| CPC A61B 5/363 (2021.01) [A61B 5/287 (2021.01); A61B 5/316 (2021.01); A61B 5/335 (2021.01); A61B 5/352 (2021.01); A61B 5/6861 (2013.01); A61B 5/7221 (2013.01); A61N 1/36514 (2013.01); A61N 1/3956 (2013.01); A61N 1/3987 (2013.01); A61B 5/364 (2021.01); A61B 2505/07 (2013.01); A61B 2560/0468 (2013.01)] | 29 Claims |
|
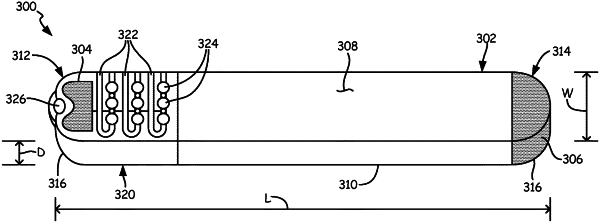
1. An insertable cardiac monitor comprising:
a housing configured for subcutaneous implantation within a patient, the housing having a length, a width, and a depth,
wherein the length is greater than the width and the width is greater than the depth,
wherein the length is within a range from 40 millimeters (mm) to 60 mm,
wherein the width is within a range from 3 mm to 10 mm, and
wherein the depth is within a range from 2 mm to 5 mm;
a distal electrode;
a proximal electrode; and
circuitry comprising a processer within the housing, the circuitry configured to:
sense a cardiac signal of the patient via the distal electrode and the proximal electrode;
compare an amplitude of the cardiac signal to a threshold;
detect an R-wave based on the comparison of the amplitude of the cardiac signal to the threshold;
detect an asystole based on a comparison of the amplitude of the cardiac signal subsequent to the detected R-wave to the threshold; and
further process the cardiac signal sensed during a pause interval that is subsequent to the detected R-wave to determine whether the asystole is false in response to detecting the asystole.
|