CPC Definition - Subclass B62D
This place covers:
- Fittings for identifying vehicles in case of collision; Fittings for marking or recording collision areas
- Spare wheel stowing, holding, or mounting arrangements
- Systematic disassembly of vehicles for recovery of salvageable components, e.g. for recycling
- Steering of motor vehicles or trailers
- Arrangements for automatically controlling steering depending on driving conditions, e.g. control circuits therefor
- Steering non-deflectable wheels
- Steering endless tracks or the like
- Steering specially adapted for trailers or for vehicles having pivotally connected frames
- Power-assisted or power-driven steering
- Steering control means, e.g. steering wheel or levers
- Steering gears, e.g. means to convert control input motion to final output motion at the wheels
- Steering linkages; Stub axles or their mountings
- Understructures; Superstructures; Vehicle bodies
- Combined superstructures and frame, i.e. monocoque constructions
- Superstructures for load-carrying vehicles
- Superstructures for passenger vehicles
- Connections between superstructure sub-units
- Understructures, i.e. chassis frames on which vehicle body may be mounted
- Connections between vehicle body and frame
- Vehicle bodies characterised by stream lining
- Stabilising vehicle bodies without suspension arrangements, e.g. by movable masses or by aerodynamic means
- Motor vehicles or trailers classified according to type; Parts or accessories thereof
- Endless track vehicles
- Motor vehicles characterised by the driver not being seated
- Tractors
- Tractor trailer combinations; Road trains
- Motor vehicles or trailers predominantly for carrying passengers, e.g. omnibuses
- Trailers with driven ground wheels
- Motor vehicles having other propulsion or ground engaging means than wheels or endless tracks alone or in addition to wheels or endless tracks
This place does not cover:
Steering, or guiding on a desired track, of agricultural machines or implements | |
Emergency vehicles, unless the document concerns chassis/bodywork aspects | |
Connections between vehicles; | |
Vehicles for use on rail and road, amphibious or convertible vehicles; | |
Passenger accommodation not otherwise provided for | |
Adaptations for load transportation or to carry special loads or objects | |
Vehicles, vehicle fittings or vehicle parts not otherwise provided for | |
Air-cushion vehicles | |
Locomotives; Motor railcars | |
Body details or kinds of railway vehicles | |
Hand-propelled vehicles, e.g. hand carts, Sledges | |
Motor-cycles, including quad bikes, ATVs; | |
Balancing machines supporting a rider; motorised skateboards and the like | |
Motorized wheelchairs; personal mobility vehicles | |
Armoured vehicles, unless the document concerns chassis/bodywork/track aspects |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Vehicle wheels, castors, axles, increasing wheel adhesion; | |
Vehicle tyres, tyre inflation or tyre changing; | |
Suspension arrangements | |
Heating, cooling, ventilating or other air treating devices | |
Windows, windscreens, non-fixed roofs, doors or similar devices, protective coverings for vehicles not in use | |
Electric equipment or propulsion of electrically-propelled vehicles; | |
Power supply for electrically-propelled vehicles | |
Lighting, signalling | |
Servicing, cleaning, repairing, supporting, lifting, or manoeuvring, not otherwise provided for | |
Brake arrangements, brake control systems or parts thereof | |
Propulsion plant arrangements, auxiliary drives, transmissions, controls, instrumentation or dashboards |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Servicing, cleaning, repairing, supporting, lifting, or manoeuvring, not otherwise provided for | |
Brake arrangements, brake control systems or parts thereof | |
Steering devices applicable only to steerable undercarriages for aircraft | |
Testing of vehicles |
The indexing scheme of IPC [5] associated with group B62D 6/00, relating to driving conditions sensed and responded to are not used in CPC.
This place covers:
Means for initiating a change of driving direction of vehicles:
- External motors for turning the steering wheel; e.g. fixed to or placed on the seat.
- Remote controllers (man held apparatus) used for steering.
- Single steering systems added later.
- System allowing steering with the knee or the like, e.g. specially adapted levers
- Systems telling the vehicle driver about free parking places.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Systems for helping the driver to keep the lane | |
Automatic steering system used for parking | |
Aeroplane ground or like engaging elements |
This place covers:
- Foot steered vehicles.
- Vehicles running a previously recorded program, also learning or teaching thereoff.
- Finger-tip steering on sliding switches.
- (mechanical) systems for blocking the steering wheel in a certain position, e.g. to allow straight driving.
- Steering by shifting a load or by rotating seats.
- Steering systems for vehicles with rotating cabins.
- Steering with reign like handles.
- Steering by moving the armrest of a seat.
This place covers:
Other electric devices integrated in the steering wheel, e.g. microphones, vibrating means, (pressure) sensors, lamps, information screens.
This place does not cover:
Combination of airbags with horn switch in steering wheel |
For the characteristics of the electric devices per se, see the relevant groups for the device as such.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Airbag storage within non-rotatable hubs |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Padded linings associated with steering wheel | |
Shock absorbers using plastic deformation of members |
References B60R 21/05 and F16F 7/12 are non-limiting in the subgroup B62D 1/11. CPC will be updated/corrected once this inconsistency is resolved in IPC.
This place covers:
- Hand levers for steering control
- (Multiple function) joy-sticks
This place covers:
Special features of steering columns; bearing and bearing arrangements therefor
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
By continuous supply of energy | |
Controlling steering depending on driving conditions |
This place covers:
- Steering columns supported by elastic means.
- Steering columns being adjustable by the driver, e.g. for a comfortable position.
- Steering columns movable together with the dashboard, e.g. when dashboard is linked to a front door.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Padded linings associated with the steering column |
Reference B60R 21/05 is non-limiting in the subgroup B62D 1/18. CPC will be updated/corrected once this inconsistency is resolved in IPC.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Locking of telescopic systems in general |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Shock absorbers using plastic deformation in general |
This place covers:
Systems of actively moving steering columns in a better position to fire the airbag.
Clarification of the definition scope; initially this group involved the movement of the steering wheel for "in case of accident". Modern activation of airbags requires a similar design/motion of the steering column and so such systems are also classified in this group.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Special adaptations of automatic tractor steering | |
Devices for lifting, movable on wheels, automatically guided |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Railways |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Steering position indicators | |
Steering aids | |
Parking aids | |
Steering assistants | |
Autonomous road vehicle drive control with determination or calculation of trajectory projection | |
Control of position or course in two dimensions |
This place covers:
Mechanical means to convert the steering control input motion, e.g. by a steering wheel, to final output motion at the wheels, e.g. rack and pinion gear or the like.
This place does not cover:
Power assisted or power driven steering | |
Steering linkages | |
Steering for non-deflectable wheels |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Gearing in general |
This place covers:
- Supplying power to the steering movement by electric or hydraulic means to reduce steering force at the control input.
- Changing the transfer ratio between the steering wheel and the steering output movement by variable supply of energy, e.g. by using a superposition gear.
- Telemotors for steering.
- Mechanical means or mechanism specially adapted for power assist.
- Hydraulic means, e.g. valves specially adapted for power assist.
- Electric means, e.g. motors specially adapted for power assist.
- Safety devices or back up systems for steering if hydraulic power assist function fails.
This place does not cover:
Steering for non-deflectable wheels |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
This place covers:
For example, mechanical steering angle limiters, e.g. catch or block to limit output movement.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Hydraulic steer-by-wire systems |
This place covers:
- Means to allow manual steering in case of failure of power assist means
- Repairing failure by redundant parts
This place covers:
- Means to "disturb" e.g. by using a brake, the turning of the steering wheel or any input element.
- Tactile feedback, e.g. vibration on steering wheel or any input element.
This place covers:
Mechanical aspects of the actuator, e.g. how to impose the force to the driver.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Control aspects, e.g. calculating the feedback force |
This place covers:
Mechanism or control to achieve change of transfer ratio
- superposition gear
- electric motor with the stator connected with one part of the steering column and the rotor with the other part of the steering column
Calculating of desired steering angle to be reached by e.g. a superposition mechanism are classified in B62D 6/002
This place covers:
- Gearings (or connections) between the power steering motor and the part, which is connected to any part of the steering system, e.g. column or rack.
- Electric power steering to be mounted additionally to the vehicle, e.g. to change manual steering into power steering.
- Cooling of electric power steering motor.
- "Non-rotating" motors, e.g. linear motors.
- Use of multiple electric motors in one power steering.
- Wire harness from the battery to the electric power steering.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Combinations of electric power steering with steering locks (steering column locks) |
This place covers:
- Constructional features of the motors or the arrangement thereof, e.g. Double stator and one rotor
- Interchanging the connections of two windings on a three phase motor to make it turn in the other direction, e.g. for using the same apparatus for right hand drive and left hand drive vehicles.
- Remote controlled moving brushes of the motor.
- Using on/off-switches to operate the motor based on steering wheel torque
This place covers:
Single drive for a single wheel, e.g. one right steering motor and one left steering motor.
Combined driving and steering units for industrial trucks.
Combined driving and steering units for industrial trucks should be also classified in B62D 7/02 and relevant subgroups
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Steering by acting on the suspension system |
This place covers:
Mechanical overload clutches for suppressing torque peaks.
"Freewheeling clutches", e.g. operated by the power steering motor or the driver's torque.
This place does not cover:
Clutches used in steer-by-wire systems to connect the steering wheel to the steered wheel in case of failure, e.g. backup, |
This place covers:
- Rheological fluid clutches in "normal" electric power steering
- Viscous clutches
- Clutches controlled by mechanical movement, e.g. pinion "rolling" on rack and by this "leaning" on friction rollers
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Screw mechanisms in general |
This place covers:
Calibrating of electric steering systems as such.
Switching off of electric power steering if not needed, e.g. standstill.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Controlling steering depending on driving conditions sensed and responded to | |
Determination of steering angle | |
Measuring torque applied to steering wheels | |
Electric motor per se |
This place covers:
- Controlling the motor as such, e.g. a brushless DC-Motor;
- booster circuits to rise the voltage over the battery voltage;
- voltage reduction circuits feeding the controller if higher battery voltage feeds the motor.
This place covers:
Control of electric power steering motor during the time of returning the steering wheel, e.g. inertia compensation.
This place covers:
Blocking of the steered wheel due to catches, stops or curb stone
This place covers:
Reducing vehicle induced disturbances, e.g. braking, unbalanced wheels, "torque steer", etc
Counterbalancing by an additional motor (which can be the "normal" power steering motor) the reaction forces of a steering angle ratio change mechanism
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Changing the transfer ratio between the steering wheel and the steering gear by variable supply of energy, e.g. by using a superposition gear |
This place covers:
Recovery from (detected) failures, e.g. fixing or bridging a loose contact.
This place covers:
Detecting failure of the motor drive means, e.g. in the H-bridge.
This place covers:
- - Detecting malfunction of sensors
- - Includes also failures in the direct treatment of sensor signals, e.g. in a circuit for phase compensation.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Sensor | any sensing element or transducer used in or for electric power steering. |
This place covers:
Parametrising of hydraulic power steering systems.
Pumps directly connected with the steering motors, e.g. reversible pump to cylinder.
Controls of the hydraulic fluid supply which adjusts the pressure to facilitate the required pressure demands by the external environment, e.g. when driving on a mountainous road.
Control of electric motor driving a pump directly connected with the steering motors (hydraulic gear), see also B62D 5/046 and subgroups.
This place covers:
Supply of pressurized fluid for other consumers and also supplying the steering means
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Priority valves in general |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Valves in general |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Controlling steering depending on driving conditions sensed and responded to |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Hydraulic steering gear |
Reference B62D 3/14 is non-limiting in the subgroup B62D 5/093. CPC will be updated/corrected once this inconsistency is resolved in IPC.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Pressure yokes |
This place covers:
- Circuits or processes for controlling power steering systems, e.g. to control steering angles.
- Control of steering angle.
- Control of vehicle motion in general, e.g. yaw rate.
- Control of steering assist power depending on ambient condition.
- Control of feedback to the driver.
- Measuring or determining driver input torque.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
This place does not cover:
Adjustable by the driver, e.g. sport mode |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Stability systems acting on the brakes |
This place covers:
Measuring or estimating the road friction coefficient using the steering system or values derived from within the steering system.
This place covers:
- Classification of the driver automatically in different groups.
- Taking care of tired, e.g. almost sleeping, driver.
- Classifying automatically the road driven by the driver, e.g. town, highway, or mountain road.
- Taking into account (dynamically) changing vehicles responses due to load, tyre condition, etc.
This place covers:
Control aspects, e.g. calculating the feedback force.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Mechanical aspects of the actuator, e.g. how to impose force to the driver |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Steering dampers for cycles |
Reference B62K 21/08 is non-limiting in the subgroup B62D 6/06. CPC will be updated/corrected once this inconsistency is resolved in IPC.
This place covers:
Means on vehicle to deflect wheels, e.g. changing the steered wheel angle in relation to chassis or vehicle body. Steering linkage, stub axles and their mountings are the means to allow deflection of the wheels.
This place does not cover:
Steering specially adapted for trailers |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Power-assisted or power-driven steering |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Varying the ratio automatically based on driving conditions |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Means on vehicle for adjusting camber, castor, or toe-in |
This place does not cover:
Pivoted axes for individually pivoted wheels where the pivotal axes are situated in more than one plane transverse to the longitudinal centre line of the vehicle and provided with safety devices |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangements for automatically controlling steering depending on driving conditions sensed and responded to, e.g. control circuits |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Power-assisted fluid steering per se |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Power-assisted electrical steering per se |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Power-assisted fluid steering per se |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Power-assisted electrical steering per se |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Pivots per se | |
Ball Joints |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Steering knuckles in general |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Means for adjusting camber, castor, toe-in |
Reference B62D 17/00 is non-limiting in the subgroup B62D 7/20. CPC will be updated/corrected once this inconsistency is resolved in IPC.
This place covers:
Residual group for subject matter not covered by previous main groups
This place covers:
Using differential driving or braking to deflect steered wheels
Not only using brakes, but also using torque differences on wheels driven by electric motors.
This place covers:
Steering non-deflectable wheels or endless tracks, wherein steering to the right or to the left is governed by an alteration in the rotation speed of one side of a set of tracks or wheels moving in a continuous motion, i.e. steering by driving. There is no associated change in the steering angle of the wheels or tracks, e.g. tanks or slip-steered wheeled vehicles or control thereof.
Gearings of interest apart from this application are also classified in the relevant group of F16H covering gearings per se.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Gearings per se |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangement or mounting of transmissions in vehicles | |
Gearing in general |
This place covers:
- Endless track steering depending on steering input for steerable wheels
- Supporting steering by differential driving of non-deflectable wheels
This place does not cover:
Differentially distributing power on deflectable wheels: |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Steering endless tracks or the like | |
Steering specially adapted for trailers |
References B62D 11/00 and B62D 13/00 are non-limiting in the main group B62D 12/00. CPC will be updated/corrected once this inconsistency is resolved in IPC.
This place covers:
Stability systems for tractor-trailer combinations, e.g. counter steering or braking.
This place covers:
For example, passive indicator, "aiming" means, e.g. fingers in the car to drive along compared with a line in the outside world.
Sensing or measuring steering angle with particular detail to the sensing/measuring.
The mere mentioning of measuring or determining a steering or steering wheel angle is not sufficient for placement in B62D 15/00 and an inventive feature about the sensing/measuring is required for placement in B62D 15/00.
This place covers:
- Storing the last recorded steering angle;
- Determination of rotation speed of steering wheel;
- Measuring on the steering wheel, if there is no steering column;
- Retrieving of steering angle information in special situations, e.g. during power off;
- Checking or testing of steering angle sensors (see also B62D 5/049);
- Calibration of steering angle systems e.g. by measuring steering angle and following curvature;
- Transmission of steering angle data to other vehicle systems including steering systems.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Sensors in general |
This place covers:
Combinations of steering angle sensors and rotary connectors in close proximity to steering wheel and column
This group only covers rotary connectors when the rotary connector is combined with the steering angle with close proximity to the steering wheel and column.
This place covers:
Measuring steering angle on the king pin at the deflectable wheel or on the turn-table between tractor and trailer
This place covers:
Determination of absolute angles, e.g. absolute steering wheel angle with a relative sensor, measuring e.g. between -90° and +90°
This place does not cover:
Non-mechanical controls that are not vehicle mounted |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Parking aids |
This place covers:
Not allowing steering in the direction of obstacles.
Minimizing damages by steering in not avoidable accident
This place covers:
- Parking the car, e.g. parallel or perpendicular parking.
- Leaving (pulling out) into the traffic.
- Testing and/or finding of parking pockets.
- Testing of (automatic) parking systems.
Automatic or guided parking as such see the relevant subgroups
This place covers:
Haptically or any other means
"Automatic parking" is also, if only the steering is done automatically.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Parking aids | |
Estimation or calculation of driving parameters for road vehicle drive control systems not related to the control of a particular sub unit with interaction between the driver and the control system | |
Autonomous road vehicle drive control with determination or calculation of trajectory projection | |
Control of position or course in two dimensions | |
Image processing |
This place covers:
Projections in the windscreen or on the street ahead
This place covers:
Means or tools located on the vehicle to adjust the different angles of a wheel support, e.g. camber, castor or toe-in and toe-out, see examples
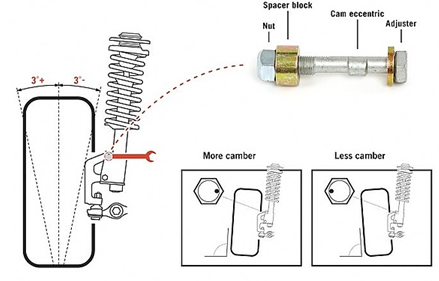

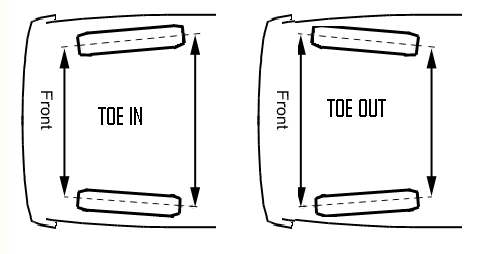
This place covers:
Levers or linkages for supporting a wheel.
Said support of wheels is considered as subject matter related to the suspension of a vehicle. Hence this group is no longer used for classifying. Classification should be given in subclass B60G instead.
This place covers:
Chassis built from frame members where the vehicle body will be mounted on, e.g.:
- Structures comprising longitudinally or transversely arranged frame members
- Structures of X-shaped or fork shaped construction
- Subframes
- Frames being adjustable
- Structures having impact absorbing means
- Structures assembled from readily detachable parts
This group does not cover subject matter primarily relating to the suspension with only a nominal recitation of frame structure, i.e. the inventive subject matter is related to suspension features and are covered by subclass B60G.
Sub-frames for mounting engines or suspension means are classified in B62D 21/11.
In order to get a classification in B62D 21/15, the understructure should have features, e.g. crush zones, crash boxes etc. which enable it to deform in a controlled fashion. If the structure is merely reinforced, then it should be given the relevant classifications elsewhere.
Beam elements which form part of a self supporting vehicle body are referred out of this group to B62D 25/00, e.g. B62D 25/082 for longitudinal beams in the engine bay to which sub-frames are attached.
This place does not cover:
Combined frame and vehicle body: | |
Beam elements forming part of a self-supporting vehicle body | |
Longitudinal beams in the engine bay to which sub-frames are attached | |
Suspension arrangements |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Understructures characterised by the material used: |
This place covers:
- Self-supporting structures which do need an additional frame, the frame and the structure forms one unit
- Spaceframes with integrated chassis in the whole shell, e.g. by using meshwork, tubes or the like
This place does not cover:
Structures having impact absorbing means | |
Superstructures or monocoque sub-units or details thereof |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Superstructures or frames characterised by the material used |
This place covers:
Fixing means for connecting vehicle body to the vehicle frame, e.g. by vibration absorbing mountings like rubber pads
This place does not cover:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
WARNING: Group B62D 24/00 and subgroups are not complete; see also other groups of B62D
This place covers:
Subunits for superstructures, e.g.
- Side panels
- Door pillars
- Fixed roofs
- Front or rear portions, e.g. bonnets, lids, dashboards or mud-guards
- Floor or bottom sub-units
The references to other areas are particularly helpful here, particularly take note of those in B62D 25/10 and B62D 25/12 for how to treat bonnet hinges, bonnet stays, openers, etc. Cabins or superstructure of the (open or closed) load compartments of utility vehicles are classified in B62D 33/00. Mudguards do not include mudguards for cycles but do include mudguards of utility vehicles.
Structures (e.g. bonnet, wing mounts) intended to deform or collapse to absorb impact forces from a non-occupant of the vehicle (e.g. pedestrian) should also be considered for classification in B60R 21/00 or indented groups.
Deformable bonnets are usually for motor cars - such documents should be classified in B62D 25/105 even if the application it is not specifically mentioned. Active protection devices which do not serve to alter the structural properties (e.g. airbags, bonnet lifters) are not classified in this group, they should be classified in B60R 21/34 and subgroups. For vehicle doors, including rear hatchback tailgates, see B60J 5/00.
The group B62D 25/085 is intended to mean front-end modules of engine compartments.
This place does not cover:
Structures having impact absorbing means | |
Superstructures of utility vehicles, e.g. load compartments or cabins | |
Running-boards, steps, or the like, as superstructure sub-unit | |
Mudguards for cycles |
The IPC group B62D25/22 "Running-boards, steps, or the like, as superstructure sub-unit" is not used in CPC; these sub-units are referred out to group B60R 3/00 (see limiting reference in main group title).
This place covers:
Rigid, resilient or readily releasable (e.g. using screwthreads) connections between super- or understructure sub-units
Please be aware that groups here should not be used for documents concerning connectors and connections in general, see subclass F16B. Documents concerning the building up of individual components (e.g. the welding of sheets to form a panel) are not classified here; neither are documents concerning the attachment components which are not part of the vehicle structure, e.g. fuel tanks.
Joining trim elements (e.g. headliners) to the vehicle are in the relevant subgroups of B60R 13/00; attachments of bumpers are in the group B60R 19/00.
Subgroup B62D 27/023 is especially directed towards structural nodes - e.g. several elements joined together by connecting means.
This place does not cover:
Connections between sub-units predominantly made of synthetic material | |
Connections of movable or detachable racks or stanchions to platforms | |
Enclosed load compartments built up with profiles of constant elongated shape, e.g. extruded, mechanically interconnected by coupling members, e.g. by clamping, riveting or bolting |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Joining trim elements (e.g. headliners) to the vehicle | |
Attachment of bumpers |
This place covers:
- Superstructures, understructures or sub-units characterised by the used material
- characterised by combining metal and synthetic material
- characterised by using predominantly special steel, light alloys, wood or synthetic material
- Structures predominantly made of synthetic material and joints therefor
This place does not cover:
Enclosed load compartments built up with flat self-supporting panels if not predominately made of synthetic material | |
Enclosed load compartments for refrigerated good vehicles |
Documents concerning the production of the material itself, or the moulding process, or metal-working process would not be given a classification here unless component details are specified.
This place covers:
- Superstructures for passenger vehicles, e.g. for carrying large number of passengers (omnibus)
- Compact cars, e.g. city cars
This main group does not include railway carriages or motorized wheelchairs or the like. Please note the definition of cycle as being a vehicle on which the operator sits (e.g. on a saddle) and has direct steering, e.g. using a steering handle.
This place does not cover:
Passenger vehicles specially adapted to co-operate with aircraft or terminal buildings |
This place covers:
- Platforms or open load compartments
- Enclosed load compartments
- Drivers's cabs or cabins and their attachment, e.g. for tiltable cabins
- Superstructures characterised by the connection of the structure to the vehicle frame
- Superstuctures comprising adjustable means
Vehicle cabs, load compartments etc. are classified in this main group, but load carrying floors for commercial vehicles are classified in group B62D 25/2054. Bonnets or lids are classified in B62D 25/10 or B62D 25/12; mudguards in B62D 25/168 or B62D 25/188.
This place does not cover:
Understuctures having impact absorbing means | |
Structures in which a load-carrying element is movable, e.g. to facilitate loading or unloading | |
Liners for load platforms or load compartments |
This place covers:
- Shaping of vehicle bodies for reducing resistance to air flow
- Devices to control or modify the boundary layer
- Spoilers
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Spoilers for stabilising vehicle bodies | |
Fluid dynamics; Influencing flow of fluid |
Spoilers which have a stabilizing function should also be classified in B62D 37/02.
Devices to control or modify the boundary layer should be classified in B62D 35/00, and should be considered for further classification in the group for influencing flow of fluid F15D 1/00.
This place covers:
Stabilising a vehicle body by forces generated with aerodynamic means (e.g. spoilers) or by movable masses, e.g. by using gyroscopes
Devices to prevent vehicles toppling over are classified according to vehicle type:
for tractors B62D 49/08; for work machines E02F 9/18; for cranes B66C 23/72.
Electronic stability control operating on brakes B60T 8/1755. Stabilising means using the control of wheel suspension are not covered by this group.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Spoilers for streamlining | |
Ground engaging vehicle fittings for supporting, lifting or manoeuvring the vehicle |
If a document concerns a spoiler which has, explicitly, a stabilizing function, then it should be given classification in B62D 37/02 as well as in B62D 35/00
This place covers:
Bodies for emergency vehicles or special vehicle bodies not provided for in other groups of this subclass
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Safety equipment |
This place covers:
Devices or methods to indicate that a vehicle has been involved in a crash, the kind of crash and where the damage occurred on the vehicle. Crash recorders are not classified in this group.
This place covers:
- Stowing, holding, or mounting arrangements for spare wheels in or on the vehicle
- Handling devices for spare wheels, e.g. for handling heavy wheels
- Anti-theft devices for spare wheels
- Protective coverings for spare wheels
If the document concerns adaptation to the vehicle structure, a further classification may also be required in B62D 25/087 and/or B62D 25/2027.
This place covers:
- Vehicles for large number of passengers, e.g. omnibus
- Vehicles which can be divided in sub-vehicles, e.g. nestable vehicles
- Vehicles which are convertible in order to modify the number of seats
This place does not cover:
Superstructures for passenger vehicles | |
Body details or kinds of railway vehicles | |
Motor-cycles, including quad bikes, ATVs; | |
Balancing machines supporting a rider; motorised skateboards and the like | |
Motorized wheelchairs; personal mobility vehicles |
B62D 47/003 means that the structure should be convertible to modify the number of seats; not that the seats should simply be removable (for removable vehicle seats see B60N 2/00). Documents which are more general and do not concern the understructure or superstructure per se or particular part thereof should be classified in this group.
This place covers:
Vehicles structures, which could be changed to allow different numbers of seats. Subject matter where the seats are simply removable are not covered by this group.
This place does not cover:
Compact cars, e.g. being foldable |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Vehicles convertible from one use to a different one |
This place covers:
- Tractors for pushing or pulling;
- Tractors for semi-trailers;
- Tractors adapted for multi-purpose use;
- Tractors for all kind of tasks, e.g. modified to take lifting devices;
- Tractors having means for preventing overturning or tipping.
This place does not cover:
Walk type tractors | |
Endless track vehicles | |
Transport means specially adapted for underground galleries |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Vehicles specially adapted for handling aircraft, e.g. aircraft tow tractors |
Generally, connections between tractors and agricultural equipment or implements are classified in A01B 59/04 and subgroups. The term "Tractors" in this group is not limited to agricultural vehicles.
Specialist tractors, e.g. street cleaning tractors, snow clearance vehicles, will be classified elsewhere according to their function.
This place covers:
- Load handling vehicles, e.g. pedestrian trucks
- Walk-type tractors, i.e. the driver is walking behind
- Vehicles where the driver is not being seated with endless tracks
- Control devices for vehicles where the driver is not being seated
- Transmission devices for vehicles where the driver is not being seated
This place does not cover:
Wheeled carriers for golf bags |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Motorised hand carts | |
Electric wheel-barrows | |
Balancing machines supporting a rider; motorised skateboards and the like |
Agricultural machines or the like where the driver walks behind the tool, e.g. lawn mower, rotary cultivator, would not typically be given a classification here, classification would be given in the related application groups for the machines. For motorised hand carts see B62B 1/00 and B62B 5/0026. For electric wheel-barrows see B62B 1/18 and B62B 5/0026.
This place covers:
Tractor-trailer combinations comprising an uniaxle tractor unit and an uniaxle trailer unit
Tractor-trailer combinations where one unit supports an essential part of the other unit's load, e.g. semi-trailers
Fifth wheel traction couplings
This place does not cover:
Articulated tracked vehicles comprising tracks for tractor and trailer | |
Traction couplings other than fifth wheel coupling |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Steering specially adapted for trailers | |
Couplings of service lines | |
Stability control acting on the braking system of tractor-trailer combinations |
Documents concerning road trains, i.e. tractor plus two or more trailers, are classified in B62D 53/005. B62D 53/125 should concern automatic coupling of the service lines happening during automatic coupling of the fifth-wheel coupling. For all other couplings of service lines see B60D 1/62 and B60D 1/64.
Regarding subgroup B62D 53/068: if the load distribution is modified by operating on the vehicle suspension (without lifting a wheel set), then the document should be classified in the relevant groups of B60G.
This place covers:
- Tracked vehicles with tracks and additional ground wheels
- Tracked vehicles using alternatively tracks or ground wheels
- Vehicles with tracks only
- Endless track units, e.g. bogies, frames or tracks
This place does not cover:
Steering aspects of endless tracked vehicles | |
Endless tracked vehicles characterised by the driver not being seated, e,g, walk-type tractors |
These endless track vehicles are also called caterpillar or crawler vehicles
If a vehicle merely has tracks, this is not a sufficient reason for classifying in B62D 55/00. For example, a mono-tracked snow mobile would only be given the classification B62D 55/07 if there were details shown of the track or track unit. Traction increasing devices which fit over individual tyres such as snow-chains are not classified here, see B60C 27/00.
Group B62D 55/253 covers flexible tracks with discrete track elements interconnected by cables or the like. Continuous tracks with embedded cables are classified in group B62D 55/242.
This place covers:
- Vehicles with ground engaging propulsion means other than wheels or endless tracks, e.g. walking members
- Vehicles having propulsion means which do not engage the ground
Humanoid robots are not systematically classified in this group. Possible areas for this subject matter are program controlled manipulators B25J 9/00; gripping heads in B25J 15/00; manipulators in general B25J.
This place does not cover:
Motorised sledges |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Endless-track vehicles for ascending or descending stairs | |
Hand carts; Sledges |
If necessary it is permissible to classify a document in both B62D 55/00 and B62D 57/00.
Please note that there are some documents concerning tracked vehicles with walking members to assist ascending stairs. These would not be classified in B62D 57/00, but in B62D 55/075 because the primary propulsion is by tracks, and due to the reference in B62D 57/024 pointing to group B62D 55/075.
The ground engaging propulsion means (e.g. walking members) are classified in the subgroup B62D 57/02.
This place covers:
Trailers with driven ground wheels or tracks, the propulsion unit being arranged either on the trailer or remote from the trailer
This place does not cover:
Ground engaging, power driven vehicle manoeuvring fittings fixed on the vehicle, e.g. fittings using additional wheel driven by an auxiliary motor |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Tractor-trailer combinations comprising uniaxial tractor and uniaxial trailer unit with a transmission shaft passing through the coupling joints | |
Vehicle manoeuvring devices separate from the vehicle |
B62D 59/00 concern trailers with driven wheels for moving the trailer when uncoupled from the tractor, e.g. for parking, manoeuvring. However, in some documents the driven trailer means are used as an auxiliary drive or alternative drive and should be (also) classified in
This place covers:
Motor vehicles or trailers characterised by the arrangement or number of wheels not covered by previous groups, e.g. with variable number of ground engaging wheels or with more than four wheels
This group does not include cycles or motorised wheelchairs or the like. Please note the definition of cycle as being a vehicle on which the operator sits (e.g. on a saddle) and has direct steering, e.g. bicycle, tricycle or quad.
This place covers:
- Modular vehicles
- Foldable, yieldable or extensible trailers
- Trailers with one axle or two wheels
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Understructures, i.e. chassis frames, characterised by the vehicle type | |
Trailer chassis | |
Semi-trailers | |
Adaptations of trailers for specific purposes |
Motor vehicles: modular vehicles does not mean vehicle with exchangeable modules for repair or change in function of the vehicle.
This place covers:
- Assembling, facilitating disassembly, or structurally modifying motor vehicles or trailers, not covered by other groups of this subclass
- Transportation, conveyor or haulage systems specially adapted for vehicle assembly lines
- Inspecting and control devices for assembly
- Joining sub-units or components to body shell or other sub-units
- Positioning of sub-units or components to body shell or to other sub-units, the subunits or components being doors, windows, openable roofs, lids, bonnets or weather strips
- Joining pre-assembled modular units
Very important is the residual character of this group "not otherwise provided for". Documents concerning the assembly or production or formation of individual components, e.g. doors, roofs, side panels, bonnets, engines, gearboxes, etc. should not be classified here, but their attachment to the body shell. This group concerns further the positioning and assembling of the body shell to the chassis.
For management of production lines, e.g. for resource allocation, planning or scheduling G06Q 10/083 ; for inventory, storage or labelling of parts, ordering of new parts, Just-In-Time delivery G06Q 10/087 .
For control of productions lines [i.e. direct connections to machines] see G05B 19/418 or see the relevant technology, for instance B23 or B05, and as well for the details of the processes.
Concerning B62D 65/024 "Positioning of sub-units or components with respect to body shell or other sub-units or components": when the centring is achieved by features of the component itself, then the document should be classified according to the component; the classification B62D 65/024 and lower is given in addition to the groups B62D 65/04 - B62D 65/16 where the component is specified.
This place covers:
Disassembly lines or processes in reverse, not for recycling of individual components or recycling of construction materials.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
General arrangement of separating plants | |
Recovery of plastics |