Version: 2026.01
Loading Scheme...
CPC | COOPERATIVE PATENT CLASSIFICATION | |||||||||
| C12P | FERMENTATION OR ENZYME-USING PROCESSES TO SYNTHESISE A DESIRED CHEMICAL COMPOUND OR COMPOSITION OR TO SEPARATE OPTICAL ISOMERS FROM A RACEMIC MIXTURE {(brewing of beer C12C; producing vinegar C12J; producing specific peptides or proteins C07K; producing enzymes C12N 9/00; DNA or RNA concerning genetic engineering, vectors, e.g. plasmids, or their isolation, preparation or purification C12N 15/00; measuring or testing processes involving enzymes or microorganisms C12Q; measuring or testing processes involving nucleic acid amplification reactions C12Q 1/6844; fermentation processes to form a food composition, A21 or A23; compounds in general, see the relevant compound class, e.g. C01, C07)} [2018-08] NOTES
WARNINGS
|
| C12P 1/00 | Preparation of compounds or compositions, not provided for in groups C12P 3/00 - C12P 39/00, by using microorganisms or enzymes [2017-08] NOTES
|
C12P 1/02 | . | by using fungi [2013-01] |
C12P 1/04 | . | by using bacteria [2013-01] |
C12P 1/06 | . | by using actinomycetales [2013-01] |
C12P 3/00 | Preparation of elements or inorganic compounds except carbon dioxide {(recovery of carbon dioxides as by-products C12F 3/02)} [2017-08] |
C12P 5/00 | Preparation of hydrocarbons {or halogenated hydrocarbons} [2013-01] |
C12P 5/002 | . | {cyclic (compounds containing at least three condensed carbocyclic rings C12P 15/00)} [2013-01] |
C12P 5/005 | . . | {aromatic (naphthacene C12P 29/00)} [2013-01] |
C12P 5/007 | . | {containing one or more isoprene units, i.e. terpenes (carotenes C12P 23/00)} [2013-01] |
C12P 5/02 | . |
C12P 7/00 | Preparation of oxygen-containing organic compounds [2013-01] |
C12P 7/02 | . | containing a hydroxy group [2013-01] |
C12P 7/04 | . . | acyclic [2013-01] |
C12P 7/06 | . . . | Ethanol, i.e. non-beverage [2013-01] |
C12P 7/065 | . . . . | {with microorganisms other than yeasts} [2017-08] |
C12P 7/08 | . . . . | produced as by-product or from waste or cellulosic material substrate [2013-01] |
C12P 7/10 | . . . . . | substrate containing cellulosic material [2013-01] |
C12P 7/12 | . . . . . | substrate containing sulfite waste liquor or citrus waste [2013-01] |
C12P 7/14 | . . . . | Multiple stages of fermentation; Multiple types of microorganisms or re-use of microorganisms [2017-08] |
C12P 7/16 | . . . | Butanols [2013-01] |
C12P 7/18 | . . . | polyhydric [2013-01] |
C12P 7/20 | . . . . | Glycerol [2013-01] |
C12P 7/22 | . . | aromatic [2013-01] |
C12P 7/24 | . | containing a carbonyl group [2013-01] |
C12P 7/26 | . . | Ketones [2013-01] |
C12P 7/28 | . . . | Acetone-containing products [2013-01] |
C12P 7/30 | . . . . | produced from substrate containing inorganic compounds other than water [2013-01] |
C12P 7/32 | . . . . | produced from substrate containing inorganic nitrogen source [2013-01] |
C12P 7/34 | . . . . | produced from substrate containing protein as nitrogen source [2013-01] |
C12P 7/36 | . . . . | produced from substrate containing grain or cereal material [2013-01] |
C12P 7/38 | . . . | Cyclopentanone- or cyclopentadione-containing products [2013-01] |
C12P 7/40 | . | containing a carboxyl group {including Peroxycarboxylic acids} [2022-01] |
C12P 7/42 | . . | Hydroxy-carboxylic acids [2013-01] |
C12P 7/44 | . . | Polycarboxylic acids [2013-01] |
C12P 7/46 | . . . | Dicarboxylic acids having four or less carbon atoms, e.g. fumaric acid, maleic acid [2013-01] |
C12P 7/48 | . . . | Tricarboxylic acids, e.g. citric acid [2013-01] |
C12P 7/50 | . . . | having keto groups, e.g. 2-ketoglutaric acid [2013-01] |
C12P 7/52 | . . | Propionic acid; Butyric acids [2013-01] |
C12P 7/54 | . . |
C12P 7/56 | . . | Lactic acid [2013-01] |
C12P 7/58 | . . |
C12P 7/60 | . . . | 2-Ketogulonic acid [2013-01] |
C12P 7/62 | . | Carboxylic acid esters [2025-01] |
C12P 7/625 | . . | Polyesters of hydroxy carboxylic acids [2022-01] |
C12P 7/64 | . | Fats; Fatty oils; Ester-type waxes; Higher fatty acids, i.e. having at least seven carbon atoms in an unbroken chain bound to a carboxyl group; Oxidised oils or fats [2014-11] |
C12P 7/6409 | . . | Fatty acids [2022-01] |
C12P 7/6418 | . . . | by hydrolysis of fatty acid esters [2022-01] |
C12P 7/6427 | . . . | Polyunsaturated fatty acids [PUFA], i.e. having two or more double bonds in their backbone [2025-01] |
C12P 7/6431 | . . . . | Linoleic acids [18:2[n-6]] [2025-01] |
C12P 7/6432 | . . . . | Eicosapentaenoic acids [EPA] [2025-01] |
C12P 7/6434 | . . . . | Docosahexenoic acids [DHA] [2025-01] |
C12P 7/6436 | . . | Fatty acid esters [2025-01] |
C12P 7/6445 | . . . | Glycerides [2025-01] |
C12P 7/6454 | . . . . | by esterification [2025-01] |
C12P 7/6458 | . . . . | by transesterification, e.g. interesterification, ester interchange, alcoholysis or acidolysis [2025-01] |
C12P 7/6463 | . . . . | obtained from glyceride producing microorganisms, e.g. single cell oil [2022-01] |
C12P 7/6472 | . . . . | containing polyunsaturated fatty acid [PUFA] residues, i.e. having two or more double bonds in their backbone [2025-01] |
C12P 7/6481 | . . . . | Phosphoglycerides (phosphoglycerides having carboxylic acids with less than seven carbon atoms C12P 7/62) [2025-01] |
C12P 7/649 | . . . | Biodiesel, i.e. fatty acid alkyl esters [2025-01] |
C12P 7/66 | . | containing the quinoid structure [2013-01] |
C12P 9/00 | Preparation of organic compounds containing a metal or atom other than H, N, C, O, S or halogen {(phosphoglycerides, C12P 7/6481)} [2013-01] |
C12P 11/00 | Preparation of sulfur-containing organic compounds [2013-01] |
C12P 13/00 | Preparation of nitrogen-containing organic compounds [2013-01] |
C12P 13/001 | . | {Amines; Imines} [2013-01] |
C12P 13/002 | . | {Nitriles (-CN)} [2013-01] |
C12P 13/004 | . . | {Cyanohydrins} [2013-01] |
C12P 13/005 | . | {Amino acids other than alpha- or beta amino acids, e.g. gamma amino acids} [2013-01] |
C12P 13/007 | . | {Carnitine; Butyrobetaine; Crotonobetaine} [2013-01] |
C12P 13/008 | . | {containing a N-O bond, e.g. nitro (-NO2), nitroso (-NO)} [2013-01] |
C12P 13/02 | . | Amides, e.g. chloramphenicol {or polyamides; Imides or polyimides; Urethanes, i.e. compounds comprising N-C=O structural element or polyurethanes (peptides C12P 21/00 or C07K)} [2013-01] |
C12P 13/04 | . |
C12P 13/06 | . . | Alanine; Leucine; Isoleucine; Serine; Homoserine [2013-01] |
C12P 13/08 | . . | Lysine; Diaminopimelic acid; Threonine; Valine [2013-01] |
C12P 13/10 | . . | Citrulline; Arginine; Ornithine [2013-01] |
C12P 13/12 | . . | Methionine; Cysteine; Cystine [2013-01] |
C12P 13/14 | . . | Glutamic acid; Glutamine [2013-01] |
C12P 13/16 | . . . | using surfactants, fatty acids or fatty acid esters, i.e. having at least seven carbon atoms in an unbroken chain bound to a carboxyl group or a carboxyl ester group [2013-01] |
C12P 13/18 | . . . | using biotin or its derivatives [2013-01] |
C12P 13/20 | . . | Aspartic acid; Asparagine [2013-01] |
| C12P 13/22 | . . | Tryptophan; Tyrosine; Phenylalanine; 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylalanine [2016-05] NOTE
|
C12P 13/222 | . . . | {Phenylalanine} [2013-01] |
C12P 13/225 | . . . | {Tyrosine; 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylalanine} [2013-01] |
C12P 13/227 | . . . | {Tryptophan} [2013-01] |
C12P 13/24 | . . | Proline; Hydroxyproline; Histidine [2013-01] |
C12P 15/00 | Preparation of compounds containing at least three condensed carbocyclic rings {(gibbanes C12P 27/00; naphthacenes C12P 29/00)} [2017-08] |
C12P 17/00 | Preparation of heterocyclic carbon compounds with only O, N, S, Se or Te as ring hetero atoms (C12P 13/04 - C12P 13/24 take precedence) [2016-05] |
C12P 17/02 | . | Oxygen as only ring hetero atoms [2017-08] |
C12P 17/04 | . . | containing a five-membered hetero ring, e.g. griseofulvin {, vitamin C} [2017-08] |
C12P 17/06 | . . | containing a six-membered hetero ring, e.g. fluorescein [2013-01] |
C12P 17/08 | . . | containing a hetero ring of at least seven ring members, e.g. zearalenone, macrolide aglycons [2013-01] |
C12P 17/10 | . | Nitrogen as only ring hetero atom [2013-01] |
C12P 17/12 | . . | containing a six-membered hetero ring [2013-01] |
C12P 17/14 | . | Nitrogen or oxygen as hetero atom and at least one other diverse hetero ring atom in the same ring [2013-01] |
C12P 17/16 | . | containing two or more hetero rings {(thiamine open chain analogs C12P 17/167, i.e. not condensed among themselves or through a common carbocyclic ring system)} [2017-08] |
C12P 17/162 | . . | {Heterorings having oxygen atoms as the only ring heteroatoms, e.g. Lasalocid} [2016-08] |
C12P 17/165 | . . | {Heterorings having nitrogen atoms as the only ring heteroatoms} [2013-01] |
C12P 17/167 | . . | {Heterorings having sulfur atoms as ring heteroatoms, e.g. vitamin B1, thiamine nucleus and open chain analogs} [2013-01] |
C12P 17/18 | . | containing at least two hetero rings condensed among themselves or condensed with a common carbocyclic ring system, e.g. rifamycin {(e.g. Rifamycin C12P 17/189)} [2017-08] |
C12P 17/181 | . . | {Heterocyclic compounds containing oxygen atoms as the only ring heteroatoms in the condensed system, e.g. Salinomycin, Septamycin} [2013-01] |
C12P 17/182 | . . | {Heterocyclic compounds containing nitrogen atoms as the only ring heteroatoms in the condensed system (alloxazine or isoalloxazine, e.g. riboflavine C12P 25/00)} [2017-08] |
C12P 17/183 | . . . | {containing an indolo[4,3-F,G]quinoleine nucleus, e.g. compound containing the lysergic acid nucleus as well as the dimeric ergot nucleus} [2013-01] |
C12P 17/184 | . . . | {containing a beta-lactam ring, e.g. thienamycin} [2013-01] |
C12P 17/185 | . . | {Heterocyclic compounds containing sulfur atoms as ring hetero atoms in the condensed system (cepam nucleus C12P 35/00; penam nucleus C12P 37/00)} [2015-11] |
C12P 17/186 | . . . | {containing a 2-oxo-thieno[3,4-d]imidazol nucleus, e.g. Biotin} [2013-01] |
C12P 17/187 | . . . | {containing two or more directly linked sulfur atoms, e.g. epithiopiperazines} [2013-01] |
C12P 17/188 | . . | {Heterocyclic compound containing in the condensed system at least one hetero ring having nitrogen atoms and oxygen atoms as the only ring heteroatoms (ergot-alcaloids C12P 17/183)} [2013-01] |
C12P 17/189 | . . . | {containing the rifamycin nucleus} [2013-01] |
| C12P 19/00 |
C12P 19/02 | . |
C12P 19/04 | . | Polysaccharides, i.e. compounds containing more than five saccharide radicals attached to each other by glycosidic bonds [2013-01] |
C12P 19/06 | . . | Xanthan, i.e. Xanthomonas-type heteropolysaccharides [2013-01] |
C12P 19/08 | . . | Dextran [2013-01] |
C12P 19/10 | . . | Pullulan [2013-01] |
C12P 19/12 | . | Disaccharides [2013-01] |
C12P 19/14 | . | produced by the action of a carbohydrase {(EC 3.2.x)}, e.g. by alpha-amylase {, e.g. by cellulase, hemicellulase} [2017-08] |
C12P 19/16 | . | produced by the action of an alpha-1, 6-glucosidase, e.g. amylose, debranched amylopectin (non-biological hydrolysis of starch C08B 30/00) [2013-01] |
C12P 19/18 | . | produced by the action of a glycosyl transferase, e.g. alpha-, beta- or gamma-cyclodextrins [2013-01] |
C12P 19/20 | . | produced by the action of an exo-1,4 alpha-glucosidase, e.g. dextrose [2013-01] |
C12P 19/22 | . | produced by the action of a beta-amylase, e.g. maltose [2013-01] |
C12P 19/24 | . | produced by the action of an isomerase, e.g. fructose [2013-01] |
C12P 19/26 | . | Preparation of nitrogen-containing carbohydrates [2013-01] |
C12P 19/28 | . . | N-glycosides [2013-01] |
C12P 19/30 | . . . | Nucleotides [2013-01] |
C12P 19/305 | . . . . | {Pyrimidine nucleotides} [2013-01] |
C12P 19/32 | . . . . | having a condensed ring system containing a six-membered ring having two N-atoms in the same ring, e.g. purine nucleotides, nicotineamide-adenine dinucleotide [2013-01] |
C12P 19/34 | . . . . | Polynucleotides, e.g. nucleic acids, oligoribonucleotides [2013-01] |
C12P 19/36 | . . . . | Dinucleotides, e.g. nicotineamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate [2013-01] |
C12P 19/38 | . . . | Nucleosides [2013-01] |
C12P 19/385 | . . . . | {Pyrimidine nucleosides} [2013-01] |
C12P 19/40 | . . . . | having a condensed ring system containing a six-membered ring having two nitrogen atoms in the same ring, e.g. purine nucleosides [2013-01] |
C12P 19/42 | . . . | Cobalamins, i.e. vitamin B12, LLD factor [2013-01] |
C12P 19/44 | . | Preparation of O-glycosides, e.g. glucosides {(polysaccharides and not substituted disaccharides C12P 19/04, C12P 19/12)} [2017-08] |
C12P 19/445 | . . | {The saccharide radical is condensed with a heterocyclic radical, e.g. everninomycin, papulacandin} [2013-01] |
C12P 19/46 | . . | having an oxygen atom of the saccharide radical bound to a cyclohexyl radical, e.g. kasugamycin [2013-01] |
C12P 19/48 | . . . | the cyclohexyl radical being substituted by two or more nitrogen atoms, e.g. destomycin, neamin [2013-01] |
C12P 19/485 | . . . . | {Having two saccharide radicals bound through only oxygen to non-adjacent ring carbons of the cyclohexyl radical, e.g. gentamycin, kanamycin, sisomycin, verdamycin, mutamycin, tobramycin, nebramycin, antibiotics 66-40B, 66-40D, XK-62-2, 66-40, G-418, G-52 (see also C12P 19/54)} [2013-01] |
C12P 19/50 | . . . . | having two saccharide radicals bound through only oxygen to adjacent ring carbon atoms of the cyclohexyl radical, e.g. ambutyrosin, ribostamycin [2013-01] |
C12P 19/52 | . . . . . | containing three or more saccharide radicals, e.g. neomycin, lividomycin [2013-01] |
C12P 19/54 | . . . | the cyclohexyl radical being bound directly to a nitrogen atom of two or more 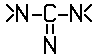 radicals, e.g. streptomycin [2013-01] radicals, e.g. streptomycin [2013-01] |
C12P 19/56 | . . | having an oxygen atom of the saccharide radical directly bound to a condensed ring system having three or more carbocyclic rings, e.g. daunomycin, adriamycin [2013-01] |
C12P 19/58 | . . | having an oxygen atom of the saccharide radical directly bound through only acyclic carbon atoms to a non-saccharide heterocyclic ring, e.g. bleomycin, phleomycin [2017-08] |
C12P 19/60 | . . | having an oxygen of the saccharide radical directly bound to a non-saccharide heterocyclic ring or a condensed ring system containing a non-saccharide heterocyclic ring, e.g. coumermycin, novobiocin {(C12P 19/605)} [2013-01] |
C12P 19/605 | . . . | {to a 1-benzopyran-2-on (or the chalcones and hydrogenated chalcones thereof, e.g. coumermycin, novobiocin, novenamin)} [2013-01] |
C12P 19/62 | . . . | the hetero ring having eight or more ring members and only oxygen as ring hetero atoms, e.g. erythromycin, spiramycin, nystatin [2013-01] |
C12P 19/623 | . . . . | {Avermectin; Milbemycin; Ivermectin; C-076} [2013-01] |
C12P 19/626 | . . . . | {Natamycin; Pimaricin; Tennecetin} [2013-01] |
C12P 19/64 | . | Preparation of S-glycosides, e.g. lincomycin [2013-01] |
C12P 21/00 |
C12P 21/005 | . | {Glycopeptides, glycoproteins} [2013-01] |
C12P 21/02 | . | having a known sequence of two or more amino acids, e.g. glutathione [2013-01] |
C12P 21/06 | . | produced by the hydrolysis of a peptide bond, e.g. hydrolysate products (preparing foodstuffs by protein hydrolysis A23J 3/00) [2013-01] |
C12P 23/00 | Preparation of compounds containing a cyclohexene ring having an unsaturated side chain containing at least ten carbon atoms bound by conjugated double bonds, e.g. carotenes (containing heterorings C12P 17/00) [2013-01] |
C12P 25/00 | Preparation of compounds containing alloxazine or isoalloxazine nucleus, e.g. riboflavin [2013-01] |
C12P 27/00 | Preparation of compounds containing a gibbane ring system, e.g. gibberellin [2013-01] |
C12P 29/00 | Preparation of compounds containing a naphthacene ring system, e.g. tetracycline (C12P 19/00 takes precedence) [2013-01] |
C12P 31/005 | . | {by fermentation or enzyme-using processes from marine organisms, e.g. Plexaura Homomalla} [2013-01] |
| C12P 33/00 | Preparation of steroids [2017-08] NOTES
|
C12P 33/005 | . | {Degradation of the lateral chains at position 17} [2013-01] |
C12P 33/02 | . | Dehydrogenating; Dehydroxylating [2013-01] |
C12P 33/04 | . . | Forming an aryl ring from A ring [2013-01] |
C12P 33/06 | . | Hydroxylating [2013-01] |
C12P 33/08 | . . | at 11 position [2013-01] |
C12P 33/10 | . . . | at 11 alpha-position [2013-01] |
C12P 33/12 | . | Acting on D ring {(carbons 13 and 14 belong to the C ring; degradation of lateral chains C12P 33/005)} [2013-01] |
C12P 33/14 | . . | Hydroxylating at 16 position [2013-01] |
C12P 33/16 | . . | Acting at 17 position [2013-01] |
C12P 33/18 | . . . | Hydroxylating at 17 position [2013-01] |
C12P 33/20 | . | containing heterocyclic rings {(reactions are also classified in groups C12P 33/00 - C12P 33/18)} [2016-05] |
C12P 35/00 | Preparation of compounds having a 5-thia-1-azabicyclo [4.2.0] octane ring system, e.g. cephalosporin [2013-01] |
C12P 35/02 | . | by desacylation of the substituent in the 7 position [2013-01] |
C12P 35/04 | . | by acylation of the substituent in the 7 position [2013-01] |
C12P 35/06 | . | Cephalosporin C; Derivatives thereof [2013-01] |
C12P 35/08 | . | disubstituted in the 7 position [2013-01] |
C12P 37/00 | Preparation of compounds having a 4-thia-1-azabicyclo [3.2.0] heptane ring system, e.g. penicillin [2013-01] |
C12P 37/02 | . | in presence of phenylacetic acid or phenylacetamide or their derivatives {not to be used} [2013-01] |
C12P 37/04 | . | by acylation of the substituent in the 6 position [2013-01] |
C12P 37/06 | . | by desacylation of the substituent in the 6 position [2013-01] |
C12P 39/00 | Processes involving microorganisms of different genera in the same process, simultaneously [2017-08] |
C12P 41/00 | Processes using enzymes or microorganisms to separate optical isomers from a racemic mixture [2017-08] |
C12P 41/001 | . | {by metabolizing one of the enantiomers} [2013-01] |
C12P 41/002 | . | {by oxidation/reduction reactions} [2013-01] |
C12P 41/003 | . | {by ester formation, lactone formation or the inverse reactions} [2013-01] |
C12P 41/004 | . . | {by esterification of alcohol- or thiol groups in the enantiomers or the inverse reaction} [2013-01] |
C12P 41/005 | . . | {by esterification of carboxylic acid groups in the enantiomers or the inverse reaction} [2013-01] |
C12P 41/006 | . | {by reactions involving C-N bonds, e.g. nitriles, amides, hydantoins, carbamates, lactames, transamination reactions, or keto group formation from racemic mixtures} [2013-01] |
C12P 41/007 | . . | {by reactions involving acyl derivatives of racemic amines} [2013-01] |
C12P 41/008 | . . | {by reactions involving carbamates} [2013-01] |
C12P 41/009 | . . | {by reactions involving hydantoins or carbamoylamino compounds} [2013-01] |