| CPC H01M 4/0469 (2013.01) [H01M 4/139 (2013.01)] | 29 Claims |
|
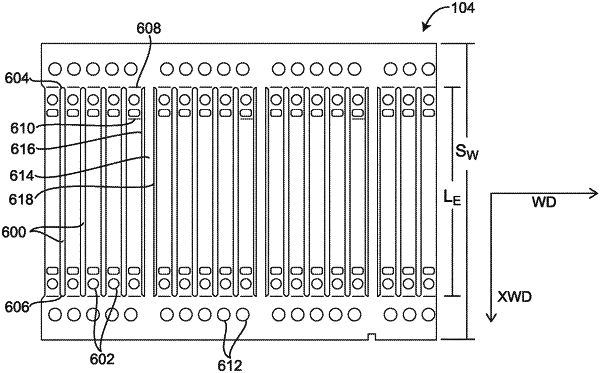
1. A process for delineating a population of electrode structures in a web, the web comprising an electrically conductive layer having opposing front and back surfaces and an electrochemically active material layer on the front surface, the back surface, or on both of the front and back surfaces, the web having a down-web direction and a cross-web direction, the down-web and cross-web directions being orthogonal to each other, the process comprising:
laser ablating the web to form a series of ablations in the web that are disposed in the down-web direction or the cross-web direction, each ablation being formed by removing a portion of the electrochemically active layer to thereby expose a portion of the electrically conductive layer;
forming a series of alignment features in the web that are disposed in the cross-web or down-web direction, the series of alignment features being formed at predetermined locations on the web;
laser machining the web to form a series of weakened tear patterns in the web in the down-web direction, the cross-web direction, or each of the cross-web direction and down-web direction that delineate members of the electrode structure population, each of the delineated members being individually bounded, at least in part, by a member of the series of weakened tear patterns that is adapted to facilitate separation of the delineated members, individually, from the web by an application of a force, the series of alignment features being used to aid in the formation of the series of weakened tear patterns; and
forming a population of tie bars between at least some of the delineated members of the electrode structure population, each of the tie bars being sized to provide additional structural stiffness to the web.
|
|
14. A process for delineating a population of electrode structures in a web, the web comprising an electrically conductive layer having opposing front and back surfaces and an electrochemically active material layer on the front surface, the back surface, or on both of the front and back surfaces, the web having a down-web direction and a cross-web direction, the down-web and cross-web directions being orthogonal to each other, the process comprising:
moving the web over a support surface, the support surface comprising a thermally conductive material;
forming a series of alignment features in the web that are disposed in the cross-web or down-web direction;
laser machining the web to form a series of weakened tear patterns in the web in the down-web direction, the cross-web direction, or each of the cross-web direction and down-web direction that delineate members of the electrode structure population, each of the delineated members being individually bounded, at least in part, by a member of the series of weakened tear patterns that is adapted to facilitate separation of the delineated members, individually, from the web by an application of a force, the series of alignment features being used to aid in the formation of the series of weakened tear patterns;
dissipating thermal energy from the laser machining using the support surface; and
forming a population of tie bars between at least some of the delineated members of the electrode structure population, each of the tie bars being sized to provide additional structural stiffness to the web.
|
|
21. A process for delineating a population of electrode structures in a web, the web comprising an electrically conductive layer having opposing front and back surfaces and an electrochemically active material layer on the front surface, the back surface, or on both of the front and back surfaces, the web having a down-web direction and a cross-web direction, the down-web and cross-web directions being orthogonal to each other, the process comprising:
forming a series of fiducial through-holes in the web that are disposed in the cross-web or down-web direction;
laser machining the web form a series of weakened tear patterns in the web in the down-web direction, the cross-web direction, or each of the cross-web direction and down-web direction that delineate members of the electrode structure population, wherein the delineated members are individually bounded, at least in part, by a member of the series of weakened tear patterns that is adapted to facilitate separation of the delineated members, individually, from the web by an application of a force, the series of fiducial through-holes being formed prior to the laser machining and used to aid in the formation of the series of weakened tear patterns;
forming a population of tie bars between at least some of the delineated members of the electrode structure population, each of the tie bars being sized to provide additional structural stiffness to the web;
controlling a tension in the web in the down-web direction during the laser machining; and
conveying the web in the down-web direction after the laser machining without releasing the delineated members from the web.
|