CPC Definition - Subclass B29D
This place covers:
the production of particular plastic or plastic-like articles; namely:
- articles with screw-threads;
- elements of slide fasteners; combined making and attaching of elements of slide fasteners;
- flat articles, e.g. films or sheets;
- optical elements, e.g. lenses, prisms;
- frames;
- gear wheels or similar articles with grooves or projections, e.g. control knobs;
- articles with corrugations;
- carriers of records containing fine grooves or impressions, e.g. disc records for needle playback, cylinder records; record discs from master stencils;
- buttons or semi-finished parts of buttons;
- hair combs or similar toothed or slotted articles;
- hollow articles;
- tubular articles;
- articles with hollow walls;
- frameless domes;
- nets or the like;
- belts or bands;
- pneumatic or solid tyres or parts thereof;
- bushes for bearings;
- footwear;
- profiled members, e.g. beams;
- wall or panel-like structures, e.g. for hulls, fuselages, or buildings;
- blades or the like, e.g. blades for turbines, propellers, or wings;
- rolling bodies, e.g. rollers, wheels, pulleys or pinions;
- countertops;
- plain balls;
- rods;
- membranes;
- sealings;
- floor coverings;
- casings, e.g. accumulator cases;
- wearing apparel, e.g. gloves, masks, bathing caps;
- filamentary materials;
- articles in the form of closed loops, e.g. rings;
- honeycomb structures;
- upholstery articles, e.g. cushions, seats;
- closure members for containers, e.g. closure caps or stoppers.
This subclass is often connected with the following subclasses, ordered decreasingly according to its incidence:
- B29C, which deals with the shaping or joining of plastics, shaping of substances in a plastic state, in general, and after-treatment of the shaped products;
- B32B, which covers layered products, i.e. products built-up of strata of flat or non-flat elements, e.g. cellular or honeycomb form, as well the method of making these products;
- G02B, which refers to optical elements, characterised by the material of which they are made, and also optical systems or apparatuses that make use thereof;
- B60C, which deals with constructional aspects of vehicle tyres or parts thereof and several aspects related to vehicle tyres, such as, tyre inflation, tyre changing, connecting valves to inflatable elastic bodies in general, devices or arrangements related to tyres;
- C08L, which contains compositions of macromolecular compounds;
- A43B, which treats of footwear or part thereof characterised by the material, shape or by the assembling of the individual parts.
This place does not cover:
Making granules | |
Making preforms | |
Shaping composites, i.e. plastics material comprising reinforcements, fillers or preformed parts, e.g. inserts | |
Methods and apparatuses for making layered products |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Plastic collars | |
Footwear or part thereof characterised by the material, shape or by the assembling of the individual parts | |
Seats or covers for all kinds of closets, made of plastic materials | |
Manufacture of rings from wire | |
Machines, devices or processes for grinding or polishing | |
Layered products, i.e. products built-up of strata of flat or non-flat elements, e.g. cellular or honeycomb form | |
Constructional form of tyres or parts thereof; tyre inflation; tyre changing | |
Connection of valves to tyres or rims | |
Sealing or packing elements; sealings formed by liquid or plastics material | |
Compositions of macromolecular compounds | |
Woven fabrics, methods of weaving and looms | |
Making nets by knotting of filamentary material, making knotted carpets or tapestries and knotting not otherwise provided for | |
Driving-belts made of plastics with reinforcement bonded by the plastic material | |
V-belts made of plastics with reinforcement bonded by the plastic material | |
Protection helmets made of plastics or plastic head-shield | |
Testing static or dynamic balance of tyres for wheeled vehicles | |
Optical elements, characterised by the material of which they are made; optical systems or apparatuses that make use thereof | |
Spectacles; sunglasses or goggles insofar as they have the same features as spectacles; contact lenses | |
Plastic bearings | |
Information storage based on relative movement between record carrier and transducer |
- The working of plastics is, as far as possible, classified primarily according to the particular shaping technique used, e.g. in subclass B29C.
- Classification according to production of particular articles in subclass B29D is restricted to:
- combined operations for making the particular article which are not fully classifiable in subclass B29C.
- Products per se are not classified in this class. However, if a product is characterised by the way it is produced and not by its structure or composition, the production method should be classified in this class.
- In this subclass it is desirable to add the Indexing Codes of the subclass B29K.
- Inventive and additional information disclosed in documents to be classified should be identified by allocation the appropriate classification symbols provided in B29D. In particular attention should be paid to the so called break down Indexing Codes, forming a further subdivision of a group or a subgroup, which are only present at additional information level.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Plastic | is defined as a macromolecular compound or composition based on such a compound |
In a plastic state | refers to a state in which the material is more or less easily deformable, locally or as a whole, by force in any direction, to assume and retain any desired shape |
Bearing | a plastic device to allow constrained relative motion between two or more parts, typically rotation or linear movement |
Bush | a thin plastic sleeve or tubular lining serving as a bearing or guide. |
Carrier of records | a kind of plastic support that enables some information to be recorded on |
This place covers:
- combined operations for making screw-threads, which are not fully classifiable in subclass B29C
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in B29D 1/00
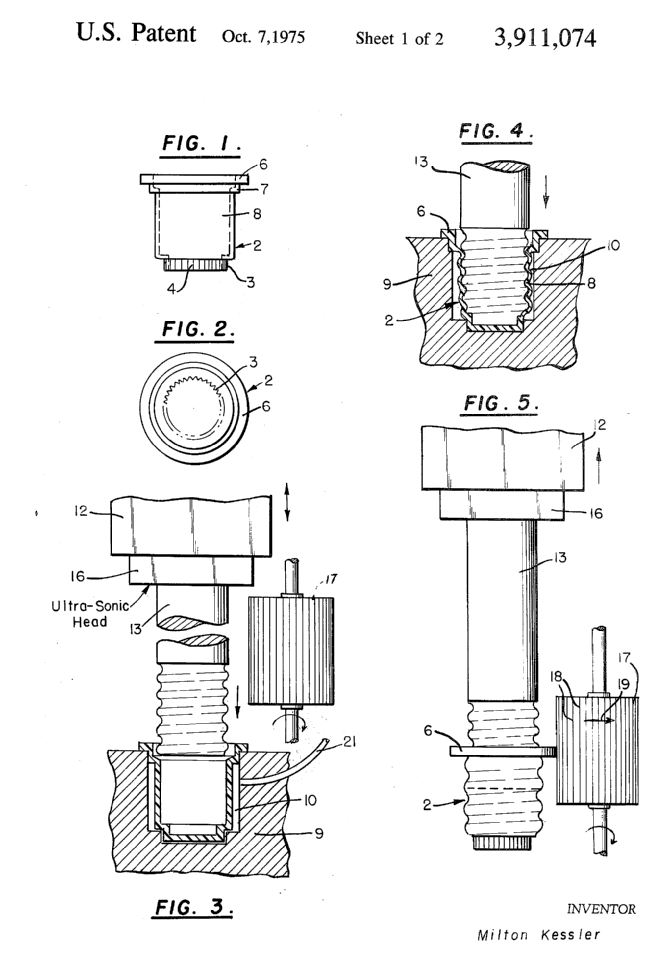
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Making screw threads by injection moulding |
This place covers:
- combined operations for making fibre reinforced screw-threads, which are not fully classifiable in subclass B29C
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in B29D 1/005
Fibrous reinforcements are at least present in the threaded part of the moulded article
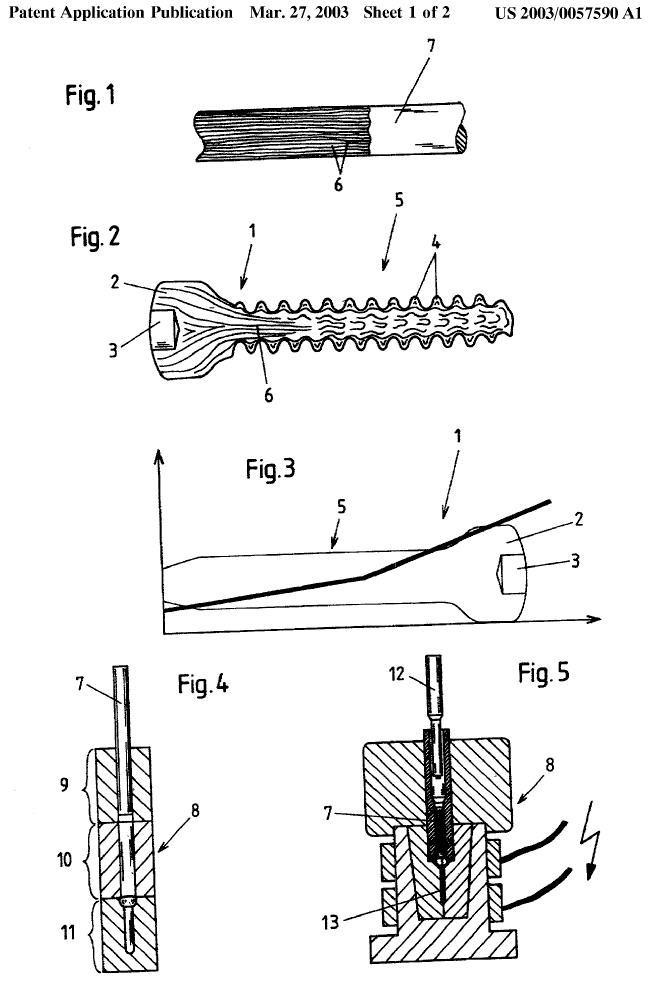
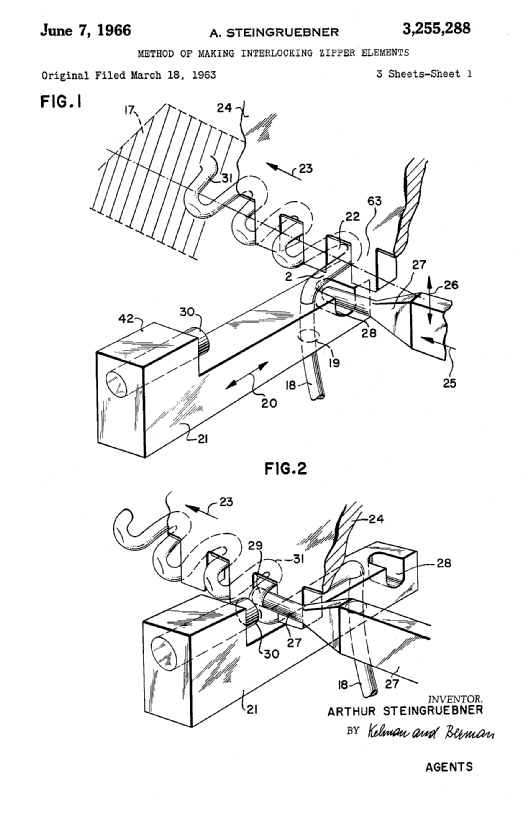
This place covers:
- combined making and attaching of elements of slide fasteners, which are not fully classifiable in subclass B29C
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in B29D 5/00
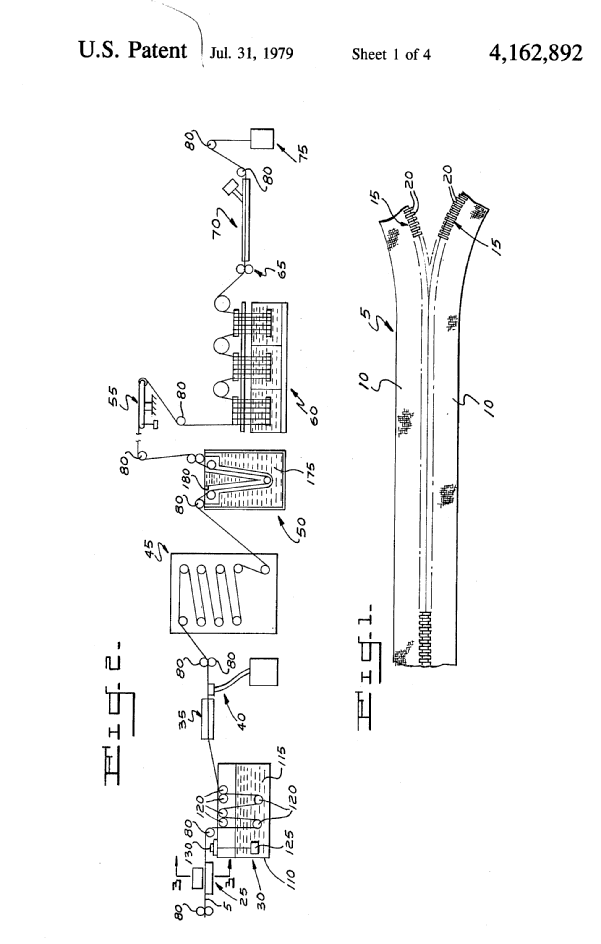
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Slide fasteners per se |
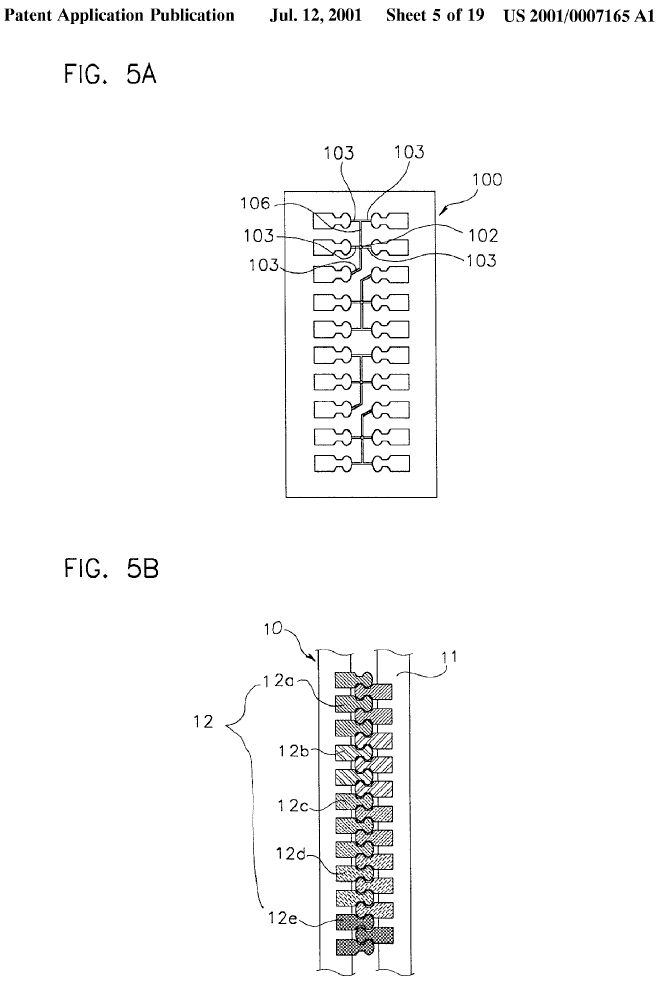
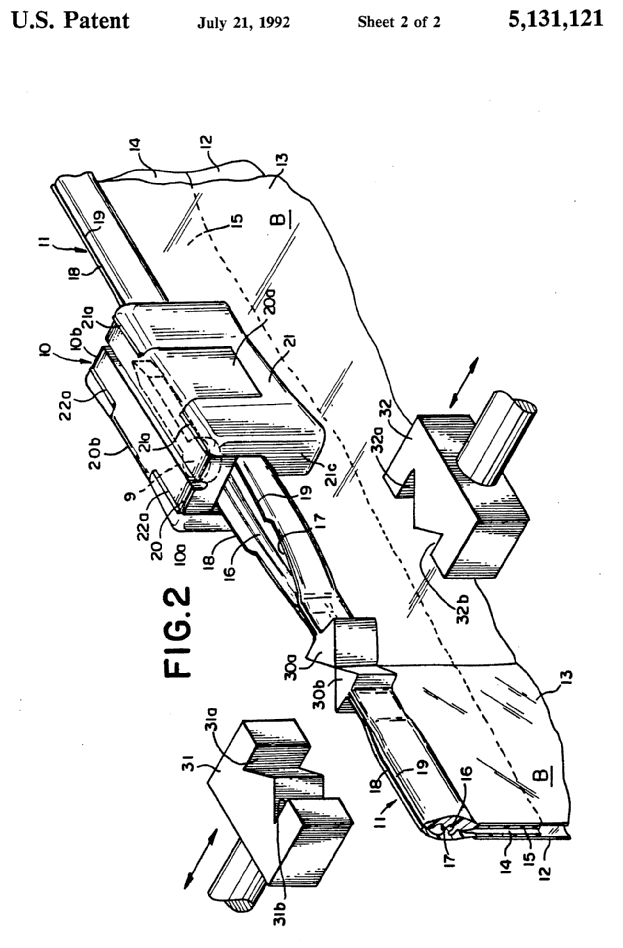
This place covers:
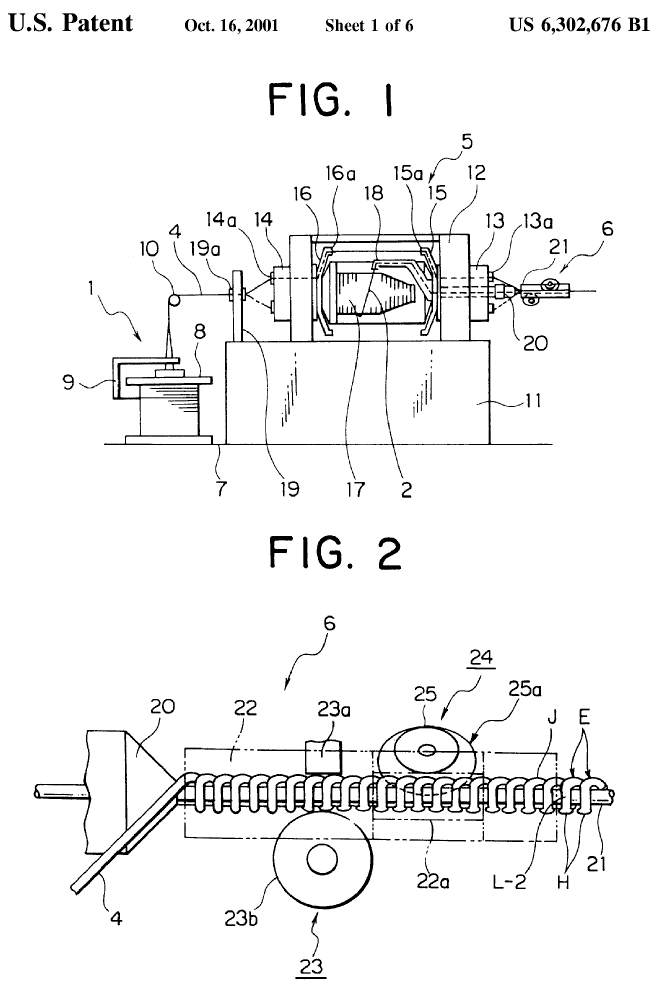
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in B29D 5/06
Helix elements for these type of fasteners commonly have the appearance of a coil compression spring as shown in figure 2 below. Such elements can however contain local protrusions, changes in cross section of the wire or other detailing
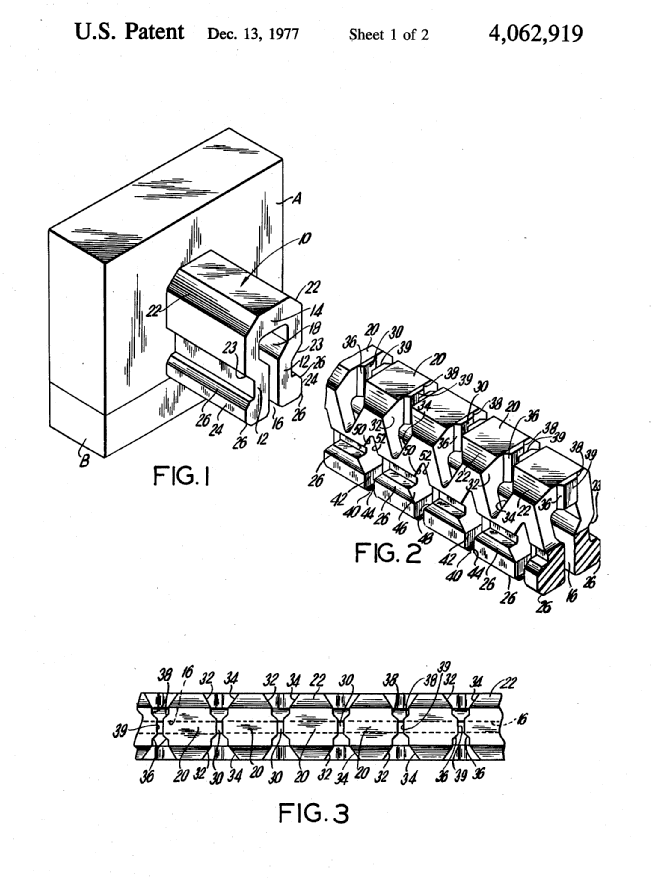
This place covers:
e.g. closure element typically used in "zip bags". The cross section of the elements being predominantly constant over the length of the slide fastener and the respective cross sectional shapes being such that it allows engaging and disengaging functionality (e.g. male/female type of cross sections)
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in B29D 5/10
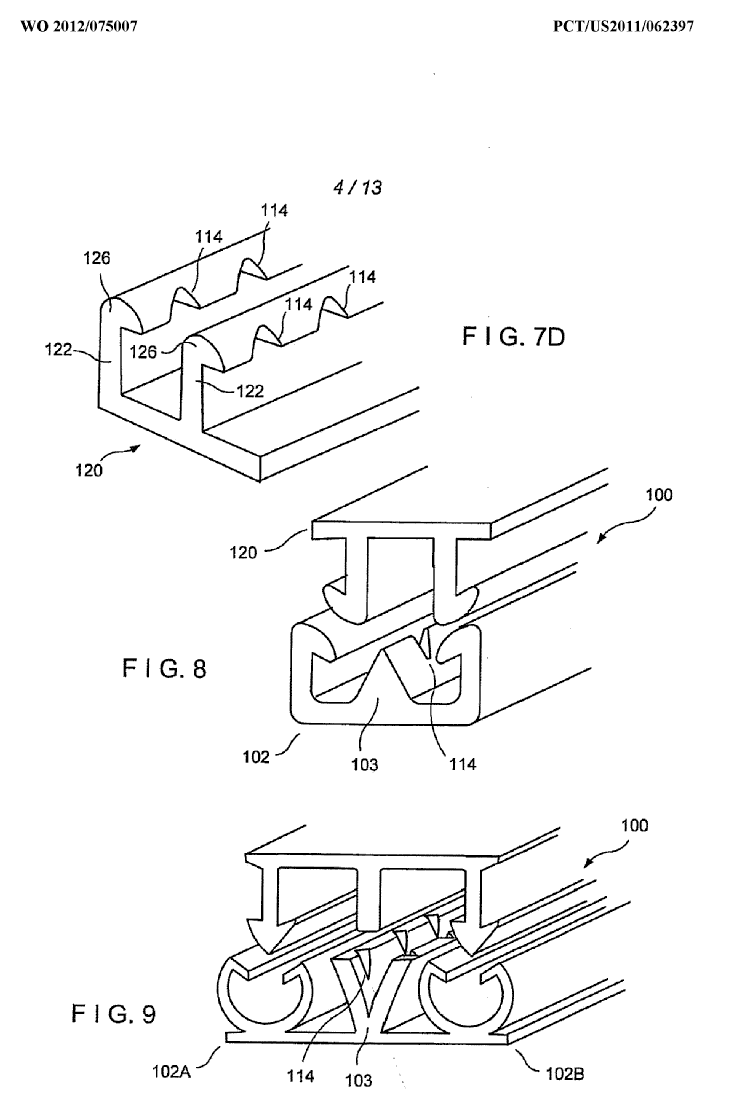
(figures 8 and 9)
This place covers:
Manufacturing of flat articles characterised by special physical or application properties (e. g. good sliding properties, high conductivity, antistatic properties, easily tearable, sealable, printable etc.)
This place does not cover:
Shaping films or sheets by stretching | |
Manufacture of films or sheets characterised by the chemical composition |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Film laminates |
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms:
- "films", "sheets", "webs", "tapes", "ribbons", "slabs", "plates", "plaques" and "boards"
This place covers:
Methods for making optical elements of polymeric materials
This place covers:
- combined operations for making frames, which are not fully classifiable in subclass B29C
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in B29D 12/00

FR2576839
This place covers:
- combined operations for making spectacle frames, which are not fully classifiable in subclass B29C
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Constructional form of spectacle frames |
This place covers:
- combined operations for making gear wheels, which are not fully classifiable in subclass B29C
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Gear wheels per se |
This place covers:
- combined operations for making articles with corrugations, which are not fully classifiable in subclass B29C
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in B29D 16/00
US5169590 

Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Corrugating metal | |
Extrusion moulding using dies or die parts movable in a closed circuit, e.g. for making corrugated articles: | |
Producing corrugated articles by winding and joining | |
Corrugating paper |
This place covers:
- combined operations for making records containing fine grooves or impressions, which are not fully classifiable in subclass B29C
- producing record discs from master stencils
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in B29D 17/00
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Recording sound or other information using formed grooves or the equivalent |
This place covers:
- combined operations for making buttons or semi-finished parts of buttons, which are not fully classifiable in subclass B29C
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in B29D 19/00
GB464736
This place covers:
- combined operations for making hair combs or similar toothed or slotted articles, which are not fully classifiable in subclass B29C
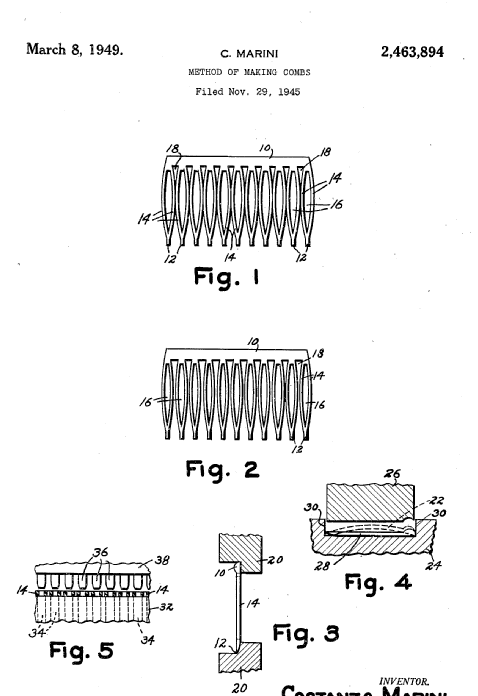
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in B29D 21/00
US2463894
This place covers:
- combined operations for making hollow articles, which are not fully classifiable in subclass B29C
This place does not cover:
Producing tubular articles | |
Producing pneumatic tyres |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Construction of fluid springs |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Tyre inner tubes with ends as such |
This place covers:
- combined operations for making tubular articles, which are not fully classifiable in subclass B29C
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in B29D 23/00
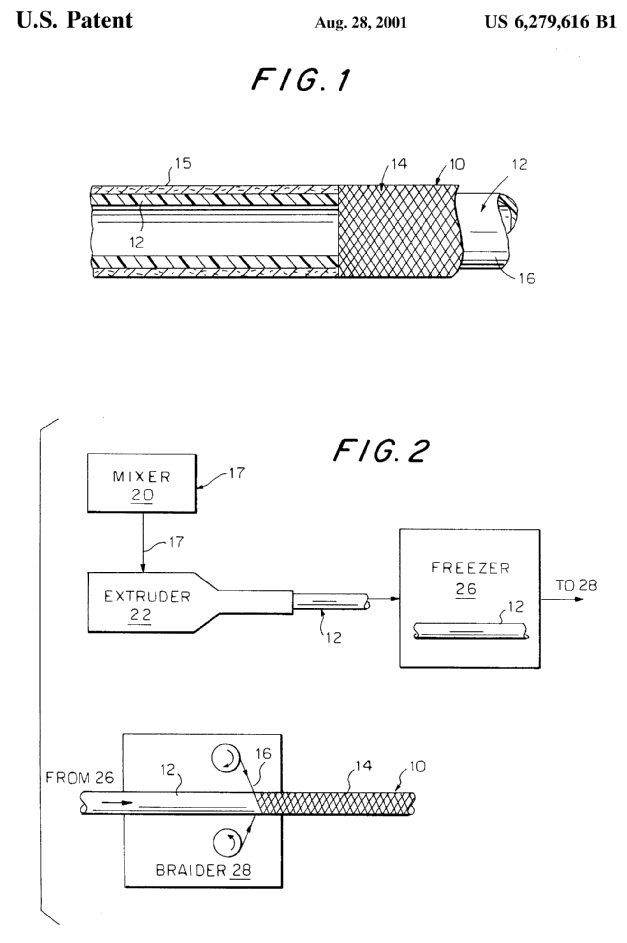
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Corrugated plastic hoses |
This place covers:
- combined operations for making articles with hollow walls, which are not fully classifiable in subclass B29C
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Producing wall or panel like structure for hulls, fuselage or buildings | |
General building construction: walls, e.g. partitions; roofs; floors; ceilings; insulation or other protection of buildings |
This place covers:
- combined operations for making frameless domes, which are not fully classifiable in subclass B29C
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in B29D 25/00
US3795559
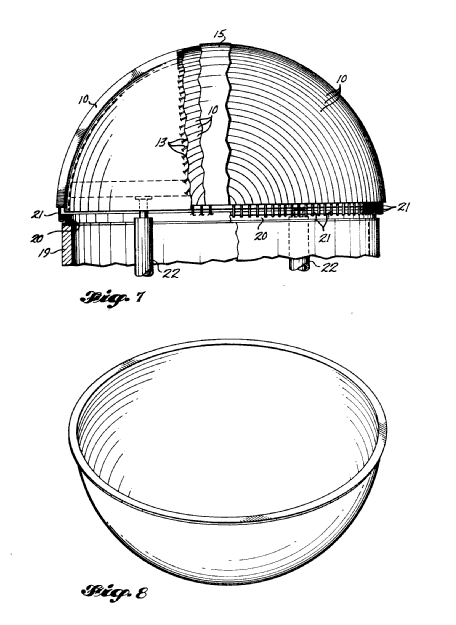
This place covers:
The production of reticular products like nets, grids, meshes, lattices not limited to a specific application.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Nets for protecting crops or plants | |
Nets for animals | |
Screens | |
Non-woven fabrics | |
Grids for geological applications |
This place covers:
The manufacture of belts or bands, either essentially consisting or plastics (including rubber or the like), or comprising various kinds of reinforcements embedded in a matrix of plastic material, including rubber or the like.
This place does not cover:
Producing belts as tyre components |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
In this group it is desirable to identify the type of produced belt or band by allocating the appropriate Indexing Codes as provided in the subclass B29L, e.g.:
- belts or bands: B29L 2029/00;
- conveyor belts: B29L 2031/7092;
- driving belts: B29L 2031/7094;
- fourdrinier belts: B29L 2031/733
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Belt | is a loop of flexible material used to link two or more rotating shafts mechanically. Belts may be used as a source of motion, to transmit power, or to track relative movement. |
Conveyor belt | is one application where the belt is adapted to continually carry a load between two points. |
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms:
- English words "band", "strip", "tape" and "ribbon"
- German words "riemen", "gürtel", and "band"
- French words "bande", "courroie", and "ceinture"
This place covers:
the manufacture of driving belts (aka synchronous belts) comprising patterns of typically tooth-shaped protruding elements. These elements mesh with the grooves of a pulley in a synchronous belt drive. Timing belts maintain constant speed during power transmission and do not slip.
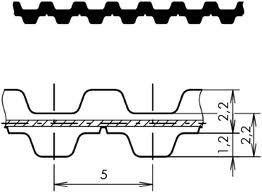
This place covers:
Making of double-toothed belts, i.e. belts being provided with teeth-like protrusions on both sides of the belts, namely on the upper and lower sides.
An illustrative schematic example thereof is the following:
This place covers:
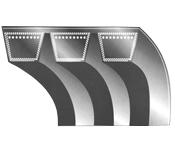
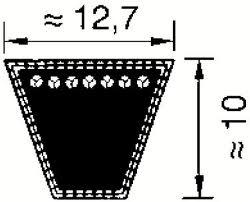
Making of driving belts having a wedge-shaped cross-section
An illustrative schematic example thereof is the following:
This place covers:
Making of multi-ribbed driving belts, that is belts having a plurality of rib-like elements, typically extending parallel to each other and to the longitudinal direction of the belt
An illustrative schematic example thereof is the following:

This place covers:
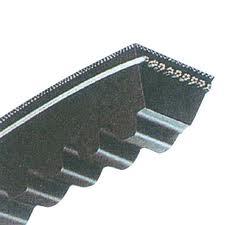
Making of cogged belts being a driving belt designed to avoid slipping; a.k.a.: timing belts or synchronous belts . The belts are typically provided with a plurality of protrusions moulded onto their inner surface.
An illustrative schematic example thereof is the following:
This place covers:
Methods and apparatuses for manufacturing pneumatic or solid tyres or parts thereof.
This group also covers the following manufacturing issues:
- resilient fillings for rubber tyres: B29D 30/04;
- injection moulding specially adapted for tyres or parts thereof: B29D 30/0678;
- centrifugal casting specially adapted for tyres or parts thereof: B29D 30/0679;
- building up green tyres on toroidal cores: B29D 30/10;
- building green tyres on cylindrical drums: B29D 30/20;
- tyre building drums: B29D 30/24;
- curing the the green tyres using vulcanizers or presses: B29D 30/0601;
- tyre moulds with incorporated heating or cooling means using liquids, gas or steam: B29D 30/0601;
- flexible cores for vulcanizing tyres: B29D 30/0654;
- after-treatment specially adapted for vulcanising tyres: B29D 30/0633;
- cooling tyres during post cure inflation: B29D 30/0643;
- retreading tyres: B29D 30/54;
- seals on envelopes used in tyre retreading: B29D 30/542;
- applying spikes to the tyre tread: B29D 30/66.
Most of the modern pneumatic radial tyres are manufactured according to the following main steps:
- a carcass including the tyre beads is built either on a toroidal core (the shape of said core being substantially correspondent to the shape of the finished tyre), or on a cylindrical drum; thereafter, the carcass built on the cylindrical drum is expanded into the final toroidal shape;
- the belt and the tread are applied to the toroidally expanded carcass;
- the sidewalls are applied to the toroidally expanded carcass;
- the green tyre so obtained is cured in a suitable mould.
Other tyre manufacturing techniques include casting, centrifugal casting, compression moulding, injection moulding.
This place does not cover:
Producing inner tubes | |
Producing tyre components by a single moulding technique, not including injection moulding or centrifugal casting | |
Means for sealing or repairing damaged tyres | |
Self-sealing arrangements or agents | |
Repairing of tyres |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Producing hollow articles | |
Producing tubular articles | |
Selectively separating reinforcements from matrix material by destroying the interface bound before desintegrating the matrix to particles or powder, e.g. from tyres or belts | |
Cores or mandrels in general, e.g. inflatable | |
Bags, bleeder sheets or cauls for isostatic pressing | |
Constructional forms of tyres or parts therof | |
Connection of valves to inflatable elastic bodies | |
Sealing compositions per se: see section C, e.g. | |
Testing of tyres |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Tyre (also spelled as tire) | a ring-shaped, typically toroidal, covering for a wheel, usually made of rubber reinforced with cords of steel, nylon or other material. It may be either solid or hollow and inflated (see pneumatic tyre), and is mounted over the rim of a wheel to provide traction, resistance to wear and to provide flexible cushion that absorbs shock while keeping the wheel in close contact with the ground |
Bias-ply tyre | a pneumatic tyre having crossed layers of ply cord running diagonally to the tread. See also: radial tyre |
Green tyre | a pneumatic tyre which has not yet undergone the moulding and vulcanizing process. Since the rubber is uncured, the green tyre is tacky, soft and not capable of maintaining its shape |
Pneumatic tyre | a tyre made of reinforced rubber, holding compressed air. Pneumatic tyres consist of bands of corded fabric, or "plies," coated with rubber. Bias ply tyres have the plies overlaid at an angle to the other layers. Radial tyres have all plies laid at 90 degrees to the tyre body or casing. See also: solid tyre |
Radial tyre | a particular type of tyre construction which utilizes beads that run perpendicular (90 degrees) to the direction of travel, stretched from bead to bead. They are typically reinforced with steel or nylon belts. See also: bias-ply tyre |
Run-Flat tyre | a type of tyre that permits travel with reduced internal pressure (deflated) for a limited mileage range at a limited speed |
Solid tyre | solid tyres have no hollow center and hold no air (non-pneumatic tyre). They are typically made of plastic or a composite of rubber/plastic and are used mostly on lawnmowers, skateboards, scooters, etc. The fact that pneumatic tyres can be punctured and lose air pressure makes them unsuitable for certain applications. For instance, tyres used by the military, in construction and on forklifts are often made with solid rubber or filled with resilient foam |
Studded tyre | tyre that comes with small metal studs embedded into the tread blocks, or holes where studs can be manually inserted, to provide better traction in inclement driving conditions |
Tubeless tyre | a pneumatic tyre which does not require a rubber inner tube to hold the air pressure. Tubeless tyres have a stiff bead on the edges of the sidewall that form an airtight seal with the wheel, eliminating the need for an inner tube .See also: solid tyre, inner tube, inner liner |
Apex (aka bead filler) | tyre component made from a very hard rubber compound, which is extruded so as to form a wedge; it is joined to bead core on its radially external surface |
Bead | the innermost portion of a tyre on either side, where it seats to the rim. A bead is reinforced with concentric steel wires to ensure a tight seal against the rim. It also prevents damage to the tyre during installation and removal |
Bead ring (aka bead core) | a structure composed of high tensile strength steel wire formed into hoops which function as anchors for the plies and hold the tyre assembly onto the rim of the wheel |
Belt (aka breaker) | one or more layers of rubber-coated tyre cord or rubber-encased steel cords located directly beneath the tread that run circumferentially in the crown of the tyre. The belt purpose is to reinforce the tread and help maintain a tyre's shape under a wide variety of conditions including tyre pressure variations, centrifugal forces and cornering and braking forces, for example. Belts also improve tread wear and help resist damage from impacts and penetration |
Bias Ply (aka as Cross-Ply) | bias ply tyres have belts that run diagonally across and on top of each other from bead to bead, typically at angles in the range of 30 to 40 degrees. This provides the advantage of allowing the tyre body more flexibility. This allows for a smoother ride over rough surfaces |
Carcass (aka casing) | a typical structural part of a pneumatic tyre, comprising a network of cords or other reinforcing elements embedded in rubber, which typically gives the tyre its shape. The tread or sidewalls are not part of the carcass |
Chafer | a narrow strip of rubber-coated abrasion-resistant material folded around the outside of the bead that protects the carcass cords against wear and cutting by the rim, distributes flex above the rim, and prevents dirt and moisture from getting into the tyre |
Cord | a strand of fabric, typically made of nylon, steel, rayon, fiberglass, polyester, or some combination of these materials, used in the making of carcass plies, belts or other reinforcing parts |
Crown | the entire outer perimeter of the contact surface of a tyre. This area houses the tread pattern of a tyre |
Inner Liner | the layer of air-impervious rubber (typically butyl rubber) that coats the inside of a tubeless tyre |
Inner Tube | the rubber balloon in the shape of a long circular tube which is inserted into a tyre to retain air pressure. Most automotive tyres are tubeless |
Ply | a layer of fabric cord extending from bead to bead, that forms much of the body of a tyre between tread and inner lining |
Retreading | the practice of applying a new tread to a used tyre casing. Most commonly used on medium and heavy commercial trucks tyres |
Safety Strips (aka Overlays) | two substantially continuous reinforcing strips wound symmetrically over the lateral edges of the belt, designed to maintain the integrity of the tyre and prevent catastrophic tread separations by decreasing stresses at the belt edges |
Shoulder | the upper rounded portion of the sidewall just below the tread edge and affects tyre heat behaviour and cornering characteristics |
Sidewall | the portion of a tyre between the bead and the tread pattern. It is typically compounded of rubber with high flex and weather resistance to control the ride and provide support |
Sipes | small slits cut into tread blocks that help evacuate water away from the crown of the tyre for improved wet traction. Sipes also provide "biting edges" for improved traction on ice- and snow-covered roads |
Tread | the part of a tyre designed to make contact with the road surface. The tread is made from tough rubber for high traction and low wear |
Tread blocks | individual sections of the tread separated by lateral grooves |
Tread pattern | the arrangement of grooves, blocks, sipes and channels on the tread that permit water to drain away from the footprint |
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms:
- English words " tire" and "tyre"
- German words "reifen" and "luftreifen"
- French expressions "pneumatique", "pneu", and "bandage pneumatique"
This place does not cover:
Pretreatment, e.g. coating of, or impregnating of reinforcements or fillers |
This place covers:
manipulating, supporting, grasping, holding tyres or parts thereof (e.g. baskets or the like), with no specific relation to loading/unloading the press or the mould.
This place does not cover:
Loading/unloading the tyre curing press press |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Gripping heads | |
Article or material handling devices associated with conveyors | |
Storing webs, tapes, or filamentary material, e.g. on reels | |
Internally-expanding grippers for handling hollow articles |
This place covers:
accessories, details or auxiliary operations, related to producing pneumatic or solid tyres or parts thereof, not covered by groups B29D 30/0005, B29D 30/0016, B29D 30/005, B29D 30/02, B29D 30/04 and B29D 30/06
This place does not cover:
Packaging annular articles, e.g. tyres |
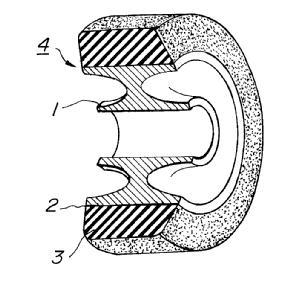
This place covers:
An illustrative schematic example thereof is the following:
US 4244413
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Non-inflatable or solid tyres |
This place covers:
methods of providing pneumatic tyres with a resilient filler to provide cushioning of the vehicle ride. The filler is typically a foamed elastomeric material, normally expanded in situ. This group also covers the materials used therefor
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Non-inflatable or solid tyre characterised by means for increasing resiliency |
This place covers:
apparatuses and methods of curing tyres, wherein the vulcanizing medium (typically steam, hot nitrogen or other hot fluids) comes directly in contact with the tyre during vulcanization; also known as "bladderless" curing: an inflatable vulcanizing bladder or core, preventing contact between the steam or the vulcanizing fluid on one side and the tyre from the other side, is not present.
This place covers:
apparatuses and methods of loading the vulcanizing presses or moulds with green (i.e. uncured) tyres and to unload the cured (i.e. vulcanized) tyres from the vulcanizing presses or moulds.
This place does not cover:
Manipulating, supporting, grasping, holding tyres, e.g. baskets or the like, with no specific relation with loading or unloading the presses or the moulds |
Typically, the tyre vulcanizing press (a.k.a. tyre vulcanizer) is an apparatus comprising the following sub-assemblies:
- one or more metallic mould(s);
- devices for opening, closing, locking and unlocking the mould(s) [e.g. mechanical means: levers, kinematical systems, actuators, etc.);
- devices for introducing/removing the toroidal bladder (when present) inside the toroidal space formed by the closed mould;
- devices for supplying to /removing from the bladder, the vulcanizing medium (e.g. steam, Nitrogen), which pressurizes the uncured
- tyre and supplies thermal energy for carrying out the vulcanization;
- devices for supplying thermal energy to the tyre mould;
- various devices (sensors, etc.) for controlling the vulcanization.
The tyre loaders/unloaders (which are typically kinds of "manipulators" for inserting the green tyre inside the open mould and removingthe cured tyre from the open mould) are typically NOT part of the tyre mould and NOT part of the press: in the sense that when the press is closed and/or the mould containing the tyre is closed, during the vulcanization cycle, the tyre loaders/unloaders remain outside the press/mould.
This place covers:
Machines (presses) comprising moulds with radially movable sectors and means for opening or closing the moulds, means for exerting pressure and means for supplying fluids and/or energy for curing the tyres including means for controlling the vulcanizing process. A mould with radially movable sectors typically comprises two substantially disc-shaped plates for moulding the tyre sidewalls and a plurality of circumferential sectors (aka segments) for moulding the tyre tread. The sectors are movable synchronously inward, to form a continuous cavity and to mould the tyre tread, and are movable synchronously outward, to allow the removal of the cured tyre from the mould.
WO03/041933 - A
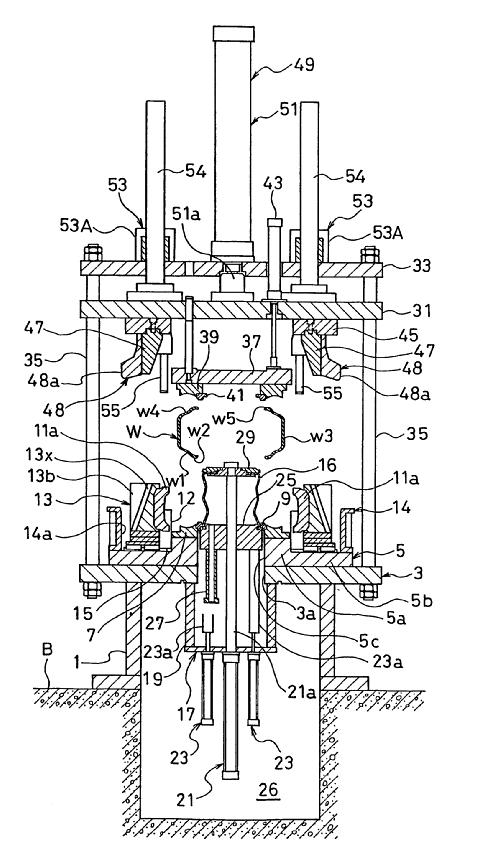
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Presses in general |
This place covers:
constructional features of moulds for vulcanizing tyres, e.g. details of the moulding surface (ribs, grooves, sipes, venting plugs, means, porous surfaces), means for opening/closing the mould or mould segments, details of fluid circulating means (channels), sensors.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Moulds or cores, characterised by the shape of the moulding surface, e.g. ribs, grooves |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Moulds or cores in general |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Porous moulds |
This place covers:
mould with radially movable sectors typically comprising two substantially disc-shaped plates for moulding the tyre sidewalls and a plurality of circumferential sectors (aka segments) for moulding the tyre tread
An illustrative schematic example thereof is the following
EP 1232843 - A 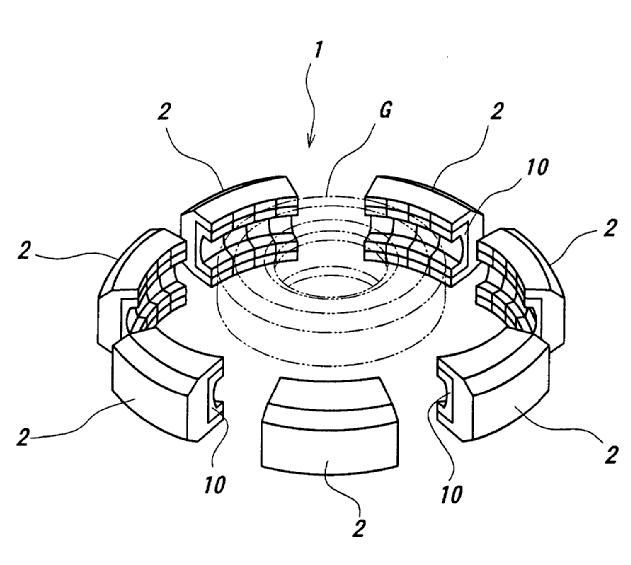
This place covers:
- improving tyre uniformity, e.g. by adding or removing material, or deforming the tyre;
- measuring tyre uniformity;
- marking, labelling tyres;
- awling, venting tyres.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Machines or devices designed for grinding surfaces of revolution on work, including those which also grind adjacent plane surfaces; Accessories therefor; Single-purpose machines or devices; For grinding tyres | |
Measuring or gauging equipment for controlling the feed movement of the grinding tool or work; Arrangements of indicating or measuring equipment, e.g. for indicating the start of the grinding operation, taking regard of the load; For grinding tyres | |
Testing static or dynamic balance of machines or structures | |
Determining imbalance | |
Compensating imbalance | |
Testing of vehicles; Of wheeled or endless-tracked vehicles; Of tyres |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Cooling in moulding processes in general |
This place covers:
tyre-vulcanising presses comprising a plurality of curing moulds, the moulds being for instance stacked upon each other, or arranged side by side
An illustrative schematic example of B29D 30/065 is the following:
US 3827839
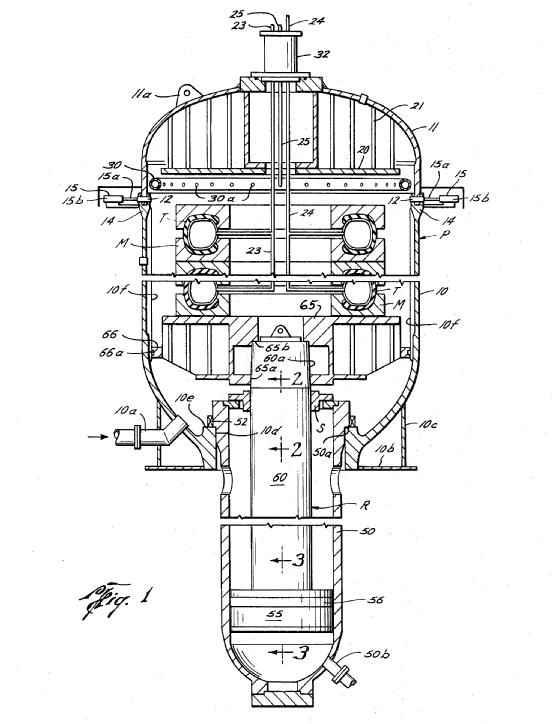
This place covers:
Inflatable vulcanizing bladders or corse, which are heat-resistant and are inserted inside the tyre toroidal cavity, preventing contact between the steam or the vulcanizing fluid on the one side and the tyre inner surface on the other side.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Heating or curing during moulding, using liquids, gas or steam |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Inflatable pneumatic tyres with impervious liner or coating on the inner wall of the tyre |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in B29D 30/3057
WO 2009068939 – A
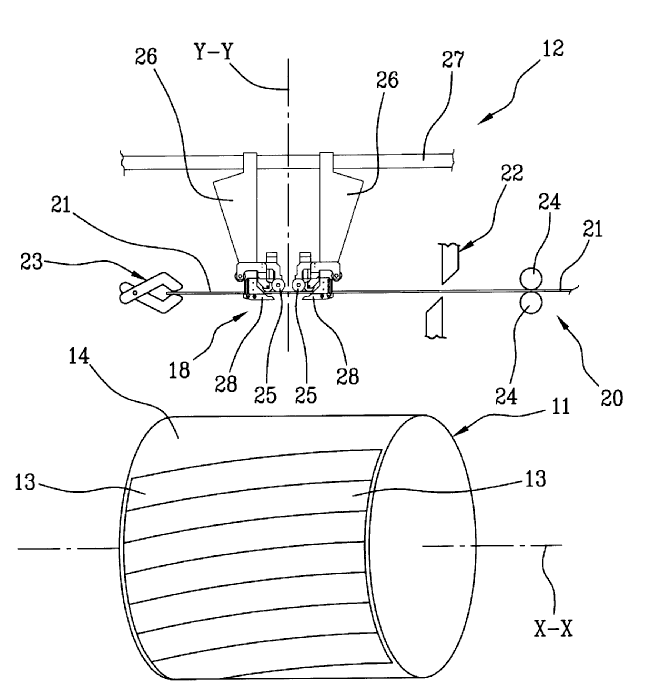
This place does not cover:
Coating or impregnating of reinforcements or fillers |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Reinforcing cords or wires for rubber or plastic articles, the cords being characterised by an anti-corrosive or adhesion-promoting coating |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Chemical pretreatment of textile inserts before building the tyre | |
Pretreatment of reinforcements or fillers | |
Treating fibres, threads, yarns, fabrics with macromolecular compounds |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Joining of performed parts |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Single butt to butt joints in general |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Single lap to lap joints, i.e. overlap joints | |
Single bevel to bevel joints, e.g. mitre joints |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Joining devices characterised by the movement of the joining tools |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Joining devices characterised by the movement of the joining tools |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Joining devices characterised by the movement of the joining tools |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Positioning the parts to be joined, e.g. aligning, indexing or centring |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Positioning the parts to be joined by using stops |
This place covers:
the manufacture of bead-rings or bead-cores, typically by winding a plurality of turns of a continuous steel wire to form a substantially un-stretchable ring.
This group also covers the application of the filler rubber or apex to the bead core, unless otherwise specified.
This place does not cover:
Pretreatment of reinforcements or fillers; coating or impregnating | |
Coating wires to promote adhesion to rubber/plastics: reinforcing cords for rubber or plastic articles; the wires being characterised by an anti-corrosive or adhesion promoting coating |
This place covers:
- manufacturing of tyre treads;
- retreading;
- application of anti-skid spikes or studs to the tread.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Tyre tread bands per se; tread patterns; anti-skid inserts |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Tread | part of the tyre which protects the carcass plies from mechanical damage and the effects of moisture. The thickest part, the section in contact with the road, has patterned projections and recesses of various sizes and shapes; the tread pattern determines the adhesion between the tyre and the road, rolling resistance, resistance to abrasion, performance under difficult road conditions, running noise, and ease of control. |
This place covers:
Retreading of tyres, i.e. processes and means to fit a worn tyre with a new tread.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Machines or devices designed for grinding surfaces of revolution on work, including those which also grind adjacent plane surfaces; accessories therefor; single-purpose machines or devices; for grinding tyres | |
Measuring or gauging equipment for controlling the feed movement of the grinding tool or work; arrangements of indicating or measuring equipment, e.g. for indicating the start of the grinding operation; taking regard of the load; for grinding tyres |
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms:
- (EN)"retreading", "recapping", (DE)"runderneuerung" and (FR)"rechapage"
This place covers:
the application of uncured bands of rubber tread to the tyre casing, either during the manufacture of a new tyre or in tyre retreading. Camel back is a synonym of rubber tread (see glossary).
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Camelback (or "camel-back" or "camel back") is a strip of uncured rubber, which becomes the tyre tread once applied on the carcass; this strip has a certain profile and a width corresponding to the tread of the tyre; usually on one side of this strip there is a link film providing adherence between tread and carcass. The expression derives from the characteristic shape of this strip having a convex curve suggesting a camel's hump.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Structure or arrangement of belts or breakers, crown-reinforcing or cushioning layers |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
The breaker is a tyre component which is designed to provide a strong bond between the carcass plies and the outermost rubber layer (the tread); it is usually made of several layers of rubberized textile or metal cord. In bias-ply tyres the cords of the breaker run at the same angle as the carcass plies; in radial-ply tyres they run at an angle of 70°–85°, thus forming an inextensible belt that carries the major portion of the forces acting on the tyres as a result of inflation pressure and external loads. Because of the combination of flexible carcass plies and a stiff breaker, radial-ply tyres have a longer life, consume less power in overcoming rolling friction, and possess other service advantages over bias-ply tyres.
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms:
- "belt" and "breaker"
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Tyre sidewalls | |
Decorating or marking the sidewalls | |
Protecting the sidewalls against exterior elements |
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms:
- "side-wall" and "sidewall"
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Protecting, decorating, marking tyre sidewalls |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Protecting, decorating, marking tyre sidewalls |
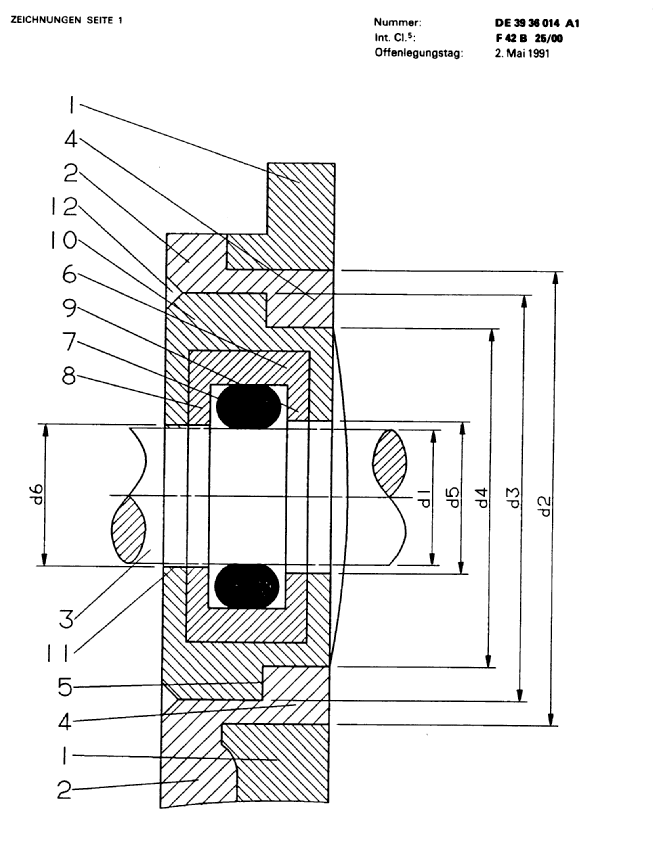
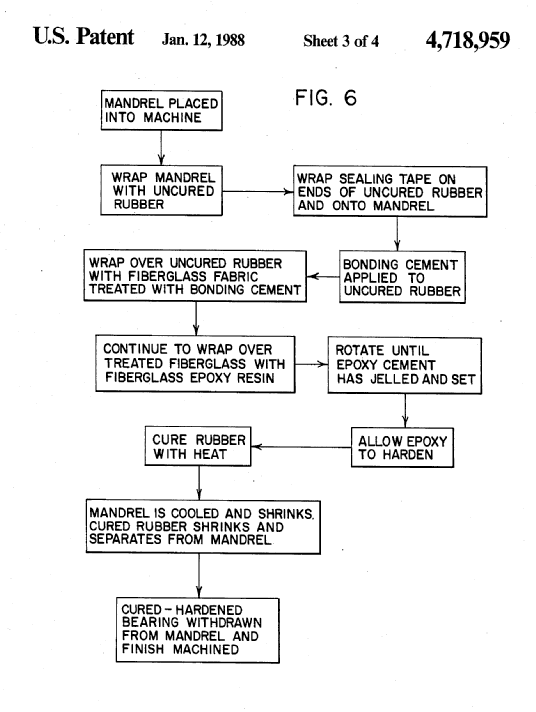
This place covers:
- combined operations for making bushes for bearings, which are not fully classifiable in subclass B29C
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in B29D 33/00
This place covers:
Producing a footwear or a part of it using moulding technique.
A43B relating to footwear itself, part of it, shape and use of it, etc...
A43C relating to attachments for footwear, including the lace and the studs.
A43D relating to machines to produce footwear (with the exception of B29D 35/00 dedicated to the moulding)
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Relating respectivelly in case of injection moulding or compression moulding is used in the procecess of producing a footwear (meaning also part of it) | |
When the whole shoe is moulded in one piece | |
When the sole is moulded to the upper assembly | |
In case part of the footwear is produced, and also if the mould is of interest |
This place covers:
Producing a footwear (meaning also part of it) using injection moulding.
This place covers:
Producing a footwear (meaning also part of it) using compression moulding/vulcanisation.
This place covers:
Complete whole shoes moulded in one piece.
This place covers:
Footwear where the sole is moulded to the upper assembly.
This place does not cover:
Footwear assembled by cementing/gluing a sole to an upper assembly.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
When the preformed sole is moulded to the upper assembly |
This place covers:
Footwear made by moulding a preformed sole to the upper assembly.
This place covers:
Parts of the footwear produced by moulding, and also the moulds thereof.
This place covers:
Methods of making articles as provided in the subgroups only
This place covers:
- combined operations for making wall or panel-like structures provided with ribs, which are not fully classifiable in subclass B29C
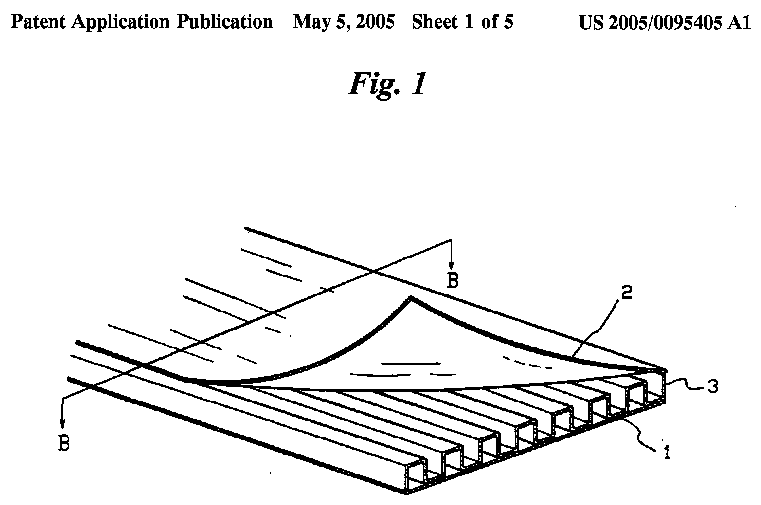
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in B29D 99/0014
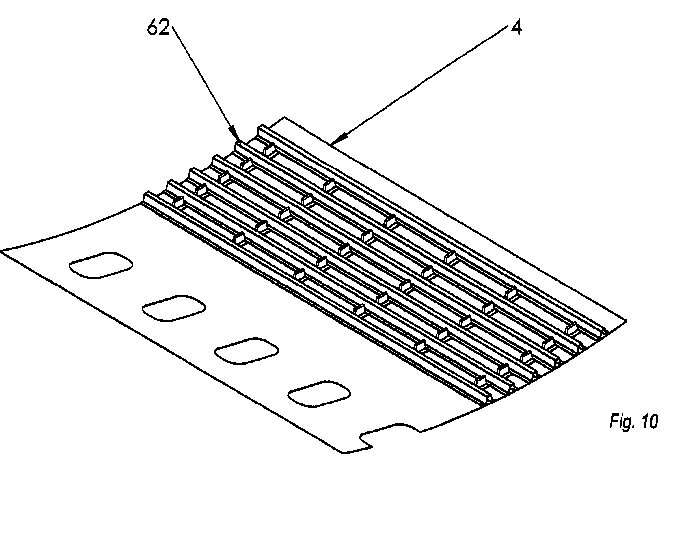
DE1020090600706
This place covers:
- combined operations for making blades, which are not fully classifiable in subclass B29C
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Blades for propellers | |
Blades for rotors | |
Blades of composite material | |
Construction of rotors of wind motors |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Hollow blades |
This place covers:
- combined operations for making rolling bodies, the rollers or cylinders having an axial length of several times the diameter, which are not fully classifiable in subclass B29C
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Moulding shells for rollers of printing machines |
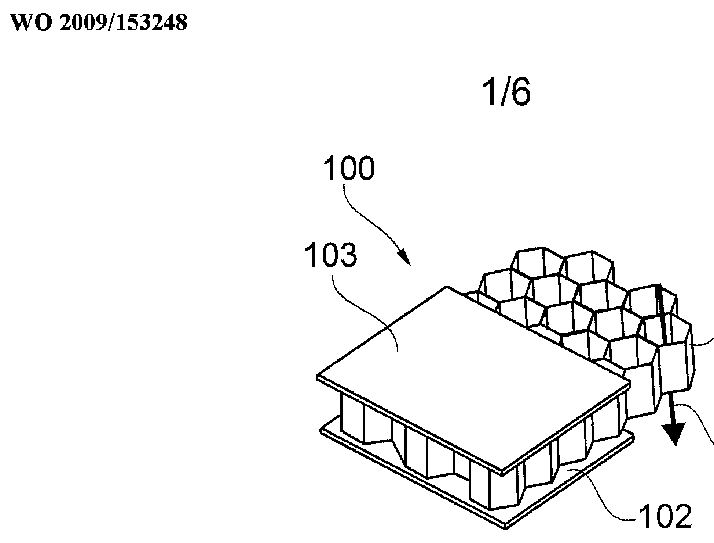
This place covers:
- combined operations for making honeycomb, which are not fully classifiable in subclass B29C
This place does not cover:
Making honeycomb structures of papers | |
Honeycomb structures of porous ceramic ware and the preparation thereof |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Honeycomb filters | |
Filtering structures for exhaust or silencing apparatus |