| CPC G10L 15/144 (2013.01) [G06N 3/08 (2013.01); G06N 20/00 (2019.01); G06F 16/285 (2019.01); G06F 2203/011 (2013.01); G10L 17/26 (2013.01); G10L 2015/0631 (2013.01)] | 19 Claims |
|
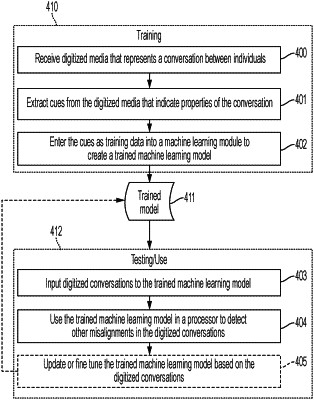
1. A method comprising:
receiving digitized media that represents a conversation between individuals;
extracting cues from the digitized media that indicate properties of the conversation;
entering the cues as training data into a machine learning module to create a trained machine learning model that detects misalignments in subsequent conversations between individuals, wherein misalignment is a lack of agreement and mutual understanding between the individuals of content and context of the content of the subsequent conversations; and
using the trained machine learning model in a processor to detect other misalignments in subsequent digitized conversations;
wherein the trained machine learning model detects misalignments in subsequent digitized conversations between individuals by determining a probability of each cue occurring in the subsequent digitized conversations under a normalcy model.
|