CPC Definition - Subclass H04M
This place covers:
- Subscriber equipment (fixed and mobile phones), e.g. Constructional features of telephone sets, User interfaces for telephones.
- Telecommunication systems including subscriber equipment and exchanges, e.g.
- Interconnection arrangements between switching centres,
- Interconnection arrangements not involving centralized switching,
- Metering arrangements,
- Time-controlling arrangements,
- Time-indicating arrangements,
- Party line systems,
- Prepayment telephone systems,
- Current supply arrangements for telephone systems,
- Computer telephony integration (CTI),
- SPIT and SPAM prevention in telephony;
- Telephonic communication systems combined with other electrical systems;
- Testing arrangements peculiar to telephonic communication systems.
With regard to mobile telephony, H04M covers communication systems using wireless extensions, i.e. wireless links without selective communication, e.g. cordless telephones, which are covered by group H04M 1/72, whereas H04W covers communication networks for selectively establishing one or a plurality of wireless communication links between a desired number of users or between users and network equipments, for the purpose of transferring information via these wireless communication links.
With regard to VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol), voice is considered in this context to be a specific form of "digital information". Since the Internet Protocol and IP networks are classified in H04L (H04L 12/00, data switching networks and real-time session management in data packet switching networks H04L 65/1066, Session management in data packet switching networks H04L 67/14), the transmission of voice over IP networks should be classified in H04L.
When VoIP is used to emulate or simulate services, the service, as presented to the user, is still classified in H04M. Any implementation details are however classified in H04L, for example SPIT and SPAM prevention in VoIP should be classified in H04M 3/436 or H04M 1/663.
VoIP is not covered by any single class, subclass, group or subgroup but rather classified as evolution of existing technologies. Therefore, aspects of VoIP are not fully classified in H04M and H04L, but also in other classes which have been used for classification of aspects related to telephonic communication, H04M and transmission of digital information, H04L such as by the Internet protocol.
This place does not cover:
Circuits for controlling other apparatus via a telephone cable and not involving telephone switching apparatus |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Counting mechanisms | |
Information storage based on relative movement between record carrier and transducer | |
Arrangements of electric cables or lines between relatively-movable parts | |
Multiplex transmission between switching centres | |
Selecting | |
Transducers | |
Wireless communication networks |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Exchange | Synonym for telephone switch. |
Satellite | A kind of exchange the operation of which depends upon control signals received from a supervisory exchange. |
Subscriber | General term for a user of terminal equipment, e.g. for the user of a telephone set, or for any equipment used by subscribers, e.g. telephones for public use. |
Substation | Subscriber or monitoring equipment which may connect a single subscriber to a line without choice as to subscriber. |
Switching centres | Include exchanges and satellites. |
Voice mail system | A centralized system for managing telephone messages for a large group of users. |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
PSTN | Public Switched Telephony Network. |
ISDN | Integrated Services Digital Network. |
ISUP | ISDN User Part. |
SIP | Session Initiation Protocol. |
H.323 | A standard protocol used for Packet-Based Multimedia Communications Systems. |
CTI | Computer telephony integration. A technology that allows interactions on a telephone and a computer to be integrated or co-ordinated. Common application interfaces and protocols for monitoring and controlling calls comprise Computer Supported Telecommunications Applications, CSTA, Java Telephony Application Programming Interface, JTAPI, Telephony Server Application Programming Interface, TSAPI, or Telephony Application Programming Interface, TAPI. |
Gatekeeper | A gatekeeper provides a number of services to terminals, gateways and devices, e.g. endpoint registration, address resolution, admission control and user authentication. |
Call agent | A call agent handles specific services to users e.g. alert the called party, send and receive voice data. |
IMS; IP Multimedia Subsystem | An architectural framework for delivering internet protocol, IP, multimedia to a mobile user. |
Softswitch | A central device in a telephone network which connects calls from one phone line to another, e.g. control connections at the junction point between circuit and packet networks. |
PBX | Private Branch Exchanges, e.g. for making connections among the internal telephones of a private organization. |
XDSL | Digital Subscriber Line. A family of technologies that provides digital data transmission over the wires of a local telephone network. |
Party line system | An arrangement in which two or more customers are connected directly to the same link or circuit. |
SPAM | The abuse of electronic messaging systems to send unsolicited bulk messages indiscriminately. |
SPIT | Spam over Internet Telephony, i.e. unwanted, automatically dialled, pre-recorded phone calls using Voice over Internet Protocol, VoIP. |
This place covers:
Substation equipment, e.g. for use by subscribers;
Arrangements for indicating or recording called number or number of calling subscriber at the substation equipment;
Arrangements for answering calls and for recording messages and conversations at the substation equipment;
Substation extension, e.g. cordless telephones;
Arrangements for testing;
User guidance features in telephone sets;
Devices for signalling identity of wanted subscriber, e.g. telephone directories;
Substation equipment including speech amplifiers;
Arrangements for preventing unauthorized or fraudulent calling.
User interfaces for telephones applications.
Arrangements for services at the substation equipment are classified here. Arrangements for services at exchanges are classified at H04M 3/00
Public telephone booth E04H 1/14.
Subscriber network interface devices H04Q 1/028.
Terminal devices adapted for wireless communication networks H04W 88/02 (not for constructional features of portable telephones).
Portable transceivers H04B 1/3827
This place does not cover:
Subscriber services or facilities provided at exchanges | |
Prepayment telephone coin boxes | |
Current supply arrangements |
Transmission systems employing electromagnetic waves other than radio waves: H04B 10/00
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Portable telephone sets | |
Casings, cabinets or drawers for electric apparatus in general |
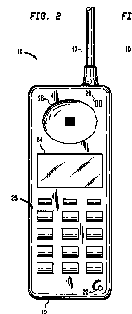
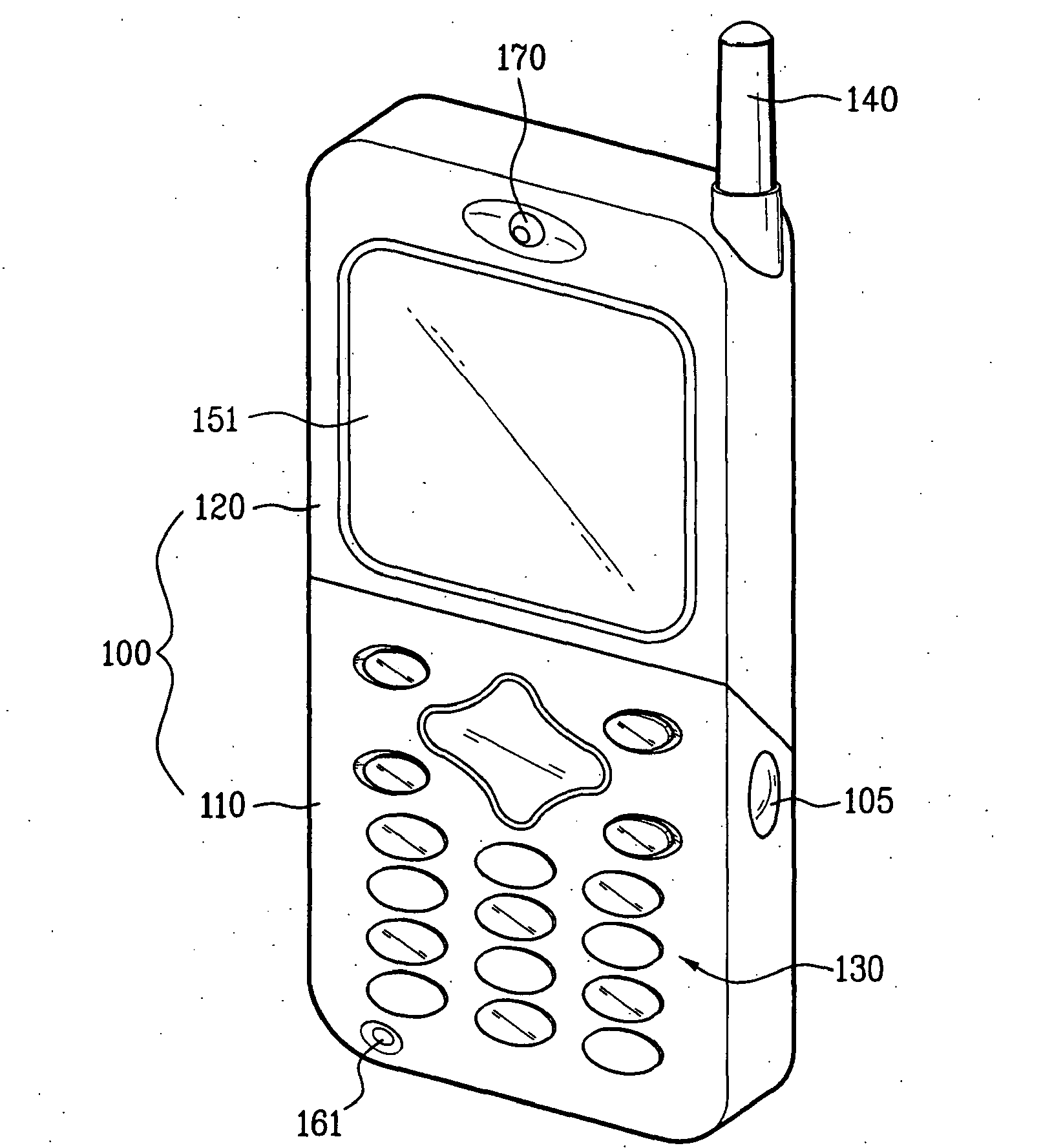
This place covers:
Constructional features of portable telephones. It is irrelevant whether they are mobile phones or handsets of a cordless phone having a local base station (e.g. DECT) at the user's premises. This group is intended to contain only candy-bar type telephone having no moving parts. For portable telephones having moving parts see below.
Example:
For portable computers: G06F 1/1613
For portable transceivers per se: H04B 1/3827
For wristwatch telephones: H04B 1/385
For SIM card holding means: H04B 1/3816
For constructional features of portable transmitters: H04B 1/034
For constructional features of casing for electrical apparatus in general: H05K 5/00
For constructional features of portable and battery operated apparatuses: H05K 5/0086
For antenna support and mounting means for mobile phones: H01Q 1/241
Toy telephones: A63H 33/3016
This place does not cover:
Constructional features of telephone transmitters or receivers, e.g. telephone handsets |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Construction or mounting dials | |
Arrangements for reducing RF exposure to the user |
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms:
- mobile, cellular,
- cordless, wireless, portable, hand-held,
- smartphone, cellphone, handy,
- appliance, terminal, station
This place covers:
Protective covers or auxiliary enclosures for mobile telephones holding the device during use without hampering said use. The covers or enclosures for mobile telephones are in principle detachable, but intended to remain on the mobile telephone during use. The cover or enclosure provides features, e.g. openings, notches or bumpers, that enable the use of the mobile phone. The protection can be various, e.g. to hazardous environments, for improving heat dissipation or resistance to shocks.
Illustrative examples of subject matter classified in this place:
1.

2.

Protective covers or auxiliary enclosures for mobile telephones that are intended to hold the device during use are classified in H04M 1/0203 while receptacles for storing portable audio devices, portable handheld communication devices or portable computing devices where the device must be removed for use are classified in A45C 11/001, A45C 11/002 and A45C 11/003, respectively.
In the context of subclass A45C, storing is understood as to refer to putting or keeping something in a receptacle for future use.
Enclosures for carrying portable computers with peripheral devices, like a printer or a charger, are classified in G06F 1/1628.
Holders or carriers being worn by a user for portable audio devices, portable handheld communication devices and portable computing devices to facilitate transporting or carrying, where the device is not in use or being passively used, are classified in groups A45F 5/1508, A45F 5/1516 and A45F 5/1525, respectively.
Protective covers or auxiliary enclosures for portable computers that are intended to hold the device during use without hampering said use are classified in G06F 1/1629.
Constructional features, like venting or EMI shielding means, of electronic housings not characterised by the inner electronic arrangements are classified in H05K 5/00.
Supports for positioning or steadying a device relative to a person with the intent of using the device are classified in F16M 13/04.
This place does not cover:
Receptacles for storing portable handheld communication devices, e.g. pagers or smart phones |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Telephone sets specially adapted for use in ships, mines or other places exposed to adverse environment | |
Receptacles for storing portable audio devices like headphones or digital music players | |
Receptacles for storing portable computing devices, e.g. laptops, tablets or calculators | |
Holders or carriers for portable audio devices | |
Holders or carriers for portable handheld communication devices | |
Holders or carriers for portable computing devices | |
Supports for positioning or steadying a device relative to a person | |
Protective covers or auxiliary enclosures for portable computers | |
Arrangements for carrying or protecting portable transceivers | |
Casings, cabinets or drawers for electric apparatus |
Features relating to further aspects concerning hygiene, e.g. integrated sanitizers or antiviral aspects are identified by allocating further classification in H04M 1/17.
Features relating to further improving the user comfort by providing a decorative aspect are identified by allocating further classification in H04M 1/0283.
Fastening means of holding devices supporting portable telephones are classified in H04M 1/04.
This place covers:
Main aspect is the motion of body parts. This group is intended for documents that do not fit in any of the lower level groups.
Example EP1843554
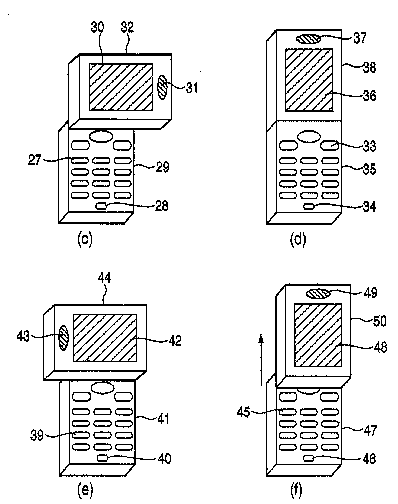
For portable computers: G06F 1/1615
Documents are only classified in this class when none of the lower classes applies.
This place covers:
Neither rotatable nor foldable in the sense of the definitions of the classes H04M 1/0225 or H04M 1/0214: the axis of the movement is neither perpendicular nor parallel to the plane defined by the bodies in the closed position.
This group is for portable telephones having moving parts and that do not fit in any of the groups H04M 1/021, H04M 1/0214, H04M 1/0225 or H04M 1/0235.
Example: EP1659700
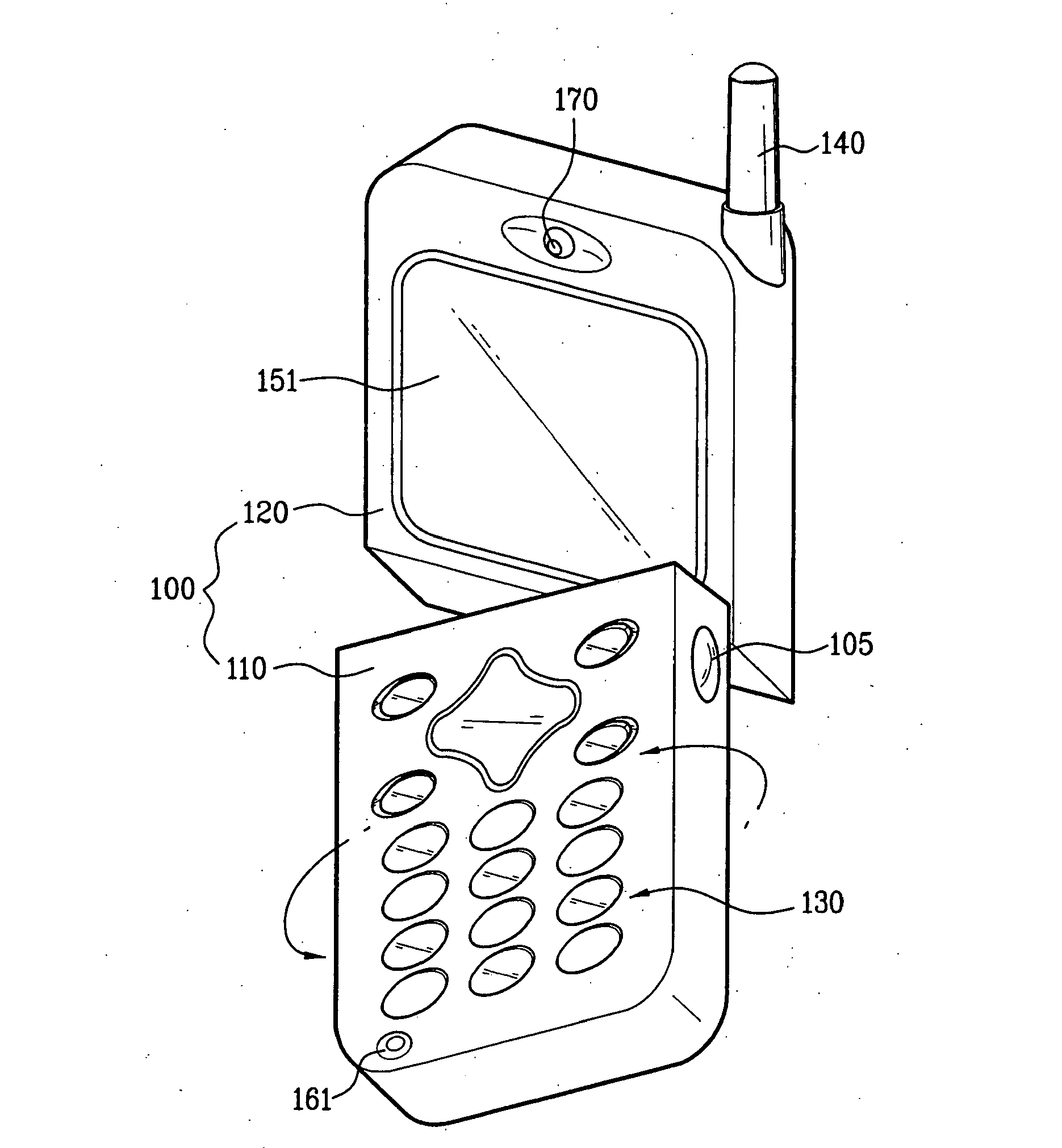
This place covers:
Only foldable and rotatable phones without mechanical details of the hinge would be classified here (when combined with translation movement H04M 1/0235).
Example: US2004/0203485
This place does not cover:
Slidable or telescopic telephones |
This place covers:
This group is for documents disclosing details of the hinge mechanism that allow two degrees of freedom in the sense defined in the group H04M 1/021, i.e. folding around a first axis and rotating around a second axis, which is perpendicular to the first one.
Example:EP1298890
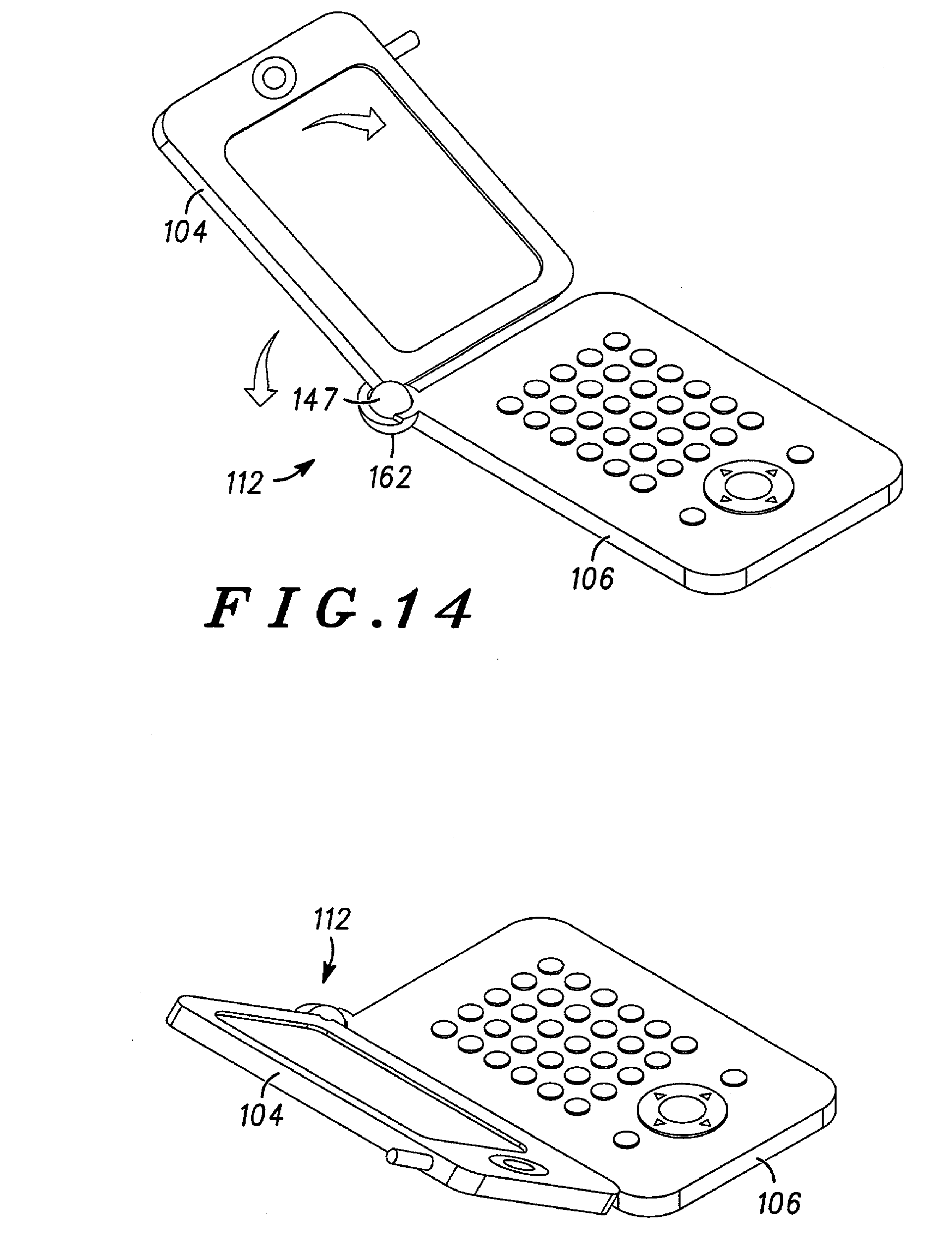
This place covers:
Only foldable and portable phone without mechanical details of the hinge.
Example:EP1595386 :
Foldable portable computers: G06F 1/1616.
Hinges for doors or windows E05D.
Hinged covers or doors H02B 1/38.
Hinges for casing of electrical apparatuses H05K 5/0226.
This place does not cover:
Slidable or telescopic telephones |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Using combined folding and rotation motions |
Indexing Codes will be converted to index classes and considered as additional information
This place covers:
This group contains constructional details concerning the hinge. If the document does not provide any details concerning the hinge, the document should be classified in the group H04M 1/0214.
Example:EP1641224
For portable computers: G06F 1/1681
Hinges for doors and windows: E05D
Flexible line connectors wound around the rotation axis for electrical connection of the two folding parts: H01R 35/00
Hinges including optical fibres between different housings: G02B 6/3604
This place covers:
This group is for hinges (folding in one direction) that contain input/out means like push buttons, a thumb wheel or other navigational tools. Additionally, folding portable telephones having cameras integrated in the hinge are classified here as well.
Example: US2005221865
This place covers:
This group is for folding portable telephones wherein the hinge comprises two paralles axes.
Example: EP1510905
This place covers:
Portable communication devices foldable along two directional axis which are perpendicular to each other (Dual-axis hinge).
Example: US2006112519
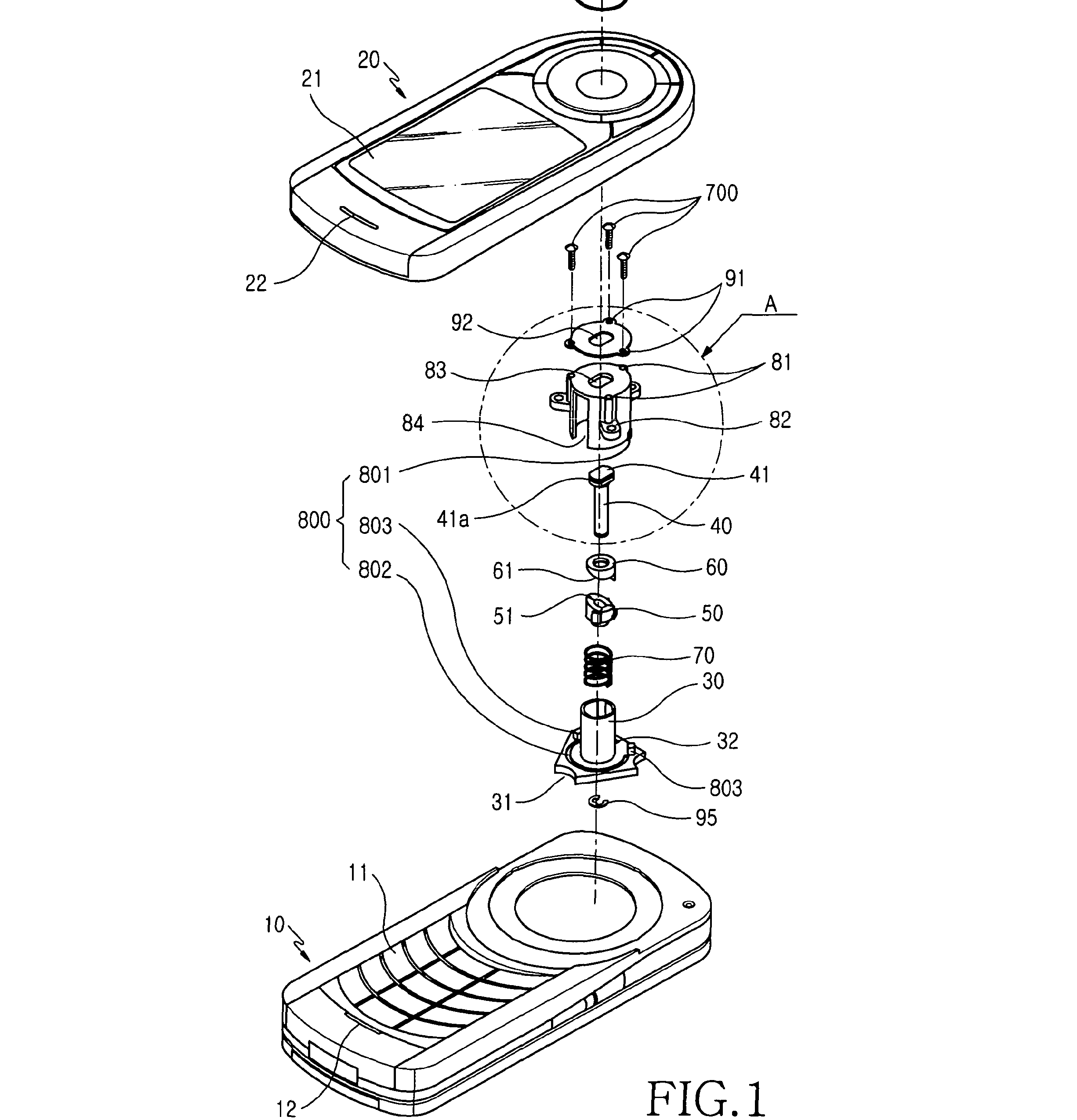
This place covers:
This group covers rotatable telephones whose body parts rotate relative to each other in the same plane as in the following Example: EP1349350
For portable computers: G06F 1/1622
This place does not cover:
Slidable or telescopic telephones |
This place covers:
This group contains constructional details concerning the hinge. If the document does not provide any details concerning the hinge, the document should be classified in the group H04M 1/0225.
For example: EP1615406
For portable computers: G06F 1/1681
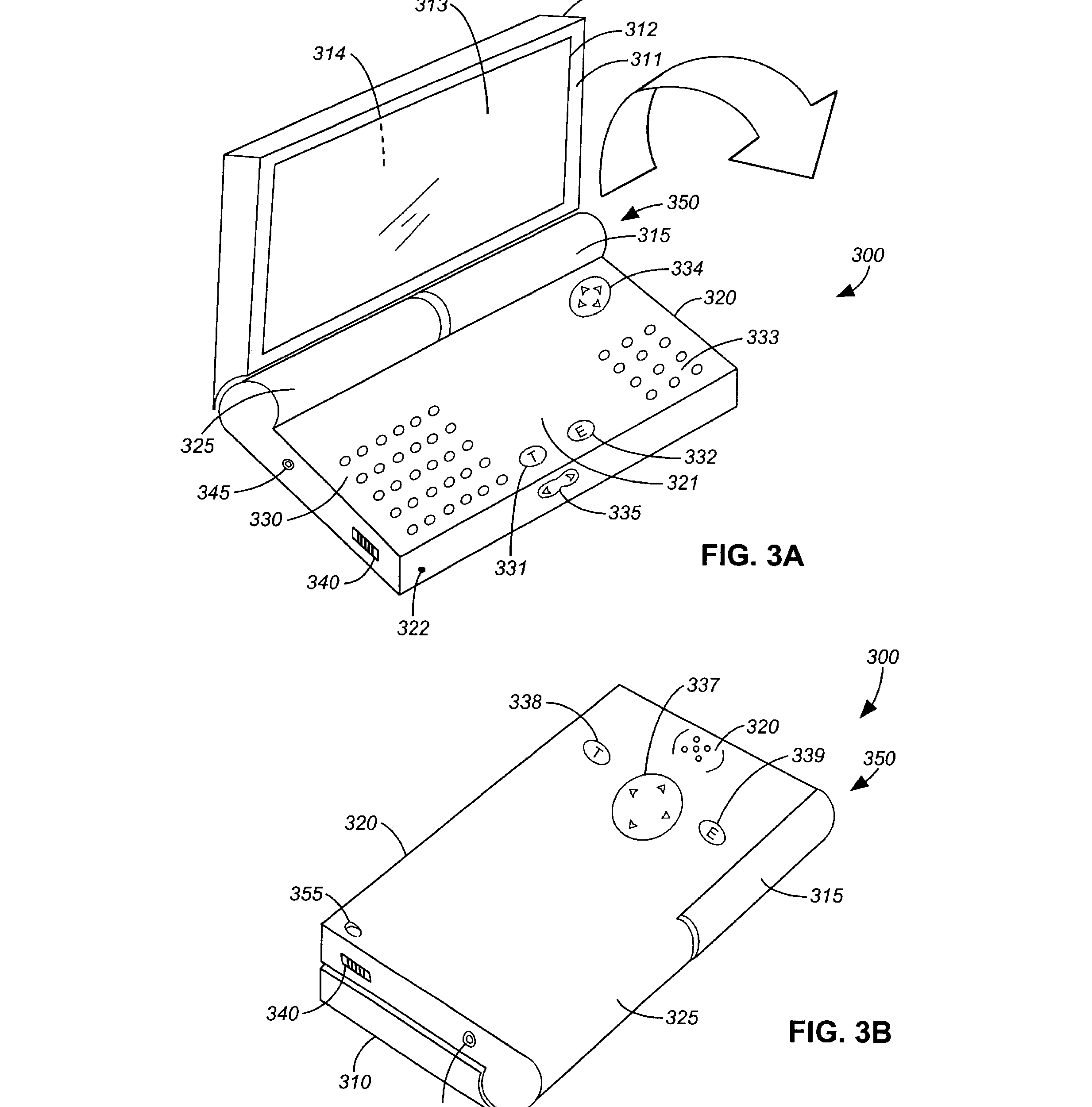
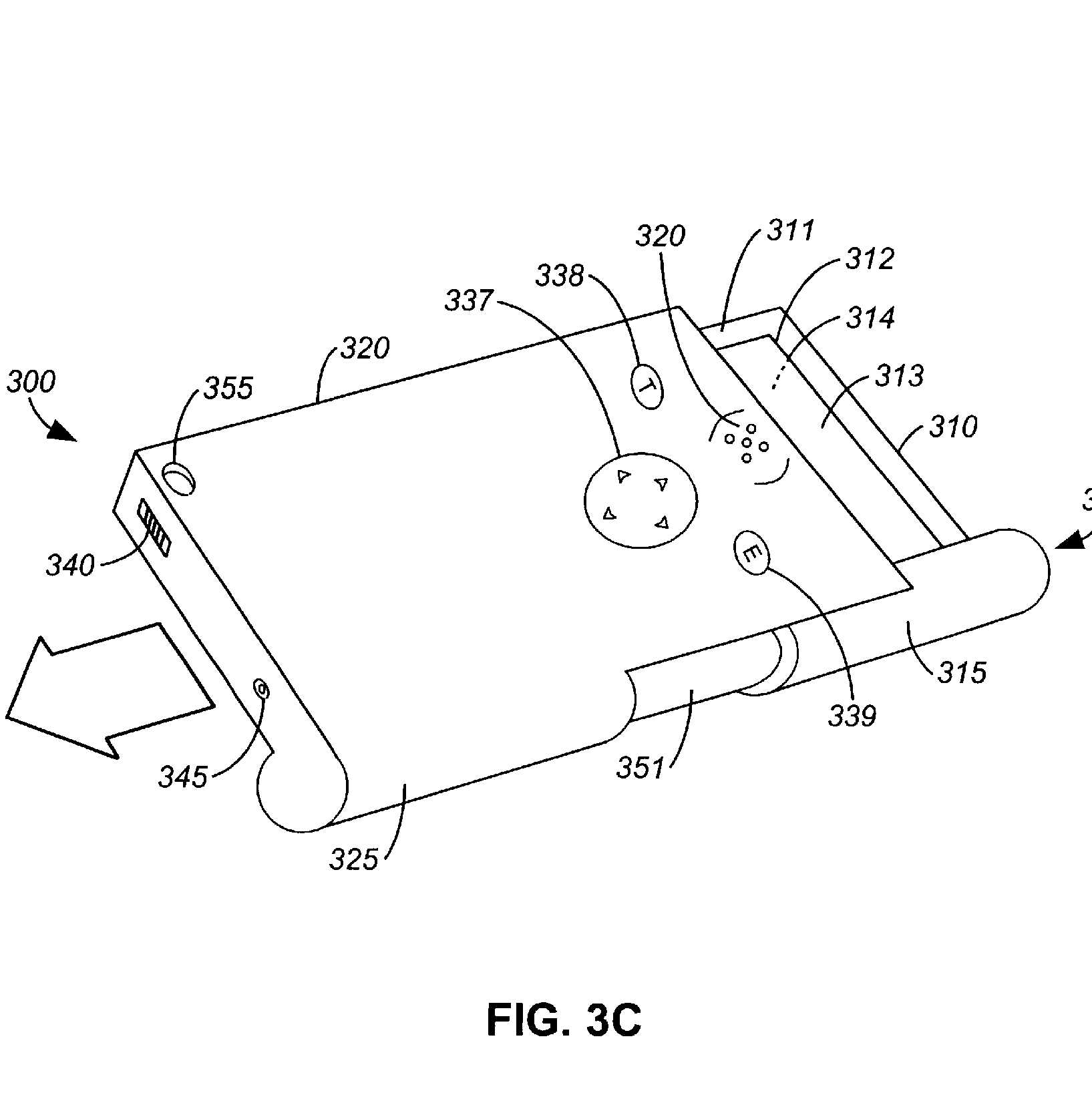
This place covers:
This group is for hinges (rotating in one direction) that contain input/out means like push buttons, a thumb wheel or other navigational tools. Additionally, rotating portable telephones having cameras integrated in the hinge are classified here as well.
For example: US2005280731
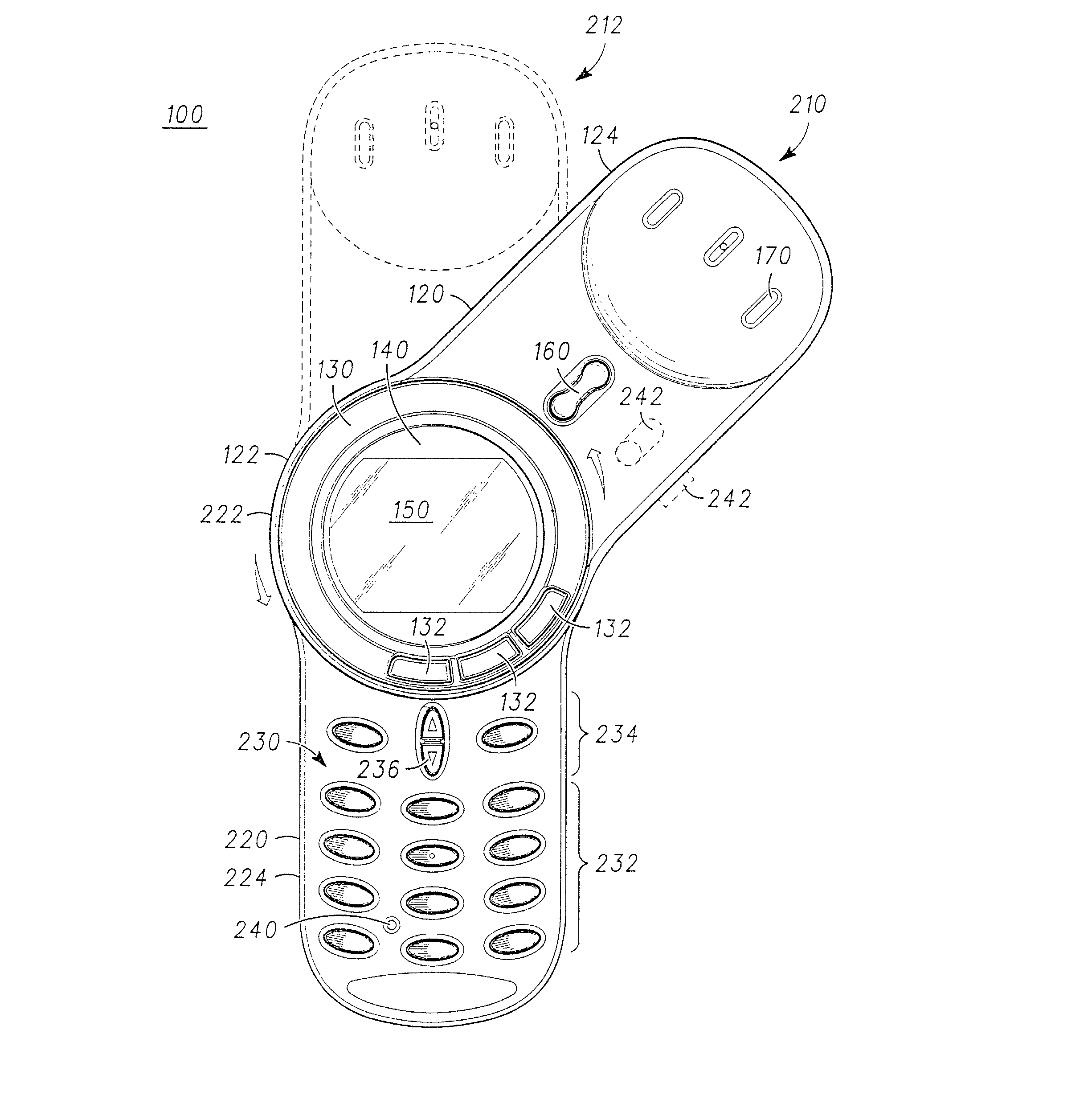
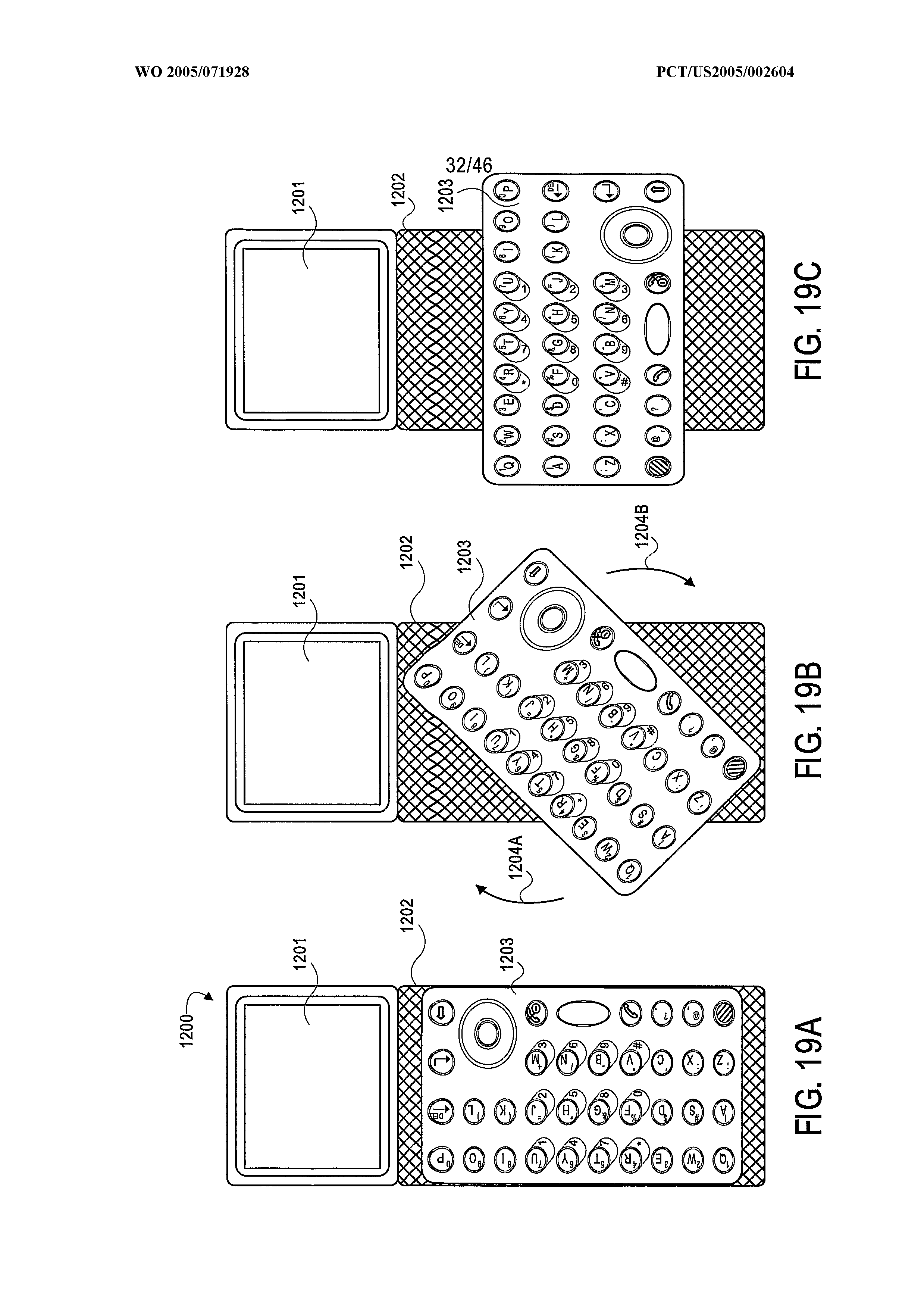
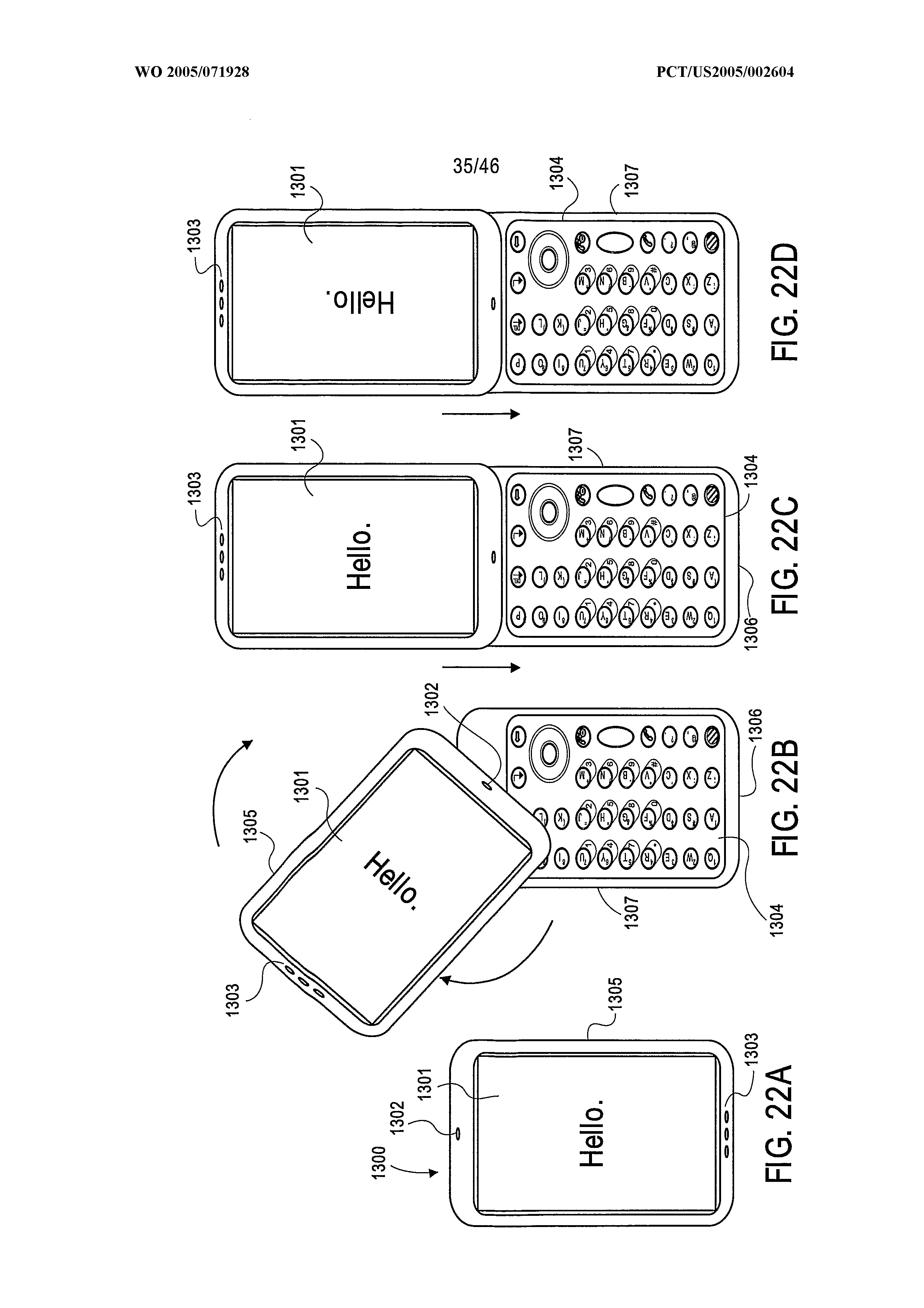
This place covers:
This group is intended for rotating portable telephones wherein one of the rotating parts is a keyboard. If the document contains details of the hinge, the document is additionally classified in H04M 1/0227.
If there are a plurality of keyboards, the indexing code H04M 2250/18 is allocated as well.
For example: WO2005071928
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Construction or mounting of dials |
This place covers:
This group is intended for rotating portable telephones wherein one of the rotating parts is a display. If the document contains details of the hinge, the document is additionally classified in H04M 1/0227.
If there are a plurality of displays, the indexing code H04M 2250/16 is allocated as well.
For example: US2005088075
For portable computers: G06F 1/1622
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
For mounting a display module on a telephone set |
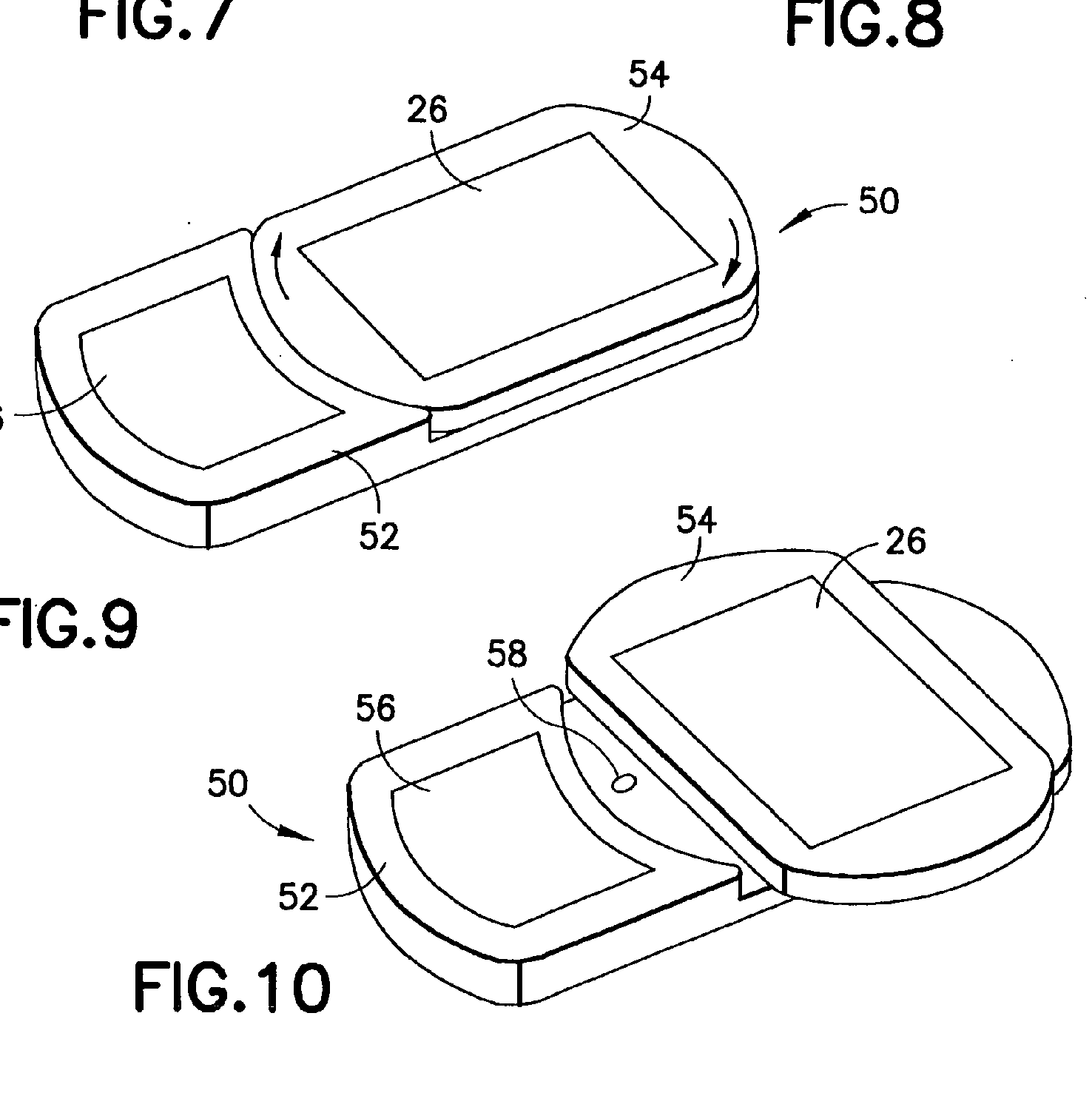
This place covers:
Slidable telephones without mechanical details of the hinge.
Some examples of movement combinations:
EP1540836: Foldable and slidable.
Classes:H04M 1/0235: Main aspect.
H04M 1/0214: Foldable as additional information.
WO2005071928: Rotatable and slidable.
Classes:
H04M 1/0235: Main aspect.
H04M 1/0233: Rotatable display as additional information.
For portable computers: G06F 1/1624
Not only slidable phones would be classified here, but every possible combination (except from foldable and rotatable, classified under H04M 1/021). Thus, the non-translational movement receives an Indexing Code as the following:
Slidable + Foldable
H04M 1/0235 + H04M 1/0214 as additional information.
Slidable + Rotatable
H04M 1/0235 + H04M 1/0225 as additional information.
Slidable + Rotatable + Foldable
H04M 1/0235 + H04M 1/021 as additional information.
This place covers:
This group contains constructional details concerning the sliding mechanism (e.g. sliding bars, springs and so on). If the document does not provide any details concerning the hinge, the document should be classified in the group H04M 1/0235.
For example: EP1648145
For portable computers: G06F 1/1681
This place covers:
This group conatins portable telephones wherein the housing parts can slide in two different directions (typically one perpendicular to the other one). If the document discloses mechanical details of the hinge, the code H04M 1/0237 is additionally allocated.
For example: WO2005071928
This place covers:
Portable telephones having moving parts (folding, rotating, sliding) whereby the position of the moving parts is detected and is used for performing an action (e.g. selecting an operating mode, answering a call, switch on/off a display or its backlight).
For example: US2005136853
'The method comprises the steps of detecting a relative position of the first electronic element relative to the second electronic element, and selecting an operational mode of the device based on the relative position'
Classification:
H04M 1/0241: Relative position.
H04M 1/0212: Details of foldable and rotatable hinge as additional information.
For portable computers |
When the main aspect is the relative position of the body parts, then the type of movement would be classified as Indexing Code or additional information.
Foldable and rotatable phones with relative position detectors are classified here, as their functionality depends on a combination of both open/close positions and the relative angle between housings.
This place covers:
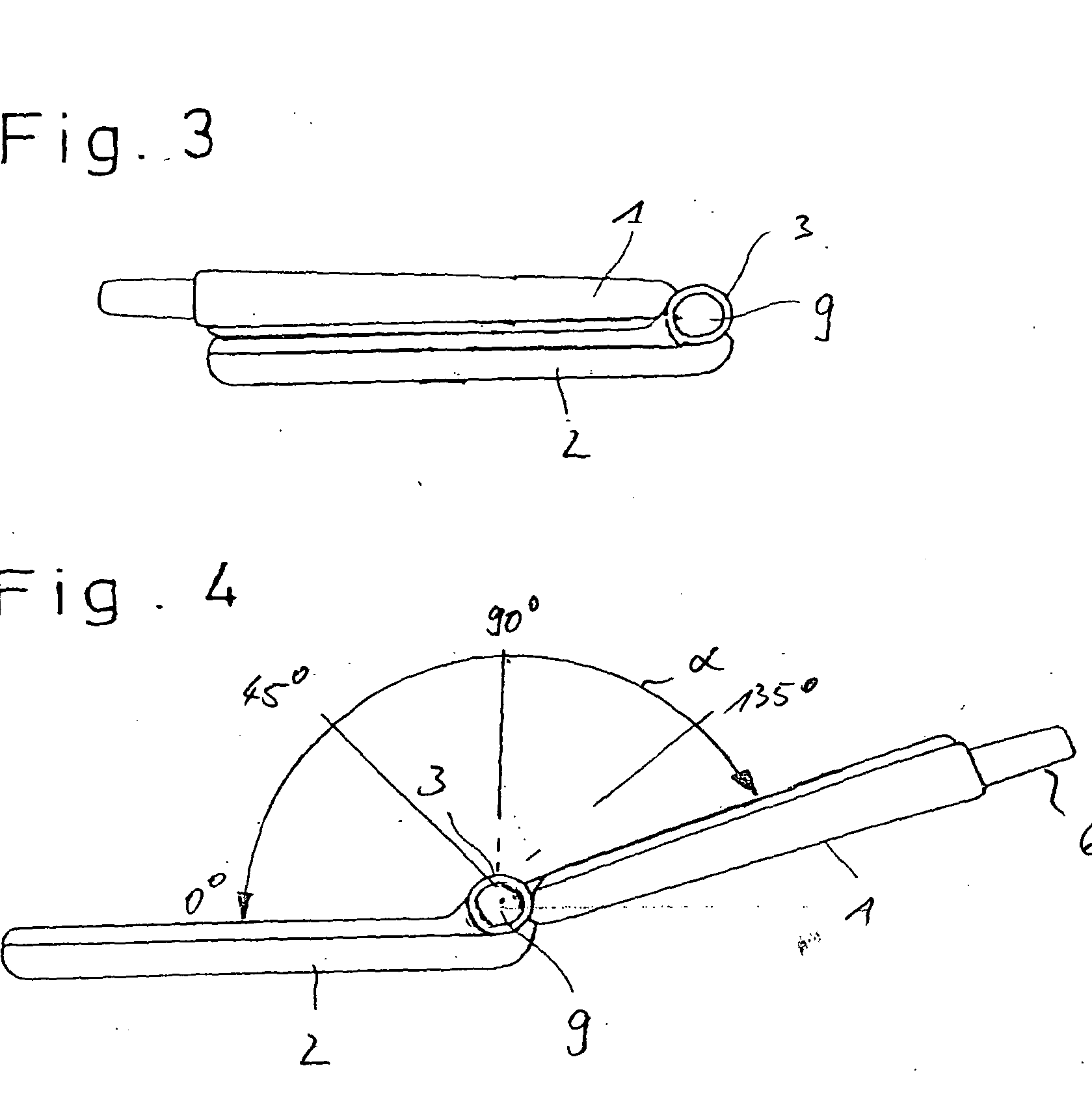
Mainly for rotatable phones, which apart from close (0°) and open (90° or 180°) positions have other 'intermediate' positions, with different functionalities.
Example: US2006035685
'the second housing ( 120 ) may have multiple positions relative to the first housing ( 220 ) in which each position activates a particular function of the device ( 100 ).'
Classification:
H04M 1/0243: Relative angle.
H04M 1/0227: Important details of rotatable hinge as additional information.
However, there are also those foldable telephones which detect not only an open/close condition, but the whole range:
Example: EP1601165
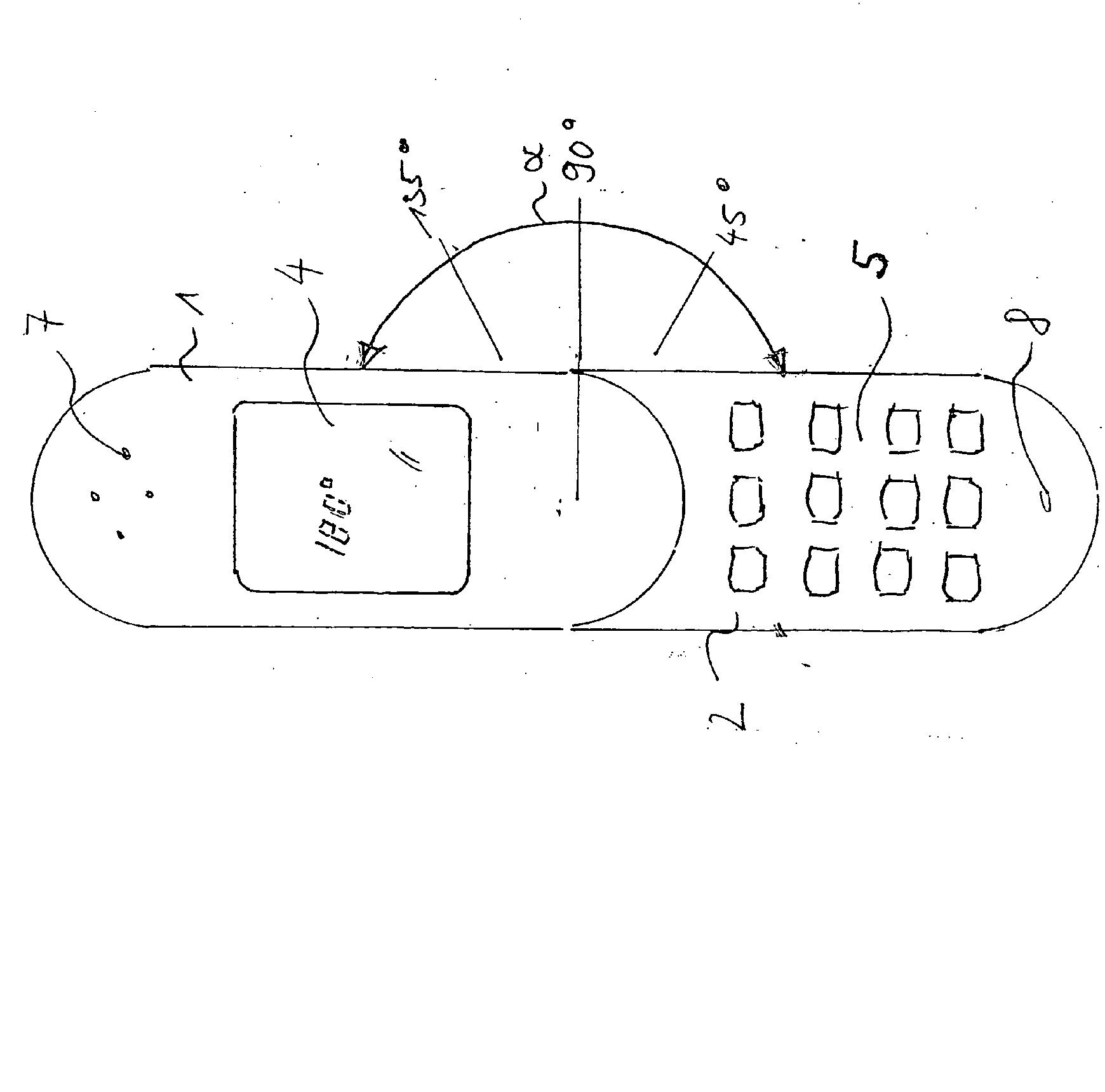
the relative angle of aperture controls foldable or rotatable phone. Classification:
H04M 1/0243: Relative angle.
H04M 1/0214: Foldable phone as additional information.
H04M 1/0225: Rotatable phone as additional information.
This place covers:
Mainly for foldable and slidable phone.
Example US2003064688
Slidable telephone with position detectors to control its functionality. Classification:
H04M 1/0245: Open/close condition.
H04M 1/0235: Slidable phone without important constructional hinge details as additional information.
For portable computers: G06F 1/1677
This place covers:
Portable telephones having at least three movable parts (folding, rotating, sliding). The type of movement is classified as additional information.
Example EP1396982: 3-body rotatable telephone.
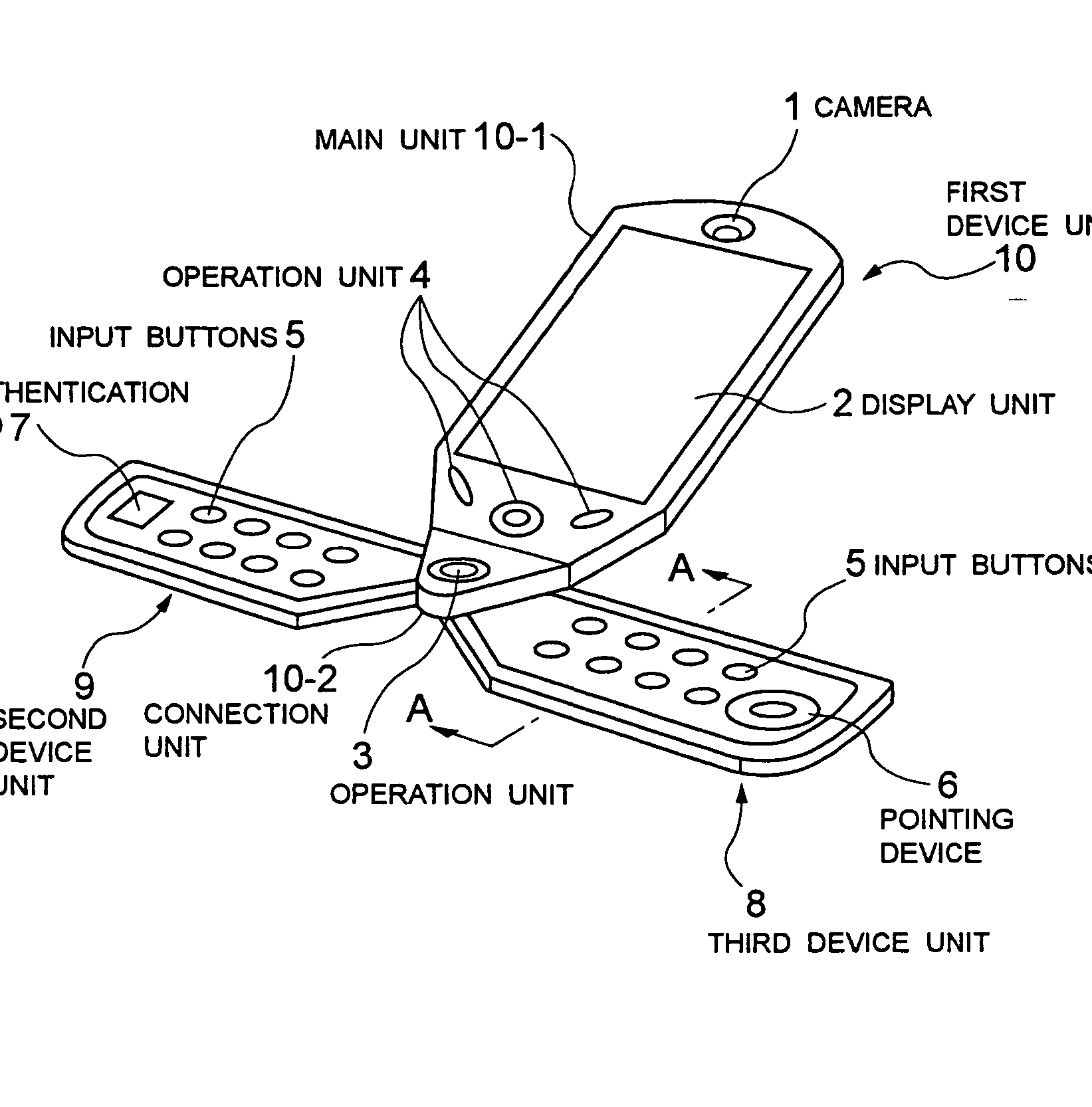
Classes:
H04M 1/0247: Main aspect.
H04M 1/0231: Rotatable keypad as additional information.
This place covers:
Constructional assembly of a mobile phone. Details about the interconnection of the main housing parts. How the device is kept together.
For user replaceable housings having a decorative purpose see H04M 1/0283.
This class is also for application dealing with methods disclosing how to assemble the telephone set during manufacturing.
Example: EP2180668
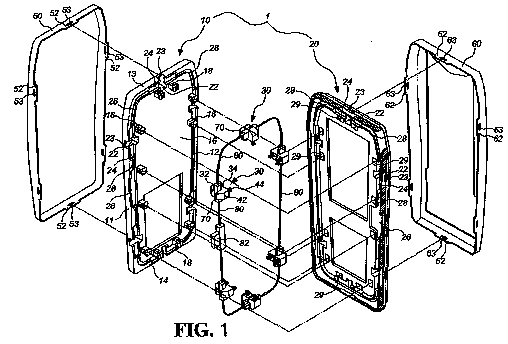
Casing and cabinets comprising several parts forming a closed housing: H05K 5/00
This place covers:
When the connection is done by pressing the housing portions together (press-fit or snap-on mechanism).
Also for applications where a special tool is required to separate the housing.
Example: EP2219349
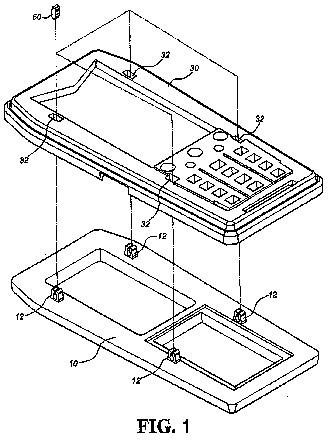
Other examples:
US2004053649
DE10314171
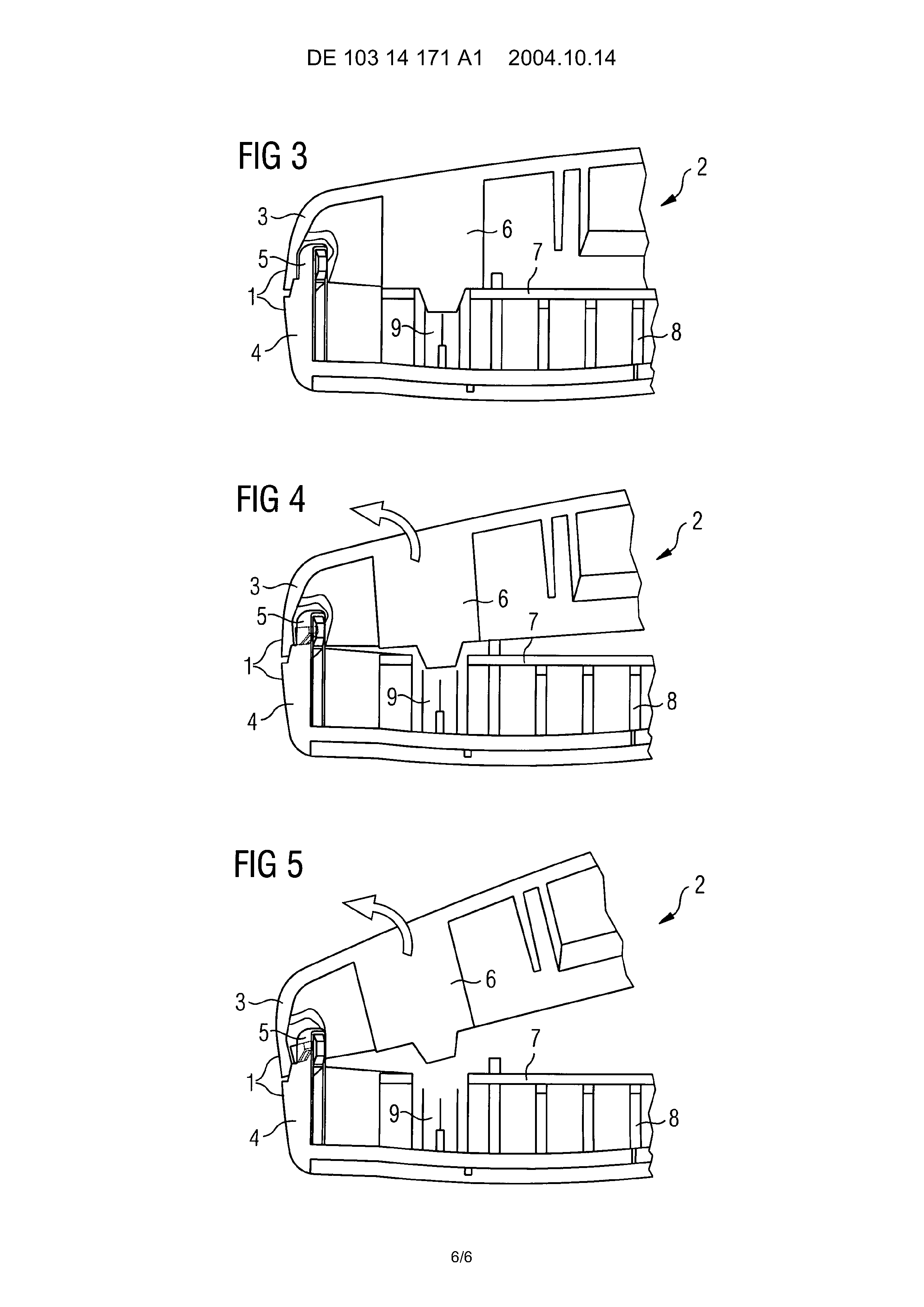
.
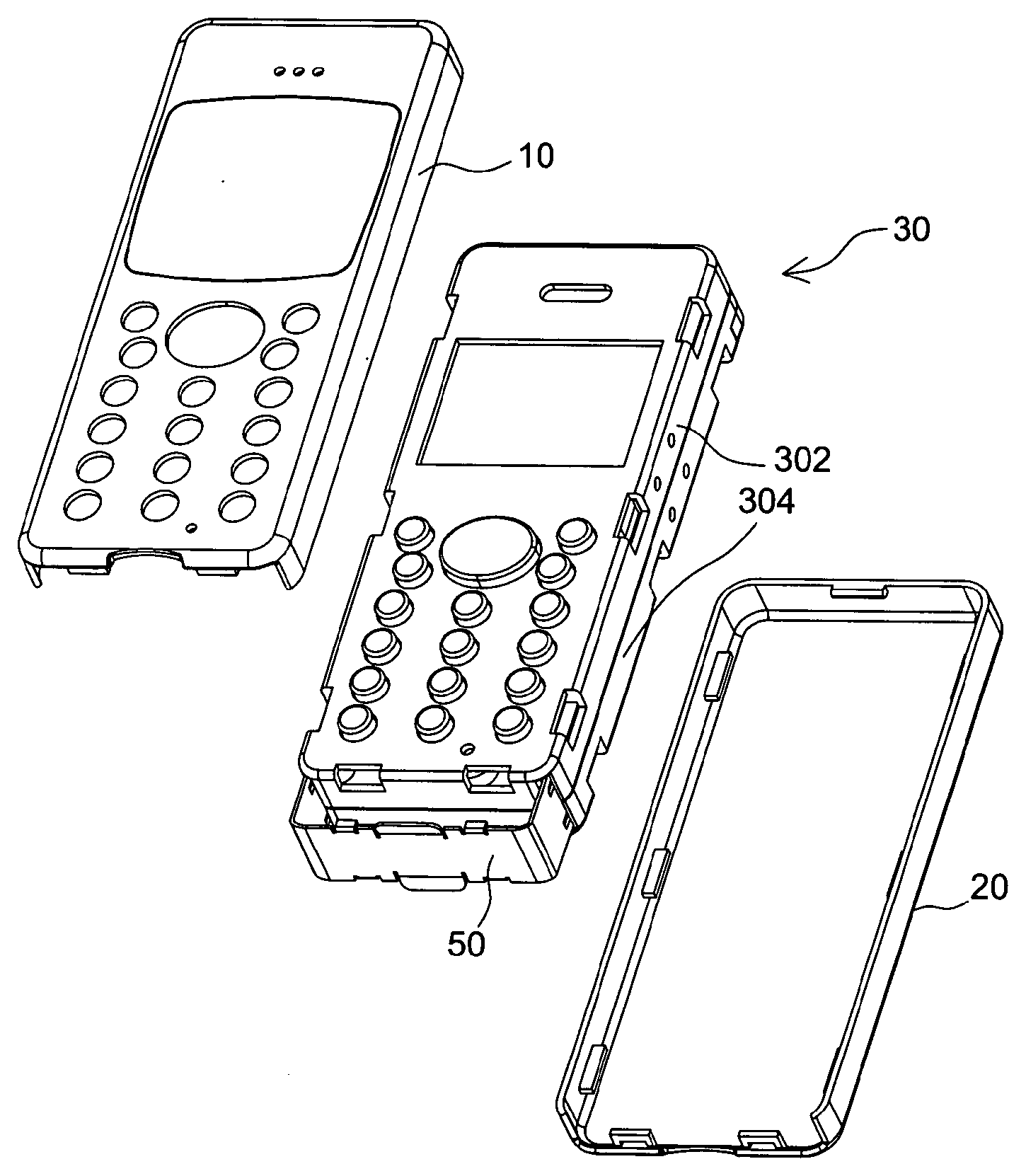
This place covers:
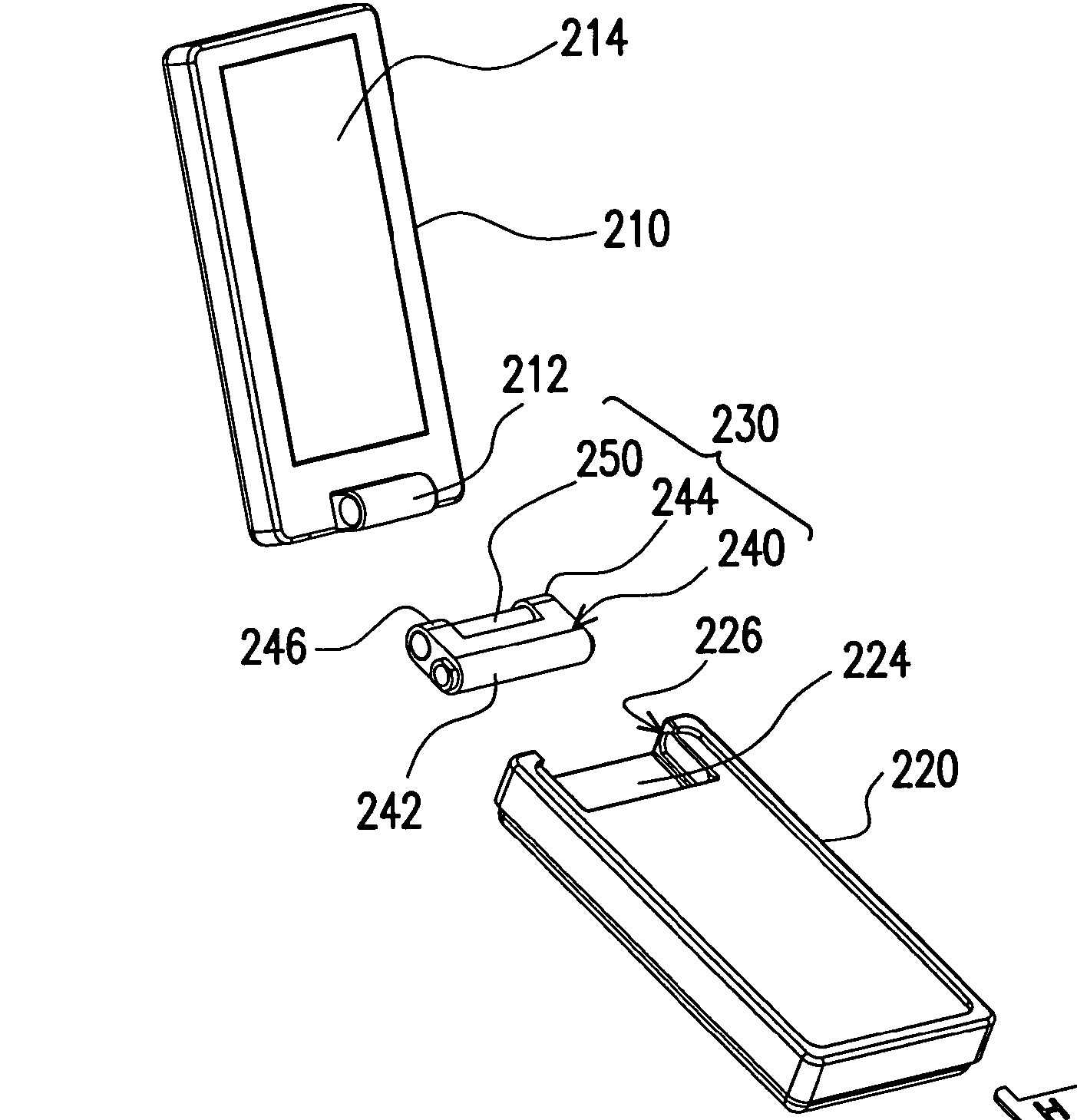
Mechanical assembly of a portable communication device comprising a plurality of detachable modules.
Example: WO2008017728. A communication device comprises a first structural module (101) with a power source (120), as well as second (102), and third (103) structural modules
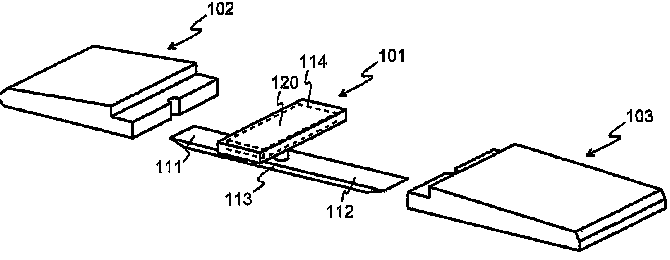
For personal computers: G06F 1/1656
Detachable keyboards for portable computers: G06F 1/1669
For a detachable accessory providing an expanded functionality to the communication device when connected to the same: H04M 1/72409.
This place covers:
Mechanical assembly of a portable communication device comprising a plurality of detachable modules which may communicate between each other via a wireless link when they are detached from each other
Example: US2008167080. An improved portable mobile phone is disclosed wherein the mobile phone comprises two modules and the mobile phone can function properly when the two modules are physically connected as well as when the two modules are detached
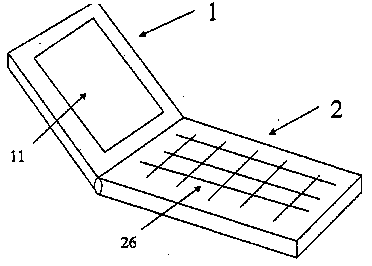
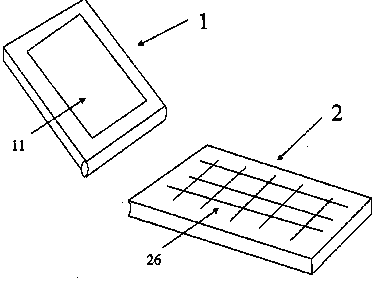 .
.
For an accessory providing an expandable functionality to the communication device and communicating with the same by using a short range radio link as the Bluetooth® interface: H04M 1/72412.
This place covers:
The headset is fitted in a special compartment of the device when not in use.
Example :US2008090626
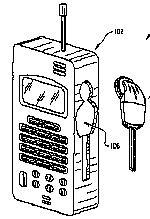
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Constructional features of headsets for use on head, throat or breast | |
Headsets for earphones to a mobile phone for hands-free use |
This place covers:
Mounting of specific components other than acoustic transducers like microphones and speakers.
The latching mechanism 10 is configured for mounting an accessory member 32 to a housing 31 of a portable electronic device 30.
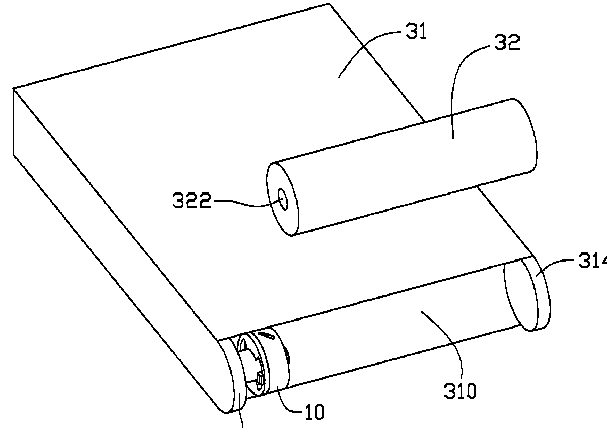
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Constructional features of telephone transmitters or receivers, e.g. of speakers or microphones | |
For portable computers |
This place covers:
Mounting of a battery module in a portable communication device
Example: WO9966697
For portable computers | |
For general aspect of mounting batteries in a portable device housing | |
For battery mounting in a portable transceiver | |
Portable or battery operated apparatus |
This place covers:
Mounting of a camera module in a portable communication device.
Example EP1267576. A camera module (30) is rotatably assembled between the inner sides of the rotary hinge support portions.
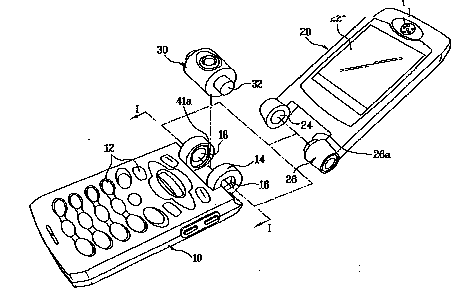
For a camera module in portable computers: G06F 1/1686
For constructional details of videotelephones: H04N 7/142
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Photo or video cameras per se | |
Television cameras |
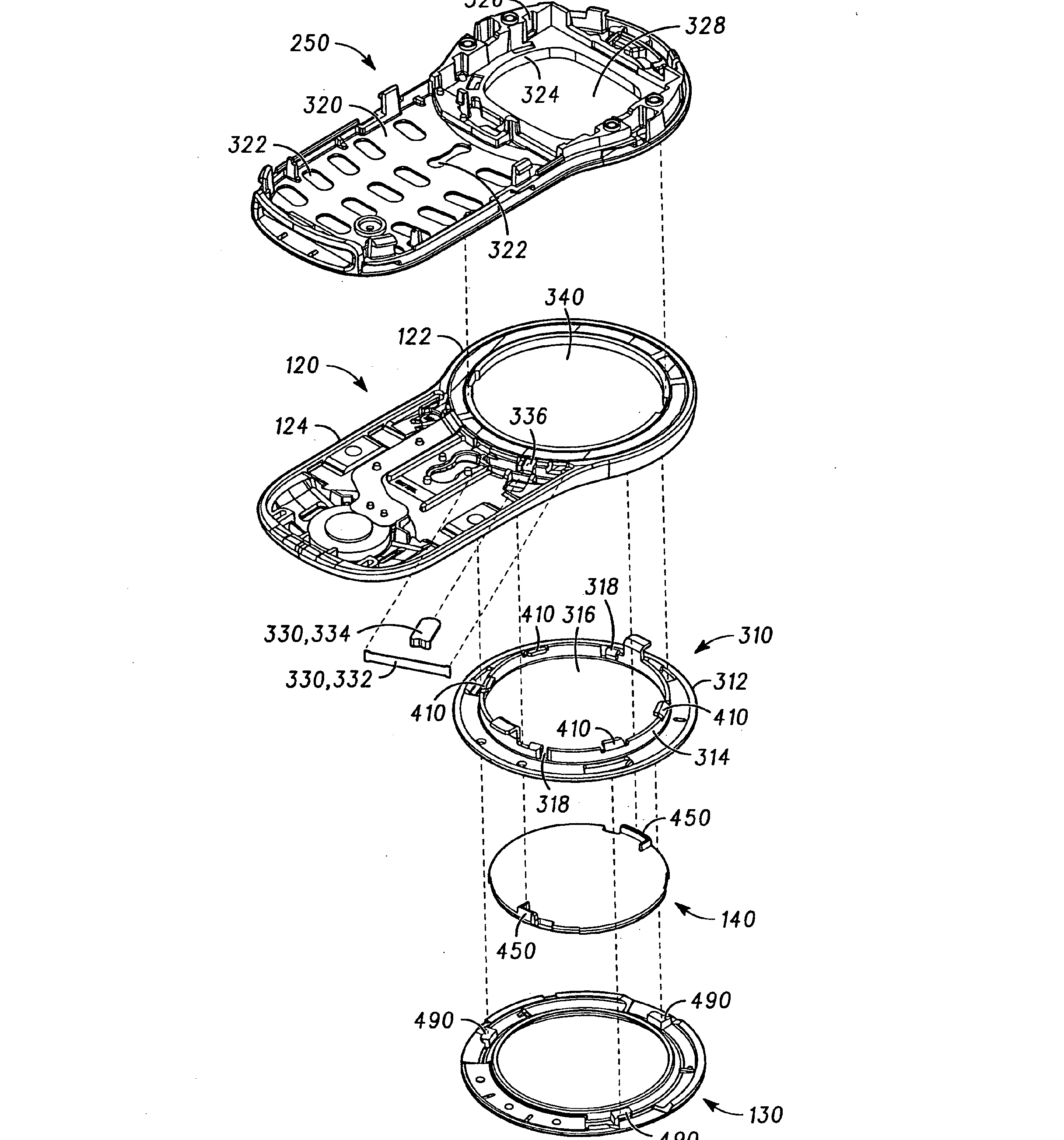
This place covers:
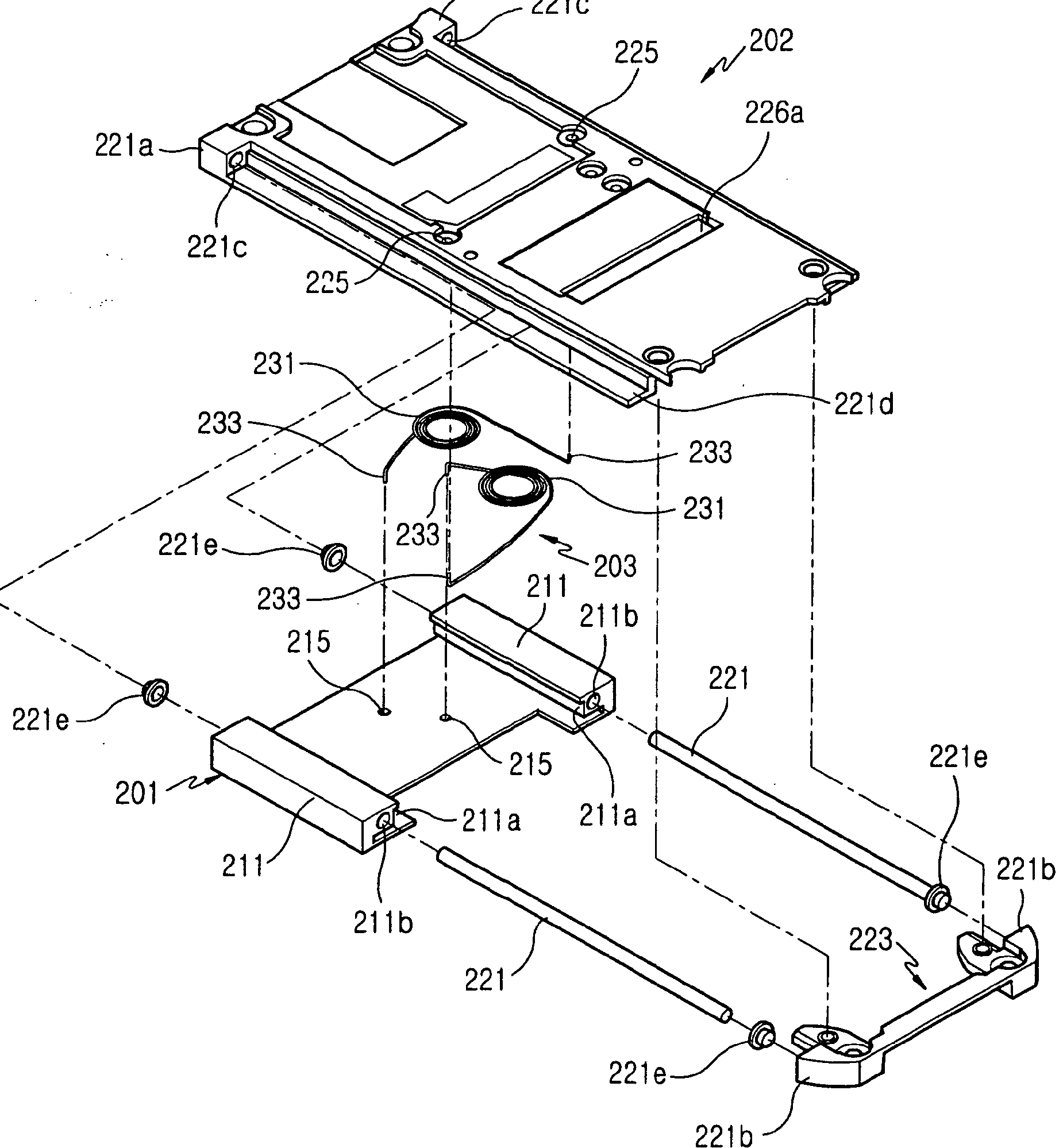
Mounting of a display module in a portable communication device
In the device (100), the flat-board-like display unit (200) provided with a display drive section (213) that drives a liquid crystal display section (211) is attached to a first case (110) with a metal rear plate (160) there between.
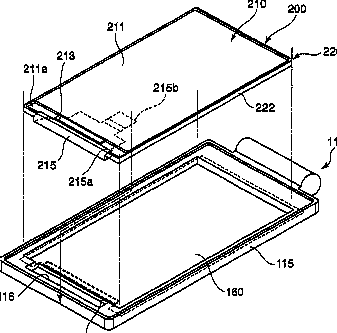 .
.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Mechanical mounting details of display modules for fixed telephones | |
For portable computers |
This place covers:
The display being extendable and retractable.
Example :WO2005114309. The display device has an inner housing with inner slot through which a bend region of a rollable display device portion is disposed.
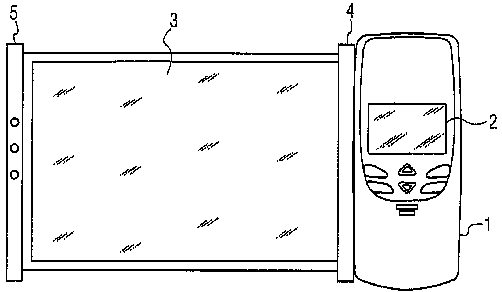
For personal computers: G06F 1/1652
This place covers:
A corrective lens (6), adapted to magnify the characters shown on the display, being associated with the display.
Example EP1643734
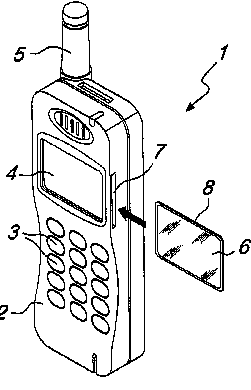
For magnifying glasses per se: G02B 25/002
This place covers:
Mounting of an electrical connector in a portable communication device for connecting an accessory or external apparatus.
Example EP2239928. A portable electronic device includes a first slidable body (110), a second body (120), a motion assembly (132), a connector (140), and an ejector (150)
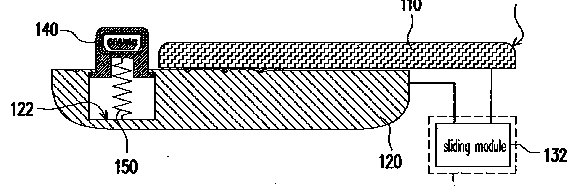
Connectors per se: H01R
This place covers:
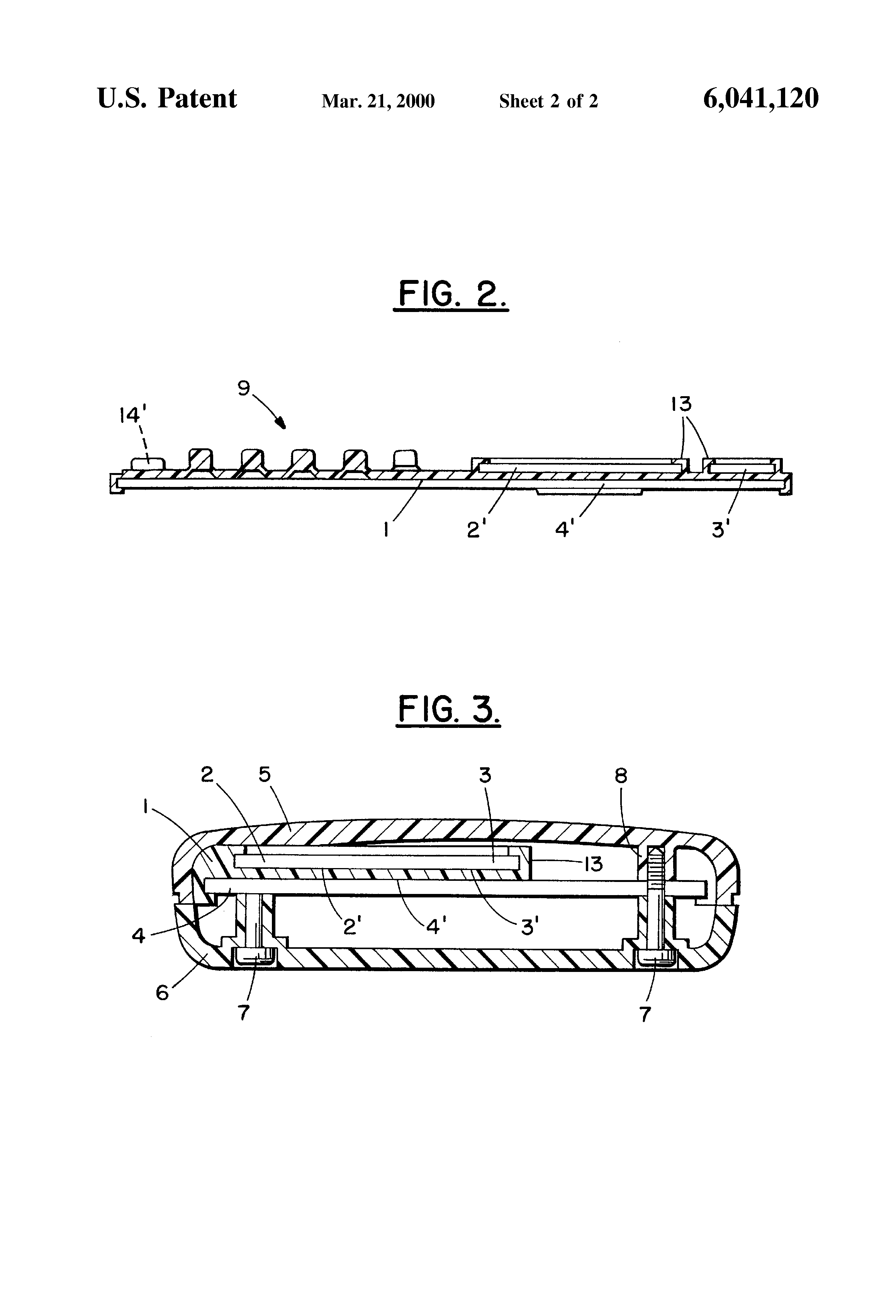
Means for securing a printed circuit boards to the inside of a portable telephone.
Examples:
US6728112. A fastening module (1) for a printed circuit board (10) of a portable electronic device includes the printed circuit board and a casing (20). The casing includes at least one supporting plate (23, 25) and at least one clamp (22).
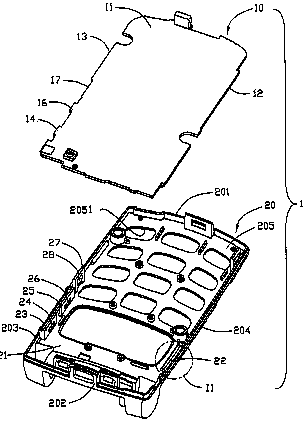
US6041120
Manufacturing printed circuits and assembling with electrical components: H05K 3/00
This place covers:
Portable telephones having means for improving the user comfort or ergonomics.
Example US2010210329. Hand held, ergonomic grip having a portable telephone device removably coupled thereto
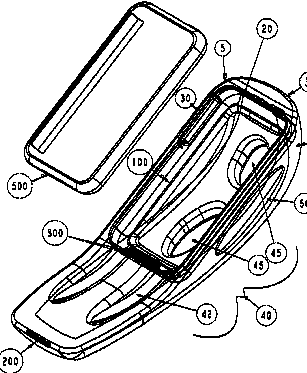
Personal computers with ergonomic disposition of keys: G06F 1/1664
Ergonomic functions for miniature keyboards : H01H 13/84
This place covers:
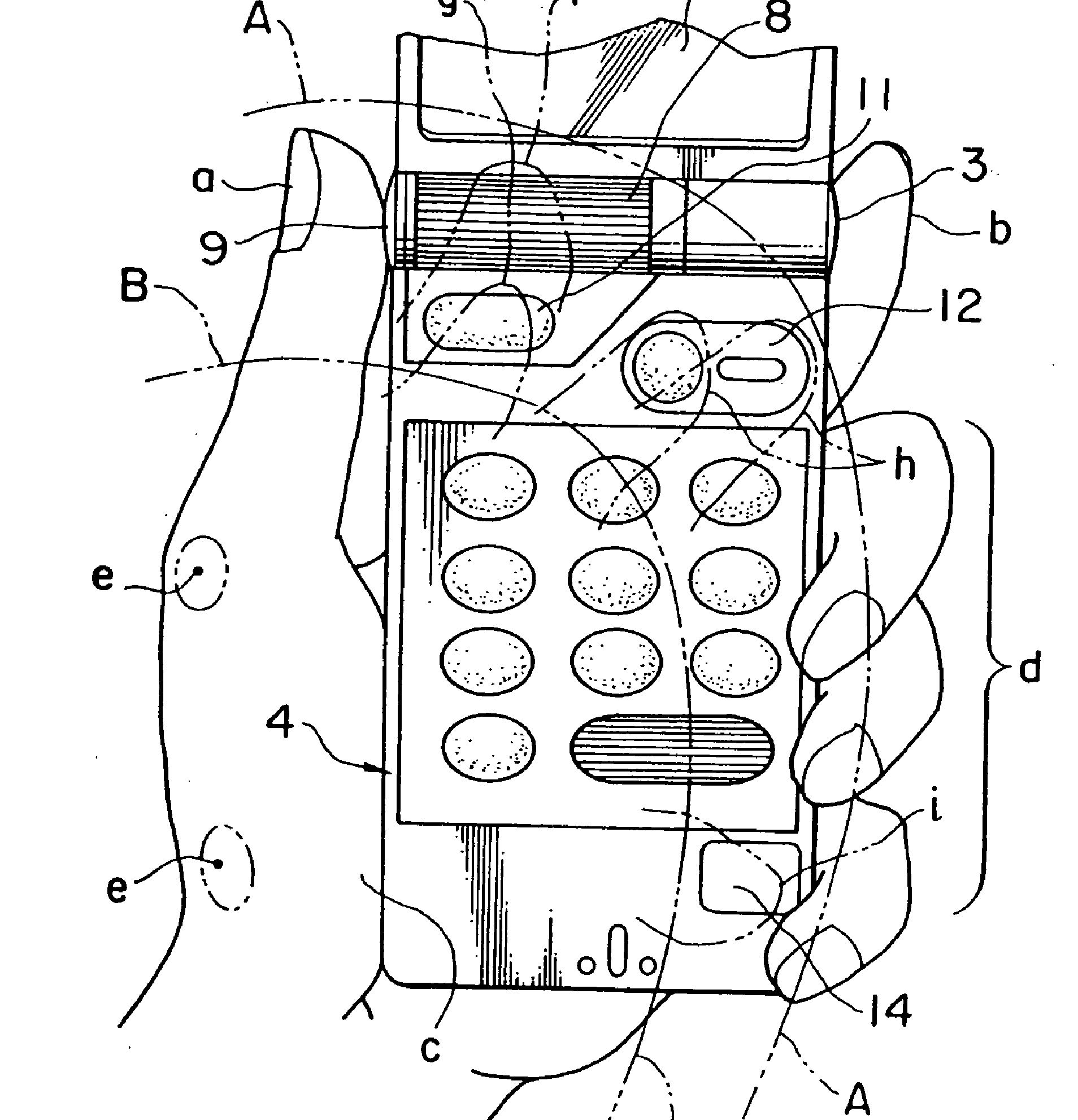
Constructional features allowing single hand use. Also for applications dealing with constructional aspects allowing right or left hand use.
An ergonomic housing that is shaped to fit comfortably in the palm of a human hand.
Example US6164853
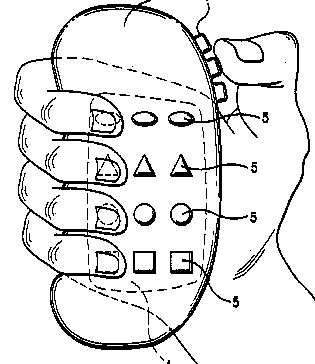
This place covers:
User replaceable covers having a decorative function. If after changing the cover there is a change in the functionality see also H04M 1/7246.
This class also includes handsets made of precious metals or with other aesthetic improvements.
Housing with decorative pattern area.
Example US2010085690
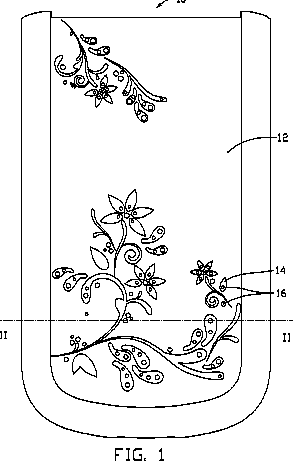
H04M 1/7246 when the exchange of a faceplate modifies the functionality of the device
This place covers:
Portable telephone having a pen shape or form factor.
Examples:
US2009251338.
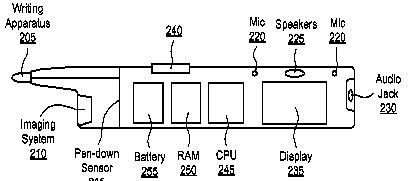
DE19922777
Pen or stylus-type devices: G06F 3/03545
This place covers:
Mechanical arrangements for connecting expansion modules to telephone sets
Example US7500880
This place covers:
Constructional features of a door telephone, intercom, or interphone.
Example US2004091092.
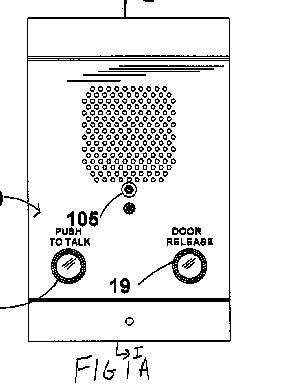
Video door telephones: H04N 7/186
Door telephone systems: H04M 11/025
This place covers:
Constructional features of junction boxes (23) for connecting a telephone set to a telephone line.
Example US2003040223.
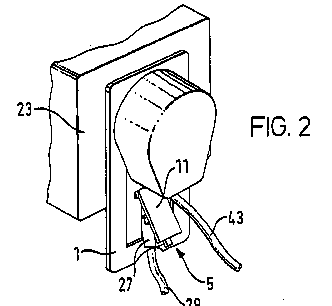
Conductive connections between two or more conductive members: H01R
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Mechanical mounting details of display modules for portable telephones |
This place covers:
Convertible desk-to-wall support for handheld devices.
Example US6130521
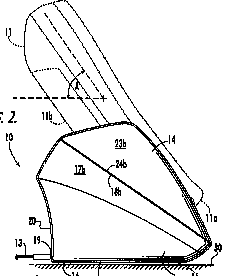
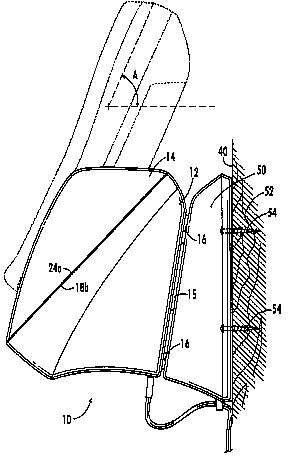
This place covers:
Mounting of a microphone and a loudspeaker in the telephone handset.
Acoustic transducers per se: H04R 1/00
Mounting of acoustic transducers in a portable computer: G06F 1/1688
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Transducers in general |
Mounting of an additional speaker/microphone in a fixed telephone set for handsfree use H04M 1/62.
This place covers:
Means for improving or changing the acoustic characteristics of acoustic transducers (microphones, loudspeakers). Resonating chambers being provided on the back of the transducer, sound channels in housings.
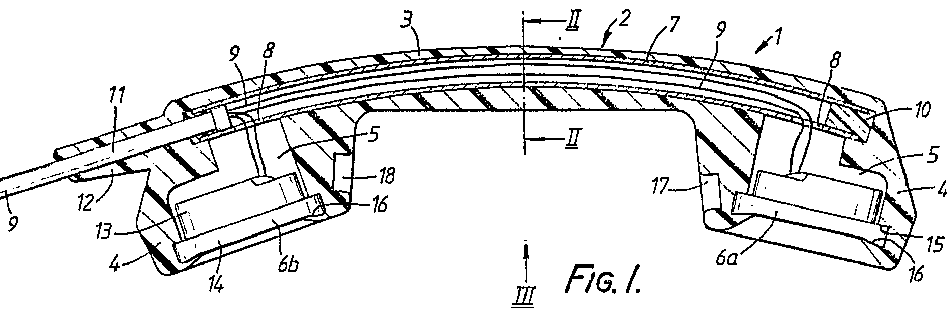
For example EP0275996 : a sound passage opening (7) is disposed on the inside of the lid, connecting with at least one sound feeding channel (8) inside the lid for guiding sound waves to the microphone (3):
This place covers:
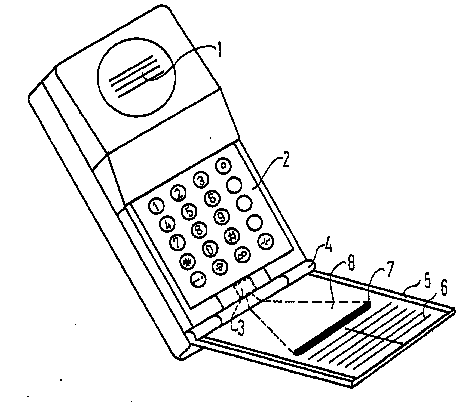
Constructional features, e.g. fastening means of a holster, holding device or docking station supporting a portable telephone.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this place:
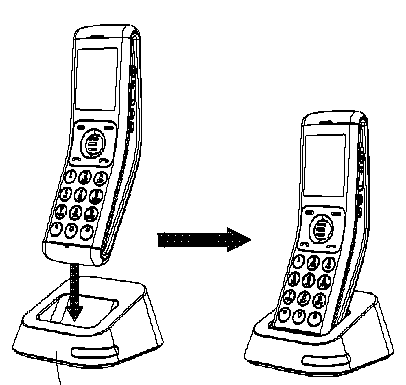
Supports for portable telephones covering constructional features of holsters, holding devices or docking stations that are supporting portable telephones directly or indirectly through connection means are classified in H04M 1/04 while supports for a hand-held apparatus or articles in general are classified in F16M 13/00.
Supports for positioning or steadying a device relative to a person with the intent of using the device are classified in F16M 13/04.
Stands or trestles as supports for articles placed thereon in general are classified in F16M 11/00.
Holders or carriers being worn by a user for portable audio devices, portable handheld communication devices and portable computing devices to facilitate transporting or carrying, where the device is not in use or being passively used, are classified in groups A45F 5/1508, A45F 5/1516 and A45F 5/1525, respectively.
Protective covers or auxiliary enclosures for portable computers that are intended to hold the device during use without hampering said use are classified in G06F 1/1629.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Protective covers or auxiliary enclosures for portable telephones | |
Supports for a fixed telephone set | |
Holders or carriers for portable audio devices | |
Holders or carriers for portable handheld communication devices | |
Holders or carriers for portable computing devices | |
Docking stations designed for portable telephones in vehicles | |
Stands or trestles as supports for apparatus or articles placed thereon | |
Other supports for positioning apparatus or articles; Means for steadying hand-held apparatus or articles | |
Supports integral with the apparatus or articles to be supported | |
Protective covers or auxiliary enclosures for portable computers | |
Docking stations designed for portable computers | |
Battery charging apparatuses | |
Arrangements for carrying or protecting portable transceivers | |
Transducers in general |
Protective covers or auxiliary enclosures for mobile phones that are intended to hold the device during use without hampering the telephonic functions are classified in H04M 1/0203.
When the docking station provides additional functionality to the portable telephone, H04M 1/72409 should be used.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
stand | a rack, base or piece of furniture for holding, supporting or displaying something |
support | element that bears the weight to keep something in position, e.g. to keep it upright |
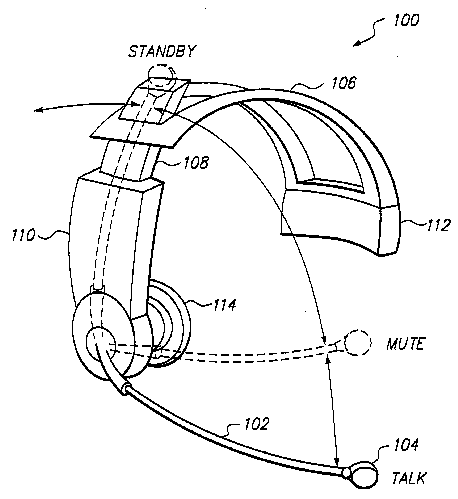
This place covers:
Constructional features of devices for adapting a telephone handset for use on head, throat or breast.
Constructional features of headsets or earphones adapted for telephone communication
Portable transceivers carried on the body: H04B 1/385
Head-up displays: G02B 27/01
Hearing aids per se: H04R 25/00
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Portable telephones adapted for handsfree use |
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms:
- earphones
- earpiece
- earset
- earplug
- headphone
- headset
- microtelephone
- hearing aid
This place covers:
Telephone cradle switch. Example: EP1005208
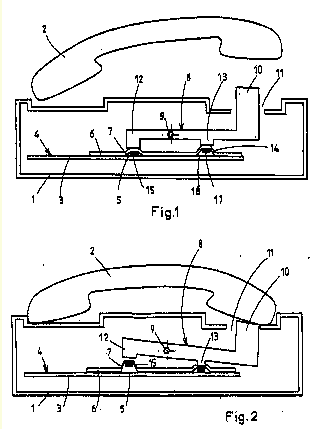
for an answering machine H04M 1/6545.
This place covers:
Supports for fixed telephone sets (meaning the whole telephone set housing).
Example:EP1467541
Stands or trestles as supports for apparatus or articles placed thereon: F16M 11/00
This place covers:
Telescopic arm and carrying platform for the telephone set
This place covers:
Means for storing or protecting a telephone cord. Typically for fixed telephone sets. Documents relating to portable telephones having means for storing or protecting the cord of a headset are also classified in this group.
For guiding electric cables in general: H02G 11/00
Devices for handling or storing cables: B65H 75/44
This place covers:
Features of telephone equipment to improve hygiene, e.g. integrated sanitizers, antiviral smartphone covers or speaker covers to prevent transmission of airborne particles.
This place does not cover:
Sanitary or hygienic devices for mouthpieces or earpieces |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Protective covers or auxiliary enclosures for portable telephones | |
Disinfection or sterilisation of materials or objects, in general; Accessories therefor |
This place covers:
Fixed telephone sets or mobile phones specially adapted for use in adverse conditions, e.g. providing protection against dust, water, extreme temperatures, chemical fumes or gases, fire or explosions.
This place does not cover:
Arrangements of transmitters, receivers, or complete sets to prevent eavesdropping |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Modified payphones | |
Telephone cabinets or booths per se | |
Protective enclosures for remote control devices | |
Dustproof, splashproof, drip-proof, waterproof or flameproof casings for keys or buttons | |
Hermetically sealed housings |
This place covers integral casings intended to improve the operability in adverse conditions. Protective covers or auxiliary enclosures for mobile phones that are intended to hold the device during use without hampering the telephonic functions are classified in H04M 1/0203.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
casings | a cover or shell, integral with or forming the telephone housing, that encloses and protects the telephone components |
This place covers:
Improvements to shock resistance of the housing, where the housing is the fixed enclosure of the telephone.
Illustrative examples of subject matter classified in this place:
1.

Figure 1 illustrates how the display panel is protected from being damaged by collisions by means of shock absorbers (90) provided under a heat dissipating plate (70) and the display panel (50).
2.

3.

4.

5.

6.

7.

Figures 2-7 illustrate several structural features for actively protecting a cover glass of a display device, when detecting that the device is in free fall. The example includes extending a bezel (104) around the display by springs or shape memory alloy, deploying an airbag (306) or parachute (356), changing the angular momentum by moving of a fluid in an internal chamber (404) or a set of balls in a track (450), so that the device lands on its side as well as deploying a suction cup (526).
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Protective covers or auxiliary enclosures for portable telephones |
This place covers:
All mechanical means for preventing noise from reaching the microphone (Directional microphones).
Voice analysis or recognition and noise suppression per se: G10L
This place covers:
Telephone sets with mechanical arrangements for preventing acoustic feedback between microphone and loudspeaker.
Example WO0049788. The telephone handset has a microphone (2) with a unidirectional direction characteristic
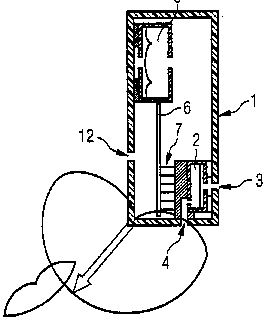
Electrical and circuit aspects of echo cancellers for two way loudspeaking telephone sets: H04M 9/08
Echo cancellers per se on line transmission systems: H04B 3/20
This place does not cover:
Constructional arrangements |
This place covers:
Structural integration of gadgets physically associated with the telephone (watches, agendas, bottle openers, thermometers, razor) which do not modify the functionality of the telephone. Personal electronics device with cosmetics compartment
Example US2009166247.
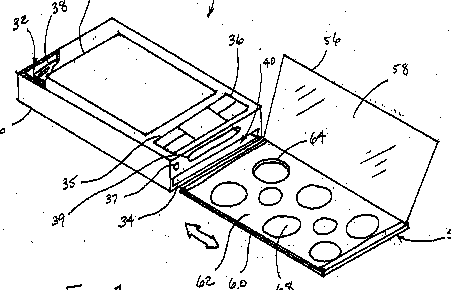
This place covers:
The auxiliary equipment is connected without modifications to the telephone's circuit.
This place covers:
Acoustic couplers for modems.
Communication by means of acoustic waves: H04B 11/00
This place covers:
Light source in combination with a fixed or portable telephone.
Includes also the backlighting of displays.
Illumination of keys per se: H01H 13/023
Illumination for keyboards: H01H 13/83
Illumination devices in combination with telephones: F21V 33/0052
Control of back illumination for visual indicators: G09G 3/3406
Combination of camera with lighting apparatus: G03B 15/03
This place covers:
This group relates to the mounting of a keyboard in the telephone set housing.
Constructional structure of an array of key-operated switches per se e.g. keyboard: H01H 13/70
Keys with feedback: H01H 13/84
For personal computers: G06F 1/1662
With ergonomic disposition of keys: G06F 1/1664
Detachable keyboards for portable computers: G06F 1/1669
H04M 1/22 takes precedence for improving visibility.
Constructional details of pointing devices for personal computers: G06F 3/033.
Special purposes keys or auxiliary keyboards for personal computers: G06F 1/1671
This place covers:
Testing arrangements located in the subscriber set.
Subscriber line supervision and monitoring circuits at the exchange: H04M 3/2272.
Automatic routine testing for subscriber lines: H04M 3/30
For wireless networks: H04W 24/06, H04W 24/08
For line transmission systems in general: H04B 3/46
Testing/monitoring in general: H04B 17/00
Testing of printed circuit boards: G01R 31/2801
Testing transducers: H04R 29/00
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring electric values | |
Testing transducers |
This place covers:
This group is only meant for fixed telephone sets.
Enhanced GUI for activating services provided by the exchange by using special function keys.
Systems providing special services or facilities to subscribers: H04M 3/42
Interaction techniques with a graphical user interface per se: G06F 3/048
This place does not cover:
User interfaces specially adapted for cordless or mobile telephones |
This place covers:
Subscriber interaction with the exchange to configure the features of the telephone set
This place does not cover:
Systems providing special services or facilities to subscribers | |
Administration or customisation of services: | |
By downloading data to substation equipment |
This place covers:
Downloading features or services related to certain keys and requested by the subscriber from the exchange.
By downloading data to the subscriber set
This place covers:
Extended functionality of a telephone set when combined with a personal computer on the subscriber side.
Arrangements which combine a telephonic equipment with a computer
Details of Application programming interfaces
Private branch exchange with computer telephony integration (CTI)
This place covers:
This group and subgroups are only meant for fixed telephone sets.
Analogous equipment in the exchange: H04M 3/42391
Devices for conversing with the deaf-blind: G09B 21/04
This place does not cover:
User interfaces for cordless or mobile telephones specially adapted for disabled users | |
Network based special services or facilities for hearing-impaired persons | |
Devices for conversing with the deaf-blind |
Hearing-aids per se
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Deaf-aid sets |
This place covers:
This group is only meant for fixed telephone sets.
User interaction with a menu display for selecting telephonic applications.
Interaction techniques with a graphical user interface per se
This place does not cover:
Same subject-matter for mobile phones. |
H04M 1/2474 takes precedence.
Text-based messaging services in telephone networks such as PSTN or ISDN
Centralised arrangements for recording text messages
Centralised arrangements providing data services like text-based messaging, instant messaging, short message service, electronic mail, or multimedia messaging
For accessing Internet
Interactive information services
This place covers:
This group has not properly evolved as the ISDN telephone sets have been classified in the group H04Q 11/0471 from their origin onwards.
ISDN terminal access circuits
Analogue to digital conversion
Telephonic communication systems adapted for simultaneous speech and data transmission
This place covers:
Telephone terminals adapted for voice communication over an internet protocol (IP).
With regard to VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol), voice is considered in this context to be a specific form of "digital information". Since the Internet Protocol and IP networks are classified in H04L (H04L 12/00, data switching networks and H04L 41/00 - H04L 69/00, real-time communication in data packet switching networks H04L 65/00), the transmission of voice over IP networks should be classified in H04L.
When VoIP is used to emulate or simulate services, the service, as presented to the user, is still classified in H04M. Any implementation details are however classified in H04L, for example SPIT and SPAM prevention in VoIP should be classified in H04M 3/436.
Networks other than PSTN/ISDN providing telephone services and including a packet-switched transport layer such as the internet protocol multimedia system H04M 7/006
Implementation or adaptation of Internet protocol [IP], of transmission control protocol [TCP] or of user datagram protocol [UDP] H04L 69/16
Network arrangements, protocols or services for supporting real-time applications in data packet communication H04L 65/00
End user terminal functionalities specially adapted for real-time communication H04L 65/1059
This place does not cover:
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) network equipment and services | |
Internet protocols |
This place covers:
General methods and devices for initiating a telephone call.
This place does not cover:
With means for preventing unauthorized or fraudulent calling |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Constructional features |
This place covers:
Telephone terminals adapted for abbreviated dialling by storing a directory consisting of a plurality of telephone numbers.
Centralized directories assistance
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Devices disposed in the exchange with arrangements for automatic redialing | |
With additional connecting arrangements for providing access to frequently wanted subscribers |
This place covers:
The telephone number is retrieved from the directory by voice recognition.
Voice recognition per se
Access to centralized directories by speech interaction
This place covers:
Telephone terminal storing only one telephone number.
This place covers:
Electromechanical arrangements.
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
For facsimile machines |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Addressing and accessing memory systems |
This place covers:
Sorting telephone directory items according to their frequency of use or other criteria.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangements for providing access to frequently wanted subscribers at the exchange |
This place covers:
Retrieving a telephone number by scrolling a list of items, e.g. names or corresponding telephone numbers, on a display.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Devices for scrolling or navigating through a menu display | |
Scrolling or panning | |
using a touch-screen or digitiser, e.g. input of commands through traced gestures |
This place covers:
Selecting a called party by means of a pictorial representation of the called party or by using interactive graphical means for accessing a directory on a display.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Interaction techniques for graphical user interfaces per se |
This place covers:
Retrieving a telephone number by matching character strings, e.g. the first letters of the name of a party to be called, with the entries of a directory.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Characters input methods by using selection from displayed items or retrieval techniques based on prediction |
This place covers:
Calling a subscriber in a different area or country by appending an area code or international prefix to the telephone number before dialling.
This place covers:
Automatic dialling or redialling systems, also for automatic dialling of a list of telephone numbers.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangements for calling back a calling subscriber | |
When the wanted subscriber ceases to be busy |
This place does not cover:
Management of directories | |
Sorting, e.g. according to history or frequency of use | |
Predictive input, predictive dialling by comparing the dialled sequence with the content of a telephone directory | |
Methods of retrieving data | |
Appending a prefix or inserting a pause to a dialling sequence | |
Automatic call origination and retry systems |
This place covers:
Using portable electronic directories, e.g. smart card storing a telephone directory and including acoustic coupling means for generating DTMF tone sequences corresponding to telephone numbers stored in the memory.
This place covers:
Using optical scanning, e.g. for scanning bar codes corresponding to telephone numbers.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Constructional details of hand-held scanners | |
Arrangements for transferring data from a sensing device to distant stations | |
Methods or arrangements for reading or recognising printed characters having additional code marks or containing code marks |
This place covers:
Telephone terminals whose directory is downloaded from another terminal or from the network.
This place covers:
Cards with magnetic band and without processor.
This place covers:
The dialling sequence is generated as a succession of pulses.
Electronic circuits for generating pulses per se: H03K 3/00
This place covers:
Circuits for generating the dialling sequence as a succession of DTMF tones.
Circuits for detecting sequences of DTMF tones: H04Q 1/45
This place covers:
E.g. Hook flash (access to additional service of the exchange by pushing the hook switch).
Party-line systems per se: H04M 13/00
Notifying the calling party with information concerning the called party: H04M 3/42093
This place covers:
Providing the called party with information about the calling party before the call is answered or during the call.
Notifying the called party with information on the calling party: H04M 3/42042
Where the information is included in the ringing tone: H04M 3/42051
For distinctive ringing: H04M 19/04
Identification of class of calling subscriber at the exchange: H04Q 3/70
Arrangements at a manual exchange: H04M 5/18
Blocking transmission of caller ID, H04M 1/571.
This place covers:
Line interface circuits for detecting the identification code of the calling party (For instance transmitted within the ringing signal).
This place covers:
A picture of the calling party is displayed.
This place covers:
A vocal announcement provides the identity of the calling party.
For distinctive ringing tones: H04M 19/04 with H04M 19/041
This place covers:
Circuit of a telephone line interface, which couples part of the signal from the handset microphone to the loudspeaker of the same handset through the hybrid circuit.
Hybrid circuit arrangements for transceivers: H04B 1/58
Hybrid circuits for line transmission systems in general: H04B 3/03
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Hybrid circuits for carrier-frequency operation |
This place covers:
Anti-side tone circuit implemented only with electronic components.
For transceivers: H04B 1/586
This place covers:
Speech amplifiers related to the transmitter (microphone) circuit.
This place covers:
Speech amplifiers related to the receiver (loudspeaker) circuit.
This place covers:
For integrated circuits performing a two-way speech circuit function.
This place covers:
Handsfree use of a fixed telephone set with external microphone and loudspeaker.
Two-way loud-speaking systems with means for suppressing echoes and acoustic feedback: H04M 9/08
Public address systems: H04R 27/00
This place does not cover:
Two-way loud-speaking telephone systems with means for conditioning the signal |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Constructional arrangements |
This place covers:
General arrangements for providing handsfree use of a mobile phone.
Arrangements for holding mobile phones in vehicles: B60R 11/0241
This place covers:
Sensing the distance between the user and the device to control the operation mode and the amplification factor of the received and/or transmitted signal.
This place covers:
Cable connection of a headset or earphone to the mobile phone for handsfree use.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Constructional features of headset devices |
This place covers:
Wireless connection between the mobile terminal and the headset.
This place covers:
Arrangements for handsfree use of a mobile terminal in a vehicle.
Arrangements for holding telephones in a vehicle: B60R 11/0241
H04M 1/6058 and H04M 1/6066 take precedence.
This place covers:
Coupling the mobile terminal with the on board audio or navigation system of the vehicle.
Navigation systems |
This place covers:
Wireless interface between the on board audio or navigation system and the mobile terminal.
Navigation systems: G01C 21/00
This place covers:
Only for fixed telephone set.
Constructional arrangements of the loudspeaker and the microphone in the telephone housing to enable handsfree use of the telephone.
This place covers:
When a call is placed to an unattended telephone set, an outgoing message OGM or pre-recorded speech announcement is played back to the calling party who is not invited in this case to record a response to the announcement.
Centralized arrangements for answering calls: H04M 3/50
Centralized dictation systems: H04M 11/10
Only for playing back a speech announcement to the calling party without recording an answer from the calling party.
Information storage per se: G11C.
This place covers:
A synthesized speech announcement is played back to the calling party.
H04M 1/642 takes precedence.
This place covers:
When a call is placed to an unattended telephone set, an outgoing message OGM or pre-recorded speech announcement is played back to the calling party who is invited in this case to record a response to the announcement, which response is also called incoming message .
Centralized arrangements for recording incoming messages: H04M 3/53
Voice mail systems: H04M 3/533
For playing back a speech announcement to the calling party and recording the calling party's answer.
Information storage per se: G11C
This place covers:
A synthesized speech announcement is played back to the calling party
H04M 1/6505 takes precedence.
This place covers:
Means for enabling the subscriber to listen to the messages which have been recorded by its telephone set during its absence by remote control.
H04M 1/658 takes precedence.
This place covers:
Specific line monitoring circuits for answering machines.
Telephone line interface circuits in general: H04M 1/738
Telephone line monitoring and detecting circuits in general: H04M 1/82
This place covers:
Answering machines with mechanical means for lifting the handset and activating the hook switch to close the line loop in response to an incoming call.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Hook switches |
This place covers:
Arrangements for recording parts or the whole speech communication in the subscriber set.
Conversation recording systems at the exchange: H04M 3/42221
This place covers:
Means for forwarding a recorded message from an unattended telephone set to a remote location corresponding to a pre-stored telephone number.
This place covers:
Telephone sets adapted for preventing unauthorized calls (incoming or outgoing calls).
This place does not cover:
Verifying user identity or authority in secret or secure digital communications |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Restricting the functionality or the communication capability of mobile telephones under specific circumstances | |
Call monitoring, e.g. for law enforcement purposes; Call tracing; Detection or prevention of malicious calls by the exchange |
This place covers:
Screening or filtering incoming calls (for instance depending on the caller identification).
Arrangements for screening incoming calls at the exchange: H04M 3/436, H04M 3/4365
This place covers:
The calling party has to dial a special code prior to the dialling of the telephone number (for instance a certain DTMF sequence). This special code is checked at the called telephone set to accept or deny the communication.
Graded services arrangements in the exchange by using authorisation codes or passwords: H04M 3/382
This place covers:
Mostly mechanical means preventing the use of a telephone set for outgoing calls.
H04M 1/677 takes precedence.
This place covers:
Circuits or functional arrangements to disable or lock the telephone set for outgoing calls. This group also includes fingerprint or biometric recognition systems to enable the use of the telephone set.
Systems for eye/iris/retina acquisition: G06V 40/19
Access control by means of physical/biometric data: G07C 9/37
Electronic locks using biometric data for granting access: G07C 9/00563
This place covers:
The user has to key in a special code to unlock the telephone set for outgoing calls.
Graded services arrangements in the exchange by using authorisation codes or passwords |
This place covers:
The user is requested to insert a smart card in the telephone set to activate the telephone set.
Graded services arrangements in the exchange by using subscriber identification cards: H04M 3/387
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
IC card mounting means in a portable telephone |
This place covers:
For instance preventing long distance calls by analysing the dialling sequence at the telephone set.
Arrangements with few programmed keys corresponding to a limited set of telephone numbers for local calls (special telephones for children).
This place covers:
Arrangements provided on the path between the local telephone and the junction box.
Eavesdropping prevention in the exchange: H04M 3/205
This place covers:
For preventing subscribers sharing the same telephone line in rural areas to listen to someone else conversation.
Lock-out or secrecy provision provided by the exchange in party-line systems |
This place covers:
Arrangements of two or more telephone sets connected to the network via the same line.
This place does not cover:
Cordless telephones |
This place covers:
Mobile telephones, i.e. cellular or wireless telephones.
Cordless telephones, i.e. devices for establishing wireless links to base stations without route selection, e.g. DECT® telephones.
Telephones adapted for both mobile and cordless operation.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Interconnection arrangements not involving centralised switching |
This place covers:
User interfaces specially adapted for the interaction of the user with mobile or cordless telephones.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Graphical user interface for managing generic applications | |
Sound input; Sound output | |
User interface programs per se | |
Measuring or estimating received signal strength | |
Selecting a network or communication service |
This place covers:
User interfaces with means for locally supporting a plurality of applications that provide extended functionality, further to the main telephone mode.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Operating the device by selecting functions from two or more displayed items, e.g. menus or icons | |
Medical applications | |
Protection of digital contents (Digital rights management: DRM) | |
Characterised by the use of a wireless device | |
Electronic marketing and advertising | |
Electronic payment applications | |
Broadcast applications for mobile receivers | |
Television applications | |
Video phones | |
Two way subscription systems |
This place covers:
Extended functionality obtained by software upgrading or downloading.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Software deployment | |
Arrangement for program loading or initiating |
This place covers:
Extended functionality obtained by connecting external accessories.
For example:
An expansion display unit (10) is provided with a display section (13) having a display surface larger than the display section (8) of the mobile terminal.
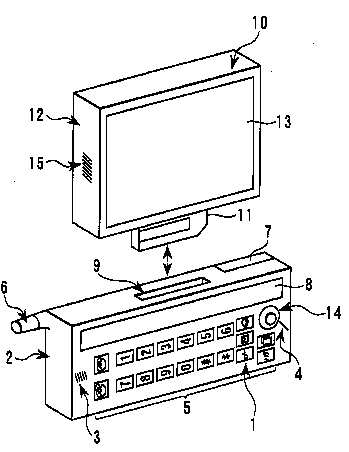
This place does not cover:
For hands-free use |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
For mechanical assembly details |
This place covers:
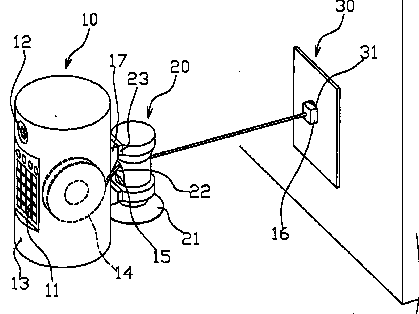
Extended functionality obtained by connecting external accessories via short-range radio links, e.g. Bluetooth®.
Illustrative example of the subject matter classified in H04M 1/72412:
A mobile phone 10 operating as a leader performs a request to establish a piconet with a computer 21, a printer 22, a PDA 23, and a headset 24 located in an operating range 20 allowing direct connection. The computer 21 can form another piconet with a speaker 30.
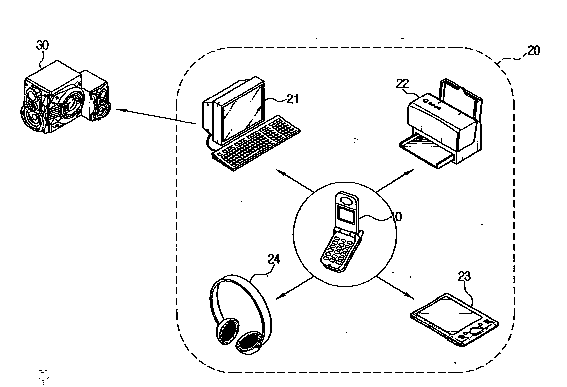
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wireless connection of a headset for handsfree use of a mobile terminal | |
Near field transmission systems | |
Discovery or management thereof, e.g. service location protocol [SLP] or web services | |
Services using short range communication | |
Discovery of other network devices in proximity of a mobile terminal |
This place covers:
Mobile or cordless telephones adapted for remote control of other appliances. For example, an appliance to be controlled is selected from a list of appliances (26) on the cellular device display (22).
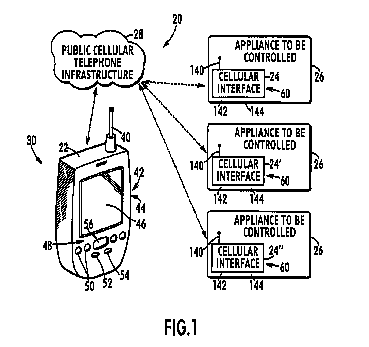
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Telephonic communication systems adapted for combination with remote control systems | |
Arrangements for transmitting signals using a radio link | |
Home automation networks | |
Remotely managing devices over a network | |
Proprietary protocols involving control of end-device applications | |
Arrangements in telecontrol or telemetry systems for selectively calling a substation from a main station |
This place covers:
Mobile or cordless telephones with applications supporting an emergency service.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Telephonic communication systems in combination with alarm systems | |
Alarm systems using wireless transmission |
This place covers:
Mobile or cordless telephones with user interfaces for interacting with game applications or for supporting graphical animations, e.g. avatars, themes or wallpapers, background screens or screen savers.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Aspects of games using an electronically generated display in general | |
Digital output to display device | |
Display control per se |
This place covers:
User interfaces for interacting with messaging applications (e.g. voice or text messaging, SMS or MMS) in mobile or cordless telephones.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Telephone answering machines for answering a telephone call | |
Mail systems for messages comprising audio and non-audio components | |
Computer-aided management of electronic mailing [e-mailing] | |
Message switching systems | |
Instant messaging |
This place does not cover:
For answering incoming calls |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Voice mail systems | |
Dictation recording and playback systems |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Computer-aided management of electronic mailing [e-mailing] | |
Instant messaging | |
Short messaging services |
This place covers:
User interfaces for interacting with image or video messaging applications, e.g. for picture transmission as attachment to a message.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Transmission of still pictures with a mobile phone | |
Videophones |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Interactive information services including a voice browser | |
Retrieval of information from the web e.g. using browsers |
This place covers:
Customisation of a mobile terminal or modification of user settings.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Telephone sets including user guidance or feature selection means facilitating their use | |
Communication control, user profiles |
This place covers:
Adapting the functionality of mobile or cordless telephones according to schedules, e.g. using calendar applications.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Office automation, time management, e.g. reminders or meetings | |
Network applications for presence management |
This place covers:
Adapting the functionality of cordless or mobile telephones according to events detected by a context application or according to their physical environment, e.g. by using sensors.
This place covers:
Adapting the functionality of mobile or cordless telephones according to their locations.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Network applications adapted for the location of the user terminal | |
User location related services provided by wireless communication networks |
This place covers:
Adapting terminal functionality by connection of exchangeable housing parts, e.g. by using interchangeable faceplates
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
For changing aesthetic appearance |
This place covers:
Partial suppression of functionality, e.g. of ringing in theatres or hospitals.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electronic means for preventing unauthorised calls | |
Network access restriction based on user location |
This place covers:
For operating the device by selecting telephonic functions on menu displays, e.g. simple accept/reject icons.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
User interaction with a menu display for generic applications |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Telephonic functions | Any functions connected with the primary reason for having telephones, e.g. diverting incoming or outgoing calls to voicemail, forwarding incoming or outgoing calls to another device, sending a response message, listing all available modes for communicating with desired call parties. |
This place covers:
Portable communication devices adapted for disabled people.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Fixed telephone sets for disabled persons | |
Devices for conversing with the deaf-blind |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electric hearing aids |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangements for improving visibility of characters on dials |
This place covers:
Cordless telephones used as extension of a telephone base station by communicating via a wireless link with the base station.
With regard to mobile telephony, H04M covers communication systems using wireless extensions, i.e. wireless links without selective communication, e.g. cordless telephones, which are covered by group H04M 1/72, whereas H04W covers communication networks for selectively establishing one or a plurality of wireless communication links between a desired number of users or between users and network equipment, for the purpose of transferring information via these wireless communication links.
This place does not cover:
User interfaces specially adapted forcordless telephones |
This place covers:
Cordless telephones registered with the same and unique base station.
This place covers:
Radio link set-up procedure between a cordless phone and the base station.
This place covers:
Radio link set-up procedure by using a control channel.
This place covers:
Radio link set-up procedure by selecting and using an idle communication channel.
This place covers:
Placing calls on hold.
Intercom functions between at least two cordless telephones registered with the same base station.
Direct communication links between two handsets without intervention of the base station. Transfer communication modes to redirect calls to other telephones.
This place covers:
For registration of a cordless telephone with a base station.
This place covers:
For cordless telephones only.
For mobile and cellular phones: H04W 52/02
For personal computers: G06F 1/3203
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Switching on/off the receiving circuit |
This place covers:
This group refers to the head group H04M 1/725 and relates only to cordless telephones
Wireless PBX: H04W 84/16
This place covers:
For cordless telephones.
This place covers:
Line interface circuits for fixed telephone sets.
Analogous interface circuits for subscriber telephone lines at the exchange: H04M 3/005
Modems and ADSL lines: H04M 11/06
This place does not cover:
Circuit arrangements in which low-frequency speech signals proceed in one direction on the line H04M 1/78
This place covers:
Arrangements located at the subscriber side.
This place covers:
Circuit arrangements located at the subscriber side.
This place covers:
Line impedance adaptation implemented in the subscriber set.
Control of transmission and equalising in line transmission systems in general: H04B 3/04
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Transmission in general |
This place covers:
Circuits arrangements on the subscriber side.
Call holding circuits at the exchange: H04M 3/4283
Line supervising and monitoring at the exchange: H04M 3/2209
Line monitoring in transmission systems in general: H04B 3/46
For detecting caller identification H04M 1/573.
This place covers:
- Telephonic communication services, in particular supplementary services specifically adapted for telephonic communication provided by networks comprising any type of switching devices, such as telephone exchanges, telephone switches, softswitches, call agents or and call state control function or control protocols, such as ISDN User part [ISUP], H.323 and SIP;
- Telephone exchanges or telephone switches, in particular digital switches which work by connecting two or more digital circuits together, according to a dialed telephone number. This main group covers both switches of Public Switched Telephone Networks, PSTN, and Private Branch Exchanges [PBX];
- Application servers for information services, call distribution and queuing services, messaging services and conference services;
- Arrangements for providing information services, such as Interactive Voice Response Systems, Voice Portals or Voice Browsers;
- Centralised arrangements for answering requiring operator intervention (also referred to as a call centers), usually employing call queuing and call distribution;
- Centralised arrangements for recording messages for absent or busy subscribers (also referred to as Voice Mail Systems);
- Arrangements for connecting several subscribers to a common circuit (also referred to as Conference Bridges).
- Exchanges in and services specially provided for mobile radio systems are classified in H04W 4/00-H04W 92/00.
- Implementation details and protocol details of networks comprising call agents, call controllers and call state control functions and/or employing the SIP or H.323 protocol are classified in H04L 65/1104 or H04L 65/1106.
- Protocol details of call control protocols such as Q.931 and ISDN User part (ISUP) are classified in H04Q.
This place does not cover:
Constructional details of telephone exchanges |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Selecting arrangements | |
Wireless communication networks |
This place covers:
- [Digital] line cards which are modular electronic circuits on a printed circuit board.
- The line card interfaces a telecommunication line coming from the subscriber.
- Telephone line cards used in PSTN perform so-called BORSCHT functions.
- A line card can terminate a line supporting voice POTS service, ISDN service or DSL service.
This place does not cover:
supervisory, monitoring or testing arrangements | |
in key telephone systems | |
current supply |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
And for DSL service | |
For ISDN service |
Some of the BORSCHT functions or at least related functions can be found in the following groups:
R=Ringing: | |
O=Overvoltage: | |
Monitoring and testing arrangements | |
S=Supervision: | |
T=Test access . | |
Exchange line cards of key telephone systems | |
B=Battery feed: | |
Current supply arrangements in general | |
C=CODEC | |
H=Hybrid |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
SLIC | Subscriber Line Interface Circuit |
This place covers:
Methods and arrangements for ringing or otherwise calling substations as well as call notifications services where the type of notification is adapted to the specific context of the incoming call.
This place does not cover:
Constructional details and the switching fabric of a telephone exchange |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
One-way selective calling services |
Providing distinctive or selective ringing capability can also be found in H04M 19/04 when the ringing current is generated at the substation.
If the ringing tone is used as a means to notify the called party of information on the calling party, H04M 3/42051 takes priority
This place covers:
Methods and arrangements which are specifically adapted to the troubleshooting of faults or failures.
The troubleshooting of faults or failures belongs in principle to Operations, Administration, Maintenance, and Provisioning [OAM&P], which is classified in H04M 3/22, but since it is an IPC group it has been kept on the same hierarchical level.
This place covers:
Means which are specifically adapted to telephone subscriber lines consisting of twisted copper pairs. For example the use of load coils or overvoltage protection arrangements are covered here.
This place does not cover:
Protective circuit arrangements in general |
This place covers:
Operations, Administration, Maintenance, and Provisioning OAM&P of telephonic communication services, arrangements and application servers as mentioned in the definition statement of the main group H04M 3/00 as well as individual telephone exchanges or switches.
Furthermore, it covers call monitoring, tracing and detail recording, as well as speech quality monitoring.
This group also covers OAM&P of the metallic twisted pair subscriber line, whereby testing of physical copper line parameters is covered by H04M 3/305 and xDSL line qualification testing is covered by H04M 3/306.
As far as management of networks is concerned, one has to distinguish between telephone networks and data networks.
Management of telephone networks is classified in group H04Q 3/0062, while management of data networks is classified in groups H04L 41/00 or H04L 43/00.
Testing of crosstalk effects is classified in group H04B 3/487.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Digital computers for evaluating statistical data |
This place covers:
Methods and arrangements for preventing the establishment of certain outgoing connections either by such services as outgoing call barring, i.e. by default the establishment is prevented, or call screening, i.e. by default the establishment is allowed.
Where the prevention can be [temporarily] disabled, this is classified in the hierarchically lower groups.
This place does not cover:
Queueing arrangements |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
With call distribution or queueing |
Prevention of incoming connections is classified in H04M 3/436.
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
FAC | Forced Authorization Codes |
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms:
- call restriction services
- service restriction in outgoing direction
- outgoing call barring
This place covers:
Methods and arrangements which provide supplementary telephonic communication services, that is any type of service which goes beyond basic call establishment. Arrangements for which specific subgroups exist are in particular enterprise telephonic communication servers H04M 3/42314, interactive voice response systems H04M 3/493, call or contact centers H04M 3/51, voicemail systems H04M 3/533, and telephonic conference bridges H04M 3/56.
This place does not cover:
Specially adapted for wireless communication networks |
The arrangements which provide the supplementary telephonic communication services are the ones mentioned in the definition statement of this subclass. Certain arrangement and protocol details are classified as mentioned in the passage "Relationship between large subject matter areas" of this subclass. Mobile application services, also referred to as mobile apps, using supplementary telephonic communication services are covered by H04W 4/16.
This place covers:
Methods and arrangements for establishing a connection to and from a party which has not been identified by the other party. For example the calling party only specifies a subject or a box number published in a newspaper. Also covers disposal numbers which are only usable for a limited amount of time.
Calling Line Identification Restriction [CLIR] is covered by the combination with H04M 3/42042. Connected Line Identification Restriction [COLR] is covered by the combination with H04M 3/42093
This place covers:
- Methods and arrangements providing a customized notification to the calling party that the called party is alerted, usually in the form of a customized ring-back tone. "Customized" refers to the fact that the type of notification is specific to the context of the call, for example the called party.
- The customized ring-back tone can be provided as a service to either the calling or the called party or even both.
- When the service is customised by the calling party, i.e. the calling party configures the different contexts, such configuration information is referred to as a profile and classified by H04M 3/42068.
- When the service is customised by the called party, i.e. the called party configures the different contexts, such configuration information is not explicitly classified since it is considered that by default such information is present.
- When the customized ring-back tone triggers some further activity of one of the parties such as for example storing the tone in their own profile, retrieving additional information on the tone, in particular when it relates to a piece of music or the download of the piece of music then these aspects are classified in H04M 3/42153 and/or H04M 3/42178.
- The configuration as such is classified in H04M 3/42153 but only if the way the configuration is performed are relevant.
- When the context is defined by the network operator, this is typically related to advertisements, which are to be classified in H04M 3/4878. What mainly distinguishes H04M 3/42017 from H04M 3/487 is the fact that the parties themselves can determine the context.
When the customized notification mentioned above relates to an advice of charge, the groups H04M 15/00 or H04L 12/14 take priority.
This place covers:
- The hierarchically highest groups H04M 3/42025, H04M 3/42034 and H04M 3/42085 are only used for additional information because most often the subject-matter to be classified does not relate to the identification as such but rather to the use of the identification for the customization of supplementary services or the presentation of the identification itself which are both covered by the hierarchically lower groups. These comprise in particular the groups H04M 3/42042 and H04M 3/42093 which cover the services calling line identification presentation [CLIP] and connected line identification presentation [COLP], was well as any more enhanced forms of presentation of information relating to one of the call parties.
- Furthermore, all caller-dependent services should receive H04M 3/42059 as additional information and all called party-depedent services should receive H04M 3/42102. The usage of profiles is covered by either H04M 3/42068 or H04M 3/4211.
This place covers:
The configuration of supplementary services. Whereas OAM&P as classified in H04M 3/22 also comprises configuration of network nodes by the network operator, this group specifically covers the configuration of supplementary services that are provided to subscribers as add-ons to basic telephony. Furthermore, service interactions are covered by H04M 3/4217.
This place covers:
Methods and arrangements where certain lines or connections are prioritised which for example is important when the system is overloaded due to failure or disaster situations.
Preferential services are often provided in the context of overload which often occurs when a disaster occurred. The disaster is a specific form of emergency situation. Overload in general is covered by H04M 3/367 whereas any services related to emergency situations are covered by H04M 2242/04. Mobile application services, also referred to as mobile apps, handling emergency, urgent or hazardous situations are covered by H04W 4/90.
This place covers:
Methods and arrangements for any kind of return calls, as well as for call completion on no reply [CCNR]. Call completion on busy [CCBS] is covered by H04M 3/48.
This group also covers services where the calling subscriber is a requestor of a return call in order to reverse the direction of the established call, as for example in calling card services. This group is also used for storing caller identity information in the network and inform called party about all calls that came in when he was busy/absent; i.e. even though nor "recall" is initiated; this service is often referred to as missed call notification.
Arrangements for calling back a calling subscriber in the specific context of call center queuing is covered by H04M 3/5231. Arrangements for calling back the sender of a voice mail messageis covered by H04M 3/53341.
Arrangements for calling back a calling subscriber when the wanted subscriber ceases to be busy is covered by H04M 3/48
This place covers:
Methods and arrangements for voice dialling.
When speech recognition is additional rather than inventive information, H04M 2201/40 is used. Selection by voice as provided by interactive voice response-type systems and classified by H04M 3/493 is not explicitly classified since it is implicit in such systems.
Arrangements at a terminal for service or number selection by voice is covered by H04M 1/271
This place covers:
Method and arrangements where a third party is capable of to answer someone else's telephone call, which is referred to as picking up a call.
This place covers:
Methods and arrangements for recording a telephone conversation independent of the specific context.
This place does not cover:
Recording at the subscriber's set |
If used for law enforcement purposes it should be combined with H04M 3/2281 and if used for quality assurance in call centers it should be combined with H04M 3/5175. Contrary to H04M 3/2218 it is the speech exchanged during a telephone conversation that is recorded and not any call details such as time of or parties to the call.
This place covers:
Methods and arrangements for handling a call according to one of the involved parties rather than handling it according to a telephone number with a fixed association to a line as in the classical PSTN where the telephone number identifies both, the party and the line. The classical example of what this group covers is the personal number service.
The hierarchically lower groups cover in particular the following:
- When the same line and/or substation is shared by several parties: H04M 3/42238;
- When a multi-mode terminal moves between different access networks of which at least one is a mobile extension to a fixed access point: H04M 3/42246
- When the subscriber is nomadic in that he uses different terminals: H04M 3/42263
This group should only be used when the subject-matter to be classified relates to the problem of overcoming the fixed association mentioned above because cellular and IP-based telephone networks inherently do not use addresses, such as telephone numbers, with such a fixed association.
Local number portability is covered by H04M/42N5.
Diversion of calls from one subscriber to another subscriber, i.e. from one subscription to another H04M 3/54 takes priority; Implementation details for such service in Intelligent Networks are covered by H04Q 3/005.
In patent documents the following expressions/words "follow-me"; "personal mobility"; "personal number service"; "portability"; "portable service"; "service profile"; "service 0700 in germany", "persönliche Rufnummer" often used.
This place covers:
Methods and arrangements for providing supplementary services relating to deregulated telephone networks or to special service telephone numbers. Three hierarchically lower groups are dedicated to
Carrier selection: H04M 3/42289
Local number portability: H04M 3/42297
Number translation services, in particular freephone: H04M 3/42306.
When the supplementary service is implemented by an Intelligent Network, H04M 2207/12 is allocated. Intelligent Networks in general are covered by H04Q 3/0029
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
ILEC | incumbent local exchange carrier |
CLEC | competitive local exchange carriers |
This place covers:
Methods and arrangements which are specifically adapted to a private context as for example in an office or even at home. Private in this context is the opposite of public in the Public Switched Telephone Network.
Three hierarchically lower groups are dedicated to
- Computer Telephone Integration: H04M 3/42323
- Direct Inward Dialing: H04M 3/42331
- Teleworking arrangements: H04M 3/4234
Multi-site arrangements which are classified in H04M 7/009
This place covers:
Methods and arrangements where the service adapts its behaviour to the spatial context of the subscriber.
If the service itself is explicitly covered by one of the H04M 3/00 group, this group is allocated in combination.
This place covers:
Methods and arrangements where the service adapts its behaviour to the personal context of the subscriber, in particular its ability and/or willingness to communicate.
If the service itself is explicitly covered by one of the H04M 3/00 groups, this group is allocated in combination.
This place covers:
Methods and arrangements where text messages are transmitted as add-on to signalling mechanisms for telephonic communication. Furthermore, interactions of calls and text messages such as calls triggering a message or messages triggering a call are covered here.
This place does not cover:
Short messaging service in wireless networks |
This place covers:
Methods and arrangements for facilitating the redial of a recently called party.
Whereas in H04M 3/424 the recall is initiated by the calling party, in H04M 3/48 it is initiated by the network.
This place does not cover:
Arrangements for automatic redialling at the subscriber's set |
This place covers:
Methods and arrangements for suppressing verbal communication to the party which has put the call on hold. Four hierarchically lower groups are dedicated to:
- the application of call hold in the context internet dial-up: H04M 3/4281
- circuits enabling the call hold functionality: H04M 3/4283
- providing content potentially in the form of advertising or entertaining nature to the party which has be put on hold Music-on-hold: H04M 3/4285
- notifying the party on hold of its removal from hold: H04M 3/4286
- call waiting: H04M 3/4288
This place covers:
Methods and arrangements where the call context is analysed in order to decide if the call is offered to the called party. If the party to be screened has defined upfront certain information that is being analysed as well, the hierarchically lower group H04M 3/4365 is to be used.
If the screening rules are stored in association with the calling party H04M 3/42059 is to be allocated in combination. In case of a spatial context, H04M 3/42348 and in case of a personal context (presence) H04M 3/42365 is to be allocated in combination. If the call which is not offered to the called party is not terminated but forwarded (diverted) to a different party, H04M 3/54 takes priority.
In patent documents the following expressions/words "do not disturb" and "incoming call barring" are often used.
This place does not cover:
Additional connecting arrangements for providing access to frequently-wanted subscribers, e.g. abbreviated dialing at the subscriber's set | |
Automatic redialing |
This place covers:
Methods and arrangements for alerting a number of substations of the same call. If the substations are alerted at the same time then the hierarchically lower group H04M 3/465 is to be used. This group covers features such as call coverage and call hunting.
Call distribution is to be classified in H04M 3/523. If all the substations to be alerted are associated with the same subscriber, the subject-matter is to be classified as a personal number service in H04M 3/42229. If for a specific context only one alternative [substation] is defined, the subject-matter is to be classified as call diversion in H04M 3/54.
In patent documents the following expressions/words "call hunting", "call hunt groups", "call-coverage" often used.
This place covers:
Methods and arrangements for calling back a calling subscriber when the wanted subscriber ceases to be busy; i.e. the calling subscriber is the served user in that even though the initial call is not established, a service is invoked which monitors the status of the called party (or both) to enable, when the calling party returns from busy, a "recall" from the calling to the called party. The conventional term is "Completion of calls on busy" [CCBS].
Call completion on no reply [CCNR] as well as any other call backs are covered by H04M 3/42195.
In patent documents the following abbreviations are often used:
CCBS | Call completion on busy subscriber |
CCBS | Completion of calls to busy subscriber |
In patent documents the following expressions/words "rückruf bei besetzt" and "anrufliste" are often used.
This place covers:
Methods and arrangements where information services are provided via voice calls. The hierarchically lower groups distinguish between non-interactive (H04M 3/4872) and interactive (H04M 3/493) services but since the information to be provided is usually determined by some sort of interaction, H04M 3/493 is to be considered the default group and H04M 3/4872 only in exceptional cases. H04M 3/493 is used for interactive voice response systems and voice portals as well as for all services provided by these systems. Voice-browser based methods and arrangements are covered by H04M 3/4938.
When the information service is location-dependent, the subject-matter is to be classified by the combination of H04M 3/487 and H04M 3/42348. Information services not provided via voice calls are covered by H04L 67/02.
This place covers:
With the exception of hierarchically lower group H04M 3/51, centralised arrangements for answering calls, that is servers without a switching function but with access to the voice path.
The hierarchically lower group H04M 3/51 covers call centers which usually imply a queuing function whereby the calls are answered before they are distributed via an automatic call distribution to a respective agent, however a call that is not queued is essentially switched as in a conventional PBX.
The hierarchically lower group H04M 3/527 covers virtual assistants which are providing the same services a human assistant (also referred to as secretary) would provide but in an automatic way. Services relate to the handling outgoing calls, supplementary services during a call, or the handling of incoming calls. Systems facilitation the interaction between a real human assistant and the party being assisted, are classified in H04M 3/5108
This place does not cover:
Information services (takes precedence) | |
Dictation recording and playback systems |
If an explicit group for a specific server exist this takes priority such as for:
- Systems providing voice announcements: H04M 3/487
- Interactive voice response systems: H04M 3/493
- Mailbox systems: H04M 3/53
- Conversation recording systems: H04M 3/42221.
This place covers:
With the exception of H04M 3/5108, call centers whereby a call center is rather a functional concept of enabling agents to handle calls, either incoming or outgoing, centrally for a legal entity like a company or a Public Safety Answering Point. H04M 3/5116 covers calls to emergency telephone numbers in general. The technical core of a call center is a queuing and distribution function which is covered by H04M 3/523. H04M 3/5108 covers methods and arrangements for facilitating the interaction between a real human assistant and the party being assisted.
This place does not cover:
Emergency calls initiated by fire, police, burglar or other alarm systems |
This place does not cover:
Unified messaging in packet-switching networks |
This place covers:
Virtual assistants which are providing the same services a human assistant (also referred to as secretary) would provide but in an automatic way.
Methods and arrangements with a human assistant like a secretary or a call center agent are covered by H04M 3/51 or H04M 3/60 when it is a switchboard operator using an attendant console. When the specific service provided by the virtual assistant is a directory service, H04M 3/4935 takes priority.
This place covers:
Mailbox systems and services, in particular voice mail systems. Other types of messaging are only covered as far as they predominantly relate to voice or are provided by telephonic communication systems such as for example fax.
This place does not cover:
Centralised arrangements for recording facsimile documents |
Services which combine telephonic communication and predominately text-based messaging are covered by H04M 7/0042 - H04M 7/0054. Predominantly text-based messaging as such is classified in H04L 51/00, e.g. e-mail or instant messaging.
This place covers:
Methods and arrangements for call diversion, that is the redirection of a call from one destination to another alternative destination.
If it is context specific if the redirection should take place and to what destination, other groups as mentioned in the title are to be allocated in combination. Many other services like personal number service, the number translation services as well as call coverage and hunt groups also direct the call to a destination not explicitly specified by the calling party but their motivation is different from that of providing per context one specific alternative for the called party. The most prevalent contexts are call forwarding unconditional, call forwarding on busy and call forwarding on no reply/no answer. It the diversion is to voice mail H04M 3/53308 takes priority.
If the diversion rules are stored in association with the calling party H04M 3/42059 is to be allocated in combination. In case of a spatial context (location), H04M 3/42348 and in case of a personal context (presence) H04M 3/42365 is to be allocated in combination. If the call which is not offered to the called party is terminated without forwarding, H04M 3/436 takes priority.
In patent documents the following expressions/words call forwarding, "call diversion", "call redirection" , "call deflection", "anrufweiterleitung", "anrufumleitung" and "anrufweiterschaltung" are often used.
This place covers:
Methods and arrangement for providing conference calling, that is a multiparty conversation. Features which facilitate the user interaction with the conference arrangements are covered by H04M 3/563.
This place does not cover:
Computer conferences | |
Video conference systems |
When the application does not predominantly relates to multiparty conversation but multiparty collaboration the subject-matter is to be classified in either H04L 12/1813 for computer conferences or H04N 7/15 for video conference systems. Only in case of different medias supplementing a predominantly audio-based conference, H04M 3/567 is to be used.
Audio processing such as mixing and spatial distribution is only covered as long as it does not relate to sound field processing per se which is covered by H04S 7/30 or echo suppression which is covered by H04M 9/02.
Protocols for floor control are covered by H04L 65/403.
This place does not cover:
Arrangements for multi-party communication with floor control, e.g. for conferences | |
Arrangements for multi-party communication with distributed floor control, e.g. for conferences | |
Arrangements for multi-party communication without distributed floor control, e.g. for conferences |
This place covers:
Method and arrangements for transferring an ongoing call. The term "transfer" is to be construed narrowly because documents related to services like call forwarding use the term "transfer" where, contrary to the present case, the call is not "ongoing"
Substation line holding circuits are covered by H04M 1/80.
This place covers:
Methods and arrangements where a switchboard operator is been given access to telephonic communication services, for example via an attendant console of a private branch exchange.
Whereas the switchboard operator is an intermediate person which initially answers the call in order to assist in finding the final destination a call center operator is in general the final destination.
If the intermediate is an interactive voice response system H04M 3/5166 takes priority.
The following expressions are often used in this context: switchboard operator, attendant console, receptionist
This place covers:
Arrangement which provide for manually connecting a group of telephone lines mutually to one another or to an outside line by way of plug and socket. When the manual operation only consists in the [numerical] selection of the other line, then this is covered by H04M 3/60.
This place does not cover:
Jacks, jack-plugs |
This place covers:
Interconnection arrangements between switching centres, id est telephonic communication networks rather than individual switches.
Internet telephony and traditional circuit-switched telephony requiring interworking between the two, see in this respect also ITU-T Recommendation Y.2261, "PSTN/ISDN evolution to NGN".
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Whereas H04M relates to telephonic communications in general, in the context of H04M 7/00 distinction is made between circuit-switched CS and packet-switched PS networks providing telephonic communications.
In this respect, some groups relate only to CS, others to the interworking of CS and PS, H04M 7/009 is used independent of CS or PS and H04M 7/006 is used only for PS.
H04M 7/0003: CS-PS-interworking
H04M 7/0012: CS-PS-interworking
H04M 7/0024: CS-PS-interworking
H04M 7/006: PS
H04M 7/009: CS-PS agnostic
H04M 7/0096: CS (not active)
H04M 7/06: only used for CS-PS-interworking
H04M 7/08: CS (not active)
H04M 7/12: CS-PS-interworking
H04M 7/14: CS (not active)
H04M 7/16: CS (not active)
This place covers:
Arrangements which allow interactions on a telephone and a computer to be integrated or coordinated. The main focus of this group relates to architectural modifications in terms of nodes and their interaction which are potentially more generic than a single service.
Furthermore, this group covers Application Programming Interfaces for telephonic communication networks such as CSTA, JTAPI, TSAPI and TAPI for private networks but also Parlay, Parlay X and its successors for public networks.
Specific services provided over already existing arrangements covered by this group are covered by H04M 7/0024. Private Branch Exchanges with Computer Telephony Integration arrangements are covered by H04M 3/42323 and Call or Contact Centers with Computer Telephony Integration arrangements are covered by H04M 3/5183.
This place covers:
Services which combine telephonic communication with data services and the combined service is predominantly a telephonic communication service. E.g. Click to dial is covered by H04M 7/003.
If the combined service is predominantly a data service than H04L takes priority. Modifications, in particular regarding the arrangement or the application programming interface which are more generic and not specific to an individual service are covered by H04M 7/0012. In other words, platform modifications are covered by H04M 7/0012 whereas individual services are covered in H04M 7/0024.
This place does not cover:
Network streaming of media packets |
This place covers:
Methods and arrangements where telephonic communication is provided over packet-switched networks.
Access arrangements for conventional telephones, in particular residential gateways.
OAM&P and security aspects in the context of packet-switched telephony if they are specific to telephonic communications.
H04L 65/00 takes precedence. This group is only to be used in combination with a group in H04M 3/00 and any aspects not specific to the type of network are covered only be H04M 3/00 and lower groups whereby in particular the special services are classified in H04M 3/42 and lower. Furthermore, any modifications to the packet-switched network that are required to provide the telephonic communication service are covered by H04L. If the telephonic communication is provided over a network where packet-switched and circuit-switched networks interact, this is covered by H04M 7/1205
Security aspects in packet-switched networks in general are covered by H04L 63/00 and OAM&P for packet-switched networks in general is covered by H04L 41/00 and H04L 41/06.
This place covers:
Multi-site arrangements for what is covered otherwise by H04M 3/42314.
This place covers:
This group relates to circuit-switched networks but is not active.
This place covers:
Common channel signalling but only in relation to packet-switched network [signalling] such as SIGTRAN which relates to SS7 over IP, Bearer Independent Call Control BICC, or SIP-T which relates to the encapsulation of SS7 in SIP.
Protocol interworking without encapsulation is covered by H04M 7/126
This place covers:
This group relates to circuit-switched networks but is not active.
This place does not cover:
Phantom working in transmission of digital information |
This place covers:
Methods and arrangements for interworking circuit-switched and packet-switched telephonic communications networks.
This place covers:
Methods and arrangements where it can be distinguished between access and core network and only the access network is being modified.
This place covers:
Methods and arrangements where the networks that are being interconnected are hierarchically on the same level, contrary to H04M 7/121 where the access network is hierarchically lower than the core network. When the circuit-switched network is a wireless core network this is covered by H04M 7/1235 and when the packet-switched network is an IP Multimedia System this is covered by H04M 7/123
This place covers:
Methods and arrangements where the circuit-switched network is involved for the establishment of calls between terminals directly connected to packet-switched networks
This group essentially covers Personal Computer to Personal computer scenarios, whereas other scenarios are covered by H04M 7/1245
This place covers:
Methods and arrangements where at least one terminal is directly connected to a circuit-switched network, Also covers IP trunking.
This group essentially covers Phone to Personal Computer, Personal Computer to Phone and Phone to Phone scenarios, whereas Personal Computer to Personal Computer scenarios are covered by H04M 7/124.
This place covers:
Details of circuit-switched packet-switched gateways which are not covered explicitly by any of the groups H04M 7/126, H04M 7/1275, H04M 7/128, H04M 7/1285, H04M 7/129, H04M 7/1295.
This place does not cover:
Data switching network gateways |
This place covers:
Interworking of signalling systems for circuit-switched systems such as SS7 or DSS1, and signalling systems for packet-switched systems such as SIP or H.323.
This place covers:
Methods in gateways directed to handle a plurality of subscribers. These are potentially carrier-graded gateways rather than residential gateways which are covered by H04M 7/0069
This place covers:
Methods and arrangements which provide for the interworking of address of the different signalling systems as mentioned with respect to H04M 7/126, in particular E.164 telephone numbers, also referred to as E.164 Number Mapping, and SIP Uniform Resource Identifiers.
This place covers:
Methods and arrangements relating to path-finding.
Least cost routing is covered by H04M 15/00.
This place covers:
Methods and arrangements for handling call progress tones known from circuit-switched networks in packet-switched network
Methods and arrangements for providing ringing current or supervisory tones in circuit-switched networks is covered by H04M 19/02.
This place covers:
Methods and arrangements for handling DTMF tones known from circuit-switched networks in packet-switched networks.
This place covers:
Private Branch Exchanges, e.g. for making connections among the internal telephones of a private organization.
Key telephone systems, i.e. a telephone system in which the telephones have multiple buttons to directly select individual Central Office lines (without dialling a 9 as in PBX).
Acoustic echo cancelling, acoustic echo suppression for telephone systems.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Constructional features of cordless telephones | |
Speech Amplifiers | |
Substation extension arrangements using two or more extension per lines | |
Automatic or semi automatic exchanges | |
Subscriber line circuits (from the central exchange office) | |
Arrangements for connecting several subscribers to a common circuit, i.e. affording conference facilities | |
Paging systems | |
Door telephones | |
Methods for damping of acoustic waves | |
Speech analysis - synthesis techniques for redundancy reduction | |
Speech enhancement | |
Detection of presence or absence of speech signals | |
Digital adaptive filtering | |
Transceivers | |
Line echo cancelling | |
Computer conference systems | |
Video conference systems | |
Video door telephones | |
Selecting arrangements providing connection between main exchange and sub-exchange or satellite | |
Details of transducers for preventing acoustic reactions | |
Preventing of acoustic reactions in def-aids sets |
Further details of subgroups
It includes two-way communication systems between a limited number of parties as, for examples, vehicle interphone systems (door telephones H04M 11/025, video door telephones H04N 7/186, paging systems G08B 3/1008, hands free subscriber equipment H04M 1/6033).
It includes systems with subscriber controlled access to a line as key telephone systems. Subgroups are defined and clear by their title (keyboard equipment in semi-automatic systems H04M 3/62, subscriber line circuits H04M 3/005).
These groups are not anymore used as they were differentiating systems according to the type of line and access used.
Two-way loud-speaking telephone systems with means for suppressing echoes or otherwise conditioning for one or other direction of traffic. This can be done for example, estimating level of noise or speech, suppressing near and far end background noise, introducing insertion losses (controlling gain) for reducing singing phenomenon. Subgroups includes H04M 9/085, where digital techniques are used, H04M 9/087 with subdivision in different frequency bands for transmitting and receiving part and H04M 9/10 with switching of direction of transmission by voice frequency. (active noise canceling by regenerating original acoustic wave in anti-phase G10K 11/178, detection of presence or absence of speech signals in general G10L 25/78)
This important subgroup refers to the acoustic echo canceling techniques where sound emitted by a local transmitter (loudspeaker) is picked up by a receiver (microphone) and then sent to the far end user together with the voice of the near end user. With the use of adaptive filter, for example, acoustic echo is estimated and subtracted. Also aspects of residual echo (echo left after an incomplete echo cancellation), insertion of comfort noise are classified here (in vocoders H04W 84/12 ). Hybrid echo also known as line echo or electrical echo (generated in the hybrid circuit "fork" inserted between a two-wire local loop and the four wire transmission facility) is instead classified in H04B 3/23 (digital adaptive filter per se H03H 21/0012). In H04M 3/002 instead documents covering aspects of echo cancellation or echo suppression on the network side (Central Office) are covered. Prevention of acoustic reactions in hearing aids is covered by H04R 25/45 .
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
ABF | Adaptive Beamformer |
AEC | Acoustic Echo Canceller |
AGC | Automatic Gain Control |
AP | Affine Projection |
APA | Affine Projection Algorithm |
AR | Auto-recursive |
CPE | Customer Premise Equipment: any phone equipment (key systems, PBX's, answering machines, etc.) which reside on the customers premises |
ERLE | Echo Return Loss Enhancement |
FIR | Finite Impulse Response |
GSC | Generalized Sidelobe Canceller |
HKTS | Hybrid Key Telephone System: telephone system that can be used as a PBX or as a Key Telephone System |
IIR | Infinite impulse response |
KSU | Key Service Unit (common control unit of a KTS) |
KTS | Key Telephone System |
LMS | Least Mean Square (algorithm used in echo cancelling) |
MDF | Multi Delay Filter |
MMSE | Minimum Mean Square Error |
MSE | Mean Square Error |
NLMS | Normalized Least Mean Square (algorithm used in echo cancelling) |
PNLMS | Proportionate NLMS |
RLS | Recursive Least Square (algorithm used in echo cancelling) |
SAEC | Stereophonic AEC |
SER | Signal to Echo Ratio |
SPNLMS | Sparse partial update NLMS |
SVD | Singular Value Decomposition |
VAD | Voice Activity detector |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
For line transmission in general |
This place covers:
Telephonic communication systems adapted for combination with other electrical systems e.g. combinations with application servers or physical implementation of xDSL-systems.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
This place covers:
Typically, electricity or gas meters are read from a remote location via the telephone network. Other types of meters may be used: water, tank fluid level, vending machine stock level, environmental and pollution conditions. Generally, two alternative models are used for remote meter reading: polling and alert, alerts being triggered by thresholds or timers.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Remote reading of utility meters | |
Tele-metering in general | |
The metering is transmitted by a channel of a phone connection dedicated to data (e.g. SMS, GPRS) | |
Reporting to a device located outside the home and the home network | |
Web-based protocols | |
Relates to telemetry by calling (a) substation/s from a main station, but not using the telephone network |
If the main aspect is remote control via the telephone line and there is also a remote meter reading via the telephone line, then classification in both H04M 11/002 and H04M 11/007 is expected.
If the meter level is an indication of an alarm condition, subgroup H04M 11/04 is preferred
Some documents might have aspects to be classified both in H04M 11/002, H04M 11/062 and G08C 17/02 (e.g. remote control by telephone and the reception device in a home is forwarding the remote control to signals after conversion to specific appliances).
This place covers:
Telemetering via telephone connection using recorded signals, e.g. speech.
This place covers:
Controlling devices via the telephone line is the subject of this subgroup.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Remote control in general | |
Remote control via wireless link | |
Remote control via home network | |
Controlling appliance services in a home-network | |
Web-based protocols |
Documents where the remote control consists solely in the setting of parameters for remote reading by telephone should be classified in H04M 11/002 only and not in H04M 11/007.
Some documents might have aspects to be classified both in H04M 11/002, H04M 11/007 and G08C 17/02 (e.g. if you remote control by telephone and the reception device in a home is forwarding the remote control to signals after conversion to specific appliances)
This place covers:
A sound is produced in order to reach a person or a subgroup of person immediately. A telephonic communication system has to be used for this purpose.
The telephonic communication system is a private system, such as an intercom (H04M 11/025) or an annunciator systems for hospitals (H04M 11/027).
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Signalling in general |
This place covers:
H04M 11/022 relates to pagers, which are end subscriber devices allowing simplex transmission or reception of text. Paging techniques used in the context of a wired telephone network or in the context of local premises are classified in this subgroup.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Finding location | |
Personal communication services | |
Special services or facilities | |
Paging systems | |
Determination of the location of a subscriber | |
Personal calling arrangements or devices | |
Public address systems | |
Paging techniques as integral part of wireless networks |
This place covers:
The door phone systems, are classified in H04M 11/025 unless they are part of a closed circuit television system for monitoring premises.
This place does not cover:
Constructional features of door telephones |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Interconnection arrangements not including central switching | |
Locks | |
Systems for screening visitors and access control | |
Door telephones adapted for closed circuit television systems |
This place covers:
Systems for calling nurses in a hospital that use a telephonic system.
This place covers:
Use of the telephone network in alarm notification.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
For portable telephones for use in emergency situation | |
For call centres used for emergency applications | |
Special services or facilities for emergency applications | |
With determination of the subscriber location use | |
Signalling in general | |
Alarm systems in general | |
Broadcast systems adapted for emergency communications | |
Provision and call routing of emergency telephone numbers | |
Services facilitating emergency connection |
This place covers:
Use of the telephone network in alarm notification using recorded signals, e.g. speech.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Alarm systems in general | |
Alarm systems in which the location of the alarm condition is signalled to a central station, e.g. fire or police telegraphic systems | |
Characterised by the transmission medium | |
Using recorded signals, e.g. speech | |
Provision and call routing of emergency telephone numbers |
This place covers:
This subgroup relates to transmitting simultaneously speech and data on the telephone line. "Simultaneous" does not include only the case where data and speech are transmitted exactly at the same time, but more generally the cases where data and voice are both transmitted on the same telephone connection, for instance competing for time access to this resource.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Telephone sets using digital voice transmission, (e.g. Internet phones) | |
Telegraphy in general | |
Packet multiplexing, where some packets are generated from data and others from voice |
Avoid classifying in H04M 11/06. Use H04M 11/062, H04M 11/064, H04M 11/066, H04M 11/068 instead.
This place covers:
This subgroup contains many documents -- some are very old-- where it is taken advantage of the fact that "sounds" above a certain frequency can not be heard by modulating data above this frequency. However, many recent documents relate to xDSL equipments (modems and concentrators). The xDSL family allows high speed access to the Internet and multimedia services over the local loop. The local loop is formed of an unshielded twisted pair (UTP) and connects the subscriber xDSL modem at customer premises to subscriber line concentrator like a DSLAM (Digital Subscriber Line Access Multiplexer) at the central office for connection to a broadband network. Splitters, comprising filters for each frequency band, are necessary so that the subscriber telephone and the data equipments do not interfere. The data bands definition, and the techniques for combining the data signals in the data bands depend on the type of xDSL: ADSL (Asymmetric DSL), SDSL (Symmetric DSL), HDSL (High speed DSL), VDSL (Very high speed DSL), MDSL (Multirate DSL), RADSL (Low Rate Adaptive DSL).
As an example, the frequency bands of ADSL are as follows. The voice part of the spectrum (the lowest 4 kHz) is separated from the rest by a passive filter, called a POTS splitter. ADSL makes use of advanced modulation techniques, such as discrete multitone (DMT) technology. DMT divides the bandwidth from about 10 kHz into a set of 265 independent subchannels, each 4 kHz wide. By measuring the quality of the subchannels and then assigning a bit-rate to each based on its quality, DMT customizes the transmit signal for every line. In doing so, it automatically avoids regions of the frequency spectrum that are too noisy or too attenuated to support reliable communications. If the quality of a subchannel degrades enough to affect a system's error performance, the data rate on that subchannel is lowered and the excess traffic moves to a subchannel capable of supporting it. The result is robust communications over single twisted pairs. As its name implies, ADSL transmits data asymmetrically at different rates upstream toward the central office and downstream toward the subscriber.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Access interface units for simultaneous transmission of speech and data, e.g. digital subscriber line (DSL) access interface units | |
Testing a digital subscriber line using xDSL modems | |
Testing of physical copper line parameters, e.g. capacitance or resistance | |
xDSL line qualification | |
Constructional details of impedance networks whose electrical mode of operation is not specified or applicable to more than one type of network of radio frequency interference filters. This is relevant for the LPF and HPF in the splitter | |
Testing crosstalk effects – includes Dynamic Spectrum Management used in optimization of DSL transmission parameters | |
Negotiation of transmission parameters prior to the communication (transmission speed and modulation) | |
Internet access | |
Modulated-carrier systems and analog front ends; means for connecting modulators, demodulators or transceivers to a transmission line | |
Documents having features related to the DMT modulation | |
Signal structure of multicarrier modulation systems | |
Constructional details of splitters | |
DSL access multiplexers |
This place covers:
This subgroup relates to transferring data on the telephone line and interrupting the data transfer when there is voice to be transmitted.
In a first aspect, this subsubgroup relates to techniques that take advantage of the fact that speech is mostly composed of silences. During these silences, data can be sent without the subscriber noticing it, provided that it is replaced at the receiving telephone by blanks. In order to receive and remove the data, the start and the end of the data segments is signalled from one end to the other.
In a second aspect, this subgroup also concerns techniques for interrupting a data communication which was happening when no any voice communication was going on the telephone line. The objective of such systems is to avoid that the subscriber can not use his telephone for voice communication when for instance his modem is transmitting data.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Notifying a called subscriber of an incoming call during an ongoing call, e.g. Call Waiting |
This place covers:
In band modems (voice band, narrow band). Since base band transmission on the telephone network is not possible, data needs to be modulated. Modems allow the modulation of data so that data can be sent instead of speech via the telephone network. Most modems have several operating modes and need to exchange training sequences before exchanging data. Circuit details of the galvanic isolation between the line side and the subscriber side are a topics of particular interest
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Details about acoustic couplers between a telephone and an external device | |
Telephone devices for the deaf | |
Negotiation of transmission parameters prior to communication - Handshaking - such as transmission speed and modulation type | |
Modulation techniques in general | |
Telemetry and telecontrol details |
In patent documents the following abbreviations are often used:
TTY | teletypewriter |
In patent documents the following expressions/words "analog modem", "digital modem", "dialup modem", " fax modem", " in band modem", "smart modem", " voice modem" are often used.
This place covers:
Time division multiplexing at the telephone subscriber end. Very often, there is an equipment for multiplexing speech and data on the phone line.
This place does not cover:
Integrated services digital networks |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Time division multiplexing systems |
This place covers:
A special arrangement at the telephony end subscriber side for handling in a special way information received via phone line which relates to a special service. The information transmitted relates for example to time, gaming information, route navigation or electronic messages.
Voice or sound, e.g. DTMF Digital Tone Multi Frequency, is usually interpreted by an automatic device, which may carry out voice recognition.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Means for retrieving and displaying personal data about calling party | |
Telephony special services | |
Display of information about the caller (CLID) | |
Arrangements in the network for providing information services, e.g. recorded voice services, time announcement | |
Interactive Voice Response systems | |
Browsing from a telephone or fax | |
Systems in which the information is continuously available on a carrier over the whole network | |
Intra-layer communication | |
In OSI layer 7 | |
Video communication | |
Two way working for television |
This place covers:
Minitel /videotext systems since television receivers are meant to include any screen display working in conjunction with the telephone. The situation where the class H04M 11/08 would have been given but the device has a display.
This place covers:
Centralised dictation systems accessible via the telephone network for recording and playback. Playback may involve tape recorder features. What characterizes the word dictation is that the ultimate purpose of dictation is to have the text typed or written, but at a later stage. The word "centralised" specifies that the system considered is not just at the subscriber side. Use of voice mail systems for dictation.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangements for recording conversations in a (mobile) phone | |
Combinations of dictation devices with cordless phones | |
Arrangements for recording conversations within the telephone network, e.g. in an exchange | |
Voice mail servers | |
Information storage based on relative movement between record carrier and transducer | |
Dictation systems as such |
This place covers:
Arrangements in which two or more customers are connected directly to the same link or circuit.
Substation equipment | |
Exchange equipment, automatic, manual | |
Metering arrangements |
This place covers:
Charging or billing arrangements, e.g. generation of metering signals, tariffs, rating plans, charge calculations and bill generation details for voice wireline and wireless communications, including VoIP. Also, rating/charging for added value services or other services using prepaid calling cards, SIM cards or the mobile phone itself, insofar as these services are metered, rated and billed by the network operator.
When documents disclose aspects of charging or billing in combination with aspects of wired or wireless data or voice communication, e.g. voice over IP (VoIP, VoLTE), then multiple classification should be considered in groups H04L 12/14, H04M 15/00, H04M 17/00 or H04W 4/24.
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Telephonic communication systems adapted for combination with other electrical systems | |
Prepayment of wireline communication systems, wireless communication systems or telephone systems | |
Charging, metering or billing arrangements specially adapted for data communications, e.g. authentication, authorisation and accounting [AAA] framework | |
Accounting or billing for services specially adapted for wireless communications |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Substation equipment, e.g. for use by subscribers | |
Arrangements for supervision, monitoring or testing for metering arrangements or prepayment telephone systems | |
Systems providing special services or facilities to subscribers | |
Counting mechanisms; Counting of objects not otherwise provided for | |
Payment architectures, schemes or protocols | |
Commerce | |
Mechanisms actuated by objects other than coins to free or to actuate vending, hiring, coin or paper currency dispensing or refunding apparatus | |
Complete banking systems; Coded card-freed arrangements adapted for dispensing or receiving monies or the like and posting such transactions to existing accounts | |
Pulse technique |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
call | any kind of communication |
This place covers:
I.e. third party can be a predetermined communication line of the user if he initiates a communication from another device and asks to be billed on his main device
This place covers:
Calling party is the party initiating the communication i.e. A-party
This place covers:
Calculation of charges at substation, e.g. at the mobile terminal, or notify subscriber of charges e.g. Advice-of-Charge (AoC)
This place covers:
Metering or calculation of charges not controlled from an exchange, i.e. autonomous calculations of charges in the terminal
This place covers:
Distributed metering or calculation of charges, e.g. in different nodes like for mobiles between HLR and VLR, or between the terminal and the billing function
This place covers:
Metering,charging or billing preventing arrangements i.e. parameters, characteristics that identify whether to charge for a service or not
WARNING: Groups H04M 15/44 - H04M 15/90 do not correspond to former or current IPC groups.
This place covers:
Billing record details, i.e. parameters, identifiers, structure of Call Data Record (CDR), or Toll Ticket (TT), or Automatic Message Accounting (AMA)
This place covers:
Dynamic individual rates, e.g. individual communication rate determination method allowing the service provider to dynamically generate an individual rate plan for the user
This place covers:
Augmented, consolidated or itemized billing statement, e.g. additional billing information, bill presentation, layout, format, e-mail, fax, printout, itemized bill per service or per account, cumulative billing, consolidated billing
This place covers:
On line or real-time flexible customization or negotiation between user and provider or operator, or between operators and providers
This place covers:
Fraud detection or prevention means related to metering, charging /billing in wire-line or wireless, voice or data
This place does not cover:
Fraud detection and prevention in wireless networks |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Detection or protecting against malicious traffic | |
Fraud detection and prevention in wireless networks |
This place covers:
Secure and trusted billing, e.g. trusted elements, encryption, digital signature, codes or double check mechanisms to secure billing calculation and information
This place does not cover:
Wireless network security |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Network security | |
Wireless network security |
This place covers:
Connection to several service providers
This place covers:
Interconnection, inter-operator accounting or billing, billing agreements between different operators, e.g. billing identifier added on the CDR in order to cross charge the other operator
This place covers:
Resellers-retail or service providers billing, e.g. agreements with telephone service operator, activation, charging/recharging of accounts, bill directly reseller's customers
This place covers:
Independent billing system i.e. billing system owned by resellers or service providers (not by the operator)
This place covers:
Arrangements for mediation, i.e. device or program to reformat CDRs from one or more switches in order to adapt to one or more billing program formats
This place covers:
Revenue sharing between telecommunication operators and service providers or location owners (e.g. for public telephones, etc.)
This place covers:
Hybrid network i.e. charging, billing arrangements for connection made over different networks, e.g. wireless and PSTN, ISDN, etc.
This place does not cover:
Telephonic communication systems adapted for combination with other electrical systems |
This place covers:
VoIP charging/billing
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Voice over IP, VoIP Protocols and Services |
This place covers:
IMS charging or billing, i.e. Integrated Multimedia messaging Subsystem charging/billing; IMS in general, see H04L 65/1016; IMS based services and session control, see H04L 65/40, H04L 65/1066.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
IP multimedia subsystem [IMS] | |
Real-time session management in data packet switching networks | |
Session initiation protocol [SIP] | |
Support for real-time services or applications in data packet switching networks |
This place covers:
Network monitoring; statistics on usage on A-party or B-party number, on used services, etc
This place does not cover:
Network monitoring per se |
This place covers:
Real time metering, charging or billing
This place covers:
Charging/billing only for the actual communication time, i.e. billing the user for the actual time used by the service, not for the time awaiting responses due to network problems; Billing the user when there is a satisfied QoS, only for the time the user receives communication data
This place covers:
Service related metering or charging or billing
This place covers:
Trigger specification e.g. trigger or code input into a device to specify a service
This place covers:
Charging based on the content carried by the SIP messages
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Real-time session management in data packet switching networks | |
Session initiation protocol [SIP] |
This place covers:
OCS i.e. Online Charging System , unified online charging and online control capabilities that can be used as a unified charging engine for all network services, making it a core basis for convergent billing in the network
This place covers:
Policy and Charging System
This place covers:
Sending billing related information over a non-traffic network channel or another connection than the one actually used, e.g. signaling, D-channel, data and voice
This place covers:
Payment of value-added services, mainly when their charges are added on the telecommunications bill, e.g. payment of non-telecom services, m-commerce, on-line banking, etc.
This place covers:
Administration or customization aspects, or modify settings or limits or counter-check correct charges
This place covers:
Account settings, e.g. users, terminals, limits, numbers or payment
This place covers:
Modify recharging resources, e.g. banking, credit or phone account
This place covers:
Activate new subscriber or card
This place covers:
Administration or customization by the user
This place covers:
Administration or customization aspects like modify account settings, checking accounts using Internet or WAP, etc. i.e. on-line real-time billing, able to see billing information while in communication via the internet
This place covers:
Using the user's device e.g. phone, PDA, etc
This place covers:
Administration or customization by the operator
This place covers:
Re-credit user, i.e. repay user with the amount or free time after finding an error in calculating the charges
This place covers:
Details of metering, charging or billing backups
This place covers:
Customization according to wishes of subscriber, e.g. customer preferences, friends and family, selecting services or billing options, Personal Communication Systems (PCS)
This place covers:
Account location specifications
This place covers:
Card based account, e.g. smart card, SIM card or USIM)
This place covers:
Account identification via service number, e.g. calling card
This place covers:
Account identification by SIM, e.g. smart card account in SCP, SDP or SN
This place covers:
Synchronization of distributed accounts
This place covers:
Linked or grouped accounts, or devices, or users, or user access,
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Systems involving a hierarchy between servers | |
Wireless access security |
This place covers:
Linked or grouped accounts, shared by users, e.g. group accounts or one account for different users, primary-secondary
This place covers:
Linked or grouped accounts, shared by technologies, e.g. one account for different access technologies (PSTN or wireless) , or prepay and post-pay
This place covers:
Linked or grouped accounts for closed Subscriber Group (in 3GPP) i.e. group of subscribers that belong to a restricted access group of cells and differentiated charging is applied e.g. CSG or femto-cells, Home Node B (HNB) cells, Home e-Node B (HeNB),
This place covers:
Multiple accounts per user
This place covers:
Multiple accounts per user per terminal or location; Mobile with multiple directory numbers
This place covers:
Multiple accounts per user per service, e.g. prepay and post-pay
This place covers:
Multiple accounts per user per technology, e.g. PSTN or wireless
This place covers:
Account specifications on parallel communications
This place covers:
Redistribute amount between accounts
This place covers:
Redistribute amount between accounts dynamically
This place covers:
Redistribute amount between accounts by user request
This place covers:
Reserve amount on the account , e.g. according to estimated costs for a typical communication duration or according to the estimated volume to be transferred
This place covers:
Virtual purses i.e. prepaid value is distributed between user specific virtual purses each associated with a respective metered resource
This place covers:
Rating aspects, e.g. rating parameters or tariff determination aspects, reduced or increased tariffs. General billing plans, e.g. numbering plans, rate centers c
This place covers:
Rating dependent on class of subscriber
This place covers:
Rating depending on the Quality of service (QoS)
This place covers:
Rating depending on determined tariff or charge band
This place covers:
Rating depending on load situation, e.g. Current network load, traffic load or available resources
This place covers:
Location dependent rating, e.g. business or home
This place covers:
Roaming or handoff depending rating]
This place covers:
Select cheaper transport technology for a given service, e.g. use for data connection WLAN rather than GSM/UMTS/GPRS or use company's communication network rather than a public network
This place covers:
Select least cost route depending on origin or type of service
This place covers:
Group MMS or SMS; Point-to-multi-point services, broadcast services
This place covers:
Reduced rates or discounts, e.g. time-of-day reductions, volume discounts, cell discounts, group billing, frequent calling destination(s) or user history list
This place covers:
Increased rates i.e. increase price of communication in order to avoid user misuse e.g. spam messaging billing differentiation
This place covers:
Trial service i.e. free of charge or reduced charging of a service for trial purposes
This place covers:
Dynamic pricing, e.g. change of tariff during call
This place covers:
Criteria, parameters used for performing billing operations, metric aspects
This place covers:
Time based data metric aspects, e.g. VoIP or circuit switched packet data
This place covers:
Aspects of data metering or packet based metering,.
(used only for additional classification of documents in order to cover all different aspects of billing metrics e.g. : time, data, in the same billing structure)
classification is done in H04L 12/14.
This place covers:
Based on the number of used channels, e.g. bundling channels or frequencies or CDMA codes
This place covers:
Pulse based metering, charging.
Based on the number of used services, e.g. call forwarding or call barring
This place covers:
Based on the number of used services, e.g. call forwarding or call barring
This place covers:
Money or currency based metering, charging
This place covers:
Charging for signaling or unsuccessful connection
This place covers:
Time (before or after or during communication) or frequency (in regular intervals, dynamically) of notifications to the user e.g. display messages related to user's balance, Advice of Charge (AoC), etc.
This place does not cover:
Notification of users, e.g. alerting for incoming communication or change of service |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
AoC | Advice of Charge |
This place covers:
Dynamic change of the length or frequency of the length of the notification interval, e.g. depending on the remaining available prepaid credit
This place covers:
Types of notifications to the user e.g. display messages announcements, flashing indication
This place does not cover:
Notification of users, e.g. alerting for incoming communication or change of service |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
AoC | Advice of Charge |
In patent documents the following expressions/words "advice of charge or aoc", "notification or notify or notice", "display", "announcement", "alert", "message" and "optical indication" are often used.
This place covers:
Types of notifications to the user announcements, e.g. IVR dialogue, intelligent peripheral or switch
This place covers:
Types of messages, e.g. alphanumeric text, SMS, MMS, EMS or www-based messaging service
This place covers:
Types of optical notifications, e.g. flashing indication of a lamp, icon, soft-key or symbo
This place covers:
Types of tone, notifications to the user, e.g. beeper, sound, wave
This place covers:
Notifications send when a specific condition, service or event is met
This place does not cover:
Notification of users, e.g. alerting for incoming communication or change of service |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
AoC | Advice of Charge |
In patent documents the following expressions/words "advice of charge or aoc", "notification or notify or notice", "display", "announcement" and "alert" are often used.
This place covers:
Notifications send when there is low balance or limit reached , e.g. zero-credit
This place covers:
Notification when a successful event, e.g. successful recharge or delivery of a service
This place covers:
Notifications send when there is an Unsuccessful event, e.g. service rejected due to low credit
This place covers:
Notifications send when there are cumulative charges
This place covers:
Notifications send when the system should request users acknowledgement prior to use
This place covers:
When and how the notifications or AOCs are send
This place covers:
Notifications send to multiple parties, e.g. multi party AOC
This place covers:
Notifications send to a predetermined or undetermined destination, e.g. notifying a prepaid accounting server of a successful delivery of a service, a connection, or chargeable content to a mobile terminal
This place covers:
Provision for limiting connection, or expenditure e.g. limit on communication expenses or account
This place covers:
Provision for limiting expenditure by continue allow grace, e.g. accept negative balance
This place covers:
Provision for limiting or expenditure by continue alternative, i.e. alternative account to continue use, e.g. Alternate Billing Service (ABS)
This place covers:
linked escalation limits, establish, first or second limit
This place covers:
Provision for limiting connection, or expenditure per application
This place covers:
Provision for limiting connection, or expenditure per terminal
This place covers:
Provision for limiting connection, or expenditure per user or user related number
This place covers:
severing connection after predetermined time or data, etc. or upon reaching limit or blocking the device
Selecting arrangements |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Provisions for intelligent networking |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
AIN | Advanced Intelligent Network |
IN | Intelligent Network |
This place covers:
Charging, metering aspects using Bluetooth® or near field, i.e. wireless communication links like Bluetooth®, Wi-Fi®, near field used to communicate charging or billing related information.
This place covers:
Prepaid aspects for wire-line and wireless communications, including VoIP. Also, any other prepaid related aspect like recharging functionality, usage and features of calling cards, SIM.
When documents disclose aspects of charging or billing in combination with aspects of wired or wireless data or voice communication, e.g. voice over IP (VoIP, VoLTE), then multiple classification should be considered in groups H04L 12/14, H04M 15/00, H04M 17/00 or H04W 4/24.
This place does not cover:
Using a coded card to authorise calls from a telephone set |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Telephonic communication systems adapted for combination with other electrical systems | |
Arrangements for metering, time-control or time indication; Metering, charging or billing arrangements for voice wireline or wireless communications | |
Charging, metering or billing arrangements specially adapted for data communications, e.g. authentication, authorisation and accounting [AAA] framework | |
Accounting or billing for services specially adapted for wireless communications |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Substation equipment, e.g. for use by subscribers | |
Arrangements for supervision, monitoring or testing for metering arrangements or prepayment telephone systems | |
Systems providing special services or facilities to subscribers | |
Counting mechanisms; Counting of objects not otherwise provided for | |
Payment architectures, schemes or protocols | |
Commerce | |
Mechanisms actuated by objects other than coins to free or to actuate vending, hiring, coin or paper currency dispensing or refunding apparatus | |
Complete banking systems; Coded card-freed arrangements adapted for dispensing or receiving monies or the like and posting such transactions to existing accounts | |
Pulse technique |
This place covers:
Disposable prepaid communication devices e.g. wireless disposable telephones
This place covers:
Cocot systems, private ownership of payphones
This place covers:
Coin-freed or check-freed systems e.g. card operated phones or mobiles, public telephones or booths, etc.
This place does not cover:
Coin-freed or check-freed apparatus per se |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Cordless telephones, mobiles |
This place covers:
Credit establishment i.e. establishment of credit (codes, vouchers, etc. ) for the payment of telecommunication services .
This place covers:
With automatic recharging of account or card with predetermined amount at threshold, e.g. if limit is reached during connection the account is recharged automatically
This place covers:
With automatic recharging of account or card at threshold and the payment method is selected interactively by the user
This place covers:
Code type e.g. alphanumeric code, bar code, pattern, punched holes, temporarily valid code, etc
This place covers:
Pay as you go i.e. user establishes payment in advance or while on line but no contract is required as for prepaid account details and usage
This place covers:
- Feeding from Central Office Exchange to telephone sub stations (Battery function of Subscriber Line Interface Circuits, SLIC).
- Arrangements for providing ringing current to telephone substations (Ringing function of Subscriber Line Interface Circuit).
- Ringing current generated at substation, in particular ringing alerts for alerting a user of incoming calls.
- Current supply source generated at the sub station.
- Subgroup details:
- H04M 19/001: This group cover the arrangements at the exchanger for providing current to substation. A SLIC should provide the so called BORSCHT (Battery, Over voltage, Ringing, Signalling, Coding, Hybrid, Testing) functions: this group covers the "B" function. SLIC in general covered by H04M 3/005.Over voltage covered by H04M 3/18. Off hook detection covered by H04M 3/2272.
- Subgroups cover details about circuits that are clear from the title of the subgroups themselves.
- H04M 19/02: This group cover the "R" function of a SLIC. Subgroups cover details that are clear from the title of the subgroups itself.
- H04M 19/04: This group cover ringing current generated at the substation. Ringing tones (as well as visual and tactile alerts) for alerting user of an incoming call should be classified here. Ring back tones are instead covered by H04M 3/42017. Audible, visible and tactile signalling in generals are covered by G08B group.
- H04M 19/06: Current supply source at subordinate switching centre charged from main exchange.
- H04M 19/08: In case substation is powered locally, from mains for example. Adjacent fields includes circuit arrangements for charging batteries (H02J 7/00), circuit arrangements for emergency or stand by power supply (H02J 9/00).
If the current supply refer to the selecting equipment part of the exchange then this aspect is covered by H04Q 1/28.
This place does not cover:
Customized ring back tones | |
Uninterrupted power supply for computers | |
Current supply arrangements over Ethernet |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Portable communication terminals with means for adapting by the user the functionality or the communication capability of the terminal under specific circumstances | |
Subscriber line interface circuits (SLIC) | |
Over voltage protection in line interface circuits | |
Subscriber line supervision circuits e.g. off hook detection | |
Paging systems | |
Door telephones | |
Power supply means for computers | |
Audible signalling system in general | |
Visible signalling system in general | |
Tactile signalling systems in general | |
Details of transformers | |
Circuit arrangements for charging or depolarising batteries or for supplying loads from batteries | |
Circuit arrangement for emergency or standby power supply | |
Arrangements for feeding power to a repeater over a transmission line | |
Systems for transmission via power distribution lines | |
Arrangements for feeding power in transmission systems employing electromagnetic waves other than radio waves, e.g. light, infrared |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
BORSCHT | Battery, Over voltage, Ringing, Signalling, Coding, Hybrid, Testing |
SLIC | Subscriber Line Interface Circuit |
AEC | Acoustic Echo Canceller |
CPE | Customer Premise Equipment: any phone equipment (key systems, PBX's, answering machines, etc.) which reside on the customers premises |
HKTS | Hybrid Key Telephone System: telephone system that can be used as a PBX or as a Key Telephone System |
KTS | Key Telephone System |
PBX | Private Branch Exchange |
UPS | Uninterrupted Power Supply |
CO | Central Office |
RBT | Ring Back Tone |
RTTL | Ring Tone Transfer Language |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Speech synthesis; Text to speech synthesisers |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Speech recognition |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adaption to the speaker for speech recognition |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Speaker identification or verification |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Quality of service monitoring for automatic or semi-automatic exchanges in telephonic communication | |
Quality of speech transmission monitoring for automatic or semi-automatic exchanges in telephonic communication |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Data switching networks for stock exchange and similar applications |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Route determination based on the nature of the carried application in data switching networks |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Data switching networks providing special services for broadcast or conference |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Network arrangements, protocols or services for supporting real-time applications in data packet communication |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Unified messaging, e.g. interactions between e-mail, instant messaging or converged IP messaging [CPM] |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Messages including annexed information, e.g. attachments in packet-switching networks |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Monitoring or handling of messages in packet-switching networks, using selective forwarding |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Monitoring or handling of messages in packet-switching networks, providing notification on incoming messages |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangements for conducting the computer conference, e.g. admission, detection, selection or grouping of participants |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Computer conference organisation arrangements |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangements for conducting the computer conference, e.g. admission, detection, selection or grouping of participants |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Network arrangements for conference optimisation or adaptation |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Computer conference organisation arrangements |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangements for conducting the computer conference, e.g. admission, detection, selection or grouping of participants |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangements for conducting the computer conference, e.g. admission, detection, selection or grouping of participants |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Tracking arrangements for later retrieval, e.g. recording contents, participants activities or behaviour, network status |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
User-to-user messaging in packet-switching networks, transmitted according to store-and-forward or real time protocols using automatic reactions in messaging within packet-switching networks |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Supporting social networking services within packet-switching networks |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Least cost routing, i.e. provision for selecting the lowest cost tariff |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Personal communication services related to one subscriber independent of his terminal and/or location | |
Information service where the information is dependent on the location of the subscriber |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Telephonic subscriber devices including a GPS signal receiver |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Digitisers, e.g. for touch screens or touch pads |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Constructional features concerning the integration of cameras in portable phones |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Constructional features for a projector or beamer module assembly in portable telephone sets, e.g. cordless phones, mobile phones or bar-type handsets |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
User interfaces specially adapted for cordless or mobile telephones with local support of applications by software upgrading or downloading | |
User interfaces specially adapted for cordless or mobile telephones with interactive means for internal management of messages |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Recording arrangements for recording conversations |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Character input methods using prediction or retrieval techniques for converting discrete items of information into a coded form |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Devices for calling a subscriber whereby a plurality of signals may be stored simultaneously, controlled by voice recognition | |
Speech recognition |