Version: 2025.08
Loading Scheme...
This area was updated. Please refer to the CPC Notices of Changes and Notices of Editorial Corrections for more information.
CPC | COOPERATIVE PATENT CLASSIFICATION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A61K | PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES (devices or methods specially adapted for bringing pharmaceutical products into particular physical or administering forms A61J 3/00; chemical aspects of, or use of materials for deodorisation of air, for disinfection or sterilisation, or for bandages, dressings, absorbent pads or surgical articles A61L; soap compositions C11D) [2025-08] NOTES
WARNINGS
|
| A61K 6/00 |
A61K 6/15 | . | Compositions characterised by their physical properties [2020-01] |
A61K 6/16 | . . | Refractive index [2020-01] |
A61K 6/17 | . . | Particle size [2020-01] |
A61K 6/18 | . . | causing dental retraction, e.g. compositions for widening the sulcus for making dental impressions or removing teeth [2020-01] |
A61K 6/19 | . . | Self-expanding, e.g. for filling teeth [2020-01] |
A61K 6/20 | . | Protective coatings for natural or artificial teeth, e.g. sealings, dye coatings or varnish [2020-01] |
A61K 6/25 | . | Compositions for detecting or measuring, e.g. of irregularities on natural or artificial teeth [2020-01] |
A61K 6/30 | . | Compositions for temporarily or permanently fixing teeth or palates, e.g. primers for dental adhesives [2020-01] |
A61K 6/35 | . . | Preparations for stabilising dentures in the mouth [2020-01] |
A61K 6/40 | . |
A61K 6/50 | . | Preparations specially adapted for dental root treatment [2020-01] |
A61K 6/52 | . . | Cleaning; Disinfecting [2020-01] |
A61K 6/54 | . . | Filling; Sealing [2020-01] |
A61K 6/56 | . . | Apical treatment [2020-01] |
A61K 6/58 | . . | specially adapted for dental implants [2020-01] |
A61K 6/60 | . | comprising organic or organo-metallic additives [2020-01] |
A61K 6/61 | . . | Cationic, anionic or redox initiators [2020-01] |
A61K 6/62 | . . | Photochemical radical initiators [2020-01] |
A61K 6/64 | . . | Thermal radical initiators [2020-01] |
A61K 6/65 | . . | Dyes [2020-01] |
A61K 6/66 | . . . | Photochromic dyes [2020-01] |
A61K 6/68 | . . . | Thermochromic dyes [2020-01] |
A61K 6/69 | . . | Medicaments [2020-01] |
A61K 6/70 | . | comprising inorganic additives [2020-01] |
A61K 6/71 | . . | Fillers [2020-01] |
A61K 6/72 | . . . | comprising nitrogen-containing compounds [2020-01] |
A61K 6/73 | . . . | comprising sulfur-containing compounds [2020-01] |
A61K 6/74 | . . . | comprising phosphorus-containing compounds [2020-01] |
A61K 6/75 | . . . . | Apatite [2020-01] |
A61K 6/76 | . . . | comprising silicon-containing compounds [2020-01] |
A61K 6/77 | . . . | Glass [2020-01] |
A61K 6/78 | . . | Pigments [2020-01] |
A61K 6/79 | . . | Initiators [2020-01] |
A61K 6/80 | . | Preparations for artificial teeth, for filling teeth or for capping teeth [2020-01] |
A61K 6/802 | . . | comprising ceramics [2020-01] |
A61K 6/804 | . . . | comprising manganese oxide [2020-01] |
A61K 6/807 | . . . | comprising magnesium oxide [2020-01] |
A61K 6/809 | . . . | comprising beryllium oxide [2020-01] |
A61K 6/811 | . . . | comprising chromium oxide [2020-01] |
A61K 6/813 | . . . | comprising iron oxide [2020-01] |
A61K 6/816 | . . . | comprising titanium oxide [2020-01] |
A61K 6/818 | . . . | comprising zirconium oxide [2020-01] |
A61K 6/82 | . . . | comprising hafnium oxide [2020-01] |
A61K 6/822 | . . . | comprising rare earth metal oxides [2020-01] |
A61K 6/824 | . . . | comprising transition metal oxides [2020-01] |
A61K 6/827 | . . . | Leucite [2020-01] |
A61K 6/829 | . . | comprising cermet composites [2020-01] |
A61K 6/831 | . . | comprising non-metallic elements or compounds thereof, e.g. carbon [2020-01] |
A61K 6/833 | . . . | Glass-ceramic composites [2020-01] |
A61K 6/836 | . . . | Glass [2020-01] |
A61K 6/838 | . . . | Phosphorus compounds, e.g. apatite [2020-01] |
A61K 6/84 | . . | comprising metals or alloys [2020-01] |
A61K 6/842 | . . . | Rare earth metals [2020-01] |
A61K 6/844 | . . . | Noble metals [2020-01] |
A61K 6/847 | . . . | Amalgams [2020-01] |
A61K 6/849 | . . | comprising inorganic cements [2020-01] |
A61K 6/851 | . . . | Portland cements [2020-01] |
A61K 6/853 | . . . | Silicates [2020-01] |
A61K 6/856 | . . . | Pozzolans [2020-01] |
A61K 6/858 | . . . | Calcium sulfates, e.g, gypsum [2020-01] |
A61K 6/86 | . . . | Al-cements [2020-01] |
A61K 6/862 | . . . | Ca-Al-sulfate-cements [2020-01] |
A61K 6/864 | . . . |
A61K 6/867 | . . . | Ammonium cements [2020-01] |
A61K 6/869 | . . . | Zeolites [2020-01] |
A61K 6/871 | . . . | Quartz; SiO2 [2020-01] |
A61K 6/873 | . . . | Carbonates [2020-01] |
A61K 6/876 | . . . | Calcium oxide [2020-01] |
A61K 6/878 | . . . | Zirconium oxide [2020-01] |
A61K 6/88 | . . . | Chromium oxide [2020-01] |
A61K 6/882 | . . . | Carbides [2020-01] |
A61K 6/884 | . . | comprising natural or synthetic resins [2020-01] |
A61K 6/887 | . . . | Compounds obtained by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds [2020-01] |
A61K 6/889 | . . . . | Polycarboxylate cements; Glass ionomer cements [2020-01] |
A61K 6/891 | . . . | Compounds obtained otherwise than by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds [2020-01] |
A61K 6/893 | . . . . | Polyurethanes [2020-01] |
A61K 6/896 | . . . . | Polyorganosilicon compounds [2020-01] |
A61K 6/898 | . . . | Polysaccharides [2020-01] |
A61K 6/90 | . | Compositions for taking dental impressions [2020-01] |
| A61K 8/00 | Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations [2023-02] NOTES
|
A61K 8/0204 | . . | {Specific forms not provided for by any of groups A61K 8/0208 - A61K 8/14} [2016-05] |
A61K 8/0208 | . . | {Tissues; Wipes; Patches} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/0212 | . . | {Face masks} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/0216 | . . | {Solid or semisolid forms} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/022 | . . . | {Powders; Compacted Powders} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/0225 | . . . . | {Granulated powders} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/0229 | . . . | {Sticks} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/0233 | . . . | {Distinct layers, e.g. core/shell sticks} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/0237 | . . . . | {Striped compositions} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/0241 | . . | {Containing particulates characterized by their shape and/or structure (see also A61K 8/04, A61K 8/11, and A61K 8/14, further aspects are classified in A61K 2800/40 and subcodes)} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/0245 | . . . | {Specific shapes or structures not provided for by any of the groups of A61K 8/0241} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/025 | . . . | {Explicitly spheroidal or spherical shape} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/0254 | . . . | {Platelets; Flakes} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/0258 | . . . . | {Layered structure} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/0262 | . . . . . | {Characterized by the central layer} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/0266 | . . . . . | {Characterized by the sequence of layers} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/027 | . . . | {Fibers; Fibrils} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/0275 | . . . | {Containing agglomerated particulates} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/0279 | . . . | {Porous; Hollow} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/0283 | . . . | {Matrix particles} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/0287 | . . . . | {the particulate containing a solid-in-solid dispersion} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/0291 | . . | {Micelles} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/0295 | . . | {Liquid crystals} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/03 | . . | Liquid compositions with two or more distinct layers [2013-01] |
A61K 8/04 | . . | Dispersions; Emulsions [2013-01] |
A61K 8/042 | . . . | {Gels} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/044 | . . . | {Suspensions} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/046 | . . . | {Aerosols; Foams} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/06 | . . . | Emulsions [2013-01] |
A61K 8/11 | . . | Encapsulated compositions [2013-01] |
A61K 8/14 | . . | Liposomes; Vesicles [2013-01] |
| A61K 8/18 | . | characterised by the composition [2015-01] NOTE
|
A61K 8/19 | . . | containing inorganic ingredients [2013-01] |
A61K 8/20 | . . . | Halogens; Compounds thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 8/21 | . . . . | Fluorides; Derivatives thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 8/22 | . . . | Peroxides; Oxygen; Ozone [2013-01] |
A61K 8/23 | . . . | Sulfur; Selenium; Tellurium; Compounds thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 8/24 | . . . | Phosphorous; Compounds thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 8/25 | . . . | Silicon; Compounds thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 8/26 | . . . | Aluminium; Compounds thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 8/27 | . . . | Zinc; Compounds thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 8/28 | . . . | Zirconium; Compounds thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 8/29 | . . . | Titanium; Compounds thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 8/30 | . . | containing organic compounds [2013-01] |
A61K 8/31 | . . . | Hydrocarbons [2013-01] |
A61K 8/33 | . . . | containing oxygen [2013-01] |
A61K 8/34 | . . . . | Alcohols [2013-01] |
A61K 8/342 | . . . . . | {Alcohols having more than seven atoms in an unbroken chain} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/345 | . . . . . | {containing more than one hydroxy group} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/347 | . . . . . | {Phenols} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/35 | . . . . | Ketones, e.g. benzophenone [2013-01] |
A61K 8/36 | . . . . | Carboxylic acids; Salts or anhydrides thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 8/361 | . . . . . | {Carboxylic acids having more than seven carbon atoms in an unbroken chain; Salts or anhydrides thereof} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/362 | . . . . . | Polycarboxylic acids [2013-01] |
A61K 8/365 | . . . . . | Hydroxycarboxylic acids; Ketocarboxylic acids [2013-01] |
A61K 8/368 | . . . . . | with carboxyl groups directly bound to carbon atoms of aromatic rings [2019-05] |
A61K 8/37 | . . . . | Esters of carboxylic acids [2013-01] |
A61K 8/375 | . . . . . | {the alcohol moiety containing more than one hydroxy group} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/38 | . . . . | Percompounds, e.g. peracids [2013-01] |
A61K 8/39 | . . . . | Derivatives containing from 2 to 10 oxyalkylene groups [2013-11] |
A61K 8/40 | . . . |
A61K 8/41 | . . . . | Amines [2013-01] |
A61K 8/411 | . . . . . | {Aromatic amines, i.e. where the amino group is directly linked to the aromatic nucleus} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/413 | . . . . . | {Indoanilines; Indophenol; Indoamines} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/415 | . . . . . | {Aminophenols} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/416 | . . . . . | {Quaternary ammonium compounds (A61K 8/35 takes precedence)} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/418 | . . . . . | {containing nitro groups} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/42 | . . . . | Amides [2013-01] |
A61K 8/43 | . . . . | Guanidines [2013-01] |
A61K 8/44 | . . . . | Aminocarboxylic acids or derivatives thereof, e.g. aminocarboxylic acids containing sulfur; Salts; Esters or N-acylated derivatives thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 8/442 | . . . . . | {substituted by amido group(s)} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/445 | . . . . . | {aromatic, i.e. the carboxylic acid directly linked to the aromatic ring} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/447 | . . . . . | {containing sulfur} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/45 | . . . . | Derivatives containing from 2 to 10 oxyalkylene groups [2013-11] |
A61K 8/46 | . . . |
A61K 8/463 | . . . . | {containing sulfuric acid derivatives, e.g. sodium lauryl sulfate} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/466 | . . . . | {containing sulfonic acid derivatives; Salts} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/49 | . . . | containing heterocyclic compounds [2013-01] |
A61K 8/4906 | . . . . | {with one nitrogen as the only hetero atom} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/4913 | . . . . . | {having five membered rings, e.g. pyrrolidone carboxylic acid} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/4926 | . . . . . | {having six membered rings} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/4933 | . . . . . | {having sulfur as an exocyclic substituent, e.g. pyridinethione} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/494 | . . . . | {with more than one nitrogen as the only hetero atom} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/4946 | . . . . . | {Imidazoles or their condensed derivatives, e.g. benzimidazoles} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/4953 | . . . . . | {containing pyrimidine ring derivatives, e.g. minoxidil} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/496 | . . . . . | {Triazoles or their condensed derivatives, e.g. benzotriazoles} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/4966 | . . . . . | {Triazines or their condensed derivatives} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/4973 | . . . . | {with oxygen as the only hetero atom} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/498 | . . . . . | {having 6-membered rings or their condensed derivatives, e.g. coumarin} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/4986 | . . . . | {with sulfur as the only hetero atom} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/4993 | . . . . | {Derivatives containing from 2 to 10 oxyalkylene groups} [2013-11] |
A61K 8/55 | . . . | Phosphorus compounds [2013-01] |
A61K 8/553 | . . . . | {Phospholipids, e.g. lecithin} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/556 | . . . . | {Derivatives containing from 2 to 10 oxyalkylene groups} [2013-11] |
A61K 8/58 | . . . | containing atoms other than carbon, hydrogen, halogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur or phosphorus [2013-01] |
A61K 8/60 | . . . | Sugars; Derivatives thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 8/602 | . . . . | {Glycosides, e.g. rutin} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/604 | . . . . | {Alkylpolyglycosides; Derivatives thereof, e.g. esters} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/606 | . . . . | {Nucleosides; Nucleotides; Nucleic acids} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/608 | . . . . | {Derivatives containing from 2 to 10 oxyalkylene groups} [2013-11] |
| A61K 8/63 | . . . | Steroids; Derivatives thereof [2013-01] NOTE
|
A61K 8/64 | . . . | Proteins; Peptides; Derivatives or degradation products thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 8/645 | . . . . | {Proteins of vegetable origin; Derivatives or degradation products thereof} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/65 | . . . . | Collagen; Gelatin; Keratin; Derivatives or degradation products thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 8/66 | . . . . | Enzymes [2013-01] |
A61K 8/67 | . . . | Vitamins [2013-01] |
A61K 8/671 | . . . . | {Vitamin A; Derivatives thereof, e.g. ester of vitamin A acid, ester of retinol, retinol, retinal} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/673 | . . . . | {Vitamin B group} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/675 | . . . . . | {Vitamin B3 or vitamin B3 active, e.g. nicotinamide, nicotinic acid, nicotinyl aldehyde (tocopheryl nicotinate A61K 8/678)} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/676 | . . . . | {Ascorbic acid, i.e. vitamin C} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/678 | . . . . | {Tocopherol, i.e. vitamin E} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/68 | . . . | Sphingolipids, e.g. ceramides, cerebrosides, gangliosides [2013-01] |
A61K 8/69 | . . . | containing fluorine [2013-01] |
A61K 8/70 | . . . . | containing perfluoro groups, e.g. perfluoroethers [2013-01] |
A61K 8/72 | . . | containing organic macromolecular compounds [2013-01] |
A61K 8/73 | . . . | Polysaccharides [2013-01] |
A61K 8/731 | . . . . | {Cellulose; Quaternized cellulose derivatives} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/732 | . . . . | {Starch; Amylose; Amylopectin; Derivatives thereof} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/733 | . . . . | {Alginic acid; Salts thereof} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/735 | . . . . | {Mucopolysaccharides, e.g. hyaluronic acid; Derivatives thereof} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/736 | . . . . | {Chitin; Chitosan; Derivatives thereof} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/737 | . . . . | {Galactomannans, e.g. guar; Derivatives thereof} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/738 | . . . . | {Cyclodextrins} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/81 | . . . | obtained by reactions involving only carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds [2013-01] |
A61K 8/8111 | . . . . . | {Homopolymers or copolymers of aliphatic olefines, e.g. polyethylene, polyisobutene; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/8117 | . . . . . | {Homopolymers or copolymers of aromatic olefines, e.g. polystyrene; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/8147 | . . . . . | {Homopolymers or copolymers of acids; Metal or ammonium salts thereof, e.g. crotonic acid, (meth)acrylic acid; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/8152 | . . . . . | {Homopolymers or copolymers of esters, e.g. (meth)acrylic acid esters; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/8158 | . . . . . | {Homopolymers or copolymers of amides or imides, e.g. (meth) acrylamide; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/8176 | . . . . . | {Homopolymers of N-vinyl-pyrrolidones. Compositions of derivatives of such polymers} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/8182 | . . . . . | {Copolymers of vinyl-pyrrolidones. Compositions of derivatives of such polymers} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/84 | . . . | obtained by reactions otherwise than those involving only carbon-carbon unsaturated bonds [2016-11] |
A61K 8/85 | . . . . | Polyesters [2013-01] |
A61K 8/86 | . . . . | Polyethers [2013-01] |
A61K 8/87 | . . . . | Polyurethanes [2013-01] |
A61K 8/88 | . . . . | Polyamides [2013-01] |
A61K 8/89 | . . . . | Polysiloxanes [2013-01] |
A61K 8/891 | . . . . . | saturated, e.g. dimethicone, phenyl trimethicone, C24-C28 methicone or stearyl dimethicone [2013-01] |
A61K 8/892 | . . . . . . | modified by a hydroxy group, e.g. dimethiconol [2013-01] |
A61K 8/893 | . . . . . . | modified by an alkoxy or aryloxy group, e.g. behenoxy dimethicone or stearoxy dimethicone [2013-01] |
A61K 8/894 | . . . . . . | modified by a polyoxyalkylene group, e.g. cetyl dimethicone copolyol [2013-01] |
A61K 8/895 | . . . . . | containing silicon bound to unsaturated aliphatic groups, e.g. vinyl dimethicone [2013-01] |
A61K 8/896 | . . . . . | containing atoms other than silicon, carbon, oxygen and hydrogen, e.g. dimethicone copolyol phosphate [2013-01] |
A61K 8/897 | . . . . . . | containing halogen, e.g. fluorosilicones [2013-01] |
A61K 8/898 | . . . . . . | containing nitrogen, e.g. amodimethicone, trimethyl silyl amodimethicone or dimethicone propyl PG-betaine [2013-01] |
A61K 8/899 | . . . . . . | containing sulfur, e.g. sodium PG-propyldimethicone thiosulfate copolyol [2013-01] |
A61K 8/90 | . . . |
A61K 8/91 | . . . |
A61K 8/92 | . . | Oils, fats or waxes; Derivatives thereof, e.g. hydrogenation products thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 8/922 | . . . | {of vegetable origin} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/925 | . . . | {of animal origin} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/927 | . . . | {of insects, e.g. shellac} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/96 | . . | containing materials, or derivatives thereof of undetermined constitution [2017-08] |
A61K 8/965 | . . . | {of inanimate origin} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/97 | . . . | from algae, fungi, lichens or plants; from derivatives thereof [2021-02] |
A61K 8/9706 | . . . . | Algae [2021-02] |
A61K 8/9711 | . . . . . | Phaeophycota or Phaeophyta [brown algae], e.g. Fucus [2021-02] |
A61K 8/9717 | . . . . . | Rhodophycota or Rhodophyta [red algae], e.g. Porphyra [2021-02] |
A61K 8/9722 | . . . . . | Chlorophycota or Chlorophyta [green algae], e.g. Chlorella [2021-02] |
A61K 8/9728 | . . . . | Fungi, e.g. yeasts [2021-02] |
A61K 8/9733 | . . . . | Lichens [2021-02] |
A61K 8/9739 | . . . . | Bryophyta [mosses] [2021-02] |
A61K 8/9741 | . . . . | Pteridophyta [ferns] [2021-02] |
A61K 8/9749 | . . . . . | Filicopsida or Pteridopsida [2017-08] |
A61K 8/9755 | . . . . | Gymnosperms [Coniferophyta] [2021-02] |
A61K 8/9761 | . . . . . | Cupressaceae [Cypress family], e.g. juniper or cypress [2017-08] |
A61K 8/9767 | . . . . . | Pinaceae [Pine family], e.g. pine or cedar [2017-08] |
A61K 8/9771 | . . . . | Ginkgophyta, e.g. Ginkgoaceae [Ginkgo family] [2021-02] |
A61K 8/9778 | . . . . | Gnetophyta, e.g. Ephedraceae [Mormon-tea family] [2021-02] |
A61K 8/9783 | . . . . | Angiosperms [Magnoliophyta] [2021-02] |
A61K 8/9789 | . . . . . | Magnoliopsida [dicotyledons] [2017-08] |
A61K 8/9794 | . . . . . | Liliopsida [monocotyledons] [2017-08] |
A61K 8/98 | . . . | of animal origin [2013-01] |
A61K 8/981 | . . . . | {of mammals or bird} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/982 | . . . . . | {Reproductive organs; Embryos, Eggs} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/983 | . . . . . | {Blood, e.g. plasma} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/985 | . . . . . | {Skin or skin outgrowth, e.g. hair, nails} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/986 | . . . . . | {Milk; Derivatives thereof, e.g. butter} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/987 | . . . . | {of species other than mammals or birds} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/988 | . . . . . | {Honey; Royal jelly, Propolis} [2013-01] |
A61K 8/99 | . . . | from microorganisms other than algae or fungi, e.g. protozoa or bacteria [2021-02] |
| A61K 9/00 | Medicinal preparations characterised by special physical form {(nuclear magnetic resonance contrast preparations or magnetic resonance imaging contrast preparations A61K 49/18; preparations containing radioactive substances A61K 51/12)} [2021-05] NOTE
|
A61K 9/0002 | . | {Galenical forms characterised by the drug release technique; Application systems commanded by energy} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/0004 | . . | {Osmotic delivery systems; Sustained release driven by osmosis, thermal energy or gas} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/0007 | . . | {Effervescent (A61K 9/0065 takes precedence)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/0009 | . . | {involving or responsive to electricity, magnetism or acoustic waves; Galenical aspects of sonophoresis, iontophoresis, electroporation or electroosmosis (microelectromechanical systems A61K 9/0097)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/0012 | . | {Galenical forms characterised by the site of application} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/0014 | . . | {Skin, i.e. galenical aspects of topical compositions (non-active ingredients are additionally classified in A61K 47/00; A61K 9/0009, A61K 9/0021, A61K 9/7015, A61K 9/7023 take precedence; cosmetic preparations A61K 8/00, A61Q; preparations for wound dressings or bandages A61L 26/00)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/0017 | . . . | {Non-human animal skin, e.g. pour-on, spot-on} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/0019 | . . | {Injectable compositions; Intramuscular, intravenous, arterial, subcutaneous administration; Compositions to be administered through the skin in an invasive manner (non-active ingredients are additionally classified in A61K 47/00)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/0021 | . . . | {Intradermal administration, e.g. through microneedle arrays, needleless injectors (mechanical aspects A61M)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/0024 | . . . | {Solid, semi-solid or solidifying implants, which are implanted or injected in body tissue (compositions for intravenous administration, normal injectable solutions or dispersions for, e.g. subcutaneous administration A61K 9/0019; brain implants A61K 9/0085; (coated) prostheses, catheters or stents A61L)} [2016-08] |
A61K 9/0026 | . . . | {Blood substitute; Oxygen transporting formulations; Plasma extender} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/0029 | . . . | {Parenteral nutrition; Parenteral nutrition compositions as drug carriers} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/0031 | . . | {Rectum, anus} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/0034 | . . | {Urogenital system, e.g. vagina, uterus, cervix, penis, scrotum, urethra, bladder; Personal lubricants} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/0036 | . . . | {Devices retained in the vagina or cervix for a prolonged period, e.g. intravaginal rings, medicated tampons, medicated diaphragms} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/0039 | . . . | {Devices retained in the uterus for a prolonged period, e.g. intrauterine devices for contraception} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/0041 | . . | {Mammary glands, e.g. breasts, udder; Intramammary administration} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/0043 | . . | {Nose} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/0046 | . . | {Ear} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/0048 | . . | {Eye, e.g. artificial tears} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/0051 | . . . | {Ocular inserts, ocular implants} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/0053 | . . | {Mouth and digestive tract, i.e. intraoral and peroral administration (rectal administration A61K 9/0031)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/0056 | . . . | {Mouth soluble or dispersible forms; Suckable, eatable, chewable coherent forms; Forms rapidly disintegrating in the mouth; Lozenges; Lollipops; Bite capsules; Baked products; Baits or other oral forms for animals} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/0058 | . . . . | {Chewing gums (non-medicinal aspects, preparing chewing gum A23G 4/00; chewing gum for care of the teeth or oral cavity, e.g. with breath freshener A61Q 11/00)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/006 | . . . | {Oral mucosa, e.g. mucoadhesive forms, sublingual droplets; Buccal patches or films; Buccal sprays} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/0063 | . . . | {Periodont} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/0065 | . . . | {Forms with gastric retention, e.g. floating on gastric juice, adhering to gastric mucosa, expanding to prevent passage through the pylorus} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/0068 | . . . | {Rumen, e.g. rumen bolus} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/007 | . . | {Pulmonary tract; Aromatherapy} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/0073 | . . . | {Sprays or powders for inhalation; Aerolised or nebulised preparations generated by other means than thermal energy; (nasal sprays A61K 9/0043; inhalation of vapours of volatile or heated drugs, e.g. essential oils or nicotine, A61K 9/007; devices A61M)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/0075 | . . . . | {for inhalation via a dry powder inhaler [DPI], e.g. comprising micronized drug mixed with lactose carrier particles} [2018-01] |
A61K 9/0078 | . . . . | {for inhalation via a nebulizer such as a jet nebulizer, ultrasonic nebulizer, e.g. in the form of aqueous drug solutions or dispersions} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/008 | . . . . | {comprising drug dissolved or suspended in liquid propellant for inhalation via a pressurized metered dose inhaler [MDI]} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/0082 | . . . | {Lung surfactant, artificial mucus} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/0085 | . . | {Brain, e.g. brain implants; Spinal cord} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/0087 | . | {Galenical forms not covered by A61K 9/02 - A61K 9/7023} [2016-05] |
A61K 9/009 | . . | {Sachets, pouches characterised by the material or function of the envelope (with gastric retention A61K 9/0065; sachets which are not administered but function merely as a container are classified according to the content, e.g. sachets comprising powder for reconstitution of a drink A61K 9/0095)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/0092 | . . | {Hollow drug-filled fibres, tubes of the core-shell type, coated fibres, coated rods, microtubules or nanotubes} [2021-05] |
A61K 9/0095 | . . | {Drinks; Beverages; Syrups; Compositions for reconstitution thereof, e.g. powders or tablets to be dispersed in a glass of water; Veterinary drenches (A61K 9/0007 takes precedence; eatable gels or foams A61K 9/0056; oral mucosa adhesive forms A61K 9/006)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/0097 | . . | {Micromachined devices; Microelectromechanical systems [MEMS]; Devices obtained by lithographic treatment of silicon; Devices comprising chips (intradermal microneedle arrays A61K 9/0021; MEMS in general B81B 7/02)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/02 | . | Suppositories; Bougies; Bases therefor; {Ovules}(apparatus for making A61J 3/08; devices for introducing into the body A61M 31/00) [2013-01] |
A61K 9/025 | . . | {characterised by shape or structure, e.g. hollow layered, coated} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/06 | . | Ointments; Bases therefor; {Other semi-solid forms, e.g. creams, sticks, gels (composition of ointments, creams or gels A61K 47/00)} [2020-01] |
A61K 9/08 | . |
A61K 9/10 | . | Dispersions; Emulsions {(A61K 9/06 takes precedence; composition of dispersions, emulsions A61K 47/00)} [2020-01] |
A61K 9/107 | . . |
A61K 9/1075 | . . . | {Microemulsions or submicron emulsions; Preconcentrates or solids thereof; Micelles, e.g. made of phospholipids or block copolymers (A61K 9/0026 takes precedence)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/113 | . . . |
A61K 9/12 | . . | Aerosols; Foams {(A61K 9/0043, A61K 9/0056, A61K 9/006, A61K 9/0073 take precedence; spray-films A61K 9/7015)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/122 | . . . | {Foams; Dry foams (edible foams A61K 9/0056)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/124 | . . . | {characterised by the propellant} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/127 | . . | Synthetic bilayered vehicles, e.g. liposomes or liposomes with cholesterol as the only non-phosphatidyl surfactant [2025-01] |
A61K 9/1271 | . . . | Non-conventional liposomes, e.g. PEGylated liposomes or liposomes coated or grafted with polymers (liposomes as conjugates {A61K 47/6911}) [2025-01] |
A61K 9/1272 | . . . . | comprising non-phosphatidyl surfactants as bilayer-forming substances, e.g. cationic lipids or non-phosphatidyl liposomes coated or grafted with polymers (lipids as modifying agents {A61K 47/543}) [2025-01] |
A61K 9/1273 | . . . . | Polymersomes; Liposomes with polymerisable or polymerised bilayer-forming substances [2025-01] |
A61K 9/1274 | . . . | Non-vesicle bilayer structures, e.g. liquid crystals, tubules, cubic phases or cochleates; Sponge phases [2025-01] |
A61K 9/1275 | . . . | Lipoproteins or protein-free species thereof, e.g. chylomicrons; Artificial high-density lipoproteins [HDL], low-density lipoproteins [LDL] or very-low-density lipoproteins [VLDL]; Precursors thereof [2025-01] |
A61K 9/1276 | . . . | Globules of milk; Constituents thereof [2025-01] |
A61K 9/1277 | . . . | Preparation processes; Proliposomes [2025-01] |
A61K 9/1278 | . . . . | Post-loading, e.g. by ion or pH gradient [2025-01] |
A61K 9/14 | . |
A61K 9/141 | . . | {Intimate drug-carrier mixtures characterised by the carrier, e.g. ordered mixtures, adsorbates, solid solutions, eutectica, co-dried, co-solubilised, co-kneaded, co-milled, co-ground products, co-precipitates, co-evaporates, co-extrudates, co-melts; Drug nanoparticles with adsorbed surface modifiers ((co) spray-dried products A61K 9/16, (co) lyophilised products A61K 9/19; the carrier being chemically bound to the active ingredient A61K 47/50)} [2017-08] |
A61K 9/143 | . . . | {with inorganic compounds} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/145 | . . . | {with organic compounds} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/146 | . . . | {with organic macromolecular compounds} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/148 | . . . | {with compounds of unknown constitution, e.g. material from plants or animals (with oils, fats, waxes, shellac A61K 9/145)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/16 | . . | Agglomerates; Granulates; Microbeadlets {; Microspheres; Pellets; Solid products obtained by spray drying, spray freeze drying, spray congealing,(multiple) emulsion solvent evaporation or extraction (A61K 9/20 takes precedence if the final form is a tablet; microspheres with drug-free outer coating, microcapsules A61K 9/50; mixture of different granules, microcapsules, (coated) microparticles A61K 9/5084; nanoparticles A61K 9/51)} [2017-08] |
A61K 9/1605 | . . . | {Excipients; Inactive ingredients} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/1611 | . . . . | {Inorganic compounds} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/1617 | . . . . | {Organic compounds, e.g. phospholipids, fats} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/1623 | . . . . . | {Sugars or sugar alcohols, e.g. lactose; Derivatives thereof; Homeopathic globules} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/1629 | . . . . | {Organic macromolecular compounds} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/1635 | . . . . . | {obtained by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polyvinyl pyrrolidone, poly(meth)acrylates} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/1641 | . . . . . | {obtained otherwise than by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polyethylene glycol, poloxamers} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/1647 | . . . . . . | {Polyesters, e.g. poly(lactide-co-glycolide)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/1652 | . . . . . | {Polysaccharides, e.g. alginate, cellulose derivatives; Cyclodextrin (homeopathic globules A61K 9/1623)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/1658 | . . . . . | {Proteins, e.g. albumin, gelatin} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/1664 | . . . . | {Compounds of unknown constitution, e.g. material from plants or animals (oils, fats, waxes, shellac A61K 9/1617)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/167 | . . . | {with an outer layer or coating comprising drug; with chemically bound drugs or non-active substances on their surface (with further drug-free outer coating A61K 9/5073)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/1676 | . . . . | {having a drug-free core with discrete complete coating layer containing drug (adsorbates of liquid drug formulations on inert powders without simultaneous granulation step A61K 9/141; with further drug-free outer coating A61K 9/5078; drug conjugated to non-active particles A61K 47/6921)} [2017-08] |
A61K 9/1682 | . . . | {Processes} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/1688 | . . . . | {resulting in pure drug agglomerate optionally containing up to 5% of excipient} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/1694 | . . . . | {resulting in granules or microspheres of the matrix type containing more than 5% of excipient} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/19 | . . | lyophilised {, i.e. freeze-dried, solutions or dispersions (lyophilised products with subsequent particle size reduction A61K 9/14; granules or pellets made by lyphilisation A61K 9/1682; solid oral dosage forms made by lyophilisation A61K 9/2095; lyophilisation additives A61K 47/00)} [2017-08] |
A61K 9/20 | . | Pills, tablets, {discs, rods (A61K 9/0004, A61K 9/0007, A61K 9/0056, A61K 9/0065 take precedence; for reconstitution of a drink A61K 9/0095)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/2004 | . . | {Excipients; Inactive ingredients} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/2009 | . . . | {Inorganic compounds} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/2013 | . . . | {Organic compounds, e.g. phospholipids, fats} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/2018 | . . . . | {Sugars, or sugar alcohols, e.g. lactose, mannitol; Derivatives thereof, e.g. polysorbates} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/2022 | . . . | {Organic macromolecular compounds} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/2027 | . . . . | {obtained by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polyvinyl pyrrolidone, poly(meth)acrylates} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/2031 | . . . . | {obtained otherwise than by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polyethylene glycol, polyethylene oxide, poloxamers} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/2036 | . . . . . | {Silicones; Polysiloxanes} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/204 | . . . . . | {Polyesters, e.g. poly(lactide-co-glycolide)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/2045 | . . . . . | {Polyamides; Polyaminoacids, e.g. polylysine} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/205 | . . . . | {Polysaccharides, e.g. alginate, gums; Cyclodextrin} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/2054 | . . . . . | {Cellulose; Cellulose derivatives, e.g. hydroxypropyl methylcellulose} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/2059 | . . . . . | {Starch, including chemically or physically modified derivatives; Amylose; Amylopectin; Dextrin} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/2063 | . . . . | {Proteins, e.g. gelatin} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/2068 | . . . | {Compounds of unknown constitution, e.g. material from plants or animals (oils, fats, waxes, shellac A61K 9/2013)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/2072 | . . | {characterised by shape, structure or size; Tablets with holes, special break lines or identification marks; Partially coated tablets; Disintegrating flat shaped forms (A61K 9/0004, A61K 9/0056, A61K 9/0065 take precedence)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/2077 | . . . | {Tablets comprising drug-containing microparticles in a substantial amount of supporting matrix; Multiparticulate tablets} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/2081 | . . . . | {with microcapsules or coated microparticles according to A61K 9/50} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/2086 | . . . | {Layered tablets, e.g. bilayer tablets; Tablets of the type inert core-active coat (active cores with a complete drug-free outer coat A61K 9/28)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/209 | . . . . | {containing drug in at least two layers or in the core and in at least one outer layer} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/2095 | . . | {Tabletting processes; Dosage units made by direct compression of powders or specially processed granules, by eliminating solvents, by melt-extrusion, by injection molding, by 3D printing (mechanical aspects A61J 3/00)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/28 | . . | Dragees; Coated pills or tablets {, e.g. with film or compression coating (A61K 9/2072 takes precedence, e.g. partially coated tablets A61K 9/2072, coated multilayer tablets A61K 9/2086, tablets with drug-coated core A61K 9/209)} [2016-08] |
A61K 9/2806 | . . . | {Coating materials} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/2813 | . . . . | {Inorganic compounds} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/282 | . . . . | {Organic compounds, e.g. fats} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/2826 | . . . . . | {Sugars or sugar alcohols, e.g. sucrose; Derivatives thereof} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/2833 | . . . . | {Organic macromolecular compounds} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/284 | . . . . . | {obtained by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polyvinyl pyrrolidone} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/2846 | . . . . . . | {Poly(meth)acrylates} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/2853 | . . . . . | {obtained otherwise than by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polyethylene glycol, polyethylene oxide, poloxamers, poly(lactide-co-glycolide)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/286 | . . . . . | {Polysaccharides, e.g. gums; Cyclodextrin} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/2866 | . . . . . . | {Cellulose; Cellulose derivatives, e.g. hydroxypropyl methylcellulose} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/2873 | . . . . . | {Proteins, e.g. gelatin} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/288 | . . . . | {Compounds of unknown constitution, e.g. material from plants or animals (oils, fats, waxes, shellac A61K 9/282)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/2886 | . . . | {having two or more different drug-free coatings; Tablets of the type inert core-drug layer-inactive layer (of the type active core-drug layer-inactive layer A61K 9/209)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/2893 | . . . | {Tablet coating processes (mechanical aspects A61J 3/06)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/48 | . | Preparations in capsules, e.g. of gelatin, of chocolate {(A61K 9/0004 takes precedence; bite capsules A61K 9/0056)} [2017-08] |
A61K 9/4808 | . . | {characterised by the form of the capsule or the structure of the filling; Capsules containing small tablets; Capsules with outer layer for immediate drug release (capsules filled with granules or microparticles A61K 9/16; filled with microcapsules or coated microparticles A61K 9/50; with mixture of different granules, microcapsules, (coated) microparticles A61K 9/5084)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/4816 | . . | {Wall or shell material} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/4825 | . . . | {Proteins, e.g. gelatin (gelatin capsule shells with substantial amounts of other macromolecular substances A61K 9/4816)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/4833 | . . | {Encapsulating processes; Filling of capsules (mechanical aspects A61J 3/07)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/4841 | . . | {Filling excipients; Inactive ingredients} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/485 | . . . | {Inorganic compounds} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/4858 | . . . | {Organic compounds} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/4866 | . . . | {Organic macromolecular compounds} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/4875 | . . . | {Compounds of unknown constitution, e.g. material from plants or animals (oils, fats, waxes, shellac A61K 9/4858)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/4883 | . . | {Capsule finishing, e.g. dyeing, aromatising, polishing} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/4891 | . . | {Coated capsules; Multilayered drug free capsule shells (with drug coating for immediate release A61K 9/4808; osmotic devices A61K 9/0004)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/50 | . . | Microcapsules {having a gas, liquid or semi-solid filling; Solid microparticles or pellets surrounded by a distinct coating layer, e.g. coated microspheres, coated drug crystals (A61K 9/2081 takes precedence; particles with a single coating comprising drug A61K 9/167)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/5005 | . . . | {Wall or coating material} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/501 | . . . . | {Inorganic compounds} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/5015 | . . . . | {Organic compounds, e.g. fats, sugars} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/5021 | . . . . | {Organic macromolecular compounds} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/5026 | . . . . . | {obtained by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polyvinyl pyrrolidone, poly(meth)acrylates} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/5031 | . . . . . | {obtained otherwise than by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polyethylene glycol, poly(lactide-co-glycolide)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/5036 | . . . . . | {Polysaccharides, e.g. gums, alginate; Cyclodextrin} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/5042 | . . . . . . | {Cellulose; Cellulose derivatives, e.g. phthalate or acetate succinate esters of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/5047 | . . . . . . . | {Cellulose ethers containing no ester groups, e.g. hydroxypropyl methylcellulose} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/5052 | . . . . . | {Proteins, e.g. albumin} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/5057 | . . . . . . | {Gelatin} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/5063 | . . . . | {Compounds of unknown constitution, e.g. material from plants or animals (oils, fats, waxes, shellac A61K 9/5015)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/5068 | . . . . . | {Cell membranes or bacterial membranes enclosing drugs (with additional exogenous lipids A61K 9/127; virus envelopes A61K 9/5184)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/5073 | . . . | {having two or more different coatings optionally including drug-containing subcoatings} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/5078 | . . . . | {with drug-free core} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/5084 | . . . | {Mixtures of one or more drugs in different galenical forms, at least one of which being granules, microcapsules or (coated) microparticles according to A61K 9/16 or A61K 9/50, e.g. for obtaining a specific release pattern or for combining different drugs (tablets containing such a mixture A61K 9/2077)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/5089 | . . . | {Processes} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/5094 | . . . | {Microcapsules containing magnetic carrier material, e.g. ferrite for drug targeting} [2018-01] |
A61K 9/51 | . . . | Nanocapsules; {Nanoparticles; (nanotubes A61K 9/0092; polymeric micelles A61K 9/1075; polymersomes A61K 9/1273; pure drug nanoparticles A61K 9/14; drug nanoparticles with adsorbed surface modifiers A61K 9/141; conjugates, e.g. between drug and non-active nanoparticles, A61K 47/50; preparations for in vivo diagnosis A61K 49/00; with radioactive substances A61K 51/00)} [2017-08] |
A61K 9/5107 | . . . . | {Excipients; Inactive ingredients} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/5115 | . . . . . | {Inorganic compounds} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/5123 | . . . . . | {Organic compounds, e.g. fats, sugars} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/513 | . . . . . | {Organic macromolecular compounds; Dendrimers} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/5138 | . . . . . . | {obtained by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polyvinyl pyrrolidone, poly(meth)acrylates} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/5146 | . . . . . . | {obtained otherwise than by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polyethylene glycol, polyamines, polyanhydrides} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/5153 | . . . . . . . | {Polyesters, e.g. poly(lactide-co-glycolide)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/5161 | . . . . . . | {Polysaccharides, e.g. alginate, chitosan, cellulose derivatives; Cyclodextrin} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/5169 | . . . . . . | {Proteins, e.g. albumin, gelatin} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/5176 | . . . . . | {Compounds of unknown constitution, e.g. material from plants or animals (oils, fats, waxes, shellac A61K 9/5123)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/5184 | . . . . . . | {Virus capsids or envelopes enclosing drugs (with additional exogenous lipids A61K 9/127; bacterial membranes A61K 9/5068)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/5192 | . . . . | {Processes} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/70 | . | Web, sheet or filament bases {; Films; Fibres of the matrix type containing drug (hollow drug-filled fibres A61K 9/0092)} [2021-05] |
A61K 9/7007 | . . | {Drug-containing films, membranes or sheets (A61K 9/0041, A61K 9/0043, A61K 9/006, A61K 9/0063 take precedence)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/7015 | . . | {Drug-containing film-forming compositions, e.g. spray-on} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/7023 | . . | {Transdermal patches and similar drug-containing composite devices, e.g. cataplasms (galenical aspects of iontophoretic devices A61K 9/0009; microneedle arrays A61K 9/0021; buccal patches A61K 9/006)} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/703 | . . . | {characterised by shape or structure; Details concerning release liner or backing; Refillable patches; User-activated patches} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/7038 | . . . . | {Transdermal patches of the drug-in-adhesive type, i.e. comprising drug in the skin-adhesive layer} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/7046 | . . . . . | {the adhesive comprising macromolecular compounds} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/7053 | . . . . . . | {obtained by reactions only involving carbon to carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polyvinyl, polyisobutylene, polystyrene} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/7061 | . . . . . . . | {Polyacrylates} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/7069 | . . . . . . | {obtained otherwise than by reactions only involving carbon to carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polysiloxane, polyesters, polyurethane, polyethylene oxide} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/7076 | . . . . . | {the adhesive comprising ingredients of undetermined constitution or reaction products thereof, e.g. rosin or other plant resins} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/7084 | . . . . | {Transdermal patches having a drug layer or reservoir, and one or more separate drug-free skin-adhesive layers, e.g. between drug reservoir and skin, or surrounding the drug reservoir; Liquid-filled reservoir patches} [2013-01] |
A61K 9/7092 | . . . . | {Transdermal patches having multiple drug layers or reservoirs, e.g. for obtaining a specific release pattern, or for combining different drugs} [2013-01] |
| A61K 31/00 | Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients [2023-05] NOTES
|
A61K 31/01 | . | Hydrocarbons [2013-01] |
A61K 31/015 | . . | carbocyclic [2013-01] |
A61K 31/02 | . | Halogenated hydrocarbons [2013-01] |
A61K 31/025 | . . | carbocyclic [2013-01] |
A61K 31/03 | . . . | aromatic [2013-01] |
A61K 31/035 | . . | having aliphatic unsaturation [2013-01] |
A61K 31/04 | . | Nitro compounds [2013-01] |
A61K 31/045 | . | Hydroxy compounds, e.g. alcohols; Salts thereof, e.g. alcoholates [2013-01] |
A61K 31/047 | . . | having two or more hydroxy groups, e.g. sorbitol [2013-01] |
| A61K 31/05 | . . | WARNING
|
A61K 31/055 | . . . | the aromatic ring being substituted by halogen [2013-01] |
A61K 31/06 | . . . | the aromatic ring being substituted by nitro groups [2013-01] |
A61K 31/065 | . . | Diphenyl-substituted acyclic alcohols [2013-01] |
A61K 31/07 | . . |
A61K 31/075 | . | Ethers or acetals [2013-01] |
A61K 31/08 | . . | acyclic, e.g. paraformaldehyde [2013-01] |
A61K 31/085 | . . | having an ether linkage to aromatic ring nuclear carbon [2013-01] |
A61K 31/09 | . . . | having two or more such linkages [2013-01] |
A61K 31/095 | . | Sulfur, selenium, or tellurium compounds, e.g. thiols [2013-01] |
A61K 31/10 | . . | Sulfides; Sulfoxides; Sulfones [2013-01] |
A61K 31/105 | . . |
A61K 31/11 | . | Aldehydes [2013-01] |
A61K 31/115 | . . | Formaldehyde [2013-01] |
A61K 31/12 | . | Ketones [2013-01] |
A61K 31/121 | . . | acyclic [2013-01] |
A61K 31/122 | . . | having the oxygen directly attached to a ring, e.g. quinones, vitamin K1, anthralin [2013-01] |
A61K 31/125 | . . . | Camphor; Nuclear substituted derivatives thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 31/13 | . |
A61K 31/131 | . . | acyclic [2017-08] |
A61K 31/132 | . . | having two or more amino groups, e.g. spermidine, putrescine [2013-01] |
A61K 31/133 | . . | having hydroxy groups, e.g. sphingosine [2013-01] |
A61K 31/135 | . . |
A61K 31/136 | . . . | having the amino group directly attached to the aromatic ring, e.g. benzeneamine [2013-01] |
A61K 31/137 | . . . | Arylalkylamines, e.g. amphetamine, epinephrine, salbutamol, ephedrine {or methadone} [2017-08] |
A61K 31/138 | . . . | Aryloxyalkylamines, e.g. propranolol, tamoxifen, phenoxybenzamine (atenolol A61K 31/165; pindolol A61K 31/404; timolol A61K 31/5377) [2017-08] |
A61K 31/14 | . . |
A61K 31/145 | . . | having sulfur, e.g. thiurams (>N—C(S)—S—C(S)—N< and >N—C(S)—S—S—C(S)—N<), Sulfinylamines (—N=SO), Sulfonylamines (—N=SO2) (isothiourea A61K 31/155) [2017-08] |
A61K 31/15 | . . | Oximes (>C=N—O—); Hydrazines (>N—N<); Hydrazones (>N—N=) {; Imines (C—N=C)} [2017-08] |
A61K 31/155 | . . | Amidines ( 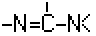 ), e.g. guanidine (H2N—C(=NH)—NH2), isourea (N=C(OH)—NH2), isothiourea (—N=C(SH)—NH2) [2017-08] ), e.g. guanidine (H2N—C(=NH)—NH2), isourea (N=C(OH)—NH2), isothiourea (—N=C(SH)—NH2) [2017-08] |
A61K 31/16 | . | Amides, e.g. hydroxamic acids [2013-01] |
A61K 31/164 | . . | of a carboxylic acid with an aminoalcohol, e.g. ceramides [2017-08] |
A61K 31/165 | . . | having aromatic rings, e.g. colchicine, atenolol, progabide [2013-01] |
A61K 31/166 | . . . | having the carbon of a carboxamide group directly attached to the aromatic ring, e.g. procainamide, procarbazine, metoclopramide, labetalol [2013-01] |
A61K 31/167 | . . . | having the nitrogen of a carboxamide group directly attached to the aromatic ring, e.g. lidocaine, paracetamol [2013-01] |
A61K 31/17 | . . | having the group >N—C(O)—N< or >N—C(S)—N<, e.g. urea, thiourea, carmustine (isoureas, isothioureas A61K 31/155; sulfonylureas A61K 31/64) [2017-08] |
A61K 31/175 | . . . | having the group 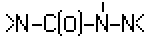 , >N—C(O)—N=N— or , >N—C(O)—N=N— or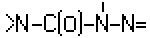 , e.g. carbonohydrazides, carbazones, semicarbazides, semicarbazones; Thioanalogues thereof [2017-08] , e.g. carbonohydrazides, carbazones, semicarbazides, semicarbazones; Thioanalogues thereof [2017-08] |
A61K 31/18 | . . |
| A61K 31/185 | . | Acids; Anhydrides, halides or salts thereof, e.g. sulfur acids, imidic, hydrazonic or hydroximic acids (hydroxamic acids A61K 31/16; peroxy acids A61K 31/327) [2023-05] NOTE
|
A61K 31/19 | . . |
A61K 31/191 | . . . | having two or more hydroxy groups, e.g. gluconic acid [2013-01] |
| A61K 31/192 | . . . | having aromatic groups, e.g. sulindac, 2-aryl-propionic acids, ethacrynic acid {(cannabinoids A61K 31/658)} [2023-05] WARNING
|
A61K 31/194 | . . . | having two or more carboxyl groups, e.g. succinic, maleic or phthalic acid [2013-01] |
A61K 31/195 | . . . | having an amino group [2013-01] |
A61K 31/196 | . . . . | the amino group being directly attached to a ring, e.g. anthranilic acid, mefenamic acid, diclofenac, chlorambucil [2013-01] |
A61K 31/197 | . . . . | the amino and the carboxyl groups being attached to the same acyclic carbon chain, e.g. gamma-aminobutyric acid [GABA], beta-alanine, epsilon-aminocaproic acid or pantothenic acid (carnitine A61K 31/205) [2024-01] |
A61K 31/198 | . . . . . | Alpha-amino acids, e.g. alanine or edetic acid [EDTA] (betaine A61K 31/205; proline A61K 31/401; tryptophan A61K 31/405; histidine A61K 31/4172; peptides not degraded to individual amino acids A61K 38/00) [2024-01] |
A61K 31/20 | . . . | having a carboxyl group bound to a chain of seven or more carbon atoms, e.g. stearic, palmitic, arachidic acids [2013-01] |
A61K 31/201 | . . . . | having one or two double bonds, e.g. oleic, linoleic acids [2013-01] |
A61K 31/202 | . . . . | having three or more double bonds, e.g. linolenic (eicosanoids, e.g. leukotrienes A61K 31/557) [2013-01] |
A61K 31/203 | . . . . | Retinoic acids {; Salts thereof} [2023-08] |
A61K 31/205 | . . | Amine addition salts of organic acids; Inner quaternary ammonium salts, e.g. betaine, carnitine [2013-01] |
A61K 31/21 | . | Esters, e.g. nitroglycerine, selenocyanates [2013-01] |
A61K 31/215 | . . | of carboxylic acids [2013-01] |
A61K 31/216 | . . . | of acids having aromatic rings, e.g. benactizyne, clofibrate [2013-01] |
A61K 31/22 | . . . | of acyclic acids, e.g. pravastatin [2013-01] |
A61K 31/221 | . . . . | with compounds having an amino group, e.g. acetylcholine, acetylcarnitine [2013-01] |
A61K 31/222 | . . . . | with compounds having aromatic groups, e.g. dipivefrine, ibopamine [2013-01] |
A61K 31/223 | . . . . | of alpha-aminoacids [2013-01] |
A61K 31/225 | . . . . | Polycarboxylic acids [2013-01] |
A61K 31/23 | . . . . | of acids having a carboxyl group bound to a chain of seven or more carbon atoms [2013-01] |
A61K 31/231 | . . . . . | having one or two double bonds [2013-01] |
A61K 31/232 | . . . . . | having three or more double bonds, e.g. etretinate [2013-01] |
A61K 31/235 | . . . | having an aromatic ring attached to a carboxyl group [2013-01] |
A61K 31/24 | . . . . | having an amino or nitro group [2013-01] |
A61K 31/245 | . . . . . |
A61K 31/25 | . . . | with polyoxyalkylated alcohols, e.g. esters of polyethylene glycol [2013-01] |
A61K 31/255 | . . | of sulfoxy acids or sulfur analogues thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 31/26 | . . | Cyanate or isocyanate esters; Thiocyanate or isothiocyanate esters [2017-08] |
A61K 31/265 | . . | of carbonic, thiocarbonic, or thiocarboxylic acids, e.g. thioacetic acid, xanthogenic acid, trithiocarbonic acid [2013-01] |
A61K 31/27 | . . | of carbamic or thiocarbamic acids, meprobamate, carbachol, neostigmine [2013-01] |
A61K 31/275 | . | Nitriles; Isonitriles [2013-01] |
A61K 31/277 | . . | having a ring, e.g. verapamil [2013-01] |
A61K 31/28 | . | Compounds containing heavy metals [2013-01] |
A61K 31/282 | . . | Platinum compounds [2013-01] |
A61K 31/285 | . . | Arsenic compounds [2013-01] |
A61K 31/29 | . . | Antimony or bismuth compounds [2013-01] |
A61K 31/295 | . . | Iron group metal compounds [2013-01] |
A61K 31/30 | . . | Copper compounds [2013-01] |
A61K 31/305 | . . | Mercury compounds [2013-01] |
A61K 31/31 | . . . | containing nitrogen [2013-01] |
A61K 31/315 | . . | Zinc compounds [2013-01] |
A61K 31/32 | . . | Tin compounds [2013-01] |
A61K 31/325 | . |
A61K 31/327 | . | Peroxy compounds, e.g. hydroperoxides, peroxides, peroxyacids [2013-01] |
A61K 31/33 | . | Heterocyclic compounds [2013-01] |
A61K 31/335 | . . | having oxygen as the only ring hetero atom, e.g. fungichromin [2013-01] |
A61K 31/336 | . . . | having three-membered rings, e.g. oxirane, fumagillin [2013-01] |
A61K 31/337 | . . . | having four-membered rings, e.g. taxol [2013-01] |
A61K 31/34 | . . . | having five-membered rings with one oxygen as the only ring hetero atom, e.g. isosorbide [2013-01] |
A61K 31/341 | . . . . | not condensed with another ring, e.g. ranitidine, furosemide, bufetolol, muscarine [2013-01] |
A61K 31/343 | . . . . | condensed with a carbocyclic ring, e.g. coumaran, bufuralol, befunolol, clobenfurol, amiodarone [2013-01] |
A61K 31/345 | . . . . |
A61K 31/35 | . . . | having six-membered rings with one oxygen as the only ring hetero atom [2013-01] |
A61K 31/351 | . . . . | not condensed with another ring [2013-01] |
| A61K 31/352 | . . . . | WARNING
|
A61K 31/353 | . . . . . | 3,4-Dihydrobenzopyrans, e.g. chroman, catechin [2013-01] |
A61K 31/355 | . . . . . . | Tocopherols, e.g. vitamin E [2013-01] |
A61K 31/357 | . . . | having two or more oxygen atoms in the same ring, e.g. crown ethers, guanadrel [2013-01] |
A61K 31/36 | . . . . | Compounds containing methylenedioxyphenyl groups, e.g. sesamin [2014-02] |
A61K 31/365 | . . . | Lactones [2013-01] |
A61K 31/366 | . . . . | having six-membered rings, e.g. delta-lactones [2013-01] |
A61K 31/37 | . . . . . | Coumarins, e.g. psoralen [2013-01] |
A61K 31/375 | . . . . | Ascorbic acid, i.e. vitamin C; Salts thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 31/38 | . . | having sulfur as a ring hetero atom [2013-01] |
A61K 31/381 | . . . | having five-membered rings [2013-01] |
A61K 31/382 | . . . |
A61K 31/385 | . . . | having two or more sulfur atoms in the same ring [2013-01] |
A61K 31/39 | . . . | having oxygen in the same ring [2013-01] |
A61K 31/395 | . . | having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins [2022-01] |
A61K 31/396 | . . . | having three-membered rings, e.g. aziridine [2016-11] |
A61K 31/397 | . . . | having four-membered rings, e.g. azetidine [2013-01] |
A61K 31/40 | . . . | having five-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom, e.g. sulpiride, succinimide, tolmetin, buflomedil [2013-01] |
A61K 31/401 | . . . . | Proline; Derivatives thereof, e.g. captopril [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4015 | . . . . | having oxo groups directly attached to the heterocyclic ring, e.g. piracetam, ethosuximide [2013-01] |
A61K 31/402 | . . . . | 1-aryl substituted, e.g. piretanide [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4025 | . . . . | not condensed and containing further heterocyclic rings, e.g. cromakalim [2013-01] |
A61K 31/403 | . . . . | condensed with carbocyclic rings, e.g. carbazole [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4035 | . . . . . | Isoindoles, e.g. phthalimide [2013-01] |
A61K 31/404 | . . . . . | Indoles, e.g. pindolol [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4045 | . . . . . . | Indole-alkylamines; Amides thereof, e.g. serotonin, melatonin [2013-01] |
A61K 31/405 | . . . . . . | Indole-alkanecarboxylic acids; Derivatives thereof, e.g. tryptophan, indomethacin [2013-01] |
A61K 31/407 | . . . . | condensed with other heterocyclic ring systems, e.g. ketorolac, physostigmine [2013-01] |
A61K 31/409 | . . . . | having four such rings, e.g. porphine derivatives, bilirubin, biliverdine (hemin, hematin A61K 31/555) [2017-08] |
A61K 31/41 | . . . | having five-membered rings with two or more ring hetero atoms, at least one of which being nitrogen, e.g. tetrazole [2013-01] |
A61K 31/415 | . . . . | 1,2-Diazoles [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4152 | . . . . . | having oxo groups directly attached to the heterocyclic ring, e.g. antipyrine, phenylbutazone, sulfinpyrazone [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4155 | . . . . . | non condensed and containing further heterocyclic rings [2013-01] |
A61K 31/416 | . . . . . | condensed with carbocyclic ring systems, e.g. indazole [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4162 | . . . . . | condensed with heterocyclic ring systems [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4164 | . . . . | 1,3-Diazoles [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4166 | . . . . . | having oxo groups directly attached to the heterocyclic ring, e.g. phenytoin [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4168 | . . . . . | having a nitrogen attached in position 2, e.g. clonidine [2013-01] |
A61K 31/417 | . . . . . | Imidazole-alkylamines, e.g. histamine, phentolamine [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4172 | . . . . . | Imidazole-alkanecarboxylic acids, e.g. histidine [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4174 | . . . . . | Arylalkylimidazoles, e.g. oxymetazolin, naphazoline, miconazole [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4178 | . . . . . | not condensed 1,3-diazoles and containing further heterocyclic rings, e.g. pilocarpine, nitrofurantoin [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4184 | . . . . . | condensed with carbocyclic rings, e.g. benzimidazoles [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4188 | . . . . . | condensed with other heterocyclic ring systems, e.g. biotin, sorbinil [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4192 | . . . . | 1,2,3-Triazoles [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4196 | . . . . | 1,2,4-Triazoles [2013-01] |
A61K 31/42 | . . . . | Oxazoles [2013-01] |
A61K 31/421 | . . . . . | 1,3-Oxazoles, e.g. pemoline, trimethadione [2013-01] |
A61K 31/422 | . . . . . | not condensed and containing further heterocyclic rings [2013-01] |
A61K 31/423 | . . . . . | condensed with carbocyclic rings [2013-01] |
A61K 31/424 | . . . . . | condensed with heterocyclic ring systems, e.g. clavulanic acid [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4245 | . . . . | Oxadiazoles [2013-01] |
A61K 31/425 | . . . . | Thiazoles [2013-01] |
A61K 31/426 | . . . . . | 1,3-Thiazoles [2013-01] |
A61K 31/427 | . . . . . | not condensed and containing further heterocyclic rings [2013-01] |
A61K 31/428 | . . . . . | condensed with carbocyclic rings [2013-01] |
A61K 31/429 | . . . . . | condensed with heterocyclic ring systems [2013-01] |
A61K 31/43 | . . . . . . | Compounds containing 4-thia-1-azabicyclo [3.2.0] heptane ring systems, i.e. compounds containing a ring system of the formula 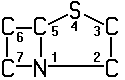 , e.g. penicillins, penems [2016-08] , e.g. penicillins, penems [2016-08] |
A61K 31/431 | . . . . . . . | containing further heterocyclic rings, e.g. ticarcillin, azlocillin, oxacillin [2013-01] |
A61K 31/433 | . . . . | Thidiazoles [2013-01] |
A61K 31/435 | . . . | having six-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4353 | . . . . | ortho- or peri-condensed with heterocyclic ring systems [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4355 | . . . . . | the heterocyclic ring system containing a five-membered ring having oxygen as a ring hetero atom [2013-01] |
A61K 31/436 | . . . . . | the heterocyclic ring system containing a six-membered ring having oxygen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. rapamycin [2016-11] |
A61K 31/4365 | . . . . . | the heterocyclic ring system having sulfur as a ring hetero atom, e.g. ticlopidine [2013-01] |
A61K 31/437 | . . . . . | the heterocyclic ring system containing a five-membered ring having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. indolizine, beta-carboline [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4375 | . . . . . | the heterocyclic ring system containing a six-membered ring having nitrogen as a ring heteroatom, e.g. quinolizines, naphthyridines, berberine, vincamine [2013-01] |
A61K 31/438 | . . . . | The ring being spiro-condensed with carbocyclic or heterocyclic ring systems [2019-05] |
A61K 31/439 | . . . . | the ring forming part of a bridged ring system, e.g. quinuclidine (8-azabicyclo [3.2.1] octanes A61K 31/46) [2013-01] |
A61K 31/44 | . . . . | Non condensed pyridines; Hydrogenated derivatives thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4402 | . . . . . | only substituted in position 2, e.g. pheniramine, bisacodyl [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4406 | . . . . . |
A61K 31/4409 | . . . . . | only substituted in position 4, e.g. isoniazid, iproniazid [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4412 | . . . . . | having oxo groups directly attached to the heterocyclic ring [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4415 | . . . . . |
A61K 31/4418 | . . . . . | having a carbocyclic group directly attached to the heterocyclic ring, e.g. cyproheptadine [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4422 | . . . . . | 1,4-Dihydropyridines, e.g. nifedipine, nicardipine [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4425 | . . . . . | Pyridinium derivatives, e.g. pralidoxime, pyridostigmine [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4427 | . . . . . | containing further heterocyclic ring systems [2013-01] |
A61K 31/443 | . . . . . . | containing a five-membered ring with oxygen as a ring hetero atom [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4433 | . . . . . . | containing a six-membered ring with oxygen as a ring hetero atom [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4436 | . . . . . . | containing a heterocyclic ring having sulfur as a ring hetero atom [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4439 | . . . . . . | containing a five-membered ring with nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. omeprazole (nicotine A61K 31/465) [2013-01] |
A61K 31/444 | . . . . . . | containing a six-membered ring with nitrogen as a ring heteroatom, e.g. amrinone [2013-01] |
A61K 31/445 | . . . . . | Non condensed piperidines, e.g. piperocaine [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4453 | . . . . . . | only substituted in position 1, e.g. propipocaine, diperodon [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4458 | . . . . . . | only substituted in position 2, e.g. methylphenidate [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4462 | . . . . . . | only substituted in position 3 [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4465 | . . . . . . | only substituted in position 4 [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4468 | . . . . . . | having a nitrogen directly attached in position 4, e.g. clebopride, fentanyl [2013-01] |
A61K 31/45 | . . . . . . | having oxo groups directly attached to the heterocyclic ring, e.g. cycloheximide [2013-01] |
A61K 31/451 | . . . . . . | having a carbocyclic group directly attached to the heterocyclic ring, e.g. glutethimide, meperidine, loperamide, phencyclidine, piminodine [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4515 | . . . . . . |
A61K 31/452 | . . . . . . |
A61K 31/4523 | . . . . . . | containing further heterocyclic ring systems [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4525 | . . . . . . . | containing a five-membered ring with oxygen as a ring hetero atom [2013-01] |
A61K 31/453 | . . . . . . . | containing a six-membered ring with oxygen as a ring hetero atom [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4535 | . . . . . . . | containing a heterocyclic ring having sulfur as a ring hetero atom, e.g. pizotifen [2013-01] |
A61K 31/454 | . . . . . . . | containing a five-membered ring with nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. pimozide, domperidone [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4545 | . . . . . . . | containing a six-membered ring with nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. pipamperone, anabasine [2013-01] |
A61K 31/455 | . . . . . | Nicotinic acids, e.g. niacin; Derivatives thereof, e.g. esters, amides [2013-01] |
A61K 31/46 | . . . . | 8-Azabicyclo [3.2.1] octane; Derivatives thereof, e.g. atropine, cocaine [2013-01] |
A61K 31/465 | . . . . | Nicotine; Derivatives thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 31/47 | . . . . | Quinolines; Isoquinolines [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4704 | . . . . . | 2-Quinolinones, e.g. carbostyril [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4706 | . . . . . | 4-Aminoquinolines; 8-Aminoquinolines, e.g. chloroquine, primaquine [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4709 | . . . . . | Non-condensed quinolines and containing further heterocyclic rings [2013-01] |
A61K 31/472 | . . . . . | Non-condensed isoquinolines, e.g. papaverine [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4725 | . . . . . . | containing further heterocyclic rings [2013-01] |
A61K 31/473 | . . . . . | ortho- or peri-condensed with carbocyclic ring systems, e.g. acridines, phenanthridines [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4738 | . . . . . | ortho- or peri-condensed with heterocyclic ring systems [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4741 | . . . . . . | condensed with ring systems having oxygen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. tubocuraran derivatives, noscapine, bicuculline [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4743 | . . . . . . | condensed with ring systems having sulfur as a ring hetero atom [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4745 | . . . . . . | condensed with ring systems having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. phenantrolines (yohimbine derivatives, vinblastine A61K 31/475; ergoline derivatives A61K 31/48) [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4747 | . . . . . | spiro-condensed [2017-08] |
A61K 31/4748 | . . . . . | forming part of bridged ring systems (strychnine A61K 31/475; morphinan derivatives A61K 31/485) [2013-01] |
A61K 31/475 | . . . . . | having an indole ring, e.g. yohimbine, reserpine, strychnine, vinblastine (vincamine A61K 31/4375) [2013-01] |
A61K 31/48 | . . . . . | Ergoline derivatives, e.g. lysergic acid, ergotamine [2013-01] |
A61K 31/485 | . . . . . | Morphinan derivatives, e.g. morphine, codeine [2013-01] |
A61K 31/49 | . . . . . | Cinchonan derivatives, e.g. quinine [2013-01] |
A61K 31/495 | . . . | having six-membered rings with two {or more} nitrogen atoms as the only ring heteroatoms, e.g. piperazine {or tetrazines}(A61K 31/48 takes precedence {; with three nitrogen atoms A61K 31/53}) [2013-01] |
A61K 31/496 | . . . . | Non-condensed piperazines containing further heterocyclic rings, e.g. rifampin, thiothixene or sparfloxacin [2024-01] |
A61K 31/4965 | . . . . | Non-condensed pyrazines [2013-01] |
A61K 31/497 | . . . . . | containing further heterocyclic rings [2013-01] |
A61K 31/498 | . . . . | Pyrazines or piperazines ortho- and peri-condensed with carbocyclic ring systems, e.g. quinoxaline, phenazine [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4985 | . . . . | Pyrazines or piperazines ortho- or peri-condensed with heterocyclic ring systems [2013-01] |
A61K 31/499 | . . . . | Spiro-condensed pyrazines or piperazines [2013-01] |
A61K 31/4995 | . . . . | Pyrazines or piperazines forming part of bridged ring systems [2013-01] |
A61K 31/50 | . . . . | Pyridazines; Hydrogenated pyridazines [2013-01] |
A61K 31/501 | . . . . . | not condensed and containing further heterocyclic rings [2013-01] |
A61K 31/502 | . . . . . | ortho- or peri-condensed with carbocyclic ring systems, e.g. cinnoline, phthalazine [2013-01] |
A61K 31/5025 | . . . . . | ortho- or peri-condensed with heterocyclic ring systems [2013-01] |
A61K 31/503 | . . . . . | spiro-condensed [2013-01] |
A61K 31/504 | . . . . . | forming part of bridged ring systems [2013-01] |
A61K 31/505 | . . . . | Pyrimidines; Hydrogenated pyrimidines, e.g. trimethoprim [2013-01] |
A61K 31/506 | . . . . . | not condensed and containing further heterocyclic rings [2013-01] |
A61K 31/51 | . . . . . . | Thiamines, e.g. vitamin B1 [2013-01] |
A61K 31/513 | . . . . . | having oxo groups directly attached to the heterocyclic ring, e.g. cytosine [2013-01] |
A61K 31/515 | . . . . . . | Barbituric acids; Derivatives thereof, e.g. sodium pentobarbital [2014-02] |
A61K 31/517 | . . . . . | ortho- or peri-condensed with carbocyclic ring systems, e.g. quinazoline, perimidine [2013-01] |
A61K 31/519 | . . . . . | ortho- or peri-condensed with heterocyclic rings [2013-01] |
A61K 31/52 | . . . . . . | Purines, e.g. adenine [2013-01] |
A61K 31/522 | . . . . . . . | having oxo groups directly attached to the heterocyclic ring, e.g. hypoxanthine, guanine, acyclovir [2013-01] |
A61K 31/525 | . . . . . . | Isoalloxazines, e.g. riboflavins, vitamin B2 [2013-01] |
A61K 31/527 | . . . . . | spiro-condensed [2013-01] |
A61K 31/529 | . . . . . | forming part of bridged ring systems [2013-01] |
A61K 31/53 | . . . | having six-membered rings with three nitrogens as the only ring hetero atoms, e.g. chlorazanil, melamine (melarsoprol A61K 31/555 {; with four nitrogen atoms A61K 31/495}) [2013-01] |
A61K 31/535 | . . . | having six-membered rings with at least one nitrogen and one oxygen as the ring hetero atoms, e.g. 1,2-oxazines [2013-01] |
A61K 31/5355 | . . . . | Non-condensed oxazines and containing further heterocyclic rings [2017-08] |
A61K 31/536 | . . . . | ortho- or peri-condensed with carbocyclic ring systems [2013-01] |
A61K 31/5365 | . . . . | ortho- or peri-condensed with heterocyclic ring systems [2013-01] |
A61K 31/537 | . . . . | spiro-condensed or forming part of bridged ring systems [2013-01] |
A61K 31/5375 | . . . . | 1,4-Oxazines, e.g. morpholine [2013-01] |
A61K 31/5377 | . . . . . | not condensed and containing further heterocyclic rings, e.g. timolol [2013-01] |
A61K 31/538 | . . . . . | ortho- or peri-condensed with carbocyclic ring systems [2013-01] |
A61K 31/5383 | . . . . . | ortho- or peri-condensed with heterocyclic ring systems [2013-01] |
A61K 31/5386 | . . . . . | spiro-condensed or forming part of bridged ring systems [2017-08] |
A61K 31/539 | . . . . | having two or more oxygen atoms in the same ring, e.g. dioxazines [2013-01] |
A61K 31/5395 | . . . . | having two or more nitrogen atoms in the same ring, e.g. oxadiazines [2013-01] |
A61K 31/54 | . . . | having six-membered rings with at least one nitrogen and one sulfur as the ring hetero atoms, e.g. sulthiame [2013-01] |
A61K 31/541 | . . . . | Non-condensed thiazines containing further heterocyclic rings [2017-08] |
A61K 31/5415 | . . . . | ortho- or peri-condensed with carbocyclic ring systems, e.g. phenothiazine, chlorpromazine, piroxicam [2013-01] |
A61K 31/542 | . . . . | ortho- or peri-condensed with heterocyclic ring systems [2013-01] |
A61K 31/545 | . . . . . | Compounds containing 5-thia-1-azabicyclo [4.2.0] octane ring systems, i.e. compounds containing a ring system of the formula: 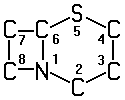 , e.g. cephalosporins, {cefaclor, or cephalexine} [2013-01] , e.g. cephalosporins, {cefaclor, or cephalexine} [2013-01] |
A61K 31/546 | . . . . . . | containing further heterocyclic rings, e.g. cephalothin [2013-01] |
A61K 31/547 | . . . . | spiro-condensed or forming part of bridged ring systems [2013-01] |
A61K 31/548 | . . . . | having two or more sulfur atoms in the same ring [2013-01] |
A61K 31/549 | . . . . | having two or more nitrogen atoms in the same ring, e.g. hydrochlorothiazide [2013-01] |
A61K 31/55 | . . . | having seven-membered rings, e.g. azelastine, pentylenetetrazole [2013-01] |
A61K 31/551 | . . . . | having two nitrogen atoms, e.g. dilazep [2013-01] |
A61K 31/5513 | . . . . . | 1,4-Benzodiazepines, e.g. diazepam {or clozapine} [2013-01] |
A61K 31/5517 | . . . . . . | condensed with five-membered rings having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. imidazobenzodiazepines, triazolam [2013-01] |
A61K 31/553 | . . . . | having at least one nitrogen and one oxygen as ring hetero atoms, e.g. loxapine, staurosporine [2013-01] |
A61K 31/554 | . . . . | having at least one nitrogen and one sulfur as ring hetero atoms, e.g. clothiapine, diltiazem [2022-01] |
| A61K 31/5545 | . . . | {having eight-membered rings not containing additional condensed or non-condensed nitrogen-containing 3-7 membered rings} [2022-01] NOTE
|
A61K 31/555 | . . | containing heavy metals, e.g. hemin, hematin, melarsoprol [2013-01] |
A61K 31/557 | . | Eicosanoids, e.g. leukotrienes {or prostaglandins} [2013-01] |
A61K 31/5575 | . . | having a cyclopentane, e.g. prostaglandin E2, prostaglandin F2-alpha [2017-08] |
A61K 31/5578 | . . | having a pentalene ring system, e.g. carbacyclin, iloprost [2013-01] |
A61K 31/558 | . . | having heterocyclic rings containing oxygen as the only ring hetero atom, e.g. thromboxanes [2013-01] |
A61K 31/5585 | . . . | having five-membered rings containing oxygen as the only ring hetero atom, e.g. prostacyclin [2013-01] |
A61K 31/559 | . . | having heterocyclic rings containing hetero atoms other than oxygen [2013-01] |
| A61K 31/56 | . | Compounds containing cyclopenta[a]hydrophenanthrene ring systems; Derivatives thereof, e.g. steroids [2021-02] NOTE
|
A61K 31/565 | . . | not substituted in position 17 beta by a carbon atom, e.g. estrane, estradiol [2013-01] |
A61K 31/566 | . . . | having an oxo group in position 17, e.g. estrone [2013-01] |
A61K 31/567 | . . . | substituted in position 17 alpha, e.g. mestranol, norethandrolone [2013-01] |
A61K 31/568 | . . . | substituted in positions 10 and 13 by a chain having at least one carbon atom, e.g. androstanes, e.g. testosterone [2013-01] |
A61K 31/5685 | . . . . | having an oxo group in position 17, e.g. androsterone [2013-01] |
A61K 31/569 | . . . . | substituted in position 17 alpha, e.g. ethisterone [2013-01] |
A61K 31/57 | . . | substituted in position 17 beta by a chain of two carbon atoms, e.g. pregnane or progesterone [2021-02] |
A61K 31/573 | . . . | substituted in position 21, e.g. cortisone, dexamethasone, prednisone or aldosterone [2021-02] |
A61K 31/575 | . . | substituted in position 17 beta by a chain of three or more carbon atoms, e.g. cholane, cholestane, ergosterol, sitosterol [2013-01] |
A61K 31/58 | . . | containing heterocyclic rings, e.g. danazol, stanozolol, pancuronium or digitogenin (digitoxin {A61K 31/7048}) [2021-02] |
A61K 31/585 | . . . | containing lactone rings, e.g. oxandrolone, bufalin [2013-01] |
A61K 31/59 | . | Compounds containing 9, 10- seco- cyclopenta[a]hydrophenanthrene ring systems [2013-01] |
A61K 31/592 | . . | 9,10-Secoergostane derivatives, e.g. ergocalciferol, i.e. vitamin D2 [2013-01] |
A61K 31/593 | . . | 9,10-Secocholestane derivatives, e.g. cholecalciferol, i.e. vitamin D3 [2013-01] |
A61K 31/60 | . | Salicylic acid; Derivatives thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 31/603 | . . | having further aromatic rings, e.g. diflunisal [2013-01] |
A61K 31/606 | . . | having amino groups [2013-01] |
A61K 31/609 | . . |
A61K 31/612 | . . | having the hydroxy group in position 2 esterified, e.g. salicylsulfuric acid (fosfosal A61K 31/661) [2013-01] |
A61K 31/616 | . . . | by carboxylic acids, e.g. acetylsalicylic acid [2017-08] |
A61K 31/618 | . . | having the carboxyl group in position 1 esterified, e.g. salsalate [2013-01] |
A61K 31/621 | . . . | having the hydroxy group in position 2 esterified, e.g. benorylate [2013-01] |
A61K 31/625 | . . | having heterocyclic substituents, e.g. 4-salicycloylmorpholine, (sulfasalazine A61K 31/635) [2013-01] |
A61K 31/63 | . | Compounds containing para-N-benzenesulfonyl-N-groups, e.g. sulfanilamide, p-nitrobenzenesulfonyl hydrazide [2013-01] |
A61K 31/635 | . . | having a heterocyclic ring, e.g. sulfadiazine [2020-08] |
A61K 31/64 | . | Sulfonylureas, e.g. glibenclamide, tolbutamide, chlorpropamide [2013-01] |
A61K 31/65 | . | Tetracyclines [2013-01] |
A61K 31/655 | . | Azo (—N=N—), diazo (=N2), azoxy (>N—O—N< or N(=O)—N<), azido (—N3) or diazoamino (—N=N—N<) compounds [2017-08] |
| A61K 31/658 | . | {o-phenolic cannabinoids, e.g. cannabidiol, cannabigerolic acid, cannabichromene or tetrahydrocannabinol} [2023-05] WARNING
|
A61K 31/66 | . | Phosphorus compounds [2013-01] |
A61K 31/661 | . . | Phosphorus acids or esters thereof not having P—C bonds, e.g. fosfosal, dichlorvos, malathion {or mevinphos} [2017-08] |
A61K 31/6615 | . . . | Compounds having two or more esterified phosphorus acid groups, e.g. inositol triphosphate, phytic acid [2013-01] |
A61K 31/662 | . . | Phosphorus acids or esters thereof having P—C bonds, e.g. foscarnet, trichlorfon [2017-08] |
A61K 31/663 | . . . | Compounds having two or more phosphorus acid groups or esters thereof, e.g. clodronic acid, pamidronic acid [2013-01] |
A61K 31/664 | . . | Amides of phosphorus acids [2013-01] |
A61K 31/665 | . . | having oxygen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. fosfomycin [2013-01] |
A61K 31/67 | . . | having sulfur as a ring hetero atom [2013-01] |
A61K 31/675 | . . | having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. pyridoxal phosphate [2013-01] |
A61K 31/683 | . . | Diesters of a phosphorus acid with two hydroxy compounds, e.g. phosphatidylinositols [2013-01] |
A61K 31/685 | . . . | one of the hydroxy compounds having nitrogen atoms, e.g. phosphatidylserine, lecithin [2013-01] |
A61K 31/688 | . . . | both hydroxy compounds having nitrogen atoms, e.g. sphingomyelins [2017-08] |
A61K 31/69 | . | Boron compounds [2013-01] |
A61K 31/695 | . | Silicon compounds [2013-01] |
| A61K 31/70 | . | NOTE
|
A61K 31/7004 | . . | Monosaccharides having only carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms [2017-08] |
A61K 31/7008 | . . | Compounds having an amino group directly attached to a carbon atom of the saccharide radical, e.g. D-galactosamine, ranimustine [2013-01] |
A61K 31/7012 | . . | Compounds having a free or esterified carboxyl group attached, directly or through a carbon chain, to a carbon atom of the saccharide radical, e.g. glucuronic acid, neuraminic acid (gluconic acid A61K 31/191; ascorbic acid A61K 31/375) [2013-01] |
A61K 31/7016 | . . |
A61K 31/702 | . . | Oligosaccharides, i.e. having three to five saccharide radicals attached to each other by glycosidic linkages [2013-01] |
A61K 31/7024 | . . | Esters of saccharides [2013-01] |
A61K 31/7028 | . . | Compounds having saccharide radicals attached to non-saccharide compounds by glycosidic linkages [2013-01] |
A61K 31/7032 | . . . | attached to a polyol, i.e. compounds having two or more free or esterified hydroxy groups, including the hydroxy group involved in the glycosidic linkage, e.g. monoglucosyldiacylglycerides, lactobionic acid, gangliosides [2017-08] |
A61K 31/7034 | . . . | attached to a carbocyclic compound, e.g. phloridzin [2013-01] |
A61K 31/7036 | . . . . | having at least one amino group directly attached to the carbocyclic ring, e.g. streptomycin, gentamycin, amikacin, validamycin, fortimicins [2013-01] |
A61K 31/704 | . . . . | attached to a condensed carbocyclic ring system, e.g. sennosides, thiocolchicosides, escin, daunorubicin {(digitoxin A61K 31/7048)} [2013-01] |
A61K 31/7042 | . . | Compounds having saccharide radicals and heterocyclic rings [2013-01] |
A61K 31/7048 | . . . | having oxygen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. leucoglucosan, hesperidin, erythromycin, nystatin {, digitoxin or digoxin} [2021-02] |
A61K 31/7052 | . . . | having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. nucleosides, nucleotides [2013-01] |
A61K 31/7056 | . . . . | containing five-membered rings with nitrogen as a ring hetero atom [2013-01] |
A61K 31/706 | . . . . | containing six-membered rings with nitrogen as a ring hetero atom [2013-01] |
A61K 31/7064 | . . . . . | containing condensed or non-condensed pyrimidines [2013-01] |
A61K 31/7068 | . . . . . . | having oxo groups directly attached to the pyrimidine ring, e.g. cytidine, cytidylic acid [2013-01] |
A61K 31/7072 | . . . . . . . | having two oxo groups directly attached to the pyrimidine ring, e.g. uridine, uridylic acid, thymidine, zidovudine [2013-01] |
A61K 31/7076 | . . . . . . | containing purines, e.g. adenosine, adenylic acid [2013-01] |
A61K 31/708 | . . . . . . . | having oxo groups directly attached to the purine ring system, e.g. guanosine, guanylic acid [2013-01] |
A61K 31/7084 | . . | Compounds having two nucleosides or nucleotides, e.g. nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide, flavine-adenine dinucleotide [2013-01] |
A61K 31/7088 | . . | Compounds having three or more nucleosides or nucleotides [2013-01] |
A61K 31/7105 | . . . | Natural ribonucleic acids, i.e. containing only riboses attached to adenine, guanine, cytosine or uracil and having 3'-5' phosphodiester links [2013-01] |
A61K 31/711 | . . . | Natural deoxyribonucleic acids, i.e. containing only 2'-deoxyriboses attached to adenine, guanine, cytosine or thymine and having 3'-5' phosphodiester links [2013-01] |
A61K 31/7115 | . . . | Nucleic acids or oligonucleotides having modified bases, i.e. other than adenine, guanine, cytosine, uracil or thymine [2013-01] |
A61K 31/712 | . . . | Nucleic acids or oligonucleotides having modified sugars, i.e. other than ribose or 2'-deoxyribose [2013-01] |
A61K 31/7125 | . . . | Nucleic acids or oligonucleotides having modified internucleoside linkage, i.e. other than 3'-5' phosphodiesters [2013-01] |
A61K 31/713 | . . . | Double-stranded nucleic acids or oligonucleotides [2013-01] |
A61K 31/7135 | . . | Compounds containing heavy metals [2013-01] |
A61K 31/714 | . . . | Cobalamins, e.g. cyanocobalamin, i.e. vitamin B12 [2013-01] |
A61K 31/715 | . . | Polysaccharides, i.e. having more than five saccharide radicals attached to each other by glycosidic linkages; Derivatives thereof, e.g. ethers, esters [2013-01] |
A61K 31/716 | . . . | Glucans [2013-01] |
A61K 31/717 | . . . . | Celluloses [2013-01] |
A61K 31/718 | . . . . | Starch or degraded starch, e.g. amylose, amylopectin [2013-01] |
A61K 31/719 | . . . . | Pullulans [2013-01] |
A61K 31/721 | . . . . | Dextrans [2013-01] |
A61K 31/722 | . . . . | Chitin, chitosan [2013-01] |
A61K 31/723 | . . . . | Xanthans [2013-01] |
A61K 31/724 | . . . . | Cyclodextrins [2013-01] |
A61K 31/726 | . . . | Glycosaminoglycans, i.e. mucopolysaccharides (chondroitin sulfate, dermatan sulfate A61K 31/737) [2013-01] |
A61K 31/727 | . . . . | Heparin; Heparan [2013-01] |
A61K 31/728 | . . . . | Hyaluronic acid [2013-01] |
A61K 31/729 | . . . | Agar; Agarose; Agaropectin [2013-01] |
A61K 31/731 | . . . | Carrageenans [2013-01] |
A61K 31/732 | . . . | Pectin [2013-01] |
A61K 31/733 | . . . | Fructosans, e.g. inulin [2013-01] |
A61K 31/734 | . . . | Alginic acid [2013-01] |
A61K 31/736 | . . . | Glucomannans or galactomannans, e.g. locust bean gum, guar gum [2013-01] |
A61K 31/737 | . . . | Sulfated polysaccharides, e.g. chondroitin sulfate, dermatan sulfate (A61K 31/727 takes precedence) [2013-01] |
A61K 31/738 | . . . | Cross-linked polysaccharides [2013-01] |
A61K 31/739 | . . . | Lipopolysaccharides [2013-01] |
A61K 31/74 | . | Synthetic polymeric materials [2013-01] |
A61K 31/745 | . . | Polymers of hydrocarbons [2013-01] |
A61K 31/75 | . . . | of ethene [2013-01] |
A61K 31/755 | . . | Polymers containing halogen [2013-01] |
A61K 31/76 | . . . | of vinyl chloride [2013-01] |
A61K 31/765 | . . | Polymers containing oxygen [2013-01] |
A61K 31/77 | . . . | of oxiranes [2013-01] |
A61K 31/775 | . . . | Phenolic resins [2013-01] |
A61K 31/78 | . . . | of acrylic acid or derivatives thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 31/785 | . . | Polymers containing nitrogen [2013-01] |
A61K 31/787 | . . . | containing heterocyclic rings having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom [2013-01] |
A61K 31/79 | . . . . | Polymers of vinyl pyrrolidone [2013-01] |
A61K 31/795 | . . | Polymers containing sulfur [2013-01] |
A61K 31/80 | . . | Polymers containing hetero atoms not provided for in groups A61K 31/755 - A61K 31/795 [2016-05] |
A61K 33/00 | Medicinal preparations containing inorganic active ingredients [2013-01] |
A61K 33/02 | . | Ammonia; Compounds thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 33/04 | . | Sulfur, selenium or tellurium; Compounds thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 33/06 | . | Aluminium, calcium or magnesium; Compounds thereof {, e.g. clay} [2017-08] |
A61K 33/08 | . . | Oxides; Hydroxides [2013-01] |
A61K 33/10 | . . | Carbonates; Bicarbonates [2013-01] |
A61K 33/12 | . . | Magnesium silicate [2013-01] |
A61K 33/14 | . | Alkali metal chlorides; Alkaline earth metal chlorides [2013-01] |
A61K 33/16 | . | Fluorine compounds [2013-01] |
A61K 33/18 | . | Iodine; Compounds thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 33/20 | . | Elemental chlorine; Inorganic compounds releasing chlorine [2013-01] |
A61K 33/22 | . | Boron compounds [2013-01] |
A61K 33/24 | . | Heavy metals; Compounds thereof [2022-01] |
A61K 33/241 | . . | Lead; Compounds thereof [2022-01] |
A61K 33/242 | . . | Gold; Compounds thereof [2022-01] |
A61K 33/243 | . . | Platinum; Compounds thereof [2022-01] |
A61K 33/244 | . . | Lanthanides; Compounds thereof (medicinal preparations containing radioactive lanthanides for use in therapy or testing in vivo A61K 51/00) [2022-01] |
A61K 33/245 | . . | Bismuth; Compounds thereof [2019-01] |
A61K 33/26 | . . | Iron; Compounds thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 33/28 | . . | Mercury; Compounds thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 33/30 | . . | Zinc; Compounds thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 33/32 | . . | Manganese; Compounds thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 33/34 | . . | Copper; Compounds thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 33/36 | . . | Arsenic; Compounds thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 33/38 | . . | Silver; Compounds thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 33/40 | . | Peroxides [2013-01] |
A61K 33/42 | . | Phosphorus; Compounds thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 33/44 | . | Elemental carbon, e.g. charcoal, carbon black [2013-01] |
| A61K 35/00 | Medicinal preparations containing materials or reaction products thereof with undetermined constitution [2015-01] NOTES
|
A61K 35/02 | . |
A61K 35/04 | . . | Tars; Bitumens; Mineral oils; Ammonium bituminosulfonate [2015-01] |
A61K 35/06 | . . . | Mineral oils, e.g. paraffinic oils or aromatic oils based on aromatic hydrocarbons [2015-01] |
A61K 35/08 | . . | Mineral waters; Sea water [2015-01] |
A61K 35/10 | . . | Peat; Amber; Turf; Humus [2015-01] |
A61K 2035/11 | . | {Medicinal preparations comprising living procariotic cells} [2013-01] |
A61K 2035/115 | . . | {Probiotics} [2013-01] |
| A61K 35/12 | . | Materials from mammals; Compositions comprising non-specified tissues or cells; Compositions comprising non-embryonic stem cells; Genetically modified cells (vaccines or medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies A61K 39/00) [2020-01] NOTE
|
A61K 2035/122 | . . | {for inducing tolerance or supression of immune responses} [2013-01] |
A61K 2035/124 | . . | {the cells being hematopoietic, bone marrow derived or blood cells} [2013-01] |
A61K 2035/126 | . . | {Immunoprotecting barriers, e.g. jackets, diffusion chambers} [2013-01] |
A61K 2035/128 | . . . | {capsules, e.g. microcapsules} [2013-01] |
A61K 35/13 | . . |
A61K 35/14 | . . | Blood; Artificial blood (perfluorocarbons A61K 31/02; umbilical cord blood A61K 35/51; haemoglobin A61K 38/42) [2015-01] |
A61K 35/15 | . . . | Cells of the myeloid line, e.g. granulocytes, basophils, eosinophils, neutrophils, leucocytes, monocytes, macrophages or mast cells; Myeloid precursor cells; Antigen-presenting cells, e.g. dendritic cells (presenting a specific antigen A61K 39/00; therapeutic combinations of antibodies, or fragments thereof, and blood-derived cells A61K 39/00) [2025-01] |
A61K 35/16 | . . . |
A61K 35/17 | . . . | Lymphocytes; B-cells; T-cells; Natural killer cells; Interferon-activated or cytokine-activated lymphocytes (when activated by a specific antigen A61K 39/00) [2025-01] |
A61K 35/18 | . . . |
A61K 35/19 | . . . | Platelets; Megacaryocytes [2015-01] |
A61K 35/20 | . . | Milk; Whey; Colostrum [2015-01] |
A61K 35/22 | . . | Urine; Urinary tract, e.g. kidney or bladder; Intraglomerular mesangial cells; Renal mesenchymal cells; Adrenal gland [2015-01] |
A61K 35/24 | . . | Mucus; Mucous glands; Bursa; Synovial fluid; Arthral fluid; Excreta; Spinal fluid (saliva A61K 35/38) [2015-01] |
A61K 35/26 | . . | Lymph; Lymph nodes; Thymus; Spleen; Splenocytes; Thymocytes [2015-01] |
A61K 35/28 | . . | Bone marrow; Haematopoietic stem cells; Mesenchymal stem cells of any origin, e.g. adipose-derived stem cells [2015-01] |
A61K 35/30 | . . | Nerves; Brain; Eyes; Corneal cells; Cerebrospinal fluid; Neuronal stem cells; Neuronal precursor cells; Glial cells; Oligodendrocytes; Schwann cells; Astroglia; Astrocytes; Choroid plexus; Spinal cord tissue [2015-01] |
A61K 35/32 | . . | Bones; Osteocytes; Osteoblasts; Tendons; Tenocytes; Teeth; Odontoblasts; Cartilage; Chondrocytes; Synovial membrane [2015-01] |
A61K 35/33 | . . | Fibroblasts [2015-01] |
A61K 35/34 | . . | Muscles; Smooth muscle cells; Heart; Cardiac stem cells; Myoblasts; Myocytes; Cardiomyocytes (vascular smooth muscle A61K 35/44) [2015-01] |
A61K 35/35 | . . | Fat tissue; Adipocytes; Stromal cells; Connective tissues (adipose-derived stem cells A61K 35/28; collagen A61K 38/39) [2015-01] |
A61K 35/36 | . . | Skin; Hair; Nails; Sebaceous glands; Cerumen; Epidermis; Epithelial cells; Keratinocytes; Langerhans cells; Ectodermal cells (islets of Langerhans A61K 35/39) [2015-01] |
A61K 35/37 | . . | Digestive system [2013-01] |
A61K 35/38 | . . . | Stomach; Intestine; Goblet cells; Oral mucosa; Saliva [2015-01] |
A61K 35/39 | . . . |
A61K 35/407 | . . . | Liver; Hepatocytes [2015-01] |
A61K 35/413 | . . . | Gall bladder; Bile [2015-01] |
A61K 35/42 | . . | Respiratory system, e.g. lungs, bronchi or lung cells [2015-01] |
A61K 35/44 | . . | Vessels; Vascular smooth muscle cells; Endothelial cells; Endothelial progenitor cells [2015-01] |
A61K 35/48 | . . | Reproductive organs [2013-01] |
A61K 35/50 | . . . | Placenta; Placental stem cells; Amniotic fluid; Amnion; Amniotic stem cells [2015-01] |
A61K 35/51 | . . . | Umbilical cord; Umbilical cord blood; Umbilical stem cells [2015-01] |
A61K 35/52 | . . . | Sperm; Prostate; Seminal fluid; Leydig cells of testes [2015-01] |
A61K 35/54 | . . . | Ovaries; Ova; Ovules; Embryos; Foetal cells; Germ cells [2015-01] |
A61K 35/545 | . . . . | Embryonic stem cells; Pluripotent stem cells; Induced pluripotent stem cells; Uncharacterised stem cells [2015-01] |
A61K 35/55 | . . | Glands not provided for in groups A61K 35/22 - A61K 35/545, e.g. thyroids, parathyroids or pineal glands [2015-01] |
A61K 35/56 | . | Materials from animals other than mammals [2016-05] |
A61K 35/57 | . . | Birds; Materials from birds, e.g. eggs, feathers, egg white, egg yolk or endothelium corneum gigeriae galli [2015-01] |
A61K 35/58 | . . |
A61K 35/583 | . . . |
A61K 35/586 | . . . | Turtles; Tortoises, e.g. terrapins [2015-01] |
A61K 35/60 | . . | Fish, e.g. seahorses; Fish eggs [2015-01] |
A61K 35/612 | . . | Crustaceans, e.g. crabs, lobsters, shrimps, krill or crayfish; Barnacles [2015-01] |
A61K 35/614 | . . | Cnidaria, e.g. sea anemones, corals, coral animals or jellyfish [2015-01] |
A61K 35/616 | . . | Echinodermata, e.g. starfish, sea cucumbers or sea urchins [2015-01] |
A61K 35/618 | . . | Molluscs, e.g. fresh-water molluscs, oysters, clams, squids, octopus, cuttlefish, snails or slugs [2015-01] |
A61K 35/62 | . . | Leeches; Worms, e.g. cestodes, tapeworms, nematodes, roundworms, earth worms, ascarids, filarias, hookworms, trichinella or taenia [2015-01] |
A61K 35/63 | . . |
A61K 35/64 | . . . | Insects, e.g. bees, wasps or fleas [2015-01] |
A61K 35/644 | . . . . | Beeswax; Propolis; Royal jelly; Honey [2015-01] |
A61K 35/646 | . . . | Arachnids, e.g. spiders, scorpions, ticks or mites [2015-01] |
A61K 35/648 | . . . | Myriapods, e.g. centipedes or millipedes [2015-01] |
A61K 35/65 | . . | Amphibians, e.g. toads, frogs, salamanders or newts [2015-01] |
A61K 35/655 | . . | Aquatic animals other than those covered by groups A61K 35/57 - A61K 35/65 [2015-01] |
A61K 35/66 | . |
A61K 35/68 | . . | Protozoa, e.g. flagella, amoebas, sporozoans, plasmodium or toxoplasma [2015-01] |
A61K 35/74 | . . |
A61K 35/741 | . . . |
A61K 35/742 | . . . . | Spore-forming bacteria, e.g. Bacillus coagulans, Bacillus subtilis, clostridium or Lactobacillus sporogenes [2015-01] |
A61K 35/744 | . . . . | Lactic acid bacteria, e.g. enterococci, pediococci, lactococci, streptococci or leuconostocs [2015-01] |
A61K 35/745 | . . . . . | Bifidobacteria [2015-01] |
A61K 35/747 | . . . . . | Lactobacilli, e.g. L. acidophilus or L. brevis [2015-01] |
A61K 35/748 | . . . | Cyanobacteria, i.e. blue-green bacteria or blue-green algae, e.g. spirulina (algae, microalgae or microphytes A61K 36/02) [2015-01] |
A61K 35/76 | . . | Viruses; Subviral particles; Bacteriophages [2015-01] |
A61K 35/761 | . . . | Adenovirus [2015-01] |
A61K 35/763 | . . . | Herpes virus [2015-01] |
A61K 35/765 | . . . | Reovirus; Rotavirus [2015-01] |
A61K 35/766 | . . . | Rhabdovirus, e.g. vesicular stomatitis virus [2015-01] |
A61K 35/768 | . . . | Oncolytic viruses not provided for in groups A61K 35/761 - A61K 35/766 [2015-01] |
| A61K 36/00 | Medicinal preparations of undetermined constitution containing material from algae, lichens, fungi or plants, or derivatives thereof, e.g. traditional herbal medicines {(antigens from pollen A61K 39/36)} [2013-01] NOTE
|
A61K 36/02 | . | Algae [2013-01] |
A61K 36/03 | . . | Phaeophycota or phaeophyta (brown algae), e.g. Fucus [2013-01] |
A61K 36/04 | . . | Rhodophycota or rhodophyta (red algae), e.g. Porphyra [2017-08] |
A61K 36/05 | . . | Chlorophycota or chlorophyta (green algae), e.g. Chlorella [2013-01] |
A61K 36/06 | . | Fungi, e.g. yeasts [2013-01] |
A61K 36/062 | . . | Ascomycota [2013-01] |
A61K 36/064 | . . . | Saccharomycetales, e.g. baker's yeast [2013-01] |
A61K 36/066 | . . . | Clavicipitaceae [2013-01] |
A61K 36/068 | . . . . | Cordyceps [2013-01] |
| A61K 36/07 | . . | Basidiomycota, e.g. Cryptococcus [2024-05] WARNING
|
| A61K 36/071 | . . . | {Agaricus} [2024-05] WARNING
|
A61K 36/074 | . . . | Ganoderma [2013-01] |
A61K 36/076 | . . . | Poria [2013-01] |
| A61K 36/078 | . . . | {Psilocybe} [2024-05] WARNING
|
A61K 36/09 | . | Lichens [2013-01] |
A61K 36/10 | . | Bryophyta (mosses) [2024-05] |
A61K 36/11 | . | Pteridophyta or Filicophyta (ferns) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/12 | . . | Filicopsida or Pteridopsida [2013-01] |
A61K 36/126 | . . . | Drynaria [2013-01] |
A61K 36/13 | . | Coniferophyta (gymnosperms) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/14 | . . | Cupressaceae (Cypress family), e.g. juniper or cypress [2013-01] |
A61K 36/15 | . . | Pinaceae (Pine family), e.g. pine or cedar [2013-01] |
A61K 36/16 | . | Ginkgophyta, e.g. Ginkgoaceae (Ginkgo family) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/17 | . | Gnetophyta, e.g. Ephedraceae (Mormon-tea family) [2017-08] |
| A61K 36/18 | . | Magnoliophyta (angiosperms) [2024-05] WARNING
|
| A61K 36/185 | . . | Magnoliopsida (dicotyledons) [2024-05] WARNING
|
A61K 36/19 | . . . | Acanthaceae (Acanthus family) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/195 | . . . . | Strobilanthes [2013-01] |
A61K 36/20 | . . . | Aceraceae (Maple family) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/21 | . . . | Amaranthaceae (Amaranth family), e.g. pigweed, rockwort or globe amaranth [2013-01] |
A61K 36/22 | . . . | Anacardiaceae (Sumac family), e.g. smoketree, sumac or poison oak [2013-01] |
A61K 36/23 | . . . | Apiaceae or Umbelliferae (Carrot family), e.g. dill, chervil, coriander or cumin [2013-01] |
A61K 36/232 | . . . . | Angelica [2013-01] |
A61K 36/233 | . . . . | Bupleurum [2013-01] |
A61K 36/234 | . . . . | Cnidium (snowparsley) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/235 | . . . . | Foeniculum (fennel) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/236 | . . . . | Ligusticum (licorice-root) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/237 | . . . . | Notopterygium [2013-01] |
A61K 36/238 | . . . . | Saposhnikovia [2013-01] |
A61K 36/24 | . . . | Apocynaceae (Dogbane family), e.g. plumeria or periwinkle [2013-01] |
A61K 36/25 | . . . | Araliaceae (Ginseng family), e.g. ivy, aralia, schefflera or tetrapanax [2013-01] |
A61K 36/254 | . . . . | Acanthopanax or Eleutherococcus [2013-01] |
A61K 36/258 | . . . . | Panax (ginseng) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/26 | . . . | Aristolochiaceae (Birthwort family), e.g. heartleaf [2013-01] |
A61K 36/264 | . . . . | Aristolochia (Dutchman's pipe) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/268 | . . . . | Asarum (wild ginger) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/27 | . . . | Asclepiadaceae (Milkweed family), e.g. hoya [2013-01] |
A61K 36/28 | . . . | Asteraceae or Compositae (Aster or Sunflower family), e.g. chamomile, feverfew, yarrow or echinacea [2013-01] |
A61K 36/282 | . . . . | Artemisia, e.g. wormwood or sagebrush [2013-01] |
A61K 36/284 | . . . . | Atractylodes [2013-01] |
A61K 36/285 | . . . . | Aucklandia [2013-01] |
A61K 36/286 | . . . . | Carthamus (distaff thistle) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/287 | . . . . | Chrysanthemum, e.g. daisy [2013-01] |
A61K 36/288 | . . . . | Taraxacum (dandelion) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/289 | . . . . | Vladimiria [2013-01] |
A61K 36/29 | . . . | Berberidaceae (Barberry family), e.g. barberry, cohosh or mayapple [2013-01] |
A61K 36/296 | . . . . | Epimedium [2013-01] |
A61K 36/30 | . . . | Boraginaceae (Borage family), e.g. comfrey, lungwort or forget-me-not [2013-01] |
A61K 36/31 | . . . | Brassicaceae or Cruciferae (Mustard family), e.g. broccoli, cabbage or kohlrabi [2013-01] |
A61K 36/315 | . . . . | Isatis, e.g. Dyer's woad [2013-01] |
A61K 36/32 | . . . | Burseraceae (Frankincense family) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/324 | . . . . | Boswellia, e.g. frankincense [2013-01] |
A61K 36/328 | . . . . | Commiphora, e.g. mecca myrrh or balm of Gilead [2013-01] |
A61K 36/33 | . . . | Cactaceae (Cactus family), e.g. pricklypear or Cereus [2013-01] |
A61K 36/34 | . . . | Campanulaceae (Bellflower family) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/342 | . . . . | Adenophora [2013-01] |
A61K 36/344 | . . . . | Codonopsis [2013-01] |
A61K 36/346 | . . . . | Platycodon [2013-01] |
| A61K 36/348 | . . . | {Cannabaceae} [2024-05] WARNING
|
A61K 36/3482 | . . . . | {Cannabis} [2024-05] |
A61K 36/3486 | . . . . | {Humulus} [2024-05] |
A61K 36/35 | . . . | Caprifoliaceae (Honeysuckle family) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/355 | . . . . | Lonicera (honeysuckle) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/36 | . . . | Caryophyllaceae (Pink family), e.g. babysbreath or soapwort [2013-01] |
A61K 36/37 | . . . | Celastraceae (Staff-tree or Bittersweet family), e.g. tripterygium or spindletree [2013-01] |
A61K 36/38 | . . . | Clusiaceae, Hypericaceae or Guttiferae (Hypericum or Mangosteen family), e.g. common St. Johnswort [2013-01] |
A61K 36/39 | . . . | Convolvulaceae (Morning-glory family), e.g. bindweed [2013-01] |
A61K 36/40 | . . . | Cornaceae (Dogwood family) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/41 | . . . | Crassulaceae (Stonecrop family) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/42 | . . . | Cucurbitaceae (Cucumber family) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/424 | . . . . | Gynostemma [2013-01] |
A61K 36/428 | . . . . | Trichosanthes [2013-01] |
A61K 36/43 | . . . | Cuscutaceae (Dodder family), e.g. Cuscuta epithymum or greater dodder [2013-01] |
A61K 36/44 | . . . | Ebenaceae (Ebony family), e.g. persimmon [2013-01] |
A61K 36/45 | . . . | Ericaceae or Vacciniaceae (Heath or Blueberry family), e.g. blueberry, cranberry or bilberry [2013-01] |
A61K 36/46 | . . . | Eucommiaceae (Eucommia family), e.g. hardy rubber tree [2013-01] |
A61K 36/47 | . . . | Euphorbiaceae (Spurge family), e.g. Ricinus (castorbean) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/48 | . . . | Fabaceae or Leguminosae (Pea or Legume family); Caesalpiniaceae; Mimosaceae; Papilionaceae [2013-01] |
A61K 36/481 | . . . . | Astragalus (milkvetch) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/482 | . . . . | Cassia, e.g. golden shower tree [2013-01] |
A61K 36/483 | . . . . | Gleditsia (locust) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/484 | . . . . | Glycyrrhiza (licorice) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/485 | . . . . | Gueldenstaedtia [2013-01] |
A61K 36/486 | . . . . | Millettia [2013-01] |
A61K 36/487 | . . . . | Psoralea [2013-01] |
A61K 36/488 | . . . . | Pueraria (kudzu) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/489 | . . . . | Sophora, e.g. necklacepod or mamani [2013-01] |
A61K 36/49 | . . . | Fagaceae (Beech family), e.g. oak or chestnut [2013-01] |
A61K 36/50 | . . . | Fumariaceae (Fumitory family), e.g. bleeding heart [2013-01] |
A61K 36/505 | . . . . | Corydalis [2013-01] |
A61K 36/51 | . . . | Gentianaceae (Gentian family) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/515 | . . . . | Gentiana [2013-01] |
A61K 36/52 | . . . | Juglandaceae (Walnut family) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/53 | . . . | Lamiaceae or Labiatae (Mint family), e.g. thyme, rosemary or lavender [2013-01] |
A61K 36/532 | . . . . | Agastache, e.g. giant hyssop [2013-01] |
A61K 36/533 | . . . . | Leonurus (motherwort) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/534 | . . . . | Mentha (mint) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/535 | . . . . | Perilla (beefsteak plant) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/536 | . . . . | Prunella or Brunella (selfheal) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/537 | . . . . | Salvia (sage) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/538 | . . . . | Schizonepeta [2013-01] |
A61K 36/539 | . . . . | Scutellaria (skullcap) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/54 | . . . | Lauraceae (Laurel family), e.g. cinnamon or sassafras [2013-01] |
A61K 36/55 | . . . | Linaceae (Flax family), e.g. Linum [2013-01] |
A61K 36/56 | . . . | Loganiaceae (Logania family), e.g. trumpetflower or pinkroot [2013-01] |
A61K 36/57 | . . . | Magnoliaceae (Magnolia family) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/575 | . . . . | Magnolia [2013-01] |
| A61K 36/577 | . . . | {Malvaceae (Mallow family)} [2024-05] WARNING
|
A61K 36/5775 | . . . . | {Hibiscus} [2024-05] |
A61K 36/5777 | . . . . | {Theobroma, e.g. cocao or cocoa} [2024-05] |
A61K 36/58 | . . . | Meliaceae (Chinaberry or Mahogany family), e.g. Azadirachta (neem) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/59 | . . . | Menispermaceae (Moonseed family), e.g. hyperbaena or coralbead [2013-01] |
A61K 36/60 | . . . | Moraceae (Mulberry family), e.g. breadfruit or fig [2013-01] |
A61K 36/605 | . . . . | Morus (mulberry) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/61 | . . . | Myrtaceae (Myrtle family), e.g. teatree or eucalyptus [2013-01] |
A61K 36/62 | . . . | Nymphaeaceae (Water-lily family) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/63 | . . . | Oleaceae (Olive family), e.g. jasmine, lilac or ash tree [2013-01] |
A61K 36/634 | . . . . | Forsythia [2013-01] |
A61K 36/638 | . . . . | Ligustrum, e.g. Chinese privet [2013-01] |
A61K 36/64 | . . . | Orobanchaceae (Broom-rape family) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/65 | . . . | Paeoniaceae (Peony family), e.g. Chinese peony [2013-01] |
A61K 36/66 | . . . | Papaveraceae (Poppy family), e.g. bloodroot [2013-01] |
A61K 36/67 | . . . | Piperaceae (Pepper family), e.g. Jamaican pepper or kava [2013-01] |
A61K 36/68 | . . . | Plantaginaceae (Plantain Family) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/69 | . . . | Polygalaceae (Milkwort family) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/70 | . . . | Polygonaceae (Buckwheat family), e.g. spineflower or dock [2013-01] |
A61K 36/704 | . . . . | Polygonum, e.g. knotweed [2013-01] |
A61K 36/708 | . . . . | Rheum (rhubarb) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/71 | . . . | Ranunculaceae (Buttercup family), e.g. larkspur, hepatica, hydrastis, columbine or goldenseal [2013-01] |
A61K 36/714 | . . . . | Aconitum (monkshood) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/716 | . . . . | Clematis (leather flower) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/718 | . . . . | Coptis (goldthread) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/72 | . . . | Rhamnaceae (Buckthorn family), e.g. buckthorn, chewstick or umbrella-tree [2013-01] |
A61K 36/725 | . . . . | Ziziphus, e.g. jujube [2013-01] |
A61K 36/73 | . . . | Rosaceae (Rose family), e.g. strawberry, chokeberry, blackberry, pear or firethorn [2013-01] |
A61K 36/732 | . . . . | Chaenomeles, e.g. flowering quince [2013-01] |
A61K 36/734 | . . . . | Crataegus (hawthorn) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/736 | . . . . | Prunus, e.g. plum, cherry, peach, apricot or almond [2013-01] |
A61K 36/738 | . . . . | Rosa (rose) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/739 | . . . . | Sanguisorba (burnet) [2013-01] |
| A61K 36/74 | . . . | Rubiaceae (Madder family) [2024-05] WARNING
|
| A61K 36/742 | . . . . | {Coffea, e.g. coffee} [2024-05] WARNING
|
A61K 36/744 | . . . . | Gardenia [2013-01] |
A61K 36/746 | . . . . | Morinda [2013-01] |
A61K 36/748 | . . . . | Oldenlandia or Hedyotis [2013-01] |
A61K 36/75 | . . . | Rutaceae (Rue family) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/752 | . . . . | Citrus, e.g. lime, orange or lemon [2013-01] |
A61K 36/754 | . . . . | Evodia [2013-01] |
A61K 36/756 | . . . . | Phellodendron, e.g. corktree [2013-01] |
A61K 36/758 | . . . . | Zanthoxylum, e.g. pricklyash [2013-01] |
A61K 36/76 | . . . | Salicaceae (Willow family), e.g. poplar [2013-01] |
A61K 36/77 | . . . | Sapindaceae (Soapberry family), e.g. lychee or soapberry [2013-01] |
A61K 36/78 | . . . | Saururaceae (Lizard's-tail family) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/79 | . . . | Schisandraceae (Schisandra family) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/80 | . . . | Scrophulariaceae (Figwort family) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/804 | . . . . | Rehmannia [2013-01] |
A61K 36/808 | . . . . | Scrophularia (figwort) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/81 | . . . | Solanaceae (Potato family), e.g. tobacco, nightshade, tomato, belladonna, capsicum or jimsonweed [2013-01] |
A61K 36/815 | . . . . | Lycium (desert-thorn) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/82 | . . . | Theaceae (Tea family), e.g. camellia [2013-01] |
A61K 36/83 | . . . | Thymelaeaceae (Mezereum family), e.g. leatherwood or false ohelo [2013-01] |
A61K 36/835 | . . . . | Aquilaria [2013-01] |
A61K 36/84 | . . . | Valerianaceae (Valerian family), e.g. valerian [2013-01] |
A61K 36/85 | . . . | Verbenaceae (Verbena family) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/855 | . . . . | Clerodendrum, e.g. glorybower [2013-01] |
A61K 36/86 | . . . | Violaceae (Violet family) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/87 | . . . | Vitaceae or Ampelidaceae (Vine or Grape family), e.g. wine grapes, muscadine or peppervine [2013-01] |
A61K 36/88 | . . | Liliopsida (monocotyledons) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/882 | . . . | Acoraceae (Calamus family), e.g. sweetflag or Acorus calamus [2013-01] |
A61K 36/884 | . . . | Alismataceae (Water-plantain family) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/886 | . . . | Aloeaceae (Aloe family), e.g. aloe vera [2013-01] |
A61K 36/888 | . . . | Araceae (Arum family), e.g. caladium, calla lily or skunk cabbage [2013-01] |
A61K 36/8884 | . . . . | Arisaema, e.g. Jack in the pulpit [2013-01] |
A61K 36/8888 | . . . . | Pinellia [2013-01] |
A61K 36/889 | . . . | Arecaceae, Palmae or Palmaceae (Palm family), e.g. date or coconut palm or palmetto [2013-01] |
A61K 36/8895 | . . . . | Calamus, e.g. rattan [2013-01] |
A61K 36/89 | . . . | Cyperaceae (Sedge family) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/8905 | . . . . | Cyperus (flatsedge) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/894 | . . . | Dioscoreaceae (Yam family) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/8945 | . . . . | Dioscorea, e.g. yam, Chinese yam or water yam [2013-01] |
A61K 36/896 | . . . | Liliaceae (Lily family), e.g. daylily, plantain lily, Hyacinth or narcissus [2013-01] |
A61K 36/8962 | . . . . | Allium, e.g. garden onion, leek, garlic or chives [2013-01] |
A61K 36/8964 | . . . . | Anemarrhena [2013-01] |
A61K 36/8965 | . . . . | Asparagus, e.g. garden asparagus or asparagus fern [2013-01] |
A61K 36/8966 | . . . . | Fritillaria, e.g. checker lily or mission bells [2013-01] |
A61K 36/8967 | . . . . | Lilium, e.g. tiger lily or Easter lily [2013-01] |
A61K 36/8968 | . . . . | Ophiopogon (Lilyturf) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/8969 | . . . . | Polygonatum (Solomon's seal) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/898 | . . . | Orchidaceae (Orchid family) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/8984 | . . . . | Dendrobium [2013-01] |
A61K 36/8988 | . . . . | Gastrodia [2013-01] |
A61K 36/899 | . . . | Poaceae or Gramineae (Grass family), e.g. bamboo, corn or sugar cane [2013-01] |
A61K 36/8994 | . . . . | Coix (Job's tears) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/8998 | . . . . | Hordeum (barley) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/90 | . . . | Smilacaceae (Catbrier family), e.g. greenbrier or sarsaparilla [2013-01] |
A61K 36/902 | . . . | Sparganiaceae (Bur-reed family) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/904 | . . . | Stemonaceae (Stemona family), e.g. croomia [2013-01] |
A61K 36/906 | . . . | Zingiberaceae (Ginger family) [2013-01] |
A61K 36/9062 | . . . . | Alpinia, e.g. red ginger or galangal [2013-01] |
A61K 36/9064 | . . . . | Amomum, e.g. round cardamom [2013-01] |
A61K 36/9066 | . . . . | Curcuma, e.g. common turmeric, East Indian arrowroot or mango ginger [2013-01] |
A61K 36/9068 | . . . . | Zingiber, e.g. garden ginger [2013-01] |
| A61K 38/00 | Medicinal preparations containing peptides (peptides containing beta-lactam rings A61K 31/00; cyclic dipeptides not having in their molecule any other peptide link than those which form their ring, e.g. piperazine-2,5-diones, A61K 31/00; ergot alkaloids of the cyclic peptide type A61K 31/48; containing macromolecular compounds having statistically distributed amino acid units A61K 31/74; medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies A61K 39/00; medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients, e.g. peptides as drug carriers, A61K 47/00) [2016-05] NOTES
|
A61K 38/005 | . | {Enzyme inhibitors (protease inhibitors A61K 38/55)} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/01 | . | Hydrolysed proteins; Derivatives thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 38/011 | . . | {from plants} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/012 | . . | {from animals} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/014 | . . . | {from connective tissue peptides, e.g. gelatin, collagen} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/015 | . . . . | {from keratin} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/017 | . . . | {from blood} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/018 | . . . | {from milk} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/02 | . | Peptides of undefined number of amino acids; Derivatives thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 38/03 | . | Peptides having up to 20 amino acids in an undefined or only partially defined sequence; Derivatives thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 38/04 | . | Peptides having up to 20 amino acids in a fully defined sequence; Derivatives thereof ({enzyme inhibitors A61K 38/005;} gastrins {A61K 38/2207}, somatostatins A61K 38/31, melanotropins A61K 38/34 {; protease inhibitors A61K 38/55}) [2023-08] |
A61K 38/043 | . . | {Kallidins; Bradykinins; Related peptides} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/046 | . . | {Tachykinins, e.g. eledoisins, substance P; Related peptides} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/05 | . . | Dipeptides [2013-01] |
A61K 38/06 | . . | Tripeptides [2013-01] |
A61K 38/063 | . . . | {Glutathione} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/066 | . . . | {TRH, thyroliberin, thyrotropin releasing hormone} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/07 | . . | Tetrapeptides [2013-01] |
A61K 38/08 | . . |
A61K 38/085 | . . . | {Angiotensins} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/09 | . . . | Luteinising hormone-releasing hormone [LHRH] {, i.e. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone [GnRH]}; Related peptides [2016-08] |
A61K 38/095 | . . . | Oxytocins; Vasopressins; Related peptides [2021-08] |
A61K 38/10 | . . |
A61K 38/105 | . . . | {Bombesin; Related peptides} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/12 | . . | Cyclic peptides {, e.g. bacitracins; Polymyxins; Gramicidins S, C; Tyrocidins A, B or C (A61K 38/043 - A61K 38/046 take precedence)} [2016-05] |
A61K 38/13 | . . . | Cyclosporins [2013-01] |
A61K 38/14 | . . | Peptides containing saccharide radicals; Derivatives thereof {, e.g. bleomycin, phleomycin, muramylpeptides or vancomycin} [2016-08] |
A61K 38/15 | . . | Depsipeptides; Derivatives thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 38/16 | . | Peptides having more than 20 amino acids; Gastrins; Somatostatins; Melanotropins; Derivatives thereof {(enzyme inhibitors A61K 38/005)} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/162 | . . | {from virus} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/164 | . . | {from bacteria} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/166 | . . . | {Streptokinase} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/168 | . . | {from plants} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/17 | . . |
A61K 38/1703 | . . . | {from vertebrates} [2020-05] |
A61K 38/1706 | . . . . | {from fish} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/1709 | . . . . | {from mammals} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/1716 | . . . . . | {Amyloid plaque core protein} [2020-05] |
A61K 38/1719 | . . . . . | {Muscle proteins, e.g. myosin or actin} [2020-05] |
A61K 38/1722 | . . . . . | {Plasma globulins, lactoglobulins} [2020-05] |
A61K 38/1725 | . . . . . | {Complement proteins, e.g. anaphylatoxin, C3a or C5a} [2020-05] |
A61K 38/1729 | . . . . . | {Cationic antimicrobial peptides, e.g. defensins} [2020-05] |
A61K 38/1732 | . . . . . | {Lectins} [2020-05] |
A61K 38/1735 | . . . . . | {Mucins, e.g. human intestinal mucin} [2020-05] |
A61K 38/1738 | . . . . . | {Calcium binding proteins, e.g. calmodulin} [2020-05] |
A61K 38/1741 | . . . . . | {alpha-Glycoproteins} [2020-05] |
A61K 38/1745 | . . . . . | {C-reactive proteins} [2020-05] |
A61K 38/1748 | . . . . . | {Keratin; Cytokeratin} [2020-05] |
A61K 38/1751 | . . . . . | {Bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein [BPI]} [2020-05] |
A61K 38/1754 | . . . . . | {Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins} [2020-05] |
A61K 38/1758 | . . . . . | {p53} [2020-05] |
A61K 38/1761 | . . . . . | {Apoptosis related proteins, e.g. Apoptotic protease-activating factor-1 (APAF-1), Bax, Bax-inhibitory protein(s)(BI; bax-I), Myeloid cell leukemia associated protein (MCL-1), Inhibitor of apoptosis [IAP] or Bcl-2} [2020-05] |
A61K 38/1767 | . . . | {from invertebrates} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/177 | . . . | {Receptors; Cell surface antigens; Cell surface determinants} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/1774 | . . . . | {Immunoglobulin superfamily (e.g. CD2, CD4, CD8, ICAM molecules, B7 molecules, Fc-receptors, MHC-molecules)} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/1777 | . . . . | {Integrin superfamily} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/178 | . . . . | {Lectin superfamily, e.g. selectins} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/1783 | . . . . | {Nuclear receptors, e.g. retinoic acid receptor [RAR], RXR, nuclear orphan receptors} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/1787 | . . . . | {for neuromediators, e.g. serotonin receptor, dopamine receptor} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/179 | . . . . | {for growth factors; for growth regulators} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/1793 | . . . . | {for cytokines; for lymphokines; for interferons} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/1796 | . . . . | {for hormones (for neuromediators A61K 38/1787)} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/18 | . . . | Growth factors; Growth regulators [2013-01] |
A61K 38/1808 | . . . . | {Epidermal growth factor [EGF] urogastrone} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/1816 | . . . . | {Erythropoietin [EPO]} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/1825 | . . . . | {Fibroblast growth factor [FGF]} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/1833 | . . . . | {Hepatocyte growth factor; Scatter factor; Tumor cytotoxic factor II} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/1841 | . . . . | {Transforming growth factor [TGF]} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/185 | . . . . | {Nerve growth factor [NGF]; Brain derived neurotrophic factor [BDNF]; Ciliary neurotrophic factor [CNTF]; Glial derived neurotrophic factor [GDNF]; Neurotrophins, e.g. NT-3} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/1858 | . . . . | {Platelet-derived growth factor [PDGF]} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/1866 | . . . . . | {Vascular endothelial growth factor [VEGF]} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/1875 | . . . . | {Bone morphogenic factor; Osteogenins; Osteogenic factor; Bone-inducing factor} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/1883 | . . . . | {Neuregulins, e.g.. p185erbB2 ligands, glial growth factor, heregulin, ARIA, neu differentiation factor} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/1891 | . . . . | {Angiogenesic factors; Angiogenin} [2015-09] |
A61K 38/19 | . . . | Cytokines; Lymphokines; Interferons [2013-01] |
A61K 38/191 | . . . . | {Tumor necrosis factors [TNF], e.g. lymphotoxin [LT], i.e. TNF-beta} [2016-08] |
A61K 38/193 | . . . . | {Colony stimulating factors [CSF]} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/195 | . . . . | {Chemokines, e.g. RANTES} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/196 | . . . . | {Thrombopoietin} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/20 | . . . . | Interleukins [IL] [2013-01] |
A61K 38/2006 | . . . . . | {IL-1} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/2013 | . . . . . | {IL-2} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/202 | . . . . . | {IL-3} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/2026 | . . . . . | {IL-4} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/2033 | . . . . . | {IL-5} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/204 | . . . . . | {IL-6} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/2046 | . . . . . | {IL-7} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/2053 | . . . . . | {IL-8} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/206 | . . . . . | {IL-9} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/2066 | . . . . . | {IL-10} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/2073 | . . . . . | {IL-11} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/208 | . . . . . | {IL-12} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/2086 | . . . . . | {IL-13 to IL-16} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/2093 | . . . . . | {Leukaemia inhibitory factor [LIF]} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/21 | . . . . | Interferons {[IFN]} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/212 | . . . . . | {IFN-alpha} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/215 | . . . . . | {IFN-beta} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/217 | . . . . . | {IFN-gamma} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/22 | . . . | Hormones (derived from pro-opiomelanocortin, pro-enkephalin or pro-dynorphin A61K 38/33, e.g. corticotropin A61K 38/35) [2013-01] |
A61K 38/2207 | . . . . | {Gastrins; Cholecystokinins [CCK]} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/2214 | . . . . | {Motilins} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/2221 | . . . . | {Relaxins} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/2228 | . . . . | {Corticotropin releasing factor [CRF] (Urotensin)} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/2235 | . . . . | {Secretins} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/2242 | . . . . | {Atrial natriuretic factor complex: Atriopeptins, atrial natriuretic protein [ANP]; Cardionatrin, Cardiodilatin} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/225 | . . . . | {Calcitonin gene related peptide} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/2257 | . . . . | {Prolactin} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/2264 | . . . . | {Obesity-gene products, e.g. leptin} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/2271 | . . . . | {Neuropeptide Y} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/2278 | . . . . | {Vasoactive intestinal peptide [VIP]; Related peptides (e.g. Exendin)} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/2285 | . . . . | {Endothelin, vasoactive intestinal contractor [VIC]} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/2292 | . . . . | {Thymosin; Related peptides} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/23 | . . . . | Calcitonins [2013-01] |
A61K 38/24 | . . . . | Follicle-stimulating hormone [FSH]; Chorionic gonadotropins, e.g. HCG; Luteinising hormone [LH]; Thyroid-stimulating hormone [TSH] [2013-01] |
A61K 38/25 | . . . . | Growth hormone-releasing factor [GH-RF], i.e. somatoliberin [2024-01] |
A61K 38/26 | . . . . | Glucagons [2013-01] |
A61K 38/27 | . . . . | Growth hormone [GH], i.e. somatotropin [2024-01] |
A61K 38/28 | . . . . | Insulins [2013-01] |
A61K 38/29 | . . . . | Parathyroid hormone, i.e. parathormone; Parathyroid hormone-related peptides [2024-01] |
A61K 38/30 | . . . . | Insulin-like growth factors, i.e. somatomedins, e.g. IGF-1, IGF-2 {(insulin-like growth factor binding protein A61K 38/1754)} [2024-01] |
A61K 38/31 | . . . . | Somatostatins [2013-01] |
A61K 38/32 | . . . . | Thymopoietins [2013-01] |
A61K 38/33 | . . . | derived from pro-opiomelanocortin, pro-enkephalin or pro-dynorphin [2013-01] |
A61K 38/34 | . . . . | Melanocyte stimulating hormone [MSH], e.g. alpha- or beta-melanotropin [2013-01] |
A61K 38/35 | . . . . | Corticotropin [ACTH] [2013-01] |
A61K 38/36 | . . . | Blood coagulation or fibrinolysis factors [2013-01] |
A61K 38/363 | . . . . | {Fibrinogen} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/366 | . . . . | {Thrombomodulin} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/37 | . . . . | Factors VIII [2013-01] |
A61K 38/38 | . . . | Albumins [2013-01] |
A61K 38/385 | . . . . | {Serum albumin} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/39 | . . . | Connective tissue peptides, e.g. collagen, elastin, laminin, fibronectin, vitronectin, cold insoluble globulin [CIG] [2013-01] |
A61K 38/395 | . . . | {Alveolar surfactant peptides; Pulmonary surfactant peptides} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/40 | . . . | Transferrins, e.g. lactoferrins, ovotransferrins [2013-01] |
A61K 38/41 | . . | Porphyrin- or corrin-ring-containing peptides [2013-01] |
A61K 38/415 | . . . | {Cytochromes} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/42 | . . . | Haemoglobins; Myoglobins [2013-01] |
| A61K 38/43 | . . | Enzymes; Proenzymes; Derivatives thereof [2013-01] NOTE
|
A61K 38/44 | . . . | Oxidoreductases (1) [2013-01] |
A61K 38/443 | . . . . | {acting on CH-OH groups as donors, e.g. glucose oxidase, lactate dehydrogenase (1.1)} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/446 | . . . . | {Superoxide dismutase (1.15)} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/45 | . . . | Transferases (2) [2013-01] |
A61K 38/46 | . . . | Hydrolases (3) [2013-01] |
A61K 38/465 | . . . . | {acting on ester bonds (3.1), e.g. lipases, ribonucleases} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/47 | . . . . | acting on glycosyl compounds (3.2), e.g. cellulases, lactases [2013-01] |
A61K 38/48 | . . . . | acting on peptide bonds (3.4) [2013-01] |
A61K 38/4806 | . . . . . | {from animals other than mammals, e.g. snakes} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/4813 | . . . . . | {Exopeptidases (3.4.11. to 3.4.19)} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/482 | . . . . . | {Serine endopeptidases (3.4.21)} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/4826 | . . . . . . | {Trypsin (3.4.21.4) Chymotrypsin (3.4.21.1)} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/4833 | . . . . . . | {Thrombin (3.4.21.5)} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/484 | . . . . . . | {Plasmin (3.4.21.7)} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/4846 | . . . . . . | {Factor VII (3.4.21.21); Factor IX (3.4.21.22); Factor Xa (3.4.21.6); Factor XI (3.4.21.27); Factor XII (3.4.21.38)} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/4853 | . . . . . . | {Kallikrein (3.4.21.34 or 3.4.21.35)} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/486 | . . . . . . | {Elastase (3.4.21.36 or 3.4.21.37)} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/4866 | . . . . . . | {Protein C (3.4.21.69)} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/4873 | . . . . . | {Cysteine endopeptidases (3.4.22), e.g. stem bromelain, papain, ficin, cathepsin H} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/488 | . . . . . | {Aspartic endopeptidases (3.4.23), e.g. pepsin, chymosin, renin, cathepsin E} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/4886 | . . . . . | {Metalloendopeptidases (3.4.24), e.g. collagenase} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/4893 | . . . . . . | {Botulinum neurotoxin (3.4.24.69)} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/49 | . . . . . | Urokinase; Tissue plasminogen activator [2013-01] |
A61K 38/50 | . . . . | acting on carbon-nitrogen bonds, other than peptide bonds (3.5), e.g. asparaginase [2013-01] |
A61K 38/51 | . . . | Lyases (4) [2013-01] |
A61K 38/52 | . . . | Isomerases (5) [2013-01] |
A61K 38/53 | . . . | Ligases (6) [2013-01] |
A61K 38/54 | . . . | Mixtures of enzymes or proenzymes covered by more than a single one of groups A61K 38/44 - A61K 38/46 or A61K 38/51 - A61K 38/53 [2016-05] |
A61K 38/55 | . . | Protease inhibitors [2013-01] |
A61K 38/553 | . . . | {Renin inhibitors} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/556 | . . . | {Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors} [2013-01] |
A61K 38/56 | . . . | from plants [2013-01] |
A61K 38/57 | . . . |
A61K 38/58 | . . . . | from leeches, e.g. hirudin, eglin [2013-01] |
| A61K 39/00 | Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies (materials for immunoassay G01N 33/53) [2025-01] NOTES
|
A61K 39/0001 | . | {Archaeal antigens} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/0002 | . | {Fungal antigens, e.g. Trichophyton, Aspergillus, Candida} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/0003 | . | {Invertebrate antigens} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/0005 | . | {Vertebrate antigens (from snakes A61K 39/38)} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/0006 | . . | {Contraceptive vaccins; Vaccines against sex hormones} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/0007 | . . | {Nervous system antigens; Prions} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/0008 | . . | {Antigens related to auto-immune diseases; Preparations to induce self-tolerance} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/001 | . . | {Preparations to induce tolerance to non-self, e.g. prior to transplantation} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/0011 | . . | {Cancer antigens} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001102 | . . . | {Receptors, cell surface antigens or cell surface determinants} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001103 | . . . . | {Receptors for growth factors} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001104 | . . . . . | {Epidermal growth factor receptors [EGFR]} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001106 | . . . . . | {Her-2/neu/ErbB2, Her-3/ErbB3 or Her 4/ErbB4} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001107 | . . . . . | {Fibroblast growth factor receptors [FGFR]} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001108 | . . . . . | {Platelet-derived growth factor receptors [PDGFR]} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001109 | . . . . . | {Vascular endothelial growth factor receptors [VEGFR]} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/00111 | . . . . . | {Hepatocyte growth factor receptor [HGFR or c-met]} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001111 | . . . . | {Immunoglobulin superfamily} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001112 | . . . . . | {CD19 or B4} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001113 | . . . . . | {CD22, BL-CAM, siglec-2 or sialic acid- binding Ig-related lectin 2} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001114 | . . . . . | {CD74, Ii, MHC class II invariant chain or MHC class II gamma chain} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001116 | . . . . | {Receptors for cytokines} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001117 | . . . . . | {Receptors for tumor necrosis factors [TNF], e.g. lymphotoxin receptor [LTR] or CD30} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001118 | . . . . . | {Receptors for colony stimulating factors [CSF]} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001119 | . . . . . | {Receptors for interleukins [IL]} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/00112 | . . . . . | {Receptors for interferons [IFN]} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001121 | . . . . . | {Receptors for chemokines} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001122 | . . . . | {Ephrin Receptors [Eph]} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001124 | . . . . | {CD20} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001126 | . . . . | {CD38 not IgG} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001128 | . . . . | {CD44 not IgG} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001129 | . . . . | {Molecules with a "CD" designation not provided for elsewhere} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/00113 | . . . | {Growth factors} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001131 | . . . . | {Epidermal growth factor [EGF]} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001132 | . . . . | {Fibroblast growth factors [FGF]} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001133 | . . . . | {Platelet-derived growth factor [PDGF]} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001134 | . . . . | {Transforming growth factor [TGF]} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001135 | . . . . | {Vascular endothelial growth factor [VEGF]} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001136 | . . . | {Cytokines} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001138 | . . . . | {Tumor necrosis factors [TNF] or CD70} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001139 | . . . . | {Colony stimulating factors [CSF]} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/00114 | . . . . | {Interleukins [IL]} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001141 | . . . . | {Interferons [IFN]} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001142 | . . . . | {Chemokines} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001144 | . . . | {Hormones, e.g. calcitonin} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001148 | . . . | {Regulators of development} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001149 | . . . . | {Cell cycle regulated proteins, e.g. cyclin, CDC, CDK or INK-CCR} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/00115 | . . . . | {Apoptosis related proteins, e.g. survivin or livin} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001151 | . . . . . | {p53} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001152 | . . . | {Transcription factors, e.g. SOX or c-MYC} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001153 | . . . . | {Wilms tumor 1 [WT1]} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001154 | . . . | {Enzymes} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001156 | . . . . | {Tyrosinase and tyrosinase related proteinases [TRP-1 or TRP-2]} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001157 | . . . . | {Telomerase or TERT [telomerase reverse transcriptase]} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001158 | . . . . | {Proteinases} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001159 | . . . . . | {Matrix metalloproteinases [MMP]} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/00116 | . . . . . | {Serine proteases, e.g. kallikrein} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001161 | . . . . . | {Caspases} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001162 | . . . . | {Kinases, e.g. Raf or Src} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001163 | . . . . | {Phosphatases} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001164 | . . . . | {GTPases, e.g. Ras or Rho} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001166 | . . . | {Adhesion molecules, e.g. NRCAM, EpCAM or cadherins} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001168 | . . . . | {Mesothelin [MSLN]} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001169 | . . . | {Tumor associated carbohydrates} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/00117 | . . . . | {Mucins, e.g. MUC-1} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001171 | . . . . | {Gangliosides, e.g. GM2, GD2 or GD3} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001172 | . . . . | {Sialyl-Thomson-nouvelle antigen [sTn]} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001173 | . . . . | {Globo-H} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001174 | . . . | {Proteoglycans, e.g. glypican, brevican or CSPG4} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001176 | . . . | {Heat shock proteins} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001178 | . . . | {Tumor rejection antigen precursor [TRAP]} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/00118 | . . . | {from embryonic or fetal origin} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001181 | . . . . | {Alpha-feto protein} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001182 | . . . . | {Carcinoembryonic antigen [CEA]} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001184 | . . . | {Cancer testis antigens, e.g. SSX, BAGE, GAGE or SAGE} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001186 | . . . . | {MAGE} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001188 | . . . . | {NY-ESO} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001189 | . . . . | {PRAME} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/00119 | . . . | {Melanoma antigens} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001191 | . . . . | {Melan-A/MART} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001192 | . . . . | {Glycoprotein 100 [Gp100]} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001193 | . . . | {Prostate associated antigens e.g. Prostate stem cell antigen [PSCA]; Prostate carcinoma tumor antigen [PCTA]; PAP or PSGR} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001194 | . . . . | {Prostate specific antigen [PSA]} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001195 | . . . . | {Prostate specific membrane antigen [PSMA]} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001196 | . . . | {Fusion proteins originating from gene translocation in cancer cells} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001197 | . . . . | {Breakpoint cluster region-abelson tyrosine kinase [BCR-ABL]} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/001198 | . . . . | {Pml-RARalpha} [2025-01] |
A61K 39/0012 | . . | {Lipids; Lipoproteins} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/0013 | . | {Therapeutic immunisation against small organic molecules, e.g. cocaine, nicotine} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/0015 | . | {Combination vaccines based on measles-mumps-rubella} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/0016 | . | {Combination vaccines based on diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/0017 | . . | {Combination vaccines based on whole cell diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/0018 | . . | {Combination vaccines based on acellular diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/002 | . | Protozoa antigens [2013-01] |
A61K 39/005 | . . | Trypanosoma antigens [2013-01] |
A61K 39/008 | . . | Leishmania antigens [2013-01] |
A61K 39/012 | . . | Coccidia antigens [2013-01] |
A61K 39/015 | . . | Hemosporidia antigens, e.g. Plasmodium antigens [2013-01] |
A61K 39/018 | . . . | Babesia antigens, e.g. Theileria antigens [2013-01] |
A61K 39/02 | . | Bacterial antigens [2013-01] |
A61K 39/0208 | . . | {Specific bacteria not otherwise provided for} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/0216 | . . | {Bacteriodetes, e.g. Bacteroides, Ornithobacter, Porphyromonas} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/0225 | . . | {Spirochetes, e.g. Treponema, Leptospira, Borrelia} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/0233 | . . | {Rickettsiales, e.g. Anaplasma} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/0241 | . . | {Mollicutes, e.g. Mycoplasma, Erysipelothrix} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/025 | . . | {Enterobacteriales, e.g. Enterobacter} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/0258 | . . . | {Escherichia} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/0266 | . . . | {Klebsiella} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/0275 | . . . | {Salmonella} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/0283 | . . . | {Shigella} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/0291 | . . . | {Yersinia} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/04 | . . | Mycobacterium, e.g. Mycobacterium tuberculosis [2013-01] |
A61K 39/05 | . . | {Actinobacteria, e.g. Actinomyces, Streptomyces, Nocardia, Bifidobacterium, Gardnerella}, Corynebacterium; Propionibacterium {(Mycobacterium A61K 39/04)} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/07 | . . | Bacillus [2013-01] |
A61K 39/08 | . . | Clostridium, e.g. Clostridium tetani [2013-01] |
A61K 39/085 | . . | Staphylococcus [2013-01] |
A61K 39/09 | . . | {Lactobacillales, e.g. aerococcus, enterococcus, lactobacillus, lactococcus}, streptococcus [2013-01] |
A61K 39/092 | . . . | {Streptococcus} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/095 | . . | Neisseria [2013-01] |
A61K 39/098 | . . | {Brucella} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/099 | . . | {Bordetella} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/10 | . . | {Brucella; Bordetella, e.g. Bordetella pertussis; Not used, see subgroups} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/102 | . . | {Pasteurellales, e.g. Actinobacillus}, Pasteurella; Haemophilus [2013-01] |
A61K 39/104 | . . | {Pseudomonadales, e.g.} Pseudomonas [2013-01] |
A61K 39/1045 | . . . | {Moraxella} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/105 | . . | {Delta proteobacteriales, e.g. Lawsonia; Epsilon proteobacteriales, e.g. campylobacter, helicobacter} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/106 | . . | {Vibrio; Campylobacter; Not used, see subgroups} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/107 | . . | {Vibrio} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/114 | . . | Fusobacterium [2013-01] |
A61K 39/116 | . . | Polyvalent bacterial antigens [2020-05] |
A61K 39/118 | . | Chlamydiaceae, e.g. Chlamydia trachomatis or Chlamydia psittaci [2014-02] |
A61K 39/12 | . | Viral antigens [2013-01] |
A61K 39/125 | . . | Picornaviridae, e.g. calicivirus [2013-01] |
A61K 39/13 | . . . | Poliovirus [2013-01] |
A61K 39/135 | . . . | Foot- and mouth-disease virus [2013-01] |
A61K 39/145 | . . | Orthomyxoviridae, e.g. influenza virus [2013-01] |
A61K 39/15 | . . | Reoviridae, e.g. calf diarrhea virus [2013-01] |
A61K 39/155 | . . | Paramyxoviridae, e.g. parainfluenza virus [2013-01] |
A61K 39/165 | . . . | Mumps or measles virus [2013-01] |
A61K 39/17 | . . . | Newcastle disease virus [2013-01] |
A61K 39/175 | . . . | Canine distemper virus [2013-01] |
A61K 39/187 | . . | Hog cholera virus [2013-01] |
A61K 39/193 | . . | Equine encephalomyelitis virus [2013-01] |
A61K 39/20 | . . | Rubella virus [2013-01] |
A61K 39/205 | . . | Rhabdoviridae, e.g. rabies virus [2013-01] |
A61K 39/21 | . . | Retroviridae, e.g. equine infectious anemia virus [2013-01] |
A61K 39/215 | . . | Coronaviridae, e.g. avian infectious bronchitis virus [2017-08] |
A61K 39/225 | . . . | Porcine transmissible gastroenteritis virus [2013-01] |
A61K 39/23 | . . | Parvoviridae, e.g. feline panleukopenia virus [2013-01] |
A61K 39/235 | . . | Adenoviridae [2013-01] |
A61K 39/245 | . . | Herpetoviridae, e.g. herpes simplex virus [2013-01] |
A61K 39/25 | . . . | Varicella-zoster virus [2013-01] |
A61K 39/255 | . . . | Marek's disease virus [2013-01] |
A61K 39/265 | . . . | Infectious rhinotracheitis virus [2013-01] |
A61K 39/27 | . . . | Equine rhinopneumonitis virus [2013-01] |
A61K 39/275 | . . | Poxviridae, e.g. avipoxvirus [2013-01] |
A61K 39/285 | . . . | Vaccinia virus or variola virus [2013-01] |
A61K 39/29 | . . | Hepatitis virus [2013-01] |
A61K 39/292 | . . . | {Serum hepatitis virus, hepatitis B virus, e.g. Australia antigen} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/295 | . . | Polyvalent viral antigens (vaccinia virus or variola virus A61K 39/285); Mixtures of viral and bacterial antigens [2020-05] |
A61K 39/35 | . | Allergens [2013-01] |
A61K 39/36 | . . | from pollen [2013-01] |
A61K 39/38 | . | Antigens from snakes [2013-01] |
A61K 39/385 | . | Haptens or antigens, bound to carriers [2013-01] |
A61K 39/39 | . | characterised by the immunostimulating additives, e.g. chemical adjuvants [2013-01] |
A61K 39/395 | . | Antibodies (agglutinins A61K 38/36 {; as drug carriers A61K 47/50}); Immunoglobulins; Immune serum, e.g. antilymphocytic serum [2017-08] |
A61K 39/39508 | . . | {from milk, i.e. lactoglobulins} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/39516 | . . | {from serum, plasma} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/39525 | . . . | {Purification} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/39533 | . . | {against materials from animals} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/39541 | . . . | {against normal tissues, cells} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/3955 | . . . | {against proteinaceous materials, e.g. enzymes, hormones, lymphokines} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/39558 | . . . | {against tumor tissues, cells, antigens} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/39566 | . . . | {against immunoglobulins, e.g. anti-idiotypic antibodies} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/39575 | . . | {against materials from other living beings excluding bacteria and viruses, e.g. protozoa, fungi, plants} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/39583 | . . | {against materials not provided for elsewhere, e.g. haptens, coenzymes} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/39591 | . . | {Stabilisation, fragmentation} [2013-01] |
A61K 39/40 | . . | bacterial [2013-01] |
A61K 39/42 | . . | viral [2013-01] |
A61K 39/44 | . . | Antibodies bound to carriers [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/505 | . | {comprising antibodies} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/507 | . . | {Comprising a combination of two or more separate antibodies} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/51 | . | {comprising whole cells, viruses or DNA/RNA} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/515 | . . | {Animal cells} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/5152 | . . . | {Tumor cells} [2025-01] |
A61K 2039/5154 | . . . | {Antigen presenting cells [APCs], e.g. dendritic cells or macrophages} [2025-01] |
A61K 2039/5156 | . . . | {expressing foreign proteins} [2025-01] |
A61K 2039/5158 | . . . | {Antigen-pulsed cells, e.g. T-cells} [2025-01] |
A61K 2039/517 | . . | {Plant cells} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/52 | . . | {Bacterial cells; Fungal cells; Protozoal cells} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/521 | . . . | {inactivated (killed)} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/522 | . . . | {avirulent or attenuated} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/523 | . . . | {expressing foreign proteins} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/525 | . . | {Virus} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/5252 | . . . | {inactivated (killed)} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/5254 | . . . | {avirulent or attenuated} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/5256 | . . . | {expressing foreign proteins} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/5258 | . . . | {Virus-like particles} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/53 | . . | {DNA (RNA) vaccination} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/54 | . | {characterised by the route of administration} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/541 | . . | {Mucosal route} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/545 | . | {characterised by the dose, timing or administration schedule} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/55 | . | {characterised by the host/recipient, e.g. newborn with maternal antibodies} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/552 | . . | {Veterinary vaccine} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/555 | . | {characterised by a specific combination antigen/adjuvant} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/55505 | . . | {Inorganic adjuvants} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/55511 | . . | {Organic adjuvants} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/55516 | . . . | {Proteins; Peptides} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/55522 | . . . | {Cytokines; Lymphokines; Interferons} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/55527 | . . . . | {Interleukins} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/55533 | . . . . . | {IL-2} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/55538 | . . . . . | {IL-12} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/55544 | . . . | {Bacterial toxins} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/5555 | . . . | {Muramyl dipeptides} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/55555 | . . . | {Liposomes; Vesicles, e.g. nanoparticles; Spheres, e.g. nanospheres; Polymers} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/55561 | . . . | {CpG containing adjuvants; Oligonucleotide containing adjuvants} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/55566 | . . . | {Emulsions, e.g. Freund's adjuvant, MF59} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/55572 | . . . | {Lipopolysaccharides; Lipid A; Monophosphoryl lipid A} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/55577 | . . . | {Saponins; Quil A; QS21; ISCOMS} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/55583 | . . . | {Polysaccharides} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/55588 | . . | {Adjuvants of undefined constitution} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/55594 | . . . | {from bacteria} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/57 | . | {characterised by the type of response, e.g. Th1, Th2} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/572 | . . | {cytotoxic response} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/575 | . . | {humoral response} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/577 | . . | {tolerising response} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/58 | . | {raising an immune response against a target which is not the antigen used for immunisation} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/585 | . . | {wherein the target is cancer} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/60 | . | {characteristics by the carrier linked to the antigen} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/6006 | . . | {Cells} [2024-08] |
A61K 2039/6012 | . . | {Haptens, e.g. di- or trinitrophenyl (DNP, TNP)} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/6018 | . . | {Lipids, e.g. in lipopeptides} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/6025 | . . | {Nucleotides} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/6031 | . . | {Proteins} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/6037 | . . . | {Bacterial toxins, e.g. diphteria toxoid [DT], tetanus toxoid [TT]} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/6043 | . . . | {Heat shock proteins} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/605 | . . . | {MHC molecules or ligands thereof} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/6056 | . . . | {Antibodies} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/6062 | . . . | {Muramyl peptides} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/6068 | . . . | {Other bacterial proteins, e.g. OMP} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/6075 | . . . | {Viral proteins} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/6081 | . . . | {Albumin; Keyhole limpet haemocyanin [KLH]} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/6087 | . . | {Polysaccharides; Lipopolysaccharides [LPS]} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/6093 | . . | {Synthetic polymers, e.g. polyethyleneglycol [PEG], Polymers or copolymers of (D) glutamate and (D) lysine} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/62 | . | {characterised by the link between antigen and carrier} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/622 | . . | {non-covalent binding} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/625 | . . | {binding through the biotin-streptavidin system or similar} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/627 | . . | {characterised by the linker} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/64 | . | {characterised by the architecture of the carrier-antigen complex, e.g. repetition of carrier-antigen units} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/645 | . . | {Dendrimers; Multiple antigen peptides} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/70 | . | {Multivalent vaccine} [2013-01] |
A61K 2039/80 | . | {Vaccine for a specifically defined cancer} [2021-08] |
A61K 2039/804 | . . | {Blood cells [leukemia, lymphoma]} [2018-08] |
A61K 2039/812 | . . | {Breast} [2018-08] |
A61K 2039/82 | . . | {Colon} [2018-08] |
A61K 2039/828 | . . | {Stomach} [2018-08] |
A61K 2039/836 | . . | {Intestine} [2018-08] |
A61K 2039/844 | . . | {Liver} [2018-08] |
A61K 2039/852 | . . | {Pancreas} [2018-08] |
A61K 2039/86 | . . | {Lung} [2018-08] |
A61K 2039/868 | . . | {kidney} [2018-08] |
A61K 2039/876 | . . | {Skin, melanoma} [2018-08] |
A61K 2039/884 | . . | {prostate} [2018-08] |
A61K 2039/892 | . . | {Reproductive system [uterus, ovaries, cervix, testes]} [2018-08] |
| A61K 40/00 | Cellular immunotherapy (medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies A61K 39/00) [2025-05] NOTES
|
A61K 40/10 | . | characterised by the cell type used [2025-01] |
A61K 40/11 | . . | T-cells, e.g. tumour infiltrating lymphocytes [TIL] or regulatory T [Treg] cells; Lymphokine-activated killer [LAK] cells [2025-01] |
A61K 40/13 | . . | B-cells [2025-01] |
A61K 40/15 | . . | Natural-killer [NK] cells; Natural-killer T [NKT] cells [2025-01] |
A61K 40/17 | . . | Monocytes; Macrophages [2025-01] |
A61K 40/19 | . . | Dendritic cells [2025-01] |
A61K 40/20 | . | characterised by the effect or the function of the cells [2025-01] |
A61K 40/22 | . . | Immunosuppressive or immunotolerising [2025-01] |
A61K 40/24 | . . | Antigen-presenting cells [APC] [2025-01] |
A61K 40/30 | . | characterised by the recombinant expression of specific molecules in the cells of the immune system [2025-01] |
A61K 40/31 | . . | Chimeric antigen receptors [CAR] [2025-01] |
A61K 40/32 | . . | T-cell receptors [TCR] [2025-01] |
A61K 40/33 | . . | Antibodies; T-cell engagers [2025-01] |
A61K 40/34 | . . | Antigenic peptides [2025-01] |
A61K 40/35 | . . | Cytokines [2025-01] |
A61K 40/36 | . . | Immune checkpoint inhibitors [2025-01] |
A61K 40/40 | . | characterised by antigens that are targeted or presented by cells of the immune system [2025-01] |
A61K 40/405 | . . | {Invertebrates antigens} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/41 | . . | Vertebrate antigens [2025-01] |
A61K 40/412 | . . . | {Contraceptive or sex hormones} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/414 | . . . | {Nervous system antigens} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/416 | . . . | {Antigens related to auto-immune diseases; Preparations to induce self-tolerance} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/418 | . . . | {Antigens related to induction of tolerance to non-self} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/42 | . . . | Cancer antigens [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4201 | . . . . | {Neoantigens} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4202 | . . . . | {Receptors, cell surface antigens or cell surface determinants} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4203 | . . . . . | {Receptors for growth factors} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4204 | . . . . . . | {Epidermal growth factor receptors [EGFR]} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4205 | . . . . . . | {Her-2/neu/ErbB2, Her-3/ErbB3 or Her 4/ ErbB4} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4206 | . . . . . . | {Fibroblast growth factor receptors [FGFR]} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4207 | . . . . . . | {Platelet-derived growth factor receptors [PDGFR]} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4208 | . . . . . . | {Vascular endothelial growth factor receptors [VEGFR]} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4209 | . . . . . . | {Hepatocyte growth factor receptor [HGFR] or c-met]} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/421 | . . . . . | {Immunoglobulin superfamily} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4211 | . . . . . . | {CD19 or B4} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4212 | . . . . . . | {CD22, BL-CAM, siglec-2 or sialic acid binding Ig-related lectin 2} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4213 | . . . . . . | {CD74, Ii, MHC class II invariant chain or MHC class II gamma chain} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4214 | . . . . . | {Receptors for cytokines} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4215 | . . . . . . | {Receptors for tumor necrosis factors [TNF], e.g. lymphotoxin receptor [LTR], CD30} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4216 | . . . . . . | {Receptors for colony stimulating factors [CSF]} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4217 | . . . . . . | {Receptors for interleukins [IL]} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4218 | . . . . . . | {Receptors for interferons [IFN]} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4219 | . . . . . . | {Receptors for chemokines} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/422 | . . . . . | {Ephrin Receptors [Eph]} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4221 | . . . . . | {CD20} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4222 | . . . . . | {CD38 not IgG} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4223 | . . . . . | {CD44 not IgG} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4224 | . . . . . | {Molecules with a "CD" designation not provided for elsewhere} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4225 | . . . . | {Growth factors} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4226 | . . . . . | {Epidermal growth factor [EGF]} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4227 | . . . . . | {Fibroblast growth factors [FGF]} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4228 | . . . . . | {Platelet-derived growth factor [PDGF]} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4229 | . . . . . | {Transforming growth factor [TGF]} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/423 | . . . . . | {Vascular endothelial growth factor [VEGF]} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4231 | . . . . | {Cytokines} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4232 | . . . . . | {Tumor necrosis factors [TNF] or CD70} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4233 | . . . . . | {Colony stimulating factors [CSF]} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4234 | . . . . . | {Interleukins [IL]} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4235 | . . . . . | {Interferons [IFN]} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4236 | . . . . . | {Chemokines} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4237 | . . . . | {Hormones, e.g. calcitonin} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4238 | . . . . | {Regulators of development} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4239 | . . . . . | {Cell cycle regulated proteins, e.g. cyclin, CDC, CDK or INK-CCR} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/424 | . . . . . | {Apoptosis related proteins, e.g. survivin or livin} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4241 | . . . . . . | {p53} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4242 | . . . . | {Transcription factors, e.g. SOX or c-MYC} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4243 | . . . . . | {Wilms tumor 1 [WT1]} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4244 | . . . . | {Enzymes} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4245 | . . . . . | {Tyrosinase or tyrosinase related proteinases [TRP-1 or TRP-2]} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4246 | . . . . . | {Telomerase or [telomerase reverse transcriptase [TERT]} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4247 | . . . . . | {Proteinases} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4248 | . . . . . . | {Matrix metalloproteinases [MMP]} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4249 | . . . . . . | {Serine proteases, e.g. kallikrein} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/425 | . . . . . . | {Caspases} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4251 | . . . . . | {Kinases, e.g. Raf or Src} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4252 | . . . . . | {Phosphatases} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4253 | . . . . . | {GTPases, e.g. Ras or Rho} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4254 | . . . . | {Adhesion molecules, e.g. NRCAM, EpCAM or cadherins} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4255 | . . . . . | {Mesothelin [MSLN]} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4256 | . . . . | {Tumor associated carbohydrates} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4257 | . . . . . | {Mucins, e.g. MUC-1} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4258 | . . . . . | {Gangliosides, e.g. GM2, GD2 or GD3} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4259 | . . . . . | {Sialyl-Thomson-nouvelle antigen [sTn]} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/426 | . . . . . | {Globo-H} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4261 | . . . . | {Proteoglycans, e.g. glypican, brevican or CSPG4} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4262 | . . . . | {Heat shock proteins} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4263 | . . . . | {Tumor rejection antigen precursor [TRAP]} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4264 | . . . . | {from embryonic or fetal origin} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4265 | . . . . . | {Alpha-feto protein} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4266 | . . . . . | {Carcinoembryonic antigen [CEA]} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4267 | . . . . | {Cancer testis antigens, e.g. SSX, BAGE, GAGE or SAGE} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4268 | . . . . . | {MAGE} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4269 | . . . . . | {NY-ESO} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/427 | . . . . . | {PRAME} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4271 | . . . . | {Melanoma antigens} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4272 | . . . . . | {Melan-A/MART} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4273 | . . . . . | {Glycoprotein 100 [Gp100]} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4274 | . . . . | {Prostate associated antigens e.g. Prostate stem cell antigen [PSCA]; Prostate carcinoma tumor antigen [PCTA]; Prostatic acid phosphatase [PAP]; Prostate-specific G-protein-coupled receptor [PSGR]} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4275 | . . . . . | {Prostate specific antigen [PSA]} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4276 | . . . . . | {Prostate specific membrane antigen [PSMA]} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4277 | . . . . | {Fusion proteins originating from gene translocation in cancer cells} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4278 | . . . . . | {Breakpoint cluster region-abelson tyrosine kinase [BCR-ABL]} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4279 | . . . . . | {Pml-RARalpha} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/428 | . . . . | {Undefined tumor antigens, e.g. tumor lysate or antigens targeted by cells isolated from tumor} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4285 | . . . | {Lipids; Lipoproteins} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/429 | . . | {Small organic molecules e.g. cocaine or nicotine} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/43 | . . | Protozoan antigens [2025-01] |
A61K 40/432 | . . . | {Trypanosoma antigens} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/434 | . . . | {Leishmania antigens} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/436 | . . . | {Coccidia antigens} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/438 | . . . | {Hemosporidia antigens, e.g. Plasmodium antigens} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4385 | . . . . | {Babesia antigens, e.g. Theileria antigens} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/44 | . . | Fungal antigens [2025-01] |
A61K 40/45 | . . | Bacterial antigens [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4512 | . . . | {Bacteriodetes, e.g. Bacteroides, Ornithobacter or Porphyromonas} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4514 | . . . | {Spirochetes, e.g. Treponema, Leptospira or Borrelia} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4516 | . . . | {Rickettsiales, e.g. Anaplasma} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4518 | . . . | {Mollicutes, e.g. Mycoplasma or Erysipelothrix} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/452 | . . . | {Enterobacteriales, e.g. Enterobacter} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4522 | . . . . | {Yersinia} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4524 | . . . | {Mycobacterium, e.g. Mycobacterium tuberculosis} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4526 | . . . | {Corynebacterium or Propionibacterium, Actinobacteria, e.g. Actinomyces, Streptomyces, Nocardia, Bifidobacterium or Gardnerella} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4528 | . . . | {Bacillus} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/453 | . . . | {Clostridium, e.g. Clostridium tetani} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4532 | . . . | {Staphylococcus} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4534 | . . . | {Streptococcus} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4536 | . . . | {Lactobacillales, e.g. aerococcus, enterococcus, lactobacillus or lactococcus} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4538 | . . . | {Neisseria} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/454 | . . . | {Brucella; Bordetella, e.g. Bordetella pertussis} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4542 | . . . | {Pasteurellales, e.g. Actinobacillus, Pasteurella; Haemophilus} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4544 | . . . | {Pseudomonadales, e.g. Pseudomonas} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4546 | . . . . | {Moraxella} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4548 | . . . | {Delta proteobacteriales, e.g. Lawsonia; Epsilon proteobacteriales} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/455 | . . . | {Vibrio; Campylobacter} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/456 | . . . | {Escherichia; Klebsiella} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4562 | . . . | {Salmonella; Shigella} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4564 | . . . | {Fusobacterium} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4566 | . . . | {Polyvalent bacterial antigens} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/4568 | . . . | {Chlamydiaceae, e.g. Chlamydia trachomatis or Chlamydia psittaci} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/46 | . . | Viral antigens [2025-01] |
A61K 40/48 | . . | Allergens [2025-01] |
A61K 40/482 | . . . | {from pollen} [2025-01] |
A61K 40/50 | . | characterised by the use of allogeneic cells [2025-01] |
A61K 41/00 | Medicinal preparations obtained by treating materials with wave energy or particle radiation {; Therapies using these preparations} [2020-01] |
A61K 41/0004 | . | {Homeopathy; Vitalisation; Resonance; Dynamisation, e.g. esoteric applications; Oxygenation of blood} [2013-01] |
| A61K 41/0023 | . | {Aggression treatment or altering} [2025-05] NOTE
|
A61K 41/0028 | . | {Disruption, e.g. by heat or ultrasounds, sonophysical or sonochemical activation, e.g. thermosensitive or heat-sensitive liposomes, disruption of calculi with a medicinal preparation and ultrasounds} [2016-08] |
A61K 41/0033 | . . | {Sonodynamic cancer therapy with sonochemically active agents or sonosensitizers, having their cytotoxic effects enhanced through application of ultrasounds (ultrasound therapy per se A61N 7/00)} [2013-01] |
A61K 41/0038 | . | {Radiosensitizing, i.e. administration of pharmaceutical agents that enhance the effect of radiotherapy (radiotherapy per se A61N 5/10)} [2013-01] |
A61K 41/0042 | . | {Photocleavage of drugs in vivo, e.g. cleavage of photolabile linkers in vivo by UV radiation for releasing the pharmacologically-active agent from the administered agent; photothrombosis or photoocclusion} [2013-01] |
| A61K 41/0047 | . | {Sonopheresis, i.e. ultrasonically-enhanced transdermal delivery, electroporation of a pharmacologically active agent} [2025-05] NOTE
|
A61K 41/0052 | . | {Thermotherapy; Hyperthermia; Magnetic induction; Induction heating therapy} [2017-08] |
A61K 41/0057 | . | {Photodynamic therapy with a photosensitizer, i.e. agent able to produce reactive oxygen species upon exposure to light or radiation, e.g. UV or visible light; photocleavage of nucleic acids with an agent} [2013-01] |
A61K 41/0061 | . . | {5-aminolevulinic acid-based PDT: 5-ALA-PDT involving porphyrins or precursors of protoporphyrins generated in vivo from 5-ALA} [2013-01] |
A61K 41/0066 | . . | {Psoralene-activated UV-A photochemotherapy (PUVA-therapy), e.g. for treatment of psoriasis or eczema, extracorporeal photopheresis with psoralens or fucocoumarins} [2013-01] |
A61K 41/0071 | . . | {PDT with porphyrins having exactly 20 ring atoms, i.e. based on the non-expanded tetrapyrrolic ring system, e.g. bacteriochlorin, chlorin-e6, or phthalocyanines} [2013-01] |
A61K 41/0076 | . . | {PDT with expanded (metallo)porphyrins, i.e. having more than 20 ring atoms, e.g. texaphyrins, sapphyrins, hexaphyrins, pentaphyrins, porphocyanines} [2013-01] |
A61K 41/008 | . . | {Two-Photon or Multi-Photon PDT, e.g. with upconverting dyes or photosensitisers} [2013-01] |
A61K 41/0085 | . | {Mossbauer effect therapy based on mossbauer effect of a material, i.e. re-emission of gamma rays after absorption of gamma rays by the material; selective radiation therapy, i.e. involving re-emission of ionizing radiation upon exposure to a first ionizing radiation} [2013-01] |
A61K 41/009 | . | {Neutron capture therapy, e.g. using uranium or non-boron material} [2013-01] |
A61K 41/0095 | . . | {Boron neutron capture therapy, i.e. BNCT, e.g. using boronated porphyrins} [2013-01] |
A61K 41/10 | . | Inactivation or decontamination of a medicinal preparation prior to administration to an animal or a person [2020-01] |
A61K 41/13 | . . | by ultrasonic waves [2020-01] |
A61K 41/17 | . . | by ultraviolet [UV] or infrared [IR] light, X-rays or gamma rays [2020-01] |
A61K 45/00 | Medicinal preparations containing active ingredients not provided for in groups A61K 31/00 - A61K 41/00 [2016-05] |
A61K 45/05 | . | {Immunological preparations stimulating the reticulo-endothelial system, e.g. against cancer} [2015-10] |
A61K 45/06 | . | Mixtures of active ingredients without chemical characterisation, e.g. antiphlogistics and cardiaca [2013-01] |
A61K 47/00 | Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient [2017-08] |
A61K 47/02 | . | Inorganic compounds [2013-01] |
A61K 47/06 | . | Organic compounds, e.g. natural or synthetic hydrocarbons, polyolefins, mineral oil, petrolatum or ozokerite [2017-08] |
A61K 47/08 | . . | containing oxygen, {e.g. ethers, acetals, ketones, quinones, aldehydes, peroxides} [2013-01] |
A61K 47/10 | . . . | Alcohols; Phenols; Salts thereof, e.g. glycerol; Polyethylene glycols [PEG]; Poloxamers; PEG/POE alkyl ethers [2017-08] |
A61K 47/12 | . . . | Carboxylic acids; Salts or anhydrides thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 47/14 | . . . | Esters of carboxylic acids, e.g. fatty acid monoglycerides, medium-chain triglycerides, parabens or PEG fatty acid esters [2017-08] |
A61K 47/16 | . . | containing nitrogen, {e.g. nitro-, nitroso-, azo-compounds, nitriles, cyanates} [2013-01] |
A61K 47/18 | . . . | Amines; Amides; Ureas; Quaternary ammonium compounds; Amino acids; Oligopeptides having up to five amino acids [2017-08] |
A61K 47/183 | . . . . | {Amino acids, e.g. glycine, EDTA or aspartame} [2021-02] |
A61K 47/186 | . . . . | {Quaternary ammonium compounds, e.g. benzalkonium chloride or cetrimide} [2021-02] |
A61K 47/20 | . . | containing sulfur, e.g. dimethyl sulfoxide [DMSO], docusate, sodium lauryl sulfate or aminosulfonic acids [2021-02] |
A61K 47/22 | . . | Heterocyclic compounds, e.g. ascorbic acid, tocopherol or pyrrolidones [2021-02] |
A61K 47/24 | . . | containing atoms other than carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, halogen, nitrogen or sulfur, e.g. cyclomethicone or phospholipids [2017-08] |
A61K 47/26 | . . | Carbohydrates, e.g. sugar alcohols, amino sugars, nucleic acids, mono-, di- or oligo-saccharides; Derivatives thereof, e.g. polysorbates, sorbitan fatty acid esters or glycyrrhizin [2021-02] |
A61K 47/28 | . . | Steroids, e.g. cholesterol, bile acids or glycyrrhetinic acid [2021-02] |
A61K 47/30 | . | Macromolecular organic or inorganic compounds, e.g. inorganic polyphosphates [2017-08] |
A61K 47/32 | . . | Macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. carbomers {, poly(meth)acrylates, or polyvinyl pyrrolidone} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/34 | . . | Macromolecular compounds obtained otherwise than by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polyesters, polyamino acids, polysiloxanes, polyphosphazines, copolymers of polyalkylene glycol or poloxamers (A61K 47/10 takes precedence) [2017-08] |
A61K 47/36 | . . | Polysaccharides; Derivatives thereof, e.g. gums, starch, alginate, dextrin, hyaluronic acid, chitosan, inulin, agar or pectin [2017-08] |
A61K 47/38 | . . . | Cellulose; Derivatives thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 47/40 | . . . | Cyclodextrins; Derivatives thereof [2017-08] |
A61K 47/42 | . . | Proteins; Polypeptides; Degradation products thereof; Derivatives thereof, e.g. albumin, gelatin or zein (oligopeptides having up to five amino acids {A61K 47/183}; polyamino acids A61K 47/34) [2017-08] |
A61K 47/44 | . | Oils, fats or waxes according to two or more groups of A61K 47/02-A61K 47/42; Natural or modified natural oils, fats or waxes, e.g. castor oil, polyethoxylated castor oil, montan wax, lignite, shellac, rosin, beeswax or lanolin (synthetic glycerides, e.g. medium-chain triglycerides, A61K 47/14) [2017-08] |
A61K 47/46 | . | Ingredients of undetermined constitution or reaction products thereof, e.g. skin, bone, milk, cotton fibre, eggshell, oxgall or plant extracts [2017-08] |
A61K 47/50 | . | the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates [2017-08] |
A61K 47/51 | . . | the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent [2017-08] |
A61K 47/52 | . . . | the modifying agent being an inorganic compound, e.g. an inorganic ion that is complexed with the active ingredient [2017-08] |
A61K 47/54 | . . . | the modifying agent being an organic compound [2017-08] |
A61K 47/541 | . . . . | {Organic ions forming an ion pair complex with the pharmacologically or therapeutically active agent} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/542 | . . . . | {Carboxylic acids, e.g. a fatty acid or an amino acid} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/543 | . . . . | {Lipids, e.g. triglycerides; Polyamines, e.g. spermine or spermidine} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/544 | . . . . . | {Phospholipids} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/545 | . . . . | {Heterocyclic compounds (A61K 47/558 takes precedence)} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/546 | . . . . . | {Porphyrines; Porphyrine with an expanded ring system, e.g. texaphyrine} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/548 | . . . . | {Phosphates or phosphonates, e.g. bone-seeking (phospholipids A61K 47/544)} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/549 | . . . . | {Sugars, nucleosides, nucleotides or nucleic acids} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/551 | . . . . . | {one of the codrug's components being a vitamin, e.g. niacinamide, vitamin B3, cobalamin, vitamin B12, folate, vitamin A or retinoic acid} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/552 | . . . . . | {one of the codrug's components being an antibiotic} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/554 | . . . . | {the modifying agent being a steroid plant sterol, glycyrrhetic acid, enoxolone or bile acid} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/555 | . . . . | {pre-targeting systems involving an organic compound, other than a peptide, protein or antibody, for targeting specific cells} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/556 | . . . . . | {enzyme catalyzed therapeutic agent [ECTA]} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/557 | . . . . . | {the modifying agent being biotin} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/558 | . . . . | {the modifying agent being a chemiluminescent acceptor} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/559 | . . . . | {Redox delivery systems, e.g. dihydropyridine pyridinium salt redox systems} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/56 | . . . | the modifying agent being an organic macromolecular compound, e.g. an oligomeric, polymeric or dendrimeric molecule [2017-08] |
A61K 47/58 | . . . . | obtained by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. poly[meth]acrylate, polyacrylamide, polystyrene, polyvinylpyrrolidone, polyvinylalcohol or polystyrene sulfonic acid resin [2017-08] |
A61K 47/585 | . . . . . | {Ion exchange resins, e.g. polystyrene sulfonic acid resin} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/59 | . . . . | obtained otherwise than by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polyureas or polyurethanes [2017-08] |
A61K 47/593 | . . . . . | {Polyesters, e.g. PLGA or polylactide-co-glycolide} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/595 | . . . . . | {Polyamides, e.g. nylon (polyamino acids A61K 47/62)} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/60 | . . . . . | the organic macromolecular compound being a polyoxyalkylene oligomer, polymer or dendrimer, e.g. PEG, PPG, PEO or polyglycerol [2017-08] |
A61K 47/605 | . . . . . | {the macromolecule containing phosphorus in the main chain, e.g. poly-phosphazene} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/61 | . . . . | the organic macromolecular compound being a polysaccharide or a derivative thereof [2017-08] |
A61K 47/62 | . . . | the modifying agent being a protein, peptide or polyamino acid [2017-08] |
A61K 47/64 | . . . . | Drug-peptide, drug-protein or drug-polyamino acid conjugates, i.e. the modifying agent being a peptide, protein or polyamino acid which is covalently bonded or complexed to a therapeutically active agent (peptidic linkers A61K 47/65) [2017-08] |
A61K 47/641 | . . . . . | {Branched, dendritic or hypercomb peptides} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6415 | . . . . . | {Toxins or lectins, e.g. clostridial toxins or Pseudomonas exotoxins} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/642 | . . . . . | {the peptide or protein in the drug conjugate being a cytokine, e.g. IL2, chemokine, growth factors or interferons being the inactive part of the conjugate} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6425 | . . . . . | {the peptide or protein in the drug conjugate being a receptor, e.g. CD4, a cell surface antigen, i.e. not a peptide ligand targeting the antigen, or a cell surface determinant, i.e. a part of the surface of a cell} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/643 | . . . . . | {Albumins, e.g. HSA, BSA, ovalbumin or a Keyhole Limpet Hemocyanin [KHL]} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6435 | . . . . . | {the peptide or protein in the drug conjugate being a connective tissue peptide, e.g. collagen, fibronectin or gelatin} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/644 | . . . . . | {Transferrin, e.g. a lactoferrin or ovotransferrin} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6445 | . . . . . | {Haemoglobin} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/645 | . . . . . | {Polycationic or polyanionic oligopeptides, polypeptides or polyamino acids, e.g. polylysine, polyarginine, polyglutamic acid or peptide TAT} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6455 | . . . . . . | {Polycationic oligopeptides, polypeptides or polyamino acids, e.g. for complexing nucleic acids} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/646 | . . . . . | {the entire peptide or protein drug conjugate elicits an immune response, e.g. conjugate vaccines} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/65 | . . . . | Peptidic linkers, binders or spacers, e.g. peptidic enzyme-labile linkers [2017-08] |
A61K 47/66 | . . . . | the modifying agent being a pre-targeting system involving a peptide or protein for targeting specific cells [2017-08] |
A61K 47/68 | . . . | the modifying agent being an antibody, an immunoglobulin or a fragment thereof, e.g. an Fc-fragment [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6801 | . . . . | {Drug-antibody or immunoglobulin conjugates defined by the pharmacologically or therapeutically active agent} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6803 | . . . . . | {Drugs conjugated to an antibody or immunoglobulin, e.g. cisplatin-antibody conjugates} [2025-05] |
A61K 47/68031 | . . . . . . | {the drug being an auristatin} [2025-05] |
A61K 47/68033 | . . . . . . | {the drug being a maytansine} [2025-05] |
A61K 47/68035 | . . . . . . | {the drug being a pyrrolobenzodiazepine} [2025-05] |
A61K 47/68037 | . . . . . . | {the drug being a camptothecin [CPT] or derivatives} [2025-05] |
A61K 47/6805 | . . . . . . | {the drug being a vinca alkaloid} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6807 | . . . . . . | {the drug or compound being a sugar, nucleoside, nucleotide, nucleic acid, e.g. RNA antisense} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6809 | . . . . . . . | {Antibiotics, e.g. antitumor antibiotics anthracyclins, adriamycin, doxorubicin or daunomycin} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6811 | . . . . . . | {the drug being a protein or peptide, e.g. transferrin or bleomycin} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6813 | . . . . . . . | {the drug being a peptidic cytokine, e.g. an interleukin or interferon} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6815 | . . . . . . . | {Enzymes} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6817 | . . . . . . . | {Toxins} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6819 | . . . . . . . . | {Plant toxins} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6821 | . . . . . . . . . | {Plant heterodimeric toxins, e.g. abrin or modeccin} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6823 | . . . . . . . . . . | {Double chain ricin} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6825 | . . . . . . . . . | {Ribosomal inhibitory proteins, i.e. RIP-I or RIP-II, e.g. Pap, gelonin or dianthin} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6827 | . . . . . . . . . . | {Ricin A} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6829 | . . . . . . . . | {Bacterial toxins, e.g. diphteria toxins or Pseudomonas exotoxin A} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6831 | . . . . . . . . | {Fungal toxins, e.g. alpha sarcine, mitogillin, zinniol or restrictocin} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6833 | . . . . . . . . | {Viral toxins} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6835 | . . . . | {the modifying agent being an antibody or an immunoglobulin bearing at least one antigen-binding site} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6839 | . . . . . | {the antibody targeting material from viruses} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6841 | . . . . . . | {the antibody targeting a RNA virus} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6843 | . . . . . | {the antibody targeting a material from animals or humans} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6845 | . . . . . | {the antibody targeting a cytokine, e.g. growth factors, VEGF, TNF, a lymphokine or an interferon} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6847 | . . . . . | {the antibody targeting a hormone or a hormone-releasing or -inhibiting factor} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6849 | . . . . . | {the antibody targeting a receptor, a cell surface antigen or a cell surface determinant} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6851 | . . . . . | {the antibody targeting a determinant of a tumour cell} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6853 | . . . . . . | {Carcino-embryonic antigens} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6855 | . . . . . . | {the tumour determinant being from breast cancer cell} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6857 | . . . . . . | {the tumour determinant being from lung cancer cell} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6859 | . . . . . . | {the tumour determinant being from liver or pancreas cancer cell} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6861 | . . . . . . | {the tumour determinant being from kidney or bladder cancer cell} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6863 | . . . . . . | {the tumour determinant being from stomach or intestines cancer cell} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6865 | . . . . . . | {the tumour determinant being from skin, nerves or brain cancer cell} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6867 | . . . . . . | {the tumour determinant being from a cell of a blood cancer} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6869 | . . . . . . | {the tumour determinant being from a cell of the reproductive system: ovaria, uterus, testes, prostate} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6871 | . . . . . | {the antibody targeting an enzyme} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6873 | . . . . . | {the antibody targeting an immunoglobulin; the antibody being an anti-idiotypic antibody} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6875 | . . . . . | {the antibody being a hybrid immunoglobulin} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6877 | . . . . . . | {the antibody being an immunoglobulin containing regions, domains or residues from different species} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6879 | . . . . . . | {the immunoglobulin having two or more different antigen-binding sites, e.g. bispecific or multispecific immunoglobulin} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6881 | . . . . . | {Cluster-antibody conjugates, i.e. the modifying agent consists of a plurality of antibodies covalently linked to each other or of different antigen-binding fragments covalently linked to each other} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6883 | . . . . . | {Polymer-drug antibody conjugates, e.g. mitomycin-dextran-Ab; DNA-polylysine-antibody complex or conjugate used for therapy} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6885 | . . . . . . | {the conjugate or the polymer being a starburst, a dendrimer, a cascade} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6887 | . . . . . | {Antibody-chelate conjugates using chelates for therapeutic purposes (radioactive substances, e.g. for use in radio diagnosis or radiotherapy, A61K 51/10; antibody-chelates for use in MRI A61K 49/14)} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6889 | . . . . | {Conjugates wherein the antibody being the modifying agent and wherein the linker, binder or spacer confers particular properties to the conjugates, e.g. peptidic enzyme-labile linkers or acid-labile linkers, providing for an acid-labile immuno conjugate wherein the drug may be released from its antibody conjugated part in an acidic, e.g. tumoural or environment} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6891 | . . . . | {Pre-targeting systems involving an antibody for targeting specific cells} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6893 | . . . . . | {clearing therapy or enhanced clearance, i.e. using an antibody clearing agents in addition to T-A and D-M} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6895 | . . . . . | {Rescue therapy; Agonist-antagonist; Antidotes; Targeted rescue or protection, e.g. by folic acid-folinic acid or conjugated to antibodies} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6897 | . . . . . | {Pre-targeting systems with two or three steps using antibody conjugates; Ligand-antiligand therapies} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6899 | . . . . . | {Antibody-Directed Enzyme Prodrug Therapy [ADEPT]} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/69 | . . | the conjugate being characterised by physical or galenical forms, e.g. emulsion, particle, inclusion complex, stent or kit [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6901 | . . . | {Conjugates being cells, cell fragments, viruses, ghosts, red blood cells or viral vectors} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6903 | . . . | {the form being semi-solid, e.g. an ointment, a gel, a hydrogel or a solidifying gel} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6905 | . . . | {the form being a colloid or an emulsion} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6907 | . . . . | {the form being a microemulsion, nanoemulsion or micelle} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6909 | . . . . . | {Micelles formed by phospholipids} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6911 | . . . . | {the form being a liposome} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6913 | . . . . . | {the liposome being modified on its surface by an antibody} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6915 | . . . . . | {the form being a liposome with polymerisable or polymerized bilayer-forming substances, e.g. polymersomes} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6917 | . . . . | {the form being a lipoprotein vesicle, e.g. HDL or LDL proteins} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6919 | . . . . | {the form being a ribbon or a tubule cochleate} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6921 | . . . | {the form being a particulate, a powder, an adsorbate, a bead or a sphere} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6923 | . . . . | {the form being an inorganic particle, e.g. ceramic particles, silica particles, ferrite or synsorb} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6925 | . . . . | {the form being a microcapsule, nanocapsule, microbubble or nanobubble} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6927 | . . . . | {the form being a solid microparticle having no hollow or gas-filled cores} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6929 | . . . . . | {the form being a nanoparticle, e.g. an immuno-nanoparticle} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6931 | . . . . . . | {the material constituting the nanoparticle being a polymer} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6933 | . . . . . . . | {the polymer being obtained by reactions only involving carbon to carbon, e.g. poly(meth)acrylate, polystyrene, polyvinylpyrrolidone or polyvinylalcohol} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6935 | . . . . . . . | {the polymer being obtained otherwise than by reactions involving carbon to carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polyesters, polyamides or polyglycerol} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6937 | . . . . . . . . | {the polymer being PLGA, PLA or polyglycolic acid} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6939 | . . . . . . . | {the polymer being a polysaccharide, e.g. starch, chitosan, chitin, cellulose or pectin} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6941 | . . . . | {the form being a granulate or an agglomerate} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6943 | . . . | {the form being a pill, a tablet, a lozenge or a capsule} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6949 | . . . | {inclusion complexes, e.g. clathrates, cavitates or fullerenes} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6951 | . . . . | {using cyclodextrin (cyclodextrins used as simple excipients A61K 47/40)} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6953 | . . . | {the form being a fibre, a textile, a slab or a sheet} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6955 | . . . | {the form being a plaster, a bandage, a dressing or a patch} [2017-08] |
A61K 47/6957 | . . . | {the form being a device or a kit, e.g. stents or microdevices} [2017-08] |
A61K 48/00 | Medicinal preparations containing genetic material which is inserted into cells of the living body to treat genetic diseases; Gene therapy [2024-01] |
A61K 48/0008 | . | {characterised by an aspect of the 'non-active' part of the composition delivered, e.g. wherein such 'non-active' part is not delivered simultaneously with the 'active' part of the composition} [2013-01] |
A61K 48/0016 | . . | {wherein the nucleic acid is delivered as a 'naked' nucleic acid, i.e. not combined with an entity such as a cationic lipid} [2013-01] |
A61K 48/0025 | . . | {wherein the non-active part clearly interacts with the delivered nucleic acid} [2018-01] |
A61K 48/0033 | . . . | {the non-active part being non-polymeric} [2013-01] |
A61K 48/0041 | . . . | {the non-active part being polymeric} [2013-01] |
A61K 48/005 | . | {characterised by an aspect of the 'active' part of the composition delivered, i.e. the nucleic acid delivered} [2013-01] |
A61K 48/0058 | . . | {Nucleic acids adapted for tissue specific expression, e.g. having tissue specific promoters as part of a contruct} [2013-01] |
A61K 48/0066 | . . | {Manipulation of the nucleic acid to modify its expression pattern, e.g. enhance its duration of expression, achieved by the presence of particular introns in the delivered nucleic acid} [2013-01] |
A61K 48/0075 | . | {characterised by an aspect of the delivery route, e.g. oral, subcutaneous} [2013-01] |
A61K 48/0083 | . | {characterised by an aspect of the administration regime} [2013-01] |
A61K 48/0091 | . | {Purification or manufacturing processes for gene therapy compositions} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/00 | Preparations for testing in vivo [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0002 | . | {General or multifunctional contrast agents, e.g. chelated agents} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0006 | . . | {Skin tests, e.g. intradermal testing, test strips, delayed hypersensitivity} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0008 | . . | {Screening agents using (non-human) animal models or transgenic animal models or chimeric hosts, e.g. Alzheimer disease animal model, transgenic model for heart failure} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/001 | . | {Preparation for luminescence or biological staining} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0013 | . . | {Luminescence} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0015 | . . . | {Phosphorescence} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0017 | . . . | {Fluorescence in vivo} [2013-01] |
| A61K 49/0019 | . . . . | {characterised by the fluorescent group, e.g. oligomeric, polymeric or dendritic molecules} [2023-08] NOTE
|
A61K 49/0021 | . . . . . | {the fluorescent group being a small organic molecule} [2023-08] |
A61K 49/0023 | . . . . . . | {Di-or triarylmethane dye (xanthene dyes A61K 49/0041)} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0026 | . . . . . . | {Acridine dyes} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0028 | . . . . . . | {Oxazine dyes} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/003 | . . . . . . | {Thiazine dyes} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0032 | . . . . . . | {Methine dyes, e.g. cyanine dyes} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0034 | . . . . . . . | {Indocyanine green, i.e. ICG, cardiogreen} [2015-10] |
A61K 49/0036 | . . . . . . | {Porphyrins (used in photodynamic therapy A61K 41/0071 or A61K 41/0076; used as targeting group or modifying agent for targeting a therapeutic compound A61K 47/546)} [2017-08] |
A61K 49/0039 | . . . . . . | {Coumarin dyes} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0041 | . . . . . . | {Xanthene dyes, used in vivo, e.g. administered to a mice, e.g. rhodamines, rose Bengal (in vivo G01N)} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0043 | . . . . . . . | {Fluorescein, used in vivo} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0045 | . . . . . | {the fluorescent agent being a peptide or protein used for imaging or diagnosis in vivo} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0047 | . . . . . . | {Green fluorescent protein [GFP]} [2013-01] |
| A61K 49/005 | . . . . | {characterised by the carrier molecule carrying the fluorescent agent} [2025-05] NOTE
|
A61K 49/0052 | . . . . . | {Small organic molecules (oligomers, polymers, dendrimers A61K 49/0054)} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0054 | . . . . . | {Macromolecular compounds, i.e. oligomers, polymers, dendrimers} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0056 | . . . . . | {Peptides, proteins, polyamino acids} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0058 | . . . . . | {Antibodies} [2013-01] |
| A61K 49/006 | . . | {Biological staining of tissues in vivo, e.g. methylene blue or toluidine blue O administered in the buccal area to detect epithelial cancer cells, dyes used for delineating tissues during surgery} [2025-05] NOTE
|
| A61K 49/0063 | . . | {characterised by a special physical or galenical form, e.g. emulsions, microspheres} [2025-05] NOTE
|
A61K 49/0065 | . . . | {the luminescent/fluorescent agent having itself a special physical form, e.g. gold nanoparticle} [2013-01] |
| A61K 49/0067 | . . . . | {quantum dots, fluorescent nanocrystals} [2025-05] NOTE
|
| A61K 49/0069 | . . . | {the agent being in a particular physical galenical form} [2025-05] NOTE
|
A61K 49/0071 | . . . . | {solution, solute} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0073 | . . . . | {semi-solid, gel, hydrogel, ointment} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0076 | . . . . | {dispersion, suspension, e.g. particles in a liquid, colloid, emulsion} [2013-01] |
| A61K 49/0078 | . . . . . | {microemulsion, nanoemulsion} [2025-05] NOTE
|
A61K 49/008 | . . . . . | {lipoprotein vesicle, e.g. HDL or LDL proteins} [2013-01] |
| A61K 49/0082 | . . . . . | {micelle, e.g. phospholipidic micelle and polymeric micelle} [2025-05] NOTE
|
| A61K 49/0084 | . . . . . | {liposome, i.e. bilayered vesicular structure} [2025-05] NOTE
|
A61K 49/0086 | . . . . . . | {Polymersome, i.e. liposome with polymerisable or polymerized bilayered-forming substances} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0089 | . . . . | {Particulate, powder, adsorbate, bead, sphere} [2013-01] |
| A61K 49/0091 | . . . . . | {Microparticle, microcapsule, microbubble, microsphere, microbead, i.e. having a size or diameter higher or equal to 1 micrometer} [2025-05] NOTE
|
A61K 49/0093 | . . . . . . | {Nanoparticle, nanocapsule, nanobubble, nanosphere, nanobead, i.e. having a size or diameter smaller than 1 micrometer, e.g. polymeric nanoparticle} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0095 | . . . . . . . | {Nanotubes} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0097 | . . . . | {Cells, viruses, ghosts, red blood cells, viral vectors, used for imaging or diagnosis in vivo} [2013-01] |
| A61K 49/04 | . |
A61K 49/0404 | . . | {containing barium sulfate} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0409 | . . | {Physical forms of mixtures of two different X-ray contrast-enhancing agents, containing at least one X-ray contrast-enhancing agent which is not a halogenated organic compound} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0414 | . . . | {Particles, beads, capsules or spheres} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0419 | . . . . | {Microparticles, microbeads, microcapsules, microspheres, i.e. having a size or diameter higher or equal to 1 micrometer} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0423 | . . . . | {Nanoparticles, nanobeads, nanospheres, nanocapsules, i.e. having a size or diameter smaller than 1 micrometer} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0428 | . . . . . | {Surface-modified nanoparticles, e.g. immuno-nanoparticles} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0433 | . . | {containing an organic halogenated X-ray contrast-enhancing agent} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0438 | . . . | {Organic X-ray contrast-enhancing agent comprising an iodinated group or an iodine atom, e.g. iopamidol} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0442 | . . . | {Polymeric X-ray contrast-enhancing agent comprising a halogenated group} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0447 | . . . | {Physical forms of mixtures of two different X-ray contrast-enhancing agents, containing at least one X-ray contrast-enhancing agent which is a halogenated organic compound} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0452 | . . . . | {Solutions, e.g. for injection} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0457 | . . . . | {Semi-solid forms, ointments, gels, hydrogels} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0461 | . . . . | {Dispersions, colloids, emulsions or suspensions} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0466 | . . . . . | {Liposomes, lipoprotein vesicles, e.g. HDL or LDL lipoproteins, phospholipidic or polymeric micelles} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0471 | . . . . . | {Perflubron, i.e. perfluoroctylbromide, C8F17Br emulsions} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0476 | . . . . | {Particles, beads, capsules, spheres} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/048 | . . . . . | {Microparticles, microbeads, microcapsules, microspheres, i.e. having a size or diameter higher or equal to 1 micrometer} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0485 | . . . . . | {Nanoparticles, nanobeads, nanospheres, nanocapsules, i.e. having a size or diameter smaller than 1 micrometer} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/049 | . . . . . . | {Surface-modified nanoparticles, e.g. immune-nanoparticles} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/0495 | . . . . | {intended for oral administration} [2013-01] |
| A61K 49/08 | . . | characterised by the carrier [2016-08] NOTE
|
| A61K 49/085 | . . . | {conjugated systems} [2025-05] NOTE
|
| A61K 49/10 | . . . | Organic compounds [2013-01] NOTE
|
| A61K 49/101 | . . . . | {the carrier being a complex-forming compound able to form MRI-active complexes with paramagnetic metals} [2025-05] NOTE
|
A61K 49/103 | . . . . . | {the complex-forming compound being acyclic, e.g. DTPA} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/105 | . . . . . . | {the metal complex being Gd-DTPA} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/106 | . . . . . | {the complex-forming compound being cyclic, e.g. DOTA} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/108 | . . . . . . | {the metal complex being Gd-DOTA} [2013-01] |
| A61K 49/12 | . . . . | Macromolecular compounds [2013-01] NOTE
|
A61K 49/122 | . . . . . | {dimers of complexes or complex-forming compounds} [2013-01] |
| A61K 49/124 | . . . . . | {dendrimers, dendrons, hyperbranched compounds} [2025-05] NOTE
|
A61K 49/126 | . . . . . | {Linear polymers, e.g. dextran, inulin, PEG} [2013-01] |
| A61K 49/128 | . . . . . . | {comprising multiple complex or complex-forming groups, being either part of the linear polymeric backbone or being pending groups covalently linked to the linear polymeric backbone} [2025-05] NOTE
|
| A61K 49/14 | . . . . | Peptides, e.g. proteins [2013-01] NOTE
|
A61K 49/143 | . . . . . | {the protein being an albumin, e.g. HSA, BSA, ovalbumin} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/146 | . . . . . | {the peptide being a polyamino acid, e.g. poly-lysine} [2013-01] |
| A61K 49/16 | . . . . . | Antibodies; Immunoglobulins; Fragments thereof [2013-01] NOTE
|
| A61K 49/18 | . . | characterised by a special physical form, e.g. emulsions, microcapsules, liposomes [2013-01] NOTE
|
A61K 49/1803 | . . . | {Semi-solid preparations, e.g. ointments, gels, hydrogels} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/1806 | . . . | {Suspensions, emulsions, colloids, dispersions} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/1809 | . . . . | {Micelles, e.g. phospholipidic or polymeric micelles} [2013-01] |
| A61K 49/1812 | . . . . | {liposomes, polymersomes, e.g. immunoliposomes} [2025-05] NOTE
|
A61K 49/1815 | . . . . | {compo-inhalant, e.g. breath tests} [2013-01] |
| A61K 49/1818 | . . . | {particles, e.g. uncoated or non-functionalised microparticles or nanoparticles} [2025-05] NOTE
|
A61K 49/1821 | . . . . | {coated or functionalised microparticles or nanoparticles} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/1824 | . . . . . | {coated or functionalised nanoparticles (liposomes A61K 49/1812; nanoemulsions A61K 49/1806; micelles A61K 49/1809)} [2017-08] |
A61K 49/1827 | . . . . . . | {having a (super)(para)magnetic core, being a solid MRI-active material, e.g. magnetite, or composed of a plurality of MRI-active, organic agents, e.g. Gd-chelates, or nuclei, e.g. Eu3+, encapsulated or entrapped in the core of the coated or functionalised nanoparticle} [2016-08] |
A61K 49/183 | . . . . . . . | {having a (super)(para)magnetic core coated or functionalised with an inorganic material or being composed of an inorganic material entrapping the MRI-active nucleus, e.g. silica core doped with a MRI-active nucleus} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/1833 | . . . . . . . | {having a (super)(para)magnetic core coated or functionalised with a small organic molecule (oligomeric, polymeric, dendrimeric A61K 49/1851)} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/1836 | . . . . . . . . | {the small organic molecule being a carboxylic acid having less than 8 carbon atoms in the main chain} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/1839 | . . . . . . . . | {the small organic molecule being a lipid, a fatty acid having 8 or more carbon atoms in the main chain, or a phospholipid} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/1842 | . . . . . . . . | {the small organic molecule being a phosphate or a phosphonate, not being a phospholipid} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/1845 | . . . . . . . . | {the small organic molecule being a carbohydrate (monosaccharides, discacharides)} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/1848 | . . . . . . . . | {the small organic molecule being a silane} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/1851 | . . . . . . . | {having a (super)(para)magnetic core coated or functionalised with an organic macromolecular compound, i.e. oligomeric, polymeric, dendrimeric organic molecule (peptide or protein A61K 49/1866; polyamino acid A61K 49/1872; antibody A61K 49/1875)} [2017-08] |
A61K 49/1854 | . . . . . . . . | {the organic macromolecular compound being obtained by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. poly(meth)acrylate, polyacrylamide, polyvinylpyrrolidone, polyvinylalcohol} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/1857 | . . . . . . . . | {the organic macromolecular compound being obtained otherwise than by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. PLGA} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/186 | . . . . . . . . . | {the organic macromolecular compound being polyethyleneglycol [PEG]} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/1863 | . . . . . . . . | {the organic macromolecular compound being a polysaccharide or derivative thereof, e.g. chitosan, chitin, cellulose, pectin, starch} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/1866 | . . . . . . . | {the nanoparticle having a (super)(para)magnetic core coated or functionalised with a peptide, e.g. protein, polyamino acid} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/1869 | . . . . . . . . | {coated or functionalised with a protein being an albumin, e.g. HSA, BSA, ovalbumin} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/1872 | . . . . . . . . | {coated or functionalised with a polyamino acid, e.g. polylysine, polyglutamic acid} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/1875 | . . . . . . . | {coated or functionalised with an antibody} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/1878 | . . . . . . | {the nanoparticle having a magnetically inert core and a (super)(para)magnetic coating} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/1881 | . . . . . . . | {wherein the coating consists of chelates, i.e. chelating group complexing a (super)(para)magnetic ion, bound to the surface} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/1884 | . . . . | {Nanotubes, nanorods or nanowires} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/1887 | . . . . | {Agglomerates, clusters, i.e. more than one (super)(para)magnetic microparticle or nanoparticle are aggregated or entrapped in the same maxtrix} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/189 | . . . | {Host-guest complexes, e.g. cyclodextrins} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/1893 | . . . . | {Molecular sieves} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/1896 | . . . | {not provided for elsewhere, e.g. cells, viruses, ghosts, red blood cells, virus capsides} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/20 | . . | containing free radicals {, e.g. trityl radical for overhauser} [2016-08] |
A61K 49/22 | . | Echographic preparations; Ultrasound imaging preparations {; Optoacoustic imaging preparations} [2023-08] |
A61K 49/221 | . . | {characterised by the targeting agent or modifying agent linked to the acoustically-active agent} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/222 | . . | {characterised by a special physical form, e.g. emulsions, liposomes} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/223 | . . . | {Microbubbles, hollow microspheres, free gas bubbles, gas microspheres} [2017-08] |
A61K 49/225 | . . . | {Microparticles, microcapsules (gas-filled to be classified in A61K 49/223)} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/226 | . . . | {Solutes, emulsions, suspensions, dispersions, semi-solid forms, e.g. hydrogels} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/227 | . . . | {Liposomes, lipoprotein vesicles, e.g. LDL or HDL lipoproteins, micelles, e.g. phospholipidic or polymeric} [2013-01] |
A61K 49/228 | . . . | {Host-guest complexes, clathrates, chelates} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/00 | Preparations containing radioactive substances for use in therapy or testing in vivo [2022-01] |
A61K 51/02 | . | characterised by the carrier {, i.e. characterised by the agent or material covalently linked or complexing the radioactive nucleus} [2017-08] |
A61K 51/025 | . . | {inorganic Tc complexes or compounds} [2013-01] |
| A61K 51/04 | . . | Organic compounds [2017-08] NOTE
|
A61K 51/0402 | . . . | {carboxylic acid carriers, fatty acids (amino acids A61K 51/0406)} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/0404 | . . . | {Lipids, e.g. triglycerides; Polycationic carriers (polycationic carriers being oligomers, polymers, dendrimers A61K 47/56; fatty acids A61K 51/0402; cholesterol A61K 51/0493)} [2017-08] |
A61K 51/0406 | . . . . | {Amines, polyamines, e.g. spermine, spermidine, amino acids, (bis)guanidines} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/0408 | . . . . | {Phospholipids (liposomes encapsulating the radioactive probe or having no radiolabelled phospholipids A61K 51/1231)} [2013-01] |
| A61K 51/041 | . . . | {Heterocyclic compounds} [2025-05] NOTE
|
A61K 51/0412 | . . . . | {having oxygen as the only ring hetero atom, e.g. fungichromin} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/0414 | . . . . . | {having three-membered rings, e.g. oxirane, fumagillin} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/0417 | . . . . . | {having four-membered rings, e.g. taxol} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/0419 | . . . . . | {having five-membered rings with one oxygen as the only ring hetero atom, e.g. isosorbide} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/0421 | . . . . . | {having six-membered rings with one oxygen as the only ring hetero atom} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/0423 | . . . . . | {having two or more oxygen atoms in the same ring, e.g. crown ethers, guanadrel} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/0425 | . . . . . | {compounds containing methylenedioxyphenol groups, e.g. sesamin} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/0427 | . . . . . | {Lactones} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/0429 | . . . . | {having sulfur as a ring hetero atom} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/0431 | . . . . . | {having five-membered rings} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/0434 | . . . . . | {having six-membered rings, e.g. thioxanthenes (thiothixene A61K 51/0459)} [2023-08] |
A61K 51/0436 | . . . . . | {having two or more sulfur atoms in the same ring} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/0438 | . . . . . | {having oxygen in the same ring} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/044 | . . . . | {having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine, rifamycins (rifampin A61K 51/0459)} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/0442 | . . . . . | {having three-membered rings, e.g. aziridine} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/0444 | . . . . . | {having four-membered rings, e.g. azetidine} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/0446 | . . . . . | {having five-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom, e.g. sulpiride, succinimide, tolmetin, buflomedil} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/0448 | . . . . . . | {tropane or nortropane groups, e.g. cocaine} [2013-01] |
| A61K 51/0451 | . . . . . . | {having four such rings, e.g. phorphine derivatives, bilirubin, biliverdine (hemin, hematin A61K 51/0472)} [2025-05] NOTE
|
A61K 51/0453 | . . . . . | {having five-membered rings with two or more ring hetero atoms, at least one of which being nitrogen, e.g. tetrazole} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/0455 | . . . . . | {having six-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/0457 | . . . . . . | {Vesamicol} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/0459 | . . . . . | {having six-membered rings with two nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, e.g. piperazine} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/0461 | . . . . . | {having six-membered rings with three nitrogens as the only ring hetero atoms, e.g. chlorazanil, melamine (melarsoprol A61K 51/0472)} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/0463 | . . . . . | {having six-membered rings with at least one nitrogen and one oxygen as the ring hetero atoms, e.g. 1,2-oxazines} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/0465 | . . . . . | {having six-membered rings with at least one nitrogen and one sulfur as the ring hetero atoms, e.g. sulthiame} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/0468 | . . . . . | {having seven-membered rings, e.g. azelastine, pentylenetetrazole} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/047 | . . . . . . | {Benzodiazepines} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/0472 | . . . . | {containing heavy metals, e.g. hemin, hematin, melarsoprol} [2013-01] |
| A61K 51/0474 | . . . | {complexes or complex-forming compounds, i.e. wherein a radioactive metal (e.g. 111In3+) is complexed or chelated by, e.g. a N2S2, N3S, NS3, N4 chelating group} [2025-05] NOTE
|
A61K 51/0476 | . . . . | {complexes from monodendate ligands, e.g. sestamibi} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/0478 | . . . . | {complexes from non-cyclic ligands, e.g. EDTA, MAG3} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/048 | . . . . . | {DTPA (diethylenetriamine tetraacetic acid)} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/0482 | . . . . | {chelates from cyclic ligands, e.g. DOTA} [2013-01] |
| A61K 51/0485 | . . . . | {Porphyrins, texaphyrins wherein the nitrogen atoms forming the central ring system complex the radioactive metal} [2025-05] NOTE
|
A61K 51/0487 | . . . . | {Metallocenes, i.e. complexes based on a radioactive metal complexed by two cyclopentadienyl anions} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/0489 | . . . | {Phosphates or phosphonates, e.g. bone-seeking phosphonates; (phospholipids: A61K 51/0408; nucleotides or nucleic acids: A61K 51/0491)} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/0491 | . . . | {Sugars, nucleosides, nucleotides, oligonucleotides, nucleic acids, e.g. DNA, RNA, nucleic acid aptamers} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/0493 | . . . | {Steroids, e.g. cholesterol, testosterone} [2013-01] |
| A61K 51/0495 | . . . | {Pretargeting} [2025-05] NOTE
|
| A61K 51/0497 | . . . | {conjugates with a carrier being an organic compounds} [2025-05] NOTE
|
A61K 51/06 | . . . | Macromolecular compounds {, carriers being organic macromolecular compounds, i.e. organic oligomeric, polymeric, dendrimeric molecules (peptides, proteins, polyamino acids A61K 51/08; antibodies A61K 51/10)} [2017-08] |
| A61K 51/065 | . . . . | {conjugates with carriers being macromolecules} [2025-05] NOTE
|
A61K 51/08 | . . . | Peptides, e.g. proteins {, carriers being peptides, polyamino acids, proteins} [2017-08] |
A61K 51/081 | . . . . | {the protein being an albumin, e.g. human serum albumin [HSA], bovine serum albumin [BSA], ovalbumin} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/082 | . . . . | {the peptide being a RGD-containing peptide} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/083 | . . . . | {the peptide being octreotide or a somatostatin-receptor-binding peptide} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/084 | . . . . | {the peptide being oxytocin} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/085 | . . . . | {the peptide being neurotensin} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/086 | . . . . | {the peptide being alphaMSH, alpha melanocyte stimulating hormone} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/087 | . . . . | {the peptide being an annexin, e.g. annexin V} [2013-01] |
| A61K 51/088 | . . . . | {conjugates with carriers being peptides, polyamino acids or proteins (antibodies A61K 51/10)} [2025-05] NOTE
|
A61K 51/10 | . . . . | Antibodies or immunoglobulins; Fragments thereof {, the carrier being an antibody, an immunoglobulin or a fragment thereof, e.g. a camelised human single domain antibody or the Fc fragment of an antibody} [2020-05] |
A61K 51/1006 | . . . . . | {the antibody being against or targeting material from viruses} [2020-05] |
A61K 51/1009 | . . . . . | {against material from bacteria} [2020-05] |
A61K 51/1012 | . . . . . | {against material from fungi, lichens or algae} [2020-05] |
A61K 51/1015 | . . . . . | {against material from plants} [2020-05] |
A61K 51/1018 | . . . . . | {against material from animals or humans} [2020-05] |
A61K 51/1021 | . . . . . | {against cytokines, e.g. growth factors, VEGF, TNF, lymphokines or interferons} [2020-05] |
A61K 51/1024 | . . . . . | {against hormones, hormone-releasing or hormone-inhibiting factors} [2020-05] |
A61K 51/1027 | . . . . . | {against receptors, cell-surface antigens or cell-surface determinants} [2020-05] |
A61K 51/103 | . . . . . . | {against receptors for growth factors or receptors for growth regulators} [2020-05] |
A61K 51/1033 | . . . . . . | {against receptors for cytokines, lymphokines or interferons} [2020-05] |
A61K 51/1036 | . . . . . . | {against hormone receptors} [2020-05] |
A61K 51/1039 | . . . . . . | {against T-cell receptors} [2020-05] |
A61K 51/1042 | . . . . . . . | {against T-cell receptor (TcR)-CD3 complex} [2020-05] |
A61K 51/1045 | . . . . . | {against animal or human tumor cells or tumor cell determinants} [2020-05] |
A61K 51/1048 | . . . . . . | {the tumor cell determinant being a carcino embryonic antigen} [2020-05] |
A61K 51/1051 | . . . . . . | {the tumor cell being from breast, e.g. the antibody being herceptin} [2020-05] |
A61K 51/1054 | . . . . . . | {the tumor cell being from lung} [2020-05] |
A61K 51/1057 | . . . . . . | {the tumor cell being from liver or pancreas} [2020-05] |
A61K 51/106 | . . . . . . | {the tumor cell being from kidney or bladder} [2020-05] |
A61K 51/1063 | . . . . . . | {the tumor cell being from stomach or intestines} [2020-05] |
A61K 51/1066 | . . . . . . | {the tumor cell being from skin} [2020-05] |
A61K 51/1069 | . . . . . . | {the tumor cell being from blood cells, e.g. the cancer being a myeloma} [2020-05] |
A61K 51/1072 | . . . . . . | {the tumor cell being from the reproductive system, e.g. ovaria, uterus, testes or prostate} [2020-05] |
A61K 51/1075 | . . . . . | {the antibody being against an enzyme} [2020-05] |
A61K 51/1078 | . . . . . | {the antibody being against an immunoglobulin, i.e. being an (anti)-anti-idiotypic antibody} [2020-05] |
A61K 51/1084 | . . . . . | {the antibody being a hybrid immunoglobulin} [2020-05] |
A61K 51/1087 | . . . . . . | {the immunoglobulin comprises domains from different animal species, e.g. chimeric immunoglobulins} [2020-05] |
A61K 51/109 | . . . . . . | {immunoglobulins having two or more different antigen-binding sites or multifunctional antibodies} [2020-05] |
| A61K 51/1093 | . . . . . | {conjugates with carriers being antibodies} [2025-05] NOTE
|
A61K 51/1096 | . . . . . . | {radioimmunotoxins, i.e. conjugates being structurally as defined in A61K 51/1093, and including a radioactive nucleus for use in radiotherapeutic applications} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/12 | . | characterised by a special physical form, e.g. emulsion, microcapsules, liposomes {, characterized by a special physical form, e.g. emulsions, dispersions, microcapsules (liposomes A61K 51/1234)} [2017-08] |
A61K 51/1203 | . . | {in a form not provided for by groups A61K 51/1206 - A61K 51/1296, e.g. cells, cell fragments, viruses, virus capsides, ghosts, red blood cells, viral vectors} [2016-05] |
A61K 51/1206 | . . | {Administration of radioactive gases, aerosols or breath tests} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/121 | . . | {Solutions, i.e. homogeneous liquid formulation} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/1213 | . . | {Semi-solid forms, gels, hydrogels, ointments, fats and waxes that are solid at room temperature} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/1217 | . . | {Dispersions, suspensions, colloids, emulsions, e.g. perfluorinated emulsion, sols} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/122 | . . . | {Microemulsions, nanoemulsions} [2017-08] |
A61K 51/1224 | . . . | {Lipoprotein vesicles, e.g. HDL and LDL proteins} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/1227 | . . . | {Micelles, e.g. phospholipidic or polymeric micelles} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/1231 | . . . | {Aerosols or breath tests, e.g. administration of gasses, emanators} [2013-01] |
| A61K 51/1234 | . . . | {Liposomes} [2025-05] NOTE
|
A61K 51/1237 | . . . . | {Polymersomes, i.e. liposomes with polymerisable or polymerized bilayer-forming substances} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/1241 | . . | {particles, powders, lyophilizates, adsorbates, e.g. polymers or resins for adsorption or ion-exchange resins} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/1244 | . . . | {microparticles or nanoparticles, e.g. polymeric nanoparticles} [2017-08] |
A61K 51/1248 | . . . . | {nanotubes} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/1251 | . . . . | {micro- or nanospheres, micro- or nanobeads, micro- or nanocapsules} [2017-08] |
A61K 51/1255 | . . . | {Granulates, agglomerates, microspheres} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/1258 | . . | {Pills, tablets, lozenges} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/1262 | . . | {Capsules} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/1265 | . . . | {Microcapsules} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/1268 | . . | {host-guest, closed hollow molecules, inclusion complexes, e.g. with cyclodextrins, clathrates, cavitates, fullerenes} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/1272 | . . | {Sponges} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/1275 | . . | {Fibers, textiles, slabbs, or sheets} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/1279 | . . | {Plasters, bandages, dressings, patches or adhesives} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/1282 | . . | {Devices used in vivo and carrying the radioactive therapeutic or diagnostic agent, therapeutic or in vivo diagnostic kits, stents} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/1286 | . . . | {Ampoules, glass carriers carrying the therapeutic or in vivo diagnostic agent} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/1289 | . . . | {Devices or containers for impregnation, for emanation, e.g. bottles or jars for radioactive water for use in radiotherapy} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/1293 | . . | {Radioactive cosmetics, e.g. radioactive bathsalts, soaps} [2013-01] |
A61K 51/1296 | . . | {Radioactive food, e.g. chocolates, drinks} [2013-01] |
A61K 2121/00 | Preparations for use in therapy [2013-01] |
A61K 2123/00 | Preparations for testing in vivo [2013-01] |
| A61K 2236/00 | Isolation or extraction methods of medicinal preparations of undetermined constitution containing material from algae, lichens, fungi or plants, or derivatives thereof, e.g. traditional herbal medicine [2013-01] NOTE
|
A61K 2236/10 | . | Preparation or pretreatment of starting material [2013-01] |
A61K 2236/11 | . . | involving culturing conditions, e.g. cultivation in the dark or under defined water stress [2013-01] |
A61K 2236/13 | . . | involving cleaning, e.g. washing or peeling [2013-01] |
A61K 2236/15 | . . | involving mechanical treatment, e.g. chopping up, cutting or grinding [2013-01] |
A61K 2236/17 | . . | involving drying, e.g. sun-drying or wilting [2013-01] |
A61K 2236/19 | . . | involving fermentation using yeast, bacteria or both; enzymatic treatment [2024-08] |
A61K 2236/30 | . | Extraction of the material [2013-01] |
A61K 2236/31 | . . | involving untreated material, e.g. fruit juice or sap obtained from fresh plants [2013-01] |
A61K 2236/33 | . . | involving extraction with hydrophilic solvents, e.g. lower alcohols, esters or ketones [2013-01] |
A61K 2236/331 | . . . | using water, e.g. cold water, infusion, tea, steam distillation or decoction [2024-08] |
A61K 2236/333 | . . . | using mixed solvents, e.g. 70% EtOH [2013-01] |
A61K 2236/35 | . . | Extraction with lipophilic solvents, e.g. Hexane or petrol ether [2013-01] |
A61K 2236/37 | . . | Extraction at elevated pressure or temperature, e.g. pressurized solvent extraction [PSE], supercritical carbon dioxide extraction or subcritical water extraction [2013-01] |
A61K 2236/39 | . . | Complex extraction schemes, e.g. fractionation or repeated extraction steps [2013-01] |
A61K 2236/50 | . | Methods involving additional extraction steps [2013-01] |
A61K 2236/51 | . . | Concentration or drying of the extract, e.g. Lyophilisation, freeze-drying or spray-drying [2013-01] |
A61K 2236/53 | . . | Liquid-solid separation, e.g. centrifugation, sedimentation or crystallization [2013-01] |
A61K 2236/55 | . . | Liquid-liquid separation; Phase separation [2013-01] |
A61K 2239/00 | Indexing codes associated with cellular immunotherapy of group A61K 40/00 [2025-01] |
A61K 2239/10 | . | characterized by the structure of the chimeric antigen receptor [CAR] [2023-05] |
A61K 2239/11 | . . | Antigen recognition domain [2023-05] |
A61K 2239/13 | . . . | Antibody-based [2023-05] |
A61K 2239/15 | . . . | Non-antibody based [2023-05] |
A61K 2239/17 | . . | Hinge-spacer domain [2023-05] |
A61K 2239/21 | . . | Transmembrane domain [2023-05] |
A61K 2239/22 | . . | Intracellular domain [2023-05] |
A61K 2239/23 | . . | On/off switch [2023-05] |
A61K 2239/24 | . . . | Dimerizable CARs; CARs with adapter [2023-05] |
A61K 2239/25 | . . . | Suicide switch [2023-05] |
A61K 2239/27 | . | characterized by targeting or presenting multiple antigens [2023-05] |
A61K 2239/28 | . . | Expressing multiple CARs, TCRs or antigens [2023-05] |
A61K 2239/29 | . . | Multispecific CARs [2023-05] |
A61K 2239/30 | . . | Mixture of cells [2023-05] |
A61K 2239/31 | . | characterized by the route of administration [2023-05] |
A61K 2239/38 | . | characterised by the dose, timing or administration schedule [2023-05] |
A61K 2239/39 | . | characterised by a specific adjuvant, e.g. cytokines or CpG [2023-05] |
A61K 2239/46 | . | characterised by the cancer treated [2023-05] |
A61K 2239/47 | . . | Brain; Nervous system [2023-05] |
A61K 2239/48 | . . | Blood cells, e.g. leukemia or lymphoma [2023-05] |
A61K 2239/49 | . . | Breast [2023-05] |
A61K 2239/50 | . . | Colon [2023-05] |
A61K 2239/51 | . . | Stomach [2023-05] |
A61K 2239/52 | . . | Intestine [2023-05] |
A61K 2239/53 | . . | Liver [2023-05] |
A61K 2239/54 | . . | Pancreas [2023-05] |
A61K 2239/55 | . . | Lung [2023-05] |
A61K 2239/56 | . . | Kidney [2023-05] |
A61K 2239/57 | . . | Skin; melanoma [2023-05] |
A61K 2239/58 | . . | Prostate [2023-05] |
A61K 2239/59 | . . | Reproductive system, e.g. uterus, ovaries, cervix or testes [2023-05] |
| A61K 2300/00 | Mixtures or combinations of active ingredients, wherein at least one active ingredient is fully defined in groups A61K 31/00 - A61K 41/00 [2023-05] NOTE
|
| A61K 2800/00 |
A61K 2800/10 | . | General cosmetic use [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/20 | . | Chemical, physico-chemical or functional or structural properties of the composition as a whole [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/21 | . . | Emulsions characterized by droplet sizes below 1 micron [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/22 | . . | Gas releasing [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/222 | . . . | Effervescent [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/24 | . . | Thermal properties [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/242 | . . . | Exothermic; Self-heating; Heating sensation [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/244 | . . . | Endothermic; Cooling; Cooling sensation [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/26 | . . | Optical properties [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/262 | . . . | Transparent; Translucent [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/28 | . . | Rubbing or scrubbing compositions; Peeling or abrasive compositions; Containing exfoliants [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/30 | . . | Characterized by the absence of a particular group of ingredients [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/31 | . . . | Anhydrous [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/33 | . . . | Free of surfactant [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/34 | . . . | Free of silicones [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/40 | . | Chemical, physico-chemical or functional or structural properties of particular ingredients [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/41 | . . | Particular ingredients further characterized by their size [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/412 | . . . | Microsized, i.e. having sizes between 0.1 and 100 microns [2017-08] |
A61K 2800/413 | . . . | Nanosized, i.e. having sizes below 100 nm [2017-08] |
A61K 2800/42 | . . | Colour properties [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/43 | . . . | Pigments; Dyes [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/432 | . . . . | Direct dyes [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/4322 | . . . . . | in preparations for temporarily coloring the hair further containing an oxidizing agent [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/4324 | . . . . . | in preparations for permanently dyeing the hair [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/434 | . . . . | Luminescent, Fluorescent; Optical brighteners; Photosensitizers [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/436 | . . . . | Interference pigments, e.g. Iridescent, Pearlescent [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/437 | . . . . | Diffractive phenomena; Photonic arrays [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/438 | . . . . | Thermochromatic; Photochromic; Phototropic [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/45 | . . . | Colour indicators, e.g. pH- or Redox indicators [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/47 | . . | Magnetic materials; Paramagnetic compounds [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/48 | . . | Thickener, Thickening system [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/49 | . . | Solubiliser, Solubilising system [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/51 | . . | Chelating agents [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/52 | . . | Stabilizers [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/522 | . . . | Antioxidants; Radical scavengers [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/524 | . . . | Preservatives [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/526 | . . . | Corrosion inhibitors [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/54 | . . | Polymers characterized by specific structures/properties [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/542 | . . . | characterized by the charge [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/5422 | . . . . | nonionic [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/5424 | . . . . | anionic [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/5426 | . . . . | cationic [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/5428 | . . . . | amphoteric or zwitterionic [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/544 | . . . | Dendrimers, Hyperbranched polymers [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/546 | . . . | Swellable particulate polymers [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/548 | . . . | Associative polymers [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/56 | . . | Compounds, absorbed onto or entrapped into a solid carrier, e.g. encapsulated perfumes, inclusion compounds, sustained release forms [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/57 | . . | Compounds covalently linked to a(n inert) carrier molecule, e.g. conjugates, pro-fragrances [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/58 | . . | Metal complex; Coordination compounds [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/59 | . . | Mixtures [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/591 | . . . | Mixtures of compounds not provided for by any of the codes A61K 2800/592 - A61K 2800/596 [2016-05] |
A61K 2800/592 | . . . | Mixtures of compounds complementing their respective functions [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/5922 | . . . . | At least two compounds being classified in the same subclass of A61K 8/18 [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/594 | . . . | Mixtures of polymers [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/596 | . . . | Mixtures of surface active compounds [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/60 | . . | Particulates further characterized by their structure or composition [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/61 | . . . | Surface treated [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/612 | . . . . | By organic compounds [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/614 | . . . . | By macromolecular compounds [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/62 | . . . . | Coated [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/621 | . . . . . | by inorganic compounds [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/622 | . . . . . | by organic compounds [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/623 | . . . . . | Coating mediated by organosilicone compounds [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/624 | . . . . . | by macromolecular compounds [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/63 | . . . . . | More than one coating [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/65 | . . . | Characterized by the composition of the particulate/core [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/651 | . . . . | The particulate/core comprising inorganic material [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/652 | . . . . | The particulate/core comprising organic material [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/654 | . . . . | The particulate/core comprising macromolecular material [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/70 | . | Biological properties of the composition as a whole [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/72 | . . | Hypo-allergenic [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/74 | . | Biological properties of particular ingredients [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/75 | . . | Anti-irritant [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/77 | . . | Perfumes having both deodorant and antibacterial properties [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/78 | . . | Enzyme modulators, e.g. Enzyme agonists [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/782 | . . . | Enzyme inhibitors; Enzyme antagonists [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/80 | . | Process related aspects concerning the preparation of the cosmetic composition or the storage or application thereof [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/805 | . . | Corresponding aspects not provided for by any of codes A61K 2800/81 - A61K 2800/95 [2016-05] |
A61K 2800/81 | . . | Preparation or application process involves irradiation [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/82 | . . | Preparation or application process involves sonication or ultrasonication [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/83 | . . | Electrophoresis; Electrodes; Electrolytic phenomena [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/84 | . . | Products or compounds obtained by lyophilisation, freeze-drying [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/85 | . . | Products or compounds obtained by fermentation, e.g. yoghurt, beer, wine [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/86 | . . | Products or compounds obtained by genetic engineering [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/87 | . . | Application Devices; Containers; Packaging [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/872 | . . . | Pencils; Crayons; Felt-tip pens [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/874 | . . . | Roll-on [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/88 | . . | Two- or multipart kits [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/882 | . . . | Mixing prior to application [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/884 | . . . | Sequential application [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/91 | . . | Injection [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/92 | . . | Oral administration [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/94 | . . | Involves covalent bonding to the substrate [2013-01] |
A61K 2800/95 | . . | Involves in-situ formation or cross-linking of polymers [2013-01] |