CPC Definition - Subclass G03B
This place covers:
Details not specific to the following types of photographic apparatus: cameras, projectors, or printers
- Film-strip handling
- Focusing arrangements
- Adjustment of optical system relative to image or object surface, other than for focusing
Details of cameras
- Control of exposure by setting shutters, diaphragms, or filters separately or conjointly, in particular remote control
- Exposure-making shutters
- Diaphragms
- Filters or other obturators specially adapted for photographic purposes
- Optical viewfinders
- Devices used in connection with camera focusing, including focusing aids or autofocus systems
- Special procedures or apparatus for taking photographs
Photographic apparatus
- Cameras
- Projectors or projection-type viewers, or their details
- Devices for changing pictures in viewing apparatus or projectors
- Viewers giving motion-picture effects by persistence of vision
- Photographic printing apparatus, or their details
- Combinations of cameras, projectors, or photographic printing apparatus with nonphotographic non-optical apparatus
- Camera modules (i.e. integrated lens and imaging units), specially adapted for embedding in other devices
Photographic techniques and processes
Processes – and solely those processes – characterised by the use or manipulation of apparatus classifiable in this subclass, in particular
- Associated working of cameras or projectors with sound-recording or -reproducing means
- Colour photography, other than mere exposure or projection of a colour film
- Stereoscopic photography
- Panoramic or wide-screen photography
- Photographing extended surfaces
- Photographing internal surfaces
- High-speed photography
- Other special photographic techniques
- Obtaining records using waves other than optical waves, or visualising such records by using optical means
- Testing correct operation of photographic apparatus or parts thereof
Photographic processes are covered by subclass G03B when the process relates to the exposure of the photosensitive medium, in order to generate the latent image, whereas subclass G03C covers the photographic processes that involve a chemical transformation of the photosensitive medium, such that the latent image is transformed into a visible and permanent record.
The printing of a record obtained via the processes or apparatus of subclass H04N is classified in class B41 if the only chemical processing involved consists in the after-treatment of ink applied to the recording surface but is classified in subclass G03B if a latent image is produced.
Subclass H04N covers the electronic image capturing apparatus or processes where an electronic image sensor converts an optical image into electrical signals, e.g. by controlling the electronic image sensor or by processing the electrical signals.
Subclass H04N covers the electronic image projection apparatus or processes where an electronic image modulator converts electrical signals into an optical image, e.g. by controlling the electronic image modulator or by processing the electrical signals.
Therefore, when the following subject matter is classified in this subclass, it is desirable to also classify it in subclass H04N, when some aspects are considered of interest for search purposes:
- Digital still cameras, or their details
- Projectors or projection-type viewers using an electronic spatial light modulator, or their details
- Video cameras, CCTV cameras, surveillance cameras and camcorders, or details thereof
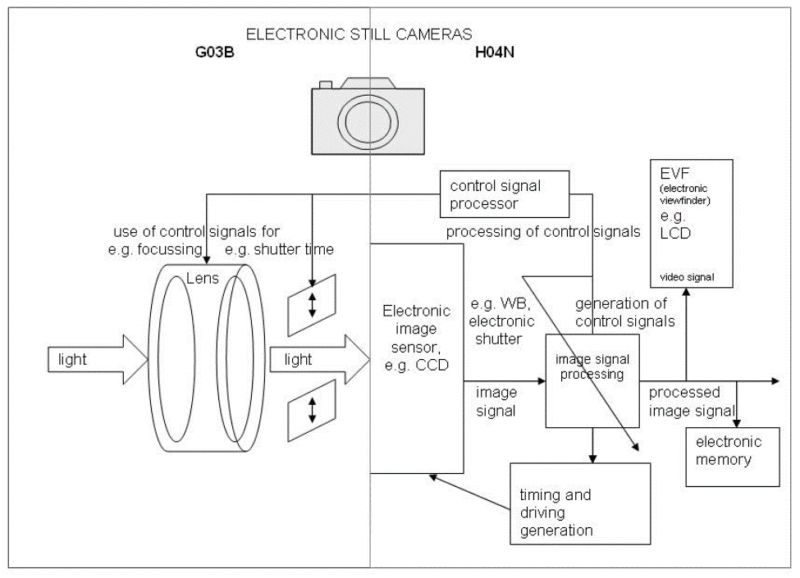
In the above image, elements on the left side correspond to G03B (e.g. light, use of control signals for focusing and shutter time). Elements on the right side correspond to H04N (e.g. control signal processor, processing of control signals, electronic image sensor, electronic shutter, generation of control signals, image signal processing, timing and driving generation, EVF, LCD, processed signal memory, and electronic memory).
Thus, in G03B aspects of apparatus or methods for taking photographs using an electronic image sensor [EIS] for image capture are classified insofar as they correspond to those of said apparatus or methods for taking photographs using light sensitive film, i.e. insofar not peculiar to the presence or use of the EIS, e.g. mounting of optical elements or flashes, and their related controls insofar they are not peculiar to the presence of the EIS, e.g. exposure, focus, (opto-) mechanical motion blur (anti-shake);
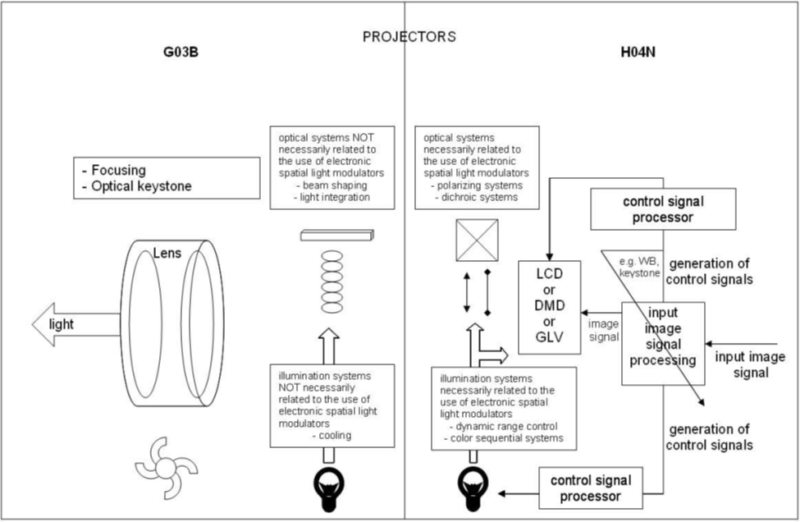
In G03B, aspects of apparatus or methods for projecting or viewing images using an electronic spatial light modulator [ESLM] are classified insofar as they correspond to those of said apparatus or methods for projecting or viewing images using film stock, photographic film or slides, i.e. insofar as not peculiar to the presence of the ESLM, e.g. mounting of optical elements not peculiar to the presence of the ESLM, and their related controls not peculiar to the presence of the ESLM, e.g. cooling, beam shaping, optical keystone correction.
As far as processes are concerned, only processes characterised by the use or manipulation of apparatus classified in G03B.
This place does not cover:
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by photographical inspection | |
Objective-type instruments for examining the eyes specially adapted for eye photography | |
Photographic composing devices | |
Photogrammetry; Photographic surveying | |
Recording indications of measuring instruments by photographic means | |
Indicating the weight by photographic recording | |
Photometry using photographic effects | |
Measuring linear or angular speed using photographic means; Measuring differences of linear or angular speeds using photographic means | |
Photographic dosimeters | |
Microscopes arranged for photographic purposes or projection purposes | |
Arrangements for producing a permanent visual presentation of the output data by photographic printing | |
Photographic arrangements structurally combined with discharge tubes or lamps | |
Photographic arrangements structurally combined with cathode-ray tubes or electron-beam tubes | |
Photographic arrangements structurally combined with discharge tubes with provision for introducing objects or material to be exposed to the discharge | |
Particle spectrometers or separator tubes with detection performed by photographic film | |
Projectors or projection-type viewers using an electronic spatial light modulator | |
Video cameras; Digital still cameras |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Photographic exposure meters | |
Adjusting means for lenses adapted for automatic focusing | |
Systems for automatic generation of focusing signals | |
Means for focusing of apparatus for photomechanical production of textured or patterned surfaces | |
Image data processing, in general | |
Information storage based on relative movement between record carrier and transducer; Static stores | |
Transforming light or analogous information into electric image information | |
Transforming X-rays into electric image information | |
Transforming infrared radiation into electric image information | |
Processing or use of electrical image signals from the EIS for the generation of camera control signals. e.g. focusing, exposure control, electronic blur correction, display in electronic viewfinder | |
Transforming light into electric information using solid-state image sensors | |
Optical elements or arrangements associated with solid state imager structures; |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Photography | Process of recording pictures by means of capturing light on a light-sensitive medium, e.g. silver halide based chemical or an electronic image sensor. Light patterns reflected or emitted from objects expose such a light sensitive medium during a timed exposure, usually through a photographic lens in a device known as a camera |
Camera | Apparatus or arrangements for taking photographs |
Projector | Device displaying image information by projection of light patterns, usually through an optical lens, wherein the light patterns are generated by illuminating an image, e.g. film or slide, or by converting an electric image signal into an optical signal using an electronic spatial light modulator |
EIS | Electronic image sensor: optoelectronic transducer, converting optical image information into an electrical signal susceptible of being processed, stored, transmitted or displayed |
Additional sensor | Sensor, other than the electronic image sensor, used for controlling a camera |
ESLM | Electronic spatial light modulator: optoelectronic transducer converting electric signals representing image information into optical image information |
Record | Photographs or any other kind of latent, directly-visible or permanent storage of pictorial information, which consist of an imagewise distribution of a quantity, e.g. an electric charge pattern, recorded on a carrier member |
Optical | Applies to visible light but also to ultraviolet radiation or infrared radiation |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
AE | Automatic Exposure |
AF | Auto Focus |
APS | Advanced Photographic System |
DEP | Double Exposure Prevention |
DSLR | Digital Single Lens Reflex Camera |
EVF | Electronic Viewfinder |
OVF | Optical Viewfinder |
SLR | Single Lens Reflex Camera |
This place covers:
Mechanical and electromechanical details of driving and guiding a focusing lens or other optical elements in photographic devices.
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Focusing aids for cameras | |
Means for focusing for cameras | |
Means for automatic focusing of projectors or projection-type viewers | |
Means for automatic focusing of photographic printing apparatus or copying cameras |
This place covers:
Mechanical and electromechanical details of driving and guiding a power operated focusing lens or other optical elements for focusing .
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Means for automatic focusing of projectors or projection type viewers | |
Means for automatic focusing of photographic printing apparatus or copying cameras |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Algorithms, control systems and user interfaces for performing autofocusing and for generating focusing signals in photographic cameras as long as the focusing signal is not generated in the main electronic image sensor | |
Means for automatic focusing of projectors or projection type viewers | |
Means for automatic focusing of photographic printing apparatus or copying cameras | |
Driving means for the movement of one or more optical elements | |
Motorized focusing of fixed focus lenses in general | |
Motorized focusing of variable focus lenses in general | |
Systems for automatic generation of focusing signals in general | |
Algorithms, control systems and user interfaces for performing autofocusing and for generating focusing signals in photographic cameras based on image signal provided by the main electronic image sensor |
This place does not cover:
Mechanism for delaying opening of shutter separate from shutter |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Optical filters per se |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Accessories in general |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Hoods or caps for eliminating unwanted light from lenses, viewfinders or focusing aids | |
Reflex cameras with single objective and a movable reflector or a partly-transmitting mirror | |
Cameras with paired lenses, one of which forms image on photographic material and the other forms a corresponding image on a focusing screen | |
Optical rangefinders | |
Automatic focusing in general | |
Systems for automatic generation of focusing signals | |
Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source | |
Focus control based upon image signals from electronic image sensors |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Viewfinders per se | |
Electronic viewfinders |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Zoom viewfinders per se |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
This place covers:
Algorithms, control systems and user interfaces for performing autofocusing and for generating focusing signals in photographic cameras as long as the focusing signal is not generated in the main electronic image sensor.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Mechanical and electromechanical details of arrangements for focusing | |
Mechanical and electromechanical details of driving and guiding a power operated focusing lens or other optical elements for focusing | |
Systems for automatic generation of focusing signals in general | |
Algorithms, control systems and user interfaces for performing autofocusing and for generating focusing signals in photographic cameras based on image signal provided by the main electronic image sensor |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Functional features or details of lighting devices or systems thereof; Structural combinations of lighting devices with other articles, not otherwise provided for |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Control of exposure in accordance with both the intensity of the flash source and the distance of the flash source from object, e.g. in accordance with "guide number" of flash bulb and the focusing of the camera | |
Testing correct operation of photographic apparatus or parts thereof, e.g. flash apparatus | |
Light sources using charges of combustible material | |
Circuit arrangements for light sources using a charge of combustible material |
This place covers:
e.g. flash units without mechanical connection to the camera
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Discharge lamps | |
Circuit arrangements or apparatus for igniting or operating discharge lamps |
This place does not cover:
High-speed photography |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Plates or blocks in which tracks of nuclear particles are made visible by after treatment, using photographic emulsion |
This place does not cover:
Lens barriers, covers, shields (for retractable lenses) if not integral part of camera body |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Indicating depth of field |
This place does not cover:
Of film strips |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Counting mechanisms |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Microscopes | |
Telescopes |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Processing apparatus |
This place covers:
external battery compartments, support of camera body
This place does not cover:
Camera cases |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Lens caps | |
Camera tripods | |
Stands or trestles as support for apparatus or articles placed thereon | |
Means for attachment of apparatus allowing quick-release | |
Movement that the support can allow for the object to be supported | |
Tripods | |
Monopod or tripod having a central telescopic column | |
Tripods with telescopic legs | |
Means for supporting on, or holding steady relative to, a person, |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Details of cameras or camera bodies;Accessories therefor |
This place covers:
e.g. cameras with a (movable) ground glass screen.
This place does not cover:
Plate or cut-film cameras with provision for alternative use with roll film |
This place does not cover:
Motion-picture cameras with non-intermittently running film |
This place does not cover:
Devices for changing pictures |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Optical distortion correction, e.g. keystone | |
Viewers, other than projection viewers, giving motion-picture effects by persistence of vision, e.g. zoetrope | |
Photographic printing apparatus | |
Tables specially adapted to be used with domestic photographic projectors | |
Lighting devices or systems producing a varying lighting effect | |
Optical projection comparators | |
Interactive projectors (whiteboards) with input means to control the projection | |
Television systems' projection arrangements for image reproduction | |
Electronic correction of distortions, e.g. video signal processing | |
Laser projectors using scanning devices | |
Projectors peculiar to the use of an electronic spatial light modulator |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Projection screens |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Condensers | |
Microscope condensers |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Light pointers |
This place does not cover:
Means for fixing the film on the axis of a reel or spindle | |
Means for fixing the film on the periphery of a reel |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Holders for containing light sensitive material and adapted to be inserted within the camera, e.g. cassettes specially adapted for motion picture film |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Film-strip handling of general interest for cameras, projectors or printers |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Mechanical linking of shutter and intermittent feed for altering frame speed or regulating constancy of film speed |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Tables specially adapted to be used with domestic photographic projectors |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Film-strip handling of general interest for cameras, projectors or printers | |
Telescopes, e.g. binoculars; Periscopes; Instruments for viewing the inside of hollow bodies | |
Viewing or reading apparatus |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Picture | Any flat representation, whether transparent or not, e.g. produced by photography, writing, or printing |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
High-speed photography |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Film-strip handling of general interest for cameras, projectors or printers |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Controlling or varying light intensity, spectral composition, or exposure time in photographic printing apparatus |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Processing apparatus per se |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Gas processing apparatus |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Heat development apparatus |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Systems for automatic generation of focusing signals |
This place does not cover:
Means for automatic focusing for projection printing apparatus |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Projection optics for slit exposure |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Producing marks on the film in cameras |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Projection optics for electro-photographic copiers |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Registration or positioning of originals, masks, frames, photographic sheets or textured or patterned surfaces in photo-mechanical production of textured or patterned surfaces, e.g. of integrated circuits |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Controlling or varying light intensity, spectral composition, or exposure time in photographic printing apparatus |
This place does not cover:
Automatic registration or positioning of originals with respect to each other or the photosensitive layer |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Apparatus relating to the handling of copy material for electrographic processes using a charge pattern |
This place does not cover:
Automatic registration or positioning of originals with respect to each other or the photosensitive layer |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Apparatus relating to the handling of originals for electrographic processes using a charge pattern |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Exposure meters per se | |
Control of light, e.g. intensity, colour, phase |
This place does not cover:
Combinations with flash apparatus |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes | |
Arrangements specially adapted for eye photography | |
Theodolites combined with cameras | |
Structural combination of reactor core or moderator structure with viewing means, e.g. with television camera, periscope, window | |
Optical or photographic arrangements structurally combined with the vessel | |
Optical or photographic arrangements structurally combined | |
Optical or photographic arrangements associated with the tube |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Time-pieces combined with other articles which do not interfere with the running or time-keeping of the time-piece |
G03B 29/00 covers constructional details of the combination of cameras with other non-optical apparatus. On the other hand, G03B 30/00 covers the camera modules themselves, which are to be embedded in other devices.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Optical viewing arrangements for vehicles | |
Mounting of cameras operative during drive; Arrangement of controls thereof relative to the vehicle | |
Mounting of lenses in general | |
Mechanisms for focusing or varying magnification | |
Miniaturized objectives characterized by the optical design | |
Television cameras |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Cinematographic processes of taking pictures or printing combined with sound-recording | |
Record carriers characterised by the selection of the material and comprising cinematographic film or slide with integral magnetic track |
This place does not cover:
Stereoscopic colour photography |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Printing apparatus | G03F35/00 |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Colour photography using lenticular screens integral with film |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Colour photography using lenticular screens integral with film |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Panoramic or wide-screen photography | |
Photogrammetry |
This place does not cover:
Automatic registration or positioning of originals with respect to each other or the photosensitive layer |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes |
This place does not cover:
Associated working of cameras or projectors with sound-recording or -reproducing means | |
Colour photography, other than mere exposure or projection of a colour film | |
Stereoscopic photography | |
Panoramic or wide-screen photography;Photographing extended surfaces, e.g. for surveying;Photographing internal surfaces, e.g. of pipe | |
High-speed photography |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Investigating or analysing materials using electromagnetic radiation, other than infrared, visible or ultraviolet radiation, e.g. microwaves, or particles | |
Investigating or analysing materials by the use of ultrasonic, sonic or infrasonic waves; Visualisation of the interior of objects by transmitting ultrasonic or sonic waves through the object | |
Radar or analogous systems specially adapted for mapping or imaging | |
Sonar systems specially adapted for mapping or imaging | |
Holography |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Circuit arrangements for obtaining a series of X-ray photographs or for X-ray cinematography |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Controlling or varying light intensity in photographic printing apparatus by transforming the picture information intermediately into electrical signals |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Apparatus for radiation diagnosis, applications or adaptations for dentistry | |
Individual packages for X-ray film, e.g. for dental applications |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Diffraction optics systems using spatial filters; | |
Optics for phase object visualising |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring specific variables |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Time-interval measuring |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Imaging systems in general using optical elements for stabilisation of the lateral and angular position of the image |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Control of cameras for stable pick-up of the scene |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Mountings for lenses with mechanism for focusing by relative axial movement of several lenses |