| CPC G06F 9/30054 (2013.01) [G06F 9/45516 (2013.01); G06F 21/53 (2013.01); H04L 9/0894 (2013.01); G06F 2221/033 (2013.01)] | 17 Claims |
|
1. A method comprising:
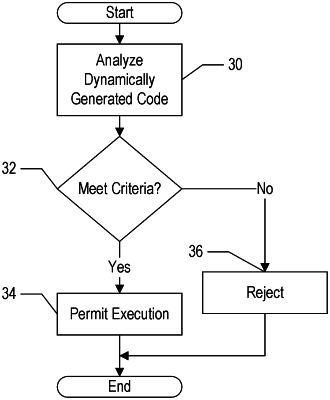
monitoring, in a monitor circuit in a processor in a computer system, a dynamically-generated code sequence being executed in a dynamic code execution region of the computer system to ensure that the dynamically-generated code sequence meets execution criteria, wherein the execution criteria specify that:
none of a set of prohibited instructions is present in the dynamically-generated code sequence;
a branch target that is outside the dynamic code execution region is:
cryptographically signed with one of a set of one or more cryptographic keys; and
within one of one or more predefined address ranges outside of the dynamic code execution region;
detecting a violation of the execution criteria by the monitor circuit; and
forcing, by the monitor circuit, an exception based on detecting the violation.
|