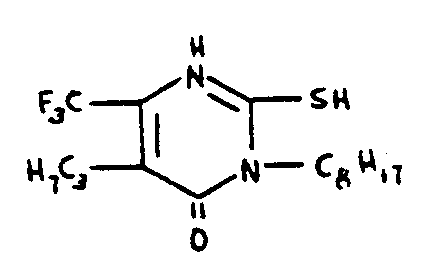
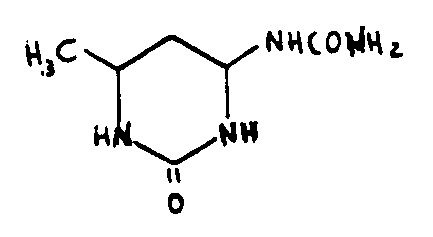
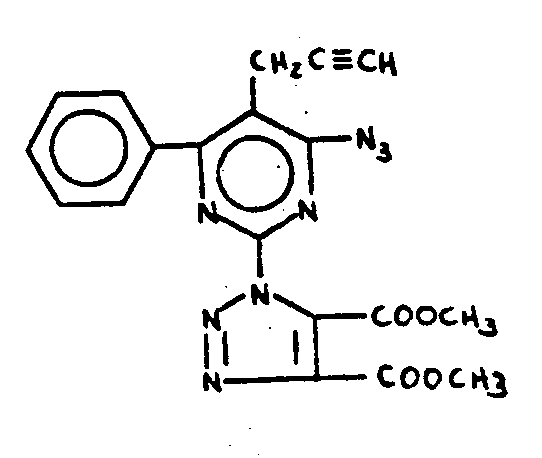
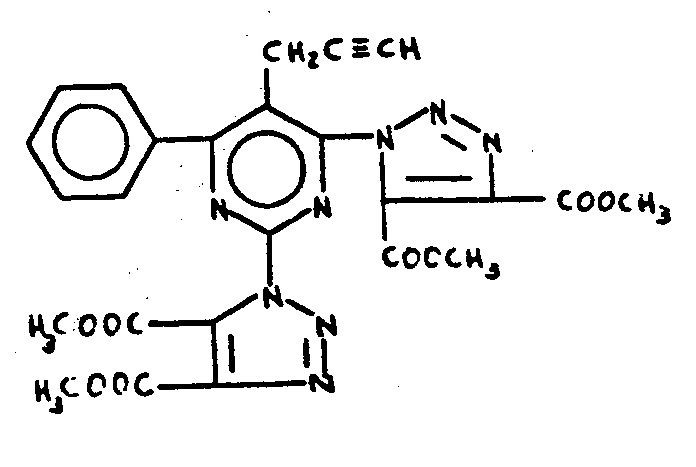
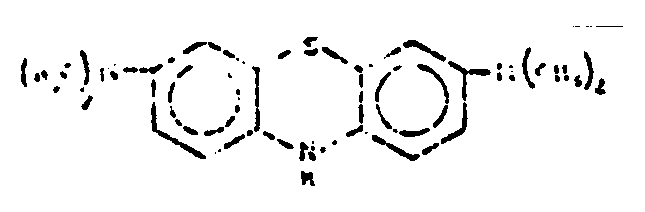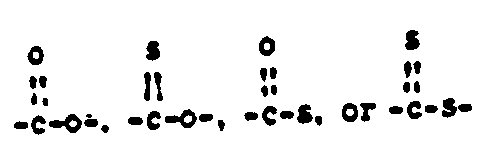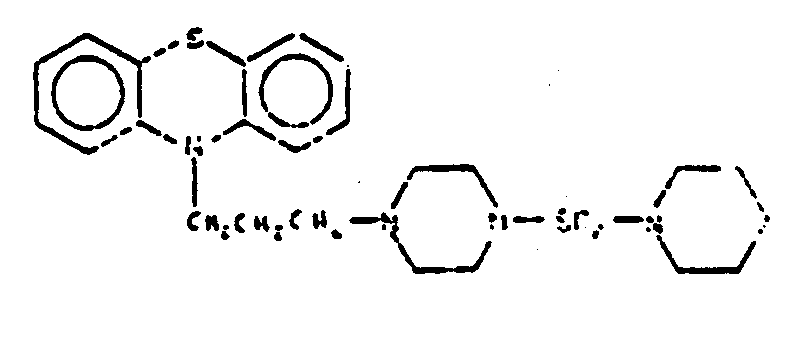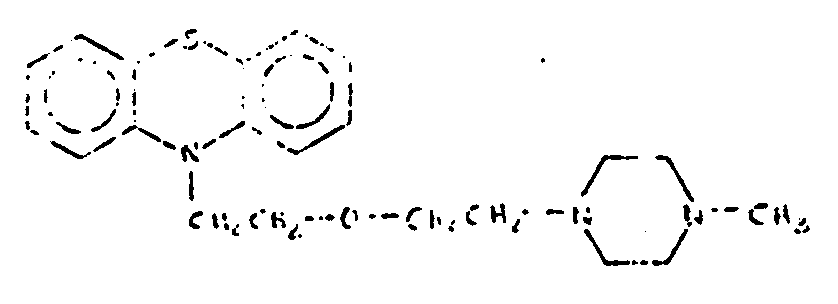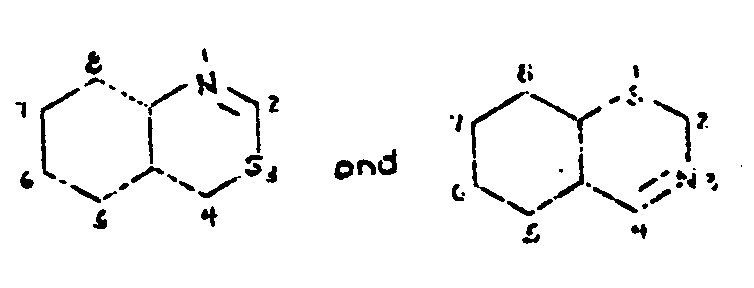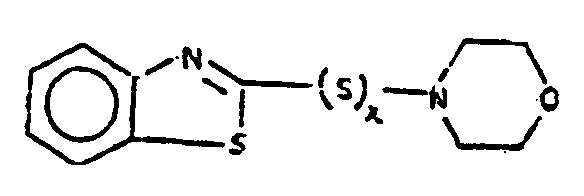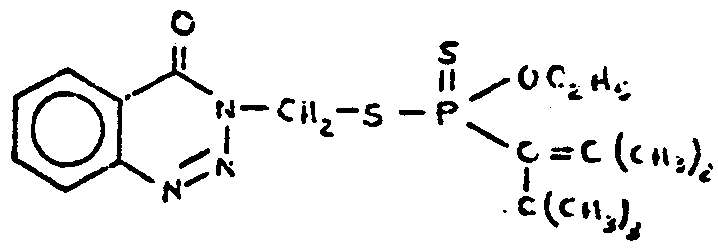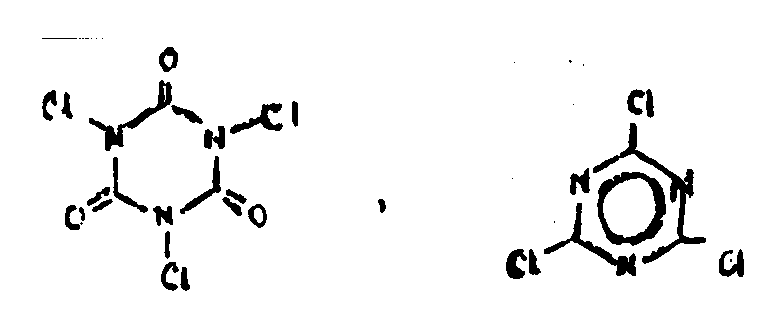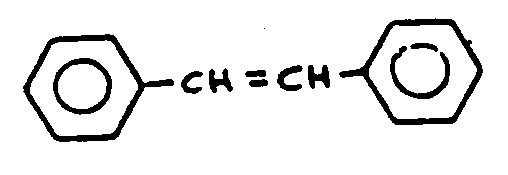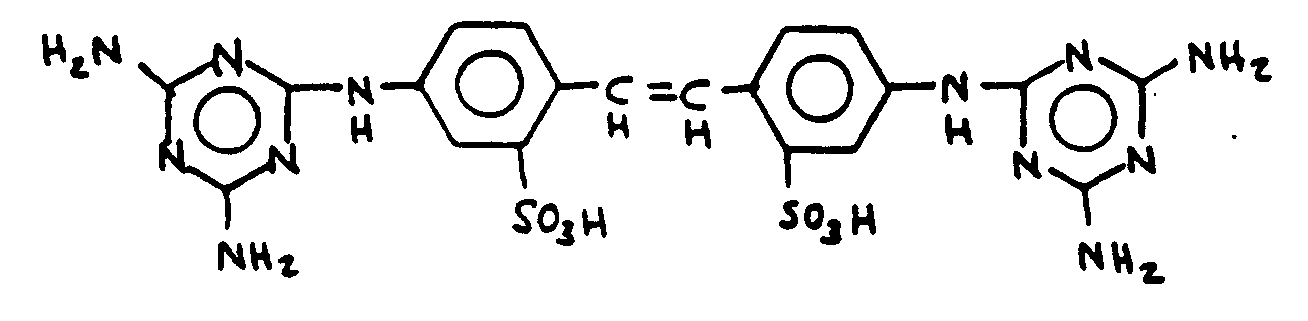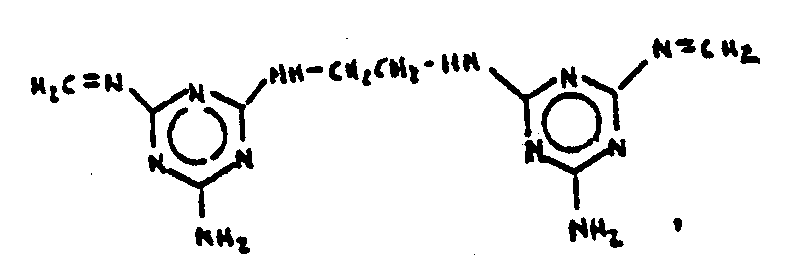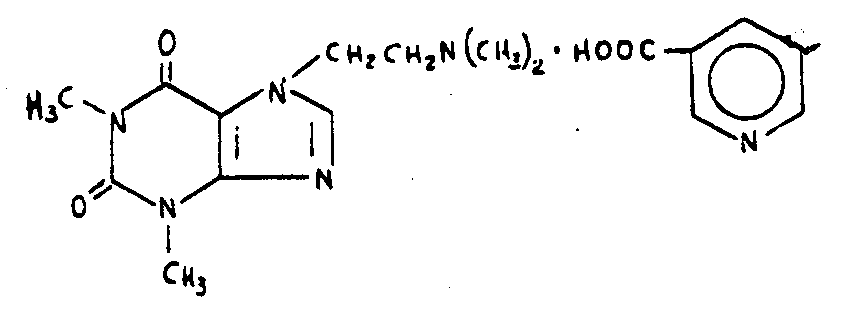![[Search a list of Patent Appplications for class 544]](../as.gif) CLASS 544, CLASS 544, | ORGANIC COMPOUNDS -- PART OF THE CLASS 532-570 SERIES |
| Click here for a printable version of this file | |
SUBCLASSES
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 1]](../ps.gif) 1 1 | Hetero ring is six-membered having two or more ring hetero atoms of which at least one is nitrogen (e.g., selenazines, etc.) | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 1. Compounds under Class 540, ... which contain a six-membered
hetero ring having two or more ring hetero atoms of which at least
one is nitrogen.
SEE OR SEARCH CLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 2]](../ps.gif) 2 2 | Six-membered hetero ring consists of oxygen, sulfur, nitrogen and carbon (e.g., oxathiazines, etc.) |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 1. Compounds wherein the six- membered hetero ring includes at least one atom each of oxygen, sulfur, nitrogen and carbon and contains no other elements as ring members. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 3]](../ps.gif) 3 3 | Six-membered hetero ring consists of sulfur, nitrogen, and carbon |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 1. Compounds wherein the six- membered hetero ring includes at least one atom each of sulfur, nitrogen and carbon and contains no other elements as ring members. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 4]](../ps.gif) 4 4 | Heavy metal or aluminum containing | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 3. Compounds which include aluminum or a metal having a specific
gravity greater than four.
| |||
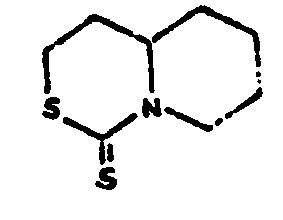
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 5]](../ps.gif) 5 5 | Plural sulfurs in the six-membered hetero ring (e.g., dithiazines, etc.) |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 3. Compounds wherein the six-membered hetero ring contains at least two ring sulfurs in addition to the nitrogen and carbon. | |
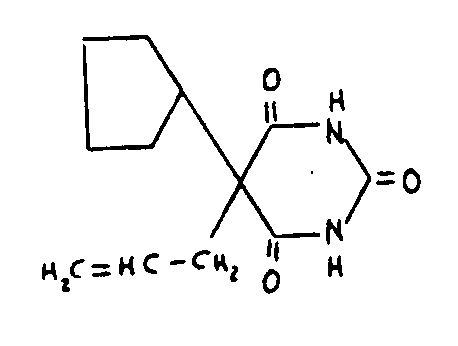
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 6]](../ps.gif) 6 6 | Spiro |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 3. Compounds which contain a spiro ring system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 7]](../ps.gif) 7 7 | Plural nitrogens in the six-membered hetero ring (e.g., thiatriazines, etc.) |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 3. Compounds wherein the six-membered hetero ring contains at least two atoms of nitrogen in addition to the sulfur and carbon. | |
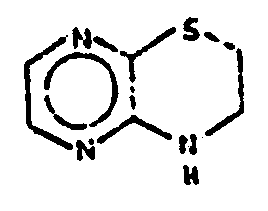
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 8]](../ps.gif) 8 8 | Thiadiazines |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 7. Compounds wherein the six-membered hetero ring consists of two nitrogen atoms, one sulfur atom and three carbon atoms. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 9]](../ps.gif) 9 9 | Polycyclo ring system having the thiadiazine ring as one of the cyclos |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 8. Compounds wherein the thiadiazine ring is one of the cyclos of a polycyclo ring system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 10]](../ps.gif) 10 10 | Bicyclo ring system having the thiadiazine ring as one of the cyclos |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 9. Compounds wherein the polycyclo ring system consists of two rings, one of which is the thiadiazine ring. | |
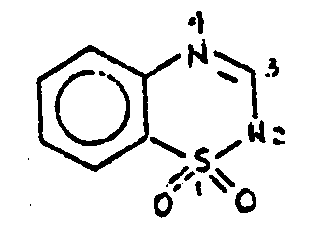
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 11]](../ps.gif) 11 11 | Benzothiadiazines |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 10. Compounds wherein the bicyclo ring system consists of the thiadiazine ring and a benzene ring. | |
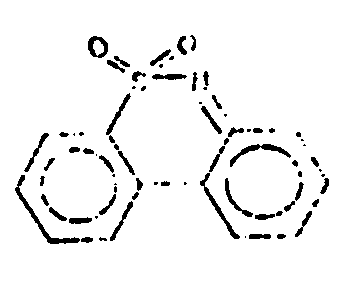
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 12]](../ps.gif) 12 12 | 1,2,4-benzothiadiazines | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 11. Compounds wherein the sulfur atom is in the 1-position and
the nitrogen atoms are in the 2- and 4-positions of the six-membered
hetero ring.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 13]](../ps.gif) 13 13 | Sulfamyl or substituted sulfamyl containing | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 12. Compounds which contain a sulfamyl or substituted sulfamyl
group; viz., -SO2N or -SO2N=.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 14]](../ps.gif) 14 14 | Polycyclo ring system having the six-membered hetero ring as one of the cyclos |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 3. Compounds wherein the six-membered hetero ring is one of the cyclos of a polycyclo ring system. | |
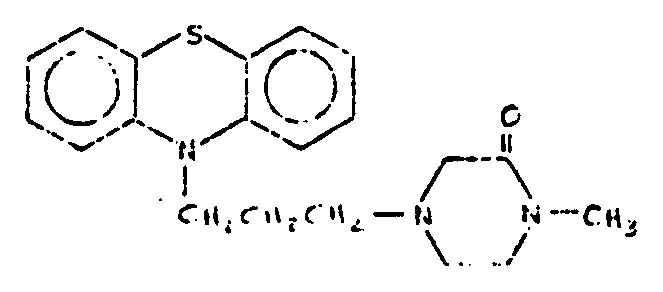
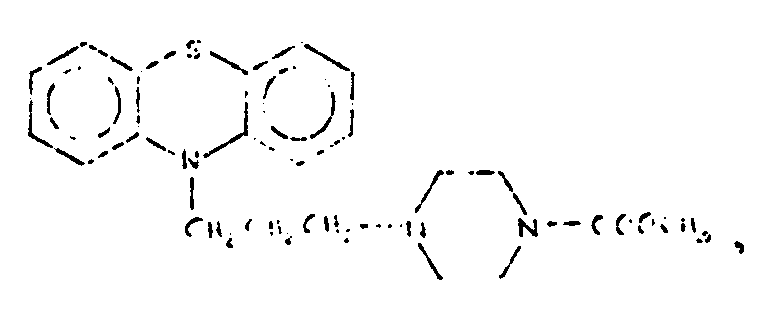
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 31]](../ps.gif) 31 31 | Phenothiazine as three cyclos of polycyclo ring system having at least four cyclos | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 14. Compounds wherein the polycyclo ring system contains four
or more rings of which three form the phenothiazine structure.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 32]](../ps.gif) 32 32 | Tricyclo ring system having the six-membered hetero ring as one of the cyclos | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 14. Compounds in which the polycyclo ring system consists of
three rings, one of which is the six-membered hetero ring.
| |||
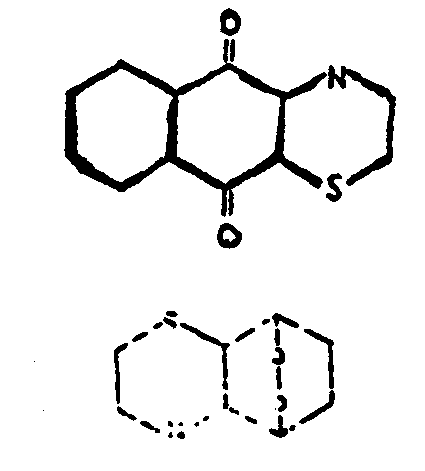
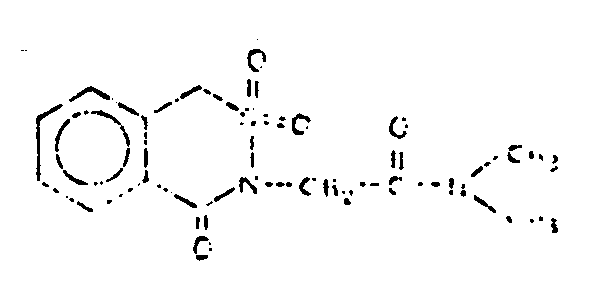
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 33]](../ps.gif) 33 33 | 1,2- or 2,1-Thiazine ring in the tricyclo ring system (e.g., hydrogenated 1,2-benzothiazine in tricyclo ring system, etc.) | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 32. Compounds in which the ring sulfur and ring nitrogen of
the six-membered hetero ring are in adjacent positions.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 34]](../ps.gif) 34 34 | Plural ring nitrogens in the tricyclo ring system | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 32. Compounds wherein the tricyclo ring system contains at least
two ring nitrogens.
| |||
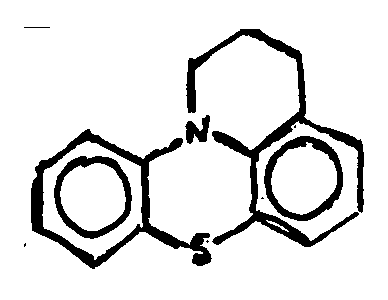
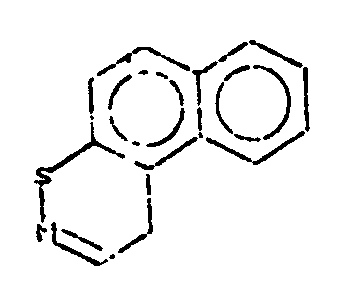
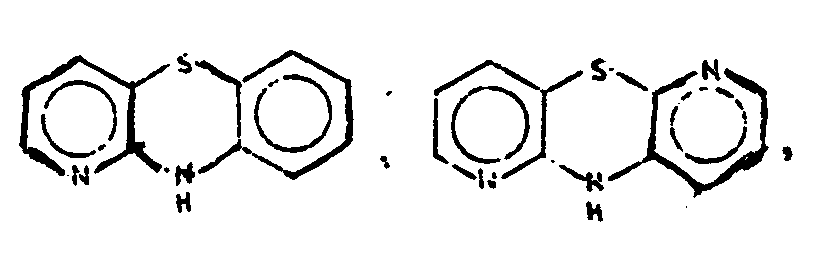
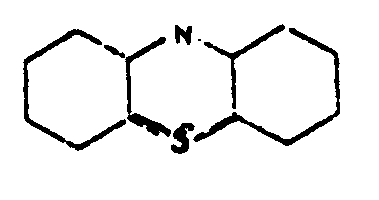
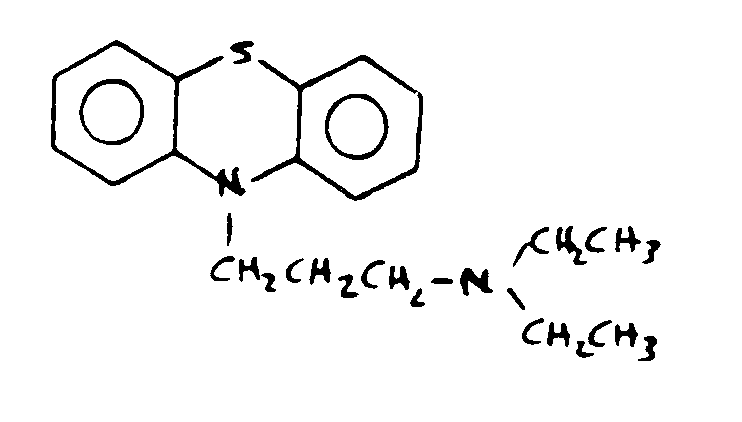
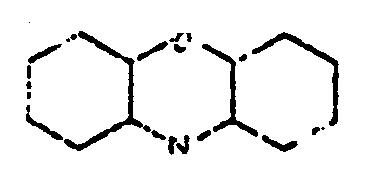
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 35]](../ps.gif) 35 35 | Phenothiazines (including hydrogenated) |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 32. Compounds wherein the tricyclo ring system has the following
basic structure, in which the bonds between ring members may be
double or single bonds.
| |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 36]](../ps.gif) 36 36 | Purification or recovery |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 35. Processes wherein the phenothiazine containing compound is separated from impurities or from the reaction mixture. | |
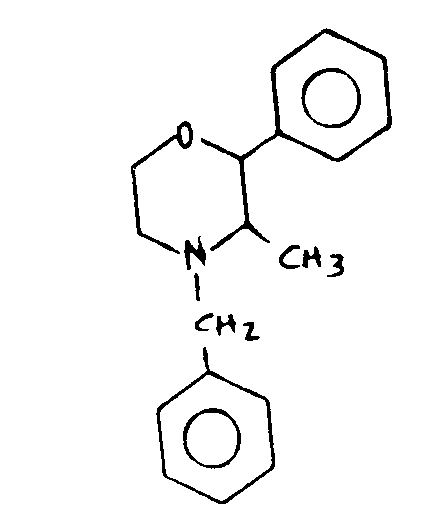
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 37]](../ps.gif) 37 37 | Nitrogen bonded directly to phenothiazine ring system | ||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 35. Compounds which include nitrogen bonded directly to the
phenothiazine ring system.
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 38]](../ps.gif) 38 38 | Carbon bonded directly to ring nitrogen of phenothiazine ring system |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 35. Compounds which contain carbon bonded directly to the ring nitrogen of the phenothiazine ring system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 39]](../ps.gif) 39 39 | Divalent chalcogen double bonded directly to the carbon |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 38. Compounds wherein divalent chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium or tellurium) is double bonded directly to the carbon which is bonded directly to the ring nitrogen of the phenothiazine ring system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 40]](../ps.gif) 40 40 | Additional chalcogen bonded directly to the carbon |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 39. Compounds which include the structure below bonded directly
to the ring nitrogen of the phenothiazine ring system, or an analog
of another chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium or tellurium).
| |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 41]](../ps.gif) 41 41 | Nitrogen containing substituent bonded to nitrogen of phenothiazine ring system | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 38. Compounds wherein a nitrogen containing substituent is bonded
directly to the ring nitrogen of the phenothiazine ring system.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 42]](../ps.gif) 42 42 | Nitrogen containing hetero ring in the nitrogen containing substituent (e.g., oxazole, etc.) | ||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 41. Compounds in which the nitrogen containing substituent includes
a hetero ring, which hetero ring has at least nitrogen as a ring
hetero atom.
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 43]](../ps.gif) 43 43 | Plural hetero rings in the nitrogen containing substituent | ||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 42. Compounds in which the nitrogen containing substituent includes
at least two hetero rings.
| |||||
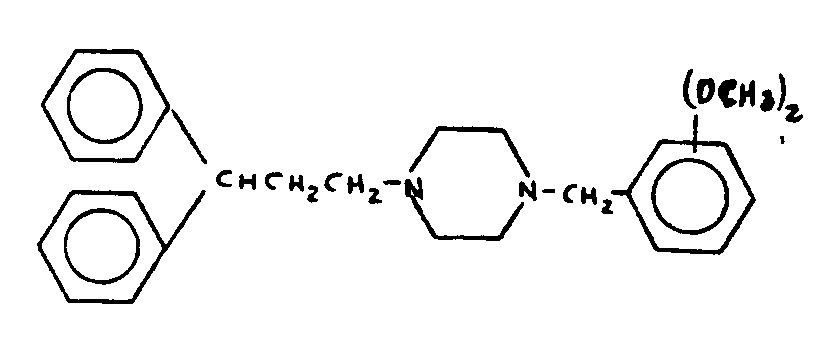
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 44]](../ps.gif) 44 44 | Piperazine ring in the nitrogen containing substituent |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 42. Compounds in which the hetero ring in the nitrogen containing substituent is a fully hydrogenated six-membered ring having nitrogen in the 1- and 4-positions and carbon in the other four positions. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 45]](../ps.gif) 45 45 | Chalcogen in the nitrogen containing substituent | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 44. Compounds which include chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur,
selenium or tellurium) in the nitrogen containing substituent.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 46]](../ps.gif) 46 46 | Chalcogen in the nitrogen containing substituent |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 42. Compounds which include chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium or tellurium) in the nitrogen containing substituent. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 47]](../ps.gif) 47 47 | Bicyclo ring system having the six-membered hetero ring as one of the cyclos | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 14. Compounds wherein the polycyclo ring system consists of
exactly two rings, one of which is the six-membered hetero ring.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 48]](../ps.gif) 48 48 | Three or more ring hetero atoms in the bicyclo ring system | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 47. Compounds wherein the bicyclo ring system contains at least
one ring hetero atom in addition to the ring sulfur and ring nitrogen
of the thiazine ring.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 49]](../ps.gif) 49 49 | Benzothiazines (including hydrogenated) | ||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 47. Compounds wherein the bicyclo ring system consists of a
benzene ring sharing two adjacent carbons of the six-membered hetero
ring.
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 50]](../ps.gif) 50 50 | 1,3- or 3,1-benzothiazines | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 49. Compounds wherein the ring hetero atoms of the benzothiazine
ring system are in the 1-and 3-positions.
| |||
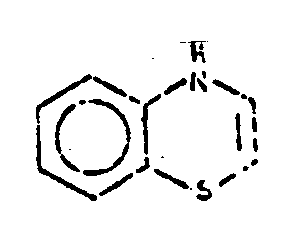
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 51]](../ps.gif) 51 51 | 1,4-benzothiazines | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 49. Compounds wherein the sulfur and nitrogen atoms of the benzothiazine
ring system are in para-position to each other.
| |||
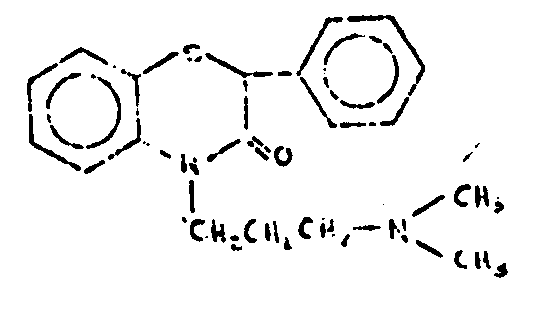
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 52]](../ps.gif) 52 52 | Double bonded divalent chalcogen containing | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 51. Compounds which include a double bonded divalent chalcogen
(i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium or tellurium).
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 53]](../ps.gif) 53 53 | 1,3-thiazines | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 3. Compounds wherein the six-membered hetero ring has sulfur
in the 1-position, nitrogen in the 3-position and carbon in the
other four positions.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 54]](../ps.gif) 54 54 | Double bonded divalent chalcogen containing |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 53. Compounds which include a double bonded divalent chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium or tellurium). | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 55]](../ps.gif) 55 55 | Additional hetero ring containing |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 53. Compounds which include an additional hetero ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 56]](../ps.gif) 56 56 | 1,4-thiazines |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 3. Compounds wherein the six-membered hetero ring has sulfur in the 1-position, nitrogen in the 4-position and carbon in the other four positions. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 57]](../ps.gif) 57 57 | Phosphorus containing |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 56. Compounds which include phosphorus in a salt or attached by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 58.1]](../ps.gif) 58.1 58.1 | Double bonded divalent chalcogen containing |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 56. Compounds which include double bonded divalent chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium). | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 58.2]](../ps.gif) 58.2 58.2 | Divalent chalcogen double bonded directly to the thiazine ring |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 58.1. Compounds wherein divalent chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium) is double bonded directly to the thiazine ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 58.4]](../ps.gif) 58.4 58.4 | Having -C(=X)-, wherein X is chalcogen, bonded directly to the thiazine ring |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 58.1. Compounds wherein a group, in which X is chalcogen (i.e. oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium), is bonded directly to the thiazine ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 58.5]](../ps.gif) 58.5 58.5 | Additional hetero ring containing | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 58.1. Compounds which include an additional hetero ring.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 58.6]](../ps.gif) 58.6 58.6 | Ring nitrogen in the additional hetero ring, which is six-membered | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 58.5. Compounds having, in addition to the thiazine ring, a six-membered
hetero ring which has at least one ring nitrogen.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 58.7]](../ps.gif) 58.7 58.7 | Ring chalcogen in the additional hetero ring | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 58.5. Compounds having, in addition to the thiazine ring, a hetero
ring which includes a ring chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium,
or tellurium).
| |||
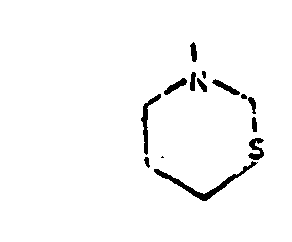
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 59]](../ps.gif) 59 59 | Thiomorpholines (i.e., fully hydrogenated 1,4-thiazines) |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 56. Compounds in which the six-membered hetero ring contains no double bonds. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 60]](../ps.gif) 60 60 | Additional hetero ring containing | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 59. Compounds which include an additional hetero ring.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 61]](../ps.gif) 61 61 | The additional hetero ring is one of the cyclos in a bicyclo ring system | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 60. Compounds wherein the additional hetero ring is a cyclo
in a bicyclo ring system.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 62]](../ps.gif) 62 62 | Benzo is the other cyclo |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 61. Compounds wherein a benzene ring is the other cyclo of the bicyclo ring system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 63]](../ps.gif) 63 63 | Six-membered hetero ring consists of oxygen, nitrogen and carbon (e.g., 1,2-oxazines, etc) | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 1. Compounds in which the six-membered hetero ring consists
of oxygen, nitrogen and carbon.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 64]](../ps.gif) 64 64 | Heavy metal or aluminum containing | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 63. Compounds which contain aluminum or a metal with a specific
gravity greater than 4.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 65]](../ps.gif) 65 65 | Plural oxygens in the six-membered hetero ring |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 63. Compounds wherein the six-membered ring contains at least two ring oxygens. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 66]](../ps.gif) 66 66 | Plural nitrogens in the six-membered hetero ring |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 63. Compounds wherein the six-membered ring contains at least two ring nitrogens. | |
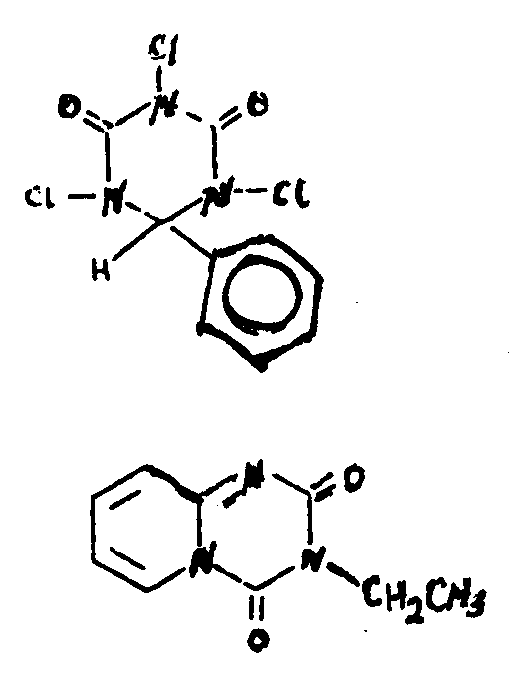
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 67]](../ps.gif) 67 67 | 1,3,5-oxadiazines |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 66. Compounds wherein oxygen is in the 1-position, nitrogen is in the 3- and 5-positions and carbon is in the remaining three positions of the six-membered hetero ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 68]](../ps.gif) 68 68 | Oxygen bonded directly to the six-membered hetero ring |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 66. Compounds in which oxygen is bonded directly to the six-membered ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 69]](../ps.gif) 69 69 | Boron or silicon containing |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 63. Compounds which contain boron or silicon. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 70]](../ps.gif) 70 70 | Spiro |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 63. Compounds which contain a spiro ring system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 71]](../ps.gif) 71 71 | Spiro oxazine |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 70. Compounds wherein at least one of the rings in the spiro ring system is a six-membered hetero ring consisting of oxygen, nitrogen and carbon. | |
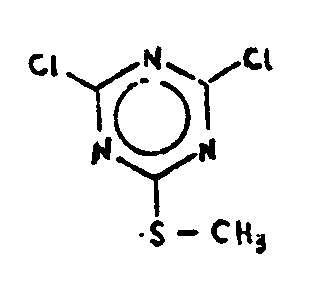
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 72]](../ps.gif) 72 72 | Plural oxazine rings |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 63. Compounds having at least two six-membered hetero rings each consisting of one ring oxygen, one ring nitrogen and four ring carbons. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 73]](../ps.gif) 73 73 | Polycyclo ring system having oxazine ring as at least one of the cyclos |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 72. Compounds in which at least one of the six-membered hetero rings is a cyclo of a polycyclo ring system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 74]](../ps.gif) 74 74 | Plural 1,4-oxazine rings are cyclos in the polycyclo ring system |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 73. Compounds wherein the polycyclo ring system contains at least two of the six-membered hetero rings, each having its oxygen in the 1-position and its nitrogen in the 4-position. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 75]](../ps.gif) 75 75 | Pentacyclo ring system having the oxazine rings as cyclos |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 74. Compounds in which the polycyclo ring system is composed of exactly five rings. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 76]](../ps.gif) 76 76 | Plural nitrogens bonded directly to the pentacyclo ring system |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 75. Compounds in which two or more nitrogen atoms are directly bonded to the pentacyclo ring system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 77]](../ps.gif) 77 77 | Acyclic nitrogen is bonded directly to a -C(=X)- group, wherein X is chalcogen |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 76. Compounds which contain nitrogen bonded directly to a group, wherein X is chalcogen (i.e. oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium). | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 78]](../ps.gif) 78 78 | Plural morpholine rings (i.e., plural fully hydrogenated 1, 4-oxazine rings) | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 72. Compounds which contain at least two of the six-membered
hetero rings, each having its oxygen in the 1-position, its nitrogen
in the 4-position, and having no double bonds between ring members,
i.e., morpholine rings.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 79]](../ps.gif) 79 79 | Polycyclo ring system |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 78. Compounds which contain a polycyclo ring system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 80]](../ps.gif) 80 80 | Ring nitrogen in the polycyclo ring system |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 79. Compounds in which a nitrogen containing hetero ring is part of the polycyclo ring system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 81]](../ps.gif) 81 81 | Four or more ring nitrogens in the polycyclo ring system | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 80. Compounds in which the polycyclo ring system contains at
least four ring nitrogens.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 82]](../ps.gif) 82 82 | Additional nitrogen containing hetero ring (e.g., thiazole, etc.) |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 78. Compounds which have, in addition to the morpholine rings, another hetero ring which has a ring nitrogen. | |
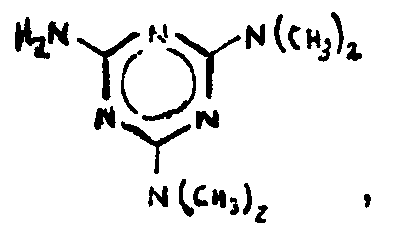
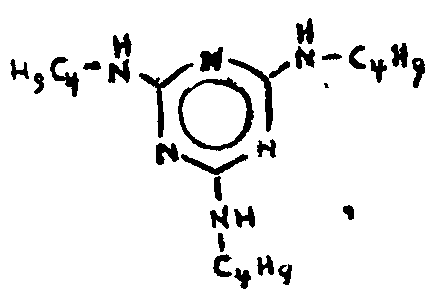
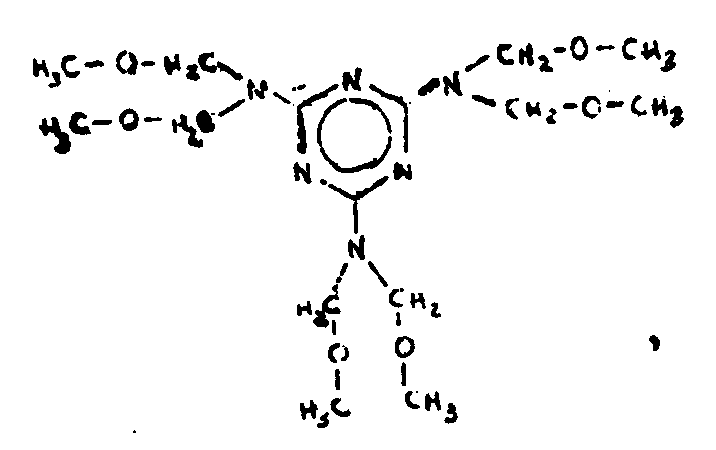
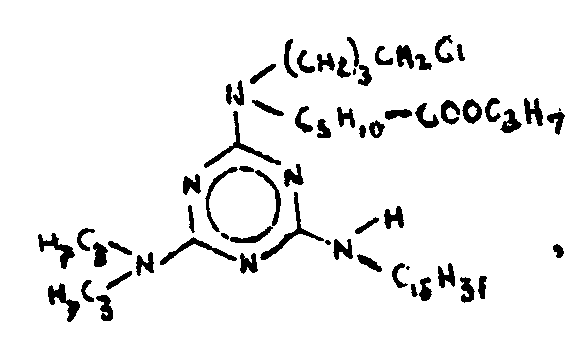
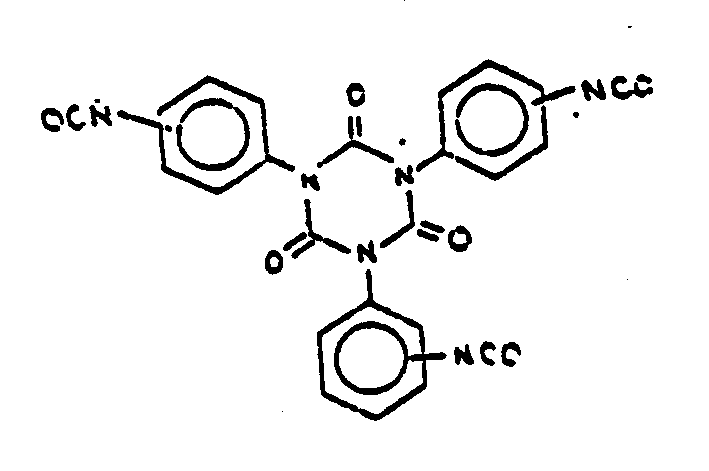
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 83]](../ps.gif) 83 83 | Triazine |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 82. Compounds in which the additional hetero ring is six-membered having three ring nitrogens and three ring carbons. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 84]](../ps.gif) 84 84 | Phosphorus attached directly or indirectly to a morpholine ring by nonionic bonding |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 78. Compounds wherein phosphorus is attached directly or indirectly to a morpholine ring by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 85]](../ps.gif) 85 85 | Sulfur attached directly or indirectly to a morpholine ring by nonionic bonding |
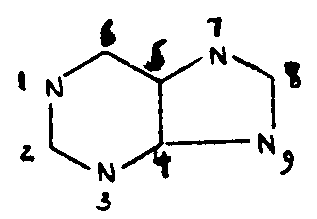
| This subclass is indented under subclass 78. Compounds wherein sulfur is attached directly or indirectly to a morpholine ring by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 86]](../ps.gif) 86 86 | Nitrogen attached directly or indirectly to a morpholine ring by nonionic bonding |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 78. Compounds wherein nitrogen is attached directly or indirectly to a morpholine ring by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 87]](../ps.gif) 87 87 | Oxygen attached directly or indirectly to a morpholine ring by nonionic bonding |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 78. Compounds wherein oxygen is attached directly or indirectly to a morpholine ring by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 88]](../ps.gif) 88 88 | 1,3-Oxazines |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 63. Compounds wherein the six-membered hetero ring has oxygen in the 1-position, nitrogen in the 3-position and carbons in the remaining four positions. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 89]](../ps.gif) 89 89 | Polycyclo ring system having the oxazine ring as one of the cyclos | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 88. Compounds wherein the six-membered hetero ring is a cyclo
in a polycyclo ring system.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 90]](../ps.gif) 90 90 | Bicyclo ring system having the oxazine ring as one of the cyclos |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 89. Compounds in which the polycyclo ring system consists of exactly two rings. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 91]](../ps.gif) 91 91 | Three or more ring hetero atoms in the bicyclo ring system |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 90. Compounds wherein the bicyclo ring system includes at least one ring hetero atom in addition to the ring oxygen and ring nitrogen of the six-membered hetero ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 92]](../ps.gif) 92 92 | Chalcogen bonded directly to the oxazine ring |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 90. Compounds wherein chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium or tellurium) is bonded directly to the six-membered hetero ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 93]](../ps.gif) 93 93 | Plural oxygens bonded directly to the oxazine ring |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 92. Compounds wherein at least two oxygen atoms are bonded directly to the six-membered hetero ring. | |
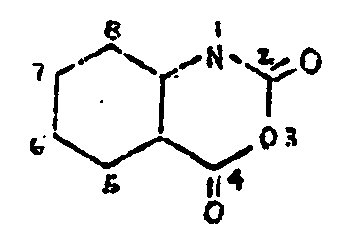
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 94]](../ps.gif) 94 94 | Plural oxygens bonded directly to the oxazine ring 3,1-Benzoxazine-2,4- diones (including hydrogenated) |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 93. Compounds which contain the isatoic anhydride configuration,
wherein there may be double or single bonds between ring members.
| |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 95]](../ps.gif) 95 95 | Three or more ring hetero atoms in the polycyclo ring system |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 89. Compounds wherein the polycyclo ring system includes at least one ring hetero atom in addition to the ring oxygen and ring nitrogen of the six-membered hetero ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 96]](../ps.gif) 96 96 | Additional hetero ring containing |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 88. Compounds which contain a hetero ring in addition to the six-membered hetero ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 97]](../ps.gif) 97 97 | Chalcogen bonded directly to the oxazine ring |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 88. Compounds wherein chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium or tellurium) is bonded directly to the six-membered hetero ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 98]](../ps.gif) 98 98 | 1,4-Oxazines |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 63. Compounds wherein the six-membered hetero ring has oxygen in the 1-position, nitrogen in the 4-position and carbons in the remaining four positions. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 99]](../ps.gif) 99 99 | Polycyclo ring system having the oxazine ring as one of the cyclos | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 98. Compounds wherein the six-membered hetero ring is one of
the cyclos of a polycyclo ring system.
| |||
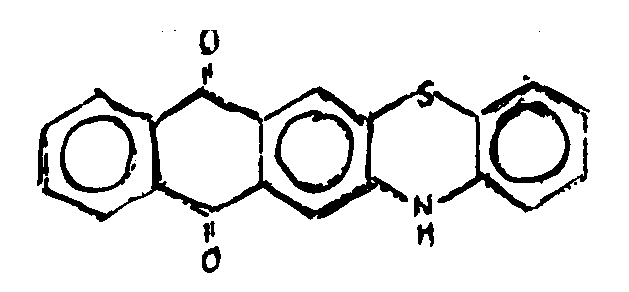
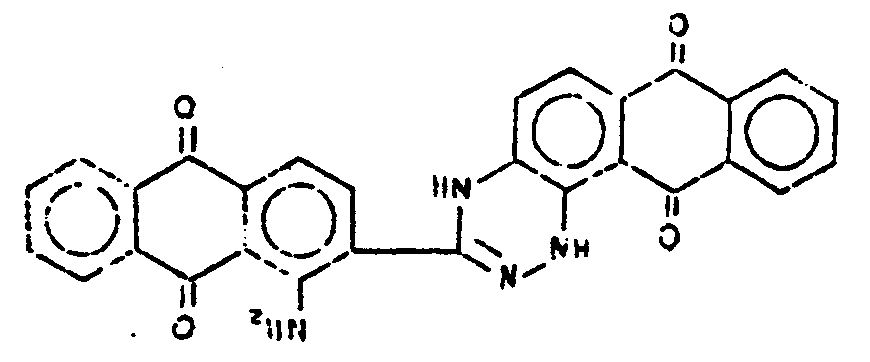
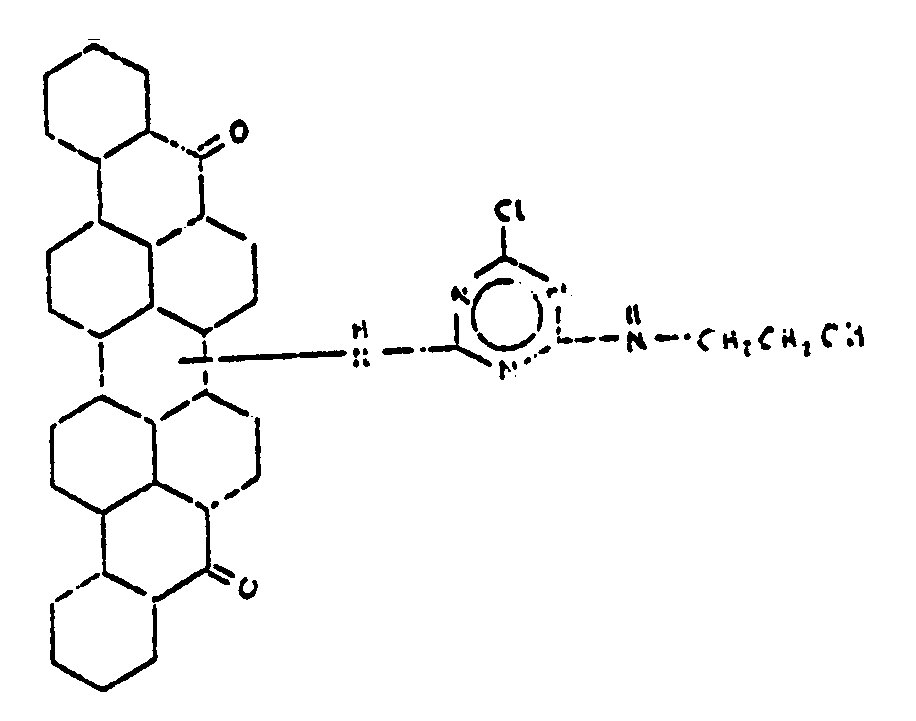
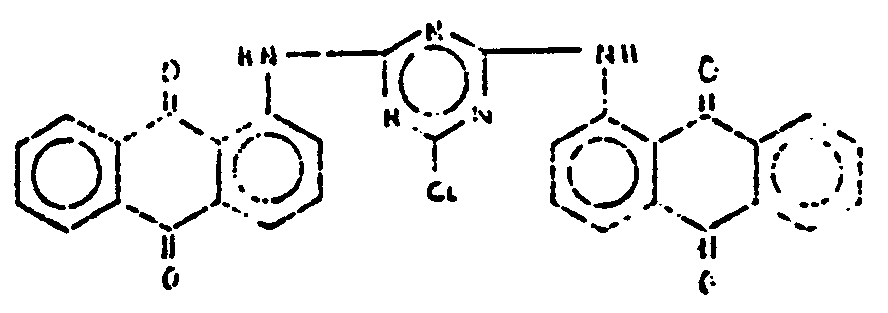
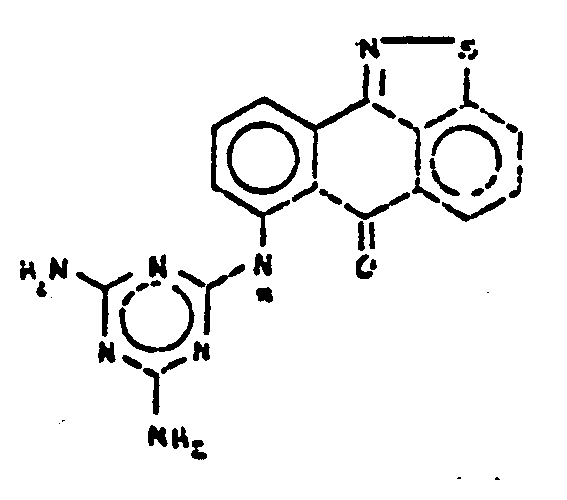
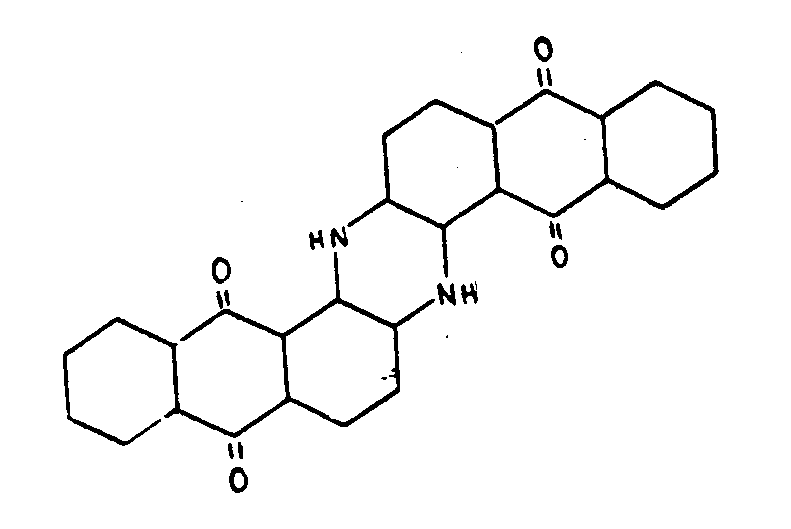
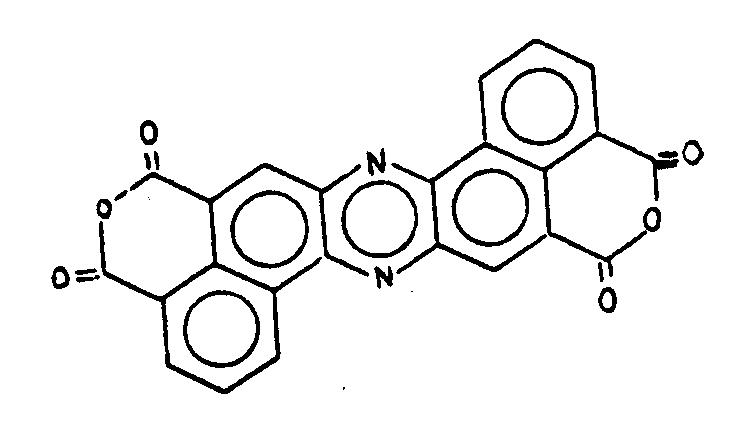
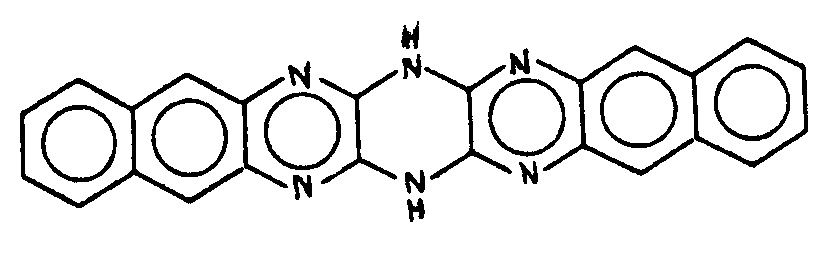
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 100]](../ps.gif) 100 100 | Anthrone or anthraquinone in the polycyclo ring system |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 99. Compounds which contain anthrone or anthraquinone as three cyclos of the polycyclo ring system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 101]](../ps.gif) 101 101 | Tricyclo ring system having the oxazine ring as one of the cyclos |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 99. Compounds wherein the polycyclo ring system consists of three rings. | |
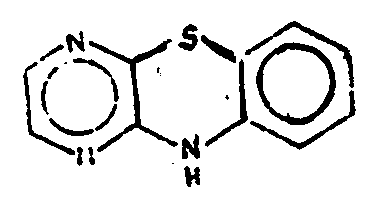
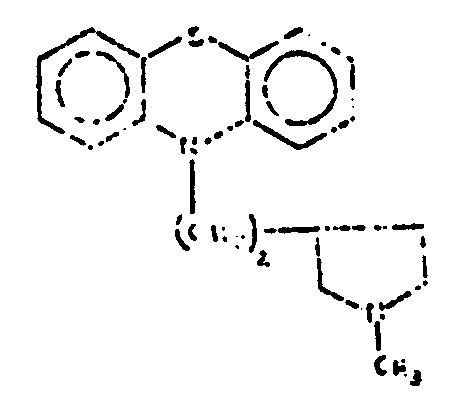
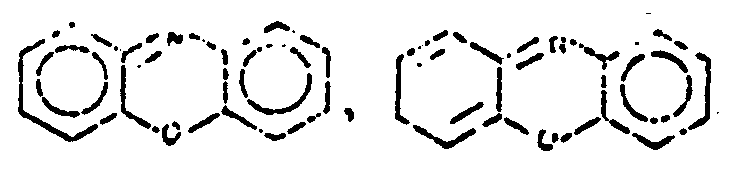
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 102]](../ps.gif) 102 102 | Phenoxazines (including hydrogenated) | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 101. Compounds wherein the tricyclo ring system has the following
basic structure, illustrated below, in which the bonds between ring
members may be single or double bonds.
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 103]](../ps.gif) 103 103 | Plural nitrogens bonded directly to the phenoxazine |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 102. Compounds wherein two or more nitrogen atoms are bonded directly to the phenoxazine ring system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 104]](../ps.gif) 104 104 | Sulfur containing |
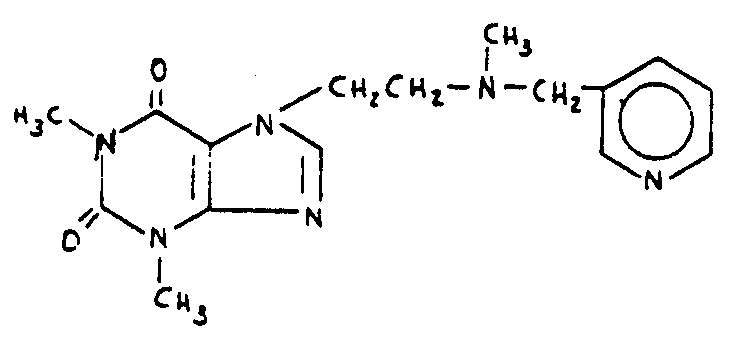
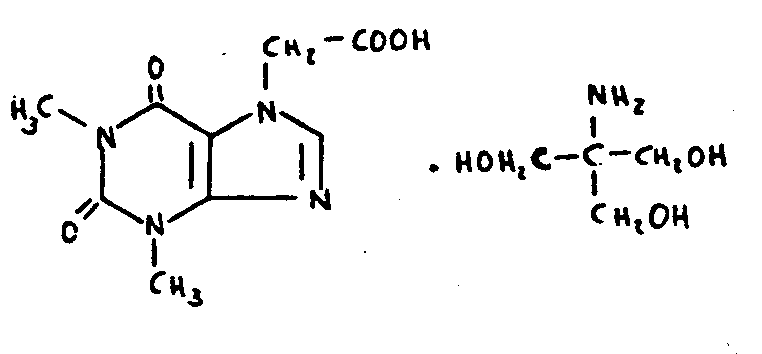
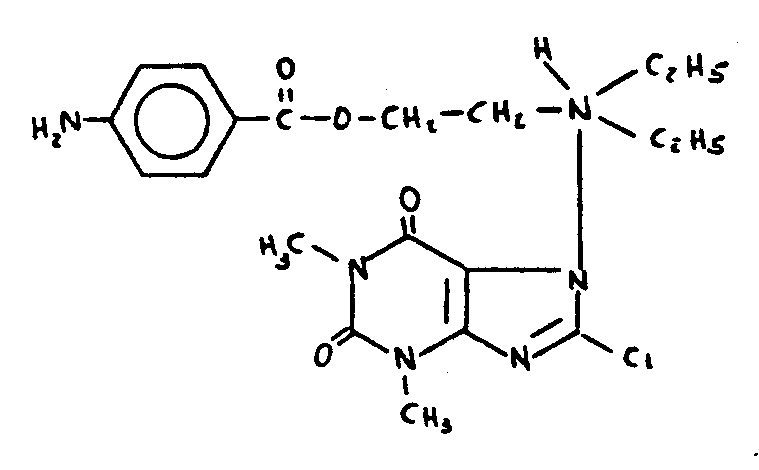
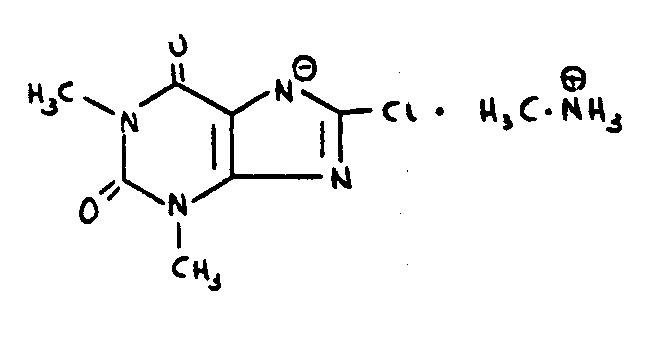
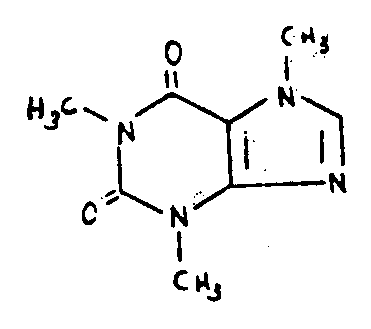
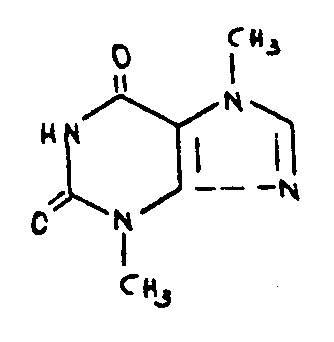
| This subclass is indented under subclass 102. Compounds which include sulfur. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 105]](../ps.gif) 105 105 | Bicyclo ring system having the oxazine ring as one of the cyclos (e.g., benzoxazines, etc.) |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 99. Compounds in which the polycyclo ring system consists of two rings. | |
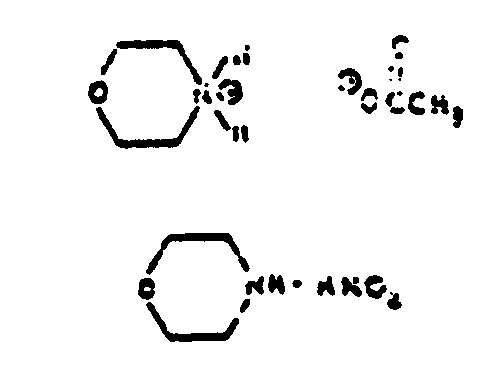
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 106]](../ps.gif) 106 106 | Morpholines (i.e., fully hydrogenated 1,4-oxazines |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 98. Compounds wherein the six-membered hetero ring, having oxygen in the 1-position and nitrogen in the 4-position, has no double bonds between ring members. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 107]](../ps.gif) 107 107 | Addition salts of morpholine which is unsubstituted or hydrocarbyl substituted only | ||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 106. Compounds which are acid addition salts of (a) unsubstituted
morpholine, or (b) morpholine substituted by hydrocarbon radicals
only.
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 108]](../ps.gif) 108 108 | N, N-dihydrocarbyl morpholinium | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 107. Compounds in which the nitrogen atom of the morpholine ring
is disubstituted with hydrocarbon moieties.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 109]](../ps.gif) 109 109 | Hetero ring in ionically bonded moiety | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 107. Compounds which contain a hetero ring in the portion of
the compound which is ionically bonded to the morpholine ring.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 110]](../ps.gif) 110 110 | Phosphorus or sulfur in ionically bonded moiety |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 107. Compounds which include phosphorus or sulfur in the portion of the compound which is ionically bonded to the morpholine ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 111]](../ps.gif) 111 111 | Additional nitrogen containing hetero ring (e.g., thiazetidine, etc.) |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 106. Compounds having, in addition to the morpholine ring, a hetero ring which includes a ring nitrogen. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 112]](../ps.gif) 112 112 | Triazine ring |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 111. Compounds in which the additional hetero ring is six-membered consisting of three ring nitrogens and three ring carbons. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 113]](../ps.gif) 113 113 | 1,3,5-Triazine ring |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 112. Compounds in which the three ring nitrogens of the additional six-membered hetero ring occupy the 1, 3, 5-positions. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 114]](../ps.gif) 114 114 | Diazine ring |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 111. Compounds in which the additional hetero ring is six-membered consisting of two ring nitrogens and four ring carbons. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 115]](../ps.gif) 115 115 | The diazine ring is one of the cyclos in a polycyclo ring system |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 114. Compounds in which the additional six-membered hetero ring is one of the cyclos of a polycyclo ring system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 116]](../ps.gif) 116 116 | The diazine ring is one of the cyclos in a bicyclo ring system |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 115. Compounds in which the polycyclo ring system consists of exactly two rings. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 117]](../ps.gif) 117 117 | Three or more ring hetero atoms in the bicyclo ring system | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 116. Compounds wherein the bicyclo ring system contains at least
one ring hetero atom in addition to the two ring nitrogens of the
additional six-membered hetero ring.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 118]](../ps.gif) 118 118 | Four or more ring nitrogens in the bicyclo ring system |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 117. Compounds wherein the bicyclo ring system cont | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 119]](../ps.gif) 119 119 | Acyclic nitrogen containing |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 116. Compounds which include acyclic nitrogen. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 120]](../ps.gif) 120 120 | 1,4-Diazine ring |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 114. Compounds in which the nitrogen atoms of the additional six-membered hetero ring are in the 1, 4-positions. | |
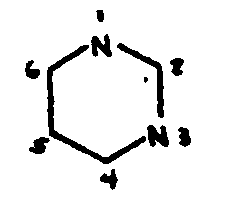
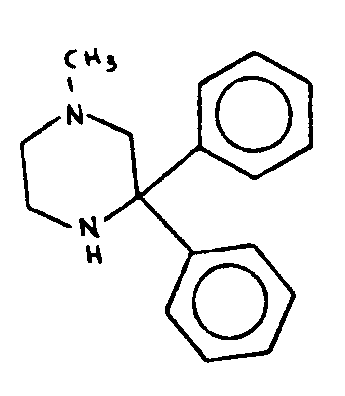
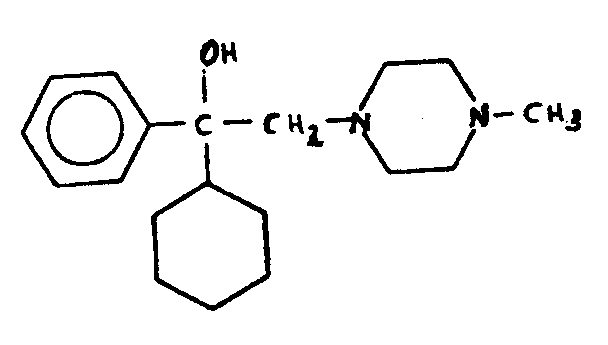
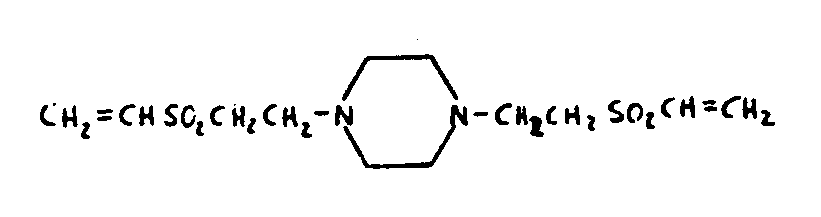
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 121]](../ps.gif) 121 121 | Piperazine ring |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 120. Compounds in which the additional six-membered hetero ring is completely hydrogenated. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 122]](../ps.gif) 122 122 | 1,3-Diazine ring |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 114. Compounds in which the nitrogen atoms of the additional six-membered hetero ring are in the 1, 3-positions. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 123]](../ps.gif) 123 123 | Oxygen bonded directly to the diazine ring |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 122. Compounds in which oxygen is bonded directly to the additional six-membered hetero ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 124]](../ps.gif) 124 124 | Six-membered ring consisting of one nitrogen and five carbons (e.g., pyridine, etc.) |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 111. Compounds in which the additional hetero ring is a six-membered ring consisting of one ring nitrogen and five ring carbons. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 125]](../ps.gif) 125 125 | The additional six-membered hetero ring is one of the cyclos in a polycyclo ring system |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 124. Compounds in which the additional six-membered hetero ring is a cyclo of a polycyclo ring system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 126]](../ps.gif) 126 126 | The additional six-membered hetero ring is one of the cyclos in a tricyclo ring system |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 125. Compounds in which the polycyclo ring system consists of exactly three rings. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 127]](../ps.gif) 127 127 | The additional six-membered hetero ring is one of the cyclos in a bicyclo ring system |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 125. Compounds in which the polycyclo ring system consists of exactly two rings. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 128]](../ps.gif) 128 128 | Quinoline or isoquinoline (including hydrogenated) |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 127. Compounds wherein the bicyclo ring system is characterized by having a six-membered carbocyclic ring ortho-fused to two carbons of the additional six-membered hetero ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 129]](../ps.gif) 129 129 | Piperidine ring |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 124. Compounds in which the additional six-membered hetero ring has no double bonds between ring members. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 130]](../ps.gif) 130 130 | Double bonded divalent chalcogen containing |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 129. Compounds which include double bonded divalent chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium or tellurium). | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 131]](../ps.gif) 131 131 | Double bonded divalent chalcogen containing |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 124. Compounds which include double bonded divalent chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium or tellurium). | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 132]](../ps.gif) 132 132 | Five-membered hetero ring having two or more ring hetero atoms of which at least one is nitrogen |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 111. Compounds in which the additional hetero ring is five-membered having two or more ring hetero atoms, at least one of which is nitrogen. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 133]](../ps.gif) 133 133 | The five-membered hetero ring has at least sulfur and nitrogen as ring hetero atoms |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 132. Compounds in which the five-membered hetero ring contains a ring sulfur, in addition to the ring nitrogen, as a ring hetero atom. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 134]](../ps.gif) 134 134 | Plural sulfurs or nitrogens in the five-membered hetero ring (e.g., thiatriazole, etc.) |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 133. Compounds in which the five-membered hetero ring contains at least two ring nitrogens or at least two ring sulfurs. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 135]](../ps.gif) 135 135 | Benzothiazoles (including hydrogenated) | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 133. Compounds wherein a six-membered carbocyclic ring is ortho-fused
to two carbons of the five-membered hetero ring forming a bicyclo ring
system.
| |||
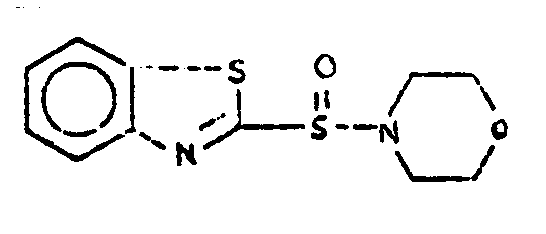
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 136]](../ps.gif) 136 136 | Polysulfide containing chain between morpholine ring and benzothiazole ring system | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 135. Compounds which contain a polysulfide linkage between the
bicyclo ring system and the morpholine ring.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 137]](../ps.gif) 137 137 | The five-membered hetero ring has at least oxygen and nitrogen as ring hetero atoms |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 132. Compounds in which the five-membered hetero ring contains a ring oxygen, in addition to the ring nitrogen, as a ring hetero atom. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 138]](../ps.gif) 138 138 | Oxadiazole ring (including hydrogenated) |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 137. Compounds in which the five-membered hetero ring consists of one ring oxygen, two ring nitrogens and two ring carbons. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 139]](../ps.gif) 139 139 | 1,3-Diazole ring (including hydrogenated) |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 132. Compounds in which the five-membered hetero ring has ring nitrogens in the 1- and 3-positions and ring carbons in the remaining three positions. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 140]](../ps.gif) 140 140 | 1,2-Diazole ring (including hydrogenated) |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 132. Compounds in which the five-membered hetero ring has ringnitrogens in the 1- 2- positions and ring carbons in the remaining three positions. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 141]](../ps.gif) 141 141 | Five-membered hetero ring consisting of one nitrogen and four carbons |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 111. Compounds in which the five-membered hetero ring consists of one ring nitrogen and four ring carbons. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 142]](../ps.gif) 142 142 | The five-membered hetero ring is one of the cyclos in a polycyclo ring system |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 141. Compounds in which the five-membered hetero ring is one of the cyclos of a polycyclo ring system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 143]](../ps.gif) 143 143 | The five-membered hetero ring is one of the cyclos in a bicyclo ring system |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 142. Compounds in which the polycyclo ring system consists of exactly two rings. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 144]](../ps.gif) 144 144 | Chalcogen bonded directly to the bicyclo ring system |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 143. Compounds in which chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium or tellurium) is bonded directly to the bicyclo ring system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 145]](../ps.gif) 145 145 | Sulfur containing hetero ring (e.g., thioxane, etc.) |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 106. Compounds having, in addition to the morpholine ring, a hetero ring which includes a ring sulfur. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 146]](../ps.gif) 146 146 | Thiophene ring (including hydrogenated) |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 145. Compounds wherein the additional hetero ring consists of one ring sulfur and four ring carbons. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 147]](../ps.gif) 147 147 | Additional oxygen containing hetero ring |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 106. Compounds having, in addition to the morpholine ring, a hetero ring which includes a ring oxygen. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 148]](../ps.gif) 148 148 | Plural ring hetero atoms in the additional hetero ring |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 147. Compounds wherein the additional hetero ring contains at least two ring hetero atoms. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 149]](../ps.gif) 149 149 | The additional hetero ring is six-membered |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 147. Compounds wherein the additional hetero ring is six-membered. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 150]](../ps.gif) 150 150 | The additional six-membered hetero ring is one of the cyclos in a polycyclo ring system |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 149. Compounds in which the additional hetero ring is a cyclo in a polycyclo ring system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 151]](../ps.gif) 151 151 | The additional six-membered hetero ring is one of the cyclos in a bicyclo ring system |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 150. Compounds in which the polycyclo ring system consists of exactly two rings. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 152]](../ps.gif) 152 152 | The additional hetero ring is five-membered |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 147. Compounds wherein the additional hetero ring is five-membered. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 153]](../ps.gif) 153 153 | The five-membered hetero ring is one of the cyclos in a polycyclo ring system |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 152. Compounds in which the additional hetero ring is a cyclo in a polycyclo ring system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 154]](../ps.gif) 154 154 | Polycyclo-carbocyclic ring system having at least three cyclos |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 106. Compounds having a polycyclo ring system which contains at least three carbocyclic rings. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 155]](../ps.gif) 155 155 | Tricyclo having three six-membered carbocyclic rings |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 154. Compounds in which the polycyclo ring system consists of exactly three six-membered carbocyclic rings. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 156]](../ps.gif) 156 156 | Anthrone or anthraquinone |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 155. Compounds wherein the tricyclo ring system is part of an anthrone or anthraquinone nucleus, or a hydrogenated form thereof. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 157]](../ps.gif) 157 157 | Phosphorus attached directly or indirectly to morpholine ring by nonionic bonding |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 100. Compounds wherein phosphorus is attached directly or indirectly to the morpholine ring by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 158]](../ps.gif) 158 158 | Sulfur attached directly or indirectly to morpholine ring by nonionic bonding |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 106. Compounds wherein sulfur is attached directly or indirectly to the morpholine ring by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 159]](../ps.gif) 159 159 | Nitrogen attached directly or indirectly to morpholine ring by nonionic bonding |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 158. Compounds wherein nitrogen is attached directly or indirectly to the morpholine ring by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 160]](../ps.gif) 160 160 | Double bonded divalent sulfur |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 159. Compounds wherein the sulfur is a double bonded divalent atom (=S). | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 161]](../ps.gif) 161 161 | Double bonded divalent sulfur |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 158. Compounds wherein the sulfur is a double bonded divalent atom (=S). | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 162]](../ps.gif) 162 162 | Nitrogen attached directed or indirectly to morpholine ring by nonionic bonding |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 106. Compounds wherein nitrogen is attached directly or indirectly to the morpholine ring by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 163]](../ps.gif) 163 163 | Cyano containing |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 162. Compounds which contain the -C=N group. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 164]](../ps.gif) 164 164 | Morpholine ring bonded directly to the nitrogen |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 162. Compounds wherein nitrogen is attached directly to the morpholine ring by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 165]](../ps.gif) 165 165 | Carbocyclic ring bonded directly to the nitrogen |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 162. Compounds wherein nitrogen is attached directly to a carbocyclic ring by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 166]](../ps.gif) 166 166 | Morpholine ring bonded directly to the carbocyclic ring |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 165. Compounds wherein the morpholine ring is bonded directly to the carbocyclic ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 167]](../ps.gif) 167 167 | Nitro bonded directly to the carbocyclic ring |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 165. Compounds wherein the -NO2 group is bonded directly to the carbocyclic ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 168]](../ps.gif) 168 168 | Oxygen double bonded and acyclic nitrogen bonded directly to the same carbon | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 162. Compounds which contain a carbon atom to which acyclic nitrogen
is bonded directly and to which oxygen is attached directly by a
double bond.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 169]](../ps.gif) 169 169 | A ring bonded directly to the carbon |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 168. Compounds in which the carbon atom is bonded directly to a ring in addition to being bonded to acyclic nitrogen and double bonded to oxygen. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 170]](../ps.gif) 170 170 | Oxygen attched directly or indirectly to morpholine ring by nonionic bonding |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 106. Compounds wherein oxygen is attached directly or indirectly to the morpholine ring by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 171]](../ps.gif) 171 171 | The oxygen is in a -COO- group | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 170. Compounds in which the oxygen is part of a O - group.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 172]](../ps.gif) 172 172 | Carbonyl of -COO- group bonded directly to a ring |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 171. Compounds wherein the carbon of the O - group is bonded directly to a ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 173]](../ps.gif) 173 173 | The oxygen is bonded directly to a ring |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 170. Compounds wherein oxygen is bonded directly to a ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 174]](../ps.gif) 174 174 | Ether containing |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 173. Compounds having the formula ROR", wherein R and R" are organic radicals, at least one of which is a ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 175]](../ps.gif) 175 175 | The oxygen is in a carbonyl group | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 170. Compounds wherein the oxygen is double bonded directly to
acyclic carbon.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 176]](../ps.gif) 176 176 | The carbonyl is bonded directly to nitrogen of morpholine ring |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 175. Compounds wherein the acyclic carbon of the carbonyl group is bonded directly to the nitrogen of the morpholine ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 177]](../ps.gif) 177 177 | Ether containing |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 170. Compounds having the formula ROR", wherein R and R" are organic radicals, one which contains the morpholine ring. | |
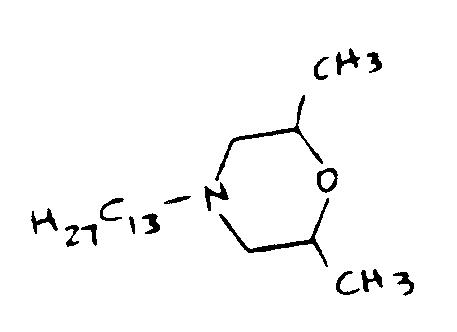
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 178]](../ps.gif) 178 178 | N-hydrocarbyl morpholines | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 106. Compounds in which a hydrocarbon substituent is bonded directly
to the nitrogen of the morpholine ring.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 179]](../ps.gif) 179 179 | Tetrazines |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 1. Compounds in which the six-membered hetero ring consists of four ring nitrogens and two ring carbons. | |
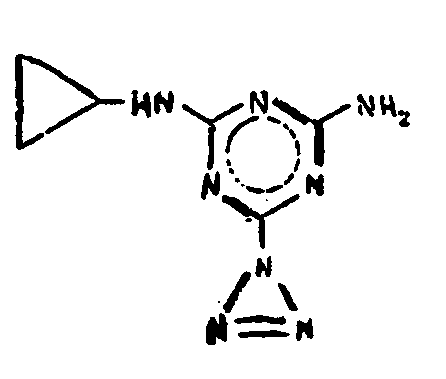
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 180]](../ps.gif) 180 180 | Triazines | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 1. Compounds wherein the six-membered hetero ring consists
of three ring nitrogens and three ring carbons.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 181]](../ps.gif) 181 181 | Heavy metal or aluminum containing | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 180. Compounds which contain aluminum or a metal having a specific
gravity greater than 4.
| |||
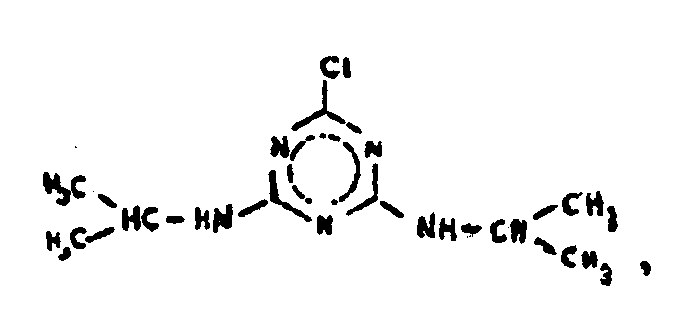
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 182]](../ps.gif) 182 182 | Asymmetrical (e.g., 1, 2, 4-triazines, etc.) | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 180. Compounds in which two of the ring nitrogens of the six-membered
hetero ring are bonded directly to each other.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 183]](../ps.gif) 183 183 | Polycyclo ring system having the asymmetrical triazine ring as one of the cyclos | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 182. Compounds wherein the asymmetrical six-membered hetero ring
is a cyclo in a polycyclo ring system.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 184]](../ps.gif) 184 184 | Four or more ring hetero atoms in the polycyclo ring system | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 183. Compounds wherein the polycyclo ring system contains a ring
hetero atom in addition to the three ring nitrogens in the six-membered
hetero ring.
| |||
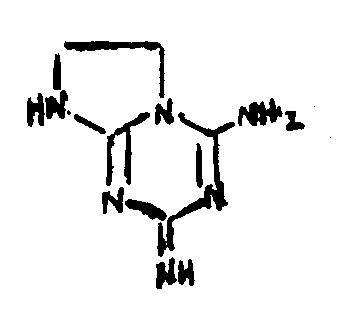
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 185]](../ps.gif) 185 185 | Hexamethylenetetramines |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 180. Compounds having the following basic structure and derivatives
thereof wherein the hexamethylene tetramine ring system is not destroyed.
| |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 186]](../ps.gif) 186 186 | Processes |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 185. Processes in which hexamethylene tetramine or derivatives thereof are produced, separated from impurities or separated from the reaction mixture. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 187]](../ps.gif) 187 187 | Anthrone or anthraquinone containing | ||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 180. Compounds which contain anthrone or anthraquinone.
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 188]](../ps.gif) 188 188 | Polycyclo ring system having the anthrone or anthraquinone and at least one hetero ring as cyclos | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 187. Compounds wherein anthrone or anthraquinone is part of a
polycyclo ring system which contains at least one hetero ring.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 189]](../ps.gif) 189 189 | Sulfur containing |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 187. Compounds which contain sulfur. | |
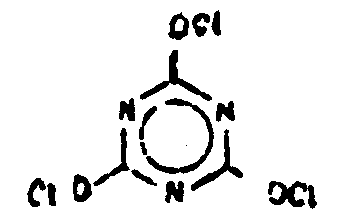
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 190]](../ps.gif) 190 190 | Cyanuric chloride or dichloroisocyanuric acid salt | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 180. Compounds which are chlorinated derivatives of cyanuric
or isocyanuric acid, and salts thereof.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 191]](../ps.gif) 191 191 | Processes utilizing cyanogen chloride reactant |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 190. Processes for the production of cyanuric chloride or a dichloro-iso-cyanuric acid salt which utilize cyanogen chloride as a (N = C- C1) reactant. | |
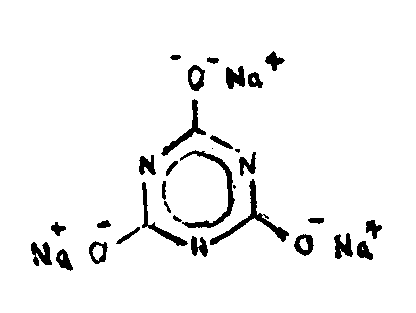
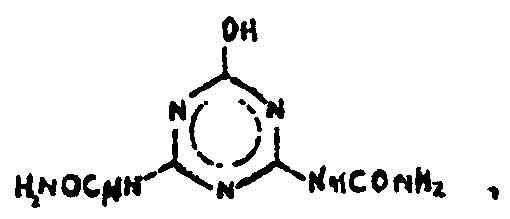
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 192]](../ps.gif) 192 192 | Cyanuric acid per se or salt thereof | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 180. Compounds termed cyanuric acid, which exists in two forms
as shown by the equilibrium.
‘normal’ cyanuric acid isocyanuric acidand salts thereof.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 193]](../ps.gif) 193 193 | Trimerization process to form the triazine ring | ||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 180. Processes wherein the six-membered hetero ring is formed
by a trimerization reaction of a monomer.
| |||||
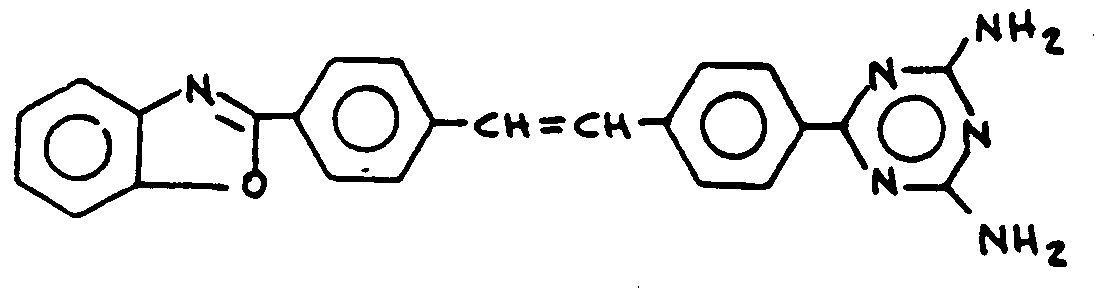
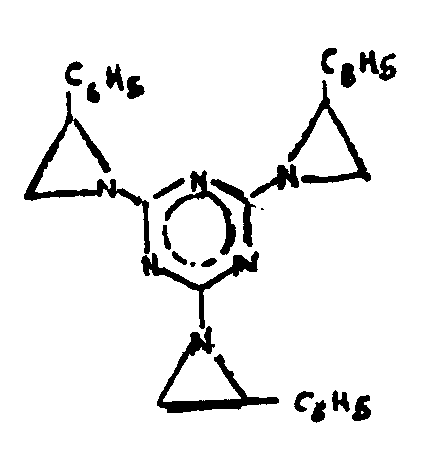
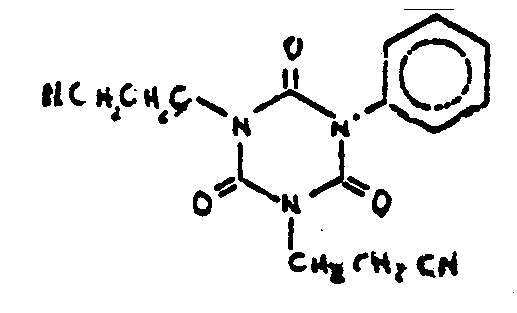
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 193.1]](../ps.gif) 193.1 193.1 | Stilbene containing | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 180. Stilbene containing:Compounds which contains the group,
illustrated below, wherein only hydrogen may be replaced.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 193.2]](../ps.gif) 193.2 193.2 | Plural triazine rings containing: | ||
Compounds under subclss 193.1 which contain at least two
triazine rings.
| |||
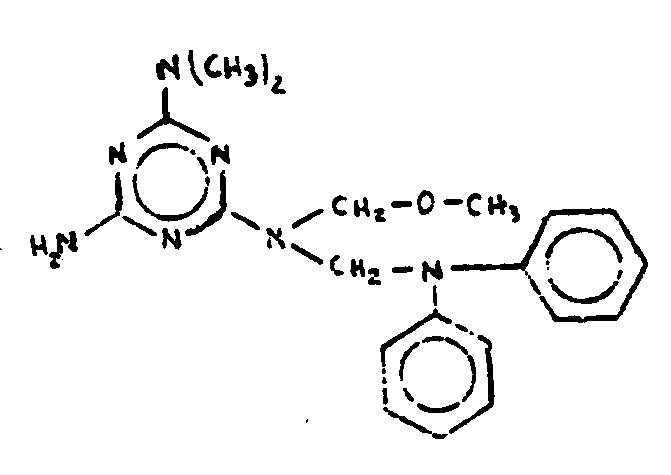
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 194]](../ps.gif) 194 194 | Substituent nitrogen bonded directly to carbon of the triazine ring | ||||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 180. Compounds wherein nitrogen, in addition to the three ring
nitrogens, is bonded directly to a ring carbon of the six-membered
hetero ring.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 195]](../ps.gif) 195 195 | Phosphorus containing |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 194. Compounds which contain phosphorus. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 196]](../ps.gif) 196 196 | Three substituent nitrogens bonded directly to the three carbons of the triazine ring | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 194. Compounds wherein nitrogen, other than the three ring nitrogens,
is bonded directly to each of the three ring carbons of the six-membered hetero
ring.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 197]](../ps.gif) 197 197 | Additional ring containing | ||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 196. Compounds in which there is a ring addition to the six-membered
hetero ring.
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 198]](../ps.gif) 198 198 | Hetero ring | ||||||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 197. Compounds in which the additional ring is a hetero ring.
| |||||||||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 199]](../ps.gif) 199 199 | Halogen or sulfur containing |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 196. Compounds which contain a halogen or sulfur. | |
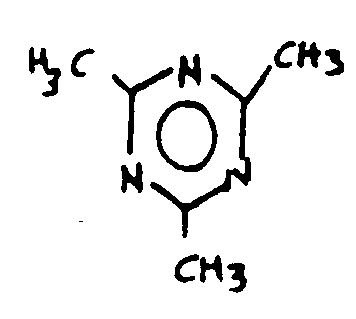
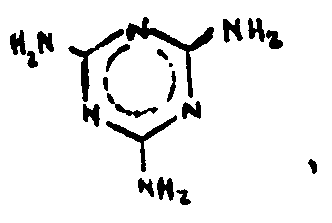
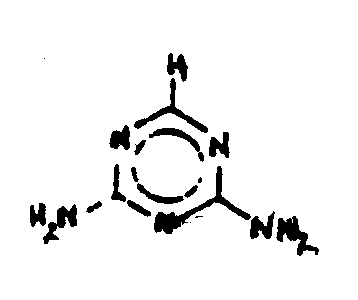
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 200]](../ps.gif) 200 200 | Melamine per se, or salt thereof |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 196. Compounds having the structure below or salts thereof.
| |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 201]](../ps.gif) 201 201 | Processes utilizing urea or biuret reactant |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 200. Processes wherein melamine is produced from urea or biuret. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 202]](../ps.gif) 202 202 | Processes utilizing cyanamide or dicyanamide reactant |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 200. Processes wherein melamine is produced from cyanamide or dicyanamide. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 203]](../ps.gif) 203 203 | Purification or recovery |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 200. Processes wherein melamine is separated from impurities or from the reaction mixture. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 204]](../ps.gif) 204 204 | Two substituent nitrogens bonded directly to two carbons of the triazine ring | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 194. Compounds wherein nitrogen, other than the three ring nitrogens,
is bonded directly to two of the three ring carbons of the six-membered hetero
ring.
| |||
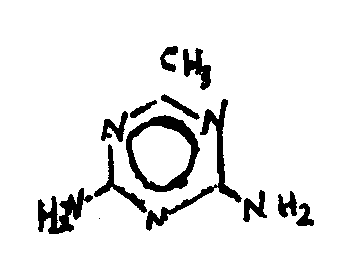
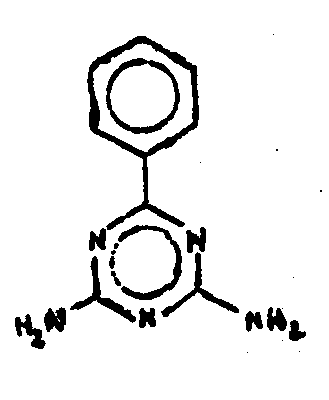
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 205]](../ps.gif) 205 205 | Guanamines | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 204. Compounds wherein hydrogen or carbon is bonded directly
to the remaining ring carbon of the six-membered hetero ring.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 206]](../ps.gif) 206 206 | Additional ring containing | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 205. Compounds which contain a ring in addition to the six-membered
hetero ring.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 207]](../ps.gif) 207 207 | Hetero ring | ||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 206. Compounds wherein the additional ring is a hetero ring.
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 208]](../ps.gif) 208 208 | Additional ring containing | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 204. Compounds which contain a ring in addition to the six-membered
hetero ring.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 209]](../ps.gif) 209 209 | Hetero ring | ||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 208. Compounds wherein the additional ring is a hetero ring.
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 210]](../ps.gif) 210 210 | Sulfur containing |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 204. Compounds which contain sulfur. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 211]](../ps.gif) 211 211 | Additional ring containing |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 194. Compounds which contain a ring in addition to the six-membered hetero ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 212]](../ps.gif) 212 212 | Hetero ring | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 211. Compounds in which the additional ring is a hetero ring.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 213]](../ps.gif) 213 213 | Sulfur containing |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 194. Compounds which contain sulfur. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 214]](../ps.gif) 214 214 | Phosphorus containing |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 180. Compounds which contain phosphorus. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 215]](../ps.gif) 215 215 | Chalcogen or halogen containing substituent |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 180. Compounds having a substituent containing chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium or tellurium) or halogen bonded directly or indirectly to the six-membered hetero ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 216]](../ps.gif) 216 216 | Bonded to triazine ring carbon | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 215. Compounds wherein the chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium
or tellurium) or halogen containing substituent is bonded to a ring
carbon of the six-membered hetero ring.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 217]](../ps.gif) 217 217 | Halogen bonded directly to triazine ring carbon | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 216. Compounds wherein a halogen is bonded directly to a ring
carbon of the six-membered hetero ring.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 218]](../ps.gif) 218 218 | Chalcogen bonded directly to triazine ring carbon | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 217. Compounds wherein chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium
or tellurium) is bonded directly to a ring carbon of the six-membered hetero
ring.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 219]](../ps.gif) 219 219 | Chalcogen bonded directly to triazine ring carbon | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 216. Compounds wherein chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium,
tellurium) is bonded directly to a ring carbon of the six-membered
hetero ring.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 220]](../ps.gif) 220 220 | Divalent chalcogen double bonded directly to triazine ring carbon | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 219. Compounds wherein divalent chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur,
selenium or tellurium) is double bonded directly to a ring carbon
of the six-membered hetero ring.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 221]](../ps.gif) 221 221 | To three ring carbons | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 220. Compounds wherein divalent chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur,
selenium or tellurium) is double bonded directly to each of the
ring carbons of the six-membered hetero ring.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 222]](../ps.gif) 222 222 | Nitrogen containing substituent | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 221. Compounds which contain nitrogen in a substituent.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 223]](../ps.gif) 223 223 | To two ring carbons | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 200. Compounds wherein divalent chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur,
selenium or tellurium) is double bonded directly to two of the ring
carbons of the six-membered hetero ring.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 224]](../ps.gif) 224 224 | The six-membered hetero ring consists of two nitrogens and four carbons (e.g., 1,2-diazines, etc.): |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 1. Compounds in which the six-membered hetero ring consists of two ring nitrogens and four ring carbons. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 225]](../ps.gif) 225 225 | Heavy metal or aluminum containing: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 224. Compounds which contain aluminum or a metal with a specific gravity greater than 4. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 226]](../ps.gif) 226 226 | Arsenic or zinc containing: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 225. Compounds which contain arsenic or zinc. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 227]](../ps.gif) 227 227 | Mercury containing: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 225. Compounds which contain mercury. | |
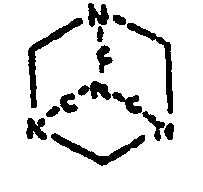
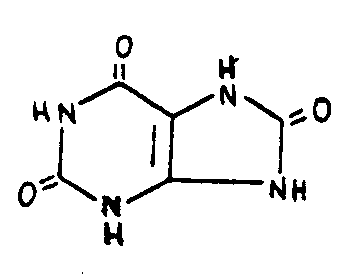
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 228]](../ps.gif) 228 228 | Purine containing (including hydrogenated): |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 227. Compounds which contain a purine nucleus of the following
basic structure in which the bonds between ring members may be single
or double bonds.
| |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 229]](../ps.gif) 229 229 | Boron or silicon containing: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 224. Compounds which contain boron or silicon. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 230]](../ps.gif) 230 230 | Spiro: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 224. Compounds which contain a spiro ring system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 231]](../ps.gif) 231 231 | Spiro diazine: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 230. Compounds wherein at least one of the rings in the spiro ring system is a six-membered hetero ring consisting of two nitrogens and four carbons. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 232]](../ps.gif) 232 232 | Phosphorus attached directly or indirectly to a 1,2-diazine ring by nonionic bonding: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 224. Compounds wherein phosphorus is attached directly or indirectly by nonionic bonding to the six-membered hetero ring which has the two ring nitrogens in the 1- and 2-positions. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 233]](../ps.gif) 233 233 | Polycyclo ring system having a 1,2-diazine ring as one of the cyclos: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 224. Compounds wherein the six-membered hetero ring has the two
ring nitrogens in the 1- and 2-positions and is a cyclo in a polycyclo
ring system.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 234]](../ps.gif) 234 234 | Tricyclo ring system having the 1,2-diazine ring as one of the cyclos: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 233. Compounds wherein the polycyclo ring system consists of three rings. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 235]](../ps.gif) 235 235 | Bicyclo ring system having the 1,2-diazine ring as one of the cyclos: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 233. Compounds wherein the polycyclo ring system consists of two rings. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 236]](../ps.gif) 236 236 | At least three ring nitrogens in the bicyclo ring system: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 235. Compounds wherein the bicyclo ring system includes at least one ring nitrogen in addition to the two ring nitrogens of the six-membered hetero ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 237]](../ps.gif) 237 237 | Phthalazines (including hydrogenated): |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 235. Compounds wherein the bicyclo ring system has the following
basic structure in which the bonds between ring members may be single
or double bonds.:
| |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 238]](../ps.gif) 238 238 | 1,2-diazines which contain an additional hetero ring: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 224. Compounds wherein the six-membered hetero ring has the two ring nitrogens in the 1-and 2-positions and which contain an additional hetero ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 239]](../ps.gif) 239 239 | Chalcogen bonded directly to ring carbon of a 1,2-diazine ring: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 224. Compounds wherein chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium) is bonded directly to a ring carbon of the six-membered hetero ring which has the two ring nitrogens in the 1- and 2-positions. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 240]](../ps.gif) 240 240 | Plural chalcogens bonded directly: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 239. Compounds wherein at least two chalcogen atoms are bonded
directly to the six-membered hetero ring.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 241]](../ps.gif) 241 241 | Halogen attached directly to the 1,2-diazine ring by nonionic bonding: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 239. Compounds wherein halogen is attached directly to the six-membered hetero ring by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 242]](../ps.gif) 242 242 | 1,3-diazines: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 224. Compounds wherein the six-membered hetero ring has nitrogens
in the 1- and 3-positions, and carbons in the remaining four positions.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 243]](../ps.gif) 243 243 | Phosphorus attached directly or indirectly to the diazine ring by nonionic bonding: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 242. Compounds wherein phosphorus is attached directly or indirectly to the six-membered hetero ring by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 244]](../ps.gif) 244 244 | Polycyclo ring system having the diazine ring as one of the cyclos: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 243. Compounds wherein the six-membered hetero ring is one of the cyclos in a polycyclo ring system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 245]](../ps.gif) 245 245 | Polycyclo ring system having the diazine ring as one of the cyclos: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 242. Compounds wherein the six-membered hetero ring is one of
the cyclos in a polycyclo ring system.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 246]](../ps.gif) 246 246 | Tetracyclo ring system having the diazine ring as one of the cyclos: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 245. Compounds wherein the polycyclo ring system consists of four rings. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 247]](../ps.gif) 247 247 | Three or more ring hetero atoms in the tetracyclo ring system: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 246. Compounds wherein the tetracyclo ring system includes at
least one ring hetero atom in addition to the two ring nitrogens
of the six-membered hetero ring.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 248]](../ps.gif) 248 248 | Ring carbon is shared by three of the cyclos (e.g., anthrapyrimidine, etc.): | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 246. Compounds wherein three of the cyclos of the tetracyclo
ring system have a ring carbon which is common to each of them.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 249]](../ps.gif) 249 249 | Tricyclo ring system having the diazine ring as one of the cyclos: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 245. Compounds wherein the polycyclo ring system consists of three rings. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 250]](../ps.gif) 250 250 | Three or more ring hetero atoms in the tricyclo ring system: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 249. Compounds wherein the tricyclo ring system includes at least
one ring hetero atom in addition to the two ring nitrogens of the
six-membered hetero ring.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 251]](../ps.gif) 251 251 | Four or more ring nitrogens in the tricyclo ring system: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 250. Compounds wherein the tricyclo ring system includes at least two ring nitrogens in addition to the two ring nitrogens of the six-membered hetero ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 252]](../ps.gif) 252 252 | Ring nitrogen is shared by two of the cyclos: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 249. Compounds in which a ring nitrogen is a member of two of
the rings in the tricyclo ring system.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 253]](../ps.gif) 253 253 | Bicyclo ring system having the diazine ring as one of the cyclos: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 245. Compounds in which the polycyclo ring system consists of two rings. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 254]](../ps.gif) 254 254 | At least five ring hetero atoms in the bicyclo ring system: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 253. Compounds wherein the bicyclo ring system includes at least three ring hetero atoms in addition to the two ring nitrogens of the six-membered hetero ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 255]](../ps.gif) 255 255 | Four ring hetero atoms in the bicyclo ring system: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 253. Compounds wherein the bicyclo ring system includes two ring hetero atoms in addition to the two ring nitrogens of the six-membered hetero ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 256]](../ps.gif) 256 256 | Four ring nitrogens in the bicyclo ring system: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 255. Compounds wherein the bicyclo ring system contains four ring nitrogens. | |
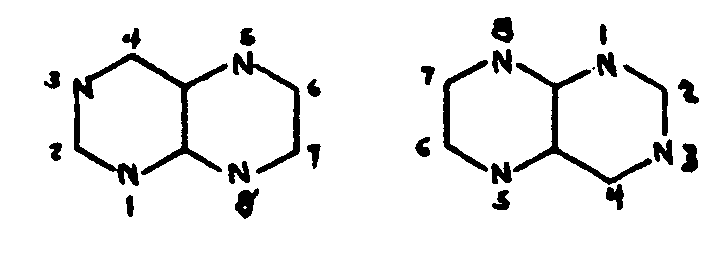
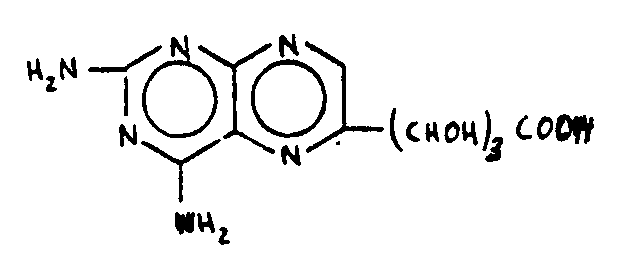
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 257]](../ps.gif) 257 257 | Pterdines (including hydrogenated): | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 256. Compounds wherein the bicyclo ring system has the following
basic structure in which the bonds between ring members may be single
or double bonds.:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 258]](../ps.gif) 258 258 | Nitrogen bonded directly to the pteridine ring system: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 257. Compounds wherein nitrogen is bonded directly to the pteridine ring system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 259]](../ps.gif) 259 259 | Plural nitrogens bonded directly to the pteridine ring system: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 258. Compounds wherein two or more nitrogen atoms are bonded directly to the pteridine ring system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 260]](../ps.gif) 260 260 | At 2- and 4-positions: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 259. Compounds wherein nitrogen atoms are bonded directly to
the 2- and 4-position carbons of the pteridine ring system.
| |||
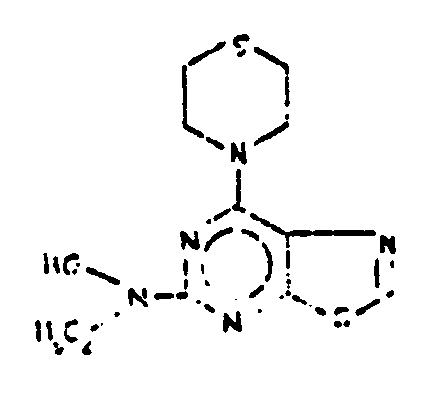
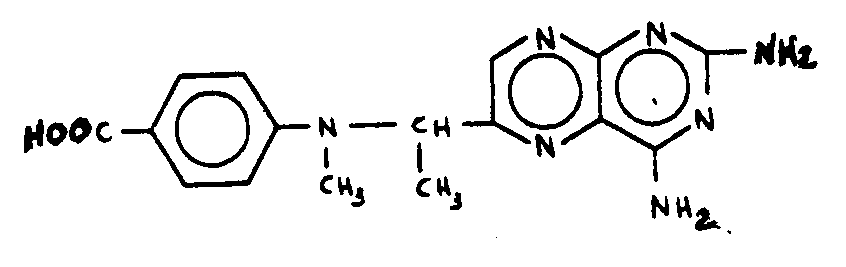
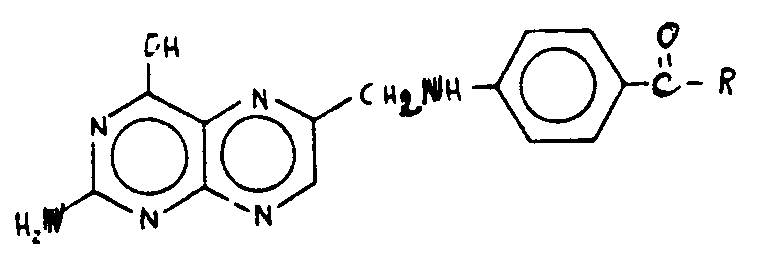
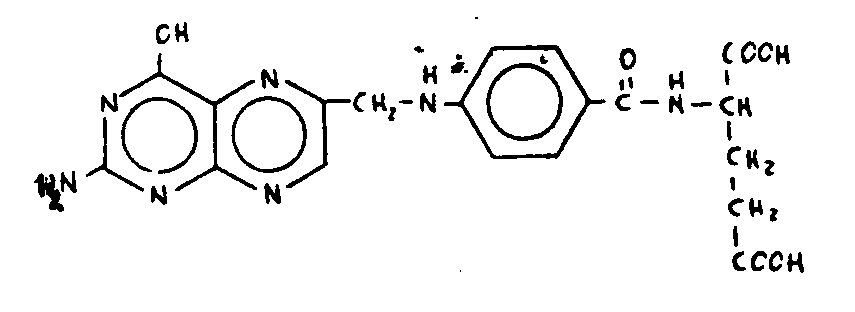
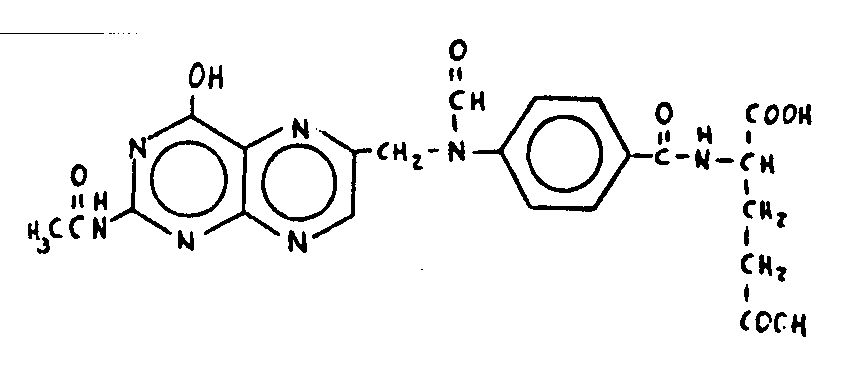
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 261]](../ps.gif) 261 261 | Pteroyl per se or having -C(=X)-, wherein X is chalcogen, bonded directly to acyclic nitrogen of otherwise unsubstituted pteroyl: | ||||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 258. Compounds which contain the structure, per se, wherein
R is a radical; and derivatives thereof wherein one or more of the
hydrogens attached to the acyclic nitrogens shown in the structure
is replaced by , in which X is chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur,
selenium, or tellurium), and no other substitution is made in the structure
shown.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 262]](../ps.gif) 262 262 | The other cyclo in the bicyclo ring system is five-membered: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 256. Compounds wherein a five-membered ring is the other cyclo of the bicyclo ring system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 263]](../ps.gif) 263 263 | Ring nitrogen is shared by the two cyclos: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 262. Compounds in which a ring nitrogen is a member of both of
the rings in the bicyclo ring system.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 264]](../ps.gif) 264 264 | Purines (including hydrogenated): |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 262. Compounds wherein the bicyclo ring system has the following
basic structure, in which the bonds between ring members may be
single or double bonds:
| |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 265]](../ps.gif) 265 265 | Chalcogen bonded directly to ring carbon of the purine ring system: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 264. Compounds wherein chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium) is bonded directly to a ring carbon of the purine ring system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 266]](../ps.gif) 266 266 | At 2-, 6-, and 8-positions: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 265. Compounds wherein chalcogens (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium,
or tellurium) are bonded directly to the 2-, 6-, and 8-positions
of the purine ring system.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 267]](../ps.gif) 267 267 | At 2- and 6- positions (e.g., theophyllines etc.): |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 265. Compounds wherein chalcogens (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium) are bonded directly to the 2- and 6- positions of the purine ring system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 268]](../ps.gif) 268 268 | Additional polycyclo ring system, which is not another purine, having a hetero ring as one of the cyclos: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 267. Compounds which contain a nonpurine polycyclo ring system,
having a hetero ring as one of the cyclos, in addition to the purine
ring system.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 269]](../ps.gif) 269 269 | Additional hetero ring which is unsaturated and is not one of the cyclos of a purine ring system: | ||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 267. Compounds having, in addition to the purine ring system,
a hetero ring which has at least one double bond between ring members.
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 270]](../ps.gif) 270 270 | Plural ring nitrogens in the additional hetero ring: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 269. Compounds wherein the additional hetero ring contains at least two ring nitrogens. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 271]](../ps.gif) 271 271 | Having -C(=X)-, wherein X is chalcogen, attached directly or indirectly to the purine ring system by nonionic bonding or halogen bonded directly at 8-position (e.g., theophylline acetate, 8-chlorotheophylline, etc.): | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 267. Compounds wherein either a group, in which X is chalcogen
(i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium), is attached directly
or indirectly to the purine ring system by nonionic bonding, or
a halogen is bonded directly to the 8-position of the purine ring
system.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 272]](../ps.gif) 272 272 | Nitrogen attached directly or indirectly to the purine ring system by nonionic bonding: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 267. Compounds wherein nitrogen is attached directly or indirectly to the purine ring system by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 273]](../ps.gif) 273 273 | Positions other than 2- and 6- are unsubstituted or hydrocarbyl substituted only (e.g., theophylline, etc.): |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 267. Compounds wherein the purine ring system, at positions other than 2- and 6-, is unsubstituted or substituted by hydrocarbon radicals only. | |
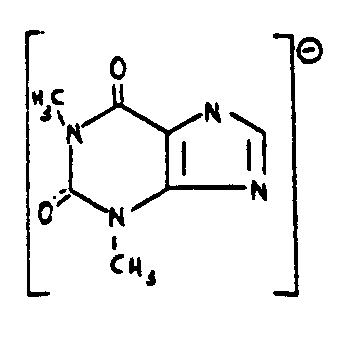
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 274]](../ps.gif) 274 274 | Caffeine per se, theobromine per se, or salt thereof: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 273. Compounds which have one of the following structures or
salts thereof.
| |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 275]](../ps.gif) 275 275 | Recovery from natural or waste materials: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 274. Compounds wherein caffeine, theobromine, or a salt thereof, is separated from impurities or from a reaction mixture. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 276]](../ps.gif) 276 276 | Nitrogen attached directly or indirectly to the purine ring system by nonionic bonding: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 265. Compounds wherein nitrogen is attached directly or indirectly to the purine ring system by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 277]](../ps.gif) 277 277 | Nitrogen attached directly or indirectly to the purine ring system by nonionic bonding: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 264. Compounds wherein nitrogen is attached directly or indirectly to the purine ring system by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 278]](../ps.gif) 278 278 | Three ring hetero atoms in the bicyclo ring system: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 253. Compounds wherein the bicyclo ring system includes a ring
hetero atom in addition to the two ring nitrogens of the six-membered
hetero ring.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 279]](../ps.gif) 279 279 | Three ring nitrogens in the bicyclo ring system: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 278. Compounds wherein the bicyclo ring system contains three ring nitrogens. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 280]](../ps.gif) 280 280 | The other cyclo in the bicyclo ring system is five-membered: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 279. Compounds wherein a five-membered ring is the other cyclo of the bicyclo ring system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 281]](../ps.gif) 281 281 | Ring nitrogen is shared by the two cyclos: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 280. Compounds in which a ring nitrogen is a member of both of
the rings in the bicyclo ring system.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 282]](../ps.gif) 282 282 | Ring nitrogen is shared by the two cyclos: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 253. Compounds in which a ring nitrogen is a member of both of
the rings in the bicyclo ring system.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 283]](../ps.gif) 283 283 | The other cyclo in the bicyclo ring system is a benzene ring (e.g., quinazoline, etc.): | ||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 253. Compounds wherein the bicyclo ring system consists of a
benzene ring and the six-membered hetero ring.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 284]](../ps.gif) 284 284 | Additional unsaturated hetero ring having at least nitrogen as a ring hetero atom: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 283. Compounds having, in addition to the bicyclo ring system, a hetero ring which has at least one double bond between ring members and at least one ring nitrogen. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 285]](../ps.gif) 285 285 | Chalcogen bonded directly at 2- and 4- positions: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 283. Compounds wherein chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium,
or tellurium) is bonded directly at the 2- and 4- positions of the
bicyclo ring system.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 286]](../ps.gif) 286 286 | Chalcogen bonded directly at 2-position: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 283. Compounds wherein chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium) is bonded directly at the 2-position of the bicyclo ring system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 287]](../ps.gif) 287 287 | Chalcogen bonded directly at 4-position: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 283. Compounds wherein chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium) is bonded directly at the 4-position of the bicyclo ring system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 288]](../ps.gif) 288 288 | Sulfur bonded directly at 6- position: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 287. Compounds wherein sulfur is bonded directly at the 6-position
of the bicyclo ring system.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 289]](../ps.gif) 289 289 | Carbocyclic ring bonded directly at 2-position: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 287. Compounds wherein a carbocyclic ring is bonded directly at the 2-position of the bicyclo ring system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 290]](../ps.gif) 290 290 | Carbocyclic ring bonded directly at 3-position: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 287. Compounds wherein a carbocyclic ring is bonded directly at the 3-position of the bicyclo ring system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 291]](../ps.gif) 291 291 | Nitrogen bonded directly at 2- and 4- positions: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 283. Compounds wherein nitrogens are bonded directly at the 2- and 4-positions of the bicyclo ring system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 292]](../ps.gif) 292 292 | Nitrogen bonded directly at 2-position: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 283. Compounds wherein nitrogen is bonded directly at the 2-position of the bicyclo ring system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 293]](../ps.gif) 293 293 | Nitrogen bonded directly at 4-position: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 283. Compounds wherein nitrogen is bonded directly at the 4-position of the bicyclo ring system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 294]](../ps.gif) 294 294 | Polycyclo-carbocyclic ring system having at least three cyclos: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 242. Compounds having a polycyclo ring system which contains at least three carbocyclic rings. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 295]](../ps.gif) 295 295 | Plural diazine rings: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 242. Compounds which contain at least two of the six-membered
hetero rings, each having ring nitrogens in the 1- and 4-positions,
and carbons in the remaining four positions.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 296]](../ps.gif) 296 296 | Plural 1, 3-diazine rings: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 295. Compounds which contain at least two of the six-membered hetero rings, each having its nitrogens in the 1- and 3- positions, and carbons in the remaining four positions. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 297]](../ps.gif) 297 297 | Nitrogen attached directly at 2-position by nonionic bonding and sulfur bonded directly to the nitrogen: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 242. Compounds which include nitrogen attached directly at the
2-position of the six-membered hetero ring by nonionic bonding and
sulfur bonded directly to the nitrogen which is at the 2-position.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 298]](../ps.gif) 298 298 | Chalcogen bonded directly to diazine ring carbon: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 242. Compounds wherein chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium) is bonded directly to a ring carbon of the six-membered hetero ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 299]](../ps.gif) 299 299 | At 2-, 4-, and 6-positions (e.g., barbituric acid, etc.): |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 298. Compounds wherein chalcogens (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium) are bonded directly at the 2-, 4-, and 6-positions of the six-membered hetero ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 300]](../ps.gif) 300 300 | Additional hetero ring which is unsaturated: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 299. Compounds having, in addition to the six-membered hetero ring, a hetero ring which has at least one double bond between ring members. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 301]](../ps.gif) 301 301 | Nitrogen attached directly or indirectly to the diazine ring by nonionic bonding: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 299. Compounds wherein nitrogen is attached directly or indirectly to the six-membered hetero ring by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 302]](../ps.gif) 302 302 | Additional chalcogen attached directly or indirectly to the diazine ring by nonionic bonding: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 299. Compounds wherein an additional chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium) is attached directly or indirectly to the six-membered hetero ring by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 303]](../ps.gif) 303 303 | Halogen attached directly or indirectly to the diazine ring by nonionic bonding: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 299. Compounds wherein halogen is attached directly or indirectly to the six-membered hetero ring by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 304]](../ps.gif) 304 304 | Alicyclic ring attached directly or indirectly to the diaziane ring by nonionic bonding: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 299. Compounds wherein an alicyclic ring is attached directly
or indirectly to the six-membered hetero ring by nonionic bonding.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 305]](../ps.gif) 305 305 | Phenyl bonded directly at 5-position: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 299. Compounds wherein a univalent radical derived from benzene by removal of one hydrogen is bonded directly at the 5-position of the six-membered hetero ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 306]](../ps.gif) 306 306 | Acyclic ethylenic or acetylenic unsaturation containing: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 299. Compounds which contain ethylenic or acetylenic unsaturation
which is not between ring members of a ring.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 307]](../ps.gif) 307 307 | Plural alkyl groups bonded directly at 5-position: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 299. Compounds wherein at least two alkyl groups are bonded directly to the 5-position of the six-membered hetero ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 308]](../ps.gif) 308 308 | Plural diverse alkly groups bonded directly at 5-position: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 307. Compounds wherein at least two different alkyl groups are
bonded directly to the 5-position of the six-membered hetero ring.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 309]](../ps.gif) 309 309 | At 2-position and a 4- or 6-position: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 298. Compounds wherein chalcogens (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium,
or tellurium) are bonded directly to the 2-position and to the 4-
or 6-position of the six-membered hetero ring.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 310]](../ps.gif) 310 310 | Additional hetero ring which is unsaturated: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 309. Compounds having, in addition to the six-membered hetero ring, a hetero ring which has at least one double bond between ring members. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 311]](../ps.gif) 311 311 | Nitrogen attached directly or indirectly to the diazine ring by nonionic bonding: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 309. Compounds wherein nitrogen is attached directly or indirectly to the six-membered hetero ring by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 312]](../ps.gif) 312 312 | 5-position is unsubstituted or alkyl substituted only: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 311. Compounds wherein the 5-position of the six-membered hetero ring is unsubstituted or substituted by alkyl radicals only. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 313]](../ps.gif) 313 313 | Halogen attached directly to the diazine ring by nonionic bonding: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 309. Compounds wherein halogen is attached directly to the six-membered hetero ring by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 314]](../ps.gif) 314 314 | Additional chalcogen attached directly or indirectly to the diazine ring by nonionic bonding: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 309. Compounds wherein an additional chalcogen, (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium) is attached directly or indirectly to the six-membered hetero ring by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 315]](../ps.gif) 315 315 | At 2-position: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 298. Compounds wherein chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium) is bonded directly at the 2-position of the six-membered hetero ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 316]](../ps.gif) 316 316 | Nitrogen attached directly or indirectly to the diazine ring by nonionic bonding: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 315. Compounds wherein nitrogen is attached directly or indirectly to the six-membered hetero ring by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 317]](../ps.gif) 317 317 | The nitrogen is bonded directly at 4- or 6- position: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 316. Compounds wherein the nitrogen is bonded directly to the
4- or 6- position of the six-membered hetero ring.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 318]](../ps.gif) 318 318 | Additional chalcogen attached directly or indirectly to the diazine ring by nonionic bonding: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 315. Compounds wherein an additional chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium) is attached directly or indirectly to the six-membered hetero ring by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 319]](../ps.gif) 319 319 | At 4- or 6-position: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 298. Compounds wherein the chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium) is bonded directly at the 4- or 6-position of the six-membered hetero ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 320]](../ps.gif) 320 320 | Nitrogen attached directly at 2-position by nonionic bonding: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 319. Compounds wherein nitrogen is attached directly to the 2-position of the six-membered hetero ring by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 321]](../ps.gif) 321 321 | Carbocyclic ring containing: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 320. Compounds which contain a carbocyclic ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 322]](../ps.gif) 322 322 | Nitrogen attached directly to the diazine ring by nonionic bonding: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 242. Compounds wherein nitrogen is attached directly to the six-membered hetero ring by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 323]](../ps.gif) 323 323 | At 2-position and at 4- or 6-position: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 322. Compounds wherein the nitrogen is attached directly to the 2- and 4-position carbons of the six-membered hetero ring by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 324]](../ps.gif) 324 324 | Additional hetero ring which is unsaturated: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 323. Compounds having, in addition to the six-membered hetero
ring, a hetero ring which has at least one double bond between ring
members.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 325]](../ps.gif) 325 325 | Substituent on 5-position contains carbocyclic ring: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 323. Compounds wherein a substituent which contains a carbocyclic ring is attached to the 5-position carbon of the six-membered hetero ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 326]](../ps.gif) 326 326 | At 4- or 6-position: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 322. Compounds wherein the nitrogen is attached directly to the 4- or 6-position carbon of the six-membered hetero ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 327]](../ps.gif) 327 327 | Sulfur attached indirectly to the diazine ring by nonionic bonding (e.g., thiamines, etc.): | ||||||
This subclass is indented under subclass 326. Compounds wherein sulfur is attached indirectly to the diazine
ring by nonionic bonding.
SEE OR SEARCH THIS CLASS, SUBCLASS:
| |||||||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 328]](../ps.gif) 328 328 | Additional hetero ring which is unsaturated: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 326. Compounds having, in addition to the six-membered hetero
ring, a hetero ring which has at least one double bond between ring
members.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 329]](../ps.gif) 329 329 | Carbonyl attached directly or indirectly to the diazine ring by nonionic bonding: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 326. Compounds wherein a group is attached directly or indirectly to the diazine ring by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 330]](../ps.gif) 330 330 | At 2-position: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 322. Compounds wherein the nitrogen is attached directly to the 2-position carbon of the six-membered hetero ring by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 331]](../ps.gif) 331 331 | Additional hetero ring which is unsaturated: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 330. Compounds having, in addition to the six-membered hetero ring, a hetero ring which has at least one double bond between ring members. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 332]](../ps.gif) 332 332 | Chalcogen attached indirectly to the diazine ring by nonionic bonding: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 330. Compounds wherein chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium) is attached indirectly to the six-membered hetero ring by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 333]](../ps.gif) 333 333 | Additional hetero ring which is unsaturated: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 242. Compounds having, in addition to the six-membered hetero ring, a hetero ring which has at least one double bond between ring members. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 334]](../ps.gif) 334 334 | Halogen attached directly to the diazine ring by nonionic bonding: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 242. Compounds wherein halogen is attached directly to the six-membered hetero ring by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 335]](../ps.gif) 335 335 | Chalcogen attached indirectly to the diazine ring by nonionic bonding: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 242. Compounds wherein chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium) is attached indirectly to the six-membered hetero ring by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 336]](../ps.gif) 336 336 | 1,4-diazines: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 224. Compounds wherein the six-membered hetero ring has nitrogens in the 1-and 4-positions, and carbons in the remaining four positions. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 337]](../ps.gif) 337 337 | Phosphorus attached directly or indirectly to the diazine ring by nonionic bonding: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 336. Compounds wherein phosphorus is attached directly or indirectly to the six-membered hetero ring by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 338]](../ps.gif) 338 338 | Polycyclo ring system having the diazine ring as one of the cyclos: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 336. Compounds wherein the six-membered hetero ring is one of
the cyclos in a polycyclo ring system.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 339]](../ps.gif) 339 339 | Heptacyclo ring system having the diazine ring as one of the cyclos (e.g., indanthrones, etc.): | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 338. Compounds wherein the polycyclo ring system consists of
seven rings.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 340]](../ps.gif) 340 340 | Chalcogen attached indirectly to the heptacyclo ring system by nonionic bonding: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 339. Compounds wherein chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium) is attached indirectly to the heptacyclo ring system by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 341]](../ps.gif) 341 341 | Halogen, nitrogen, or carbon attached directly to the heptacyclo ring system by nonionic bonding: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 339. Compounds wherein halogen, nitrogen, or carbon is attached directly to the heptacyclo ring system by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 342]](../ps.gif) 342 342 | Pentacyclo ring system having the diazine ring as one of the cyclos: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 338. Compounds wherein the polycyclo ring system consists of five rings. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 343]](../ps.gif) 343 343 | Tetracyclo ring system having the diazine ring as one of the cyclos (e.g., benzophenazines, etc.): | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 338. Compounds wherein the polycyclo ring system consists of
four rings.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 344]](../ps.gif) 344 344 | Tricyclo ring system having the diazine ring as one of the cyclos: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 33. Compounds wherein the polycyclo ring system consists of three rings. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 345]](../ps.gif) 345 345 | Three or more ring hetero atoms in the tricyclo ring system: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 344. Compounds wherein the tricyclo ring system includes at least one ring hetero atom in addition to the two ring nitrogens of the six-membered hetero ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 346]](../ps.gif) 346 346 | Ring nitrogen is shared by two of the cyclos (e.g., ergot, alkaloids, etc.): | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 345. Compounds in which a ring nitrogen is a member of two of
the rings in the tricyclo ring system.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 347]](../ps.gif) 347 347 | Phenazines (including hydrogenated): |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 344. Compounds wherein the tricyclo ring system has the following
basic structure in which the bonds between ring members may be single
or double bonds..
| |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 348]](../ps.gif) 348 348 | Nitrogen attached directly to the phenazine ring system by nonionic bonding: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 347. Compounds wherein nitrogen is attached directly to the phenazine ring system by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 349]](../ps.gif) 349 349 | Bicyclo ring system having the diazine ring as one of the cyclos: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 338. Compounds in which the polycyclo ring system consists of two rings. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 350]](../ps.gif) 350 350 | Three or more ring hetero atoms in the bicyclo ring system: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 349. Compounds wherein the bicyclo ring system includes at least one ring hetero atom in addition to the two ring nitrogens of the six-membered hetero ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 351]](../ps.gif) 351 351 | Triethylene diamines: | ||
| This subclass is indented under subclass 349. Compounds wherein the bicyclo ring system has the following
basic structure:
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 352]](../ps.gif) 352 352 | Process of forming, purifying, or recovering triethylene diamine per se, or salt thereof: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 351. Compounds wherein triethylene diamine per se is formed by a chemical reaction or is separated from impurities or a reaction mixture. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 353]](../ps.gif) 353 353 | Quinoxalines (including hydrogenated): |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 349. Compounds wherein the bicyclo ring system has the following
basic structure, illustrated below, in which the bonds between ring
members may be single or double bonds.
| |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 354]](../ps.gif) 354 354 | Chalcogen bonded directly to diazine ring carbon: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 353. Compounds wherein chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium) is bonded directly to a ring carbon of the six-membered hetero ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 355]](../ps.gif) 355 355 | Having -C(=X)-, wherein X is chalcogen, bonded directly to diazine ring carbon: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 353. Compounds wherein a group, in which X is chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium), is bonded directly to a ring carbon of the six-membered hetero ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 356]](../ps.gif) 356 356 | Halogen or nitrogen attached directly to diazine ring carbon by nonionic bonding: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 353. Compounds wherein halogen or nitrogen is attached directly to a ring carbon of the six-membered hetero ring by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 357]](../ps.gif) 357 357 | Plural diazine rings: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 336. Compounds which contain at least two of the six-membered hetero rings, each having ring nitrogens in the 1- and 4-positions, and carbons in the remaining four positions. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 358]](../ps.gif) 358 358 | Piperazines (i.e., fully hydrogenated 1,4-diazines): |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 336. Compounds wherein the six-membered hetero ring, having nitrogens in the 1- and 4-positions, has single bonds only between ring members, i.e., piperazines. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 359]](../ps.gif) 359 359 | Additional hetero ring containing: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 358. Compounds which contain a hetero ring in addition to the piperazine ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 360]](../ps.gif) 360 360 | Six-membered ring consisting of one nitrogen and five carbons (e.g., pyridine, etc.): |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 359. Compounds wherein the additional hetero ring is a six-membered ring consisting of one ring nitrogen and five ring carbons. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 361]](../ps.gif) 361 361 | The additional six-membered hetero ring is one of the cyclos in a polycyclo ring system: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 360. Compounds wherein the additional six-membered hetero ring is a cyclo of a polycyclo ring system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 362]](../ps.gif) 362 362 | The additional six-membered hetero ring is one of the cyclos in a bicyclo ring system: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 361. Compounds wherein the polycyclo ring system consists of exactly two rings. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 363]](../ps.gif) 363 363 | Quinoline or isoquinoline (including hydrogenated): |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 362. Compounds wherein the bicyclo ring system is characterized by having a six-membered carbocyclic ring ortho-fused to two carbons of the additional six-membered hetero ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 364]](../ps.gif) 364 364 | At least three hetero rings containing: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 360. Compounds which contain a hetero ring in addition to the
piperazine ring and the six-membered hetero ring consisting of one
ring nitrogen and five ring carbons.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 365]](../ps.gif) 365 365 | Having -C(=X)-, wherein X is chalcogen, bonded directly to ring carbon of the additional six-membered hetero ring (e.g., nicotinic acid, etc.): | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 360. Compounds wherein a group, in which X is chalcogen (i.e.,
oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium), as bonded directly to a
ring carbon of the additional six-membered hetero ring.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 366]](../ps.gif) 366 366 | Five-membered hetero ring having two or more ring hetero atoms of which at least one is nitrogen: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 359. Compounds wherein the additional hetero ring is five-membered having two or more ring hetero atoms, at least one of which is nitrogen. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 367]](../ps.gif) 367 367 | Ring chalcogen in the five-membered hetero ring: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 366. Compounds in which the five-membered hetero ring contains a ring chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium) in addition to the ring nitrogen. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 368]](../ps.gif) 368 368 | The five-membered hetero ring is one of the cyclos in a polycyclo ring system: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 367. Compounds wherein the five-membered hetero ring is one of the cyclos of a polycyclo ring system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 369]](../ps.gif) 369 369 | 1,3-oxazole ring or 1,3-thiazole ring (including hydrogenated): |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 367. Compounds wherein the five-membered hetero ring has a ring oxygen or ring sulfur in the 1-position, a ring nitrogen in the 3-position, and ring carbons in the remaining three positions. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 370]](../ps.gif) 370 370 | 1,3-diazole ring (including hydrogenated): |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 366. Compounds wherein the five-membered hetero ring has ring nitrogens in the 1- and 3-positions, and ring carbons in the remaining three positions. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 371]](../ps.gif) 371 371 | 1,2-diazole ring (including hydrogenated): |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 366. Compounds wherein the five-membered hetero ring has ring nitrogens in the 1- and 2-positions, and ring carbons in the remaining three positions. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 372]](../ps.gif) 372 372 | Five-membered hetero ring consisting of one nitrogen and four carbons: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 359. Compounds wherein the additional hetero ring is five-membered consisting of one ring nitrogen and four ring carbons. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 373]](../ps.gif) 373 373 | The five-membered hetero ring is one of the cyclos in a bicyclo ring system: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 372. Compounds wherein the five-membered hetero ring is one of the cyclos of a bicyclo ring system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 374]](../ps.gif) 374 374 | Ring chalcogen in the additional hetero ring: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 359. Compounds having in addition to the piperazine ring, a hetero ring which includes a ring chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium). | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 375]](../ps.gif) 375 375 | Polycyclo ring system having the additional hetero ring as one of the cyclos: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 374. Compounds wherein the additional hetero ring is one of the cyclos of a polycyclo ring system. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 376]](../ps.gif) 376 376 | Bicyclo ring system having the additional hetero ring as one of the cyclos: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 375. Compounds wherein the polycyclo ring system consists of exactly two rings. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 377]](../ps.gif) 377 377 | Plural ring chalcogens in the bicyclo ring system: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 376. Compounds wherein the bicyclo ring system contains at least
two ring chalcogens.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 378]](../ps.gif) 378 378 | Plural ring chalcogens in the polycyclo ring system or the piperazine ring bonded directly to the polycyclo ring system: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 375. Compounds wherein the polycyclo ring system contains at
least two ring chalcogens (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium),
or the polycyclo ring system is bonded directly to the piperazine
ring.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 379]](../ps.gif) 379 379 | The additional hetero ring is five-membered and unsaturated (e.g., thienyl piperazines, etc.): |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 374. Compounds wherein the additional hetero ring is five-membered and has at least one double bond between ring members. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 380]](../ps.gif) 380 380 | Polycyclo-carbocyclic ring system having at least three cyclos: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 358. Compounds having a polycylco ring system which contains at least three carbocyclic rings. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 381]](../ps.gif) 381 381 | Piperazine ring bonded directly to the polycyclo-carbocyclic ring system: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 380. Compounds wherein the polycyclo-carbocyclic ring system is bonded directly to the piperazine ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 382]](../ps.gif) 382 382 | Nitrogen attached directly to the piperazine ring by nonionic bonding: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 358. Compounds wherein nitrogen is attached directly to the piperazine ring by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 383]](../ps.gif) 383 383 | Chalcogen attached directly to piperazine ring nitrogen by nonionic bonding: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 358. Compounds wherein chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium) is attached directly to a ring nitrogen of the piperazine ring by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 384]](../ps.gif) 384 384 | Chalcogen bonded directly to piperazine ring carbon: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 358. Compounds wherein chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium) is bonded directly to a ring carbon of the piperazine ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 385]](../ps.gif) 385 385 | Plural chalcogens bonded directly to piperazine ring carbons: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 384. Compounds wherein at least two chalcogen atoms (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium) are bonded directly to the six-membered hetero ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 386]](../ps.gif) 386 386 | Having -C(=X)-, wherein X is chalcogen, bonded directly to the piperazine ring: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 358. Compounds wherein a group, in which X is chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium. or tellurium), is bonded directly to the piperazine ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 387]](../ps.gif) 387 387 | Plural -C(=X)- groups bonded directly to the piperazine ring: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 386. Compounds wherein at least two groups are bonded directly to the piperazine ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 388]](../ps.gif) 388 388 | Chalcogen or acyclic nitrogen bonded directly to at least one of the -C(=X)- groups: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 387. Compounds wherein chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium), or acyclic nitrogen is bonded directly to at least one of the groups. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 389]](../ps.gif) 389 389 | The -C(=X)- is part of a -C(=X)X-group, wherein the X"s are the same or diverse chalcogens: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 386. Compounds wherein the is part of a X - group, in which
the X"s are the same or diverse chalcogens (i.e., oxygen,
sulfur, selenium, or tellurium).
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 390]](../ps.gif) 390 390 | Halogen or acyclic nitrogen bonded directly to the -C(=X)- group: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 386. Compounds wherein halogen or acyclic nitrogen is bonded directly to the group. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 391]](../ps.gif) 391 391 | Carbocyclic ring containing: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 386. Compounds which contain a carbocyclic ring.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 392]](../ps.gif) 392 392 | Phenyl or napthyl bonded directly to ring nitrogen of the piperazine ring: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 358. Compounds wherein a phenyl or napthyl group is bonded directly to a ring nitrogen of the piperazine ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 393]](../ps.gif) 393 393 | Acyclic nitrogen bonded directly to a -C(=X)- group, wherein X is chalcogen: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 392. Compounds which contain acyclic nitrogen bonded directly to a group, in which X is chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium). | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 394]](../ps.gif) 394 394 | The other ring nitrogen has a substituent which includes chalcogen single bonded to acyclic carbon: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 392. Compounds wherein the other ring nitrogen of the piperazine
ring has a substituent which includes chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur,
selenium or tellurium) singly bonded to an acyclic carbon, e.g.,
an alcohol or ether, etc.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 395]](../ps.gif) 395 395 | The other ring nitrogen is unsubstituted or alkyl substituted only, or salt thereof: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 392. Compounds wherein the other ring nitrogen of the piperazine ring is unsubstituted or alkyl substituted only, or salts thereof. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 396]](../ps.gif) 396 396 | Plural carbocyclic rings bonded directly to the same acyclic carbon: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 358. Compounds which contain at least two carbocyclic rings bonded
directly to the same acyclic carbon.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 397]](../ps.gif) 397 397 | Chalcogen bonded directly to the carbon: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 396. Compounds which contain chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur,
selenium, or tellurium) bonded directly to the acyclic carbon.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 398]](../ps.gif) 398 398 | Chalcogen attached indirectly to the piperazine ring by nonionic bonding: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 358. Compounds wherein chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium,
or tellurium) is attached indirectly to the piperazine ring by nonionic
bonding.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 399]](../ps.gif) 399 399 | The chalcogen, X is in a -C(=X)- group: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 398. Compounds wherein the chalcogen, X (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium), is in an acyclic group. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 400]](../ps.gif) 400 400 | Acyclic nitrogen bonded directly to the-C(=X)- group: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 399. Compounds wherein acyclic nitrogen is bonded directly to the group. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 401]](../ps.gif) 401 401 | The chalcogen is single bonded to both acyclic carbon and hydrogen: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 398. Compounds wherein the chalcogen is in a hydroxy group which is bonded directly to carbon. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 402]](../ps.gif) 402 402 | Nitrogen attached indirectly to the piperazine ring by nonionic bonding: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 358. Compounds wherein nitrogen is attached indirectly to the piperazine ring by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 403]](../ps.gif) 403 403 | Carbocyclic ring containing: | ||
This subclass is indented under subclass 358. Compounds which contain a carbocyclic ring.
| |||
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 404]](../ps.gif) 404 404 | N-hydrocarbyl piperazines: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 358. Compounds in which a hydrocarbon substituent is bonded directly to a ring nitrogen of the six-membered hetero ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 405]](../ps.gif) 405 405 | Additional hetero ring which is unsaturated: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 336. Compounds having, in addition to the six-membered hetero ring, a hetero ring which has at least one double bond between ring members. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 406]](../ps.gif) 406 406 | Having -C(=X)-, wherein X is chalcogen, bonded directly to the diazine ring: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 336. Compounds wherein a group, in which X is chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium), is bonded directly to the diazine ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 407]](../ps.gif) 407 407 | Nitrogen attached directly to the diazine ring by nonionic bonding: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 406. Compounds wherein nitrogen is attached directly to the six-membered hetero ring by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 408]](../ps.gif) 408 408 | Chalcogen bonded directly to diazine ring carbon: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 336. Compounds wherein chalcogen (i.e., oxygen, sulfur, selenium, or tellurium) is bonded directly to a ring carbon of the six-membered hetero ring. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 409]](../ps.gif) 409 409 | Halogen attached directly to the diazine ring by nonionic bonding: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 336. Compounds wherein halogen is attached directly to the six-membered hetero ring by nonionic bonding. | |
![[List of Patents for class 544 subclass 410]](../ps.gif) 410 410 | Unsubstituted or hydrocarbyl substituted only, or salt thereof: |
| This subclass is indented under subclass 336. Compounds wherein the six-membered hetero ring is unsubstituted or is substituted only by radicals which consist of hydrogen and carbon, or salts thereof. | |