CPC Definition - Subclass C12Q
This place covers:
Processes in which there is a direct or indirect qualitative or quantitative measurement or test of a material which contains enzymes, nucleic acids or microorganisms.
Processes in which a material containing enzymes, nucleic acids or microorganisms is used to perform a qualitative or quantitative measurement or test, e.g. testing for antimicrobial activity or cholesterol, geomicrobiological testing.
In vivo or in vitro or in silico measuring or testing processes involving nucleic acid e.g. nucleic acid hybridisation including PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction).
Compositions or test papers containing enzymes, nucleic acids or microorganisms which can be used to detect or identify a chemical compound or composition, e.g. paper strips for the testing of blood sugar.
Compositions or test papers distinguished by the use of indicators which can be used to detect or identify the presence of enzymes, nucleic acids or microorganisms.
Processes of making such test compositions.
Processes involving enzymes or microorganisms in which a process parameter is measured and that or another process parameter is varied in response to such measurement, i.e. condition responsive control.
Controlling or regulating in general is classified in G05.
This place does not cover:
Immunoassay | |
Immunoassay with enzyme label | |
Immunoassay with the carrier being a biological cell or cell fragment | |
Immunoassay for microorganisms | |
Immunoassay for venereal diseases | |
Immunoassay for enzymes and isoenzymes | |
Immunoassay for cancer | |
Immunoassay for hepatitis |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Microorganisms per se | |
Human, animal or plant cells per se | |
Viruses per se | |
Enzymes per se | |
Investigating or analysing materials by determining their chemical or physical properties | |
Chemical analysis involving blood sugar, e.g. galactose | |
Chemical analysis involving proteins, peptides and amino acids | |
Chemical analysis involving lipids, e.g. cholesterol |
In this subclass, in absence of an indication to the contrary, classification is made in the last appropriate place.
In this subclass, test media are classified in the appropriate group for the relevant test process.
In this subclass, bacteria, fungi, viruses, protozoa and algae are considered as microorganisms.
In this subclass, sub-cellular parts, unless specifically provided for, are classified with the whole cell.
Combination Sets [C-Sets]:
In this subclass, C-Sets classification is applied to the following groups, listed in the table below, if the document discloses a pertinent combination of technical features that cannot be covered by the allocation of a single symbol. The fourth column of the table indicates the place where the detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules can be found, in the definition section "Special rules of classification".
C-SETS ID | BASE SYMBOL | SUBSEQUENT SYMBOLS | C-SETS FORMULA; LOCATION OF C-SETS RULES |
#C12Qa | (C12Q, C12Q); measuring or testing processes involving in a nucleic acid; see C12Q 1/68 | ||
#C12Na | (C12N, C12Q); DNA or RNA isolation/preparation process and cell culture components; see C12N 15/10 | ||
#C12Nb | (C12N, C12Q); general methods for preparing vectors; see C12N 15/64 |
The specific C-Sets rule is located at only one place of the base symbol in the section "Special rules of classification" in the definition. If the C-Sets rule is applicable to all groups of a subclass, it is located at the subclass level only. If the same C-Sets rule is applicable to multiple groups or subgroups within the same subclass, the C-Sets rule is placed at the highest group or subgroup of the multiple groups.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Enzyme | Proteinaceous material which causes a chemical change in a starting material without being consumed in the reaction. |
Involving | When used in relation to a substance, includes the testing for the substance as well as employing the substance as a determinant or reactant in a test for a different substance. |
Microorganism | For the purposes of classification, this term includes bacteria, fungi, viruses, protozoa and algae. |
Nucleic acid | Comprises nucleic acids as in vitro compounds as well as sub-cellular parts in vivo like chromosome territories within the nucleus, plasmids, gene sequences, genetic information, mutations, polymorphisms such as SNPs, in silico base sequences, aptamers (ligand binding nucleic acids) and ribozymes (catalytic active RNA molecules). |
This place covers:
Processes in which there is a direct or indirect qualitative or quantitative measurement or test of a material which contains enzymes, nucleic acids or microorganisms.
Processes in which a material containing enzymes, nucleic acids or microorganisms is used to perform a qualitative or quantitative measurement or test, e.g. testing for antimicrobial activity or cholesterol, geomicrobiological testing.
In vivo or in vitro or in silico measuring or testing processes involving nucleic acid e.g. nucleic acid hybridisation including Polymerase Chain Reaction [PCR]. See section range C12Q 1/68 - C12Q 1/708.
Compositions or test papers containing enzymes, nucleic acids or microorganisms which can be used to detect or identify a chemical compound or composition, e.g. paper strips for the testing of blood sugar.
Compositions or test papers distinguished by the use of indicators which can be used to detect or identify the presence of enzymes, nucleic acids or microorganisms.
Processes of making such test compositions.
This place does not cover:
Measuring or testing apparatus with condition measuring or sensing means, e.g. colony counters |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Apparatus for condition-responsive control processes | |
Microorganisms per se | |
Human, animal or plant cells per se | |
Viruses per se | |
Enzymes per se | |
Investigating or analysing materials by determining their chemical or physical properties | |
Observation of the progress or of the result of processes specified in this group by any of the methods specified in groups G01N 3/00 - G01N 29/00 | |
Investigating or analysing biological material | |
Testing involving plant cells | |
Immunoassay for plant cells | |
Immunoassay for animal cells | |
Chemical analysis involving blood sugar, e.g. galactose | |
Chemical analysis involving proteins, peptides and amino acids | |
Chemical analysis involving lipids, e.g. cholesterol |
In this group, test media are classified in the appropriate group for the relevant test process.
Classification in main group C12Q 1/00 and sub-groups C12Q 1/001 - C12Q 1/66 is further refined using Indexing Codes from the range C12Q 2304/00 - C12Q 2337/52. The definitions and scope of these Indexing Codes are self evident. The codes and definitions are listed at the end of this document.
Due to the strong relationship between the range C12Q 1/00 - C12Q 1/66 and the range G01N 33/50 - G01N 33/98, "Chemical analysis of biological material", and the rather broad nature of the definitions of some of the C12Q 1/001 - C12Q 1/66 sub-groups, refinement of the classification in this area by allocation of Indexing Codes from the range G01N 2333/00 - G01N 2800/60, where possible, is considered mandatory.
Observation of the progress or of the result of processes specified in this group by any of the methods specified in groups G01N 3/00 - G01N 29/00 may require additional classification in these groups.
This place covers:
Enzyme-based Electrochemical sensors where inventive concept lies in the enzyme aspect e.g. enzyme used, how attached to electrode, enzyme mediator involvement, enzyme sensing mechanism/system.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search and classification:
Apparatus specifically adapted for solid-phase testing in biospecific ligand binding assays or immunological testing/immunoassays | |
Involving physiochemical end-point determination | |
Electrodes |
This place covers:
Enzyme electrodes where inventive concept lies in the use of or construction of a membrane on or in which an enzyme or multi-enzyme sensing system is attached or entrapped
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Membrane | Any non-conductive porous structure |
This place covers:
Inventive concept lies in chemical e.g. silylation or physical e.g. plasma treatment of the electrode membrane to alter/create functional groups for attachment of enzyme. May also include crosslinking or other treatments of membrane polymers. Overlap with G01N 33/54353, G01N 33/5436, G01N 33/54393.
Chemical functionalisation of solid-phases for ligand attachment for use in biospecific ligand binding assays or immunological testing/immunoassays G01N 33/54353.
With the ligand physically entrapped within the solid phase G01N 33/5436.
Treatment of solid-phases (e.g. coating, irradiation) for the purpose of improving reaction conditions (e.g. reduction of non-specific binding, promotion of specific binding G01N 33/54393.
This place covers:
Enzyme electrodes where the enzyme or multi-enzyme sensing system requires a mediator e.g. co-factors (NAD/FAD), ferrodoxins.
This place covers:
Enzyme electrodes directed to analysis of specific molecules or use of specific enzymes. Use of multi-enzyme systems such as oxido-reductase systems may also be classified in C12Q 1/004 if the mediator is of importance.
This place covers:
Enzyme electrodes specifically designed for the analysis of glucose.
This place covers:
Methods for determining isoenzyme profiles.Overlap with G01N 33/573, G01N 33/5735.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search and classification:
Biospecific ligand binding assays or immunological testing/immunoassays for isoenzymes |
This place covers:
Methods for detecting, measuring or identifying co-enzymes or co-factors e.g. NAD, ATP involved in enzyme reactions.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search and classification:
Biospecific ligand binding assays or immunological testing/immunoassays for co-enzymes or co-factors |
This place covers:
Methods or processes for living microorganisms which cannot be classified elsewhere in C12Q 1/00- C12Q 1/66. Includes Total Viable Organism (TVO) testing and electrophysical measurements such as ion channel current.
C12Q 1/02 and subgroups includes testing for microorganisms where the desired result indicates non-viability.
This place does not cover:
Specific binding assays/Immunoassays for microorganisms are classified in | |
For hepatitis |
This place covers:
Methods or processes for testing or evaluating non antimicrobial chemical or biological compounds such as drugs, cosmetics.
This place does not cover:
Antimicrobial activity |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Testing or evaluating the effect of chemical or biological compounds, e.g. drugs, cosmetics, using animal cells | |
Testing or evaluating the effect of chemical or biological compounds, e.g. drugs, cosmetics, using plant cells |
This place covers:
Methods or processes (qualitative testing) designed to determine the presence or identity (variety, species, genus or Gram +/-) of a microorganism, including compositions containing an indicator for presence or identity of a microorganism.
This place covers:
Methods, processes or compositions wherein the inventive concept lies in the composition or content of the culture media e.g. percentage ratio of components, compounds present in medium itself (carbon source, nitrogen source, vitamins etc.)
This place covers:
Methods and processes (quantitative testing) for numerical counting the number of viable microorganisms or viable/non-viable ratio in a sample.
This place covers:
Methods, processes or compositions involving use of a multifield media (single media permitting identification of multiple results or single item e.g. petri dish comprising more than one medium to allow multiple results) in methods and processes (quantitative testing) for numerical counting the number of viable microorganisms or viable/non-viable ratio in a sample.
This place covers:
Methods, processes or compositions involving quantitative determination of Enterobacteria e.g. Citrobacter, Serratia, Proteus, Providencia, Morganella, Yesinia, Escherichia, Shigella, Salmonella, Klebsiella, Enterobacter, Erwinia, Hafnia.
This place covers:
Methods, processes or compositions involving quantitative determination of bacteria under nitrate to nitrite reducing conditions. Some bacteria e.g. E.Coli use nitrate under anaerobic growth conditions.
This place covers:
Methods, processes or compositions involving quantitative determination of Streptococcus or Staphylococcus bacteria.
This place covers:
Methods, processes or compositions for detecting presence or kind of microorganism (qualitative testing) designed to determine the presence or identity (variety, species, genus or Gram +/-) of a microorganism. wherein the inventive concept lies in the use of radioisotopes (e.g. 11C, 13 C, 14C, 2H, 3H, 15N, 35S, 35P).
This place covers:
Methods or processes for testing of antimicrobial activity of a compound on living microorganisms.
This place covers:
Methods, processes or compositions involving the use of a multifield media (single media permitting identification of multiple results or single item e.g. petri dish comprising more than one medium to allow multiple results) in methods or processes for testing of antimicrobial activity of a compound on living microorganisms.
This place covers:
Methods or processes for testing if sterility conditions have been achieved or are being maintained. Examples are labels for food packaging, testing of medical instrument sterilization methods, air or water quality.
This place covers:
Methods for sampling/physically isolating intact microorganisms (including non-viable microorganisms) are classified in C12Q 1/24 irrespective of what becomes of them afterwards. If the isolated microorganisms are further subject to immunoassay/biospecific binding assay a further symbol from G01N 33/569 or subgroups would be added.
This place covers:
Methods, processes or compositions involving enzymes having unidentifiable EC number and enzymes which cannot be classified elsewhere in C12Q 1/26-C12Q 1/66. Classified under this symbol are methods, processes or compositions involving enzymes classified EC 6.X.X.X. These enzymes are characterised by bond formation C-O (6.1), C-S (6.2), C-N (6.3), C-C (6.4), P-O (.5), N-Met (6.6) and may commonly be known as ligase, synthase, carboxylase, cyclase, chelatase.
This place covers:
Methods, processes or compositions involving enzymes classified as EC 1.X.X.X oxidoreductases, not comprising as part of the IUB name 'dehydrogenase' (see C12Q 1/32) and which cannot be classified elsewhere in C12Q 1/26-C12Q 1/32. Enzymes are characterised by the catalysis of oxidation/reduction reactions and may comprise as part of their IUB name reductase, oxidase, synthase, dismutase, hydrogenase, oxygenase
This place covers:
Methods, processes or compositions involving peroxidase enzymes classified EC 1.11.1.X including peroxidase enzyme itself (EC 1.11.1.7).
This place covers:
Methods, processes or compositions involving catalase enzyme, EC 1.11.1.6.
This place covers:
Methods, processes or compositions involving enzymes having an EC number 1.X.X.X and which contain 'dehydrogenase' in the IUB standard enzyme name.
This place covers:
Methods, processes or compositions involving enzymes classified as EC 3.X.X.X hydrolases and which cannot be classified elsewhere in C12Q 1/37-C12Q 1/46. Enzymes are characterised by the catalysis of the addition or removal of a water molecule and may comprise as part of their IUB name hydrolase, lipase, lactonase, nuclease, nucleotidase, NTPase, helicase, amidase, sulfatase, depolymerase, glycosylase and variants e.g. ribonuclease. Methods, processes or compositions involving urease (EC 3.5.1.5) - C12Q 1/58. Methods, processes or compositions involving (phospho)lipase - C12Q 1/61.
This place covers:
Methods, processes or compositions involving enzymes classified as EC 3.4.X.X. The enzymes are classified as acting on peptide bonds and may comprise as part of the IUB name peptidase and variants e.g. dipeptidase, aminopeptidase. Methods, processes or compositions involving clotting factors - C12Q 1/56.
There are many enzymes classified in the area EC 3.4.21.X - 3.4.23.X which retain the 'original' names e.g. trypsin, complement factors, kallikrein, subtilisin, papain, Meprin A, renin.
This place covers:
Methods, processes or compositions involving enzymes classified as EC 3.2.1.X. Enzymes are characterised by hydrolysis of O - and S -glycosyl compounds and may comprise as part of the IUB name (sugar residue)sidase e.g. galactosidase, mannosidase.
There are many enzymes classified in the area EC 3.2.1.X which retain the 'original' names e.g. amylase, lysozyme, lactase.
This place covers:
Methods, processes or compositions involving enzymes classified as EC 3.1.3.X. Enzymes are characterised by hydrolysis of phosphoric monoesters and usually comprise as part of the IUB name phosphatase.
This place covers:
Methods, processes or compositions involving enzymes classified as EC 3.1.X.X having as part of the IUB name 'esterase' or variant e.g. diesterase, thioesterase. Enzymes are characterised by acting on ester bonds.
This place covers:
Methods, processes or compositions involving acetylcholinesterase, EC 3.1.1.7 or cholinesterase EC 3.1.1.8.
This place covers:
Methods, processes or compositions involving enzymes classified as EC 2.X.X.X transferases and which cannot be classified elsewhere in C12Q 1/485-C12Q 1/52. Enzymes are characterised by the transfer of a functional group and may comprise as part of their IUB name kinase, transferase, synthase, phosphorylase and variants e.g. aminotransferase.
This place covers:
Methods, processes or compositions involving enzymes classified as EC 2.7.X.X having as part of the IUB name 'kinase' or variant. Enzymes are characterised by the transfer of phosphorus-containing groups.
This place covers:
Methods, processes or compositions involving enzyme creatine (phospho)kinase, EC 2.7.3.2.
This place covers:
Methods, processes or compositions involving enzymes classified as EC 2.6.1.X and may comprise as part of the IUB name 'transaminase'. Enzymes are characterised by the transfer of nitrogenous groups.
This place covers:
Methods, processes or compositions involving enzymes classified as EC 4.X.X.X lyases and may comprise as part of the IUB name lyase, carboxylase, aldolase, hydratase and variants e.g. decarboxylase, dehydratase. Enzymes are characterised by the catalysis of reactions involving the formation of or addition to a double bond.
This place covers:
Methods, processes or compositions involving enzymes classified as EC 5.X.X.X isomerases and may comprise as part of the IUB name racemase, mutase, epimerase, isomerase, tautomerase, synthase and variants e.g. aminomutase. Enzymes are characterised by the catalysis of isomerisation reactions.
This place covers:
Methods, processes or compositions involving glucose or galactose where glucose or galactose are the final analyte or subject of the test e.g. diabetes testing, glucose demand for testing presence of microorganisms, Glucose Tolerance Test, use of glucose or galactose in the production of enzymes. Electrochemical glucose sensors where the inventive concept is in an electrode or other sensor structure to specifically enhance glucose determinations are classified in C12Q 1/006.
This place covers:
Methods, processes or compositions involving blood clotting factors e.g. thrombin, fibrinogen, thromboplastin. Includes investigation and/or identification of compounds which are present in or modulate the clotting pathway.
This place covers:
Methods, processes or compositions involving detection of urea or urease (EC 3.5.1.5). Includes measurement of Biological Nitrogen Demand. Urea electrodes where the inventive concept is in the electrode are classified in C12Q 1/001 - C12Q 1/005. Includes detection of ammonia.
This place covers:
Methods, processes or compositions involving detection of cholesterol or LDL-cholesterol. Cholesterol electrodes where the inventive concept is in the electrode are classified in C12Q 1/005.
Overlap with G01N 33/92.
This place covers:
Methods, processes or compositions involving detection of triglycerides, e.g. as biomarkers for disease, HDL, LDL, CM values or acting as substrate for determination of (phospho)lipase enzymes.
Overlap with G01N 33/92.
This place covers:
Methods, processes or compositions involving detection of uric acid, often using the enzyme uricase (EC 1.7.3.3). Includes detection of uric acid as breakdown product indicative of other analytes e.g. purine bases, nucleotides.
This place covers:
Methods, processes or compositions involving detection of microbiological degradation or contamination of in-situ hydrocarbon reserves, hydrocarbon reserve prospecting using microorganisms, monitoring of microorganism contamination of liquid hydrocarbon fuels, carbon dioxide sequestering by subterranean microorganism methane production.
This place covers:
Methods, processes or compositions involving luciferase (EC 1.13.12.X or EC 1.14.14.3).
This place covers:
All documents which cannot be classified in any of the other groups but relate to the enzymatic manipulation of nucleic acids.
Group C12Q 1/00 relates to enzymes. From group C12Q 1/68 onwards, assays and products for analysing or detecting nucleic acids are covered irrespective of whether enzymes or microorganisms are involved. Group C12Q 1/70 similarly relates to nucleic acid assays and products for analysing or detecting viruses or bacteriophages.
Nucleic acid amplification reactions are classified in group C12P 19/34 if the focus of the subject-matter is on the enzymes or the enzyme modifications per se. However, if the enzyme modification results in a changed/improved analytical effect, classification is also effected in group C12Q 1/68.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Immunization, vaccines | |
Viral antigens in a vaccine | |
Gene therapy | |
Design and fabrication of microarrays (biochips) wherein the invention resides in the synthesis of polypeptides or polynucleotides; Apparatus and devices for combinatorial chemistry or for making molecular arrays. | |
Microfluidic systems used for nucleic acid analysis like thermal cyclers (PCR-machines), capillary sequencers | |
Chemical synthesis or modification of nucleosides, nucleotides or oligonucleotides (chemically linked to other compounds, fluorescent labels). | |
Bacterial, fungal, protozoal, vertebrate antigens. | |
Antibodies | |
Undifferentiated human, animal or plant cells | |
Plant cells | |
Animal cells | |
Cells modified by introduction of foreign genetic material | |
Viruses; Bacteriophages | |
Bacterial, fungal and protozoan enzymes | |
Extraction and purification of nucleic acids from biological samples, e.g. pure separation or isolation methods; Conditions, buffers or apparatuses therefore | |
Isolating individual clones by screening libraries; making libraries | |
DNA or RNA fragments; Modified forms thereof | |
Introduction of foreign genetic material using vectors; Vectors; Use of hosts therefor; Regulation of expression | |
Bacterial vectors | |
Vectors for fungal cells | |
Introduction of foreign genetic material using processes not otherwise provided for, e.g. co-transformation | |
Animal vectors and their preparation | |
Sensors and electronic devices involving nucleic acids wherein the electrical detection is important | |
Sensors and electronic devices wherein the optical detection is important | |
Protein diagnostics and detection | |
Coulter counters | |
Computer systems using nucleic acids | |
Bioinformatics |
In groups C12Q 1/68 - C12Q 1/708, the common rule is applied, i.e. the classification is made at the most appropriate place.
Classification guidance
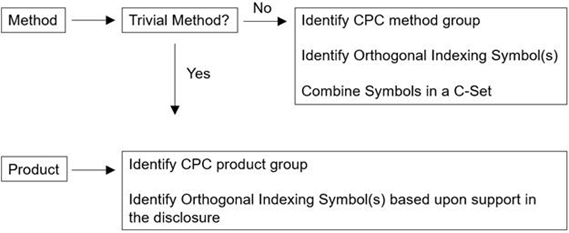
The subgroups C12Q 1/68 - C12Q 1/708 are divided in method groups and nucleic acid product groups (primers, probes, arrays, and other nucleic acid products) as shown in the tables below.
Depending on which kind of subject matter of invention is being classified (i.e. method or product), different rules for classification apply.
If the methods disclosed by an application are known or trivial, classification of such trivial methods is determined based on the use of the products identified and follows the classification guidance for products.
Orthogonal Indexing symbols C12Q 2500/00 - C12Q 2565/634 are used with the CPC method groups.
Orthogonal Indexing symbols of the groups C12Q 2600/00 - C12Q 2600/178 are used with the CPC product groups.
Classification of Nucleic acid product groups and trivial methods:
Nucleic acid product groups are shown below:
Symbol | Title |
Hybridisation probes, primers, and other nucleic acid products | |
For sex determination | |
For tissue and cell typing, e.g. hla probes | |
For diseases caused by alterations of genetic material | |
For cancer | |
For detection or identification of organisms | |
For bacteria | |
For protozoa | |
For plants, fungi, or algae | |
Specific hybridisation probes | |
For retroviruses | |
Viruses associated with AIDS | |
For herpetoviridae, e.g. herpes simplex, varicella zoster | |
For hepatitis | |
Non-A, non-B Hepatitis, excluding hepatitis D | |
For papilloma |
Classification guidance for nucleic acid products and trivial methods:
- The nucleic acid product groups C12Q 1/6876 - C12Q 1/6895 and C12Q 1/701- C12Q 1/708 are allocated as single symbols in conjunction with orthogonal Indexing symbols of the groups C12Q 2600/00 - C12Q 2600/178.
- The C12Q 2600/00 orthogonal Indexing symbols are given as independent symbols.
- The use of the C12Q 2600/00 codes is compulsory. They should be given if the claims and/or examples support a functional use as given by any of the C12Q 2600/00 symbols as shown above.
Examples for nucleic acid product groups:
Example 1. An invention is directed to the identification of the TNF haplotype TNF-1031C/-857C/-863C/-308G and its association with Crohn's Disease. The disclosure provides data showing a significant association of the haplotype with the Crohn's Disease. The invention also relates to the identification of the -857C allele. The methods and means for determining these polymorphisms and haplotypes are known in the art, therefore considered as trivial.
The nucleic acid product symbol for this invention is C12Q 1/6883.
Although the method for determining the -857C polymorphism is known, adding the orthogonal indexing symbol C12Q 2600/156 (polymorphic or mutational markers) will help in retrieving the information about use of the identified polymorphic allele, like 857C, and its association with Crohn's Disease.
The method for determining the haplotype is known. However, adding the orthogonal indexing symbol C12Q 2600/172 (Haplotypes) will aid in retrieving the information about use of haplotypes, like TNF-1031C/-857C/-863C/-308G, and its association with Crohn's Disease.
The complete classification should therefore be C12Q 1/6883, C12Q 2600/156 and C12Q 2600/172.
Example 2. An application relates to the use of the B1153 gene in testing for an allergic disease. The expression level of this gene is increased in patients with an allergic disease. The methods and means for determining the expression level are trivial.
The nucleic acid product symbol for this application is C12Q 1/6883.
The methods for determining the expression level are trivial but adding the orthogonal indexing symbol C12Q 2600/158 (expression marker) will aid in retrieving the information of use of specific expression markers, including B1153.
The complete classification should therefore be C12Q 1/6883 and C12Q 2600/158.
Example 3. An application relates to the use of a SNP for determining if a patient would benefit from an anti-cancer therapy. The methods and means for determining the SNP are trivial.
The nucleic acid product symbol for this application would be C12Q 1/6886.
The methods for determining the SNP are trivial but adding the orthogonal indexing symbol C12Q 2600/156 (polymorphic or mutational markers) will aid in retrieving information about polymorphic or mutational markers.
In addition, the application claims pharmacogenomics. If the application provides evidence-based support (e.g. examples) for this claim, orthogonal indexing symbol C12Q 2600/106 is also given. If no support is present, only the Indexing symbol for polymorphic marker C12Q 2600/156 is given.
The complete classification should therefore be:
- C12Q 1/6886 and C12Q 2600/156 if no support is present, or
- C12Q 1/6886, C12Q 2600/106 and C12Q 2600/156 if the application provides support for a pharmacogenomics claim.
Classification of non-invention information (additional information):
All subgroups in C12Q 1/68 - C12Q 1/708 can be used for classifying non-invention information (or Additional information) that compliments Invention information and is useful for searches. Such Additional information is given under the classifier's discretion. The following example illustrates how to classify non-invention information as (A) that is useful for search:
Example: An application relates to oligonucleotide probes used for the species-specific identification of parodontophathogenic bacteria by in situ hybridisation. The methods for performing the in situ hybridisation are known in the art and considered as non-invention.
The application is given C12Q 1/689 for the bacterial detection probes as Inventive information.
Although the method in situ hybridisation is known in the art, adding C12Q 1/6841 (in situ hybridisation) as Additional information will aid in retrieving the method of identifying novel bacteria by using in situ hybridisation.
In searching, the combination of C12Q 1/689 (Inventive information (I)), C12Q 1/6841(Additional information (A)), and keywords will directly lead to the most relevant documents.
The complete classification should therefore be:
- C12Q 1/689 (I)
- C12Q 1/6841(A)
Classification of methods groups as invention information:
Within C12Q 1/68 - C12Q 1/6874 and C12Q 1/6897 - C12Q 1/70, the following subgroups listed in table below are considered as method groups related to nucleic acids.
Symbol | Title |
Nucleic acid analysis utilising immunogens | |
Preparing nucleic acids for analysis, e.g. for PCR assay | |
Sequence identification involving differential detection | |
Selection methods for production or design of target specific oligonucleotide or binding molecules | |
Hybridisation assays | |
Characterised by the means of detection | |
Involving interaction of at least two labels, e.g. resonant energy transfer | |
Signal amplification | |
Release of bound marker | |
Nucleic acid detection involving sensors | |
For mutation or polymorphism detection | |
Involving restriction enzymes, e.g. rflp | |
Enhancement of hybridisation reaction | |
Nucleic acid analysis involving immobilisation; Immobilisation characterised by the carrier or coupling agent | |
Characterised by the use of probe arrays or probe chips | |
Triple helix formation in hybridisation assays | |
In situ hybridisation | |
Nucleic acid amplification reactions | |
Common amplification features | |
Preventing contamination | |
Quantitative amplification | |
Using modified primers or templates | |
Ligating adaptors | |
Allele specific amplification | |
Polymerase chain reaction [PCR] | |
Ligase chain reaction [LCR] | |
Promoter based amplification, e.g. NASBA, 3SR, TAS | |
Replicase based amplifications, e.g. Q-beta replicase | |
Methods for sequencing; sequencing using nanopores and other sequencing systems based on physical properties of nucleic acids, e.g. Atomic Force Microscopy [AFM] | |
Involving mass spectrometry | |
Involving nucleic acid arrays, e.g. sequencing by hybridisation [SBH] | |
Involving reporter genes operably linked to promoters | |
Involving viruses and Bacteriophages |
Combination sets (C-Sets):
Methods related to nucleic acids as listed above in the table are classified in the form of C-Sets, which follows C-Sets rule #C12Qa as described in below.
C-Sets statement: #C12Qa
- In these C-Sets, the base symbol, representing the type of method are taken from the groups C12Q 1/68 - C12Q 1/6874, C12Q 1/6897 and C12Q 1/70, whereas the subsequent symbols representing the essential technical features of the method are taken from the orthogonal symbols C12Q 2500/00 - C12Q 2565/634.
- Orthogonal symbols C12Q 2500/00 - C12Q 2565/634 are only used as subsequent symbols in C-Sets and should not be allocated as single symbol.
- In the C-Set, only the essential technical features of the invention, which differentiate it from the prior art, are to be represented: only exceptionally more than three technical feature (orthogonal symbols) codes should make up the C-Set. The least possible number of orthogonal symbols should be included in the C-Set.
- All indexing codes from groups C12Q 2500/00 - C12Q 2565/634 are to be used in the context literally expressed in the phrase ascribed to the code, i.e. the use of an indexing code is neither restricted by its hierarchical position in a group nor by the definition of the group in which the code is found.
- All C-Sets #C12Qa should be allocated as Invention information (INV).
C-Sets syntax rules:
- Each C-Set shall contain two or more symbols. Each C-Set shall contain one base symbol from C12Q 1/68, C12Q 1/6804 - C12Q 1/6874, C12Q 1/6897 and C12Q 1/70, and at least one subsequent symbol from C12Q 2500/00 - C12Q 2565/634.
- Duplicate symbols are not allowed in these C-Sets.
- The order of the subsequent symbols in these C-Sets is not relevant.
C-Sets examples:
#C12Qa: Nanopore sequencing is accomplished by measuring changes to an electrical current as a nucleic molecule is passed through a pore. An application discloses an improved method of nanopore sequencing using an immobilized helicase at the pore entrance:
C12Q 1/6869 is given as a base symbol for the method of sequencing
The essential technical features of the inventive method are assigned using orthogonal indexing codes as follows:
- Feature 1: C12Q 2565/631 being a biochannel or pore
- Feature 2: C12Q 2521/543 immobilized enzyme(s)
- Feature 3: C12Q 2521/513 winding/unwinding enzyme, e.g. helicase
These orthogonal indexing codes are selected to describe the essential technical features of the method, and not to capture all features of the method of nanopore sequencing, such as C12Q 2565/607 being a sensor, e.g. electrode.
Complete C-set: (C12Q 1/6869, C12Q 2521/513, C12Q 2521/543, C12Q 2565/631)
#C12Qa: An application discloses an inventive method of nucleic acid quantification using an amplification method with an external standard and a logarithmic regression for determining the initial amount of nucleic acid present:
C12Q 1/6851 is given as a base symbol for the method of quantitative amplification
The following orthogonal indexing codes in C12Q 2500/00 - C12Q 2565/634 are assigned for the essential technical features of the inventive method:
- Feature 1: C12Q 2545/113 with an external standard/control
- Feature 2: C12Q 2537/165 Mathematical modelling
Complete C-set: (C12Q 1/6851, C12Q 2537/165, C12Q 2545/113)
This place covers:
Applications characterised by immunological compounds which are used in the analysis of nucleic acids. This group also includes applications characterised by nucleic acids which are used for analysing or detecting proteins and immunogens, e.g. immuno PCR).
This place does not cover:
Immunoassay | |
Immunoassay for nucleic acids |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Antibodies |
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Immunogens | means immunological compounds such as antibodies and antigens |
This place covers:
All applications which deal with the preparation/modification of nucleic acids in order to use them or prepare them for subsequent analysis (e.g. amplification techniques (PCR), hybridisation techniques, sequencing of nucleic acids). This group also contains applications dealing with the preservation of DNA or RNA samples.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Extracting or separating nucleic acids from biological samples, e.g. pure separation or isolation methods; Conditions, buffers or apparatuses therefore | |
Extracting or separating nucleic acids from biological samples by means of a solid support carrier, e.g. particles, polymers | |
Extracting or separating nucleic acids from biological samples by chromatography, e.g. electrophoresis, ion-exchange, reverse phase | |
Extracting or separating nucleic acids from biological samples by using magnetic beads | |
Extracting or separating nucleic acids from biological samples by filtration, e.g. using filters, frits, membranes |
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
This place covers:
All documents where the invention concerns a method for determining differential expression (RNA level) and comparative genomics (genomic DNA level) and improvements to such methods. However, if the methods disclosed by an application are known, these applications are classified as products based on the use of the products identified.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
The screening and making of libraries (e.g. cDNA libraries) |
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
This place covers:
The design of primers and probes using enzymatic techniques for obtaining them.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Isolating an individual clone by screening libraries | |
Screening libraries presented on the surface of microorganisms, e.g. phage display, E. coli display | |
Ribosome/Polysome display, e.g. SPERT, ARM | |
Preparation or screening of libraries displayed on scaffold proteins | |
SELEX | |
Gene trapping, e.g. exon-, intron-, IRES-, signal sequence-trap cloning, trap vectors | |
Protein x Protein interaction, e.g. two hybrid selection | |
Directional evolution of libraries, e.g. evolution of libraries is achieved by mutagenesis and screening or selection of mixed population of organisms | |
mRNA-Display, e.g. polypeptide and encoding template are connected covalently | |
Preparation or screening of tagged libraries, e.g. tagged microorganisms by STM-mutagenesis, tagged polynucleotides, gene tags | |
Template (nucleic acid) mediated chemical library synthesis, e.g. chemical and enzymatical DNA-templated organic molecule synthesis, libraries prepared by non ribosomal polypeptide synthesis (NRPS), DNA/RNA-polymerase mediated polypeptide synthesis | |
Differential gene expression library synthesis, e.g. subtracted libraries, differential screening | |
By coupling phenotype to genotype, not provided for in other groups of this group | |
Screening libraries by altering the phenotype or phenotypic trait of the host | |
Preparation or screening gene libraries by chromosomal integration of polynucleotide sequences, HR-, site-specific-recombination, transposons, viral vectors | |
Preparation or screening of expression libraries, e.g. reporter assays | |
Design, preparation, screening or analysis of libraries using computer algorithms | |
General methods of preparing gene libraries, not provided for in other subgroups | |
Phage display | |
Bioinformatics for probe design or probe optimization |
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
This place covers:
All applications dealing with hybridisation assays which can not be classified in any of the hybridisation subgroups.
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
This place covers:
Applications dealing with the detection of hybridisation assays characterised by the detection means.
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Means of detection | the mechanism used to detect the hybridisation of a nucleic acid probe to its nucleic acid target (e.g. labels,...) |
This place covers:
All applications dealing with the detection of hybridisation events using the interaction between the labels as principle.
The use of this detection principle in non-hybridisation based techniques such as nucleic acid amplification in group C12Q 1/6844 or sequencing in group C12Q 1/6869 are not covered by C12Q 1/6818 unless the invention resides in an improvement which has general applicability also for hybridisation assays (for instance an improved Taqman probe). In this case, both C12Q 1/6818 and an amplification or sequencing group can be given.
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
This place covers:
All applications where the detection signal generated in a hybridisation reaction is amplified (for instance the use of branched probes or rolling circle amplification to amplify the hybridisation signal).
Amplification of target nucleic acids as such wherein the target amplification results in an increase of signal which is not seen as signal amplification and is not classified in C12Q 1/682.
Electronic signal amplification is not classified in group C12Q 1/682 .
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
This place covers:
All applications wherein the hybridisation detection depends on the physical separation and subsequent detection of a signalling moiety.
The use of this detection principle in non-hybridisation based techniques such as nucleic acid amplification in group C12Q 1/6844 or sequencing in group C12Q 1/6869 are not covered by group C12Q 1/6823 unless the invention resides in an improvement which has general applicability also for hybridisation assays. In this case both C12Q 1/6823 and an amplification or sequencing group can be given.
This place covers:
All applications wherein the detection of the hybridisation reaction depends on the electrical or physical properties of the label or of the nucleic acid molecules themselves.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Sensors wherein the optical detection is important | |
Sensors and electronic devices involving nucleic acids wherein the electrical detection is important |
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
This place covers:
All methods dealing with the detection of polymorphisms using an hybridisation assay and which cannot be classified in group C12Q 1/683. The detection of methylation and splice variants is seen as polymorphism detection and therefore classified in this group if the detection principle is based on an hybridisation assay.
The detection of polymorphisms using amplification based techniques is classified in group C12Q 1/6858. The use of allele specific primer extension is covered by group C12Q 1/6858 and not C12Q 1/6827.
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Sequence identification involving differential detection | |
Allele specific amplification; The detection of polymorphisms using amplification based techniques |
This place covers:
All applications dealing with the enhancement of the binding between a target and its probe, e.g. use of special buffer components, temperatures, probe modifications.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Sequence identification involving differential detection | |
Increasing the specificity or sensitivity of an amplification reaction | |
Allele specific amplification |
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
This place covers:
All applications dealing with the enzymatic and biochemical coupling of nucleic acids to solid surfaces for the use in low throughput assays and the application of those solid surfaces in the subsequent analysis of a nucleic acid.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Design and fabrication of microarrays (biochips) wherein the invention resides in the synthesis of polypeptides or polynucleotides; Apparatus and devices for combinatorial chemistry or for making molecular arrays. | |
Chemical synthesis or modification of nucleosides, nucleotides or oligonucleotides, chemically linked to other compounds (fluorescent labels) |
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
This place covers:
All nucleic acid analysis methods which depend on the use of probe arrays (biochips, microarray). If the use of the array is in the context of a method which can be classified in another group of the hybridisation based assays, e.g. C12Q 1/6813, the classifier has to decide based on the relevance of the method to classify the application in either one of these groups or even to classify the application in both groups if necessary. However, if the use is for sequencing then the application is only classified in group C12Q 1/6874.
This place does not cover:
Involving nucleic acid arrays, e.g. sequencing by hybridisation [SBH] |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Design and fabrication of microarrays (biochips) wherein the invention resides in the synthesis of polypeptides or polynucleotides; Apparatus and devices for combinatorial chemistry or for making molecular arrays. | |
Chemical synthesis or modification of nucleosides, nucleotides or oligonucleotides, chemically linked to other compounds (fluorescent labels) |
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
This place covers:
All methods dealing with the formation of a triple helix DNA conformation. This group also covers other higher order conformations of nucleic acids (quadruplex).
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
This place covers:
All applications dealing with methods for the analysis of a nucleic acid in a cell or positionally in a chromosome like Fluorescent In Situ Hybridisation [FISH].
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
This place covers:
All amplification methods which do not belong in any of the amplification groups. Generally, amplification techniques which use a mechanism for amplifying nucleic acids and for which no group exists are classified in group C12Q 1/6844. An example of such an amplification technique is strand displacement amplification [SDA].
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Microfluidic systems used for nucleic acid analysis like thermal cyclers (PCR-machines), capillary sequencers | |
Chemical synthesis of oligonucleotides |
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
This place covers:
Methods for preventing contamination in an amplification reaction such as the use of wax barriers, containers, uracil glycosylase, hot start and nested PCR. In addition, all methods relating to increasing the specificity or sensitivity of an amplification reaction are classified in this group.
This group also covers means for reducing false positive or false negative signals in an amplification reaction.
These include the use of modified nucleotides, e.g. in amplification reactions designed for amplifying GC-rich templates, special buffer components, pH, reaction conditions, etc.
If the method is designed for a specific amplification technique like PCR in group C12Q 1/686, then it is both classified in the specific amplification group, i.e. C12Q 1/686, and in C12Q 1/6848.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Methods for preventing contamination before an amplification reaction | |
Enhancement of hybridisation reactions |
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
This place covers:
Methods for the quantitative amplification of nucleic acids including the use of standards or mathematical models. This group also covers methods (both again enzymatic and mathematical) for determining the amplification efficiency.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
ICT specially adapted for hybridisation; ICT specially adapted for gene or protein expression |
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
This place covers:
Methods using modified primers or templates.
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
This place covers:
Methods where the primer or the template is modified by the ligation to an adaptor.
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
This place covers:
All methods dealing with the detection of polymorphisms using an amplification assay. The detection of methylation and splice variants is seen as polymorphism detection and therefore classified in this group if the detection principle is based on an amplification assay. This includes allele specific primer extension (also when only one dNTP or ddNTP is incorporated using a polymerase).
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Hybridisation based polymorphism detection | |
Hybridisation based polymorphism detection involving restriction enzymes | |
Sequencing |
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
This place covers:
All applications dealing with PCR and modifications/improvements thereof (e.g. Taqman, multiplex-PCR, and etc.).
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
This place covers:
All applications dealing with LCR and modifications/improvements thereof.
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
This place covers:
All applications dealing with promoter based amplification and modifications/improvements thereof.
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
NASBA | Nucleic acid sequence based amplification |
3SR | selfsustained sequence replication |
TAS | transcription-based amplification system |
This place covers:
All applications dealing with replicase based amplifications and modifications/improvements thereof.
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
This place covers:
All nucleic acid sequencing methods which cannot be classified in the subgroups for sequencing using mass spectrometry, i.e. in group C12Q 1/6872 and sequencing using solid surfaces, i.e. in group C12Q 1/6874. This group also covers methods for sequencing using nanopores and other sequencing systems based on physical properties of nucleic acids, e.g. Atomic Force Microscopy [AFM].
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Allele specific primer extension | |
Microfluidic systems used for nucleic acid analysis like thermal cyclers (PCR-machines), capillary sequencers | |
Apparatus for sequencing using nanopores or nanochannels |
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
This place covers:
All applications dealing with mass spectrometry based sequencing and modifications/improvements thereof.
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
This place covers:
All applications dealing with nucleic acid array based sequencing and modifications/improvements thereof.
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
This place covers:
All nucleic acid products used in the analysis of nucleic acids (e.g. primers, probes, controls) which cannot be classified in any of the subgroups C12Q 1/6879 - C12Q 1/6895. If an application relates both to methods and nucleic acid products, than these applications are classified in both the appropriate method and product subgroups.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Differential detection | |
Polymorphism detection by hybridisation | |
Allele specific amplification | |
Probes and primers for the detection of viruses and bacteriophages | |
Virus antigen in a vaccine | |
Modified nucleosides, nucleotides | |
Bacterial and fungal antigens | |
Protozoal antigens | |
Antibodies | |
Virus, Bacteriophages | |
Bacterial, fungal and protozoan enzymes | |
DNA or RNA fragments; Modified forms thereof | |
Bacterial vectors | |
Vectors for fungal cells | |
Animal vectors and their preparation |
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
This place covers:
All nucleic acid based diagnostic products. Those include both products for detecting the alterations (polymorphisms including methylation and splice variants) of genetic material and for detecting differential expression of a disease gene. If an application also discloses methods for detecting such polymorphisms or differential expression, the classifier should decide based on the relevance of this method to classify the application also in the appropriate method groups, e.g. C12Q 1/6827, C12Q 1/683, C12Q 1/6858, or C12Q 1/6809.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Primers and probes for cancer assays | |
Diagnostic immunoassays |
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
This place covers:
All nucleic acid based cancer diagnostic products.
This place does not cover:
Cancer diagnostic immunoassays |
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
This place covers:
All methods which use the detection of reporter genes operably linked to promoters for screening and nucleic acid analysis.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Preparation or screening of expression libraries, e.g. reporter assays | |
If the screening or the analysis focuses on protein interaction, expression or activity |
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
This place covers:
All methods which are specifically designed for the analysis of viral nucleic acids or for the analysis of nucleic acids of bacteriophages. (NOTE: According to the hierarchy this subgroup should not be limited to analysis involving nucleic acids. In practice, however, as Immunoassays/protein based Biospecific binding assays for viruses are classified in G01N, this subgroup is effectively limited to analysis of viral/bacteriophagal nucleic acids). Methods which are generally applicable to nucleic acid analysis should also be classified in the relevant C12Q 1/68 subgroup.
This place does not cover:
Immunoassay/protein based Biospecific binding assay for viruses |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Virus antigen in a vaccine | |
Virus |
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
This place covers:
All probes and primers for the detection and analysis of viruses and bacteriophages not covered by any of the subgroups C12Q 1/703 - C12Q 1/708.
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
This place covers:
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
This place covers:
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
This place covers:
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
This place covers:
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
This place covers:
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
This place covers:
See the "Special rules" section of C12Q 1/68
This place covers:
Processes involving enzymes or microorganisms in which a process parameter is measured and that or another process parameter is varied in response to such measurement.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
O-linked chromogens for determinations of hydrolase enzymes, e.g. glycosidases, phosphatases or esterases | |
N-linked chromogens for determinations of peptidases and proteinases |
Indexing codes C12Q 2500/00 - C12Q 2565/634 are only used as subsequent symbols in C-Sets and are not allocated as single symbols.
C-Sets classification:
Indexing codes C12Q 2500/00 - C12Q 2565/634 are used as subsequent symbols in C-Sets #C12Qa, #C12Na and #C12Nb. The detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules are found in the "Special rules of classification" in C12Q 1/68 for C-Set rule #C12Qa, C12N 15/10 for C-Set rule #C12Na, and C12N 15/64 for C-Set rule #C12Nb.
C-Sets searches:
C-Sets search queries may be made according to C-Set classification rules #C12Qa, #C12Na or #C12Nb, described in C12Q 1/68, C12N 15/10 or C12N 15/64, respectively.
When the detection is based on the release of pyrophosphate, classification is made in group C12Q 2565/301.
When the promoter-based amplification (e.g. NASBA, 3SR, TAS) is of relevance, classification is made in group C12Q 2531/143.
Classification in this group is not to be used for 3'-end base.
When the incorporation is made in the context of the Sanger sequencing method, i.e. oligonucleotide sequencing using primer elongation and dideoxynucleotides as chain terminators, classification is made in group C12Q 2535/101.
When the reaction requires the presence of a metal/ion, classification is made in group C12Q 2563/137.
When the method involves a ligase detection reaction [LDR], classification is made in group C12Q 2561/125.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Allele specific primer extension | |
Characterised by the capture oligonucleotide acting as a primer |
When the ligation is assessed in the context of a ligase chain reaction or of a ligase detection reaction, classification is made in groups C12Q 2531/137 or C12Q 2561/125, respectively.
When the reaction is characterized by incorporating arbitrary or random nucleotide sequences, classification is made in group C12Q 2525/179.
When the method relates to strand displacement amplification [SDA], classification is made in group C12Q 2531/119.
Classification in this group is not to be used for reactions that are implicitly known to be sequential (e.g. amplification reactions).
When the reaction is based on linear amplification, i.e. non exponential, on asymmetric PCR, on PCR, on strand displacement amplification, on rolling circle, on inverse PCR, on ligase chain reaction, on promoter based amplification or on replicase based amplification, classification is made in groups C12Q 2531/101 - C12Q 2531/149, respectively.
When the reaction step is used in the context of a quantitative measurement with a competitive internal standard/control, classification is made in group C12Q 2545/107.
When an enzyme inhibitor or activator is used in the reaction or when a non-extendable or blocking moiety is used in the reaction, classification is made in groups C12Q 2527/127 or C12Q 2525/186, respectively.
When the reaction is based on the use of an internal standard/control or on the use of a competitive internal standard/control, or finally on the use of an external standard/control, i.e. control reaction is separated from the test/target reaction, then the classification is made in groups C12Q 2545/101, C12Q 2545/107 or C12Q 2545/113, respectively.
When reactions leading to the incorporation of a peptide nucleic acid are involved, classification is made in group C12Q 2525/107.
When the label is electroactive, classification is made in group C12Q 2563/113.
When the capture moiety is a protein for target oligonucleotides, classification is made in group C12Q 2565/531.
Classification in this group is to be used when enzymes are used as labels.
When the primers are used in sequential reactions, with the exception of uses for reactions implicitly known to be sequential, e.g. amplification reactions, classification is made in group C12Q 2537/149.
When a mass label is used in nucleic acid detection, classification is made in group C12Q 2563/167.