| CPC G01N 21/6428 (2013.01) [C12Q 1/6818 (2013.01); G01N 21/6458 (2013.01); G02B 21/16 (2013.01); G02B 21/365 (2013.01); G06V 20/693 (2022.01); G06V 20/695 (2022.01); G06V 20/698 (2022.01); G16B 30/00 (2019.02); G01N 2021/6439 (2013.01); G06V 2201/03 (2022.01)] | 48 Claims |
|
1. A method of analyzing detectable signals acquired from a plurality of nucleic acid molecules, the method comprising:
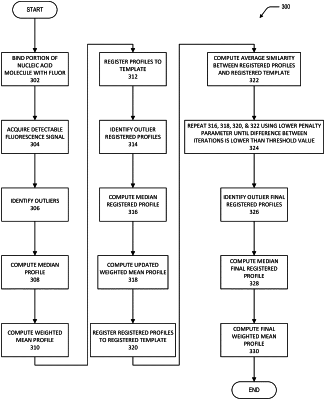
a) receiving a data set comprising profiles of detectable signal intensity versus position, the detectable signal intensity acquired from a plurality of marker molecules bound to substantially identical portions of the plurality of nucleic acid molecules and generating a consensus profile of detectable signal intensity versus position, wherein the generating the consensus profile comprises an iterative process comprising the following steps: (i) detecting outliers; (ii) computing a template on a first iteration and updating the template on subsequent iterations; (iii) register the profiles of detectable signal intensity versus position to the template; and (iv) compute an average similarity between the profiles of detectable signal intensity versus position and the template, wherein the iterative process is repeated until the average similarity is maximized, the registered profiles from step (iii) of the final iteration of the iterative process are subjected to steps (i) and (ii) and the updated template of step (ii) is the consensus profile;
b) extracting underlying genomic information from the data set; and
c) generating an output signal or a report comprising the underlying genomic information.
|