CPC Definition - Subclass D01G
This place covers:
The preliminary treatment of fibres for staple yarn spinning.
This place does not cover:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Winding or unwinding, conducting or guiding laps, webs, slivers or rovings in general, sliver or roving cans, depositing in sliver or roving cans |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Fibre | a relatively-short, elongated member of natural or artificial material |
Filament | an endless or quasi-endless, elongated member of natural (e.g. silk) or artificial material |
Yarn | a unitary assembly of fibres, usually produced by spinning |
Thread | an assembly of yarns or filaments, usually produced by twisting |
Drawing | stretching and elongating yarns or filaments |
Draft | the amount to which yarns or filaments are drawn |
This place covers:
The transformation of filaments into staple fibres, whereby a distinction is made between processes where fibres are delivered in bulk and processes where fibres are delivered in parallelised forms (e.g. ribbons, tops, slivers).
This place covers:
Processes and devices where the obtained staple fibres are delivered in randomized orientation or bulk form.
Randomized orientation can for example be found for the cutting of mineral filaments like glass, or guillotine type chopping processes of fibres to shorten them.
This place does not cover:
Processes and devices where the obtained staple fibres are delivered in parallelised form (e.g. strand, ribbon) |
This place covers:
Processes and devices where the obtained staple fibres are delivered in parallelised form (e.g. strands or ribbons).
Typically, processes like the stretch breaking or converting of synthetic filament tows are found in this group.
This place does not cover:
Processes and devices where the obtained staple fibres are delivered in randomized orientation (bulk) |
This place covers:
Mechanical and wet treatments that affect the surface of natural fibres e.g. sanding of fibres, degreasing of wool fibres.
Typically, techniques that increase surface roughness or permeability (for higher inter-fibre cohesion, higher absorption, higher binding affinity with polymers and the like).
This place covers:
Fibre sorting mechanisms and methods other than silk-dressing machines and combing, e.g. for preparing the natural fibres for a length diagram measurement step.
This place does not cover:
Silk-dressing machines | |
Combing machines |
This place covers:
The opening of compressed bales of fibres into workable fibre tufts; e.g. sawtooth grinding of cotton bales.
This place covers:
The separation of remaining non-fibre elements (e.g. seeds, vegetal contaminants) from fibres in fibre opening and cleaning apparatuses, and the opening i.e. loosening of the fibres, in order to obtain better fibre individualisation for example before carding. Typically, the group refers to blowroom equipment.
This place does not cover:
The processing of flax stalks in order to extract the flax fibres from the stalk |
This place covers:
Apparatus and processes for disintegrating fibre containing articles to obtain fibres for reuse, i.e. recycling.
This place covers:
Apparatus and processes for mixing, e.g. blending fibres or mixing fibrous and non-fibrous material.
This place covers:
The technical elements and variants of cards, as well short staple cards (cotton cards) as long staple cards (wool cards).
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Carding | a mechanical process that breaks up locks and unorganised clumps of fibre and then aligns the individual fibres so that they are more or less parallel with each other. The aim of carding is to perfect the individualisation and cleaning of staple fibres. |
This place covers:
Long staple (e.g. for wool) cards, where the carding action is performed between the workers and the main cylinder.
A worker designates a rotating cylinder of small diameter that cooperates with the main cylinder (or tambour) of the card, in order to perform the fibre carding.
This place covers:
Short staple (e.g. for cotton) cards, where the carding action is performed between flats and the main cylinder.
Flats designate longitudinal flat elements on a chain which cooperate with the main cylinder (or tambour) of the card, in order to perform the fibre carding.
This place covers:
Morel cylinder devices, where one cylinder has openings adapted to trap wool fibres entangled with burrs, while a cooperating cylinder will beat the burrs out.
This place covers:
A (rare) carding process for individualising silk staple fibres.
This place covers:
The combing out of short fibres (noils) from a carded fibre mass, in order to retain the longer fibres. The fibres are generally fed to and from the combing machine in sliver form.
This place covers:
The so-called Noble combing principle where rotating pinned elements act on a passing fibre mass to remove short fibres from it.
This place covers:
The combing technique (also called Heilmann combing technique), where combed fibre tufts are drawn out in linear manner from the combing area and are superposed.
This place covers:
E.g. heated crimping boxes, to increase fibre cohesion.
This place covers:
Partial or complete processing lines with a combination of fibre preparation machines and process steps; e.g. combed cotton producing line.
This place covers:
Apparatus and processes for feeding fibres to machines.
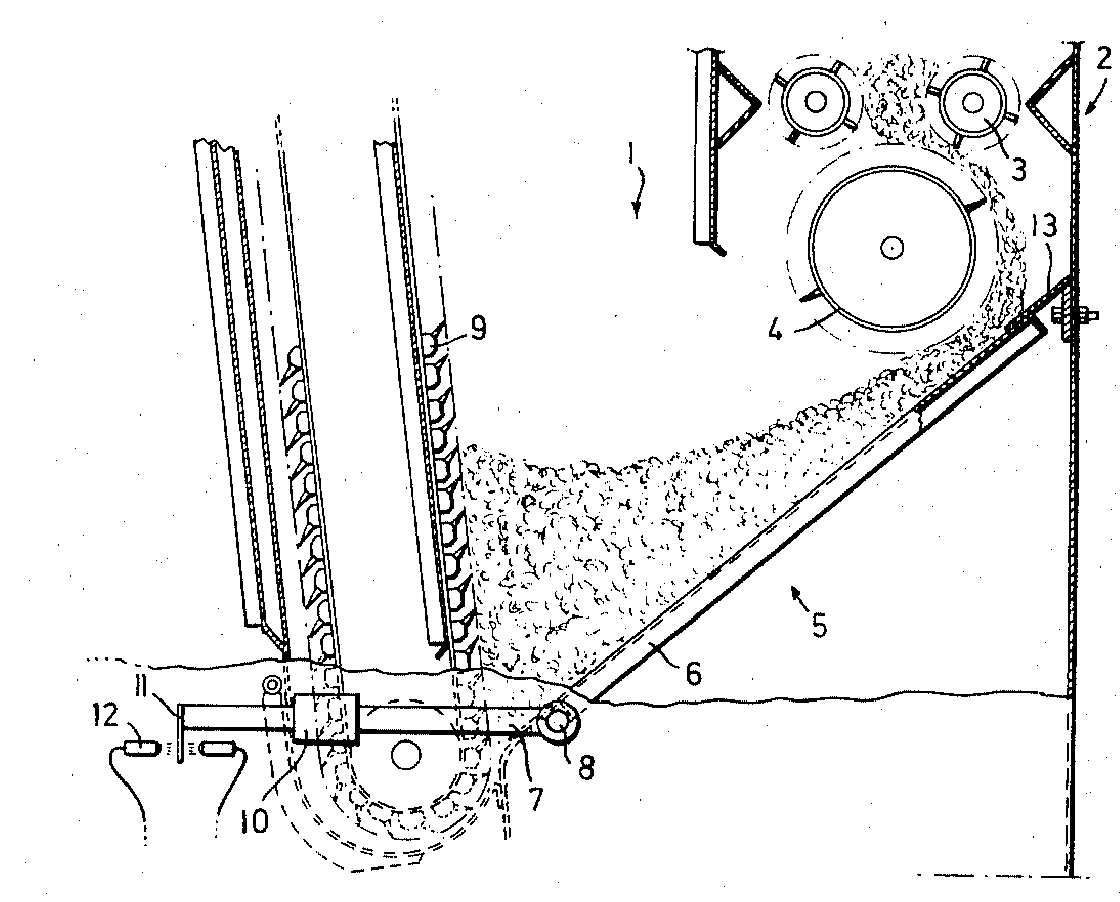
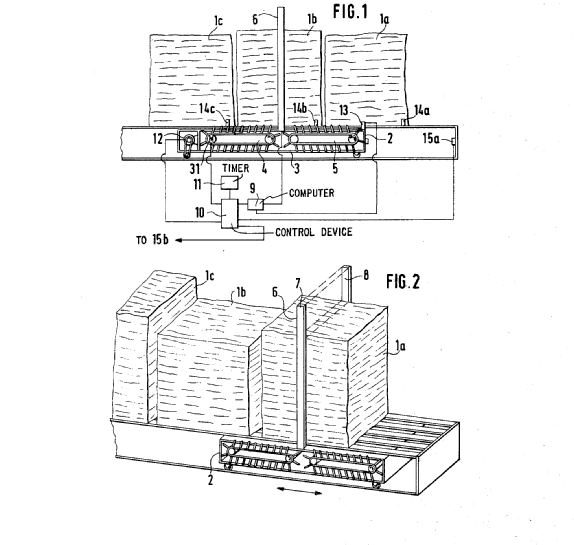
This place covers:
Fibre packing devices, that wind fibre strands into a compact package (lap) that is easier to transport, e.g.:
- cross lappers after cards;
- lapping devices after cotton combing units.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Folding limp material | |
Depositing filamentary material in cans or receptacles | |
Forming mats or batts of continuous filaments for non-woven fabrics |
This place covers:
The re-packaging of laps or slivers into bobbins, in order to accommodate specific format requirements.
This place covers:
The application of lubricant, e.g. by spraying during fibre preparation.
Lubricant can be sprayed in drafting machines to enable a better fibre gliding or a better penetration of control pins in so-called gill boxes (i.e. fibre control units with pins, placed between drafting rollers in long staple drafting arrangements).
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Moistening, sizing, oiling, waxing, colouring or drying filamentary material as additional measures during package formation | |
Treating fibres, threads, yarns, fabrics or fibrous goods made from such materials, with macromolecular compounds |
This place covers:
Warning and safety devices, as well as quality monitoring devices applied to spinning preparation machines; e.g. evenness monitors of a card output; sliver breaking detectors etc.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Warning | monitoring, as monitoring systems are used to warn in case of value deviation and/or stop the machine. |
This place covers:
Auxiliary devices used by hand to facilitate intervention of fibres; e.g. superposing sliver ends in a comb to create a sliver junction.
This place covers:
The cleaning and opening of entangled or agglomerated flax or hemp fibres, to obtain a parallelised fibre bundle (e.g. to be used as joint in connecting pipes).
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Oakum | a preparation of tarred fibre (e.g. hemp or jute) used in shipbuilding, for packing the joints of timbers in wooden vessels and the deck planking of ships, as well as cast iron plumbing applications. |