| CPC H01S 3/10046 (2013.01) [G02F 1/35 (2013.01); H01S 3/0057 (2013.01); H01S 3/0092 (2013.01); H01S 3/06791 (2013.01); H01S 3/1305 (2013.01); H01S 3/136 (2013.01); G02F 1/3503 (2021.01); G02F 1/3528 (2021.01)] | 19 Claims |
|
1. A method for controlling an optical system to a target output, the method comprising:
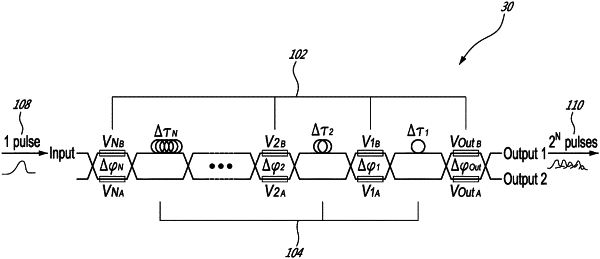
i) generating at least two optical signal components, by splitting an input optical signal provided by an optical source, using a plurality of signal modifying elements, each signal modifying element comprising a plurality of branches along which at least one optical signal arriving at the signal modifying element travels, wherein at least one of the signal modifying elements is configured so that optical signals travelling along different branches are modified in different ways, the signal modifying elements being cascaded so that respective branches thereof define multiple pathways for optical signals to travel, so that the input optical signal is split into a plurality of optical signal components that have travelled along different pathways and result with different optical properties and a controlled phase relation; and at least one switching element controlling the proportion of optical signals travelling along the different pathways and hence relative proportions and individual optical properties of the optical signal components;
ii) interacting the optical signal components generated in step i) within the optical system;
iii) characterizing a resulting output of the optical system with respect to the target output;
iv) adjusting parameters of said generating the optical signal components in step i) with results of said characterizing; and
v) repeating steps i) to iv) until the target output.
|