CPC Definition - Subclass B64C
This place covers:
- Overall fuselage shapes and concepts (only documents relating thereto are attributed the symbol B64C 1/00, when the emphasis is on aerodynamic aspects the symbol B64C 1/0009 is attributed).
- Structural features (including frames, stringers, longerons, bulkheads, skin panels and interior liners).
- Windows and doors (including hatch covers, access panels, drain masts, canopies and windscreens).
- Fuselage structures adapted for mounting power plants, floors, integral loading means (such as steps).
- Attachment of wing or tail units or stabilising surfaces to the fuselage.
- Relatively movable fuselage parts (for improving pilot's view or for reducing size for storage).
- Severable/jettisonable parts for facilitating emergency escape.
- Inflatable fuselage components.
- Fuselage adaptations for receiving aerials or radomes.
- Passive cooling of fuselage structures and sound/heat insulation (including isolation mats, and clips for mounting such mats and components such as pipes or cables).
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Aerodynamical features common to fuselages, wings, stabilising surfaces or the like |
Structures and components for helicopters falling within this main group and/or appended subgroups are additionally attributed the symbol B64C 27/04.
As an example, a helicopter fuselage with crash absorbing frames would be attributed the symbols B64C 1/062 and B64C 27/04.
This place covers:
Complete fuselage shapes for obtaining aerodynamic effects, e.g. reduced drag.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
plastic composite structures, frames, stringers, spars, beams, longerons, stringers and skins (also filament-wounded fuselage shells) (working with plastics) | |
plastic composite structures, frames, stringers, spars, beams, longerons, stringers and skins (also filament-wounded fuselage shells) (laminates) |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Specifically for wings |
This place covers:
Interior liners for aesthetic and/or protective purposes generally following the shape of the fuselage and visible from the inside in the completed fuselage.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Sound or heat insulating mat assemblies for being positioned adjacent the fuselage outer skin |
This place covers:
Complete fuselage structures (frames, stringers, skin) with the emphasis on structural features.
Assembling (e.g. moving, positioning) fuselage components (e.g. barrels) into a complete fuselage: B64F 5/10
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
This place covers:
Constructional features specially adapted for the nose of the fuselage.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Nose cones for missiles or torpedoes |
This place covers:
Constructional features specially adapted for the aft end of the fuselage.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Mountings for vertical or horizontal stabilizers | |
Mountings for auxiliary power units |
This place covers:
Aircraft fuselage bulkheads such as pressure bulkheads.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Fuselage frames | |
Cabin dividers for class separation |
Skins specifically for wings: B64C 3/26
Aircraft skin structures with integral lightning protection features are concurrently attributed the symbols B64C 1/12 and B64D 45/02 (aircraft lightning protectors).
This place does not cover:
Fairings movable in conjunction with undercarriage elements | |
Bomb doors |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Cleaning vehicle windows and windscreens |
Other structures integral with the fuselage to facilitate loading (e.g. cargo bays, cranes): B64C 1/22
This place does not cover:
Inspection hatches for engine cowls and nacelles |
Doors or door arrangements specially adapted to restrict unauthorized access are classified in this place (B64C 1/1469) and in B64D 45/0028 (multiple classification).
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Windows in vehicles | |
Windows in trains |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Pyrotechnics for shattering canopies |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Aircraft characterised by piston type power plant within or attached to the fuselage | |
Aircraft characterised by gas-turbine type power plant within or attached to the fuselage | |
Aircraft characterised by jet type power plant within or attached to the fuselage | |
Arrangements for mounting power plants in aircraft |
This place covers:
- Construction of aircraft floors.
- Decompression valves for mounting in the floor region.
This place covers:
- Aircraft floors specially adapted to freight by virtue of location, strength and/or shape(s);
- Aircraft floors with anchoring points or rails for freight;
- Aircraft seat rails.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Roller trays, Power Drive Units (PDU), clamping devices and other devices for moving and/or securing freight |
Equipment for handling freight in aircraft: B64D 9/00 - B64D 9/003
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Cargo door type ramps | |
Equipment for handling freight in aircraft |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Fuselage frames enabling folding or collapsing to reduce overall dimensions | |
Folding or collapsing wings |
This place covers:
Also includes pyrotechnics for shattering canopies.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Ejection seats | |
Ejectable capsules |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Inflatable structural components for wings | |
Varying camber of complete wings or parts thereof by inflatable elements | |
Connection of valves to inflatable elastic bodies |
This place covers:
Details of the mounting of the antenna or radome to the fuselage, e.g. hinged connections for maintenance purposes
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Antennas or radomes per se |
This place covers:
Cooling of the external fuselage skin.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Insulation mats or blankets adjacent the fuselage skin | |
Structures adapted to reduce effects of aerodynamic or other external heating on wings | |
Cooling structural parts of aircraft with air from an air-treatment apparatus (e.g. environmental control system) in the aircraft |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Cooling of the external fuselage skin | |
Insulating elements for vehicles in general |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Clips for sound or heat insulation in vehicles in general | |
Fasteners in general |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangement of elements of electric or fluid circuits specially adapted for vehicles in general | |
Supports for pipes, cables or protective tubing | |
Installations of electric cables or lines in vehicles |
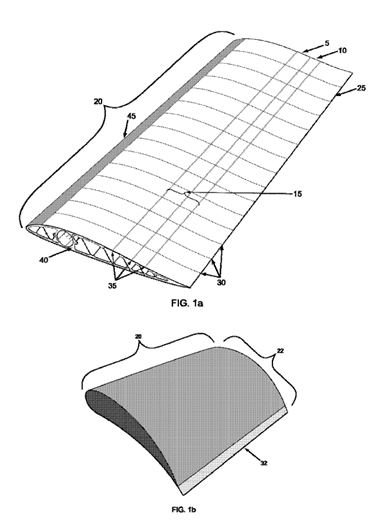
This place covers:
- Wing shapes (planform, airfoil profile, frontal aspect).
- Wing structures (spars, ribs, stringers, skin panels).
- Wing adaptations for accommodating power plants.
- Integral fuel tanks in the wings.
- Passive cooling of wing structures.
- Adjustment of complete wings or parts thereof (variable sweep, incidence, camber or area; warping, folding for storage purposes).
- Wings with fixed fences or spoilers.
This place does not cover:
Ornithopter wings |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Stabilising surfaces | |
Hang-glider wings (delta-shaped) | |
Hang-glider wings (parafoil) | |
Disc- or ring-shaped wings | |
Flying wings | |
Working with plastics |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
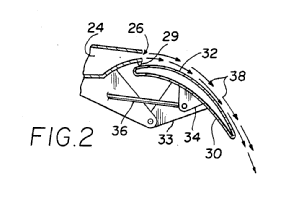
This place covers:
Shape of wing(s) when viewed from the front, e.g. dihedral, anhedral, gull-wing.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Stringers or longerons for fuselages |
Inflatable structural components for fuselages: B64C 1/34
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
For variation of shape, e.g. camber, for aerodynamical purposes | |
Connection of valves to inflatable elastic bodies |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Aircraft characterised by piston-type power plant within, or attached to, wings | |
Aircraft characterised by gas turbine-type power plant within, or attached to, wings | |
Aircraft characterised by turbofan or turbojet power plant within, or attached to, wings | |
Arrangements for mounting power plants in aircraft |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Fuel tanks |
This place covers:
Cooling of the external wing skin
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Constructions adapted to reduce effects of aerodynamic or other external heating of fuselage | |
Cooling structural parts of aircraft with air from an air-treatment apparatus (e.g. environmental control system) in the aircraft |
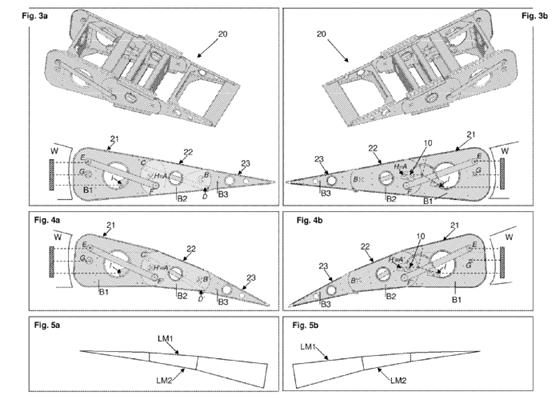
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group (variation of camber by inflatable elements):
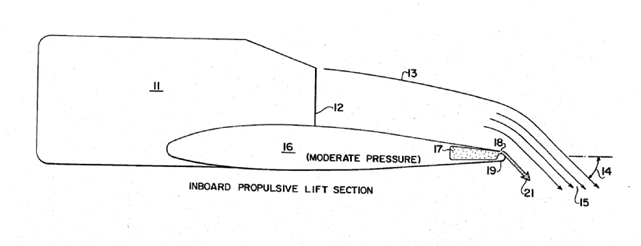
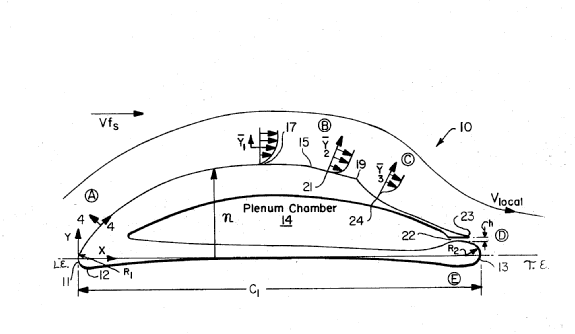
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group (wing skins are elastic; morphing, see also Glossary of Terms):

Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Connection of valves to elastic bodies | |
Inflatable elements for deicing only, e.g. inflatable leading edge boots |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Morphing | modification of wing shape by deformation, e.g. elastic skin |
This place covers:
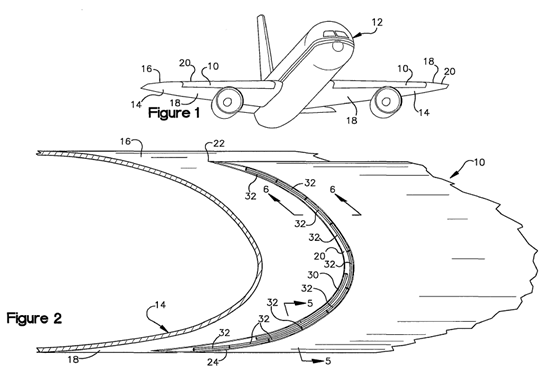
Illustrative example of variation of camber by movable elements:
This subgroup also includes documents where additionally wing skins are elastic (morphing; see also Glossary of Terms):
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Connection of valves to elastic bodies | |
Movable wing elements for deicing only | |
Inflatable elements for deicing only (e.g. inflatable leading edge boots) |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Morphing | modification of wing shape by deformation, e.g. employing elastic skin |
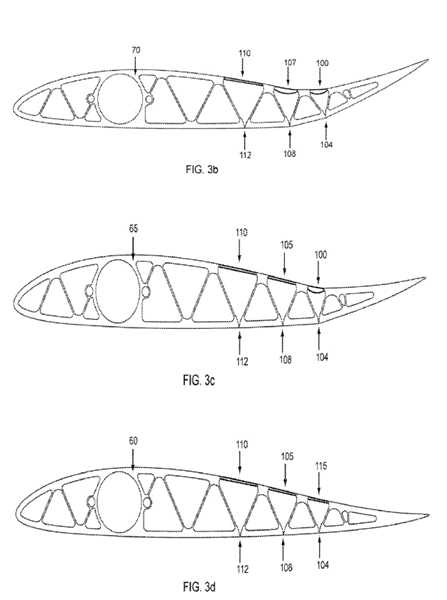
This place covers:
Integral leading or trailing edge parts of wings forming flaps by being movable by (elastic) deformation.
This place covers:
Folding wings or elements thereof to provide variable aerodynamic lift.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Folding wings or elements for reducing dimensions for storage purposes |
This place covers:
Folding or collapsible wings or elements thereof to reduce overall aircraft size for storage, as typically used by aircraft on aircraft carriers or by trailerable aircraft.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Relatively movable fuselage parts for reducing overall size for storage | |
Folding wings or elements thereof to provide variable, aerodynamic lift |
This place does not cover:
Adjustable for control purposes |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Generating vortices over aircraft surfaces not otherwise provided for |
This place covers:
Substantially fixed stabilising structures such as tailplanes, noseplanes and fins. Adjustable stabilising structures only when adjustment is limited and not for primary control purposes, e.g. an adjustable tail plane.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Attaching stabilising surfaces to fuselage |
This place covers:
Also some winglets
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Surfaces at the wing tip creating vortices |
This place covers:
For example horizontal stabilisers with limited movement about a spanwise axis for pitch trim.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Attaching stabilising surfaces to fuselages | |
Varying wing area for variation in lift |
This place covers:
Mounting control surfaces: B64C 9/02
Helicopter rotor hub fairings are concurrently attributed the symbols B64C 7/00 and B64C 27/04
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Power plant nacelles |
This place covers:
Control surfaces such as rudders, ailerons, flaps, elevators, trim/servo tabs and air brakes, as well as their mounting and balancing.
This place does not cover:
Trimming stabilising surfaces |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Systems for actuating flying-control surfaces |
This place covers:
Mechanical (hinged, sliding) connections between control surfaces (e.g. aileron) and supporting part (wings).
Gap covers and seals.
Structures and fairings not otherwise provided for: B64C 7/00
This place covers:
For example flaperons
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Fixed leading or trailing edge slots | |
Boundary-layer control |
This place does not cover:
Wings provided with fixed fences or spoilers |
This place covers:
Mainly actuating connections and linkages in the region of the flap and the supporting structure (e.g. wing), as well as further details such as covers. Aerodynamic (airflow) aspects are attributed B64C 9/18 (single flaps) or B64C 9/20 (multiple flaps).
This and the associated subgroups also covers trailing edge flaps where no slot is formed (e.g. conventional split flaps)
This place covers:
- Aerodynamic (airflow) aspects.
- Single flap in a given chordwise direction.
This place covers:
- Aerodynamic (airflow) aspects.
- Multiple flaps in a given chordwise direction.
This place covers:
Mainly actuating connections and linkages in the region of the flap and the supporting structure (e.g. wing), as well as further details such as covers. Aerodynamic (airflow) aspects are attributed B64C 9/24 (single flaps) or B64C 9/26 (multiple flaps).
This and the associated subgroups also covers leading edge flaps where no slot is formed (e.g. conventional Krüger flaps).
This place covers:
- Aerodynamic (airflow) aspects.
- Single flap in a given chordwise direction.
This place covers:
- Aerodynamic (airflow) aspects.
- Multiple flaps in a given chordwise direction.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Stabilising surfaces for retraction against or within fuselage or nacelle | |
Braking by parachutes |
This place covers:
- Propeller hubs, blades and pitch-changing mechanisms.
- Propeller vibration absorbing or balancing means. Arrangements of multiple propellers (e.g. coaxial propellers).
- Active or passive propeller measures for noise reduction (only such disclosures are attributed the symbol B64C 11/00).
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Rotors specially adapted for rotorcraft | |
Helicopter rotor blades with tips for noise reduction |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Propellers and associated components are only attributed B64C 11/00 or associated subgroup symbols when they are disclosed as being for use with aircraft, generally for producing longitudinal thrust.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Vibration damping devices for rotorcraft |
This place covers:
This and the associated subgroups B64C 11/48 and B64C 11/50 can also cover multiple propellers of the "unducted fan" or "open rotor" type.
This place does not cover:
Takes precedence |
This place covers:
- Control sticks and yokes, stick shakers, tactile or force-feedback.
- Mechanical, fluid or electric transmission means to the control surface(s), including use of autopilots, fly-by-wire and fly-by-light.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Asymmetric flap detection |
This place covers:
Control sticks and yokes as well as associated components and details in the region thereof.
Initiating means in rotorcraft: B64C 27/56
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Controlling members in general (e.g. joysticks, handles) |
This place covers:
For example longitudinal adjustment of rudder pedal assemblies.
This place covers:
- Vibrating control sticks or yokes ("stick shakers").
- Tactile cueing
Artificial feel (e.g. "force feedback") in the transmitting system: mechanical B64C 13/345, fluid B64C 13/46, electric B64C 13/507
This place covers:
Devices characterized by having two inputs actuated to effect control.
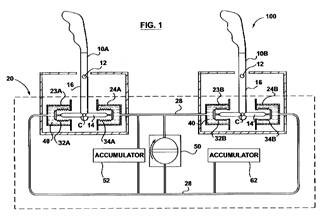
This place covers:
For example, locking a yoke against the dashboard to lock the control surfaces against wind gusts.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Locking in position to suit individual persons |
This place covers:
Also covers for example automatic rudder/aileron deflection to counter asymmetric thrust.
Automatic or condition responsive initiating members in rotorcraft: B64C 27/57.
Fly-by-wire or fly-by-light: B64C 13/503.
Automatic or condition responsive initiating members in aircraft power plant control: B64D 31/06 - B64D 31/12.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Control of position, course, altitude or attitude of land, water, air or space vehicles |
This place covers:
Autopilots, stability augmentation systems, yaw dampers, mostly in the context of the whole or a major part of the transmitting system.
This place covers:
For example radio control
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Remote controlled aircraft | |
Remote controlled toy aircraft | |
Air traffic control |
This place covers:
For example unmanned aerial vehicles, which can also be flown by a pilot (e.g. aircraft converted to "drones" or aerial targets).
This place covers:
Transmitting means between the initiating means (e.g. control stick) and the control surface (e.g. aileron).
Documents relating to power amplifying actuators (fluid, electric, mechanic) in aircraft control surfaces transmitting means are attributed this and the symbols of the associated subclasses when their use, mounting and/or function in the context of the transmitting means as a whole is described.
This place covers:
Only intermeshing toothed gearing.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Hydraulic circuits |
Automatically activated personal initiating means: B64C 13/16 - B64C 13/22.
Automatic or condition responsive personal initiating members in rotorcraft: B64C 27/57.
Automatic or condition responsive initiating members in aircraft power plant control: B64D 31/06 - B64D 31/12.
Personally activated initiating means with warning devices (e.g. "stick shakers", tactile cueing): B64C 13/10.
This place covers:
Also covers fly-by-light.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Control of position, course, altitude or attitude of land, water, air or space vehicles |
This place covers:
Control of aircraft by jet(s) generated by any means (including propellers).
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Altitude control of rotorcraft | |
Vertical take-off and landing [VTOL] aircraft | |
In-flight adjustment of the base configuration of UAVs | |
Details of jet-engine plants, e.g. of nozzles or jet pipes |
This place covers:
Thrust vectoring.
See also B64D 33/04 for arrangements of exhaust outlets or jet pipes.
This place covers:
Thrust vectoring obtained by rotating the power unit as a whole.
This place covers:
Aircraft control obtained by using dedicated jets.
This place does not cover:
Jet flaps |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Boundary layer control |
This place covers:
This group contains documents concerning aircraft stabilisation which are not classified in e.g. B64C 5/00.
This place covers:
Stability control by e.g. shifting the CoG
This place covers:
Pendulum stability is achieved when the centre of lift is above the CoG of the aircraft, or by using a dedicated pendulum.
This place covers:
A gyro is used to directly stabilize the aircraft.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Initiating means using automatic pilots | |
Automatic pilots |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Ballasting arrangements in lighter-than-air aircraft |
This place covers:
Displacement of the CoG, aimed at reaching a desired trim condition, is achieved by fuel transfer between the internal tanks of the aircraft.
This place covers:
Control of aircraft by using e.g. gyroscopic effects, vortex generators, moving aircraft parts and/or surfaces not provided for in B64C 9/00 or, in general, systems not provided for in B64C 13/00 or B64C 15/00.
This place covers:
Manual or automatic controller(s) on board one or more aircraft, embodying manual inputs or automatic control logic for aircraft sub-units of different type or different function, send(s) control signals to actuators of two or more aircraft sub-units, so that the sub-units act together to solve a particular problem or in response to a particular flying condition, e.g. in order to improve stability, comfort or safety, by managing the global dynamics of the one or more aircraft.
Illustrative examples of subject matter classified in this group:
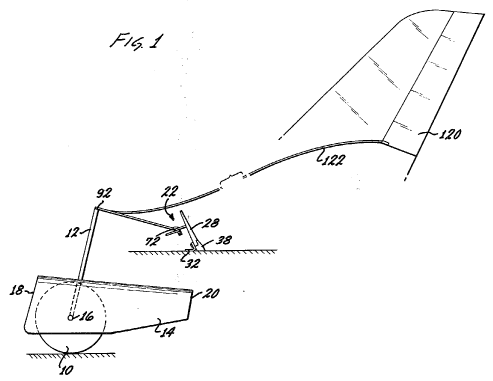
This area relates to aircraft control, function and dynamics of aircraft flying.
Classification concerning control of position, course or altitude will be placed in G05D 1/00.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Flying units formed by separate aircraft | |
Aircraft towing aircraft | |
Aircraft transported by aircraft |
Dual control apparatuses should be placed in B64C 13/12.
This place covers:
Any device/method operating within the airfoil boundary layer to influence the air flow around the airfoil, especially in order to control boundary layer separation.
This place covers:
Propulsion arrangements which ingest some or all of the aircraft surface boundary layer.
Illustrative example of the subject matter classified in this group:
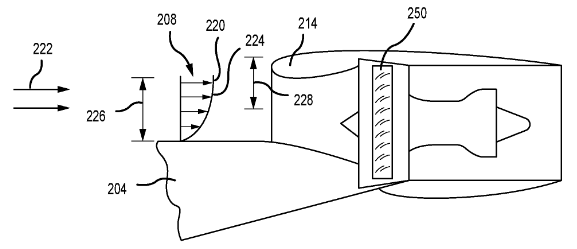
Illustrative example of the subject matter classified in this group:
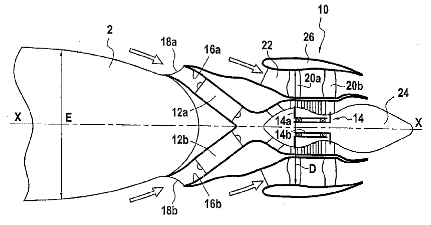
This place covers:
Cavities, slots, holes along a structural surface whereby the net flow is null.
This place covers:
Fluid is blown and sucked.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adjustable |
This place covers:
Fluid is only blown.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adjustable |
This place covers:
Fluid is only sucked.
This place does not cover:
BLI propulsion |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adjustable |
This place covers:
Fluid flow is explicitly adjustable by, e.g. valves, variable aperture or slot area, variable pump action or fluid pressure.
Always classify, in the case of blown or sucked fluid, also in B64C 21/025 or B64C 21/04 or B64C 21/06.
The properties referred to are e.g. roughness or riblets.
This place covers:
Air-flow over aircraft surfaces influenced e.g. by magnetic, electric or piezoelectric panels, by static charges, by ultrasound, by special shape, by rotating bodies.
Examples of places in relation to which this place is residual:
Attitude control by jet reaction | |
Influencing boundary layer |
Also B64C 21/00 if boundary layer explicitly involved.
Circulation control airfoils: B64C 3/141
Using Magnus effect: B64C 23/08
This place covers:
Shock wave modification devices and methods. Reduction of shock drag as main searched technical effect.
Supersonic type aircraft | |
Specific airfoil shape |
Fins mounted on wings |
This place covers:
Devices of any type (winglets, fins, turbines, splines) arranged at the wing tip.
Helicopter rotor blades tips: B64C 27/463
Fins on wings: B64C 5/08
This place covers:
A wing tip airfoil device is any separately identifiable airfoil member at the tip of the wing which creates or contributes in affecting vortices.
This place covers:
Devices having a cylindrical or spherical form which explicitly generate a force by using the Magnus effect.
Circulation control airfoils: B64C 3/141
This place covers:
- Any structure that supports/arrest the aircraft on a surface.
- Wheels supported by shock absorbers, skis, floats, pontoons or combinations thereof.
- Braking systems specific for aircraft.
- Arrester hooks. Control/actuating systems thereof.
This place does not cover:
Air-cushion alighting gear |
This place covers:
Arrangement or disposition on aircraft with respect to the aircraft structure. Inter-relationship thereof.
This place covers:
Systems for opening and closing undercarriage door bays. Fairings in general whose movement is performed in conjunction with the landing gear movement.
This place covers:
General methods and systems for operating unspecified aircraft landing gears.
This place covers:
Operating mechanisms comprising levers, pulleys, cables, gear wheels and/or characterised essentially by the kinematic aspects of the retracting/folding displacement.
Locking mechanisms: B64C 25/26
This place covers:
Operating mechanisms characterised by the control circuits/operating actuators being hydraulic or pneumatic.
This place covers:
Operating mechanisms characterised by using electrical or electromagnetic actuators.
This place covers:
Uplock assemblies for retaining and releasing landing gear systems, bracing locking devices, undercarriage locking and unlocking systems in general.
Operating systems, mechanical aspects: B64C 25/20
This place covers:
Ground lock detection devices, landing gear warning systems, landing gear verification systems.
Devices specially adapted to indicate the position of a movable element of the aircraft, e.g. landing gear |
This place covers:
Emergy release/actuation actuators and relevant control.
Devices specially adapted to indicate the position of a movable element of the aircraft, e.g. landing gear |
This place does not cover:
Arrester hooks: |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of endless-track type ground-engaging element:

This place covers:
Pre-landing acceleration devices for aircraft wheels, generally passive.
This place covers:
Motorised wheels, any type of motor or installation thereof.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Using rockets | |
Thrust reversers |
Originally meant for covering, e.g. thrust reversers, it is no longer used in this respect.
Thrust reversers shall not be classified in this group.
This place covers:
Braking methods/systems wherein the braking sequence is controlled by an electronic control unit and performed in accordance with predetermined steps, including controlling the brakes independently, to achieve a predetermined target, e.g. to achieve a predetermined deceleration rate or to optimize the braking force.
This place covers:
Regulators, disks, valves.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangements of brakes specially adapted for aircraft |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Anti-skidding regulators; electric or electronic controllers therefor |
This place covers:
Undercarriages which can be steered, relevant control systems and actuators, steering angle warning systems.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Steering devices for land vehicles | |
Ground or aircraft-carrier-deck installations for towing aircraft |
This place covers:
Wheel shimmy is a condition in which the landing gear wheel or wheels oscillate from side to side along a straight line parallel to the direction of travel of the aircraft. Documents concerning this problem are classified here.
This place covers:
Skis, skids, runners, various ground engaging structures, especially suitable for helicopters.
Safety devices for helicopters: B64C 27/006
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
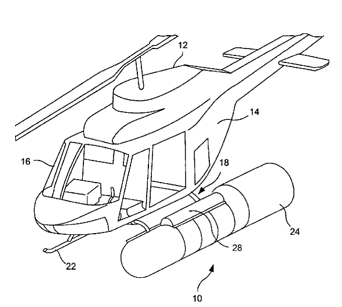
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Connection of valves to inflatable elastic bodies |
This place does not cover:
Shimmy-dampers |
This place covers:
Any shock absorber comprising hydraulic or pneumatic cylinders.
This place covers:
The ground engaging elements can be converted from e.g. wheeled to floats or skis and vice-versa depending on the specific landing surface.
This place covers:
Capturing or retrieving systems on aircraft.
This place covers:
- Vibration damping, safety devices and rotor tracking/balancing devices for rotorcraft rotors.
- Gyroplanes and autogyros, and rotors therefor.
- Helicopters, flying platforms and compound rotorcraft/helicopters.
- Rotors (including tail rotors), hubs, blades and rotor blade adjustment control (including flying controls, such as collective and pitch levers).
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Alighting gear |
This place covers:
Vibration or noise damping by means of isolators on the rotor head, suspended masses, actuators acting on the complete rotor assembly or active noise cancellation.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Rotor blade tips | |
Blade adjustment mechanism including flaps mounted on blades | |
Means acting on blades for blade adjustment |
This place covers:
For example wire cutters or detectors, helicopter-specific use of airbags, distance sensors for tail booms, rotor blade crack detection, tail rotor guards, emergency tail rotor drives or emergency anti-torque means.
Aircraft emergency devices: B64D 25/00
This place covers:
For example rotor blade tip weights or rotor blade tracking apparatus and methods.
This place does not cover:
For helicopters |
The following helicopter components are not attributed any of the symbols in B64C 27/00 but only the symbol B64C 27/04 and one of the following associated, applicable symbols:
Rotor hub fairings:B64C 7/00
Underslung loads: B64D 1/22
Mounting cameras: B64D 47/08
This place covers:
Drives which transfer motor output to the rotors at a generally 1:1 ratio.
Illustrative examples of subject matter classified in this group:
1.
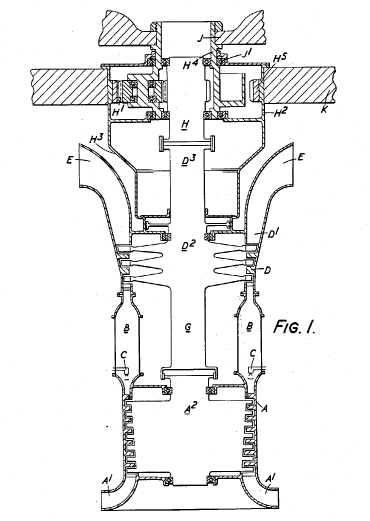
2.
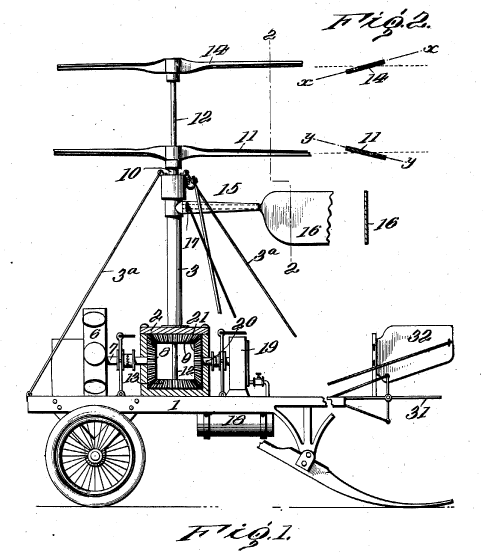
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Power transmission to rotor by electric power plant integral with rotor |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Shrouded propellers | |
With wings | |
Unmanned aerial vehicles |
This place covers:
Mostly tiltrotor aircraft requiring an anti-torque tail rotor.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Vertical take-off and landing [VTOL] aircraft, e.g. tiltrotors |
This place covers:
Rotor hubs, special or unconventional rotors.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Features common to rotors and propellers |
This place covers:
Flexbeams for rigid rotors.
Root attachment to rotor head: B64C 27/48
This place covers:
Elastomeric joints for articulated rotors
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Springs |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Having flexing arms | |
Having elastomeric joints |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Rotor blade tips |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Constructional features of propeller blades | |
Rotor blade tips | |
Rotors for wind motors |
Root attachment of propeller blades: B64C 11/04 - B64C 11/12
Foldable propeller blades: B64C 11/28
For autogyros: B64C 27/022
Transmitting means for controlling lead-lag movement of rotor blades: B64C 27/635
This place does not cover:
See-saw type construction |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
With forward-propulsion propellers pivotable to act as lifting rotors | |
Mechanisms for controlling blade adjustment or movement relative to rotor head | |
VTOL aircraft |
This place covers:
Cyclic sticks and collective levers as well as associated components and details in the region thereof.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Personal control surface initiating means in aeroplanes | |
Transmitting means, e.g. interrelated with initiating means or means acting on blades | |
Controlling members in general (e.g. joysticks, handles) |
This place covers:
Can also cover maintaining hover position or attitude.
Automatic or condition responsive initiating members in aeroplanes: B64C 13/16 - B64C 13/22
Fly-by-wire or fly-by-light: B64C 13/503
Automatic or condition responsive initiating members in aircraft power plant control: B64D 31/06 - B64D 31/12
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Control of position, course, altitude or attitude of land, water, air or space vehicles |
This place covers:
Transmitting means downstream of the cyclic stick and the collective lever.
This place does not cover:
Means acting on blades |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Transmitting means for aeroplanes | |
Initiating means |
This place covers:
Individual blade control by acting directly on the blade, e.g. by a separate actuator for each blade.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Individual rotor blade control using flaps on the blades |
This place covers:
Vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aircraft, e.g. of the tiltrotor types.
This place does not cover:
Rotorcraft |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Attitude, flight direction, or altitude control by jet reaction | |
Air-cushion vehicles | |
Details of jet-engine plants, e.g. of nozzles or jet pipes |
This place covers:
Also covers horizontal propeller/blower and airflow deflector.
This place covers:
- Complete aircraft or structural features described as facilitating supersonic/hypersonic flight, including special shapes and planforms of complete aircraft.
- Sonic boom alleviation means and methods.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Airfoil profiles |
This place covers:
- Gliders/sailplanes, accessories therefor when they cannot be classified elsewhere.- Microlight, ultralight and Light Sport Aircraft, and safety devices therefore (e.g. Ballistic Rescue Systems).
- Hang-gliders (e.g. of the "Rogallo" type).
- Man-powered (e.g. using pedals to drive a propeller) aircraft.
- Kites.
This place covers:
Also covers accessories for gliders (e.g. insect removal from leading edges) which cannot be adequately classified elsewhere.
This place does not cover:
Hang-gliders |
This place covers:
Hang-glider-type aircraft; Microlight-type aircraft, i.e. mainly very simple and light, powered single or two-seat aircraft with an open frame fuselage, but also covers light, single or two-seat aircraft when the emphasis is on low weight and simplicity, and/or when described as an "ultralight", "microlight" or "light sport aircraft".
Illustrative examples of subject matter classified in this group:
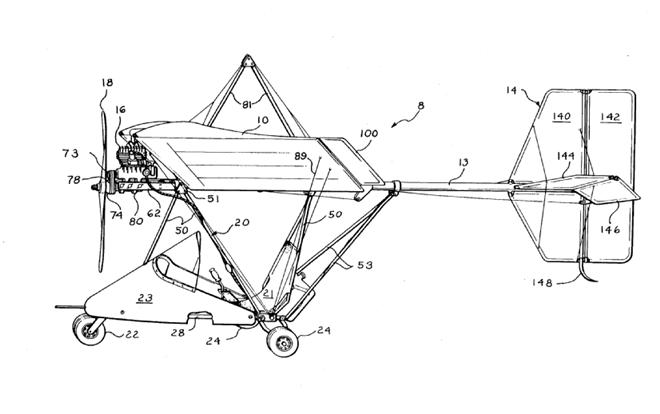
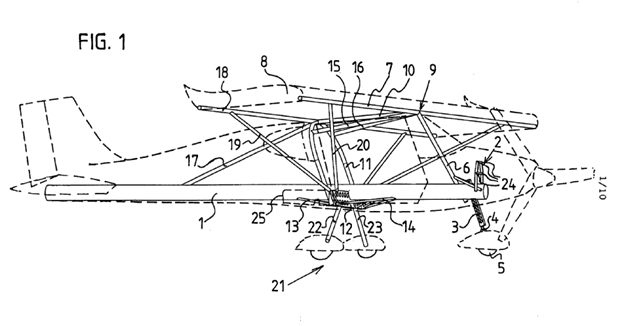
Example of "trike" or weight-shift controlled microlight:

Example of powered hang-glider:
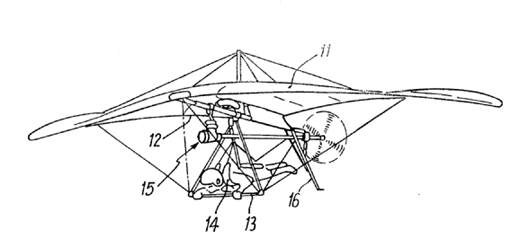
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Microlight or ultralight | Also covers the type of aircraft known in the USA as "Light Sport Aircraft" |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
ULM | Avion ultra-légèr motorisé |
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms:
- "ultralight aircraft", "light sport aircraft", "microlight aircraft" and "Ultraleichtflugzeug"(German)
- "trike"(English, German), "weight-shift control" and "gewichtskraftgesteuert" (German)
This place covers:
For example (ballistic) parachute rescue systems specially adapted to microlight aircraft or hang-gliders.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
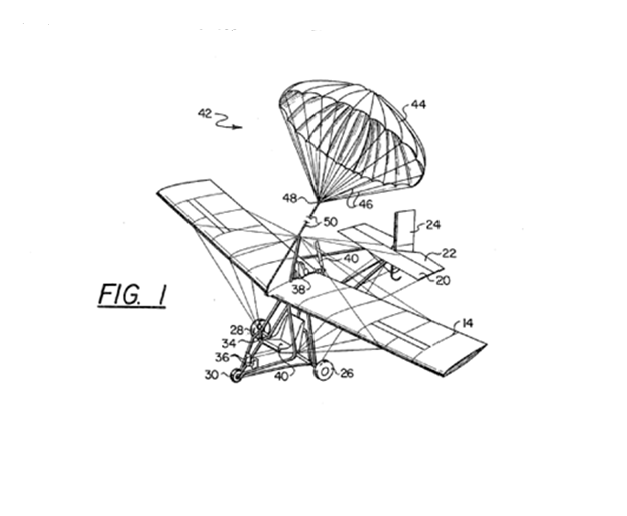
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Ejectable capsules |
This place covers:
Mainly unpowered hang-gliders with rigid, delta-shaped wings of the "Rogallo"-type.
Illustrative example of a delta-shaped wing:
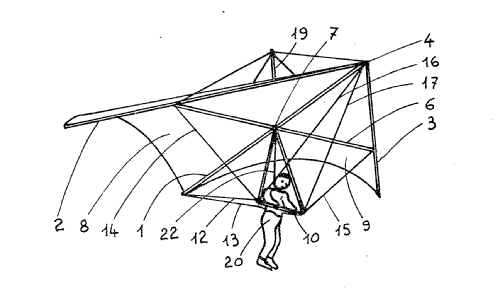
Also covers powered, microlight aircraft when comprising details of such wings.
This place covers:
Microlight aircraft - mainly powered - with a parachute or parafoil type wing attached to a rigid/substantial structure (e.g. framework or rigid seat). Also covers backpack-type powerplants for paragliders.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
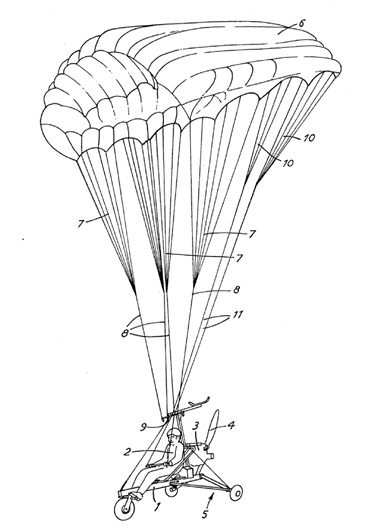
Illustrative example of subject matter (backpack-powerplant) classified in this group:
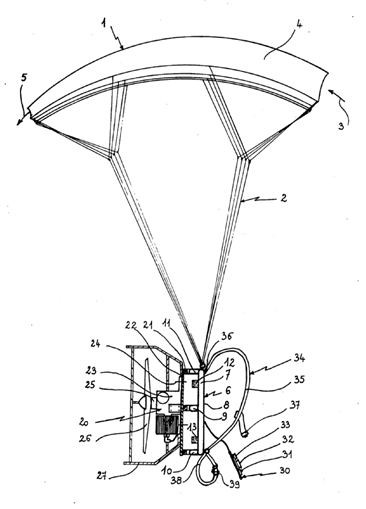
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Parachutes | |
Paragliders |
This place covers:
Propulsive power produced by the pilot, e.g. pedals connected to a propeller.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Ornithopters |
This place does not cover:
Toy aspects | |
Airborne towed targets, e.g. kites |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
For propelling water sports boards | |
For propelling vessels |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Hang-gliders | |
Advertising with kites |
This place covers:
All aircraft which fly by flapping the wings.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Toy aircraft propelled by flapping of wings | |
Ornithopter unmanned aerial vehicles |
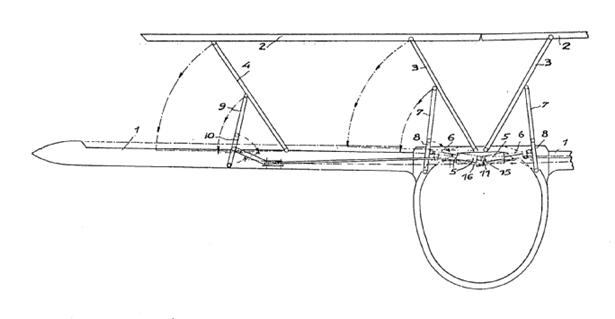
This place covers:
Illustrative example of ornithopter wings and actuating mechanism therefor:
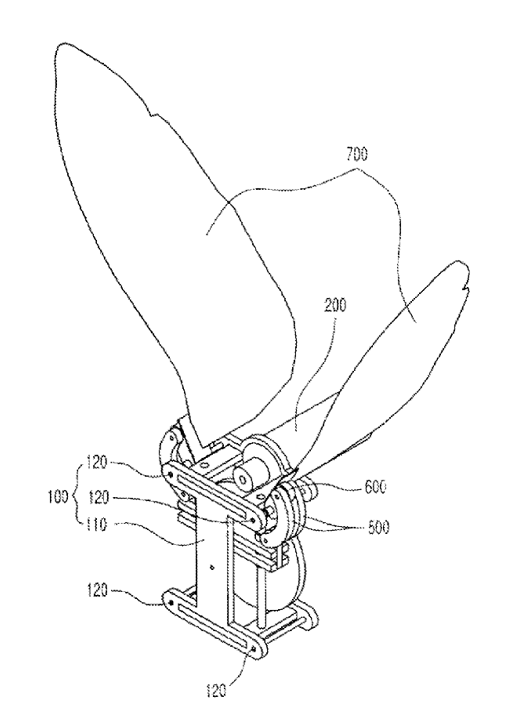
This place covers:
The word "seaplane" is used to describe two types of air/water vehicles: the floatplane and the flying boat. A floatplane has slender floats, mounted under the fuselage. Two floats are common, but other configurations are possible. Only the floats of a floatplane normally come into contact with water. The fuselage remains above water. In a flying boat, the main source of buoyancy is the fuselage, which acts like a ship's hull in the water. Most flying boats have small floats mounted on their wings to keep them stable.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Alighting gear | |
Floats |
This place covers:
Comprising devices acting in the water to generate thrust and/or slow down and/or steer the aircraft (e.g. propellers, jets, rudders).
This place covers:
Comprising lift generating devices which are peculiar to the shape of a seaplane.
This place covers:
Aircraft suitable for ground and water take-off and landing.
This place covers:
Combined road (and/or water) /air vehicles usually provided with wheels (and/or e.g. pontoons) and in-air propelling/thrust means.
This place covers:
Flying units wherein (possibly after an initial engagement phase) the multitude of (possibly different) flying vehicles (possibly including ground and/or water vehicles and/or dedicated units) are permanently connected.
This place does not cover:
Towing | |
Aircraft transported by aircraft | |
Air-refuelling |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Automatic pilots |
This place covers:
Essentially all the flying vehicles not classified in one of the previous groups, highly unconventional aircraft.
This place covers:
Flying vehicles characterised by sustainment without aerodynamic lift, engine thrust or buoyant gas. Lifting arrangements which violate the laws of physics, e.g. closed-loop systems.
Illustrative example of a flying saucer:
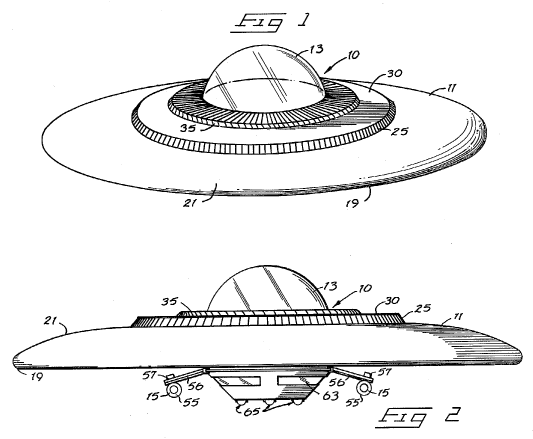
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Rotorcraft characterized by having shrouded rotors, e.g. flying platforms | |
Aircraft having disc or ring-shaped wings | |
Aircraft having annular wings with radial airflow | |
Inertia motors |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
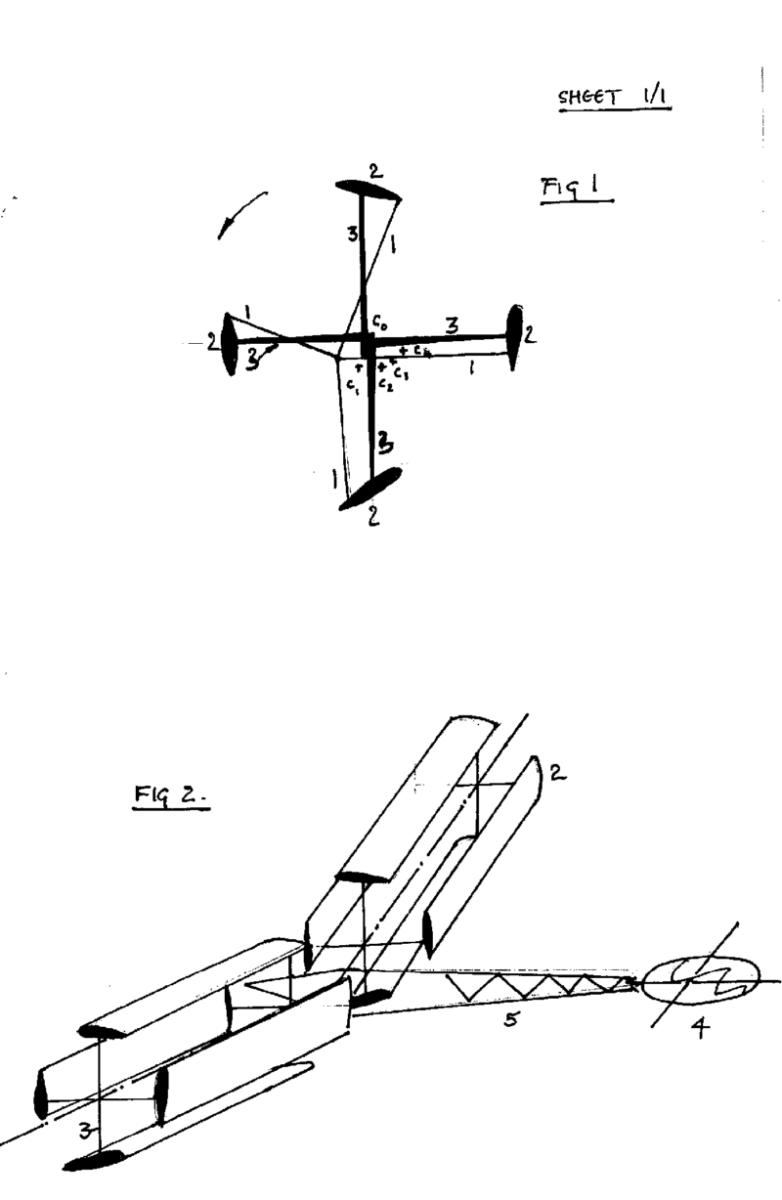
This place does not cover:
Rotorcraft | |
Ornithopters |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Paddle wheels | |
Using Magnus effect | |
Rotorcraft unmanned aerial vehicles | |
Ornithopter unmanned aerial vehicles |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Captive toy aircraft | |
Tethered unmanned aerial vehicles |
This place covers:
Remotely piloted flying vehicles in general.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Unmanned aerial vehicles |
This place covers:
Devices including rotors, wings, propellers, turbojets to be "worn" by a user.
Illustrative examples of subject matter classified in this group:
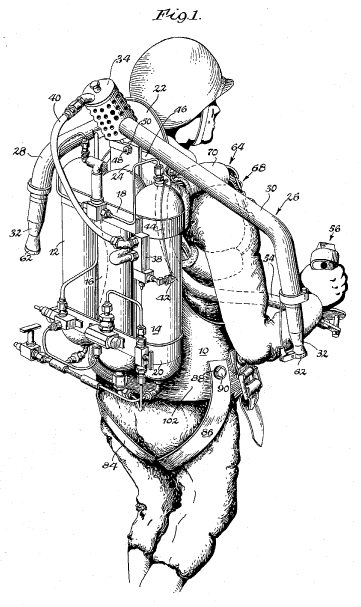
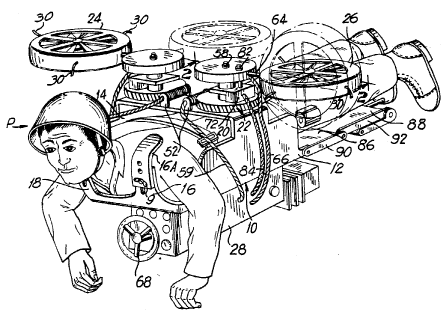
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Ornithopters | |
Sports garments, e.g. for skydiving | |
Power-driven personal watercraft for hydroflight sports | |
Parachutes | |
Rotary wing parachutes |
This place covers:
MAVs (microaerial vehicles), usually for military purposes, any maximum dimension of which does not exceed 15 cm (6 inches).
This place covers:
Aircraft that lack symmetry with respect to a longitudinal vertical plane.
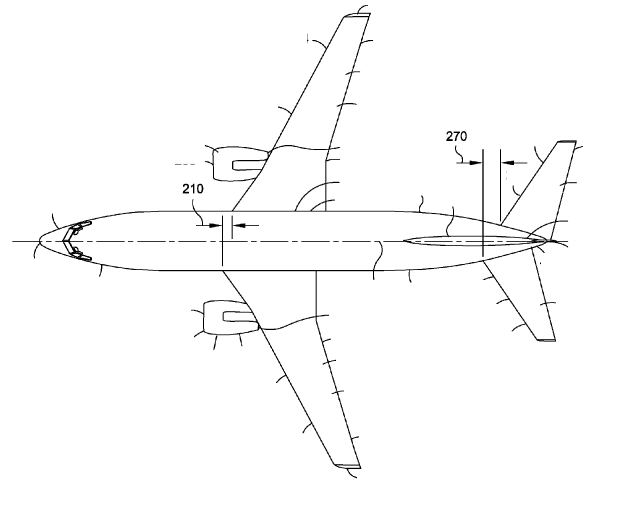
Examples of places in relation to which this place is residual:
Rotorcraft asymmetry due to placement of auxiliary rotor or fluid-jet device for counter-balancing lifting rotor torque |
Flying units formed by separate aircraft: B64C 37/02
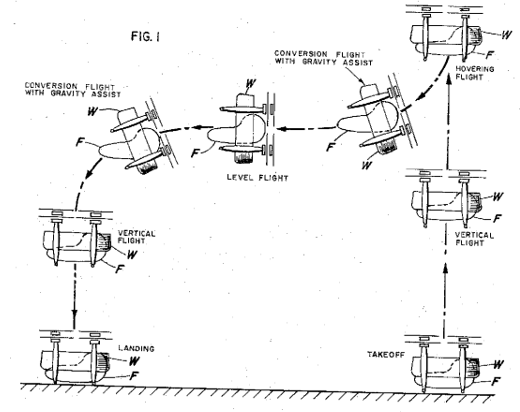
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
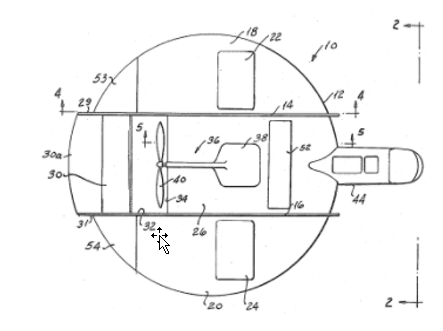
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Aircraft capable of landing or taking-off vertically, having its flight directional axis vertical when grounded | |
Flying saucers |
This place covers:
Aircraft having ring-shaped wings wherein the air flow in level flight is parallel to an axis of revolution of said ring
Illustrative examples of annular wings:
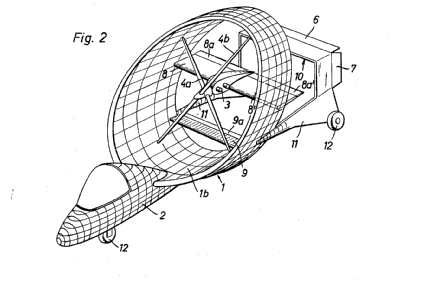
This place covers:
Illustrative example of annular wing with radial airflow:
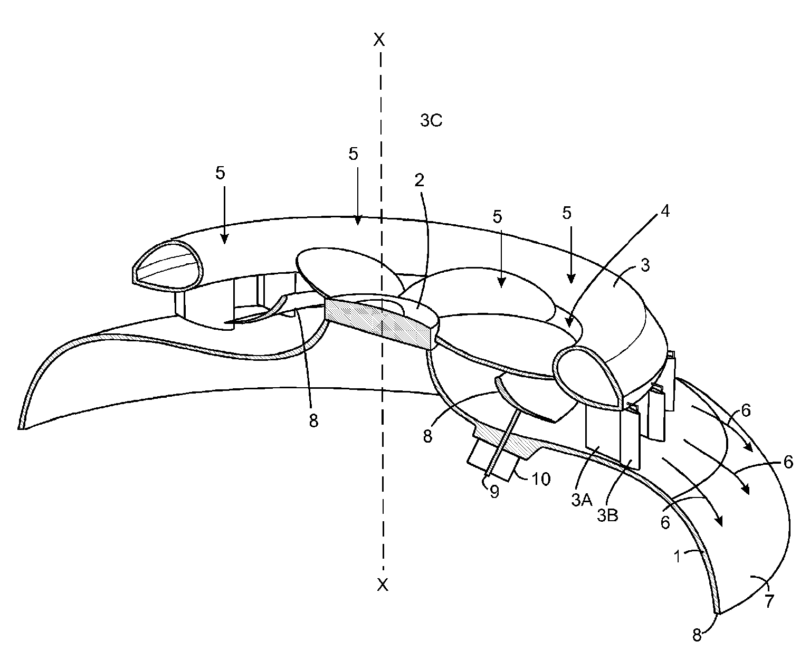
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Flying saucers |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of channel wings:
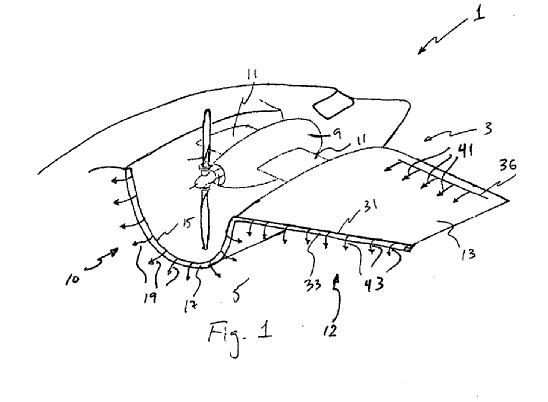
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Frontal shape of wings |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of multiple wings joined at the tips:
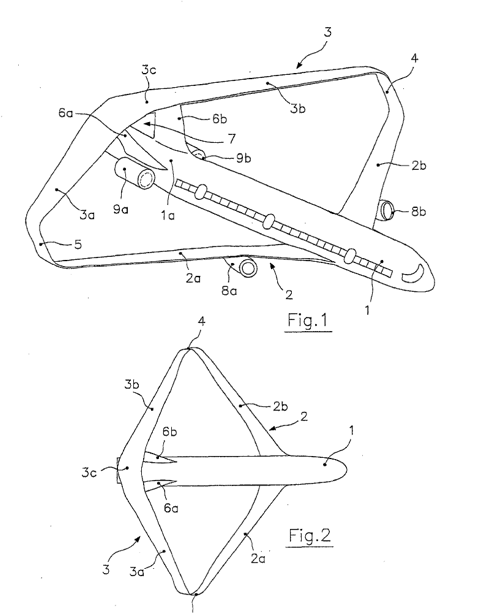
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Frontal shape of wings |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Having disc- or ring-shaped wings | |
Canard-type aircraft |
This place covers:
This group includes e.g. the BWB (blended-wing-body)-type aircraft
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Flying saucers |