| CPC G06F 30/20 (2020.01) [A61C 13/34 (2013.01)] | 4 Claims |
|
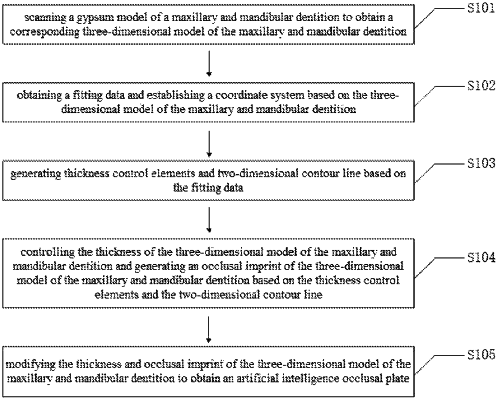
1. A design method of an orthognathic surgical occlusal plate based on artificial intelligence, comprising;
scanning a gypsum model of a maxillary and mandibular dentition to obtain a corresponding three-dimensional model of the maxillary and mandibular dentition;
obtaining a fitting data and establishing a coordinate system based on the three-dimensional model of the maxillary and mandibular dentition;
generating thickness control elements and two-dimensional contour line based on the fitting data;
controlling the thickness of the three-dimensional model of the maxillary and mandibular dentition and generating an occlusal imprint of the three-dimensional model of the maxillary and mandibular dentition based on the thickness control elements and the two-dimensional contour line;
modifying the thickness and occlusal imprint of the three-dimensional model of the maxillary and mandibular dentition to obtain an artificial intelligence occlusal plate;
wherein the obtaining the fitting data and establishing the coordinate system based on the three-dimensional model of the maxillary and mandibular dentition, comprises;
obtaining the planes fitted by the points of the three-dimensional model of the maxillary and maxillary dentition, including the maxillary fitting plane and the mandibular fitting plane;
establishing a polar coordinate system by a plane where a main axis and a lateral axis are located to calculate the angle θ of all the points of the maxillary and mandibular dentition model according to all the points in the maxillary and mandibular dentition model;
wherein the establishing the polar coordinate system by the plane where the main axis and the lateral axis are located to calculate the angle θ of all the points of the maxillary and mandibular dentition model according to all the points in the maxillary and mandibular dentition model, comprises:
combining all the points in the maxillary and mandibular dentition model into a point set, and obtain the overall center point, central plane, main axis, lateral axis and normal vector through principal component analysis; and establishing a polar coordinate system through the plane where the main axis and lateral axis are located to calculate the angle θ of all points of the maxillary and mandibular model;
wherein the generating thickness control elements and two-dimensional contour lines based on the fitting data, comprises:
simplifying the occlusal plate and judging the opening according to the fitting data,
generating thickness control elements;
generating two-dimensional contour lines;
wherein the simplifying the occlusal plate and judging the opening according to the fitting data, comprises;
simplifying both the maxillary fitting plane and the mandibular fitting plane into a U shape, and equally dividing both the maxillary fitting plane and the mandibular fitting plane into 20 intervals in the range of [−π,π), calculating a distribution of the angle θ of all points, and finding out angle interval without points, so as to judge the opening of the U-shaped, and correct the direction of the main axis towards a central incisor;
wherein the generating thickness control elements, comprises:
extruding the maxillary fitting plane and mandibular fitting plane outward respectively to obtain a maxillary assembly and a mandibular assembly;
wherein the generating two-dimensional contour lines, comprises:
fitting the points concentrated in the range of (−π/2, π/2), that is, fitting the points in the U-shaped semicircle area, to inner and outer contour curves of a semicircular area of the U-shaped plate, and fitting the points beyond the range of (−π/2, π/2) as a straight line segment, connecting the straight line segment with the inner and outer contour curves to obtain a complete two-dimensional contour line of the U-shaped plate, and then smoothing the two-dimensional contour line of the U-shaped plate.
|