| CPC H04W 64/00 (2013.01) [H04L 43/0864 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
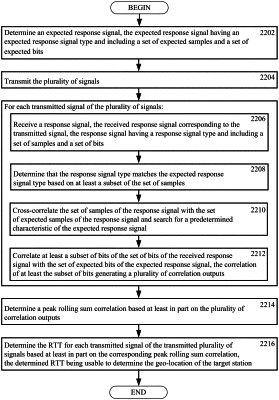
1. A method in a wireless device (WD) for determining a geo-location of a target station using round-trip times (RTTs) of a plurality of signals transmitted by the WD to the target station and a plurality of response signals received from the target station corresponding to the plurality of signals transmitted by the WD, each response signal having a response signal type and including a set of samples and a set of bits, the method comprising:
for each transmitted signal of the plurality of signals:
determining that the response signal type of the corresponding response signal matches an expected response signal type based on at least a subset of the set of samples, the expected response signal type corresponding to an expected response signal comprising a set of expected samples and a set of expected bits;
correlating at least a subset of bits of the set of bits of the response signal with the set of expected bits of the expected response signal, the correlation of at least the subset of bits generating a plurality of correlation outputs;
summing the correlation outputs corresponding to a set number of signals of the plurality of signals, at least the set number of signals being transmitted in a burst by the WD; and
determining the RTT based at least in part on a peak of the sum of the correlation outputs, the determined RTT being usable to determine the geo-location of the target station.
|