| CPC B60W 30/09 (2013.01) [B60W 30/0956 (2013.01); B60W 10/18 (2013.01); B60W 10/20 (2013.01); B60W 2552/53 (2020.02); B60W 2554/4029 (2020.02)] | 7 Claims |
|
1. A driving support system that supports driving of a vehicle, the driving support system comprising:
a storage device that stores driving environment information indicating a driving environment of the vehicle; and
a processor that executes a risk avoidance control for reducing a risk of collision with an object in front of the vehicle, based on the driving environment information, wherein:
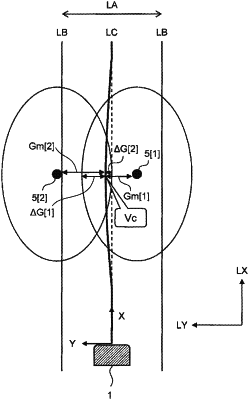
a risk potential field represents a risk value as a function of position;
an obstacle potential field is the risk potential field in which the risk value is maximum at a position of the object and decreases as a distance from the object increases;
a lane longitudinal direction is a direction along which a lane in which the vehicle is present extends;
a vehicle center potential field is the risk potential field in which a valley of the risk value extends in the lane longitudinal direction from a position of the vehicle;
a position of the valley in the vehicle center potential field changes with the position of the vehicle;
the risk avoidance control includes a steering control for steering the vehicle;
the processor sets the vehicle center potential field and the obstacle potential field based on the driving environment information, sets a sum of the vehicle center potential field and the obstacle potential field as a first risk potential field, and executes the steering control such that the vehicle follows a first valley, the first valley being the valley of the risk value represented by the first risk potential field;
the risk avoidance control further includes a deceleration control for decelerating the vehicle;
the processor sets a second risk potential field including the obstacle potential field;
a second valley is a valley of the risk value represented by the second risk potential field;
a correction gap is a lateral distance between the object and the second valley; and
when the correction gap is smaller than a predetermined gap and a suppression amount is larger than a threshold value, the processor executes the deceleration control, the suppression amount being a difference between the predetermined gap and the correction gap.
|