wherein in the latter case the reactive carbon-carbon group stays intact without cleavage of fragments). The macromolecular compounds are themselves classified in C08G 61/00-C08G 61/127.
Macromolecular compounds per se obtained by polyaddition reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds wherein the reactive carbon-carbon group stays intact without cleavage of fragments are classified in C08F. Compositions based on monomers of such polymers are also classified in C08F.
This main group includes metathesis polymerization products, but it does not include common addition polymers such as polymethylmethacrylate.
Macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions forming a carbon-carbon bond in the main chain other than polymers obtained by reactions only involving the polyaddition of carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds are classified in C08G 61/00. Compositions based on monomers of such polymers are also placed in C08G 61/00.
Coating compositions and other polymer compositions for similar uses, e.g. paints, inks, woodstains and printing pastes, are classified in C09D.
Relationship with other main groups of the same subclass C09J:
Adhesives based on polymers prepared by condensation reactions of aldehydes or ketones with phenols only are classified in groups C09J 161/04 - C09J 161/16, since C09J 161/00-C09J 161/34 take precedence.
For the same reasons, adhesives based on condensation polymers of aldehydes or ketones only are classified in C09J 161/02. Adhesives of polymers, which may otherwise be formed by carbon-carbon bond formation, but which are prepared by condensation reactions other than those involving the formation of carbon-carbon bonds in the main chain are classified in the appropriate groups, e.g. C09J 179/04 for adhesives based on polypyrrole formed from amines and polyketones. Polyketone-based adhesives are classified in C09J 173/00.
This place does not cover:
Adhesives based on rubbers or on their derivatives | |
Adhesives based on condensation polymers of aldehydes or ketones |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adhesive bandages, dressings or absorbent pads | |
Surgical adhesives | |
Catalysts in general | |
Layered products characterised by the connection of layers, using an adhesive | |
Layered products essentially comprising synthetic resin | |
Containers, packaging elements or packages for web or tape-like material, e.g. dispenser for dispensing tape | |
Condensation polymers of aldehydes with phenols only; compositions comprising such polycondensates | |
Condensation polymers of aldehydes with aromatic hydrocarbons or halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons only; (adhesive) compositions comprising such polycondensates | |
Macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions forming a carbon-to-carbon link in the main chain of the macromolecule | |
Poly(ether ketones) obtained by reactions forming an ether link in the main chain of the macromolecule; (adhesive) compositions comprising such polycondensates | |
Polycondensates having nitrogen-containing heterocyclic rings in the main chain of the macromolecules obtained by reactions forming a linkage containing nitrogen, including polypyrroles; compositions comprising such polycondensates | |
Complementary aspects concerning C08G 61/00 | |
Bonding of a preformed macromolecular material to the same or other solid material such as metal, glass, leather, e.g. using adhesives | |
Connecting constructional elements or machine parts by sticking or pressing them together, e.g. cold pressure welding ; Compositions and coating compositions based on polymers according to main group C08G 61/00 are classified in main groups | |
Connecting constructional elements or machine parts by sticking or pressing them together, e.g. cold pressure welding |
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Addition polymers | An addition polymer is a polymer which is formed by an addition reaction (polyaddition), where monomers bond together via rearrangement of bonds without the loss of any atom or molecule. This is in contrast to a condensation polymer which is formed by a condensation reaction where a molecule, such as water, is lost during the formation. |
Condensation polymers | Condensation polymers are macromolecules formed by means of reactions in which water or some other simple molecule is eliminated from 2 or more monomer molecules as they combine to form the polymer (polycondensation). |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
ADMET | Acyclic diene metathesis |
ROMP | Ring-opening metathesis polymerisation |
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions wherein the major component is a polymer of C08G 63/00.
This place does not cover:
Adhesives based on polyester-amides | |
Adhesives based on polyester-imides |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adhesive processes in general | |
Adhesives in the form of films or foils | |
Chemical aspects of and materials for bandages, dressings, absorbent pads or surgical articles | |
Layered products comprising polyesters | |
Bonding of preformed macromolecular material | |
Polymer compositions of polyesters | |
Coating compositions of polyesters |
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
PBT | Polybutylene terephthalate |
PCL | Polycaprolactone |
PEA | Polyethylene adipate |
PEN | Polyethylene naphthalate |
PET | Polyethylene terephthalate |
PGA | Polyglycolic acid |
PHA | Polyhydroxyalkanoate |
PLA | Polylactic acid |
PTT | Polytrimethylene terephthalate |
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions wherein the major component is a polymer of C08G 64/00
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adhesive processes in general | |
Adhesives in the form of films or foils | |
Layered products comprising polycarbonates | |
Bonding of preformed macromolecular material | |
Polymer compositions of polycarbonates | |
Coating compositions of polycarbonates | |
Polycarbonate record carriers |
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
This place does not cover:
Adhesives based on polyacetals | |
Adhesives based on epoxy resins | |
Adhesives based on polythioether-ethers | |
Adhesives based on polyethersulfones |
Same rules apply as for C08L 71/00 - C08L 71/14.
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
The same rules as for C08L 73/00 - C08L 73/02 apply.
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions of polymers of C08G 18/00 or C08G 71/00.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adhesives processes | |
Preparations for medical, dental or toilet purposes | |
Processes for applying liquid materials to surfaces | |
Shaping or joining plastics | |
Mould release agents | |
Layered products comprising polyurethanes | |
Working up of polyurethanes to porous or cellular articles | |
Use of inorganic or non-macromolecular organic substances as compounding ingredients | |
Polymer compositions wherein the major component is a polymer of C08G 18/00 or C08G 71/00 | |
Coating compositions characterized by their physical nature or their effects produced | |
Coating compositions of polyurethanes or polyureas | |
Materials for sealing |
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
CPP | Copolymer polyol |
DABCO | 1,4-Diazabicyclo(2.2.2)octane |
DMPA | Dimethylol propionic acid |
EDA | Ethylene diamine |
EO | Ethylen oxide |
HDI | Hexane diisocyanate |
H12MDI | Dicyclohexylmethane diisocyanate |
IEM | Isocyanato ethyl methacrylate |
IPDI | Isophorone diisocyanate |
Jeffamine | Amine capped polyether |
MDI | 4,4-Methylenebis(phenyl)isocyanate |
PEG | Polyethyleneglycol |
PIR | Polyisocyanurate |
PMDI | Polymethylene poly(phenylisocyanate) |
PO | Propylene oxide |
PPG | Polypropylene glycol |
PTMO | Polytetramethylene oxide |
TDI | Toluene diisocyanate |
TMP | Trimethylol propane |
TMXDI | Trimethylol propane |
TPU | Tetramethylxylylene diisocyanate |
XDI | Xylylene diisocyanate |
This place covers:
Adhesives based on compositions of polyamides derived from
- omega-amino carboxylic acids or from lactams which correspond to subgroup C08G 69/02, e.g. nylon 6
- alpha-amino carboxylic which correspond to subgroups C08G 69/10
polyamines and polycarboxylic acids which correspond to subgroup C08G 69/26, e.g. nylon 66.
- aromatically bound amino and carboxyl groups of amino-carboxylic acids or of polyamines and polycarboxylic acids which correspond to subgroup C08G 69/32
- adhesives based on compositions of polyester-amides which correspond to subgroup C08G 69/44
This place does not cover:
Adhesives based on polyhydrazides | |
Adhesives based on polyamideimides or polyamide acids |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Hollow fibres membranes | |
Treatment of rubber | |
Macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions involving carbon to carbon bonds | |
Processes of polymerisation | |
Post‑polymerisation treatments | |
Macromolecular compounds obtained otherwise than by reactions only involving carbon to carbon bonds | |
Processes of treating or compounding macromolecular substances | |
Processes of crosslinking | |
Manufacture of articles or shaped materials containing macromolecular substances, e.g. films | |
Coating of shaped articles made of macromolecular substances | |
Workingup of macromolecular substances to porous or cellular materials | |
Compounding ingredients | |
Tubes | |
Optical articles, optical parts, e.g. contact lenses | |
Photosensitive films | |
Printed circuits |
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
This place covers:
Adhesives compositions of:
- Polyamines or polyethyleneimines.
- Polycondensates having nitrogen-containing heterocyclic rings in the main chain, e.g. polyhydrazides, polyhydrazides, polytriazoles, polyamino-triazoles, polybenzimidazoles or polyoxadiazoles.
- Polyimides, polyester-imides, polyamide-imides, polyamide acids, (unsaturated) polyimide precursors.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Hollow fibres membranes | |
Treatment of rubber | |
Macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions involving carbon to carbon bonds | |
Processes of polymerisation | |
Post‑polymerisation treatments | |
Macromolecular compounds obtained otherwise than by reactions only involving carbon to carbon bonds | |
Processes of treating or compounding macromolecular substances | |
Processes of crosslinking | |
Manufacture of articles or shaped materials containing macromolecular substances, e.g. films | |
Coating of shaped articles made of macromolecular substances | |
Working‑up of macromolecular substances to porous or cellular materials | |
Compounding ingredients | |
Tubes | |
Optical articles, optical parts, e.g. contact lenses | |
Photosensitive films | |
Printed circuits |
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions comprising macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions forming in the main chain of the macromolecule a linkage containing silicon with or without sulfur, nitrogen, oxygen or carbon only (Si-based macromolecular compounds in accordance with C08G 77/00 or "Si-based polymers" hereunder), for example:
- polysilicates (corresponding to group C08G 77/02),
- polysiloxanes (corresponding to group C08G 77/04),
- block- or graft-copolymers containing polysiloxane sequences (corresponding to group C08G 77/42) or
- polymers in which at least two but not all the silicon atoms are connected by linkages other than oxygen atoms (corresponding to group C08G 77/48).
Adhesive compositions of derivatives of such polymers.
Adhesive compositions made from mixtures of different reactive silanes (sol-gel compositions) are classified in the respective subclass of C09J 183/00. It is assumed that in such mixtures there has always been formed a siloxane polymer via hydrolysis/condensation.
The groups for adhesive compositions are structured in analogy to the coating compositions C09D 183/00.
C-Sets classification:
In this group, multiple C-Sets, specifically C-Sets #C9Jc, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si), #C9Jc(Si)2, #C9Jf(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)2 are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of classification of the following places
- See C-Sets #C9Jc, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si) in C09J 101/00.
- See C-sets #C9Jc(Si)2 and #C9Jf(Si)2 present in this group below.
C-Sets statement: #C9Jc(Si)2, #C9Jf(Si)2
#C9Jc(Si)2, and #C9Jf(Si)2 are a special use of #C9Dc and #C9Df, are applied for a composition comprising two or more Si-based polymers in accordance with C08G 77/00.
- In groups C09J 183/02 - C09J 183/16, the feature relating to an adhesive composition comprising one Si-based polymer in majority with one Si-based polymer in minority optionally with non Si-based polymer is classified in the form of C-Sets.
- In #C9Jc(Si)2, the base symbol, representing the polymer in majority, is taken from the groups C09J 183/02 - C09J 183/16, whereas the subsequent symbol(s) representing the silicon-based macromolecular compound(s) in minority is (are) taken from the group C08L 83/00 and optionally from the groups C08L 1/00 - C08L 101/16 for any other polymer.
- In #C9Jf(Si)2, the base symbol, representing the polymer in majority, is taken from the groups C09J 183/02 - C09J 183/16, whereas the subsequent symbol(s) representing the silicon-based macromolecular compound(s) in minority is (are) taken from the group C08L 83/00 and optionally from the groups C08L 1/00 - C08L 101/16 for any other polymer and further subsequent symbols representing compound(s) used as an additive(s), is (are) taken from the groups C08K 3/00 - C08K 13/08.
- In addition to C-Sets, one or more additional symbols are allocated, which are selected from the range C08G 77/02 - C08G 77/62 corresponding to each of the Si-based macromolecular compound components detailed in the C-Set.
- A single symbol is given according to the macromolecular constituent present in the highest proportion.
C-Sets syntax rules:
- C-Sets of #C9Jc(Si)2 shall contain at least two symbols.
- C-Sets of #C9Jf(Si)2 shall contain at least three symbols.
- While duplicate symbols are allowed in these C-Sets, only one symbol selected from the range C09J 183/02 - C09J 183/16 is permitted per C-Set.
C-Sets examples:
- #C9Jc
Example 1: An adhesive composition comprising, in descending amounts by weight, an epoxy-substituted polysiloxane in accordance with C08G 77/14 and a polyester in accordance with C08G 63/02 is classified as (C09J 183/06, C08L 67/02) and in C08G 77/14 (ADD).
Example 2: An adhesive composition comprising, in descending amounts by weight, a polyester in accordance with C08G 63/02 and an alkoxy-substituted polysiloxane in accordance with C08G 77/18 is classified as (C09J 167/02, C08L 83/04) and in C08G 77/18 (ADD).
- #C9Jc(Si)
Example 3: An adhesive composition comprising, in descending amounts by weight, a polyester in accordance with C08G 63/02, an amine-substituted polysiloxane in accordance with C08G 77/26 and an epoxy-substituted polysiloxane in accordance with C08G 77/14 is classified as (C09J 167/02, C08L 83/08, C08L 83/00) and in C08G 77/14 and C08G 77/26.
- #C9Jc(Si)2
Example 4: An adhesive composition comprising, in descending amounts by weight, a vinyl-substituted polysiloxane in accordance with C08G 77/20 and a polysiloxane bearing Si-H groups in accordance with C08G 77/12 is classified as (C09J 183/04, C08L 83/00) and in C08G 77/12 (ADD) and C08G 77/20 (ADD).
Example 5: An adhesive composition comprising, in descending amounts by weight, a vinyl-substituted polysiloxane in accordance with C08G 77/20, an epoxy-substituted polysiloxane in accordance with C08G 77/14 and a polysiloxane bearing Si-H groups in accordance with C08G 77/12 is classified as (C09J 183/04, C08L 83/00, C08L 83/00) and in C08G 77/12 (ADD), C08G 77/14 (ADD) and C08G 77/20 (ADD).
Example 6: An adhesive composition comprising, in descending amounts by weight, a silanol-substituted polysiloxane in accordance with C08G 77/16, a polysiloxane bearing Si-H groups in accordance with C08G 77/12 and a polyester in accordance with C08G 63/02 is classified as (C09J 183/04, C08L 83/00, C08L 67/02) and in C08G 77/12 (ADD) and C08G 77/16 (ADD).
Example 7: An adhesive composition comprising, in descending amounts by weight, a halogen group-bearing polysiloxane in accordance with C08G 77/24, a polyester in accordance with C08G 63/02 and an epoxy-substituted polysiloxane in accordance with C08G 77/14 is classified as (C09J 183/08, C08L 67/02, C08L 83/00) and in C08G 77/14 (ADD) and C08G 77/24 (ADD).
- #C9Jf
Example 8: An adhesive composition comprising, in descending amounts by weight, an epoxy-substituted polysiloxane in accordance with C08G 77/14 and a polyester in accordance with C08G 63/02 and a resorcinol phosphate is classified as (C09J 183/06, C08L 67/02, C08K 5/523) and in C08G 77/14 (ADD).
Example 9: An adhesive composition comprising, in descending amounts by weight, a polyester in accordance with C08G 63/02 and an alkoxy-substituted polysiloxane in accordance with C08G 77/18 and silica is classified as (C09J 167/02, C08L 83/04, C08K 3/36) and in C08G 77/18 (ADD).
- #C9Jf(Si)
Example 10: An adhesive composition comprising, in descending amounts by weight, a polyester in accordance with C08G 63/02, an amine-substituted polysiloxane in accordance with C08G 77/26 and an epoxy-substituted polysiloxane in accordance with C08G 77/14 and carbon black is classified as (C09J 167/02, C08L 83/08, C08L 83/00, C08K 3/04) and in C08G 77/14 (ADD) and C08G 77/26 (ADD).
- #C9Jf(Si)2
Example 11: An adhesive composition comprising, in descending amounts by weight, a vinyl-substituted polysiloxane in accordance with C08G 77/20 and a polysiloxane bearing Si-H groups in accordance with C08G 77/12 and silica is classified as (C09J 183/04, C08L 83/00, C08K 3/36) and in C08G 77/12 (ADD) and C08G 77/20 (ADD).
Example 12: An adhesive composition comprising, in descending amounts by weight, a vinyl-substituted polysiloxane in accordance with C08G 77/20, an epoxy-substituted polysiloxane in accordance with C08G 77/14 and a polysiloxane bearing Si-H groups in accordance with C08G 77/12 and silica is classified as (C09J 183/04, C08L 83/00, C08L 83/00, C08K 3/36) and in C08G 77/12 (ADD), C08G 77/14 (ADD) and C08G 77/20 (ADD).
Example 13: An adhesive composition comprising, in descending amounts by weight, a silanol-substituted polysiloxane in accordance with C08G 77/16, a polysiloxane bearing Si-H groups in accordance with C08G 77/12 and a polyester in accordance with C08G 63/02 and a phenol is classified as (C09J 183/04, C08L 83/00, C08L 67/02, C08K 5/13) and in C08G 77/12 (ADD) and C08G 77/16 (ADD).
Example 14: An adhesive composition comprising, in descending amounts by weight, a halogen group-bearing polysiloxane in accordance with C08G 77/24, a polyester in accordance with C08G 63/02 and an epoxy-substituted polysiloxane in accordance with C08G 77/14 and a phenol is classified as (C09J 183/08, C08L 67/02, C08L 83/00, C08K 5/13) and in C08G 77/14 (ADD) and C08G 77/24 (ADD).
C-Sets searches:
Since multiple C-Sets classifications are applicable to this group C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J 101/00 and this group above, as well as other related subclasses, e.g. C08K and C08L.
In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Application of siloxanes as pressure sensitive adhesives (PSAs) | |
Release adhesive composition on which the PSA is applied |
From 01.09.2010 onwards, an adhesive composition containing two or more siloxanes is searched and classified in (C09J 183/04, C08L 83/04), and then given additional Indexing Codes for the respective siloxanes, e.g. C08G 77/12 for Si-H siloxane and C08G 77/20 for vinyl-siloxane.
This place does not cover:
Adhesive compositions obtained by polymerising a compound having a carbon-to-carbon double bond on to a polysiloxane |
Attention is drawn to the CPC Definitions of C08G 77/42.
Attention is drawn to the CPC Definitions of the respective C08G 77/00 classes.
Attention is drawn to the CPC Definitions of the respective C08G 77/00 classes.
C09J 183/10 takes precedence over this group.
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions based on macromolecular compounds corresponding to groups C08G 79/00, e.g. containing Al or Sn.
The same rules as for C08L 85/00-C08L 85/04 apply.
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions of unspecific macromolecular compounds, obtained by step polymerisation reactions or addition polymerization reactions.
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
This place covers:
Covalently or ionically crosslinked gels are classified in C08H.
A composition based on proteins or derivatives thereof is classified in C08L.
Coating compositions based on proteins or derivatives thereof are classified in C09D.
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Foodstuff preparations |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Composition comprising proteins or protein derivatives | |
Coating composition comprising proteins or protein derivatives |
Last place priority rule:
Within each subgroup of this group, in the absence of an indication to the contrary, classification is made in the last appropriate place.
Classification guidance:
- Reference A23J 3/00 is non-limiting in the subclass/main group/subgroup C08L 89/00. CPC will be updated/corrected once this inconsistency is resolved in IPC.
- The subject-matter disclosed in both the claims and the examples of a patent document is to be classified.
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
- If C09J 189/00 relates to an adhesive composition of proteins or derivatives, classification is given in the form of C-Sets (i.e. #C9J(c)) according to the relative weight percentage of the polymer constituents.
- The polymer in majority is given a symbol as a base symbol, and the polymers in minority are given symbols as subsequent symbols in the form of C-Sets.
- In addition, a single symbol is given according to the macromolecular constituent present in the highest proportion.
- If all the constituents are present in equal weight percentage, the composition is classified according to each of these constituents.
- In the case that several polymers can be in majority, separate C-Sets should be made based on each polymer in majority and its component(s) in minority.
- Orthogonal indexing codes C08L 2201/00 - C08L 2555/86 are also given if applicable.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions based on drying oils, vulcanised oils, e.g. factice, linoxyn or (mineral) waxes.
Covalently or ionically crosslinked gels are classified in C08H.
A composition based on oils, fats, waxes or derivatives thereof is classified in C08L.
Coating compositions based on oils, fats, waxes or derivatives thereof are classified in C09D.
The use of oils, fats and waxes in cosmetics and other toilet preparations is further classified in one of A61Q together with A61K 8/92.
Galenical compositions comprising natural resins are classified in A61K 9/00.
The use of oils, fats and waxes as carriers in medicinal preparations is classified in A61K 47/44.
The use of oils, fats and waxes in lubricants is classified in C10M.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Vulcanised oils, e.g. factice | |
Composition comprising oils, fats or waxes | |
Coating composition comprising oils, fats or waxes | |
Polishing compositions, ski waxes | |
Soaps, detergent compositions |
Last place priority rule:
Within each subgroup of this group, in the absence of an indication to the contrary, classification is made in the last appropriate place.
Classification guidance:
- The subject-matter disclosed in both the claims and the examples of a patent document is to be classified.
- Oils, fats and waxes in solution, or together with other macromolecular compounds, or together with an inorganic or non-macromolecular organic additive are considered as a composition and are thus classified according to the rules of C08L.
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
- If C09J 191/00 relates to an adhesive composition containing oils, fats and waxes, classification is given in the form of C-Sets according to the relative weight percentage of the polymer constituents.
- The polymer in majority is given a symbol as a base symbol, and the polymers in minority are given symbols as subsequent symbols in the form of C-Sets.
- In addition, a single symbol is given according to the macromolecular constituent present in the highest proportion.
- If all the constituents are present in equal weight percentage, the composition is classified according to each of these constituents.
- In the case that several polymers can be in majority, separate C-Sets should be made based on each polymer in majority and its component(s) in minority.
- Orthogonal indexing codes C08L 2201/00 - C08L 2555/86 are also given if applicable.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
This place covers:
Adhesives or binders based on natural resins or their derivatives corresponding to the following groups: C09F 1/00
Covalently or ionically crosslinked gels are classified in C08H.
A composition based on natural resins or their derivatives is classified in C08L.
Coating compositions based on natural resins or their derivatives are classified in C09D.
Grafted natural resins obtained by reaction of an unsaturated monomer onto a natural resin are classified in C08F 253/00.
Galenical compositions comprising natural resins are classified in A61K 9/00.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Composition comprising natural resins | |
Coating composition comprising natural resins | |
Purification or chemical modification of natural resins | |
Polishing compositions |
Last place priority rule:
Within each subgroup of this group, in the absence of an indication to the contrary, classification is made in the last appropriate place.
Classification guidance:
- The subject-matter disclosed in both the claims and the examples of a patent document is to be classified.
- Adhesive compositions based on natural resins in solution, or together with other macromolecular compounds, or together with an inorganic or non-macromolecular organic additive are considered as a composition and are thus classified according to the rules of C09J.
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
- If C09J 193/00 relates to an adhesive composition containing natural resins, classification is given in the form of C-Sets according to the relative weight percentage of the polymer constituents.
- The polymer in majority is given a symbol as a base symbol, and the polymers in minority are given symbols as subsequent symbols in the form of C-Sets.
- In addition, a single symbol is given according to the macromolecular constituent present in the highest proportion.
- If all the constituents are present in equal weight percentage, the composition is classified according to each of these constituents.
- In the case that several polymers can be in majority, separate C-Sets should be made based on each polymer in majority and its component(s) in minority.
- Orthogonal indexing codes C08L 2201/00 - C08L 2555/86 are also given if applicable.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
This place covers:
- Compositions of bitumen or asphalt used for adhesive applications other than adhering aggregate.
- Aqueous compositions of bitumen or asphalt, e.g. emulsions, used for adhesive applications other than adhering aggregate.
Relationship with the main group C08L 95/00:
Since the main group C09J 195/00 is seen as a "related field" of C08L 95/00, explicit reference is made to all references, definitions, terms and rules explained in said main group C08L 95/00.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Coating or adhering of aggregate | |
Coating applications | |
Sealing materials |
Classification guidance:
- The subgroup C09J 195/00 or C09J 195/005 should be used only if the claims of the application explicitly encompass a bituminous adhesive as such.
- In addition a C08L 95/00 code in combination with the relevant orthogonal indexing code(s) (C08L 2555/00 - C08L 2555/86) characterising essential features should also be given if the adhesive composition is mainly characterised by the bituminous composition, either by its constituents and/or by its parameters.
- Example 1: An adhesive composition for adhering 2 metal substrates to each other comprising bitumen is classified in C09J 195/00.
- Example 2: An adhesive composition for adhering aggregate comprising bitumen is classified in C08L 95/00.
- Example 3: An adhesive composition comprising bitumen for mere coating a substrate is classified in C09J 195/00.
- Example 4: An adhesive composition comprising a mixture of bitumen and bees wax is classified in C09J 195/00 and C08L 95/00 and C08L 2555/64.
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
In this group, several terms (or expressions) are used having the meaning as indicated in the group C08L 95/00
In this group, several synonyms and keywords are used as indicated in the group C08L 95/00
This place covers:
Covalently or ionically crosslinked gels are classified in C08H.
This place does not cover:
Adhesives based on polysaccharides |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adhesive or binder based on natural macromolecular compounds or of derivatives thereof not provided for in groups C08L 89/00 - C08L 97/00, e.g. flours | |
Macromolecular compounds derived from lignin | |
Macromolecular compounds derived from lignocellulosic materials | |
Composition comprising lignin-containing materials | |
Coating composition comprising lignin-containing materials |
Last place priority rule:
Within each subgroup of this group, in the absence of an indication to the contrary, classification is made in the last appropriate place.
Classification guidance:
- The subject-matter disclosed in both the claims and the examples of a patent document is to be classified.
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
- If C09J 197/00 relates to a Lignin-containing adhesive composition, classification is given in the form of C-Sets (i.e. #C9J(c)) according to the relative weight percentage of the polymer constituents.
- The polymer in majority is given a symbol as a base symbol, and the polymers in minority are given symbols as subsequent symbols in the form of C-Sets.
- In addition, a single symbol is given according to the macromolecular constituent present in the highest proportion.
- If all the constituents are present in equal weight percentage, the composition is classified according to each of these constituents.
- In the case that several polymers can be in majority, separate C-Sets should be made based on each polymer in majority and its component(s) in minority.
- Orthogonal indexing codes C08L 2201/00-C08L 2555/86 are also given if applicable.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
This place covers:
Adhesives based on natural macromolecular compounds or derivatives thereof, corresponding to the following groups: C08H 99/00
Covalently or ionically crosslinked gels are classified in C08H.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adhesive/binder based on starch or derivatives thereof | |
Adhesive/binder based on lignin-containing materials, e.g. lignin, cork, lignocellulose or wood | |
Natural macromolecular compounds or derivatives thereof | |
Composition comprising natural macromolecular compounds | |
Coating compositions comprising natural macromolecular compounds |
Last place priority rule:
Within each subgroup of this group, in the absence of an indication to the contrary, classification is made in the last appropriate place.
Classification guidance:
- The subject-matter disclosed in both the claims and the examples of a patent document is to be classified.
- Adhesive composition of natural macromolecular materials in solution, or together with other macromolecular compounds, or together with an inorganic or non-macromolecular organic additive are considered as a composition and are thus classified according to the rules of C09J.
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
- If C09J 199/00 relates to a Lignin-containing adhesive composition, classification is given in the form of C-Sets (i.e. #C9J(c)) according to the relative weight percentage of the polymer constituents.
- The polymer in majority is given a symbol as a base symbol, and the polymers in minority are given symbols as subsequent symbols in the form of C-Sets.
- In addition, a single symbol is given according to the macromolecular constituent present in the highest proportion.
- If all the constituents are present in equal weight percentage, the composition is classified according to each of these constituents.
- In the case that several polymers can be in majority, separate C-Sets should be made based on each polymer in majority and its component(s) in minority.
- Orthogonal indexing codes C08L 2201/00 - C08L 2555/86 are also given if applicable.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
This place covers:
Adhesive compositions based on unspecified macromolecular compounds.
C-Sets classification:
In this group, C-Sets (#C9Jc, #C9Je, #C9Jf, #C9Jc(Si) and #C9Jf(Si)) are used for classification. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the Special rules of C09J 101/00.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses. In addition, #C8Lz, #C9Dz, and #C9Jz Search Rules may be followed to search for polymers in documents classified prior to April 2012.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
In this group, several terms (or expressions) are used having the meaning as indicated in the group C08L 95/00.
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms:
In this group, several synonyms and keywords are used as indicated in the group C08L 95/00.
This place covers:
A symbol from C09J 5/00 or C09J 7/00 must be allocated for the indexing codes under C09J 2203/00 to be allocated as well.
Example:
An adhesive process used in the fabrication of shoes involving the pre-treatment of a substrate is classified in C09J 2203/362 and in C09J 5/02.
An adhesive tape with a paper carrier used as masking tape for painting is classified in C09J 7/21 and in C09J 2203/31.
This place covers:
Additional features of adhesives in the form of films or foils (C09J 7/00).
This place covers:
Additional features of adhesives in the form of films or foils with parameters being the characterising feature when the adhesive itself is not specified.
This place covers:
Additional features of adhesives in the form of films or foils characterised by the presence of essential components.
This place covers:
Classification guidance:
The indexing scheme of C09J 2400/00 covers the use of materials in adhesive processes in general or adhesives in the form of films or foils and is used as single symbols or in C-Sets (in the case of blends or copolymers) in conjunction with groups C09J 5/00 and C09J 7/00.
Use of indexing codes as single symbols:
In groups C09J 2401/00 - C09J 2499/008, each indent within a given group points to a particular material, monomer or (co)polymer in a specific layer, e.g.
C09J 2401/00: presence of cellulose in the adhesive layer
C09J 2401/001: presence of cellulose in the barrier layer
C09J 2401/003: presence of cellulose in the primer coating
C09J 2401/005: presence of cellulose in the release coating
C09J 2401/006: presence of cellulose in the substrate
C09J 2401/008: presence of cellulose in the pretreated surface to be joined
Orthogonal indexing codes within C09J 2400/00 – C09J 2499/008 can be allocated as single symbol(s) and/or in C-Sets.
Combination sets (C-Sets):
C-Sets statement: #C9Jg
- In groups C09J 2400/00 – C09J 2499/008 blends of material or resins used within the same layer of adhesives in the form of films or foils are classified in the form of C-Sets.
- In #C9Jg, the base symbol, representing the first material or (co)polymer in a given layer, is taken from groups C09J 2400/00 – C09J 2499/008, whereas the subsequent symbol(s), representing the second or further material or (co)polymer in the same layer, is (are) taken from the corresponding groups in C09J 2400/00 – C09J 2499/008.
C-Sets syntax rules:
- Each C-Set shall contain two or more symbols.
- Duplicate symbols are allowed in these C-Sets.
- In these C-Sets the symbols are arranged in alphanumerical order.
C-Sets examples:
- #C9Jg: A blend of a poly(meth)acrylate polymer (C09J 2433/00) and a polyolefin resin (C09J 2423/00) in an adhesive layer is classified as (C09J 2423/00, C09J 2433/00).
- #C9Jg: A blend of two distinct poly(meth)acrylate polymers (C09J 2433/00) in an adhesive layer is classified as (C09J 2433/00, C09J 2433/00).
- #C9Jg: A blend of a poly(meth)acrylate (C09J 2433/001) and PVC resin (C09J 2427/001) in a barrier layer is classified as (C09J 2427/001, C09J 2433/001).
- #C9Jg: A blend of a polyamide (C09J 2477/003), polyimide (C09J 2479/083), and a polyester (C09J 2467/003) resin in a primer coating layer is classified as (C09J 2467/003, C09J 2477/003, C09J 2479/083).
- #C9Jg: A blend of a polyethylene (C09J 2423/046) and polypropylene resin (C09J 2423/106) in a substrate layer is classified as (C09J 2423/046, C09J 2423/106).
- #C9Jg: A blend in a pretreated surface to be joined of a polyester (C09J 2467/008) and a polycarbonate resin (C09J 2469/008) is classified as (C09J 2467/008, C09J 2469/008).
a.
C-Sets statement: #C9Jh
- In groups C09J 2400/00 – C09J 2499/008, the nature of the monomers in a (co)polymer used within a given layer of adhesives in the form of films or foils is classified in the form of C-Sets.
- In #C9Jh, the base symbol, representing the first monomer in a (co)polymer in a given layer, is taken from groups C09J 2400/00 – C09J 2499/008, whereas the subsequent symbols, representing the second or further monomer in a (co)polymer in the same layer, are taken from the corresponding groups in C09J 2400/00 – C09J 2499/008. In addition, the indexing code C09J 2301/414 must be given as a separate symbol.
b.
C-Sets syntax rules:
- Each C-Set shall contain two or more symbols.
- Duplicate symbols are allowed in these C-Sets.
- In these C-Sets the symbols are arranged in alphanumerical order.
c.
C-Sets examples:
- #C9Jh: A copolymer of polyethylene (C09J 2423/04) and polyvinyl alcohol (C09J 2429/00) in an adhesive layer is classified as (C09J 2423/04, C09J 2429/00) and in C09J 2301/414.
- #C9Jh: A copolymer of a tetrafluoroethylene (C09J 2427/005) and ethylene (C09J 2423/045) in a release coating layer is classified as (C09J 2423/045, C09J 2427/005) and in C09J 2301/414.
d.
For searches using C-Sets:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Sets classification rules described in C09J and related subclasses.