CPC Definition - Subclass H04J
This place covers:
Multiplex Communication having circuits or apparatus for combining or dividing signals for the purpose of transmitting the signals simultaneously or sequentially over the same transmission path, and monitoring arrangements therefor.
Class H04 Electric communication technique covers electrical communication systems with propagation paths employing beams of corpuscular radiation, acoustic waves or electromagnetic waves. Subclass H04J refers to multiplex communication in general. If the multiplex communication is specially adapted for particular applications classification is made in other subclasses of class H04.
This place does not cover:
Optical monitoring arrangements, independent of the multiplexing method | |
Selecting arrangements for multiplex systems |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Use of multiplexing in transmission systems for measured values, control or similar signals | |
Arrangements for transmission of digital information affording multiple use of the transmission path | |
Systems for the simultaneous or sequential transmission of more than one television signal |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Optical elements, systems or apparatus | |
Addressing or transmission in computers | |
Electronic switching or gating | |
Transmission in general | |
Relay systems | |
Broadcast communication | |
Data switching networks | |
Modulated-carrier systems | |
Telephonic Communication | |
Selecting techniques | |
Stereophonic systems | |
Wireless communication networks |
This place covers:
Frequency Division Multiplexing, FDM, by multiplexing two or more data sources. Covers particularly hierarchical multiplexing electrical frequencies in stages of power of 2, e.g. 8kHz, 64Khz.
This place does not cover:
FDM in satellite systems | |
FDM in radio system | |
OFDM | |
OFDM synchronization |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Hybrid TDM/FDM | |
SCM | |
FDM in CATV or HFC networks |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
FDM | Frequency Division Multiplexing |
OFDM | Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing |
SCM | Multiplexing of electrical subcarriers on an optical wavelength |
CATV | CAble Television Systems |
HFC | Hybrid Fiber Coax |
TDM | Time Division Multiplex |
This place covers:
Systems for transposing frequency channels carrying information onto frequency carriers Covers also FDM multiplexers, demultiplexers
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
TDM/FDM conversion of transmultiplexing |
H04J 1/08 takes precedence
This place covers:
Frequency translators, FDM multiplexers, demultiplexers, operating with digital techniques
This place does not cover:
Group modulators /demodulators used for transmultiplexing FDM TDM |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Digital Filters |
H04J 1/08 takes precedence
This place does not cover:
- Channel allocation |
This place does not cover:
Branching filters |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Discrete frequency-selective devices, e.g. stubs, waveguides, directional filters |
This place covers:
Frequency allocation, including by demand or to reduce intermodulation;
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
In line transmission | |
In baseband systems |
This place covers:
Hierarchical frame structures, the structure repeats continuously at a fixed rate. Typically these are standard TDM frame structures at 8kHz rate like PDH, SDH or OTN. Other fixed rates frames should also be classified here and related fields.
- fixed length Ethernet (H04L 12/40)
Synchronization of TDM Frames
Packet transmission is classified for some specific applications:
Transmission of synchronous services like voice via packets, e.g. VoIP, is classified in H04J 3/0632, when the source clock is recovered.
Alignment of packets using packet flags should be in H04J 3/0602 for fixed line systems and in H04L 7/04 in wireless, satellite or radio systems.
Ranging of packets in an uplink in systems with a TDM frame defined in the downlink, see H04J 3/0682.
Note 1: Ranging or time alignment of a radio/wireless channel preferably in H04W 56/00. For radio/wireless systems data transmitted via a fixed network, e.g. connections between Mobile Switching Centre (MSC) and Base Station (BS) or between several Access Points (AP), documents referring to specific data of the radio/wireless channel are in H04W 56/00, e.g. alignment for handover.
Allocation of packets within a TDM frame, e.g. Ethernet in OTN payload, see H04J 3/16 or lower.
Allocation of packets in an uplink of a systems with a TDM frame defined above in the downlink, H04J 3/1694.
Note 1 : This group refers to the allocation of the bandwidth.
Note 3 : Allocation of timeslots in PON, H04Q 11/0001 takes precedence
Synchronization of TDMA or packets in the meaning of time alignment, the minimum entity of detection or correction is a bit. Smaller sub-bit values refer to bit synchronization of H04L 7/00
This place does not cover:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Simulcast or Single Frequency Networks | |
Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic; arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols | |
Packet networks | |
Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security | |
Network arrangements, protocols or services for supporting real-time applications in data packet communication | |
Network protocols for data switching network services Network arrangements or protocols for supporting network services or applications | |
Digital audio for loudspeakers |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
SDH | Synchronous Digital Hierarchy |
SONET | Synchronous Optical NETwork |
OTN | Optical Transport Network |
MulDex | Multiplexer/Demultiplexer |
This place does not cover:
Electronic switching or gating |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Pulse counters | |
Pulse distributors in general | |
SerDes not adapted for data communication of telecommunication |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
SerDes | Serializer / Deserializer |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
CRT | Cathode Ray tubes |
This place covers:
Details of multiplexing or demultiplexing of bits or bytes in arrangements specially adapted for time multiplexing.
Distributors with transistors or integrated circuits
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Timing and clocking in MulDex | |
Higher level of abstraction of hierarchical PDH MulDex | |
Details of discrete elements, e.g. transistors |
Details of bit and byte multiplexers or demultiplexers per se, e.g. 2:1 pulse multiplexers and tree structures thereof, H03M 9/00 takes precedence.
This place covers:
Synchronization of TDM networks and some specific synchronization arrangements in TDMA or packet networks.
Synchronization of TDM networks covers:
Detection of FAW and alignment of frames, H04J 3/0602;
Absorbing of phase or frequency differences by buffers, H04J 3/062;
Distribution of synchronization information and organisation of the synchronization network, H04J 3/0635.
Specific synchronization arrangement of packet or TDMA networks are:
Distribution of synchronization information and organisation of the synchronization network, H04J 3/0635
Source clock recovery over packet or ATM networks, e.g. VoIP, H04J 3/0632.
Synchronization of wireless network when mobility of radio channel is relevant, H04W 56/00.
This place does not cover:
Smaller, sub-bit, values refer to bit synchronization |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Synchronization in computer networks, e.g. Time of Day | |
Buffers between clock domains |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
FAW | Frame Alignment Word |
This place covers:
A FAW is used as synchronising information for a TDM frame.
This place does not cover:
Specific FAW | |
Details of the FAW detector | |
Detection of packet headers, e.g. HDLC flag |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Special synchronization information, e.g. for packet or mobile transmission |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
FAW | Frame Alignment Word |
This place covers:
Design rules of constructing FAW.
variable FAW, e.g. for low rate signalling, depending on the synchronization state.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Signalling in TDM |
FAW of standardized frames, e.g. T1, SONET, SDH or OTN are known per se are not classified here. Their detection is classified in H04J 3/0608.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
FAW | Frame Alignment Word |
UW | Unique Word |
This place covers:
Detection of FAW by correlators, state machines, forward or backward protection.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Digital correlators | |
Detectors of UW for packet detection or symbol synchronisation |
This place covers:
PN codes used for synchronisation, if the PN synchronisation signals is varying during transmission, e.g. by a feedback Shift-register. Fixed synchronisation signals, e.g. unique words or FAW signals, are not to be classified in this group. This also applies even if the synchronisation signal can be presented as a state of such a PN-code generator. Only if the generator shifts, then the document is classified here.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
PN codes used for synchronization in other transmission systems, e.g. packet or mobile |
H04J 3/0608 takes precedence for detection
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
PN code | Pseudo-Noise or Pseudorandom code |
This place covers:
Rate differences are compensated in a lossless way, e.g. by an elastic buffer or FIFO
This place does not cover:
Pulse stuffing | |
Speed conversion in computers | |
Speed conversion, e.g. 8 kHz to 9,2 kHz |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
FIFO | First In First Out buffer |
This place covers:
Compensation of fluctuating rates in SDH/SONET or OTN
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
PDH/SDH interfaces, e.g. desynchronizers |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
OTN | Optical Transport Network |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
PDH/SDH interfaces, e.g. desynchronizers | |
Slot or bandwidth allocation in PDH |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
PDH | Plesiochronous Digital Hierarchy |
This place covers:
Recovery of source clock of Continuous Bit Rate (CBO) service, e.g. VoIP. The invention is located at the edge of the packet network and the output is a stream of bits, e.g. control of playout rate.
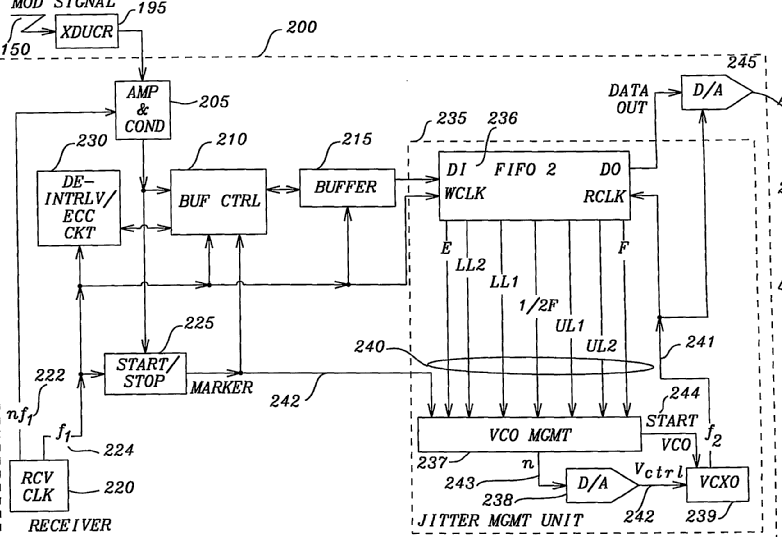
This place does not cover:
Queuing arrangements in packet switching elements | |
Synchronising systems for the synchronous transmission of a pulse code modulated video signal with one or more other pulse code modulated signals |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Flow control or congestion control |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
FIFO | First In First Out buffer or elastic buffer |
RTS | Residual Time Stamps signalling a source clock offset compared to the network clock |
SRTS | Synchronous Residual time stamps signalling a source clock offset compared to the network clock |
SFET | Synchronous Frequency Encoding Technique signalling a source clock offset compared to the network clock |
CES | Circuit Emulating Switching |
This place covers:
Distribution of synchronisation information among nodes, e.g. leader-follower signalling or SSM.
TOD synchronization.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Clock synchronization path among nodes of more than two levels | |
In combination with delay compensation using timestamp to determine RTD | |
Clock synchronization in Computer Networks, e.g. TOD | |
Synchronisation of Ring Networks | |
Data switching networks with synchronous transmission |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
SSM | Synchronization Status Message |
RTD | Round Trip Delay |
NTP | Network Time Protocol |
PTP | Precision Time Protocol |
TOD | Time Of Day |
This place covers:
Signalling to prevent or recover from a failure in the synchronization network.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Fail safe arrangements within the node | |
Monitoring and fail safe arrangements in general | |
Fail safe arrangements for synchronizers in general |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
APS | Automatic Protection Switching |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Bus network with centralized control in which slots are of a TDMA packet structure |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
TTP | Time Triggered Protocol |
This place covers:
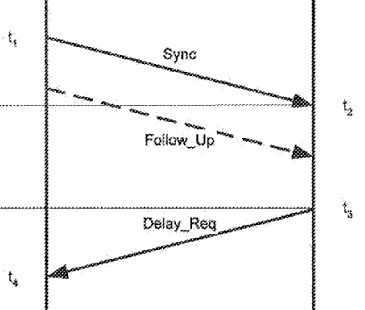
This place does not cover:
Arrangements for monitoring round trip delays in packet switching networks |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Delay compensation for other types of time multiplexing, e.g. TDM/TDMA in a star configuration | |
Time supervision arrangements, e.g. real time clock | |
Timer mechanisms used in protocols of packet data networks |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
NTP | Network Time Protocol |
PTP | Precision Time Protocol |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
NTP | Network Time Protocol |
PTP | Precision Time Protocol |
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms:
- "PTP" and "IEEE 1588"
This place covers:
Adding or modification of delay information, e.g. residence time in PTP
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Interconnection of networks |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
PTP | Precision Time Protocol |
This place covers:
Exchange of synchronization information, e.g. buffer fill.Coupling clocks, e.g. by adding weighted signals of clock or phase errors.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Clock selection in a TDM node |
This place covers:
Determination or initialisation of clock distribution path among more than two levels of nodes according to parameters, e.g. priority, path length, number of hops, clock quality, statistics.Avoidance of clock loops or timing islands.
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
SSM | Synchronisation Status Message |
This place covers:
RTD measurement in TDM or TDMA networks for the purpose of timing adjustment, clock correction or time alignment.
This place does not cover:
Bidirectional timestamps, e.g. NTP or PTP for compensation of clock drift and for compensation of propagation delays | |
Synchronization in mobile networks |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
RTD measurement and compensation in satellite systems | |
RTD measurement for network management or monitoring | |
PON in general |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
PON | Passive Optical Network |
CATV | CAble TeleVision |
RTD | Round Trip Delay |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Monitoring and fail safe arrangements in general | |
Fail safe arrangements of PLL | |
Fail safe arrangements for synchronizers in general |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
APS | Automatic Protection Switching |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
TTP | Time Triggered Protocol |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
PTP | Precision Time Protocol |
This place covers:
Variable length stuffing; self marking stuff indications
This subgroup does not refer to stuffing of packet flags as line coding to interrupt a long sequence of identical bit values.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Fill bit or bits in non-TDM formats, | |
Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic; arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols | |
Line coding | |
Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security | |
Network arrangements, protocols or services for supporting real-time applications in data packet communication | |
Network protocols for data switching network services Network arrangements or protocols for supporting network services or applications |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
WTJ | Waiting Time Jitter |
STM | Stuff Threshold Modulation |
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms:
- "justification" and "stuffing"
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
PDH buffering | |
PDH framing formats and slot allocation |
This place covers:
Stuffing in OTN
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Buffer arrangements for synchronization in SDH/SONET or OTN |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
OTN | Optical Transport Network |
This place covers:
ADM Add Drop Multiplexers
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
ADM | Add Drop Multiplexer |
This place covers:
Protection in TDM ring networks
This place does not cover:
Protection in TDM networks in general | |
Protection in optical ring networks | |
Protection in packet ring networks, e.g. RPR |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
CW | Clockwise |
CCW | Counter Clockwise |
UPSR | Unidirectional Protection Switched Ring |
BLSR | Bidirectional Line Switched Ring |
This place covers:
Bit stealing for signalling, e.g. winking in PDH T1.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
LSB bit dropping for making bandwidth available for user payload |
This place covers:
Protection Switching; Testing of TDM systems.
This place does not cover:
Monitoring or Protection Switching of TDM rings | |
Protection switching of SDH/SONET or OTN |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Network management |
This place covers:
Covering variable time slot allocation.
H04J 3/1605 fixed standard frame structures.
H04J 3/1611 SDH
H04J 3/1623 PDH
H04J 3/1652 OTN;
H04J 3/1682 statistical multiplexers, allocation changes per frame cycle
H04J 3/1694 distributed multiplexers, e.g. access multiplexer
This place covers:
Refers to systems according to ITU recommendations G.707 - G.709 in the versions of 1990 (SDH/SONET)
Radio, satellite and microwave transmission according to the standards mentioned above.
Covers switches, nodes and Cross-connects and respective internal or proprietary formats
This place does not cover:
Interactions with OTN |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
SDH/SONET or OTN ring networks |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
SPE | Synchronous Payload Envelope |
This place covers:
SPE carries ATM cells or payload data packets
H04J 2203/0082 Services, Interaction of SDH with non-ATM protocols
H04J 2203/0083 Support of the IP protocol
H04J 2203/0085 Support of Ethernet
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Stuffing, destuffing and desynchronization | |
SDH/SONET or OTN ring networks | |
Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic; arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols | |
Packet networks in general | |
Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security | |
Network arrangements, protocols or services for supporting real-time applications in data packet communication | |
Network protocols for data switching network services Network arrangements or protocols for supporting network services or applications |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
PoS | Packet over SONET |
GFP | Generic Framing Procedure |
SPE | Synchronous Payload Envelope |
This place covers:
Covers switches, nodes and Cross-connects and respective internal or proprietary formats.
Also covers transport of packets via a plesiochronous network, e.g. "ATM over E1".
This place covers:
Time slot allocation according to rules, e.g. to evenly distributed slots to various users while minimizing the distance to ideal evenly distributed slot allocation for a single user.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Splitting time slots to smaller entities or concatenating time slots to larger entities | |
Time slot allocation according the instantaneous needs of the sources to be multiplexed |
This place covers:
Format conversion of PDH frames of different standards, e.g. ETSI and ANSI
This place covers:
DS0, DS1, DS3 or European PDH, PCM30/32, E1 to E4 according to ITU recommendation G.703. Covers the hardware structure of programmable TDM multiplexer, e.g. internal construction by bus, as described in ITU recommendation G.797.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electronic details of multiplexers or demultiplexers, e.g. multiplexing of bits or bytes |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
MULDEX | Multiplexer Demultiplexer |
This place covers:
Variable allocation of elementary units like time slots, subslots or fragments. The allocation can be modified by splitting elementary units or by combining elementary units to units of larger bandwidth. The overall frame length remains constant.
This place covers:
Refers to systems according to ITU recommendation G.707 - G.709 in the versions of 2000.
Covers radio and microwave transmission according to the standards mentioned above.
Covers switches, nodes and Cross-connects and respective internal or proprietary formats.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
SDH/SONET or OTN ring networks | |
SDH/SONET as preceding technology to OTN | |
Optical wavelength-division multiplex systems | |
WDM optical network architectures |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
SPE | Synchronous Payload Envelope |
H04J 3/1664 takes precedence for payloads with different packet types
H04J 3/1664 takes precedence
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Fee space optical transmission with PPM or PWM | |
General PPM or PWM transmission | |
PPM or PWM modulation |
This place covers:
Allocation of bandwidth changes instantaneously, e.g. on demand or according to buffer fill.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Distributed multiplexers, e.g. access multiplexers | |
Packet multiplexing in general | |
Hybrid switching, e.g. moveable boundary between CS and PS | |
Voice over Date multiplexing for a single user | |
Statistical multiplexing for video or multimedia |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
CS | Circuit Switched service |
PS | Packet Switched service |
This place does not cover:
Reducing bandwidth of signals in general | |
Reducing bandwidth of signals in PCM-systems |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
LSB dropping of bit stealing for transporting signalling | |
Digital Speech Interpolation (DSI) | |
Digital Circuit Multiplication (DCM) |
This place does not cover:
Time slot allocation in Passive Optical Networks | |
Time slot allocation in wireless networks |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Time slot allocation in computer networks via CATV or HFC |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
CATV | CAble TeleVision |
HFC | Hybrid Fibre Coax |
This place does not cover:
DTX in wireless networks for power saving |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Distributed multiplexers, e.g. access multiplexers | |
Speech analysis | |
Silence suppression in packet networks |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
DTX | Discontinuous Transmission |
Comfort Noise | Introduction of noise signal to have a more comfortable audio signal during speech pauses |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
TASI | Time Assignment Speech Interpolation |
DSI | Digital Speech Interpolation |
This place does not cover:
PRMA (Packet Reservation Multiple Access), |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
VAD | |
Instant speaker's algorithm in telephony systems |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
VAD | Voice Activity Detection |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Frame conversion |
This place covers:
Different symbol rates in the slots of the TDM frame.
Different or variable user rates or source rates are classified under H04J 3/1605 or sub-groups.
CDMA and Spread-spectrum communication, H04J 13/00 takes precedence.
This place does not cover:
Variable length frames or packets to avoid errors |
This place covers:
Generic packet or ATM multiplexing
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Packet multiplexing in general |
This place covers:
Time frequency encoded transmission. The combination of time and frequency is determined by the receiver address and the transmitted information.
Transmission of address by Pulse Position Modulation (PPM).
Random sampling of analog sources
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
RADA | Random Access Discrete Address |
This place does not cover:
Time and Frequency allocation of OFDM systems |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Allocation of time/frequency in radio systems |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
OFDM | Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing |
This place covers:
Translation of TDM into FDM and vice versa.
This place covers:
Simultaneous transmission of analog and digital, e.g. by overmodulation
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
FAW having a special amplitude | |
Multiple use of the transmission path the signals being represented by different amplitude or polarities, e.g. quadriplex | |
Synchronization signal having a special amplitude |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
FAW | Frame Alignment Word of a TDM frame |
This place does not cover:
Modification of modulation constellation |
This place covers:
Orthogonal multiplex systems at the physical layer, techniques relating to problems arising from the multiplexing of users / base stations. Aspects that are covered include
cell search, i.e. how a mobile phone finds the identity of base stations;
interference handling and cancellation, at the transmitter, the receiver or both, especially
subtractive interference cancellation
intercell interference cancellation at the physical layer.
Examples of orthogonal multiplexing techniques are OFDMA [Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access ], SC-FDMA [ Single Carrier Frequency Division Multiple Access ].
Examples of systems using orthogonal multiplexing are LTE [ Long Term Evolution ], LTE-advanced.
Code multiplexing techniques, orthogonal or not, are classified in H04J 13/00 if the focus is on the code multiplexing aspects and in H04B 1/69 if the focus is on the implementation of the spread-spectrum technique (e.g. details of how the signals are physically transmitted, received and processed).
This place does not cover:
Narrowband interference reduction | |
Direct sequence spread spectrum | |
Frequency Hopping | |
Spatial processing techniques | |
Allocation of channels of OFDM systems | |
Details of Linear Filters and Decision Feedback Equalisers | |
Sequence estimation techniques, including multi user sequence estimation | |
Correlative coding in synchronous or start-stop systems | |
OFDM modulation techniques | |
OFDM frequency synchronisation techniques | |
Power management | |
Local resource allocation of wireless systems |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Cell search in CDMA systems | |
Interference aspects in CDMA systems | |
Broadcast communication | |
Modulated-carrier systems | |
Telephonic Communication | |
Discovery of network devices for network data management | |
Processing access restriction or access information |
Additional information is classified with the corresponding CPC codes. Classification of additional information is compulsory.
This place covers:
Code division multiplexing techniques which are related to the division of the communication medium according to codes.
Aspects that are covered include types of codes, generation of codes and allocation of codes to channels.
With regard to spread-spectrum techniques, the borderline between H04J 13/00 and H04B 1/69 should be determined based on whether the features relevant for classification are focused on the code multiplexing aspects or the implementation of the spread-spectrum technique (e.g. details of how the signals are physically transmitted, received and processed).
Documents classified in H04J 13/00 containing aspects of spectral spreading of interest for search, may also be classified in group H04B 1/69.
With regard to systems that use frequency hopping as a means to divide the communication medium, it has been agreed that that frequency hopping is excluded from H04J 13/00 even if it is used within the context of multiple access. Because the concepts dealt with in H04J 13/00 do not have relevance for FH-CDMA even though frequency hopping can be used for CDMA (i.e. FH-CDMA), this subject-matter is exclusively classified in H04B 1/713.
This place does not cover:
MC-CDMA | |
Details of the signal processing which are covered by systems that use frequency hopping as a means to divide the communication medium |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Implementation of the spread-spectrum technique |
Additional information is classified with the corresponding CPC codes. Classification of additional information is compulsory.
When classifying in this group, any aspect of spread spectrum techniques not specific to frequency hopping, and which is considered to represent information of interest for search, may also be classified in group H04B 1/69.
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
CDMA | Code Division Multiple Access |
MC-CDMA | Multi-carrier Code Division Multiple Access |
OVSF | Orthogonal variable spreading factor |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Frequency-division multiplex systems | |
Electrical Time-division multiplex systems | |
Combined time-division and frequency-division multiplex systems | |
Multiplex systems in which the amplitudes or durations of the signals in individual channels are characteristic of those channels | |
Multiplex systems in which each channel is represented by a different type of modulation of the carrier | |
Orthogonal multiplex systems | |
Code division multiplex systems | |
Optical coupling devices, e.g. optical fibres, optical gratings | |
Optical integrated multiplexers and demultiplexers devices, e.g. AWG, optical interferometers | |
Optical coupling with wavelength selective means | |
Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating, or modulating; Non-linear optics | |
Demodulating light; Transferring the modulation of modulated light; Frequency-changing of light | |
Laser, amplifier per se | |
Optical Transmission | |
Optical switching per se |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
ADM | Add-drop multiplex |
CDC | Colourless, directionless or contentionless |
DCN | Data center network |
OAM | Orbital angular momentum |
OAMP | Operation, administration, maintenance or provisioning |
OLT | Optical line termination |
ONU | Optical network unit |
ROADM | Reconfigurable optical add/drop multiplexers |
SCM | Sub-carrier multiplexing |
TDM | Time division multiplexing |
TOADM | Tunable optical add/drop multiplexers |
WDM | Wavelength division multiplexing |
WDM-PON | WDM Passive Optical Network |
WSS | Wavelength selective switches |
This place covers:
Coherence Multiplex for data transmission
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Sensor systems | |
Coherent homodyne or heterodyne systems |
This place covers:
Optical code division multiplexing systems
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electrical code division multiplexing |
This place covers:
Orthogonal optical code division multiplexing systems
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electrical orthogonal multiplexing systems |
This place covers:
Wavelength division multiplex systems, in general, as well as WDM equipment terminal, e.g. WDM sources and WDM receivers.
This place covers:
Optical add and drop multiplexing systems for WDM systems
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
OADM | Optical Add and Drop multiplexing |
This place covers:
Internal arrangements details of OADM for WDM systems
This place covers:
OADM arrangements that first broadcast the input signals, typically implemented with an optical splitter at the input of the OADM, and then select among the signals before they are output.
This place covers:
OADM arrangements that first selects among the input signals at the input of the OADM and then combines the signals before they are output, typically implemented with an optical combiner at the output of the OADM
This place covers:
OADM arrangements that allow express channels to be directly brought from the input of the OADM to the input of the OADM, typically for minimising the insertion losses incurred by those channels.
This place covers:
OADM arrangements that include multiplexing and/or demultiplexing using interleavers, e.g. processing the odd and even WDM channels separately.
This place covers:
OADM arrangements where multiplexing and/or demultiplexing are implemented by a cascading of multiple stages.
This place covers:
Reconfigurable or tuneable OADM arrangements where the optical channels that are actually added or dropped can be changed during the operation of the OADM.
This place covers:
OADM arrangements where the reconfiguration is accomplish by using optical switches or wavelength selective switches.
This place covers:
Colourless and/or directionless and/or contentionless reconfigurable ADM arrangements where there is no dependency to wavelength and/or for any added and dropped channels, any direction can be selected and/or for any added and dropped channels the same wavelength can be selected.
This place covers:
Reconfigurable ADM arrangements where channels are multicast/broadcast to a plurality of directions, e.g. multicast OADM (MC-OADM).
This place covers:
OADM arrangements where the groups of channel or wave bands are processed together.
This place covers:
Architectures aspects of OADM in WDM systems in terms of how they relate to the WDM networks where they are in.
This place covers:
OADM architectures that are prepared to be used in bidirectional networks, meaning that the ports of the OADM are input and output ports at the same time and consequently the fibres connected at those ports transmit optical WDM signals in both directions.
This place covers:
OADM architectures that have more than one input and/or more than one output (the degree of a node in a network is defined as the number of input plus output ports of such node).
This place covers:
OADM architectures constituted by modules that are repeated to increase the capabilities of the node, typically to upgrade the number of channels that can be added or dropped.
This place covers:
OADM architectures that are used for interconnecting different WDM networks, e.g. interconnected rings.
This place covers:
Power control in a WDM system. Subject covers equalizing power of the different wavelengths, e.g. to keep the total optical power constant or to control the optical power per channel in a WDM system so as to maintain constant a particular performance related characteristic. Also covers control of power transients due to add and drop wavelengths, wavelength switching, e.g. caused by protection switching, or wavelength re-allocation.
This place covers:
Arrangements for controlling/equalizing the optical power per channel or for groups of channels in a WDM system by adding a signal not carrying data, e.g. dummy wavelength(s), noise or pilot signal.
This place covers:
Arrangements for controlling/equalizing the optical power per channel or for groups of channels in a WDM system by adding/dropping/reallocating data channels, e.g. by adding/dropping/shuffling channel(s).
This place covers:
Arrangements for controlling/equalizing the optical power per channel or for groups of channels in a WDM system by controlling attenuation/gain of the data channel(s).
This place covers:
Controlling/equalizing the optical power per channel or for group of channels in a WDM system where management of power control is central, e.g. configured by the Network Management System (NMS).
This place covers:
Controlling/equalizing the optical power per channel or for group of channels in a WDM system where each node of the system acts independently to control/equalize power.
This place covers:
Conversion from WDM signals into OTDM or vice versa to facilitate the multiplexing or demultiplexing of optical channels.
This place covers:
WDM irregular allocation plans, typically to overcome non-linear effects or to accommodate optical channels of different bit rate. This group covers also regular schemes in which carriers remain unused, e.g. to avoid interference.
This place covers:
Fixed carrier allocation according to service or for a particular use, e.g. dummy channels to keep the power constant.
This place covers:
Wavelength allocation and assignment for WDM and the application of management to WDM networks. It covers routing, e.g. use of tables for wavelength routing, and wavelength allocation algorithms, dynamic allocation of wavelengths and use of a dedicated wavelength for OAM, e.g. optical service channel, and pilot tones for OAM. It also covers optical channel and optical multiplex identification and labelling, optical signalling in WDM networks and WDM networks restoration (in network restoration, as opposed to network protection, all available resources in the network are considered when looking for a new path to be established).
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Monitoring of optical transmission parameters in general |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Optical transmission using a single light source for multiple stations |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Routing or path finding of packets in data switching networks |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Route fault recovery of packets in data switching networks |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Organization of routing tables of packets in data switching networks |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangements for monitoring or testing transmission systems using a supervisory or additional signal for monitoring of optical transmission parameters |
This place covers:
Spectrum allocation/assignment/optimisation for WDM systems, e.g. allocating flex-grid slots for channels, assigning super-channels or optimising spectral resources via de-fragmentation.
This place covers:
WDM arrangements for medium access of radio-frequencies networks; wavelength allocation rules for such arrangement, e.g. any haul transport network for LTE/5G networks, for example via PON.
This place does not cover:
Radio-over-fibre arrangements |
This place covers:
WDM optical networks defined by the type of interconnection between WDM nodes
This place covers:
WDM systems using a point to point network connection between two WDM nodes.
This place covers:
Multiple WDM nodes connected to two adjacent WDM nodes, except for the two nodes constituting the bus head-end, and using a common optical fibre supporting a WDM signal.
This place covers:
A common WDM node is connected via multiple fibres to a multiplicity of other WDM nodes. It also covers the case of star networks, where multiple WDM nodes are interconnected to other WDM nodes using multiple optical fibres each supporting a WDM signal, typically using a star coupler.
This place covers:
WDM architecture where all WDM nodes are connected to two adjacent nodes using a common optical fibre supporting a WDM signal.
This place covers:
WDM architecture where each WDM node is typically connected to every other node using multiple optical fibres, each supporting a WDM signal.
This place covers:
WDM networks where different layers of interconnection between the different WDM nodes. Each layer can be of the same type of network architecture or of different types.
This place covers:
WDM architecture of Data Centre Networks (DCN).
This place covers:
Protection aspects in WDM systems, typically switching from a protected resource to a protection resource when a failure occurs. As opposed to network restoration, network protection considers only resources that have a priori been labelled as protection resources.
This place covers:
Protection is carried out at the level of the whole WDM multiplex.
This place covers:
A WDM multiplex is duplicated and transmitted simultaneously using two WDM multiplex signals. The selection of which WDM signal to receive is done at the WDM level and at the receiver end, typically without considering any specific signalling from the transmitter end.
This place covers:
A WDM multiplex is transmitted using working resources and in case that a failure occurs, then the WDM multiplex is switched to the protection resource, typically shared by different nodes. At the receiver end the WDM signal coming via the protection resource is selected, typically this mechanism involves switching or bridging at both transmitter and receiver ends at the WDM multiplex level any requires some signalling between transmitter and receiver ends. The protection WDM multiplex can be used by low priority traffic until protection takes place.
This place covers:
A WDM channel is duplicated and transmitted simultaneously using two WDM channels. The selection of which WDM channel to receive is done at the channel level and at the receiver end, typically without considering any specific messaging from the transmitter end.
This place covers:
WDM channels are transmitted using working resources and in case that a failure occurs, then the WDM channel is switched to the protection resource, typically shared by different WDM channels. At the receiver end the WDM signal coming via the protection resource is selected, typically this mechanism involves switching or bridging at both transmitter and receiver ends at the channel level any requires some signalling between transmitter and receiver ends. The protection channels can be used by low priority traffic until protection takes place.
This place covers:
WDM is duplicated to protect the equipment against internal faults.
This place covers:
Sub-carrier multiplexing system, e.g. for CATV.
This place covers:
WDM arrangements, e.g. equipment, included in terminals or line to enable WDM transmission.
This place does not cover:
ADM arrangements | |
WDM network architectures |
This place covers:
WDM arrangements, e.g. equipment for end terminals, e.g. WDM transmitters/receivers or wavelength converters.
This place covers:
Multiplexers or demultiplexers, e.g. odd/even multiplexing or multistage.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Optical coupling, mixing or splitting |
This place covers:
Systems where the different modes of transmission in the optical fibres are used to multiplex different channels of information.
This place covers:
Systems where either optical wireless (i.e. free space), multiplexing (e.g. MIMO) or space division multiplexing (e.g. multicore) is used for multiplexing different channels of information.
This place covers:
Systems where the different cores of a multicore fibre are used to multiplex different channels of information.
This place does not cover:
Mode multiplex systems |
This place covers:
System where the different states of polarisation of the light are used to multiplex different channels of information.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Optical transmitters using polarisation modulation | |
Optical receivers processing orthogonal polarisation components |
This place covers:
Systems where different orbital angular momenta of the light phase are used to multiplex different channels of information.
This place covers:
Systems using optical time division multiplexing (OTDM). Time multiplexing of optical pulses.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Optical synchronisation |
This place covers:
Optical add and drop multiplexing systems for OTDM systems.
This place covers:
Medium access in OTDM systems.
This place does not cover:
Time-division multiplex systems with variable time allocation to individual channels within a transmission cycle |