CPC Definition - Subclass B23Q
This place covers:
General components that are used in any kind of machine tool, such as machine beds, feeding devices, workpiece holding means, workpiece conveying means, tool changing means, chip evacuating means, etc...
Machine configurations combining different kinds of machining operations, such as drilling, milling, turning, or cutting, e.g. sawing.
In the subclass B23Q, a machine tool is considered to be a mechanical working machine that removes material from a workpiece with a mechanical cutting edge to perform a shaping operation, essentially through drilling, milling, turning, or cutting, e.g. sawing.
B23Q is in general related to machine tools in the sense of the wording as being referred to above, not related to a particular result. There are, however, subclasses that are specially dedicated to specific machining techniques and their corresponding equipment or methods. Classification is done in the specific subclasses and not in B23Q, if the process or apparatus is fully covered in said specific subclasses.
B21 deals with mechanical working of metal without removing material.
B23B is the subclass for machines or components dedicated to turning or boring operations. In particular, group B23B 31/00 relates to chucks and group B23B 27/00 to tools for turning or boring machines. B23C is the subclass for milling, B23D for slotting or sawing, B23F for making gears, B23G for thread cutting, B23H for electro discharge machining, B23K for welding, B24 for grinding or polishing.
B25B relates to clamps, vices or chucks as such, with no special relation to a specific configuration of a machine tool. B25J deals with manipulators.
The subclasses B25C, B25D, B25F deal with portable power driven tools. B25H refers to workshop equipment, e.g. work benches. Subclass B26D relates to cutting and severing, B26F to perforating and punching.
Transport or storage devices not used in particular handling or treatment are covered by B65G.
F16 is a general class of mechanical components (such as linear guides and bearings) that are used in machine tools, as well as in other technical fields.
Group G05B 19/00 covers program control systems.
H10P 72/00 covers apparatus specially adapted for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices, e.g. wafers, during manufacture or treatment thereof.
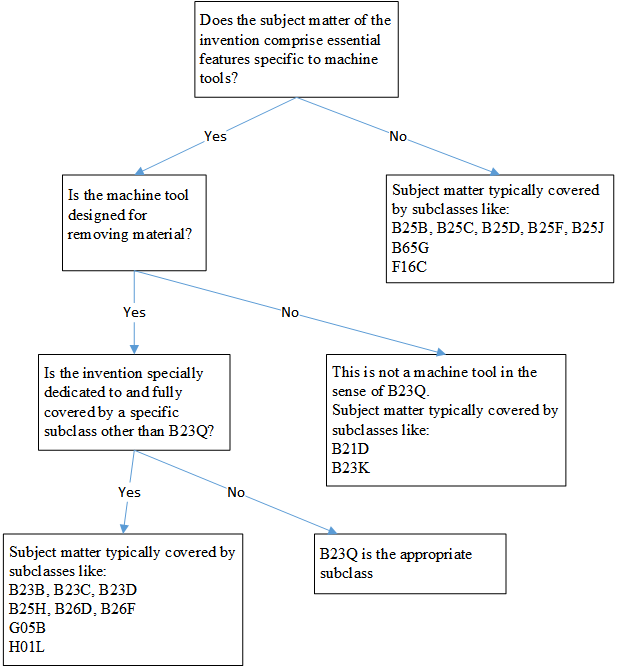
As guidance for finding the appropriate subclass, reference is made to the following flow chart:
This place does not cover:
Tools of the kind used in lathes or boring machines |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Machine tool | a mechanical working machine that removes material from a workpiece with a mechanical cutting edge to perform a shaping operation essentially through drilling, milling, turning, or cutting, e.g. sawing. The workpiece is generally made of metal, wood or plastic and is not a human body, food or cloth. |
Controlling | influencing a variable in any way, e.g. changing its direction or its value (including changing it to or from zero), maintaining it constant, limiting its range of variation |
Regulation | maintaining a variable automatically at a desired value or within a desired range of values. The desired value or range may be fixed, or manually varied, or may vary with time according to a predetermined "programme" or according to variation of another variable. Regulation is a form of control |
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms:
- "automatic control" and" regulation"
This place covers:
Features relating to the transfer of energy (mechanical, hydraulic or pneumatic) or signals in the machine tool.
Features relating to the bed or frame of the machine tool, spatial disposition of the linear guides, degrees of freedom of the tool or workpiece.
Features of the structure supporting the workpiece.
Means for guiding or stopping the movement of slides or spindles carrying the tool or the workpiece.
The groups B23Q 1/48 - B23Q 1/62 do not cover parallel kinematic structures as such, without special application in a machine tool, which is covered by B25J 9/00, B25J 17/00.
This place does not cover:
Members which are comprised in the general build-up of a form of machine, whereby said machine is a metal-working machines, or constructional combinations thereof, built-up from units designed so that at least some of the units can form parts of different machines or combinations | |
Positioning supports for measuring arrangements | |
Motorised alignment for optical elements | |
Handling of mask or wafer | |
Adjusting or compensating devices for optical apparatuses | |
Piezoelectric or electrostrictive positioners |
The following table summarises the content of the groups, wherein
P means a purely translational movement along an axis (Prismatic)
R means a purely rotational movement around an axis
A means a perpendicular relationship between two consecutive moving axes
E means a parallel relationship between two consecutive moving axes
I means a 45° inclination between two consecutive moving axes
O means other relative orientation between two consecutive moving axes.
The machines are classed according to their axis configuration, starting from the bed (fixed portion) and going towards the last moving portion (usually the tool or the workpiece, or a spindle or a supporting surface for a workpiece).
The rotation of the cutting tool in the spindle (milling, drilling, etc.) is not considered here as a rotational movement R.
To illustrate the meaning of the symbols P, R, A, E, the drawings below indicate the relation between the symbol(s) and the actual movement:
Group | Content (Comments) |
R and P | |
RAP | |
RAPAR | |
RAPER | |
RAPAP | |
RAPEP | |
REP | |
REPAR | |
REPER | |
REPER | |
REPEP | |
PAR | |
PARAR | |
PARER | |
PARAP | |
PAREP | |
PER | |
PERAR | |
PERER | |
PERAP | |
PEREP | |
R and R | |
R | |
R' (Rotation axis is perpendicular to the supporting surface) | |
R'' (Rotation axis is parallel to the supporting surface) | |
R''' ( Using a ring or tube structure where the workpiece is fixed coaxially to its rotating axis.Related group for welding: B23K 37/0452) | |
ROR,RIR | |
RAR | |
RARAR | |
RARER | |
RARAP | |
RAREP | |
RAR' (The last rotation of the supporting surface is perpendicular to the surface on which the last rotation is mounted to) | |
RAR'' (The last rotation of the supporting surface is parallel to the surface on which the last rotation is mounted to) | |
R and R w. spherical joint (At least 2 degrees of freedom in rotation, using a spherical surface joint) | |
joint and additional rotation ( - Parallel kinematic structures, using spherical surface joints or other kind of joints, where the movement is induced by a rotating element (EP1529597).- Structures using a spherical surface joint, and comprising an additional dof in rotation (US1,927,675)) | |
joint and additional translation ( - Parallel kinematic structures, using spherical surface joints or other kind of joints, where the movement is induced by a sliding/translating element (WO2005/120780) or by a telescopic element (WO2006/054935).- Structures using a spherical surface joint, and comprising an additional dof in translation (US5,544,968)). | |
RER | |
REREAR | |
RERER | |
RERAP | |
REREP | |
P and P | |
P | |
P' (Translation perpendicular to the working/supporting surface) | |
POP,PIP | |
PEP | |
PEPAR | |
PEPER | |
PEPAP | |
PEPEP | |
PAP (Use this group when the perpendicular axes are not piled, that is that both axes are at a same level (not one on top of the other; JP3234488)) | |
PAP | |
PAPAR | |
PAPER | |
PAPAP | |
PAPEP |
Further details of subgroups:
Means for adjusting height or inclination of the machine on the floor or on a support surface.
Means for clamping pallets or similar exchangeable parts in a fixed place on the machine, usually engaging a male and a female part (e.g. "quick clamping cylinder").
Special features of the frame, the bed, the portal of the machine, or the arrangement of the ways (linear guides) on the machine.
Machines where a portal, bridge or gantry is an important feature are classified in B23Q 1/012.
Inventions concerning the kinematical structure of the machine tool: how the movement is guided, number and relative arrangement of the axes.
Inventions relating to the extension of a tool holder or a tool.
This place covers:
Means for transferring energy (electrical, hydraulic or pneumatic) or signals through moving parts of the machine.
This place does not cover:
Devices for coolant flowing through the spindle | |
Rotary joints for coolant through the spindle |
This place covers:
Mostly workpiece supports for specially shaped workpieces (large or flexible) or variety of workpiece shapes or special cutting applications requiring special features of the workpiece support.
This place does not cover:
Vices composed of a plurality of parts adapting to the shape of the workpiece | |
Holders for printed circuit boards |
This place does not cover:
Movable or adjustable work or tool supports with sliding pairs and rotating pairs, whereby particular mechanisms with screw pairs are being used |
See table provided under B23Q 1/00 for summary of kinematic connections
This place covers:
Inventions relating to the bearings configuration or the housing of a working spindle.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Grinding spindles with magnetic or electromagnetic bearings | |
General features relating to bearings or other spindles |
This place covers:
Guides or fences for guiding the movement of workpieces (B23Q 3/005).
Devices for tightly holding a workpiece on a table or support in order to machine it (B23Q 3/06 - B23Q 3/08).
Any holding, supporting or positioning device for a workpiece, directed to the machining of the workpiece.
Arrangements for the automatic insertion or removal of a cutting tool from the spindle or tool holder of the machine tool (B23Q 3/155).
Arrangements for replacing, inserting or removing multi-spindle head modules:
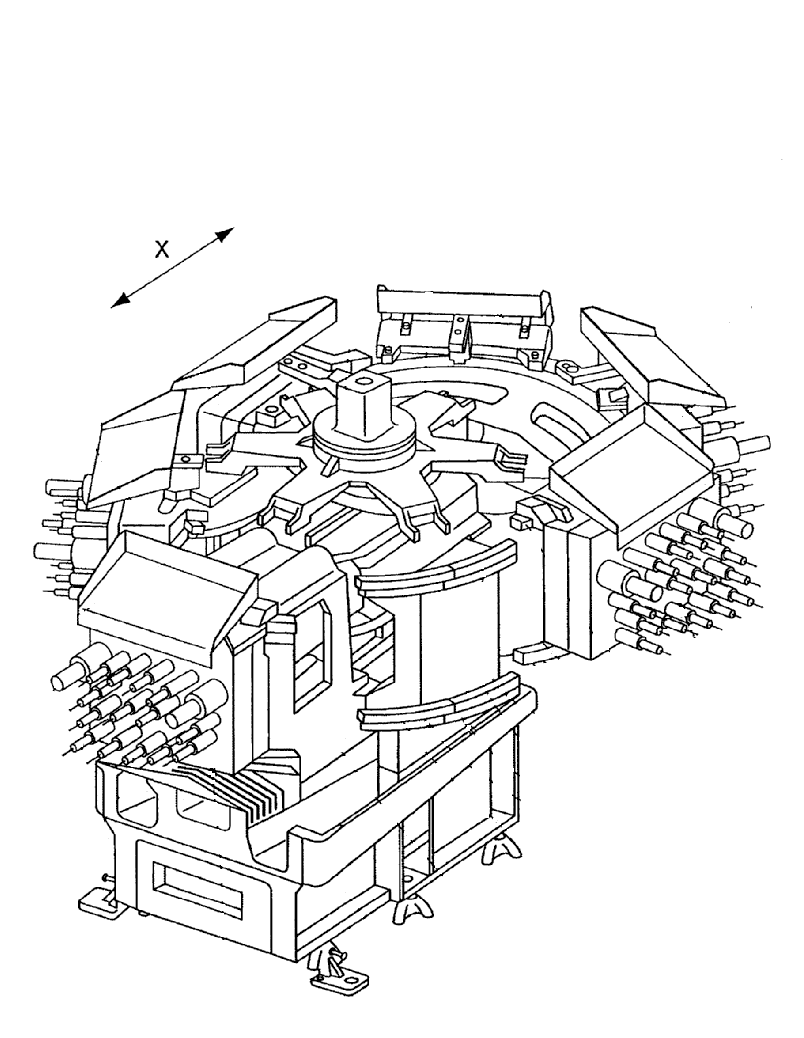
Illustrative document B23Q 2003/1558
This place does not cover:
Work-tables or other parts, e.g. faceplates, normally not incorporating means for securing work | |
Automatic position control | |
Food cutting boards | |
Workpiece support for dies | |
Rotary tool heads for turning-machines | |
Non-driven tool holders | |
General features of turrets | |
Drawbars in spindles | |
For electrical discharge machining | |
For welding | |
Means for securing grinding wheels | |
Mountings for abrasive wheels | |
Clamps, vices or chucks as such, with no special relation to a specific configuration of a machine tool. | |
Chucks for percusive tools | |
Work benches for manual work | |
Devices for securing circular saw blades | |
For assembling or manufacturing aircrafts | |
Devices for holding circuit boards | |
For holding semiconductors or wafers |
While the classes B23Q 3/1572 - B23Q 3/15766 are subclasses of B23Q 3/15713, they shall be also used for devices with direct insertion of the tool in the spindle (B23Q 3/15706).
The documents shall thus receive a classification symbol in one of the B23Q 3/15706 or B23Q 3/15713 groups and eventually one of the groups B23Q 3/1572 - B23Q 3/15766.
Arrangements for automatic insertion or removal of tools are classified in the appropriate entries foreseen in the groups B23Q 3/155 through B23Q 3/15793, and when comprising guards, fences, doors or any other kind of housing for protection of some parts of said arrangements, then additional classification in B23Q 11/08 is required.
This place covers:
Means for pressing a workpiece against a guide, fence or table. Usually mounted on a structure over the machine table or on the spindle head. If the means is mounted directly on the table and presses the workpiece downwards against the table, then classify in B23Q 3/069.
This place does not cover:
Pressure rollers for feeding timber in sawing machines |
This place covers:
Guides or fences for workpieces.
This place does not cover:
Devices for conveying work in sawing machines | |
Guide fences for sawing machines | |
Guide fences for wood working |
This place does not cover:
handling workpieces or tools by means of grippers specially adapted for use in connection with arrangements for automatic insertion or removal of tools |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangements for automatic insertion or removal of rotary tools by a transfer device taking a single tool from a storage device comprising rotating or circulating storage means and inserting it into a spindle |
This place covers:
Devices for holding the tools in the storage means (grippers) or special features relating to the tool holder in the spindle for the automatic tool exchange.
This place covers:
Mechanisms for producing a rotational or reciprocating movement (driving) or translational movement (feeding) of a workpiece or tool, in a machine tool.
This place does not cover:
Automatic control or regulation of feed movement, cutting velocity or position of tool or work | |
Methods for copying | |
Control systems or devices for copying directly from a pattern or a master model; Devices for use in copying manually | |
Boring or drilling machines or devices characterised by the drive, e.g. by fluid-pressure drive, pneumatic power drive | |
Constructional features of components specially designed for boring or drilling machines; Accessories therefor | |
Numerical control [NC], i.e. automatically operating machines, in particular machine tools, e.g. in a manufacturing environment, so as to execute positioning, movement or co-ordinated operations by means of program data in numerical form |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Vibratory toolholders | |
Ultrasonic boring | |
Gearings, speed selectors for power driven hand tools | |
Ultrasonic cutting of gems, jewels | |
General features of fluid pressure drives accelerating or decelerating the stroke | |
General mechanisms or mechanical components not specific to a machine tool | |
General mechanical drives with varying speed ratio | |
Cam or ballscrew mechanisms as such | |
Linear motors as such |
This place covers:
Arrangements concerning the conveying of workpieces between machine tools or to the loading/unloading of machine tools.
The classes correspond either to the type of conveying means used B23Q 7/001 - B23Q 7/08 or to the relationship between the machining stations of a production line that are linked by conveying means B23Q 7/14 - B23Q 7/1421.
This place does not cover:
Indexing rotating tables as such | |
Simultaneous operations on different machining stations, incorporated in a same machine. Transfer of the workpiece within such a machine. | |
Handling sheet metal, metal tubes or metal profiles | |
Conveying bar stock in a lathe | |
Vacuum work grippers | |
Program-controlled manipulators | |
General aspects of gripping heads | |
Feed chains for timber | |
Pallets for loads to be lifted | |
Separating articles from piles |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
General aspects of article conveyors |
If the work is carried on a pallet or cart loosely mounted on a conveyor means, the document should be classified in B23Q 7/1426 or subclasses of it.
The classification of new documents in groups B23Q 7/14 - B23Q 7/1421 should be avoided, since the classification in B23Q 39/00 or B23Q 41/00 is preferred.
Further details of subgroups:
Machining of the workpiece during its conveying (GB2273077).
Devices for catching a finished workpiece (DE202006003047U).
Arrangements for gripping a workpiece by using the tool holder means (EP1637279) or mounted on the tool spindle (EP2253422).
The workpieces are consecutively conveyed to the next working device, the working devices being placed in series (linearly or not) corresponding to the the sequence of working.
A long workpiece is axially transported and one end of it is machined and cut from the rest of the workpiece.
This place covers:
Arrangements for supporting, fixing or guiding a portable machine tool in combination with guide means that position the machine tool relative to the workpiece.
Machine tools that are mounted on the surface of large workpieces (such as aircrafts), or that are fixed to a large workpiece with a special profile (such as beam or tube).
Machines that are automatically guided by means supported directly on the workpiece, e.g. via an automatic cart or crawler (B23Q 9/0007).
Machines that are manually guided by means supported directly on the workpiece (B23Q 9/0014).
This place does not cover:
Turning machine for reconditioning wheel sets without removing same from the vehicle | |
For tapping pipes | |
Hand-held or like portable drilling machines, e.g. drill guns; Equipment therefor | |
Tables for sawing machines | |
Portable stands or supports for positioning portable tools or work to be operated on thereby | |
Portable hand-operated wood-milling machines; Routers |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Portable hand-operated wood-milling machines; Routers |
Further details of subgroups:
Automatic machine usually used for machining large workpieces which require high machining accuracy (e.g. aeronautic components, pipes, or profiles), wherein the machine or the guide means are supported by the workpiece. If the guide means form part of the machine, then classify also in B23Q 9/0028 or B23Q 9/0035; if they are independent from the machine and fixed on the workpiece, then classify also in B23Q 9/0042 through B23Q 9/0057.
Smaller portable machine that is manually guided by the operator, wherein the machine or the guide means are supported by the workpiece. If the guide means form part of the machine, then classify also in B23Q 9/0028 or B23Q 9/0035; if they are independent from the machine and fixed on the workpiece, then classify also in B23Q 9/0042 through B23Q 9/0057.
The machine or the guide means are supported by a support independent from the workpiece. If the guide means form part of the machine, then classify in B23Q 9/0071; if they are independent from the machine and fixed to the support, then classify in B23Q 9/0078.
This class takes precedence over B23Q 9/0014.
Here are classified machines that are secured to workpieces with a special shape such as beams or tubes, to which the securing means are specially adapted. If the workpiece is secured on the surface of the workpiece with standard fixing means, then classify in B23Q 9/0014.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Portable machine tool | A machine that is brought to the workpiece. Either the workpiece is very large (aircraft fuselage, long beams or tubes) or the machine is very light and easy to transport. |
This place covers:
Arrangements reducing or eliminating thermal influences in the machining accuracy (B23Q 11/0003).
Arrangements reducing or eliminating the influence of gravity on the machine (B23Q 11/001).
Arrangements reducing or eliminating undesired vibrations in parts of the machine (B23Q 11/0032).
Arrangements for removing or evacuating from the working area cutting chips produced during machining (B23Q 11/0042).
Arrangements protecting the operator from possible injuries or noise (B23Q 11/0078).
Arrangements for removing scrap from the teeth of cutting devices (B23Q 11/02).
Arrangements for preventing overload of tools for preventing their damage (B23Q 11/04).
Safety devices for specially adapted for disc shaped cutters like saws (B23Q 11/06).
Coverings for protecting parts of machine tools from dust, chips, cutting fluids, etc or for protecting the operator from flying cutting chips, centrifugated tools or cutting fluid (B23Q 11/08).
Arrangements for cooling or lubricating the interface between the tool and the workpiece or the tool itself. Special cooling or lubricating strategies, coolant nozzles, cooling liquid filtration systems (B23Q 11/10).
Arrangements for cooling or lubricating other parts of the machine than the tool and workpiece (bearings, spindle, motors, ballscrew, linear guides, frame (B23Q 11/12).
Arrangements for maintaining a constant temperature in parts of the machine tool, meaning the use of a certain temperature control strategy (B23Q 11/14).
This place does not cover:
Preventing escape of dirt or fumes from the working area; suction systems |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Safety devices in general, not specially designed for a machine tool |
Further details of subgroups:
Constructional or design measures intended to facilitate the evacuation of the chips by their own weight.
This class should not be used if a more specific class in another field exists (see classes cited in B23Q 11/0078).
Systems for filtering the cutting liquid for separating the chips from the liquid.
Nozzle suited to be adapted to different tools, so that its position or the direction of the cutting liquid jet can be adjusted to the geometry of the tool.
General features relating to the distribution of coolant to the machine tools, coolant dispensing devices independent of the machine, etc.
This place does not cover:
Automatic compensation of tool deflection due to temperature or force |
Constructional or design measures intended to prevent negative influences of varying temperatures are classified in B23Q 11/0003.
If thermal dilation occurs, but measures are taken to compensate for it, then classify in B23Q 11/0007 (e.g. EP1989019).
This place does not cover:
Automatic compensation of tool deflection due to temperature or force | |
Tool balancers for portable tools |
This place does not cover:
Detection or control of chatter | |
Boring bars with vibration reducing means | |
Vibration damping in sawing machines |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Counterweights for suppressing vibrations in general | |
Numerical control for compensation of load, inertia or temperature |
This place covers:
Chip collectors or chip conveyors placed under or next to a machine tool, in order to catch and convey the chips from the working area to the outside.
If the invention is focussed on the separating of the chips from the coolant, then classify rather in B23Q 11/1069 (filtration).
This place does not cover:
Removing or collecting chips in sawing machines | |
Dust removing means in manipulators | |
Means for removing cut-out material or waste in punching or perforating machines | |
Arrangements for removing bark-zones, chips, waste, or dust, specially designed for use in connection with wood-working machines |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Cleaning workpieces in general | |
Conveying materials in general, other than cutting chips |
This place does not cover:
Protective coverings placed between the working area and the operator | |
Chambers provided with manipulation devices | |
Devices for braking the circular saw blade or the saw spindle | |
Devices for arresting movement of the saw chain | |
Safety guards for wood saws |
This place does not cover:
Tool covers | |
Arrangements for covering or protecting the waysfixed to the carriage or bearing body movable along the guide rail |
This place covers:
If the invention concerns a specific kind of tool with features concerning its cooling or lubricating, it should be classified in the corresponding class of the tool.
Arrangements for cooling or lubricating tools or work incorporated in the tool may be classified in the relevant place for the tool.
Examples of places in relation to which this place is residual:
Cutting tools with special provision for cooling | |
Drills with lubricating or cooling equipment | |
Features relating to lubricating or cooling for milling-cutters | |
Devices for lubricating or cooling circular saw blades | |
Devices for lubricating or cooling straight or strap saw blades | |
Reaming tools with means for lubricating or cooling |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Feed or discharge mechanisms for settling tanks (sedimentation) | |
Filters in general | |
Equipment for cooling the grinding surfaces, e.g. devices for feeding coolant |
This place covers:
Equipment used in combination with a tool when the tool is not in operation, e.g. tool covers avoiding injury of an operator or damage of the tool.
This place covers:
Control while the tool acts upon the workpiece. Control before or after the tool acts upon the workpiece.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Control of manipulators | |
Microprocessor control of machines | |
Numerical control of machine-tools |
This place covers:
Mechanical stops for positively defining a position of a part of the machine tool by abutment against the stop (B23Q 16/001 - B23Q 16/002).
Mechanisms of peck feed drills for periodically retracting the drill from the bored hole and advancing it again to the previous working position. Other mechanisms allowing to bring the tool back to a previous working position after an interruption (B23Q 16/003).
Equipment for measuring the distance just before contact or detecting the contact between two machine parts (B23Q 16/005).
This place does not cover:
Detection of contact between tool and workpiece |
If the stop is in a hollow spindle, then classify in B23Q 16/002
If the relative movement is locked by an intermediate member mounted on the support and insertable in an aperture of the indexing part, then classify in B23Q 16/04-B23Q 16/065.
If the relative movement is stopped by a sort of clamping means or meshing means (hirth ring), then classify in B23Q 16/08-B23Q 16/102.
If the indexing movement is a rotation and the clamping means is a disc or a drum brake, then classify in B23Q 16/105 or B23Q 16/107 respectively.
These classes concern details for locking or clamping the indexing part in the indexing position, so that it does not move relative to the fixed support.
If the relative movement is locked by an intermediate member mounted on the support and insertable in an aperture of the indexing part, then classify in
If the relative movement is stopped by a sort of clamping means or meshing means (hirth ring), then classify in B23Q 16/08-B23Q 16/102.
If the indexing movement is a rotation and the clamping means is a disc or a drum brake, then classify in B23Q 16/105 or B23Q 16/107 respectively.
Further details of subgroups:
See, for example, US-5,765,448.
Device consisting of a plurality of abutting stops at different positions or of different lengths, in a common carrier, used for detemining a position or length of a machine part.
Positive angle adjustment of a pivotable table. See, for example, US-3,861,088.
Equipment for bringing a linearly or rotatably moving part to one of a plurality of consecutive predefined indexing positions.
Details concerning the elements that assure the accurate positioning at the indexing point.
Details concerning the mechanism that produces the movement from an indexing point to the next.
Means for varying the distance between two consecutive indexing points or between various consecutive machine parts separated from each other by the same distance.
Additional means for adjusting the position of the indexing part around the normal indexing position.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Reciprocating or oscillating movement | Linear movement |
Continuous movement or continuous drive | Rotary movement or rotary drive |
This place covers:
Arrangements for measuring any parameters, such as tool or workpiece dimensions, vibrations, positions of machine parts, etc.
Arrangements for detecting any machine condition, such as "tool or workpiece are safely clamped", "the machine parts are in a good state", for managing the life of the tools or other parts of the machine, etc.
If the amplitude of a force is analysed in the time domain, then classify in B23Q 17/0966.
If the force is analysed in the frequence domain (vibration), then classify in B23Q 17/0971.
The documents should rather be classified in B23Q 17/0914-B23Q 17/0947 as far as possible.
If the referencing is done by contacting the workpiece with the tool, then classify in B23Q 17/2241.
Further details of subgroups:
Controlling whether a tool or workpiece holder is correctly holding (correct position or correct holding force).
Depending on whether the parameter controlled is a position of a part or a force, pressure or deformation acting on a part, the document should be classified in B23Q 17/003 or B23Q 17/005 respectively.
As opposed to B23Q 17/002, this class deals only with the detecting of the presence or absence of a tool or workpiece in its holder, and not to the quality of the holding action.
Controlling the right, smooth functioning of parts of the machine, except the tool. Details concerning life management of a specific part (how long can this part still work correctly before it must be replaced or maintained?) are classified in B23Q 17/008.
Analysing the quality (dimensions, roughness, temperature, etc.) of the machined workpiece.
Special details of arrangements for measuring vibrations in machine tools.
Special arrangements in machine tools for measuring the position of the workpiece or the tool relative to the machine or relative to each other.
Arrangements for correcting position errors or for adjusting the tool and the workpiece relative to each other.
Arrangements for detecting or preventing collisions between parts (tool, workpiece, slides, etc. ) of the machine tool.
Adjusting the tool into its holder or into the tool head, for example for correcting an eccentricity or an inclination error.
Arrangements for adjusting the position of the tool or the spindle relative to the workpiece or to a reference part in the machine.
Arrangements using optical devices (lenses, electromagnetic waves, radar, cameras, etc.) for measuring, detecting a certain machine state, or facilitating the working in a machine tool.
This place covers:
Details concerning the control of the condition of the tool (level of wear, broken tool, dimensions, temperature, machining forces, etc.). Depending on whether the control is performed before/after machining or during machining, classify in B23Q 17/0904 - B23Q 17/0947 or B23Q 17/0952 - B23Q 17/099 respectively.
This place does not cover:
Accessories for positioning, for tool-setting for measuring probes |
This place covers:
The tool is measured in an apparatus (presetting device) independent from the machine tool.
This place does not cover:
Clamping a tool in a tool holder by heating and shrinking the holder (tool length setting device) |
This place covers:
Measurement of workpiece characteristics, in a machine tool or directly related to the functioning of the machine tool.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring instruments in general |
This place covers:
Using light beams projected on the working area for helping the operator to guide the tool or workpiece to the desired target.
This place does not cover:
Optical guiding devices for hand tools |
This place covers:
Arrangements for compensating any irregularities, such as wear, in the functioning of the machine tool.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Automatic control of parts of a machine tool | |
Program control systems |
This place covers:
Special machine configurations allowing to produce works of particular shape.
This place does not cover:
Grinding non circular cross sections | |
Numerical control for generating special surfaces |
This place covers:
General methods for copying a shape.
This class is not used anymore for classifying. It contains some old documents that deal with the reproduction of a shape on a workpiece.
This place does not cover:
Tracing or scanning a model for preparing numerical control data |
This place covers:
Arrangements allowing a tool to copy a pattern or model.
Arrangements allowing a cutting tool to machine a workpiece for reproducing the shape of a physical master model (e.g. a key). The shape of the master model is detected either with or without physical contact and the corresponding information is transferred to the axis of a machine tool.
This place does not cover:
Using a copying machine for making dental prostheses |
This place covers:
Machine tools made of special modules allowing the machine to be reconfigured.
Modules adapted to make reconfigurable machines.
Machines not made of modular elements but being convertible into different working configurations (e.g., from horizontally working into vertically working; B23Q 37/002).
This place covers:
Machine tools made of a plurality of sub-assemblies, wherein each-subassembly can perform a machining operation, either simultaneously or consecutively, either on a same workpiece or not.
This place does not cover:
Turning-machines with two or more working-spindles |
Further details of subgroups:
There is a single operating station, i.e. either a single workholder for a plurality of toolheads (B23Q 39/021 - B23Q 39/027) or a plurality of workholders ready to be operated on by a single toolhead (B23Q 39/028).
In these classes, "same working direction" means that the toolheads operate on the workpiece from the same side, with similar inclination of the tool. "Different working direction" means that the toolheads operate on the workpiece from different sides or with different inclination of the tool.
Several workpieces are machined simultaneously at different stations by different tool heads.
This place covers:
Machining lines with a plurality of machining stations of different types, with a special arrangement or organisation of the machines, characterised not by the end product or the machining technology but by the relationship between the machines.
This place does not cover:
Advancing work in multistage presses | |
Assembly with two or more workstations | |
Total factory control |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Combinations of conveyors in general |
Further details of subgroups:
Details relating to the transfer of the work between the machines.
If the details correspond to a specific transfer device, then classify in the corresponding group in B23Q 7/00 - B23Q 7/103.
Details relating to the relative spatial arrangements of the machines in the factory.
Details relating to the organisation of the working of the machines or to the distribution or flow of the workpieces between the machines.
General details relating to the maintenance of efficient working conditions in the machines, such as parts or tool wear control, checking of quality, optimisation of working conditions.