CPC Definition - Subclass G06K
This place covers:
Methods or arrangements for reading printed or written characters; for graph-reading or for converting the pattern of mechanical parameters into electrical signals; for printing of data in the shape of alphanumeric or other characters from a record carrier; for verifying the correctness of markings on a record carrier; for sensing record carriers; and for marking the record carrier in digital fashion.
Arrangements for producing a permanent visual presentation of the output data.
Column-detection devices.
Conveying record carriers from one station to another, e.g. from stack to punching mechanism.
Record carriers for use with machines and with at least a part designed to carry digital markings.
Information retrieval from punched cards designed for manual use or handling by machine, and apparatus for handling such cards, e.g. marking or correcting.
Arrangements for preparing the data output from a computer for printing, e.g. computer or network printers insofar as they are involved in outputting the result of a computation, like a document.
This place does not cover:
Image or video recognition or understanding |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Postal sorting | |
Hand-held input or output devices for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by a digital computer, e.g. light-pens, joysticks, mice or trackballs |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Printing per se | |
Transponders powered by received radio waves, e.g. passive transponders | |
Tags attached to, or associated with, an object, in order to enable detection of the object | |
Magnetic head applications | |
Magnetic alloy thin films, such as used in magnetoresistive applications in magnetic heads | |
Magnetic alloy thin films, such as used in magnetic thin film media applications | |
Magnetic alloy thin films, such as used in static memory applications | |
Responders; Transponders | |
Near-field transmission systems using transceiver |
G06K 17/00 covers methods or arrangements for effecting co-operative working between equipments covered by two or more main groups G06K 1/00-G06K 15/00.
G06K 19/00 takes precedence over G06K 21/00.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Record carrier | means a body, such as a cylinder, disc, card, tape, or wire, capable of permanently holding information, which can be read-off by a sensing element movable relative to the recorded information or by electrical contacting or non-contacting means |
Data | is a synonym for information |
This place covers:
This groups covers details of card punching machines and methods using such machines as well as the printing of optically readable codes, such as barcodes, in particular in relation to the difficulties of said printing on the material being printed on.
G06K 1/121 is related to B41J (printing in general). G06K 1/126 is related to B23K 26/00(laser marking of workpieces, e.g. metal workpieces)
Reading and writing of magnetic stripes, RFIDs, and of smart cards is classified in G06K 7/00.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Translating markings on a record carrier into printed data on the same record carrier, i.e. Interpreting |
Methods of marking or printing of barcodes and other optically detectable digital codes should be classified in G06K 1/12 and lower
Only G06K 1/12 is presently active as the methods of card punching are practically obsolete.
Typically G06K 1/121, problems associated to the difference between the theoretically desirable bar code and the real printed barcode and how this has its effect on the quality (readability) of the barcode:
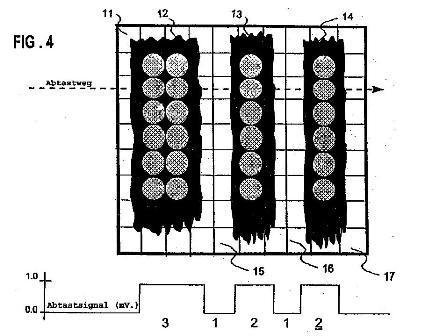
and G06K 1/126 typically is related to laser marking of optical codes, e.g. on workpieces:
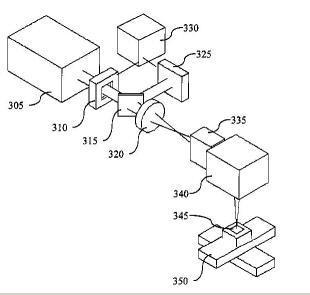
This group was originally created for classification of various card punching systems and methods. With these systems being nowadays obsolete, the only relevant group being in use is that of G06K 1/12 which focuses on methods and systems particular for marking machine readable codes such as bar codes on various substrates and the particular problems related thereto, e.g. to avoid bleeding in the printing process so that the bars constituting the barcode are "sharp".
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms:
- "barcode", "bar code", "optical code" and "marking"
This place covers:
- Methods or arrangements for verifying the correctness of markings on a record carrier;
- Column detection devices;
- Correctness of marking may be assessed by detecting physical properties, check-digit, plausibility check or by comparing with stored data.
- Examples:
- Bar code data is compared with data in memory,
- Spectral light of bar code is compared with predetermined spectrum;
- Production line with a marking device, followed by a verification device to check correctness of the marking; see illustration herebelow:
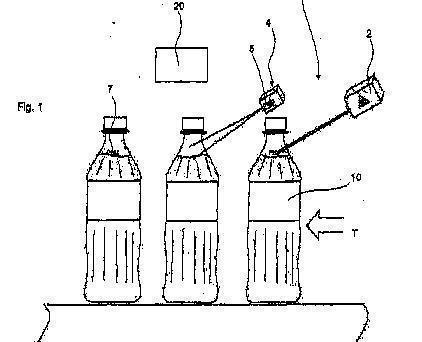
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Devices for scanning or checking the printed matter for quality control | |
Error detection or correction by redundancy in data representation, e.g. by using checking codes. | |
Testing paper currency, securities, bonds or similar valuable papers for genuineness by testing patterns thereon, e.g. comparing to a reference in a memory |
This place covers:
This group covers the arrangements for reading and writing of devices such as non-contact smart cards, contact smart cards, barcodes, magnetic stripes and other digitally records included on a handheld object, such as a card, or e.g. printed or otherwise included on a label for attachment to an object, for identification of the object.
This place does not cover:
Methods or arrangements for marking the record carrier in digital fashion | |
Pattern recognition | |
Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding | |
Character recognition, recognising digital ink or document-oriented image-based pattern recognition |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Identification of animals | |
Marking of poultry and the like | |
Receptacle for credit cards, such as etuis | |
Check-out counters, e.g. including a barcode scanner | |
Implanted circuitry (for diagnostics) | |
Detecting for diagnostic purposes | |
Sorting of articles according to an identifier or destination marking | |
Sorting using a machine readable code | |
Printing of security markings | |
Card filing arrangements | |
Printed mater of special format, e.g. identity or credit cards | |
Containers for laboratory use carrying an identifier, e.g. an RFID or barcode | |
Indicating train identities using tags | |
Transponders fixed to bicycles | |
Labelling machines, e.g. fixing machines to fix a label with a bar code to a package | |
Refuse receptacles carrying identification means | |
Article conveyance distributing the articles according to bodily destination marks, e.g. in production lines | |
Stacking and de-stacking of flat articles, e.g. stacking plural card shaped objects | |
Marking arrangements for laundry purposes, e.g. to track laundry using RFID tags | |
Paper including security elements, e.g. methods to create a paper support carrying an RFID | |
Details of vessels, means for coding or identifying them | |
Recording measures values, e.g. using sensors | |
Position detection of objects using reflection of radio waves on passive responders, e.g. with exchange of information between interrogator and responder | |
Tags for enabling detection of objects, e.g. to locate underground oil pipes or landmines | |
Scanning systems | |
Computer security in general | |
Business methods using RFIDs or barcodes or the like | |
Tachographs using smart cards or the like for recording | |
Access control using an identification card, opening of card doors using a transponder | |
Payment using cards | |
Cash registers using barcode scanning | |
Partner search systems using transponders | |
Anti-theft systems using transponders or the like | |
Identification of vehicles | |
Labels, tags, tickets and security seals | |
Recording reproducing or erasing on magnetic carriers in general | |
Optical recording on flat record carriers other than barcode recording | |
Optical recording on CDs, DVDs and the like | |
CD's with transponders | |
Circuit means for protection against loss of information of semiconductor storage device, e.g. on cards against alpha rays inducing soft errors | |
Contactless power supplies for memory stores | |
Manufacturing coils not particular for non contact smart cards | |
Antennas design details | |
SAW circuits not for record carriers | |
SIM card connection arrangements particular for mobile phones | |
Near field transmission systems not RFID type | |
Wireless local area networks | |
Mobile phones with a barcode reading functionality | |
Digital cameras combined with a further device (e.g. a mobile phone) | |
Wireless networks in general | |
Conductive patterns on PCBs other than on smart cards | |
Casings cabinets drawers for interchangeable modules | |
Faraday type of protections of electrical circuits | |
Cards including details of the manufacturing of the semiconductor device |
G06K 7/0004 is for classification of combined arrangements, like a device incorporating a barcode reader and an RFID reader.
G06K 7/0013 is for classification of constructional details and functions of contact card readers, such may be the housing of the reader, the entry slots of the reader, the peculiarities of the contact arrangements for contacting the contacts on the smart card or memory card, protection arrangements for protecting the circuits of the card reader against intrusion or unwanted inspection.
G06K 7/084 is for classification of magnetic stripe reading arrangements. Typically these magnetic stripes are included on a card shaped object as the classical credit card.
G06K 7/10009 is for classification of arrangements for interogating wireless record carriers, such as RFIDs and non-contacts smart cards. Typically, the arrangements comprise arrangements to resolve collision between plural RFIDs that try communicating with an interrogator at the same time, arrangements for controlling the power of the interrogation field, arrangements allowing the interrogator to mimick an RFID or transponder or vice versa, protocols for RFID interrogators, protection arrangements and antenna arrangements adapted for RFID interrogation.
G06K 7/10544 is for classification of constructional aspects of barcode reading arrangements, such as arrangements for focalisation, cameras, mirrors, handheld readers.
G06K 7/1099 is for classification of arrangements using X-Rays to retrieve identification codes on objects.
G06K 7/12 is for classification of barcode reading systems where the color of the light that is used is of importance, e.g. using UV or IR to illuminate invisible fluorescent barcodes.
G06K 7/14 is primarily for classification of software for barcode readers in particular algorithms to locate or retrieve a barcode from an image.
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms:
- "smart card connector", "card connector", "card reader", "interrogator", "RFID", "transponders" and "tag reader"
This place covers:
Reader/writers capable of handling different information recording principles, either on respective data carriers or on data carriers having information recorded according to a plurality of recording principles.
Examples:
- combined chip card / magnetic stripe card reader,
- combined contactless / contact IC-card readers,
- combined barcode / RFID readers.
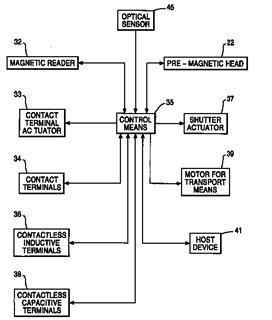
In particular readers/writers that combine two types of readers in one and the same device and where a synergetic interaction between the two is present need to be classified inhere.
This place covers:
G06K 7/0013 deals with arrangements for connecting a smart card to a card reader, for example:
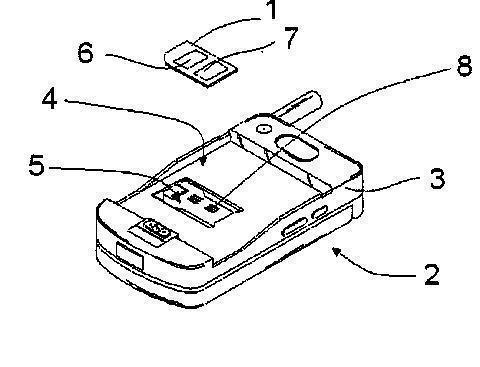
or
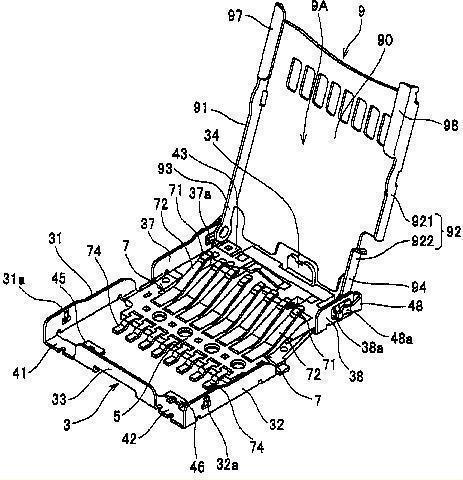
but also with arrangements for connecting a variety of memory cards, such as MMC, memory sticks, SD cards and the like; see illustration here below:
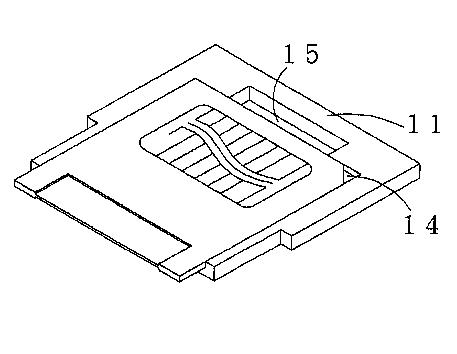
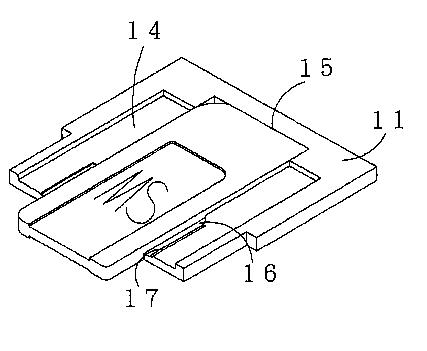
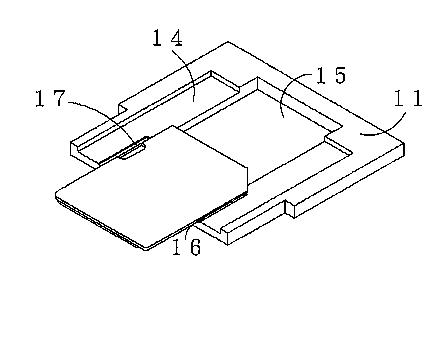
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Information storage based on relative movement between record carrier and transducer in general |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Information storage based on relative movement between record carrier and transducer in general |
This place covers:
Ancillary aspects of RFID interrogators such as collision resolution, energy usage, antenna arrangements and security of the interrogation process.
Example:
arrangement to interrogate a cloud of transponders.
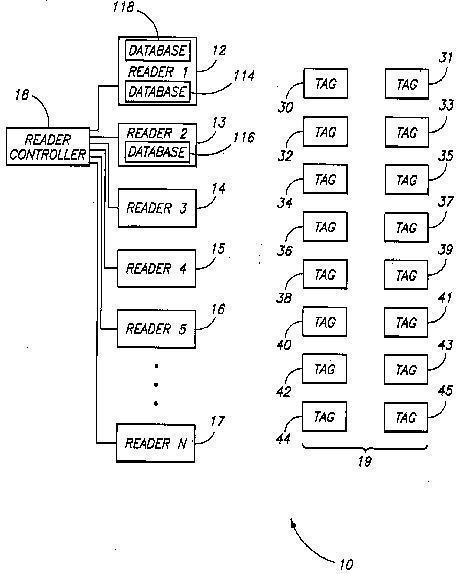
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Systems using the reflection or reradiation of radio waves, e.g. radar | |
Reading of smart cards, dongles, for authentication and access control in computer systems | G06F21/00N5A2D2 |
Communication between electronic keys and locks, e.g. car keys with transponders | |
Mutual authentication between data carrier and terminal or host | G07F7/10D4 |
Transmitter circuits | |
Near field transmission systems | |
Transmission power control in radio transmission systems | |
Secure transmission, encryption, protection against differential power attacks (DPA) | |
Wireless local area networks, home automation | H04L12/28W |
Wireless communication networks |
This place does not cover:
Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic; arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols | |
Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security | |
Network arrangements, protocols or services for supporting real-time applications in data packet communication | |
Network arrangements or protocols for supporting network services or applications |
This place covers:
G06K 7/10544 is reserved mainly for barcode reader systems, e.g. construction of the typical checkout counter multi-window systems:
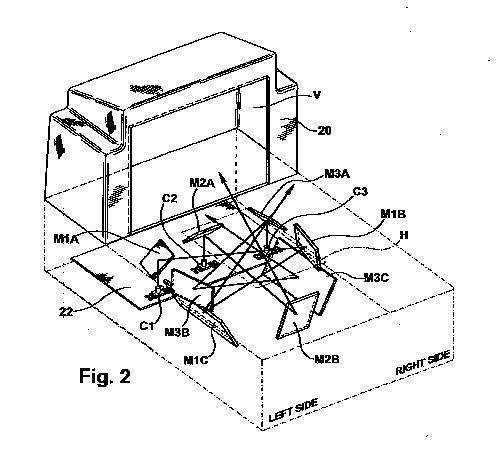
This place covers:
Details of handheld barcode readers are to be classified herein.
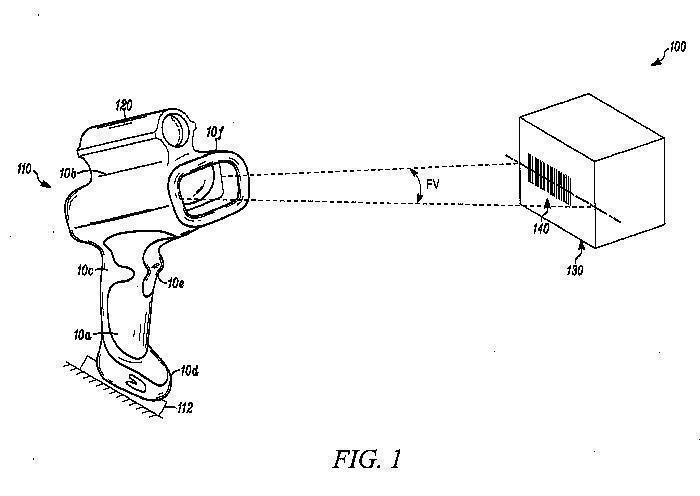
This place covers:
Optical code readers, such as barcode readers, with special adaptations for reading barcodes in a selected predetermined wavelength range, e.g. barcode readers particularly adapted for colour barcodes or barcode readers for barcodes that are invisible under regular illumination conditions but become visible when illuminated by a special light source, such as UV light:
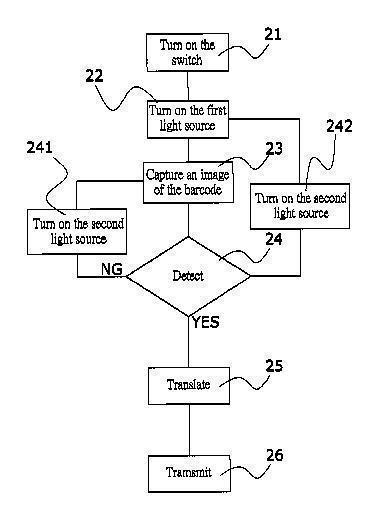
This is related to the Indexing Code G06K 2019/06225 where color and other wavelength specific optical codes are classified.
Bar code and optical code readers adapted for reading and illuminating targets that emit specific wavelengths, e.g. fluorescent targets, invisible targets only visible in infrared or UV.
In patent documents the following words are often use:
Infrared, UV, ultraviolet, fluorescence, color.
This place covers:
Barcode decoding methods and algorithms that are applied after the raw barcode material, such as the 2D image of a barcode, resides in the memory of a computer system. For example this groups covers algorithms that are applied after the image of the barcode has been taken by a CCD or CMOS based imager and the image is in the memory of a computer system and can be subjected to image processing techniques for retrieving, correcting and decoding the bar code in the image.
Algorithms for decoding bar codes should be classified here, in addition to methods for detecting bar codes, for error correction of bar code images imaged by a CCD camera.
This group and its groups are no longer used for the classification of new documents as from 1 January 2006. Documents relating to methods and arrangements for input to a computer are classified under G06F 3/033 and G06F 3/041.
Before 1 January 2006, groups G06K 11/00 - G06K 11/06 were already not used because of obsolence, whereas other groups under G06K 11/06, deleted in 2006, were used to classify costructional details of computer pointing devices now classified under G06F 3/033 and digitizers technologies now classified under G06F 3/041.
This place covers:
Arrangements for moving data carriers, such a smart cards, into and out of a data carrier reader device
This place does not cover:
Conveying record carriers combined with another operation, e.g. with reading |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
G06K 13/06 is for classification of mechanisms that assist in correct guiding of the card in the card reader
G06K 13/08 is for classification of aspects for inserting and ejection of cards into and out from card readers.
G06K 13/08 contains in particular the arrangements for inserting and ejection of cards, like card ejectors using a spring and a heart shaped cam to arrive at a push-push card insertion-ejection arrangement.
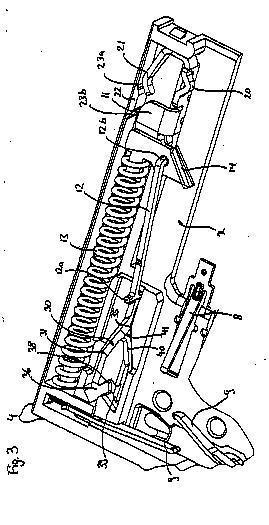
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
card magazines in general |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
features of interest apart from data processing | |
magnetic-tape drive |
This place covers:
Digital data processing in printers and related to the printing of computer output data.
Control of digital printing means, not otherwise provided for.
This place does not cover:
Printing or plotting combined with another operation, e.g. with conveying |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Photocomposing | |
Construction of print heads | |
Control and analysis of mechanical parameters involving printing test patterns | |
Light beam scanning systems using movable or deformable optical elements | |
Digital data processing in computers and related to printing | |
Two-dimensional image generation | |
Special arrangements for scanning and reproduction of pictures, e.g. photographs, facsimile |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
To rip (verb) | to generate a pixel map of an image |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
PDL | Page Description Language |
RIP | Raster Image Processing |
This place covers:
- Methods or arrangements for effecting co-operative working between equipments covered by two or more of the preceding main groups, e.g. automatic card files incorporating conveying and reading operations.
- Methods or systems involving reading and writing of identification or authentication codes on record carriers, or reading of codes and transporting of carriers.
Further classification information:
G06K 17/0022 contains inventory control systems:
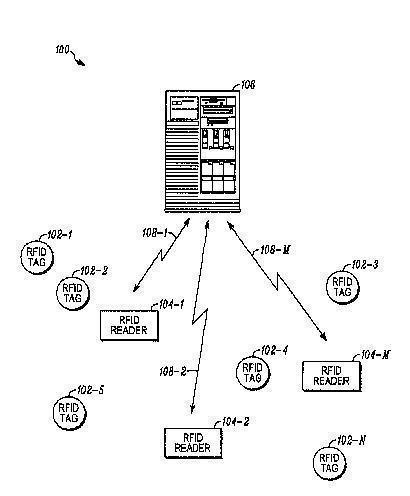
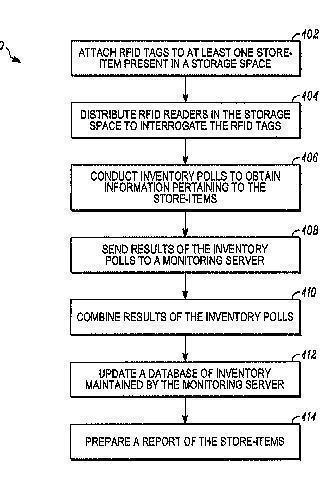
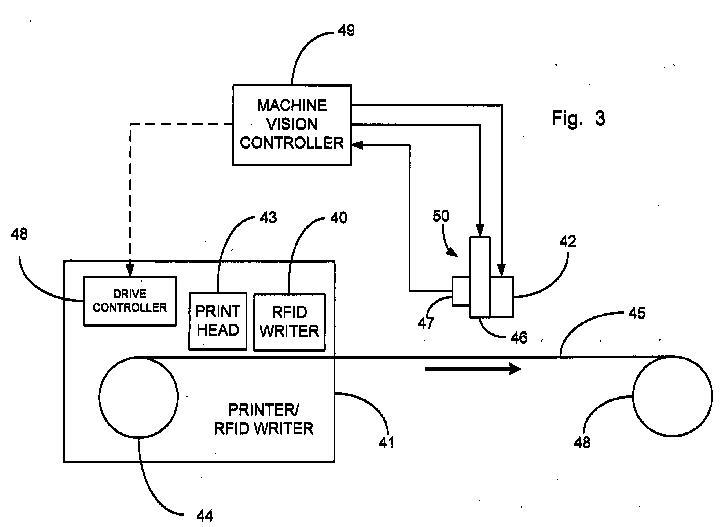
G06K 17/0025 covers combined RFID - printing systems, like the typical RFID label writers:
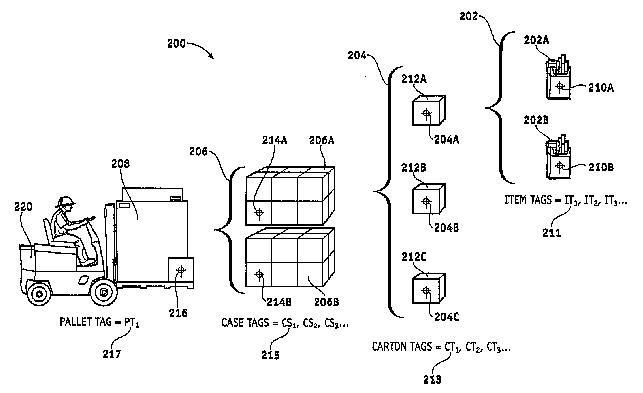
G06K 17/0029 covers arrangements to deal with grouped articles with each article having an identifier:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Correctness verifcation | |
Collecting milk | |
Medical systems in general | |
Test tubes with identification means | |
Labelling machines using RFIDs | |
Collecting waste | |
Logistics using RFIDs or barcodes | |
Inventory control using RFIDs or barcodes | |
Access-control involving the use of a pass, e.g. tag, transponder | |
Personalization of a card | |
Theft detection systems using tags | |
ICT specially adapted for the handling or processing of patient-related medical or healthcare data stored on portable record carriers, e.g. on smartcards, RFID tags or CD |
The particular use of a record carrier, if of importance to the invention, should be classified in the corresponding G06K 17/00 groups.
Examples of such uses are:
G06K 17/0025 covers devices combining in a single entity printing and RFID writing.
G06K 17/0029 covers arrangements for interrogating grouped objects carrying identifiers, such as a carton with an RFID containing multiple cigarette packages each having an RFID.
G06K 17/00 is used for classification of arrangements and methods where a plurality of objects is tagged with an identifier and some logistic process is carried out using the arrangement. Further classification is made in G06Q, particularly if the technical effect of the identifiers that are used is common knowledge.
This place covers:
In this main group primarily hand holdable devices or artifacts are classified that contain at least one digital marking, such as RFIDs, smart cards, magnetic stripe cards, barcodes, optical codes, and non-intelligent resonating digital marks without.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Record carriers adapted for controlling specific machines, see the appropriate subclass for the machine | |
Plastic moulding techniques for card shaped objects, such as smart cards | |
Lamination suitable for card shaped articles | |
Form printing | |
Printing or marking of cards not characterised by the kind of marking | |
File cards | |
Operating system software for smart cards | |
Data input/out arrangements, such as buses, to transfer data from/to smart cards | |
General arrangements for computer security | |
Arrangements on smart cards for sensing fingerprints | |
Cards for automatic access control systems | |
Record carriers made for e.g. of paper or other flexible material, suitable fo use as a banknote | |
Smart cards for payment | |
Antitheft arrangements using RFIDs | |
Labels for tamper secure fixing to objects | |
Record carriers in general | |
Recording by magnetisation or demagnetisation of a record carrier | |
Details of memory layout in smart cards | |
Security software for smart cards and RFIDs using encryption | |
Manufacturing of printed circuits on a smart card | |
Manufacturing of the integrated circuit in a smart card |
Amongst the various groups under G06K 19/00, the following groups are the most important, in particular in that these groups are most frequently used:
Constructional details of optical codes, such as barcodes | |
Magnetic stripes as used on e.g. credit cards. | |
Functionality of contact based smart cards | |
Arrangements for protection the integrated circuit in smart card against intrusion | |
Constructional details for non-contact smart cards, RFIDs, transponders or wireless tags | |
Functionality of non-contact smart cards, RFIDs, transponders or wireless tags | |
Constructional details for contact-based smart cards |
This place covers:
The selected material of the record carrier achieves an extra effect which is not directly related to the function as record carrier.
Examples:
- record carrier made of a material that withstands gastric acids so that it may be brought in the stomach of cattle, or
- a tag with special adaptations to the material to attach it to a garment, like
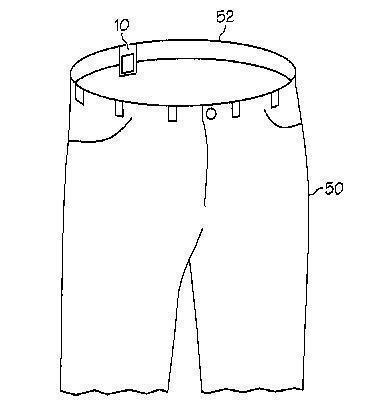
or a metal data carrier

Counterexample:
bar code printed in a colour material only visible under UV light: G06K 19/06046.
This place covers:
Different peculiar form factors.
Examples:
- circular RFID tag to be attached to a DVD
- identification wrist band for newborn babies in hospitals
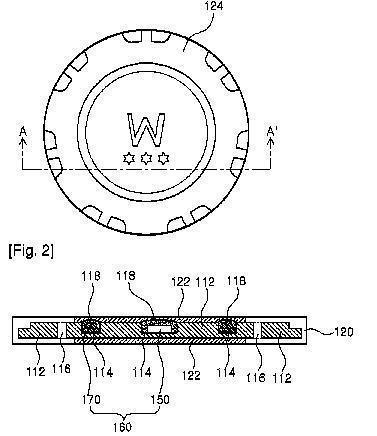
- credit card with a non-standard shape (e.g. one rounded corner as a marketing gag)
- casino chips with RFID
This place covers:
Examples:
- label coding data by spectral signatures
- using characters having small modifications to code digital data in a text
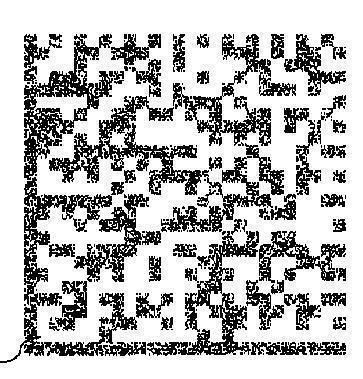
- printed data code
- barcodes like a 2D barcode where each barcode pixel is a barcode itself:
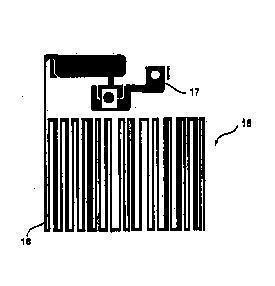
but also barcodes where the barcode is at the same time an antenna of an RFID like device (needs also a classification in G06K 19/07749):
Holographic, diffractive or retroreflective recording | |
Wavelength selection | |
Miniature code |
This place covers:
Digital optical markings arranged in one dimension in space, such as the well known 1D barcodes
This place covers:
Markings arranged in more than one dimension in space.
Examples: Code 49, DataMatrix, MaxiCode, PDF 471.
This place covers:
Constructional details of optically detectable markings (e.g. kind of material or physical properties).
Example: encoded optical identification elements including an optical substrate having a diffraction grating with refractive index variations (e.g. WO2005027031).
See G06K 19/08 and lower if there is a combined effect with an other type of code.
This place covers:
The marking codes at least one bit (e.g. present/not present), data carriers for magnetically detectable purely analog "signatures" or signals should not be classified here.
Examples:
- classical banking/credit card with a magnetic stripe;
- bar codes printed with magnetic ink;
- security tags comprising magnetic elements coding digital information (security tags per se: see G08B).
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Magnetic theft detection tags | |
Magnetic recording with relative movement between data carrier and transducer | |
Magnetic alloy thin films as used in magnetoresistive application in static memory applications |
This place covers:
Constructional details of the magnetically detectable markings (e.g. kind of material or physical properties).
Consider classifying in G06K 19/08 and groups if there is a combined effect with another type of code.
This place covers:
For example:
- punched cards;
- credit card with Braille characters.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Relief-type marking |
This place covers:
For example:
- bar codes printed with conductive ink;
- card comprising pencil markings to be sensed by their conductivity;
- cards carrying a passive LC circuit.
This place covers:
Record carriers that do not comprise a logical or integrated circuit and that reflect a digital code upon interrogation by an electromagnetic field.
Examples:
record carrier comprising a plurality of resonating LC circuits
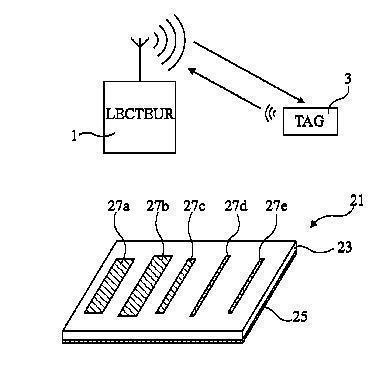
or e.g.
or surface acoustic wave (SAW) transponders
This place covers:
Data carriers, such as smart cards or RFID tags that comprise at least one integrated circuit.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
EEPROM memories |
This place covers:
data carriers with integrated circuits and with a wireless communication means.
Examples:
RFID tags and contactless chip cards (ISO 14443, 15693, 18000).
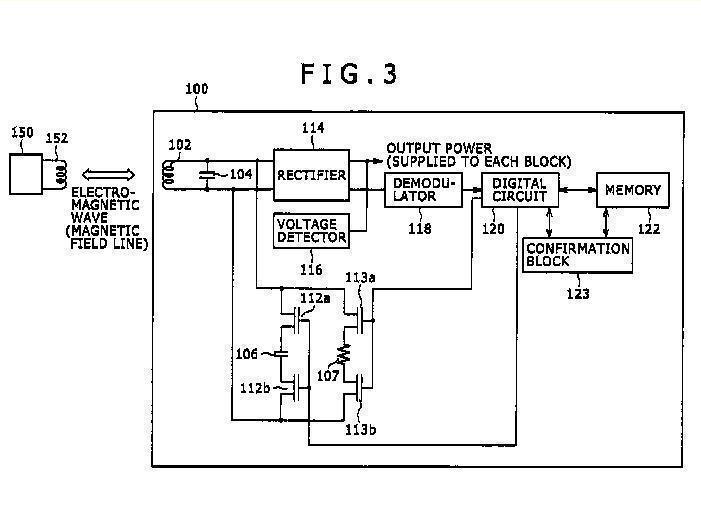
This place does not cover:
System using reflection of radio waves using passive responders radiating a codes signal | |
System with exchange of information between initiator and responder | |
Near-field transmission systems |
This place covers:
In this group security related aspects realized by means on the card or the RFID device are found, e.g. arrangements to protect the circuits on a smart card against intrusion.
This place does not cover:
At least some of the measures for preventing access to the data in the integrated circuit should be hardware based, pure software solutions, e.g. encryption, should not be classified in G06K. In these cases the classes of the related fields mentioned below should be considered.
Protection against unauthorised use of computer memory |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Security arrangements in computer systems | |
Smart cards for payment | |
Secure smart card communication using encryption |
This place covers:
Arrangements that blcok electromagnetic fields that are used to attempt access to wireless record carriers, wherein the arrangements carry out the blocking without the use of logical and/or intelligent [circuits]
Examples: metallic screens around an RFID tag for blocking an interrogation field in order to make sure that the RFID tag cannot be interrogated without permission
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Screening against electric or magnetic fields | |
Screening of semiconductor devices |
Shielding measures intended to protect the stored data belong in this class. This class is not used if shielding measures are intended to minimize undesired effects of mounting on e.g. metal and other electromagnetically interfering objects/surfaces. In this case: use class G06K 19/07771.
This place covers:
Arrangements comprising logical circuits that are suitable to actively and intelligently, using logical operations, interfere with an electromagnetic field that is used in an attempt to access information in record carrier
Example:
Blocking chipcard which prevents communication of other cards by repeated response under violation of waiting times defined in the communication protocol.
This place covers:
Arrangements on the record carrier that are suitable to switch at least a part of the logical circuit on the record carrier from an active to an inactive state or from an inactive to an active state in order to protect the contents of the record carrier or to provide priviliged access to contents or processes on the data carrier.
Example:
Chip card in which the antenna is only connected to the chip if a user presses a mechanical switch.
This place covers:
Arrangements on the record carrier that are in place such that it is made difficult for a reerse engineer to anlayze the construction of the circuit on the record carrier using non-invasive techniques.
Example:
Chipcard IC writing to dummy cells even if no real write operation is required.
This place covers:
Arrangements that deactivate temporarily or for good part of the logical circuit in the record carrier if a detection circuit on the same record carrier detects sings of attempted tampering with the record carrier. The "detection" may be an active process on the record carrier that continuously monitors if tampering is attempted, or the detection may be directly lead to destruction of a circuit that is being tampered.
Example:
For instance, a chip is covered by a conductive cage, wherein the integrity of the cage is being actively monitored. If one of the wires of the cage is broken this is seen as a voltage drop by the monitoring circuit and the chip is warned of this fact.
This place covers:
Arrangements that deactivate temporarily or for good part of the logical circuit in the record carrier if a detection circuit on the same record carrier detects signs of attempted tampering with the record carrier, wherein the antenna is destructed upon the detected tampering. The detection in this case is directly also destruction of the circuit.
Example:
An RFID tag that is fixed to an object such that the RFID tag antenna will tear or break when detached from the object. In order to tamper with the RFID tag, the FRID tag needs to be detached from the object.
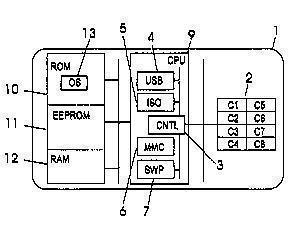
This place covers:
All kinds of constructional peculiarities related to manufacturing, materials, special devices included in the data carrier like displays, sensors, batteries, etc are to be classified and searched. Also MMC cards are found here when no special features clearly for other fields are under consideration.
Examples:
removable sim cards
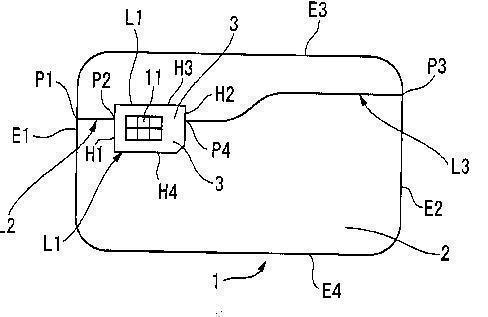
or special arrangements for avoiding breaking of the integrated circuit on a smart card:
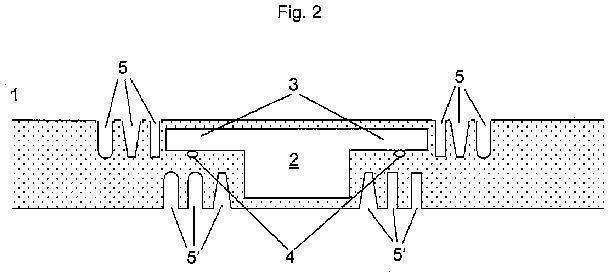
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Holders, etuis, cases, for credit cards or the like | |
Injection molding for cards | |
Processes for making labels or tags | |
Interconnection between memories and computers | |
Acces protection for memory cards | |
Access control with a pass containing electronic elements | |
Memory | |
Connection arrangements for memory cards | |
Housings for electronic devices, such as memory sticks or other memory cards |
This place covers:
Record carriers with an integrated circuit chip and with galvanic contacts at the surface of said record carriers, such as ISO 7816 smart cards.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Sensing record carriers by galvanic contacts | |
Arrangements for conducting current for flat cards |
This place covers:
Record carriers with an integrated circuit chip wherein the integrated circuit chip is mounted into a card body, or the like, as a module.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Encapsulation of chip modules |
This place covers:
G06K 19/07749 is for constructional details particular for non-contact data carriers, such RFIDs, e.g. methods of placing the antenna wire on the data carrier:
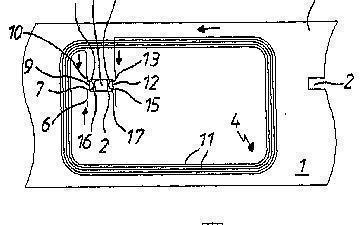
This place covers:
G06K 19/08 and lower contains data carriers with two different types of markings, e.g., a bar code and a magnetic stripe on the same data carrier.
This place covers:
This head group is not used anymore to classify new documents. Please classify in its lower subgroup G06L19/086 instead.
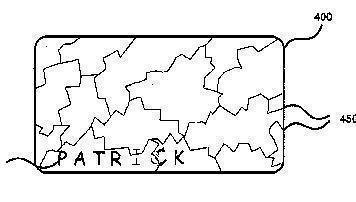
This place covers:
Markings consisting of randomly placed or oriented elements, the randomness of the elements being for generating a unique identifying signature of the record carrier, e.g., randomly placed magnetic fibres or magnetic particles in the body of credit card.
Example:
A card comprising a pattern of random cracks from which a digital signature is derived.
This place covers:
Record carriers that comprise a first type and a different second type of digital marking wherein one of these digital markings is particularly suited for authenticating the record carrier. Examples:
copy protected DVD comprising a required decoding key in an RFID transponder incorporated in the DVD body.
This place does not cover:
Verification of coded identity or credit cards in mechanisms actuated by them |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Identification cards not to be read by a machine | |
Card operated payment systems |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
tools for perforating in general |