| CPC G06F 21/6245 (2013.01) [G06F 40/295 (2020.01); G06N 20/00 (2019.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
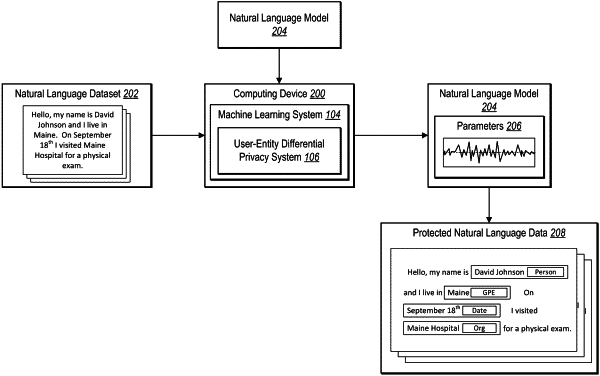
1. In a digital medium environment for natural language processing, a computer-implemented method for implementing differential privacy that protects data owners and sensitive textual information within textual datasets comprising:
determining a set of sensitive data points based on sampled users and sampled sensitive entities from a natural language dataset, wherein each sensitive data point is associated with at least one sampled user and comprises at least one sampled sensitive entity; and
generating, utilizing the set of sensitive data points, a natural language model that simultaneously provides protection for users and sensitive entities represented within the natural language dataset via user-entity differential privacy by:
determining an average gradient corresponding to the set of sensitive data points using a user-entity estimator;
determining a noise scale for the user-entity estimator based on the sampled users and the sampled sensitive entities associated with the set of sensitive data points; and
generating parameters for the natural language model using the average gradient and the noise scale.
|