| CPC G06T 7/0012 (2013.01) [G06F 18/217 (2023.01); G06F 18/2148 (2023.01); G06N 5/04 (2013.01); G06N 20/00 (2019.01); G06V 20/69 (2022.01); G16H 10/20 (2018.01); G16H 50/20 (2018.01); G06V 2201/03 (2022.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
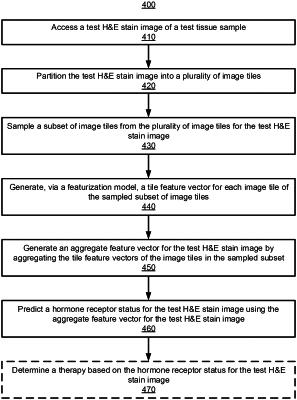
1. A method for predicting hormone receptor status using machine learning comprising:
partitioning a test H&E stain image of a test tissue sample into a plurality of non-overlapping image tiles;
sampling a subset of non-overlapping image tiles from the plurality of non-overlapping image tiles of the test H&E stain image;
generating a feature vector for the test H&E stain image based on the sampled subset of non-overlapping image tiles; and
predicting a hormone receptor status by applying a machine-learned prediction model to the feature vector for the test H&E stain image, wherein the machine-learned prediction model is trained using a first set of H&E stain images from a first set of tissue samples having a positive hormone receptor status and a second set of H&E stain images from a second set of tissue samples having a negative hormone receptor status.
|