| CPC G06F 17/16 (2013.01) [G01M 99/005 (2013.01); G05B 23/0281 (2013.01); G06F 11/079 (2013.01); G06F 17/18 (2013.01); G06N 20/00 (2019.01); H04L 41/0631 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A system, comprising:
a memory that stores computer executable components; and
a processor, operably coupled to the memory, and that executes the computer executable components stored in the memory, wherein the computer executable components comprise:
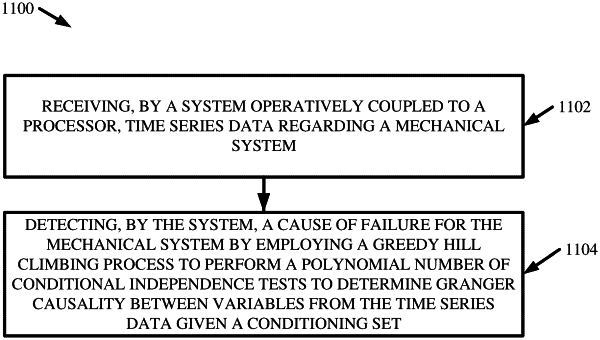
a maintenance component that detects a cause of failure for a second system by employing a greedy hill climbing process to perform a number of conditional independence tests to determine a causality between variables from time series data of the second system given a conditioning set.
|