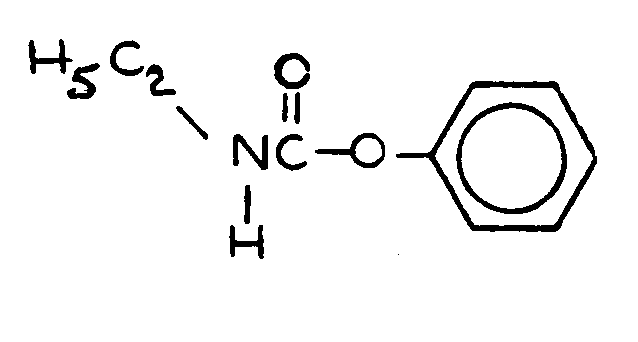
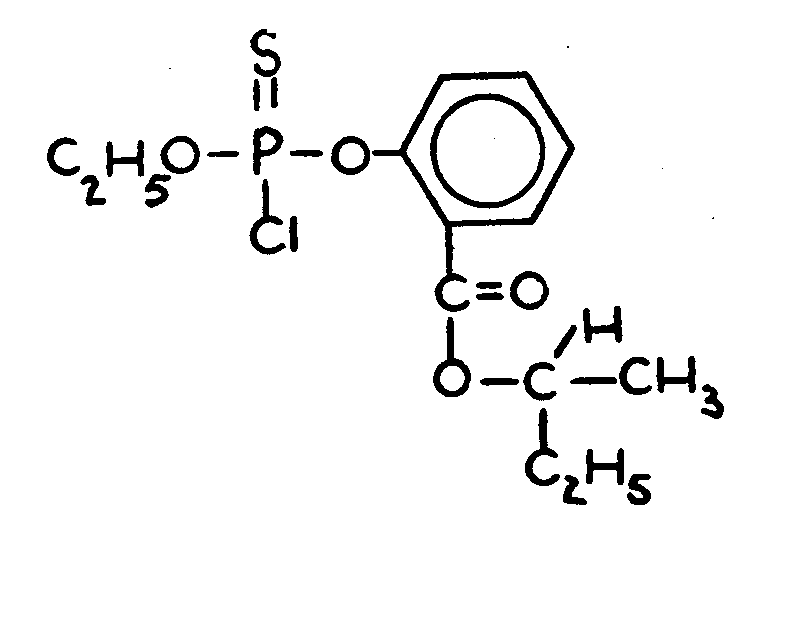
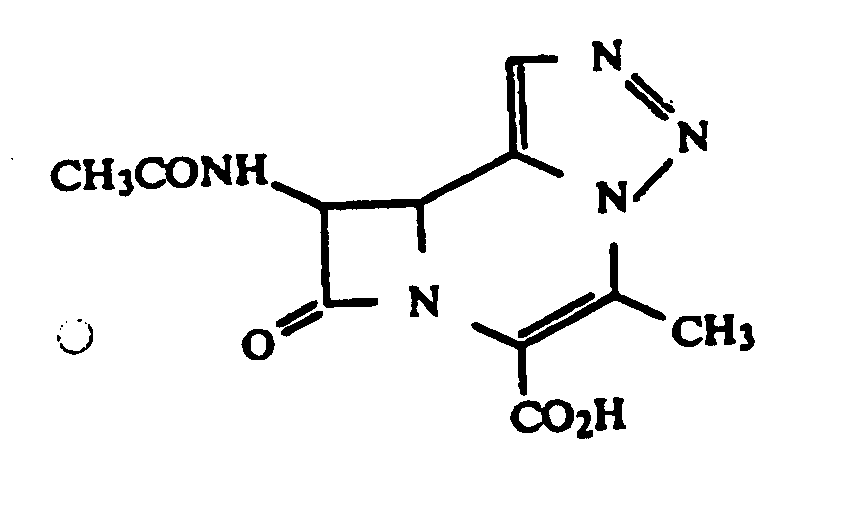
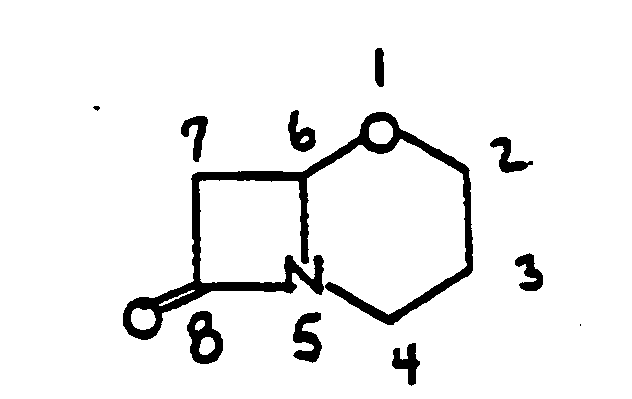
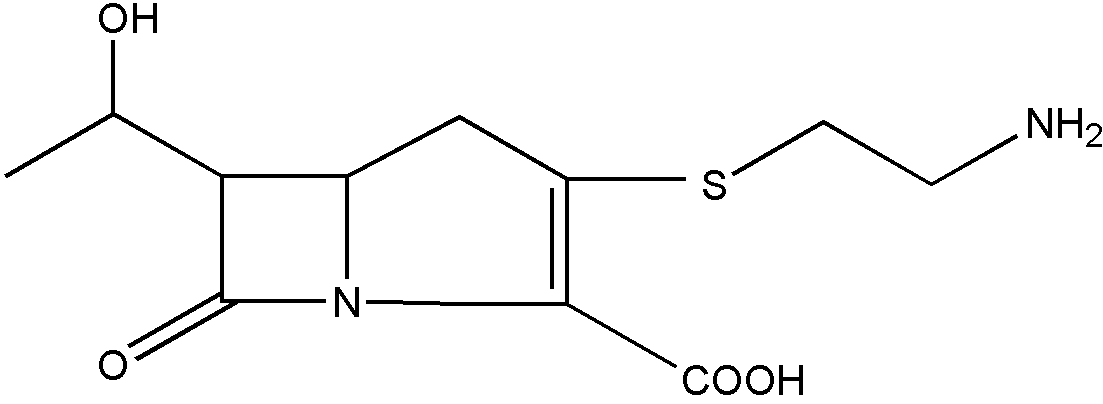
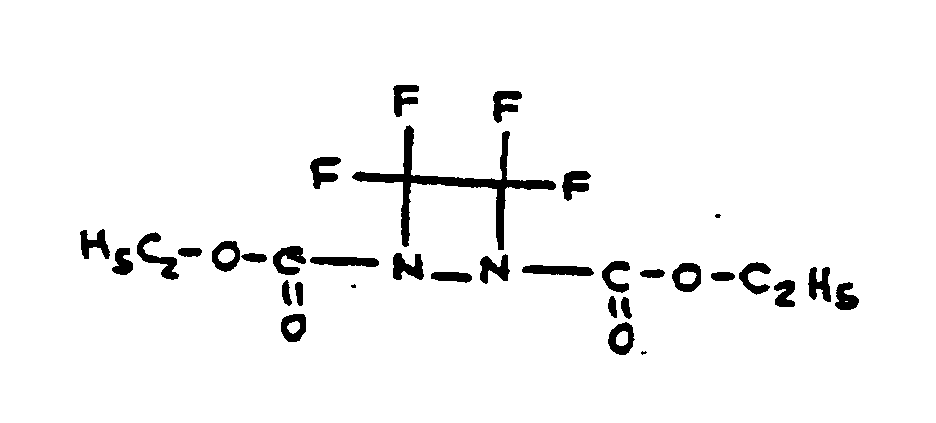
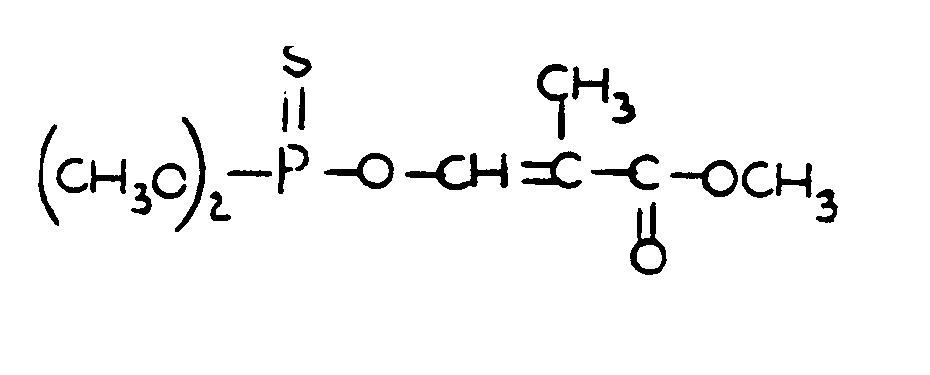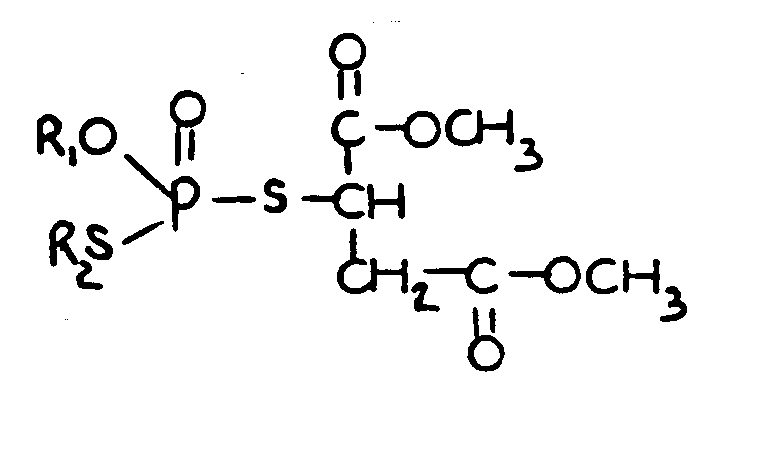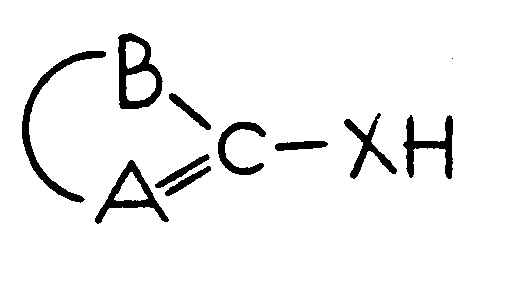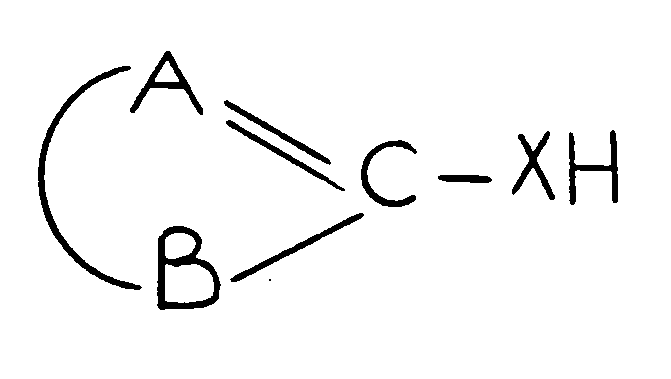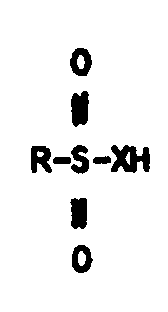SECTION I - CLASS DEFINITION
Class 514 is an integral part of Class 424. It incorporates
all the definitions and rules as to subject matter of Class 424.
SECTION II - LINES WITH OTHER CLASSES AND WITHIN THIS CLASS
A. GENERAL STATEMENT OF CLASS SUBJECT MATTER
(1) Official subclasses 1-789 do not provide for cross-reference
patents which are originally classified in Class 260 (Compound area)
or in the Class 530-570 series or in Class 585. Cross-reference
patents that are originally classified in the Class 520 series are
allowed.
(2) The cross-reference rule elaborated above means that a
specific compound having a disclosed or even specifically claimed
utility (i.e., compound X useful as an anti-cancer drug) will be
classifiable only in Class 260 or in the Class 530-570 series or
in class 585.
B. OFFICIAL CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS:
(1) Peptide and protein art collections (subclasses 800-809).
(2) Specifically disclosed disease condition and pharmaceutical
effect (subclasses 810-935).
The official cross-reference art collections subclasses 800-935
take patents dating from Jan.1, 1965. These collections provide
for data from all classes including Classes 260, 530-570, and Class
585.
C. OFFICIAL CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS:
Subclasses 936-975 provide for specifically disclosed carrier
specified nonbioactive ingredient (subclasses 936-975).
This art collection provides (1) data from Class 260 (Compounds
) and Classes 530-570 series and Class 585 dating from Jan. 1, 1965,
and (2) data from all other classes regardless of date.
Class 514 and Class 424 differ in scope as to cross-referencing
procedure. Those subclasses identified as Class 424 will accept
cross-references from all classes including 424, 260, Classes 530-570
series and Class 585 as has been done in the past. An exception
within Class 424 are subclasses 1.11+ wherein the 514 rule
is respected and therefore cross-referencing is not accepted.
SCHEDULE OUTLINE OF CLASS 514
The schedule is divided into a number of parts, each of which
is distinct and provides for different types of subject matter.
The following is a breakdown of the major areas and indicates the
type of subject matter provided therein.
(A) Subclasses 1-768 provide for the subject matter proper
under Class 424 containing a designated organic active ingredient
(DOAI), methods of making such compositions and methods of using
such compositions. Also included herein are method of using a specified DOAI.
(B) Subclasses 769-771 provide for subject matter relating
to a designated inorganic nonactive ingredient (See Glossary below)
other than water or designated elemental nonactive material (See
Glossary). These subclasses provide for compositions which may
have an organic active material and which active material does not
qualify as a DOAI as well as to methods of preparing or using such
compositions. These subclasses also provide for compositions containing
a designated inorganic nonactive material other than water or designated
elemental material and which composition qualifies as subject matter
proper for Class 424 and is not provided higher in the classification
schedule as well as to methods of preparing or using such compositions.
(C) Subclasses 772-788 provide for subject matter relating
to a designated organic nonactive ingredient (See GLOSSARY) other
than a hydrocarbon. These subclasses provide for compositions which
may have an organic active material and which active material does not
qualify as a DOAI as well as to methods of preparing or using such
compositions.
(D) Subclass 789 is the miscellaneous subclass for subject
matter proper in Class 424 or 514. This subclass provides for compositions,
methods of preparing or using same.
(E) Subclasses 800-809 are art collections pertaining to protein
and peptide and relate to subject matter only in Class 514.
(F) Subclasses 810-935 are art collections pertaining to specifically
disclosed disease condition and pharmaceutical effect and relate
to subject matter only in Class 514.
(G) Subclasses 936-975 are art collections pertaining to specifically
disclosed carrier system; physical form or specified nonbioactive
ingredient and relate to subject matter only in Class 514.
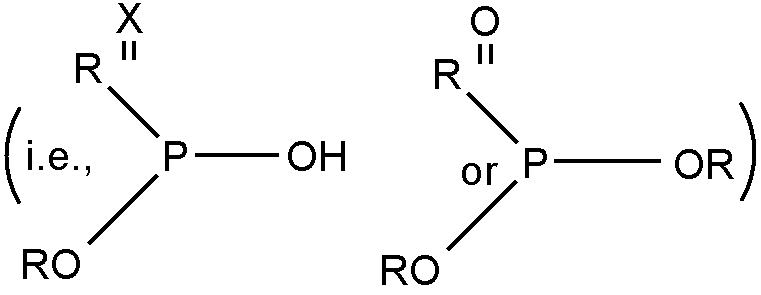
DESIGNATED ORGANIC ACTIVE INGREDIENT (DOAI)
DOAI is when (a) the active ingredient is identified by at
least one chemical atom, e.g., organic phosphorus compound, etc.
or (b) the active ingredient is identified as a generic type of
chemical compound, e.g., alcohol, ether, etc.
The term active denotes a physiological, pharmacological or
biological effect.
For purposes of this class organic active ingredient although
inherently reciting the presence of a carbon atom is considered
to be too broad and therefore will not be considered as DOAI"s
is as follows: chalcogen, carboxylic acid, phosphorus containing,
organic alkali or earth metal compound, hydrocarbon, halogenated hydrocarbon,
etc.
The following list below is not exhaustive and merely emumerates
certain materials that will not be considered as DOAI"s,
e.g., organic compound, solvent, biocide, pharmaceutically active,
medicine, preservative, diabetes active, pesticidal, active against
rabies, antihistamine, anti-tussive, anti-caries, crystalline, antioxidant, etc.
It is important to remember that function of a material or even
amount, e.g., pharmaceutical, etc., even if specific, e.g., diabetes
active, etc., or 2% of a diabetes active ingredient, etc.,
does not meet any of the necessary criteria elaborated in 1 and
2 above. Function or amount therefore does not qualify as rendering
an ingredient as "Designated".
RULES CONCERNING THE USE OF DOAI IN THE SCHEDULE
For purposes of Class 514, certain rules as to patent placement
have been adopted. These rules pertain only to the subject matter
in Class 514 and are not to be extrapolated to areas in Class 424.
The rules adopted pertaining to the use of the term "DOAI" are
as follows:
(A) In those subclasses which recite a designated organic
active ingredient (DOAI) in the title, the indented subclasses merely
pertain to a further elaboration of the DOAI and do not relate to
any other ingredient. An example of this is (subclass 497 in Class
514) which recites nitrogen containing and is indented under (subclass
496) which recites mercury and which in turn is indented under (subclass
492) heavy metal containing DOAI. The meaning of (subclass 497)
is that an active ingredient contains both nitrogen and mercury
atoms as part of a single molecule.
(B) In those subclasses which recite "with" as
in (subclass 168) under a specified DOAI, such use is consistent
with the term as used in other classes in that, at least two separate
materials must be present, one of which is the DOAI and the other "with" ingredient.
The "with" ingredient need not have an active
function for Class 514 unless the subclass specifically requires
an "active with ingredient" as in subclass 154.
EXAMPLES OF PATENT PLACEMENT WITHIN THE CLASS
Patentee Claims
(A) A biocide and starch as a carrier. The original classification
is with the starch in subclass 778, since a chemical atom of the
biocide is not recited.
(B) 2% of a biocide and starch as a carrier. Same
classification as in (A) above, since 2% is not considered
sufficient to be DOAI.
(C) An organic phosphorus containing biocide and starch as
carrier. Original classification is on the basis of the biocide
since an atom is recited. Entirely proper to look at disclosure
to see the type of phosphorus compound encompassed by the term "organic
phosphorus".
(D) A synergistic mixture of two biocides at least one of which
is formaldehyde classifiable in subclasses 694+. The disclosure
recites that the other biocide can be a organic phosphorus compound
classifiable in subclasses 75+. Since the claim has only
one DOAI recited (i.e., formaldehyde) original classification is
in the formaldehyde species.
(E) A synergistic mixture of two biocides one of which is
formaldehyde and the other is malathion. Formaldehyde is classified
in subclass 694 and malathion is classified in subclass 122. The
original is classified with malathion in subclass 122 as per normal
classification rules.
RULES CONCERNING PLACEMENT OF SALTS WITHIN CLASS 514 AND SEARCH
THEREFOR
Classification Practice
(A) Inorganic salts of organic materials are considered as
organic and classified with the organic materials only, even when
the organic material is not a DOAI by definition (see Glossary).
No weight in the classification system is given to the inorganic
material. However, when the inorganic segment of the salt is specifically
claimed or disclosed as the only active segment of the salt molecule
original classification is proper on the basis of the inorganic
segment and cross-referenced to the organic material.
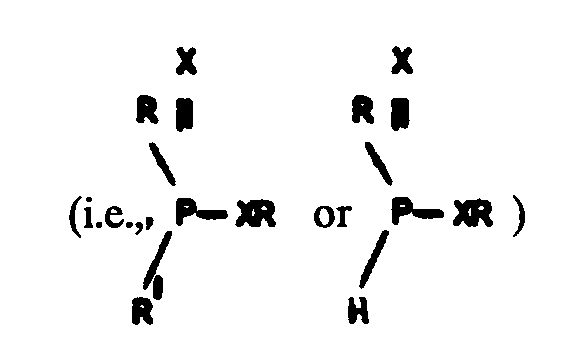
Example 1. R--R. SO4
classified on the basis of
R--R
segment only
Example 2 Organic. SO4
or
Organic pesticide. SO4 classified on
the basis of the disclosed organic or organic pesticide material
only.
Example 3. Organic. SO4
or
Amine. SO4
Wherein activity is recited only in the SO4 segment, original
classification is with SO4 segment, cross-reference
is highly desirable with the disclosed organic or amine material.
(B) When a nonsalt DOAI material (see section 2, Glossary)
as well as a salt thereof are claimed a prima facie nonrebuttal
presumption is established that only the nonsalt active material
is effective, even if the salt is specifically claimed and even
if different 424 utility is noted for the specific salt. The claims
are classified as original with the nonsalt DOAI material and a
cross-reference to the salt area, even if higher in the classification schedule
is unnecessary.
(C) When an organic salt of a DOAI is solely specifically
claimed (i.e., nonsalt species of material is not claimed) the following
classification rules will apply:
(1) Both segments of the solely claimed salt, i.e., anion and
cation, are designated
(a) both segments are claimed or disclosed as active for the
utility intended, or where no evidence is shown that a particular
segment is active or inactive (both through claims or disclosure),
the entire molecule will be considered a DOAI and classified on
the basis of the first appearing segment in the schedule hierarchy,
an example of this is the treatment of amine-critic acid: original classification
with citric acid is proper since both segments of the molecule are
active and since amine is classified lower in the 514 schedule hierarchy
then citric acid or
(b) only one particular segment is claimed or disclosed as
active, the original classification is to the designated active
segment and cross-referenced to the nonactive segment area if said
nonactive segment is higher in the classification schedule.
(2) Only one segment of the solely claimed salt, i.e., anion
or cation, is designated, the original classification is with the
active segment, even if the active segment is nondesignated, e.g., "an
amine salt of an organic compound" wherein the pesticide
or organic compound is specifically claimed or disclosed to be active
for the utility intended. Classification is on the basis of the
disclosed pesticide or the organic compound and cross-referenced
to the amine area if the amine is higher in the schedule hierarchy
than the disclosed species of the pesticide or organic compound.
However, when the nondesignated segment is claimed as "a
pharmaceutically acceptable acid (or base or equivalent thereof),
e.g., "an amine salt of a therapeutically acceptable or
compatible acid", no weight is given to the "acceptable
or compatible acid" and classification is based only on
the designated segment, i.e., the amine.
Examination Practice
Due to the nature of the system of classification elaborated
above a search to be complete must at times entail searching in
a multiplicity of subclasses.
(A) Claims drawn to solely a salt. Claims are classified and
searched as in Classification Practice, C, above.
(B) Claims drawn to a nonsalt DOAI and also to a salt thereof,
either in a dependant claim or in a Markush group. Classified only
with the nonsalt species but searched in all salt species which
are classified higher in the classification schedule than the nonsalt
species.
The rules for determining Class placement of the Original
Reference (OR) for claimed chemical compositions are set forth in
the Class Definition of Class 252 in the section LINES WITH OTHER
CLASSES AND WITHIN THIS CLASS, subsection COMPOSITION CLASS SUPERIORITY,
which includes a hierarchical ORDER OF SUPERIORITY FOR COMPOSITION CLASSES.
CLASS 514 TERMS
The following frequently used terms in Class 514 are referenced
in References to The Current Class, below. These terms have also
been entered into the Index of the U.S. Patent Classification.
A
Acronycines; Allantion; Amantadine; Amphetamine; Ampicillin;
Amprotropine; Aspirin; Atropine
B
Barbituric acid; Benzocaine; Benzomorphans; Biotin
C
Capsaicin; Cephalocporins; Chlorpheniramine; Cholecalciferol;
Chrysanthemic acid; Cobalamin; Codeine; Colchicine; Cortisone; Cupreine;
Cycloheximide; Cyproheptadine; Cysteine ester
D
DDT; DDVP; Dextromethorphan; Dyphylline
E
Ephedrine; Estradiol;
F
Fluspirilene
G
Glaucine; Glucamine; Griseofulvin
H
Hexachlorophene; Hydrocortisone
I
Isoniazid
M
Malathion; Melatonin; Meperidine; Methadone; Methapyrilene;
Methomyl; Morphinans; Morphine;
N
Nandrolone; Niacinamide; Nortestosterone
O
Oxolinic acid
P
Parathion; Pencillin G; Perimidines; Phenylephrine; Phenyltoloxamine;
Pilocarpine; Pimozide; Piromidic acid; Perdnisolone; Procaine; Progesterone;
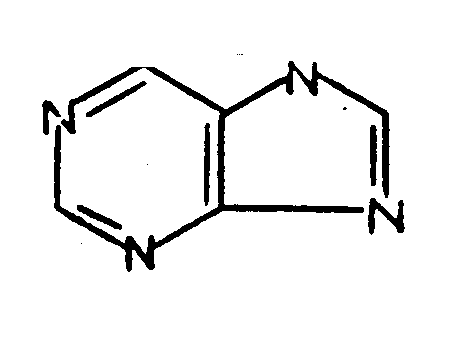
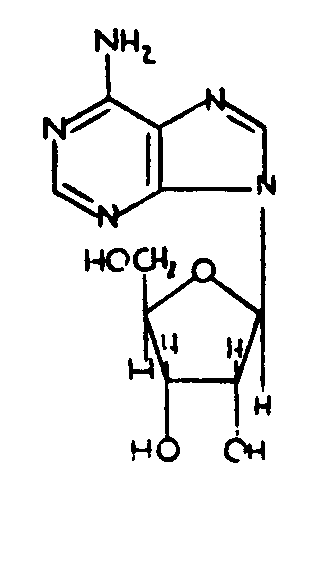
Psoralen; Pteridine; Purines
Q
Quinicine; Quinidine; Quinine; Quinoxaline
R
Riboflavins
S
Salinomycin; Scopolamine
T
Tartaric acid; Tetracycline; Theophilline; Thiamines; Tocopherois;
Tryptophan; Tyrosine; Tripelennamine
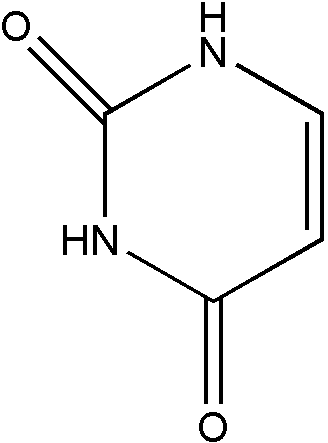
U
Uracil
V
Vinblastine; Vincamine; Viquidil
SECTION III - SUBCLASS REFERENCES TO THE CURRENT CLASS
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 52, | Cobalamin |
| 122, | Malathion |
| 132, | Parathion |
| 136, | DDVP |
| 152, | Tetracycline |
| 167, | Cholecalciferol |
| 165, | Aspirin |
| 178, | Nortestosterone |
| 179, | Hydrocortisone |
| 179, | Cortisone |
| 178+, | Nandrolone |
| 179, | Perdnisolone |
| 177, | Progesterone |
| 182, | Estradiol |
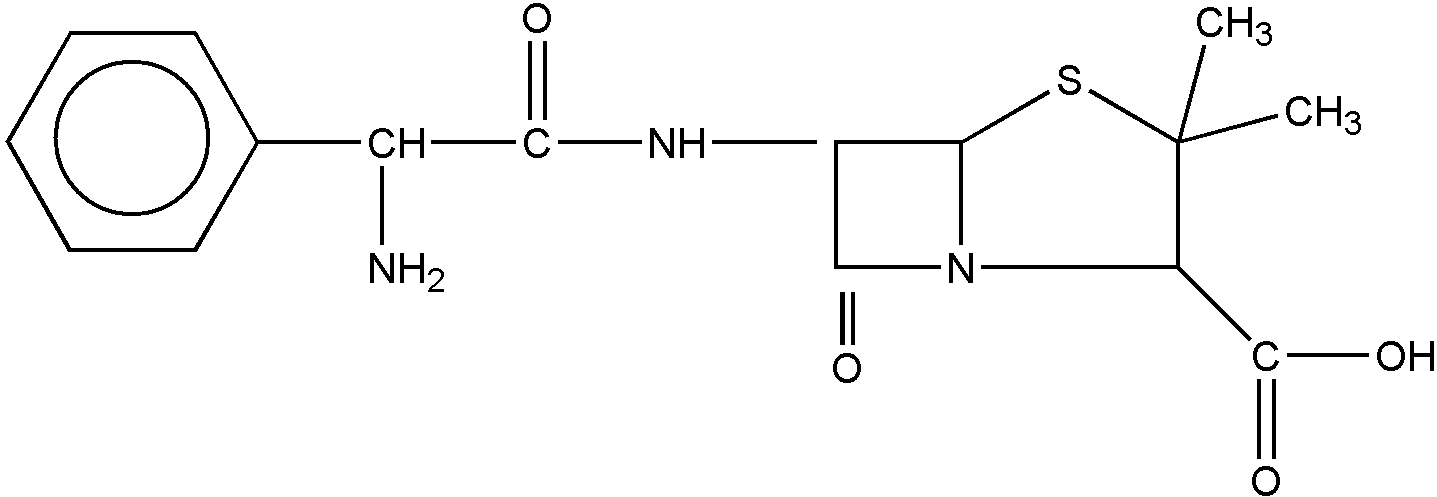
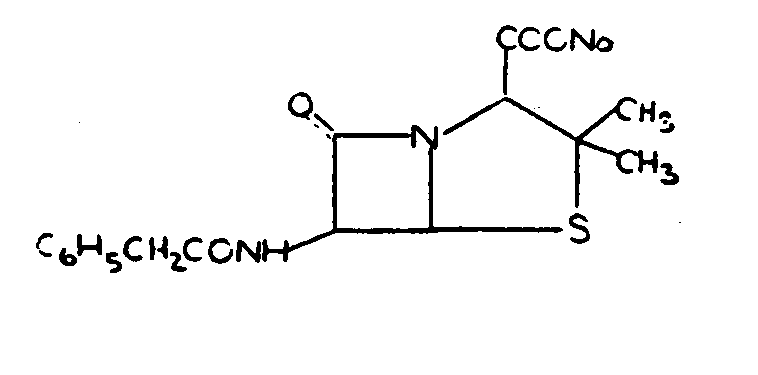
| 198, | Ampicillin |
| 199, | Pencillin G |
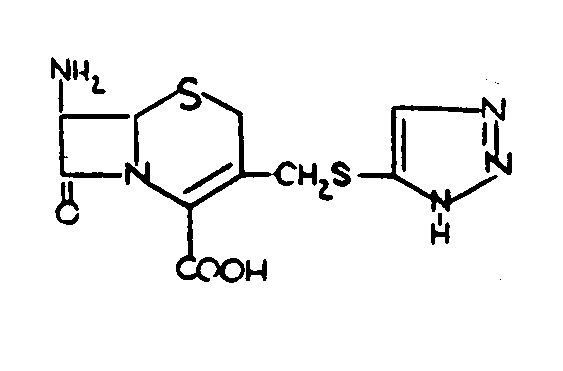
| 200+, | Cephalocporins |
| 249, | Pteridine |
| 249, | Quinoxaline |
| 251, | Riboflavins |
| 263.1 | through 263.4 , Purines |
| 263.34, | Theophilline |
| 263.36, | Dyphylline |
| 269, | Perimidines |
| 270, | Barbituric acid |
| 274, | Uracil |
| 276, | Thiamines |
| 278, | Fluspirilene |
| 282, | Codeine |
| 283, | Vincamine |
| 283, | Vinblastine |
| 285, | Acronycines |
| 282, | Morphine |
| 284, | Glaucine |
| 289, | Dextromethorphan |
| 289, | Morphinans |
| 291, | Oxolinic acid |
| 291, | Scopolamine |
| 295, | Benzomorphans |
| 303, | Piromidic acid |
| 305, | Cupreine |
| 305, | Quinidine |
| 305, | Quinine |
| 314, | Quinicine |
| 314, | Viquidil |
| 323, | Pimozide |
| 325, | Cyproheptadine |
| 328, | Cycloheximide |
| 330, | Meperidine |
| 336, | Methapyrilene |
| 352, | Tripelennamine |
| 354, | Isoniazid |
| 355, | Niacinamide |
| 357, | Chlorpheniramine |
| 387, | Biotin |
| 390, | Allantion |
| 397, | Pilocarpine |
| 415, | Melatonin |
| 419, | Tryptophan |
| 455, | Psoralen |
| 458, | Tocopherois |
| 460, | Salinomycin |
| 462, | Griseofulvin |
| 477, | Methomyl |
| 534, | Amprotropine |
| 534, | Atropine |
| 535, | Benzocaine |
| 535, | Procaine |
| 550, | Cysteine ester |
| 567, | Tyrosine |
| 572, | Chrysanthemic acid |
| 574, | Tartaric acid |
| 627, | Capsaicin |
| 629, | Colchicine |
| 648, | Methadone |
| 651, | Phenyltoloxamine |
| 653, | Ephedrine |
| 653, | Phenylephrine |
| 654, | Amphetamine |
| 656, | Amantadine |
| 669, | Glucamine |
| 735, | Hexachlorophene |
| 748, | DDT |
SECTION IV - GLOSSARY
The following terms have been used in a number of
subclass titles throughout Class 514. For convenience, these often
used terms have been arranged into a Glossary. When any of these
terms is used in particular subclass titles in Class 514, their
meaning is to be consistent with the meaning in this Glossary.
ACYCLIC
Denotes a compound devoid of any ring-containing moiety.
Thus an acyclic chain may contain any atom as long as it is not
a member of a ring.
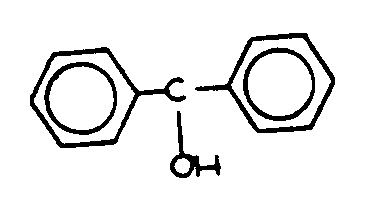
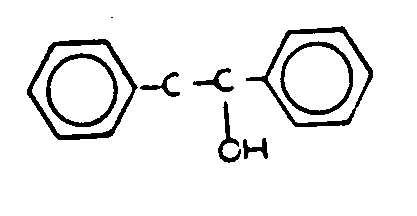
ALCOHOL
Denotes an organic compound having the general structure
C-OH wherein the carbon atom bound to the oxygen atom of the hydroxyl
group cannot be doubled bonded to oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium
or triple bonded to nitrogen. The terms as used herein includes
phenols.
ALDEHYDE
Denotes an organic compound having the general structure
-C-[C(=O)]n-H or
H-[C(=O)]n-H (n
is 1 or more and wherein the carbon atom bonded to the-[C(=O)]-n group
is not double bonded to oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium,
or triple bonded to nitrogen.
ALICYCLIC RING OR RING SYSTEM
This term denotes a carbocyclic ring which is not a benzene
ring or a polycyclo carbocyclic ring system which does not have
a benzene ring as one of the cyclos.
AMINE-
Denotes an organic compound having a nitrogen atom single
or double bonded to a carbon atom and wherein the carbon atom bonded
to the nitrogen atom is devoid of a double bond to oxygen, sulfur,
selenium, or tellurium or triple bonded to nitrogen. In addition,
those compounds wherein the same nitrogen atom is bonded to a -C(=X)-
group (X is O, S, Se, or Te) and to a carbon atom which is not double
bonded to oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium, are not considered
as being amines, e.g.,
-C-NH-C(X=)-
Although amides may be considered chemically as amines, it
has been found expedient for this class to exclude compounds containing
only amide nitrogen herefrom. Therefore, as used throughout this
area, the term amide is not to be confused as being an amine. A compound,
however, which contains a nitrogen atom bonded to a non -C(=X)-
carbon atom and which contains either a nitrogen atom bonded to
a -C(=X)- group or an amide group, is considered as being
an amine.
AMINO NITROGEN
Denotes any nitrogen in an organic compound other than
a nitrogen in an inorganic ion of an addition salt, a nitro (-NO2)
or nitroso (-NO). Component parts of an "adduct" will
be considered to be attached to each other ionically except if it
is clear that the mode of attachment is nonionic.
ARYL RING OR RING SYSTEM
This term denotes a benzene ring or a polycyclo carbocyclic
ring system having a benzene ring as one of the cyclos.
ATTACHED DIRECTLY OR BONDED DIRECTLY
These terms are used to show that specified moieties
are connected by bonds only.
ATTACHED INDIRECTLY
This term denotes that at least one atom, as well as bond,
connects specified moieties.
BENZENE RING
This term includes in all cases except where there are explicit
limitations to the contrary, substituted benzene rings, including
substitution in the form of an additional fused or bridged ring
or ring system.
BICYCLO RING SYSTEM
This term denotes a polycyclo ring system which contains
exactly two rings.
CARBOCYCLIC
This term denotes a ring or ring system where all ring members
are carbons.
CHAIN
This term denotes a plurality of atoms which connect specified
groups or atoms. The atoms of the chain must be nonionically attached
to each other and to the specified groups or atoms. If the chain
may not include any ring members it will be designated as acyclic.
When the chain may include ring members the title will state that the
chain may include a ring. The chain ends where it attaches to the
specified groups or atoms and does not include any part of them.
The chain may have substituents but the substituents are not part
of the chain.
DESIGNATED ELEMENTAL NONACTIVE INGREDIENT
Denotes an elemental material either metallic or nonmetallic
and which is identified by its chemical nature, e.g., iron, silver,
etc., or is identified in a generic manner, e.g., alkali metal atom,
etc. The term nonactive as used herein denotes the absence of any
physiological, pharmacological or biological affect attributed to
the elemental material.
DESIGNATED INORGANIC NONACTIVE INGREDIENT
Denotes an inorganic compound which is identified by at
least one chemical atom, e.g., sodium-containing, etc., or is identified
as a generic type of inorganic chemical compound, e.g., alkali metal-containing,
etc. The term nonactive as used herein denotes the absence of any
physiological, pharmacological or biological affect attributed to
the inorganic material.
DESIGNATED ORGANIC ACTIVE INGREDIENT (DOAI) DENOTES
(1) The active ingredient is identified by at least one chemical
atom, e.g., organic phosphorus compound, etc., or (2) The active
ingredient is identified as a generic type of chemical atom, e.g.,
alcohol, ether, etc. The term active denotes the presence of a physiological, pharmacological
or biological affect.
DESIGNATED ORGANIC NONACTIVE INGREDIENT DENOTES
(1) A nonactive ingredient is identified by at least
one chemical atom or (2) the nonactive ingredient is identified
as a generic type of chemical compound, e.g., starch, etc. The
term nonactive denotes the absence of any physiological, pharmacological
or biological affect attributed to the organic material.
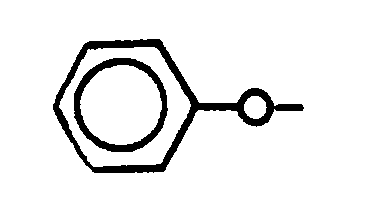
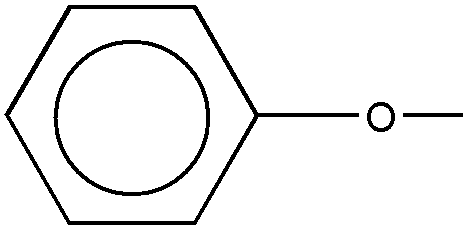
ETHER
Denotes an organic compound having oxygen bonded directly
to two carbon atoms, which carbons cannot be double bonded to oxygen,
sulfur, selenium, or tellurium, or triple bonded to nitrogen.
FATTY ACID
Denotes an aliphatic monocarboxylic acid having an unbroken
chain of at least seven carbon atoms bonded to the carboxyl group.
FUSED OR BRIDGED RING SYSTEM
Denotes a ring system having at least two rings which (a)
share with each other two adjacent ring atoms, or (b) share with
each other three or more ring atoms and wherein each ring having
shared atoms is either a heterocyclic ring or a carbocyclic ring.
HALOGENATED HYDROCARBON
Denotes a compound containing only carbon, hydrogen, and
halogen, or only carbon and halogen.
HETERO RING
Denotes the presence of one or more carbon atoms covalently
bonded in a closed ring with at least one atom of oxygen, nitrogen,
sulfur, selenium or tellurium and having no other atoms in the ring.
INCLUDING HYDROGENATED
Denotes that a ring system which by definition has ring unsaturation
possesses a degree of saturation which may be different than the
ring system definition would normally indicate.
KETONE (INCLUDING KETENE)
Denotes an organic compound having the general structure
-C-[C(=O)]n -C-
(n is 1 or more) and whereinthe carbon atoms
bonded to the-[C(=O)]ngroup
are not double bonded to oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium.
Ketone as used throughout includes ketene.
NONIONIC BONDING
As used in regard to bonding or attachment of specified moieties
denotes the absence of ionic bonding between the moieties. If the
moieties are attached directly, the bonds between them must be covalent
or coordinate. If the moieties are attached indirectly, each atom
of the connecting chain must be attached by covalent or coordinate
bonding to another atom of the connecting chain or to one of the
moieties. However, the connecting chain may have substituents thereon
which include ionic bonding. Some examples will be given of compounds which
could be classified in a subclass having the following titles: "Oxygen
attached indirectly to the six-membered hetero ring by nonionic
bonding".
Two typical compounds which would be classified in such a
subclass are:
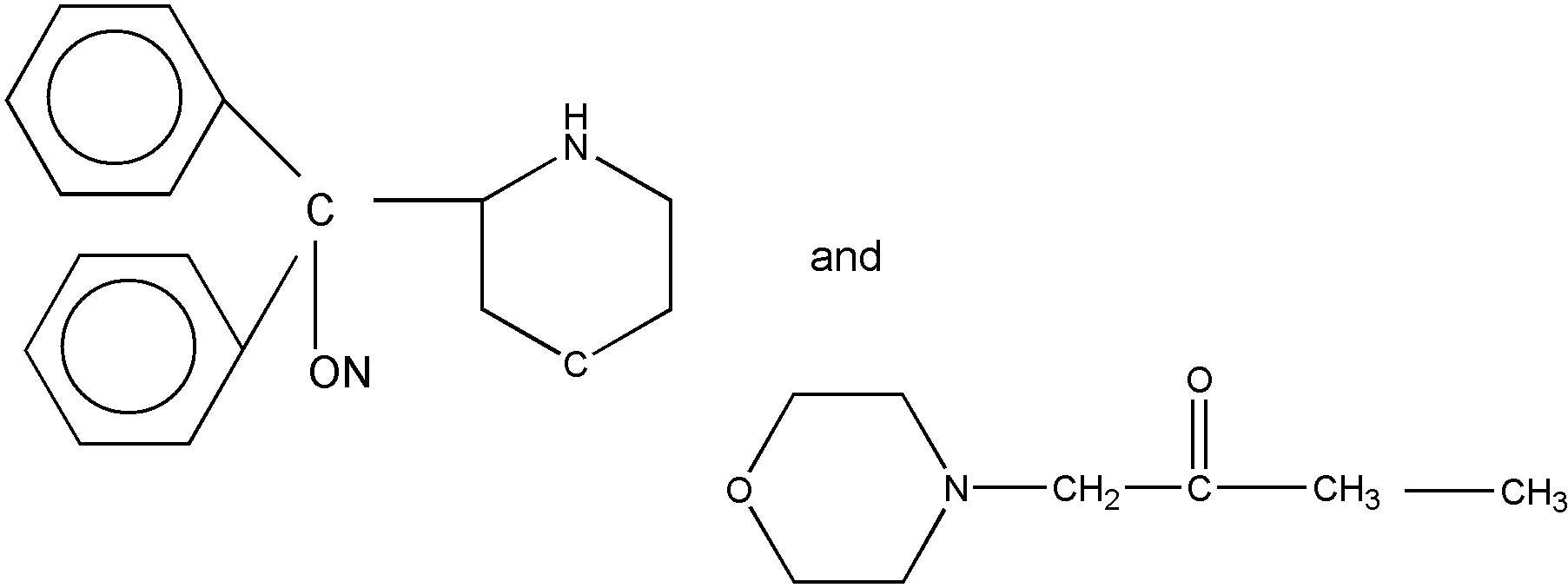
The following three compounds would also be classified in
such a subclass but they are not typical.
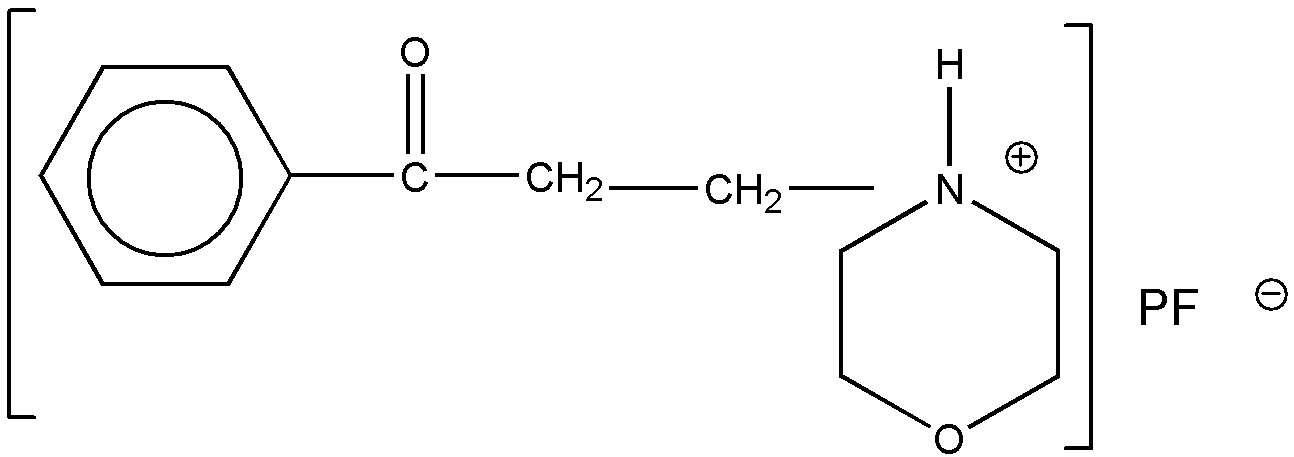
The three atypical examples are considered to meet the title
since there is a chain of atoms between the hetero ring and the
oxygen in which each atom is connected to the hetero ring, the oxygen,
or another atom of the chain by nonionic bonding. The ionic bonding between
the ring nitrogen and the oxygen in the two betaine inner salts
is additional and does not keep the betaines out of such a subclass. However,
a structure, such as
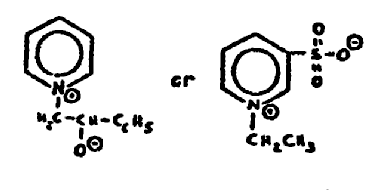
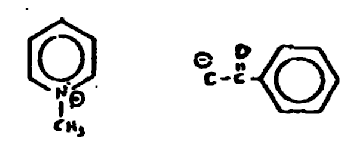
is excluded since no oxygen is attached to the six-membered
hetero ring by nonionic bonding. The oxygen of an N—oxide,
for example,
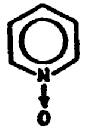
is considered attached to the ring by nonionic bonding (coordinated
bonding).
POLYCYCLO RING SYSTEM
This term denotes a compound which contains fused or bridged
rings. The polycyclo ring system must contain at least two rings
and each ring of the system must share two or more of its atoms
with another ring of the system. All ring members must be attached
to each other by nonionic bonding. The polycyclo ring system is
usually only a moiety within a compound. Indents such as bicyclo
and tricyclo are meant to limit the number of rings or cyclos in
the polycyclo ring system to exactly two rings and three rings,
respectively.
For polycyclo systems having bridges it should be remembered
that the system is regarded as composed only of the smallest number
of smallest rings that will account for all atoms and valences.
This is in accord with the nomenclature employed by The Ring Index.
Second Edition, (1960).
An example of the use of this system of nomenclature is as
follows. The compound (Ia)
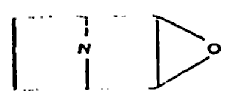
can also be written as (Ib)
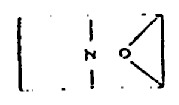
Said compound should also be considered as a (C4N—C4N—C2O)
tricyclo system as in (Ia), rather than as a (C4N—C4
NO—C2O) tricyclo system as possibly
seen in (Ib). The former interpretationis the one with smallest
number of smallest rings that accounts for all atoms and valences.
Some additional illustrative examples of the principle set forth
above are: (II)
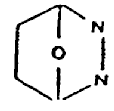
Compound II is considered as a bicyclo system composed of
a C2N2O ring and a C4O
ring; it is not considered a diazine
ring for classification. Further, 3—aza—bicyclo [3.1.0] hexane

is classified with pyrrolidines considering the structure
a five-membered ring and a three-membered ring rather than with
piperidines which would require considering it a six-membered ring.
However, see page XI of The Ring Index for an explanation of "valence
bridges".
Similarly, the structure is considered to be a pentacyclo
ring system have three six-membered carbocyclic rings, one five-membered hetero
ring consisting of one ring oxygen and four ring carbons, and one
six-membered ring consisting of one ring nitrogen and five ring carbons.
Betaine inner salts are sometimes shown as ring structures,
etc.,
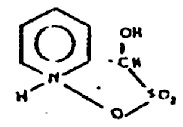
However, this is not a polycyclo ring system because nonionic
bonding does not exist between the N and O atoms. The bonding between
them is ionic and such as compound is classified as:
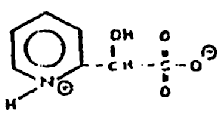
Additionally, a structure of the type:
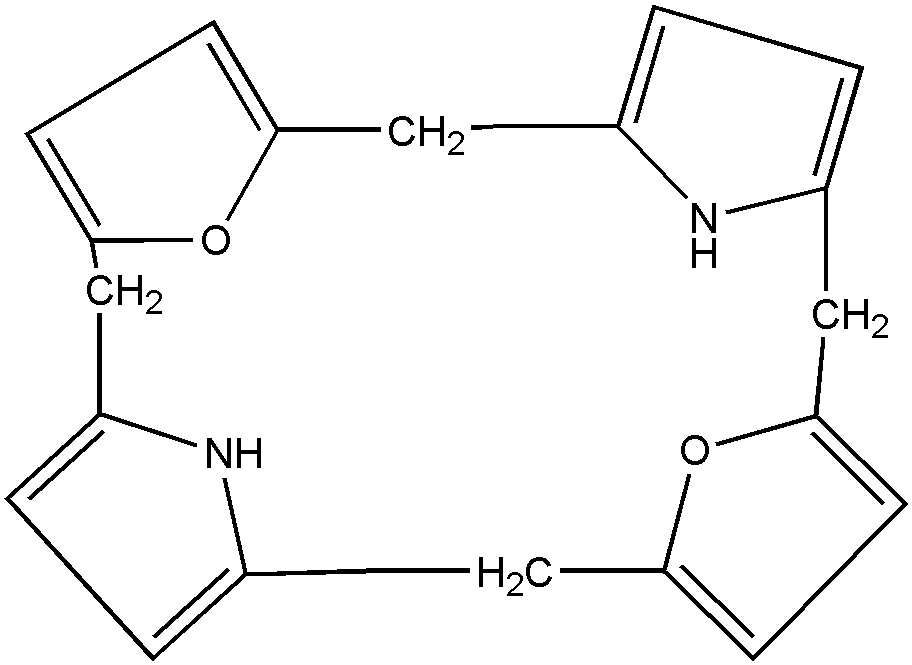
is considered to be a polycyclo ring system composed of five
rings:
C4N—C4O—C4N—C4O—C12N2O2.
SPIRO AND SPIRO RING SYSTEM
These terms denote the sharing of one common ring member
only by exactly two rings. The following two structures are illustrative:
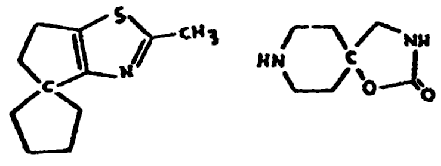
A structure such as:
is excluded because the carbon atom shared by two rings is
also shared by a third ring.
The common ring member must be attached to two ring members
of each of the rings by nonionic bonding. Therefore, stuctures such
as:
are also excluded from consideration as "spiro ring
systems" because ionic bonding exists between the hetero
ring atom and an acyclic atom (an oxygen atom in both of these cases) in
the formation of these betaine inner salts. These structures will
be considered and classified as:
TRICYCLO RING SYSTEM
This term denotes a polycyclo ring system which contains
exactly three rings.
SUBCLASSES
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 1]](../ps.gif) 1 1 | DESIGNATED ORGANIC ACTIVE INGREDIENT CONTAINING (DOAI): |
| | Subject matter under Class 424 definition which contains
a designated organic active ingredient, e.g., coal tar, coal tar
oil, etc.
| | (1)
Note. See Class Definition, Glossary, for the definition
of "DOAI". |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 731, | for a composition containing creosote or a coal
tar acid. |
| 800, | and 801-809, for art collections pertaining to subclasses
1-21. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 208, | Mineral Oils: Processes and Products,
subclass 2 for a coal tar or coal tar oil which has the property
of killing, repelling or preventing the growth of insects, fungi
or bacteria and the process of preparing same. |
|
| | |
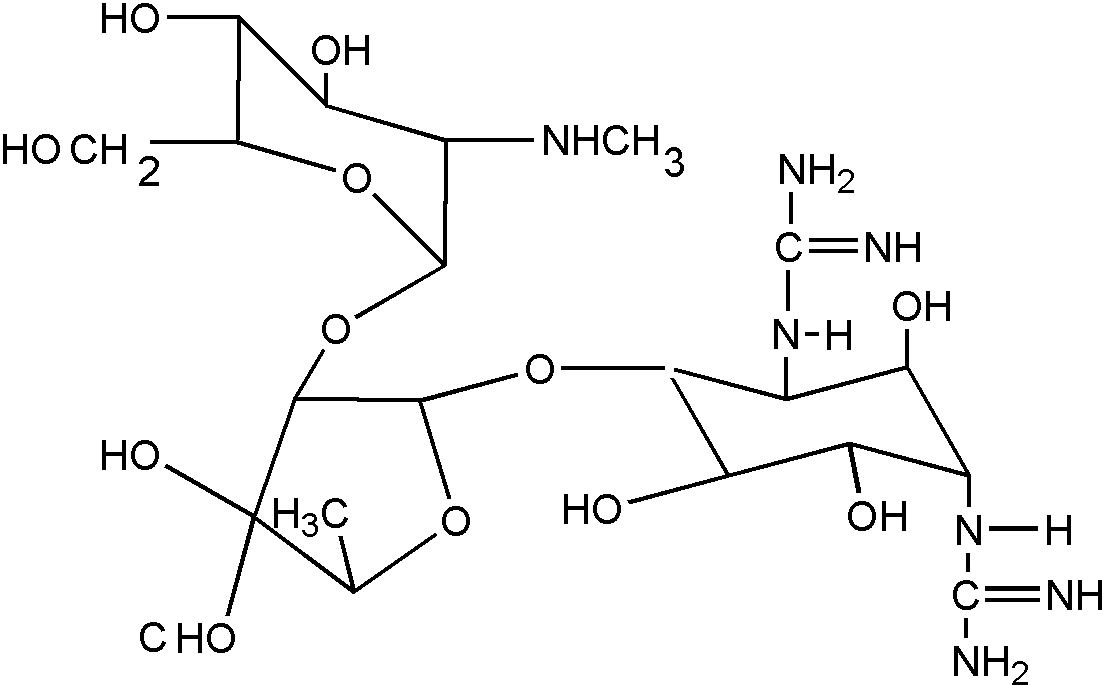
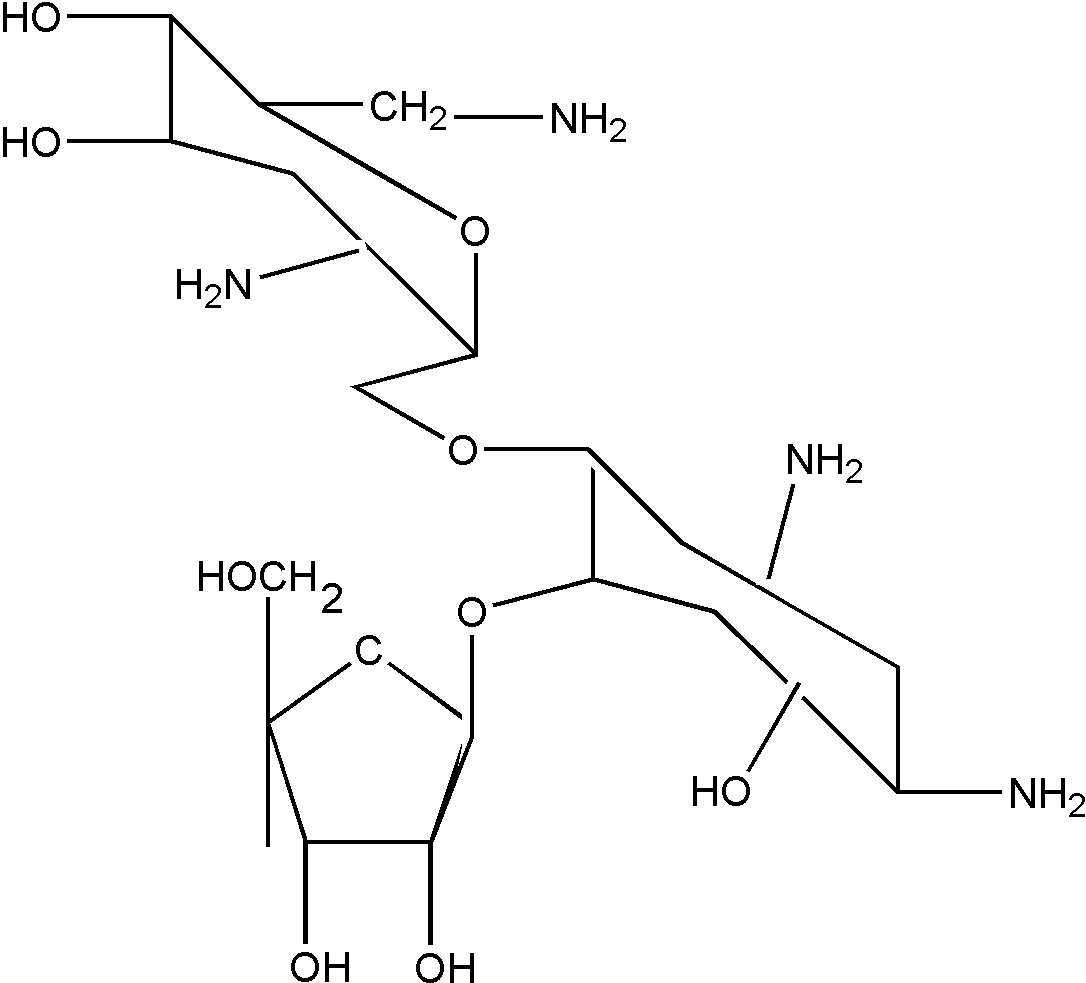
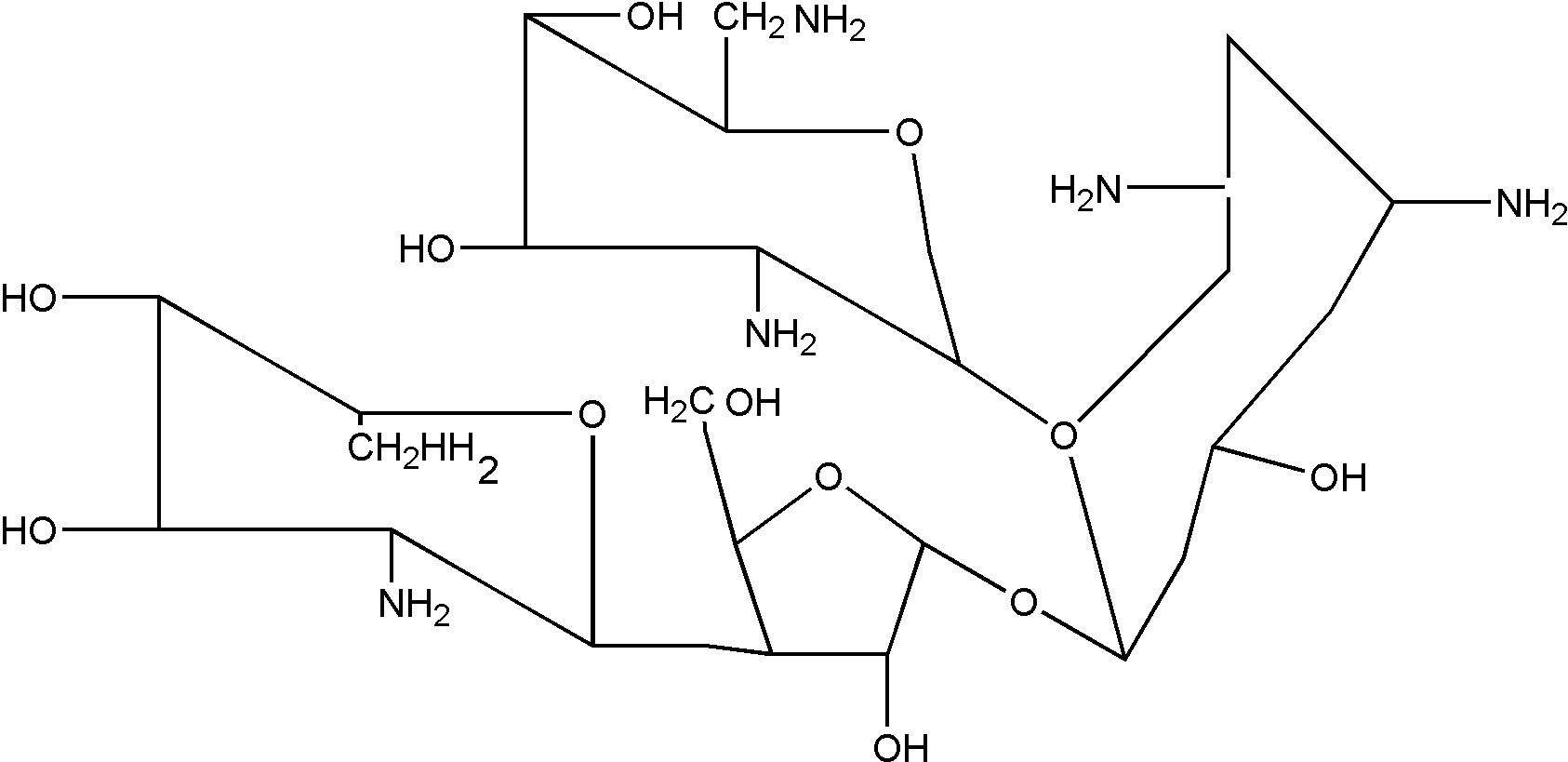
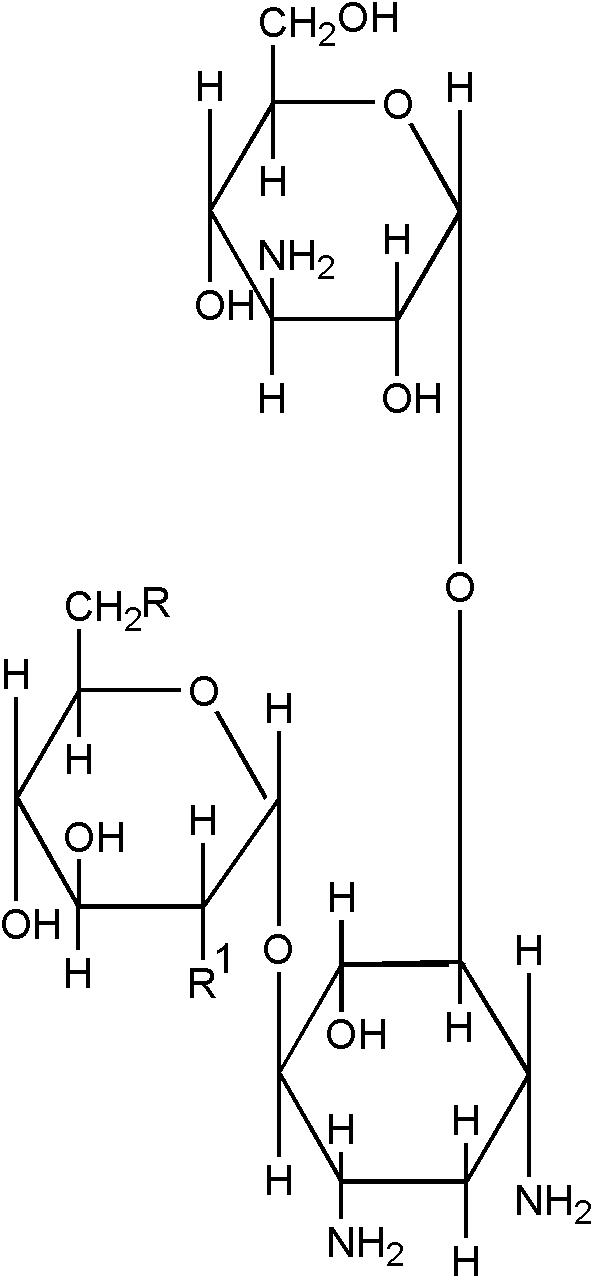
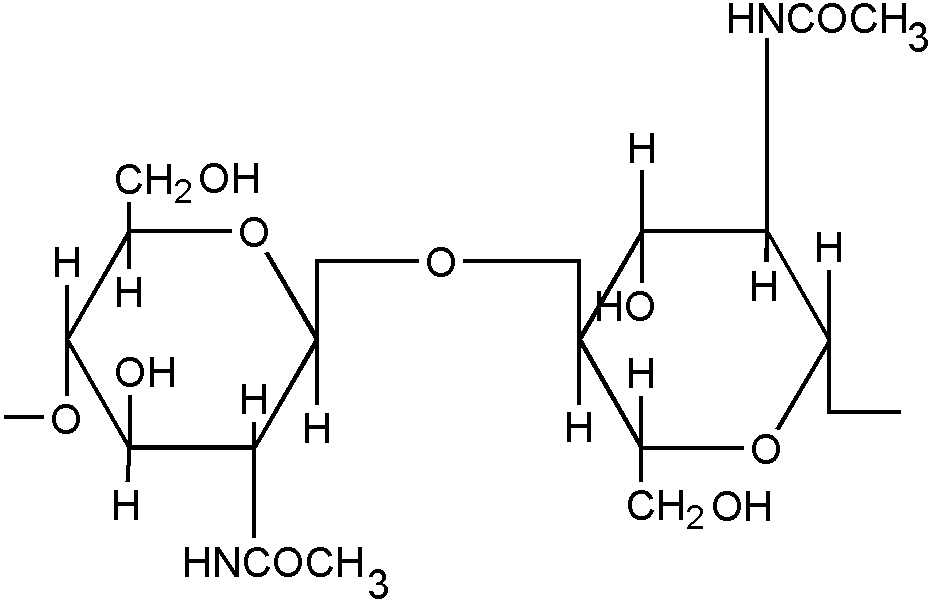
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 1.1]](../ps.gif) 1.1 1.1 | Peptide (e.g., protein, etc.) containing DOAI: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1. Subject matter wherein the designated organic active ingredient (DOAI) contains
two or more amino acids joined covalently by peptide bonds.
| | (1)
Note. A peptide bond is an amide bond between the
carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another. For
purposes of classification, the terms "peptide" and "protein" are used
interchangeably. |
| | (2)
Note. For the purposes of this and indented subclasses, language
such as "a pharmaceutical (or medicinal, bio-affecting, etc.) composition
comprising protein ’X’" is considered
a composition and is proper for this area as if it is a true composition
comprising two or more ingredients. |
| | (3)
Note. A derivative is classified with the peptide
when its function or utility is analogous to the named peptide and
its structure corresponds to approximately half or more of the amino
acid residues of the named peptide. The product of side
chain substitution, C or N terminal chain will be classified
with the named peptide as related peptides. The product of
a replacement reaction will be classified as a related peptide so
long as less than half the amino acid residues of the named peptide
have been replaced. The product of a removal reaction or
a partial sequence (i.e., fragments) will
be classified as a related peptide if half the amino acid residues
of the named peptide are present. Polypeptides which are
formed by joining the named peptide of identical sequence to the
named peptide should be originally classified on the basis of the named
peptide and cross-referenced to the appropriate subclasses. |
| | (4)
Note. In the case where peptides are joined by covalent
bonding, as by S-S bonds through cysteine, the
number of amino acids in the peptide is the sum of the individual
chains. |
| | (5)
Note. Subclasses herein provide for the delivery
of a peptide (DOAI) which has a biological effect. For
subclasses wherein the terms "affecting" or "utilizing" are
used, the peptide administered is not always the substance
named in the subclass title, rather the peptide administered
may have an effect on this substance which may be naturally occurring within
the living body. |
| | (6)
Note. A peptide acting as a potentiator or synergist
for a nonpeptide active ingredient (DOAI) is considered
as being an active ingredient (DOAI). |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 424, | Drug, Bio-Affecting and Body
Treating Compositions,
subclasses 94.1 through 94.67for enzyme containing pharmaceutical or bio-affecting
compositions. |
| 530, | Chemistry: Natural Resins or Derivatives; Peptides
or Proteins; Lignins or Reaction Products Thereof,
subclasses 300 through 345for peptides, per se, and methods
of preparing same; and subclasses 350-427 for proteins, per
se, and methods of preparing the same. |
| 930, | Peptide or Protein Sequence,
subclasses 10 through 320for peptide or protein sequences or four or more amino
acids. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 1.2]](../ps.gif) 1.2 1.2 | Transporter affecting or utilizing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is a transporter
peptide, or wherein a peptide is administered which has
an effect on a transporter.
| | (1)
Note. Transporters facilitate the carrying of molecular
contents across the cell membrane. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 1.3]](../ps.gif) 1.3 1.3 | Prodrug utilizing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide is part of a molecule
capable of being converted in vivo by chemical or enzymatic modifications
of its structure into an active agent. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 1.4]](../ps.gif) 1.4 1.4 | Sepsis affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide affects an acute systemic (bodywide) inflammatory response (also
known as systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS)) to
the spread of a micro-organism or its toxin in the blood
or tissues.
| | (1)
Note. In sepsis, widespread release of inflammatory
cytokines (especially, interleukin-1 (IL-1), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and
tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF alpha)) and
cytotoxic enzymes damage the endothelium which can result in tissue
edema, hypotension, and intravascular thrombosis, and
ultimately organ dysfunction or failure, and death. |
| | (2)
Note. The terms "sepsis," "severe
sepsis," and "septic shock" are
used to denote different extents of inflammation and infection. Severe
sepsis is sepsis with organ dysfunction, hypotension, or hyperperfusion. Septic
shock is sepsis-induced hypotension despite adequate fluid
resuscitation. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 2.3, | through 3.2, for a peptide composition which
is effective in destroying or inhibiting the growth of a micro-organism
when sepsis is not present. |
| 15.6, | for a peptide composition which affects the pressure
of blood flow against the walls of the arteries, either to
raise or lower said pressure. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 1.5]](../ps.gif) 1.5 1.5 | Respiratory distress syndrome (e.g., ARDS, IRDS, etc.) affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide is useful in treating
respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) including
acute/adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and
infant respiratory distress syndrome (IRDS).
| | (1)
Note. ARDS is respiratory failure in adults or children
resulting from various injuries to the lung including massive transfusion, chest
trauma, neurological injury, and sepsis. It
is characterized by pulmonary edema, difficult rapid breathing, and
hypoxemia. |
| | (2)
Note. Infant respiratory distress syndrome (IRDS) or
neonatal respiratory distress syndrome is also called hyaline membrane
disease. It is a condition in newborn babies, in
which the lungs are deficient in surfactant, preventing
their proper expansion and causing the formation of hyaline material
in the lung spaces. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 15.5, | for a peptide composition which affects or utilizes
surfactant protein (e.g., SP-A, SP-B, etc.). |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 1.6]](../ps.gif) 1.6 1.6 | Pneumonia affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide is useful in treating
pneumonia, an illness of the lung characterized by inflammation, abnormal
alveolar filling with fluid, and consolidation of lung
tissue followed by resolution.
| | (1)
Note. Pneumonia is chiefly caused by infection and
is usually accompanied by fever, cough, chest
pain, and difficulty in breathing. |
| | (2)
Note. Included but not limited thereto are bacterial
pneumonia, viral pneumonia, atypical pneumonia, bronchial
pneumonia, etc. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 1.7]](../ps.gif) 1.7 1.7 | Asthma affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide is useful in treating
asthma, a chronic respiratory system disorder marked by
recurring episodes of airway obstruction that is triggered by various stimuli
such as allergens, rapid change in air temperature, and
environmental tobacco smoke. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 1.8]](../ps.gif) 1.8 1.8 | Cystic fibrosis affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide is useful in treating
cystic fibrosis, a hereditary disease involving the functional
disorder of the exocrine (mucus) glands of the
lungs, liver, pancreas, and intestines, wherein
abnormally viscous mucus is produced.
| | (1)
Note. Cystic fibrosis is manifested by faulty digestion
due to a deficiency of pancreatic enzymes, by difficulty
in breathing due to mucus accumulation in airways, and
by excessive loss of salt in the sweat. It is also called
fibrocystic disease of the pancreas, mucoviscoidosis, or
mucoviscidosis. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 1.9]](../ps.gif) 1.9 1.9 | Arteriosclerosis (e.g., atherosclerosis, etc.) affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide is useful in treating
arteriosclerosis, an abnormal thickening and hardening
of the arterial walls.
| | (1)
Note. Different types of arteriosclerosis are atherosclerosis, arteriosclerosis
obliterans, medial calcific sclerosis, etc. |
| | (2)
Note. Atherosclerosis is the most common form of
arteriosclerosis. It is a hardening of an artery specifically
due to an atheromatous plaque containing cholesterol (free
lipid), atheroma (abnormal fatty deposits), etc. |
| | (3)
Note. Arteriosclerosis is distinct from arteriolosclerosis, which
is the hardening of arterioles. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 2.1]](../ps.gif) 2.1 2.1 | Endotoxin (e.g., LPS, etc.) affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered affects
endotoxin.
| | (1)
Note. Endotoxin is a poisonous substance found inside
pathogens such as bacteria. It is a structural component
in the bacteria, for example, lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and
lipooligosaccharide (LOS), separable
from the cell body only when the bacteria are lysed. It
may cause fever and inflammation in a host. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.4, | for endotoxin affecting peptide compositions used
in the treatment of sepsis. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 2.3]](../ps.gif) 2.3 2.3 | Micro-organism destroying or inhibiting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is effective
in destroying or inhibiting the growth of a single-celled
organism which is of microscopic or ultramicroscopic size (0.2-200 micrometers).
| | (1)
Note. For the purposes of this subclass and indented
subclasses, the term "micro-organism" includes
bacteria, actinomycetales, fungi (e.g., molds), protozoa, and
viruses. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 804, | for a cross-reference art collection of subject
matter containing a phleomycin peptide or derivative. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 2.4]](../ps.gif) 2.4 2.4 | Bacterium (e.g., Bacillus, etc.) destroying
or inhibiting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 2.3. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is effective
in destroying bacteria or in inhibiting their growth.
| | (1)
Note. The destroying or inhibiting can involve treating
a living host that has a bacterial infection or to preclude the
possible infection of a living host by a bacteria. Furthermore, a
peptide that is useful in destroying or inhibiting the growth of
bacteria in any nonliving environment is also properly classified herein, e.g., room, etc. |
| | (2)
Note. Bacteria are microscopic single-cell
organisms that have neither a membrane-bounded nucleus
or other membrane bounded organelles. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 2.5]](../ps.gif) 2.5 2.5 | Lactoferrin: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 2.4. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is lactoferrin, an
iron-binding protein of very high affinity found in milk, tears, mucus, bile, and
some white blood cells. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 2.6]](../ps.gif) 2.6 2.6 | Streptococcus: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 2.4. Subject matter wherein the bacterium is of the genus Streptococcus.
| | (1)
Note. Streptococcus is a spherical Gram-positive
bacterium. |
| | (2)
Note. Streptococcus bacteria can cause streptococcal
pharyngitis or streptococcal sore throat (strep throat), meningitis, endocarditis, etc. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 2.7]](../ps.gif) 2.7 2.7 | Staphylococcus (e.g., Staphylococcus
aureus, etc.): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 2.4. Subject matter wherein the bacterium is of the genus Staphylococcus.
| | (1)
Note. Staphylococcus is a Gram-positive spherical
bacterium. |
| | (2)
Note. Staphylococcus bacteria are generally responsible
for, for example, toxic shock syndrome, food
poisoning, etc. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 2.8]](../ps.gif) 2.8 2.8 | Gram negative bacterium (e.g., Escherichia coli, salmonella, Helicobacter, etc.): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 2.4. Subject matter wherein the bacterium is considered to be
Gram negative or does not retain the purple dye when stained by
Gram’s stain.
| | (1)
Note. Gram staining is an empirical method to distinguish
Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria based
on structural and composition differences in their cell walls. Gram-negative
bacterium has a lipid outer layer and a thinner inner layer than
Gram-positive bacterium and loses the purple color after
decolorization in the Gram test. It is proper to classify
an organism here considered to be Gram negative on the basis of
phylogenetic relationship but which does not display the expected
Gram staining characteristics, e.g., it
stains Gram positive, etc.). | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 2.9]](../ps.gif) 2.9 2.9 | Cyclopeptide utilizing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 2.4. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is a cyclic
structure, wherein the cyclic structure is formed by peptide
bonding, disulfide bonding, hydrocarbon bonding, or
other types of bonding and has at least a dipeptide as an integral
part thereof.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 3.6, | for a composition containing a cyclopeptide used
in the treatment of a fungal infection. |
| 21.1, | for a composition containing a cyclopeptide for
a function/utility not provided by a specific function/utility subclass
in this class. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 930, | Peptide or Protein Sequence,
subclass 260 for peptides or proteins with intrachain cysteine-cysteine
bridges and subclass 270 for other cyclic peptides or proteins. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 3.1]](../ps.gif) 3.1 3.1 | Glycopeptide utilizing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 2.4. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is bonded
to a carbohydrate.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 20.9, | for a composition containing a glycopeptide for
a function/utility not provided by a specific function/utility subclass
in this class. |
| 804, | for a cross-reference art collection of subject
matter containing a phleomycin peptide or derivative. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 3.2]](../ps.gif) 3.2 3.2 | Amphiphilic or oligomer modified peptide (e.g., magainin, peptide
nucleic acid, or PEGylated peptide, etc.) utilizing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 2.4. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is characterized
by the coexistence of a hydrophobic domain and a hydrophilic domain which
can be due to a chemically attached lipophilic group or spatial
segregation of hydrophobic and hydrophilic amino acid residues in the
tertiary structure (e.g., alpha-helix, etc.), or the
peptide administered is covalently functionalized by repeated organic
functional moieties (e.g., nucleic
acid or ethylene glycol, etc.).
| | (1)
Note. Examples of peptides included in this subclass
are magainin, peptide nucleic acid, and PEGylated
peptide. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 3.3]](../ps.gif) 3.3 3.3 | Fungus (e.g., athlete’s
foot, ringworm, etc.) destroying
or inhibiting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 2.3. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is effective
in destroying fungi or in inhibiting their growth.
| | (1)
Note. The destroying or inhibiting can involve treating
a living host that has a fungal infection or to preclude the possible
infection of a living host with a fungus. Furthermore a
peptide that is useful in destroying or inhibiting the growth of fungus
in any nonliving environment is also properly classified herein (e.g., room, etc.). |
| | (2)
Note. Fungi are organisms that belong to the kingdom
Fungi. They contain a chitinous cell wall (e.g., molds, yeasts, etc.). | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 3.4]](../ps.gif) 3.4 3.4 | Candida (e.g., Candida
albicans, etc.): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 3.3. Subject matter wherein the fungus is of the genus Candida.
| | (1)
Note. Candida albicans is the most common cause of
vaginal infection Candidiasis is also called yeast infection or thrush. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 3.6]](../ps.gif) 3.6 3.6 | Cyclopeptide utilizing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 3.3. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is a cyclic
structure, wherein the cyclic structure is formed by peptide
bonding, disulfide bonding, hydrocarbon bonding, or
other types of bonding, and has at least a dipeptide as an
integral part thereof.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 21.1, | for a composition containing a cyclopeptide for
a function/utility not provided by a specific function/utility subclass
in this class. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 930, | Peptide or Protein Sequence,
subclass 260 for peptides or proteins with intrachain cysteine-cysteine
bridges and subclass 270 for other cyclic peptides or proteins. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 3.7]](../ps.gif) 3.7 3.7 | Virus destroying or inhibiting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 2.3. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is effective
in destroying a virus or in inhibiting its growth.
| | (1)
Note. The destroying or inhibiting can involve treating
a living host that has a viral infection or to preclude the possible infection
of a living host with a virus. Furthermore, a
peptide that is useful in destroying or inhibiting the growth of
a virus in any nonliving environment is also properly classified
herein (e.g., room, etc.). |
| | (2)
Note. A virus is encapsulated RNA or DNA enclosed
within a protective protein coat. Outside of a host cell
a virus is unable to grow or reproduce. |
| | (3)
Note. The following are some of the diseases caused
by a virus (e.g., Polio, smallpox, the
common cold, chickenpox, shingles, herpes, rabies, Ebola, AIDS, etc.). | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 3.8]](../ps.gif) 3.8 3.8 | Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 3.7. Subject matter wherein the virus is the human immunodeficiency
virus (HIV), the causative agent of Acquired
Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS).
| | (1)
Note. HIV refers to any of a group of viruses that
infect and destroy cells of the immune system causing the marked reduction
in their numbers that leads to a diagnosis of AIDS. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 3.9]](../ps.gif) 3.9 3.9 | Cluster of differentiation protein (e.g., CD4, etc.) affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 3.8. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered affects
cluster of differentiation molecules found on the surface of a leukocyte.
| | (1)
Note. Cluster of differentiation proteins are a group
of cell surface molecules present on leukocytes. |
| | (2)
Note. CD4 is a primary receptor used by the human
immunodeficiency virus (HIV) to gain entry into
host T-cells. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 4.2]](../ps.gif) 4.2 4.2 | Herpesviridae: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 3.7. Subject matter wherein the virus is of the family herpesviridae, which
can cause inflammation of the skin or mucous membranes characterized
by watery blisters.
| | (1)
Note. Some members of the herpesviridae family of
viruses which cause disease in humans include herpes simplex virus-1, herpes
simplex-2, varicella zoster virus, Epstein-Barr
virus, cytomegalovirus, etc. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 4.3]](../ps.gif) 4.3 4.3 | Hepatitis: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 3.7. Subject matter wherein the virus is the hepatitis virus (e.g., hepatitis
A, B, C, D, E, etc.) which damages
the liver. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 4.4]](../ps.gif) 4.4 4.4 | Protozoa destroying or inhibiting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 2.3. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is effective
in destroying a unicellular eukaryotic organism or in inhibiting
its growth (e.g., amoebas, ciliates, flagellates, sporozoans, etc.). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 4.5]](../ps.gif) 4.5 4.5 | Insect destroying or inhibiting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is effective
in destroying insects or in inhibiting their growth.
| | (1)
Note. Insects are arthropods of the class Insecta. |
| | (2)
Note. Included but not limited thereto are cockroaches, ants, beetles, moths, grasshoppers, bees, wasps, helicoverpa zea, lepidoptera, etc. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 4.7]](../ps.gif) 4.7 4.7 | Lactation affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered affects
the formation or secretion of milk by the mammary glands of female
animals. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 4.8]](../ps.gif) 4.8 4.8 | Weight regulation affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered affects
body weight (e.g., treating
obesity, increasing feed efficiency and weight gain of animals, varying
the fat-flesh ratio, etc.).
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 426, | Food or Edible Material: Processes, Compositions, and
Products, for compositions wherein the nutritional ingredients (e.g., fat, carbohydrate, or protein, etc.) are
varied to achieve a certain fat-flesh ratio in an animal, or for
compositions intended to nourish an animal by natural oral ingestion, which
may contain an additive necessary to maintain the normal metabolism
of the animal (e.g., vitamins, minerals, amino
acids, etc.). |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 4.9]](../ps.gif) 4.9 4.9 | Appetite or satiation affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 4.8. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered affects
hunger sensations, cravings, or the sensation
of fullness or gratification derived from oral consumption of food. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 5.1]](../ps.gif) 5.1 5.1 | Growth hormone (GH) or derivative utilizing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 4.8. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is growth
hormone or a derivative thereof.
| | (1)
Note. Growth hormone is alternatively known as somatotrophin, somatotropin, somatotropic
hormone, somatotrophic hormone, STH, human
growth hormone. |
| | (2)
Note. Somatotrophin contains 191 amino acids. |
| | (3)
Note. Somatotrophin has important functions, which
include stimulating body growth and strengthening bones and tendons
in humans. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 5.2]](../ps.gif) 5.2 5.2 | Neuropeptide (e.g., NPY, PYY, dynorphin, etc.) or
derivative utilizing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 4.8. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is a neuropeptide
derived from neural tissues or a derivative thereof.
| | (1)
Note. Neuropeptide Y (NPY) is a
36 amino acid peptide neurotransmitter found in the brain and autonomic
system. NPY increases food intake and increases the proportion
of energy stored as fat. |
| | (2)
Note. Peptide YY (PYY) is a 36
amino acid peptide produced by neurons in the brainstem, and
released by L cells in the gastrointestinal tract, especially
the ileum and colon in response to feeding. It inhibits
gastric motility, increases efficiency of digestion and
nutrient absorption, and decreases appetite. |
| | (3)
Note. Dynorphin is an opioid peptide that arises
from the precursor protein prodynorphin. Dynorphin is produced
in the arcuate nucleus and in orexin neurons of the lateral hypothalamus
and affects the control of appetite. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 5.4]](../ps.gif) 5.4 5.4 | Iron affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered promotes
or inhibits iron absorption, uptake, storage, or
recycling to treat conditions including iron insufficiency and iron
overload (e.g., by reducing
gastrointestinal side effects, improving bioavailability, or
binding iron).
| | (1)
Note. Iron as a metal is an important component of
proteins and enzymes responsible for regulating cell growth, differentiation, and
oxygen transport. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 5.5]](../ps.gif) 5.5 5.5 | Nutrition enhancement or support: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered contributes
to improved absorption or utilization of a nutrient, or
wherein the peptide composition administered to nourish an animal is
designed to be delivered to the animal via routes other than the
alimentary canal (e.g., by rectal
or parenteral injection, etc.) or via
a tube through the alimentary canal or stomach wall.
| | (1)
Note. Improved absorption or utilization of nutrients
may promote wound healing or increase resistance to disease. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 426, | Food or Edible Material: Processes, Compositions, and
Products, for compositions intended to nourish an animal
by natural oral ingestion, which may contain an additive
necessary to maintain the normal metabolism of the animal (e.g., vitamins, minerals, amino
acids, etc.). |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 5.8]](../ps.gif) 5.8 5.8 | Leptin or derivative affecting or utilizing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is leptin
or a derivative thereof, or wherein the peptide is administered
which has an effect on leptin.
| | (1)
Note. Leptin is a naturally occurring hormone which
affects appetite and regulates energy intake and energy expenditure. |
| | (2)
Note. Leptin has a molecular weight of 16,000
daltons. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 5.9]](../ps.gif) 5.9 5.9 | Insulin or derivative utilizing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is insulin
or a derivative thereof, in which neither a peptide chain
nor a disulfide link between chains is broken.
| | (1)
Note. Insulin is a peptide hormone produced in the
Islets of Langerhans in the pancreas. While the position
and/or kind of amino acids in the chain(s) may
vary (depending on the animal from which it originates), it
appears that insulin contains at least an "A" chain
of 21 acid units linked by disulfide moieties to a "B." An
additional disulfide moiety bridges the 6 and 11 positions of chain A. |
| | (2)
Note. A synthetic form of insulin is classified as
if it is naturally occurring. |
| | (3)
Note. It is proper to classify a peptide here if
it is characterized as insulin or a derivative thereof. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
| 8.5, | for a composition containing an insulin-like
growth factor. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 530, | Chemistry: Natural Resins or Derivatives; Peptides
or Proteins; Lignins or Reaction Products Thereof,
subclass 303 for insulin, per se. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 6.1]](../ps.gif) 6.1 6.1 | Truncated insulin: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 5.9. Subject matter wherein the insulin contains fewer amino
acids than natural insulin (i.e., one or
more of the amino acid residues on the insulin molecule are absent (e.g., Phe
at B25 position is deleted, etc.).
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 6.2, | for insulin wherein an amino acid of the A-chain
is substituted with another amino acid and the insulin contains
the same number of amino acids as natural insulin. |
| 6.3, | for insulin wherein an amino acid of the B-chain
is substituted with another amino acid and the insulin contains the
same number of amino acids as natural insulin. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 6.2]](../ps.gif) 6.2 6.2 | A-chain modified insulin: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 5.9. Subject matter wherein the A-chain structure of insulin
is changed (e.g., one or more
amino acids are added to the A-chain, a different amino
acid is substituted for the amino acid normally found in that position
of the A-chain, etc.). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 6.3]](../ps.gif) 6.3 6.3 | B-chain modified insulin: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 5.9. Subject matter wherein the B-chain structure of insulin
is changed (e.g., one or more
amino acids are added to the B-chain, a different amino
acid is substituted for the amino acid found in that position of
the B-chain, etc.). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 6.5]](../ps.gif) 6.5 6.5 | With an additional active ingredient: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 5.9. Subject matter wherein the insulin is admixed with another
active ingredient.
| | (1)
Note. A potentiator is considered as an active ingredient
and can be an additional peptide or a nonpeptide. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 6.6]](../ps.gif) 6.6 6.6 | With protamine: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 6.5. Subject matter wherein the insulin or derivative is admixed
with protamine.
| | (1)
Note. Protamine is a positively charged polypeptide
which prolongs the effect of insulin. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 6.8]](../ps.gif) 6.8 6.8 | Blood sugar affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered has an effect
on the concentration of sugar in the blood.
| | (1)
Note. Glucose and other sugars are transported via
the blood stream, and are the primary sources of energy
for the cells. |
| | (2)
Note. Glucose is the primary blood sugar. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 6.9]](../ps.gif) 6.9 6.9 | Diabetes: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 6.8. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is useful
in treating diabetes.
| | (1)
Note. Diabetes as defined by the American Diabetes
Association (2008) is a condition where a subject
has a fasting plasma glucose level (FPG) above
126 mg/dl, while a level between 100 and 125 mg/dl
is considered pre-diabetes. For purposes of this
subclass, any FPG level of 100 mg/dl or higher
is considered as being diabetic. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 7.1]](../ps.gif) 7.1 7.1 | Somatostatin or derivative affecting or utilizing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 6.9. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is somatostatin
or a derivative thereof, or wherein a peptide is administered
which has an effect on somatostatin.
| | (1)
Note. Somatostatin is alternatively known as growth
hormone inhibiting hormone (GHIH) or somatotropin release-inhibiting
factor (SRIF). |
| | (2)
Note. Somatostatin is secreted in the digestive system
and in the hypothalamus. It inhibits both insulin and glucagon
secretion. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
| 806, | for a cross-reference art collection of subject
matter involving peptide compositions having somatostatin-like activity. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 7.2]](../ps.gif) 7.2 7.2 | Glucagon, glucagon-like peptide (e.g., GLP-1, etc.) or
derivative affecting or utilizing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 6.9. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is glucagon, a
glucagon-like peptide, or a derivative thereof, or
wherein a peptide is administered which has an effect on glucagon or
a glucagon-like peptide.
| | (1)
Note. Glucagon is a 29 amino acid polypeptide hormone
that is produced by the pancreas that promotes an increase in the sugar
content of the blood by increasing the rate of glycogen breakdown
in the liver. |
| | (2)
Note. GLP-1 is derived from the same precursor
as glucagon, which is proglucagon. GLP-1
inhibits glucagon and stimulates secretion of insulin. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 7.3]](../ps.gif) 7.3 7.3 | Type I diabetes: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 6.9. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is useful
in treating Type I diabetes (i.e., Insulin-Dependent
Diabetes Mellitus (IDDM)), an
autoimmune disease that results in destruction of insulin-producing
beta cells of the pancreas. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 7.4]](../ps.gif) 7.4 7.4 | Lipid or cholesterol affecting (e.g., dyslipidemia, etc.): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered has an effect
on lipid or cholesterol levels in the body.
| | (1)
Note. Lipid (e.g., fats, oils, sterols, waxes, etc.) is
a water-insoluble biomolecule or organic compound which
is a structural constituent of a living cell affecting, modulating, or
regulating cellular metabolic functions together with carbohydrates
and proteins or peptides. |
| | (2)
Note. Cholesterol is an important constituent of
cell membranes as a lipid, responsible for permeability
of metabolites and nutrients across the cell membrane of an animal
cell. |
| | (3)
Note. Dyslipidemia is characterized by abnormal concentrations
of lipids or lipoproteins in the blood. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 7.5]](../ps.gif) 7.5 7.5 | Protein tyrosine kinase (PTK) affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered affects
protein tyrosine kinase (PTK) which catalyzes
the phosphorylation of tyrosine residues in a protein.
| | (1)
Note. Phosphorylation of proteins by kinases is an
important mechanism in signal transduction for regulation of enzyme
activity. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 7.6]](../ps.gif) 7.6 7.6 | Growth factor or derivative affecting or utilizing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is a growth
factor or a derivative thereof, which regulates cell proliferation, development, migration, or
differentiation of cells or tissues, or wherein the peptide
administered has an effect on a growth factor.
| | (1)
Note. The term "growth factor" is
meant to encompass any secretory factor that is growth stimulatory
or growth inhibitory (i.e., that
will stimulate or inhibit clonal expansion of cells). |
| | (2)
Note. The term "growth factor" is
sufficient for placement of a peptide into this subclass. |
| | (3)
Note. Cytokines produced by both immune cells (i.e., antigen-presenting cells, lymphocytes, basophils, dendritic cells, granulocytes, helper
T-cells, leukocytes, macrophages, and
mast cells) and other cell types and cytokines where the origin
is unspecified (not claimed, disclosed, or
otherwise known) are cross-referenced here as
appropriate. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
| 9.7, | through 13.1, for a peptide hormone, especially
subclass 11.3 for a growth hormone. |
| 18.9, | for a peptide composition which affects apoptosis. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 424, | Drug, Bio-Affecting and Body
Treating Compositions,
subclasses 85.1 through 85.7for compositions containing cytokines, soluble
immune mediators, produced by the cells of the immune system
(i.e., antigen-presenting
cells, lymphocytes, basophils, dendritic
cells, granulocytes, helper T-cells, leukocytes, macrophages, and mast
cells) and cytokines produced by both immune cells and
other cell types. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 7.7]](../ps.gif) 7.7 7.7 | Erythropoietin (EPO) or derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 7.6. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is erythropoietin (EPO) or
a derivative thereof, or wherein the peptide administered has
an effect on erythropoietin.
| | (1)
Note. EPO is a glycoprotein (a protein with
a sugar attached to it). It is a growth hormone
produced by the kidney that promotes the formation of red blood cells
in the bone marrow. Human EPO has a molecular weight of
approximately 34,000 daltons. |
| | (2)
Note. It is proper to classify a peptide in this
subclass if it is characterized as an erythropoietin growth factor
regardless of function. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 7.8]](../ps.gif) 7.8 7.8 | Thrombopoietin (TPO) or derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 7.6. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is thrombopoietin (TPO) or
a derivative thereof, or wherein the peptide administered has
an effect on TPO.
| | (1)
Note. TPO is a glycoprotein (a protein with
a sugar attached to it). It is a hormone produced
mainly by the liver and the kidney that regulates the production of
platelets by the bone marrow. |
| | (2)
Note. It is proper to classify a peptide in this
subclass if it is characterized as an thrombopoietin growth factor
regardless of function. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 7.9]](../ps.gif) 7.9 7.9 | Hematopoiesis affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 7.6. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is a growth
factor that has an effect on the formation and development of blood
cells. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 8.1]](../ps.gif) 8.1 8.1 | Vascular endothelial growth factor (e.g., VEGF-A, VEGF-B, etc.) or
derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 7.6. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is vascular
endothelial growth factor or a derivative thereof, or wherein
the peptide administered has an effect on vascular endothelial growth
factor.
| | (1)
Note. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a signaling
peptide that stimulates the formation of new blood vessels, as
well as new blood vessels from pre-existing ones. It
is also important in the development of the embryonic circulatory
system. |
| | (2)
Note. Vascular endothelial growth factors (e.g., VEGF-A, VEGF-B, VEGF-C, placenta
growth factor (PIGF), etc.) are
a subfamily of growth factors. |
| | (3)
Note. It is proper to classify a peptide in this
subclass if it is characterized as an endothelial or vascular growth
factor regardless of function. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
| 13.3, | for a peptide composition which affects angiogenesis. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 8.2]](../ps.gif) 8.2 8.2 | Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) or derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 7.6. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is platelet-derived
growth factor (PDGF) or a derivative thereof, or
wherein the peptide administered has an effect on PDGF.
| | (1)
Note. PDGF plays a significant role in blood vessel
formation, as well as the growth of blood vessels from
already existing blood vessel tissue. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 8.3]](../ps.gif) 8.3 8.3 | Nerve tissue or nerve cell growth affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 7.6. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is a growth
factor which affects the proliferation, development, migration, or differentiation
of nerve cells or nerve tissues.
| | (1)
Note. Nervous tissue is the material composed of
neurons that make up the brain, spinal cord, and
network of nerves around the body. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 8.4]](../ps.gif) 8.4 8.4 | Nerve growth factor (NGF) or derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 8.3. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is nerve
growth factor (NGF) or a derivative thereof, or
wherein the peptide administered has an effect on NGF.
| | (1)
Note. NGF is a naturally occurring peptide in the
body which stimulates growth and differentiation of the sympathetic sensory
nerves. It consists of alpha, beta, and
gamma polypeptide chains. |
| | (2)
Note. It is proper to classify a peptide in this
subclass if it is characterized as a nerve growth factor regardless
of function. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 8.5]](../ps.gif) 8.5 8.5 | Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) or
derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 7.6. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is an insulin-like
growth factor (IGF) or a derivative thereof, or
wherein the peptide administered has an effect on IGF.
| | (1)
Note. IGF may also be called somatomedin. |
| | (2)
Note. Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), insulin-like
growth factor-2 (IGF-2), etc. are
part of a complex system that cells use to communicate with their physiologic
environment and which has a high sequence similarity to insulin. |
| | (3)
Note. IGF-1 is also called somatomedin C
and IGF-2 is also called somatomedin A. |
| | (4)
Note. It is proper to classify a peptide in this
subclass if it is categorized as IGF, regardless of use. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 8.6]](../ps.gif) 8.6 8.6 | Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) or derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 8.5. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is insulin-like
growth factor 1 (IGF-1) or a derivative
thereof, or wherein the peptide administered has an effect
on IGF-1.
| | (1)
Note. IGF-1 may also be called somatomedin
C. |
| | (2)
Note. IGF-1 is a natural hormone consisting
of 79 amino acids in a single chain with 3 intra-molecular
disulfide bridges with a molecular weight of 7,649 daltons. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 8.7]](../ps.gif) 8.7 8.7 | Insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP) or
derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 8.5. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is insulin-like
growth factor binding protein (IGFBP) or a derivative
thereof, or wherein the peptide administered has an effect on
IGFBP.
| | (1)
Note. IGFBP is a family of cysteine rich (16-20
cysteines) proteins which binds IGF. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 8.8]](../ps.gif) 8.8 8.8 | Bone morphogenic protein (BMP) or derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 7.6. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is a bone
morphogenic protein (BMP) or derivative thereof, or
wherein the peptide administered has an effect on BMP.
| | (1)
Note. BMPs are generally involved in the formation
of bone or cartilage. |
| | (2)
Examples of BMPs include osteogenic protein-1 (OP-1), BMP-3, OP-2, BMP-4, etc. |
| | (3)
Note. It is proper to classify a peptide in this
subclass if it is categorized as BMP, regardless of use. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 8.9]](../ps.gif) 8.9 8.9 | Transforming growth factor (TGF) or derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 7.6. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is a transforming
growth factor (TGF) or a derivative thereof, or
wherein the peptide administered has an effect on TGF.
| | (1)
Note. TGF (e.g., TGF-beta, etc.) is
generally involved in inducing cellular transformation and in stimulating
the growth of normal cells. |
| | (2)
Note. It is proper to classify a peptide in this
subclass if it is characterized as TGF, regardless of use. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 9.1]](../ps.gif) 9.1 9.1 | Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) or derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 7.6. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is a fibroblast
growth factor (FGF) or a derivative thereof, or
wherein the peptide administered has an effect on FGF.
| | (1)
Note. FGFs are particularly involved in wound healing, angiogenesis, and embryonic
development. |
| | (2)
Note. The FGF family consists of four members: FGFR1, FGFR2, FGFR3, and FGFR4. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
| 9.4, | for a peptide composition which affects wound healing
or repair. |
| 13.3, | for a peptide composition which affects angiogenesis. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 9.2]](../ps.gif) 9.2 9.2 | Keratinocyte growth factor (KGF) or derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 9.1. Subject matter wherein the fibroblast growth factor administered
is keratinocyte growth factor (KGF) or a derivative
thereof, or wherein the peptide administered has an effect
on KGF.
| | (1)
Note. KGF, also known as fibroblast growth
factor 7 (FGF7), has an important role
in wound healing or repair. |
| | (2)
Note. KGF stimulates the growth of epithelial cells
in the skin and in the lining of the mouth, stomach, and
intestines. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
| 9.4, | for a peptide composition which affects wound healing
or repair. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 9.3]](../ps.gif) 9.3 9.3 | Fibronectin or derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 7.6. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is fibronectin
or a derivative thereof, or wherein the peptide administered
has an effect on fibronectin.
| | (1)
Note. Fibronectin is a glycopeptide growth factor
of 2,000 daltons molecular weight with two polypeptide
chains linked by disulfide bonds. |
| | (2)
Note. Functions of fibronectin include cellular adhesion
mediation, cell shape, and migration control. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 9.4]](../ps.gif) 9.4 9.4 | Wound healing or wound repair affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 7.6. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is a growth
factor or derivative thereof, which affects the natural
process of regenerating internal or external tissues which have
been damaged, or wherein the peptide administered has an
effect on a growth factor whose function is to regenerate internal
and external tissues which have been damaged.
| | (1)
Note. Wound healing or repair is a complex and dynamic
process of restoring cellular structures and tissue layers. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 9.5]](../ps.gif) 9.5 9.5 | Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) or derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 7.6. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is hepatocyte
growth factor (HGF) or a derivative thereof, or
wherein the peptide administered has an effect on HGF.
| | (1)
Note. HCF, also known as scatter factor, is
a polypeptide involved in cellular growth, motility, and
morphogenesis. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 9.6]](../ps.gif) 9.6 9.6 | Epidermal growth factor (EFG) or epidermal
growth factor-like or derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 7.6. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is an epidermal
growth factor (EGF) or epidermal growth factor-like (EGF-like), or
a derivative thereof, or wherein the peptide administered
has an effect on EFG.
| | (1)
Note. EGF stimulates and sustains the replication
of epidermal cells (of ectodermal or endodermal origin). |
| | (2)
Note. Human EGF is a 6,045-dalton
protein with 53 amino acid residues and 3 intramolecular disulfide
bonds. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 9.7]](../ps.gif) 9.7 9.7 | Hormone or derivative affecting or utilizing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is a hormone, which
affects, enhances, or modulates the carrying of
information for metabolic function from host cell to target cell
or wherein the peptide administered has an effect on a hormone.
| | (1)
Note. The term "hormone" is sufficient for
placement of a peptide into this subclass. It is not necessary
that the peptide described as a "hormone" be used
for that purpose. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 9.8]](../ps.gif) 9.8 9.8 | Fertility: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 9.7. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is a hormone, or
a derivative thereof, which affects the physiological mechanisms
or conditions that inhibit or promote ability to produce offspring, or
wherein a peptide is administered which has an effect on a hormone which
is involved in inhibiting or promoting the ability to produce offspring. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 9.9]](../ps.gif) 9.9 9.9 | Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) or derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 9.8. Subject matter wherein the peptide hormone administered
is follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), which
is normally produced by the pituitary gland or a derivative thereof, or
wherein the peptide administered has an effect on FSH.
| | (1)
Note. FSH promotes reproductive function by stimulating
the growth of follicles in the ovary or inducing the formation of
sperm in the testes. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 10.1]](../ps.gif) 10.1 10.1 | Luteinizing hormone (LH) or derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 9.8. Subject matter wherein the peptide hormone administered
is luteinizing hormone (LH) or a derivative thereof, or
wherein the peptide administered has an effect on LH.
| | (1)
Note. LH controls the length and sequence of the
female menstrual cycle, including ovulation, preparation
of the uterus for implantation of a fertilized egg, and
ovarian production of both estrogen and progesterone. In
males, it stimulates the testes to produce androgen. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
| 10.2, | for a peptide which affects androgen or estrogen. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 10.3]](../ps.gif) 10.3 10.3 | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) or
derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 9.8. Subject matter wherein the peptide hormone administered
is gonadatropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) or
a derivative thereof, or wherein the peptide administered
has an effect on gonadatropin-releasing hormone.
| | (1)
Note. GnRH, also known as luteinizing-hormone
releasing hormone (LHRH), is a decapeptide
which stimulates the synthesis and secretion of the gonadotropins from
the anterior pituitary. |
| | (2)
Note. Gonadotropins include luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle
stimulating hormone (FSH), and human
chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
| 800, | for a cross-reference art collection of subject
matter involving compositions containing peptides that influence
the release of luteinizing hormone. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 10.4]](../ps.gif) 10.4 10.4 | Cetrorelix, leuprolide, or deslorelin
utilizing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 10.3. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is cetrorelix, leuprolide, or
deslorelin, synthetic analogues of naturally occurring gonadotropin-releasing
hormone.
| | (1)
Note. Cetrorelix is a synthetic decapeptide which
acts as an injectable GnRH antagonist. |
| | (2)
Note. Leuprorelin, which is a synonym for
leuprolide, is a synthetic nonapeptide analogue of GnRH. |
| | (3)
Note. Deslorelin is a synthetic nonapeptide analogue
of the natural GnRH. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 10.5]](../ps.gif) 10.5 10.5 | Ovulation affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 10.3. Subject matter wherein the gonadotropin-releasing
hormone (i.e., GnRH) or
derivative thereof, administered affects the process in
the menstrual cycle during which a mature ovarian follicle ruptures
and discharges an ovum (i.e., oocyte, female
gamete, egg). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 10.7]](../ps.gif) 10.7 10.7 | Melanocortin (e.g., melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH), etc.) or
derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 9.7. Subject matter wherein the peptide hormone administered
is a melanocortin, which is normally produced by the pituitary
gland or a derivative thereof, or wherein the peptide administered
has an effect on a melanocortin.
| | (1)
Note. Melanocortins are known to be involved in regulating
other hormones involved in cell pigmentation. |
| | (2)
Melanocortins include melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH), etc. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 10.8]](../ps.gif) 10.8 10.8 | Corticotropin or derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 10.7. Subject matter wherein the melanocortin administered is
corticotropin, which is normally produced by the pituitary
gland, or a derivative thereof, or wherein the
peptide administered has an effect on corticotropin.
| | (1)
Note. Corticotropin is also known as adrenocorticotropin (ACTH). |
| | (2)
Note. Corticotropin stimulates the adrenal glands
to produce cortisol and other steroid hormones. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
| 805, | for a cross-reference art collection of subject
matter involving a peptide composition having adrenocorticotropic
activity. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 10.9]](../ps.gif) 10.9 10.9 | Vasopressin or derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 9.7. Subject matter wherein the peptide hormone administered
is vasopressin, which is normally produced by the pituitary
gland, or a derivative thereof, or wherein the
peptide administered has an effect on vasopressin.
| | (1)
Note. Vasopressin, also called antidiuretic
hormone (ADH), is involved in the regulatory
function of the circulatory system, including constricting
blood vessels, raising blood pressure so as to help keep
a regular balance of salts in the blood, and controlling
the amount and frequency of urination. Without vasopressin, too
much water is lost in the urine. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
| 11.6, | for a composition containing oxytocin or a derivative
thereof. |
| 807, | for a cross-reference art collection of subject
matter involving a peptide composition related to oxytoxin, vasopressin, or
a derivative thereof. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 11.1]](../ps.gif) 11.1 11.1 | Somatostatin or derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 9.7. Subject matter wherein the peptide hormone administered
is somatostatin or a derivative thereof, or wherein the
peptide administered has an effect on somatostatin.
| | (1)
Note. Somatostatin is also known as growth hormone
inhibiting hormone (GHIH) or somatotropin release-inhibiting
factor (SRIF). |
| | (2)
Note. Somatostatin is secreted in the digestive system
and in the hypothalamus. Somatostatin inhibits both insulin and
glucagon secretion and also inhibits the secretion of several gastrointestinal hormones (e.g., gastrin, etc.) and
affects nutrient absorption and motility in the gastrointestinal
tract. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
| 806, | for a cross-reference art collection of subject
matter involving peptide compositions having somatostatin-like activity. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 11.2]](../ps.gif) 11.2 11.2 | Growth-hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) or
derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 9.7. Subject matter wherein the peptide hormone administered
is growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) or
a derivative thereof, which stimulates the release of growth
hormone, or wherein the peptide administered has an effect on
GHRH.
| | (1)
Note. GHRH is also known as growth-hormone-releasing
factor (GRF or GHRF) or somatocrinin. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 11.3]](../ps.gif) 11.3 11.3 | Growth hormone (GH) or derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 9.7. Subject matter wherein the peptide hormone administered
is growth hormone (GH), normally produced
by the anterior lobe of pituitary gland which stimulates growth
and cell reproduction in humans and other animals, or a derivative
thereof, or wherein the peptide administered has an effect
on GH.
| | (1)
Note. GH is alternatively known as somatotrophin, somatotropin, somatotropic
hormone, somatotrophic hormone, STH, and
human growth hormone (hGH). |
| | (2)
Note. Human somatotrophin contains 191 amino acids. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 11.4]](../ps.gif) 11.4 11.4 | Human growth hormone (hGH) or derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 11.3. Subject matter wherein the growth hormone administered is
human growth hormone (hGH) or a derivative thereof, or
wherein the peptide administered has an effect on hGH.
| | (1)
Note. HGH consists of 191 amino acids and has a molecular
weight of 22,124 daltons. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 11.5]](../ps.gif) 11.5 11.5 | Prolactin or derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 9.7. Subject matter wherein the peptide hormone administered
is prolactin, which is normally produced by the pituitary
gland, or a derivative thereof, or wherein the
peptide administered has an effect on prolactin.
| | (1)
Note. Prolactin is alternatively known as lactogenic
hormone, lactotropin, luteotropic hormone, and
luteotropin. |
| | (2)
Note. Human prolactin is a single chain polypeptide
of 199 amino acids with a molecular weight of approximately 24,000
daltons. The molecule is folded due to the activity of
three disulfide bonds. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 11.6]](../ps.gif) 11.6 11.6 | Oxytocin or derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 9.7. Subject matter wherein the peptide hormone administered
is oxytocin or a derivative thereof, or wherein the peptide
administered has an effect on oxytocin.
| | (1)
Note. Oxytocin is a polypeptide hormone secreted
by the posterior portion of the pituitary gland. Oxytocin
stimulates the contraction of smooth muscle of the uterus during
childbirth and facilitates ejection of milk from the mammary glands. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
| 807, | for a cross-reference art collection of subject
matter involving a peptide composition related to oxytoxin, vasopressin, or
a derivative thereof. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 11.7]](../ps.gif) 11.7 11.7 | Glucagon, glucagon-like peptide (e.g., GLP-1, GLP-2, etc.) or
derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 9.7. Subject matter wherein the peptide hormone administered
is glucagon or a glucagon-like peptide, or a derivative
thereof, or wherein the peptide administered has an effect
on glucagon or glucagon-like peptide.
| | (1)
Note. Glucagon is a polypeptide hormone that is produced
by the pancreas that promotes an increase in the sugar content of
the blood by increasing the rate of glycogen breakdown in the liver. |
| | (2)
Note. Examples of glucagon-like peptides
include GLP-1 which inhibits glucagon and stimulates the
release of insulin, and GLP-2 which enhances intestinal
growth and function. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 11.8]](../ps.gif) 11.8 11.8 | Parathyroid hormone (PTH) or derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 9.7. Subject matter wherein the peptide hormone administered
is parathyroid hormone (PTH), which is
derived from the parathyroid gland, or a derivative thereof, or
wherein the peptide administered has an effect on PTH.
| | (1)
Note. PTH, also known as parathormone, is
a polypeptide containing 84 amino acids produced by the parathyroid glands
that regulate the amount of calcium and phosphorus in the body. PTH has
a molecular weight of approximately 9,500 daltons. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 11.9]](../ps.gif) 11.9 11.9 | Calcitonin or derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 9.7. Subject matter wherein the peptide hormone administered
is calcitonin or a derivative thereof, or wherein the peptide
administered has an effect on calcitonin.
| | (1)
Note. Calcitonin is a peptide hormone containing
32 amino acids produced by the thyroid gland that lowers the levels of
calcium and phosphate in the blood and promotes the formation of
bones. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
| 808, | for a cross-reference art collection of subject
matter involving a peptide composition related to calcitonin or
a derivative thereof. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 12.1]](../ps.gif) 12.1 12.1 | Muscle contraction affecting (e.g., muscle twitch, muscle
relaxation, etc.): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 9.7. Subject matter wherein the peptide hormone administered
affects the process leading to shortening or tensing of a muscle
or muscle fiber in action or movement, or wherein the peptide
administered has an effect on a hormone which affects muscle contraction.
| | (1)
Note. The muscle may lengthen, shorten, or
remain the same while under tension. |
| | (2)
Note. A muscle relaxant alleviates muscle contraction
and reduces muscle spasm and twitch. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 12.2]](../ps.gif) 12.2 12.2 | Anti-inflammatory: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 9.7. Subject matter wherein the peptide hormone administered
affects conditions characterized by redness, warmth, swelling, or
pain, or wherein the peptide administered has an effect on
a hormone which affects inflammation.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 18.7, | for skin affecting anti-inflammatory peptide
compositions which are not hormones. |
| 803, | for a cross-reference art collection of subject
matter wherein the peptide composition has kinin-like activity. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 12.3]](../ps.gif) 12.3 12.3 | Gastrin hormone or derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 9.7. Subject matter wherein the peptide hormone administered
is gastrin, which is normally produced by the G cells, or
a derivative thereof, or wherein the peptide administered
has an effect on gastrin.
| | (1)
Note. G cells are specialized cells in the stomach
that secrete gastrin. |
| | (2)
Note. Forms of gastrin include gastrin-34, gastrin-17, gastrin-14, etc. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
| 19.7, | for a composition containing bombesin or a derivative
thereof. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 12.4]](../ps.gif) 12.4 12.4 | Natriuretic peptide or derivative (e.g., atrial natriuretic
peptide, brain natriuretic peptide, etc.): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 9.7. Subject matter wherein the peptide hormone administered
is a natriuretic peptide, which induces natriuresis, or
a derivative thereof, or wherein the peptide administered
has an effect on a natriuretic peptide hormone.
| | (1)
Note. Examples of natriuretic peptides include atrial
natriuretic peptide (ANP), brain natriuretic
peptide (BNP), etc. |
| | (2)
Note. Natriuresis is the process of excretion of
sodium in the urine via the action of the kidneys. Natriuresis
lowers the concentration of sodium in the blood and also tends to
lower blood volume because osmotic forces tend to make water follow
sodium out of the body’s blood circulation and into the
urine. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 12.5]](../ps.gif) 12.5 12.5 | Bradykinin or derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 9.7. Subject matter wherein the peptide hormone administered
is bradykinin or a derivative thereof, or wherein the peptide
administered has an effect on bradykinin.
| | (1)
Note. Bradykinin is a nonapeptide that that causes
blood vessels to enlarge, and therefore causes blood pressure
to lower. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
| 803, | for a cross-reference art collection of subject
matter wherein the peptide composition has kinin-like activity. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 12.6]](../ps.gif) 12.6 12.6 | Cholecystokinin (CCK) or derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 9.7. Subject matter wherein the peptide hormone administered
is cholecystokinin (CCK), or a derivative
thereof, or wherein the peptide administered has an effect
on CCK.
| | (1)
Note. CCK, also known as pancreozymin, is
a peptide hormone secreted especially by the duodenal mucosa that regulates
the emptying of the gallbladder and secretion of enzymes by the
pancreas, and that has also been found in the brain. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 12.7]](../ps.gif) 12.7 12.7 | Relaxin or derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 9.7. Subject matter wherein the peptide hormone administered
is relaxin or a derivative thereof, or wherein the peptide
administered has an effect on relaxin.
| | (1)
Note. Relaxin is a peptide hormone produced by the
corpus luteum that facilitates birth by causing relaxation of the pelvic
ligaments. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 12.8]](../ps.gif) 12.8 12.8 | Secretin or derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 9.7. Subject matter wherein the peptide hormone administered
is secretin or a derivative thereof, or wherein the peptide
administered has an effect on secretin.
| | (1)
Note. Secretin is an intestinal hormone capable of
stimulating secretion of digestive enzymes from the pancreas and bile
from the liver. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 12.9]](../ps.gif) 12.9 12.9 | Thymosin (e.g., thymosin
alpha 1, thymosin beta 4, etc.) or
derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 9.7. Subject matter wherein the peptide hormone administered
is thymosin or a derivative thereof, or wherein the peptide
administered has an effect on thymosin.
| | (1)
Note. Thymosin is an actin-binding protein
in cells isolated from the thymus. |
| | (2)
Note. Examples of thymosins include thymosin alpha
1, thymosin beta 4, etc. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 13.1]](../ps.gif) 13.1 13.1 | Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) or
derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 9.7. Subject matter wherein the peptide hormone administered
is vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) or a derivative
thereof, or wherein the peptide administered has an effect
on VIP.
| | (1)
Note. VIP is a peptide hormone containing 28 amino
acid residues produced in many areas of the human body, including the
gut, pancreas, and suprachiasmatic nuclei of the
hypothalamus in the brain. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 13.2]](../ps.gif) 13.2 13.2 | Digestive tract ulcer affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is useful
in treating or preventing the erosion of the lining of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract.
| | (1)
Note. Ulcers are normally caused by the imbalance
of the acidic environment in the regions of the GI tract which include the
stomach, duodenum, and intestines. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 13.4]](../ps.gif) 13.4 13.4 | Blood substitute: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is part
of a biocompatible composition which in its use mimics blood in
performing the normal vital physiological functions normally associated
with blood in a living organism.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 13.5, | for a peptide composition containing a blood protein
or a peptide composition which affects the blood. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 13.5]](../ps.gif) 13.5 13.5 | Blood affecting or blood protein utilizing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is a blood
protein, or wherein the peptide administered affects the
specialized biological fluid as an essential carrier or medium of
metabolic nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and other
waste products in a living organism.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 424, | Drug, Bio-Affecting and Body
Treating Compositions,
subclasses 529 through 534for therapeutic or body treating compositions containing
an extract or material of undetermined chemical constitution derived
from blood. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 13.6]](../ps.gif) 13.6 13.6 | Fibrin or derivative affecting or utilizing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 13.5. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is fibrin, an
essential component for blood clotting over a wound site, or
a derivative thereof, or wherein a peptide is administered
which has an effect on fibrin.
| | (1)
Note. Fibrin is formed by the action of thrombin
on fibrinogen when blood clots. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
| 802, | for a cross-reference art collection of subject
matter wherein the peptide composition is related to fibrinopeptides, blood-coagulation
factors, or derivatives. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 13.7]](../ps.gif) 13.7 13.7 | Coagulation affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 13.5. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered affects
the process by which the blood forms clots.
| | (1)
Note. Coagulation is an important part of hemostasis (i.e., the
cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel) whereby
a damaged blood vessel wall is covered by clot-forming
constituents to stop bleeding and begin repair of the damaged vessel. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 802, | for a cross-reference art collection of subject
matter wherein the peptide composition is related to fibrinopeptides, blood-coagulation
factors, or derivatives. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 13.9]](../ps.gif) 13.9 13.9 | Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 13.8. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered affects
glycoprotein IIb/IIIa (GP IIb/IIIa), an
integrin found on the surface of platelets.
| | (1)
Note. GP IIb/IIIa is a receptor for fibrinogen
and aids in platelet activation. |
| | (2)
Note. GP IIb/IIIa inhibitors can be used to
prevent blood clots in an effort to decrease the risk of heart attack
or stroke. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 14.1]](../ps.gif) 14.1 14.1 | Factor VIII or derivative affecting or utilizing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 13.7. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is factor
VIII or a derivative thereof, or wherein the peptide administered
has an effect on blood coagulation factor VIII.
| | (1)
Note. Factor VIII is a glycoprotein found in blood
plasma that plays a crucial role in blood clotting. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 14.3]](../ps.gif) 14.3 14.3 | Factor VIIa affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 14.2. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered affects
coagulation factor VIIa.
| | (1)
Note. Factor VIIa (trypsin-like
serine protease) is the activated form of factor VII. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 424, | Drug, Bio-Affecting and Body
Treating Compositions,
subclass 94.64 for therapeutic or body-treating compositions
containing factor VIIa. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 14.4]](../ps.gif) 14.4 14.4 | Factor Xa affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 14.2. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered affects
coagulation factor Xa, a serine endopeptidase which cleaves
prothrombin to yield the active thrombin.
| | (1)
Note. Factor Xa may also be known as thrombokinase. |
| | (2)
Note. Factor Xa is the activated form of Factor X. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 424, | Drug, Bio-Affecting and Body
Treating Compositions,
subclass 94.64 for therapeutic or body-treating compositions
containing factor Xa. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 14.5]](../ps.gif) 14.5 14.5 | Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) utilizing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 14.4. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is tissue
factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) or a derivative
thereof, or wherein the peptide administered has an effect
on tissue factor pathway inhibitor, a single-chain
polypeptide which can reversibly inhibit factor Xa. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 14.6]](../ps.gif) 14.6 14.6 | Urokinase affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 14.2. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered affects
urokinase, a proteolytic enzyme involved in the process
of thrombolysis, which is the dissolution of blood clots.
| | (1)
Note. Urokinase may also be known as urokinase-type
plasmninogen activator (uPA). |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 424, | Drug, Bio-Affecting and Body
Treating Compositions,
subclass 94.64 for therapeutic or body-treating compositions
containing urokinase. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 14.7]](../ps.gif) 14.7 14.7 | Thrombin affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 14.2. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered affects
thrombin, the coagulation protein formed from prothrombin
that facilitates the clotting of blood by catalyzing conversion
of soluble fibrinogen to insoluble strands of fibrin.
| | (1)
Note. Thrombin may also be known as factor IIa. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 424, | Drug, Bio-Affecting and Body
Treating Compositions,
subclass 94.64 for therapeutic or body-treating compositions
containing thrombin. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 14.8]](../ps.gif) 14.8 14.8 | Hirudin or derivative utilizing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 14.7. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is hirudin
or a derivative thereof.
| | (1)
Note. Hirudin contains 65 amino acids. |
| | (2)
Note. Hirudin is normally derived from the buccal
glands of leeches and affects the coagulation properties of blood
and is known to inhibit thrombin. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 14.9]](../ps.gif) 14.9 14.9 | Thrombosis affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 13.7. Subject matter wherein the peptide affects the undesired
formation of a clot, or thrombus, inside a blood
vessel obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system (e.g., by preventing
the formation of a clot or dissolving an existing clot). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 15.1]](../ps.gif) 15.1 15.1 | Oxidative stress affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 13.5. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered affects
the condition of increased oxidant production in blood cells, characterized
by the release of free oxygen radicals and resulting in cellular
degeneration, or a disorder resulting from a shortage of
oxygen, such as ischemia or reperfusion injury. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 15.2]](../ps.gif) 15.2 15.2 | Albumin or derivative affecting or utilizing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 13.5. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is albumin, a
common protein found in the blood, or a derivative thereof, or
wherein the peptide administered has an effect on albumin.
| | (1)
Note. Albumin is a major plasma protein which is
an integral transporter of nutrients within the body.
Albumin may also assist in maintaining blood volume in the arteries
and veins. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 15.3]](../ps.gif) 15.3 15.3 | Plasma protein affecting or utilizing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 13.5. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is a plasma
protein, or wherein the peptide administered has an effect
on a plasma protein.
| | (1)
Note. Plasma is the liquid part of the blood and
lymphatic fluid, which makes up about half of its volume. Plasma
is the colorless constituent of the blood in which the red and white
blood corpuscles are suspended and is composed of water, dissolved
proteins, glucose, clotting factors, etc. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 15.4]](../ps.gif) 15.4 15.4 | Kidney affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. The subclass is indented Subject matter wherein
the peptide administered affects the kidney, an organ with
numerous metabolic functions, whose primary role is to
maintain the homeostatic balance of bodily fluids.
| | (1)
Note. Three important homeostatic functions of the
kidney include:
| | (a)
Filter waste materials out of the blood and pass them out
of the body as urine. |
| | (b)
Regulate blood pressure and the levels of metabolites (e.g., water, salts, minerals
in the body, etc.). |
| | (c)
Produce hormones that control other body functions. | |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 15.6, | for a peptide composition which affects blood pressure. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 15.5]](../ps.gif) 15.5 15.5 | Surfactant protein (e.g., SP-A, SP-B, etc.) or derivative
affecting or utilizing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is surfactant
protein or a derivative thereof, or wherein the peptide
administered has an effect on a surfactant protein.
| | (1)
Note. Surfactant protein is a component of the pulmonary
surfactant system. Pulmonary surfactant is a lipid-protein
complex which is synthesized and secreted by the respiratory epithelium
of the lungs to the alveolar spaces. The main function
of the pulmonary surfactant is to reduce the surface tension at
the air/liquid interface in the lung, thereby
minimizing the work of breathing. |
| | (2)
Note. Surfactant proteins include SP-A, SP-B, SP-C, and
SP-D. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
| 1.5, | for a peptide composition which affects respiratory
distress syndrome (e.g., ARDS, IRDS, etc.). |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 15.6]](../ps.gif) 15.6 15.6 | Blood pressure affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered affects
the pressure of blood flow against the walls of the arteries, either
to raise or lower said pressure.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 803, | for a cross-reference art collection of subject
matter wherein the peptide composition has kinin-like activity. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 15.7]](../ps.gif) 15.7 15.7 | Hypertension: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 15.6. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is useful
in treating patients who suffer from high blood pressure (i.e., a
systolic pressure of 120 mm/Hg or higher and a diastolic pressure
of 80 mm/Hg or higher).
| | (1)
Note. Technically, patients having a systolic
blood pressure of 140 mm/Hg and a diastolic blood pressure
of 90 mm/Hg are considered as having hypertension, or
high blood pressure, whereas patients whose systolic pressure
is between 120 and 139 mm/Hg, and whose diastolic pressure
is between 80 and 90 mm/Hg are considered pre-hypertensive. For purposes
of this subclass, pre-hypertension is considered
to be the same as hypertension. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 15.8]](../ps.gif) 15.8 15.8 | Renin inhibitor affecting or utilizing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 15.7. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered affects
the activity of a renin inhibitor, or wherein the peptide
administered is a renin inhibitor and inhibits the enzyme renin.
| | (1)
Note. Renin is a part of the renin-angiotensin
system which is a group of related substances which act together
to regulate blood pressure as well as the body’s salt and
water balance. Renin, also known as angiotensinogenase, is
an enzyme secreted by the kidneys that catalyzes the formation of
angiotensin 1. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 15.9]](../ps.gif) 15.9 15.9 | Dipeptide renin inhibitor: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 15.8. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered, which
inhibits rennin, consists of an uninterrupted chain of
only two amino acid residues. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 16.1]](../ps.gif) 16.1 16.1 | Endothelin (e.g., ET-2, ET-3, etc.) or
derivative affecting or utilizing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 15.7. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is endothelin, which
is produced by the vascular endothelium, or a derivative
thereof, or wherein the peptide administered has an effect
on endothelin.
| | (1)
Note. Endothelin is a 21-amino acid peptide
that functions as a vasoconstricting peptide and also maintains
a delicate balance between vasodilation and vasoconstriction in
controlling hypertension. |
| | (2)
Note. Examples of endothelin include endothelin-1 (ET-1), endothelin-2 (ET-2), and
endothelin-3 (ET-3). |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 16.2]](../ps.gif) 16.2 16.2 | Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 15.7. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered affects
angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) that converts
angiotensin I to its activated form, angiotensin II.
| | (1)
Note. Angiotensin II is a peptide that can act as
a vasoconstricting agent (causing blood vessels to narrow). |
| | (2)
Note. Peptides which inhibit or slow the activity
of the enzyme ACE (ACE inhibitors), thereby
decreasing the production of Angiotensin II, can lower
the effects of hypertension by dilating blood vessels. |
| | (3)
Note. ACE is alternatively known as angiotensin I
converting enzyme, carboxycathepsin, dipeptidyl
carboxypeptidase I, kininase II, peptidase P, and peptidyl
dipeptidase I. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 16.3]](../ps.gif) 16.3 16.3 | Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered affects
angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) that converts
angiotensin I to its activated form, angiotensin II.
| | (1)
Note. Angiotensin II is a peptide that can act as
a vasoconstricting agent (causing blood vessels to narrow). |
| | (2)
Note. ACE is alternatively known as angiotensin I
converting enzyme, carboxycathepsin, dipeptidyl
carboxypeptidase I, kininase II, peptidase P, and peptidyl
dipeptidase I. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 16.6]](../ps.gif) 16.6 16.6 | Rheumatoid arthritis affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide is useful in treating
a chronic autoimmune disease, called rheumatoid arthritis, characterized
by pain, swelling, inflammation, and
destruction of the joints. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 16.7]](../ps.gif) 16.7 16.7 | Bone affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered affects
the rigid calcified connective tissue that constitutes the skeletal
framework of living organisms, or is useful in preventing conditions
that affect the bone.
| | (1)
Note. Bone is composed of a matrix of collagen, phosphate, and
other minerals. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 17.1, | for a peptide composition which affects cartilage. |
| 17.2, | for a peptide composition wherein collagen or a
derivative is affected or utilized. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 16.8]](../ps.gif) 16.8 16.8 | Osteoarthritis: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 16.7. Subject matter wherein the peptide is useful in treating
the loss of the connective tissue between two or more bones, or
in preventing the onset of osteoarthritis.
| | (1)
Note. Osteoarthritis develops when the cartilage (cushioning
at the ends of the bones) breaks down. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 16.9]](../ps.gif) 16.9 16.9 | Osteoporosis: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 16.7. Subject matter wherein the peptide is useful in treating
the loss of bone density caused by reduced calcium absorption, or
in preventing the onset of osteoporosis.
| | (1)
Note. Osteoporosis is a disease condition that leads
to reduction of bone mineral density, or disruption of
microarchitecture resulting in increased risk of fracture. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 17.1]](../ps.gif) 17.1 17.1 | Cartilage affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered affects
the connective tissue that covers the ends of bones, or
is useful in preventing the onset of conditions that affect cartilage. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 17.2]](../ps.gif) 17.2 17.2 | Collagen or derivative affecting or utilizing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is collagen
or a derivative thereof, or wherein a peptide is administered
which has an effect on collagen.
| | (1)
Note. For the purposes of this subclass, gelatin
is considered a derivative of collagen. |
| | (2)
Note. Collagen’s molecular weight is approximately
130,000 daltons. The collagen molecule contains
three peptide chains, each having 1,000 amino
acids. Nearly one third of all the residues are glycine, with
typical repeating sequences being Gly-Pro-Hyp
and Gly-Pro-Ala. The chains are arranged
in a triple helix and contain intramolecular cross-links. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
| 801, | for a cross-reference art collection of subject
matter wherein the peptide composition contains collagen, gelatin, or
derivatives. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 17.3]](../ps.gif) 17.3 17.3 | N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered affects
a type of glutamate receptor, called N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor, that
participates in excitatory neurotransmission.
| | (1)
Note. Activation of NMDA receptors results in the
opening of an ion channel that is nonselective to cations which allows
flow of sodium and small amounts of calcium into the cell and potassium
out of the cell. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 17.4, | for a peptide composition which affects an ion channel
protein. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 17.4]](../ps.gif) 17.4 17.4 | Ion channel protein affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered affects
a pore-forming protein complex, called ion channel
protein, which resides at the cell periphery.
| | (1)
Note. Ion channel proteins facilitate the diffusion
of ions across biological membranes or phospholipid bilayers. |
| | (2)
Note. Ion channels provide a high conducting, hydrophilic
pathway across the hydrophobic interior of the membrane. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 17.5]](../ps.gif) 17.5 17.5 | Mental disorder or mental illness (e.g., psychoses, etc.) affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide is useful in treating
a condition of psychological or clinical impairment or a disorder
of the normal emotional or behavioral function in an individual.
| | (1)
Note. Disorders include, but are not limited
to, mood, anxiety, psychotic, eating, developmental, personality, etc. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 17.6]](../ps.gif) 17.6 17.6 | Anti-depressant or derivative affecting or utilizing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 17.5. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is an antidepressant, an
agent used to prevent or treat clinical depression, or
a derivative thereof, or wherein the peptide administered has
an effect on an anti-depressant.
| | (1)
Note. Clinical depression is characterized by pervasive
low mood, loss of interest in normal activities, and
diminished ability to experience pleasure. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 17.7]](../ps.gif) 17.7 17.7 | Nervous system (e.g., central
nervous system (CNS), etc.) affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered affects
conditions or processes of the central or peripheral nervous systems.
| | (1)
Note. The central nervous system consists of the
brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system (PNS) extends
outside the central nervous system (CNS) and its
primary purpose is to connect the CNS to the limbs and organs. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 17.8]](../ps.gif) 17.8 17.8 | Alzheimer’s disease: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 17.7. Subject matter wherein the peptide is useful in treating
the disease called Alzheimer’s disease, marked
by loss of cognitive ability typically associated with abnormal
tissue and protein deposit buildup in the cerebral cortex. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 17.9]](../ps.gif) 17.9 17.9 | Multiple sclerosis: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 17.7. Subject matter wherein the peptide is useful in treating
the disease called multiple sclerosis, a chronic, progressive
disease marked by gradual degeneration of the nerve cells in the
central nervous system that control voluntary muscle movement. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 18.1]](../ps.gif) 18.1 18.1 | Neurotransmitter or derivative affecting or utilizing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 17.7. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is a neurotransmitter, a
substance which relays, amplifies, and modulates
signals between a neuron and another cell or a derivative thereof, or
wherein the peptide administered has an effect on a neurotransmitter.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 18.2]](../ps.gif) 18.2 18.2 | Neuropathy affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 17.7. Subject matter wherein the peptide is useful in treating
an abnormal condition or disorder, called neuropathy, characterized
by inflammation and degeneration of peripheral nervous system. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 18.3]](../ps.gif) 18.3 18.3 | Pain affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 17.7. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered suppresses
or alleviates pain or treats hyperanalgesia by increasing the body’s response
to a painful stimulus. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 18.4]](../ps.gif) 18.4 18.4 | Opioid receptor affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 18.3. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered binds to
receptors in the brain and other organs to alleviate pain.
| | (1)
Note. Opioids are narcotic drugs that are generally
prescribed to manage pain. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 18.5]](../ps.gif) 18.5 18.5 | Enkephalin or derivative affecting or utilizing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 18.3. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is enkephalin, a
pentapeptide, or a derivative thereof, or wherein
the peptide administered has an effect on enkephalin.
| | (1)
Note. Enkephalin performs opiate and analgesic activities
and has a marked affinity for opiate receptors. |
| | (2)
Note. Forms of enkephalin include Met-enkephalin, Leu-enkephalin, etc. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
| 809, | for a cross-reference art collection of subject
matter involving neurological peptides related to enkephalin or endorphin. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 18.6]](../ps.gif) 18.6 18.6 | Skin affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered affects
a natural protective body covering, excluding hair and
nails, which is the site of the sense of touch.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 424, | Drug, Bio-Affecting and Body
Treating Compositions,
subclass 78.02 for a topical body preparation containing solid
synthetic organic polymer as designated organic active ingredient (DOAI). |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 18.7]](../ps.gif) 18.7 18.7 | Anti-inflammatory: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 18.6. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is useful
in treating inflammatory conditions of the skin characterized by
redness, warmth, swelling, or pain. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 18.8]](../ps.gif) 18.8 18.8 | Cosmetic enhancement or care: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 18.6. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is useful
in beautifying and improving the appearance of the skin.
| | (1)
Note. Included herein are skin creams for the improvement
of beauty, especially that of the complexion of the skin. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 424, | Drug, Bio-Affecting and Body
Treating Compositions,
subclass 59 for a topical sun or radiation screening, or tanning
preparation; subclass 62 for a composition which bleaches
or removes color from live skin; subclass 63 for a composition
which is applied topically for coloring the skin in either a limited
or overall area (e.g., blemish cover, cheek
rouge, eye shadow, etc.); subclass
69 for face or body powders for grooming, adorning, or
absorbing; subclass 70.1 for a nontherapeutic composition
for grooming or adorning the scalp; and subclass 78.02
for a topical body preparation containing solid synthetic organic
polymer as designated organic active ingredient (DOAI). |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 18.9]](../ps.gif) 18.9 18.9 | Apoptosis affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered affects
the death of cells characterized by a programmed sequence of events
which leads to the elimination of cells without releasing harmful
substances into the surrounding area. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 19.1]](../ps.gif) 19.1 19.1 | Cellular adhesion affecting or cell adhesion molecule ( placeCAM) affecting
or utilizing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered affects
the cell adhesion process or the peptide administered is a cell
adhesion molecule.
| | (1)
Note. Cellular adhesion is the binding of a cell
to another cell or to an extracellular matrix. Cellular
adhesion is regulated by specific CAMs that interact with molecules
on opposing cells or surfaces. |
| | (2)
Note. CAMs are integral membrane proteins that have
cytoplasmic, transmembrane, and extracellular
domains. |
| | (3)
Note. Examples of CAMs include intercellular adhesion
molecule (ICAM), vascular-cell
adhesion molecule (VCAM), endothelial
leukocyte adhesion molecule-1 (ELAM-1), etc. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 19.3]](../ps.gif) 19.3 19.3 | Cancer: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 19.2. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is useful
in treating or preventing a malignant growth caused by abnormal
and uncontrolled cell division. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 19.4]](../ps.gif) 19.4 19.4 | Breast: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 19.3. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is useful
in treating or preventing a malignant growth associated with the
breast. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 19.5]](../ps.gif) 19.5 19.5 | Prostate: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 19.3. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is useful
in treating or preventing a malignant growth associated with the
prostate gland. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 19.6]](../ps.gif) 19.6 19.6 | Leukemia: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 19.3. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is useful
in treating or preventing a malignant condition of the blood or
bone marrow, called leukemia, which is characterized
by an abnormal proliferation (production by multiplication) of
blood cells, usually white blood cells (leukocytes). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 19.7]](../ps.gif) 19.7 19.7 | Bombesin or derivative affecting or utilizing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 19.3. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is bombesin, or
a derivative thereof, or wherein the peptide administered
has an effect on bombesin.
| | (1)
Note. Bombesin is a polypeptide which has been shown
to play a role in cancer. Bombesin may stimulate the growth
or migration of certain cancer cells. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 19.8]](../ps.gif) 19.8 19.8 | Metastasis affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 19.3. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered affects
the spreading, settling down, and growth of a
cancerous tumor from one organ or part to another nonadjacent healthy
organ or part. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 19.9]](../ps.gif) 19.9 19.9 | Cyclopeptide utilizing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 19.3. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is a cyclic
structure, wherein the cyclic structure is formed by peptide
bonding, disulfide bonding, hydrocarbon bonding, or
other types of bonding, and has at least a dipeptide as an
integral part thereof.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 930, | Peptide or Protein Sequence,
subclass 260 for peptides or proteins with intrachain cysteine-cysteine
bridges and subclass 270 for other cyclic peptides or proteins. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 20.1]](../ps.gif) 20.1 20.1 | Protease inhibitor affecting or utilizing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered affects
the activity of a protease inhibitor or wherein the peptide administered
is a protease inhibitor and inhibits the activity of protease.
| | (1)
Note. Protease inhibitors prevent proteases from
splitting proteins into peptides. |
| | (2)
Note. A protease is an enzyme which degrades proteins
into smaller component peptides. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 20.3]](../ps.gif) 20.3 20.3 | Serine protease inhibitor affecting or utilizing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 20.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered affects
the activity of a serine protease inhibitor, or wherein
the peptide administered is a serine protease inhibitor and inhibits
the activity of a serine protease.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 424, | Drug, Bio-Affecting and Body
Treating Compositions,
subclass 94.64 for therapeutic or body-treating compositions
containing serine proteases. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 20.4]](../ps.gif) 20.4 20.4 | Elastase inhibitor affecting or utilizing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 20.3. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered affects
the activity of an elastase inhibitor or wherein the peptide administered
is an elastase inhibitor and inhibits the activity of the enzyme
elastase.
| | (1)
Note. Elastase hydrolyzes proteins, including
elastin which is responsible for the elastic properties of vertebrate
tissues. |
| | (2)
Note. Elastases include pancreatic elastase, neutrophil
elastase, etc. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 424, | Drug, Bio-Affecting and Body
Treating Compositions,
subclass 94.64 for therapeutic or body-treating compositions
containing elastase. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 20.5]](../ps.gif) 20.5 20.5 | Cyclosporine or derivative utilizing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is a cyclic
oligopeptide, called cyclosporine, or a derivative
thereof.
| | (1)
Note. Cyclosporine is used to inhibit organ transplant
rejection. |
| | (2)
Note. Cyclosporine is also known as ciclosporin and
cyclosporin. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 1.1, | for definition of the term "derivative." |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 20.6]](../ps.gif) 20.6 20.6 | G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered affects
G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR), which
affects signal transmission into the cell.
| | (1)
Note. GPCRs constitute a large and diverse family
of proteins whose primary function is to transduce extracellular
stimuli into intracellular signals. GPCRs are found only
in eukaryotes. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 20.7]](../ps.gif) 20.7 20.7 | Hair affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide is useful in treating
or preventing conditions affecting the fine, flexible peptide
strands that grow from the follicles on the skin. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 20.8]](../ps.gif) 20.8 20.8 | Eye affecting: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide is useful in treating
or preventing conditions of the eye, the organ that detects
light and sends signals along the optic nerve to the visual and
other areas of the brain. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 21.1]](../ps.gif) 21.1 21.1 | Cyclopeptide utilizing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1.1. Subject matter wherein the peptide administered is a cyclic
structure, wherein the cyclic structure is formed by peptide
bonding, disulfide bonding, hydrocarbon bonding, or
other types of bonding, and has at least a dipeptide as an
integral part thereof.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 930, | Peptide or Protein Sequence,
subclass 260 for peptides or proteins with intrachain cysteine-cysteine
bridges and subclass 270 for other cyclic peptides or proteins. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 22]](../ps.gif) 22 22 | Lignin or derivative DOAI: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1. Subject matter wherein the organic active ingredient is
lignin or a reaction derivative thereof, e.g., lignin
sulfonate, etc.
| | (1)
Note. Lignin is a noncarbohydrate, polymeric
substance found in wood. It is isolated directly from
wood or wood products or from the treatment of wood, e.g., waste
sulfite liquor or black liquor. The structure of the lignin
monomer is not completely known. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 23]](../ps.gif) 23 23 | Carbohydrate (i.e., saccharide
radical containing) DOAI: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1. Subject matter wherein the organic active ingredient is
a saccharide or polysaccharide, the monomeric saccharide
radical units of which contain at least five carbon atoms, or their
reaction products wherein the carbon skeleton of the saccharide
or polysaccharide of the unit is not destroyed.
| | (1)
Note. Included herein is cellulose, cellulose
derivatives, starch, starch derivatives, tannins, O-glycosides, N-glycosides
and S-glycosides. |
| | (2)
Note. Alcohols and acids corresponding to carbohydrates
are excluded. |
| | (3)
Note. Cascara sagrada is excluded herefrom and is
classified with plant extracts. See Search Notes below. |
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 251, | for a composition containing riboflavin DOAI. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 424, | Drug, Bio-Affecting and Body
Treating Compositions,
subclasses 725 through 779for plant extracts. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 24]](../ps.gif) 24 24 | S-glycoside: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 23. Subject matter wherein the saccharide is a thioacetal derivative
of a cyclic form of sugars in which the hydrogen atom of the hemithioacetal sulfhydryl
group has been replaced by an alkyl, aralkyl or aryl group.
| | (1)
Note. A S-glycoside is a compound having
a sugar moiety connected to an aglycone moiety via sulfur. |
| | (2)
Note. An aglycone is a noncarbohydrate material, e.g., benzene, indoxyl, alkyl, anthracene, etc. |
| | (3)
Note. The cyclic sugars referred to in the definition
are normally pyranoses or furanoses. |
| | (4)
Note. Glycosides derived from aldoeses are referred
to as aldosides, and those ketoses are ketosides. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 25]](../ps.gif) 25 25 | O-glycoside: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 23. Subject matter wherein the saccharide is an acetal derivative
of a cyclic form of sugars in which the hydrogen atom of the hemiacetal hydroxyl
has been replaced by an alkyl, aralkyl or aryl group.
| | (1)
Note. An O-glycoside is a compound having
a sugar moiety connected to an aglycone moiety via oxygen. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 41]](../ps.gif) 41 41 | Kanamycin or derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 40. Subject matter wherein the organic active ingredient is
Kanamycin or a derivative thereof, i.e., as
illustrated below, wherein R is NH2 and
R" is NH2 or OH.
Kanosamin, deoxystreptamine |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 42]](../ps.gif) 42 42 | N-glycoside: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 23. Subject matter wherein the saccharide is a glycosidic derivative
or the cyclic form of saccharides or polysaccharides in which an
aglycone portion is attached through nitrogen to the saccharide
moiety by substituting it for the hemiacetal hydroxyl of the sugar.
| | (1)
Note. The aglycone can be noncyclic. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 44]](../ps.gif) 44 44 | Polynucleotide (e.g., RNA, DNA, etc.): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 43. Subject matter which has the following structure, illustrated
below, wherein n is a whole number equal or greater than
two, R" is H or OH and R" is purine or pyrimidine
or a substituted purine or pyrimidine.
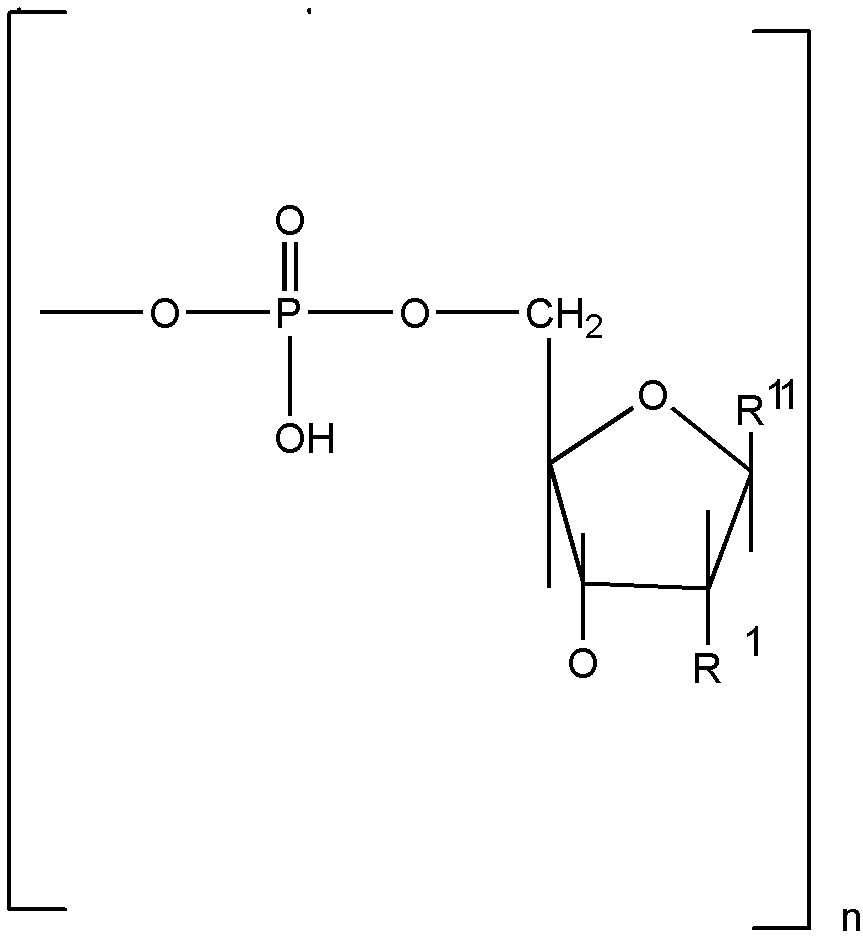
| | (1)
Note. Substituted pyrimidine or purine includes
only those derivatives which are substituted on rather than in the respective
ring position, i.e., illustrated below, is
present in the structure. The internal ring bonding may
be altered by tautomerism or by the addition of substituents without
excluding a compound from this subclass.
Or 
| SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 536, | Organic Compounds, appropriate subclasses for nucleosides, nucleotides and
polynucleotides like RNA or DNA compounds as well as chemical methods
for synthesizing these compounds. Search specifically
subclasses 23.1+ for fragments of DNA which could have utility in
recombinant processes or gene therapy and subclasses 26.4+ for
vitamin B-12 and its derivatives. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 53]](../ps.gif) 53 53 | Disaccharide: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 23. Subject matter wherein the organic active ingredient contains
two saccharide radicals bonded via a glycosidic linkage and which
on hydrolysis yields two units of monosaccharides (e.g., sucrose, lactose, maltose, etc.). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 54]](../ps.gif) 54 54 | Polysaccharide |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 23. Subject matter wherein the organic active ingredient contains
more than two saccharide radicals directly or indirectly bonded
together. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 56]](../ps.gif) 56 56 | Heparin or derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 54. Subject matter wherein the polysaccharide has the following
repeating unit, illustrated below, wherein the
degree of sulfation of the individual components in the polysaccharide
chain, and derivatives thereof.
| | (1)
Note. Heparin is a substance which can be found
in various tissues of mammals, especially the lung, spleen, liver
and muscle, and has been used medicinally for coagulation
of blood and metabolism of lipids. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 58]](../ps.gif) 58 58 | Dextrin or derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 54. Subject matter wherein the polysaccharide consists of various
gummy polysaccharides produced by thermal or acid degradation of
starch, and derivatives of such compounds.
| | (1)
Note. Dextrins are carbohydrates, intermediate
between starch and sugars. Degradation of dextrins yields
maltose and glucose. |
| | (2)
Note. Derivatives of dextrins which remain gummy
polysaccharides are classified herein. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 59]](../ps.gif) 59 59 | Dextran or derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 54. wherein the polysaccharide is composed of D-glucose
units which are linked by 1, 6 glucosidic bonds.
| | (1)
Note. Dextrin and dextrine are not variant spelling
of "Dextran", instead they are respectively
a starch hydrolysis product and a variant spelling of dextrin. |
| | (2)
Note. Controlled hydrolysis of native dextran yields
clinical dextran of lower molecular weight which is useful as a blood
plasma substitute. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 60]](../ps.gif) 60 60 | Starch or derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 54. Subject matter wherein the polysaccharide has amylose and
amylopectin as their main components.
| | (1)
Note. Starches are heterogeneous in that the amylose
and amylopectin occur in different ratios to each other. |
| | (2)
Note. Starches yield dextrins upon extensive thermal
of acid degradation and yield glucose upon completed hydrolysis. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 65]](../ps.gif) 65 65 | Pyrethrum plant derived material or plant derive rotenone
compound containing DOAI: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1. Subject matter which contains pyrethrum plant derived material
or plant derived rotenone compound containing material, e.g., ground pyrethrum
flowers or extract of cube root or derris root, etc.
| | (1)
Note. This subclass does not contain chemically
identified derivatives of naturally occurring pyrethrum plant derived material
or plant derived rotenone containing material since such derivatives are
classified on the basis of the chemical structure. |
| | (2)
Note. Synthetically produced active compounds which
would be identical with the active constituents of pyrethrum or
rotenone containing plant such as derris root, cube root
are not classified herein but are classified of the chemical structure
of the synthetically produced compound. See, for
example, subclass 531 for allethrins. |
| | (3)
Note. The active constituents of pyrethrum includes
pyrethrins I and II, cinerins I and II and jasmolins I
and II. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 66]](../ps.gif) 66 66 | With heterocyclic compound: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 65. Subject matter which contains a heterocyclic compound in
addition to the pyrethrum derived material or plant derived rotenone
compound. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 68]](../ps.gif) 68 68 | With carboxylic acid ester: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 65. Subject matter which contains a carboxylic acid ester in
addition to the pyrethrum derived material or plant derived rotenone
compound. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 78]](../ps.gif) 78 78 | Lecithins: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 77. Subject matter wherein the inner salt contains the following
structurewherein R is an organic radical.
, etc. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 95]](../ps.gif) 95 95 | Sulfur containing hetero ring: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 75. Subject matter in which the organo-phosphorus compound
contains a heterocyclic ring which contains at least one sulfur
atom as a ring member. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 98]](../ps.gif) 98 98 | Oxygen in the hetero ring: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 95. Subject matter in which the organo-phosphorus compound
contains a heterocyclic ring which contains at least one sulfur
atom and at least one oxygen atom as ring members. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 104]](../ps.gif) 104 104 | Benzene ring in the alcohol moiety: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 103. Subject matter in which the polyphosphorus compound corresponds
to the structure -P-X-(R)-X-P-, wherein
R is the residue of a polyhydric alcohol which is aromatic in nature (i.e., contains
a benzene ring and wherein X is chalcogen). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 109]](../ps.gif) 109 109 | P-X-X containing (X is chalcogen): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 75. Subject matter in which the organo-phosphorus compound
has a single phosphorus atom linked directly to a chalcogen atom
which in turn is linked directly to another chalcogen atom, e.g., as
illustrated below, wherein X is chalcogen.
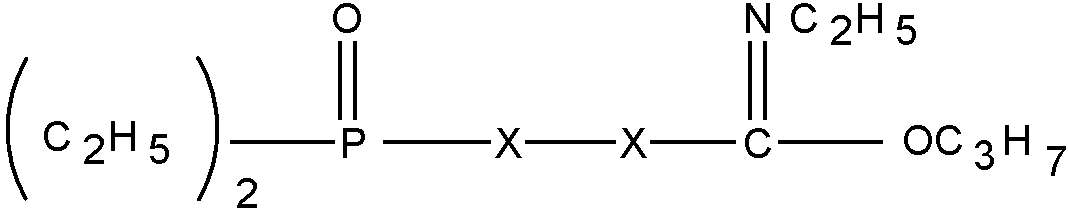
, etc. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 122]](../ps.gif) 122 122 | Malathion: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 121. Subject matter wherein the organo-phosphorus compound
is malathion, i.e.,

, etc. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 127]](../ps.gif) 127 127 | Thioether, sulfoxide or sulfone: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 126. Subject matter in which the organo-phosphorus compound
contains sulfur in the form of a thioether, sulfoxide or
sulfone group.
| | (1)
Note. This subclass contains the groups: C-S-C; C- C, and
C- C | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 134]](../ps.gif) 134 134 | Acyclic carbon to carbon unsaturation: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 75. Subject matter wherein the organo-phosphorus compound
has at least one unsaturated group between adjacent carbon atoms
and wherein said unsaturation is present other than as an aromatic
compound, e.g.,
, etc. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 135]](../ps.gif) 135 135 | Alkyne |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 134. Subject matter wherein the unsaturation is in the form of
a triple bond, e.g.,
, etc. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 137]](../ps.gif) 137 137 | Nitrogen bonded directly to phosphorus: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 75. Subject matter wherein the organo-phosphorus compound
has at least one phosphorus to nitrogen bond.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 118, | when another nitrogen atom other than nitro or nitroso
is present in the molecule which nitrogen is not directly bonded
to phosphorus. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 142]](../ps.gif) 142 142 | (CX-)(C)P(C),(CX-)(RX-)P (C), (CX-) P (XH)(XH
or (CX-)P(-XR) containing (X
is chalcogen: R is C or H) (e.g., phosphinite, phosphonite, phosphite, etc.): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 75. Subject matter in which the organo-phosphorus compound
is (a) an ester or phosphinous acid (i.e., first
illustration below), (b) an
ester of phosphonous acid, as in the second illustration, below, or (c) an
ester of phosphorus acid, as in the third illustration, below, wherein
R or R in any of the above formulas is an organic radical and X
is chalcogen.
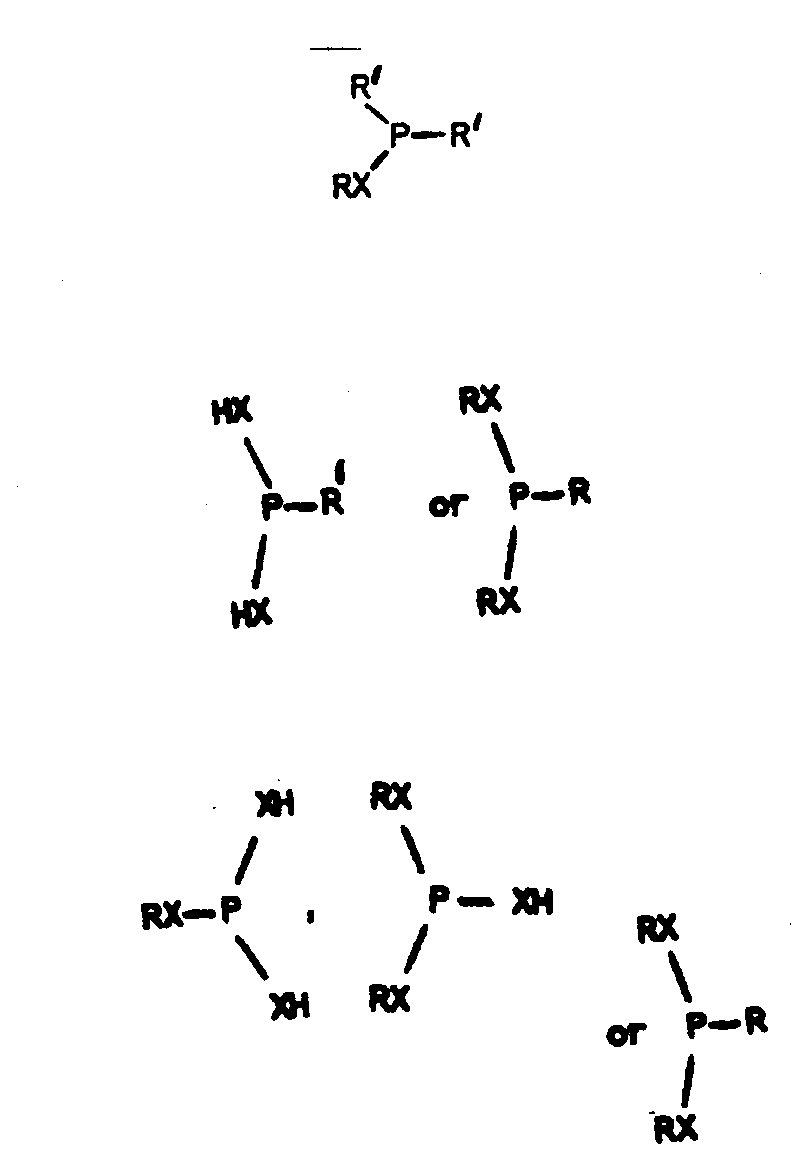
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 144]](../ps.gif) 144 144 | Triester: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 143. Subject matter which the organo-phosphorus compound
is a triester of orthophosphoric acid, illustrated below, wherein
X is chalcogen.
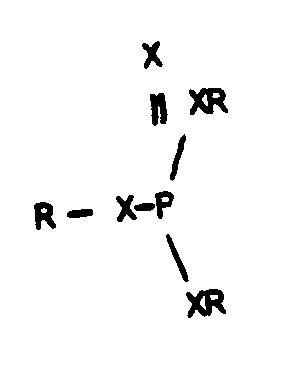
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 145]](../ps.gif) 145 145 | Three benzene rings bonded directly to chalcogen: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 144. Subject matter wherein the organo-phosphorus compound
has three benzene rings attached directly to chalcogens which are
bonded directly to a single phosphorus atom.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 146, | for the compound, illustrated below, which
is considered to have only two benzene rings attached to chalcogens which
are bonded directly to phosphorus.
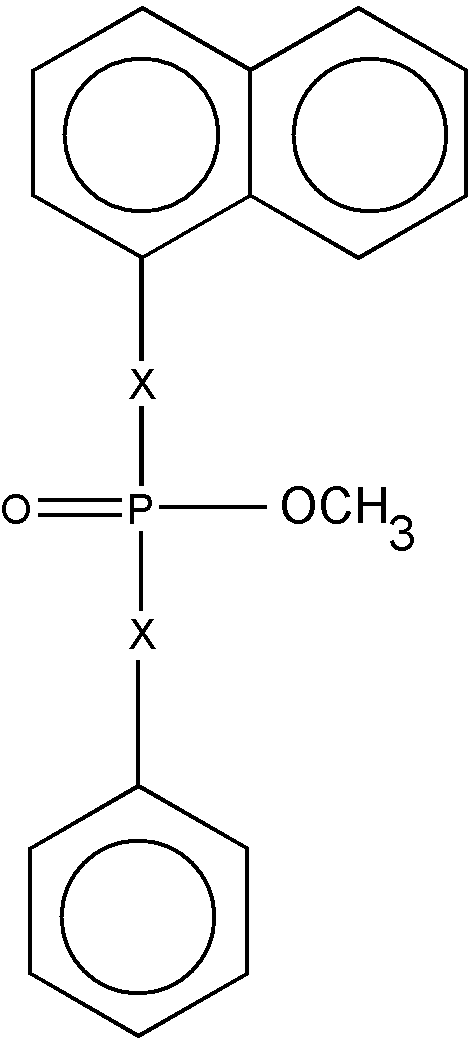
| |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 146]](../ps.gif) 146 146 | Two benzene rings bonded directly to chalcogen: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 144. Subject matter wherein the organo-phosphorus compound
has at least two benzene rings attached directly to chalcogens which
are bonded to a single phosphorus atom.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 147, | for the compound, illustrated below, which
is considered to have only one benzene ring bonded to chalcogen which
is bonded directly to phosphorus.
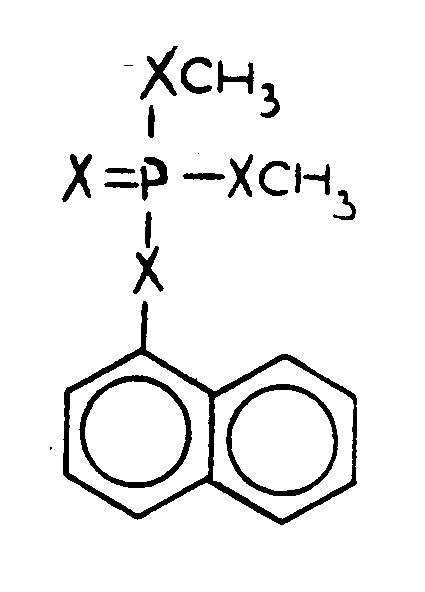
| |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 148]](../ps.gif) 148 148 | Diester: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 143. Subject matter wherein the organo-phosphorus compound
has the formula, illustrated below, wherein R
is an organic radical and X is chalcogen.
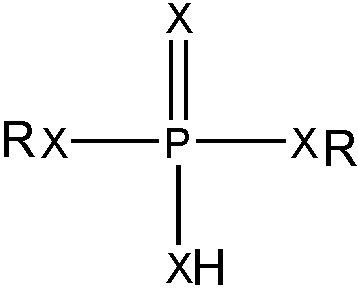
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 149]](../ps.gif) 149 149 | Azoxy DOAI: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1. Subject matter wherein the active DOAI contains the azoxy
group, i.e., -N(O)=N-, wherein each
nitrogen is bonded directly to carbon.
| | (1)
Note. Subject matter containing a -N=N- groups
as part of a ring is classified in subclass 183. |
| | (2)
Note. The azoxy group may also be represented
as shown below.
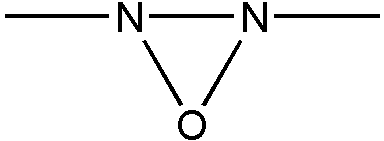
| |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 151]](../ps.gif) 151 151 | Acyclic C-N=N-N containing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 150. Subject matter wherein the active ingredient contains the
C-N=N-N grouping e.g.,
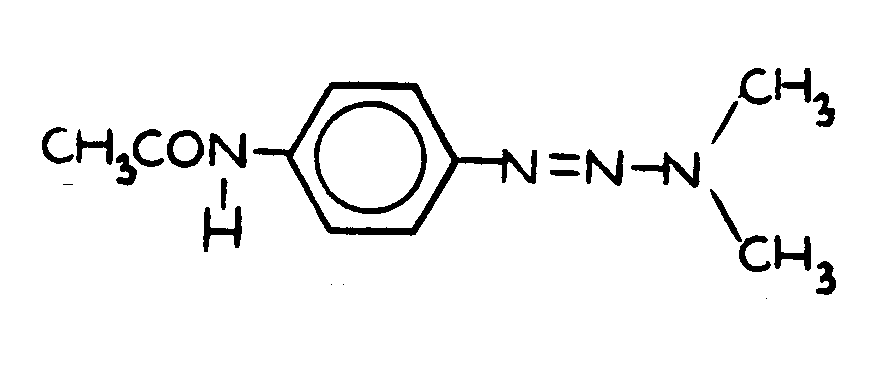
,etc.
| | (1)
Note. Subject matter which contains -N=N-N- as
part of a ring is classified in subclass 183. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 153]](../ps.gif) 153 153 | With stabilizer or preservative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 152. Subject matter wherein an additional agent is present which
is disclosedas a stabilizer or preservative for the 3,10-dihydroxy-2-naphthacenecarboxamide
compound. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 156]](../ps.gif) 156 156 | Hetero ring containing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 155. Subject matter wherein the active ingredient having at least
one group, shown in the first illustration below, also
contains a heterocyclic group, e.g., sulfapyridine, shown
in the second illustration, below.
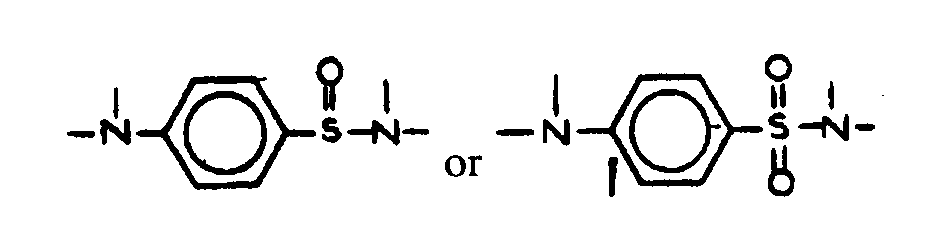
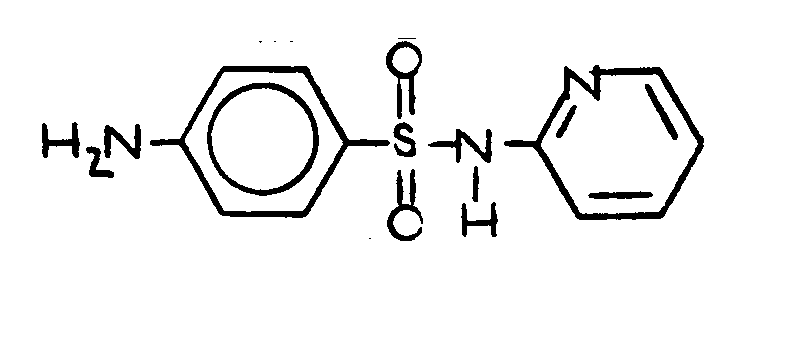
,etc. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 159]](../ps.gif) 159 159 | Ortho-hydroxybenzoic acid (i.e., salicylic acid) or
derivative DOAI: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1. Subject matter wherein the organic active ingredient contains
salicylic acid as shown in the first illustration, below, or
a derivative thereof which contains the moiety, as shown
in the second illustration, below, said derivative being
other than another ring fused onto the benzoic acid moiety or the
ortho-hydroxybenzoic acid salts of a bioactive organic
compound.
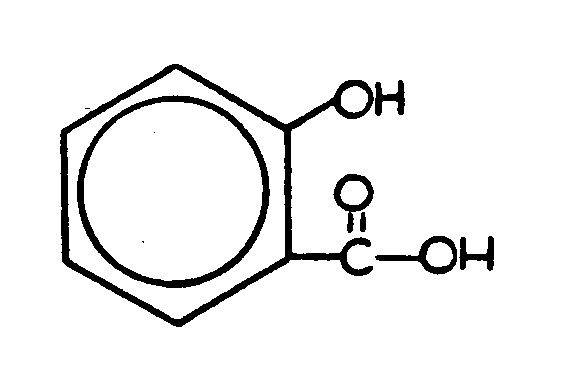
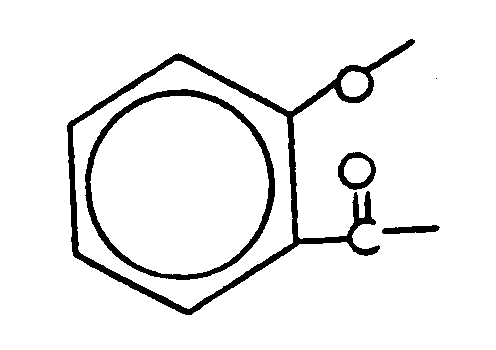
| | (1)
Note. This subclass includes ring structures derived
from the carboxy and hydroxyl moieties. |
| | (2)
Note. The ortho-hydroxybenzoic acid salts
of organic compounds are excluded herefrom and are classified in
the appropriate subclasses below based on the bioactive compound. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 169]](../ps.gif) 169 169 | Cyclopentanohydrophenanthrene ring system DOAI: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1. Subject matter wherein the organic active ingredient has
the cyclopentanohydrophenanthrene nucleus, illustrated
below, and may contain double bond between its members.
| | (1)
Note. Included herein is lanolin as the active ingredient. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 172]](../ps.gif) 172 172 | Hetero ring containing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 169. Subject matter wherein the cyclopentanohydrophenanthrene
ring containing compound contains a heterocyclic ring.
Included herein are:
and 
, etc. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 173]](../ps.gif) 173 173 | Spiro ring system: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 172. Subject matter wherein a spiro ring is attached directly
or indirectly to a carbon of the cyclopentanohydrophenanthrene nucleus. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 179]](../ps.gif) 179 179 | Modified C-ring (except methyl in 13-position) (e.g., double
bond containing substituted, etc.): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 178. Subject matter wherein the C-ring of the cyclopentanohydrophenanthrene
ring system contains a double bond or is substituted, other
than -CH3 in 13-position, i.e., 18-methyl.
| | (1)
Note. For the purpose of this classification, the
C-ring is defined as including positions 8, 9, 11, 12, 13, and
14. |
| | (2)
Note. See subclass 169 for the numbering system
of a cyclopentanohydrophenanthrene nucleus. |
| | (3)
Note. This subclass contains for example:
,etc. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 181]](../ps.gif) 181 181 | 21-position substituted: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 178. Subject matter wherein the carbon in the 21 position is
directly bonded to an atom other than carbon or hydrogen.
| | (1)
Note. This subclass contains, for example:
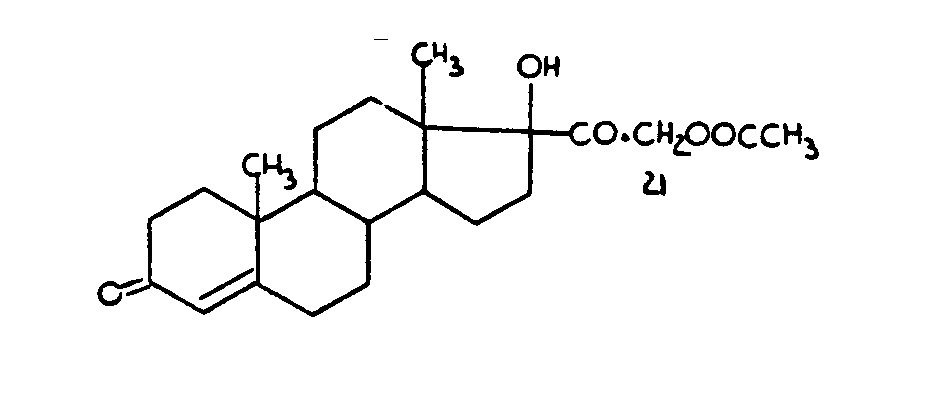
, etc. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 183]](../ps.gif) 183 183 | Heterocyclic carbon compounds containing a hetero ring
having chalcogen (i.e., O, S, Se, or
Te) or nitrogen as the only ring hetero atoms DOAI: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1. Subject matter which includes a compound containing a ring
composed of carbon and at least one element from the group consisting
of nitrogen, sulfur, selenium, tellurium
and oxygen as DOAI.
| | (1)
Note. Excluded herefrom are those carbon compounds
wherein the only heterocyclic nucleus present is produced by salt
formation between amino and acid groups, e.g., betaines, which
are placed with the corresponding open chain compounds, particularly
subclass 556. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 185]](../ps.gif) 185 185 | Polycyclo ring system: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 184. Subject matter wherein the heterocyclic compound which includes
a heavy metal is a part of a fused ring or bridged ring system. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 189]](../ps.gif) 189 189 | Tin: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 184. Subject matter wherein the heavy metal is tin. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 192]](../ps.gif) 192 192 | 1-thia-4-aza-bicyclo (3.2.0.) heptane
ring containing (including dehydrogenated) e.g., penicillins, etc.): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 183. Subject matter wherein the heterocyclic compound contains
a 1-thia- 4- aza-bicyclo (3.2.0) heptane
ring system having the following structure, and may contain
a double bond between ring members, e.g., penicillins, etc.
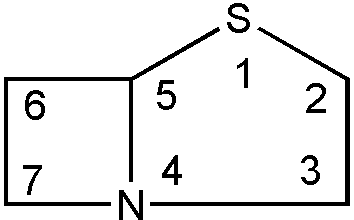
| | (1)
Note. The Ring Index uses a different system for
numbering the ring members. However, in the indents
hereunder which refer to positions, the numbers shown in the
definition are employed. |
| | (2)
Note. Patents reciting broadly "penicillins," "penicillin
type," or "penicillin drugs" are
placed herein. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 435, | Chemistry: Molecular Biology and Microbiology,
subclass 43 for processes of producing penicillin by microbial
fermentation. |
| 540, | Organic Compounds,
subclasses 304+ for a penicillin compound, per se. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 194]](../ps.gif) 194 194 | 6,6-di-substituted: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 192. Subject matter wherein the bicyclo heptane ring system contains
two substituents other than hydrogen in 6-position. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 201]](../ps.gif) 201 201 | 7,7-di-substituted: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 200. Subject matter wherein the bicyclo octane ring system contains
two substituents other than hydrogen in 7-position. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 210.01]](../ps.gif) 210.01 210.01 | Hetero ring is four-membered and includes at least
one ring nitrogen: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 183. Subject matter which contains a heterocyclic ring consisting
of four atoms, at least one of which is nitrogen.
| | (1)
Note. The heterocyclic ring may include other hetero
atoms of the group set forth in the definition of subclass 183 and
the relative positions of the hetero atoms may vary. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 540, | Chemistry, Carbon Compounds, Part of
the Class 532-570 Series,
subclasses 200 through 364for a compound which includes a four-membered
lactam ring. |
| 548, | Carbon Compounds, Part of the 532-570
Series,
subclasses 950 through 953,for a compound which includes a non-lactam
four-membered hetero ring containing nitrogen. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 210.05]](../ps.gif) 210.05 210.05 | Plural ring hetero atoms in the bicyclo ring system: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 210.04. Subject matter wherein the bicyclo ring system contains
an additional hetero atom (i.e. nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or
tellurium).
| | (1)
Note. An example of an active ingredient provided
for herein is,
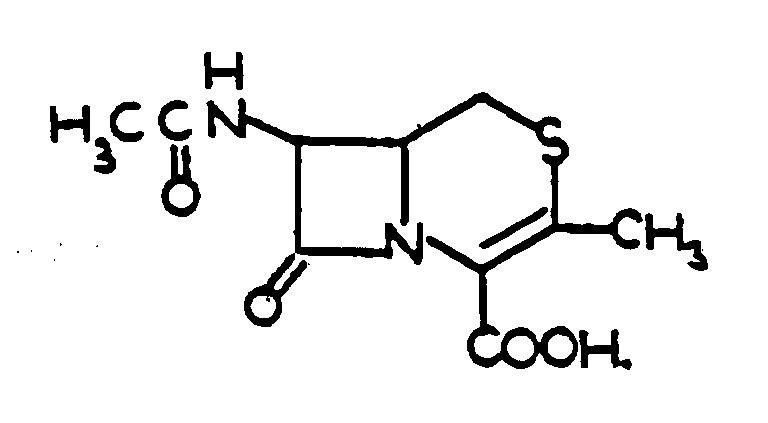
| SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 192, | for when the additional hetero atom is sulfur, and
the bicyclo ring system is 1-thia-4-aza-bicyclo (3.2.0) heptane. |
| 200, | for when the hetero atom is sulfur, and the
bicyclo ring system is 1-thia-5-aza- bicyclo (4.2.0) octane. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 211.01]](../ps.gif) 211.01 211.01 | Hetero ring contains seven members including nitrogen,
carbon, and chalcogen: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 183. Subject matter which contains a hetero ring having exactly
seven members consisting of carbon, nitrogen and chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or
tellurium as its only ring members).
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 540, | Chemistry, Carbon Compounds, Part of
the 532-570 Series,
subclasses 488 through 491for seven-membered lactams containing
a chalcogen ring atom in the lactam ring, subclasses 544
through 552 for non-lactam seven-membered hetero
ring compounds which include nitrogen and chalcogen as ring atoms
of the seven-membered hereto ring. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 212.01]](../ps.gif) 212.01 212.01 | Hetero ring is seven-membered consisting of one
nitrogen and six carbons: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 183. Subject matter wherein the hetero ring has seven members
and consists of one ring nitrogen and six carbon atoms.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 540, | Chemistry, Carbon Compounds, Part of
the 530-570 Series,
subclasses 519 through 540for a lactam ring compound wherein the ring consists
of nitrogen and six carbon atoms, and subclasses 576-612
for a non-lactam compound having a hetero ring consisting
one nitrogen and six carbons. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 212.02]](../ps.gif) 212.02 212.02 | Spiro: |
| | Subject matter under 212.01 wherein a ring is spiro
fused directly or indirectly to the seven-membered hetero
ring.
| | (1)
Note. An example of an active ingredient provided
herein is:
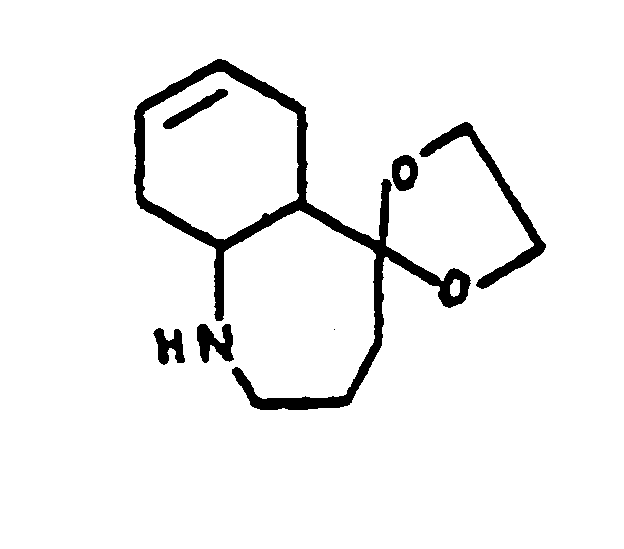
| |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 223.5]](../ps.gif) 223.5 223.5 | With additional active ingredient: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 223.2. Subject matter in which, in addition to the 1,2, 4-benzothiadiazine-1, 1-dioxide
compound, an additional active ingredient is present.
| | (1)
Note. This subclass provides for subject matter
wherein plural nonidentical 1,2, 4-benzothiadiazine-1, 1-dioxide
compounds are each present as active ingredients. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 223.8]](../ps.gif) 223.8 223.8 | 1,3,5-thiadiazines: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 222.5. Subject matter in which the six-membered hetero
ring has the following basic structure, which may contain
double bonds between ring members:
| | (1)
Note. An example of an active ingredient provided
for herein is:
| |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 224.8]](../ps.gif) 224.8 224.8 | Phenothiazines (including hydrogenated): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 224.5. Subject matter in which the polycyclo ring system has the
following basic structure, which may contain double bonds
between ring members:
| | (1)
Note. An example of an active ingredient provided
for herein is:
| |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 226.8]](../ps.gif) 226.8 226.8 | 1, 3-thiazines: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 222.2. Subject matter in which the hetero ring has the following
basic structure, which may contain double bonds between
ring members:
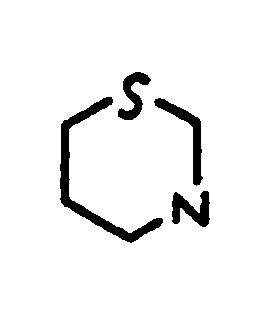
| | (1)
Note. An example of an ingredient provided for herein
is:
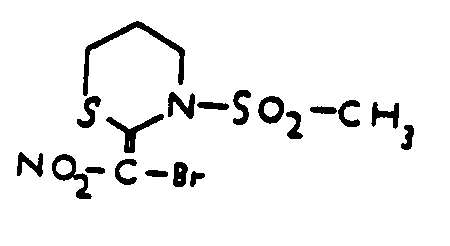
| |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 227.5]](../ps.gif) 227.5 227.5 | 1, 4-thiazines: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 222.2. Subject matter in which the hetero ring has the following
basic structure, which may contain double bonds between
ring members:
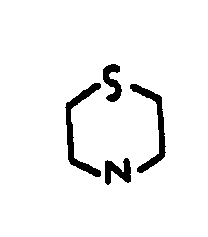
| | (1)
Note. An example of an active ingredient provided
for herein is:
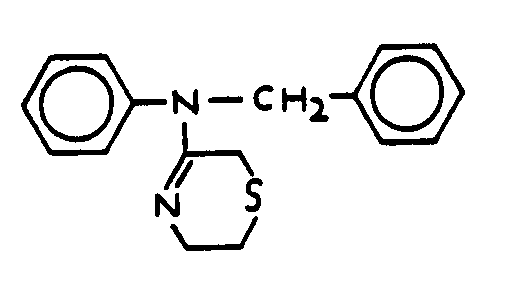
| |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 230.8]](../ps.gif) 230.8 230.8 | Chalcogen bonded directly to ring carbon of 1, 4-oxazine
ring: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 228.8. Subject matter in which the six-membered hetero
ring has the following basic structure which may contain double
bonds between ring members, as illustrated below, and
in which chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium) is
bonded directly to a ring carbon of the six-membered hetero
ring.
| | (1)
Note. An example of an active ingredient provided
for herein is:

| |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 234.8]](../ps.gif) 234.8 234.8 | Quinoxalines (including hydrogenated): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 234.5. Subject matter in which the bicyclo ring system has the
following basic structure which may contain double bonds between
ring members:
| | (1)
Note. An example of an active ingredient provided
for herein is:
| |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 251]](../ps.gif) 251 251 | Isoalloxazine (e.g., riboflavins, vitamin
B2, etc.): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 250. Subject matter in which the 1,4, diazine
is part of a radical having the following structure:
| | (1)
Note. In a derivative, the ring structure and
carbonyl moieties must remain intact. Any position on
the ring may be substituted. |
| | (2)
Note. This subclass provides for a vitamin B2 (or
G) composition. |
| | (3)
Note. A patent with a claim directed to a riboflavin
composition will be placed here and not in subclass 23. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 252.1]](../ps.gif) 252.1 252.1 | 1,4 diazines: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 247. Subject matter wherein the six-membered hetero
ring is a 1, 4-diazine ring..
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 544, | Carbon Compounds,
subclasses 336 through 410,for compounds which include a 1,4-diazine
ring. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 252.15]](../ps.gif) 252.15 252.15 | Spiro ring system containing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 252.14. Subject matter wherein the active ingredient containing
the diazine rings includes a spiro ring system.
| | (1)
Note. Neither the 1,4-diazine
ring nor the 1,3-diazine ring has to be part of
the spiro ring system. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 263.1]](../ps.gif) 263.1 263.1 | Purine (including hydrogenated): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 262.1. Subject matter wherein the bicyclo ring system is the
purine nucleus, (illustrated below) including
hydrogenated forms thereof.

SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 45, | for bio-affecting or body treating compositions
containing as the active ingredient N-glycoside with the
aglycone portion being a purine or a substituted purine. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 266.22]](../ps.gif) 266.22 266.22 | Piperidinyl or tetrahydropyridyl: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 266.21. Subject matter wherein the six membered hetero ring is a
piperidine or a tetrahydropyridine ring that is attached directly
or indirectly to the quinazoline ring system through its ring carbon. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 270]](../ps.gif) 270 270 | Barbituric acid or derivative (including thioanalogs): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 269. Subject matter wherein the 1,3-diazine
is of the structure, illustrated below, wherein
X is oxygen or sulfur or the enol form thereof and R and/or
R" are hydrogen, alkyl or aryl.

| | (1)
Note. For this subclass, the three keto groups
must be present on the 1,3 diazine ring. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 271]](../ps.gif) 271 271 | Two or more barbituric acid compounds or with an additional
active ingredient or stabilizer: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 270. Subject matter which contains two or more compounds each
having the moiety, as shown below, or one compound
having said moiety and an additional organic active ingredient or stabilizing
agent.
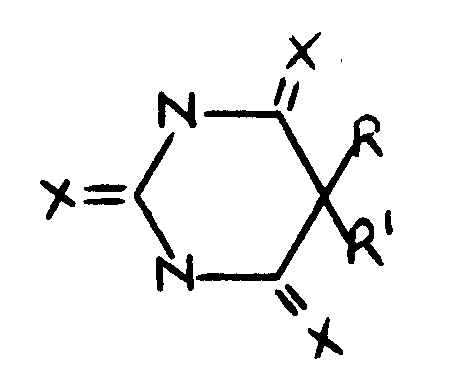
| | (1)
Note. Included herein is the combination of barbituric
acid and a salt thereof and complexes of two or more active ingredients, or
active ingredient complexed with stabilizing agent. |
| | (2)
Note. Potentiating and synergistic agents are considered
active ingredients. |
| | (3)
Note. See section II, Glossary, for
the definition of a stabilizing agent. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 315]](../ps.gif) 315 315 | Piperidines: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 277. Subject matter wherein the six-membered hetero
ring, consisting of one nitrogen and five carbons, contains
no double bonds between ring members, i.e., the
piperidine ring. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 336]](../ps.gif) 336 336 | Additional hetero ring containing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 277. Subject matter which contains an additional hetero ring
in the compound other than the six-membered hetero ring
consisting of one nitrogen and five carbons, i.e., an
additional hetero ring other than a pyridine or partially hydrogenated
pyridine ring. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 355]](../ps.gif) 355 355 | At 3-position: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 354. Subject matter wherein the C=O group is attached
directly to the 3-position of the six-membered
hetero ring e.g.,
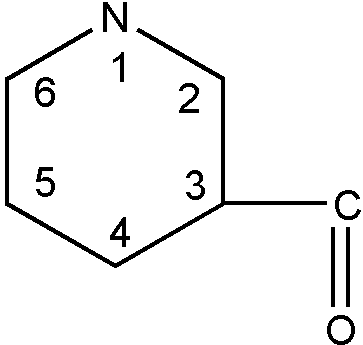
, etc. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 364]](../ps.gif) 364 364 | Oxadiazoles (including hydrogenated): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 361. Subject matter wherein the hetero ring contains one ring
oxygen and two ring nitrogens as the only hetero atoms of the ring
and may have a double bond between ring members, e.g.,
, etc. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 365]](../ps.gif) 365 365 | 1,3-thiazoles (including hydrogenated): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 359. Subject matter wherein the five-membered hetero
ring is a 1,3-thiazole ring which includes the
following basic ring structure, as illustrated below, and
may contain a double bond between ring members.
| | (1)
Note. See section II, Glossary, for
the definition of "including hydrogenated". | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 372]](../ps.gif) 372 372 | 1,2-thiazoles (including hydrogenated): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 359. Subject matter wherein the five-membered hetero
ring is a 1,2-thiazole ring which includes the
following basic ring structure, illustrated below, and
may contain a double bond between ring members.
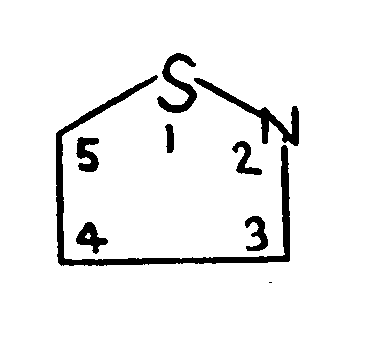
| | (1)
Note. See section II, Glossary, for
the definition of "including hydrogenated". | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 374]](../ps.gif) 374 374 | 1,3-oxazoles (including hydrogenated): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 359. Subject matter wherein the five-membered hetero
ring is a 1,3-oxazole ring which includes the
following basic ring structure, illustrated below, and
may contain a double bond between ring members.
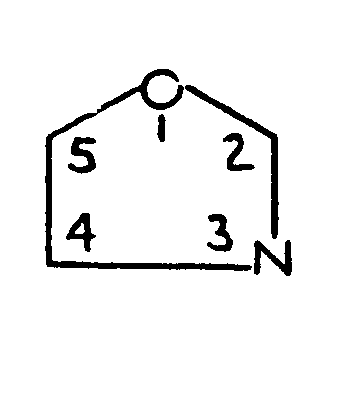
| | (1)
Note. See section II, Glossary, for
the definition "including hydrogenated". | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 378]](../ps.gif) 378 378 | 1,2-oxazoles (including hydrogenated): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 359. Subject matter wherein the five-membered hetero
ring is a 1,2-oxazole ring which includes the
following basic ring structure, illustrated below, and
may contain a double bond between ring members.
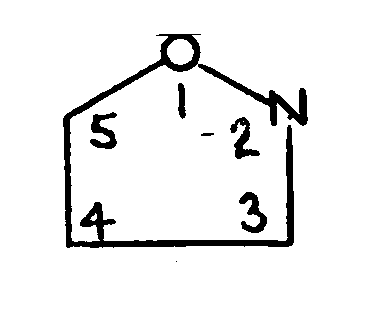
| | (1)
Note. See section II, Glossary, for
the definition "including hydrogenated". | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 385]](../ps.gif) 385 385 | 1,3-diazoles: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 359. Subject matter wherein the five-membered hetero
ring is a 1,3-diazole ring which includes the following
basic ring structure, illustrated below, and may
contain a double bond between ring members.
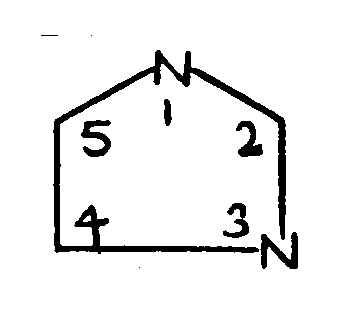
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 386]](../ps.gif) 386 386 | Divalent chalcogen or acyclic nitrogen double bonded directly
to ring carbon of the diazole ring, or tautomeric equivalent: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 385. Subject matter wherein a ring carbon of the 1,3-diazole
ring is bonded directly by a double bond to divalent chalcogen or
acyclic nitrogen, or to a group which may tautomerize thereto (e.g., hydroxyl, sulfhydryl, acyclic
amino, etc.).
| | (1)
Note. (A) all 1,3-diazoles
having the following structure, as shown in the first illustration,
are classified in this and indented subclasses; (B) the
aminoimidazole, for example, as shown in the second
illustration below, is included in this subclass though
its imino tautomer, as shown in the third illustration
below, may not be present in significant amounts; (C) salts
in which the labile hydrogen of, for example, an
hydroxy, sulfhydryl or amino tautomer is replaced with
a metal or amine salt are classified here.
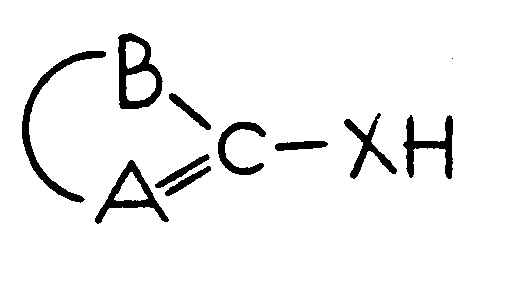
X is chalcogen or NR; A is N or CR"; Bis the remainingring members of the 1,3-diazole; R
is H or a substituent; R" isH or a substituent
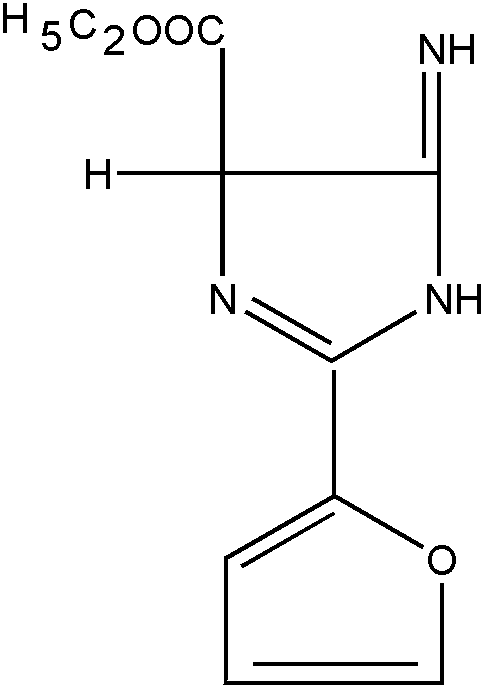
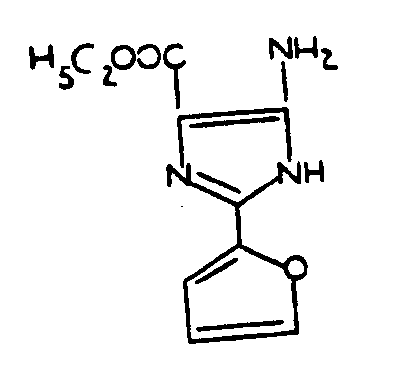
| |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 396]](../ps.gif) 396 396 | Imidazoles: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 385. Subject matter wherein the 1,3-diazole
ring is imidazole which contains two double bonds between the ring
members. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 400]](../ps.gif) 400 400 | At imidazole ring carbon: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 399. Subject matter wherein the chalcogen or nitrogen is bonded
indirectly to a ring carbon of the imidazole ring and not through
any of the hetero atoms. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 401]](../ps.gif) 401 401 | 2-imidazolines: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 385. Subject matter wherein the 1,3-diazole
ring contains one double bond between 2-carbon and 3-nitrogen. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 403]](../ps.gif) 403 403 | 1,2-diazoles: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 359. Subject matter wherein the five-membered hetero
ring is a 1,2-diazole ring which includes the following
basic ring structure, as illustrated below, and
may contain a double bond between ring members.

|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 404]](../ps.gif) 404 404 | Divalent chalcogen or acyclic nitrogen double bonded directly
to ring carbon of the diazole ring, or tautomeric equivalent: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 403. Subject matter wherein a ring carbon of the 1,2-diazole
ring is bonded directly by a double bond to divalent chalcogen or
acyclic nitrogen, or to a group which may tautomerize thereto (e.g., hydroxyl, sulfhydryl, acyclic
amino, etc.).
| | (1)
Note. (A) all 1,2-diazoles
having the following structure, shown in the first illustration, are
classified in this and indented subclasses; (B) the
hydroxy pyrazole, for example, as shown in the second
illustration below, is included in this subclass though
its oxo tautomer, as shown in the third illustration below, may
not be present in significant amounts; (C) Salts
in which the labile hydrogen of, for example, an
hydroxy, sulfhydryl or amino tautomer is replaced with
a metal ion or amine salt are classified here.
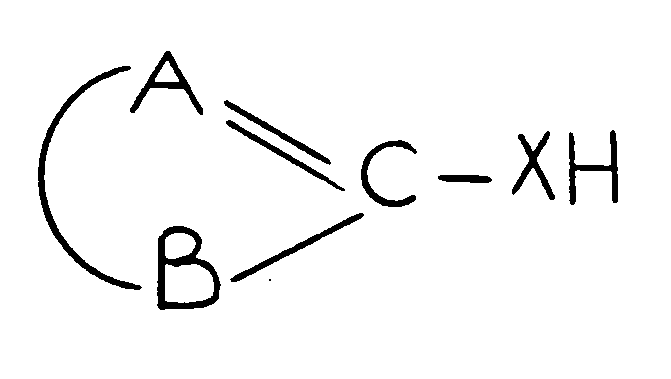
X is chalcogen or NR; A is N or CR"; Bis the remainingring members of the 1,2-diazole; R
is H or a substituent; R" isH or a substituent
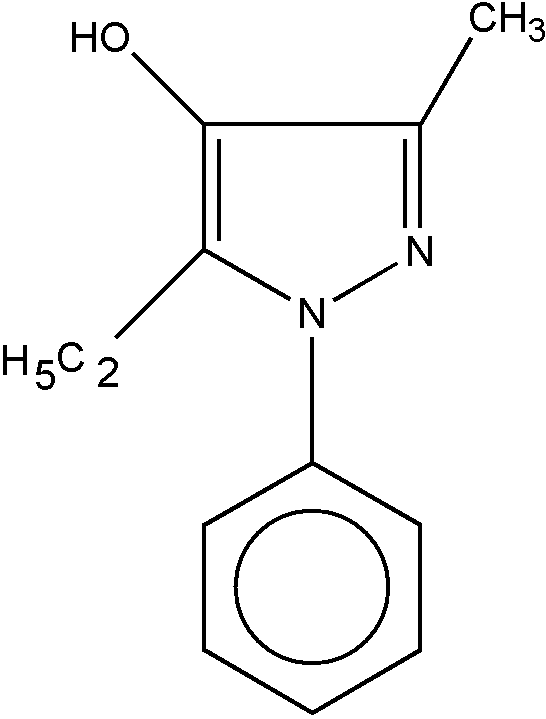
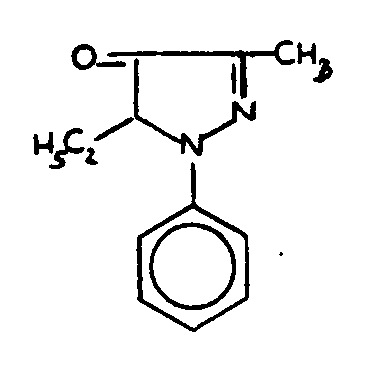
| |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 406]](../ps.gif) 406 406 | Pyrazoles: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 403. Subject matter wherein the 1,2-diazole
ring is pyrazole which contains two double bonds between ring members. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 409]](../ps.gif) 409 409 | Spiro ring system: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 408. Subject matter which contains a spiro ring system, e.g.,
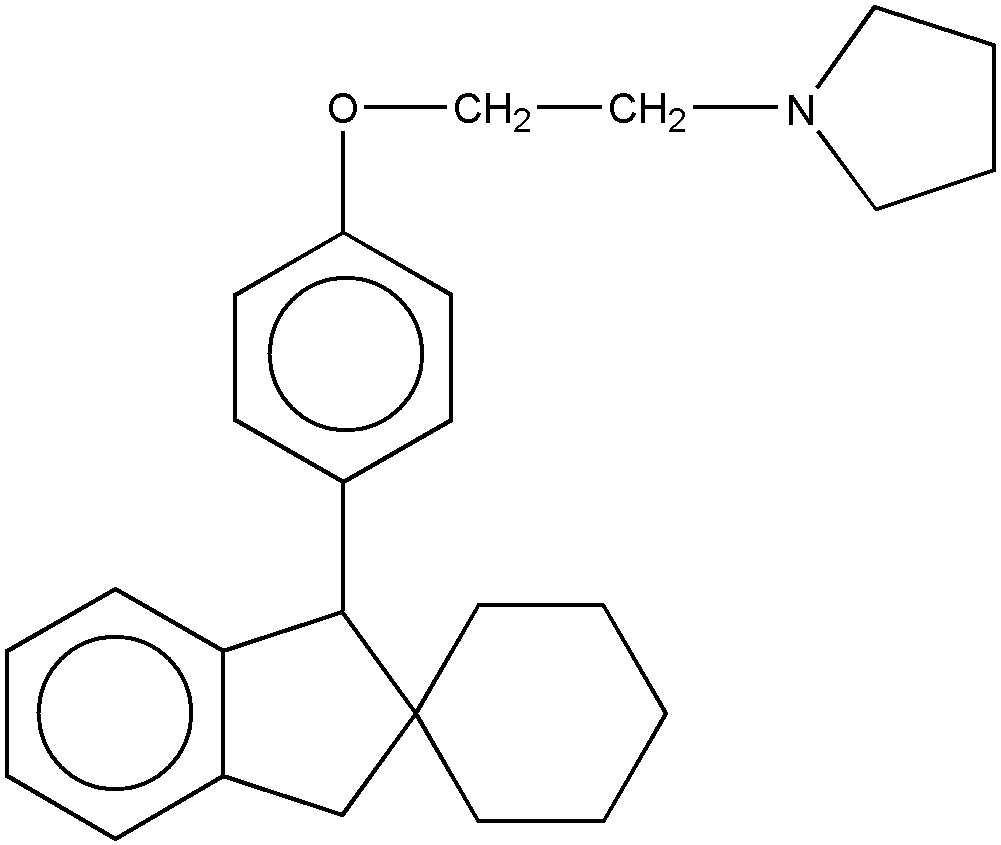
, etc.
| | (1)
Note. See section II, Glossary, for
the definition of "spiro ring system". | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 430]](../ps.gif) 430 430 | Sulfur containing hetero ring: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 183. Subject matter wherein the hetero ring has sulfur as a ring
hetero atom.
| | (1)
Note. Inner sulfonium salts, even when represented
in cyclic form are excluded herefrom. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 444]](../ps.gif) 444 444 | Additional hetero ring: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 438. Subject matter wherein an additional hetero ring is present.
| | (1)
Note. Examples of compounds Provided for herein
are:
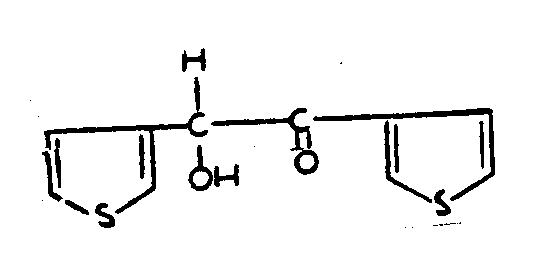
, etc. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 458]](../ps.gif) 458 458 | Tocopherols (e.g., vitamin
E, etc.): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 456. Subject matter wherein the bicyclo ring system includes
the following structure, in the first illustration below, or
ether, ester of the hydroxyl group thereof, e.g., as
shown in the second illustration below.
, etc.
| | (1)
Note. The several tocopherols differ by methyl substitution
on the benzo ring. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 462]](../ps.gif) 462 462 | Spiro ring system: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 461. Subject matter which contains a spiro ring system, e.g.,
, etc.
| | (1)
Note. See section IV, Glossary, for
the definition of "spiro ring system." | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 474]](../ps.gif) 474 474 | Ascorbic acid or derivative (e.g., vitamin
c, etc.): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 473. Subject matter which has the following structure, as
illustrated below, or derivative thereof.
| | (1)
Note. A derivative of ascorbic acid includes the
replacement of hydroxyl hydrogen with acyl, alkyl or metal
to give the ester, ether or alcoholate of a metal. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 478]](../ps.gif) 478 478 | N-C (=X)-X-C
containing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 476. Subject matter in which the active ingredient is an ester
of carbamic acid, i.e., H-XN (X
is chalcogen) and which contains the NX-C group, e.g.,
, etc. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 479]](../ps.gif) 479 479 | With an additional active ingredient: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 478. Subject matter which contains a compound having the grouping, as
shown below, and an additional organic active ingredient.
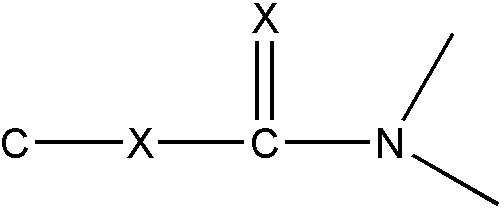
| | (1)
Note. Synergistic and potentiating agents are considered
active ingredients. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 480]](../ps.gif) 480 480 | Polycyclo ring system attached by nonionic bonding: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 478. Subject matter wherein the compound contains a polycyclo
ring system, e.g.,
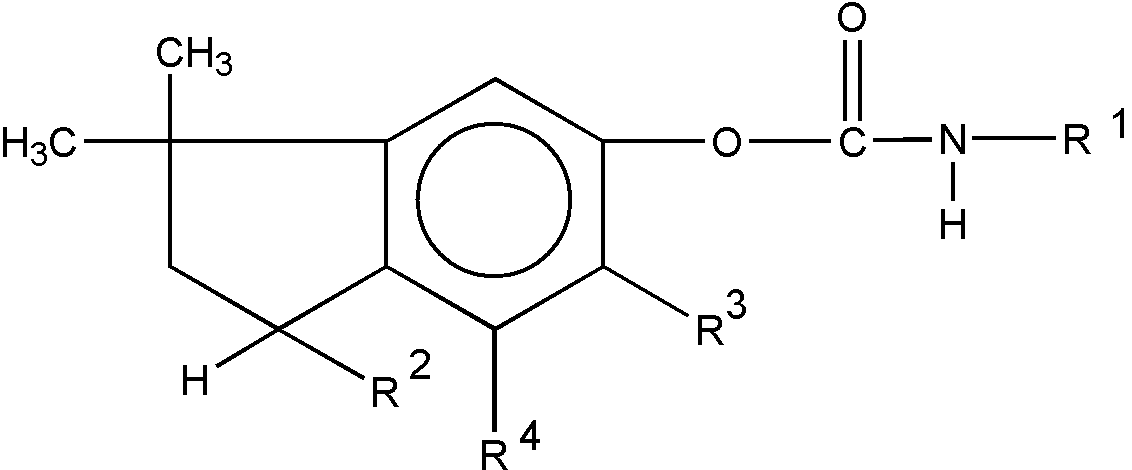
, etc.
| | (1)
Note. Compounds wherein the polycyclo system is
ionically bonded to the moiety containing the grouping, as shown
below, are excluded from this subclass.
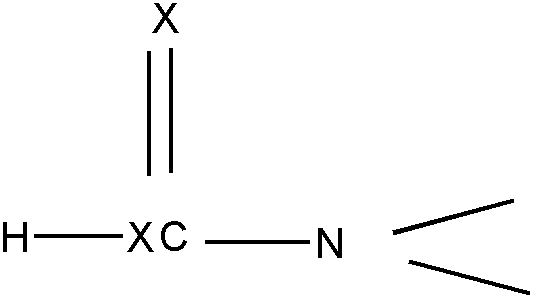
| |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 482]](../ps.gif) 482 482 | N-C(=X)-N, N-C (=N)N, N-N, nitrogen directly
bonded to oxygen by nonionic bonding or cyano containing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 478. Subject matter which contains the grouping NN (e.g., ureido);NN, (e.g., guanido); N-N (e.g., hydrazo, etc.), cyano
or a nitrogen bonded directly to oxygen by nonionic bonding.
| | (1)
Note. This subclass contains, for example,
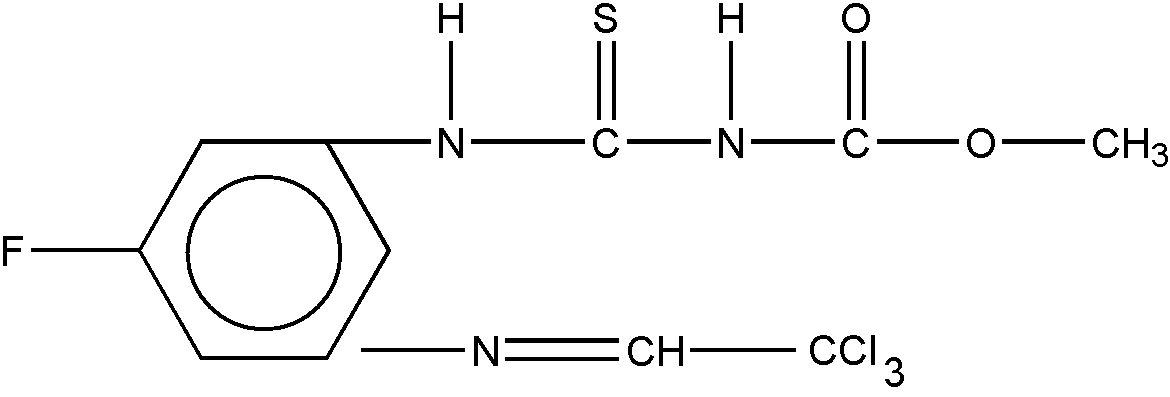
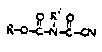
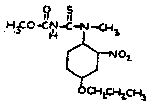
, etc. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 488]](../ps.gif) 488 488 | Ring in alcohol moiety: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 485. Subject matter wherein the organic active ingredient also
contains a ring in the alcohol moiety.
| | (1)
Note. This subclass contains, e.g.,
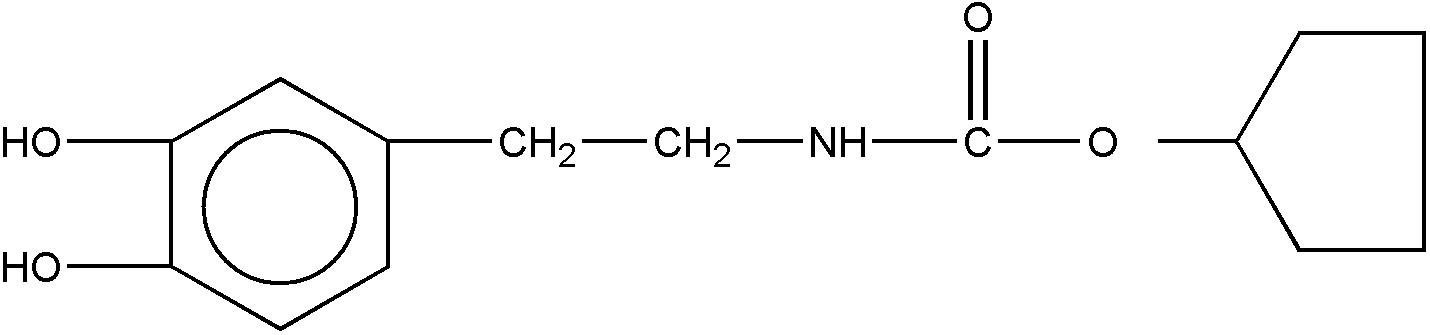
, etc. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 489]](../ps.gif) 489 489 | Ring in alcohol moiety: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 478. Subject matter wherein the active ingredient contains a
ring in the alcohol moiety.
| | (1)
Note. This subclass contains, e.g.,
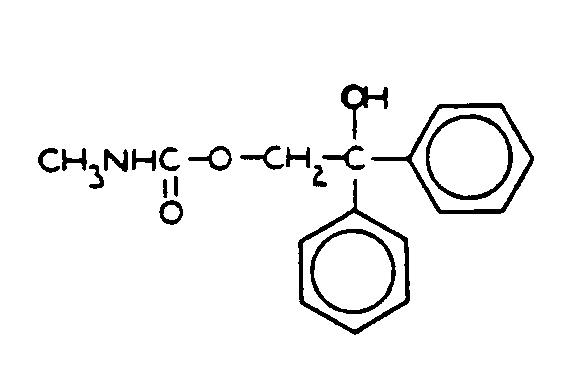
, etc. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 491]](../ps.gif) 491 491 | With an additional active ingredient: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 476. Subject matter which contains a compound having the grouping
NX and an additional organic active ingredient.
| | (1)
Note. Synergistic and potentiating agents are considered
active ingredients. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 492]](../ps.gif) 492 492 | Heavy metal containing DOAI: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1. Subject matter in which the DOAI contains a heavy metal, i.e., a
metal whose specific gravity is greater than 4.
| | (1)
Note. Many patents in this and indented subclasses
are drawn to compositions containing heavy metal salts of organic compounds. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 493]](../ps.gif) 493 493 | Tin: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 492. Subject matter in which the heavy metal is tin. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 494]](../ps.gif) 494 494 | Zinc: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 492. Subject matter in which the heavy metal is zinc. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 498]](../ps.gif) 498 498 | Lead: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 492. Subject matter in which the heavy metal is lead. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 500]](../ps.gif) 500 500 | With an additional active ingredient: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 499. Subject matter which contains a compound which contains
copper and also an additional active ingredient.
| | (1)
Note. Synergistic and potentiating agents are considered
active ingredients. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 502]](../ps.gif) 502 502 | Iron: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 492. Subject matter in which the heavy metal is iron. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 506]](../ps.gif) 506 506 | Ester DOAI: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1. Subject matter wherein the DOAI is identical in structure
with a compound formed by replacing the hydroxyl of an alcohol or
phenol by an acid radical. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 510]](../ps.gif) 510 510 | Polycyclo ring system: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 506. Subject matter wherein the ester contains a polycyclo ring
system in either the alcohol or acid portion of the molecule.
| | (1)
Note. This subclass contains, for example:
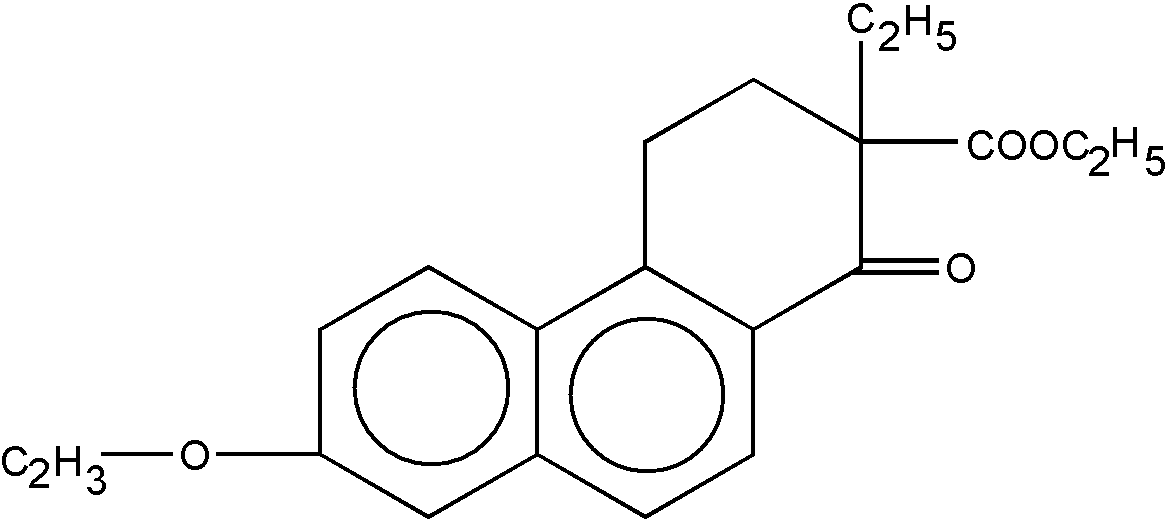
, etc. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 515]](../ps.gif) 515 515 | With an additional active ingredient: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 514. Subject matter wherein the organic active ingredient contains
a compound having the group -CNX or -XCN and an
additional organic active ingredient.
| | (1)
Note. Synergistic and potentiating agents are considered
active ingredients. |
| | (2)
Note. The starting solid polymer may be subjected
to a number of aftertreating steps the sequence or numbers of which will
not affect classification. The important criteria is that
every reaction be considered proceeding from the starting solid
polymer to the final product. This is consistent with
the classification rules set out in the Class 520 Series. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 520]](../ps.gif) 520 520 | Benzene ring containing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 303. Subject matter in which the cyano or isocyano containing
compound also contains a benzene ring.
| | (1)
Note. This subclass contains, for example:
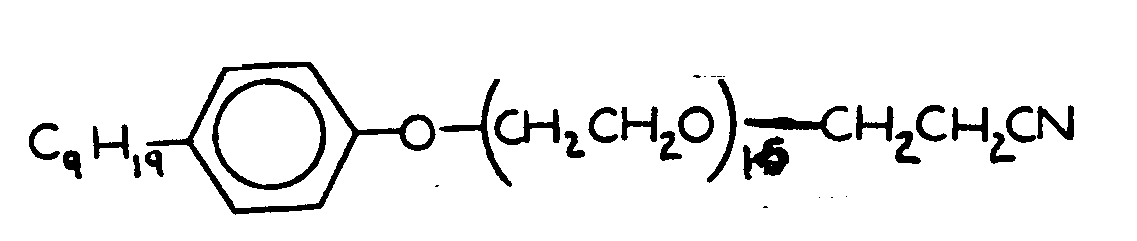
, etc. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 521]](../ps.gif) 521 521 | C=O other than as ketone or aldehyde: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 520. Subject matter in which the cyano or isocyano and benzene
ring containing compound also contains a C=D (carbonyl) other
than as a ketone or aldehyde.
| | (1)
Note. This subclass contains, for examples:
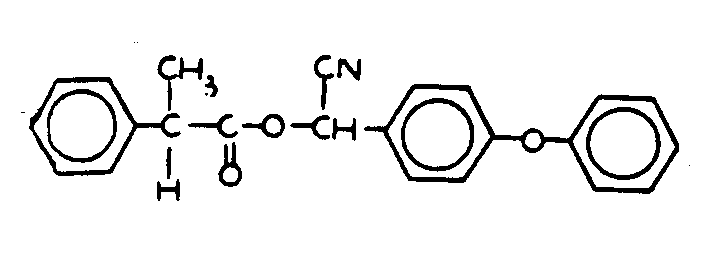
, etc. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 523]](../ps.gif) 523 523 | Additional nitrogen other than cyano: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 520. Subject matter wherein the cyano and benzene containing
compound also contains an additional nitrogen other than as in a
cyano or isocyano grouping.
| | (1)
Note. This subclass contains, for example:
, etc. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 526]](../ps.gif) 526 526 | Acyclic: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 519. Subject matter wherein the cyano containing compound is
acyclic.
| | (1)
Note. This subclass contains, for example:
, etc. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 527]](../ps.gif) 527 527 | C=O other than as ketone or aldehyde: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 526. Subject matter wherein the acyclic cyano containing compound
contains a C=O (carbonyl) other than
as ketone or aldehyde.
| | (1)
Note. This subclass contains, for example:
, etc. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 528]](../ps.gif) 528 528 | C(=O)N containing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 527. Subject matter wherein the carbonyl group is present in
the form of a carboxamide grouping,
| | (1)
Note. This subclass contains, for example:
, etc. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 531]](../ps.gif) 531 531 | Z contains a cyclopropyl or cyclopropene ring: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 529. Subject matter wherein Z is or contains a cyclopropyl or
cyclopropene moiety.
| | (1)
Note. This subclass contains for example:
, etc. |
| | (2)
Note. A Compound which contains plural ZO-Y
radicals is proper for the subclasses hereunder if the A (or
Y) of any of the radicals meets the requirements for Z (or
Y) in the subclass. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 540]](../ps.gif) 540 540 | Nitrogen in Y moiety: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 538. Subject matter wherein at least one nitrogen atom is also
present in the Y radical.
| | (1)
Note. This subclass contains, for example:
, etc. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 543]](../ps.gif) 543 543 | Z forms a phenoxyl alky or phenoxy alkenyl radical: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 532. Subject matter wherein Z is a substituted or unsubstituted
Phenoxy alkyl or phenoxy alkenyl radical.
| | (1)
Note. This subclass contains, for example, as
illustrated below, wherein an oxyalkyl or oxyalkenyl group
is between the phenyl and carbonyl of the ester function. |
| |
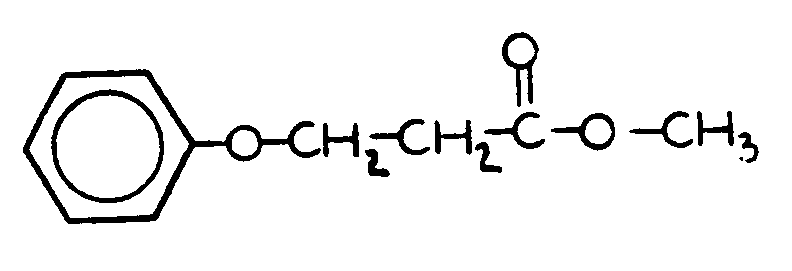
, etc. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 545]](../ps.gif) 545 545 | Ketone in Z radical: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 532. Subject matter wherein a ketone grouping is present in the
Z moiety.
| | (1)
Note. This subclass contains, for example:
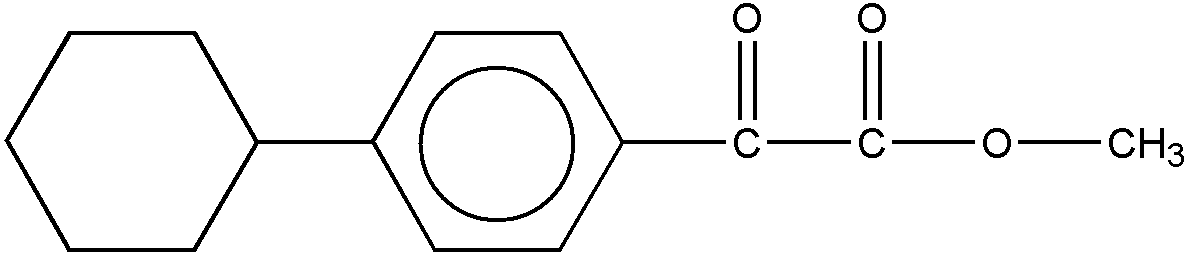
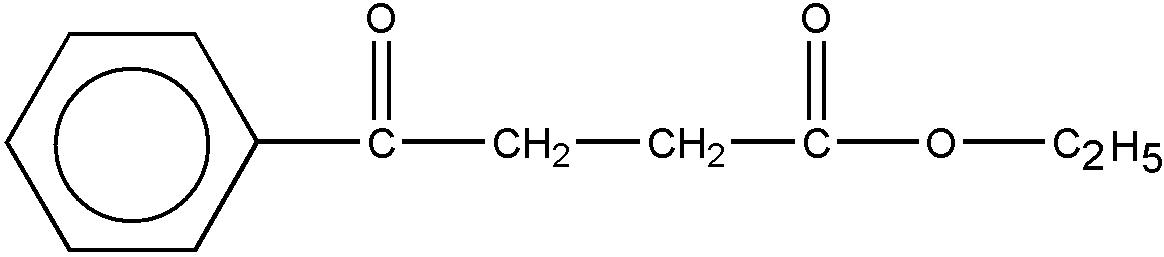
, etc. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 548]](../ps.gif) 548 548 | Ring in alcohol moiety: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 547. Subject matter wherein the Y moiety contains a carbocyclic
ring.
| | (1)
Note. This subclass contains, for example:
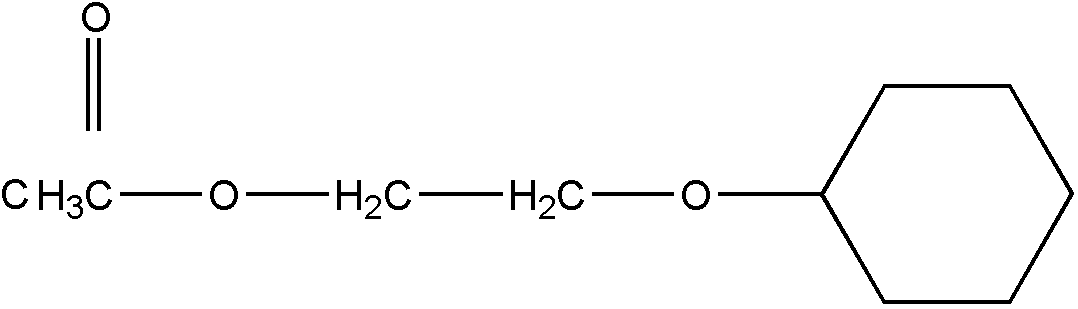
, etc. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 553]](../ps.gif) 553 553 | Radical -XH acid, or anhydride, acid
halide or salt thereof (X is chalcogen) DOAI: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1. Subject matter which contains a DOAI which has the structure
M-A-X-H where A is sulfur, selenium, tellurium, as
illustrated below, wherein X,Y and Z are Chalcogens, n=1
or 2 and X is not identical to A, anhydride acid halide
or salt thereof, M being any radical not provided for above.
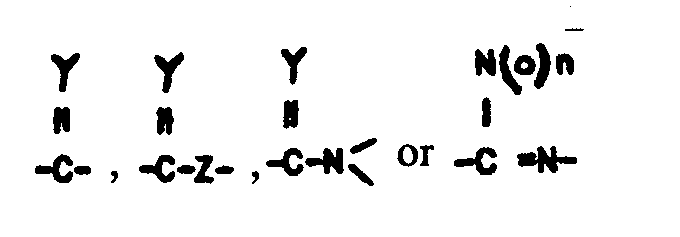
| | (1)
Note. Unless otherwise provided for, the salt
of an acid is classified on the basis of the corresponding acid. |
| | (2)
Note. This subclass specifically provides for acyclic
anhydrides and acyclic acyl halides. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 554]](../ps.gif) 554 554 | Amine addition salt of the acid: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 553. Subject matter in which the active ingredient is an addition
salt of an amine and an organic acid.
| | (1)
Note. For the purpose of this and indented subclasses, amines
are compounds identical in constitution with the derivatives of
ammonia (NH3) wherein the
nitrogen atom thereof is bonded to at least one carbon of an organic
radical. |
| | (2)
Note. This subclass contains, for example:
, etc. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 558]](../ps.gif) 558 558 | Higher fatty acid or salt thereof: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 557. Subject matter wherein the acyl group has an unbroken chain
of at least seven acyclic carbon atoms bonded to the carbon of the
carbonyl group, i.e., higher
fatty acids. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 559]](../ps.gif) 559 559 | Ring containing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 558. Subject matter wherein the organic active ingredient contains
a carbocyclic ring attached indirectly or directly to the higher
fatty acid chain. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 566]](../ps.gif) 566 566 | Polycarboxylic acid: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 864. Subject matter wherein the active ingredient has at least
two C(=O)-O groups bonded to
carbons of the active ingredient.
| | (1)
Note. The O groups can be bonded to the same or
different carbons. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 569]](../ps.gif) 569 569 | Polycyclo ring system: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 568. Subject matter wherein the active ingredient has a fused
or bridged ring system therein which is not ionically bonded. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 575]](../ps.gif) 575 575 | Hydroxamic acid or salt thereof: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 553. Subject matter wherein the acid is hydroxamic acid on a
salt thereof, i.e., RC(=O)- NOH, wherein
R is hydrogen or an organic radical bonded to the C=O by
a carbon. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 577]](../ps.gif) 577 577 | Polycyclo ring system: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 576. Subject matter wherein the active ingredient contains a
fused or bridged ring system which is nonionically bonded. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 579]](../ps.gif) 579 579 | Nitrogen containing other than solely as a nitrogen in
an inorganic ion of an addition salt, a nitro or a nitroso, DOAI: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1. Subject matter which includes a compound containing nitrogen
in a form other that as nitrogen in an inorganic ion of an addition
salt, nitro or nitroso.
| | (1)
Note. This group of compounds includes for example, ureas, thioureas, amides, amidines, azines, hydrazones, carbodimides, oximes, hydroxylamines and
amines, inter alia, as well as their inorganic
acid salts. |
| | (2)
Note. This subclass is residual for alicyclic amines
not specifically provided for below. |
| | (3)
Note. This subclass contains, for example:
, etc. |
| | (4)
Note. If amino nitrogen is present, the compound
may additionally contain nitro, nitroso or nitrogen in
an inorganic ion of an addition salt. |
| | (5)
Note. Component parts of an "adduct" will
be considered to be attached to each other ionically, except
if it is clear that the mode of attachment is nonionic. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 580]](../ps.gif) 580 580 | Thioureas (i.e., N-C(=S)-N: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 579. Subject matter containing the grouping NN.
| | (1)
Note. N=N is not provided for in this subclass; see
appropriate subclass and in particular subclass 631. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 588]](../ps.gif) 588 588 | Ureas (i.e., N-C(=O)N: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 579. Subject matter which contains the grouping NN.
| | (1)
Note. This subclass contains, for example, adducts
of urea with inorganic compounds such as hydrogen peroxide or calcium
nitrate. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 603]](../ps.gif) 603 603 | Nitrogen in Q: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 602. Subject matter wherein the residue of the aromatic sulfonamide
contains nitrogen, e.g.,
, etc. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 604]](../ps.gif) 604 604 | Q is monocyclic: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 602. Subject matter wherein the residue of the aromatic sulfonic
acid is monocyclic, i.e., Q
contains only one ring. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 618]](../ps.gif) 618 618 | Sulfur in R: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 613. Subject matter wherein the residue of the carboxylic acid (R) also
contains sulfur. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 621]](../ps.gif) 621 621 | C=O in R: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 617. Subject matter wherein the carboxylic acid residue (R) contains
a C=O group. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 625]](../ps.gif) 625 625 | R is acyclic: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 613. Subject matter wherein the carboxylic acid residue (R) does
not contain a ring. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 668]](../ps.gif) 668 668 | Polyether: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 667. Subject matter wherein the compound contains more than one
C-O-C group. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 670]](../ps.gif) 670 670 | Monoether: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 667. Subject matter wherein the compound contains only one C-O-C
group. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 675]](../ps.gif) 675 675 | Ketone DOAI: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1. Subject matter wherein the organic active ingredient is
a Ketone.
| | (1)
Note. See section II, Glossary, for
the definition of Ketone. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 681]](../ps.gif) 681 681 | Bicyclo: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 680. Subject matter wherein the polycyclo ring system is a bicyclo
ring system. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 693]](../ps.gif) 693 693 | Aldehyde DOAI: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1. Subject matter which includes an aldehyde.
| | (1)
Note. See section II, Glossary, for
definition of aldehyde. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 711]](../ps.gif) 711 711 | Acyclic: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 708. Subject matter wherein the compound does not contain a ring. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 712]](../ps.gif) 712 712 | Thioether: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 706. Subject matter in which the compound has the R-S-R
structure wherein the R"s are diverse or identical organic radicals. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 715]](../ps.gif) 715 715 | Ether DOAI: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1. Subject matter which includes a compound containing an oxygen
atom which is bonded to carbons of two discrete organic radicals
and has the grouping R-O-R wherein the R"s are diverse
or identical organic radicals. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 722]](../ps.gif) 722 722 | Acyclic: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 715. Subject matter wherein the compound does not contain a ring. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 735]](../ps.gif) 735 735 | Nuclear halogenated: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 734. Subject matter wherein the compound contains a halogen bonded
directly to a nuclear carbon of a benzene ring. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 737]](../ps.gif) 737 737 | Nuclear halogenated: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 731. Subject matter wherein the compound contains a halogen bonded
directly to a nuclear carbon of a benzene ring. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 742]](../ps.gif) 742 742 | Polynitro: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 740. Subject matter wherein the compound contains at least two -NO2 groups. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 745]](../ps.gif) 745 745 | Alkyne: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 744. Subject matter wherein the compound contains a triple bond
between two carbon atoms. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 747]](../ps.gif) 747 747 | Carbocyclic: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 743. Subject matter wherein the halogenated hydrocarbon contains
a ring in which all ring members are carbons. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 752]](../ps.gif) 752 752 | Alkyne: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 751. Subject matter wherein the compound contains a triple bond
between two carbon atoms. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 756]](../ps.gif) 756 756 | Bicyclo: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 755. Subject matter wherein the polycyclo ring system consists
of exactly two rings. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 762]](../ps.gif) 762 762 | Hydrocarbon DOAI: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 1. Subject matter which includes a compound consisting of carbon
and hydrogen atoms only. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 763]](../ps.gif) 763 763 | Carbocyclic: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 762. Subject matter wherein the compound contains at least one
ring in which all of the members are carbon. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 769]](../ps.gif) 769 769 | DESIGNATED INORGANIC NONACTIVE INGREDIENT OR ELEMENTAL MATERIAL
OTHER THAT WATER: |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter wherein the composition contains an organic
nonactive ingredient or elemental material other than water.
| | (1)
Note. This and indented subclasses provide for compositions
which (a) do not contain a designated pharmacologically or
biologically active ingredient or which (b) are
solely disclosed or claimed as useful as inert additives or carriers
for an active ingredient of this class, e.g., diluent
or carrier. |
| | (2)
Note. Within this subclass are compositions which
may contain an organic active ingredient which does not meet the
definition of the designated organic active ingredient (DOAI). |
| | (3)
Note. See section II, Glossary, for
the definition "DOAI". |
| | (4)
Note. A Claim of the type: "A
pharmaceutical composition containing a medicament or drug and l-20
percent by weight of aluminum oxide and 5-20 percent by
weight of sodium bicarbonate" is properly classified under
the subclass. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 772]](../ps.gif) 772 772 | DESIGNATED ORGANIC NONACTIVE INGREDIENT CONTAINING OTHER THAN
HYDROCARBON: |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter wherein the composition contains a nonbioactive
organic compound.
| | (1)
Note. This and indented subclasses provide for compositions
which (a) do not contain a pharmacologically or
biologically active ingredient or which (b) are solely
disclosed or claimed as useful as inert additives or carriers for
an active ingredient of this class. For example: topical
preparations, e.g., face cream, etc., which
are not specifically provided for as special subclasses and which
do not contain a designated active ingredient are classified in
this and indented subclasses. |
| | (2)
Note. Within this subclass are compositions which
may contain an organic active ingredient which does not meet the
definition of the designated organic active ingredient (DOAI). |
| | (3)
Note. See section II, Glossary, for
the definition of "DOAI". |
| | (4)
Note. A claim of the type: "A
pharmaceutical composition containing a medicament or drug and 1-20
percent by weight glycerin, 1-10 percent by weight ethyl
alcohol and 5-10 percent by weight of an cationic surfactant" is
properly classified under this subclass. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 516, | Colloid Systems and Wetting Agents; Subcombinations
Thereof; Processes of Making, Stabilizing, Breaking, or Inhibiting, appropriate subclasses for subject matter relating
to: colloid systems (such as sols*, emulsions, dispersions, foams, aerosols, smokes, gels, or
pastes) or wetting agents (such as leveling, penetrating, or spreading); subcombination
compositions of colloid systems containing at least an agent specialized
and designed for or peculiar to use in making or stabilizing colloid
systems; compositions and subcombination compositions specialized
and designed for or peculiar to use in breaking (resolving) or
inhibiting colloid systems; processes of making the compositions
or systems of the class; processes of breaking (resolving) or inhibiting
colloid systems; in each instance, when generically
claimed or when there is no hierarchically superior provision in
the USPC for the specifically claimed art. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 772.1]](../ps.gif) 772.1 772.1 | Aftertreated solid synthetic organic polymer (e.g., grafting, blocking, etc.): |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 772. Subject matter wherein the designated organic nonactive
ingredient is a solid synthetic organic polymer which has been aftertreated, e.g., a
saponified starch acrylonitrile graft copolymer, polyacrylic
acid neutralized with sodium hydroxide, etc.
| | (1)
Note. The chemical after treatment of a solid synthetic
organic polymer may be to remove or add a group or element or a combination
of both procedures. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 522, | Synthetic Resins or Natural Rubbers, for the process of treating a solid polymer utilizing
wave energy. |
| 525, | Synthetic Resins or Natural Rubbers, appropriate subclasses for the aftertreatment of
solid synthetic organic polymers. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 772.2]](../ps.gif) 772.2 772.2 | Polyvinyl alcohol: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 772.1. Subject matter wherein the solid polymer is polyvinyl alcohol, e.g., obtained
from the hydrolysis of polyvinyl acetate or copolymers thereof, etc. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 772.3]](../ps.gif) 772.3 772.3 | Solid synthetic organic polymer: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 772. Subject matter wherein the designated organic nonactive
ingredient is a solid synthetic polymer, e.g., a
pharmaceutical preparation containing a bio-degradable
polymer derived from a monomer mixture comprising 2, 2-bis (epsilon-caprolactone-4-yl) propane, gamma-valerolactone
and epsilon-caprolactone, etc.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| 78.01+, | for a pharmaceutical composition which contains
a solid synthetic organic polymer which functions as a designated
organic active ingredient. |
| 78.08, | for a more thorough discussion on polymers which
are proper for Classes 424, 514, and Class 520
Series. |
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 522, | Synthetic Resins or Natural Rubbers, for the process of preparing a solid polymer utilizing
wave energy. |
| 526, | Synthetic Resins or Natural Rubbers, for the perparation of solid synthetic polymers
derived from ethylenic monomers only, e.g., acrylic
acid, etc. |
| 527, | Synthetic Resins or Natural Rubbers, for the preparation of solid synthetic polymers
derived from the reaction between a natural product and other chemical
intermediates, e.g., a carbohydrate
and polyisocyanate, a protein and an ethylenic reactant, etc. |
| 528, | Synthetic Resins or Natural Rubbers,
subclasses 1+ for the preparation of a solid synthetic polymer
derived from at least one saturated reactant, e.g., toluene
diisocyanate and polyethylene glycol, etc.; subclasses
480+ treating a solid polymer merely with heat. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 772.4]](../ps.gif) 772.4 772.4 | Polymer from ethylenic monomers only: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 772.3. Subject matter wherein the polymer is derived from ethylenic
monomers only, e.g., a self-microencapsulating
pesticidal composition contains polymethyl methacrylate, a
cosmetic moisturizing composition contains a copolymer from acrolein
and sodium acrylate, etc.
| | (1)
Note. See Class 424, subclass 78.17
for the definition of an ethylenic monomer. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 772.5]](../ps.gif) 772.5 772.5 | Heterocyclic monomer: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 772.4. Subject matter wherein the solid polymer is derived from
a heterocyclic monomer, e.g., a cosmetic
composition containing a copolymer derived from vinyl ether and
maleic anhydride, a cosmetic emulsion containing a copolymer derived
from vinylpyrrolidone, vinyl acetate, and vinyl
myristate, etc. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 772.6]](../ps.gif) 772.6 772.6 | Carboxylic acid containing monomer: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 772.4. Subject matter wherein the solid polymer is derived from
an ethylenically unsaturated monomer containing a carboxylic acid
group, e.g., acrylic acid, maleic
acid, fumaric acid, etc. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 773]](../ps.gif) 773 773 | Peptide containing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 772. Subject matter wherein the nonbioactive organic compound
is a peptide which is not degraded to the constituent amino acids, e.g., collagen, etc. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 777]](../ps.gif) 777 777 | Carbohydrate or lignin, or derivative: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 772. Subject matter wherein the nonbioactive organic compound
is a carbohydrate or lignin or derivative thereof wherein the carbon
skeleton of the carbohydrate is not destroyed except as noted below.
| | (1)
Note. Alcohols and acids corresponding to carbohydrates
are excluded from this subclass and compositions containing such
compounds are in appropriate subclasses below. |
| | (2)
Note. Lignin is a noncarbohydrate, polymeric
substance found in wood. It is isolated directly from
wood or wood products or from the compositions derived from the
treatment of wood, e.g., waste
sulfite liquor or black liquor. The structure of the lignin
monomer is not completely know. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 782]](../ps.gif) 782 782 | Natural gum or resin: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 772. Subject matter wherein the nonbioactive organic compound
is a natural gum or resin, e.g., natural
rubber, latex, rosin, etc. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 783]](../ps.gif) 783 783 | Plant extract or plant material of undetermined constitution: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 772. Subject matter wherein the nonbioactive organic compound
is a plant extract of plant product of undetermined chemical constitution including
essential oils.
| | (1)
Note. An extract is considered to be of determined
constitution when sufficient information as to its chemical structure is
available to permit classification based upon its chemical structure. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 786]](../ps.gif) 786 786 | Glyceride: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 785. Subject matter wherein the ester is derived from glycerol.
| | (1)
Note. The fats and oils and mainly triglycerides
of fatty acids, e.g., tripalmitin. | |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 788.1]](../ps.gif) 788.1 788.1 | SOLID SYNTHETIC ORGANIC POLYMER DERIVED SOLELY FROM HYDROCARBON
REACTANTS AS DESIGNATED ORGANIC NONACTIVE INGREDIENT CONTAINING: |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter wherein the composition contains a solid
synthetic organic polymer derived solely from hydrocarbon reactants, e.g., polystyrene, etc.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 424, | Drug, Bio-Affecting and Body
Treating Compositions,
subclasses 78.01+ for a pharmaceutical composition which contains
a solid synthetic organic polymer which functions as a designated
organic active ingredient; subclass 78.08 for
a more thorough discussion on polymers which are proper for Classes
424, 514 and 520 Series. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 789]](../ps.gif) 789 789 | MISCELLANEOUS (E.G., HYDROCARBONS, ETC.): |
| | This subclass is indented under the class definition. Subject matter not otherwise provided for, e.g., hydrocarbons, etc. |
| | |
CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS
| | (1)
Note. The following subclasses are collections of
published disclosures pertaining to various specified aspects relating to
drug, bioaffecting and body treating compositions and which
aspects do not form appropriate bases for subclasses in the foregoing
classification (i.e., subclasses
superior hetero in the schedule). These disclosures
relate to Class 514 subject matter only. |
| | (2)
Note. The general outline of the developed cross-reference
art collections is as follows:
| | (A)
Subclasses 800-809 provide for disclosures relating
to PEPTIDE AND PROTEIN. |
| | (B)
Subclasses 810-935 provide for disclosures drawn
to SPECIFICALLY DISCLOSES DISEASE CONDITION AND PHARMACEUTICAL EFFECT.
| | (1)
This are collection will take patents dating from January, 1965
to date, e.g., Classes 71, 424, 514, 260, and
the 530-570 series, etc. |
| | (2)
References crossed into this are collection should have specific, disclosed compositions
or examples of use. A mere statement or mention of a utility
or composition, unless actually claimed, is generally
insufficient. | |
| | (C)
Subclasses 936-975 are drawn to a number of various
art concepts.
| | (1)
Subclasses 936-947 drawn to LIQUID CARRIER, DILUENT
OR SOLVENT, subclasses 948-956 drawn to SOLID
CARRIER OR SOLID DILUENT, subclasses 957-959 drawn
to GASEOUS OR GAS EMITTING CARRIER OR PROPELLANT, subclasses 960-965
drawn to PILL, LOZENGE, TABLET OR CAPSULE, subclasses 966-969
drawn to SUPPOSITORY BOUGIE OR BASE, subclasses 970-975 drawn
to SPECIAL DESIGNATED INGREDIENT. |
| | (2)
These art collections provide (a) data from
Class 260 (Compounds) and Classes 530-570
series and Class 585 dating from January 1, 1965, (b) and data
from all other classes regardless of date. |
| | (3)
References crosses into these art collections should have
specific, disclosed compositions or methods where the inventive
concept or point of novelty resides in the carrier system, the
form of the composition or have designated ingredients, e.g., stabilizers, etc. | | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 800]](../ps.gif) 800 800 | LHRH LIKE: |
| | Subject matter involving a compositions containing peptides
that influence the release of lutenizing hormone. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 801]](../ps.gif) 801 801 | COLLAGEN, GELATIN OR DERIVATIVE THEREOF: |
| | Subject matter wherein the peptide composition contain collagen, gelatin
of derivative. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 802]](../ps.gif) 802 802 | FIBRINOPEPTIDES, BLOOD-COAGULATION FACTORS
OR DERIVATIVE: |
| | Subject matter wherein the peptide composition is related
to fibrinopeptides, blood-coagulation factors
or derivative. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 803]](../ps.gif) 803 803 | KININ OR DERIVATIVE: |
| | Subject matter wherein the peptide composition has Kinin-like
activities. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 804]](../ps.gif) 804 804 | PHLEOMYCIN SERIES OR DERIVATIVE: |
| | Subject matter containing a phleomycin peptide or derivative. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 805]](../ps.gif) 805 805 | ADRENOCORTICOTROPIC HORMONE OR DERIVATIVE: |
| | Subject matter involving peptide composition having adrenocorticotropic
activity. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 806]](../ps.gif) 806 806 | SOMATOSTATIN OR DERIVATIVE: |
| | Subject matter involving peptide compositions having somatostatin-like
activity. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 807]](../ps.gif) 807 807 | OXYTOXIN, VASOPRESSIN OR DERIVATIVE: |
| | Subject matter involving peptide composition related to
oxytoxin, vasopressin or a derivative thereof. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 808]](../ps.gif) 808 808 | CALCITONIN OR DERIVATIVES: |
| | Subject matter involving peptide composition related to
calcitonin or a derivative thereof. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 809]](../ps.gif) 809 809 | ENKEPHALIN, ENDORPHIN OR DERIVATIVES: |
| | Subject matter involving neurological peptides related to
enkephalin or endorphin. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 810]](../ps.gif) 810 810 | ADDICTION: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment of the state of being
devoted or given up to a practice or habit or to something habit
forming to the extent that cessation causes severe trauma. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 811]](../ps.gif) 811 811 | Alcohol: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 810. Subject matter wherein the addictive substance is alcohol. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 812]](../ps.gif) 812 812 | Narcotic: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 810. Subject matter wherein the addictive substance is a narcotic. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 813]](../ps.gif) 813 813 | Tobacco: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 810. Subject matter wherein the addictive substance is tobacco. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 814]](../ps.gif) 814 814 | ANEMIA: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment of anemia. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 816]](../ps.gif) 816 816 | ANESTHETIC, GENERAL: |
| | Subject matter involving a general anesthetic effect. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 817]](../ps.gif) 817 817 | ANESTHETIC, TOPICAL: |
| | Subject matter involving a topical anesthetic effect. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 818]](../ps.gif) 818 818 | ANESTHETIC, LOCAL: |
| | Subject matter involving a local anesthetic effect. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 819]](../ps.gif) 819 819 | ANTACID, ORAL: |
| | Subject matter involving an antacid effect when administered
orally. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 821]](../ps.gif) 821 821 | ANTIARRHYTHMIC: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment or prevention of
arrhythmia in a patient in need thereof. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 822]](../ps.gif) 822 822 | ANTICOAGULATION: |
| | Subject matter involving an anticoagulation effect. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 823]](../ps.gif) 823 823 | ANTIDOTE: |
| | Subject matter involving an antidote (prevents or
counteracts) for a poison or other noxious substance. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 824]](../ps.gif) 824 824 | ARTERIOSCLEROSIS: |
| | Subject matter involving treatment of arteriosclerosis. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 825]](../ps.gif) 825 825 | ARTHRITIS: |
| | Subject matter involving treatment of arthritis. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 826]](../ps.gif) 826 826 | ASTHMA: |
| | Subject matter involving treatment or alleviation of the
symptoms of asthma. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 827]](../ps.gif) 827 827 | ASTRINGENT, NONFACIAL: |
| | Subject matter involving an astringent effect. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 829]](../ps.gif) 829 829 | BITE OR STING: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment or alleviation of
discomfort or other symptoms caused by a bite or sting. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 830]](../ps.gif) 830 830 | Insect: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 829. Subject matter wherein the bite or sting is from an insect. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 832]](../ps.gif) 832 832 | BLOOD SUBSTITUTE: |
| | Subject matter involving a substance which is a substitute
for blood or blood component. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 833]](../ps.gif) 833 833 | BLOOD PLASMA EXTENDER: |
| | Subject matter involving extending or increasing the amount
of blood plasma in a patient in need thereof. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 834]](../ps.gif) 834 834 | COAGULANT: |
| | Subject matter involving the enhancing of coagulation. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 835]](../ps.gif) 835 835 | CARIES: |
| | Subject matter involving treatment or prevention of caries. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 836]](../ps.gif) 836 836 | CHELATE: |
| | Subject matter involving a material which acts as a chelating
agent. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 837]](../ps.gif) 837 837 | CHOLERA: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment or prevention of
cholera. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 838]](../ps.gif) 838 838 | CIRRHOSIS: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment or alleviation of
the symptoms of cirrhosis of the liver. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 839]](../ps.gif) 839 839 | CONTACT LENS TREATMENT: |
| | Subject matter involving treatment of contact lens such
as sterilization or cleaning. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 841]](../ps.gif) 841 841 | CONTRACEPTIVE: |
| | Subject matter involving prevention of conception. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 842]](../ps.gif) 842 842 | Nonmammal: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 841. Subject matter wherein conception is prevented in nonmammals, e.g., insects, etc. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 844]](../ps.gif) 844 844 | COSMETIC, FACIAL: |
| | Subject matter involving facial cosmetics. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 849]](../ps.gif) 849 849 | COUGH AND COLD PREPARATION: |
| | Subject matter involving relief of the symptoms of a cough
or a cold. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 851]](../ps.gif) 851 851 | CYSTIC FIBROSIS: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment or prevention of
cystic fibrosis. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 852]](../ps.gif) 852 852 | DANDRUFF: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment or prevention of
dandruff. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 853]](../ps.gif) 853 853 | DECONGESTANT: |
| | Subject matter involving a decongestant effect. |
| | |
| | DERMATITIS: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment of the skin and problems
related thereto. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 858]](../ps.gif) 858 858 | Athlete"s foot: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment or prevention of
athlete"s foot fungus. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 859]](../ps.gif) 859 859 | Acne: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment or prevention of
acne. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 860]](../ps.gif) 860 860 | Cellulitis: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment of a cellulitis condition. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 861]](../ps.gif) 861 861 | Eczema: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment of eczema. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 863]](../ps.gif) 863 863 | Psoriasis: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment or prevention of
psoriasis. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 864]](../ps.gif) 864 864 | Seborrhea: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment or prevention of
seborrhea. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 865]](../ps.gif) 865 865 | Diaper rash: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment or prevention of
diaper rash. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 866]](../ps.gif) 866 866 | DIABETES: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment or prevention of
diabetes. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 867]](../ps.gif) 867 867 | DIARRHEA: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment or alleviation of
the symptoms of diarrhea in animals. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 868]](../ps.gif) 868 868 | DISTEMPER: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment or prevention of
distemper. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 869]](../ps.gif) 869 869 | DIURETIC: |
| | Subject matter involving substances which yield a diuretic
effect. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 870]](../ps.gif) 870 870 | EDEMA: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment or prevention of
edema. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 871]](../ps.gif) 871 871 | Topical: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 870. Subject matter wherein the treatment of prevention calls
for topical application. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 872]](../ps.gif) 872 872 | EMESIS (MOTION SICKNESS-NAUSEA): |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment or prevention of
emesis. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 873]](../ps.gif) 873 873 | EMOLLIENT: |
| | Subject matter involving a specified emollient. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 874]](../ps.gif) 874 874 | ESTROGENIC AGENT (NONCONTRACEPTIVE): |
| | Subject matter involving a chemical agent used to obtain
an estrogenic effect when administered to a patient. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 875]](../ps.gif) 875 875 | FLEA CONTROL: |
| | Subject matter involving the control or prevention of fleas. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 876]](../ps.gif) 876 876 | Collar type: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 875. Subject matter wherein the control and prevention is obtained
from a collar type structure. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 877]](../ps.gif) 877 877 | GALLSTONE: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment or prevention of
gallstone. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 878]](../ps.gif) 878 878 | GERIATRICS: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment or prevention of
problems associated with aging. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 880]](../ps.gif) 880 880 | HAIR TREATMENT (THERAPEUTIC-SCALP): |
| | Subject matter involving application to the head or scalp
of a therapeutic composition. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 881]](../ps.gif) 881 881 | Shampoo: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 880. Subject matter wherein the composition is applied in the
form of a shampoo. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 882]](../ps.gif) 882 882 | HEMORRHOID PREPARATION: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment or alleviation of
symptoms of hemorrhoids. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 883]](../ps.gif) 883 883 | HODGKIN"S DISEASE: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment or prevention of
Hodgkin"s disease. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 884]](../ps.gif) 884 884 | HYPOGLYCEMIA: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment or prevention of
hypoglycemia. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 885]](../ps.gif) 885 885 | IMMUNE RESPONSE AFFECTING DRUG: |
| | Subject matter involving the enhancing or reducing of an
immune response in a patient. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 886]](../ps.gif) 886 886 | INFLAMMATION, SKIN: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment of skin inflammation. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 888]](../ps.gif) 888 888 | INFLUENZA: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment or prevention of
influenza. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 889]](../ps.gif) 889 889 | INTERFERON INDUCER: |
| | Subject matter involving the inducement of the production
of interferon. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 890]](../ps.gif) 890 890 | IRRITANT (E.G., TEAR
GAS, ETC.): |
| | Subject matter involving production of an irritating effect. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 891]](../ps.gif) 891 891 | KIDNEY STONE: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment or prevention of
kidney stone. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 892]](../ps.gif) 892 892 | LAXATIVE: |
| | Subject matter involving the inducement of a laxative effect
in a subject needing said treatment. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 893]](../ps.gif) 893 893 | LIVER DISORDER: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment of liver disorder (excludes
cirrhosis of the liver). |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 895]](../ps.gif) 895 895 | MALARIA: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment or prevention of
malaria. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 896]](../ps.gif) 896 896 | MEASLES: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment or prevention of
measles. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 897]](../ps.gif) 897 897 | Rubella: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 896. Subject matter wherein the type of measles to be treated
is rubella. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 898]](../ps.gif) 898 898 | MENINGITIS: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment or prevention of
meningitis. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 899]](../ps.gif) 899 899 | MENSTRUAL DISORDER: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment, prevention
or alleviation of symptoms of a menstrual disorder. |
| | |
| | MOUTH TREATMENT: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment of the mouth. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 900]](../ps.gif) 900 900 | Periodontitis: |
| | Subject matter under mouth treatment involving the treatment
or prevention of periodontitis. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 901]](../ps.gif) 901 901 | Mouthwash: |
| | Subject matter under mouth treatment involving the use of
a mouthwash. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 902]](../ps.gif) 902 902 | Gingival: |
| | Subject matter under mouth treatment involving the treatment
or prevention of disorders of the gingiva. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 903]](../ps.gif) 903 903 | MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment, prevention
or alleviation of symptoms of multiple sclerosis. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 904]](../ps.gif) 904 904 | MULTIPLE VITAMINS: |
| | Subject matter involving a composition which contains two
or more vitamins. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 905]](../ps.gif) 905 905 | With mineral: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 904. Subject matter wherein the multiple vitamin composition
also contains one or more minerals. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 906]](../ps.gif) 906 906 | MUSCLE RELAXANT: |
| | Subject matter involving a muscle relaxing effect. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 907]](../ps.gif) 907 907 | MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment, prevention
or alleviation of symptoms of muscular dystrophy. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 908]](../ps.gif) 908 908 | LEUKEMIA: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment or prevention of
leukemia. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 909]](../ps.gif) 909 909 | OBESITY: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment of obesity. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 910]](../ps.gif) 910 910 | Anorectic: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 909. Subject matter wherein the treatment is a chemical means
for reduction or suppression of appetite. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 912]](../ps.gif) 912 912 | OPHTHALMIC: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment of an ophthalmic
disorder. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 915]](../ps.gif) 915 915 | Wetting agent: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 912. Subject matter wherein a composition acts as a wetting agent
or an artificial tear. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 916]](../ps.gif) 916 916 | PYRETIC: |
| | Subject matter involving alleviating fever. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 917]](../ps.gif) 917 917 | RADIOACTIVE, ANTI-: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment or counter-acting
of the effect of exposure to a radioactive substance or source. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 918]](../ps.gif) 918 918 | REPELLENT: |
| | Subject matter involving the repelling of a living organism
from any site or locus. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 919]](../ps.gif) 919 919 | Insect: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 918. Subject matter wherein the organism beign repelled is an
insect. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 920]](../ps.gif) 920 920 | Mammal: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 918. Subject matter wherein the organism being repelled is a
mammal. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 921]](../ps.gif) 921 921 | SHOCK: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment of shock in a patient. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 922]](../ps.gif) 922 922 | SIDE EFFECT REDUCTION BY INCORPORATION OF A SECOND DESIGNATED
INGREDIENT: |
| | Subject matter involving the reducing or eliminating of
an undesirable side effect of a given drug by concurrent administration
of a second designated compound. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 923]](../ps.gif) 923 923 | SLEEP AID (INSOMNIA): |
| | Subject matter involving inducing sleep. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 924]](../ps.gif) 924 924 | TUBERCULOSIS: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment or prevention of
tuberculosis. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 925]](../ps.gif) 925 925 | ULCER TREATMENT: |
| | Subject matter involving the treatment, alleviation
of symptoms or prevention of an ulcer. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 926]](../ps.gif) 926 926 | Duodenal: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 925. Subject matter wherein the ulcer is in the duodenal area
of the digestive tract. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 929]](../ps.gif) 929 929 | VASODILATOR: |
| | Subject matter involving a dilation of the blood vessels
on administration. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 930]](../ps.gif) 930 930 | VASOCONSTRICTOR (NONDECONGESTANT): |
| | Subject matter involving a constriction of the blood vessels. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 931]](../ps.gif) 931 931 | VENEREAL DISEASE: |
| | Subject matter involving treatment, alleviation of
symptoms or prevention of a venereal disease. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 934]](../ps.gif) 934 934 | Virus: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 931. Subject matter wherein the venereal disease is viral. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 935]](../ps.gif) 935 935 | UTERINE MOTILITY: |
| | Subject matter involving the increasing of fertility by
increasing uterine motility. |
| | |
| | LIQUID CARRIER, DILUENT OR SOLVENT |
| | Specifically disclosed composition or method where the inventive
concept or point of novelty resides in the carrier system which
is in liquid form. This area of the art collection also includes
those disclosures wherein specified ingredients are disclosed for
the purpose of describing the carrier system used in combination
with an active ingredient. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 936]](../ps.gif) 936 936 | DMSO CONTAINING: |
| | Subject matter involving using a composition which contains
dimethyl sulfoxide as a designated nonactive ingredient. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 937]](../ps.gif) 937 937 | DISPERSION OR EMULSION: |
| | Subject matter involving a composition in the form of a
dispersion or emulsion.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 516, | Colloid Systems and Wetting Agents; Subcombinations
Thereof; Processes of Making, Stabilizing, Breaking, or Inhibiting,
subclasses 9+ for continuous liquid phase colloid systems (e.g., foams, emulsions, suspensions, dispersions) or
agents for such systems or making or stabilizing such systems or
agents, when generically claimed or when there is no hierarchically superior
provision in the USPC for the specifically claimed art. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 938]](../ps.gif) 938 938 | Oil-water type: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 937. Subject matter wherein the dispersion or emulsion contains
both an oil and water. This subclass covers both oil-in-water
and water-in-oil type emulsions.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 516, | Colloid Systems and Wetting Agents; Subcombinations
Thereof; Processes of Making, Stabilizing, Breaking, or Inhibiting,
subclasses 9+ for continuous liquid phase colloid systems (e.g., foams, emulsions, suspensions, dispersions) or
agents for such systems or making or stabilizing such systems or
agents, when generically claimed or when there is no hierarchically superior
provision in the USPC for the specifically claimed art. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 939]](../ps.gif) 939 939 | Mineral oil-water type: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 938. Subject matter wherein the oil is mineral oil.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 516, | Colloid Systems and Wetting Agents; Subcombinations
Thereof; Processes of Making, Stabilizing, Breaking, or Inhibiting,
subclasses 9+ for continuous liquid phase colloid systems (e.g., foams, emulsions, suspensions, dispersions) or
agents for such systems or making or stabilizing such systems or
agents, when generically claimed or when there is no hierarchically superior
provision in the USPC for the specifically claimed art. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 940]](../ps.gif) 940 940 | Quick break type: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 939. Subject matter wherein the mineral oil emulsion is of the
quick breaking type.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 516, | Colloid Systems and Wetting Agents; Subcombinations
Thereof; Processes of Making, Stabilizing, Breaking, or Inhibiting,
subclasses 9+ for continuous liquid phase colloid systems (e.g., foams, emulsions, suspensions, dispersions) or
agents for such systems or making or stabilizing such systems or
agents, when generically claimed or when there is no hierarchically superior
provision in the USPC for the specifically claimed art. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 941]](../ps.gif) 941 941 | Polyoxyalkylated compound containing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 939. Subject matter wherein the emulsion contains a polyoxyalkylated
compound as the emulsifying agent.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 516, | Colloid Systems and Wetting Agents; Subcombinations
Thereof; Processes of Making, Stabilizing, Breaking, or Inhibiting,
subclasses 9+ for continuous liquid phase colloid systems (e.g., foams, emulsions, suspensions, dispersions) or
agents for such systems or making or stabilizing such systems or
agents, when generically claimed or when there is no hierarchically superior
provision in the USPC for the specifically claimed art. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 942]](../ps.gif) 942 942 | Organic sulfonate, sulfate or sulfite containing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 939. Subject matter wherein the emulsion contains an organic
sulfonate, sulfate or sulfite compound as the emulsifying
agent.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 516, | Colloid Systems and Wetting Agents; Subcombinations
Thereof; Processes of Making, Stabilizing, Breaking, or Inhibiting,
subclasses 9+ for continuous liquid phase colloid systems (e.g., foams, emulsions, suspensions, dispersions) or
agents for such systems or making or stabilizing such systems or
agents, when generically claimed or when there is no hierarchically superior
provision in the USPC for the specifically claimed art. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 943]](../ps.gif) 943 943 | Higher fatty acid or derivative containing: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 939. Subject matter wherein the emulsion contains a higher fatty
acid or a derivative thereof as the emulsifying agent.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 516, | Colloid Systems and Wetting Agents; Subcombinations
Thereof; Processes of Making, Stabilizing, Breaking, or Inhibiting,
subclasses 9+ for continuous liquid phase colloid systems (e.g., foams, emulsions, suspensions, dispersions) or
agents for such systems or making or stabilizing such systems or
agents, when generically claimed or when there is no hierarchically superior
provision in the USPC for the specifically claimed art. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 944]](../ps.gif) 944 944 | GEL: |
| | Subject matter involving a gel form and containing specified
ingredients to give a gel.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 516, | Colloid Systems and Wetting Agents; Subcombinations
Thereof; Processes of Making, Stabilizing, Breaking, or Inhibiting,
subclasses 98+ for colloid systems of continuous or semicontinuous
solid phase with discontinuous liquid phase (gels, pastes, flocs, coagulates) or
agents for such systems or making or stabilizing such systems or agents, when
generically claimed or when there is no hierarchically superior
provision in the USPC for the specifically claimed art. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 945]](../ps.gif) 945 945 | FOAM: |
| | Subject matter involving a foam and containing specified
ingredients to form said foam.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 516, | Colloid Systems and Wetting Agents; Subcombinations
Thereof; Processes of Making, Stabilizing, Breaking, or Inhibiting,
subclasses 10+ for foam colloid systems or agents for such systems
or making or stabilizing such systems or agents, when generically claimed
or when there is no hierarchically superior provision in the USPC for
the specifically claimed art. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 946]](../ps.gif) 946 946 | PENETRANT OR ABSORBENT (ENHANCES PENETRATION INTO
SUBJECT TREATED): |
| | Subject matter involving the increasing or enhancing of
the rate or amount of active ingredient absorbed into the treated
subject. This includes topical application as well as
absorption through the digestive tract.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 516, | Colloid Systems and Wetting Agents; Subcombinations
Thereof; Processes of Making, Stabilizing, Breaking, or Inhibiting,
subclasses 198+ for wetting agents (e.g., spreading, penetrating, leveling) or
methods of making such agents, when generically claimed
or when there is no hierarchically superior provision in the USPC for
the specifically claimed art. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 947]](../ps.gif) 947 947 | Topical application: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 946. Subject matter wherein application is to the skin and absorption
is through the skin.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 516, | Colloid Systems and Wetting Agents; Subcombinations
Thereof; Processes of Making, Stabilizing, Breaking, or Inhibiting,
subclasses 198+ for wetting agents (e.g., spreading, penetrating, leveling) or
methods of making such agents, when generically claimed
or when there is no hierarchically superior provision in the USPC for
the specifically claimed art. |
|
| | |
| | SOLID CARRIER OR SOLID DILUENT |
| | Specifically disclosed composition or method where the inventive
concept or point of novelty resides in the carrier system which
is in the form of a solid. This area of the art collection also
includes those disclosures wherein specified ingredients are disclosed
for the purpose of describing the carrier system used in combination
with an active ingredient. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 948]](../ps.gif) 948 948 | SOLID CANDY TYPE: |
| | Subject matter involving an active ingredient in combination
with a candy type base or carrier system. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 949]](../ps.gif) 949 949 | NATURALLY DERIVED CLAY (E.G., BENTONITE, ETC.): |
| | Subject matter involving the use of a natural clay as a
solid carrier component. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 950]](../ps.gif) 950 950 | MACROMOLECULAR (OTHER THAN SYNTHETIC RESINS): |
| | Subject matter involving a solid carrier component which
is a high molecular weight polymeric type material. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 951]](../ps.gif) 951 951 | POWDERS, GRANULES OR PARTICLES OF SPECIFIED MESH
OR PARTICLE SIZE: |
| | Subject matter involving a composition in which an active
ingredient is in combination with a solid carrier in the form of
a powder, granule or particle of specified particle size
or shape. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 952]](../ps.gif) 952 952 | Wettable: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 951. Subject matter wherein the particles, powder or granules
are intended to be readily mixed with water or other solvent. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 953]](../ps.gif) 953 953 | SHAPED FORMS ADAPTED FOR NONINGESTIBLE USE OTHER THAN SUPPOSITORY
TYPE (E.G., FILMS, INSERTS, ETC.): |
| | Subject matter involving an active ingredient in combination
with a solid carrier having a designated shape or form. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 954]](../ps.gif) 954 954 | Ocular: |
| | This subclass is indented under subclass 953. Subject matter wherein the composition is for application
to the eye. |
| | |
| | GASEOUS OR GAS EMITTING CARRIER OR PROPELLANT |
| | Specifically disclosed composition or method where the inventive
concept or point of novelty resides in the carrier system which
is either gaseous or gas emitting. This area of the art collection
also includes those disclosures wherein specified ingredients are
disclosed for the purpose of describing the carrier system. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 957]](../ps.gif) 957 957 | VAPOR EMITTING COMPOSITION: |
| | Subject matter involving application or distribution of
an active ingredient using a vapor or gas.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 516, | Colloid Systems and Wetting Agents; Subcombinations
Thereof; Processes of Making, Stabilizing, Breaking, or Inhibiting,
subclasses 1+ for continuous gas or vapor phase colloid system (e.g., smoke, fog, aerosol, cloud, mist) or
agents for such systems or making or stabilizing such systems or
agents, when generically claimed or when there is no hierarchically
superior provision in the USPC for the specifically claimed art. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 958]](../ps.gif) 958 958 | FOR SMOKING OR INHALING: |
| | Subject matter involving a combination of an active ingredient
with a carrier system which allows administration by smoking or
inhaling.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 516, | Colloid Systems and Wetting Agents; Subcombinations
Thereof; Processes of Making, Stabilizing, Breaking, or Inhibiting,
subclasses 1+ for continuous gas or vapor phase colloid system (e.g., smoke, fog, aerosol, cloud, mist) or
agents for such systems or making or stabilizing such systems or
agents, when generically claimed or when there is no hierarchically
superior provision in the USPC for the specifically claimed art. |
|
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 959]](../ps.gif) 959 959 | BREATHING GASES: |
| | Subject matter involving inhalation of a breathing gas such
as oxygen containing gas and supplements thereto.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| 516, | Colloid Systems and Wetting Agents; Subcombinations
Thereof; Processes of Making, Stabilizing, Breaking, or Inhibiting,
subclasses 1+ for continuous gas or vapor phase colloid system (e.g., smoke, fog, aerosol, cloud, mist) or
agents for such systems or making or stabilizing such systems or
agents, when generically claimed or when there is no hierarchically
superior provision in the USPC for the specifically claimed art. |
|
| | |
| | PILL, LOZENGE, TABLET OR CAPSULE |
| | Specifically disclosed composition or method where the inventive
concept or point of novelty resides in the carrier system which
takes the form of a pill, lozenge, tablet or capsule.
This area of the art collection also includes those disclosures
wherein specified ingredients are dissolved for the purpose of describing
this form of carrier system used in combination with an active ingredient. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 960]](../ps.gif) 960 960 | SIGNIFICANT TABLET FORMULATION (E.G., DESIGNATED
EXCIPIENT, DISINTEGRANT, GLYDENT OR LUBRICANT, ETC.): |
| | Subject matter involving designated nonactive ingredient
which involves in a tableting process. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 962]](../ps.gif) 962 962 | CAPSULE (E.G., GELATIN, ETC.): |
| | Subject matter involving a capsuling material or composition. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 964]](../ps.gif) 964 964 | SUSTAINED OR DIFFERENTIAL RELEASE TYPE: |
| | Subject matter involving a combination of an active ingredient
and a carrier system which permits or results in a sustained or
diffeential release of said active ingredient. |
| | |
| | SUPPOSITORY BOUGIE BASE |
| | Specifically disclosed composition or method of preparation
wherein the composition is in the form of a suppository, bougy
or a base therefor. The group takes only those references wherein
the inventive concept or point of novelty resides in the make-up
of the carrier system rather than the active ingredient. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 966]](../ps.gif) 966 966 | RECTAL: |
| | Subject matter involving a form for rectal administration. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 967]](../ps.gif) 967 967 | VAGINAL: |
| | Subject matter involving a form for vaginal application
or administration. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 968]](../ps.gif) 968 968 | URETHRAL: |
| | Subject matter involving a form for urethral application
or administration. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 969]](../ps.gif) 969 969 | OINTMENT OR SALVE BASE: |
| | Subject matter involving a base which is to be combined
with an active ingredient to give an ointment or salve base. |
| | |
| | SPECIAL DESIGNATED INGREDIENT |
| | Specifically disclosed or claimed composition or preparation
which contains, in addition to the active ingredient, at
least one special designated ingredient which has a purpose or is
present other than as a carrier or excipient. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 970]](../ps.gif) 970 970 | CONTAINING DESIGNATED INGREDIENT TO STABILIZE AN ACTIVE
INGREDIENT: |
| | Subject matter involving a designated ingredient which will
act to stabilize an active ingredient. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 974]](../ps.gif) 974 974 | CONTAINING DESIGNATED INGREDIENT TO REDUCE NOXIOUS EFFECTS OF
ACTIVE INGREDIENT (E.G., TASTE, MASKING, ODOR
REDUCING, ETC.): |
| | Subject matter involving a designated ingredient which is
intended to reduce the noxious effects of the active ingredient
present. |
| | |
![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 975]](../ps.gif) 975 975 | CHARACTERIZED BY TYHE DESIGNATED SURFACTANT USED: |
| | Subject matter involving a designated ingredient which is
to act as a surfactant. |
| | |
FOREIGN ART COLLECTIONS
The definitions below correspond to abolished subclasses
from which these collections were formed. See the Foreign
Art Collection schedule of this class for specific correspondence. [Note: The
titles and definitions for indented art collections include all
the details of the one(s) that are hierarchically
superior. |
| FOR 100 | 1,2 or 1,4-diazine compound
having two or more hetero rings: |
| | Foreign art collection which is a 1,2 or
1,4-diazine which has heterocyclic substituent. |
| | |
| FOR 101 | Hetero other than 1,2 or 1,4-diazine
is part of a polycyclo ring system: |
| | Foreign art collection wherein the heterocyclic
substituent is part of a polycyclo substituent. |
| | |
| FOR 102 | Diazine is bonded directly to the polycyclo ring system: |
| | Foreign art collection wherein the 1,2
or the 1,4 diazine is bonded directly to the polycyclo
ring system. |
| | |
| FOR 103 | 1,4-diazines: |
| | Foreign art collection in which the ring nitrogen
occupy the 1, and the 4-positions of the diazine
nucleus. |
| | |
| FOR 104 | Hetero ring is four-membered and includes at
least one nitrogen: |
| | Foreign art collection which contains a heterocyclic
ring consisting of four atoms, at least one of which is
nitrogen.
| | (1)
Note. The heterocyclic ring may include other hetero
atoms of the group set forth in the definition of subclass 183 and
the relative positions of the hetero atoms may vary. | |
| | |
| FOR 105 | Hetero ring is seven-membered and includes at
least one nitrogen and at least one hetero atom other than nitrogen: |
| | Foreign art collection which contains a heterocyclic
ring consisting of seven atoms, at least one of which is
nitrogen and at least one other hetero atom, other than
nitrogen.
| | (1)
Note. See Glossary for definition of het atom. | |
| | |
| FOR 106 | Hetero ring is seven-membered consisting of one
nitrogen and six carbon atoms: |
| | Foreign art collection which contains a seven-mem
heterocyclic ring consisting of six carbon atoms and one nitrogen
atom. |
| | |
| FOR 107 | Polycyclic ring system having the seven-membered
hetero ring as one of the cyclos: |
| | Foreign art collection wherein the seven-membered
hetero ring is one of the cyclos of a polycyclo ring system. |
| | |
| FOR 108 | Ring nitrogen is shared by two or three of the cyclos: |
| | Foreign art collection wherein the ring nitrogen
of the seven-membered hetero ring is also a member of one
or two additional cyclos in the polycyclo ring system. |
| | |
| FOR 109 | Peptide containing (e.g., protein, peptones, fibrinogen, etc.) DOAI: |
| | Foreign art collection which contains a protein
or its reaction product, e.g., peptides, peptones, fibrinogen, etc., wherein
the protein molecule is not degraded to the constituent amino-acids.
| | (1)
Note. The term "peptide unit" used herein
is intended to mean the group N-C-(=O) or
beta-alanine. | |
| | |
| FOR 110 | Insulin or derivative: |
| | Foreign art collection identical to the extract of
the pancreas, known as insulin or a derivative thereof, in
which neither a peptide chain nor a disulfide link between chains
is broken.
| | (1)
Note. While the position and/or kind of amino
acids in the chain(s) may vary (depending
on the animal from which derived), it appears
that insulin contains at least an "A" chain of
21 acid units linked by disulfide moieties to a "B." An additional
disulfide moiety bridges the 6 and 11 positions of chain A. | |
| | |
| FOR 111 | With an additional active ingredient: |
| | Foreign art collection which contains insulin and
an additional active ingredient.
| | (1)
Note. For this subclass, an organic potentiator
for insulin is considered an active ingredient. | |
| | |
| FOR 112 | Iodine containing: |
| | Foreign art collection in which the peptide moiety
contains iodine or the peptide moiety is reacted with or complexed
to iodine containing compound. |
| | |
| FOR 113 | Heavy metal containing (e.g., hemoglobin, etc.): |
| | Foreign art collection which contains a heavy metal
atom.
| | (1)
Note. See Glossary for a definition of the term "heavy
metal." | |
| | |
| FOR 114 | Phosphorus containing: |
| | Foreign art collection which contains phosphorus
in the peptide compound. |
| | |
| FOR 115 | Glycoprotein (carbohydrate containing): |
| | Foreign art collection which contains a carbohydrate
or derivative thereof attached to the peptide. |
| | |
| FOR 116 | Cyclopeptides: |
| | Foreign art collection wherein the amino acid chain
forms a cyclic structure; said cyclo structures can be
formed by peptide bonding, disulfide bonding, hydrocarbon bonding
or other types of connection that define the cyclo structures as
having at least a dipeptide as an integral part thereof. |
| | |
| FOR 117 | Bicyclic: |
| | Foreign art collection wherein a compound has two
cyclic groups containing an amino acid chain. |
| | |
| FOR 118 | Monocyclic: |
| | Foreign art collection wherein a compound has only
one cyclic group containing an amino acid chain. |
| | |
| FOR 119 | 25 or more peptide repeating units in known peptide chain
structure: |
| | Foreign art collection wherein a peptide chain has
25 or more peptide units in an uninterrupted chain. |
| | |
| FOR 120 | 16 to 24 peptide repeating units in known peptide chain: |
| | Foreign art collection which contains an uninterrupted
peptide chain of 16 to 24 peptide units. |
| | |
| FOR 121 | 12 to 15 peptide repeating units in known peptide chain: |
| | Foreign art collection which contains an uninterrupted
peptide chain of 12 to 15 peptide units. |
| | |
| FOR 122 | 9 to 11 peptide repeating units in known peptide chain: |
| | Foreign art collection which contains an uninterrupted
peptide chain of 9 to 11 peptide units. |
| | |
| FOR 123 | 7 or 8 peptide repeating units in known peptide chain: |
| | Foreign art collection which contains an uninterrupted
peptide chain of 7 or 8 peptide units. |
| | |
| FOR 124 | 5 or 6 peptide repeating units in known peptide chain: |
| | Foreign art collection which contains an uninterrupted
peptide chain of 5 or 6 peptide units. |
| | |
| FOR 125 | 3 or 4 peptide repeating units in known peptide chain: |
| | Foreign art collection which contains an uninterrupted
peptide chain of 3 or 4 peptide units. |
| | |
| FOR 126 | 2 peptide repeating units in known peptide chain: |
| | Foreign art collection which contains an uninterrupted
peptide chain of 2 peptide units. |
| | |
| FOR 127 | Guanidine containing: |
| | Foreign art collection wherein the peptide compound
contains the guanidine group. |
| | |
| FOR 128 | Produced by or extracted from animal tissue: |
| | Foreign art collection which is derived from
animal material. |
| | |
![[Search a list of Patent Appplications for class 514]](../as.gif) CLASS 514,
CLASS 514,

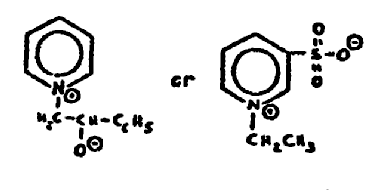
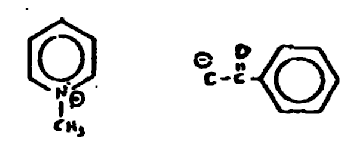






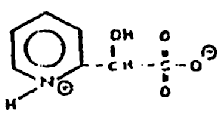





![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 1]](../ps.gif) 1
1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 1.1]](../ps.gif) 1.1
1.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 1.2]](../ps.gif) 1.2
1.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 1.3]](../ps.gif) 1.3
1.3![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 1.4]](../ps.gif) 1.4
1.4![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 1.5]](../ps.gif) 1.5
1.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 1.6]](../ps.gif) 1.6
1.6![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 1.7]](../ps.gif) 1.7
1.7![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 1.8]](../ps.gif) 1.8
1.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 1.9]](../ps.gif) 1.9
1.9![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 2.1]](../ps.gif) 2.1
2.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 2.2]](../ps.gif) 2.2
2.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 2.3]](../ps.gif) 2.3
2.3![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 2.4]](../ps.gif) 2.4
2.4![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 2.5]](../ps.gif) 2.5
2.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 2.6]](../ps.gif) 2.6
2.6![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 2.7]](../ps.gif) 2.7
2.7![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 2.8]](../ps.gif) 2.8
2.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 2.9]](../ps.gif) 2.9
2.9![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 3.1]](../ps.gif) 3.1
3.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 3.2]](../ps.gif) 3.2
3.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 3.3]](../ps.gif) 3.3
3.3![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 3.4]](../ps.gif) 3.4
3.4![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 3.5]](../ps.gif) 3.5
3.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 3.6]](../ps.gif) 3.6
3.6![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 3.7]](../ps.gif) 3.7
3.7![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 3.8]](../ps.gif) 3.8
3.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 3.9]](../ps.gif) 3.9
3.9![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 4.1]](../ps.gif) 4.1
4.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 4.2]](../ps.gif) 4.2
4.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 4.3]](../ps.gif) 4.3
4.3![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 4.4]](../ps.gif) 4.4
4.4![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 4.5]](../ps.gif) 4.5
4.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 4.6]](../ps.gif) 4.6
4.6![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 4.7]](../ps.gif) 4.7
4.7![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 4.8]](../ps.gif) 4.8
4.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 4.9]](../ps.gif) 4.9
4.9![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 5.1]](../ps.gif) 5.1
5.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 5.2]](../ps.gif) 5.2
5.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 5.3]](../ps.gif) 5.3
5.3![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 5.4]](../ps.gif) 5.4
5.4![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 5.5]](../ps.gif) 5.5
5.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 5.6]](../ps.gif) 5.6
5.6![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 5.7]](../ps.gif) 5.7
5.7![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 5.8]](../ps.gif) 5.8
5.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 5.9]](../ps.gif) 5.9
5.9![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 6.1]](../ps.gif) 6.1
6.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 6.2]](../ps.gif) 6.2
6.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 6.3]](../ps.gif) 6.3
6.3![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 6.4]](../ps.gif) 6.4
6.4![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 6.5]](../ps.gif) 6.5
6.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 6.6]](../ps.gif) 6.6
6.6![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 6.7]](../ps.gif) 6.7
6.7![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 6.8]](../ps.gif) 6.8
6.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 6.9]](../ps.gif) 6.9
6.9![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 7.1]](../ps.gif) 7.1
7.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 7.2]](../ps.gif) 7.2
7.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 7.3]](../ps.gif) 7.3
7.3![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 7.4]](../ps.gif) 7.4
7.4![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 7.5]](../ps.gif) 7.5
7.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 7.6]](../ps.gif) 7.6
7.6![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 7.7]](../ps.gif) 7.7
7.7![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 7.8]](../ps.gif) 7.8
7.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 7.9]](../ps.gif) 7.9
7.9![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 8.1]](../ps.gif) 8.1
8.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 8.2]](../ps.gif) 8.2
8.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 8.3]](../ps.gif) 8.3
8.3![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 8.4]](../ps.gif) 8.4
8.4![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 8.5]](../ps.gif) 8.5
8.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 8.6]](../ps.gif) 8.6
8.6![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 8.7]](../ps.gif) 8.7
8.7![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 8.8]](../ps.gif) 8.8
8.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 8.9]](../ps.gif) 8.9
8.9![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 9.1]](../ps.gif) 9.1
9.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 9.2]](../ps.gif) 9.2
9.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 9.3]](../ps.gif) 9.3
9.3![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 9.4]](../ps.gif) 9.4
9.4![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 9.5]](../ps.gif) 9.5
9.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 9.6]](../ps.gif) 9.6
9.6![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 9.7]](../ps.gif) 9.7
9.7![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 9.8]](../ps.gif) 9.8
9.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 9.9]](../ps.gif) 9.9
9.9![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 10.1]](../ps.gif) 10.1
10.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 10.2]](../ps.gif) 10.2
10.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 10.3]](../ps.gif) 10.3
10.3![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 10.4]](../ps.gif) 10.4
10.4![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 10.5]](../ps.gif) 10.5
10.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 10.6]](../ps.gif) 10.6
10.6![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 10.7]](../ps.gif) 10.7
10.7![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 10.8]](../ps.gif) 10.8
10.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 10.9]](../ps.gif) 10.9
10.9![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 11.1]](../ps.gif) 11.1
11.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 11.2]](../ps.gif) 11.2
11.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 11.3]](../ps.gif) 11.3
11.3![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 11.4]](../ps.gif) 11.4
11.4![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 11.5]](../ps.gif) 11.5
11.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 11.6]](../ps.gif) 11.6
11.6![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 11.7]](../ps.gif) 11.7
11.7![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 11.8]](../ps.gif) 11.8
11.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 11.9]](../ps.gif) 11.9
11.9![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 12.1]](../ps.gif) 12.1
12.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 12.2]](../ps.gif) 12.2
12.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 12.3]](../ps.gif) 12.3
12.3![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 12.4]](../ps.gif) 12.4
12.4![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 12.5]](../ps.gif) 12.5
12.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 12.6]](../ps.gif) 12.6
12.6![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 12.7]](../ps.gif) 12.7
12.7![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 12.8]](../ps.gif) 12.8
12.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 12.9]](../ps.gif) 12.9
12.9![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 13.1]](../ps.gif) 13.1
13.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 13.2]](../ps.gif) 13.2
13.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 13.3]](../ps.gif) 13.3
13.3![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 13.4]](../ps.gif) 13.4
13.4![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 13.5]](../ps.gif) 13.5
13.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 13.6]](../ps.gif) 13.6
13.6![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 13.7]](../ps.gif) 13.7
13.7![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 13.8]](../ps.gif) 13.8
13.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 13.9]](../ps.gif) 13.9
13.9![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 14.1]](../ps.gif) 14.1
14.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 14.2]](../ps.gif) 14.2
14.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 14.3]](../ps.gif) 14.3
14.3![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 14.4]](../ps.gif) 14.4
14.4![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 14.5]](../ps.gif) 14.5
14.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 14.6]](../ps.gif) 14.6
14.6![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 14.7]](../ps.gif) 14.7
14.7![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 14.8]](../ps.gif) 14.8
14.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 14.9]](../ps.gif) 14.9
14.9![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 15.1]](../ps.gif) 15.1
15.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 15.2]](../ps.gif) 15.2
15.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 15.3]](../ps.gif) 15.3
15.3![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 15.4]](../ps.gif) 15.4
15.4![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 15.5]](../ps.gif) 15.5
15.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 15.6]](../ps.gif) 15.6
15.6![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 15.7]](../ps.gif) 15.7
15.7![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 15.8]](../ps.gif) 15.8
15.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 15.9]](../ps.gif) 15.9
15.9![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 16.1]](../ps.gif) 16.1
16.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 16.2]](../ps.gif) 16.2
16.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 16.3]](../ps.gif) 16.3
16.3![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 16.4]](../ps.gif) 16.4
16.4![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 16.5]](../ps.gif) 16.5
16.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 16.6]](../ps.gif) 16.6
16.6![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 16.7]](../ps.gif) 16.7
16.7![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 16.8]](../ps.gif) 16.8
16.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 16.9]](../ps.gif) 16.9
16.9![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 17.1]](../ps.gif) 17.1
17.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 17.2]](../ps.gif) 17.2
17.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 17.3]](../ps.gif) 17.3
17.3![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 17.4]](../ps.gif) 17.4
17.4![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 17.5]](../ps.gif) 17.5
17.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 17.6]](../ps.gif) 17.6
17.6![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 17.7]](../ps.gif) 17.7
17.7![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 17.8]](../ps.gif) 17.8
17.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 17.9]](../ps.gif) 17.9
17.9![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 18.1]](../ps.gif) 18.1
18.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 18.2]](../ps.gif) 18.2
18.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 18.3]](../ps.gif) 18.3
18.3![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 18.4]](../ps.gif) 18.4
18.4![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 18.5]](../ps.gif) 18.5
18.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 18.6]](../ps.gif) 18.6
18.6![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 18.7]](../ps.gif) 18.7
18.7![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 18.8]](../ps.gif) 18.8
18.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 18.9]](../ps.gif) 18.9
18.9![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 19.1]](../ps.gif) 19.1
19.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 19.2]](../ps.gif) 19.2
19.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 19.3]](../ps.gif) 19.3
19.3![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 19.4]](../ps.gif) 19.4
19.4![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 19.5]](../ps.gif) 19.5
19.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 19.6]](../ps.gif) 19.6
19.6![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 19.7]](../ps.gif) 19.7
19.7![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 19.8]](../ps.gif) 19.8
19.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 19.9]](../ps.gif) 19.9
19.9![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 20.1]](../ps.gif) 20.1
20.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 20.2]](../ps.gif) 20.2
20.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 20.3]](../ps.gif) 20.3
20.3![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 20.4]](../ps.gif) 20.4
20.4![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 20.5]](../ps.gif) 20.5
20.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 20.6]](../ps.gif) 20.6
20.6![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 20.7]](../ps.gif) 20.7
20.7![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 20.8]](../ps.gif) 20.8
20.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 20.9]](../ps.gif) 20.9
20.9![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 21.1]](../ps.gif) 21.1
21.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 21.2]](../ps.gif) 21.2
21.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 21.3]](../ps.gif) 21.3
21.3![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 21.4]](../ps.gif) 21.4
21.4![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 21.5]](../ps.gif) 21.5
21.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 21.6]](../ps.gif) 21.6
21.6![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 21.7]](../ps.gif) 21.7
21.7![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 21.8]](../ps.gif) 21.8
21.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 21.9]](../ps.gif) 21.9
21.9![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 21.91]](../ps.gif) 21.91
21.91![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 21.92]](../ps.gif) 21.92
21.92![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 22]](../ps.gif) 22
22![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 23]](../ps.gif) 23
23![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 24]](../ps.gif) 24
24![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 25]](../ps.gif) 25
25![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 26]](../ps.gif) 26
26![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 27]](../ps.gif) 27
27![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 28]](../ps.gif) 28
28![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 29]](../ps.gif) 29
29![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 30]](../ps.gif) 30
30![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 31]](../ps.gif) 31
31![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 32]](../ps.gif) 32
32![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 33]](../ps.gif) 33
33![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 34]](../ps.gif) 34
34![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 35]](../ps.gif) 35
35![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 36]](../ps.gif) 36
36![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 37]](../ps.gif) 37
37![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 38]](../ps.gif) 38
38![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 39]](../ps.gif) 39
39![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 40]](../ps.gif) 40
40![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 41]](../ps.gif) 41
41![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 42]](../ps.gif) 42
42![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 43]](../ps.gif) 43
43![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 44]](../ps.gif) 44
44![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 45]](../ps.gif) 45
45![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 46]](../ps.gif) 46
46![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 47]](../ps.gif) 47
47![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 48]](../ps.gif) 48
48![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 49]](../ps.gif) 49
49![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 50]](../ps.gif) 50
50![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 51]](../ps.gif) 51
51![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 52]](../ps.gif) 52
52![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 53]](../ps.gif) 53
53![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 54]](../ps.gif) 54
54![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 55]](../ps.gif) 55
55![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 56]](../ps.gif) 56
56![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 57]](../ps.gif) 57
57![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 58]](../ps.gif) 58
58![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 59]](../ps.gif) 59
59![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 60]](../ps.gif) 60
60![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 61]](../ps.gif) 61
61![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 62]](../ps.gif) 62
62![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 63]](../ps.gif) 63
63![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 64]](../ps.gif) 64
64![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 65]](../ps.gif) 65
65![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 66]](../ps.gif) 66
66![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 67]](../ps.gif) 67
67![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 68]](../ps.gif) 68
68![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 69]](../ps.gif) 69
69![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 70]](../ps.gif) 70
70![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 71]](../ps.gif) 71
71![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 72]](../ps.gif) 72
72![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 73]](../ps.gif) 73
73![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 74]](../ps.gif) 74
74![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 75]](../ps.gif) 75
75![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 76]](../ps.gif) 76
76![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 77]](../ps.gif) 77
77![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 78]](../ps.gif) 78
78![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 79]](../ps.gif) 79
79![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 80]](../ps.gif) 80
80![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 81]](../ps.gif) 81
81![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 82]](../ps.gif) 82
82![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 83]](../ps.gif) 83
83![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 84]](../ps.gif) 84
84![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 85]](../ps.gif) 85
85![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 86]](../ps.gif) 86
86![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 87]](../ps.gif) 87
87![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 88]](../ps.gif) 88
88![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 89]](../ps.gif) 89
89![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 90]](../ps.gif) 90
90![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 91]](../ps.gif) 91
91![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 92]](../ps.gif) 92
92![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 93]](../ps.gif) 93
93![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 94]](../ps.gif) 94
94![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 95]](../ps.gif) 95
95![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 96]](../ps.gif) 96
96![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 97]](../ps.gif) 97
97![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 98]](../ps.gif) 98
98![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 99]](../ps.gif) 99
99![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 100]](../ps.gif) 100
100![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 101]](../ps.gif) 101
101![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 102]](../ps.gif) 102
102![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 103]](../ps.gif) 103
103![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 104]](../ps.gif) 104
104![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 105]](../ps.gif) 105
105![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 106]](../ps.gif) 106
106![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 107]](../ps.gif) 107
107![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 108]](../ps.gif) 108
108![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 109]](../ps.gif) 109
109![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 110]](../ps.gif) 110
110![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 111]](../ps.gif) 111
111![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 112]](../ps.gif) 112
112![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 113]](../ps.gif) 113
113![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 114]](../ps.gif) 114
114![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 115]](../ps.gif) 115
115![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 116]](../ps.gif) 116
116![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 117]](../ps.gif) 117
117![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 118]](../ps.gif) 118
118![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 119]](../ps.gif) 119
119![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 120]](../ps.gif) 120
120![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 121]](../ps.gif) 121
121![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 122]](../ps.gif) 122
122![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 123]](../ps.gif) 123
123![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 124]](../ps.gif) 124
124![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 125]](../ps.gif) 125
125![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 126]](../ps.gif) 126
126![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 127]](../ps.gif) 127
127![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 128]](../ps.gif) 128
128![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 129]](../ps.gif) 129
129![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 130]](../ps.gif) 130
130![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 131]](../ps.gif) 131
131![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 132]](../ps.gif) 132
132![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 133]](../ps.gif) 133
133![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 134]](../ps.gif) 134
134![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 135]](../ps.gif) 135
135![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 136]](../ps.gif) 136
136![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 137]](../ps.gif) 137
137![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 138]](../ps.gif) 138
138![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 139]](../ps.gif) 139
139![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 140]](../ps.gif) 140
140![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 141]](../ps.gif) 141
141![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 142]](../ps.gif) 142
142![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 143]](../ps.gif) 143
143![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 144]](../ps.gif) 144
144![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 145]](../ps.gif) 145
145![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 146]](../ps.gif) 146
146![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 147]](../ps.gif) 147
147![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 148]](../ps.gif) 148
148![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 149]](../ps.gif) 149
149![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 150]](../ps.gif) 150
150![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 151]](../ps.gif) 151
151![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 152]](../ps.gif) 152
152![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 153]](../ps.gif) 153
153![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 154]](../ps.gif) 154
154![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 155]](../ps.gif) 155
155![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 156]](../ps.gif) 156
156![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 157]](../ps.gif) 157
157![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 158]](../ps.gif) 158
158![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 159]](../ps.gif) 159
159![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 160]](../ps.gif) 160
160![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 161]](../ps.gif) 161
161![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 162]](../ps.gif) 162
162![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 163]](../ps.gif) 163
163![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 164]](../ps.gif) 164
164![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 165]](../ps.gif) 165
165![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 166]](../ps.gif) 166
166![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 167]](../ps.gif) 167
167![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 168]](../ps.gif) 168
168![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 169]](../ps.gif) 169
169![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 170]](../ps.gif) 170
170![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 171]](../ps.gif) 171
171![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 172]](../ps.gif) 172
172![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 173]](../ps.gif) 173
173![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 174]](../ps.gif) 174
174![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 175]](../ps.gif) 175
175![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 176]](../ps.gif) 176
176![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 177]](../ps.gif) 177
177![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 178]](../ps.gif) 178
178![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 179]](../ps.gif) 179
179![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 180]](../ps.gif) 180
180![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 181]](../ps.gif) 181
181![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 182]](../ps.gif) 182
182![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 183]](../ps.gif) 183
183![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 184]](../ps.gif) 184
184![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 185]](../ps.gif) 185
185![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 186]](../ps.gif) 186
186![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 187]](../ps.gif) 187
187![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 188]](../ps.gif) 188
188![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 189]](../ps.gif) 189
189![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 190]](../ps.gif) 190
190![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 191]](../ps.gif) 191
191![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 192]](../ps.gif) 192
192![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 193]](../ps.gif) 193
193![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 194]](../ps.gif) 194
194![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 195]](../ps.gif) 195
195![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 196]](../ps.gif) 196
196![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 197]](../ps.gif) 197
197![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 198]](../ps.gif) 198
198![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 199]](../ps.gif) 199
199![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 200]](../ps.gif) 200
200![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 201]](../ps.gif) 201
201![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 202]](../ps.gif) 202
202![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 203]](../ps.gif) 203
203![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 204]](../ps.gif) 204
204![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 205]](../ps.gif) 205
205![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 206]](../ps.gif) 206
206![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 207]](../ps.gif) 207
207![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 208]](../ps.gif) 208
208![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 209]](../ps.gif) 209
209![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 210.01]](../ps.gif) 210.01
210.01![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 210.02]](../ps.gif) 210.02
210.02![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 210.03]](../ps.gif) 210.03
210.03![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 210.04]](../ps.gif) 210.04
210.04![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 210.05]](../ps.gif) 210.05
210.05![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 210.06]](../ps.gif) 210.06
210.06![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 210.07]](../ps.gif) 210.07
210.07![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 210.08]](../ps.gif) 210.08
210.08![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 210.09]](../ps.gif) 210.09
210.09![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 210.1]](../ps.gif) 210.1
210.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 210.11]](../ps.gif) 210.11
210.11![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 210.12]](../ps.gif) 210.12
210.12![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 210.13]](../ps.gif) 210.13
210.13![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 210.14]](../ps.gif) 210.14
210.14![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 210.15]](../ps.gif) 210.15
210.15![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 210.16]](../ps.gif) 210.16
210.16![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 210.17]](../ps.gif) 210.17
210.17![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 210.18]](../ps.gif) 210.18
210.18![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 210.19]](../ps.gif) 210.19
210.19![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 210.20]](../ps.gif) 210.20
210.20![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 210.21]](../ps.gif) 210.21
210.21![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 211.01]](../ps.gif) 211.01
211.01![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 211.02]](../ps.gif) 211.02
211.02![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 211.03]](../ps.gif) 211.03
211.03![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 211.04]](../ps.gif) 211.04
211.04![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 211.05]](../ps.gif) 211.05
211.05![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 211.06]](../ps.gif) 211.06
211.06![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 211.07]](../ps.gif) 211.07
211.07![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 211.08]](../ps.gif) 211.08
211.08![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 211.09]](../ps.gif) 211.09
211.09![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 211.1]](../ps.gif) 211.1
211.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 211.11]](../ps.gif) 211.11
211.11![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 211.12]](../ps.gif) 211.12
211.12![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 211.13]](../ps.gif) 211.13
211.13![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 211.14]](../ps.gif) 211.14
211.14![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 211.15]](../ps.gif) 211.15
211.15![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 212.01]](../ps.gif) 212.01
212.01![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 212.02]](../ps.gif) 212.02
212.02![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 212.03]](../ps.gif) 212.03
212.03![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 212.04]](../ps.gif) 212.04
212.04![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 212.05]](../ps.gif) 212.05
212.05![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 212.07]](../ps.gif) 212.07
212.07![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 212.08]](../ps.gif) 212.08
212.08![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 213.01]](../ps.gif) 213.01
213.01![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 214.01]](../ps.gif) 214.01
214.01![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 214.02]](../ps.gif) 214.02
214.02![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 214.03]](../ps.gif) 214.03
214.03![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 215]](../ps.gif) 215
215![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 216]](../ps.gif) 216
216![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 217]](../ps.gif) 217
217![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 217.01]](../ps.gif) 217.01
217.01![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 217.02]](../ps.gif) 217.02
217.02![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 217.03]](../ps.gif) 217.03
217.03![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 217.04]](../ps.gif) 217.04
217.04![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 217.05]](../ps.gif) 217.05
217.05![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 217.06]](../ps.gif) 217.06
217.06![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 217.07]](../ps.gif) 217.07
217.07![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 217.08]](../ps.gif) 217.08
217.08![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 217.09]](../ps.gif) 217.09
217.09![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 217.1]](../ps.gif) 217.1
217.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 217.11]](../ps.gif) 217.11
217.11![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 217.12]](../ps.gif) 217.12
217.12![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 218]](../ps.gif) 218
218![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 219]](../ps.gif) 219
219![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 220]](../ps.gif) 220
220![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 221]](../ps.gif) 221
221![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 222.2]](../ps.gif) 222.2
222.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 222.5]](../ps.gif) 222.5
222.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 222.8]](../ps.gif) 222.8
222.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 223.2]](../ps.gif) 223.2
223.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 223.5]](../ps.gif) 223.5
223.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 223.8]](../ps.gif) 223.8
223.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 224.2]](../ps.gif) 224.2
224.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 224.5]](../ps.gif) 224.5
224.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 224.8]](../ps.gif) 224.8
224.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 225.2]](../ps.gif) 225.2
225.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 225.5]](../ps.gif) 225.5
225.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 225.8]](../ps.gif) 225.8
225.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 226.2]](../ps.gif) 226.2
226.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 226.5]](../ps.gif) 226.5
226.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 226.8]](../ps.gif) 226.8
226.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 227.2]](../ps.gif) 227.2
227.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 227.5]](../ps.gif) 227.5
227.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 227.8]](../ps.gif) 227.8
227.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 228.2]](../ps.gif) 228.2
228.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 228.5]](../ps.gif) 228.5
228.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 228.8]](../ps.gif) 228.8
228.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 229.2]](../ps.gif) 229.2
229.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 229.5]](../ps.gif) 229.5
229.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 229.8]](../ps.gif) 229.8
229.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 230.2]](../ps.gif) 230.2
230.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 230.5]](../ps.gif) 230.5
230.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 230.8]](../ps.gif) 230.8
230.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 231.2]](../ps.gif) 231.2
231.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 231.5]](../ps.gif) 231.5
231.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 231.8]](../ps.gif) 231.8
231.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 232.2]](../ps.gif) 232.2
232.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 232.5]](../ps.gif) 232.5
232.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 232.8]](../ps.gif) 232.8
232.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 233.2]](../ps.gif) 233.2
233.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 233.5]](../ps.gif) 233.5
233.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 233.8]](../ps.gif) 233.8
233.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 234.2]](../ps.gif) 234.2
234.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 234.5]](../ps.gif) 234.5
234.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 234.8]](../ps.gif) 234.8
234.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 235.2]](../ps.gif) 235.2
235.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 235.5]](../ps.gif) 235.5
235.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 235.8]](../ps.gif) 235.8
235.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 236.2]](../ps.gif) 236.2
236.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 236.5]](../ps.gif) 236.5
236.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 236.8]](../ps.gif) 236.8
236.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 237.2]](../ps.gif) 237.2
237.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 237.5]](../ps.gif) 237.5
237.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 237.8]](../ps.gif) 237.8
237.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 238.2]](../ps.gif) 238.2
238.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 238.5]](../ps.gif) 238.5
238.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 238.8]](../ps.gif) 238.8
238.8![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 239.2]](../ps.gif) 239.2
239.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 239.5]](../ps.gif) 239.5
239.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 241]](../ps.gif) 241
241![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 242]](../ps.gif) 242
242![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 243]](../ps.gif) 243
243![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 244]](../ps.gif) 244
244![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 245]](../ps.gif) 245
245![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 246]](../ps.gif) 246
246![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 247]](../ps.gif) 247
247![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 248]](../ps.gif) 248
248![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 249]](../ps.gif) 249
249![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 250]](../ps.gif) 250
250![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 251]](../ps.gif) 251
251![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 252.01]](../ps.gif) 252.01
252.01![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 252.02]](../ps.gif) 252.02
252.02![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 252.03]](../ps.gif) 252.03
252.03![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 252.04]](../ps.gif) 252.04
252.04![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 252.05]](../ps.gif) 252.05
252.05![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 252.06]](../ps.gif) 252.06
252.06![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 252.1]](../ps.gif) 252.1
252.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 252.11]](../ps.gif) 252.11
252.11![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 252.12]](../ps.gif) 252.12
252.12![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 252.13]](../ps.gif) 252.13
252.13![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 252.14]](../ps.gif) 252.14
252.14![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 252.15]](../ps.gif) 252.15
252.15![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 252.16]](../ps.gif) 252.16
252.16![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 252.17]](../ps.gif) 252.17
252.17![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 252.18]](../ps.gif) 252.18
252.18![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 252.19]](../ps.gif) 252.19
252.19![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 252.2]](../ps.gif) 252.2
252.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 253.01]](../ps.gif) 253.01
253.01![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 253.02]](../ps.gif) 253.02
253.02![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 253.03]](../ps.gif) 253.03
253.03![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 253.04]](../ps.gif) 253.04
253.04![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 253.05]](../ps.gif) 253.05
253.05![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 253.06]](../ps.gif) 253.06
253.06![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 253.07]](../ps.gif) 253.07
253.07![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 253.08]](../ps.gif) 253.08
253.08![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 253.09]](../ps.gif) 253.09
253.09![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 253.1]](../ps.gif) 253.1
253.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 253.11]](../ps.gif) 253.11
253.11![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 253.12]](../ps.gif) 253.12
253.12![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 253.13]](../ps.gif) 253.13
253.13![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 254.01]](../ps.gif) 254.01
254.01![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 254.02]](../ps.gif) 254.02
254.02![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 254.03]](../ps.gif) 254.03
254.03![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 254.04]](../ps.gif) 254.04
254.04![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 254.05]](../ps.gif) 254.05
254.05![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 254.06]](../ps.gif) 254.06
254.06![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 254.07]](../ps.gif) 254.07
254.07![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 254.08]](../ps.gif) 254.08
254.08![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 254.09]](../ps.gif) 254.09
254.09![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 254.1]](../ps.gif) 254.1
254.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 254.11]](../ps.gif) 254.11
254.11![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 255.01]](../ps.gif) 255.01
255.01![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 255.02]](../ps.gif) 255.02
255.02![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 255.03]](../ps.gif) 255.03
255.03![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 255.04]](../ps.gif) 255.04
255.04![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 255.05]](../ps.gif) 255.05
255.05![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 255.06]](../ps.gif) 255.06
255.06![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 256]](../ps.gif) 256
256![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 257]](../ps.gif) 257
257![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 258.1]](../ps.gif) 258.1
258.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 259.1]](../ps.gif) 259.1
259.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 259.2]](../ps.gif) 259.2
259.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 259.3]](../ps.gif) 259.3
259.3![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 259.31]](../ps.gif) 259.31
259.31![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 259.4]](../ps.gif) 259.4
259.4![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 259.41]](../ps.gif) 259.41
259.41![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 259.5]](../ps.gif) 259.5
259.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 260.1]](../ps.gif) 260.1
260.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 261.1]](../ps.gif) 261.1
261.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 262.1]](../ps.gif) 262.1
262.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 263.1]](../ps.gif) 263.1
263.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 263.2]](../ps.gif) 263.2
263.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 263.21]](../ps.gif) 263.21
263.21![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 263.22]](../ps.gif) 263.22
263.22![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 263.23]](../ps.gif) 263.23
263.23![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 263.24]](../ps.gif) 263.24
263.24![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 263.3]](../ps.gif) 263.3
263.3![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 263.31]](../ps.gif) 263.31
263.31![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 263.32]](../ps.gif) 263.32
263.32![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 263.33]](../ps.gif) 263.33
263.33![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 263.34]](../ps.gif) 263.34
263.34![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 263.35]](../ps.gif) 263.35
263.35![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 263.36]](../ps.gif) 263.36
263.36![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 263.37]](../ps.gif) 263.37
263.37![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 263.38]](../ps.gif) 263.38
263.38![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 263.4]](../ps.gif) 263.4
263.4![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 264.1]](../ps.gif) 264.1
264.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 264.11]](../ps.gif) 264.11
264.11![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 265.1]](../ps.gif) 265.1
265.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 266.1]](../ps.gif) 266.1
266.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 266.2]](../ps.gif) 266.2
266.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 266.21]](../ps.gif) 266.21
266.21![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 266.22]](../ps.gif) 266.22
266.22![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 266.23]](../ps.gif) 266.23
266.23![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 266.24]](../ps.gif) 266.24
266.24![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 266.3]](../ps.gif) 266.3
266.3![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 266.31]](../ps.gif) 266.31
266.31![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 266.4]](../ps.gif) 266.4
266.4![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 267]](../ps.gif) 267
267![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 268]](../ps.gif) 268
268![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 269]](../ps.gif) 269
269![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 270]](../ps.gif) 270
270![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 271]](../ps.gif) 271
271![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 272]](../ps.gif) 272
272![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 273]](../ps.gif) 273
273![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 274]](../ps.gif) 274
274![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 275]](../ps.gif) 275
275![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 276]](../ps.gif) 276
276![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 277]](../ps.gif) 277
277![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 278]](../ps.gif) 278
278![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 279]](../ps.gif) 279
279![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 280]](../ps.gif) 280
280![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 281]](../ps.gif) 281
281![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 282]](../ps.gif) 282
282![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 283]](../ps.gif) 283
283![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 284]](../ps.gif) 284
284![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 285]](../ps.gif) 285
285![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 286]](../ps.gif) 286
286![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 287]](../ps.gif) 287
287![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 288]](../ps.gif) 288
288![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 289]](../ps.gif) 289
289![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 290]](../ps.gif) 290
290![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 291]](../ps.gif) 291
291![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 292]](../ps.gif) 292
292![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 293]](../ps.gif) 293
293![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 294]](../ps.gif) 294
294![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 295]](../ps.gif) 295
295![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 296]](../ps.gif) 296
296![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 297]](../ps.gif) 297
297![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 298]](../ps.gif) 298
298![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 299]](../ps.gif) 299
299![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 300]](../ps.gif) 300
300![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 301]](../ps.gif) 301
301![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 302]](../ps.gif) 302
302![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 303]](../ps.gif) 303
303![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 304]](../ps.gif) 304
304![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 305]](../ps.gif) 305
305![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 306]](../ps.gif) 306
306![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 307]](../ps.gif) 307
307![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 308]](../ps.gif) 308
308![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 309]](../ps.gif) 309
309![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 310]](../ps.gif) 310
310![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 311]](../ps.gif) 311
311![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 312]](../ps.gif) 312
312![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 313]](../ps.gif) 313
313![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 314]](../ps.gif) 314
314![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 315]](../ps.gif) 315
315![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 316]](../ps.gif) 316
316![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 317]](../ps.gif) 317
317![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 318]](../ps.gif) 318
318![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 319]](../ps.gif) 319
319![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 320]](../ps.gif) 320
320![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 321]](../ps.gif) 321
321![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 322]](../ps.gif) 322
322![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 323]](../ps.gif) 323
323![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 324]](../ps.gif) 324
324![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 325]](../ps.gif) 325
325![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 326]](../ps.gif) 326
326![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 327]](../ps.gif) 327
327![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 328]](../ps.gif) 328
328![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 329]](../ps.gif) 329
329![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 330]](../ps.gif) 330
330![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 331]](../ps.gif) 331
331![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 332]](../ps.gif) 332
332![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 333]](../ps.gif) 333
333![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 334]](../ps.gif) 334
334![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 335]](../ps.gif) 335
335![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 336]](../ps.gif) 336
336![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 337]](../ps.gif) 337
337![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 338]](../ps.gif) 338
338![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 339]](../ps.gif) 339
339![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 340]](../ps.gif) 340
340![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 341]](../ps.gif) 341
341![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 342]](../ps.gif) 342
342![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 343]](../ps.gif) 343
343![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 344]](../ps.gif) 344
344![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 345]](../ps.gif) 345
345![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 346]](../ps.gif) 346
346![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 347]](../ps.gif) 347
347![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 348]](../ps.gif) 348
348![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 349]](../ps.gif) 349
349![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 350]](../ps.gif) 350
350![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 351]](../ps.gif) 351
351![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 352]](../ps.gif) 352
352![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 353]](../ps.gif) 353
353![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 354]](../ps.gif) 354
354![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 355]](../ps.gif) 355
355![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 356]](../ps.gif) 356
356![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 357]](../ps.gif) 357
357![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 358]](../ps.gif) 358
358![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 359]](../ps.gif) 359
359![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 360]](../ps.gif) 360
360![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 361]](../ps.gif) 361
361![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 362]](../ps.gif) 362
362![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 363]](../ps.gif) 363
363![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 364]](../ps.gif) 364
364![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 365]](../ps.gif) 365
365![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 366]](../ps.gif) 366
366![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 367]](../ps.gif) 367
367![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 368]](../ps.gif) 368
368![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 369]](../ps.gif) 369
369![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 370]](../ps.gif) 370
370![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 371]](../ps.gif) 371
371![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 372]](../ps.gif) 372
372![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 373]](../ps.gif) 373
373![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 374]](../ps.gif) 374
374![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 375]](../ps.gif) 375
375![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 376]](../ps.gif) 376
376![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 377]](../ps.gif) 377
377![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 378]](../ps.gif) 378
378![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 379]](../ps.gif) 379
379![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 380]](../ps.gif) 380
380![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 381]](../ps.gif) 381
381![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 382]](../ps.gif) 382
382![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 383]](../ps.gif) 383
383![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 384]](../ps.gif) 384
384![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 385]](../ps.gif) 385
385![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 386]](../ps.gif) 386
386![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 387]](../ps.gif) 387
387![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 388]](../ps.gif) 388
388![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 389]](../ps.gif) 389
389![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 390]](../ps.gif) 390
390![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 391]](../ps.gif) 391
391![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 392]](../ps.gif) 392
392![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 393]](../ps.gif) 393
393![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 394]](../ps.gif) 394
394![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 395]](../ps.gif) 395
395![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 396]](../ps.gif) 396
396![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 397]](../ps.gif) 397
397![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 398]](../ps.gif) 398
398![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 399]](../ps.gif) 399
399![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 400]](../ps.gif) 400
400![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 401]](../ps.gif) 401
401![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 402]](../ps.gif) 402
402![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 403]](../ps.gif) 403
403![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 404]](../ps.gif) 404
404![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 405]](../ps.gif) 405
405![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 406]](../ps.gif) 406
406![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 407]](../ps.gif) 407
407![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 408]](../ps.gif) 408
408![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 409]](../ps.gif) 409
409![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 410]](../ps.gif) 410
410![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 411]](../ps.gif) 411
411![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 412]](../ps.gif) 412
412![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 413]](../ps.gif) 413
413![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 414]](../ps.gif) 414
414![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 415]](../ps.gif) 415
415![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 416]](../ps.gif) 416
416![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 417]](../ps.gif) 417
417![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 418]](../ps.gif) 418
418![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 419]](../ps.gif) 419
419![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 420]](../ps.gif) 420
420![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 421]](../ps.gif) 421
421![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 422]](../ps.gif) 422
422![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 423]](../ps.gif) 423
423![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 424]](../ps.gif) 424
424![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 425]](../ps.gif) 425
425![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 426]](../ps.gif) 426
426![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 427]](../ps.gif) 427
427![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 428]](../ps.gif) 428
428![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 429]](../ps.gif) 429
429![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 430]](../ps.gif) 430
430![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 431]](../ps.gif) 431
431![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 432]](../ps.gif) 432
432![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 433]](../ps.gif) 433
433![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 434]](../ps.gif) 434
434![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 435]](../ps.gif) 435
435![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 436]](../ps.gif) 436
436![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 437]](../ps.gif) 437
437![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 438]](../ps.gif) 438
438![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 439]](../ps.gif) 439
439![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 440]](../ps.gif) 440
440![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 441]](../ps.gif) 441
441![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 442]](../ps.gif) 442
442![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 443]](../ps.gif) 443
443![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 444]](../ps.gif) 444
444![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 445]](../ps.gif) 445
445![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 446]](../ps.gif) 446
446![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 447]](../ps.gif) 447
447![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 448]](../ps.gif) 448
448![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 449]](../ps.gif) 449
449![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 450]](../ps.gif) 450
450![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 451]](../ps.gif) 451
451![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 452]](../ps.gif) 452
452![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 453]](../ps.gif) 453
453![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 454]](../ps.gif) 454
454![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 455]](../ps.gif) 455
455![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 456]](../ps.gif) 456
456![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 457]](../ps.gif) 457
457![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 458]](../ps.gif) 458
458![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 459]](../ps.gif) 459
459![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 460]](../ps.gif) 460
460![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 461]](../ps.gif) 461
461![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 462]](../ps.gif) 462
462![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 463]](../ps.gif) 463
463![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 464]](../ps.gif) 464
464![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 465]](../ps.gif) 465
465![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 466]](../ps.gif) 466
466![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 467]](../ps.gif) 467
467![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 468]](../ps.gif) 468
468![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 469]](../ps.gif) 469
469![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 470]](../ps.gif) 470
470![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 471]](../ps.gif) 471
471![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 472]](../ps.gif) 472
472![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 473]](../ps.gif) 473
473![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 474]](../ps.gif) 474
474![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 475]](../ps.gif) 475
475![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 476]](../ps.gif) 476
476![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 477]](../ps.gif) 477
477![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 478]](../ps.gif) 478
478![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 479]](../ps.gif) 479
479![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 480]](../ps.gif) 480
480![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 481]](../ps.gif) 481
481![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 482]](../ps.gif) 482
482![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 483]](../ps.gif) 483
483![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 484]](../ps.gif) 484
484![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 485]](../ps.gif) 485
485![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 486]](../ps.gif) 486
486![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 487]](../ps.gif) 487
487![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 488]](../ps.gif) 488
488![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 489]](../ps.gif) 489
489![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 490]](../ps.gif) 490
490![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 491]](../ps.gif) 491
491![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 492]](../ps.gif) 492
492![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 493]](../ps.gif) 493
493![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 494]](../ps.gif) 494
494![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 495]](../ps.gif) 495
495![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 496]](../ps.gif) 496
496![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 497]](../ps.gif) 497
497![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 498]](../ps.gif) 498
498![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 499]](../ps.gif) 499
499![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 500]](../ps.gif) 500
500![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 501]](../ps.gif) 501
501![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 502]](../ps.gif) 502
502![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 503]](../ps.gif) 503
503![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 504]](../ps.gif) 504
504![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 505]](../ps.gif) 505
505![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 506]](../ps.gif) 506
506![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 507]](../ps.gif) 507
507![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 508]](../ps.gif) 508
508![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 509]](../ps.gif) 509
509![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 510]](../ps.gif) 510
510![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 511]](../ps.gif) 511
511![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 512]](../ps.gif) 512
512![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 513]](../ps.gif) 513
513![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 514]](../ps.gif) 514
514![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 515]](../ps.gif) 515
515![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 516]](../ps.gif) 516
516![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 517]](../ps.gif) 517
517![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 518]](../ps.gif) 518
518![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 519]](../ps.gif) 519
519![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 520]](../ps.gif) 520
520![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 521]](../ps.gif) 521
521![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 522]](../ps.gif) 522
522![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 523]](../ps.gif) 523
523![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 524]](../ps.gif) 524
524![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 525]](../ps.gif) 525
525![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 526]](../ps.gif) 526
526![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 527]](../ps.gif) 527
527![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 528]](../ps.gif) 528
528![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 529]](../ps.gif) 529
529![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 530]](../ps.gif) 530
530![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 531]](../ps.gif) 531
531![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 532]](../ps.gif) 532
532![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 533]](../ps.gif) 533
533![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 534]](../ps.gif) 534
534![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 535]](../ps.gif) 535
535![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 536]](../ps.gif) 536
536![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 537]](../ps.gif) 537
537![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 538]](../ps.gif) 538
538![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 539]](../ps.gif) 539
539![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 540]](../ps.gif) 540
540![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 541]](../ps.gif) 541
541![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 542]](../ps.gif) 542
542![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 543]](../ps.gif) 543
543![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 544]](../ps.gif) 544
544![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 545]](../ps.gif) 545
545![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 546]](../ps.gif) 546
546![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 547]](../ps.gif) 547
547![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 548]](../ps.gif) 548
548![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 549]](../ps.gif) 549
549![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 550]](../ps.gif) 550
550![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 551]](../ps.gif) 551
551![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 552]](../ps.gif) 552
552![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 553]](../ps.gif) 553
553![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 554]](../ps.gif) 554
554![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 555]](../ps.gif) 555
555![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 556]](../ps.gif) 556
556![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 557]](../ps.gif) 557
557![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 558]](../ps.gif) 558
558![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 559]](../ps.gif) 559
559![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 560]](../ps.gif) 560
560![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 561]](../ps.gif) 561
561![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 562]](../ps.gif) 562
562![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 563]](../ps.gif) 563
563![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 564]](../ps.gif) 564
564![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 565]](../ps.gif) 565
565![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 566]](../ps.gif) 566
566![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 567]](../ps.gif) 567
567![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 568]](../ps.gif) 568
568![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 569]](../ps.gif) 569
569![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 570]](../ps.gif) 570
570![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 571]](../ps.gif) 571
571![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 572]](../ps.gif) 572
572![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 573]](../ps.gif) 573
573![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 574]](../ps.gif) 574
574![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 575]](../ps.gif) 575
575![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 576]](../ps.gif) 576
576![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 577]](../ps.gif) 577
577![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 578]](../ps.gif) 578
578![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 579]](../ps.gif) 579
579![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 580]](../ps.gif) 580
580![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 581]](../ps.gif) 581
581![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 582]](../ps.gif) 582
582![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 583]](../ps.gif) 583
583![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 584]](../ps.gif) 584
584![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 585]](../ps.gif) 585
585![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 586]](../ps.gif) 586
586![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 587]](../ps.gif) 587
587![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 588]](../ps.gif) 588
588![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 589]](../ps.gif) 589
589![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 590]](../ps.gif) 590
590![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 591]](../ps.gif) 591
591![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 592]](../ps.gif) 592
592![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 593]](../ps.gif) 593
593![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 594]](../ps.gif) 594
594![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 595]](../ps.gif) 595
595![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 596]](../ps.gif) 596
596![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 597]](../ps.gif) 597
597![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 598]](../ps.gif) 598
598![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 599]](../ps.gif) 599
599![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 600]](../ps.gif) 600
600![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 601]](../ps.gif) 601
601![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 602]](../ps.gif) 602
602![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 603]](../ps.gif) 603
603![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 604]](../ps.gif) 604
604![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 605]](../ps.gif) 605
605![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 606]](../ps.gif) 606
606![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 607]](../ps.gif) 607
607![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 608]](../ps.gif) 608
608![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 609]](../ps.gif) 609
609![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 610]](../ps.gif) 610
610![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 611]](../ps.gif) 611
611![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 612]](../ps.gif) 612
612![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 613]](../ps.gif) 613
613![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 614]](../ps.gif) 614
614![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 615]](../ps.gif) 615
615![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 616]](../ps.gif) 616
616![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 617]](../ps.gif) 617
617![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 618]](../ps.gif) 618
618![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 619]](../ps.gif) 619
619![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 620]](../ps.gif) 620
620![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 621]](../ps.gif) 621
621![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 622]](../ps.gif) 622
622![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 623]](../ps.gif) 623
623![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 624]](../ps.gif) 624
624![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 625]](../ps.gif) 625
625![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 626]](../ps.gif) 626
626![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 627]](../ps.gif) 627
627![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 628]](../ps.gif) 628
628![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 629]](../ps.gif) 629
629![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 630]](../ps.gif) 630
630![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 631]](../ps.gif) 631
631![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 632]](../ps.gif) 632
632![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 633]](../ps.gif) 633
633![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 634]](../ps.gif) 634
634![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 635]](../ps.gif) 635
635![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 636]](../ps.gif) 636
636![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 637]](../ps.gif) 637
637![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 638]](../ps.gif) 638
638![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 639]](../ps.gif) 639
639![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 640]](../ps.gif) 640
640![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 641]](../ps.gif) 641
641![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 642]](../ps.gif) 642
642![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 643]](../ps.gif) 643
643![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 644]](../ps.gif) 644
644![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 645]](../ps.gif) 645
645![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 646]](../ps.gif) 646
646![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 647]](../ps.gif) 647
647![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 648]](../ps.gif) 648
648![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 649]](../ps.gif) 649
649![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 650]](../ps.gif) 650
650![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 651]](../ps.gif) 651
651![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 652]](../ps.gif) 652
652![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 653]](../ps.gif) 653
653![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 654]](../ps.gif) 654
654![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 655]](../ps.gif) 655
655![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 656]](../ps.gif) 656
656![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 657]](../ps.gif) 657
657![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 658]](../ps.gif) 658
658![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 659]](../ps.gif) 659
659![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 660]](../ps.gif) 660
660![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 661]](../ps.gif) 661
661![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 662]](../ps.gif) 662
662![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 663]](../ps.gif) 663
663![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 664]](../ps.gif) 664
664![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 665]](../ps.gif) 665
665![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 666]](../ps.gif) 666
666![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 667]](../ps.gif) 667
667![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 668]](../ps.gif) 668
668![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 669]](../ps.gif) 669
669![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 670]](../ps.gif) 670
670![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 671]](../ps.gif) 671
671![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 672]](../ps.gif) 672
672![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 673]](../ps.gif) 673
673![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 674]](../ps.gif) 674
674![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 675]](../ps.gif) 675
675![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 676]](../ps.gif) 676
676![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 677]](../ps.gif) 677
677![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 678]](../ps.gif) 678
678![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 679]](../ps.gif) 679
679![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 680]](../ps.gif) 680
680![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 681]](../ps.gif) 681
681![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 682]](../ps.gif) 682
682![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 683]](../ps.gif) 683
683![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 684]](../ps.gif) 684
684![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 685]](../ps.gif) 685
685![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 686]](../ps.gif) 686
686![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 687]](../ps.gif) 687
687![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 688]](../ps.gif) 688
688![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 689]](../ps.gif) 689
689![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 690]](../ps.gif) 690
690![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 691]](../ps.gif) 691
691![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 692]](../ps.gif) 692
692![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 693]](../ps.gif) 693
693![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 694]](../ps.gif) 694
694![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 695]](../ps.gif) 695
695![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 696]](../ps.gif) 696
696![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 697]](../ps.gif) 697
697![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 698]](../ps.gif) 698
698![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 699]](../ps.gif) 699
699![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 700]](../ps.gif) 700
700![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 701]](../ps.gif) 701
701![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 702]](../ps.gif) 702
702![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 703]](../ps.gif) 703
703![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 704]](../ps.gif) 704
704![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 705]](../ps.gif) 705
705![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 706]](../ps.gif) 706
706![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 707]](../ps.gif) 707
707![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 708]](../ps.gif) 708
708![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 709]](../ps.gif) 709
709![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 710]](../ps.gif) 710
710![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 711]](../ps.gif) 711
711![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 712]](../ps.gif) 712
712![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 713]](../ps.gif) 713
713![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 714]](../ps.gif) 714
714![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 715]](../ps.gif) 715
715![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 716]](../ps.gif) 716
716![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 717]](../ps.gif) 717
717![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 718]](../ps.gif) 718
718![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 719]](../ps.gif) 719
719![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 720]](../ps.gif) 720
720![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 721]](../ps.gif) 721
721![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 722]](../ps.gif) 722
722![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 723]](../ps.gif) 723
723![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 724]](../ps.gif) 724
724![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 725]](../ps.gif) 725
725![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 726]](../ps.gif) 726
726![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 727]](../ps.gif) 727
727![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 728]](../ps.gif) 728
728![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 729]](../ps.gif) 729
729![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 730]](../ps.gif) 730
730![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 731]](../ps.gif) 731
731![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 732]](../ps.gif) 732
732![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 733]](../ps.gif) 733
733![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 734]](../ps.gif) 734
734![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 735]](../ps.gif) 735
735![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 736]](../ps.gif) 736
736![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 737]](../ps.gif) 737
737![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 738]](../ps.gif) 738
738![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 739]](../ps.gif) 739
739![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 740]](../ps.gif) 740
740![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 741]](../ps.gif) 741
741![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 742]](../ps.gif) 742
742![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 743]](../ps.gif) 743
743![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 744]](../ps.gif) 744
744![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 745]](../ps.gif) 745
745![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 746]](../ps.gif) 746
746![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 747]](../ps.gif) 747
747![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 748]](../ps.gif) 748
748![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 749]](../ps.gif) 749
749![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 750]](../ps.gif) 750
750![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 751]](../ps.gif) 751
751![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 752]](../ps.gif) 752
752![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 753]](../ps.gif) 753
753![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 754]](../ps.gif) 754
754![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 755]](../ps.gif) 755
755![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 756]](../ps.gif) 756
756![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 757]](../ps.gif) 757
757![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 758]](../ps.gif) 758
758![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 759]](../ps.gif) 759
759![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 760]](../ps.gif) 760
760![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 761]](../ps.gif) 761
761![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 762]](../ps.gif) 762
762![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 763]](../ps.gif) 763
763![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 764]](../ps.gif) 764
764![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 765]](../ps.gif) 765
765![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 766]](../ps.gif) 766
766![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 767]](../ps.gif) 767
767![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 768]](../ps.gif) 768
768![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 769]](../ps.gif) 769
769![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 770]](../ps.gif) 770
770![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 771]](../ps.gif) 771
771![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 772]](../ps.gif) 772
772![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 772.1]](../ps.gif) 772.1
772.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 772.2]](../ps.gif) 772.2
772.2![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 772.3]](../ps.gif) 772.3
772.3![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 772.4]](../ps.gif) 772.4
772.4![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 772.5]](../ps.gif) 772.5
772.5![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 772.6]](../ps.gif) 772.6
772.6![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 772.7]](../ps.gif) 772.7
772.7![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 773]](../ps.gif) 773
773![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 774]](../ps.gif) 774
774![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 775]](../ps.gif) 775
775![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 776]](../ps.gif) 776
776![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 777]](../ps.gif) 777
777![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 778]](../ps.gif) 778
778![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 779]](../ps.gif) 779
779![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 780]](../ps.gif) 780
780![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 781]](../ps.gif) 781
781![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 782]](../ps.gif) 782
782![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 783]](../ps.gif) 783
783![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 784]](../ps.gif) 784
784![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 785]](../ps.gif) 785
785![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 786]](../ps.gif) 786
786![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 787]](../ps.gif) 787
787![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 788]](../ps.gif) 788
788![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 788.1]](../ps.gif) 788.1
788.1![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 789]](../ps.gif) 789
789![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 800]](../ps.gif) 800
800![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 801]](../ps.gif) 801
801![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 802]](../ps.gif) 802
802![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 803]](../ps.gif) 803
803![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 804]](../ps.gif) 804
804![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 805]](../ps.gif) 805
805![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 806]](../ps.gif) 806
806![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 807]](../ps.gif) 807
807![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 808]](../ps.gif) 808
808![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 809]](../ps.gif) 809
809![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 810]](../ps.gif) 810
810![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 811]](../ps.gif) 811
811![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 812]](../ps.gif) 812
812![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 813]](../ps.gif) 813
813![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 814]](../ps.gif) 814
814![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 815]](../ps.gif) 815
815![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 816]](../ps.gif) 816
816![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 817]](../ps.gif) 817
817![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 818]](../ps.gif) 818
818![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 819]](../ps.gif) 819
819![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 820]](../ps.gif) 820
820![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 821]](../ps.gif) 821
821![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 822]](../ps.gif) 822
822![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 823]](../ps.gif) 823
823![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 824]](../ps.gif) 824
824![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 825]](../ps.gif) 825
825![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 826]](../ps.gif) 826
826![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 827]](../ps.gif) 827
827![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 828]](../ps.gif) 828
828![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 829]](../ps.gif) 829
829![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 830]](../ps.gif) 830
830![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 831]](../ps.gif) 831
831![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 832]](../ps.gif) 832
832![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 833]](../ps.gif) 833
833![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 834]](../ps.gif) 834
834![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 835]](../ps.gif) 835
835![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 836]](../ps.gif) 836
836![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 837]](../ps.gif) 837
837![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 838]](../ps.gif) 838
838![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 839]](../ps.gif) 839
839![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 840]](../ps.gif) 840
840![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 841]](../ps.gif) 841
841![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 842]](../ps.gif) 842
842![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 843]](../ps.gif) 843
843![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 844]](../ps.gif) 844
844![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 845]](../ps.gif) 845
845![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 846]](../ps.gif) 846
846![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 847]](../ps.gif) 847
847![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 848]](../ps.gif) 848
848![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 849]](../ps.gif) 849
849![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 850]](../ps.gif) 850
850![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 851]](../ps.gif) 851
851![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 852]](../ps.gif) 852
852![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 853]](../ps.gif) 853
853![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 854]](../ps.gif) 854
854![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 855]](../ps.gif) 855
855![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 858]](../ps.gif) 858
858![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 859]](../ps.gif) 859
859![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 860]](../ps.gif) 860
860![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 861]](../ps.gif) 861
861![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 862]](../ps.gif) 862
862![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 863]](../ps.gif) 863
863![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 864]](../ps.gif) 864
864![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 865]](../ps.gif) 865
865![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 866]](../ps.gif) 866
866![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 867]](../ps.gif) 867
867![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 868]](../ps.gif) 868
868![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 869]](../ps.gif) 869
869![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 870]](../ps.gif) 870
870![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 871]](../ps.gif) 871
871![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 872]](../ps.gif) 872
872![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 873]](../ps.gif) 873
873![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 874]](../ps.gif) 874
874![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 875]](../ps.gif) 875
875![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 876]](../ps.gif) 876
876![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 877]](../ps.gif) 877
877![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 878]](../ps.gif) 878
878![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 879]](../ps.gif) 879
879![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 880]](../ps.gif) 880
880![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 881]](../ps.gif) 881
881![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 882]](../ps.gif) 882
882![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 883]](../ps.gif) 883
883![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 884]](../ps.gif) 884
884![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 885]](../ps.gif) 885
885![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 886]](../ps.gif) 886
886![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 887]](../ps.gif) 887
887![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 888]](../ps.gif) 888
888![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 889]](../ps.gif) 889
889![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 890]](../ps.gif) 890
890![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 891]](../ps.gif) 891
891![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 892]](../ps.gif) 892
892![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 893]](../ps.gif) 893
893![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 894]](../ps.gif) 894
894![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 895]](../ps.gif) 895
895![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 896]](../ps.gif) 896
896![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 897]](../ps.gif) 897
897![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 898]](../ps.gif) 898
898![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 899]](../ps.gif) 899
899![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 900]](../ps.gif) 900
900![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 901]](../ps.gif) 901
901![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 902]](../ps.gif) 902
902![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 903]](../ps.gif) 903
903![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 904]](../ps.gif) 904
904![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 905]](../ps.gif) 905
905![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 906]](../ps.gif) 906
906![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 907]](../ps.gif) 907
907![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 908]](../ps.gif) 908
908![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 909]](../ps.gif) 909
909![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 910]](../ps.gif) 910
910![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 911]](../ps.gif) 911
911![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 912]](../ps.gif) 912
912![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 913]](../ps.gif) 913
913![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 914]](../ps.gif) 914
914![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 915]](../ps.gif) 915
915![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 916]](../ps.gif) 916
916![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 917]](../ps.gif) 917
917![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 918]](../ps.gif) 918
918![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 919]](../ps.gif) 919
919![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 920]](../ps.gif) 920
920![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 921]](../ps.gif) 921
921![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 922]](../ps.gif) 922
922![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 923]](../ps.gif) 923
923![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 924]](../ps.gif) 924
924![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 925]](../ps.gif) 925
925![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 926]](../ps.gif) 926
926![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 927]](../ps.gif) 927
927![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 928]](../ps.gif) 928
928![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 929]](../ps.gif) 929
929![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 930]](../ps.gif) 930
930![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 931]](../ps.gif) 931
931![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 932]](../ps.gif) 932
932![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 933]](../ps.gif) 933
933![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 934]](../ps.gif) 934
934![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 935]](../ps.gif) 935
935![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 936]](../ps.gif) 936
936![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 937]](../ps.gif) 937
937![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 938]](../ps.gif) 938
938![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 939]](../ps.gif) 939
939![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 940]](../ps.gif) 940
940![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 941]](../ps.gif) 941
941![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 942]](../ps.gif) 942
942![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 943]](../ps.gif) 943
943![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 944]](../ps.gif) 944
944![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 945]](../ps.gif) 945
945![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 946]](../ps.gif) 946
946![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 947]](../ps.gif) 947
947![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 948]](../ps.gif) 948
948![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 949]](../ps.gif) 949
949![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 950]](../ps.gif) 950
950![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 951]](../ps.gif) 951
951![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 952]](../ps.gif) 952
952![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 953]](../ps.gif) 953
953![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 954]](../ps.gif) 954
954![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 955]](../ps.gif) 955
955![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 956]](../ps.gif) 956
956![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 957]](../ps.gif) 957
957![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 958]](../ps.gif) 958
958![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 959]](../ps.gif) 959
959![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 960]](../ps.gif) 960
960![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 961]](../ps.gif) 961
961![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 962]](../ps.gif) 962
962![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 963]](../ps.gif) 963
963![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 964]](../ps.gif) 964
964![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 965]](../ps.gif) 965
965![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 966]](../ps.gif) 966
966![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 967]](../ps.gif) 967
967![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 968]](../ps.gif) 968
968![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 969]](../ps.gif) 969
969![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 970]](../ps.gif) 970
970![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 971]](../ps.gif) 971
971![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 972]](../ps.gif) 972
972![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 973]](../ps.gif) 973
973![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 974]](../ps.gif) 974
974![[List of Patents for class 514 subclass 975]](../ps.gif) 975
975