CPC Definition - Subclass H02S
This place covers:
- Photovoltaic [PV] power plants, e.g. mobile PV generator systems
- Combination of PV power plants with other systems for generation of electric energy
- Supporting structures for PV modules
- Structural details of PV modules not involving light conversion
- Components or accessories specially adapted for PV modules, e.g. cleaning arrangements, optical components, electrical components, thermal components
- Monitoring or testing of PV systems, e.g. load balancing or fault identification
- Testing of PV devices
This place does not cover:
Arrangements for obtaining electrical energy from radioactive sources | |
Light sensitive inorganic semiconductor devices | |
Light sensitive organic semiconductor devices | |
Thermoelectric devices | |
Pyroelectric devices |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Space applications, e.g. power supply for satellites made of solar cell modules | |
Solar heat collectors | |
Systems for regulating electric power to the maximum power available from a generator, e.g. from PV cells | |
Electric power networks; Circuit arrangements or systems for supplying or distributing electric power; Systems for storing electric energy |
In this subclass, the classification symbols are to be only indicated as Inventive (I).
This place covers:
- PV power plants
- Hybrid diesel-PV energy systems
- Hybrid wind-PV energy systems
- Hybrid hydroelectric-PV energy systems
- PV power plants comprising energy storage means integrated therein or associated therewith
- Thermophotovoltaic systems
- Mobile PV generators
This place covers:
PV power plants combined with a supplementary source of electric energy, e.g. combined with a diesel generator or a hydroelectric power plant
This place does not cover:
PV energy systems combined with gas-turbine plants |
This place covers:
Electric power generators, where wind turbines are combined with PV modules, e.g.:
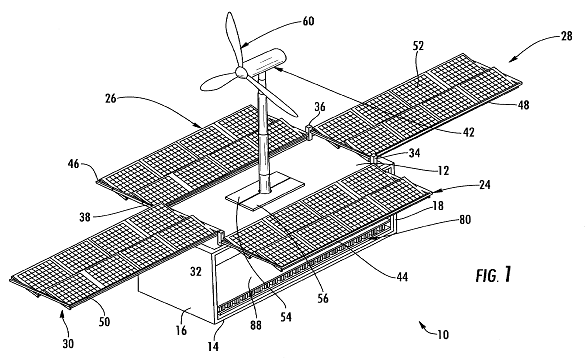
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wind Motors per se |
This place covers:
PV power plants including rechargeable batteries for energy storage.
This place does not cover:
Energy storage means, e.g. batteries, structurally associated with PV modules, e.g. directly mounted onto the module |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Secondary accumulators structurally combined with charging apparatus, e.g. solar battery charging system | |
Circuit arrangements for charging batteries with solar cells | |
Energy storage means directly associated or integrated with the PV cell |
This place covers:
Systems formed by an infrared radiation emitting source and by a (an array of) low band-gap solar cell(s) which are specifically sensitive to the infrared spectrum emitted by the source. Generally two types of system are the most common one: one in which a special emitter (of refractory materials) is heated (e.g. by a gas flame) and emits a specially adapted infrared spectrum, the other in which the solar light is concentrated in a cavity and converted by the solar cells situated in the cavity.
This subgroup is used to classify documents covering aspects of the systems, including the specific radiators.
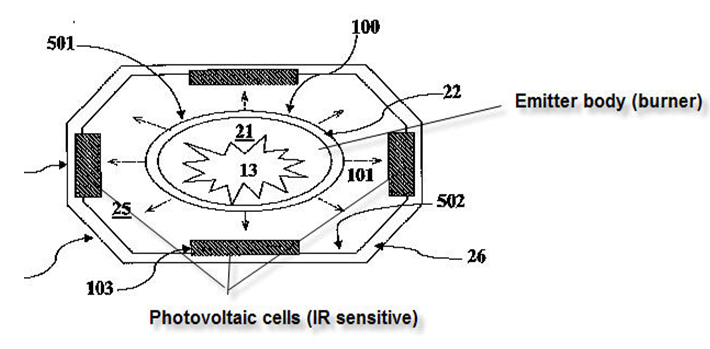
Documents featuring photovoltaic cells optimized for IR radiation spectrum are classified and found in the solar cell groups covering the cell structure or the cell materials (H10F 10/10 and subgroups).
Cells for TPV described independently from the TPV system are classified in the groups according to materials, structure, etc (H10F 10/10) since they merely refer to solar cells specifically sensitive to IR (IR forming also a part of the solar spectrum)
This place does not cover:
Photovoltaic cells specially adapted for conversion or sensing of infrared [IR] radiation | |
Thermoelectric devices |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Burners |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
TPV | Thermophotovoltaic |
This place covers:
PV generator systems being movable or displaceable to provide power to devices external to the generator.
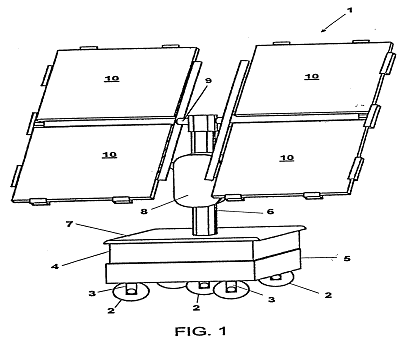
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Collapsible or foldable PV modules |
This place covers:
- Mechanical structures for supporting one or a plurality of PV modules.
- Floating structures for supporting one or a plurality of PV modules.
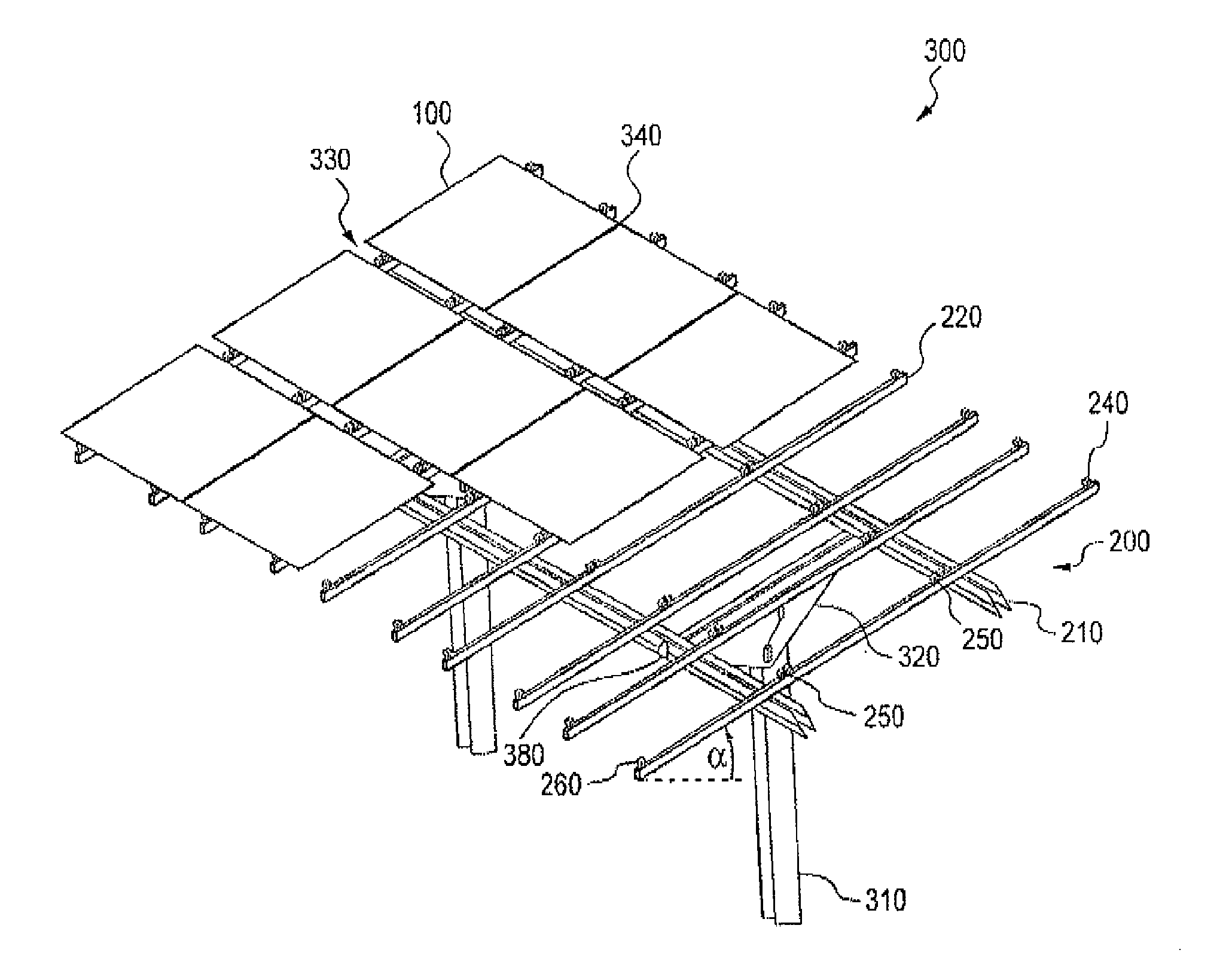
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Other supports for positioning apparatus or articles per se |
Supporting structures also intended for use with solar heat collectors should also be classified in groups F24S 50/20 or F24S 25/00
This place covers:
Supporting structures directly fixed to the ground, where there is no element between the photovoltaic module supporting structure and the ground. The supporting structure does not have any further function other than supporting the photovoltaic module, e.g. a street lamp with a photovoltaic module is an immovable object which should be classified in H02S 20/20.
This place does not cover:
Supporting structures being movable or adjustable, e.g. for angle adjustment |
This place covers:
Supporting structures directly fixed to an immovable object, e.g. a street lamp or a parking device having a photovoltaic module.
This place does not cover:
Supporting structures being movable or adjustable, e.g. for angle adjustment |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Mobile PV generators |
This place covers:
PV modules specially adapted for being used and mounted on sound barriers for road or railways, e.g. using the available surfaces of said barriers to produce electrical power.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Sound barriers per se |
Aspects of such PV modules specifically relating to PV applications should be classified in this subgroup, architectural aspects of the barrier walls are covered elsewhere (E01F 8/00).
This place covers:
Supporting structure specially adapted for integrating PV modules in buildings, e.g. PV modules mounted on the façade:
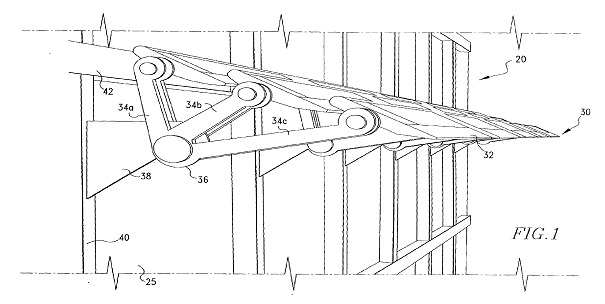
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Roof tile elements | |
Building materials integrated with PV modules, e.g. façade elements |
This place covers:
- Solar PV modules adapted for house roofs, disposed within roof tiles
- Special structural arrangements for installations on house roofs
- Wind protection devices (deflectors) associated with the PV supporting structures
- Ballast devices
- Solar PV modules integrated with Carports.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Roof covering aspects of energy collecting devices, e.g. including solar panels |
This place covers:
Photovoltaic devices integrated to or associated with one roof tile.
Example:
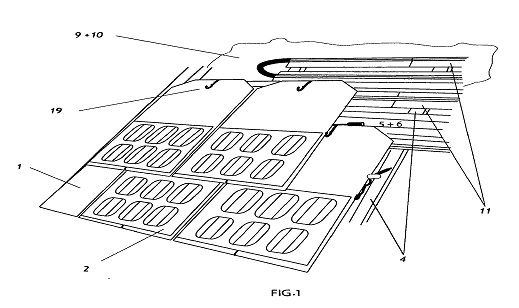
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Roof covering by making use of tiles | |
Roof covering by making use of flat or curved slabs | |
Solar heat collectors having working fluid conveyed through collector, e.g. solar thermal tiles |
This place does not cover:
Roof tile elements |
This place covers:
Movable structures to make a photovoltaic module mobile, e.g. solar PV modules integrated in an automobile.
Adjustable structures to adjust the position of the photovoltaic module, e.g. for angle adjustment.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Floating supporting structures | |
Roof tile elements |
This place covers:
Example:
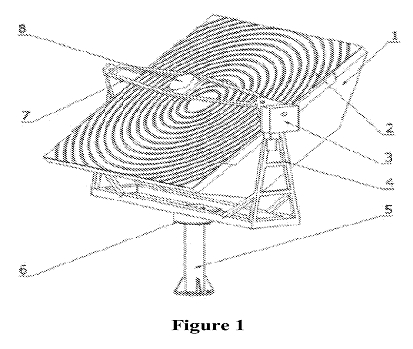
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Solar tracking for solar heat collectors | |
Direction- finders for determining the direction from which electromagnetic waves are being received | |
Control of position or direction |
This place covers:
- Frame structures
- Collapsible or foldable PV modules
This place does not cover:
Device aspects of modules of electrolytic light sensitive devices | |
Semiconductor device aspects of inorganic PV modules | |
Semiconductor device aspects of organic PV modules |
This place covers:
Frames or parts of frames specially adapted for PV modules, where the frame is not part of a housing or supporting structure. The frames covered by this subgroup are a result of the PV module manufacturing process and surround the laminate layers of the module.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Supporting structures for PV modules | |
Collapsible or foldable PV modules | |
Solar thermal collectors, including mechanical mounting aspects of solar modules, when also suitable for solar thermal collectors | |
Direction-findings for determining the direction from which light is being received, e.g. forming part of solar tracking systems |
This place covers:
PV modules specially adapted for being collapsible, rollable, or foldable, e.g. for jalousies, umbrellas, handbags.
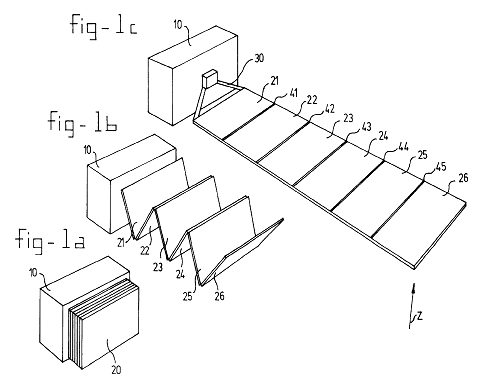
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Mechanical arrangements of foldable PV modules in satellites |
If the collapsible/foldable property is due to a special frame, then the subject matter is additionally classified in H02S 30/10.
This place covers:
- Cleaning arrangements in combination with PV modules, e.g. means for removing snow
- Optical components in combination with PV modules, e.g. light-concentrating means
- Electrical components in combination with PV modules, e.g. junction boxes, module-to-module interconnection
- Thermal components in combination with PV modules, e.g. cooling means
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Snow traps for roof coverings |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Optical elements in general |
This place covers:
Example:
Photovoltaic assembly with concentration (1) and spectral splitting (6, 7) of collected light beam:
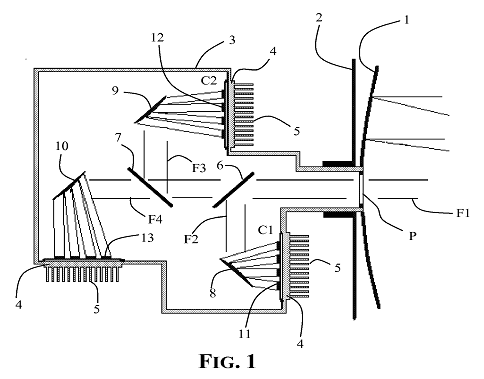
This place does not cover:
Light-reflecting or light-concentrating means directly associated with the PV cell or integrated with the PV cell |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Solar heat collectors having concentrating elements |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electric line connectors; Electric current collectors |
This place covers:
- DC/AC inverter means directly associated with the PV module, e.g. inverter on the backside of the PV module.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
This place covers:
- Junction boxes associated with and connected with the PV module, e.g. one box per module for electrical connection, or comprising bypass diodes.
This place covers:
Electrical interconnection between two or more PV modules.
Example:
- Electrical contacts 34 and 36 are used for interconnecting two PV modules:
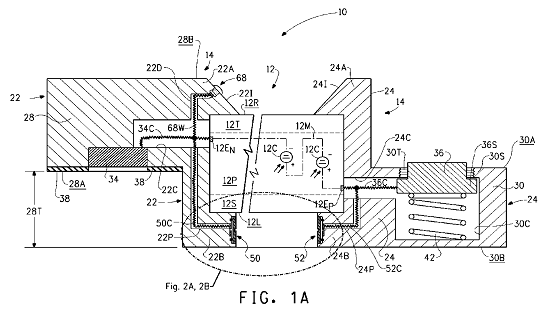
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Conductive pastes as such | |
Particular structures for electrical interconnecting of adjacent thin film solar cells in the module | |
Interconnection between solar cells inside a PV module | |
Electrodes of PV cells |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
"Interconnection" in this case means electrical connection, not mechanical.
This place covers:
Energy storage means which are mechanically connected PV modules or specially adapted to integrate with the PV modules. Electrical connection between batteries and photovoltaic modules are not classified in this subgroup, as well as batteries not being part of the photovoltaic module itself.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Battery charging utilising light sensitive cells |
This place does not cover:
Thermophotovoltaic systems |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Cooling means directly associated or integrated with the PV cell |
This place covers:
- Hybrid PV modules, producing warm water and electricity at the same time
Example:
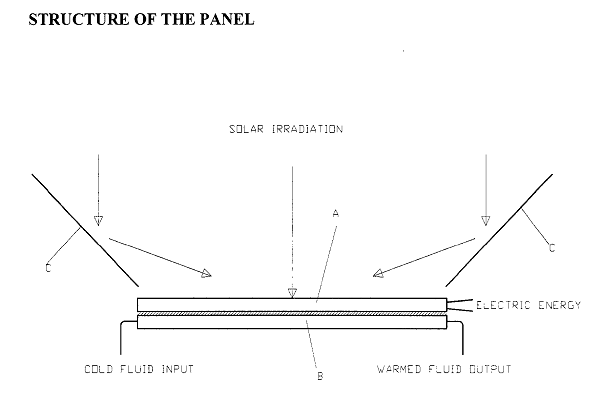
This place does not cover:
Means to utilise heat energy directly associated with the PV cell or integrated with the PV cell |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Using solar heat per se |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Testing of electric apparatus, lines, or components for short-circuits, discontinuities, leakage, or incorrect line connection | |
Burglar, theft or intruder alarms |
This place covers:
- Testing of electrical properties of PV devices in the dark state, e.g. short circuit test
- Testing of electrical properties, e.g. I-V characteristics, of PV devices under solar simulators
This place does not cover:
Testing of semiconductor devices during manufacturing |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Lighting devices intended for fixed installation, e.g. solar simulators | |
Testing of general semiconductor devices | |
Testing of electrical properties of electrical power supplies | |
Electroluminescent light sources |
This place covers:
- Testing of optical responses e.g. electroluminescence, light reflection or light absorption, of PV devices
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Investigating or analysing materials by fluorescence or phosphorescence | |
Investigating or analysing materials by electroluminescence |
This place covers:
This group is to be used only in rare situations where the subject matter is appropriate for H02S but does not clearly belong in any of the above main groups.