CPC Definition - Subclass G21B
This place covers:
Reactors in which energy release is caused by the controlled fusion of atomic nuclei, namely:
Thermonuclear fusion reactors.
Low-temperature nuclear fusion reactors, e.g. alleged cold fusion reactors.
This place does not cover:
Uncontrollable fusion reactions; applications thereof |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Confinement | Controlled compression of fusion nuclei to overcome their electrostatic repulsion. |
Fusion | Combination of two or more nuclei to form a heavier nucleus, a by-product of which is the release of energy. |
Thermonuclear | Relating to fusion at high temperatures. |
This place covers:
systems and components for producing energy by nuclear fusion reactions taking place in a thermonuclear plasma, in particular all parts related to the confinement, ignition and sustainment of the plasma.
This place does not cover:
Low-temperature fusion systems | |
Nuclear fission reactors | |
Investigating plasma | |
Generating plasma other than for nuclear fusion reactions |
The general rule of classification in this subclass follows the IPC rules, i.e. the invention information is classified with an EC class.
This place covers:
Reactors composed of nuclear fusion systems combined with nuclear fission systems, whereby neutrons generated by the fusion reactions are used for generating nuclear fission reactions.
This place does not cover:
Nuclear fission reactors |
This place covers:
Reactors in which nuclear fusion reactions are initiated by heating and compressing a fuel target, typically in the form of a pellet containing the nuclear fuel.
This place covers:
Reactors in which nuclear fusion reactions take place between atomic nuclei of a nuclear fuel in a plasma state, whereby magnetic fields are used to confine the plasma and electromagnetic fields are used to ignite and sustain the plasma.
This place covers:
Reactors in which the plasma containment system comprises a chamber, a magnetic field generator for applying a magnetic field in a direction substantially along a principle axis, and an annular plasma layer that comprises a circulating beam of ions, wherein the internal magnetic field reverses direction.
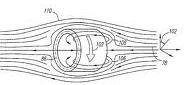
This place covers:
Closed-loop reactors in which the magnetic confinement is produced with a single coil system. As the helical twisting of field lines is achieved solely with external coils, the latter have to be twisted accordingly.
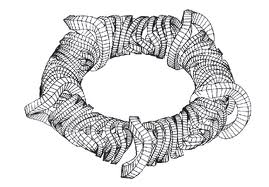
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Torsatron | Stellarator with continuous helical coils |
Heliotron | Stellarator with added poloidal field coils |
Heliac | Stellarator in which the magnetic field forms a toroidal helix |
Helias | Helical Advanced Stellarator |
This place covers:
Closed-loop reactors using magnetic fields to confine the plasma in the shape of a torus with a doughnut cross-section. A toroidal magnetic field is generated by electromagnets encircling the torus. A poloidal field is generated by a poloidal electric current that flows inside the plasma, this current being induced inside the plasma by a second set of electromagnets.
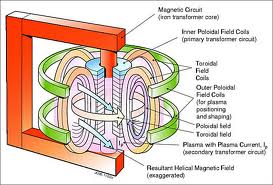
This place does not cover:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
First wall, blanket, divertor |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
ITER | International Thermonuclear Reactor |
JET | Joint European Torus |
ASDEX | Axial Symmetric Divertor Experiment |
This place covers:
Specific components of the inertial and/or magnetic fusion confinement reactors and auxiliary systems associated, e.g. electromagnets.
This place does not cover:
This place covers:
Systems and methods for recovering the tritium generated in the blanket of a nuclear fusion reactor.
This place covers:
Details of the structural elements in contact with the plasma and/or affected by the fusion generated neutrons, and auxiliary systems associated, e.g. first wall cooling systems.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
FW | First wall |
This place covers:
Systems and methods for injecting the nuclear fuel targets (e.g. pellets) into an inertial confinement reactor, and the nuclear fuel into the plasma in a magnetic confinement reactor.
This place does not cover:
Lasers and related optical systems for producing plasma by target irradiation |
This place covers:
The reactor vessel in which the fusion reactions take place, and the auxiliary systems associated, e.g. systems for creating the desired pressure conditions within the vessel.
This place covers:
Targets containing the nuclear fuel apt to generate nuclear fusion reactions under compression, e.g. pellets for irradiation by laser or charged particle beams.
This place does not cover:
Targets for producing nuclear reactions |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Lasers for target irradiation |
This place covers:
All the circuits and devices used in a nuclear fusion power plant for supplying energy to the plasma energizing systems.
This place does not cover:
Means for discharging superconducting storage windings | |
Systems for supplying RF to particle accelerators |
This place covers:
All the devices and systems used for irradiating fuel targets in an inertial confinement reactor (e.g. lasers), and the devices and systems using irradiation methods for measuring plasma parameters in nuclear fusion reactors.
This place does not cover:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangements for sustaining plasma by injection heating in laboratory systems |
This place covers:
Auxiliary equipments used for the construction, inspection, maintenance and repair of systems and components of nuclear fusion power plants.
This place covers:
Systems and components for producing energy by nuclear reactions not involving the generation of a thermonuclear plasma, e.g. fusion reactions.
This place does not cover:
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Cold fusion | Nuclear (fusion) reactions taking place at ordinary temperatures |
Thermonuclear fusion | Nuclear fusion reactions involving the generation of a plasma at extremely high temperatures(i.e. million degrees) |
This place covers:
Systems and methods for inducing fusion of hydrogen isotopes by diffusion in a host matrix, or reactions of hydrogen isotopes with the nuclei of a host matrix at ordinary temperatures.
This place covers:
Systems and methods for inducing fusion of hydrogen isotope nuclei by using the catalyzing properties of muons in a hydrogen isotope environment.
This place covers:
Systems and methods for promoting nuclear fusion at ordinary temperatures using a beam of particles reacting with other particles or with a target.
This place does not cover:
Conversion of elements by electromagnetic or particle irradiation |
This place covers:
Systems and methods for promoting nuclear fusion of a (gaseous, liquid or solid) target by subjecting it to pressure or shock waves.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Sonoluminescence |