CPC Definition - Subclass F01B
This place covers:
Machines or engines, in general or of positive-displacement type.
This place does not cover:
Rotary-piston or oscillating-piston machines or engines | |
Non-positive-displacement machines or engines, e.g. steam turbines | |
Internal-combustion engines | |
Combustion-product engine plants | |
Machines or engines, other than of positive-displacement type, for liquids | |
Positive-displacement engines driven by liquids | |
Wind motors | |
Positive-displacement machines for liquids | |
Rotary-piston, or oscillating-piston, positive-displacement machines for liquids |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Steam engine plants | |
Cyclically operating valves for machines or engines | |
Lubricating of machines or engines in general | |
Pumps for liquids or elastic fluids | |
Crankshafts, crossheads or connecting-rods | |
Flywheels | |
Gearings for interconverting rotary motion and reciprocating motion in general | |
Pistons, piston rods or cylinders, for engines in general |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
engine | a device for continuously converting fluid energy into mechanical power, thus, this term includes, for example, steam piston engines or steam turbines, per se, or internal-combustion piston engines, but it excludes single-stroke devices. |
machine | a device which could equally be an engine and a pump, and not a device which is restricted to an engine or one which is restricted to a pump. |
pump | a device for continuously raising, forcing, compressing, or exhausting fluid by mechanical or other means. Thus, this term includes fans or blowers. |
positive displacement | the way the energy of a working fluid is transformed into mechanical energy, in which variations of volume created by the working fluid in a working chamber produce equivalent displacements of the mechanical member transmitting the energy, the dynamic effect of the fluid being of minor importance, and vice versa. |
non-positive displacement | the way the energy of a working fluid is transformed into mechanical energy, by transformation of the energy of the working fluid into kinetic energy, and vice versa. |
oscillating-piston machine | a positive-displacement machine in which a fluid-engaging work-transmitting member oscillates. This definition applies also to engines and pumps. |
rotary-piston machine | a positive-displacement machine in which a fluid-engaging work-transmitting member rotates about a fixed axis or about an axis moving along a circular or similar orbit. This definition applies also to engines and pumps. |
rotary piston | the work-transmitting member of a rotary-piston machine and may be of any suitable form, e.g., like a toothed gear. |
free piston | a piston of which the length of stroke is not defined by any member driven thereby. |
cylinders | positive-displacement working chambers in general. Thus, this term is not restricted to cylinders of circular cross-section. |
main shaft | the shaft which converts reciprocating piston motion into rotary motion or vice versa. |
plant | an engine together with such additional apparatus as is necessary to run the engine. For example, a steam engine plant includes a steam engine and means for generating the steam. |
working fluid | the driven fluid in a pump or the driving fluid in an engine. The working fluid can be in a compressible, gaseous state, called elastic fluid, e.g. steam; in a liquid state; or in a state where there is coexistence of an elastic fluid and liquid phase. |
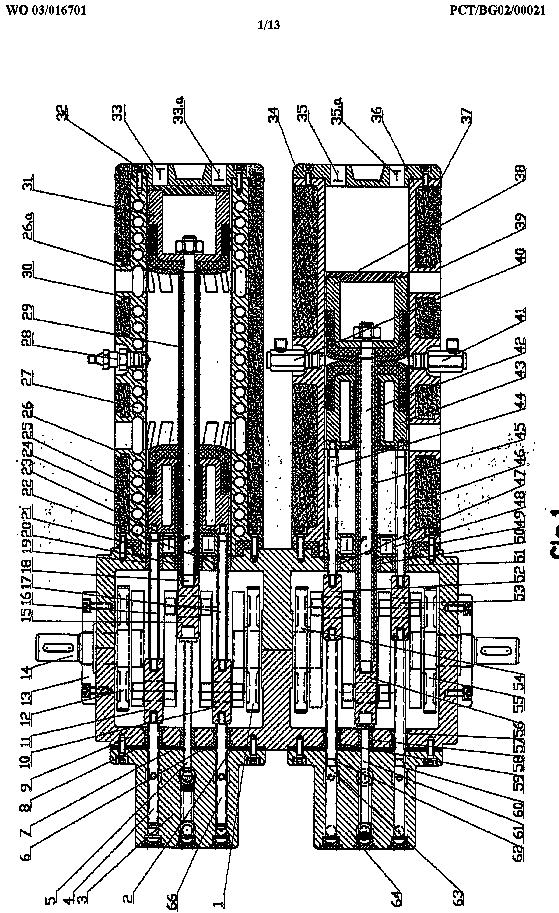
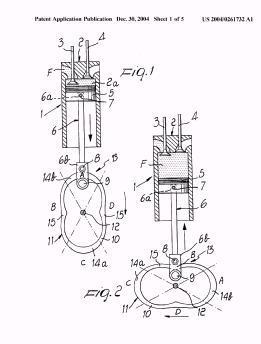
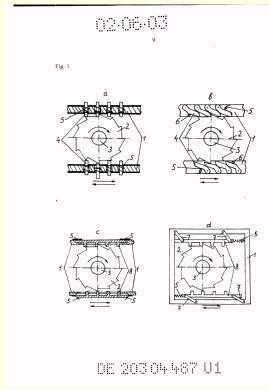
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 1/0603
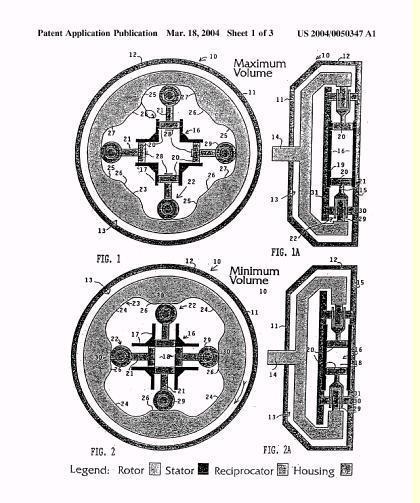
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 1/062
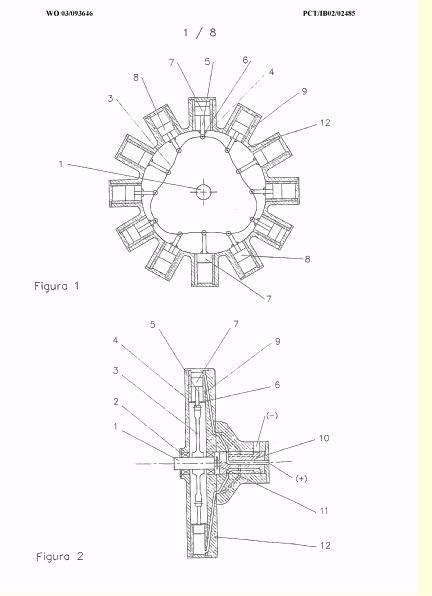
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Disengagement of connections between pistons and main shafts |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Combinations of two or more machines or engines |
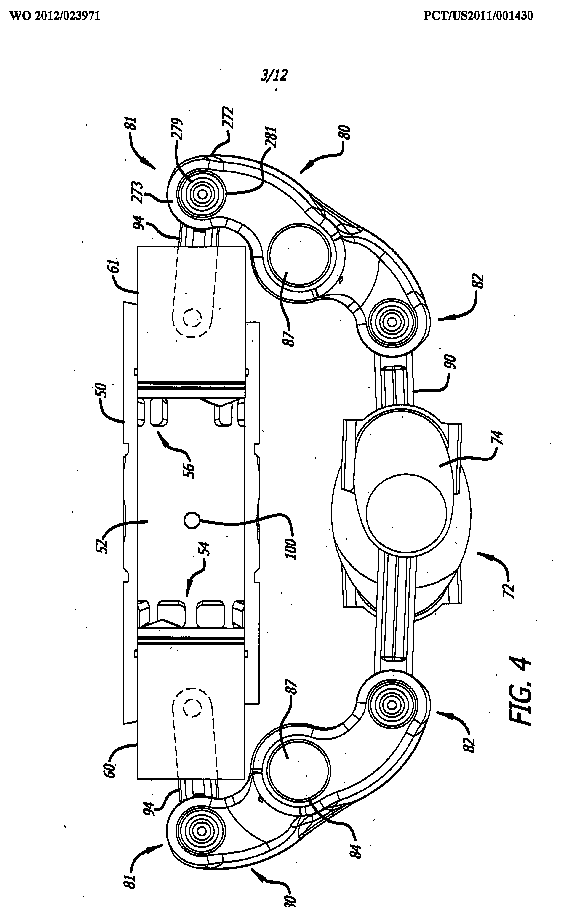
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 3/0002
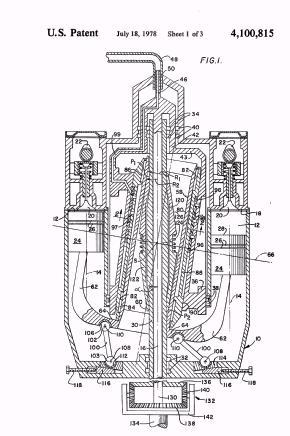
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 3/0005
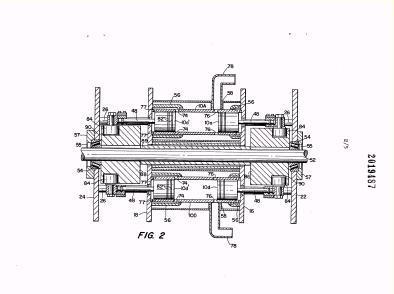
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 3/0008
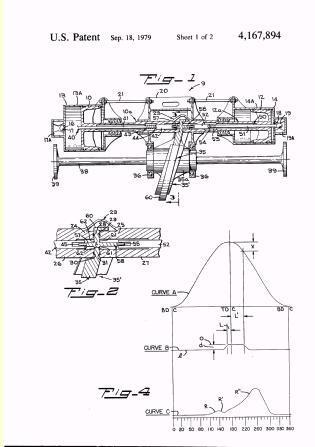
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 3/0011
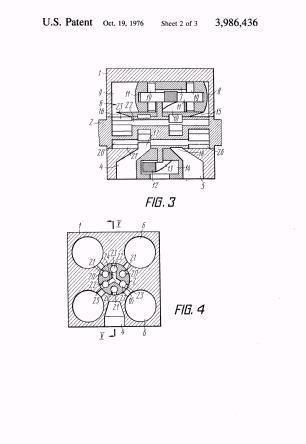
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 3/0014
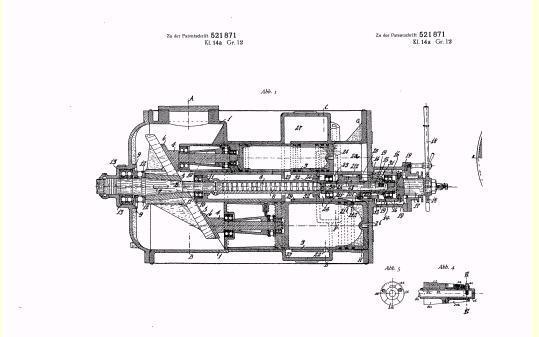
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 3/0032
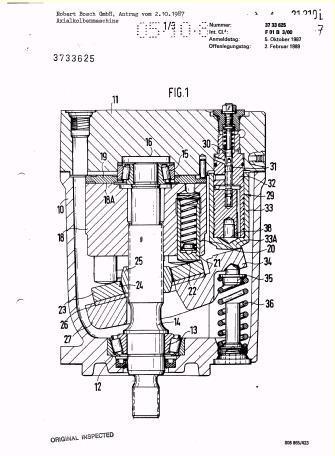
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 3/0038
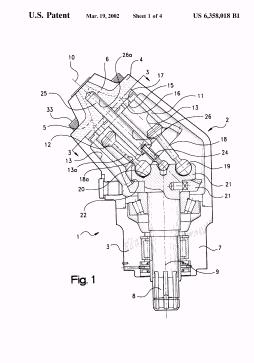
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 3/0041
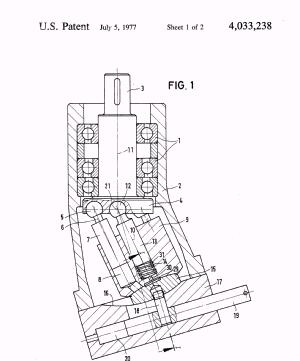
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 3/0047
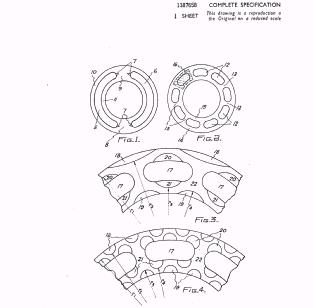
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 3/005
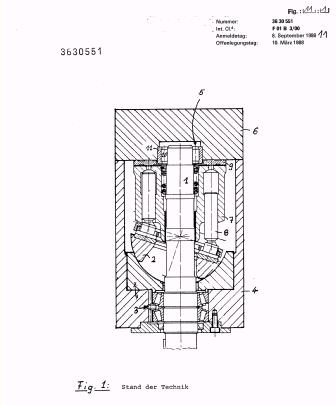
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 3/0052
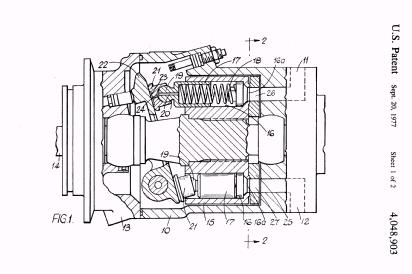
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 3/0061
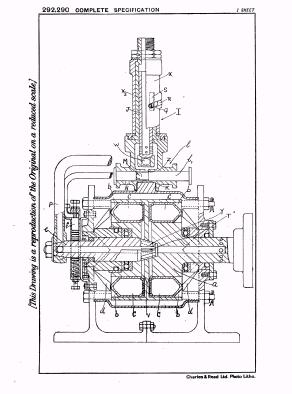

Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 3/007
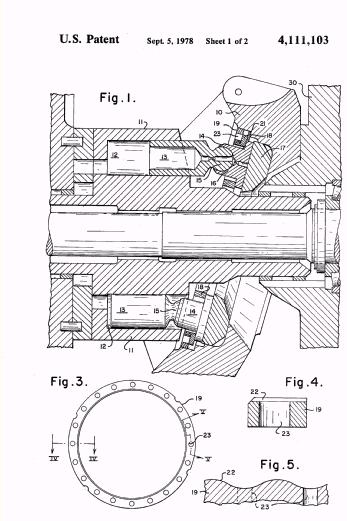
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 3/0076
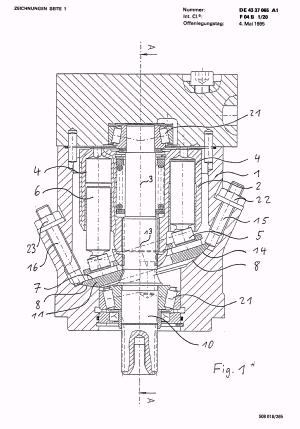
This place covers:
Reciprocating-piston machines or engines with cylinder axes coaxial with, or parallel or inclined to, main shaft axis, wherein the pistons rotate (spin) about their longitudinal axis as they reciprocate.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this place:

Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Piston motion being transmitted by curved surfaces |
This place covers:
Piston motion being transmitted by curved surfaces, e.g. by cams or grooves.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this place:

Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 3/045
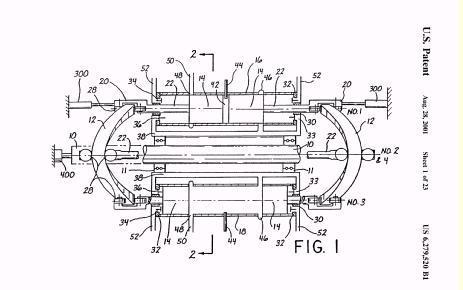
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 3/103
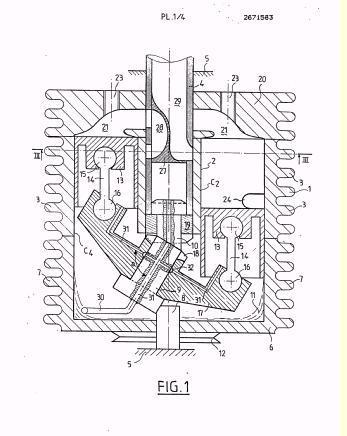
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 3/104
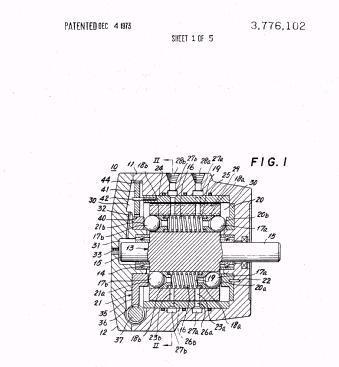
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 3/106
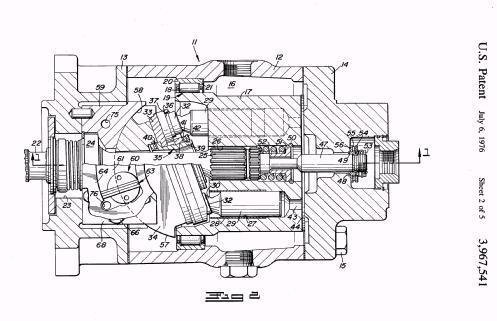
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 3/108
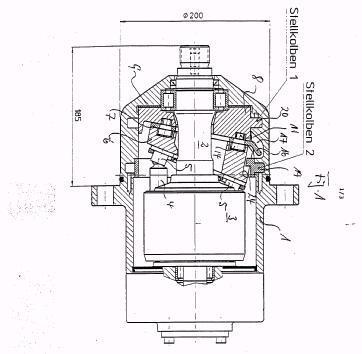
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this place:

Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Control of working-fluid admission or discharge by changing inclination of the swash plate |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 5/003
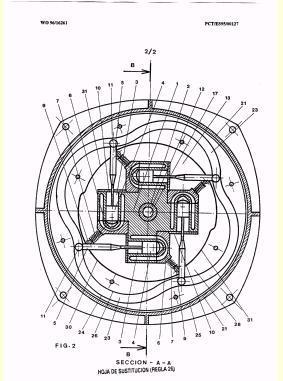
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 5/006
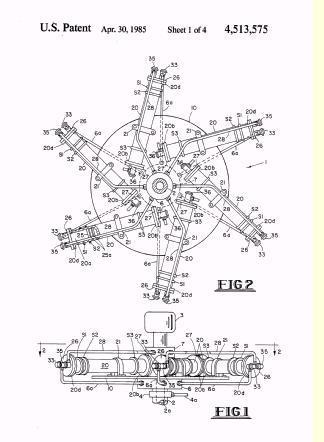
This place does not cover:
Coaxial cylinders in opposite arrangement relative to main shaft |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 7/00

This place covers:
Reciprocating-piston machines or engines characterised by connections between pistons and main shafts and not specific to groups F01B 1/00 - F01B 7/00, e.g. when no recognisable crank shaft is present or the main shaft is a cam shaft.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this place:

Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Connections disengageable during idling |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 9/023
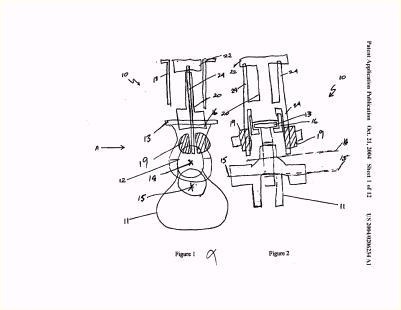
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 9/042

Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 9/047
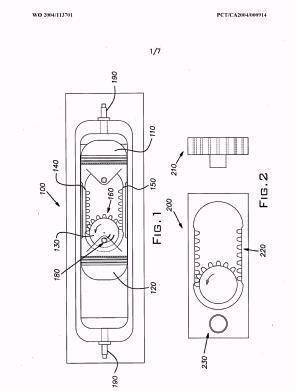
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 11/001
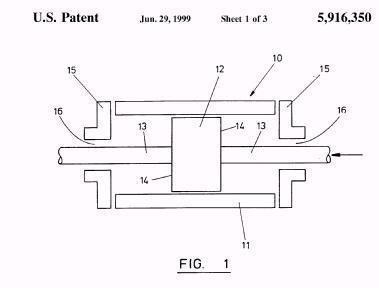
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 11/002
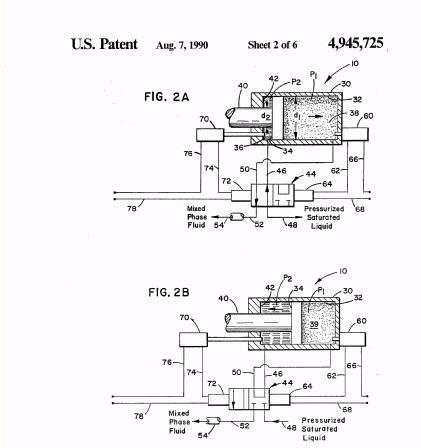
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 11/004
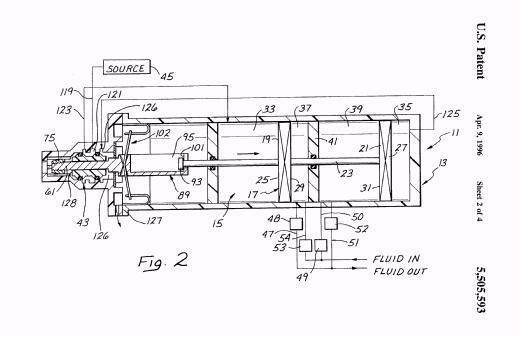
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 11/006
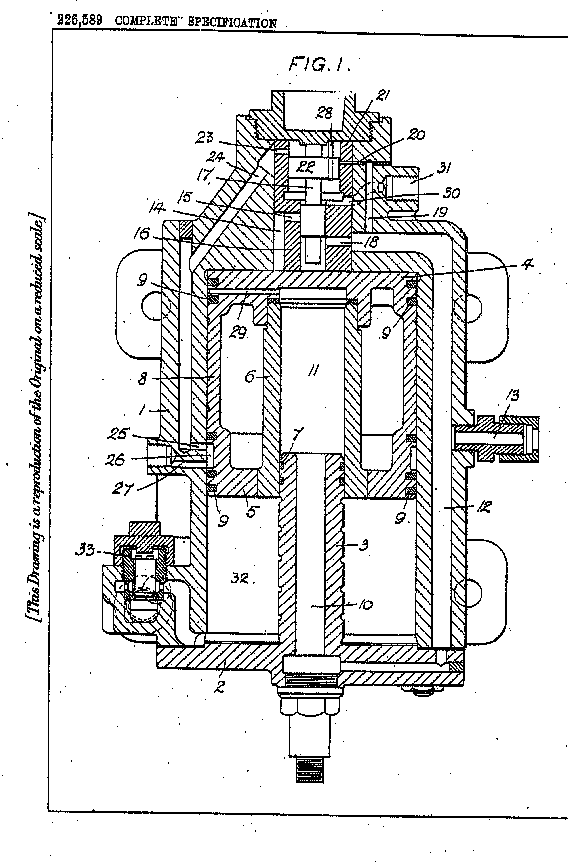
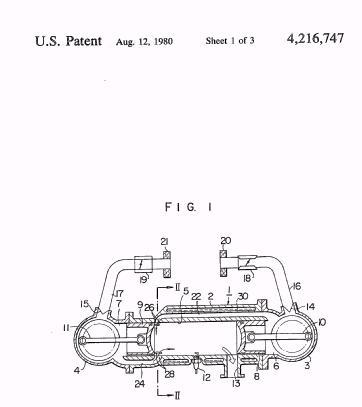
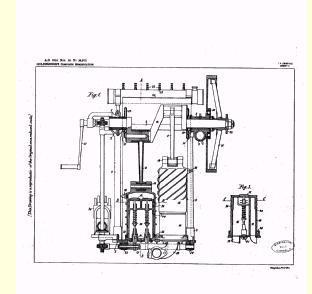
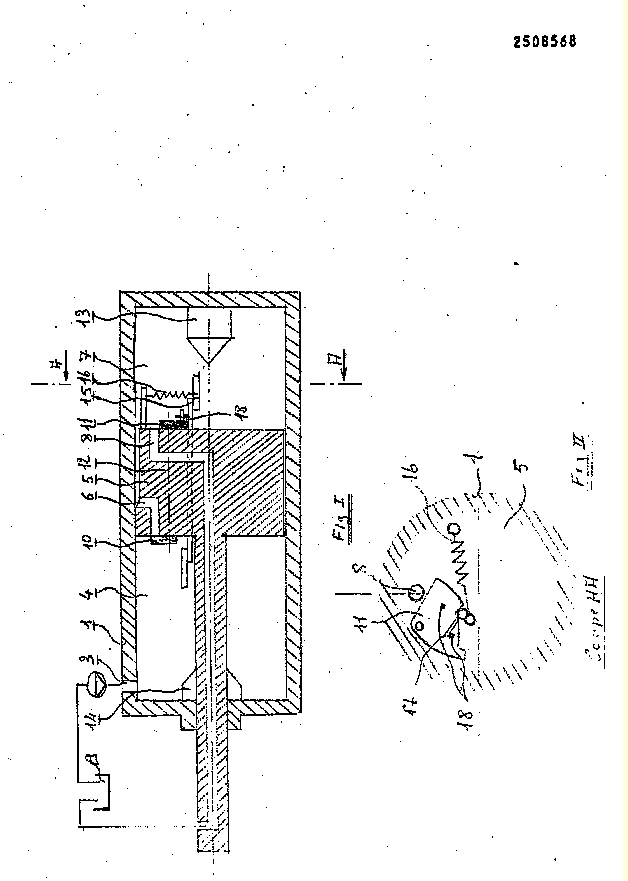
"...the steam supplied through the inlet 13 and the passage 12 enters the port 18, and acting upon the 1 upper face of the element 4 of the double piston (4,5), causes the latter to move downwards against the opposing action of the steam continuously supplied to the space 11...
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 11/007
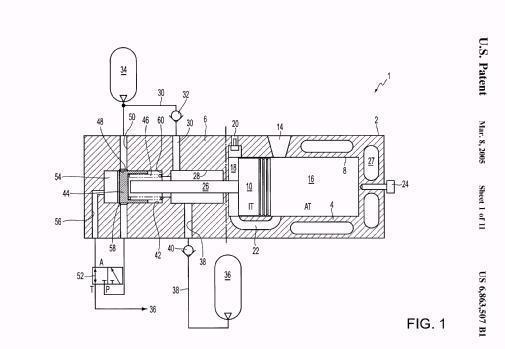
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 11/008
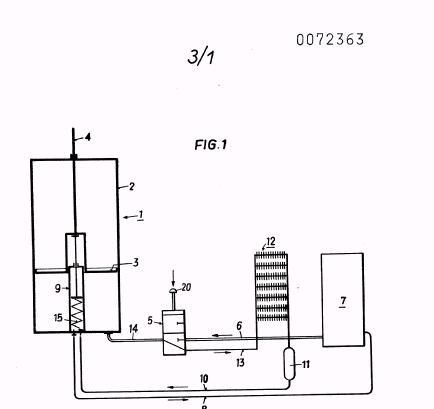
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 11/009
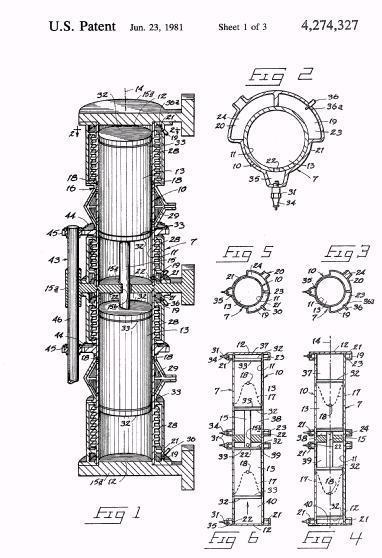
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 11/02
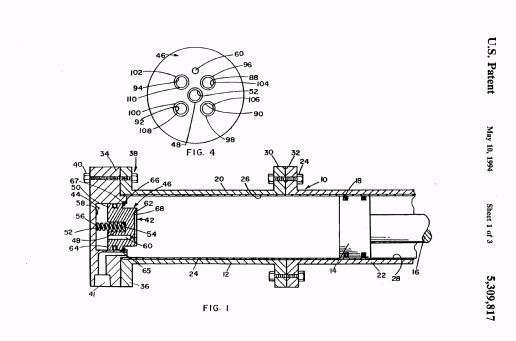
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this place:

Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Engines combined with pumps |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 11/06
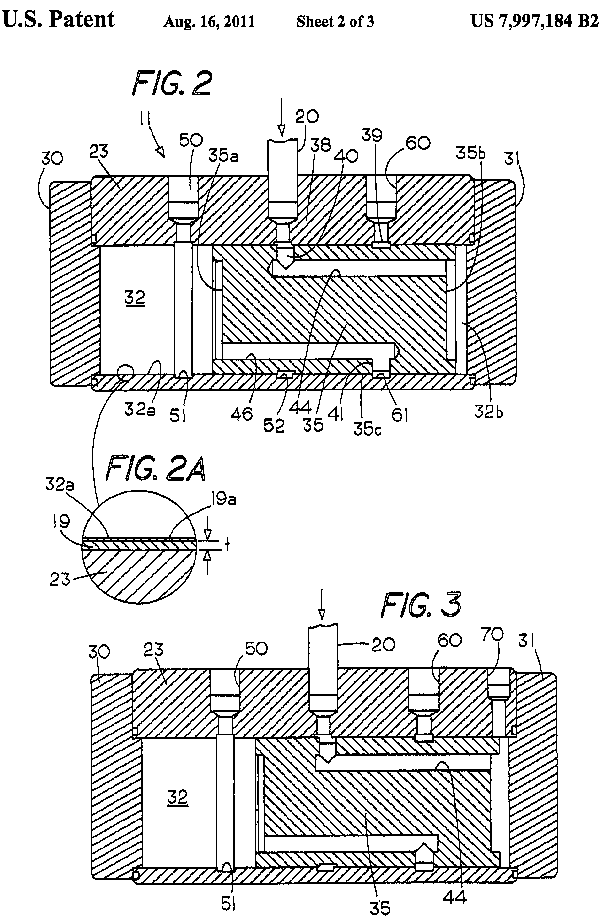
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this place:

Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Equalising or cushioning devices |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Machines or engines of flexible-wall type |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 13/02
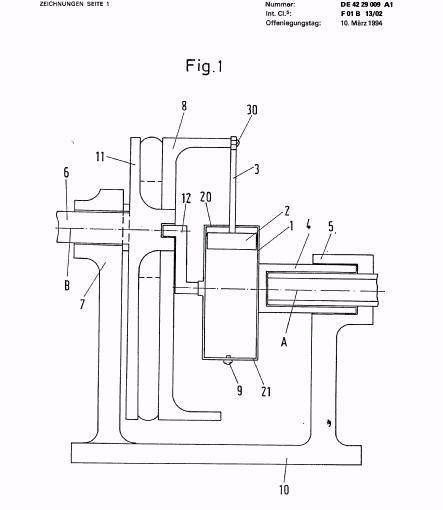
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this place:

Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Reciprocating-piston machines or engines with cylinder axes coaxial with, or parallel or inclined to, main shaft axis having rotary cylinder block |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 13/045
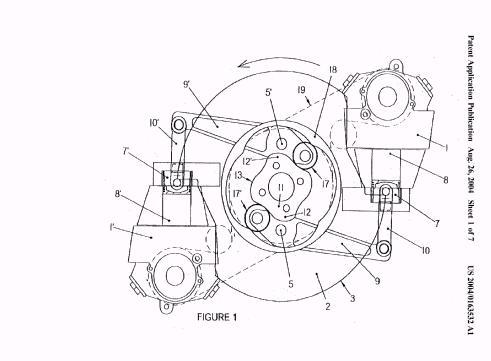
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 13/061
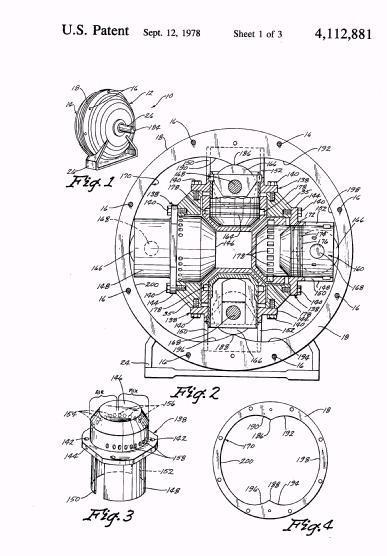
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 13/068
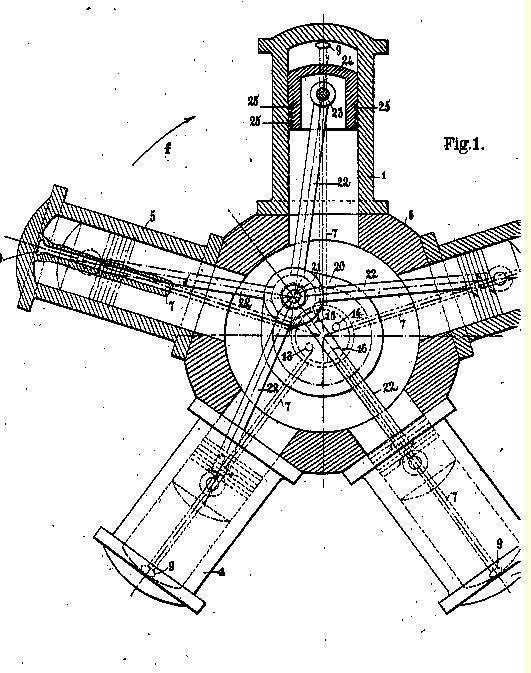
This place covers:
Reciprocating-piston machines or engines with movable cylinders other than provided for in group F01B 13/00, e.g. reciprocating-piston machines or engines having reciprocating cylinders or pivoting and oscillating cylinders.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Slide-valve gear or valve arrangements, with cylindrical, sleeve or part-annularly-shaped valves, surrounding working cylinder or piston |
This place covers:
Reciprocating-piston machines or engines characterised by use of uniflow principle:
E.g. compressed gas engines where the working fluid enter a working cylinder, expands and then exits the cylinder.
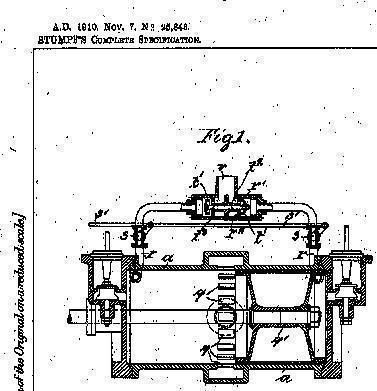
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
In patent document the word "uniflow" is often used with the meaning "open circuit where gas enters cylinder, expands, and is then released"
This place covers:
Compressed gas engines.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangement or mounting of steam or gaseous-pressure propulsion units of the piston type in vehicles | |
Arrangement or mounting of plural diverse prime-movers for mutual or common propulsion, prime movers comprising combustion engines and a chargeable fluidic accumulator for storing fluid energy |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 17/022
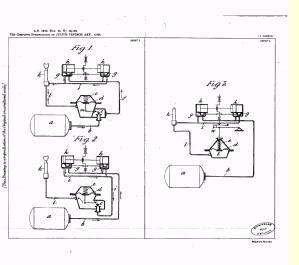
This place covers:
Separators for separating liquid or oil from compressed gas for gas engines.
This place covers:
Positive-displacement machines or engines of flexible-wall type. E.g. where the piston is made of a diaphragm or bellows.
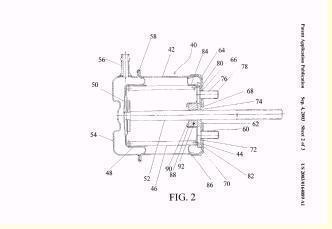
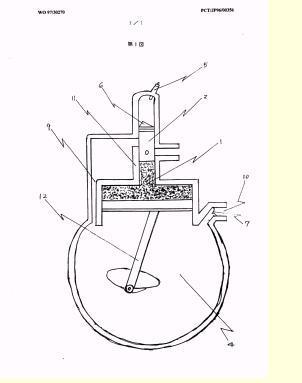
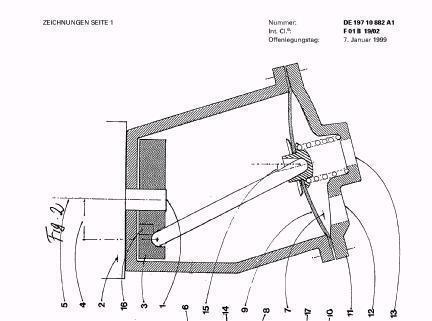
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 19/02
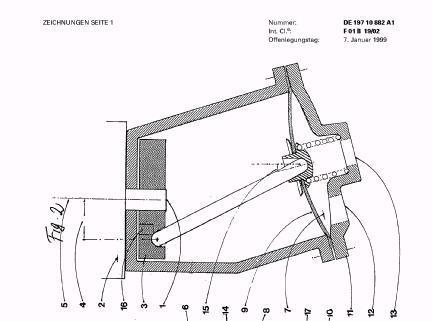
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in F01B 19/04

This place covers:
Combinations of two or more machines or engines, e.g. a combined internal combustion engine and steam engine.
This place does not cover:
Adaptations of machines or engines for special use; Combinations of engines with devices driven thereby |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Combinations of two or more positive-displacement pumps in pumping installations or systems specially adapted for elastic fluids | |
Combinations of two or more machines or pumps, each being of rotary-piston or oscillating-piston type; Pumping installations | |
Combinations of two or more pumps, each being of rotary-piston or oscillating-piston type, specially adapted for elastic fluids; Pumping installations specially adapted for elastic fluids; Multi-stage pumps specially adapted for elastic fluids | |
Combinations of two or more non-positive-displacement pumps in pumping installations or systems | |
Combinations of two or more non-positive-displacement pumps in pumping installations or systems specially adapted for elastic fluids | |
Rotary fluid gearing using pumps and motors of the volumetric type, i.e. passing a predetermined volume of fluid per revolution | |
Rotary fluid gearing of the hydrokinetic type | |
Other fluid gearing, e.g. with oscillating input or output | |
Combinations of fluid gearings for conveying rotary motion with couplings or clutches |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Reciprocating-piston machines or engines without rotary main shaft, e.g. of free-piston type | |
Rotary fluid gearing using pumps and motors of the volumetric type, i.e. passing a predetermined volume of fluid per revolution | |
Rotary fluid gearing of the hydrokinetic type | |
Other fluid gearing, e.g. with oscillating input or output | |
Combinations of fluid gearings for conveying rotary motion with couplings or clutches |
This place does not cover:
Controlling combustion engines |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Regulating or controlling in general |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Distributing or expansion valve gear |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Valves in general |
This place does not cover:
Starting combustion engines |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Turning-gear in general |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Refrigeration machines |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Machine or engine casings, other than those peculiar to steam engines |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Suppression of vibrations in systems; Means or arrangements for avoiding or reducing out-of-balance forces, e.g. due to motion |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Cooling of fluid machines or engines in general | |
Heat insulation in general |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Lubricating arrangements of fluid machines or engines in general |
Examples of places in relation to which this place is residual:
Warning devices |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring instruments or the like per se |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangements of exhaust pipes or tubes on steam engines | |
Gas-flow silencers or exhaust silencers for machines or engines in general |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Steam traps |