CPC Definition - Subclass H01G
This place covers:
Passive two-terminal electrical components used to store energy in an electrical field, typically two electrical conductors, i.e. electrodes, separated by a dielectric or dielectric medium.
Non-electrolytic, fixed capacitors, per se, e.g. thin and thick film capacitors, details thereof, e.g. electrodes, dielectrics, housings and encapsulations, and structural combinations thereof with each other, e.g. stacked, multilayer, feed-through or anti-noise capacitors, or with electrolytic devices covered by this subclass, or with other electric elements not covered by this subclass where the structure consists mainly of a capacitor. Processes of manufacture thereof. H01G 4/00.
Non-electrolytic, variable capacitors per se, in which the capacitance is varied by mechanical means, e.g. using variation of effective area of electrode, using variation of distance between electrodes, e.g. capacitors making use of microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), or using multiple capacitors. Details thereof, and structural combinations thereof with each other, with electrolytic devices covered by this subclass, or with other electric elements not covered by this subclass where the structure consists mainly of a capacitor. Processes of manufacture thereof. H01G 5/00.
Non-electrolytic, variable capacitors per se, in which the capacitance is varied by non-mechanical means, e.g. electrets, ferroelectric capacitors. Details thereof, and structural combinations thereof with each other, with electrolytic devices covered by this subclass, or with other electric elements not covered by this subclass where the structure consists mainly of a capacitor. Processes of manufacture thereof. H01G 7/00.
Electrolytic capacitors per se, e.g. liquid, solid, electric double layer, hybrid or redox capacitors, details thereof, e.g. terminals, electrolytes, electrodes, housings, and processes of manufacture thereof. Electrolytic rectifiers, detectors, switching devices, light-sensitive or temperature-sensitive devices per se, and details thereof. Structural combinations thereof with each other, with non-electrolytic capacitors or with other electric components not covered by this subclass. Processes of manufacture thereof. H01G 9/00.
Apparatus specially adapted for manufacturing capacitors; Processes specially adapted for manufacturing capacitors not provided for in other main groups of this subclass. H01G 13/00.
Structural combinations of capacitors or other devices covered by at least two different main groups of this subclass with each other. H01G 15/00.
Structural combinations of capacitors or other devices covered by at least two different main groups of this subclass with other electric elements, not covered by this subclass, e.g. RC combinations. H01G 17/00.Details common to two or more main types of devices covered by this subclass, e.g. special adaptation for mounting; cooling, heating and ventilating arrangements; housings, encapsulations and protection or prevention arrangements. H01G 2/00.
This place does not cover:
Selection of specified materials as dielectric | |
Capacitors having potential barriers |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Capacitive deionisation for electrochemical separation | |
Indicating or measuring liquid level, or level of fluent solid material by measuring variations of capacity of capacitors | |
Measuring temperature using capacitive elements | |
Impedance networks utilising capacitors, e.g. filters and circuitry thereof | |
Electret transducers | |
Printed circuits incorporating printed capacitors | |
Capacitors specially adapted for integration, e.g. stacked capacitors in DRAM | |
Thin- or thick-film solid state devices |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Powder metallurgy | |
Layered products | |
Micromechanical devices, comprising flexible or deformable elements | |
Active carbon | |
Compositions of ceramic materials | |
Polymeric films or sheets | |
Electrolytic coating by surface reaction, i.e. forming conversion layers | |
Measuring force or stress by measuring variations in capacitance | |
Measuring steady or quasi-steady pressure of a fluid or a fluent solid material by making use of variations in capacitance | |
Investigating or analysing material by investigating capacitance | |
Measuring capacitance; Measuring dielectric constants | |
Variable capacitance devices operated as switches | |
Batteries and fuel cells | |
Circuit arrangements for charging or depolarising batteries or for supplying loads from batteries | |
Casings for electrical apparatus in general |
Processes of manufacture specially adapted for manufacturing capacitors, e.g. parts thereof. e.g. dielectrics, electrodes, etc are covered by the corresponding product subgroups.
The following exceptions apply:
- Solid inorganic dielectrics vapour deposited are covered by H01G 4/08.
- Formation of the dielectric layer is covered by H01G 9/0032.
- Formation of a solid electrolyte layer is covered by H01G 9/0036.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
collector | a conductive component in intimate contact with an electrode material in an electrolytic or electric double layer capacitor |
electrolyte | an ionic conducting liquid or solid either comprised in one of the electrodes, typically the cathode, of an electrolytic capacitor or ensuring electric conduction between electrode active parts or electric double layers therein in Electric Double Layer Capacitors |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
MLCC | Multilayer Ceramic Capacitor |
EDLC | Electric Double Layer Capacitor |
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms:
- "capacitor" and "condenser"
- "supercapacitor", "ultracapacitor, "electrochemical capacitor" and "electric double layer capacitor"
- "multilayer capacitor" and "stacked capacitor"
- condenser
- capacitor
- electrochemical capacitor
- double-layer capacitor
- ultracapacitor
- supercapacitor
This place covers:
Details common to two or more main types of devices covered by this subclass, e.g. special adaptation for mounting; cooling, heating and ventilating arrangements; housings, encapsulations and protection or prevention arrangements.
This group covers details of capacitors that are not provided for in a single one of groups H01G 4/00 - H01G 11/00.
For example, encapsulations specific to fixed capacitors H01G 4/224, encapsulations specific to hybrid or EDL capacitors H01G 11/78, whereas group H01G 2/10 covers encapsulations where the type of capacitor is unspecified or the encapsulation is generally applicable to several types of capacitors as covered by groups H01G 4/00 - H01G 11/00.
This place covers:
Non-electrolytic, fixed capacitors, per se, e.g. thin or thick film capacitors, details thereof, e.g. electrodes, dielectrics, housings and encapsulations, structural combinations thereof with each other, e.g. stacked, multilayer, feed-through or anti-noise capacitors, or with electrolytic devices covered by this subclass, or with other electric elements not covered by this subclass where the structure consists mainly of a capacitor. Processes of manufacture thereof.
This place covers:
Non-electrolytic, variable capacitors per se, in which the capacitance is varied by mechanical means, e.g. using variation of effective area of electrode, using variation of distance between electrodes, e.g. capacitors making use of microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), or using multiple capacitors. Details thereof or structural combinations thereof with each other, with electrolytic devices covered by this subclass, or with other electric elements not covered by this subclass where the structure consists mainly of a capacitor. Processes of manufacture thereof.
This place covers:
Non-electrolytic, variable capacitors per se, in which the capacitance is varied by non-mechanical means, e.g. electrets, ferroelectric capacitors. Details thereof or structural combinations thereof with each other, with electrolytic devices covered by this subclass, or with other electric elements not covered by this subclass where the structure consists mainly of a capacitor. Processes of manufacture thereof.
This place covers:
Electrolytic capacitors per se, e.g. liquid or solid capacitors, details thereof, e.g. terminals, electrolytes, electrodes, housings, and processes of manufacture thereof. Electrolytic rectifiers, detectors, switching devices, light-sensitive or temperature-sensitive devices per se and details thereof. Structural combinations thereof with each other, with non-electrolytic capacitors or with other electric components not covered by this subclass. Processes of manufacture thereof.
This place covers:
Photoelectrochemical cells based on junctions between an inorganic semiconductor and an electrolyte
Photoelectrochemical cells based on a dye dissolved in the electrolyte or adsorbed on an electrode
This place does not cover:
Photo electrochemical storage cells | |
Inorganic semiconductor devices sensitive to electromagnetic or corpuscular radiation | |
Solid state light sensitive devices using an organic semiconductor as the active part |
In this group, documents are classified according to the inventive information e.g. classification symbol H01G 9/2031, while "additional information" is identified with Indexing Code symbols, e.g. H01G 9/2059.
In this subclass, Indexing Codes are mainly attributed with a view to allow retrieval of documents comprising a combination of technical characteristics, some of them being unimportant per se, and, hence, identified with an Indexing Code symbol rather than with the corresponding potential-jump barrier or surface barrier.
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
DSSC | dye sensitized solar cell |
PEC | photo electrochemical cell |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Primary cells with non-aqueous electrolyte | |
Accumulators with non-aqueous electrolyte |
This place covers:
Photo electrochemical cells having an oxide semiconductor as working electrode or having oxide semiconductor particles dispersed in the electrolyte;
examples of oxide semiconductors are: zinc oxide [ZnO], tungsten trioxide [WO3], copper oxide [CuO], niobium pent oxide [Nb2O5]
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Zinc oxides | |
Tungsten oxides |
This place covers:
Dye sensitized solar cells; the sensitizer may be a dye (organic) or an inorganic pigment, e.g. PbSe nanoparticles.
Working principle of a dye sensitized solar cell
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group.I
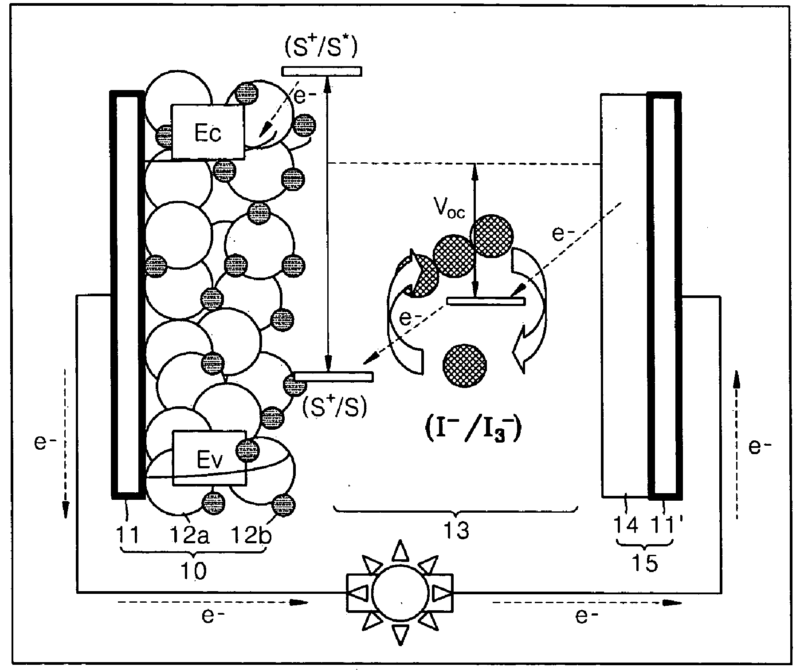
US2009173381
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Titanium oxides |
This place does not cover:
Light sensitive devices comprising an oxide semiconductor electrode |
This place covers:
- Serial interconnection of photoelectrochemical cells;
- sealing of photoelectrochemical cells;
- dye sensitized solar cells in form of a fibre;
- special provisions for filling the photoelectrochemical cell with the electrolyte or dyeing solution.
This place covers:
Hybrid capacitors, i.e. capacitors having different positive and negative electrodes; electric double-layer [EDL] capacitors; processes for the manufacture thereof or of parts thereof.
More specifically the following subjects are covered:
- Capacitors using combined reduction-oxidation reactions at electrode surfaces or at the interface electrode/electrolyte, e.g. redox arrangement or solion.
- Structural combinations, e.g. assembly or connection, of hybrid or EDL capacitors with other electric components, at least one hybrid or EDL capacitor being the main component, or multiple hybrid or EDL capacitors, e.g. arrays or modules, including stacked hybrid or EDL capacitors.
- Arrangements or processes for adjusting or protecting hybrid or EDL capacitors e.g. against electric or thermal overloads as well as reformation or processes for removal of impurities.
- Electrodes thereof, e.g. characterised by structural features of the materials making up or comprised therein or characterised by their material, e.g. based on carbon, metal oxides, conductive polymers or specially adapted for lithium-ion capacitors.
- Other components of hybrid or EDL capacitors covered include separators, electrolytes e.g., solid, liquid, current collectors and terminals.
- Cases; housings; encapsulations; mountings including gaskets or sealing and fixing or assembling a hybrid or EDL capacitive element in a housing, e.g. mounting electrodes, current collectors or terminals in containers or encapsulations.
- Processes for the manufacture of hybrid or EDL capacitors, or components thereof, including processes specially adapted for the manufacture of the electrodes.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Carbon or inorganic carbon compounds thereof | |
Active carbon compounds | |
Compositions of ceramic materials | |
Polymeric films or sheets | |
Batteries or fuel cells in general | |
Carbonaceous material for inserting or intercalating light metals | |
Carriers or collectors of a battery | |
Li-accumulators | |
Accumulators characterised by the material used as electrolytes | |
Hybrid cells, i.e. electrochemical generators having two different types of half-cells, the half-cell being an electrode-electrolyte combination of either a primary, a secondary, or a fuel cell | |
Cases, mountings of batteries | |
Separators for batteries | |
Terminals of a battery | |
Electric power networks; Circuit arrangements or systems for supplying or distributing electric power; Systems for storing electric energy | |
Circuit arrangements for charging or depolarising batteries or for supplying loads from batteries; with parallel operation in networks using both storage and other DC sources, e.g. providing buffering | |
Capacitors embedded in printed circuits | |
Casings for electrical apparatus in general | |
Thin film capacitors for integrated circuits |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
electrochemical storage device | means a battery, accumulator or capacitor |
collector | means a conductive component in intimate contact with an electrode material in an hybrid or EDL capacitor |
electrolyte | refers to an ionic-conducting liquid or solid ensuring electric conduction between electrode active parts or electric double layers, inside hybrid or EDL capacitors |
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms:
- "electrochemical capacitor", "EDL capacitor", "ultracapacitor", "supercapacitor" and "hybrid capacitor"