CPC Definition - Subclass B03C
This place covers:
- Magnetic separation
- Separating dispersed particles from gases or vapour, e.g. air, by electrostatic effect
- Separating dispersed particles from liquids by electrostatic effect
- Separating solids from solids by electrostatic effect
- Separation by high-voltage electrical fields
This place does not cover:
Separating isotopes | |
Separating solid materials using liquids or using pneumatic tables or jigs | |
Separating solids from solids by sieving, screening, sifting or by using gas currents; Separating by other dry methods applicable to bulk material, e.g. loose articles fit to be handled like bulk material |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Filters making use of electricity or magnetism | |
Separating sheets from piles | |
Magnets or magnet coils per se |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
high-voltage | voltage of 1000V (RMS) or more for alternating current and 1500V or more for direct current |
This place covers:
Separation of particles out of a fluid or a stream of particles using magnetic effects.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Separation, e.g. filters in general | |
Processes for separating dispersed particles from gases or vapours by gravity, inertia or centrifugal forces | |
Combinations of cyclones with filters, for separating particles from gases or vapours | |
Processes for separation of gases or vapours or for recovering vapours of volatile solvents from gases by centrifugal force | |
Flotation; Differential sedimentation | |
Devices for separating or removing fatty or oily substances or similar floating material from water, waste water or sewage | |
Device in sewers for separating liquid or solid substances from sewage | |
Chemical analysis of biological material | |
Measuring, investigating or testing electric or magnetic properties of materials | |
Materials for magnets or magnetic bodies |
The following indexing codes are used:
- Magnetic separation of gases from gases, e.g. oxygen from air, is classified with indexing symbol B03C 2201/16.
- Magnetic separation of particles suspended in a liquid is classified with indexing symbol B03C 2201/18.
- Magnetic separation of bulk or dry particles in mixtures is classified with indexing symbol B03C 2201/20.
- Magnetic separation characterised by magnetic field, special shape or generation is classified with indexing symbol B03C 2201/22.
- Magnetic separation characterised by parts being designed to be removable for cleaning purposes is classified with indexing symbol B03C 2201/28.
- Magnetic separation used in or with vehicles is classified with indexing symbol B03C 2201/30.
This place covers:
Magnetic separation methods that use high gradient magnetic fields.
This place does not cover:
Magnetic separation device that uses a high gradient magnetic field acting directly on the substance being separated | |
High gradient magnetic separation acting on the medium |
This place covers:
Pretreatment specially adapted for magnetic separation by addition of magnetic adjuvants that do not cause an advanced chemical reaction with the particles to be separated.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Pretreatment specially adapted for magnetic separation by chemical treatment imparting magnetic properties to the material to be separated |
This place covers:
Magnetic separation devices that use high gradient magnetic fields, wherein matrix elements, e.g. of steel wool, are disposed within the magnetic fields.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Magnetic separation methods that use high gradient magnetic fields |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Matrix elements |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Superconductive coils for open gradient separators |
This place covers:
Component parts or auxiliary operations of high gradient magnetic separators characterised by the matrix elements, e.g. details about the construction of the magnetic matrix elements.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
High gradient separators having circulating matrix or matrix elements |
This place covers:
Magnetic separators characterised by the configuration of an unobstructed or open gap employed within the magnetic field, such that the gap lacks a matrix element.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
High gradient magnetic separators |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Details about the construction of the superconductive coil |
This place covers:
Magnetic separation in which either (a) the material to be separated or (b) the separated material is moved with cylindrical means, e.g. drums or discs.
This place does not cover:
Magnetic separation with material carried by travelling fields obtained by a rotating magnetic drum |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Cylindrical magnetic plugs and dipsticks |
This place covers:
Magnetic separation with cylindrical material carriers in which either (a) the magnets are moving during operation or (b) the magnets include movable pole pieces during operation.
This place covers:
Magnetic separation with magnets moving during operation and with material carriers in the form of belts, e.g. of cross-belt type, multiple belt carriers characterised by their mutual disposition or combinations of magnetic separating belts with material carrying belts.
Illustrative examples of subject matter classified in this place:
1. Cross belt magnetic separator

This example shows a cross belt magnetic separator having a main conveyor belt (6) and cross belts (21).
2. Multiple belt carriers

This example shows multiple belt carriers characterised by their mutual disposition in which magnetic bars (6) are moved by endless conveyor chains (5) and a set of conveyor chains (13) having drive scrapers (14) at an oblique angle with respect to the magnetic bars (6).
3. Combination of magnetic separating belts with material carrying belts
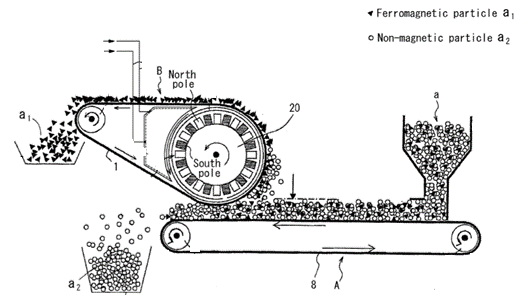
This example shows a combination of magnetic separating belts with material carrying belts in which a material carrying belt (8) is working in conjunction with another belt (1) that is magnetized by a magnetic roll (20).
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Devices whereby the material to be separated or the separated material is moved with cylindrical means |
This place does not cover:
Open gradient magnetic separators, i.e. separators in which the gap is unobstructed, characterised by the configuration of the gap |
This place covers:
Devices or methods for separating particles contained in a liquid by using magnetic plugs or dipsticks.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Lubricating systems characterised by the provision therein of lubricant venting or purifying means, e.g. of filters | |
Arrangements for purifying liquid fuel specially adapted for, or arranged on, internal-combustion engines, e.g. arrangements in the feeding system |
The following indexing codes are used:
- Magnetic separation for particles suspended in a liquid is classified with indexing symbol B03C 2201/18.
- Magnetic separation for use in medical or biological applications is classified with indexing symbol B03C 2201/26.
This place is used when the magnetic separation is part of a bigger process. However, documents disclosing the mere presence of a magnetic separation without details of the magnetic separator or of the magnetic separation process should not be classified in this place.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Sink-float separation using heavy liquids or suspensions |
This place covers:
Methods or devices using an electrostatic effect for separating dispersed particles from gases or vapours, e.g. devices that use electrostatic effects for filtering air.
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Exhaust or silencing apparatus for machines or engines having means for removing solid constituents of exhaust, using electric or electrostatic separators |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Domestic cleaning implements actuated by electrostatic attraction; Devices for cleaning same | |
Separation of gases or vapours; Recovering vapours of volatile solvents from gases; Chemical or biological purification of waste gases (e.g. engine exhaust gases, smoke, fumes, flue gases, aerosols) by electrostatic effects or by high-voltage electric fields | |
Cleaning by electrostatic means | |
Electric elements specially adapted for carrying off electrostatic charges from vehicles | |
Treatment of water, waste water, or sewage by electrochemical methods | |
Electrostatic machines | |
Carrying-off electrostatic charges in general |
When the electrostatic effect is not used for separating, it should not be classified here.
The following indexing codes are used:
- Electrostatic separation including cleaning of the device by burning trapped particles is classified with indexing symbol B03C 2201/12.
- Electrostatic separation for gas that is moved electro-kinetically is classified with indexing symbol B03C 2201/14.
- Electrostatic separation including measuring or calculating of parameters, e.g. efficiency, is classified with indexing symbol B03C 2201/24.
- Electrostatic separation for use in medical or biological applications is classified with indexing symbol B03C 2201/26.
- Electrostatic separation for use in or with vehicles is classified with indexing symbol B03C 2201/30.
- Electrostatic separation including checking the quality of the result or the well-functioning of the device is classified with indexing symbol B03C 2201/32.
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
ESP | electrostatic precipitator |
DEP | di-electrophoresis |
nDEP or pDEP | negative di-electrophoresis or positive di-electrophoresis |
This place covers:
Mechanical filtering or flow control before the actual ESP filter.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Combinations of electrostatic separators, e.g. in parallel or in series, stacked separators, dry-wet separator combinations | |
Mechanical filtering combined with the ESP filter | |
Controlling flow of gases or vapour in the ESP filter |
This place covers:
Adding water for the purpose of changing the characteristics of the gas mixture to be treated.
This place is used when the electrostatic separation is part of a bigger, specified process, e.g. part of a medical apparatus. However, documents should not be classified in this place when no (sufficient) details of the electrostatic separation are disclosed.
This place covers:
Mechanical filtering or flow control after the actual ESP filter.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Combinations of electrostatic separators, e.g. in parallel or in series, stacked separators, dry-wet separator combinations | |
Mechanical filtering combined with the ESP filter |
This place covers:
Devices wherein stationary tube electrodes are used, such as in a bundle of stationary tube electrodes.
This place covers:
Dry type plants or installations having external electricity supply for separating of dispersed particles from gases or vapour by electrostatic effect, characterised by the presence of stationary flat electrodes arranged with their flat surfaces at right angles to the gas stream, e.g. where the gas stream is forced to change direction to flow between flat electrodes or where the gas stream passes through porous electrodes.
The mere mentioning of separation between the ionizing and collecting stations does not justify classification in this place. The separation between the ionizing and collecting stations should be clearly illustrated or described.
This place does not cover:
Transportable units, e.g. for cleaning room air |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Separating particles from gases by gravity |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Separating particles from gases by centrifuges | |
Centrifuges in general | |
Selective separation of solid materials carried by, or dispersed in, gas currents using centrifugal force |
This place covers:
Mechanical filtering combined with the actual ESP filter.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Mechanical filtering before the actual ESP filter | |
Mechanical filtering after the actual ESP filter | |
Combinations of electrostatic separators, e.g. in parallel or in series, stacked separators, dry-wet separator combinations |
This place covers:
Devices where the added liquid (e.g. water) is not completely absorbed by the treated gas.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adding water for the purpose of changing the characteristics of the gas mixture to be treated | |
Liquid, or liquid-film, electrodes | |
Cleaning the electrodes, e.g. by washing |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Room air-conditioners having an electrostatic separating stage |
This place covers:
Flow control in the actual ESP filter.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Flow control before the ESP filter | |
Flow control after the ESP filter | |
Combinations of electrostatic separators, e.g. in parallel or in series, stacked separators, dry-wet separator combinations | |
Mechanical dry-type filtering, e.g. combined with the ESP filter |
This place covers:
The flow control is located at the entrance of the ESP
This place covers:
The flow control is located at the exit of the ESP
This place covers:
Particle charging or ionising stations in which particles are electrostatically charged for the purpose of separating them, e.g. using electric discharge, radioactive radiation or flames.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electrode constructions | |
Disinfection, sterilisation or deodorisation of air by ionisation | |
Air-conditioning systems applying an electrostatic field | |
Apparatus for generating ions to be introduced into non-enclosed gases | |
Ionising gases |
Indexing symbols B03C 2201/04 – B03C 2201/10 are used to describe the type of ionising electrode.
The following indexing codes are used:
- Ionising electrode wires are classified with indexing symbol B03C 2201/04.
- Ionising electrode needles are classified with indexing symbol B03C 2201/06.
- Ionising electrode rods are classified with indexing symbol B03C 2201/08.
- Ionising electrodes including two or more serrated ends or sides are classified with indexing symbol B03C 2201/10.
This place does not cover:
Liquid, or liquid-film, electrodes |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Devices wherein stationary tube electrodes are used, such as in a bundle of stationary tube electrodes | |
Collecting electrodes specially adapted for heat exchange with the gas stream |
This place covers:
Constructional details of a collecting-electrode where the collecting-electrode is a catch-space electrode used in separating dispersed particles from gases or vapor by electrostatic effect.
This place covers:
Details about the electrical power supply of the ESP, except the emergency control aspects.
This place does not cover:
Electricity supply or control systems for cleaning the electrodes |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Emergency control systems | |
Power supply for an electrostatic spraying apparatus |
This place does not cover:
Liquid, or liquid-film, electrodes |
This subgroup covers the cleaning of the electrodes, and also includes all details about cleaning the interior of the ESP.
The following indexing codes are used:
- Cleaning the device by burning of trapped particles is classified with indexing symbol B03C 2201/12.
- Parts designed to be removable for cleaning purposes is classified with indexing symbol B03C 2201/28.
- Measuring or calculating of parameters, e.g. efficiency, is classified with indexing symbol B03C 2201/24.
- Checking the quality of the result or the well-functioning of the device is classified with indexing symbol B03C 2201/32.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Control systems for applications of electricity supply techniques, e.g. electricity supply or control systems of the ESP |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Control systems for applications of electricity supply techniques, e.g. electricity supply or control systems of the ESP |
This place covers:
Devices or methods using a liquid where the purpose of the liquid is to clean the electrodes.
This place covers:
Details about the (mechanical) fixation of the electrodes (including the electrical isolators).
This place does not cover:
Electrode constructions |
This place covers:
Cleaning out collected particles that have already been removed from the electrodes or walls.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Cleaning of the electrodes |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electrostatic non-mechanical conveyors |
This place does not cover:
Centrifuges combined with other apparatus, e.g. electrostatic separators |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Settling tanks making use of electricity or magnetism, e.g. for flocculation or agglomeration of electric particles | |
Separation by electrophoresis, other than separation of solids, not fully covered by a single other group or subclass | |
Microreactors | |
Apparatus for the treatment of microorganisms or enzymes with electrical or wave energy, e.g. magnetism, sonic waves | |
Treatment of microorganisms or enzymes with electrical or wave energy, e.g. magnetism, sonic waves | |
Measuring or testing processes involving enzymes, nucleic acids or microorganisms, for methods of sampling, or inoculating or spreading a sample, and for methods of physically isolating intact microorganisms | |
Investigating or analysing materials by the use of electric, electro-chemical or magnetic means using electrophoresis | |
Analysis of biomaterial by electrical means |
The following indexing codes are used:
- Electrostatic separation, including measuring or calculating of parameters, e.g. efficiency, is classified with indexing symbol B03C 2201/24.
- Electrostatic separation for use in medical or biological applications is classified with indexing symbol B03C 2201/26.
- Electrostatic separation, including checking of the quality of the result or the well-functioning of the device, is classified with indexing symbol B03C 2201/32.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
electrostatic field or electrostatic effect | caused by electric charges that are either stationary or move very slowly (no induced magnetic forces) |
electrodynamic field or electrodynamic effect | caused by electric charges that are moving with high frequency, e.g. for creation of electromagnetic radiation from aerial or antenna |
separating | includes separation of particles from liquids as is conventionally understood, as well as the immobilisation, caging, translation or rotational motion of particles |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
ESP | electrostatic precipitator |
DEP | di-electrophoresis |
nDEP or pDEP | negative di-electrophoresis or positive di-electrophoresis |
This place covers:
Separating dispersed particles from liquids by electrostatic effect by using di-electrophoresis, or the motion of polarizable particles under the influence of an applied non-uniform electric field, with the force arising from the interaction of the field and the dipole moment induced in the particle.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Separator devices using di-electrophoresis in non-uniform electrostatic fields for separating dispersed particles from liquids | |
Separation by high-voltage electrical fields, not provided for in other groups of this subclass, such as separation of fluids from fluids by high-voltage electrical fields | |
Separation by electrophoresis, not fully covered by a single other group or subclass |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Dielectrophoresis, i.e. dielectric particles migrating towards the region of highest field strength for separating dispersed particles from liquids by electrostatic effect |
This place covers:
Devices for separating particles from fluids with electrodes arranged, such that an open-gradient electrostatic field is created.
Illustrative examples of subject matter classified in this place:
1. Electrode arrangement having an open-gradient electrostatic field
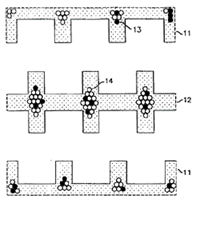
This example shows an electrode arrangement comprising interdigitated electrodes (11) and (12) that create an open-gradient electrostatic field.
2. Fluid filter having a dielectrophoretically active electrode element

This example shows a fluid filter that includes a dielectrophoretically active electrode element comprising a coiled substrate (200) upon which a pair of electrode arrays (201) are disposed.
This place covers:
Illustrative examples of subject matter classified in this place:
1. Electrode arrangement having a time-varying electric field for movement of a biological cell
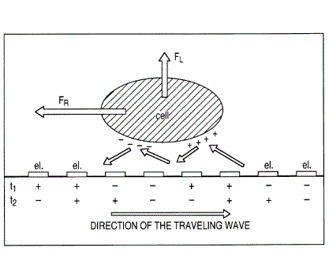
This example shows an electrode arrangement to which a time-varying electric field is applied for movement of a biological cell when polarised by the electric field.
2. Response of particles exposed to a travelling wave

This example shows the response of particles exposed to a travelling wave field with a phase shift in between neighbouring electrodes.
This place covers:
Separating solids from solids by electrostatic effect, e.g. separating particles.
This place covers:
Electrostatic separation not provided for in any single one of the other main groups of this subclass, e.g. other types of electrostatic separation, except for electrostatically separating liquids from liquids by high-voltage electrical fields.
Examples of places in relation to which this place is residual:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electro-statically separating liquids from liquids by high-voltage electrical fields, not provided for in other groups of this subclass |
This place covers:
This group is used for electrostatically separating liquids from liquids by high-voltage electrical fields, not provided for in other groups of this subclass.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Separation of liquids with coalescers | |
Separation of liquids from each other by electricity | |
Filters i.e. particle separators or filtering processes specially modified for separating dispersed particles from gases or vapours including coalescing means for the separation of liquid | |
Refining of hydrocarbons oils by electric or magnetic mean |
The following indexing code is used:
Electrostatically separating liquids from liquids, is classified with indexing symbol B03C 2201/02.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
high-voltage | voltage of 1000V (RMS) or more for alternating current and 1500V or more for direct current |