| CPC G01V 99/00 (2013.01) | 3 Claims |
|
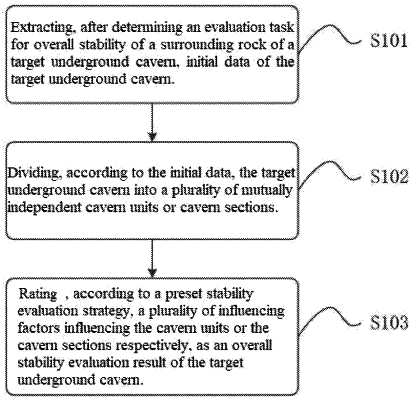
1. A quantitative assessment method for global stability of surrounding rocks of underground-caverns, comprising:
extracting initial data of a target underground cavern, wherein the initial data comprises: geological structures, rock mass structure types, lithology, initial maximum principal stress values, buried depths, included angles between initial maximum principal stress directions and a cavern axis, dimensions, a cavern axis orientation and use functions of different positions of the target underground cavern;
dividing, according to the initial data, the target underground cavern into different independent cavern units or cavern sections; and
rating, according to a preset stability assessment strategy, seven factors influencing a stability of surrounding rocks of the cavern units or the cavern sections respectively, as a global stability assessment result of the target underground cavern;
said dividing, according to the initial data, the target underground cavern into the different independent cavern units or cavern sections comprising:
dividing, according to the initial data, the target underground cavern into the different dividing, according to the initial data, the target underground cavern into the different independent cavern units or cavern sections in a preset similar judgment range;
the preset stability assessment strategy evaluating from the seven factors: a basic quality (BQ) index of the surrounding rocks, an uniaxial compressive strength Rc of the surrounding rocks, a local stability condition of the surrounding rocks, a relaxation/damage condition of the surrounding rocks, a combined relationship between the initial maximum principal stress directions of the surrounding rocks and the cavern axis, a combined relationship between a main structural plane and the cavern axis, and groundwater;
the local stability condition of the surrounding rocks being specifically evaluated from four aspects: a local deformation stability of the surrounding rocks, a block stability of the surrounding rocks, a collapse tendency of the surrounding rocks and a rockburst tendency of the surrounding rocks;
said rating, according to the preset stability assessment strategy, the seven factors influencing the stability of the surrounding rocks of the cavern units or the cavern sections respectively, as the global stability assessment result of the target underground cavern comprising:
rating, according to the preset stability assessment strategy, the seven factors influencing the stability of the surrounding rocks of the cavern units or the cavern sections respectively; and
accumulating the ratings of the seven factors, and confirming the accumulated ratings as stability assessment results of respective cavern units or cavern sections, as the global stability assessment result of the target underground cavern;
said accumulating the ratings of the seven factors, and said confirming the accumulated ratings as the stability assessment results of the respective cavern units or cavern sections comprising:
accumulating the ratings of the seven factors;
determining, based on preset global stability classifications of the surrounding rocks of the target underground cavern and rating ranges thereof, target global stability classifications corresponding to the accumulated ratings, the preset global stability classifications of the surrounding rocks of the target underground cavern being divided into four classifications: stable, basically stable, understable and unstable; and
confirming the accumulated ratings and the target global stability classifications as the stability assessment results of the respective cavern units or cavern sections, and as the global stability assessment result of the target underground cavern;
during the rating, the BQ index of the surrounding rocks comprises:
Class I, BQ>550, Class II, 550≥BQ>450, and a corresponding rating interval of a rating S1 of the BQ index of the surrounding rocks is 20≥S1≥15; Class III, 450≥BQ>350 and the corresponding rating interval of the rating S1 of the BQ index of the surrounding rocks is 15≥S1≥10; Class IV, 350≥BQ>250 and the corresponding rating interval of the rating S1 of the BQ index of the surrounding rocks is 10≥S1≥5; Class V, 250≥BQ, and the corresponding rating interval of the rating S1 of the BQ index of the surrounding rocks is 5>S1≥0;
wherein the rating S1 of the BQ index of the surrounding rocks is linearly interpolated from a lower limit of the corresponding rating interval of the rating S1 of the BQ index of the surrounding rocks to an upper limit of the corresponding rating interval of the rating S1 of the BQ index of the surrounding rocks according to the BQ index of the surrounding rocks; when there is no BQ index monitoring data available, the rating S1 of the BQ index of the surrounding rocks is performed according to qualitative description of surrounding rocks characteristics of a site; when the BQ index of the surrounding rocks is Class I, the rating S1 of the BQ index of the surrounding rocks is 20; when the surrounding rocks are hard and brittle and have a brittle failure tendency, the rating S1 of the BQ index of the surrounding rocks is linearly interpolated from the upper limit of the corresponding rating interval of the rating S1 of the BQ index of the surrounding rocks to the lower limit of the corresponding rating interval of the rating S1 of the BQ index of the surrounding rocks according to the BQ index;
during the rating, rock strength Rc/σmax of the surrounding rocks comprises:
Rc/σmax≥7, and a corresponding rating interval of a rating S2 of the rock strength Rc/σmax of the surrounding rocks is 20≥S2≥15; 7>Rc/σmax≥4, and the corresponding rating interval of the rating S2 of the rock strength Rc/σmax of the surrounding rocks is 15>S2≥10; 4>Rc/σmax≥2, and the corresponding rating interval of the rating S2 of the rock strength Rc/σmax of the surrounding rocks is 10>S2≥5; 2>Rc/σmax, and the corresponding rating interval of the rating S2 of the rock strength Rc/σmax of the surrounding rocks is 5>S2≥0;
wherein the rating S2 of the rock strength Rc/σmax of the surrounding rocks is linearly interpolated from a lower limit of the corresponding rating interval of the rating S2 of the rock strength Rc/σmax of the surrounding rocks to an upper limit of the corresponding rating interval of the rating S2 of the rock strength Rc/σmax of the surrounding rocks according to the rock strength Rc/σmax of the uniaxial compressive strength Rc of the surrounding rocks to a maximum principal stress σmax of an initial ground stress; Rc/σmax>10, and the rating S2 of the rock strength Rc/σmax of the surrounding rocks is 20; Rc/σmax<1, and the rating S2 of the rock strength Rc/σmax of the surrounding rocks is 0;
during the rating, the local stability condition of the surrounding rocks comprises:
stable, and a corresponding rating interval of a rating S3 of the local stability condition of the surrounding rocks is 20≥S3≥15; basically stable, and the corresponding rating interval of the rating S3 of the local stability condition of the surrounding rocks is 15>S3≥10; understable, and the corresponding rating interval of the rating S3 of the local stability condition of the surrounding rocks is 10>S3≥5; unstable, and the corresponding rating interval of the rating S3 of the local stability condition of the surrounding rocks is 5>S3≥0; wherein the rating S3 of the local stability condition of the surrounding rocks of a single failure type of a cavern unit or cavern section takes a lowest value in all ratings of the single failure type;
during the rating, the relaxation/damage condition of the surrounding rocks comprises:
3 meters (m)≥Dr or 0.15≥Dr/B, and a corresponding rating interval of a rating S4 of the relaxation/damage condition of the surrounding rocks is 10≥S4≥8; 6 m≥Dr≥3 m or 0.3≥Dr/B>0.15, and the corresponding rating interval of the rating S4 of the relaxation/damage condition of the surrounding rocks is 8≥S4≥5; 9 m≥Dr>6 m or 0.45≥Dr/B>0.3, and the corresponding rating interval of the rating S4 of the relaxation/damage condition of the surrounding rocks is 5>S4≥2; Dr>9 m or Dr/B>0.45, and the corresponding rating interval of the rating S4 of the relaxation/damage condition of the surrounding rocks is 2>S4≥0;
wherein a damage zone depth Dr standard is adopted when a cavern span B>20 m, and a depth-cavern span ratio DI/B standard is adopted for others; Dr takes an average value of a maximum relaxation/damage depth of a monitoring/analysis section or area; the rating S4 of the relaxation/damage condition of the surrounding rocks is linearly interpolated from an upper limit of the corresponding rating interval of the rating S4 of the relaxation/damage condition of the surrounding rocks to a lower limit of the corresponding rating interval of the rating S4 of the relaxation/damage condition of the surrounding rocks according to a value of Dr or Dr/B; when Dr≥12 m or Dr/B≥0.6, the rating S4 of the relaxation/damage condition of the surrounding rocks is 0; in a survey and design stage, Dr is predicted by numerical calculation integrated with a damage assessment index or similar physical simulation; in a construction stage, Dr is obtained by an acoustic wave velocity test, borehole imaging or numerical calculation integrated with the damage assessment index; when a disturbance degree of a construction to the surrounding rocks is a target level, the rating S4 of the relaxation/damage condition of the surrounding rocks takes the lower limit of the corresponding rating interval of the rating S4 of the relaxation/damage condition of the surrounding rocks where the Dr standard or the Dr/B standard is located; when the local stability condition of the surrounding rocks takes an assessment result of the local deformation stability or the collapse tendency, the rating S4 of the relaxation/damage condition of the surrounding rocks is 0;
during the rating, the combined relationship between the initial maximum principal stress directions of the surrounding rocks and the cavern axis comprises:
20°≥γ, and a corresponding rating interval of a rating S5 of the combined relationship between the initial maximum principal stress directions of the surrounding rocks and the cavern axis is 10≥S5≥8; 40°≥γ>20°, and the corresponding rating interval of the rating S5 of the combined relationship between the initial maximum principal stress directions of the surrounding rocks and the cavern axis is 8>S5≥6; 70°≥γ>45°, and the corresponding rating interval of the rating S5 of the combined relationship between the initial maximum principal stress directions of the surrounding rocks and the cavern axis is 6>S5>3; γ>70°, and the corresponding rating interval of the rating S5 of the combined relationship between the initial maximum principal stress directions of the surrounding rocks and the cavern axis is 3>S5>0; wherein the rating S5 of the combined relationship between the initial maximum principal stress directions of the surrounding rocks and the cavern axis is linearly interpolated from an upper limit of the corresponding rating interval of the rating S5 of the combined relationship between the initial maximum principal stress directions of the surrounding rocks and the cavern axis to a lower limit of the corresponding rating interval of the rating S5 of the combined relationship between the initial maximum principal stress directions of the surrounding rocks and the cavern axis according to a value of γ, γ refers to an included angle between an initial maximum principal stress direction of the surrounding rocks and the cavern axis, and γ is an acute angle;
during the rating, the combined relationship between the main structural plane and the cavern axis comprises:
α≥60°, β>70°, and a corresponding rating of a rating S6 of the combined relationship between the main structural plane and the cavern axis is side wall S6=8 and vault S6=10; α≥60°, 70°>β≥45°, and the corresponding rating of the rating S6 of the combined relationship between the main structural plane and the cavern axis is the side wall S6=6 and the vault S6=8; α≥60°, 45°>β≥20°, and the corresponding rating of the rating S6 of the combined relationship between the main structural plane and the cavern axis is the side wall S6=8 and the vault S6=6; α≥60°, 20°>β, the corresponding rating of the rating S6 of the combined relationship between the main structural plane and the cavern axis is the side wall S6=10 and the vault S6=2, a is an included angle between a direction of the main structural plane and the cavern axis, and B is a dip angle of the main structural plane;
60°>α≥30°, β≥70°, and the corresponding rating of the rating S6 of the combined relationship between the main structural plane and the cavern axis is the side wall S6=6 and the vault S6=8; 60°>α≥30°, 70°>β≥45°, and the corresponding rating of the rating S6 of the combined relationship between the main structural plane and the cavern axis is the side wall S6=2 and the vault S6=6; 60°>α≥300, 45°>β≥20°, and the corresponding rating of the rating S6 of the combined relationship between the main structural plane and the cavern axis is the side wall S6=8 and the vault S6=2; 60°>α≥30°, 20°>β, and the corresponding rating of the rating S6 of the combined relationship between the main structural plane and the cavern axis is the side wall S6=10 and the vault S6=0;
30°>α, β≥70°, the corresponding rating of the rating S6 of the combined relationship between the main structural plane and the cavern axis is the side wall S6=2 and the vault S6=6; 30°>α, 70°>β≥45°, and the corresponding rating of the rating S6 of the combined relationship between the main structural plane and the cavern axis is the side wall S6=0 and the vault S6=2; 30°>α, 45°>β≥20°, and the corresponding rating of the rating S6 of the combined relationship between the main structural plane and the cavern axis is the side wall S6=6 and the vault S6=0; 30°>α, 20°>β, and the corresponding rating of the rating S6 of the combined relationship between main structural plane refers to discontinuities comprising a fault, a dislocation zone, a bedding plane, fissure, an altered fracture zone, and a dike zone which run through the target underground cavern and have a scale of Class II or below; when the main structural plane is exposed in the vault and the side wall at a same time, the rating S6 of the combined relationship between the main structural plane and the cavern axis takes a lowest value of the main structural plane when exposed in the vault and the main structural plane when exposed in the side wall; when there are multiple groups of main structural planes, the rating S6 of the combined relationship between the main structural plane and the cavern axis takes a lowest of all main structural planes; if there is no main structural plane influencing the stability of the surrounding rocks of the cavern units or the cavern sections, the rating S6 of the combined relationship between the main structural plane and the cavern axis is 10;
during the rating, the groundwater comprises:
10≥Q, dry without water seepage, and a corresponding rating interval of a rating S7 of the groundwater is 5≥S7≥4; 25≥Q>10, wet or dripping water, and the corresponding rating interval of the rating S7 of the groundwater is 4>S7≥3; 125≥Q>25, rain or linear water, and the corresponding rating interval of the rating S7 of the groundwater is 3>S7≥1; Q>125, gushing water, the corresponding rating interval of the rating S7 of the groundwater is 1>S7≥0;
wherein a unit of water quantity Q per 10 m cavern length is a liter per minute (L/min)·10 m; the rating S7 of the groundwater is linearly interpolated from an upper limit of the corresponding rating interval of the rating S7 of the groundwater to a lower limit of the corresponding rating interval of the rating S7 of the groundwater according to a common logarithm of Q; when there is no Q monitoring data available, the rating S7 of the groundwater is performed according to a description of a groundwater output state; when 250≥Q, the rating S7 of the groundwater is 0; in the survey and design stage, the lower limit of the corresponding rating interval of the rating S7 of the groundwater is selected according to a buried condition of the groundwater of the site;
during the rating, the local deformation stability of the surrounding rocks in the local stability condition of the surrounding rocks comprises:
stable, a corresponding rating interval of a rating S9 of the local deformation stability of the surrounding rocks is 20≥S9≥15, a classification standard in the survey and design stage is
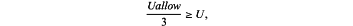 a classification standard in the construction stage is 0.2 millimeters per day (mm/d)≥v or
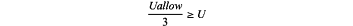 for five consecutive days; basically stable, the corresponding rating interval of the rating S9 of the local deformation stability of the surrounding rocks is 15>S9≥10, the classification standard in the survey and design stage is
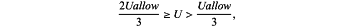 and the classification standard in the construction stage is 0.5 mm/d≥v>0.2 mm/d or
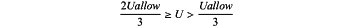 for five consecutive days; understable, the corresponding rating interval of the rating S9 of the local deformation stability of the surrounding rocks is 10>S9≥5, the classification standard in the survey and design stage is
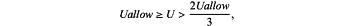 and the classification standard in the construction stage is 0.5 mm/d<v≤1 mm/d or
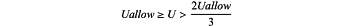 for five consecutive days; or unstable, the corresponding rating interval of the rating S9 of the local deformation stability of the surrounding rocks is 5>S9≥0, the classification standard in the survey and design stage is U>Uallow, and the classification standard in the construction stage is v>1 mm/d or U>Uallow for five consecutive days;
wherein U, v and Uallow are a relative displacement, a deformation rate and an allowable relative displacement value of measuring points in key parts of the target underground cavern respectively; a value of Uallow should be in accordance with technical specifications of rock and soil anchor stock and shotcrete support engineering; the rating S9 of the local deformation stability of the surrounding rocks is linearly interpolated from an upper limit of the corresponding rating interval of the rating S9 of the local deformation stability of the surrounding rocks to a lower limit of the corresponding rating interval of the rating S9 of the local deformation stability of the surrounding rocks according to a value of U or v; the rating S9 of the local deformation stability of the surrounding rocks is 0 when v>2 mm/d in five consecutive days or U>1.3Uallow; when double standards of U and v are adopted for rating, an assessment result of the double standards of U and v with a lowest rating is taken;
during the rating, the block stability of the surrounding rocks in the local stability condition of the surrounding rocks comprises:
stable, a corresponding rating interval of a rating S10 of the block stability of the surrounding rocks is 20≥S10≥15, and the classification standard is Fs≥Fs allow; basically stable, the corresponding rating interval of the rating S10 of the block stability of the surrounding rocks is 15>S10≥10, and the classification standard is Fs_allow>Fs≥0.9Fs_allow; understable, the corresponding rating interval of the rating S10 of the block stability of the surrounding rocks is 10>S10≥5, and the classification standard is 0.9Fs_allow>Fs>1.0; unstable, the corresponding rating interval of the rating S10 of the block stability of the surrounding rocks is 5>S10≥0, and the classification standard is 1.0>Fs;
wherein the rating S10 of the block stability of the surrounding rocks is linearly interpolated from a lower limit of the corresponding rating interval of the rating S10 of the block stability of the surrounding rocks to an upper limit of the corresponding rating interval of the rating S10 of the block stability of the surrounding rocks according to a block safety factor Fs; when Fs>1.1Fs_allow, the rating S10 of the block stability of the surrounding rocks is 20; when a potential unstable block volume V>30 m3, the rating S10 of the block stability of the surrounding rocks is the lower limit of the corresponding rating interval of the rating S10 of the block stability of the surrounding rocks where the rating S10 of the block stability of the surrounding rocks is located; an allowable block safety factor Fs_allow is a minimum safety factor according to a design code of an underground powerhouse of a hydropower station;
during the rating, the collapse tendency of the surrounding rocks in the local stability condition of the surrounding rocks comprises:
very little, a corresponding rating interval of a rating S11 of the collapse tendency of the surrounding rocks is 20≥S11≥15, the classification standard in the survey and design stage is 1 m≥H, and the classification standard in the construction stage is 1 m≥H or 10 m3≥V; slight, the corresponding rating interval of the rating S11 of the collapse tendency of the surrounding rocks is 15>S11≥10, the classification standard in the survey and design stage is 3 m≥H>1 m, and the classification standard in the construction stage is 3 m>H>1 m or 30 m3≥V>10 m3; medium, the corresponding rating interval of the rating S11 of the collapse tendency of the surrounding rocks is 10>S11≥5, the classification standard in the survey and design stage is 6 m≥H>3 m, and the classification standard in the construction stage is 6 m≥H>3 m or 100 m3≥V>30 m3; strong, the corresponding rating interval of the rating S11 of the collapse tendency of the surrounding rocks is 5>S11≥0, the classification standard in the survey and design stage is H>6 m, and the classification standard in the construction stage is H>6 m or V>100 m3;
wherein the rating S11 of the collapse tendency of the surrounding rocks is linearly interpolated from an upper limit of the corresponding rating interval of the rating S11 of the collapse tendency of the surrounding rocks to a lower limit of the corresponding rating interval of the rating S11 of the collapse tendency of the surrounding rocks according to a collapse height H or a common logarithm of a collapse volume V; when H≥9 m or V≥300 m3, the rating S11 of the collapse tendency of the surrounding rocks is 0; when double standards of H and V are adopted for rating, an assessment result of the double standards of H and V with a lowest rating is taken;
during the rating, the rockburst tendency of the surrounding rocks in the local stability condition of the surrounding rocks comprises:
very little, a corresponding rating interval of a rating S12 of the rockburst tendency of the surrounding rocks is 20≥S12≥15, the classification standard in the survey and design stage is 0.3≥σθ/Rc, and the classification standard in the construction stage is 0.3≥σθ/Rc≥0 or 0.1 m>Df; slight, the corresponding rating interval of the rating S12 of the rockburst tendency of the surrounding rocks is 15>S12≥10, the classification standard in the survey and design stage is 0.5≥σθ/Rc>0.3, and the classification standard in the construction stage is 0.5≥σθ/Rc>0.3 or 0.5 m≥Df>0.1 m; medium, the corresponding rating interval of the rating S12 of the rockburst tendency of the surrounding rocks is 10>S12≥5, the classification standard in the survey and design stage is 0.7≥σθ/Rc>0.5, and the classification standard in the construction stage is 0.7≥σθ/Rc>0.5 or 1 m≥Df>0.5 m; strong, the corresponding rating interval of the rating S12 of the rockburst tendency of the surrounding rocks is 5>S12≥0, the classification standard in the survey and design stage is σθ/Rc>0.7, and the classification standard in the construction stage is σθ/Rc>0.7 or Df>1 m;
wherein the rating S12 of the rockburst tendency of the surrounding rocks is linearly interpolated from an upper limit of the corresponding rating interval of the rating S12 of the rockburst tendency of the surrounding rocks to a lower limit of the corresponding rating interval of the rating S12 of the rockburst tendency of the surrounding rocks according to a ratio σθ/Rc of a tangential compressive stress σθ of the surrounding rocks to the uniaxial compressive strength Rc of the surrounding rocks, or linearly interpolated from the upper limit of the corresponding rating interval of the rating S12 of the rockburst tendency of the surrounding rocks to the lower limit of the corresponding rating interval of the rating S12 of the rockburst tendency of the surrounding rocks according to a spalling/brittle failure depth Df; when σθ/Rc≥0.9 or Df≥3 m, the rating S12 of the rockburst tendency of the surrounding rocks is 0; when double standards of σθ/Rc and Df are configured for rating, an assessment result of the double standards of σθ/Rc and Df with a lowest rating is taken; and σθ is obtained by an elastic numerical calculation result of underground cavern excavation; and
during the rating, the stability assessment results of the respective cavern units or cavern sections comprise:
stable, a corresponding rating interval of a rating S of the stability assessment results of the respective cavern units or cavern sections is 100≥S≥80; basically stable, the corresponding rating interval of the rating S of the stability assessment results of the respective cavern units or cavern sections is 80>S≥60; understable, the corresponding rating interval of the rating S of the stability assessment results of the respective cavern units or cavern sections is 60>S≥30; unstable, the corresponding rating interval of the rating S of the stability assessment results of the respective cavern units or cavern sections is S<30;
wherein the quantitative assessment method further comprises: guiding an excavation operation on the target underground cavern according to the global stability assessment result of the target underground cavern.
|