CPC Definition - Subclass B61K
This place covers:
All auxiliary devices or methods needed to make railways safer, faster or energy efficient.
This place covers:
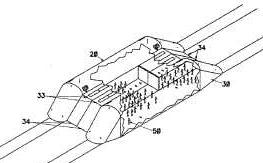
Transit systems or methods wherein passengers or freights board and exit during moving of vehicles or wherein rail vehicles are coupled or uncoupled during motion.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this place:
This place covers:
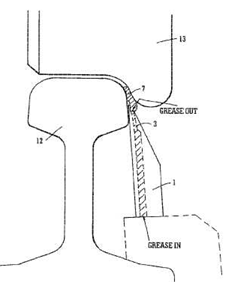
Devices or methods for the application of lubricant onto the surface of rails or wheels.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this place:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Lubricating for vehicles | |
Lubrication for locomotives | |
Lubricating compositions characterised by the base-material being a non-macromolecular organic compound | |
Lubricating in general |
This place covers:
- Portable derailing devices;
- Devices for lifting a rail vehicle while standing on the rail;
- Re-railer apparatus for placing derailed railway vehicle back onto the track.
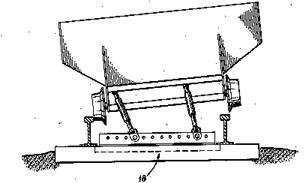
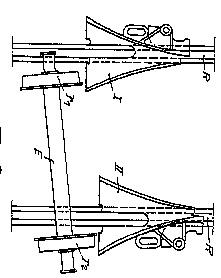
Illustrative examples of subject matter classified in this place:
1.
2.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Overhead travelling cranes comprising one or more substantially horizontal girders the ends of which are directly supported by wheels or rollers running on tracks carried by spaced supports | |
Capstans; Winches; Tackles, e.g. pulley blocks; Hoists | |
Hoisting, lifting, hauling or pushing, not otherwise provided for, e.g. devices which apply a lifting or pushing force directly to the surface of a load | |
Lifts with platforms suspended from ropes, cables or chains |
This place covers:
Devices fixed to railway track or permanent way, and methods associated with such devices, for stopping or retarding the movement of railway vehicles.
Illustrative examples of subject matter classified in this place:
1.
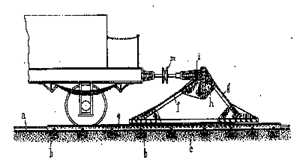
2.
This place does not cover:
Retarders of the mushroom type |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electrodynamic brake systems for vehicles in general | |
Methods, circuits or devices for controlling the propulsion of electrically-propelled vehicles, e.g. their traction-motor speed, to achieve a desired performance; Adaptation of control equipment on electrically-propelled vehicles for remote actuation from a stationary place, from alternative parts of the vehicle or from alternative vehicles of the same vehicle train |
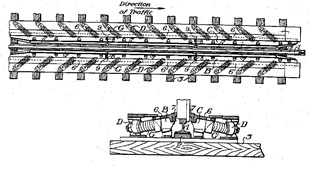
This place covers:
Means combined with a track using sand or materials which have a retarding effect on the wheels.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this place:
1a.

1b.

Figures 1a and 1b illustrate a top and cross view of a sand or like track.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Preventing wheel slippage by depositing sand or like friction-increasing materials |
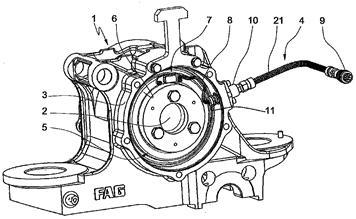
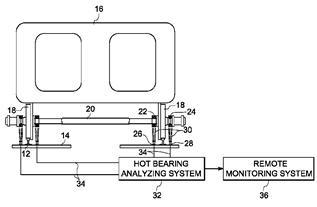
This place covers:
- Methods for detecting of imbalance in wheels of rail vehicle;
- Train wheel bearing temperature detection;
- Sensors for rail vehicle wheel bearing unit;
- Methods or devices for contactless measurement of the deformation or wear of railroad tracks;
- Acoustic monitoring of railcar running gear.
Illustrative examples of subject matter classified in this place:
1.
2.
Examples of places in relation to which this place is residual:
Track-building in general | |
Applications of measuring apparatus or devices for track-building purposes |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Manufacturing wheels | |
Reconditioning wheel sets without removing same from the vehicle; Underfloor wheel lathes for railway vehicles | |
Railway wheels | |
Brakes for railway vehicles coming into operation in case of accident, derailment or damage of rolling stock or superstructure | |
Arrangements for adjusting wheel-braking force to meet varying vehicular or ground-surface conditions | |
Railway control, warning or safety means | |
Measuring arrangements characterised by the use of infrasonic, sonic or ultrasonic vibrations | |
Weighing apparatus or methods adapted for weighing railway vehicles | |
Measuring mechanical vibrations | |
Radiation pyrometry for sensing the radiation of moving bodies | |
Casings for radiation pyrometry, e.g. infrared or optical thermometry | |
Thermometers for measuring temperature of moving solid bodies | |
Testing of railway vehicles | |
Investigating materials by determining their chemical or physical properties | |
Investigating presence of flaws | |
Investigating of materials by the use of ultrasonic waves | |
Measuring speed | |
Navigation for trains using radio waves |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Applications of measuring apparatus or devices for track-building purposes |
This place covers:
Illustrative examples of subject matter classified in this place:
1.
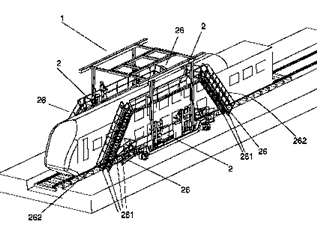
2.
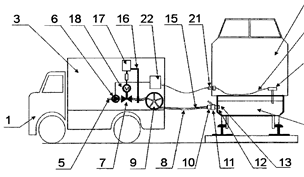
Examples of places in relation to which this place is residual:
Filling stations for steam- or pneumatic-accumulator locomotives | |
Water or fuel supply fittings on locomotives |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Lifting or lowering rail vehicle axles or wheels | |
Transport or storage devices | |
Conveying materials in bulk | |
Refuelling locomotives with solid fuels | |
Washing or cleaning boilers |
This place covers:
Other auxiliary devices and methods not classified in B61K 1/00 - B61K 11/00.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this place:
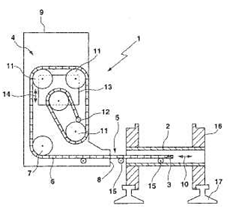
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Safety belts or body harnesses |
Examples of places in relation to which this place is residual:
Safety devices for preventing passengers from being injured by movements of doors or variations in air pressure |