| CPC G06Q 30/0203 (2013.01) | 20 Claims |
|
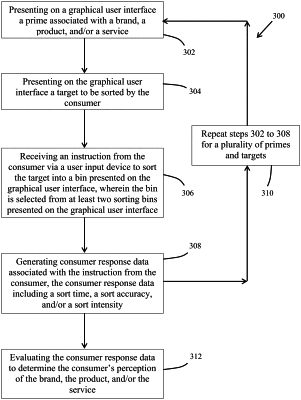
1. A computer-implemented method of assessing perception, the method comprising:
(a) presenting a graphical user interface on a device of a user, the graphical user interface comprising: a three-dimensional depiction of a first sorting bin and a second sorting bin, wherein the first sorting bin appears to be close to the user and the second sorting bin appears to be far from the user; an accuracy gauge; and a speed gauge;
(b) presenting a prime on the graphical user interface;
(c) presenting a target on the graphical user interface;
(d) receiving an instruction from the user to sort the target into either the first sorting bin or the second sorting bin, wherein an accurate sort instruction comprises either a natural approach reaction or a natural avoidance reaction;
(e) determining an accuracy and a speed associated with the instruction from the user, wherein the accuracy gauge and the speed gauge provide a real-time indication of the accuracy of the instruction and the speed of the instruction;
(f) repeating steps (b) to (e) for a plurality of primes and targets; and
(g) determining the user's perception of at least one prime based on the determined accuracy and speed for the plurality of primes and targets.
|