| CPC H02K 1/30 (2013.01) [H02K 1/02 (2013.01); H02K 1/276 (2013.01); H02K 7/006 (2013.01); H02K 15/03 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
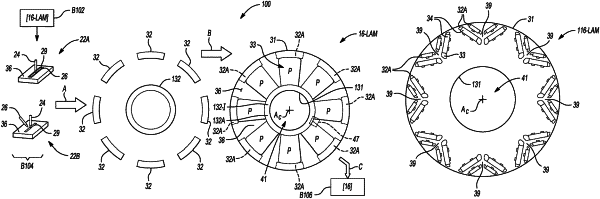
1. A method for constructing an annular lamination for a rotary electric machine, the method comprising:
forming the annular lamination from a ferrous core material having a first relative magnetic permeability, wherein the annular lamination defines a plurality of through-openings, such that a peripheral bridge of the ferrous core material extends between the through-openings and a perimeter surface of the annular lamination; and
diffusing an alloy material having a second relative magnetic permeability that is less than the first relative magnetic permeability into the peripheral bridge to thereby form an austenitic bridge, wherein diffusing the alloy material includes (i) performing a direct powder injection process or a wire injection process in conjunction with application of heat from a heat source, or (ii) using a deposition process prior to a laser treatment process.
|