| CPC H01M 8/04664 (2013.01) [H01M 8/04671 (2013.01); H01M 8/04858 (2013.01); H01M 8/04932 (2013.01); H01M 2250/20 (2013.01)] | 4 Claims |
|
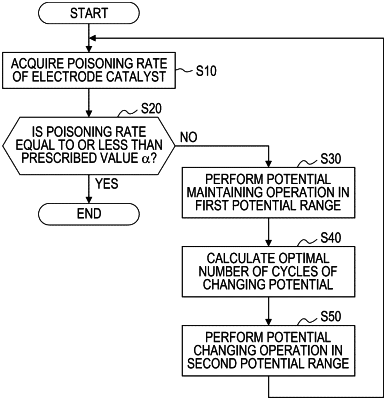
1. A control method for a fuel cell system, the control method comprising:
acquiring a poisoning rate of an electrode catalyst of a fuel cell; and
in response to the poisoning rate of the electrode catalyst being greater than a prescribed value,
performing a potential maintaining operation of maintaining a potential of the fuel cell in a first potential range, wherein in the potential maintaining operation,
hydrogen gas is supplied to an anode electrode of the fuel cell,
inert gas is supplied to a cathode electrode of the fuel cell, and
a proton pumping process is performed for sweeping the potential of the fuel cell from a lower-limit potential of the first potential range to an upper-limit potential of the first potential range at a predetermined rate; and
after the potential maintaining operation has been performed, performing a potential changing operation of repeating a cycle in which the potential of the fuel cell is changed between an upper-limit potential and a lower-limit potential of a second potential range which is higher than the first potential range, wherein
the upper-limit potential of the first potential range is equal to or lower than the lower-limit potential of the second potential range,
in the potential changing operation, the gas supplied to the cathode electrode is changed from the inert gas to oxygen gas, and
a minimum number of cycles of the potential changing operation, which is performed after the potential maintaining operation, to decrease the poisoning rate of the electrode catalyst to the prescribed value is less than a minimum number of cycles of the potential changing operation, which is performed without the potential maintaining operation.
|