| CPC G06F 12/1441 (2013.01) [G06F 13/1668 (2013.01); G06F 2212/1052 (2013.01)] | 21 Claims |
|
1. An integrated circuit configured to drive an audio transducer, the integrated circuit comprising:
first and second interfaces; and
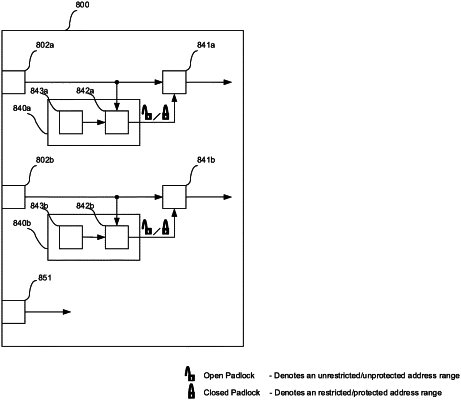
an internal addressable space comprising a plurality of address ranges;
wherein the integrated circuit stores an access permission to define an authorized subset of address ranges to which access by an external processor is permitted during runtime control of the integrated circuit;
wherein each of the first and second interfaces is coupled to the internal addressable space, and wherein each of the first and second interfaces is configured to receive a request, from the external processor, to access at least one of the address ranges of the internal addressable space; and
wherein the integrated circuit is configurable in a first state in which the external processor is permitted, via the first interface, access to the authorized subset of address ranges and is prevented, via the first interface, access to the remainder of the address ranges during runtime control of the integrated circuit and the external processor is permitted, via the second interface, access to the plurality of address ranges, and configurable in a second state in which the external processor is permitted, via the second interface, access to the authorized subset of address ranges and is prevented, via the second interface, access to the remainder of the address ranges during runtime control of the integrated circuit and the external processor is permitted, via the first interface, access to the plurality of address ranges.
|