CPC Definition - Subclass B64U
This place covers:
Aerial vehicles that do not carry a human operator and which are guided autonomously or are remotely operated or both, using various levels of automated functions. The aerial vehicles can be expendable or recoverable and may carry lethal or non-lethal payloads.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Toy aircraft; Other flying toys | |
Guided missiles |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
VTOL | Vertical Take-Off and Landing |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangements permitting vertical take-off or landing [VTOL] of aircraft, e.g. using rockets |
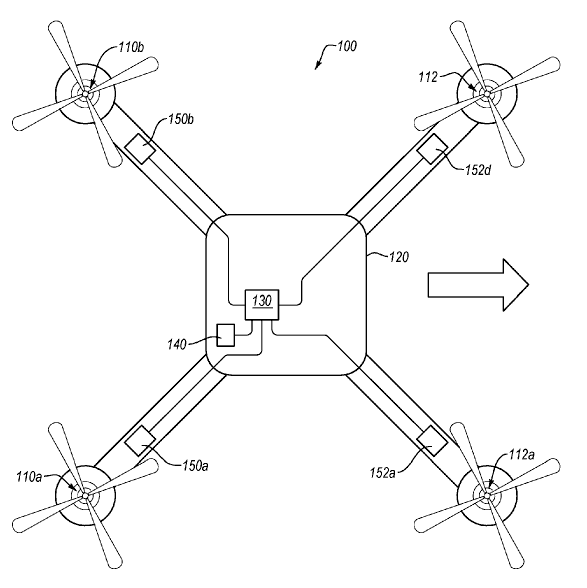
This place covers:
Aircraft generally without a preferential longitudinal axis, having one or more rotors generating a lifting thrust, wherein the lifting thrust is generally vertical, wherein pitch and roll control is normally provided by differential thrust control or a separate force generated outside the propulsors.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this place:
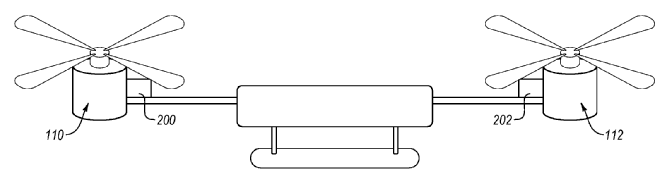
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Rotorcraft characterised by having shrouded rotors, e.g. flying platforms |
This place covers:
Vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aerial vehicles, whereby the vehicles can hover, take-off and land vertically.
This place does not cover:
Flying platforms | |
Helicopters |
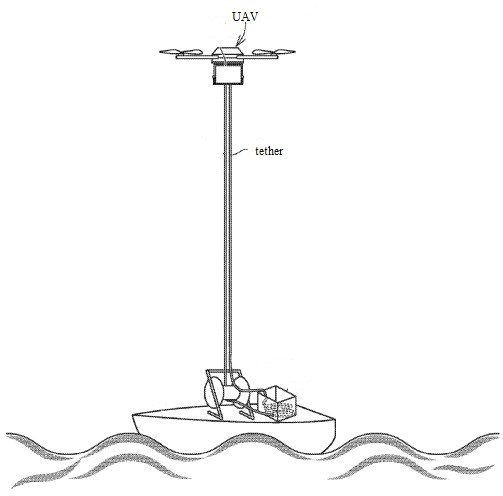
This place covers:
Unmanned aircraft which are physically linked to a person, the ground or an object at all times while it is flying.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this place:
This place covers:
UAVs whose size does not exceed 15 cm.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
MAV | Micro-Air Vehicle |
This place covers:
UAV bodies formed substantially of unitary or single-piece construction.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Supply or distribution of electrical power |
This place covers:
UAVs wherein the wings are moved to different positions along the body, e.g. by sliding or by detaching and reattaching.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
In-flight adjustment of the base configuration |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Compound rotorcraft with rotor blades fixed in flight to act as lifting surfaces |
This place does not cover:
Foldable or collapsible rotors |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
In-flight adjustment of the base configuration |
This place covers:
Devices usually in the form of a bar with a weight or paddle at each end, mounted to the rotor to aid stability.
This place covers:
Devices arranged around the rotors for protecting the rotors from contacting obstacles during flight. The devices may surround the UAV as well.
This place does not cover:
Ducted or shrouded rotors | |
Guards used as ground propulsion |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Rotorcrafts; Rotors peculiar thereto |
This place covers:
Mechanisms for actuating adjustable control surfaces or for changing the orientation of rotors, or for changing the pitch of rotor blades, while in flight to control the attitude of the aircraft or control position of the aircraft.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Controlling flying-control surfaces of aeroplanes and helicopters | |
Controlling rotors of aeroplanes and helicopters |
This place covers:
Mechanisms for adjusting the position of wings or rotors, or otherwise moving the centre of gravity relative to the body, while in flight.
This place covers:
Arrangements for receiving electrical power from an external source while in flight.
This place does not cover:
Supply or distribution of electrical power generated by photovoltaics |
This place covers:
Rolling cages, i.e. free-rolling frames, that at least partially surround the UAV and are connected thereto by at least one rotary joint. UAVs with rolling cages may be capable of movement in flight and on the ground.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this place:
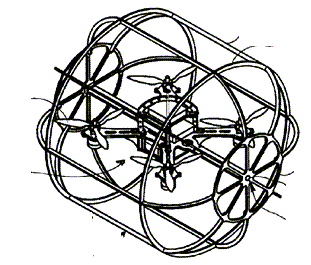
This place covers:
Wings, rotor supports or shrouds which may be adjusted in position or orientation to also act as landing gear for the UAV.
This place covers:
UAVs which are launched or take flight from a storage position within a storage container.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this place:
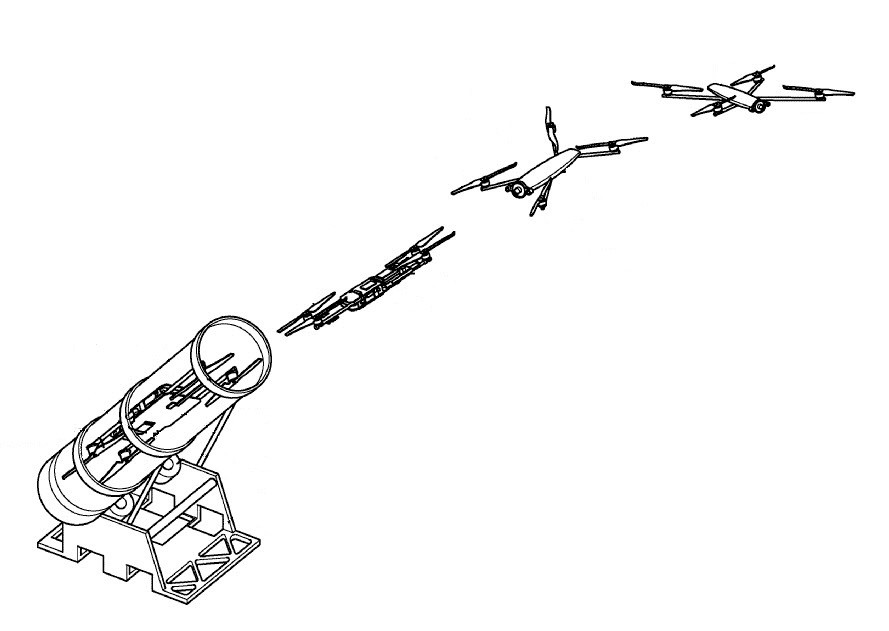
This place covers:
Arrangements to permit VTOL capability for aircraft not otherwise having the capability, e.g. using rockets or parachutes.
This place does not cover:
Rotorcrafts | |
VTOL aircraft |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Balloons per se | |
Parachutes per se |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Emergency apparatus or devices, not otherwise provided for |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Visual or acoustic landing aids |
This place covers:
Means for physically positioning or orienting the UAV on the platform during landing, e.g. using mechanical means.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this place:
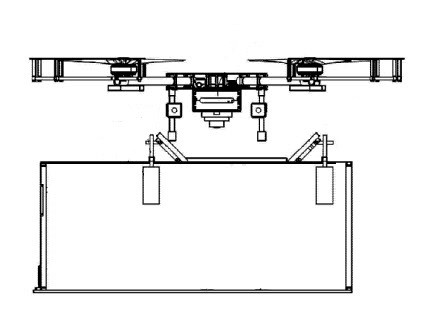
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Visual or acoustic landing aids |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Foldable or collapsible UAVs |
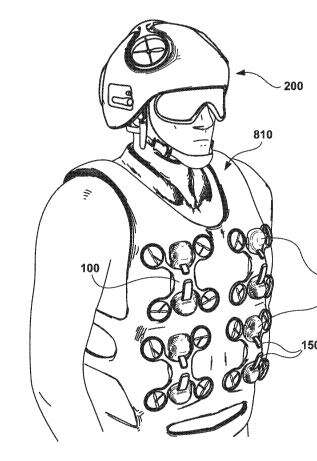
This place covers:
UAVs stored on a person by attaching to apparel, e.g. clothing, or the body itself, e.g. on the wrist.
Illustrative example 1 of subject matter classified in this place:
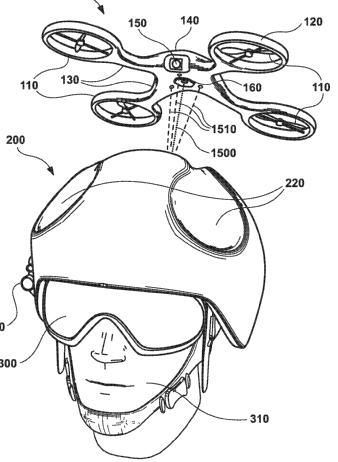
Illustrative example 2 of subject matter classified in this place: