CPC Definition - Subclass A61F
This place covers:
Apparatus, devices or methods for physically correcting or altering the body of patients or disabled persons that are directly and for prolonged periods of time (i.e. not just during acute exceptional circumstances) used on or in the body of the patient or the disabled person:
Stents and similar devices providing patency to, or preventing collapsing of, tubular structures of the body;
Prostheses, i.e. artificial substitutes or replacements for parts of the body that are either implantable into the body (e.g. blood vessels, eye parts, heart valves, bones, joints) or not implantable in the body (e.g. mammary prostheses, artificial arms, hands, legs or feet or parts thereof);
Specially adapted electrical, bioelectrical or fluid operating or control means for prostheses or sphincters;
Specially adapted means for connecting prostheses with or to the body (e.g. bandages, harnesses, sockets, stockings for the limb stump);
Specially adapted means for protecting prostheses;
Filters implantable into blood vessels;
Lengthening pieces for natural legs;
Orthopaedic methods or devices for non-surgical treatment of bones or joints, e.g. splints, casts, corsets, devices for stretching including equipment for beds or treatment tables, medical insertions for shoes, pressure pads, suspensory bandages;
Methods or devices for physically treating or correcting of the eyes (e.g. eye surgery using laser);
Apparatus specially adapted for guiding the blind by supplementing or replacing their visual perception;
Methods or devices for treatment of the ears, e.g. surgical.
Methods or devices (e.g. head or eye-gaze-direction actuated control devices, oral communication actuated control devices) for enabling patients or disabled persons to operate independent apparatus or machines (i.e. apparatus such as room lights or doors that is not a part of, or used in conjunction with the functioning of, artificial or natural parts of their body) without the application of direct force from the part of the human body that would normally be used by individuals for controlling operation of the independent apparatus or machine such as a hand, foot or their artificial equivalents.
Contraceptive devices for males (e.g. condoms, vas deferens occluders) or females (e.g. pessaries, intra-uterine type, fallopian occluders).
Devices for medical or hygienic care of living individuals that are worn by the individual or directly contact the body of the individual during their care:
Devices worn by the patient for reception of urine, faeces; colostomy devices;
Bandages or dressings, e.g. plasters, elastic stockings;
Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, absorbent garments, e.g. diapers, tampons, e.g. catamenial tampons, surgical swabs; supporting and fastening means for pads.
Heating or cooling devices for medical or therapeutic treatment of the human body and for body cavities, e.g. compresses, warming pads, pans or mats, hot water bottles, ice bags.
Protective devices for the eyes, e.g. goggles, eye-masks worn to prevent particulates or chemicals from striking the eyes.
Devices for inserting contact lenses.
Protective devices for the ears, e.g. ear plugs or earmuffs.
Auxiliary appliances for wound dressings; dispensing containers for dressings or bandages; packages or wrapping arrangements for used pads, e.g. for disposal.
Containers having various emergency medical supplies such as bandages, simple medical tools, and medicines (i.e. first-aid kits) that are intended to be used for administering initial treatment to injured or sick individuals.
If an apparatus, method, device, or material is usable for both humans and animals for the same purpose and in the same manner, and it is otherwise proper for this subclass, classification is made only in subclass A61F. Similar devices or processes to those covered by subclass A61F that are usable exclusively for animals or are used in animals in a different manner or for different purposes than for humans, are classified in subclass A01K or A61D.
Surgical apparatus or processes in general are covered by subclass A61B.
Subclass A61H provides for massage, chiropractic, or physical therapy apparatus or processes used for the treatment of disease, injuries or disability (i.e. an abnormal condition of the body) by utilisation of direct mechanical energy.
Chemical and material aspects of prostheses, structures inserted into tubular structures of human bodies, bandages, dressings, absorbent pads or surgical articles are covered by subclass A61L.
With regard to human organs and their parts, the exact distinction between the artificial devices implantable into human bodies that are proper for subclass A61F and those proper for subclass A61M is somewhat imprecise. Therefore, for analogous situations that are not specifically covered by existing groups of these subclasses, the following listings are intended to provide guidance.
Subclass A61F provides for the following replacements or substitutes for internal body organs or their parts: hollow or tubular parts of organs (e.g. bladders, tracheae, bronchi, heart valves and blood vessels, bile ducts), structural supporting or maintaining devices for such parts (e.g. stents), artificial eyes and artificial ears.
Subclass A61M provides for the following replacements or substitutes for internal body organs or their parts: artificial hearts (based on catchword index), artificial livers, artificial lungs, artificial pancreas, artificial kidneys and catheters in general.
Devices for introducing media into or onto the body, devices for taking media from the body are also covered by subclass A61M.
Spectacles, sunglasses, contact lenses or goggles insofar as they have the features of vision correction or protection against high levels of visible and ultraviolet light are covered by subclass G02C.
This place does not cover:
Dental prostheses |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Undergarments | |
Baby linen | |
Corsets or girdles | |
Brassieres | |
Cosmetic articles, e.g. wigs, hair pieces | |
Caps with means for protecting the eyes or the ears | |
Ordinary arch supports for shoes | |
Artificial nails | |
Heating or cooling means in connection with bedsteads or mattresses | |
Surgical instruments | |
Devices for closing wounds, or holding wounds closed | |
Surgical drapes | |
Chiropractic methods or devices | |
Appliances for aiding patients or disabled persons to walk | |
Massage of the genitals | |
Chemical aspects of contraception | |
Transdermal drug delivery patches | |
Chemical aspects of, or use of materials for, bandages, dressings or absorbent pads | |
Adhesives for colostomy devices | |
Surgical adhesives or cements | |
Materials for prostheses | |
Materials for colostomy devices | |
Artificial hearts, kidneys | |
Irrigators | |
Balloon catheters | |
Drainage appliances for wounds | |
Dilators | |
Valves specially adapted for medical use | |
Exercising apparatus specially adapted for particular parts of the body | |
Goggles for swimming | |
Making artificial eyes from organic plastic material | |
Arm rests for use as writing aids | |
Arrangements of tyre-inflating valves to tyres or rims | |
Diving masks | |
Safety devices for welding in general | |
Sunglasses or goggles having the same features as spectacles | |
Removable contact lenses | |
Electric heating elements |
The breakdown symbols (i.e. the non "parallel" or non "mirror" symbols) and "orthogonal" symbols are to be used for classifying the invention information (in addition to the invention symbols) in case the invention is insufficiently classified by an invention information symbol. They are also to be used for classifying the additional information. They are stored in the additional information field.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Absorbent articles | Articles adapted to absorb liquid excreted by the body. |
Dilator | A (surgical) device or instrument used to dilate, distend, enlarge, expand, stretch an opening, organ, passage, tube, canal or cavity of a human or animal body (e.g. urethrotomy, tracheotomy, nasal, anal or cervix (Hegar's dilator) or vaginal dilation, bougienage, percutaneous dilation of tissues (Byrd dilator), whereas stents are not dilators but prostheses for providing patency, or preventing collapsing of tubular structures of the body. |
Disabled person | A human being that is unable to do certain basic physical tasks (e.g. walking) due to a physical or mental impairment/condition. |
Patient | A human being awaiting or undergoing any form of (a) medical care (e.g. testing) or treatment by medical staff (e.g. doctors, dentists, midwives, chiropractors), or (b) physical tending (e.g. feeding) by care giver (e.g. hospice or nursing home staff) due to impairment. |
Stent | Balloon- or self-expandable tubular device for use in the treatment of duct-like organs typified for example by a blood vessel, biliary tract, urinary tract, digestive tract, and the like providing patency. |
Stent graft | Stent with a tubular member made of a synthetic resin affixed to the inside or outside of the stent. |
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used with the meaning indicated:
Device for fluid management | incontinence article. |
This place does not cover:
Dental prostheses | |
Artificial kidneys | |
Artificial hearts |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wigs | |
Hair pieces, inserts, rolls, pads, or the like; Toupées | |
Artificial nails | |
Materials for prostheses |
The "subdivision" Indexing Code symbols (i.e. the non "parallel" Indexing Code symbols) are used for classifying as well the invention information as the additional information. They are stored only in the additional information field".
The "orthogonal" Indexing Code symbols are also used.
Prostheses are classified in groups A61F 2/00 - A61F 2/26 or A61F 2/82 or A61F 9/00 or A61F 11/00 or subgroups thereof:
A61F 2210/00 Particular material properties.
A61F 2220/00 Fixations or connections.
A61F 2230/00 Geometry of prostheses.
A61F 2240/00 Manufacturing or designing of prostheses (specific manufacturing fields take precedance).
A61F 2250/00 Special features of prostheses.
Colostomy devices: A61F 5/445
Receptacles for taking up urine or feces: A61F 5/451
Drainage catheters: A61M 27/00
This place does not cover:
Closure means for other lumina | |
Drainage of urine without closure | |
Catheters for rectum |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Healthcare informatics |
This place does not cover:
Plugging an opening in the wall of a hollow or tubular organ |
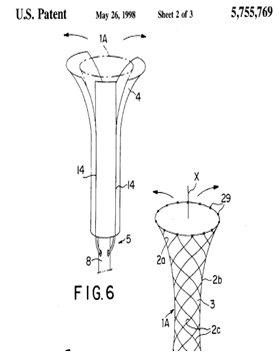
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/0009.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/0013.
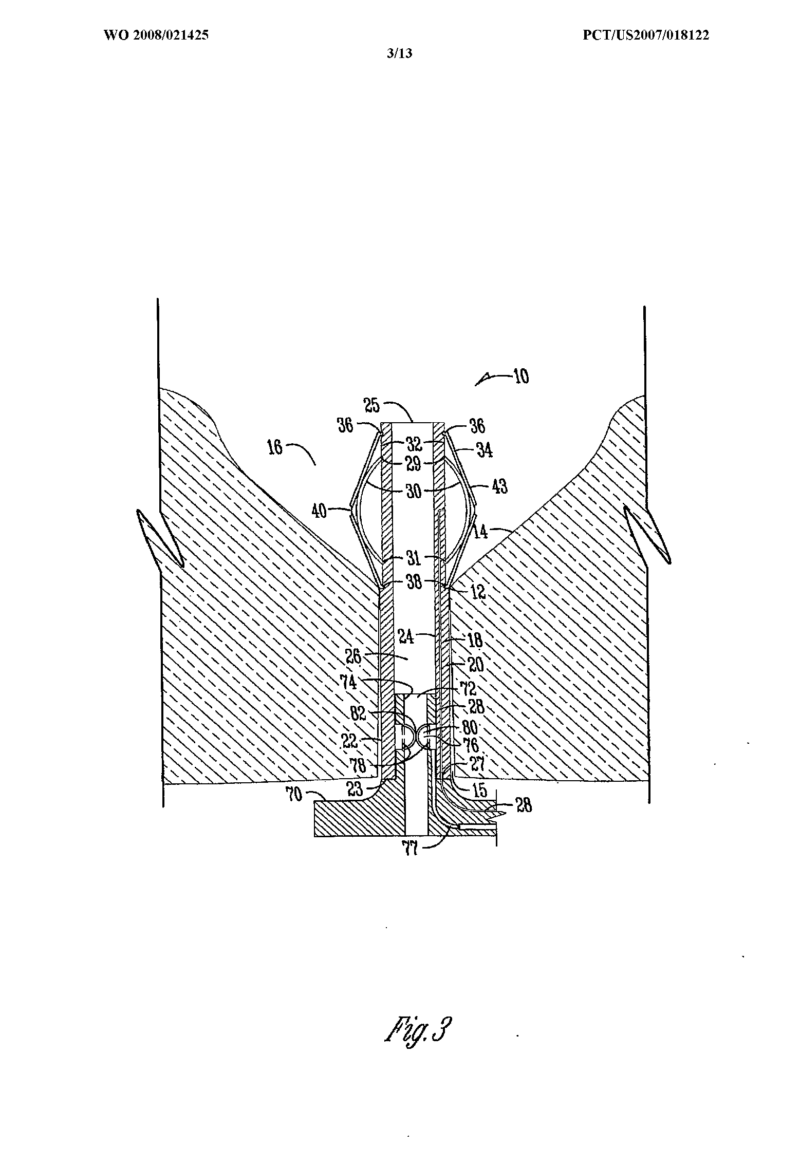
This place does not cover:
Occluding blood vessels by internal devices | |
Urethral drainage stents |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/0022
Implanted gastrointestinal electrodes for the anal tract: A61N 1/0512
Implanted gastrointestinal electrodes for the urinary tract: A61N 1/0514
This place does not cover:
Magnetic closure means placed in or outside the body opening close to the surface of the body | |
Injectable solid implants | |
Drainage implants in the urethral tract | |
Stimulation by electrodes |
Means for transferring electromagnetic energy to implants: A61F 2250/0001
This place covers:
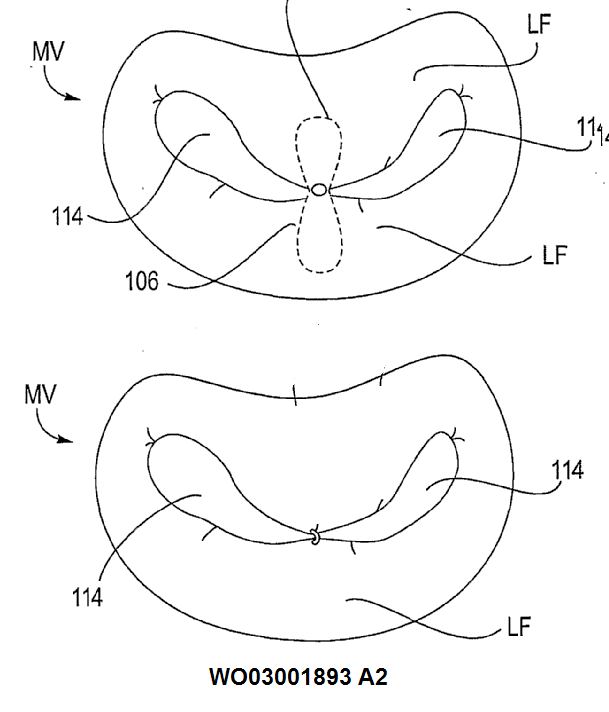
Slings or meshes for pelvic prolapse
Hernia repair meshes: A61F 2/0063
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Treatment of female stress incontinence, i.e. especially delivery devices or other devices for implantation | |
Bone anchors for fixation of slings | |
Suturing instruments |
Tampons: A61F 13/20
Pessaries, i.e. devices worn in the vagina to support the uterus: A61F 6/08
Exercising apparatus for vaginal muscles: A63B 23/20
Absorbent pads for male use: A61F 13/471
Penis implants: A61F 2/26
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Clamps or clips in general |
This place covers:
Implants are structurally confined; there are no uncontained fillers
Cosmetic fillers: A61K 8/02
Cosmetic materials containing animal cells: A61L 27/38
Knitting processes for the production of meshes: D04B 21/12
This place does not cover:
Support slings for the urethra | |
Breast lifts | |
Heart meshes, i.e. covering the external surface of the heart | |
Bandages | |
Implants for closing a vessel puncture or a septal defect | |
Mesh patterns and the fabrication thereof |
This place does not cover:
Bone surfaces | |
Materials for coating prostheses | |
Sand blasting | |
Processes for functionalising a surface | |
Inorganic coating processes |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Prosthetic joints implantable into the body with special external or bone-contacting surface for promoting ingrowth of bone tissue |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Prosthetic joints implantable into the body with special external or bone-contacting surface for retarding or preventing ingrowth of bone tissue |
Packages or dispensers for instruments: A61B 50/30
Packages in general: B65D 1/00 - B65D 90/00
This place does not cover:
Packages or dispensers for intraocular lenses | |
Packages or dispensers for dental surgery |
Implants receive their particular Indexing Code-code together with the subgroup A61F 2/0095 (Example: a package for a soft heart valve prosthesis will be classified in A61F 2/0095 (Example: a package for a soft heart valve prosthesis will be classified in A61F 2/0095 and A61F 2/2412).
Catheters for removing obstructions in lumina with perfusion capabilities: A61B 17/22
Aspiration catheters: A61M 1/84
Dilation catheters with perfusion capabilities: A61M 2025/1095
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Internal occluding devices | |
Filters used as gripping instruments | |
Snare instruments |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/013.
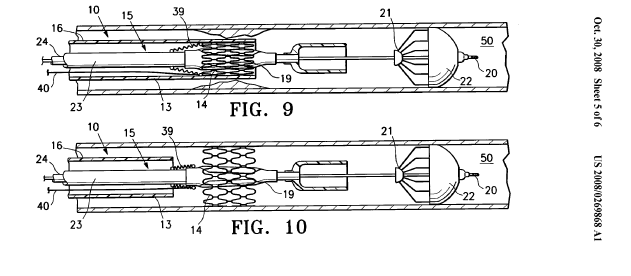
The other endovascular procedure in addition to the filtering device has to be classified in the appropriate groups such as for example:
Stent or stent-graft delivery devices: A61F 2/95
Balloon catheters: A61M 25/10
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Closure means for urethra or rectum or for artificial body openings therefor |
This place covers:
Devices which replace or supplement a natural gland and deliver enzymes.
This place does not cover:
Drug delivery | |
Hemodialysis | |
Hemofiltration | |
Other extracorporeal blood treatment |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Bioreactors for enzymes | |
Processes for producing enzymes |
Urethral drainage stents: A61M 25/0017.
This place does not cover:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Devices, other than stent-grafts, providing patency to, or preventing collapsing of, tubular structures of the body, e.g. stents | |
Bariatric or gastric sleeves | |
Tear duct implants |
Documents receiving a symbol in A61F 2/04 have to receive a further symbol information, such as:
Urinary bladders: A61F 2/042.
Bronchi: A61F 2002/043.
Oesophageal anti-reflux valves and devices: A61F 2002/044.
Tubes in the stomach: A61F 2002/045.
Trachea: A61F 2002/046.
Urethrae: A61F 2002/047.
Ureters: A61F 2002/048.
This place covers:
Tubular structures that substitute natural blood vessels, e.g. bypass grafts
This place does not cover:
Materials for artificial blood vessels | |
Artificial blood vessels as access point for injections e.g. for repeated puncture | |
Tracheal tubes |
This place covers:
Devices for creating vascular grafts by mechanical means.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this place:
1a.
1b.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Materials containing animal cells | |
Protheses made from natural tissue or living cells | |
Bioreactors for producing artificial tissue or for ex-vivo cultivation of tissue | |
Cell culture and products made of cells |
This place covers:
The artificial blood vessel has special technical features, e.g. hooks to provide a connection to a natural or artificial blood vessel.
This place does not cover:
Anastomosis in general; Anastomosis of natural blood vessels |
This place covers:
Stent-grafts for blood vessels. Stent-grafts are tubular grafts with stents embedded therein or attached to the graft material. The stent-graft for blood vessels is usually deployed within an aneurysm. The stent anchors the graft to the blood vessel wall. The graft is usually made from fabric material
External clamps or sleeves around an aneurism: A61B 17/12
Reinforcement of blood vessels, e.g. for repeated puncture: A61M 1/3655
This place does not cover:
Stent-grafts for tubular structures of the body other than blood vessels | |
Instruments for placement or removal | |
External stent or sleeve around aneurysm |
This place covers:
Artificial muscles implanted in the body.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Prostheses not implantable in the body, e.g. muscles | |
Operating or control means for prostheses | |
Sutures | |
Tendon anastomosis | |
Programme-controlled manipulators with muscles or tendons |
This place does not cover:
Guiding means for bone drills |
This place does not cover:
Suture anchors | |
Staples for connecting tendon to bone |
Documents receiving a class in A61F 2/0811 have to receive a further class information, such as:
Structure of the anchor | |
Modular anchors comprising a plurality of separate parts | |
without deformation of anchor parts, e.g. fixation screws on bone surface, extending barbs, cams, butterflies, spring-loaded pins | |
with deformation of anchor parts, e.g. expansion of dowel by set screw | |
Longitudinal channel for insertion tool running through the whole tendon anchor, e.g. for accommodating bone drill, guidewire | |
Mode of fixation of anchor to tendon or ligament | |
Fixation of a loop or U-turn, e.g. eyelets, anchor having multiple holes | |
Fixation of tendon or ligament between anchor and bone, e.g. interference screws, wedges | |
Fixation of tendon or ligament between anchor elements, e.g. by additional screws in the anchor, anchor crimped around tendon | |
Anchor integrated into tendons, e.g. bone blocks, integrated rings | |
Position of anchor in respect to the bone | |
Anchor in or on top of a bone tunnel, i.e. a hole running through the entire bone | |
Anchor in or on a blind hole or on the bone surface without formation of a tunnel |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Prostheses non-implantable in the body, i.e. artificial substitutes or replacements for muscles |
This place does not cover:
Instruments for implanting hair follicles | |
Hair cells |
This place does not cover:
Skin cells |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Materials for use in artificial skin |
This place covers:
Illustrative examples of subject matter classified in this place:
1.
2.
Figure 2 illustrates a mammary support implant.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
External mammary prostheses | |
Devices for expanding tissue |
This place covers:
All eye prostheses and replacement parts not provided for in the subclasses.
Retinal electrodes: A61N 1/0526.
Retinal implants: A61N 1/36046.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Packages or dispensers for prostheses or other implants in general | |
Exercisers for the eye | |
Shaping or joining of plastics | |
Making of artificial eyes from organic plastic material | |
Removable contact lenses |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Surgical instruments for osteosynthesis of orbital bone |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/141
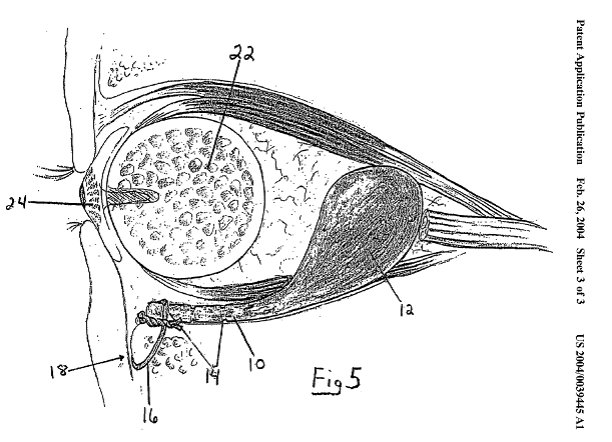
This place covers:
Artificial or natural cornea replacement implant for repair of defective corneal tissue.
Implantation instruments therefor: A61F 2/148
This place does not cover:
Optically active corneal inlay or onlays for refractive correction | |
Corneal implants for refractive correction by alteration of the shape of the cornea |
This place covers:
Optically active elements inserted between corneal layers for refractive correction.
This place does not cover:
Corneal onlays and inlays for photoablative laser surgery | |
Corneal onlays and inlays for photodisruptive laser surgery | |
Reshaping the cornea assisted by thermal and/or chemical treatment and the like |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Contact lenses for reshaping the cornea, i.e. orthokeratology |
This place covers:
Stromal or corneal implants, in general at least partial rings, shaping the cornea for refractive correction.
Contact lenses for reshaping the cornea, i.e. orthokeratology: G02C 7/04
This place covers:
Implantation instruments for corneal implants altering the shape of the cornea for refractive correction
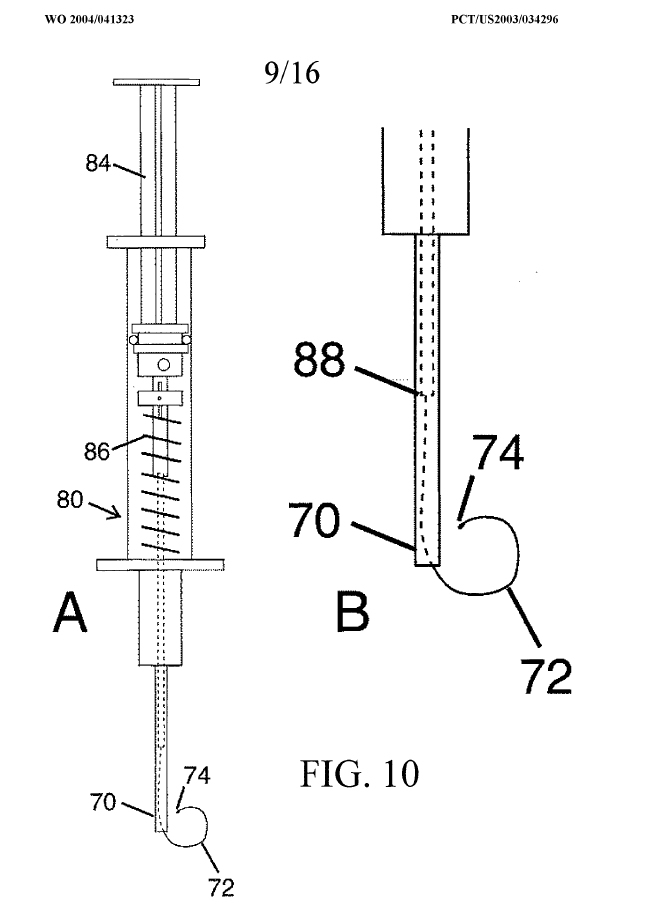
This place does not cover:
Implantation instruments for intraocular lenses |
This place covers:
An intraocular lens (IOL) is an optically active element implanted in the eye, either replacing a removed natural crystalline lens (aphakic) or for additional refractive correction of the existing crystalline lens (phakic) or a separate artificial IOL (pseudo-phakic).
An intraocular prism shifting the image on the retina slightly away from the fovea (e.g. in case of macular degeneration) is considered as an IOL.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Mirrors and prisms in general |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Phakia | the presence of the natural crystalline lens. |
Aphakia | the absence of the natural crystalline lens, either from natural causes or because it has been removed. |
Pseudophakia | substitution of the natural crystalline lens with a synthetic lens. |
Pseudophakic IOLs | are used in cataract surgery |
This place covers:
Corrective lenses for phakic or pseudophakic eyes.
PN - US2002103537 A1 20020801
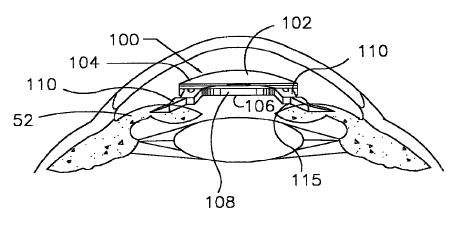
This place does not cover:
Intraocular lenses for replacing the natural cristalline lens |
Piggyback lenses: additional IOL for "fine tuning" already implanted IOL (pseudophakic), A61F 2/1602 (& A61F 2/1648) & A61F 2/1613
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Phakic eye: | having natural crystalline lens |
Pseudophakic eye | having an artificial lens replacing the natural crystalline lens |
This place covers:
Having special lens configuration and particular optical properties, e.g. pseudo-accommodative, having variable focus, aberration correcting, multipart, diffractive, variably absorbing electromagnetic radiation.
This place covers:
Pseudo-accommodative IOL having fixed power or power distribution, the brain selects the sharp image formed on the retina, neglecting blurred images.
This place does not cover:
Accommodative IOL having variable focal power |
This place covers:
A plurality of different but fixed powers usually distributed on concentric circles, bifocal lenses are comprised
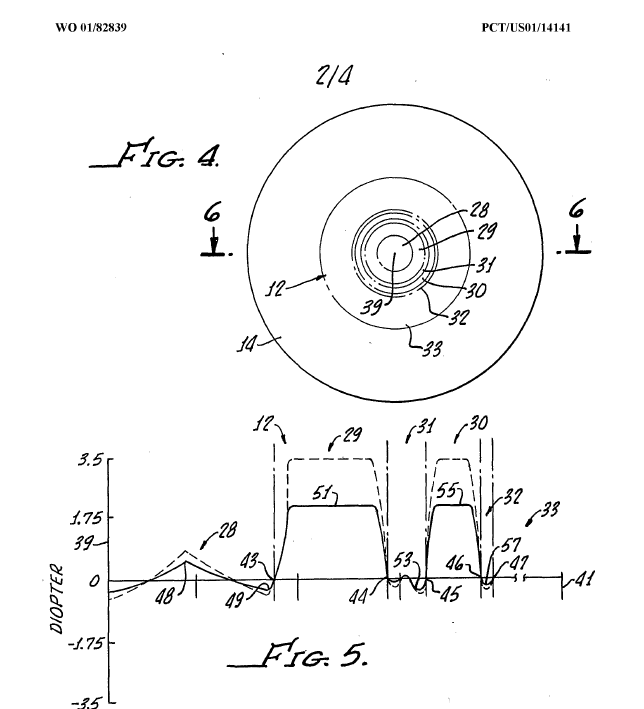
This place covers:
A different lens in each eye, with different foci, e.g. to enable near and far vision.
Term referring to a method of correcting presbyopia by using a lens corrected for distance in one eye (usually the dominant one) and a lens corrected for near in the other eye. Binocular vision is impaired with this method, especially stereoscopic vision. It is assumed that at any time one eye is focused while the other is not and the cortical visual system suppresses this latter image.
[Image taken from WIKIPEDIA]
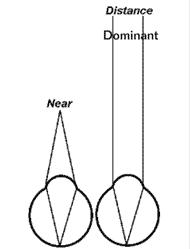
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Monovision in general |
This place covers:
Actuated by external means as e.g. mechanically, by electrical or magnetic fields, or by an internal mechanisms of the eye, as e.g. mechanically or electrically by ciliary body action or by pupillary constriction (accommodating IOL).
This place does not cover:
Pseudo-accommodative lenses simultaneously offering distinct foci to the brain |
This place covers:
Crosslinked regions of a polymeric lens have increased volume, and hence increased refractive index and increased dioptre power,
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Photosensitive materials with macromolecular compounds as photosensing material in general |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/1627
e.g. WO2009124231
For polymeric materials capable of changing focal power in response to crosslinking: A61F 2/1627 and A61F 2/1635 (or A61F 2/1635 and A61F 2/1627 depending on which effect is identified as dominant)
This place covers:
Single optical elements changing position along its optical axis (like a slide machine) or more than one optical elements changing relative distance to alter the focal power.
This place does not cover:
Changing position perpendicularly to longitudinal axis |
For more than one optically active element | |
For one or more optically active element and one or more optically inactive additional elements like e.g. movement arms |
This place covers:
Changing position vertically to visual axis, either one single optical element having irregular power distribution or at least two optic elements changing relative radial position
For more than one optical element: A61F 2/1632 and A61F 2/1648
This place covers:
Changing either shape or curvature of an external surface of the lens or e.g. of an internal interface between to immiscible fluids having different index of refraction.
Two media having different optical properties (e.g. refractive index): A61F 2250/0053
This place covers:
IOL adapted for correcting higher order optical errors either by a particular form or by particular treatment of the refracting surfaces
Aspheric IOL | |
Cylindrical IOL | |
Toric IOL | |
Special surface |
This place covers:
At least two optically active components.
Principle of different correction for the two eyes (far/near, colours, arrangement of power zones) in general: G02C
At least one optically active and at least one optically inactive component, both necessary for the performance of the IOL assembly: A61F 2/1648
Made from materials having different optical properties (e.g. index of refraction) : A61F 2250/0053
This place covers:
IOL having at least one diffractive element
Ophthalmic lenses having diffractive optical surfaces in general: G02C
IOL comprising a Fresnel lens, prism or plate: A61F 2/1656
This place covers:
The Fresnel lens reduces the amount of material required compared to a conventional spherical lens by dividing the lens into a set of concentric annular sections known as Fresnel zones.
This place covers:
Microscopically and macroscopically variable absorption, i.e. due to modification of the structure or variable size of an opening in an opaque medium (e.g. for increasing depth of focus).
Radiopaque |
This place covers:
Any kind of instrument for inserting IOL in an eye during surgery for implantation
Instruments for inserting mechanical ocular implants : A61F 2/148
Instruments for directly injecting therapeutic agents or drug eluting implants in an eye: A61F 9/0008
This place covers:
Instruments for manually (folding) and inserting an IOL in an eye during surgery, e.g. forceps-like

For manual insertion during surgery, e.g. forceps-like instruments, tweezers
This place covers:
IOL insertion instrument having a plunger for moving and ejecting the IOL actuated by rotation

This place covers:
Instruments for inserting an IOL in an eye during surgery, the plunger for moving and ejecting the IOL being actuated by being pushed
This place covers:
Instruments for inserting an IOL in an eye having a plunger that allows for different kind of actuation e.g. for advancing and for ejecting the IOL
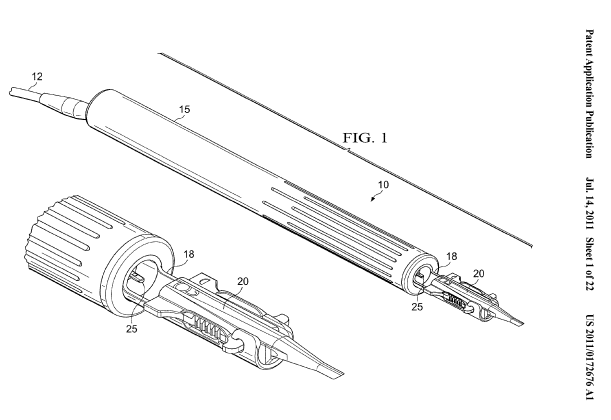
This place covers:
Insertion instruments having a lubricated surface, e.g. of the barrel, the loading chamber, the folding section or the ejecting nozzle, for reducing friction
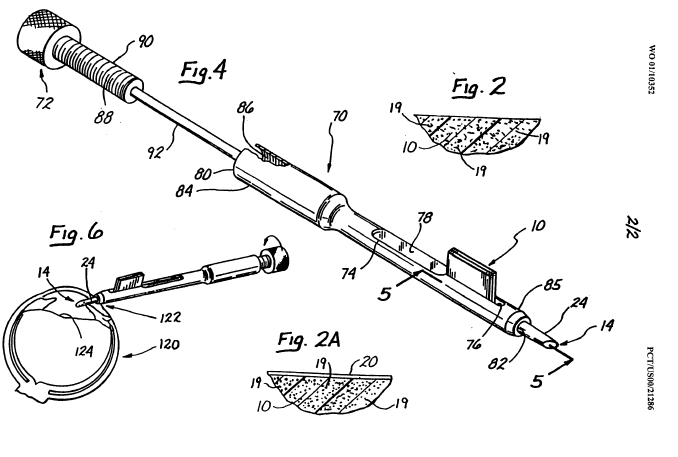
This place covers:
Insertion device having a separate cartridge, e.g. for storing (pre-packing) or for compaction of lens in order to avoid contamination due to handling of the IOL during loading in the inserter.
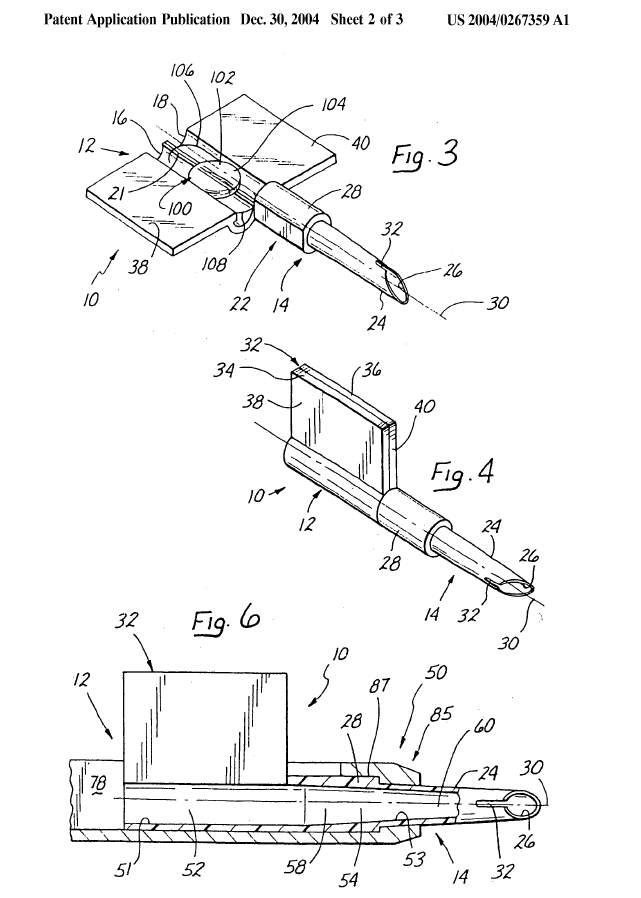
Packages or dispensers for IOL: A61F 2/1691
This place covers:
Packages and holders for IOL ; individual containers or packages suitable for encasing and/or securing intraocular lenses e.g. for shipping and/or storage before implantation 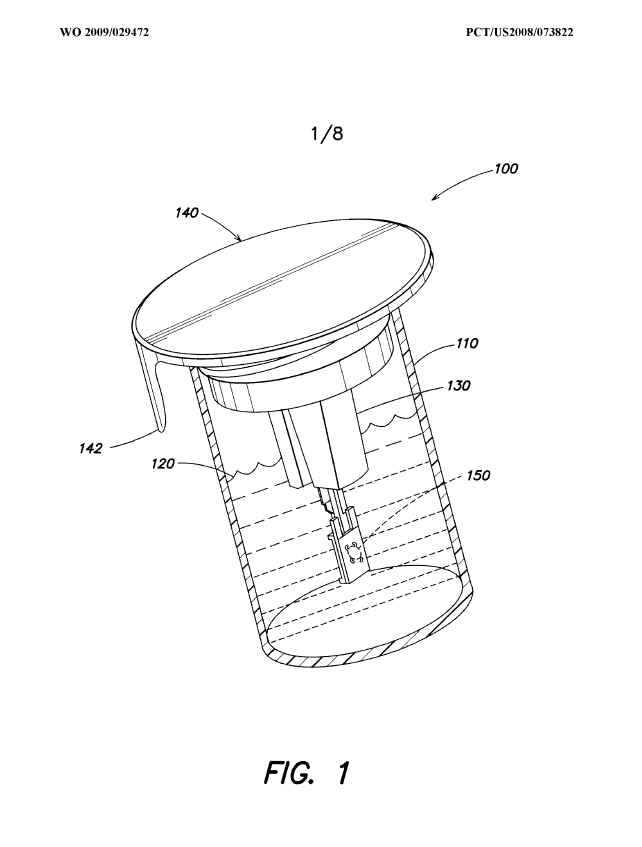
IOL insertion instruments having a separate cartridge: A61F 2/1678
This place does not cover:
Packages and holders for contact lenses |
Implantable holder for an, e.g. exchangeable, IOL |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/1694.
For example ring-shaped elements for supporting or stretching the capsular bag for easier implantation of an IOL 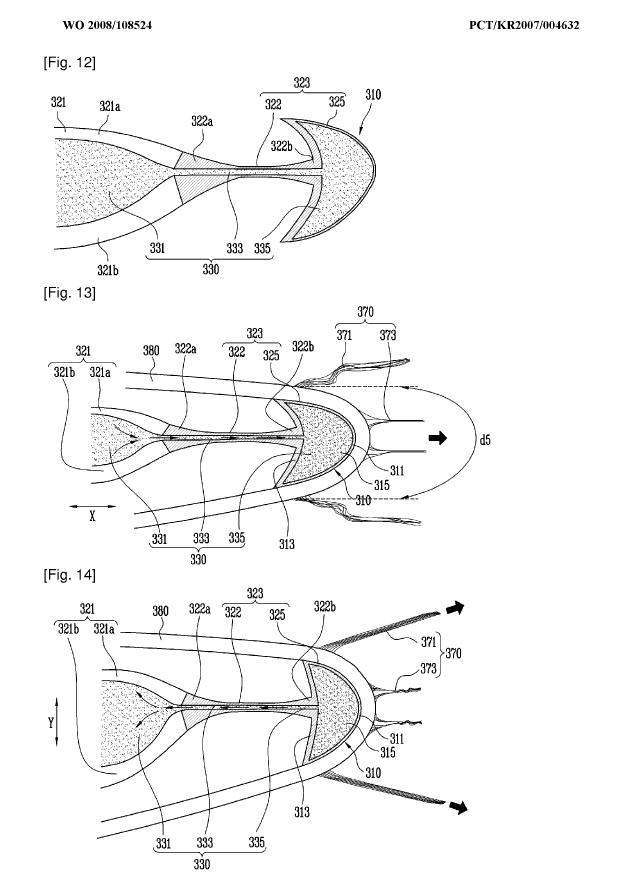
Implants for middle ear ventilation or drainage | |
Cochlear electrodes |
Implants for plugging a hole in a nasal septum: A61B 17/0057
Orthopaedic devices for correcting deformities of the nose: A61F 5/08
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Tracheae or bronchi per se | |
Tracheostomy tubes |
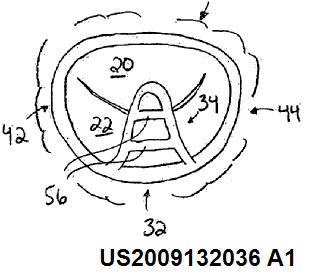
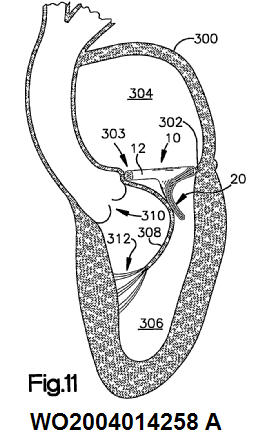
This place covers:
Vascular valves, e.g. venous valves; Heart implants, e.g. passive devices for improving the function of the native valve or the heart muscle; Transmyocardial revascularisation [TMR] devices as this is the most suitable place for.
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Esophageal, Lung/bronchial valves | |
Plugging a cardiac septal defect | |
Motor for/with heart valve |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Valvuloplasty | |
Apical access devices / heart ports |
This place does not cover:
Check valves with hinged closure members in general |
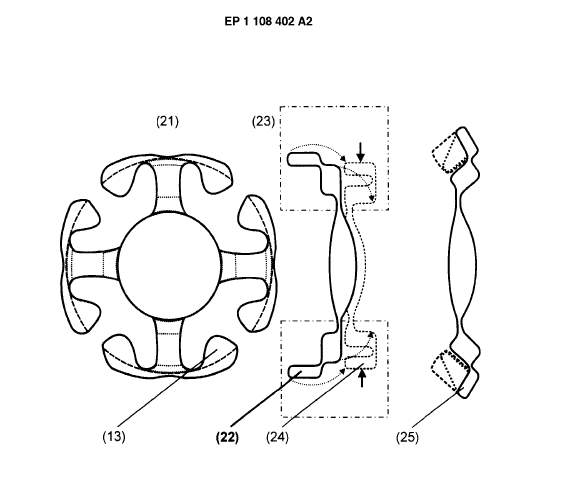
This place covers:
Sewing rings
This place does not cover:
Annuloplasty rings |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Check valves with flexible valve members in general |
Two-part valves with a docking frame into which a valve is mounted during surgery are classified in groups A61F 2/2418 and A61F 2250/006 (modular).
This place covers:
In particular cutting and forming of the prosthetic valve leaflets.
This place does not cover:
Surgical cutting instruments for a heart valve |
This place covers:
This class includes features of the valve leaflets (e.g. geometrical) in relation to their fixation to the scaffold:
This place does not cover:
Annular rigid support rings | |
Stents used for opening blocked vessels |
Stents solely used for heart valves do not get a class in A61F 2/82 but may get codes (additional information).
Two part valves with a docking frame into which a valve is mounted during surgery get both A61F 2/2418 and A61F 2250/006 (modular).
Stent-like anchor members (no class in A61F 2/82 and subgroups is given additionally, except if a stent without valve is explicitly mentioned)
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Delivery devices for annuloplasty implants or for inserts in the coronary sinus for correcting the valve shape or for implants for improving the function of a native heart valve |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Handle mechanisms | |
Heart valve crimping devices |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/243
If an additional retractable sheath is mentioned also a code (additional information) is given A61F 2/2436.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/2439
This place does not cover:
Staples connected by a thread for plicating the annulus | |
Devices for joining two adjacent leaflets at a single point, e.g. clips |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Plugging a cardiac septal defect |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/2442
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/2445
Springs for tensioning or expanding the annulus:
This place covers:
Inserts not only in the coronary sinus but also in other coronary vessels.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/2457
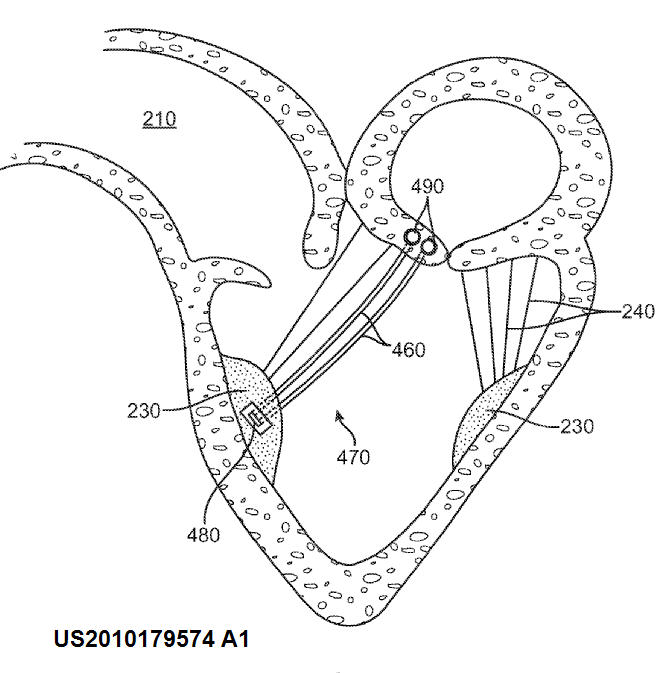
Valves with soft leaflets with artificial chordae get a class in both A61F 2/2412 (subclass where appropriate) and A61F 2/2457
This place does not cover:
Plugs per se |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/246
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/2469
This place covers:
Devices for testing the proper functioning of the prosthetic valve in vivo or in vitro
This place covers:
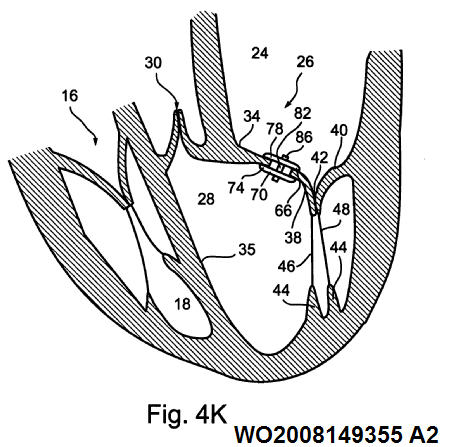
Also annuloplasty devices for venous valves and springs inside or outside the vein for reshaping the annulus.
Annuloplasty devices for venous valves and springs inside or outside the vein for reshaping the annulus. Those also get the appropriate class in A61F 2/2442. Venous valves do not get a class in A61F 2/06 or A61F 2/07
This place covers:
Bags outside the heart wall:
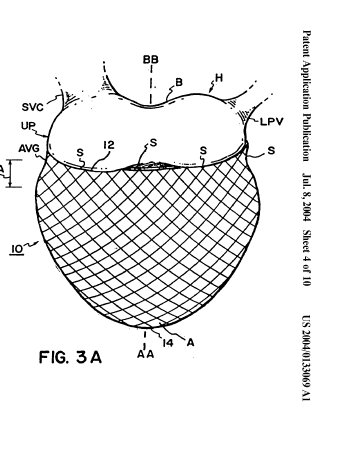
Heart splints:
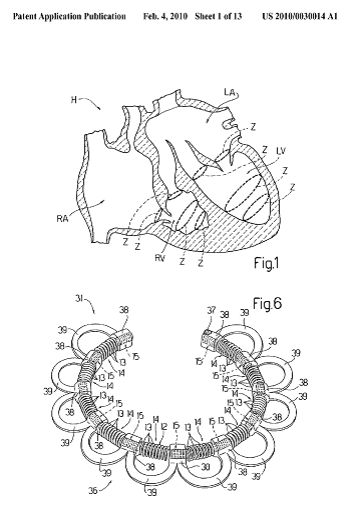
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Active ventricular assist devices, i.e. heartbags with motor |
Heart splints, i.e. two anchors connected by string to reduce heart volume: A61B 2017/048
Devices for improving valve function being external to the heart wall adjacent to the valve annulus: A61F 2/2442
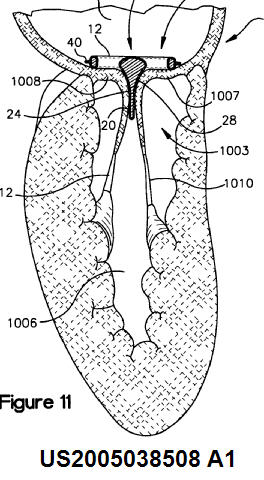
This place covers:
Also internal heart bags/meshes that pull the heart wall inside (e.g. equipped with barbs).
This place does not cover:
Membranes dividing the heart chamber volume into an active and a passive part | |
Barbs, anchors per se |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/2487
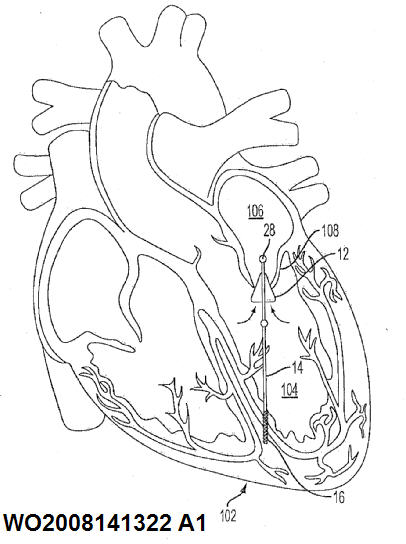
This place covers:
Also implants for revascularising the myocardium, e.g. screws.
This place does not cover:
By-pass connections, i.e. connections from heart chamber to blood vessel or from blood vessel to blood vessel | |
Anastomosis | |
Side-to-side connections, i.e. shunts between vessels (clips without an elongate tubular middle part) |
This place covers:
Also templates for artificial heart valves, annuloplasty rings or other heart implants.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring per se |
This place does not cover:
External devices for promoting erection |
If inflatable do not classify in A61F 2250/0003
This place covers:
Prosthetic bones, i.e. implants for replacing bones or parts of bones.
Surgical implants which are not prosthetic, but added to the natural bone, are classified in A61B 17/00. Examples classified in A61B 17/00 are: Bone plates, bone screws, bone fixators or devices for injection of materials into bone.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Joints | |
Means for introducing bone substitute, for implanting bone graft implants or for compacting them in the bone cavity | |
Devices for grinding or milling bone material | |
Anatomical models for scientific, medical or mathematical purposes |
Additional information is classified under A61F 2002/30001 and A61F 2310/00. Any additional information which may be useful for search must be completely classified.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Skull or cranium | |
Temporo-mandibular joints | |
Bone plates for the jaw | |
Periodontal bone regeneration for consolidating natural teeth |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/2803
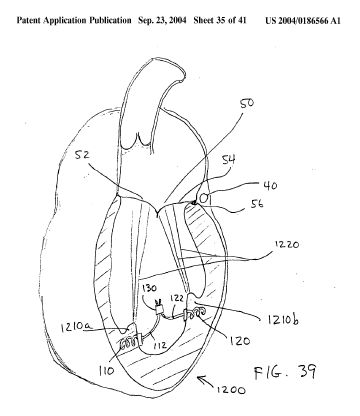
Devices for attachment of external prostheses to bone stumps are classified in both A61F 2/2814 and A61F 2/78.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Means for attaching external orthopedic prostheses to the body |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/2814
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Nets or sleeves applied to surface of endoprostheses | |
Bone plates | |
Bone regeneration in dental surgery |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/2846

Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Devices for autopsy |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/2857
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this place:
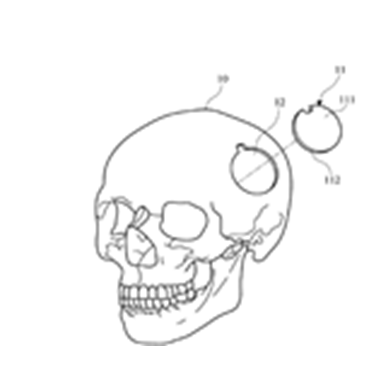
This place does not cover:
Bones for mandibular reconstruction | |
Joints for temporo-mandibular [TM] joints [TMJ] |
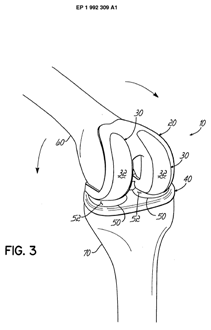
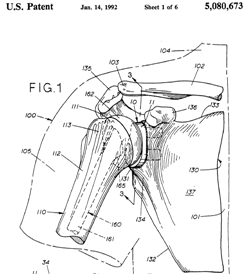
This place covers:
Prosthetic joints, i.e. implants for replacing joints or parts of joints. The classes A61F 2/30 - A61F 2/46 comprise:
Hip joints
Knee and elbow joints
Shoulder joints
Wrist, ankle, finger and toe joints
Vertebrae and vertebral joints
Tools for implanting or extracting prosthetic joints
Operating or control means
Accessories
Cartilage endoprostheses
Special articulating or bone contacting surfaces
Surgical implants which are not prosthetic, but added to the natural joint, are classified in A61B 17/00. Examples classified in A61B 17/00 are: Devices implanted between the natural articulating surfaces, devices implanted adjacent a natural joint for stabilising it.
A61F 2/30 contains implantable devices for replacing anatomical joints.
Additional information is classified under A61F 2/30 - A61F 2/48. Any additional information which may be useful for search must be completely classified.
Additional information concerning a particular anatomical joint is classified under the corresponding subgroup (A61F 2/32 - A61F 2/48).
Additional information concerning accessories is classified under A61F 2/30721.
Additional information concerning cartilage endoprostheses is classified under A61F 2/30756.
Additional information concerning external or bone-contacting surfaces of joint or bone prostheses is classified under A61F 2/30767.
Additional information concerning manufacturing of endoprostheses is classified under A61F 2/3094.
Additional information concerning anatomical joints not covered by A61F 2/32 - A61F 2/44 is classified under A61F 2/30988.
Further additional information applicable for joint or bone prostheses is classified under A61F 2002/30003 - A61F 2002/30667.
Additional information concerning the use of particular materials in joint or bone prostheses is classified under A61F 2310/00.
Additional information for which classes exist in neighbouring fields, is coded in said fields, e.g.
- Joint distractors: A61B 17/025
- Surgical staples for bones: A61B 17/0642
- Securing of bone screws: A61B 17/8033, A61B 17/8052
- Fastening to the bone by wires, bands or straps: A61B 17/842
- Fastening to the bone by screws or pins: A61B 17/86
- Packages for prostheses: A61F 2/0095
- Fixation devices for tendons or ligaments: A61F 2/08
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Tools for inserting plugs | |
Sealing collars for use during cementing |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/30723
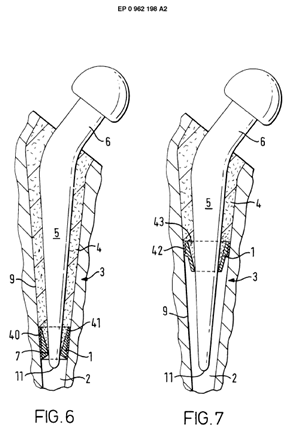
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/30724
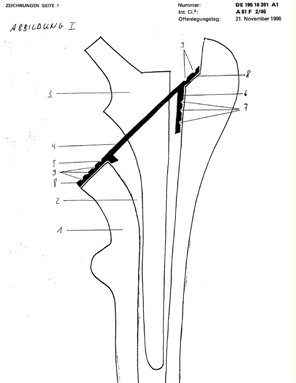
This place does not cover:
Modular inserts, sleeves or augments |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Sealing collars for use during cementing |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/30728
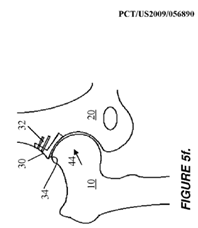
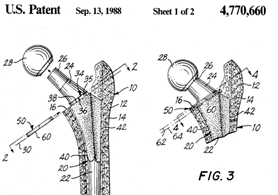
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/30734

Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Proximal parts of endoprosthetic femoral shafts | |
Non-prosthetic trochanteric devices |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/30739
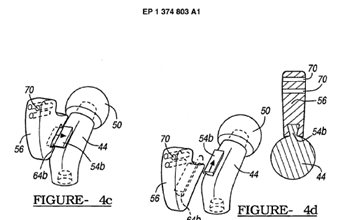
This place does not cover:
Tool for implantation with bone cement and with sealing collar for bone cavity |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Sealing membranes for retaining bone substitute |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/30742
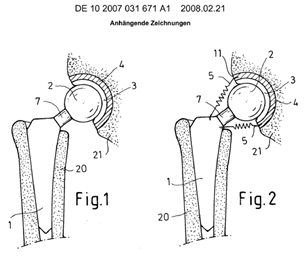
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/30744

Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Cartilage endoprostheses |
This place does not cover:
Femoral heads implanted without ablation of the shole natural femoral head |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/30756
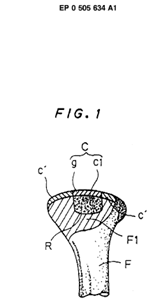
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Materials for coating prostheses |
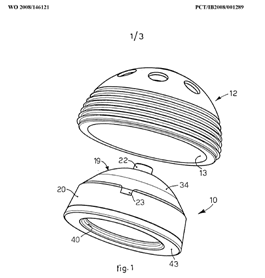
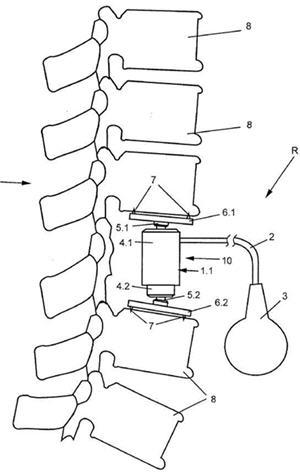
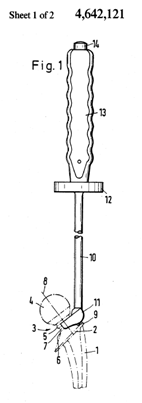
This place covers:
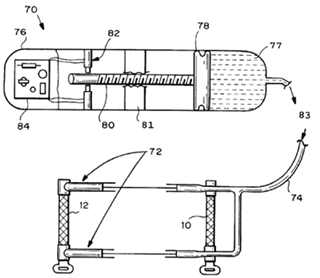
The following figures show an illustrative example of subject matter classified here. Figure 1 is a longitudinal section of a surgical implant (1) having a structured surface (2) for contact with bone tissue. A plurality of cavities (3) are mechanically produced on surface (2). The cavities (3) are provided with an undercut (5). Figure 2 is a top view on the surface region of the surgical implant shown in figure 1.

Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Etching into the surface |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Computer-assisted sizing or machining of dental prostheses | |
CAD-CAM techniques per se |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Endoprostheses for mandibular reconstruction |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/3099
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Non-prosthetic internal fixation devices for the femoral head or neck |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/3601
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Endoprosthetic cartilage |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/3603
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/3607
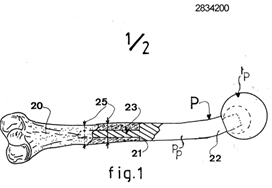
This place does not cover:
Femoral endoprostheses for replacing only the epiphyseal or metahpyseal parts of the femur |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/3609
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/3662

Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Trochanteric devices connected to said proximal parts |
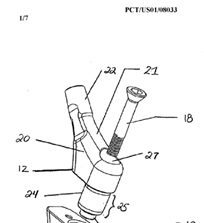
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/367
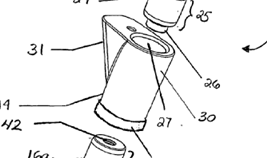
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/3672
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/3676
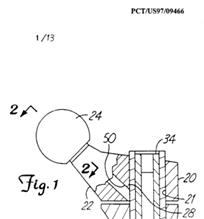
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/3804
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/3859
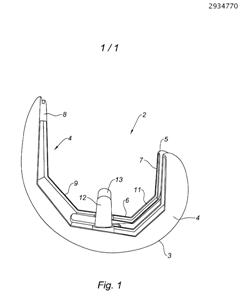
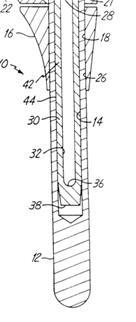
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/3868
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/3872

Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/3877
This place does not cover:
Knee prostheses with sliding tibial bearing |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/3886
This place does not cover:
Knee prostheses with sliding tibial bearing |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Replacing only the epiphyseal or metaphyseal parts of the femur |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/4014
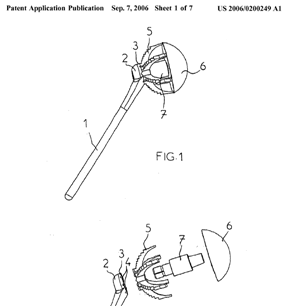
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/4059

Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/4081
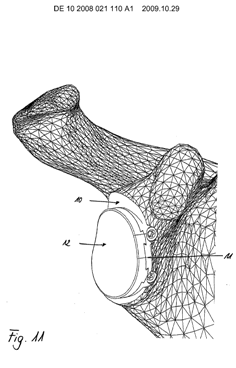
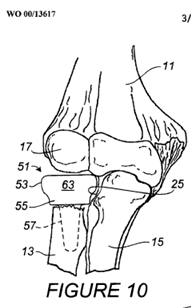
This place covers:
- facet joint prostheses,
- facet joint fusion implants, if the implant replaces the joint.
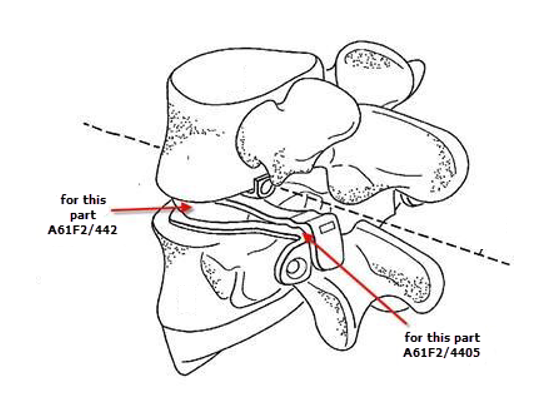
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Devices implanted between spinous or transverse processes |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/441
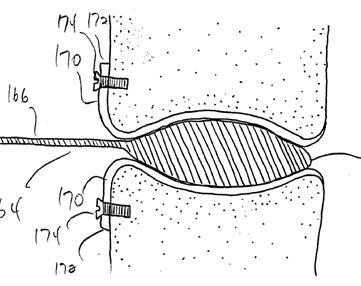
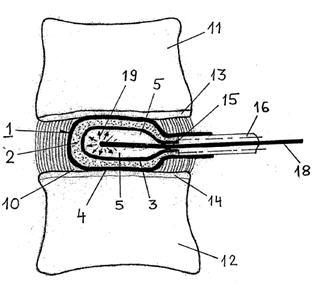
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Non-disc-shaped intervertebral inflatable pockets | |
Intervertebral fusion implants |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/442
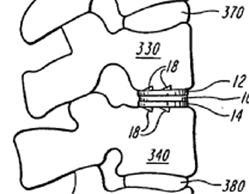
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/4425
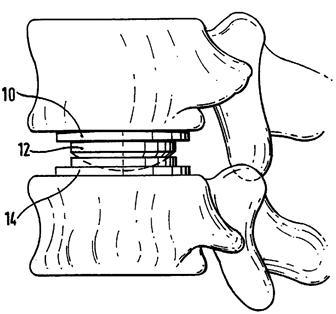
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Intervertebral discs |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/4455

Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/446
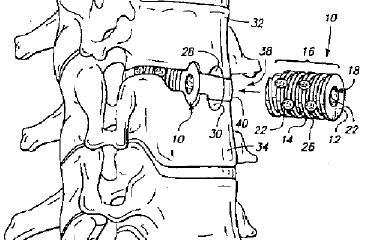
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/4465
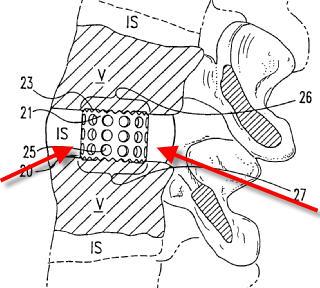
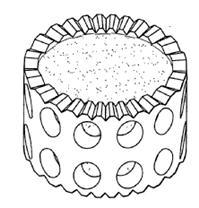
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/447
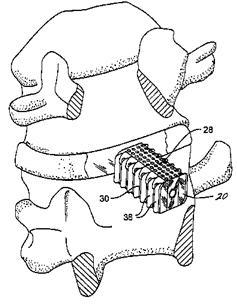
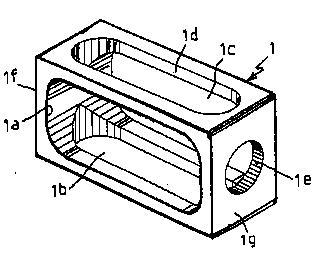
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Surgical instruments |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
For introducing bone cement |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/4605
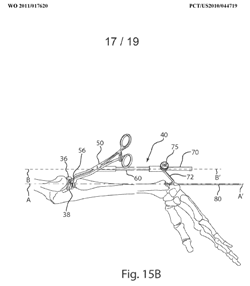
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/4607
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/4609
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/461
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/4611
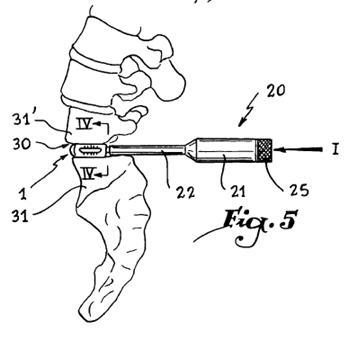
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/4612
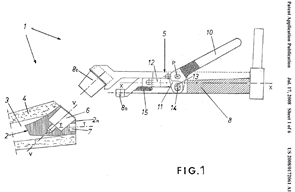
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/4614
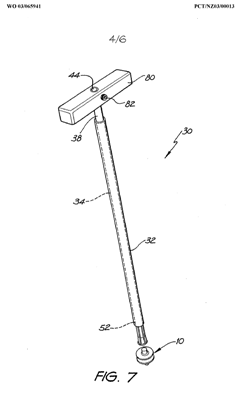
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/4618
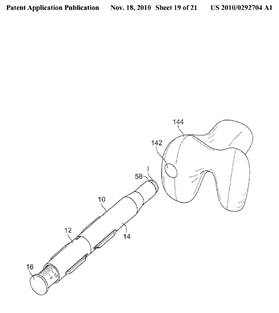
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/4637
This place does not cover:
Surgical bone cutting instruments for harvesting bone graft |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Bone prostheses | |
Bone as a prosthesis material | |
Disintegrating or milling devices | |
Cutting in general |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
For surgical instruments |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
For cleaning teeth cavities | |
Irrigators |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
This place covers:
Prostheses, i.e. artificial substitutes or replacements for parts of the body, which are NOT implantable in the body, as well as fitting and attaching measures for such devices.
This place does not cover:
Closure means for urethra or rectum or for artificial body openings therefor |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Implantable devices | |
Bone stump | |
Orthopaedic devices | |
Brassieres | |
Program-controlled manipulators | |
Exoskeleton | |
Gripping heads | |
Joints | |
Arms |
Designing or making customized prostheses, e.g. using templates, finite-element analysis or CAD-CAM techniques: A61F 2/5046
Prostheses which are not implantable; e.g. upper and lower artificial limbs, or mammary prostheses: A61F 2/54, A61F 2/60, A61F 2/52
Operating or control means for such prostheses: A61F 2/68
Means for assembling, fitting or testing prostheses: A61F 2/76
Means for attaching such prostheses to the body: A61F 2/78
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Special structural features of bone or joint prostheses having elastic means or damping means, different from springs |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Coating or prosthesis-covering structure made of elastic material, e.g. of elastomer | |
Prostheses not implantable in the body having spring elements | |
Prosthetic feet non-implantable in the body having a plate-like or strip-like spring element, e.g. an energy-storing cantilever spring keel |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Special structural features of bone or joint prostheses implantable into the body having a pocket filled with solid particles |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adjustable prosthetic joints implantable into the body |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Special structural features of bone or joint prostheses for adjusting length |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Prostheses not implantable in the body having damping means, e.g. shock absorbers |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Prosthetic implantable hinged joint, e.g. with transverse axle restricting the movement |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Artificial muscles implantable into the body |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Features concerning the anatomical functioning or articulation of the implantable prosthetic joint having rolling elements between both articulating surfaces |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Connections or couplings between prosthetic parts locked by spring biased locking mechanism | |
Implantable bone or joint prostheses having special structural features such as spring elements | |
Prostheses not implantable in the body having elastic means different from springs, e.g. including an elastomeric insert |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Special structural features of implantable bone or joint prostheses |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Prostheses not implantable in the body for adjusting length |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Implant or prostheses properties specially designed for children, e.g. having means for adjusting to their growth |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Implant or prostheses properties with identification means; Administration of patients |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Prostheses implantable into muscles, tendons or ligaments |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Features concerning the anatomical functioning or articulation of the implantable prosthetic ball-and-socket joints |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Magnetic properties of materials and coating materials of implantable prosthetic joints |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Bioelectric control of protheses not implantable in the body, e.g. myoelectric |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Means for transferring electromagnetic energy to implants for data transfer |
The bioelectrical control may be in response to physiological signals or parameters recorded from the body as found in A61B 5/389 or A61B 5/4851.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Detecting, measuring or recording bioelectric signals of the body or parts thereof | |
Electromyography |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Special tools or methods for implanting or extracting artificial joints using heating means |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Special tools or methods for implanting or extracting artificial joints using cooling means |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring instruments used for implanting artificial joints |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Testing instruments for artificial joints | |
Means for testing implantable prostheses |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Heating or cooling appliances for medical or therapeutic treatment of stumps after amputation |
Prosthetic liners or sockets with a heating or cooling function should also be classified under A61F 2007/0051 as Additional Information.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Connections or couplings between implantable prosthetic parts using adhesives |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Cosmetic coverings for prostheses not implantable in the body |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Connections or couplings between implantable prosthetic parts, retained or tied with a rope, string, thread, wire or cable |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Connections or couplings between implantable prosthetic parts, made by longitudinally pushing a protrusion into a complementarily-shaped recess, e.g. held by friction fit | |
Snap connection between implantable prosthetic parts locked by an additional locking mechanism such as a snap connection |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Connections or couplings between implantable prosthetic parts using hook and loop-type fasteners |
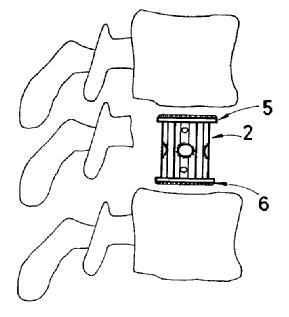
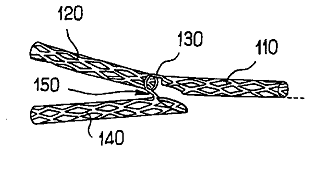
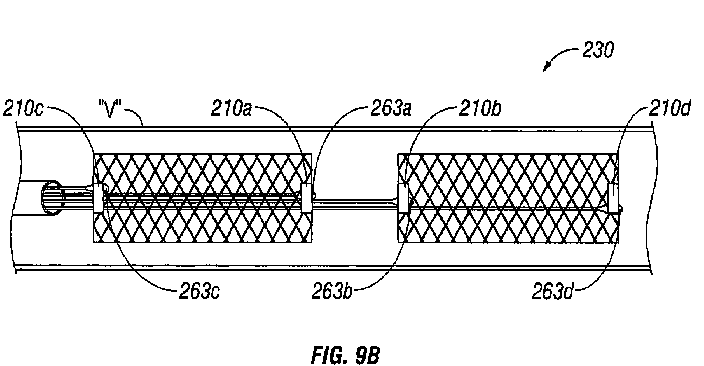
This place covers:
Stents with tubular structures deployed within a stenosis in order to widen and support the vessel. The stent is usually made from a rigid material like metal or polymer.
Illustrative examples of subject matter classified in this place:
1.
A61F 2/82 (stents), A61F 2002/065, A61F 2002/828 (means for connecting a plurality of stents).
2.
A61F 2/82 (stents), A61F 2002/067, A61F 2002/828, A61F 2/856: when it is not clear if there is a portal or if there are two stents connected, both possibilities are to be classified.
This place does not cover:
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Instruments specially adapted for placement or removal of stents or stent grafts |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Surgical instruments, devices or methods, e.g. tourniquets, for closing wounds or holding wounds closed | |
Materials for other surgical articles, e.g. stents | |
Urethral catheters | |
Dilators | |
Coating by spraying | |
Bending sheets of metals for making tubes | |
Wire-working in the manufacture of medical instruments, e.g. stents | |
Working by laser beam, e.g. welding, cutting or boring | |
Moulds or cores | |
Injection moulding | |
Etching metallic material by chemical means | |
Electroplating tubes | |
Stent braiding |
Additional information for stents is classified in breakdown codes A61F 2002/821 - A61F 2002/828 when appropriate.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/844
CLXVa. A61F 2/848
having means for fixation to the vessel wall, e.g. barbs
The following additional information is given to stents when appropriate:
Barbs | |
provided on at least one of the ends |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/852
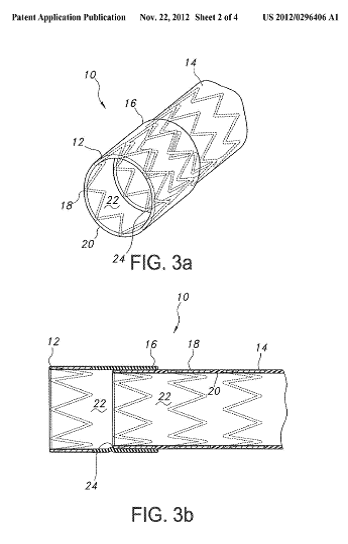
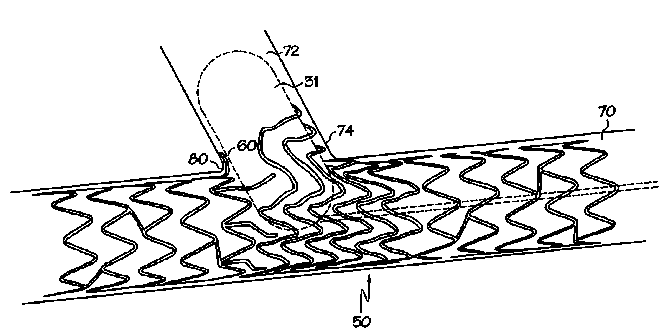
This place covers:
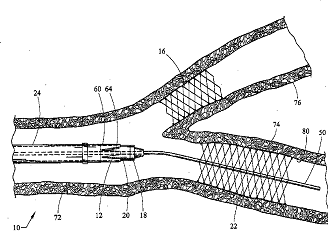
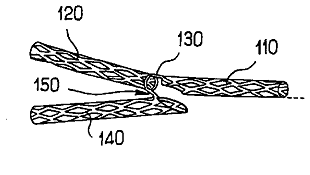
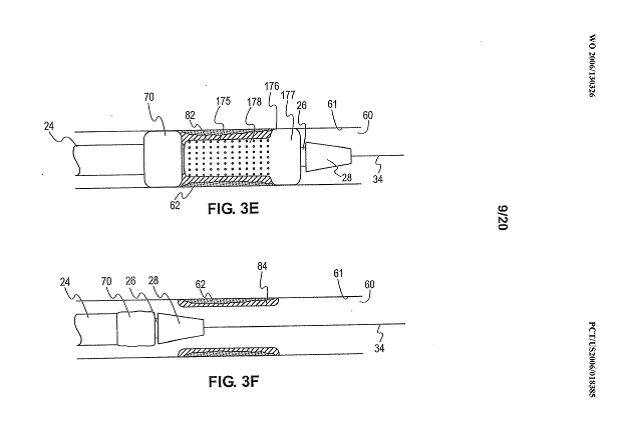
Single tubular stent with a passage in side of the stent for allowing access to secondary lumen (see passage 60 in the example drawing).
This place does not cover:
Stents or stent-grafts having a Y-shape |
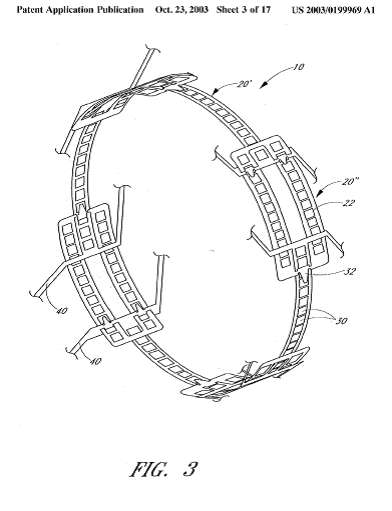
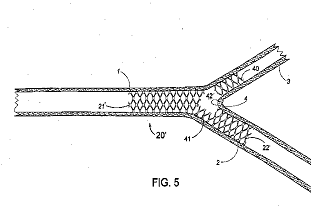
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/885
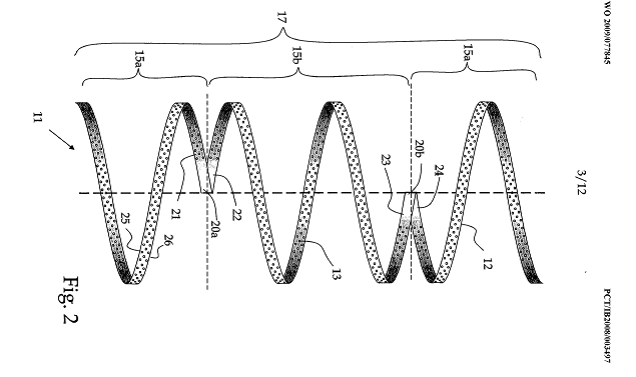
This place covers:
Single, discrete rings joined by a connector.
Stent rings which are connected in order to allow flexibility of the whole structure (see connectors (4) between stent rings (2) in the example drawing).

This place does not cover:
Stent-grafts | |
Means for connecting a plurality of stents allowing flexibility of the whole structure | |
Stents having meander bands being connected to each other by struts |
Illustrative example of a document classified in A61F 2002/828 and not A61F 2/89 to demonstrate the difference between both groups:
US2009/0254164 A
A61F 2002/828 : Stents must be "standing alone" structures (in the absence of the connector, they would still accomplish their supporting function). Do not give A61F 2250/006 "modular" if they are joined (single structure).
Illustrative example of a document classified in A61F 2/915 and not A61F 2/89 to demonstrate the difference between both groups:
US2009105809
The following additional information is given to stents when appropriate:
Frangible connectors | |
Biodegradable covering or connection |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Woven tubular fabrics |
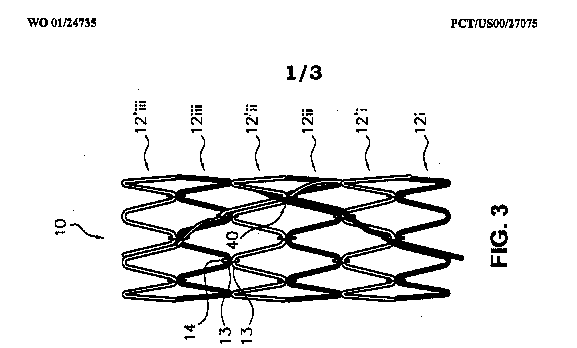
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/90
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms:
- "net", "net-like", "mesh" and "mesh-like"
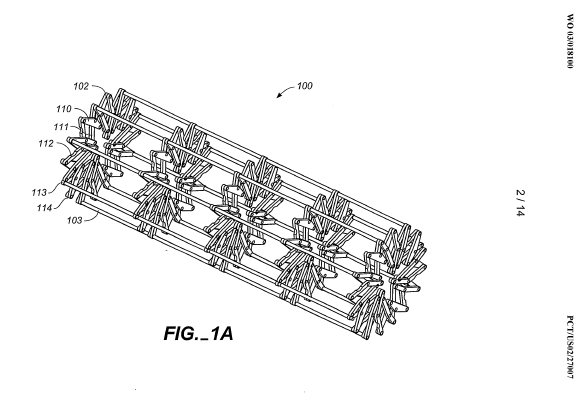
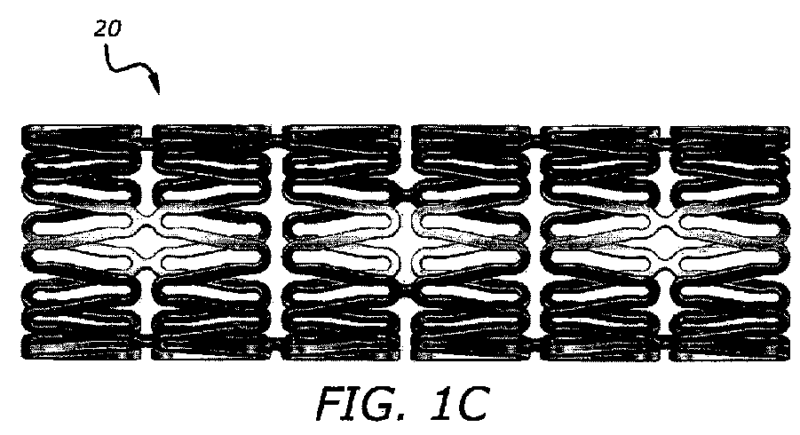
This place covers:
Net- or mesh-like stents made from perforated sheet material or tubes. Perforated sheet material or tubes are created by methods including, for example, laser cutting, etching or some other techniques.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this place: 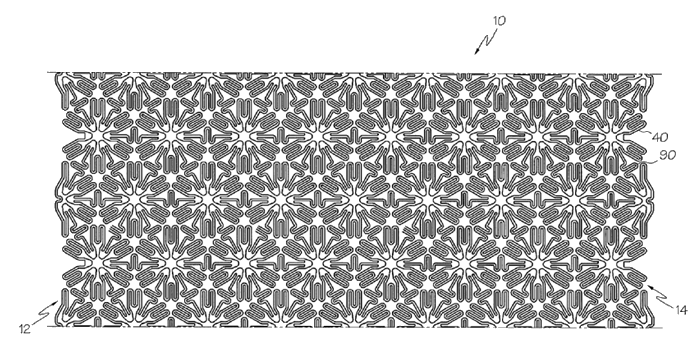
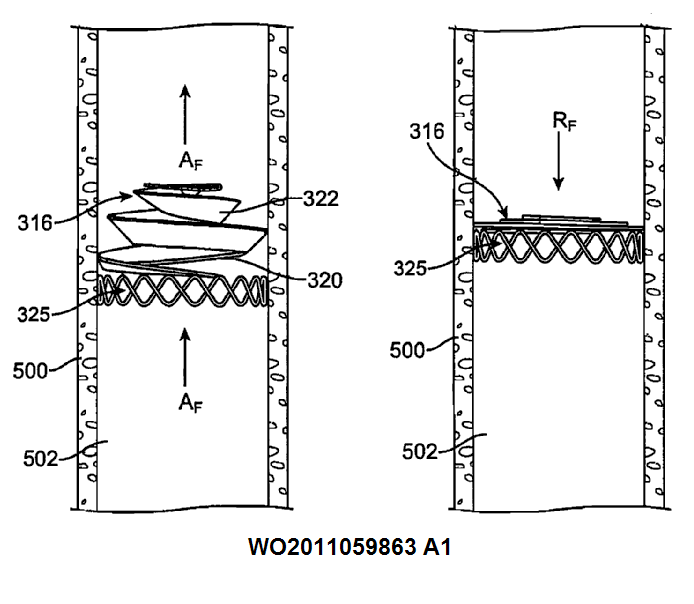
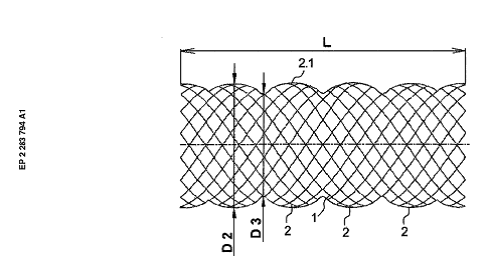
This place covers:
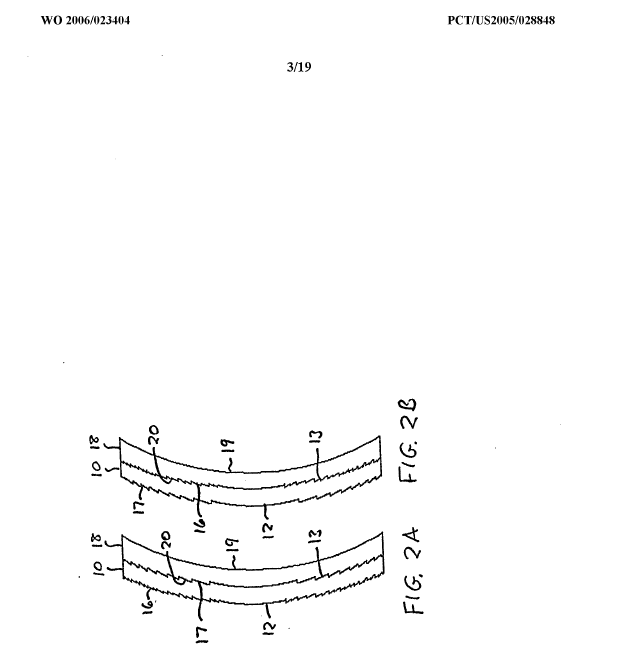
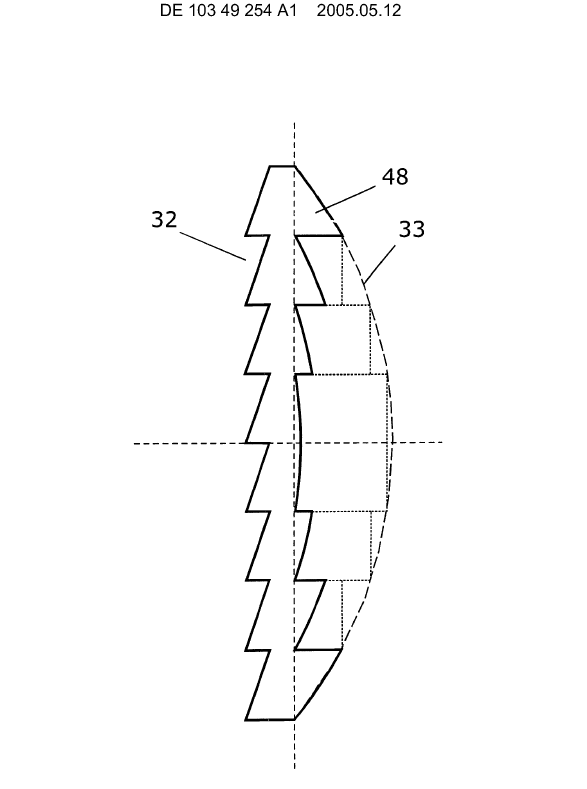
Stents having a meander or wave-like pattern. The stent comprises several meander bands. Each meander band forms peaks and throughs. The bands are connected to each other by struts (see connector 50 between bands 40 and 60 in the example drawing) or directly connected without struts.
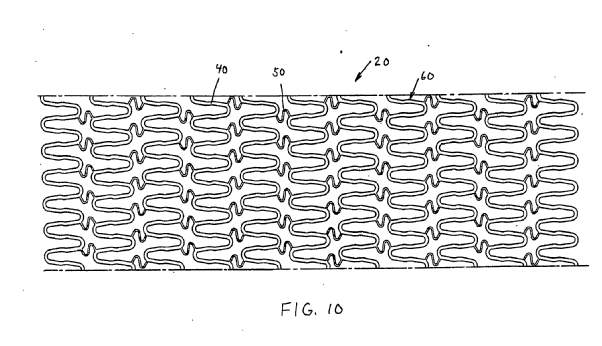
The meander structure receives further additional classification:
The meander having a difference in amplitude along the band: A61F 2002/91508
The meander having a change in frequency along the band: A61F 2002/91516
Within the whole structure different bands showing different meander characteristics, e.g. frequency or amplitude: A61F 2002/91525
Characterised by the phase between adjacent bands: A61F 2002/91533
Adjacent bands are arranged out of phase: A61F 2002/91541
Adjacent bands being connected to each other: A61F 2002/9155
Adjacent bands being connected peak to peak, i.e. bridge with each end connected to a convex side of an apex: A61F 2002/91558
Adjacent bands being connected trough to trough, i.e. bridge with each end connected to a concave side of an apex: A61F 2002/91566
Adjacent bands being connected peak to trough, i.e. bridge with one end connected to a convex side of an apex and with the other end connected to a concave side of an apex: A61F 2002/91575
Adjacent bands being connected by a bridge, whereby at least one of its ends is connected along the length of a strut between two consecutive apices within a band: A61F 2002/91583
Locking connectors, e.g. using male-female connections: A61F 2002/91591
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
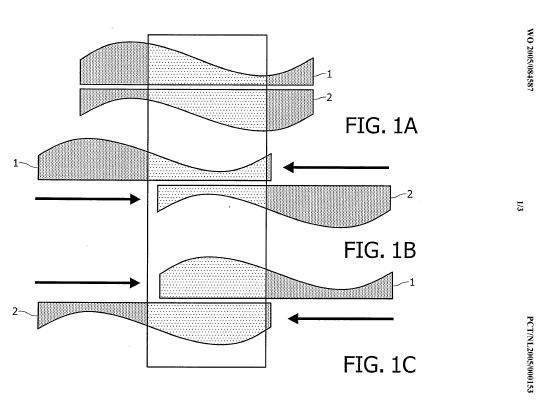
An amplitude is: 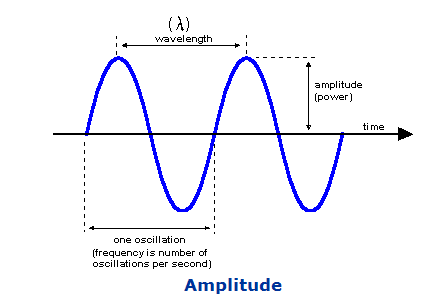
Frequency:
Sinusoidal waves of various frequencies; the bottom waves have higher frequencies than those above. The horizontal axis represents time.
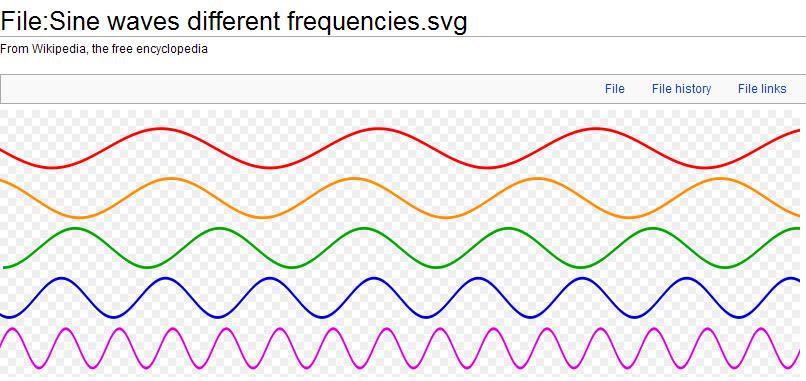
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms:
- "rolled-up" and "coiled"
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 2/945
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Means for mounting a stent or stent-graft onto or into a placement instrument | |
Instruments for placing occluding devices | |
Handles for angioplasty balloon inflation |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Having retaining means other than an outer sleeve, e.g. male-female connector between stent or stent-graft and instrument | |
The retaining means being filaments or wires | |
Handle assemblies therefor | |
For retrieval of stents or stent-grafts | |
For repositioning of stents or stent-grafts | |
Closing wounds, or holding wounds closed | |
Catheters; hollow probes |
This place does not cover:
Stents or stent-grafts having a Y-shape |
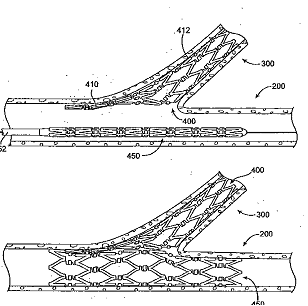
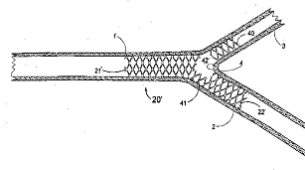
Illustrative examples of subject matter classified in A61F 2/954
and in particular to point out the differences between stents and their delivery devices having a secondary lumen or bifurcation:
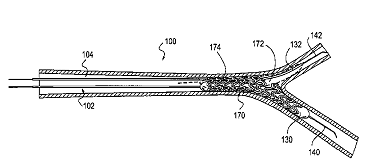
WO 02/056799

| A61F 2/856 only if stent is not described A61F 2/954 (class for delivery device for bifurcations) |
| A61F 2/954, A61F 2/856, A61F 2250/006 modular if further stents are applied NEVER A61F 2002/065 These are not Y shaped |
EP0904746 | A61F 2/954, A61F 2/856 eventually A61F 2250/0039 (differing in diameter) |
| A61F 2/954, A61F 2/82/low or A61F 2/82 /lowspecific stent class or additional information A61F 2002/067 :This additional information can be given in exceptional cases like this one, where the vessel is Y shaped even though there are no 3 distinctive stents present. |
| A61F 2/856, A61F 2/954, A61F 2002/821 (ostial) A61F 2/852 (overlapping) |
| A61F 2/82 /low (specific stent class) A61F 2002/065, A61F 2002/828 (means for connecting a plurality of stents) |
| A61F 2/82 /low (specific stent class) A61F 2002/067, A61F 2002/828, A61F 2/856 :If it is not clear if there is a portal or if there are 2 stents connected, classify both possibilities |
Means for holding the stent on the balloon, e.g. using protrusions, adhesives or an outer sleeve | |
the means being inside the balloon |
This place covers:
Retractable outer sleeves
with additional retaining means |
This place covers:
The wording in the title "released" is regarded as "expanded", i.e. "the middle portion of the stent or stent-graft is expanded first"
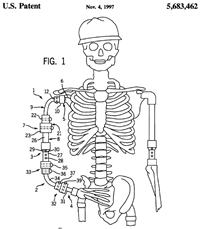
This place covers:
devices which are applied to natural legs for lengthening said legs, e.g. to compensate for a difference in length between the two legs of a user.
Artificial legs or feet or parts thereof: A61F 2/60
Shoe-like orthopaedic devices for protecting the feet against injuries after operations: A61F 5/0195
This place does not cover:
Internal fixation devices |
This place covers:
Methods or devices enabling invalids to operate a device which, otherwise, the person would not be able to, e.g. control of computers or ambulation devices like a wheel-chair.
Chairs or personal conveyances specially adapted for disabled persons, e.g. wheelchairs: A61G 5/00.
Input arrangements or combined input and output arrangements for interaction between user and computer: G06F 3/01.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
This place covers:
Orthopaedic methods or devices for non-surgical treatment of bones or joints, e.g. long-term immobilising or pressure directing devices for treating broken or deformed bones such as splints, casts or braces. Furthermore, it covers devices worn by the patient for reception of urine, faeces, catamenial or other discharge, e.g. colostomy devices. Also, devices for preventing snoring as well as for correcting stammering or stuttering are covered.
Prostheses not implantable in the body: A61F 2/50.
This place does not cover:
Bandages, dressings or absorbent pads |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Closure means for urethra or rectum | |
Penile implants | |
Operating or control means for external prostheses | |
Pessaries | |
Insoles for arch support | |
Mattress underlays | |
Devices for taking faeces samples | |
Devices for taking sperm samples | |
Devices for taking urine samples | |
Surgical instruments or methods for treatment of bones or joints, devices specially adapted therefor | |
Massage of genitals | |
Adhesive for colostomy devices | |
Devices for preventing snoring by gas treatment | |
Handcuffs |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arm-rests for use as writing aids |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Corn-pads or corn-rings |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Tourniquets |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Valves specially adapted for medical use | |
Connection of valves to inflatable elastic bodies | |
Valves per se |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Handcuffs |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Penis implants | |
Massage of the genitals |
This place covers:
- Devices worn by the patients for reception of urine, faeces, catamenial or other discharge, e.g. portable urination aids.
- Colostomy devices, e.g. worn by patients for reception of discharge.
This place does not cover:
Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels | |
Drainage appliances for wounds |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adhesives for colostomy devices | |
Materials for colostomy devices | |
Emptying devices for urine bags |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adhesives or sealing pads therefor |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Devices for influencing the respiratory system by gas treatment |
This place covers:
Contraceptive devices; pessaries and applicators therefore, which can be used by males or females, and which can be applied externally, e.g. condoms, sheaths or the like; internally, like devices worn in the vagina to support the uterus, remedy a malposition, or prevent conception; as well as implantable occluding device, e.g. for vas deferens or fallopian tubes.
Devices for promoting penis erection: A61F 5/41.
Massage of genitals: A61H 19/00.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Obstruction of tubular structures by internal devices | |
Chemical aspects of contraception |
Packages or dispensers for contraceptive devices – A61F 6/005.
Contraceptive devices for males, like condoms, sheaths or the like, e.g. combined with devices protecting against contagion – A61F 6/04.
Contraceptive device for females, like intra-vaginal or intra-uterine devices – A61F 6/08.
Occluders for vas deferens or fallopian tubes – A61F 6/20.
Note: Additional information is classified under A61F 6/00.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Surgical instruments for ligaturing of tubular organs, e.g. blood vessels or umbilical cord |
This place covers:
Heating and cooling of (parts of) a patient for therapeutic purposes not resulting in tissue destruction or intended tissue damage.
This place does not cover:
Hyperthermia using electric or magnetic fields or ultrasound |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Protective garments | |
Gloves | |
Hats, caps, hoods | |
Attachments for beds | |
Bed covers, blankets, pillows | |
Heating or cooling for surgical purposes, such as tissue removal, ablation, coagulation, etc. | |
Heating or cooling of tissue immediately around tissue treated by a surgical probe | |
Massage and therapeutic baths | |
Temperature treatment of blood in bypass of the human or animal body | |
Heating or cooling media before injection into the body | |
Heating for divers | |
Materials for the production of heat or cold by chemical reaction | |
Compression machines, plants or systems with non-reversible cycle | |
Producing ice | |
Devices using naturally cold air or cold water | |
Electric heating devices |
Documents describing treatment with a device for heating alone or a device described to be able to apply both heating and cooling (with the necessary adaptations to the heat source, e.g. a self-heating exothermic pad which is described or claimed as being equally configurable as self-cooling endothermic pad by using the appropriate chemicals) should be classified in A61F 7/00 - A61F 7/08 or A61F 7/12.
Documents related to bags, pads etc. exclusively using cooling should be classified in A61F 7/10 (e.g. chemically cooled endothermic pads only described for cooling in A61F 7/106).
As an exception in A61F 7/00, A61F 2007/0056 and A61F 2007/0063 also exclusively deal with cooling.
Further details of subgroups
A61F 2007/0001: locations on the human body for heating and cooling. Not for invention information. Headgroup A61F 2007/0001 not to be used for classification.
A61F 7/0053: Cabins, rooms chairs or other equipment for treatment with a hot or cold circulating fluid. Does not cover heating pads with a circulating fluid, those are to be classified in A61F 7/02.
A61F 2007/0054: "closed fluid circuit" refers to a device in which the circulating thermal medium, e.g. water, is not in direct contact with the treatment area;
A61F 2007/0059:"open fluid circuit" refers to a device in which the circulating thermal medium, e.g. water, is in direct contact with the treatment area;
A61F 7/007: Electrically heated or cooled devices.
A61F 7/0085: Devices for generating hot or cold treatment fluids, the devices not being in direct contact with the patient. Only the fluid is transported from the device to a separate patient heating or cooling device.
A61F 7/0097: Heating blankets. Only blankets with an active heating or cooling source, no ordinary blankets keeping warm by insulation only (to be classified in A47G 9/0207).
A61F 7/02: Compresses, poultices or other pads for heating or cooling.
A61F 7/03: Chemical heating devices. Not the chemicals as such (to be classified in C09K 5/00), only as part of a device to be used on the body for therapy.
A61F 7/08: hot water bottles for heating, refillable with a non-circulating hot or cold fluid.
A61F 7/10: Cooling bags, pads etc. exclusively used for cooling.
A61F 7/106: Chemical cooling devices. Not the chemicals as such (to be classified in C09K 5/00), only as part of a cooling device used on the body.
A61F 7/12: Cooling devices for internal body cavities.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
hyperthermia | heating of tissue up to but not beyond the point of tissue damage |
hypothermia | cooling of tissue down to but not beyond the point of tissue damage |
This place covers:
"closed fluid circuit" refers to a device in which the circulating thermal medium, e.g. water, is not in direct contact with the treatment area.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Heating or cooling appliances for medical or therapeutic treatment connected to the human body with belt or strap with pockets for receiving packs or pouches | |
Heating or cooling appliances for medical or therapeutic treatment incorporated in a pocket of clothing or garments |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Heating or cooling appliances for medical or therapeutic treatment of the human body with a closed fluid circuit, e.g. hot water | |
Heating or cooling appliances for medical or therapeutic treatment of the human body with an open fluid circuit |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Heating or cooling appliances for medical or therapeutic treatment connected to the human body with belt or strap with pockets for receiving packs or pouches | |
Heating or cooling appliances for medical or therapeutic treatment incorporated in a pocket of clothing or garments |
Documents with self-cooling as well as self-heating devices are classified here, even though the title covers only self-heating devices
This place does not cover:
Caps with means for protecting the eyes | |
Visors for helmets | |
Eye baths | |
Sunglasses or goggles having the same features as spectacles |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Retractors | |
Manipulators specially adapted for use in surgery | |
Appliances for aiding patients or disabled persons to walk | |
Exercisers for the eyes |
The "subdivision" Indexing Code symbols (i.e. the non "parallel" Indexing Code symbols) are used for classifying as well the invention information as the additional information. They are stored only in the additional information field.
The "orthogonal" Indexing Code symbols are also used.
The symbols in A61B 17/00 and A61B 18/00 are to be used for classifying additional information in case there is no appropriate symbol in A61F 9/00736, A61F 9/0079 or A61F 9/008.
This place covers:
Eye droppers
Baths for the eyes : A61H 35/02
Containers with means for dispensing liquid medicaments : A61J 1/1443
Droppers : B65D 47/18
This place does not cover:
Putting in contact lenses | |
Introducing or retaining media in cavities of the body in general |
This place covers:
Ocular inserts for drug delivery

This place does not cover:
Cornea implants for repair of corneal tissue | |
Corneal inlays or onlays for refractive correction | |
Stromal implants for refractive correction | |
Implantation instruments specially adapted therefor | |
Intraocular lenses | |
Implantation instruments for intraocular lenses | |
Pharmaceutical compositions of ocular inserts or implants | |
Contact lenses for reshaping the cornea |
This place does not cover:
Contact lens cases |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 9/0061
This place covers:
Devices particular for surgical interventions on the eye
This place does not cover:
Devices for general mechanical surgery | |
Devices for general non-mechanical surgery | |
Devices for therapy with ultrasound |
This place does not cover:
Instruments for removal of intra-ocular material |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Instruments other than toothpicks and pincettes for removing foreign bodies form the human body |
This place covers:
Instruments to help restore the lid function
Devices using ultrasonic vibrations therefore: A61F 9/00745
Capsulotomes: A61F 9/00754
Instruments with rotating or reciprocating (other than ultrasonically) elements: A61F 9/00763
This place does not cover:
Invasive laser devices to remove intra-ocular material | |
Ultrasonic cutters for general surgery | |
Devices using focused ultrasound for general tissue removal |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Plugs implanted in body vessels |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 9/00772
Example for correcting occluded lacrimal pathways (Jones tube):
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
Punctum plug | Plug, implant or instrument for the lacrimal duct |
This place does not cover:
Drainage implants in general |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61F 9/00781
Treatment of outflow of aqueous humor.
The most practiced surgery intended to reduce aqueous humor production is the cyclodestruction technique. When cyclodestruction is performed with a laser, it is called cyclophotocoagulation. High Intensity focused Ultrasound can be used to obtain a cyclodestruction.
This place covers:
Methods or devices for eye surgery (i.e. destruction, modification or removal of tissue) using electromagnetic radiation other than laser, e.g. non-coherent light or microwaves.
This place does not cover:
Mechanical eye surgery | |
Radiation therapy |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Implants of eye parts in general | |
Instruments for examination of the eyes | |
Surgery with non mechanical forms of energy in general | |
Laser surgery in general | |
Accessories for surgery or diagnosis | |
Photodynamic therapy | |
Optical components | |
Contact lenses | |
Lasers in general |
The application of non-laser electromagnetic radiation for surgical purposes covers, inter alia, applications whereby infrared or microwave radiation is applied to heat the cornea in order facilitate its shaping by a mold. The relevant information here is the application of the electromagnetic radiation, not the mold. Contact lenses in general, including orthokeratology lenses, are covered by G02C 7/04.
This place covers:
Methods or devices for eye surgery (i.e. destruction, modification or removal of tissue) using laser.
This place does not cover:
Mechanical eye surgery | |
Radiation therapy |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Implants of eye parts in general | |
Instruments for examination of the eyes | |
Surgery with non mechanical forms of energy in general | |
Laser surgery in general | |
Accessories for surgery or diagnosis | |
Photodynamic therapy | |
Optical components | |
Contact lenses | |
Lasers in general |
The scheme in A61F 9/008 contains several independent classification trees covering different aspects of a laser system for eye surgery.
The effect produced by the laser beam in the tissue should be classified in A61F 9/00802, A61F 9/00821, A61F 9/00825, or A61F 2009/00842 and lower hierarchical groups thereof
Auxiliary devices contacting the eyeball like for coupling in the surgical laser light are classified in A61F 9/009
Further aspects are then classified in codes according to:
The control or steering of the laser beam during the treatment (subgroups of A61F 2009/00844)
The calibration of any component in the laser system (A61F 2009/00855 and subgroups thereof)
The part of the eye to be treated (subgroups of A61F 2009/00861),
The planning of the irradiation before the treatment, like based on particular information or measurements (A61F 2009/00878 and subgroups thereof)
The disease to be treated (subgroups of A61F 2009/00885),
Particular algorithms or mechanisms for scanning the beam (A61F 2009/00897)
This groups cover inlays, onlays and intraocular lenses for implantation but specially adapted to be molded by a photoablative or photodisruptive beam. Implantable corneal inlays and onlays and for direct refractive correction and intraocular lenses in general are covered by A61F 2/145 and A61F 2/16.
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
This place does not cover:
Laser eye surgery |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Methods or devices for eye surgery |
This place does not cover:
Surgical scalpels and knives |
This place does not cover:
Swimming goggles |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Breathing masks | |
Diving masks |
This place does not cover:
Optical filters per se |
This place does not cover:
Welding masks with variable transmission |
This place covers:
Sleep masks.
Masks for protecting the eye after ophtalmic surgery.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this place: 
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Eye-bandages | |
Protective face-masks | |
Protectors for shampooing |
This place does not cover:
Goggles comprising special optical filters | |
Masks with movable polarising filter discs |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Walking or guiding aids for blind | |
Replacing visual perception by electrode stimulation | |
Teaching or communicating with the blind |
This place covers:
Methods or devices for surgical or non-surgical treatment of ears.
Apparatus or devices surgically implanted into the ear.
This place does not cover:
Implantable prostheses that substitute or replace internal ear parts, e.g. ear drums | |
Headwear, e.g. caps or helmets, with means for protecting the ears | |
Methods or devices to cause a change in the state of auditory consciousness | |
Electrotherapy applying electrical stimulation of the auditory system, or circuits therefor | |
Radiotherapy using optical stimulation of the auditory system | |
Electro-acoustic hearing aids |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
auditory perception | the ability to detect and interpret sounds |
hearing sense | the ability to perceive sounds by detecting vibrations or changes in the pressure of the surrounding medium through time using the auditory parts of the sensory system |
This place does not cover:
Cotton tips | |
Cleaning by suction | |
Cleaning by irrigation |
This place covers:
Processes or use of devices implanted or attached to the body not limited to the ear to stimulate the body to cause an auditory perception, i.e. vibratory devices.
This place does not cover:
Cochlear implants, i.e. electronic stimulation of auditory nerves |
This place covers:
Any kind of stimulation of the auditory system (outer ear, middle ear, inner ear, and auditory nerve) causes "auditory perception." Usually, application of vibration on the skull (like as in so called bone anchored hearing aids) causes vibrations in the cochlea that lead to auditory perception. Therefore, vibro-stimulation does not replace the auditory perception with another kind of reception (e.g. visual or tactile perception).
Illustrative example of subject matter.
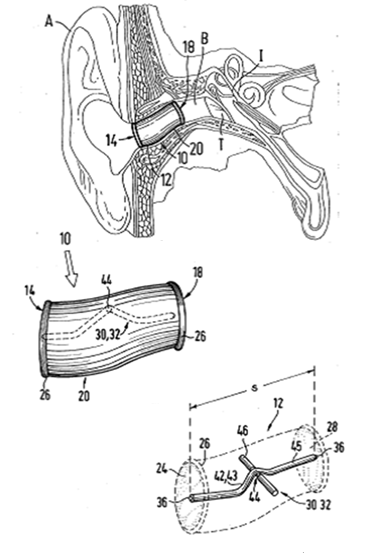
Earplugs including an inner channel: A61F 11/085
This place covers:
Only acoustic protection.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Other external protector | |
Earcaps or earmuffs for hairdresser's rooms | |
Earcaps or earmuffs for sports | |
Headphones |
This place covers:
Methods of surgically placing or implanting a device or apparatus into the ear using either invasive or minimally invasive procedures.
This place covers:
Devices used with the ear to assist the ear in the ability to hear without the use of any electric power source.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Non-electric sound-amplifying devices, e.g. non-electric megaphones | |
Methods or devices for sound-focusing or directing sound using reflection, e.g. parabolic reflectors |
This place covers:
Articles intended to be in contact with the human skin and absorb fluids excreted by the human body other than sweat, i.e. wound dressings and bandages adapted to be attached to the injured skin or to be held against the injured place. In addition to the wound dressings, this group covers also articles which are indented to be used for injured parts of the body, e.g. plaster of Paris and any kind of stiffening bandage.
Articles intended to be attached to the body or worn in conjunction with another garment or being held in place by their shape and intended to absorb excretions from a natural opening (genital, anal, nose, mouth, ear) and during surgery.
Method and apparatuses of manufacturing these articles.
A61F 5/01 - A61F 5/40 cover stiffening bandages for immobilizing extremities. The difference with A61F 13/04 - A61F 13/14 is that (with the exception of A61F 13/04) in A61F 13/06 - A61F 13/14 no rigid parts are used. If rigid parts are used, then A61F 5/01 should be taken into consideration. A61F 5/44 covers devices worn by the patient for reception of urine, faeces, catamenial or other discharge which are rather receptacles or bags other than diapers or absorbent pads.
This place does not cover:
Radioactive dressings |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Suspensory bandages | |
Contact avoiding wound protectors | |
Undergarments, e.g. garments that do not absorb excretions from a natural opening | |
Articles intended to absorb sweat | |
Bandages, poultices, compresses special adapted for veterinary purposes | |
Tissues, wipes or patches for cleaning the skin (e.g. wet wipes) | |
Chemical aspects of, or use of materials for, bandages, dressings or absorbent pads | |
Bandages or dressings with incorporated medicaments | |
Chemical aspects of, or use of materials for, liquid, gel or powder form wound dressings or bandages | |
Absorbent pads for tracheostomy |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wound bandages or dressings with lubricants |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wound bandages or dressings with wax, e.g. petroleum or bees |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Absorbent pads with a reinforcing structure, e.g. net |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Lint-free wound bandages, i.e. non-linting or fraying |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wound bandages with safety barrier for protection of the operator | |
Absorbent pads for protecting the body against ulcers | |
Absorbent pads for protecting in contaminated ambience, e.g. NBC or industrial chemicals |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wound bandages for protection of the body or articulation | |
Absorbent pads for protecting the body against ulcers | |
Absorbent pads for protecting in contaminated ambience, e.g. NBC or industrial chemicals | |
Absorbent pads used as prophylaxis |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Absorbent pads used as prophylaxis |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wound bandages or dressings with wax, e.g. petroleum or bees | |
Wound bandages not adhering to the wound | |
Absorbent pads being sprayed with lubricants |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Support means for bone substitute or for bone graft implants, e.g. membranes or plates for covering bone defects |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Coloured wound bandages or with decoration pattern or printing |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Plasters shaped as a body part |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wound bandages for protection of the body or articulation | |
Wound bandages with safety barrier for protection of the operator | |
Plasters for protection of suture stitches | |
Plasters for protection of wound surround |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Plasters for surgical sutures with cyano-acrylic adhesive | |
Plasters with adhesive connecting means | |
Adhesives for plasters | |
Plasters with means for wound humidity control with absorbent adhesives | |
Plasters with means for wound humidity control with permeable adhesive layers | |
Plasters with different adhesion of different adhesive layers | |
Plasters changing the adhesion force with strain value |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wound bandages for protection of the body or articulation | |
Wound bandages with safety barrier for protection of the operator | |
Plasters for skin protection | |
Plasters for protection of wound surround |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Plasters with adhesives for mucosae | |
Plasters with adhesives for use on wounds |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wound bandages for red nails, in-grown nails or felons (inflamed digits) |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wound bandages for burns or skin transplants |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wound bandages with alginate, not adhering to the wound | |
Plasters with hydrogel adhesive | |
Plasters with water-based adhesive | |
Plasters with adhesives for mucosae | |
Plasters with adhesives for use on wounds | |
Plasters with means for wound humidity control with hydrocolloids or superabsorbers | |
Plasters with means for wound humidity control with absorbent adhesives | |
Plasters with means for wound humidity control with fumed silica | |
Impervious plasters with viscoelastic oil-elastomer gel |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Plasters containing means with biological activity, e.g. enzymes for debriding wounds or others, collagen or growth factors |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wound bandages with net structure |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Plasters for use with needles, tubes or catheters with double adhesive layer | |
Plasters for surgical sutures with cyano-acrylic adhesive | |
Adhesives for plasters | |
Plasters with means for wound humidity control with absorbent adhesives | |
Plasters with means for wound humidity control with permeable adhesive layers | |
Plasters with different adhesion of different adhesive layers | |
Plasters changing the adhesion force with strain value |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wound bandages with alginate, not adhering to the wound | |
Plasters for use with needles, tubes or catheters with double adhesive layer | |
Plasters for surgical sutures with cyano-acrylic adhesive | |
Plasters for treating burn with hydrogel | |
Plasters with adhesive connecting means | |
Plasters with hydrogel adhesive | |
Plasters with adhesive for mucosae | |
Plasters with adhesives for use on wounds | |
Plasters with means for wound humidity control with hydrocolloids or superabsorbers | |
Plasters with means for wound humidity control with absorbent adhesives | |
Plasters with means for wound humidity control with permeable adhesive layers | |
Plasters with means for wound humidity control with fumed silica | |
Plasters with different adhesion of different adhesive layers | |
Plasters changing the adhesion force with strain value | |
Impervious plasters with viscoelastic oil-elastomer gel |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wound bandages with alginate, not adhering to the wound | |
Plasters for surgical sutures with cyano-acrylic adhesive | |
Plasters for treating burn with hydrogel | |
Plasters with hydrogel adhesive | |
Plasters with water-based adhesive | |
Plasters with adhesives for mucosae | |
Plasters with adhesives for use on wounds | |
Plasters with means for wound humidity control with absorbent adhesives | |
Plasters with means for wound humidity control with fumed silica | |
Impervious plasters with viscoelastic oil-elastomer gel |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Plasters for use with needles, tubes or catheters with double adhesive layer | |
Plasters for surgical sutures with cyano-acrylic adhesive | |
Plasters with adhesive connecting means | |
Adhesives for plasters | |
Plasters with means for wound humidity control with absorbent adhesives | |
Plasters with means for wound humidity control with permeable adhesive layers | |
Plasters changing the adhesion force with strain value |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wound bandages for protection of the body or articulation | |
Wound bandages with safety barrier for protection of the operator | |
Plasters for skin protection | |
Plasters for protection of suture stitches | |
Absorbent pads for protecting the body against ulcers | |
Absorbent pads for protecting in contaminated ambience, e.g. NBC or industrial chemicals | |
Absorbent pads used as prophylaxis |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Plasters for use with needles, tubes or catheters with double adhesive layer | |
Plasters for surgical sutures with cyano-acrylic adhesive | |
Plasters with adhesive connecting means | |
Adhesives for plasters | |
Plasters with means for wound humidity control with absorbent adhesives | |
Plasters with means for wound humidity control with permeable adhesive layers | |
Plasters with different adhesion of different adhesive layers |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wound bandages in a special way pervious to air or vapours |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Plasters with hydrogel adhesive | |
Plasters with oil-based adhesive | |
Plasters with elastomer adhesive, e.g. rubber-based |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wound bandages with triboelectric materials |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wound bandages not adhering to the wound with metallic layer |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Plasters for conducting tests |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Bandages or dressings specially adapted for feet or legs; Corn-pads; Corn-rings | |
Elastic stockings; For contracting aneurisms | |
Bandages or dressings specially adapted for fingers, hands or arms; Finger-stalls; Nail-protectors | |
Bandages or dressings specially adapted for the head or neck | |
Bandages or dressings specially adapted for the breast or abdomen | |
Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators | |
Vaccination diagnosis other than by injuring the skin, e.g. allergy test patches | |
Surgical adhesives or cements; Adhesives for colostomy devices | |
Devices for applying media, e.g. remedies, on the human body |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Transdermal patches having a drug layer or reservoir | |
Seal, e.g. to apply around a wound, for isolating the treatment area in combination with an absorbent pad for irrigating or draining the wound |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Tapes for stoma bags | |
Wound closure tapes | |
Surgical drapes | |
Attaching catheters |
This place does not cover:
Orthopaedic devices, e.g. long-term immobilising or pressure directing devices for treating broken or deformed bones such as splints, casts or braces | |
Bandages, dressings or absorbent pads specially adapted for feet or legs; Corn-pads; Corn-rings | |
Bandages, dressings or absorbent pads specially adapted for fingers, hands or arms; Finger-stalls; Nail-protectors | |
Bandages, dressings or absorbent pads specially adapted for the head or neck | |
Bandages, dressings or absorbent pads specially adapted for the breast or abdomen | |
Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Chemical aspects of orthopaedic devices |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Negative pressure wound therapy devices, i.e. devices for applying suction to a wound to promote healing, e.g. including a vacuum dressing | |
Drainage appliances for wounds in general |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Devices for domestic use for assisting in putting-on or pulling-off clothing, e.g. stockings or socks | |
For ligaturing or otherwise compressing tubular parts of the body, e.g. blood vessels, umbilical cord | |
Active massage of limbs | |
Weft knitting processes for the production of stockings |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Orthopaedic methods or devices for non-surgical treatment of bones or joints | |
Orthopaedic devices for the arms, hands or fingers | |
Restraining devices for arms | |
Slings | |
Shoulder bandages |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Ear, face, or lip protectors | |
Preparations for care of the skin |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Braces for providing support to the lower back, e.g. lumbo- sacral supports | |
Corsets or bandages for abdomen, teat or breast support | |
Brassieres for medical use or surgery |
This place covers:
Articles intended to be worn or held against the human body for absorbing excretions from natural openings.
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Articles for absorbing wound excretions | |
Adhesive bandages or dressings | |
Bandages or dressings specially adapted for absorbing wound excretions for feet or legs | |
Bandages or dressings specially adapted for absorbing wound excretions for fingers, hands or arms | |
Bandages or dressings specially adapted for absorbing wound excretions for head or neck | |
Bandages or dressings specially adapted for absorbing wound excretions for breast or abdomen |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Non-absorbent catamenial devices | |
Pessaries | |
Underwear | |
Wristbands or headbands, e.g. for absorbing sweat | |
Fittings or trimmings for hats, e.g. hat-bands | |
Insoles for insertion, e.g. footbeds or inlays | |
Tissues, wipes or patches for cleaning the skin (e.g. wet wipes) |
Investigating or analysing materials by determining their chemical or physical properties G01N.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Spraying |
Joining or sealing of preformed parts, welding of plastics materials and apparatus therefore: B29C 65/00
Corrugating in general: B31F 1/20
Vacuum drums for perforating: B26F 1/26, D06C 23/00, D04H 1/465, B29C 59/06, B29C 59/022, B29C 59/025, B29C 51/225, B29C 59/043, B29C 51/225.
This place covers:
All articles intended to be inserted within a natural opening e.g. nose plugs, dental absorbent tampons, catamenial tampons, anal plugs, ear plugs.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
A wound opening is not considered as a natural opening and articles related to wound healing | |
The swabs for cleaning wounds or absorbing wound liquids during surgery |
This place does not cover:
Portable hand-held applicators having sponges, foams, absorbent pads or swabs for dispensing or spreading integral media on the human body, e.g. swabs containing a liquid in a rupturable reservoir |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Ear cleaners other than cotton tips |
This place covers:
All articles having means for indicating the article is wet, independently of the kind of absorbent article (napkins, diapers, tampons, wound dressings) or indicator (chemical, electrical, tactile etc.).
For determining moisture content, e.g. humidity, of the fluid by the use of electric, electro-chemical, or magnetic means G01N 27/00.
This place covers:
The two- or three- dimensional shape of articles or the shape of details thereof, and is intended as a head group to branch down to either articles needing another article or adhesive to be held against the body (A61F 13/47) or articles that are self-supporting e.g. diapers (A61F 13/49).
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Absorbent articles characterised by the edge leakage prevention means having a continuous closed form, e.g. circle, ellipse, rectangle |
This place covers:
Absorbent articles that need another article or adhesive to be held against the body or articles which are held in place by the specific female or male anatomy.
This place covers:
Articles of the feminine hygiene napkin type having a reinforcing member to keep the shape in a desired form.
This place covers:
Articles of the feminine hygiene napkin type where the fold lines or grooves are intended for allowing the article to fold or bent around them rather than being a barrier.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Foldable male incontinence devices | |
Foldable interlabial articles |
This place covers:
Articles which are intended to be placed against and to be hold by the labiae of the female anatomy.
This place does not cover:
Articles intended to be worn inside the vagina e.g. tampons |
This place covers:
Articles of the feminine hygiene napkin type having a portion which is elevated in relation to the rest of the article with the intention to be in close contact with the source of excretions for acquiring easily the fluids.
This place covers:
Articles of which the dimension of the elevated portion permits the elevated portion to be inserted between the labia majora or deeper in the vagina.
This place covers:
Articles of the feminine hygiene napkin type which have means that are in a latent state. During use or just before the use of the article the means are activated to perform a function so that the shape of the article is altered, e.g. elastics that stay inactive until they become wet in order to have a flat article before use and once wet their elastic properties become active and the shape of the article changes to a curved form.
This place does not cover:
Means which upon activation perform another function than changing the shape | |
Skin enhancers |
This place covers:
Articles of the feminine hygiene napkin type which are manually or elastically adjustable to fit the body shape or to increase or decrease their absorbency
This place covers:
Articles of the feminine hygiene napkin type having a kind of barrier to prevent the liquid from leaking out of the article and soil the underwear.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
The liquid impermeable backsheet per se |
This place covers:
Articles of the feminine hygiene napkin type having wings or flaps for being wrapped over the edge of the underwear. The primary function of the flaps should be the prevention of leakage or soiling the undergarment.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Supporting means specially adapted for fastening the article on the underwear |
This place covers:
Articles which due to their form are self sustained around the waist, e.g. diapers, or pant form diapers.
This place covers:
Absorbent articles that are washable and as such reusable. If a part mostly the outer cover/chassis is washable and has an exchangeable insert but the invention relies in the washable part then this document is to be classified in this subgroup and get an Indexing Code in A61F 13/505. If however only the exchangeability of parts is disclosed so that they are to be reused several times without being of a special fabric having the possibility to be washed then this document is classified in A61F 13/505.
This place does not cover:
Fastening means per se |
This place covers:
Diapers or pants type diapers where the invention relies in the elastic or stretchable features intended to aid the article to conform to the body of the wearer.
This place does not cover:
Elastic barriers which are covered by the edge leaking prevention |
Extensible layered products B32B 5/04, B32B 5/26 – B32B 5/2795, B32B 27/12, B32B 37/144
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Layered products characterised by the non- homogeneity or physical structure characterised by structural features of a layer specified as extensible | |
Layered products characterised by the non- homogeneity, or physical structure characterised by features of foamed layer material with fibrous or filamentary layers | |
Layered products comprising synthetic resin layer next to a fibrous or filamentary layer | |
Methods or apparatus for laminating characterised by layer properties having differing mechanical properties |
This place covers:
Articles that are manually adjustable to conform the body shape or size.
This place does not cover:
The fastening means or the adjustability of the article through the fastening means |
This place covers:
Articles that have secondary absorbent material located at the side edges of the article, mostly next to the main absorbent core.
This place does not cover:
Edge leakage prevention means with the barrier having an absorbent medium |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
The difference of absorbency of the absorbent core in the X-Y direction per se |
If the secondary absorbent material is located at the end edges, then this is covered by A61F 13/49466.
This place does not cover:
Tampons, e.g. catamenial tampons; Accessories therefor | |
Reusable, washable fabric diapers |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Supporting or fastening means |
This place covers:
The outer layers of the absorbent articles whether feminine napkin tape or diapers. A backsheet is understood as the layer or composite layer that is intended to inhibit the liquid from flowing down of the article. A topsheet is understood as the layer which is in close contact with the skin for receiving the liquid.
This place does not cover:
Tampons |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wicking or transfer layers |
This place does not cover:
If the layer immediately under the topsheet is a separate layer, i.e. not laminated to the topsheet and has the function of spreading the liquid in the X-Y direction |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
If the inner layer immediately adjacent but not laminated to the backsheet is intended to distribute the liquid in the X-Y direction |
This place covers:
The material is. e.g. corrugated SELF or ring rolled so as to impart to the backsheet stretchability without being elastic.
This place does not cover:
If the inner layer immediately adjacent but not laminated to the backsheet is intended to distribute the liquid in the X-Y direction |
This place covers:
The absorbent core of the absorbent articles. If the structure of the core is intended for conforming the body fit or the leakage prevention then this is covered by the corresponding subgroups A61F 13/47, A61F 13/475 or A61F 13/49, A61F 13/494.
Chemical composition: A61L 15/16
This place does not cover:
Grooves which are intended for leakage prevention per see or for folding |
This place does not cover:
Absorbent pads characterised by specific fibre orientation or weave | |
Absorbent pads characterised by the connection of absorbent layers with each other or with the outer layers |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Homogeneous cores with tissue wrapping |
Foldable baby changing mats/supports: A47D 15/00, A47D 5/00.
This place does not cover:
If the package or packaging is not directly related to the absorbent article |
This place covers:
All means for holding in their position the absorbent articles covered by the subgroups A61F 13/45-A61F 13/51.
This place does not cover:
Fastening means for wound appliances |
This place does not cover:
If the flaps are indented to prevent leakage soiling of the undergarment |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Fabric strip fastener elements |
Hook and loop in general and the manufacturing thereof: A44B 18/00.
This place does not cover:
Support using fastening strips | |
Support using flaps | |
Tab fastener elements combining adhesive and mechanical fastening | |
Garments, holders or supports not integral with absorbent pads |
This place covers:
Articles that have means (mostly adhesive) to attached the article to the skin of the user in order to keep it in place.
This place does not cover:
Adhesive attachment of wound dressings |
This place does not cover:
Packaging of wound dressings |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Individual wrapped articles before or after use |
This place covers:
Packs, bags, packages, cases to be carried by a person and having items to be used under first aid circumstances. The items as such are not of importance.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Bags in general | |
Bags for midwives | |
Carrying bags, cases, trusses e.g. doctor bags |