2136 Pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) [R-10.2019]
[Editor Note: This MPEP section is not applicable to applications subject to examination under the first inventor to file (FITF) provisions of the AIA as set forth in 35 U.S.C. 100 (note), except for determining eligibility of SIRs as eligible prior art. See MPEP § 2159 et seq. to determine whether an application is subject to examination under the FITF provisions, and MPEP § 2150 et seq. for examination of applications subject to those provisions.]
Pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102 Conditions for patentability; novelty and loss of right to patent.
A person shall be entitled to a patent unless-
*****
- (e) the invention was described in — (1) an application for patent, published under section 122(b), by another filed in the United States before the invention by the applicant for patent or (2) a patent granted on an application for patent by another filed in the United States before the invention by the applicant for patent, except that an international application filed under the treaty defined in section 351(a) shall have the effects for the purposes of this subsection of an application filed in the United States only if the international application designated the United States and was published under Article 21(2) of such treaty in the English language.
*****
Pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) allows the use of certain international application publications and U.S. patent application publications, and certain U.S. patents as prior art under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) as of their respective U.S. filing dates, including certain international filing dates. The prior art date of a reference under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) may be the international filing date if the international filing date was on or after November 29, 2000, the international application designated the United States, and the international application was published by the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) under the Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) Article 21(2) in the English language. References based on international applications that were filed prior to November 29, 2000 are subject to the pre-AIPA version of 35 U.S.C. 102(e) (i.e., the version in force on November 28, 2000). See MPEP § 2136.03 for additional information.
In accordance with former 35 U.S.C. 157(c), a published SIR will be treated the same as a U.S. patent for all defensive purposes, usable as a reference as of its filing date in the same manner as a U.S. patent. A SIR is prior art under all applicable sections of 35 U.S.C. 102 including pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e). See MPEP § 1111.
Pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) is mostly utilized when the publication or issue date is too recent for the reference to be applied under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(a) or pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(b). In order to apply a reference under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e), the inventive entity of the application must be different from that of the cited reference. Note that, where there are joint inventors, only one inventor needs to be different for the inventive entities to be different; put another way, a rejection under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) is applicable even if there are some inventors in common between the application and the cited reference.
Below are examination guidelines on the application of pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e).
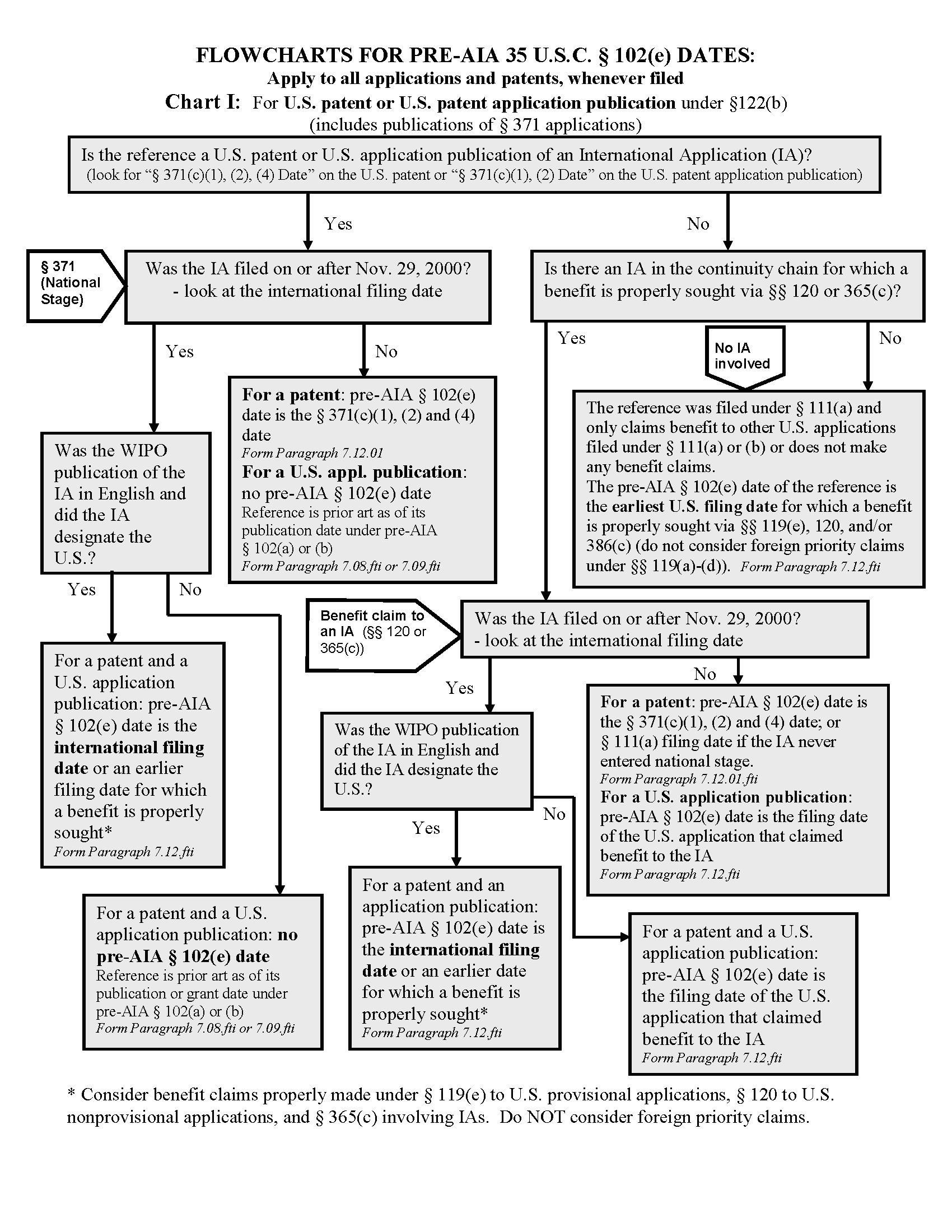
I. DETERMINE THE APPROPRIATE PRE-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) DATE FOR EACH POTENTIAL REFERENCE BY FOLLOWING THE GUIDELINES, EXAMPLES, AND FLOW CHARTS SET FORTH BELOW:- (A) The potential reference must be a U.S. patent, a U.S. application publication (35 U.S.C. 122(b)) or a WIPO publication of an international application under PCT Article 21(2) in order to apply the reference under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e).
- (B) Determine if the potential reference resulted from, or claimed the benefit of, an international application. If the reference does, go to step (C) below. The pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) date of a reference that did not result from, nor claimed the benefit of, an international application is its earliest effective U.S. filing date, taking into consideration any proper benefit claims to prior U.S. applications under 35 U.S.C. 119(e) or 120. For all benefit claims, the prior application(s) must properly support the subject matter used to make the rejection in compliance with pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 112, first paragraph or 35 U.S.C. 112(a). See MPEP § 2136.02. In addition, for benefit claims under 35 U.S.C. 119(e), at least one claim of the potential reference must be supported by the written description of the relied upon provisional application in compliance with pre- AIA 35 U.S.C. 112, first paragraph, or 35 U.S.C. 112(a), in order for the potential reference to be usable as prior art under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) as of a relied upon provisional application’s filing date. See MPEP § 2136.03, subsection III.
- (C) If the potential reference resulted from, or claimed the benefit
of, an international application, the following must be determined:
- (1) If the international application meets the following three
conditions:
- (a) an international filing date on or after November 29, 2000;
- (b) designated the United States; and
- (c) published under PCT Article 21(2) in English,
- then the international filing date is a U.S. filing date for prior art purposes under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e). If such an international application properly claims benefit to an earlier-filed U.S. or international application, or to an earlier-filed U.S. provisional application, apply the reference under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) as of the earlier filing date, provided all the conditions of pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e), 119(e), 120, 365(c), or 386(c) are met. For all benefit claims, the subject matter used in the rejection must be disclosed in the earlier-filed application in compliance with pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 112, first paragraph, or 35 U.S.C. 112(a), in order for that subject matter to be entitled to the earlier filing date under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e). See MPEP § 2136.02. In addition, for benefit claims under 35 U.S.C. 119(e), at least one claim of the potential reference must be supported by the written description of the relied upon provisional application in compliance with pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 112, first paragraph, or 35 U.S.C. 112(a), in order for the potential reference to be usable as prior art under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) as of a relied upon provisional application’s filing date. See MPEP § 2136.03, subsection III. Note, where the earlier application is an international application, the earlier international application must satisfy the same three conditions (i.e., filed on or after November 29, 2000, designated the U.S., and had been published in English under PCT Article 21(2)) for the earlier international filing date to be a U.S. filing date for prior art purposes under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e).
- (2) If the international application was filed on or after November 29, 2000, but did not designate the United States or was not published in English under PCT Article 21(2), do not treat the international filing date as a U.S. filing date for prior art purposes. In this situation, do not apply the reference as of its international filing date, its date of completion of the 35 U.S.C. 371(c)(1), (2) and (4) requirements, or any earlier filing date to which such an international application claims benefit or priority. The reference may be applied under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(a) or pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(b) as of its publication date, or pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) as of any later U.S. filing date of an application that properly claimed the benefit of the international application (if applicable).
- (3) If the international application has an international filing
date prior to November 29, 2000, apply the reference under the provisions of
pre-AIA
35 U.S.C. 102 and 374, prior to the AIPA
amendments:
- (a) For U.S. patents, apply the reference under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) as of the earlier of the date of completion of the requirements of 35 U.S.C. 371(c)(1), (2) and (4) or the filing date of the later-filed U.S. application that claimed the benefit of the international application;
- (b) For U.S. application publications and WIPO publications directly resulting from international applications under PCT Article 21(2), never apply these references under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e). These references may be applied as of their publication dates under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(a) or pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(b);
- (c) For U.S. application publications of applications that claim the benefit under 35 U.S.C. 120 or 365(c) of an international application filed prior to November 29, 2000, apply the reference under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) as of the actual filing date of the later-filed U.S. application that claimed the benefit of the international application.
- (4) Examiners should be aware that although a publication of, or a U.S. Patent issued from, an international application may not have a pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) date at all, or may have a pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) date that is after the effective filing date of the claimed invention in an application being examined (so it is not “prior art”), the corresponding WIPO publication of an international application may have an earlier pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(a) or pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(b)) date.
- (1) If the international application meets the following three
conditions:
- (D) Foreign application filing dates that are claimed (via 35 U.S.C. 119(a)-(d), (f), or 365(a) or (b)) in applications, which have been published as U.S. or WIPO application publications or patented in the U.S., may not be used as pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) dates for prior art purposes. This includes international filing dates claimed as foreign priority dates under 35 U.S.C. 365(a) or (b).
In order to illustrate the prior art dates of U.S. and WIPO publications of patent applications and U.S. patents under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e), nine examples are presented below. The examples only cover the most common factual situations that might be encountered when determining the pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) date of a reference. Examples 1 and 2 involve only U.S. application publications and U.S. patents. Example 3 involves a priority claim to a foreign patent application. Examples 4-9 involve international applications. The time lines in the examples below show the history of the prior art references that could be applied against the claims of the application under examination, or the patent under reexamination.
The examples show only the information necessary to determine a prior art date under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e). Also, the dates in the examples below are arbitrary and are presented for illustrative purposes only. Thus, for example, correlation of patent grant dates with Tuesdays or application publication dates with Thursdays may not be portrayed in the examples. All references to 35 U.S.C. 102 in the examples and flowcharts below are to the version of 35 U.S.C. 102 in effect on March 15, 2013 (the pre-AIA version).
| Example 1: Reference Publication and Patent of 35 U.S.C. 111(a) Application with no Priority/Benefit Claims. |
| For reference publications and patents of patent applications filed under 35 U.S.C. 111(a) with no claim for the benefit of, or priority to, a prior application's filing date, the prior art dates under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) accorded to these references are the earliest effective U.S. filing dates. Thus, a publication and patent of a 35 U.S.C. 111(a) application, which does not claim any benefit under either 35 U.S.C. 119(e), 120, 365(c) or 386(c), would be accorded the application’s actual filing date as its prior art date under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e). |
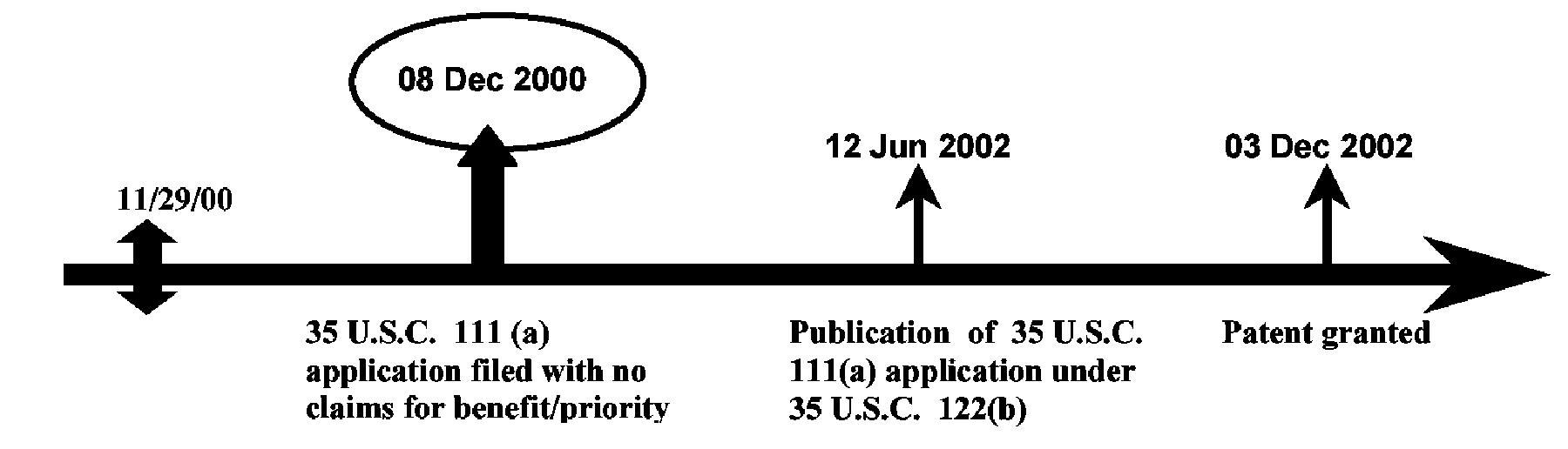
The pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e)(1) date for the Publication is 08 Dec. 2000. The pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e)(2) date for the Patent is: 08 Dec. 2000.
| Example 2: Reference Publication and Patent of 35 U.S.C. 111(a) Application with a Benefit Claim to a Prior U.S. Provisional or Nonprovisional Application. |
| For reference publications and patents of patent applications filed under 35 U.S.C. 111(a), the prior art dates under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) accorded to these references are the earliest effective U.S. filing dates. A publication and patent of a 35 U.S.C. 111(a) application that claims the benefit under 35 U.S.C. 120 of a prior nonprovisional application would be accorded the earlier filing date as its prior art date under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e), provided the earlier-filed nonprovisional application has proper support for the subject matter as required by 35 U.S.C. 120. A publication and patent of a 35 U.S.C. 111(a) application that claims benefit under 35 U.S.C. 119(e) to a prior provisional application would be accorded the earlier filing date as its prior art date under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e), provided that the provisional application has proper support for the subject matter as required by 35 U.S.C. 119(e) and that at least one claim of the reference is supported by the written description of the relied upon provisional application in compliance with pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 112, first paragraph, or 35 U.S.C. 112(a). See MPEP § 2136.03, subsection III. |
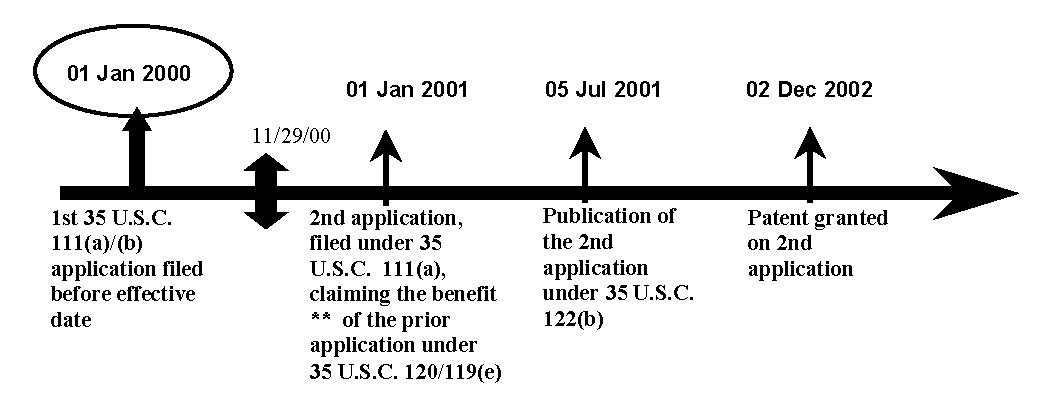
The pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e)(1) date for the Publication is: 01 Jan. 2000. The pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e)(2) date for the Patent is: 01 Jan. 2000.
| Example 3: Reference Publication and Patent of 35 U.S.C. 111(a) Application with 35 U.S.C. 119(a)-(d) Priority Claim to a Prior Foreign Application. |
| For reference publications and patents of patent applications filed under 35 U.S.C. 111(a), the prior art dates under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) accorded to these references are the earliest effective U.S. filing dates. No benefit of the filing date of the foreign application is given under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) for prior art purposes (In re Hilmer, 149 USPQ 480 (CCPA 1966)). Thus, a publication and patent of a 35 U.S.C. 111(a) application, which claims priority under 35 U.S.C. 119(a)-(d) to a prior foreign-filed application (or under 35 U.S.C. 365(a) to an international application), would be accorded its U.S. filing date as its prior art date under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e). In the example below, it is assumed that the earlier-filed U.S. application has proper support for the subject matter of the later-filed U.S. application as required by 35 U.S.C. 120. |
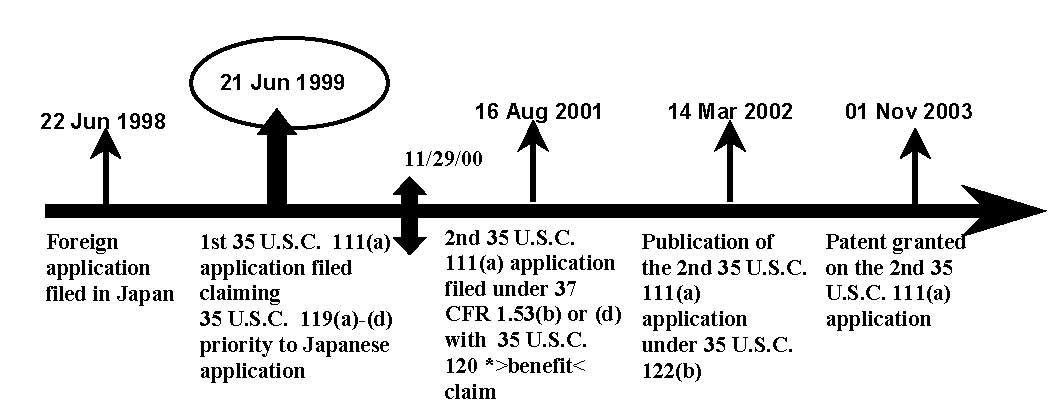
The pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e)(1) date for the Publication is: 21 June 1999. The pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e)(2) date for the Patent is: 21 June 1999.
| Example 4: References based on the national stage (35 U.S.C. 371) of an International Application filed on or after November 29, 2000 and which was published in English under PCT Article 21(2). |
| All references have the pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) prior art date of the international filing date or earlier effective U.S. filing date, regardless of whether the references are a WIPO publication, a U.S. patent application publication or a U.S. patent, of an international application (IA) that was filed on or after November 29, 2000, designated the U.S., and was published in English under PCT Article 21(2) by WIPO. No benefit of the international filing date (or of any U.S. filing dates prior to the IA), however, is given for pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) prior art purposes if the IA was published under PCT Article 21(2) in a language other than English. |
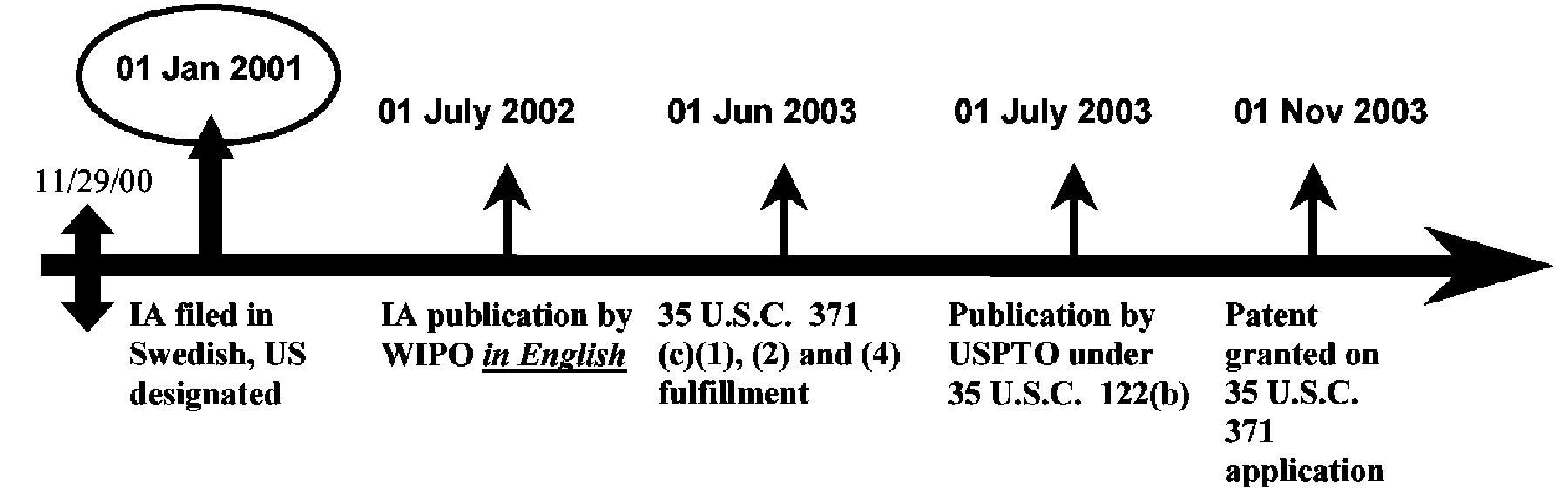
The pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e)(1) date for the IA Publication by WIPO is: 01 Jan. 2001. The pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e)(1) date for the Publication by USPTO is: 01 Jan. 2001. The pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e)(2) date for the Patent is: 01 Jan. 2001.
| Additional Benefit Claims: |
| If a later-filed U.S. nonprovisional (35 U.S.C. 111(a)) application claimed the benefit of the IA in the example above, the pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) date of the patent or publication of the later-filed U.S. application would be the international filing date, provided the earlier-filed IA has proper support for the subject matter relied upon as required by 35 U.S.C. 120. |
| If the IA properly claimed the benefit of an earlier-filed U.S. nonprovisional (35 U.S.C. 111(a)) application, the pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) date for all the references would be the filing date of the earlier-filed U.S. application, provided the earlier-filed application has proper support for the subject matter relied upon as required by 35 U.S.C. 120. |
| If the IA properly claimed the benefit of an earlier-filed U.S. provisional (35 U.S.C. 111(b)) application, the pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) date would be the filing date of the provisional application provided that the provisional application has proper support for the subject matter as required by 35 U.S.C. 119(e) and that at least one claim of the IA is supported by the written description of the relied upon provisional application in compliance with pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 112, first paragraph, or 35 U.S.C. 112(a). See MPEP § 2136.03, subsection III. |
| Example 5: References based on the national stage (35 U.S.C. 371) of an International Application filed on or after November 29, 2000 and which was not published in English under PCT Article 21(2). |
|
All references, whether the WIPO publication, the U.S. patent application publication or the U.S. patent, of an international application (IA) that was filed on or after November 29, 2000, but was not published in English under PCT Article 21(2) have no 35 U.S.C. 102(e) prior art date at all. According to pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e), no benefit of the international filing date (or of any U.S. filing dates prior to the IA) is given for pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) prior art purposes if the IA was published under PCT Article 21(2) in a language other than English, regardless of whether the international application entered the national stage. Such references may be applied under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(a) or (b) as of their publication dates, but never under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e). |
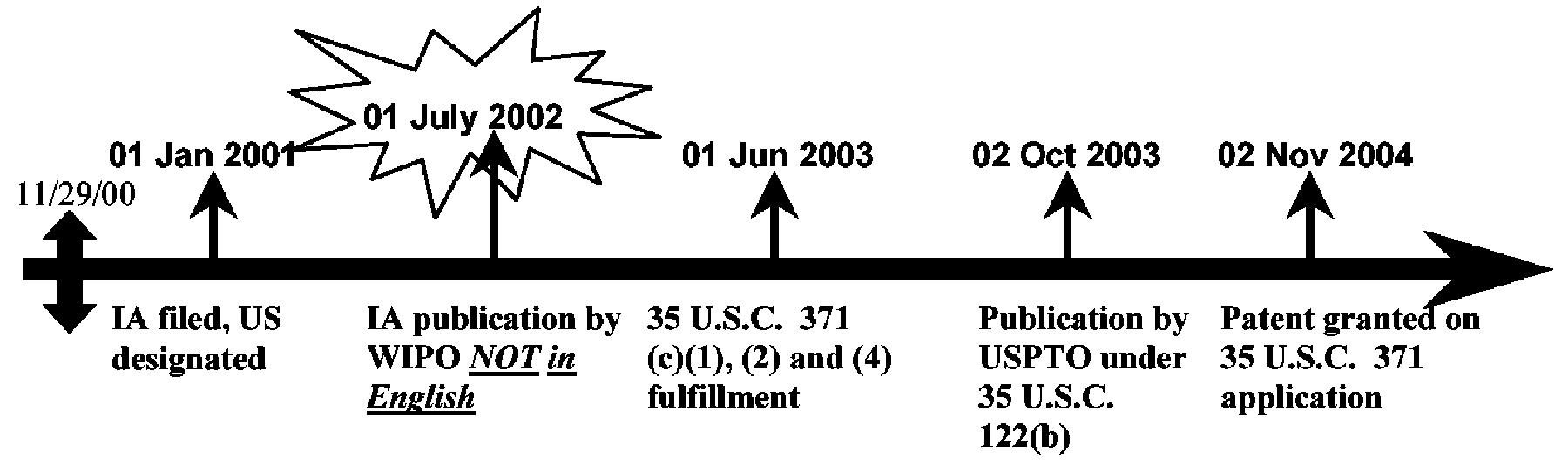
The pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e)(1) date for the IA Publication by WIPO is: None. The pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e)(1) date for the Publication by USPTO is: None. The pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e)(2) date for the Patent is: None.
| The IA publication by WIPO can be applied under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(a) or (b) as of its publication date (01 July 2002). |
| Additional Benefit Claims: |
| If the IA properly claimed the benefit of any earlier-filed U.S. application (whether provisional or nonprovisional), there would still be no pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) date for all the references. |
| If a later-filed U.S. nonprovisional (35 U.S.C. 111(a)) application claimed the benefit of the IA in the example above, the pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) date of the patent or publication of the later-filed U.S. application would be the actual filing date of the later-filed U.S. application. |
| Example 6: References based on the national stage (35 U.S.C. 371) of an International Application filed prior to November 29, 2000 (language of the publication under PCT Article 21(2) is not relevant). |
| The reference U.S. patent issued from an international application (IA) that was filed prior to November 29, 2000, has a pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) prior art date of the date of fulfillment of the requirements of 35 U.S.C. 371(c)(1), (2) and (4). This is the former pre-AIPA 35 U.S.C. 102(e). The application publications, both the WIPO publication and the U.S. publication, published from an international application that was filed prior to November 29, 2000, do not have any pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) prior art date. According to the effective date provisions as amended by Public Law 107-273, the amendments to pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) and 374 are not applicable to international applications having international filing dates prior to November 29, 2000. The application publications can be applied under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(a) or (b) as of their publication dates. |
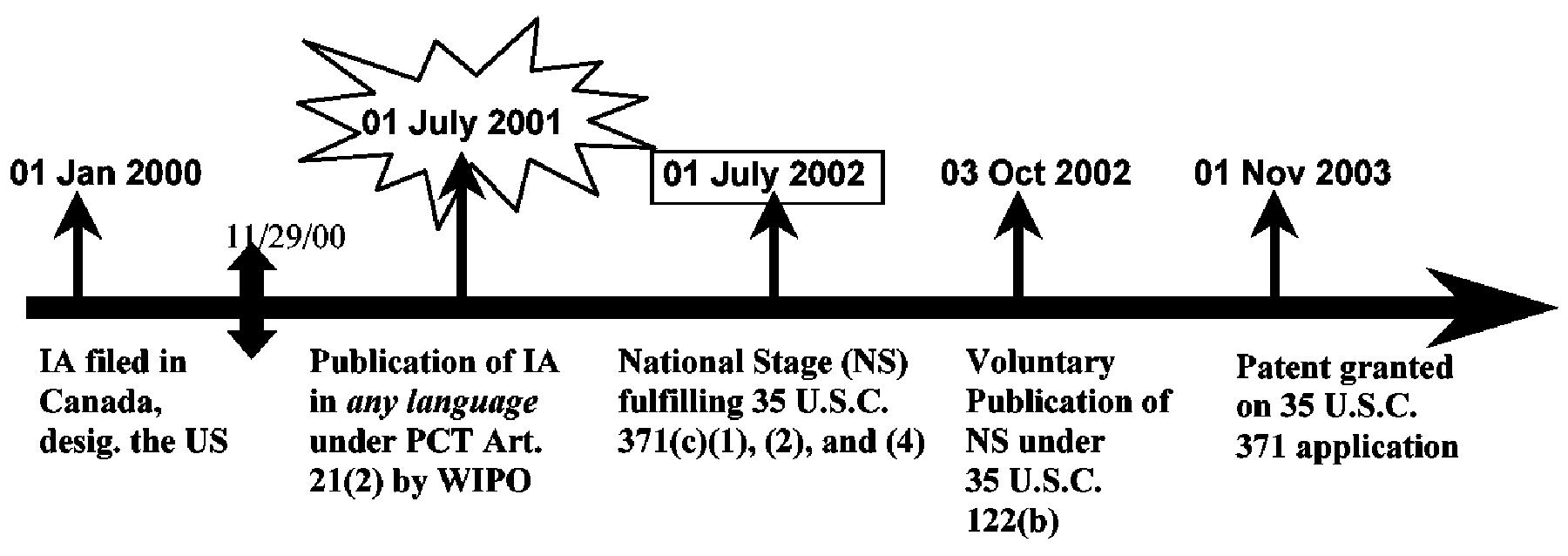
The pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e)(1) date for the IA Publication by WIPO is: None. The pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e)(1) date for the Publication by USPTO is: None. The pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) date for the Patent is: 01 July 2002.
| The IA publication by WIPO can be applied under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(a) or (b) as of its publication date (01 July 2001). |
| Additional Benefit Claims: |
| If the IA properly claimed the benefit of any earlier-filed U.S. application (whether provisional or nonprovisional), there would still be no pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e)(1) date for the U.S. and WIPO application publications, and the pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) date for the patent will still be 01 July 2002 (the date of fulfillment of the requirements under 35 U.S.C. 371(c)(1), (2) and (4)). |
| If a later-filed U.S. nonprovisional (35 U.S.C. 111(a)) application claimed the benefit of the IA in the example above, the pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e)(1) date of the application publication of the later-filed U.S. application would be the actual filing date of the later-filed U.S. application, and the pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) date of the patent of the later-filed U.S. application would be 01 July 2002 (the date that the earlier-filed IA fulfilled the requirements of 35 U.S.C. 371(c)(1), (2) and (4)). |
| If the patent was based on a later-filed U.S. application that claimed the benefit of the international application and the later filed U.S. application’s filing date is before the date the requirements of 35 U.S.C. 371(c)(1), (2) and (4) were fulfilled (if fulfilled at all), the pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) date of the patent would be the filing date of the later-filed U.S. application that claimed the benefit of the international application. |
| Example 7: References based on a 35 U.S.C. 111(a) Application which is a Continuation of an International Application, which was filed on or after November 29, 2000, designated the U.S. and was published in English under PCT Article 21(2). |
| All references, whether the WIPO publication, the U.S. patent application publication or the U.S. patent, of or claiming the benefit of, an international application (IA) that was filed on or after November 29, 2000, designated the U.S., and was published in English under PCT Article 21(2) have the pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) prior art date of the international filing date or earlier effective U.S. filing date. No benefit of the international filing date (or of any U.S. filing dates prior to the IA), however, is given for pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) purposes if the IA was published under PCT Article 21(2) by WIPO in a language other than English. In the example below, it is assumed that the earlier-filed IA has proper support for the subject matter of the later-filed U.S. application as required by 35 U.S.C. 120 and 365(c). |
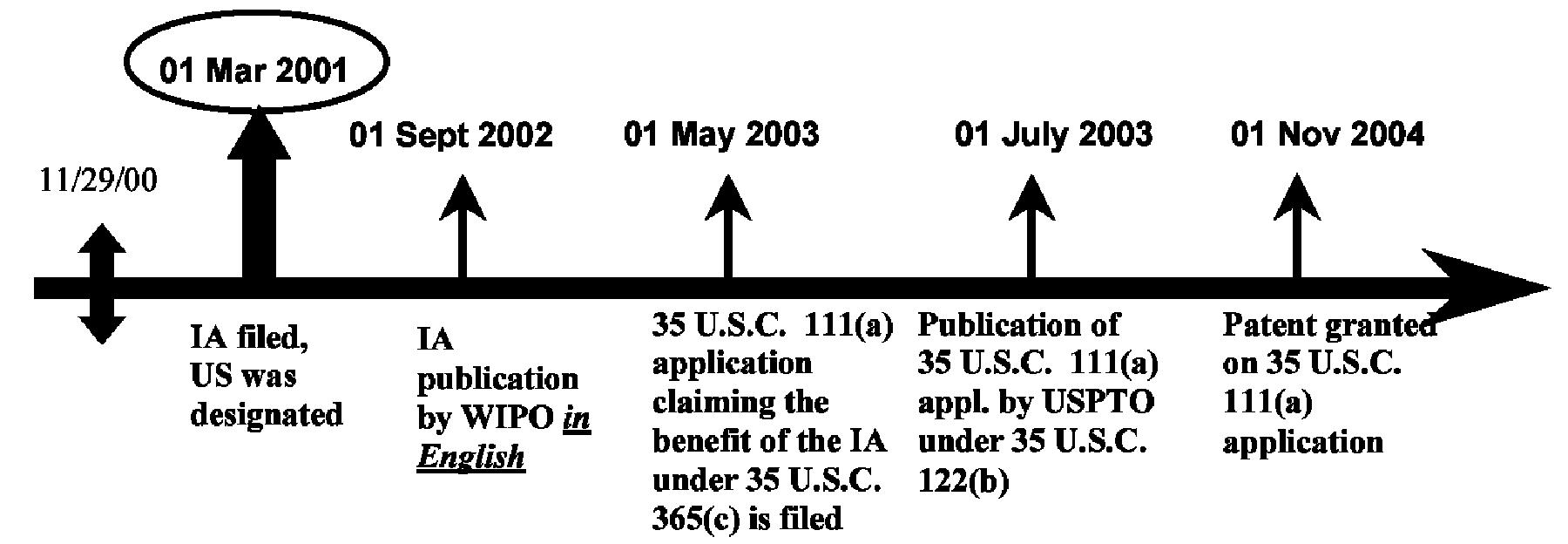
The pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e)(1) date for the IA Publication by WIPO is: 01 Mar. 2001. The pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e)(1) date for the Publication by USPTO is: 01 Mar. 2001. The pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e)(2) date for the Patent is: 01 Mar. 2001.
| Additional Benefit Claims: |
| If the IA properly claimed the benefit of an earlier-filed U.S. nonprovisional (35 U.S.C. 111(a)) application, the pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) date for all the references would be the filing date of the earlier-filed U.S. application, provided the earlier-filed application has proper support for the subject matter relied upon as required by 35 U.S.C. 120. |
| If the IA properly claimed the benefit of an earlier-filed U.S. provisional (35 U.S.C. 111(b)) application, the pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) date for all the references would be the filing date of the earlier-filed U.S. application provided that the provisional application has proper support for the subject matter as required by 35 U.S.C. 119(e) and that at least one claim of the IA is supported by the written description of the relied upon provisional application in compliance with pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 112, first paragraph, or 35 U.S.C. 112(a). See MPEP § 2136.03, subsection III. |
| If a second, later-filed U.S. nonprovisional (35 U.S.C. 111(a)) application claimed the benefit of the 35 U.S.C. 111(a) application in the example above, the pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) date of the patent or publication of the second, later-filed U.S. application would still be the international filing date of the IA, provided the earlier-filed IA has proper support for the subject matter relied upon as required by 35 U.S.C. 120 and 365(c). |
| Example 8: References based on a 35 U.S.C. 111(a) Application which is a Continuation of an International Application, which was filed on or after November 29, 2000 and was not published in English under PCT Article 21(2). |
| Both the U.S. publication and the U.S. patent of the 35 U.S.C. 111(a) continuation of an international application (IA) that was filed on or after November 29, 2000 but not published in English under PCT Article 21(2) have the pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) prior art date of the actual U.S. filing date of the 35 U.S.C. 111(a) application. No benefit of the international filing date (or of any U.S. filing dates prior to the IA) is given for pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) purposes because the IA was published under PCT Article 21(2) in a language other than English. The IA publication under PCT Article 21(2) does not have a prior art date under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e)(1) because the IA was not published in English under PCT Article 21(2). The IA publication under PCT Article 21(2) can be applied under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(a) or (b) as of its publication date. |
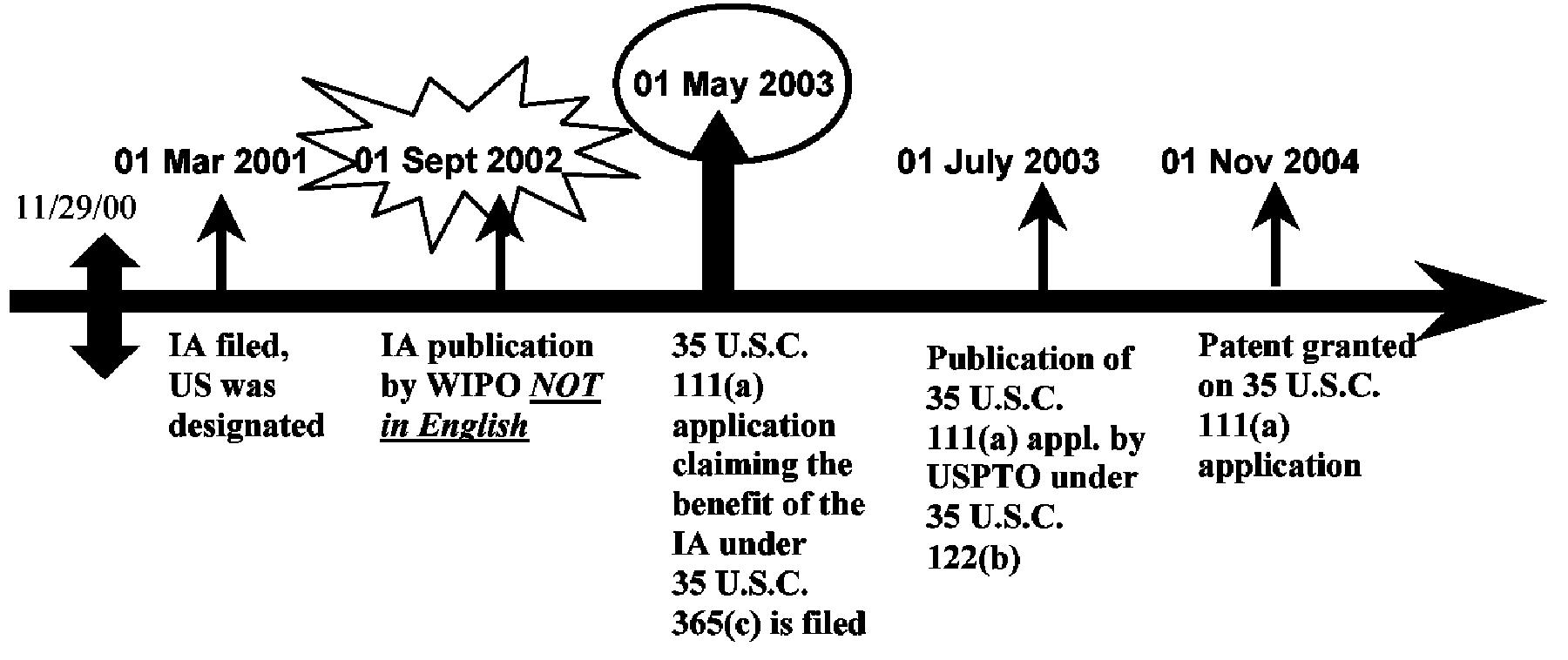
The pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e)(1) date for the IA Publication by WIPO is: None. The pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e)(1) date for the Publication by USPTO is: 01 May 2003. The pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e)(2) date for the Patent is: 01 May 2003
| The IA publication by WIPO can be applied under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(a) or (b) as of its publication date (01 Sept 2002). |
| Additional Benefit Claims: |
| If the IA properly claimed the benefit of any earlier-filed U.S. application (whether provisional or nonprovisional), there would still be no pre-AIA35 U.S.C. 102(e)(1) date for the IA publication by WIPO, and the U.S. patent application publication and patent would still have a pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) date of the actual filing date of the later-filed 35 U.S.C. 111(a) application in the example above (01 May 2003). |
| If a second, later-filed U.S. nonprovisional (35 U.S.C. 111(a)) application claimed the benefit of the 35 U.S.C. 111(a) application in the example above, the pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) date of the patent or publication of the second, later-filed U.S. application would still be the actual filing date of the 35 U.S.C. 111(a) application in the example above (01 May 2003). |
| Example 9: References based on a 35 U.S.C. 111(a) Application which is a Continuation (filed prior to any entry of the national stage) of an International Application, which was filed prior to November 29, 2000 (language of the publication under PCT Article 21(2) is not relevant). |
| Both the U.S. publication and the U.S. patent of the 35 U.S.C. 111(a) continuation (filed prior to any entry of the national stage) of an international application (IA) that was filed prior to November 29, 2000, have the pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) prior art date of their actual U.S. filing date under 35 U.S.C. 111(a). No benefit of the international filing date (or of any U.S. filing dates prior to the IA) is given for pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) prior art purposes since the IA was filed prior to November 29, 2000. The IA publication under PCT Article 21(2) does not have a prior art date under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e)(1) because the IA was filed prior to November 29, 2000. The IA publication under PCT Article 21(2) can be applied under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(a) or (b) as of its publication date. |
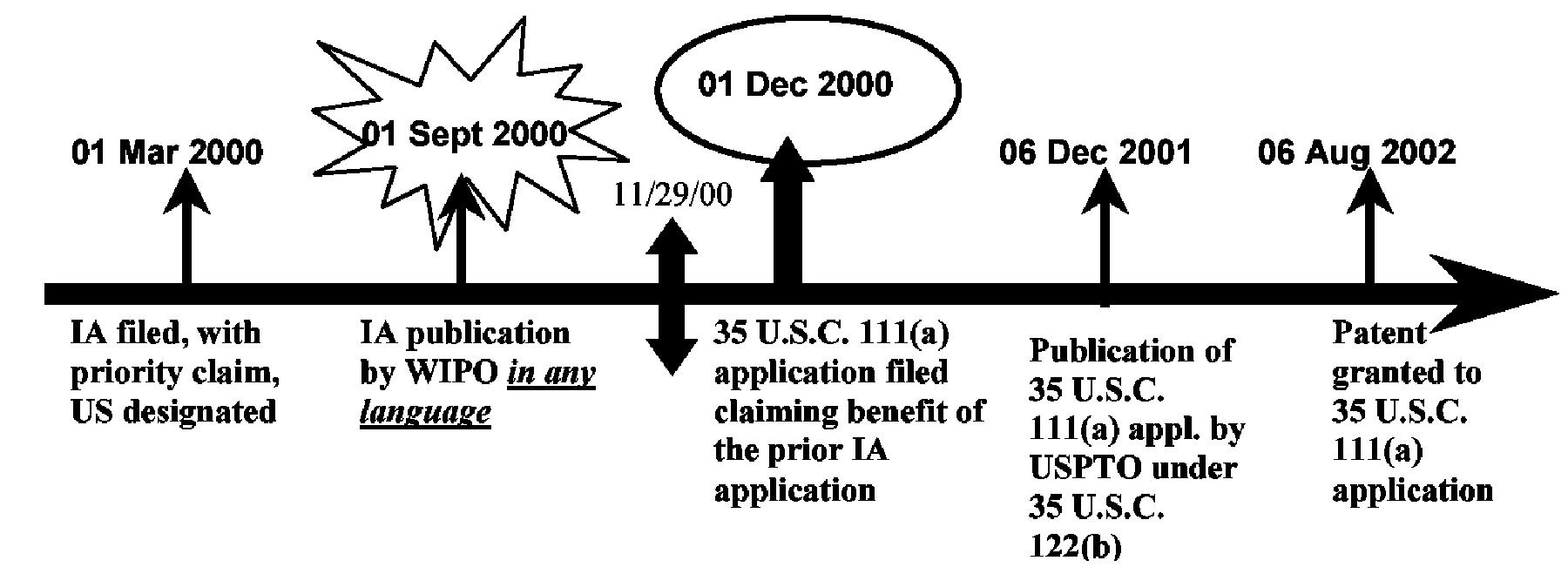
The pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e)(1) date for the IA Publication by WIPO is: None. The pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e)(1) date for the Publication by USPTO is: 01 Dec. 2000. The pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e)(2) date for the Patent is: 01 Dec. 2000.
| The IA publication by WIPO can be applied under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(a) or (b) as of its publication date (01 Sept 2000). |
| Additional Benefit Claims: |
| If the IA properly claimed the benefit of any earlier-filed U.S. application (whether provisional or nonprovisional), there would still be no pre-AIA35 U.S.C. 102(e)(1) date for the IA publication by WIPO, and the U.S. application publication and patent would still have a pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) date of the actual filing date of the later-filed 35 U.S.C. 111(a) application in the example above (01 Dec 2000). |
| If a second, later-filed U.S. nonprovisional (35 U.S.C. 111(a)) application claimed the benefit of the 35 U.S.C. 111(a) application in the example above, the pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) date of the patent or publication of the second, later-filed U.S. application would still be the actual filing date of the 35 U.S.C. 111(a) application in the example above (01 Dec 2000). |
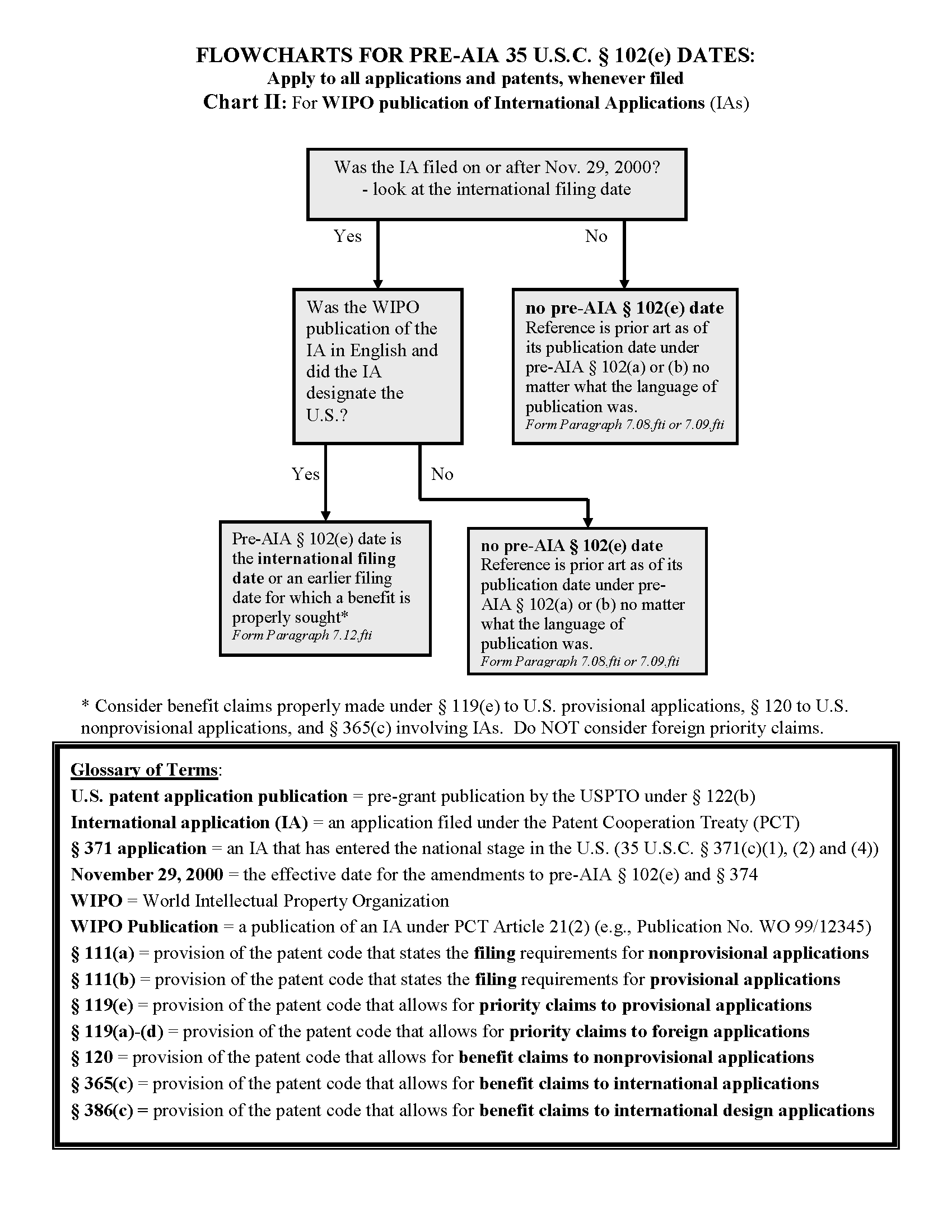
The following flowcharts provide guidance for determining the pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) date, if any, for a U.S. patent, U.S. patent application publication, or international application publication. Note that for benefit claims under 35 U.S.C. 119(e), the critical reference date under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) may be the filing date of a relied upon provisional application only if at least one of the claims in the reference patent, patent application publication, or international application publication is supported by the written description of the provisional application in compliance with pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 112, first paragraph, or 35 U.S.C. 112(a). See MPEP § 2136.03, subsection III.
2136.01 Status of Unpublished or Published as Redacted U.S. Application as a Reference Under Pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) [R-10.2019]
[Editor Note: This MPEP section is not applicable to applications subject to examination under the first inventor to file (FITF) provisions of the AIA as set forth in 35 U.S.C. 100 (note). See MPEP § 2159 et seq. to determine whether an application is subject to examination under the FITF provisions, and MPEP § 2150 et seq. for examination of applications subject to those provisions.]
If an earlier filed, copending, and unpublished U.S. patent application discloses subject matter which would anticipate the claims in a later filed pending U.S. application which has a different inventive entity, the examiner should determine whether a provisional rejection under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) of the later filed application can be made. In addition, a provisional rejection under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) may be made, in certain circumstances as described below, if the earlier filed, pending application has been published as redacted (37 CFR 1.217) and the subject matter relied upon in the rejection is not supported in the redacted publication of the patent application.
I. WHEN THERE IS NO COMMON ASSIGNEE, APPLICANT, OR INVENTOR, A U.S. APPLICATION MUST ISSUE AS A PATENT OR BE PUBLISHED AS A SIR OR AS AN APPLICATION PUBLICATION BEFORE IT IS AVAILABLE AS PRIOR ART UNDER PRE-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e)In addition to U.S. patents and SIRs, certain U.S. application publications and certain international application publications are also available as prior art under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) as of their effective U.S. filing dates (which will include certain international filing dates).
If there is no common assignee, common applicant, or common inventor and the application was not published pursuant to 35 U.S.C. 122(b), the confidential status of applications under 35 U.S.C. 122(a) must be maintained and no rejection can be made relying on the earlier filed, unpublished application, or subject matter not supported in a redacted application publication, as prior art under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e). For applications subject to pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(g), if the filing dates of the applications are within 6 months of each other (3 months for simple subject matter) then interference may be proper. See MPEP Chapter 2300. If the application with the earliest effective U.S. filing date will not be published pursuant to 35 U.S.C. 122(b), it must be allowed to issue once all the statutory requirements are met. After the patent has issued, it may be used as a reference in a rejection under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) in the still pending application as appropriate. See MPEP § 2136et seq.
II. WHEN THERE IS A COMMON ASSIGNEE, APPLICANT, OR INVENTOR, A PROVISIONAL PRE-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) REJECTION OVER AN EARLIER FILED UNPUBLISHED APPLICATION CAN BE MADEBased on the assumption that an application will ripen into a U.S. patent (or into an application publication), it is permissible to provisionally reject a later application over an earlier filed, and unpublished, application under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) when there is a common assignee, applicant, or inventor. See, e.g., In re Irish, 433 F.2d 1342, 167 USPQ 764 (CCPA 1970). In addition, a provisional pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) rejection may be made if the earlier filed copending U.S. application has been published as redacted (37 CFR 1.217) and the subject matter relied upon in the rejection is not supported in the redacted publication of the patent application. Such a provisional rejection “serves to put applicant on notice at the earliest possible time of the possible prior art relationship between copending applications” and gives applicant the fullest opportunity to overcome the rejection by amendment or submission of evidence. In addition, since both applications are pending and usually have the same assignee, more options are available to applicant for overcoming the provisional rejection than if the other application were already issued. Ex parte Bartfeld, 16 USPQ2d 1714 (Bd. Pat. App. & Int. 1990) aff’d on other grounds, 925 F.2d 1450, 17 USPQ2d 1885 (Fed. Cir. 1991). Note that provisional rejections over pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) are only authorized when there is a common inventor or assignee, otherwise the copending application prior to publication must remain confidential.
Therefore, if (1) at least one common inventor or applicant exists between the applications or the applications are commonly assigned, and (2) the effective filing dates are different; then a provisional rejection of the later-filed application should be made. The provisional rejection is appropriate in circumstances where, if the earlier-filed application is published or becomes a patent, it would constitute actual prior art under 35 U.S.C. 102. Because the earlier-filed application is not published at the time of the rejection, the rejection must be provisionally made under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e).
A provisional rejection under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) can be overcome in the same manner that a pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) rejection can be overcome. See MPEP § 2136.05. The provisional rejection can also be overcome by abandoning the applications and filing a new application containing the subject matter of both. Form paragraph 7.15.01.fti should be used when making a provisional rejection under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e).
III. PROVISIONAL REJECTION UNDER PRE-AIA 35 U.S.C. 103(a) CAN BE MADE USING PRIOR ART UNDER PRE-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e)For applications filed on or after November 29, 1999 or pending on or after December 10, 2004, a provisional rejection under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 103(a) using prior art under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) is not proper if the application contains evidence that the application and the prior art reference were owned by the same person, or subject to an obligation of assignment to the same person, at the time the invention was made. See pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 103(c).
In addition, certain non-commonly owned references may be disqualified from being applied in a rejection under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 103(a) due to the Cooperative Research and Technology Enhancement Act of 2004 (CREATE Act) (Public Law 108-453; 118 Stat. 3596 (2004)), which was enacted on December 10, 2004 and was effective for all patents granted on or after December 10, 2004.
See MPEP §§ 2146-2146.03 for information pertaining to prior art disqualified under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 103(c), evidence of common ownership, and examination procedure with respect to pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 103(c); see MPEP § 2146.03(a) for a discussion of provisional rejections under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 103(a) using provisional prior art under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e).
Pre-AIA 35 U.S.C.103(c), as amended by the CREATE Act, continues to apply only to subject matter which qualifies as prior art under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e), (f) or (g), and which is being relied upon in a rejection under 35 U.S.C. 103. It does not apply to or affect subject matter which is applied in a rejection under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102 or a double patenting rejection (see 37 CFR 1.78(c) and MPEP § 804). In addition, if the subject matter qualifies as prior art under any other subsection of pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102 (e.g., pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(a) or (b)) it will not be disqualified as prior art under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 103(c). See also MPEP § 2146et seq. for information relating to rejections under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 103 and evidence of joint research agreements.
2136.02 Content of the Prior Art Available Against the Claims [R-10.2019]
[Editor Note: This MPEP section is not applicable to applications subject to examination under the first inventor to file (FITF) provisions of the AIA as set forth in 35 U.S.C. 100 (note). See MPEP § 2159 et seq. to determine whether an application is subject to examination under the FITF provisions, and MPEP § 2150 et seq. for examination of applications subject to those provisions.]
I. A 35 U.S.C. 102(e) REJECTION MAY RELY ON ANY PART OF THE PATENT OR APPLICATION PUBLICATION DISCLOSUREUnder pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e), the entire disclosure of a U.S. patent, a U.S. patent application publication, or an international application publication having an earlier effective U.S. filing date (which will include certain international filing dates) can be relied on to reject the claims. Sun Studs, Inc. v. ATA Equip. Leasing, Inc., 872 F.2d 978, 983, 10 USPQ2d 1338, 1342 (Fed. Cir. 1989). See MPEP § 2120.01.
II. REFERENCE MUST ITSELF CONTAIN THE SUBJECT MATTER RELIED ON IN THE REJECTIONWhen a U.S. patent, a U.S. patent application publication, or an international application publication is used to reject claims under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e), the disclosure relied on in the rejection must be present in the issued patent or application publication. It is the earliest effective U.S. filing date (which will include certain international filing dates) of the U.S. patent or application publication being relied on as the critical reference date and subject matter not included in the patent or application publication itself can only be used when that subject matter becomes public. Portions of the patent application which were canceled are not part of the patent or application publication and thus cannot be relied on in a pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) rejection over the issued patent or application publication. Ex parte Stalego, 154 USPQ 52 (Bd. App. 1966). Similarly, subject matter that is disclosed in an abandoned, unpublished parent application but was not carried over into the child patent or application publication may not be relied on as prior art under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e). In re Klesper, 397 F.2d 882, 886, 158 USPQ 256, 258 (CCPA 1968). See MPEP § 901.02 for more information on availability of abandoned applications as prior art. Likewise, subject matter which is disclosed in a parent application, but not included in the child continuation-in-part (CIP) cannot be relied on in a pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) rejection over the issued or published CIP. In re Lund, 376 F.2d 982, 153 USPQ 625 (CCPA 1967) (The examiner made a pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) rejection over an issued U.S. patent which was a continuation-in-part (CIP). The parent application of the U.S. patent reference contained an example II which was not carried over to the CIP. The court held that the subject matter embodied in the canceled example II could not be relied on as of either parent or child filing date. Thus, the use of example II subject matter to reject the claims under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) was improper.).
Where a U.S. patent claims benefit to a provisional application, at least one claim of the patent must be supported by the disclosure of the relied upon provisional application in compliance with pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 112, first paragraph, in order for the patent to be usable as prior art under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) as of the relied upon provisional application’s filing date. See MPEP § 2136.03, subsection III.
III. THE SUPREME COURT HAS AUTHORIZED 35 U.S.C. 103 REJECTIONS BASED ON PRE-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e)U.S. patents may be used as of their filing dates to show that the claimed subject matter is anticipated or obvious. Obviousness can be shown by combining other prior art with the U.S. patent reference in a 35 U.S.C. 103 rejection. Hazeltine Research v. Brenner, 382 U.S. 252, 147 USPQ 429 (1965). Similarly, certain U.S. application publications and certain international application publications may also be used as of their earliest effective U.S. filing dates (which will include certain international filing dates) to show that the claimed subject matter would have been anticipated or obvious.
See MPEP § 2146et seq. for additional information on rejections under 35 U.S.C. 103 and evidence of common ownership or a joint research agreement.
2136.03 Critical Reference Date [R-10.2019]
[Editor Note: This MPEP section is not applicable to applications subject to examination under the first inventor to file (FITF) provisions of the AIA as set forth in 35 U.S.C. 100 (note). See MPEP § 2159 et seq. to determine whether an application is subject to examination under the FITF provisions, and MPEP § 2150 et seq. for examination of applications subject to those provisions.]
I. FOREIGN PRIORITY DATEPre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) is explicitly limited to certain references “filed in the United States before the invention thereof by the applicant” (emphasis added). Foreign applications’ filing dates that are claimed (via 35 U.S.C. 119(a)–(d), (f) or 35 U.S.C. 365(a)) in applications, which have been published as U.S. or WIPO application publications or patented in the U.S., may not be used as pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) dates for prior art purposes. This includes international filing dates claimed as foreign priority dates under 35 U.S.C. 365(a). Therefore, the foreign priority date of the reference under 35 U.S.C. 119(a)-(d), (f), and 35 U.S.C. 365(a) cannot be used to antedate the application filing date. In contrast, applicant may be able to overcome the pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) rejection by proving the applicant is entitled to the 35 U.S.C. 119 priority date which is earlier than the reference’s U.S. filing date. In re Hilmer, 359 F.2d 859, 149 USPQ 480 (CCPA 1966) (Hilmer I) (Applicant filed an application with a right of priority to a German application. The examiner rejected the claims over a U.S. patent to Habicht based on its Swiss priority date. The U.S. filing date of Habicht was later than the application’s German priority date. The court held that the reference’s Swiss priority date could not be relied on in a pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) rejection. Because the U.S. filing date of Habicht was later than the German priority date of the application, the rejection was reversed.). See MPEP § 216 for information on procedures to be followed in considering applicant's right of priority.
Note that certain international application (PCT) filings are considered to be “filings in the United States” for purposes of applying an application publication as prior art. See MPEP § 2120.01.
II. INTERNATIONAL (PCT) APPLICATIONS; INTERNATIONAL APPLICATION PUBLICATIONSIf the potential reference resulted from, or claimed the benefit of, an international application, the following must be determined:
- (A) If the international application meets the following three
conditions:
- (1) an international filing date on or after November 29, 2000;
- (2) designated the United States; and
- (3) published under PCT Article 21(2) in English,
the international filing date is a U.S. filing date for prior art purposes under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e). If such an international application properly claims benefit to an earlier-filed U.S. or international application, apply the reference under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) as of the earlier filing date, provided all the conditions of pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) and 35 U.S.C. 120 or 365(c) are met. In addition, the subject matter relied upon in the rejection must be disclosed in the earlier-filed application in compliance with 35 U.S.C. 112(a) /pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 112, first paragraph, in order to give that subject matter the benefit of the earlier filing date under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e).
If such an international application properly claims benefit to an earlier-filed U.S. provisional application, apply the reference under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) as of the earlier filing date, provided that the provisional application has proper support for the subject matter as required by 35 U.S.C. 119(e) and that at least one claim of the international application is supported by the written description of the relied upon provisional application in compliance with pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 112, first paragraph or 35 U.S.C. 112(a). See MPEP § 2136.03, subsection III.
Note: where the earlier application is an international application, the earlier international application must satisfy the same three conditions (i.e., filed on or after November 29, 2000, designated the U.S., and published in English under PCT Article 21(2)) for the earlier international filing date to be the U.S. filing date for prior art purposes under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e).
- (B) If the international application was filed on or after November 29, 2000, but did not designate the United States or was not published in English under PCT Article 21(2), do not treat the international filing date as a U.S. filing date. In this situation, do not apply the reference as of its international filing date, its date of completion of the 35 U.S.C. 371(c)(1), (2) and (4) requirements, or any earlier filing date to which such an international application claims benefit or priority. The reference may be applied under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(a) or (b) as of its publication date, or pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) as of any later U.S. filing date of an application that properly claimed the benefit of the international application (if applicable).
References based on international applications that were filed prior to November 29, 2000 are subject to the pre-AIPA version of 35 U.S.C. 102(e) (i.e., the version in force on November 28, 2000) as set forth below.
Former 35 U.S.C. 102 Conditions for patentability; novelty and loss of right to patent (as in force on November 28, 2000).
A person shall be entitled to a patent unless-
*****
- (e) the invention was described in a patent granted on an application for patent by another filed in the United States before the invention thereof by the applicant for patent, or on an international application by another who has fulfilled the requirements of paragraphs (1), (2), and (4) of section 371(c) of this title before the invention thereof by the applicant for patent.
*****
If an international application has an international filing date prior to November 29, 2000, the reference should be applied under the provisions of 35 U.S.C. 102 and 374 as in force on November 28, 2000 (prior to the AIPA amendments):
- (1) For U.S. patents, apply the reference under 35 U.S.C. 102(e) as in force on November 28, 2000 as of the earlier of the date of completion of the requirements of 35 U.S.C. 371(c)(1), (2) and (4) or the filing date of the later-filed U.S. application that claimed the benefit of the international application;
- (2) For U.S. application publications and WIPO publications directly resulting from international applications under PCT Article 21(2), never apply these references under 35 U.S.C. 102(e) as in force on November 28, 2000. These references may be applied as of their publication dates under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(a) or (b);
- (3) For U.S. application publications of applications that claim the benefit under 35 U.S.C. 120 or 365(c) of an international application filed prior to November 29, 2000, apply the reference under 35 U.S.C. 102(e) as in force on November 28, 2000 as of the actual filing date of the later-filed U.S. application that claimed the benefit of the international application.
Examiners should be aware that although a publication of, or a U.S. patent issued from, an international application may not be available as prior art under former 35 U.S.C. 102(e) as in force on November 28, 2000 or under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e), the corresponding WIPO publication of an international application may have an earlier pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(a) or (b) date.
III. BENEFIT OF PROVISIONAL APPLICATION UNDER 35 U.S.C. 119(e)The critical reference date under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) of a U.S. patent, a U.S. patent application publication, as well as an international application publication having prior art effect under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e), may be the filing date of a relied upon provisional application only if at least one of the claims in the reference patent, patent application publication, or international application publication is supported by the written description of the provisional application in compliance with pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 112, first paragraph, or 35 U.S.C. 112(a). See Amgen Inc. v. Sanofi, 872 F.3d 1367, 1380 (Fed. Cir. 2017); Dynamic Drinkware, LLC, v. National Graphics, Inc., 800 F.3d 1375, 116 USPQ2d 1045 (Fed. Cir. 2015). The provisional application must also describe, in compliance with pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 112, first paragraph, or 35 U.S.C. 112(a), the subject matter relied upon in the reference patent or publication to make the rejection. See MPEP § 2136, examples 2, 4, and 7.
Note that international applications which (1) were filed prior to November 29, 2000, or (2) did not designate the U.S., or (3) were not published in English under PCT Article 21(2) by WIPO, may not be used to reach back (bridge) to an earlier filing date through a priority or benefit claim for prior art purposes under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e).
IV. BENEFIT OF NONPROVISIONAL APPLICATION UNDER 35 U.S.C. 120For prior art purposes, a U.S. patent or patent application publication that claims the benefit of an earlier filing date under 35 U.S.C. 120 of a prior nonprovisional application (i.e., a continuation, divisional, or continuation-in-part application) would be accorded the earlier filing date as its prior art date under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e), provided the earlier-filed application properly supports the subject matter relied upon in any rejection in compliance with 35 U.S.C. 112(a) or pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 112, first paragraph. In other words, the subject matter used in the rejection must be disclosed in the earlier-filed application in compliance with 35 U.S.C. 112(a) or pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 112, first paragraph, in order for that subject matter to be entitled to the earlier filing date under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e).
See also MPEP § 2136, examples 2 and 5 to 9.
V. DATE OF CONCEPTION OR REDUCTION TO PRACTICEIf a reference available under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) discloses, but does not claim the subject matter of the claims being examined or an obvious variant, the reference is not prior art under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(g). Furthermore, the reference does not qualify as “prior art” under 35 U.S.C. 102 as of a date earlier than its filing date based upon any prior inventive activity that is disclosed in the U.S. patent or U.S. patent application publication in the absence of evidence that the subject matter was actually reduced to practice in this country on an earlier date. See MPEP § 2138. When the cases are not in interference, the effective date of the reference as prior art is its filing date in the United States (which will include certain international filing dates), as stated in pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e). See MPEP §§ 2120.01 and2136. The date that the prior art subject matter was conceived or reduced to practice is of no importance when pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(g) is not at issue. Sun Studs, Inc. v. ATA Equip. Leasing, Inc., 872 F.2d 978, 983, 10 USPQ2d 1338, 1342 (Fed. Cir. 1989) (The defendant sought to invalidate patents issued to Mason and Sohn assigned to Sun Studs. The earliest of these patents issued in June 1973. A U.S. patent to Mouat was found which issued in March 1976 and which disclosed the invention of Mason and Sohn. While the patent to Mouat issued after the Mason and Sohn patents, it was filed 7 months earlier than the earliest of the Mason and Sohn patents. Sun Studs submitted affidavits showing conception in 1969 and diligence to the constructive reduction to practice and therefore antedated the patent to Mouat. The defendant sought to show that Mouat conceived the invention in 1966. The court held that conception of the subject matter of the reference only becomes an issue when the claims of the conflicting patents cover inventions which are the same or obvious over one another. When pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) applies but not pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(g), the filing date of the prior art patent is the earliest date that can be used to reject or invalidate claims.).
2136.04 Different Inventive Entity; Meaning of “By Another” [R-10.2019]
[Editor Note: This MPEP section is not applicable to applications subject to examination under the first inventor to file (FITF) provisions of the AIA as set forth in 35 U.S.C. 100 (note). See MPEP § 2159 et seq. to determine whether an application is subject to examination under the FITF provisions, and MPEP § 2150 et seq. for examination of applications subject to those provisions.]
I. IF THERE IS ANY DIFFERENCE IN THE INVENTIVE ENTITY, THE REFERENCE IS “BY ANOTHER”“Another” means other than applicants, In re Land, 368 F.2d 866, 151 USPQ 621 (CCPA 1966), in other words, a different inventive entity. The inventive entity is different if not all inventors are the same. The fact that the application and reference have one or more inventors in common is immaterial. Ex parte DesOrmeaux, 25 USPQ2d 2040 (Bd. Pat. App. & Inter. 1992) (The examiner made a pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) rejection based on an issued U.S. patent to three inventors. The rejected application was a continuation-in-part of the issued parent with an extra inventor. The Board found that the patent was “by another” and thus could be used in a pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e)/103 rejection of the application.).
II. A DIFFERENT INVENTIVE ENTITY IS PRIMA FACIE EVIDENCE THAT THE REFERENCE IS “BY ANOTHER”As stated by the House and Senate reports on the bills enacting section pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) as part of the 1952 Patent Act, this subsection of 102 codifies the Milburn rule of Milburn v. Davis-Bournonville, 270 U.S. 390, 1926 C.D. 303, 344 O.G. 817 (1926). The Milburn rule authorized the use of a U.S. patent containing a disclosure of the invention as a reference against a later filed application as of the U.S. patent filing date. The existence of an earlier filed U.S. application containing the subject matter claimed in the application being examined indicates that applicant was not the first inventor. Therefore, a U.S. patent, a U.S. patent application publication or international application publication, by a different inventive entity, whether or not the application shares some inventors in common with the patent, is prima facie evidence that the invention was made “by another” as set forth in pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e). In re Mathews, 408 F.2d 1393, 161 USPQ 276 (CCPA 1969); In re Facius, 408 F.2d 1396, 161 USPQ 294 (CCPA 1969); Ex parte DesOrmeaux, 25 USPQ2d 2040 (Bd. Pat. App. & Inter. 1992). See MPEP § 2136.05et seq. for discussion of methods of overcoming pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) rejections.
2136.05 Overcoming a Rejection Under Pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) [R-10.2019]
[Editor Note: This MPEP section is not applicable to applications subject to examination under the first inventor to file (FITF) provisions of the AIA as set forth in 35 U.S.C. 100 (note). See MPEP § 2159 et seq. to determine whether an application is subject to examination under the FITF provisions, and MPEP § 2150 et seq. for examination of applications subject to those provisions. Information pertaining to overcoming pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) rejections has been moved to MPEP § 2136.05(a) for affidavits or declarations under 37 CFR 1.131 and benefit or priority claims, and to MPEP § 2136.05(b) for affidavits or declarations under 37 CFR 1.132.]
In all applications, an applicant may overcome a pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102 rejection by persuasively arguing that the claims are patentably distinguishable from the prior art, or by amending the claims to patentably distinguish over the prior art. Additional ways available to overcome a rejection based on pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102 prior art depend on the applicable paragraph of pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102. See MPEP § 2132.01 for overcoming a rejection under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(a) and MPEP § 2133.02(a) for overcoming a rejection under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(b).
A rejection based on pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) can be overcome by:
- (A) Persuasively arguing that the claims are patentably distinguishable from the prior art;
- (B) Amending the claims to patentably distinguish over the prior art;
- (C) Filing an affidavit or declaration under 37 CFR 1.132 showing that the reference invention is not by “another.” See MPEP §§ 715.01(a), 715.01(c), 716.10, and 2136.05(b);
- (D) Filing an affidavit or declaration under 37 CFR 1.131(a) showing prior invention, if the reference is not a U.S. patent or a U.S. patent application publication claiming interfering subject matter as defined in 37 CFR 41.203(a) (subject matter of a claim of one party would, if prior art, have anticipated or rendered obvious the subject matter of a claim of the opposing party and vice versa). See MPEP §§ 715 and 2136.05(b) for more information on 37 CFR 1.131(a) affidavits;
- (E) Submitting and perfecting a claim to priority under 35 U.S.C. 119(a) - (d) within the time period set in 37 CFR 1.55 and establishing that prior foreign application disclosure satisfies the enablement and written description requirements of 35 U.S.C. 112 for the subject matter claimed in the application under examination (see MPEP § 2136.05(a) for a summary of priority requirements, and MPEP §§ 213-216 for detailed information); and/or
- (F) Submitting a benefit claim under 35 U.S.C. 119(e) or 120, within the time periods set in 37 CFR 1.78 and establishing that the prior application satisfies the enablement and written description requirements of 35 U.S.C. 112 for the subject matter claimed in the application under examination (seeMPEP § 2136.05(a) for a summary of benefit requirements, and MPEP § 211et seq. for detailed information).
2136.05(a) Antedating a Pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) Reference [R-10.2019]
When a prior U.S. patent, U.S. patent application publication, or international application publication is not a statutory bar, a pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) rejection can be overcome by antedating the filing date (see MPEP § 2136.03 regarding critical reference date of pre‑AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) prior art) of the reference by submitting an affidavit or declaration under 37 CFR 1.131. The filing date of a pre‑AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) reference can also be antedated by establishing priority to, or the benefit of, the filing date of an earlier application under 35 U.S.C. 119 or 35 U.S.C. 120.
I. AFFIDAVIT OR DECLARATION UNDER 37 CFR 1.131An affidavit or declaration under 37 CFR 1.131(a) can overcome a prior art rejection under pre‑AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) by proving invention of the claimed subject matter by the inventor or at least one joint inventor prior to the effective date of the reference relied upon in the rejection.
When the claims of the reference U.S. patent or U.S. patent application publication and the application are directed to the same invention or are obvious variants, an affidavit or declaration under 37 CFR 1.131(a) is not an acceptable method of overcoming the rejection. Under these circumstances, the examiner must determine whether a double patenting rejection or interference is appropriate. If there is a common assignee or inventor between the application and patent, a double patenting rejection must be made. See MPEP § 804. Note that a terminal disclaimer does not overcome a pre‑AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) rejection. See, e.g., In re Bartfeld, 925 F.2d 1450, 17 USPQ2d 1885 (Fed. Cir. 1991). If there is no common assignee or inventor and the rejection under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) is the only possible rejection, the examiner must determine whether an interference should be declared. See MPEP Chapter 2300 for more information regarding interferences.
For information on the required contents of a 37 CFR 1.131 affidavit or declaration and the situations in which such affidavits and declarations are permitted, see MPEP § 715et seq.
An affidavit or declaration under 37 CFR 1.131 is not appropriate if the reference describes an inventor's or at least one joint inventor's own work. In this case, applicant must submit an affidavit or declaration under 37 CFR 1.132. See MPEP § 2136.05(b) for more information concerning the requirements of 37 CFR 1.132 affidavits and declarations.
II. ESTABLISHING PRIORITY TO, OR THE BENEFIT OF, AN EARLIER FILING DATEA rejection based on pre‑AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) can be overcome by:
- (A) Submitting a claim to priority under 35 U.S.C. 119(a) - (d) within the time period set in 37 CFR 1.55:
-
- (1)
- (a) for applications filed on or after September 16, 2012, by filing a corrected application data sheet under 37 CFR 1.76 which identifies a prior foreign application in accordance with 37 CFR 1.55, or
- (b) for applications filed prior to September 16, 2012, by filing a corrected application data sheet under 37 CFR 1.76 which identifies a prior foreign application in accordance with 37 CFR 1.55 or by identifying the prior foreign application in the oath or declaration under pre-AIA 37 CFR 1.63,
and
- (2) by establishing that the prior foreign application satisfies the enablement and written description requirements of 35 U.S.C. 112(a) (for applications filed on or after September 16, 2012), or 35 U.S.C. 112, first paragraph (for applications filed prior to September 16, 2012); or filing a grantable petition to accept an unintentionally delayed priority claim under 37 CFR 1.55. See MPEP §§ 213 - 216. The foreign priority filing date must antedate the reference and be perfected. The filing date of the priority document is not perfected unless applicant has filed a certified priority document in the application (and an English language translation, if the document is not in English) (see 37 CFR 1.55); and/or
- (1)
- (B) Submitting a benefit claim under
35
U.S.C. 119(e) or 120, within the time periods set in 37 CFR
1.78:
- (1)
- (a) for applications filed on or after September 16, 2012, filing an application data sheet under 37 CFR 1.76 which contains a specific reference to a prior application in accordance with 37 CFR 1.78, or
- (b) for applications filed prior to September 16, 2012, amending the specification of the application to contain a specific reference to a prior application or by filing an application data sheet under 37 CFR 1.76 which contains a specific reference to a prior application in accordance with 37 CFR 1.78,
and
- (2) establishing that the prior application satisfies the enablement and written description requirements of 35 U.S.C. 112(a) (for applications filed on or after September 16, 2012), or 35 U.S.C. 112, first paragraph (for applications filed prior to September 16, 2012) or filing a grantable petition to accept an unintentionally delayed claim under 37 CFR 1.78.
- (1)
The filing date of a prior application cannot be used to antedate a reference if the application at issue is not entitled to claim the benefit of the prior application under 35 U.S.C. 119(e), 120, 121, or 365(c). In re Costello, 717 F.2d 1346, 219 USPQ 389 (Fed. Cir. 1983).
2136.05(b) Showing The Reference Is Describing An Inventor's Or At Least One Joint Inventor's Own Work [R-07.2022]
[Editor Note: This MPEP section is not applicable to applications subject to examination under the first inventor to file (FITF) provisions of the AIA as set forth in 35 U.S.C. 100 (note). See MPEP § 2159 et seq. to determine whether an application is subject to examination under the FITF provisions, and MPEP § 2150 et seq. for examination of applications subject to those provisions. Information pertaining to overcoming pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) rejections has been moved to MPEP § 2136.05(a) for affidavits or declarations under 37 CFR 1.131.]
A rejection based on pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) can be overcome by filing an affidavit or declaration under 37 CFR 1.132 showing that the reference invention is not by “another.” “The fact that an application has named a different inventive entity than a patent does not necessarily make that patent prior art.” Applied Materials Inc. v. Gemini Research Corp., 835 F.2d 279, 15 USPQ2d 1816 (Fed. Cir. 1988). The issue turns on what the evidence of record shows as to who invented the subject matter. In re Whittle, 454 F.2d 1193, 1195, 172 USPQ 535, 537 (CCPA 1972). In fact, even if an inventor's or at least one joint inventor's work was publicly disclosed prior to the patent application, the inventor's or at least one joint inventor's own work may not be used against the application subject to pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102 unless there is a time bar under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(b). In re DeBaun, 687 F.2d 459, 214 USPQ 933 (CCPA 1982) (citing In re Katz, 687 F.2d 450, 215 USPQ 14 (CCPA 1982)). However, an affidavit or declaration under 37 CFR 1.132 that is only a naked assertion of inventorship and that fails to provide any context, explanation or evidence to support that assertion is insufficient to show that the relied-upon subject matter was the inventor’s own work. See EmeraChem Holdings, LLC v. Volkswagen Grp. of Am., Inc., 859 F.3d 1341, 123 USPQ2d 1146 (Fed. Cir. 2017) (finding that a declaration submitted by inventor Campbell insufficient to establish that he and Guth (now deceased) were inventors of the subject matter disclosed in a patent naming Campbell, Guth, Danziger, and Padron because “[n]othing in the declaration itself, or in addition to the declaration, provides any context, explanation, or evidence to lend credence to the inventor's bare assertion” and more than twenty years had passed since the alleged events occurred. Id. at 1345; 123 USPQ2d at 1149.). Therefore, when the unclaimed subject matter of a reference is an inventor's or at least one joint inventor's own invention, a prima facie case based on the patent, U.S. patent application publication, or international application publication, may be overcome by showing that the disclosure is a description of the inventor's or at least one joint inventor's own previous work. Such a showing can be made by proving that the inventor(s) of the U.S. patent, U.S. patent application publication, or the international application publication, was associated with applicant (e.g., same assignee) and learned of the inventor's or at least one joint inventor's invention from the inventor or at least one joint inventor directly or indirectly. In re Mathews, 408 F.2d 1393, 161 USPQ 276 (CCPA 1969).
In the situation where one application is first filed naming sole inventor X and then a later application is filed naming joint inventors X & Y, it must be proven that the joint invention was made first, was thereafter described in the sole inventor's patent, or was thereafter described in the sole inventor's U.S. patent application publication or international application publication, and then the joint application was filed. In re Land, 368 F.2d 866, 151 USPQ 621 (CCPA 1966).
In In re Land, separate U.S. patents to Rogers and to Land were used to reject a joint application to Rogers and Land under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e)/103. The inventors worked for the same company (Polaroid) and in the same laboratory. All the patents flowed from the same research. In addition, the patent applications were prepared by the same attorneys, were interrelated and contained cross-references to each other. The court affirmed the rejection because (1) the inventive entities of the patents (one to Rogers and one to Land) were different from the inventive entity of the joint application (Rogers and Land) and (2) Land and Rogers brought their knowledge of their individual work with them when they made the joint invention. There was no indication that the portions of the references relied on disclosed anything they did jointly. Nor was there a showing that what they did jointly was done before the filing of the reference patent applications.
See also In re Carreira, 532 F.2d 1356, 189 USPQ 461 (CCPA 1976) (The examiner rejected claims to a joint application to Carreira, Kyrakakis, Solodar, and Labana under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) and 103 in view of a U.S. patent issued to Tulagin and Carreira or a patent issued to Clark. The applicants submitted declarations under 37 CFR 1.132 by Tulagin and Clark in which each declarant stated he was “not the inventor of the use of compounds having a hydroxyl group in a position ortho to an azo linkage.” The court held that these statements were vague and inconclusive because the declarants did not disclose the use of this generic compound but rather species of this generic compound in their patents and it was the species which met the claims. The declaration that each did not invent the use of the generic compound does not establish that Tulagin and Clark did not invent the use of the species.)
MPEP § 715.01(a), § 715.01(c), and § 716.10 set forth more information pertaining to the contents and uses of affidavits and declarations under 37 CFR 1.132 for antedating references. See MPEP § 2146 for information pertaining to rejections under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e)/103 and the applicability of pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 103(c).
I. APPLICANT NEED NOT SHOW DILIGENCE OR REDUCTION TO PRACTICE WHEN THE SUBJECT MATTER DISCLOSED IN THE REFERENCE IS APPLICANT’S OWN WORKWhen the reference reflects an inventor's or at least one joint inventor's own work, evidence of diligence or reduction to practice does not need to be provided in order to establish that the inventor or at least one joint inventor invented the subject matter disclosed in the reference. A showing that the reference disclosure arose from an inventor's or at least one joint inventor's work coupled with a showing of conception by the inventor or at least one joint inventor before the filing date of the reference will overcome the pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) rejection. The showing can be made by submission of an affidavit under 37 CFR 1.132 by the inventor or at least one joint inventor who invented the subject matter. The other joint inventors, if applicable, need not submit an affidavit disclaiming inventorship, but, if submitted, a disclaimer by all other joint inventors should be considered by the examiner. In re DeBaun, 687 F.2d 459, 214 USPQ 933 (CCPA 1982) (Declaration submitted by DeBaun stated that he was the inventor of subject matter disclosed in the U.S. patent reference of DeBaun and Noll. Exhibits were attached to the declaration showing conception and included drawings DeBaun had prepared and given to counsel for purposes of preparing the application which issued as the reference patent. The court held that, even though the evidence was not sufficient to antedate the prior art patent under 37 CFR 1.131, diligence and/or reduction to practice was not required to show DeBaun invented the subject matter. Declarant’s exhibits and statement that he conceived the invention was enough to show that the subject matter in the U.S. patent reference was declarant’s own invention.).
II. CLAIMING OF INDIVIDUAL ELEMENTS OR SUBCOMBINATIONS IN A COMBINATION CLAIM OF THE REFERENCE DOES NOT ITSELF ESTABLISH THAT THE INVENTOR OR AT LEAST ONE JOINT INVENTOR INVENTED THOSE ELEMENTSThe existence of combination claims in a reference is not evidence that the inventor or at least one joint inventor invented the individual elements or subcombinations included if the elements and subcombinations are not separately claimed apart from the combination. In re DeBaun, 687 F.2d 459, 214 USPQ 933 (CCPA 1982) (citing In re Facius, 408 F.2d 1396, 1406, 161 USPQ 294, 301 (CCPA 1969)).
See also In re Mathews, 408 F.2d 1393, 161 USPQ 276 (CCPA 1969) (On September 15, 1961, Dewey filed an application disclosing and claiming a time delay protective device for an electric circuit. In disclosing the invention, Dewey completely described, but did not claim, a “gating means 19” invented by Mathews which was usable in the protective device. Dewey and Mathews were coworkers at General Electric Company, the assignee. Mathews filed his application on March 7, 1963, before the Dewey patent issued but almost 18 months after its filing. The Mathews application disclosed that “one illustration of a circuit embodying the present invention is shown in copending patent application S.N. 138,476-Dewey.” The examiner used Dewey to reject all the Mathews claims under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e). In response, Mathews submitted an affidavit by Dewey under 37 CFR 1.132. In the affidavit, Dewey stated that he did not invent the gating means 19 but had learned of the gating means through Mathews and that GE attorneys had advised that the gating means be disclosed in Dewey’s application to comply with 35 U.S.C. 112, first paragraph. The examiner argued that the only way to overcome a pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 102(e) rejection was by submitting an affidavit or declaration under 37 CFR 1.131 to antedate the filing date of the reference. The court reversed the rejection, holding that the totality of the evidence on record showed that Dewey derived his knowledge from Mathews who is “the original, first and sole inventor.”).

