| CPC B01D 53/0438 (2013.01) [B01D 53/0446 (2013.01); B01D 53/0462 (2013.01); B01D 53/0476 (2013.01); B01D 53/62 (2013.01); B01D 2257/504 (2013.01); B01D 2258/0283 (2013.01); B01D 2259/402 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
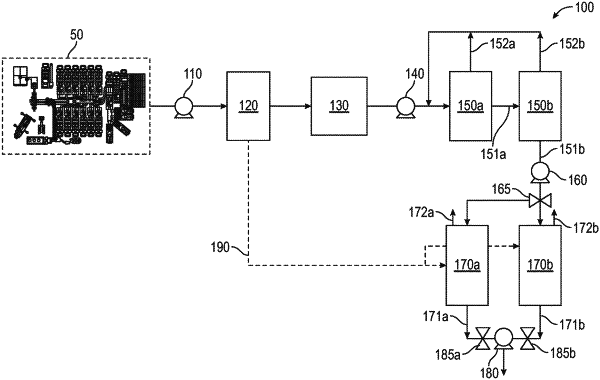
1. A method comprising:
lowering a temperature of an exhaust gas using a heat exchanger;
lowering a concentration of a particulate matter within the lowered temperature exhaust gas;
passing the lowered particulate concentration and lowered temperature exhaust gas through one or more membrane modules to produce a membrane module permeate flow that contains a higher concentration of carbon dioxide compared to a concentration of carbon dioxide in the lowered particulate concentration and lowered temperature exhaust gas; and
producing a substantially pure carbon dioxide from the membrane module permeate flow using one or more adsorbent packed beds,
wherein producing the substantially pure carbon dioxide from the membrane module permeate flow using one or more adsorbent packed beds comprises:
injecting the membrane module permeate flow into the one or more adsorbent packed beds;
extracting the substantially pure carbon dioxide from the membrane module permeate flow using a sorbent disposed within the one or more adsorbent packed beds;
releasing the membrane module permeate flow after the substantially pure carbon dioxide has been extracted; and
applying one of a pressure swing by reducing a pressure within the one or more adsorbent packed beds or a temperature swing by raising a temperature of the one or more adsorbent packed beds.
|